Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the EME programme as project number 11/117/07. The contractual start date was in November 2014. The final report began editorial review in December 2018 and was accepted for publication in June 2019. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The EME editors and production house have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the final report document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Arshad Majid reports grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation and grants from NIHR Sheffield Biomedical Research Centre during the conduct of the study. Rainer Hinz reports grants and non-financial support from GE Healthcare (Chicago, IL, USA) during the conduct of the study; and grants from the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) outside the submitted work. Karl Herholz reports non-financial support from GE Healthcare and grants from the European Commission during the conduct of the study; and grants from the Medical Research Council and GlaxoSmithKline (Brentford, UK) outside the submitted work.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2020. This work was produced by Visi et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2020 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Stroke is the third most common cause of disability in the developed world and the second leading cause of death worldwide. 1 According to the Stroke Association (London, UK), stroke is responsible for > 100,000 hospital admissions per year in the UK and the annual cost to UK society is around £26B.
Acute ischaemic stroke is typically caused by a cerebral artery occlusion because of local thrombosis or thromboembolism from a remote source. Duration and severity of the diminished cerebral blood flow are the major factors that determine the degree of the ischaemic injury. Hence, prompt reperfusion therapy using either systemic thrombolysis or endovascular mechanical thrombectomy is the mainstay of acute treatment. However, given the narrow therapeutic window, only a minority of patients are eligible and can benefit from these procedures.
Experimental and clinical studies have demonstrated the complex role of the immune system in the molecular, cellular and tissue changes that occur after acute ischaemic stroke from the early to the late phases. 2 Thus, targeting neuroinflammation became a potential novel therapeutic strategy. The broader therapeutic window could enable a wide range of patients (relative to the reperfusion procedures) to receive anti-inflammatory agents, but it might also increase the rate of systemic infectious complications. 3 Another potential pitfall can result from the complex character of the inflammatory process. Often referred to as ‘the double-edged sword’, neuroinflammation can contribute to tissue damage but also promote repair in the subacute and chronic phase. 2,4 Therefore, understanding the correlation between the grade and extent of neuroinflammation and the functional outcome could help to establish the optimum timing and monitor the anti-inflammatory treatment.
Microglia are the major resident immune cells of the brain. Activated microglia respond to pathogens and neuronal damage and then play a crucial role in mediating the inflammatory response in the brain. 5 Hence, microglial activation is a hallmark of neuroinflammation. The 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) is expressed within activated microglia, infiltrating macrophages, astrocytes and endothelial cells. Although macrophage infiltration is high in acute stroke, in the subacute phase microglia are the predominant TSPO-expressing cell type. 6 Thus, TSPO imaging by positron emission tomography (PET) has been considered an in vivo marker of activated microglia levels in the brain. 7
The first-generation TSPO ligand radiotracer 11C-labelled PK11195 has been successfully used to image activated microglia in several neurological disorders, including ischaemic stroke. 8–11 However, its short physical half-life (20 minutes) makes it impractical for routine clinical application. In contrast, 18F-labelled radiopharmaceuticals have a longer half-life, enabling transport from production to clinical sites to occur. Therefore, they can potentially be applied as diagnostic tools in routine clinical settings.
We therefore studied microglial activation in the human brain using [18F]-GE180 PET in patients after mild to moderate stroke. In the pilot study we evaluated safety, tolerability and technical feasibility by intraindividual comparison with [11C]-(R)-PK11195 and assessing the effect of the genotype on the binding. [18F]-GE180 binds with high specificity to TSPO12 but, similar to second-generation TSPO ligand tracers, affinity is influenced by a genetic polymorphism (Ala147Thr) on the TSPO gene (rs6971). 13 High-affinity binders (HABs) and low-affinity binders (LABs) express a single binding site for TSPO with either high or low affinity, respectively, whereas mixed-affinity binders (MABs) express approximately equal numbers of the HAB and LAB-binding sites. 14 The highest specific binding of [18F]-GE180 is expected in HABs, lower but still detectable binding is expected in MABs, and negligible binding is expected in LABs. If successful, this pilot study was intended to be followed by a second phase to assess the correlation between the imaging finding and clinical outcome in a larger patient sample.
Chapter 2 Patients
Eligible patients were identified and consented by Greater Manchester hospitals stroke services. Clinical assessment was performed at the screening visit 4–28 days (median 12 days) after stroke onset and the 3-month follow-up visit was 85–130 days (median 94.5 days) after stroke onset.
A total of 10 participants (eight male and two female) (aged 24–89 years, median 68 years) with ischaemic stroke of mild to moderate (modified Rankin scale score of 2–3, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score of 0–3) severity in middle cerebral artery territory were scanned. Two of these patients had received intravenous thrombolysis treatment with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Table 1 shows the demographic and clinical details.
| Participant | Age (year) | Gender | Thrombolysis | Clinical symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P002 | 68 | Male | No | L hemianopsia, L inattention, L hemiparesis |
| P005 | 86 | Male | No | R facial droop, dysarthria, mild expressive dysphasia |
| P006 | 89 | Male | No | Confusion/speech difficulty/impaired recall of events |
| P008 | 53 | Male | No | R hemiparesis and sensory loss |
| P009 | 24 | Male | No | L upper limb sensory loss, mild expressive dysphasia |
| P010 | 81 | Male | No | L hemiataxia, L sensory loss, dysarthria, |
| P011 | 68 | Female | No | Expressive dysphasia |
| P012 | 65 | Male | Yes | Expressive dysphasia, R hemianopsia |
| P014 | 70 | Male | Yes | R hemiparesis |
| P015 | 63 | Female | No | R hemiparesis, R inattention, R paraesthesia, dysarthria |
The 3-month follow-up data were collected from eight participants; two participants were lost to follow-up (Table 2).
| Participant | Modified Rankin scale score | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre stroke | Screening | 3-month follow-up | Admission | Screening | 3-month follow-up | |
| P002 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 17 | 3 | 1 |
| P005 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| P006 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| P008 | 0 | 3 | n/a | 3 | 1 | n/a |
| P009 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| P010 | 1 | 2 | 2 | Missing | 0 | 1 |
| P011 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| P012 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| P014 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 0 |
| P015 | 0 | 2 | n/a | 6 | 1 | n/a |
Chapter 3 Methods
Scanning sessions
All of the participants were scanned at the Wolfson Molecular Imaging Centre 18 to 63 days (median 34.5 days) after their stroke. The participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Philips 1.5 T; Philips, Amsterdam, the Netherlands) and PET (Siemens HRRT; Siemens, Munich, Germany) scanning using [18F]-GE180 and [11C]-(R)-PK11195 tracers.
The two PET scans were performed on two separate sessions as close to each other as possible (mean 3.4 days) but at least 1 day apart. Five participants were randomised to receive the [11C]-(R)-PK11195 at the first session (arm A) and five participants were randomised to receive the [18F]-GE180 scan at the first session (arm B).
The MRI scan was performed either during session 1 (nine participants) or during session 2 (one participant). Eight participants completed T1 inversion recovery, T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) and post-contrast-enhanced T1 sequence. Two participants completed the non-contrast sequences only because of safety reasons (allergy or impaired renal function).
Positron emission tomography image processing and analysis
The volume of interest (VOI) of ischaemic lesions (target) were defined manually using ANALYZE software (Overland Park, KS, USA) on co-registered T2-weighted FLAIR magnetic resonance (MR) scans, separately for contrast-enhancing and non-contrast-enhancing areas on co-registered T1-weighted MR scans. Contralateral mirror VOIs were then drawn manually as a reference.
A set of standard anatomical VOIs was placed on the individual PET images by warping the 83-region probabilistic brain atlas15 from template space. Using the segmented T1-weighted MR scans, a set of standard grey matter anatomical VOIs was obtained, including left and right cerebellum.
The [11C]-(R)-PK11195 PET data were acquired for 60 minutes following the administration of a 740-MBq activity intravenous bolus. Parametric maps of binding potentials were generated with the simplified reference tissue model using a bilateral grey matter cerebellar reference tissue input function. 16,17 For better comparability with the [18F]-GE180 data, [11C]-(R)-PK11195 binding potentials were converted into [11C]-(R)-PK11195 distribution volume ratios by adding the value of 1. 18
The [18F]-GE180 PET data were acquired for 30 minutes following the administration of a 200-MBq activity intravenous bolus. This short measurement time is not sufficient to calculate binding potentials. Instead, two summed images were calculated: (1) a late summed image 15–30 minutes post injection; and (2) an early summed image 0–5 minutes post injection, representing predominantly vascular activity. As shown in a previous study,13 the signal from intravascular activity of [18F]-GE180 remains very high during the scanning time. In addition to tissue activity without correction obtained from the late summed images, we estimated intravascular activity from the early summed images and then calculated tissue activity corrected for intravascular activity by subtracting the estimated intravascular activity from the late summed images.
Target-to-reference ratios (TRRs) of [18F]-GE180 were then calculated from the readouts of the late summed images without or with correction for vascular activity. TRRs of [11C]-(R)-PK11195 were obtained by dividing distribution volume ratios of the target (infarct) region through the corresponding reference (contralateral mirror) region.
Blood tests
Each participant was genotyped for the rs6971 polymorphism of the TSPO gene [single nucleotide polymorphism analysis at rs6971 locus using isolated deoxyribonucleic acid by LCG genomics (Hoddesdon, UK)] and categorised as a HAB, a MAB or a LAB. 14 Spearman’s rank-order correlation and unpaired t-tests were used to test for association of imaging parameters with genotype.
Blood samples were taken from each patient for systemic inflammatory marker [high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin 6] analysis at the [18F]-GE180 PET session (18–55 days after stroke onset).
Safety and tolerability
Each participant completed a questionnaire after receiving [18F]-GE180 PET to evaluate the tolerability of scanning. The questionnaire contained five questions asking the participant to grade the discomfort associated with the [18F]-GE180 PET procedure on a five-point scale (1 – the most discomfort, 5 – the least discomfort).
All adverse events related to trial-specific procedures were collected.
Chapter 4 Results
Characteristics of patients and their ischaemic lesions
All study participants showed ischaemic lesions associated with the recent ischaemic stroke. A total of 14 lesions in nine patients were detected on the MR scans. In one patient’s case (P006) no such lesion was identified on the MR scan, but an area of increased radiotracer binding could be located in the clinically relevant site. Two patients also demonstrated evidence [by location, admission computed tomography (CT) appearance and diffusion-weighted imaging] of old ischaemic lesions (n = 4) acquired prior to the recent clinical episode, probably asymptomatically. With regard to TSPO genotype, there were five HABs, three MABs and two LABs in the sample, which was consistent with the reported distribution in the population (Table 3).
| Participant | Recent infarct on MR | Contrast-enhancing infarct on MR scan | Old infarct on MR scan | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P002 | 5 (unilateral) | 4 | 0 | HAB |
| P005 | 2 (unilateral) | 0 | 0 | HAB |
| P006 | 0a | 0 | 0 | HAB |
| P008 | 1 | 0 | 0 | HAB |
| P009 | 1 | 0 | 0 | LAB |
| P010 | 1 | 1 | 0 | MAB |
| P011 | 1 | n/a (not given for safety reason) | 1 | HAB |
| P012 | 1 | 1 | 0 | MAB |
| P014 | 1 | n/a (not given for safety reason) | 3 (unilateral) | MAB |
| P015 | 1 | 1 | 0 | LAB |
Comparison of radiotracer uptake in ischaemic lesions
Across all lesions, the contrast between the lesion and the reference region was very similar, with [11C]-(R)-PK11195 [TRR mean 1.20, standard deviation (SD) 0.28] and [18F]-GE180 without intravascular activity correction (TRR mean 1.23, SD 0.36). With correction for [18F]-GE180 intravascular activity, the visual image contrast and TRR increased (mean 1.46, SD 0.65). Example images are shown in Figure 1. Our findings indicate the presence of microglial activation in most lesions 1–2 months after stroke, which is in line with previous studies. 6,8
FIGURE 1.
A contrast-enhancing recent ischaemic lesion (patient P012) can be identified on MRI scans in the left middle cerebral artery territory (top left). The patchy low T2 signal within the infarct area on the FLAIR image (top right) is consistent with haemorrhagic transformation, which had also been detected on the 24-hour post-thrombolysis CT scan. The infarct area shows higher radiotracer uptake than the mirror region on both the [11C]-(R)-PK11195 (bottom left) and the [18F]-GE180 PET scan (bottom middle). Correction for intravascular activity on [18F]-GE180 PET (bottom right) increased the contrast between the target and the reference region.

As expected, recent infarcts showed higher ratios with both tracers than old infarcts. The mean TRRs of old infarcts were 0.89 (SD 0.08) for [11C]-(R)-PK11195, 0.94 (SD 0.09) for [18F]-GE180 without correction for intravascular activity and 0.89 (SD 0.06) with correction for intravascular activity (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2.
[18F]-GE180 and [11C]-(R)-PK11195 uptake (TRR: mean and SD) in recent and old infarcts.

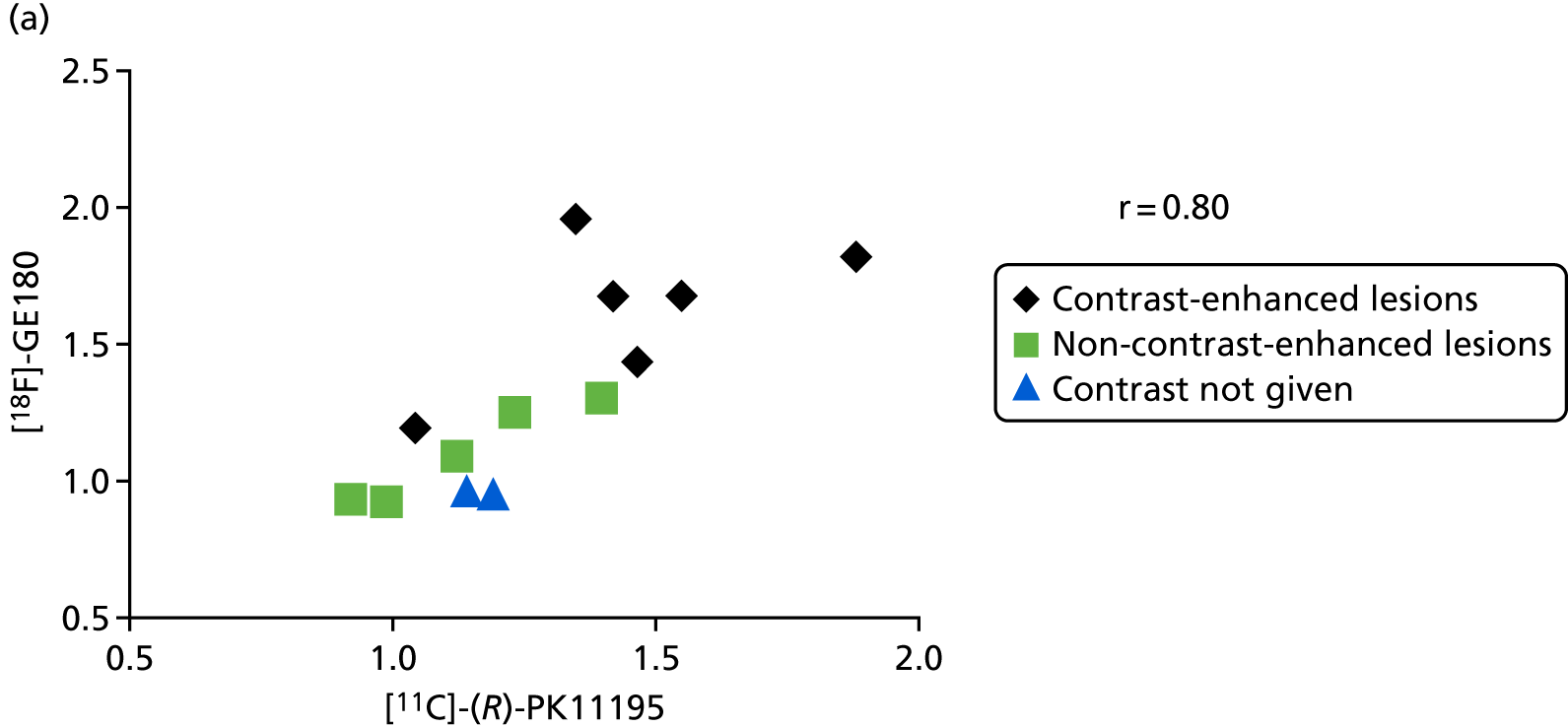
Across all lesions in HAB and MAB participants, the correlation coefficient between the tracers was 0.84 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.60 to 0.94] without (Figure 3) and 0.80 (95% CI 0.52 to 0.92) with correction for intravascular activity. The LAB participants (n = 2, P009 and P015) have been excluded from these calculations because of negligible binding of [18F]-GE180, but are included in Figure 3 and marked by green squares and blue triangles.
FIGURE 3.
Correlation of TRRs across all lesions (recent and chronic) between [11C]-(R)-PK11195 and [18F]-GE180 without correction for intravascular activity.

When restricting the analysis to recent lesions in HABs and MABs only, mean TRR was 1.29 (SD 0.26) for [11C]-(R)-PK11195, 1.32 (SD 0.36) for [18F]-GE180 without correction for intravascular activity and 1.64 (SD 0.65) with correction for intravascular activity. Correlation coefficients were 0.80 (95% CI 0.45 to 0.94) without and 0.79 (95% CI 0.42 to 0.93) with correction (Figure 4), which was similar to the results obtained in all lesions. These figures also indicate that the correlation was similar for contrast-enhancing and non-contrast-enhancing lesions while the former generally showed higher TRR values for both tracers.
FIGURE 4.
Correlation of [11C]-(R)-PK11195 TRRs across recent lesions (HABs and MABs only) with (a) [18F]-GE180 TRRs without correction for intravascular activity and (b) with correction for intravascular activity. Correlation did not depend on contrast enhancement on MRI (marked by different symbols).

The effect of genotype
Healthy tissue
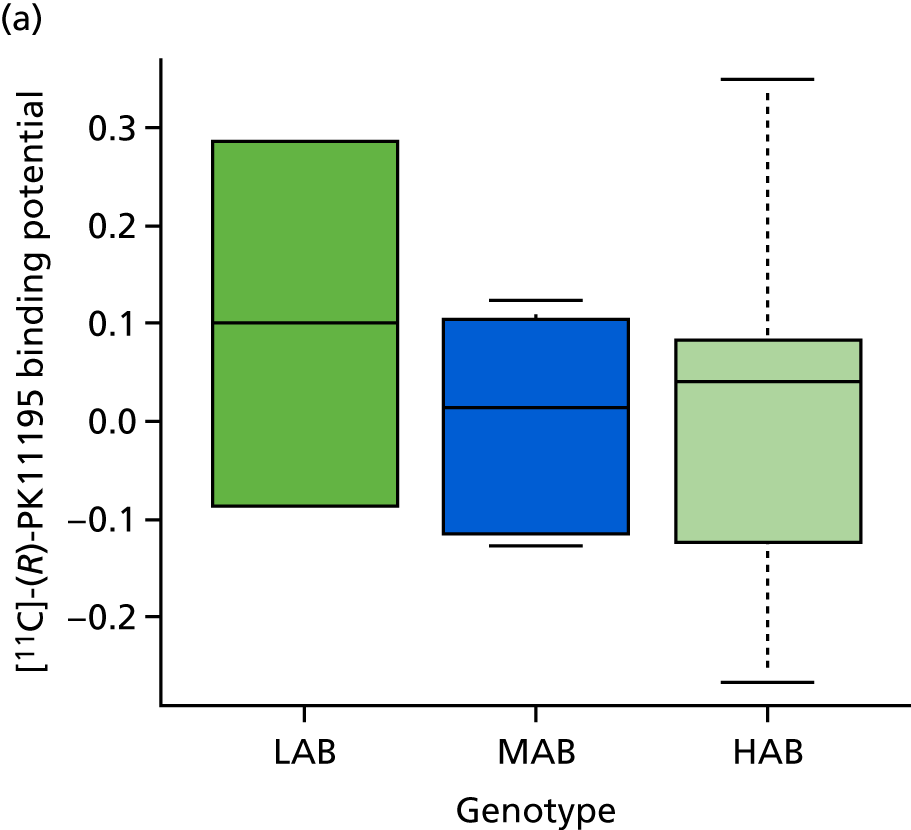
As the genotype might affect radiotracer binding (LAB < MAB < HAB), we tested that hypothesis by rank-order correlation. There was no significant association of binding [11C]-(R)-PK11195 in healthy contralateral tissue with genotype (rho = –0.14, 95% CI –0.56 to 0.34) (Figure 5a) in our sample. In contrast, there was a significant association of [18F]-GE180 tissue uptake (tissue activity concentration) with genotype (ρ = 0.64, 95% CI 0.11 to 0.89) (Figure 5b). Supressing the vascular contribution from the tissue activity, the difference between LABs and MABs and HABs became more pronounced after correction of the tissue activity of [18F]-GE180 for intravascular activity (Figure 5c), whereas the numerical correlation was somewhat less (ρ = 0.40, 95% CI –0.22 to 0.79).
FIGURE 5.
Tissue activity by genotype in normal contralateral tissue. (a) [11C]-(R)-PK11195 binding potential; (b) [18F]-GE180 tissue activity (kBq/ml) uncorrected; and (c) [18F]-GE180 tissue activity (kBq/ml) corrected for intravascular activity.


As shown in Table 4, tissue uptake of [18F]-GE180 with correction for intravascular activity in LABs was approximately 25% of the uptake in MABs and HABs. Without correction, the [18F]-GE180 uptake values in LABs were as high as 62–75% of the values in MABs and HABs. Normal tissue uptake of [18F]-GE180 with correction in MABs and HABs was approximately 60% of the total signal without correction, indicating that about 40% of the total signal came from intravascular activity.
| Genotype | [11C]-(R)-PK11195 BP | [18F]-GE180 activity (kBq/ml) | [18F]-GE180 activity (kBq/ml) – corrected | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| LAB | 0.1000 | 0.2630 | 0.7615 | 0.1761 | 0.1675 | 0.0643 |
| MAB | 0.0025 | 0.1087 | 1.0362 | 0.0951 | 0.6377 | 0.0994 |
| HAB | 0.0045 | 0.1705 | 1.2291 | 0.2877 | 0.7195 | 0.2282 |
Ischaemic lesions
A similar picture emerges in ischaemic lesions (Table 5): no correlation with genotype with [11C]-(R)-PK11195, but a significant relation with [18F]-GE180 tissue activity concentration without correction for intravascular activity (ρ = 0.50; p = 0.03) (Figure 6a) and with correction for intravascular activity (ρ = 0.53; p = 0.02 (Figure 6b).
| Genotype | [11C]-(R)-PK11195 BP | [18F]-GE180 tissue activity (kBq/ml) | [18F]-GE180 tissue activity (kBq/ml) – corrected | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| LAB | 0.3520 | 0.0085 | 0.9950 | 0.1782 | 0.4365 | 0.1888 |
| MAB | 0.0673 | 0.2230 | 1.1963 | 0.4335 | 0.8007 | 0.3426 |
| HAB | 0.2852 | 0.3766 | 1.5191 | 0.3533 | 1.0377 | 0.3110 |
FIGURE 6.
[18F]-GE180 tissue activity (kBq/ml) in ischaemic lesions by genotype. (a) Uncorrected for intravascular activity; and (b) corrected for intravascular activity.
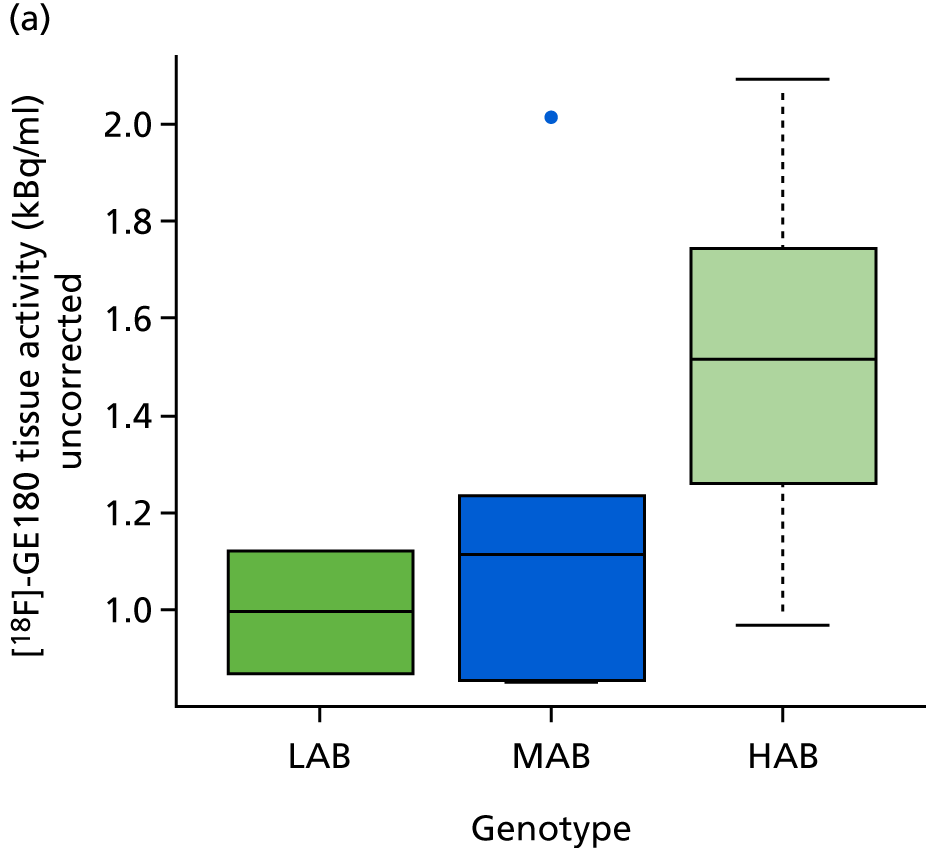

Even in participants categorised as LAB, [18F]-GE180 uptake in lesions was considerably higher (corrected activity values 0.570 and 0.303 kBq/ml) than in normal tissue (0.122 and 0.213 kBq/ml, respectively). As shown in Table 6, tissue uptake of [18F]-GE180 with correction for intravascular activity in LABs was approximately 50% of the uptake in MABs and HABs. Without correction, the [18F]-GE180 uptake values in LABs were as high as 66–83% of the values in MABs and HABs. The tissue uptake of [18F]-GE180 with correction in MABs and HABs was approximately 67% of the total uptake (without correction).
| Genotype | [11C]-(R)-PK11195 BP | [18F]-GE180 tissue activity (kBq/ml) | [18F]-GE180 tissue activity (kBq/ml) – corrected | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| LAB | 0.3520 | 0.0085 | 0.9950 | 0.1782 | 0.4365 | 0.1888 |
| MAB | 0.2127 | 0.1703 | 1.3583 | 0.2923 | 0.979 | 0.2687 |
| HAB | 0.3361 | 0.2347 | 1,5612 | 0.3324 | 1.0852 | 0.3094 |
As indicated before, older infarcts showed less radiotracer uptake with both tracers than more recent infarcts. Their distribution was not even between the three subgroups (0 out of 2 in the LABs, 3 out of 6 in the MABs, 1 out of 11 in the HABs). Thus, we also restricted the analysis to recent infarcts only (see Table 6), which did not change the contrast between the groups with [18F]-GE180.
Effect of blood–brain barrier disruption
Binding potentials measured with [11C]-(R)-PK11195 are higher in lesions with blood–brain barrier (BBB) disruption, as demonstrated by gadolinium contrast enhancement, than in those without (p = 0.02, t-test) (Figure 7).
FIGURE 7.
Effect of BBB disruption on [11C]-(R)-PK11195 binding potential in ischaemic lesions. N, no; Y, yes.

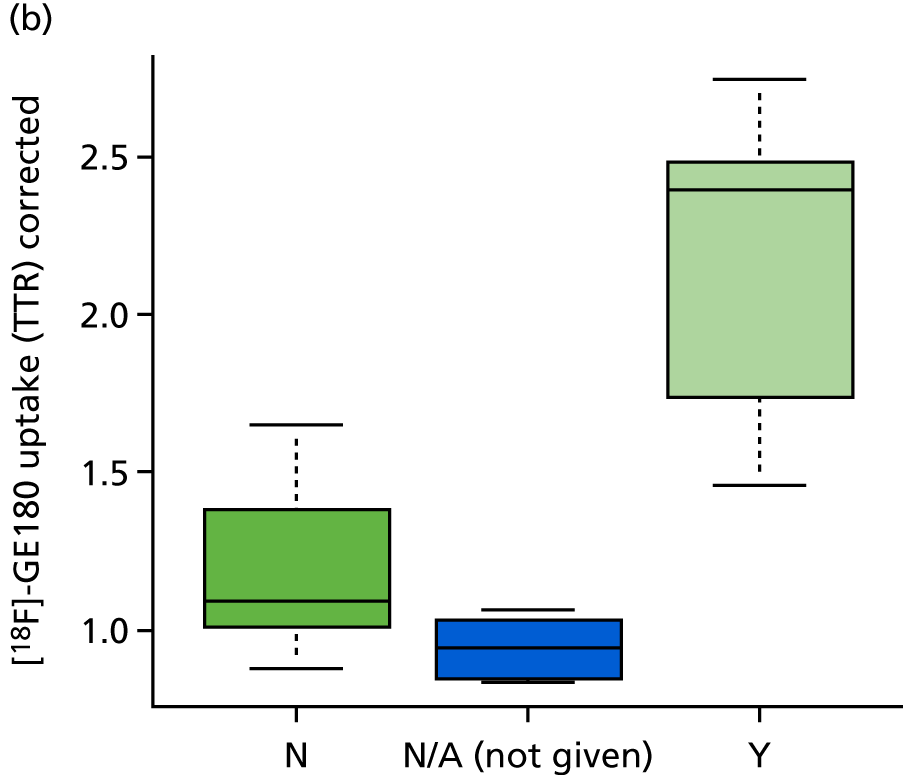
Because of the strong effect of genotype on [18F]-GE180 binding, tissue activity concentration values cannot be used without adjustment. This was done by using TRRs with lesion values divided by those in the corresponding contralateral regions of interest. Lesions with BBB disruption also show increased uptake of [18F]-GE180 [t-test; p = 0.004 (Figure 8a) without correction for intravascular activity and p = 0.003 (Figure 8b) with correction for intravascular activity] in HAB and MAB patients. The single LAB patient with BBB disruption (P015) also showed a very high lesion-to-reference ratio (1.76 without correction for intravascular activity, 4.67 with correction for intravascular activity) contrary to expected negligible specific binding (see Figure 3). This suggests that BBB damage is associated with significant non-specific radiotracer uptake that cannot be accounted for by correction for intravascular activity.
FIGURE 8.
The effect of BBB disruption on [18F]-GE180 uptake (TTR, relative to contralateral VOIs) in ischaemic lesions, HAB and MAB patients only. (a) without correction for intravascular activity; and (b) with correction for intravascular activity. N, no; Y, yes.

Uptake values in non-enhancing lesions were very small and (in this pilot sample) not significantly different from contralateral regions (Table 7).
| Contrast enhancement | [11C]-(R)-PK11195 BP | [18F]-GE180 tissue activity concentration | [18F]-GE180 tissue activity concentration – corrected | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| No | 0.0944 | 0.2899 | 1.1006 | 0.1748 | 1.2027 | 0.3096 |
| Yes | 0.5498 | 0.2391 | 1.6259 | 0.2743 | 2.2012 | 0.4934 |
Correlation between imaging and systemic inflammatory markers
Statistically significant correlation could be demonstrated between both plasma interleukin 6 and high-sensitivity CRP levels and the lesion-to-reference ratios with [11C]-(R)-PK11195 and also marginally with [18F]-GE180 (Figures 9 and 10 and Table 8).
FIGURE 9.
Rank-order scatterplot of interleukin 6 level and TTRs.

FIGURE 10.
Rank-order scatterplot of high-sensitivity CRP levels and TTRs.

| Lesion-to-reference ratio | Interleukin 6 | High-sensitivity CRP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ | 95% CI | ρ | 95% CI | |
| [11C]-(R)-PK11195 | 0.68 | 0.09 to 0.92 | 0.76 | 0.25 to 0.94 |
| [18F]-GE180 TRR | 0.63 | 0.001 to 0.90 | 0.63 | 0.001 to 0.90 |
| [18F]-GE180 with correction for intravascular activity | 0.57 | –0.09 to 0.88 | 0.61 | –0.03 to 0.90 |
Three patients (i.e. P002, P006 and P015) had elevated interleukin 6 levels (7.7, 10.4 and 13.8 pg/ml) and high-sensitivity CRP levels (8.17, 7.35, and 35 mg/l). The patients also showed higher lesion-to-reference ratios with [11C]-(R)-PK11195 (TRR median 1.47, range 1.12–1.88) and [18F]-GE180 without intravascular correction (TRR median 2.34, range 1.09–4.67) relative to the rest of the participants with normal inflammatory marker levels [[11C]-(R)-PK11195, TRR median 1.02, range 0.86–1.35; and [18F]-GE180, TRR median 1.02, range 0.84–2.74]. As seen in Table 3, patients P002 and P015 also demonstrated the presence of obvious BBB disruption (by having contrast-enhancing lesions), which also contributes to the higher radiotracer uptake.
Correlation with clinical outcome
The pilot phase of this study had not been powered to demonstrate associations with clinical outcome. None of the imaging data or plasma markers showed an obvious association with clinical outcome.
Safety and tolerability
The mean score from the 10 participants’ tolerability questionnaire was 4.36 (range 4–5), which is well above the threshold (neutral = 3) that we set to accept.
We did not observe any serious adverse events. Non-serious adverse events occurred, but had no obvious links to the radiotracer.
Chapter 5 Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study to analyse the properties of [18F]-GE180 in patients with ischaemic stroke and to compare it with [11C]-(R)-PK11195 in human participants. As to be expected with the very small amounts of injected PET radiotracer, we did not observe any serious adverse events. Although [18F]-GE180 provided very good contrast in ischaemic lesions with BBB damage, we also observed some limitations that had not been seen in the generally favourable outcome of a previous stroke study in rats. 19
Similar to previous studies of the kinetics of [18F]-GE180 in healthy human participants13,20 and in patients with glioma21 and multiple sclerosis,22 but in contrast to rodent studies,19 we found that the uptake of [18F]-GE180 in normal tissue across the intact BBB was very low.
Perfusion and blood volume in subacute ischaemic lesions can be highly variable, depending on the extent of reperfusion. 23 We therefore performed corrections for intravascular activity. We had opted for scanning times not exceeding 30 minutes, as this length of time is typically required for clinically applicable procedures in functionally impaired patients. The procedure was regarded as well tolerated as indicated by patient responses in the questionnaire. However, because of the short data acquisition time, we could not perform standard kinetic modelling and so estimated intravascular activity from data obtained during the first 5 minutes after radiotracer injection. The correction improved signal-to-background contrast of [18F]-GE180, but did not change the correlations between [18F]-GE180 and [11C]-(R)-PK11195 substantially.
As demonstrated in Figures 3 and 4, correlation was generally very good and lesion-to-background ratios were comparable, suggesting that [18F]-GE180 could possibly be used instead of [11C]-(R)-PK11195 to assess microglial activity in clinical stroke studies. We also found a correlation between systemic inflammation markers and radiotracer uptake in lesions with both tracers, confirming observations previously seen in normal participants with vascular risk factors. 24 Neither systemic nor PET markers were related to clinical outcome. However, the small sample in our pilot study had not been powered to address this question and functional deficits had been mild already at study inclusion, leaving limited room for further improvement of functional scores.
Recent infarcts showed higher radiotracer uptake with both tracers than old infarcts. In contrast with the recent lesions, most of the old infarcts demonstrated less radiotracer uptake (i.e. TRR < 1) than the contralateral reference region. In the absence of previous scans or obviously relevant clinical events, we could not establish the exact age of the old infarcts. But some details in the clinical history (e.g. an episode of possibly transitory ischaemic attack in the case of P011 and a few episodes of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in the case of P014) suggested that these might have been acquired many years before. A previous longitudinal study9 demonstrated increased [11C]-(R)-PK11195 binding 150 days after the stroke onset. The lack of inflammation in our case could perhaps be explained by the presence of an already established glial scar.
Substantial limitations for clinical use of [18F]-GE180 became obvious when analysing the effects of the genetic polymorphism and BBB damage. We found a significant association of [18F]-GE180 tissue activity concentration with genotype in both the healthy contralateral tissue and the ischaemic lesions, but not with [11C]-(R)-PK11195. When applying correction for intravascular activity of [18F]-GE180, the difference between MABs and HABs was no longer significant in healthy tissue. A similar effect was seen in other studies13,25 but not in all studies20 conducted on healthy volunteers, perhaps because of the small magnitude of the signal in a normal brain. The differences in binding of second-generation tracers across HAB/MAB/LAB classes vary depending on ligand affinity. 26 In vitro [18F]-GE180 demonstrates a binding affinity of 15 : 1 between HABs and LABs, which suggests negligible specific binding in PET scans obtained in LABs.
Owing to the limited ability of [18F]-GE180 to cross the intact BBB and, therefore, the poor penetration of the brain tissue, a significant amount of the signal in a brain region of interest is in fact from the vascular activity. As the spatial resolution of human brain imaging is unable to resolve the vasculature, we sought to apply an approximate correction for the contribution of the vascular signal by subtracting an early image. Our results suggest that a significant portion (up to 50%) of the signal seen in the infarcts in MAB and HAB patients may be caused by spillover from the vasculature.
The comparison of lesions with and without contrast enhancement suggests that BBB disruption is playing a major role in tissue uptake of [18F]-GE180 in ischaemic lesions. Although some proportion of increased uptake will probably indicate increased binding to TSPO receptors, this was also observed in LABs, which suggested that there is a large amount of non-specific uptake in ischaemic lesions with contrast enhancement. Thus, clinical interpretation of findings would need to take into account the effects of the polymorphism and BBB damage, which cannot be quantified accurately. Furthermore, assessment of BBB damage requires MR scanning with gadolinium, which, for safety reasons, could not be applied in two of our patients.
Another challenge to the interpretation of clinical studies are recent in vitro findings27 suggesting that, in contrast to findings in rodents, TSPO gene expression does not depend on microglia activation in humans.
Given the significant impact of rs6971 genotype and BBB disruption on the signal, LABs and patients not receiving contrast-enhanced MRI scans need to be excluded, which results in a substantial increase in the size of the required sample. Furthermore, the statistical analysis would have taken the presence of contrast enhancement into account as a major confounder. Considering these factors, the number of participants planned for phase 2 (n = 40), which was aiming at correlation with clinical outcome, would not have provided adequate power.
A limitation of the current study was the time window to assess TSPO binding with [18F]-GE180 (15–30 minutes post injection). Most other studies report a time window of 60 to 90 minutes as the optimal interval. Kinetic studies13,28 showed a relatively high contribution of intravascular blood activity to total observed activity, even after 60 minutes. However, with late static scans, correction for intravascular activity is not possible and we therefore chose scanning for 30 minutes immediately after injection. Analysis of kinetic data from multiple studies (compiled in Sridharan29) showed relatively little change in lesion-to-background ratios after 15 minutes. In addition, the close correlation between [18F]-GE180 and [11C]-(R)-PK11195 that was observed in our study supports the validity of using an early time window. Nevertheless, we cannot exclude that late scanning could have provided increased lesion-to-background ratios.
Chapter 6 Public and patient involvement
The study was discussed with a patient representative prior to finalising. This helped to confirm that the scanning protocol was practical and tolerable and that patient information sheets provided all of the necessary information in an appropriate manner to ensure that proper informed consent of participants was obtained. The interaction did not result in changes to the protocol. Owing to the very technical nature of the results, publications will be primarily aimed at a specialist audience and we do not anticipate support by public and patient involvement for dissemination of the results.
Chapter 7 Conclusions
This pilot study demonstrates that neuroinflammation in ischaemic stroke can be imaged by the TSPO PET radioligands [18F]-GE180 and [11C]-(R)-PK11195. Uptake in lesions, relative to contralateral tissue, is similar and highly correlated with both radiotracers. As expected, [18F]-GE180 intravascular activity is high during the entire scanning time, so correction for intravascular activity was necessary and could be performed successfully. Genotype and BBB damage have significant effects on [18F]-GE180 uptake. High uptake of [18F]-GE180 in lesions with BBB damage, even in LABs, suggests the presence of non-specific binding, whereas uptake in normal brain tissue is very low. Further studies are warranted to fully understand the influence of BBB damage on PET microglia imaging.
The very low uptake of [18F]-GE180 in normal brain tissue and the substantial confounding effect of BBB damage had not been known when designing the present study. Thus, according to our own judgement and the opinion of the Independent Data Monitoring Committee, phase 2 could not be conducted as envisaged and the study has been closed after completion of phase 1.
Acknowledgements
As a clinical trial, the study was sponsored by The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, and managed by the clinical trials unit of the University of Manchester at The Christie NHS Foundation Trust. The authors are very grateful to their staff, to the principal investigators at patient recruitment sites and their staff, to GE HealthCare staff for helpful advice, and to all staff involved in production of [11C]-(R)-PK11195, scanning and study management at the Wolfson Molecular Imaging Centre. We also thank the members of the Independent Data Monitoring Committee for its support and advice. Particular thanks go to the patient volunteers who participated in the study.
Contributions of authors
Eszter Visi (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5589-4740) (MD, neurologist) was the clinical fellow for this study. She was responsible for data acquisition and for patient care at Wolfson Molecular Imaging Centre. She also contributed significantly to data analysis and drafted the report.
Rainer Hinz (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7808-9207) (PhD, physicist) led on imaging physics and analysis of radiotracer kinetics.
Martin Punter (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6800-891X) (MD, neurologist) provided critical support to Eszter Visi as the clinical lead principal investigator at the Salford Royal Foundation Trust hyperacute stroke centre.
Arshad Majid (MD, PhD, neurologist, professor for stroke research), Alexander Gerhard and Karl Herholz jointly designed the study. Arshad Majid also provided links to patient representatives and the national and regional stroke networks to support patient recruitment.
Alexander Gerhard (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8071-6062) (MD, neurologist) was a senior lecturer, provided guidance and provided training on image data analysis to Eszter Visi.
Karl Herholz (https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8658-0151) (MD, neurologist) was a professor for clinical neuroscience, was the chief investigator for the study, designed the principal concept for data analysis, ensured compliance with regulatory requirements, and finalised the report.
All authors provided a critical review of the data and the manuscript.
Data-sharing statement
All data requests should be submitted to the corresponding author for consideration. Please note exclusive use will be retained until the publication of major outputs. Access to anonymised data may be granted following review.
Patient data
This work uses data provided by patients and collected by the NHS as part of their care and support. Using patient data is vital to improve health and care for everyone. There is huge potential to make better use of information from people’s patient records, to understand more about disease, develop new treatments, monitor safety, and plan NHS services. Patient data should be kept safe and secure, to protect everyone’s privacy, and it’s important that there are safeguards to make sure that it is stored and used responsibly. Everyone should be able to find out about how patient data are used. #datasaveslives You can find out more about the background to this citation here: https://understandingpatientdata.org.uk/data-citation.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research. The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, the MRC, NETSCC, the EME programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the EME programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Feigin VL, Krishnamurthi RV, Parmar P, Norrving B, Mensah GA, Bennett DA, et al. Update on the global burden of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in 1990–2013: the GBD 2013 study. Neuroepidemiology 2015;45:161-76. https://doi.org/10.1159/000441085.
- Iadecola C, Anrather J. The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med 2011;17:796-808. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2399.
- Emsley HC, Smith CJ, Hopkins SJ. Infection and brain-induced immunodepression after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2008;39. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.500447.
- Patel AR, Ritzel R, McCullough LD, Liu F. Microglia and ischemic stroke: a double-edged sword. Internat J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 2013;5.
- Boche D, Perry VH, Nicoll JA. Review: activation patterns of microglia and their identification in the human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2013;39:3-18. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12011.
- Thiel A, Heiss WD. Imaging of microglia activation in stroke. Stroke 2011;42:507-12. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.598821.
- Owen DR, Matthews PM. Imaging brain microglial activation using positron emission tomography and translocator protein-specific radioligands. Int Rev Neurobiol 2011;101:19-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-387718-5.00002-X.
- Thiel A, Radlinska BA, Paquette C, Sidel M, Soucy JP, Schirrmacher R, et al. The temporal dynamics of poststroke neuroinflammation: a longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging-guided PET study with 11C-PK11195 in acute subcortical stroke. J Nucl Med 2010;51:1404-12. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.110.076612.
- Gerhard A, Schwarz J, Myers R, Wise R, Banati RB. Evolution of microglial activation in patients after ischemic stroke: a [11C](R)-PK11195 PET study. Neuroimage 2005;24:591-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.09.034.
- Pappata S, Levasseur M, Gunn RN, Myers R, Crouzel C, Syrota A, et al. Thalamic microglial activation in ischemic stroke detected in vivo by PET and [11C]PK1195. Neurology 2000;55:1052-4. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.55.7.1052.
- Price CJ, Wang D, Menon DK, Guadagno JV, Cleij M, Fryer T, et al. Intrinsic activated microglia map to the peri-infarct zone in the subacute phase of ischemic stroke. Stroke 2006;37:1749-53. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000226980.95389.0b.
- Wadsworth H, Jones PA, Chau W-F, Durrant C, Fouladi N, Passmore J, et al. [18F]GE-180: A novel fluorine-18 labelled PET tracer for imaging translocator protein 18kDa (TSPO). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012;22:1308-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.12.084.
- Fan Z, Calsolaro V, Atkinson RA, Femminella GD, Waldman A, Buckley C, et al. Flutriciclamide (18F-GE180) PET: first-in-human PET study of novel third-generation in vivo marker of human translocator protein. J Nucl Med 2016;57:1753-9. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.115.169078.
- Owen DR, Yeo AJ, Gunn RN, Song K, Wadsworth G, Lewis A, et al. An 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) polymorphism explains differences in binding affinity of the PET radioligand PBR28. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2012;32:1-5. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2011.147.
- Hammers A, Chen CH, Lemieux L, Allom R, Vossos S, Free SL, et al. Statistical neuroanatomy of the human inferior frontal gyrus and probabilistic atlas in a standard stereotaxic space. Hum Brain Mapp 2007;28:34-48. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20254.
- Turkheimer FE, Edison P, Pavese N, Roncaroli F, Anderson AN, Hammers A, et al. Reference and target region modeling of [11C]-(R)-PK11195 brain studies. J Nucl Med 2007;48:158-67.
- Su Z, Herholz K, Gerhard A, Roncaroli F, Du Plessis D, Jackson A, et al. [11C]-(R)PK11195 tracer kinetics in the brain of glioma patients and a comparison of two referencing approaches. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013;40:1406-19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2447-2.
- Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J, Fujita M, Gjedde A, Gunn RN, et al. Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007;27:1533-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600493.
- Boutin H, Murray K, Pradillo J, Maroy R, Smigova A, Gerhard A, et al. 18F-GE-180: a novel TSPO radiotracer compared to 11C-R-PK11195 in a preclinical model of stroke. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2015;42:503-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2939-8.
- Feeney C, Scott G, Raffel J, Roberts S, Coello C, Jolly A, et al. Kinetic analysis of the translocator protein positron emission tomography ligand [18F]GE-180 in the human brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2016;43:2201-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3444-z.
- Albert NL, Unterrainer M, Fleischmann DF, Lindner S, Vettermann F, Brunegraf A, et al. TSPO PET for glioma imaging using the novel ligand 18F-GE-180: first results in patients with glioblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2017;44:2230-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3799-9.
- Unterrainer M, Mahler C, Vomacka L, Lindner S, Havla J, Brendel M, et al. TSPO PET with [18F] GE-180 sensitively detects focal neuroinflammation in patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2018;45:1423-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-018-3974-7.
- Heiss WD, Herholz K. Assessment of pathophysiology of stroke by positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 1994;21:455-65. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171424.
- Drake C, Boutin H, Jones MS, Denes A, McColl BW, Selvarajah JR, et al. Brain inflammation is induced by co-morbidities and risk factors for stroke. Brain Behav Immun 2011;25:1113-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.02.008.
- Zanotti-Fregonara P, Pascual B, Rizzo G, Yu M, Pal N, Beers D, et al. Head-to-head comparison of 11C-PBR28 and 18F-GE180 for the quantification of TSPO in the human brain. J Nucl Med 2018;59:1260-6. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.117.203109.
- Turkheimer FE, Rizzo G, Bloomfield PS, Howes O, Zanotti-Fregonara P, Bertoldo A, et al. The methodology of TSPO imaging with positron emission tomography. Biochem Soc Trans 2015;43:586-92. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20150058.
- Owen DR, Narayan N, Wells L, Healy L, Smyth E, Rabiner EA, et al. Pro-inflammatory activation of primary microglia and macrophages increases 18 kDa translocator protein expression in rodents but not humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2017;37:2679-90. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17710182.
- Vomacka L, Albert N, Lindner S, Unterrainer M, Mahler C, Brendel M, et al. Quantification of the new TSPO ligand [18F]GE-180 in patients with multiple sclerosis – initial results. J Nuclear Med 2017;58.
- Sridharan S. Quantitative Analysis of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) With the Second Generation Translocator Protein (TSPO) Ligand [18F]GE-180 2016. www.research.manchester.ac.uk/portal/en/theses/quantitative-analysis-of-positron-emission-tomography-pet-with-the-second-generation-translocator-protein-tspo-ligand-18fge180(01bdc97f-90f7-4db3-8268-f65e013640ab).html (accessed 17 October 2019).
List of abbreviations
- [18F]-GE180
- flutriciclamide
- BBB
- blood–brain barrier
- CI
- confidence interval
- CRP
- C-reactive protein
- CT
- computed tomography
- FLAIR
- fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- HAB
- high-affinity binder
- LAB
- low-affinity binder
- MAB
- mixed-affinity binder
- MR
- magnetic resonance
- MRI
- magnetic resonance imaging
- PET
- positron emission tomography
- SD
- standard deviation
- TRR
- target-to-reference ratio
- TSPO
- 18-kDa translocator protein
- VOI
- volume of interest
