Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the EME programme as project number 10/90/10. The contractual start date was in February 2012. The final report began editorial review in March 2014 and was accepted for publication in March 2015. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The EME editors and production house have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the final report document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Pallav L Shah has received consultancy fees from PneumRx and Olympus and organises a bronchoscopy course, which is sponsored by ERBE, Cook Medical, Superdimension, Boston Scientific, Aquilant, Broncus, Pulmonx, Olympus and PneumRx. The valves used were provided by the manufacturer, Pulmonx, free of charge. Pulmonx had no input into trial design, data analysis or data presentation.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2015. This work was produced by Zoumot et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Introduction
Despite optimal pharmacological therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) remain significantly disabled. Emphysema, the destruction of lung parenchyma, is an important feature of the disease. Loss of lung elastic recoil leads to airflow obstruction, gas trapping and increased operating lung volumes. When the condition is heterogeneous, the worst-affected areas of lung expand disproportionately, restricting the ventilation of relatively more healthy areas. Lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS), resecting the worst areas of lung, has been clearly shown to improve outcomes in selected patient groups. 1–4 The surgical intervention is, however, associated with significant morbidity and an early mortality rate of about 5%. 1,2 There is therefore considerable interest in developing novel treatment approaches that can reduce lung volumes and gas trapping, either more safely than LVRS or in patients for whom LVRS is not an option. 5
One such approach is bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR), the placement of endobronchial valves using a fibreoptic bronchoscope, to allow air to leave but not enter emphysematous areas of the lung, causing them to collapse. In the heterogeneous disease, this allows the relatively healthier lung to function better. Initial pilot work by our group6,7 and others has been encouraging. 8–13 We demonstrated that valve placement could reduce dynamic hyperinflation with improved exercise capacity associated with improvements in inspiratory capacity (IC) and gas transfer. 6 Moreover, follow-up of our original cohort has shown that all patients in whom radiological atelectasis had occurred (n = 5) were alive 6 years post procedure whereas eight of the 14 without radiological atelectasis had died (Figure 1). 14 This offers the possibility that BLVR may like LVRS, offer a survival advantage when effective in appropriately selected patients.
FIGURE 1.
Atelectasis following BLVR is associated with improved survival (p = 0.026). 14 This material has not been reviewed by European Respiratory Society prior to release; therefore the European Respiratory Society may not be responsible for any errors, omissions or inaccuracies, or for any consequences arising there from, in the content. Reproduced with permission of the European Respiratory Society: Eur Respir J 2011;37(6):1346–51; published ahead of print 2010, doi: 10.1183/09031936.00100110.

This trial report describes a study intended to address these issues. The study rationale and design, including the complete protocol15 and the full study results,16 have been published previously.
A ‘lobar’ approach has generally been adopted, with valves placed to occlude all of the segmental airways of the target lobe. This should lead to lobar atelectasis. The major problem with this approach is collateral ventilation. If the interlobar fissures have been damaged, air may enter the target lobe through the adjacent lobe, preventing atelectasis. Improvement in lung function may occur in the absence of radiological volume reduction, perhaps by the diversion of airflow to healthier lung, but benefits are greatest when atelectasis occurs. 6 However, because of the destruction of lung parenchyma in COPD, collateral ventilation may occur between lobes when the interlobar fissures are no longer intact. A large randomised controlled trial of BLVR, the Endobronchial Valve for Emphysema Palliation Trial (VENT), was published in 2010. 17 In total, 321 patients with heterogeneous emphysema were randomly assigned to receive either unilateral lobar occlusion with Zephyr endobronchial valves (Pulmonx Corporation, Redwood City, CA, USA) (Figure 2) or standard medical care. This confirmed that the treatment was effective but the overall benefits were modest, with a 6.85% difference in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) between the treatment group and the control group at 6 months’ follow-up and a 5.7% difference in 6-minute walk distance. This occurred at the expense of a modest increase in acute exacerbations.
FIGURE 2.
The Zephyr endobronchial valve.
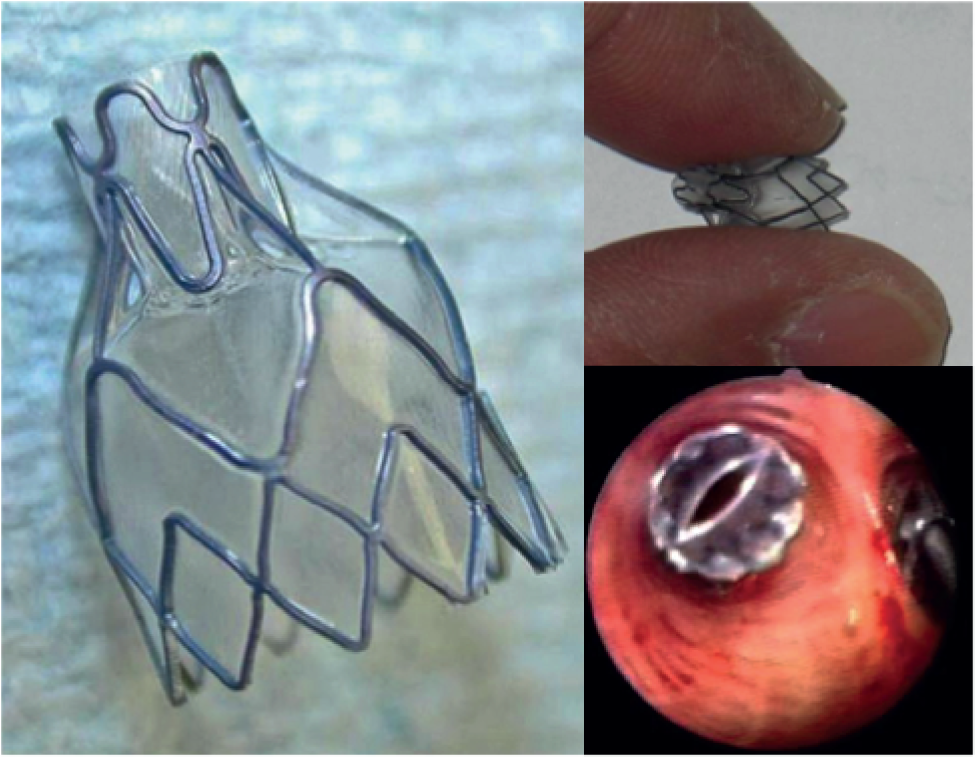
After prolonged discussion, the US Food and Drug Administration did not approve the use of these valves in emphysema because the overall group benefits were too small. However, a subgroup of ‘lobar exclusion’ patients was identified in whom pre-procedure computerised tomography (CT) showed that the interlobar fissures appeared intact and post-procedure CT confirmed that valves were satisfactorily placed (i.e. there was no airway proximal to where they were sited). 17 Post-hoc analysis of this subgroup, in whom the target lobe had been effectively isolated, revealed improvements of a similar order of magnitude to those who have been observed following LVRS, with a median 21% increase in FEV1. By contrast, the group without intact fissures had only a 2% change in FEV1 at 6 months. Heterogeneity of response is therefore to be expected and a proper assessment of the usefulness of BLVR will require the identification of a responder subgroup phenotype.
Another feature was that, although there was heterogeneity in the CT scans of people enrolled in the trial (as an entry criterion), in many, this represented a difference in lung density because of either microscopic emphysema or airways disease rather than a more macroscopic ‘lung destruction’ pattern. The latter appears to be more responsive to BLVR and it appears that a number of patients included in the VENT trial17 may not be the most responsive to BLVR. In fact, patients with the greatest heterogeneity on CT benefited the most from BLVR in the VENT study.
An endobronchial catheter-based device (Chartis™; Pulmonx, Palo Alto, CA, USA) has been developed for estimating collateral resistance, potentially allowing better target lobe selection. The Chartis system consists of a balloon occlusion catheter with a flow sensor. At bronchoscopy the catheter is inserted into the target lobe and the occlusion balloon inflated, with the aim being to completely occlude the target lobe. The balloon occludes the airway, enabling no direct flow of inspired air into the lung compartment. The Chartis console displays expiratory air flow (orange), pressure (blue) and resistance (green) measurements. The balloon is occluded for up to 5 minutes. If flow stops then it is assumed that there is no collateral ventilation; however, if there is still active flow then collateral ventilation is present. 18
A number of alternative approaches to the Zephyr valve have been or are under investigation to achieve volume reduction in patients with emphysema and are reviewed briefly here.
Lung volume reduction surgery
Novel techniques need to be considered in the context of LVRS. This involves resection of the worst-affected area of emphysematous lung. Lung volumes improve because bullous areas, which expand at the expense of more healthy lung, have been resected and because the remaining relatively healthier lung has greater elastic recoil, allowing it to empty more effectively. 19 The best evidence around the indications for this treatment comes from the National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT). 2 This multicentre trial randomised > 1200 patients to LVRS or usual care. An early finding was the identification of a high-risk group [FEV1 < 20% predicted with either a homogeneous pattern of disease or the carbon monoxide transfer factor of the lung (TLCO) < 20% predicted]. Subsequent enrolment from this patient group was stopped. Analysis was based on a priori categories of exercise capacity and pattern of emphysema. At 24 months a survival benefit was apparent in surgical patients with a low exercise capacity and upper lobe predominant emphysema. Excluding the high-risk group, procedural (90-day) mortality was 5.5% in the trial, with serious morbidity after LVRS observed in 59% of patients [persistent air leak (33%), respiratory failure (22%), pneumonia (18%), cardiac arrhythmias (24%)]. 2 A subsequent report from the trial demonstrated that the beneficial effects of LVRS were sustained, with increased survival in the LVRS group at a median 4.3 years of follow-up [0.11 deaths per person-year in the LVRS group vs. 0.13 deaths per person-year in the medical group; risk ratio 0.85, p < 0.02]. 20 Patients with upper lobe predominant emphysema and low baseline exercise capacity showed the largest benefit, with > 70% still alive at 5 years compared with < 50% of those treated medically (risk ratio 0.57, p < 0.01). This group also had improvements in exercise capacity (p < 0.001) and quality of life (p < 0.001). The cost of LVRS was US$140,000 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained at 5 years and was projected to be US$54,000 per quality-adjusted life-year gained at 10 years. 21 National and international guidelines now recommend that LVRS be considered in patients with upper lobe predominant disease and low exercise capacity. 22,23 The previous single-centre study performed at the Royal Brompton Hospital yielded similar results. 1,24 It should be noted that morbidity and mortality with modern LVRS practice [unilateral video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)] are lower than in the NETT trial, in which bilateral procedures through a median sternotomy were performed. 2,4
Spiration valve
Spiration Incorporated (Redmond, WA, USA) developed an umbrella-shaped device that, when expanded, allows air and secretions to leave but not enter the occluded lobar segment. A central proximal rod can be grasped to collapse the umbrella and allow it to be removed. In a multicentre pilot trial of 91 patients with severe heterogeneous emphysema, a mean of 6.7 valves were inserted per patient, resulting in nine pneumothoraces and one fatality. 25 Although quality of life improved in this unblinded study, lung function did not improve. This may be because a non-lobar approach (e.g. targeting only two out of three right upper lobe segmental bronchi) was adopted. A double-blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial using this device in 73 patients reported that, although non-lobar occlusion with the intrabronchial valve (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) was safe, it was also generally ineffective. 26
Polymeric lung volume reduction
Polymeric lung volume reduction (Aeris Therapeutics Incorporated, Woburn, MA, USA) involves deployment of a biodegradable gel into subsegmental bronchi bronchoscopically. The solution, which contains aminated polyvinyl alcohol and glutaraldehyde, creates a hydrogel foam when delivered to the distal airways. As gas within the foam (which fills damaged alveoli) is absorbed, the foam, which is now adherent to the alveolar tissue, collapses and as it does so it reduces lung volume and hyperinflation. An open-label multicentre exploratory Phase II clinical study with polymeric lung volume reduction hydrogel administered to eight subsegmental sites in 25 patients with upper lobe emphysema showed improvements in lung function and functional parameters, which persisted at 6 months. 27 The safety profile was acceptable in this study; however, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency has objected to the use of the AeriSeal® system in the UK on the grounds of patient safety, because of the presence of potentially toxic glutaraldehyde in the gel and two deaths in preliminary studies.
Bronchoscopic thermal vapour ablation (‘steam’)
The bronchoscopic thermal vapour ablation system (Uptake Medical, Seattle, WA, USA) delivers heated water vapour bronchoscopically, via a dedicated catheter, into the targeted emphysematous lung segments. The delivered heat causes acute tissue injury, which is followed by scarring and fibrosis, leading to lung volume reduction. In a pilot safety and feasibility study, Eberhardt et al. 28 unilaterally treated 20 patients with heterogeneous emphysema. Two patients developed pneumonia with a prolonged hospital stay, but all patients showed physiological benefits at 30 days. Longer-term follow-up data are not yet available.
Bronchoscopic instillation of autologous blood for volume reduction
The use of autologous blood and fibrinogen to trigger a scarring response and achieve volume reduction could avoid the need for expensive devices, and expensive and potentially toxic agents. Pilot work in Japan has shown promise29 and further trials are under way.
RePneu Coil© lung volume reduction
The RePneu© Coil (PneumRx Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA) is an implantable coil-like device comprising Nitinol, a super-elastic shape memory alloy. The implant is delivered bronchoscopically under fluoroscopic guidance into the targeted airways and when its sheath is removed it recoils to its original shape, preventing expansion of lung tissue. It may also act as a tensioning stent preventing larger airway collapse. A multicentre randomised controlled trial in heterogeneous emphysema has shown encouraging results, with significant improvements in lung function. 30 Safety data after more than 1350 coils have been implanted in 164 patients have shown no deaths, no device migration or expectoration, six pneumothoraces (resolved quickly with intercostal chest drain insertion) and nine cases of pneumonia in eight patients (which did not require a prolonged hospital stay). 30–34 Preliminary data suggest that the improvements seen are sustained for at least 1 year. 35
Airway bypass stents
Exhale® Airway Bypass drug-eluting stents (Broncus Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA) are placed bronchoscopically through cartilaginous airways into emphysematous lung parenchyma. CT mapping is used to target the areas with the most severe emphysema and a Doppler probe is used to avoid airway wall blood vessels. Initial pilot data in patients with homogeneous emphysema showed encouraging persistent benefits with regard to physiological and functional parameters at 6 months. 36 However, a double-blind multicentre pivotal trial has been disappointing. 37 Significant reductions in lung volumes were seen immediately post procedure but these did not persist. This appears to be because of a loss of stent patency. Although the concept of transbronchial airway bypass has been proven, the problem of stent occlusion will need to be addressed before it can be of value for patients.
Percutaneous transpleural airway bypass (‘spiracles’)
An alternative to the transbronchial approach to airway bypass is to create a transpleural pneumonostomy. This is similar to an intrabullous drainage procedure (the Brompton/Monaldi technique38) but with a permanent track being fashioned to allow a pathway for air to escape. The Portaero Pneumostoma System (Portaero Inc., Cupertino, CA, USA) creates a pneumonostomy channel through a minimally invasive transthoracic surgical approach in a procedure that takes approximately 1 hour to complete. The patient is required to change the Portaero tube daily to maintain patency. This has now been trialled in six patients with encouraging results. 39 In the four patients who retained the bypass tube for ≥ 3 months there was a 23% increase in FEV1.
Airway bypass techniques depend on collateral ventilation to be effective and are therefore likely to be most effective in patients with homogeneous disease and are less relevant to the population targeted in the present study.
Rationale for the Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction with endobronchial valves for patients with Heterogeneous emphysema and Intact interlobar Fissures study
The Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction with endobronchial valves for patients with Heterogeneous emphysema and Intact interlobar Fissures (BeLieVeR-HIFi) study involved the prospective, independent validation of the use of a medical device, the Zephyr endobronchial valve, through a double-blind randomised controlled trial. The population was patients with severe or very severe COPD [Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) stage III and IV] with a heterogeneous pattern of emphysema and intact interlobar fissures. The intervention was the placement of endobronchial valves to achieve lobar occlusion. The comparator was a control group who had a bronchoscopy and ‘sham’ valve placement. Outcomes were change in lung function, exercise capacity and health status 3 months post procedure.
The project fitted the National Institute for Health Research Efficacy and Mechanisms Evaluation programme remit because there was some initial evidence that endobronchial valves were effective but it had not been shown that a population of responders could be identified prospectively to give evidence for effect size. Inconsistency of response, probably because of collateral ventilation between lobes where the interlobar fissures are incomplete, has been a major problem in refining the use of this therapy. We aimed to demonstrate efficacy under ideal conditions, conducting the trial at a highly experienced centre and recruiting patients carefully but in a transparent and reproducible way. Confirming the effect on lung function and exercise capacity would be an essential step to allow commissioners to consider whether or not they wished to support this form of treatment.
Although a positive outcome of the trial could lead to more widespread use of bronchoscopically deployed valves, which would be of interest to device manufacturers, a potential strength of our non-commercial study was that we would define a narrow subset of patients who experience a substantial benefit, whereas commercial trials will tend to try to identify as wide a population as possible. Use of valves in patients with emphysema outside the criteria defined in this trial would need to be justified by subsequent studies.
Study hypotheses
Studies have to date demonstrated some dramatic responses to the placement of endobronchial valves in COPD but modest overall group benefits. We hypothesised that it would be possible to identify a group of COPD patients prospectively with heterogeneous emphysema and intact interlobar fissures in whom lobar occlusion, and hence lung volume reduction, could be achieved, both to a significant degree and consistently. The study therefore addressed the following questions, with outcomes assessed at 3 months post procedure:
-
Does endobronchial valve placement in this subgroup of COPD patients lead to a significant improvement in airflow obstruction (FEV1) compared with control patients?
-
Does endobronchial valve placement in this group lead to significant improvement in lung volumes [residual volume (RV), total lung capacity (TLC) and functional residual capacity (FRC)] measured by body plethysmography compared with control patients?
-
Does endobronchial valve placement in this group lead to a significant improvement in exercise capacity (endurance time at 70% of maximum workload) and dynamic hyperinflation measured during endurance cycle ergometry as isotime end-expiratory lung volume (EELV)?
-
Does endobronchial valve placement lead to an improvement in walking distance assessed using the 6-minute walk test?
-
Does endobronchial valve placement in this group lead to a significant improvement in health-related quality of life?
-
Will the benefit seen in this group be of a magnitude likely to be sufficient to justify the cost of the procedure and complications that occur?
Chapter 2 Methods
Sponsorship, ethics and registration
The study sponsor was Imperial College London. The study was approved by the London – Bentham Research Ethics Committee (reference 11/LO/1608). All patients gave written informed consent to participate. The trial was registered as ISRCTN04761234. The study design and trial protocol have been published previously. 15
Public and patient involvement
The initial study design was discussed with the Kensington and Chelsea Breathe Easy group. Once the scientific results are published we will work with the British Lung Foundation and the Imperial College and Royal Brompton media departments to ensure that they are disseminated appropriately.
Study design
The study was a double-blind, randomised, sham-controlled trial to investigate the effect of BLVR with endobronchial valves in patients with severe (GOLD stage III and IV) heterogeneous emphysema and intact interlobar fissures.
Patient recruitment
Patients were recruited from the advanced COPD clinic at Royal Brompton Hospital between March 2012 and September 2013. When clinically appropriate, patients had investigations including thoracic CT scans and pulmonary function tests to assess their eligibility for LVRS. All patients were discussed in a multidisciplinary meeting including a respiratory physician, a radiologist and a thoracic surgeon with additional physiotherapy and nursing input.
Inclusion criteria were as follows:
-
Adult patients with stable severe COPD (GOLD stage III or IV with FEV1 < 50% predicted).
-
Medical Research Council (MRC) dyspnoea score between 3 and 5.
-
TLC > 100% predicted and RV > 150% predicted, assessed using body plethysmography.
-
6-minute walk distance of < 450 m.
-
Patient on optimum medical therapy including inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta2-agonist and anticholinergic agents unless intolerant or declined to use them.
-
Thoracic CT scan demonstrating heterogeneous emphysema with a defined target lobe with lung destruction and intact adjacent interlobar fissures. Scans were reviewed by two radiologists independently and a third adjudicated on any disagreements. Radiologists agreed that the worst-affected lobe of the lung has an emphysema score of > 2 (according to the NETT scoring system), that it is at least 1 point higher than the ipsilateral lobes and that it has intact fissures visible on at least one projection.
Exclusion criteria were as follows:
-
significant comorbidity that limits exercise capacity or prognosis
-
significant daily sputum production
-
hypoxia [i.e. arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) < 6.5 kPa while breathing air]
-
smoker.
Outcome measures are described in detail later in this chapter. At baseline patients underwent full pulmonary function testing, a thoracic CT scan and a 6-minute walk test. Health status was also assessed. A symptom-limited incremental exercise test on a cycle ergometer was performed and then an endurance cycle test at 70% of peak workload with measurements of IC to track dynamic lung volumes. These measures were repeated at 90 days.
Flow through the study is described in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3.
Study flow chart. 6MWT, 6-minute walk test; CAT, COPD Assessment Test; CXR, chest radiography; FFM, fat-free mass; MDT, multidisciplinary team; PFT, pulmonary function test.

Randomisation and blinding
Two separate teams were used to maintain blinding. A treatment team (PLS, ZZ, WHM) undertook the randomised procedures and a separate assessment team (CD, MIP, NSH) was blind to study assignment and responsible for the assessments. This approach has been successfully employed in previous trials of bronchoscopic therapies for emphysema. 37
A random sequence with block randomisation was generated by trial statistician Winston Banya. Treatment allocation was obtained by the treatment team by telephoning the Imperial Clinical Trials Unit (ICTU) hotline from the bronchoscopy suite once the patient had been sedated.
Sample size
We considered an absolute difference in response between the two arms of 15% to be clinically significant. For 80% power and a significance level of 0.05, 21 subjects would be needed in each arm assuming that the mean change in FEV1 from baseline in the control group was 0 [standard deviation (SD) 2.5%] and the mean change in the group receiving BLVR was 15% (SD 25%). To allow for dropout we have increased the sample size target by 20%; hence, we aimed to recruit 50 patients in total.
Outcome measures
Lung function
Spirometry, gas transfer and lung volumes assessed by body plethysmography were measured using a CompactLab System (Jaeger; Hoechberg, Germany). 40 Lung function tests were all performed post bronchodilator. Predicted values used are those of the European Coal and Steel Community. 41,42
The primary end point was the difference in percentage change in post-bronchodilator FEV1, measured 90 days post procedure, between the treatment group and the control group. This was selected as the primary end point as it is the measure most usually accepted by regulatory authorities. This and other lung function measures were carried out in the lung function department of Royal Brompton Hospital according to international guidelines and with rigorous quality assurance in place. Plethysmographic lung volumes (TLC, RV and FRC) were also measured. It was expected that improvement in FEV1 in patients with BLVR would be accompanied by reductions in lung volumes and possibly an increase in TLCO.
Exercise
Secondary end points were change in endurance time on cycle ergometry (Tlim) at 70% of peak workload achieved at baseline with a metabolic measurement cart to allow measurement of dynamic hyperinflation. The endurance exercise tests were performed immediately after lung function testing. Patients performed IC manoeuvres each minute through the test. The IC value was subtracted from TLC to calculate EELV. Changes in EELV at isotime (the last 30-second period completed in the shorter of the two exercise tests) were compared. 6 Patients performed an initial incremental test with 5- to 10-W increments to establish the workload for the endurance test. This test was performed on a separate day from the first endurance cycle or with at least a 2-hour gap to ensure recovery.
A 6-minute walk test was also performed at last 1 hour after the cycle test to allow time to recover. As recommended in American Thoracic Society guidelines,43 two walks were performed with the best value taken.
Computerised tomography scanning
Target lobe volume change was assessed by one radiologist (DHC) as an explicatory variable and scored as follows:
-
0: no change
-
1: some volume loss (fissures shift)
-
2: segmental atelectasis (band of collapsed lung)
-
3: complete atelectasis (complete collapse).
Health status
The COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score was used to evaluate quality of life. This symptom score was developed according to a formal patient-reported outcome process and incorporates eight questions scored from 0 to 5, with higher scores representing more symptoms. It has been shown to be responsive to both exacerbations and pulmonary rehabilitation44,45 and is correlated with breathlessness and exacerbation frequency. 46 The St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire for COPD (SGRQc), a long-established health status measure for COPD, was also used. 47
Procedures
Study participants underwent bronchoscopy performed using moderate sedation [midazolam (average dose 1.9 mg) and alfentanil (Rapifen®, Janssen) (average dose 208 µg)]. The average procedure time was 25 minutes. Depending on their allocation patients had either unilateral lobar endobronchial valve placement aiming to achieve lobar atelectasis or bronchoscopy and ‘sham’ valve placement. A single operator (PLS) with expertise in interventional bronchoscopy who had performed > 50 endobronchial valve procedures before study commencement carried out all procedures.
Although target lobe selection was based on CT appearances alone, measurements of collateral ventilation using the Chartis balloon catheter system were carried out in all participants so that the accuracy of the two approaches could be compared. 48 This also served to reinforce blinding of the sham-treated patients as they underwent a ‘procedure’. Endobronchial valves were placed to occlude segmental bronchi leading to the target lobe (irrespective of Chartis results).
Patients underwent post-procedure chest radiography to check for the presence of a pneumothorax, which was reviewed by the treatment team. All were counselled and provided with an information sheet, irrespective of treatment allocation, giving advice on seeking medical attention in the presence of chest pain or sudden breathlessness. Advice was also provided for medical staff for patients presenting as an emergency.
A 1-month follow-up telephone call to ask about any adverse events was also made.
Statistical analysis and presentation
Data were entered into an electronic database developed by the ICTU using InForm version 4.6 (Oracle; Reading, UK) and analysis was performed by the trial statistician (WB) using Stata version 12 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) and SAS version 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Data were monitored by the ICTU with frequency distribution checks carried out on the data for possible outliers. Reference ranges were set before the start of the study and queries were generated on the data for any values that sat outside the predefined ranges.
Analysis was on an intention-to-treat basis as prespecified in a formal statistical analysis plan. Categorical data are presented as percentages and comparisons are carried out using the Pearson chi-square test. Normally distributed numerical data are presented as means with SDs or 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Non-normally distributed numerical data are presented as medians [interquartile ranges (IQRs)]. The two-sample independent t-test was used to compare means between the two treatment groups or the Mann–Whitney test was used for non-parametric data. A post-hoc univariate analysis of factors associated with change in cycle endurance time, using regression with the cluster option, that is, taking into account the paired nature of the data and relaxing the conditions for independence, was performed. A p-value of < 0.05 was taken to indicate statistical significance. Missing data were imputed using the Markov chain Monte Carlo method, which creates multiple imputations by using simulations from a Bayesian prediction distribution.
Collateral ventilation was measured during all bronchoscopies so that outcomes could also be compared across the two groups (excluding collateral ventilation-positive patients in intervention and control groups as predefined groups). A mixed linear model procedure was used to evaluate the effects of predefined covariables on dependent outcome variables.
In addition to this, a responder analysis was performed based on the achievement of minimum clinically important differences (MCIDs) for various parameters, prespecified as a 15% increase for FEV1, a 350-ml reduction for RV,49 a 4-point decrease for the SGRQc,47,50 a 2-point decrease for the CAT,45,51 a 105-second increase for Tlim52 and a 26-m increase for the 6-minute walk test. 53
Safety data analysis
Safety data were collected during the course of the study. Severe adverse events were defined as those resulting in death, a life-threatening illness or injury, or permanent impairment of a body structure or a body function, requiring hospital admission, prolonging existing hospitalisation or resulting in medical or surgical intervention to prevent a life-threatening illness or injury, or permanent impairment to a body structure or a body function. Pneumothorax was documented on a separate severe adverse event form with addition details.
Adverse events were recorded (severity, outcome, relationship to intervention and action taken). Expected adverse events were defined as (1) related to bronchoscopy – cough, acute exacerbation and haemoptysis – and (2) related to valve placement – pneumothorax, valve expectoration and acute exacerbation.
Chapter 3 Results
The baseline characteristics of the 50 COPD patients enrolled are presented in Table 1. Patients and control subjects were generally well matched although lung volumes were somewhat higher in the control group than in the treatment arm. Three individuals had taken part in pulmonary rehabilitation, completing within 3 months (46, 56, 63 days) of study enrolment. The mean (SD) gap between rehabilitation and enrolment was 390 (263) days.
| Characteristic | All | BLVR | Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.8 (7.4) | 62.3 (7.0) | 63.3 (7.9) |
| Gender, male/female (n) | 31/19 | 17/8 | 14/11 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 (4.8) | 24.5 (5.1) | 24.5 (4.6) |
| FEV1 (l) | 0.89 (0.32) | 0.93 (0.35) | 0.85 (0.30) |
| FEV1% predicted | 31.7 (10.2) | 31.6 (10.2) | 31.8 (10.5) |
| VC (l) | 3.13 (0.84) | 3.27 (0.85) | 2.99 (0.83) |
| FEV1/VC ratio | 0.28 (0.06) | 0.28 (0.06) | 0.29 (0.07) |
| TLC (l) | 8.33 (1.58) | 8.26 (1.53) | 8.40 (1.65) |
| TLC% predicted | 137 (14) | 132 (12) | 143 (15) |
| RV (l) | 5.17 (1.20) | 4.96 (1.11) | 5.38 (1.27) |
| RV% predicted | 232 (43) | 219 (39) | 245 (44) |
| RV/TLC (%) | 62.14 (8.12) | 60.23 (8.06) | 64.06 (7.88) |
| FRC (l) | 6.14 (1.33) | 5.99 (1.26) | 6.28 (1.40) |
| FRC% predicted | 189.9 (29.6) | 181.4 (27.9) | 198.5 (29.3) |
| TLCO (mmol/minute/kPa) | 2.98 (1.08) | 2.88 (0.95) | 3.08 (1.20) |
| TLCO% predicted | 33.8 (9.9) | 33.8 (10.8) | 33.7 (9.0) |
| VA (l) | 4.43 (1.06) | 4.34 (1.04) | 4.53 (1.09) |
| VA% predicted | 79.2 (12.9) | 77.6 (10.9) | 80.8 (14.7) |
| KCO (mmol/minute/kPa/l) | 0.66 (0.17) | 0.66 (0.18) | 0.67 (0.17) |
| KCO% predicted | 45.4 (12.1) | 45.8 (12.8) | 45.1 (11.7) |
| PaCO2 (kPa) | 4.85 (0.73) | 4.81 (0.86) | 4.90 (0.61) |
| PaO2 (kPa) | 9.60 (1.20) | 9.74 (1.45) | 9.47 (0.89) |
| MRC dyspnoea score | 4 (1) | 4 (1) | 4 (1) |
| CAT score | 25 (5) | 24 (5) | 27 (5) |
| SGRQc – symptoms | 71.23 (16.29) | 68.49 (15.78) | 73.97 (16.65) |
| SGRQc – activity | 88.35 (11.86) | 86.41 (13.51) | 90.29 (9.85) |
| SGRQc – impact | 57.14 (16.26) | 56.47 (16.92) | 57.81 (15.89) |
| SGRQc – total | 69.22 (12.78) | 67.79 (13.17) | 70.65 (12.48) |
| Pack-years smoked | 54 (24) | 56 (26) | 51 (23) |
| Exacerbation rate/year | 3 (3) | 3 (3) | 3 (2) |
| 6MWD (m) | 338 (87) | 342 (94) | 334 (81) |
| Peak workload (W) | 23 (14) | 25 (16) | 21 (11) |
| Peak VO2 (l/minute) | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.86 |
| Peak VCO2 (l/minute) | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.77 |
| Peak VE (l/minute) | 41.12 (12.76) | 41.84 (12.58) | 40.40 (13.15) |
| Tlim at 70% peak (seconds) | 305 (169) | 306 (166) | 305 (175) |
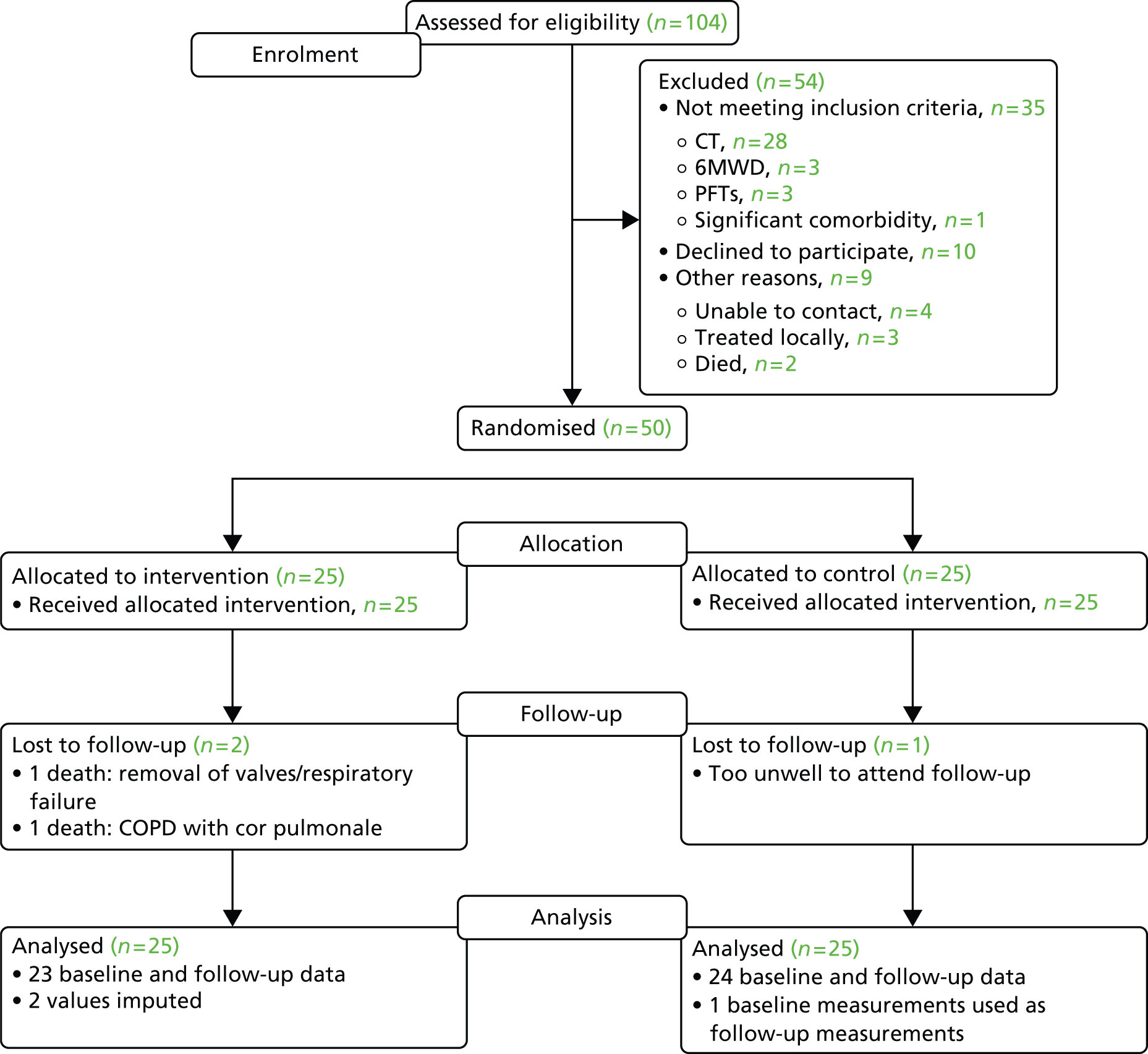
A Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) diagram describing flow through the study is provided in Figure 4. Two patients in the treatment arm died and one in the control arm was too unwell to attend for follow-up at 90 days (see later).
FIGURE 4.
Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) flow diagram. 6MWT, 6-minute walk distance; PFT, pulmonary function test.
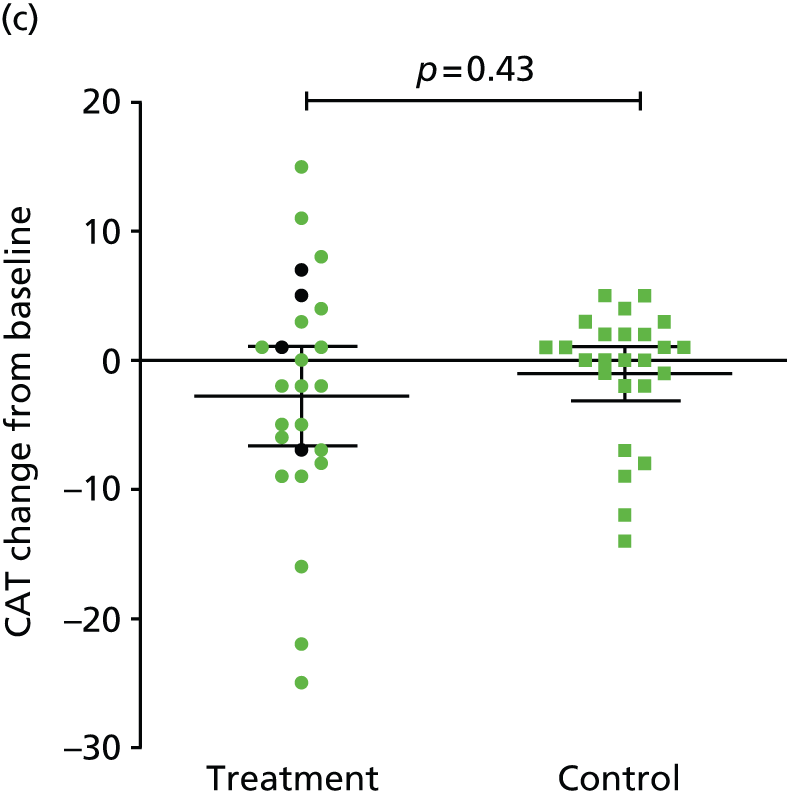
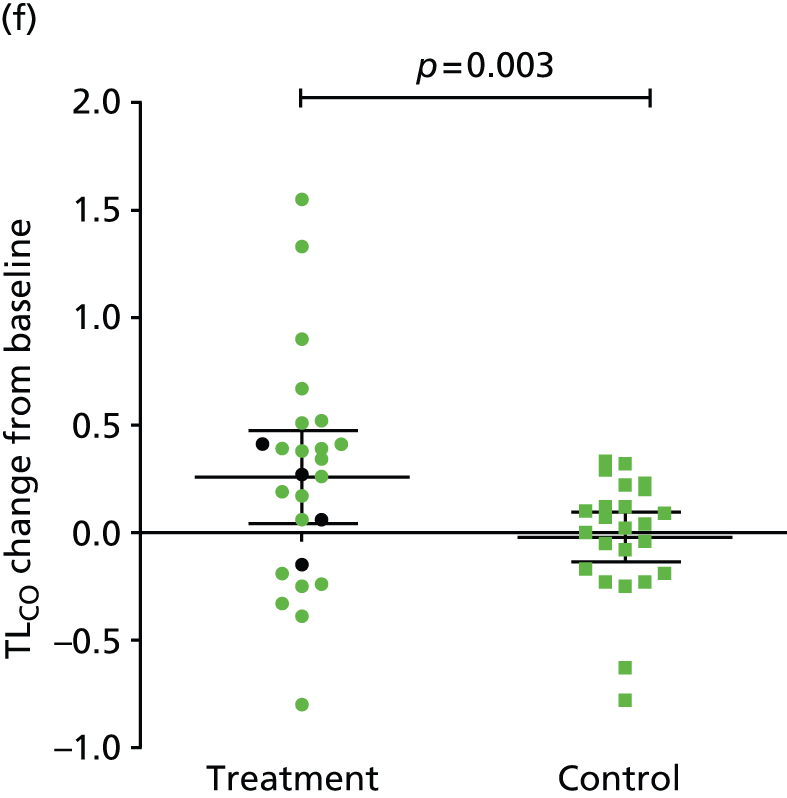
The primary end point of the study was met: FEV1 increased by 24.8% (95% CI 8.0% to 41.5%) from baseline in the treatment arm and by 3.9% (95% CI 0.7% to 7.1%) from baseline in the control arm, a between-group difference of 20.9% (95% CI 4.3% to 37.5%) (p = 0.033) (Table 2 and Figure 5). This was associated with improvements in lung volumes, gas transfer and exercise capacity. The comparative changes in gas transfer, RV and health status and exercise capacity are provided in Figure 6. No baseline parameter was associated with improvement in FEV1 (Table 3).
| Outcome | BLVR | Control | Between-group difference | p-valuea | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %ΔFEV1 | Mean (95% CI) | 24.77 (8.02 to 41.51) | 3.87 (0.66 to 7.08) | 20.89 (4.29 to 37.50) | 0.0326 |
| Median (IQR) | 8.77 (2.27 to 35.85) | 2.88 (0.00 to 8.51) | |||
| ΔFEV1 (l) | Mean (95% CI) | 0.18 (0.07 to 0.29) | 0.03 (0.00 to 0.52) | 0.16 (0.05 to 0.27) | 0.0273 |
| Median (IQR) | 0.06 (0.02 to 0.38) | 0.03 (0.00 to 0.06) | |||
| %ΔVC | Mean (95% CI) | 6.75 (0.13 to 13.36) | 1.42 (–3.43 to 6.27) | 5.37 (–2.66 to 13.31) | 0.1370 |
| Median (IQR) | 3.75 (–1.02 to 9.95) | 0.84 (–7.14 to 6.57) | |||
| ΔFEV1/VC | Mean (95% CI) | 14.80 (6.38 to 23.22) | 3.20 (–0.69 to 7.10) | 11.59 (2.56 to 20.63) | 0.0293 |
| Median (IQR) | 6.60 (2.61 to 23.04) | 0.75 (–4.96 to 9.52) | |||
| ΔTLC (l) | Mean (95% CI) | –0.35 (–0.57 to –0.13) | –0.12 (–0.24 to 0.00) | –0.24 (–0.36 to –0.11) | 0.0603 |
| Median (IQR) | –0.32 (–0.70 to 0.06) | –0.10 (–0.24 to 0.00) | |||
| ΔRV (l) | Mean (95% CI) | –0.50 (–0.82 to –0.18) | –0.13 (–0.28 to 0.02) | –0.37 (–0.72 to –0.03) | 0.0798 |
| Median (IQR) | –0.26 (–1.07 to 0.16) | –0.08 (–0.39 to 0.08) | |||
| ΔRV/TLC | Mean (95% CI) | –3.99 (–6.9 to –1.1) | –0.64 (–1.92 to 0.64) | –3.52 (–6.46 to –0.25) | 0.0715 |
| Median (IQR) | –3.95 (–8.32 to 0.66) | –1.20 (–2.46 to 1.28) | |||
| ΔFRC (l) | Mean (95% CI) | –0.47 (–0.86 to –0.08) | 0.12 (–0.15 to 0.19) | –0.59 (–0.90 to –0.08) | 0.0213 |
| Median (IQR) | –0.24 (–1.14 to 0.06) | 0.07 (–0.15 to 0.20) | |||
| ΔTLCO (mmol/minute/kPa) | Mean (95% CI) | 0.29 (0.10 to 0.49) | –0.06 (–0.19 to 0.07) | 0.35 (0.13 to 0.58) | 0.0029 |
| Median (IQR) | 0.30 (0.03 to 0.43) | 0.00 (–0.19 to 0.13) | |||
| ΔKCO (mmol/minute/kPa/l) | Mean (95% CI) | 0.05 (0.02 to 0.08) | 0.00 (–0.02 to 0.03) | 0.05 (0.01 to 0.09) | 0.0130 |
| Median (IQR) | 0.05 (0.01 to 0.11) | 0.01 (–0.03 to 0.06) | |||
| ΔMRC dyspnoea score | Mean (95% CI) | –0.52 (–0.95 to –0.09) | –0.50 (–0.81 to –0.19) | –0.02 (–0.49 to 0.53) | 0.4037 |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (–1 to 0) | 0 (–1 to 0) | |||
| ΔCAT (points) | Mean (95% CI) | –2.8 (–6.6 to 1.1) | –1.0 (–3.1 to 1.0) | –1.7 (–6.0 to 2.6) | 0.2269 |
| Median (IQR) | –2 (–7 to 3) | 0 (–2 to 2) | |||
| ΔSGRQc total (points) | Mean (95% CI) | –8.72 (–17.22 to –0.21) | –3.66 (–8.12 to 0.80) | –5.06 (–14.42 to 4.30) | 0.3454 |
| Median (IQR) | –4.4 (–16.93 to 6.76) | –3.57 (–7.67 to 2.55) | |||
| Δ6MWD (m) | Mean (95% CI) | 29 (0 to 58) | –4 (–27 to 19) | 33 (–3 to 69) | 0.0119 |
| Median (IQR) | 25 (7 to 64) | 3 (–14 to 20) | |||
FIGURE 5.
Change in FEV1 at 90 days in patients treated with endobronchial valves and control subjects who underwent sham treatment. Change in FEV1 was significantly greater in patients treated with endobronchial valves than in control subjects who underwent sham treatment (p = 0.0326). Bars are means and 95% CIs. Black symbols represent the four patients who had collateral ventilation detected using the Chartis system who were treated with endobronchial valves. Reproduced from © Davey et al. 54 Open Access article distributed under the terms of CC BY. Published by Elsevier Ltd.

FIGURE 6.
Exercise, lung function and health status responses in valve and control groups at 90 days. 6MWD, 6-minute walk distance. Black symbols indicate treated patients who had a positive Chartis measurement of collateral ventilation. p-values are for t-tests with robust variance. Error bars are means and 95% CIs.




| Factor | β (95% CI) | r 2 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| TLC% predicted | –0.0024 (–0.0065 to 0.0017) | 0.028 | 0.25 |
| RV% predicted | –0.0006 (–0.002 to 0.0008) | 0.015 | 0.40 |
| FRC% predicted | –0.0005 (–0.003 to 0.015) | 0.005 | 0.64 |
| TLCO% | 0.003 (–0.053 to 0.059) | 0.0002 | 0.92 |
| KCO% – TLCO% | –0.004 (–0.067 to 0.059) | 0.0003 | 0.90 |
| FEV1% predicted | –0.002 (–0.008 to 0.004) | 0.012 | 0.46 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | –0.0002 (–0.013 to 0.012) | 0.000 | 0.97 |
| Age (years) | 0.002 (–0.006 to 0.01) | 0.005 | 0.63 |
| Gender (male) | 0.001 (–0.109 to 0.136) | 0.001 | 0.83 |
Valve placement was associated with an improvement in Tlim (see Figure 6), accompanied by reductions in dynamic hyperinflation (Table 4). Improved Tlim was associated with improved FEV1 and reduced respiratory rate and breathlessness at isotime (Table 5). Although differences in health status measures between groups were of a similar magnitude to the MCID, they were not statistically significant (see Figure 6). The difference in 6-minute walk distance was also greater in the treatment group (see Figure 6).
| Parameter | BLVR | Control | p-valueb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tlim (seconds) | 139 (43 to 235) | –2 (–78 to 73) | 0.021 |
| Isotime | |||
| EELV (l) | –0.54 (–0.89 to –0.19) | –0.02 (–0.20 to 0.15) | 0.009 |
| IRV (l) | 0.10 (–0.05 to 0.25) | –0.08 (–0.23 to 0.07) | 0.095 |
| VE (l/minute) | 0.42 (–2.03 to 2.87) | 0.34 (–1.67 to 2.36) | 0.96 |
| RR (per minute) | –2.52 (–5.73 to 0.69) | 1.08 (–0.95 to 3.12) | 0.054 |
| Vt (ml) | 35.09 (28.61 to 41.56) | 28.18 (25.00 to 31.36) | 0.50 |
| Borg leg discomfort | –0.35 (–1.29 to 0.60) | 0.04 (–0.66 to 0.74) | 0.49 |
| Borg breathlessness | –0.46 (–1.50 to 0.59) | 0.33 (–0.56 to 1.23) | 0.24 |
| Peak | |||
| EELV (l) | –0.51 (–0.84 to –0.18) | –0.04 (–0.21 to 0.14) | 0.001 |
| IRV (l) | 0.09 (–0.04 to 0.21) | –0.07 (–0.20 to 0.07) | 0.096 |
| VE (l/minute) | 0.68 (–2.00 to 3.36) | 0.62 (–1.28 to 2.53) | 0.97 |
| RR (per minute) | –1.96 (–4.80 to 0.89) | 0.64 (–1.50 to 2.78) | 0.13 |
| Vt (ml) | 36.38 (29.96 to 42.79) | 29.29 (25.46 to 33.13) | 0.053 |
| Borg leg discomfort score | 0.02 (–0.93 to 0.97) | –0.44 (–1.01 to 0.13) | 0.38 |
| Borg dyspnoea score | 0.22 (–0.65 to 1.08) | –0.04 (–0.70 to 0.62) | 0.62 |
| Factor | Univariate regression | Multiple stepwise regression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95% CI) | r 2 | p-value | β (95% CI) | r 2 | p-value | |
| FEV1 (l) | 7.18 (2.29 to 12.07) | 0.60 | 0.005 | 3.24 (1.64 to 4.85) | 0.59 | < 0.0001 |
| VC (l) | 3.97 (1.03 to 6.90) | 0.60 | 0.009 | |||
| TLCO (mmol/minute/kPa) | 2.76 (0.88 to 4.64) | 0.57 | 0.005 | |||
| TLC (l) | –1.84 (–3.98 to 0.30) | 0.54 | 0.090 | |||
| RV (%) | –2.83 (–4.55 to –1.10) | 0.61 | 0.002 | |||
| IC (at rest) (l) | 4.32 (1.92 to 6.73) | 0.62 | 0.001 | |||
| EELV (isotime) (l) | –2.50 (–3.88 to –1.12) | 0.61 | 0.001 | |||
| IRV (isotime) (l) | 3.97 (0.63 to 7.32) | 0.57 | 0.021 | |||
| Vt (isotime) (ml) | 8.06 (1.43 to 14.68) | 0.60 | 0.018 | |||
| RR (isotime) (per minute) | –0.29 (–0.45 to –0.14) | 0.63 | < 0.0001 | –0.07 (–0.14 to –0.006) | 0.033 | |
| Borg dyspnoea score (isotime) | –0.69 (–1.08 to –0.30) | 0.58 | 0.001 | –0.26 (–0.49 to –0.02) | 0.032 | |
| Borg leg discomfort score (isotime) | –0.04 (–0.60 to 0.68) | 0.51 | 0.90 | |||
The numbers of patients achieving the MCID for lung function, health status and exercise are provided in Table 6, which shows that this was more likely to occur in the treatment arm than in the control arm. This confirms that when collateral ventilation was present the response to treatment was less.
| Parameter | BLVR, n (%) | Control (n = 24), n (%) | p-valuea | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 23) | CV+ve excluded (n = 19) | |||
| FEV1: > 15% improvement | 9 (39) | 1 (4) | 0.0044 | |
| 9 (47) | 1 (4) | 0.0022 | ||
| RV: > 0.35-l reduction49 | 11 (48) | 7 (29) | 0.2400 | |
| 11 (58) | 7 (29) | 0.0700 | ||
| 6MWD: > 26-m improvement53 | 12 (52) | 4 (17) | 0.0120 | |
| 12 (63) | 4 (17) | 0.0040 | ||
| Tlim: > 105-second improvement52 | 10 (43) | 2 (8) | 0.0080 | |
| 9 (47) | 2 (8) | 0.0050 | ||
| SGRQc: > 4-point reduction50 | 11 (48) | 11 (46) | 1.0000 | |
| 11 (58) | 11 (46) | 0.5000 | ||
| CAT: > 2-point reduction51 | 13 (57) | 7 (29) | 0.0800 | |
| 13 (68) | 7 (29) | 0.0150 | ||
In the treatment group eight patients were scored as having ‘complete collapse’ of the target lobe, five as having ‘a band of atelectasis’, two as having some volume loss and eight as showing no change. Individual patient responses in the treatment group are provided in Tables 7 and 8 together with target lobe and the presence or absence of collateral ventilation measured with the Chartis system.
| Patient number | Target lobe | Collateral ventilation | Atelectasis scorea | %ΔFEV1 | ΔRV (l) | Δ6MWD (m) | ΔSGRQc (points) | ΔTlim (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LUL | No | 2 | 24.3 | –0.43 | 78.0 | –51.1 | 25.0 |
| 2 | RUL | No | 3 | 77.2 | 0.08 | 10.0 | –10.4 | –56.0 |
| 5 | LUL | No | 3 | 51.9 | –1.42 | 149.0 | –50.9 | 570.0 |
| 12 | RUL | No | 0 | –20.5 | 0.16 | 75.0 | –4.4 | –104.0 |
| 13 | LUL | No | 1 | –3.0 | 0.51 | –225.0 | 11.8 | –61.0 |
| 19 | RUL | No | 3 | 8.8 | 0.25 | –3.0 | 7.3 | –48.0 |
| 25 | RUL | No | 0 | 6.6 | 0.08 | 64.0 | –6.1 | 11.0 |
| 28 | RUL | No | 3 | 9.0 | 0.19 | 95.0 | –14.1 | 668.0 |
| 29 | LUL | No | 2 | 37.7 | –0.19 | –36.0 | 5.0 | 36.0 |
| 38 | LLL | No | 3 | 147.2 | –1.54 | 55.0 | –8.1 | 546.0 |
| 41 | LUL | No | 3 | 35.8 | –1.07 | 60.0 | 6.8 | 42.0 |
| 43 | LUL | No | 3 | 102.4 | –0.15 | 30.0 | 10.4 | 180.0 |
| 44 | LUL | No | 1 | 0.0 | –0.26 | 7.0 | –3.2 | –59.0 |
| 46 | LUL | No | 3 | 25.5 | 0.34 | 9.0 | –2.5 | 158.0 |
| 49 | RUL | No | 0 | 6.5 | –1.85 | 135.0 | –35.3 | 182.0 |
| 20b | LUL | No | 2 | 9.4 | –1.81 | 5.0 | –18.9 | 273.0 |
| 21b | RUL | No | 0 | 4.1 | –0.24 | 94.0 | –49.7 | 338.0 |
| 35c | LUL | No | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 18c | RUL | NA | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 31 | LUL | NA | 0 | 5.6 | –0.65 | 29.0 | –4.9 | 304.0 |
| 7 | RUL | NA | 0 | 19.8 | –1.48 | 16.0 | –16.9 | 116.0 |
| 4 | RUL | Yes | 0 | –4.2 | 0.42 | 64.0 | 4.7 | –8.0 |
| 26 | LUL | Yes | 0 | 2.3 | –1.58 | 9.0 | –9.4 | 573.0 |
| 33 | LUL | Yes | 2 | 4.0 | 0.52 | 15.0 | 15.5 | –26.0 |
| 39 | LUL | Yes | 2 | –2.2 | –0.64 | –35.0 | 18.9 | –27.0 |
| Patient number | Target lobe | Collateral ventilation | %ΔFEV1 | Atelectasisa | Number of MCIDs reached | ΔFEV1 > 15% | ΔRV > 350 ml | Δ6MWD > 26 m | ΔSGRQc > 4 points | ΔTlim > 105 seconds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LUL | No | 24.3 | 2 | 2 | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| 2 | RUL | No | 77.2 | 3 | 5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 5 | LUL | No | 51.9 | 3 | 5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 12 | RUL | No | –20.5 | 0 | 0 | No | No | No | No | No |
| 13 | LUL | No | –3.0 | 1 | 0 | No | No | No | No | No |
| 19 | RUL | No | 8.8 | 3 | 3 | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 25 | RUL | No | 6.6 | 0 | 0 | No | No | No | No | No |
| 28 | RUL | No | 9.0 | 3 | 4 | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 29 | LUL | No | 37.7 | 2 | 3 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 38 | LLL | No | 147.2 | 3 | 5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 41 | LUL | No | 35.8 | 3 | 4 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| 43 | LUL | No | 102.4 | 3 | 4 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| 44 | LUL | No | 0.0 | 1 | 0 | No | No | No | No | No |
| 46 | LUL | No | 25.5 | 3 | 2 | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| 49 | RUL | No | 6.5 | 0 | 4 | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 20b | LUL | No | 9.4 | 2 | 2 | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| 21b | RUL | No | 4.1 | 0 | 3 | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 35c | LUL | No | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 18c | RUL | NA | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 31 | LUL | NA | 5.6 | 0 | 2 | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| 7 | RUL | NA | 19.8 | 0 | 3 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| 4 | RUL | Yes | –4.2 | 0 | 1 | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| 26 | LUL | Yes | 2.3 | 0 | 2 | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| 33 | LUL | Yes | 4.0 | 2 | 0 | No | No | No | No | No |
| 39 | LUL | Yes | –2.2 | 2 | 1 | No | No | Yes | No | No |
Imputation of values for missing patients was prespecified for the analysis. However, if the three patients in whom 90-day data were unavailable are excluded, the difference in FEV1 response was still significant [treatment group: mean +23.8% (SD 38.7%) (95% CI 7.10% to 40.57%) vs. control: mean 4.0% (SD 7.9%) (95% CI 0.70% to 7.37%); between-group difference 19.8% (p = 0.018)].
Adverse events
Adverse events are outlined in Table 9. There were two deaths in the treatment arm before 90 days. One patient developed a troublesome cough and a decision was taken to remove his valves 49 days after they had been placed. At the time of removal a tension pneumothorax developed with an ongoing significant air leak. He progressed to respiratory failure, dying 17 days later despite intensive care treatment including endotracheal tube intubation and use of a Novalung device (Novalung® GmbH, Heilbronn, Germany). The second patient died suddenly 3 days after valve placement. At post mortem there was no evidence of pneumonia or pneumothorax and a diagnosis of death from COPD with cor pulmonale was made.
| Adverse event | BLVR (n = 25) | Control (n = 25) | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events | Patients | Events | Patients | ||
| Exacerbation (total) | 23 | 22 | 0.42 | ||
| 16 | 20 | 0.35 | |||
| Requiring hospitalisation | 5 | 3 | 0.70 | ||
| Pneumonia (respiratory tract infection with radiographic changes) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.49 |
| Pneumothorax | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 |
| Death | 2 | 0 | 0.49 | ||
| Respiratory failure | 1 | 0 | 1.00 | ||
| COPD with cor pulmonale | 1 | 0 | 1.00 | ||
| Expectorated valve | 5 | 4 | – | – | NA |
| Removal of valves | 2 | 2 | – | – | NA |
| Seizure (unrelated) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 |
One patient in the control group was too unwell to attend for follow-up because of a spontaneous pneumothorax with prolonged air leak, with onset 66 days after his sham bronchoscopy. In addition, two patients in the treatment arm had pneumothoraces, which both responded to intercostal tube drainage, one at 3 and one at 12 days post procedure.
Four patients expectorated a valve before 3 months. These were replaced in three out of four individuals before their follow-up visit. The patients were instructed not to inform the assessment team of these additional procedures.
In one patient the valve was removed because the patient felt more breathless and had an externally audible wheeze. This was because of a high degree of collateral ventilation and continuing expiratory airflow through the valve. Removal was uneventful.
Chapter 4 Discussion
The main finding of this trial is that placement of endobronchial valves in patients with severe COPD who have heterogeneous emphysema and intact interlobar fissures on CT scan produces statistically and clinically significant improvements in lung function. There is a risk of pneumothorax associated with the intervention, which needs to be considered when selecting patients.
Significance of the findings
The data suggest that, in appropriately selected patients, endobronchial valve placement results in improvements in lung function that are of a similar order of magnitude to those that have been seen with LVRS. 1,2,4 This prospective study confirms the retrospective analysis of the VENT trial. 17 When collateral ventilation is absent, lobar atelectasis is more likely to occur, which is a key determinant of effectiveness associated with improved lung function response6,17 and survival. 14
There is a significant overlap between the indications for BLVR and those for LVRS and it may be that a stepwise approach with bronchoscopic techniques considered at an earlier stage to defer, prevent or act as a bridge to LVRS is required. Alternatively, it may be that LVRS is the definitive treatment that should be offered earlier. Prospective trials comparing LVRS and valve placement will be needed to clarify this.
The scale of potential valve treatment remains to be established. It has been estimated that about 16,000 COPD patients in the UK may be eligible for LVRS and, given the powerful evidence base, the lack of a systematic approach to this is a failure of the UK and other health systems. 4,55,56 There are so far no reliable data on the proportion of patients who have intact interlobar fissures and who would therefore be suitable for BLVR, but it is likely that several thousand UK patients could benefit.
Safety
In part, bronchoscopic treatment for emphysema has been developed for people considered to be too disabled to withstand LVRS, but caution is needed given the pneumothorax risk. Pneumothorax can occur when valve placement leads to a change in the conformation of the lung, producing tears in the lung parenchyma. Pneumothorax is therefore, to an extent, a marker of effective lobar occlusion. As such, better patient selection will mean an increase in the pneumothorax rate to levels much higher than in trials to date, in which patient selection has been poor. In the present study it occurred in two treated patients (8%) and there was also one spontaneous pneumothorax in a control patient (4%). The management of pneumothorax in this context is conventional, usually with intercostal tube drainage. It is therefore important that patients are selected who are considered likely to be able to withstand the associated acute lung function impairment a pneumothorax will cause. It is likely that the pneumothorax rate in properly selected patients will be between 10% and 20%. Our clinical practice is now to allow an inpatient stay of 3 nights after valve placement, although later pneumothorax can also occur. 6
One death occurred as a result of valve removal, indicated because of a troublesome cough. An important learning point is to limit the force used to try to extract valves and to have a low threshold for abandoning a flexible bronchoscopy approach and converting to a rigid bronchoscopy. This is in general carried out by a thoracic surgeon and highlights the need for collaboration within an integrated team. The other death was not obviously mechanistically linked to valve placement and may have been coincidental (as was the pneumothorax in the control patient), although it occurred only a few days after valve placement. It remains to be established what the ‘true’ mortality rate is and it is important to resist extrapolating from a relatively small series. By analogy, we described a zero surgical mortality rate in our experience with unilateral VATS LVRS between 2000 and 2012. 4 It would, however, be absurd to suggest that the ‘true’ mortality rate for LVRS is zero.
Exacerbations have been described previously as a complication of valve placement and early after placement a degree of irritation causing an ‘exacerbation-like’ pattern of symptoms can occur. 6,10,17,26 In the present study, exacerbations occurred in the majority of patients, reflecting the severity of the population, but there was no significant difference in the occurrence of exacerbations between the two study arms.
Although the success rate of valve placement was higher than in previous studies because of the inclusion of only patients with intact interlobar fissures, the presence of collateral ventilation assessed using the Chartis system was associated with no benefit from treatment. The ideal strategy for selecting patients in whom lobar exclusion can be achieved remains to be defined and will remain unclear as refinements in technology and CT scoring of fissure integrity evolve. Direct measurement with the Chartis system is not always possible for technical reasons (approximately 10%) and in other studies it has been assessed as 75% accurate. 57 It adds cost and time to procedures and this will need to be weighed against the likely increase in the responder rate. The positive and negative predictive power of collateral ventilation measured with the Chartis system will vary depending on the CT criteria used in the initial selection strategy. In addition, in some patients ideal positioning of the valves is not possible because of patient anatomy, for example insufficient length of bronchus to place the valve adequately, leading to early expectoration, or difficult access to a particular segment, which may impact on the effectiveness of valves as a treatment strategy.
Methodological issues
A strength of the study was the blinding of patients and assessors. The presence of a sham bronchoscopy procedure meant that a more confident estimate could be made of changes in health status, which have often been large in unblinded studies, even in the absence of significant changes in lung function. 26 The assessment of collateral ventilation in all participants using the Chartis system meant that control subjects also underwent a ‘procedure’, which helped to maintain the blinding. Although subjects in whom a pneumothorax occurred or who expectorated a valve were unblinded, valves are difficult to visualise on chest radiographs and this maintained blinding of physicians and patients alike if they underwent investigations for a clinical deterioration in the absence of a pneumothorax.
Follow-up was for a short period as the purpose of the study was to test the hypothesis that a responder phenotype could be prospectively identified. Previous data have shown that a response to treatment is associated with improved survival in the longer term14 but there has been a need to produce a response rate with treatment that justifies the upfront cost of the procedure. The cohort will be followed up longer term although following the end of the trial patients will be offered the opportunity to have open-label valves or LVRS.
Chapter 5 Conclusion and future work
The present study demonstrates that, in patients with heterogeneous emphysema and intact interlobar fissures, endobronchial valve placement is effective in improving lung function to a clinically significant extent. However, this is not without risks, including, in particular, the possibility of pneumothorax. Clinicians and patients considering BLVR need to be aware that the procedure carries a risk of death. Given the need for careful selection of patients it will be important for this, and other lung volume reduction techniques, to be delivered in the context of a multidisciplinary team able to offer a range of approaches. 4,56
Further work is needed to establish how this technique should best be deployed relative to LVRS2,4 and other developing techniques such as lung volume reduction coils30 and bronchoscopic thermal vapour ablation. 58 Specifically, a randomised controlled trial of valve placement compared with unilateral VATS LVRS is needed. This will need to take a pragmatic approach to allow for adjustments and replacements of valves, thus reproducing real clinical practice rather than simply comparing a single event – valve placement or surgery. It will also need to be of sufficient duration to balance the early complications related to LVRS against possible longer-term relative benefits in terms of lung function, exercise capacity and health status as well as relative safety and survival benefits.
Patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency have tended to be excluded from trials and it is not yet known whether or not the typical lower lobe pattern of emphysema seen in this group of patients will benefit from BLVR. LVRS has not generally been beneficial in patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and so a trial of endobronchial valves in this specific patient group is needed.
Acknowledgements
Our thanks to members of the Data Monitoring Committee: Michael Roughton (Chairperson), Statistician, Rsquared Statistics Ltd, Bromley, Kent; Dr Tudor P Toma, Lewisham Hospital; Professor Emma Baker, St George’s Hospital; and Dr Philip Ind, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust.
Contribution of authors
Zaid Zoumot, William H McNulty and Pallav L Shah performed the procedures.
Claire Davey performed the assessments.
Simon Jordan, David M Hansell, Michael I Polkey, Pallav L Shah and Nicholas S Hopkinson developed the study.
Denis H Carr, Simon Jordan, Matthew D Hind, Michael B Rubens, Michael I Polkey and Nicholas S Hopkinson were involved in patient selection.
Winston Banya with Nicholas S Hopkinson and Claire Davey developed the statistical analysis plan and performed the analyses.
Zaid Zoumot, Claire Davey and Nicholas S Hopkinson, prepared the first draft of this paper, which all authors subsequently contributed to and approved.
Nicholas S Hopkinson is the guarantor.
Publication
Davey C, Zoumot Z, Jordan S, McNulty WH, Carr DH, Hind MD, et al. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction with endobronchial valves for patients with heterogeneous emphysema and intact interlobar fissures (the BeLieVeR-HIFi study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015;386:1066–73.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research. The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, MRC, NETSCC, the EME programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the EME programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Geddes D, Davies M, Koyama H, Hansell D, Pastorino U, Pepper J, et al. Effect of lung-volume-reduction surgery in patients with severe emphysema. N Engl J Med 2000;343:239-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200007273430402.
- National Emphysema Treatment Trial Research Group . A randomized trial comparing lung-volume-reduction surgery with medical therapy for severe emphysema. N Engl J Med 2003;348:2059-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa030287.
- Ferguson GT, Fernandez E, Zamora MR, Pomerantz M, Buchholz J, Make BJ. Improved exercise performance following lung volume reduction surgery for emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;157:1195-203. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.157.4.9705008.
- Clark SJ, Zoumot Z, Bamsey O, Polkey MI, Dusmet M, Lim E, et al. Surgical approaches for lung volume reduction in emphysema. Clin Med 2014;14:122-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.14-2-122.
- Hopkinson NS. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction: indications, effects and prospects. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2007;13:125-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MCP.0b013e328012e053.
- Hopkinson NS, Toma TP, Hansell DM, Goldstraw P, Moxham J, Geddes DM, et al. Effect of bronchoscopic lung volume reduction on dynamic hyperinflation and exercise in emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005;171:453-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200407-961OC.
- Toma TP, Hopkinson NS, Hillier J, Hansell DM, Morgan C, Goldstraw PG, et al. Bronchoscopic volume reduction with valve implants in patients with severe emphysema. Lancet 2003;361:931-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12762-6.
- Snell GI, Holsworth L, Borrill ZL, Thomson KR, Kalff V, Smith JA, et al. The potential for bronchoscopic lung volume reduction using bronchial prostheses: a pilot study. Chest 2003;124:1073-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.124.3.1073.
- Yim AP, Hwong TM, Lee TW, Li WW, Lam S, Yeung TK, et al. Early results of endoscopic lung volume reduction for emphysema. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004;127:1564-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.10.005.
- Wan IY, Toma TP, Geddes DM, Snell G, Williams T, Venuta F, et al. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction for end-stage emphysema: report on the first 98 patients. Chest 2006;129:518-26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.129.3.518.
- Venuta F, de Giacomo T, Rendina EA, Ciccone AM, Diso D, Perrone A, et al. Bronchoscopic lung-volume reduction with one-way valves in patients with heterogenous emphysema. Ann Thorac Surg 2005;79:411-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.07.048.
- de Oliveira HG, Macedo-Neto AV, John AB, Jungblut S, Prolla JC, Menna-Barreto SS, et al. Transbronchoscopic pulmonary emphysema treatment: 1-month to 24-month endoscopic follow-up. Chest 2006;130:190-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.130.1.190.
- Wood DE, McKenna RJ, Yusen RD, Sterman DH, Ost DE, Springmeyer SC, et al. A multicenter trial of an intrabronchial valve for treatment of severe emphysema. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;133:65-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.06.051.
- Hopkinson NS, Kemp SV, Toma TP, Hansell DM, Geddes DM, Shah PL, et al. Atelectasis and survival after bronchoscopic lung volume reduction for COPD. Eur Respir J 2011;37:1346-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00100110.
- Davey C, Zoumot Z, Jordan S, Carr DH, Polkey MI, Shah PL, et al. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction with endobronchial valves for patients with heterogeneous emphysema and intact interlobar fissures (the BeLieVeR-HIFi trial): study design and rationale. Thorax 2015;70:288-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205127.
- Davey C, Zoumot Z, Jordan S, McNulty WH, Carr DH, Hind MD, et al. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction with endobronchial valves for patients with heterogeneous emphysema and intact interlobar fissures (The BeLieVeR-HIFi study) – a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015.
- Sciurba FC, Ernst A, Herth FJ, Strange C, Criner GJ, Marquette CH, et al. A randomized study of endobronchial valves for advanced emphysema. N Engl J Med 2010;363:1233-44. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0900928.
- Aljuri N, Freitag L. Validation and pilot clinical study of a new bronchoscopic method to measure collateral ventilation before endobronchial lung volume reduction. J Appl Physiol 2009;106:774-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.91075.2008.
- Fessler H, Scharf S, Permutt S. Improvement in spirometry following lung volume reduction surgery. application of a physiologic model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:34-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.165.1.2101149.
- Naunheim KS, Wood DE, Mohsenifar Z, Sternberg AL, Criner GJ, DeCamp MM, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients receiving lung-volume-reduction surgery versus medical therapy for severe emphysema by the National Emphysema Treatment Trial Research Group. Ann Thorac Surg 2006;82:431-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2006.05.069.
- Criner GJ, Cordova F, Sternberg AL, Martinez FJ. The NETT part II: lessons learned about lung volume reduction surgery. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011;184:881-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201103-0455CI.
- Celli BR, MacNee W. ATS/ERS Task Force . Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD: a summary of the ATS/ERS position paper. Eur Respir J 2004;23:932-46. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.04.00014304.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Adults in Primary and Secondary Care (Partial Update). London: NICE; 2010.
- Lim E, Ali A, Cartwright N, Sousa I, Chetwynd A, Polkey M, et al. Effect and duration of lung volume reduction surgery: mid-term results of the Brompton trial. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;54:188-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-872953.
- Springmeyer SC, Bolliger CT, Waddell TK, Gonzalez X, Wood DE. Treatment of heterogeneous emphysema using the spiration IBV valves. Thorac Surg Clin 2009;19:247-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.thorsurg.2009.02.005.
- Ninane V, Geltner C, Bezzi M, Foccoli P, Gottlieb J, Welte T, et al. Multicentre European study for the treatment of advanced emphysema with bronchial valves. Eur Respir J 2012;39:1319-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00019711.
- Herth FJ, Gompelmann D, Stanzel F, Bonnet R, Behr J, Schmidt B, et al. Treatment of advanced emphysema with emphysematous lung sealant (AeriSeal®). Respiration 2011;82:36-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000322649.
- Eberhardt R, Schmidt B, Ernst A, Ficker J, Snell GI, Herth FJ. Germany pilot safety and feasibility study of bronchoscopic thermal vapor ablation (BTVA) for lung volume reduction in patients with heterogeneous emphysema with upper lobe predominance. Chest 2009;136. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.136.4_MeetingAbstracts.78S.
- Kanoh S, Kobayashi H, Motoyoshi K. Intrabullous blood injection for lung volume reduction. Thorax 2008;63:564-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thx.2007.087957.
- Shah PL, Zoumot Z, Singh S, Bicknell SR, Ross ET, Quiring J, et al. RESET trial Study Group . Endobronchial coils for the treatment of severe emphysema with hyperinflation (RESET): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med 2013;1:233-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70047-X.
- Herth FJ, Eberhard R, Gompelmann D, Slebos DJ, Ernst A. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction with a dedicated coil: a clinical pilot study. Ther Adv Respir Dis 2010;4:225-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1753465810368553.
- Deslee G, Klooster K, Hetzel M, Stanzel F, Kessler R, Marquette C, et al. Lung volume reduction coil treatment for patients with severe emphysema: a European multicentre trial. Thorax 2014;69:980-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205221.
- Slebos DJ, Klooster K, Ernst A, Herth FJ, Kerstjens HAM. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction coil treatment of patients with severe heterogeneous emphysema. Chest 2012;142:574-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-0730.
- Klooster K, Ten Hacken NH, Slebos DJ. The lung volume reduction coil for the treatment of emphysema: a new therapy in development. Expert Rev Med Devices 2014;11:481-9.
- Zoumot Z, Kemp SV, Singh S, Bicknell SR, McNulty WH, Hopkinson NS, et al. Endobronchial coils for severe emphysema are effective up to 12 months following treatment: medium term and cross-over results from a randomised controlled trial. PLOS ONE 2015;10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122656.
- Lausberg HF, Chino K, Patterson GA, Meyers BF, Toeniskoetter PD, Cooper JD. Bronchial fenestration improves expiratory flow in emphysematous human lungs. Ann Thorac Surg 2003;75:393-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0003-4975(02)04553-8.
- Shah PL, Slebos DJ, Cardoso PF, Cetti E, Voelker K, Levine B, et al. Bronchoscopic lung-volume reduction with Exhale airway stents for emphysema (EASE trial): randomised, sham-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet 2011;378:997-1005. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61050-7.
- Venn GE, Williams PR, Goldstraw P. Intracavity drainage for bullous, emphysematous lung disease: experience with the Brompton technique. Thorax 1988;43:998-1002. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thx.43.12.998.
- Moore AJ, Cetti E, Haj-Yahia S, . Unilateral extrapulmonary airway bypass in advanced emphysema. Ann Thorac Surg 2010;89:899-906. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.10.067.
- Boutou AK, Shrikrishna D, Tanner RJ, Smith C, Kelly JL, Ward SP, et al. Lung function indices for predicting mortality in COPD. Eur Respir J 2013;42:616-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00146012.
- Quanjer PH, Tammeling GJ, Cotes JE, Pedersen OF, Peslin R, Yernault JC. Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Report Working Party Standardization of Lung Function Tests, European Community for Steel and Coal. Official Statement of the European Respiratory Society. Eur Respir J Suppl n.d.;16:5-40.
- Clark EH, Woods RL, Hughes JM. Effect of blood transfusion on the carbon monoxide transfer factor of the lung in man. Clin Sci Mol Med 1978;54:627-31.
- American Thoracic Society . ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;166:111-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.166.1.at1102.
- Jones PW, Harding G, Berry P, Wiklund I, Chen WH, Kline Leidy N. Development and first validation of the COPD Assessment Test. Eur Respir J 2009;34:648-54. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00102509.
- Dodd JW, Hogg L, Nolan J, Jefford H, Grant A, Lord VM, et al. The COPD Assessment Test (CAT): response to pulmonary rehabilitation. A multicentre, prospective study. Thorax 2011;66:425-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thx.2010.156372.
- Kelly JL, Bamsey O, Smith C, Lord VM, Shrikrishna D, Jones PW, et al. Health status assessment in routine clinical practice: the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease assessment test score in outpatients. Respiration 2012;84:193-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000336549.
- Meguro M, Barley EA, Spencer S, Jones PW. Development and validation of an improved, COPD-specific version of the St George’s respiratory questionnaire. Chest 2007;132:456-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.06-0702.
- Shah PL, Herth FJ. Current status of bronchoscopic lung volume reduction with endobronchial valves. Thorax 2014;69:280-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-203743.
- Hartman JE, Ten Hacken NH, Klooster K, Boezen HM, de Greef MH, Slebos DJ. The minimal important difference for residual volume in patients with severe emphysema. Eur Respir J 2012;40:1137-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00219111.
- Schünemann HJ, Griffith L, Jaeschke R, Goldstein R, Stubbing D, Guyatt GH. Evaluation of the minimal important difference for the feeling thermometer and the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire in patients with chronic airflow obstruction. J Clin Epidemiol 2003;56:1170-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0895-4356(03)00115-X.
- Kon SS, Canavan JL, Jones SE, Nolan CM, Clark AL, Dickson MJ, et al. Minimum clinically important difference for the COPD Assessment Test: a prospective analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2014;2:195-203. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70001-3.
- Casaburi R. Factors determining constant work rate exercise tolerance in COPD and their role in dictating the minimal clinically important difference in response to interventions. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2005;2:131-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1081/COPD-200050576.
- Puhan MA, Chandra D, Mosenifar Z, Ries A, Make B, Hansel NN, et al. The minimal important difference of exercise tests in severe COPD. Eur Respir J 2011;37:784-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00063810.
- Davey C, Zoumot Z, Jordan S, McNulty WH, Carr DH, Hind MD, et al. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction with endobronchial valves for patients with heterogeneous emphysema and intact interlobar fissures (the BeLieVeR-HIFi study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015;386:1066-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60001-0.
- McNulty W, Jordan S, Hopkinson NS. Attitudes and access to lung volume reduction surgery for COPD: a survey by the British Thoracic Society. BMJ Open Respir Res 2014;1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000023.
- Zoumot Z, Jordan S, Hopkinson NS. Emphysema: time to say farewell to therapeutic nihilism. Thorax 2014;69:973-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205667.
- Herth FJ, Eberhardt R, Gompelmann D, Ficker JH, Wagner M, Ek L, et al. Radiological and clinical outcomes of using Chartis™ to plan endobronchial valve treatment. Eur Respir J 2013;41:302-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00015312.
- Emery MJ, Eveland RL, Eveland K, Couetil LL, Hildebrandt J, Swenson ER. Lung volume reduction by bronchoscopic administration of steam. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;182:1282-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201001-0102OC.
List of abbreviations
- BLVR
- bronchoscopic lung volume reduction
- CAT
- COPD Assessment Test
- CI
- confidence interval
- COPD
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CT
- computerised tomography
- EELV
- end-expiratory lung volume
- FEV1
- forced expiratory volume in 1 second
- FRC
- functional residual capacity
- GOLD
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
- IC
- inspiratory capacity
- ICTU
- Imperial Clinical Trials Unit
- IQR
- interquartile range
- LVRS
- lung volume reduction surgery
- MCID
- minimum clinically important difference
- MRC
- Medical Research Council
- NETT
- National Emphysema Treatment Trial
- PaO2
- arterial oxygen tension
- RV
- residual volume
- SD
- standard deviation
- SGRQc
- St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- TLC
- total lung capacity
- TLCO
- carbon monoxide transfer factor
- Tlim
- endurance time on cycle ergometry
- VATS
- video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery
- VENT
- Endobronchial Valve for Emphysema Palliation Trial