Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned by the HTA programme on behalf of the Department of Health as project number 09/19/01. The contractual start date was in February 2009. The draft report began editorial review in August 2009 and was accepted for publication in December 2009. As the funder, by devising a commissioning brief, the HTA programme specified the research question and study design. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the referees for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
None
Permissions
Copyright statement
© 2010 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO. This journal may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NETSCC, Health Technology Assessment, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2010 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Background
Type 2 diabetes and its treatment
Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is usually seen in people who are overweight or obese, and the prevalence is increasing. In most patients it is a progressive disease, in the sense that treatment starts with diet and other lifestyle measures, such as physical activity, but that tablet therapy is soon required, and progression to needing insulin is common as time passes. This is not invariable, in that some people manage to lose weight and be physically active and may not progress to needing intensified treatment.
The problems underlying progression of disease are twofold. Firstly, overweight and obesity make the body less sensitive to insulin (‘insulin resistance’), so that the pancreas needs to produce more to keep blood glucose levels normal. Secondly, there is progressive failure of the function of the beta cells in the pancreas, so that insulin production cannot be maintained. By the time someone is diagnosed with T2DM, they have usually lost about half of their beta-cell capacity.
Progression may mean that patients go through the following treatment stages:
-
Diet and physical activity, aiming to achieve weight loss and reduce insulin needs and resistance.
-
Treatment with a single oral drug, usually metformin.
-
Treatment with two oral drugs, usually by adding a sulphonylurea to the metformin.
-
Treatment with three oral drugs.
-
The addition of insulin, usually with a once-daily long-acting (‘basal’) insulin, taken along with metformin and a perhaps reduced dose of sulphonylurea.
-
When that fails, moving to more complex insulin regimens, such as adding short-acting insulin at mealtimes, or twice-daily mixed insulins, with the sulphonylurea being discontinued.
Each step in the treatment pathway is triggered by rising blood glucose levels. The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guideline CG661 recommends that the target should usually be a glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) level of 6.5% or less. HbA1c is a blood test, taken by a doctor or nurse, and measured in a laboratory, and gives average blood glucose levels over the past 2–3 months. The HbA1c test measures the amount of glucose attached to the haemoglobin molecule.
If not well controlled, diabetes will increase the risk of heart disease, blindness, renal failure, amputation and other complications, so patients need to keep their blood glucose under as good control as possible. To do so, they need to know what it is. They will usually have their HbA1c level measured at intervals, which will let them know if control is poor. However, HbA1c level, being an average, will not explain why control is poor. Blood glucose can fluctuate from hour to hour, and blood glucose testing with meters and strips can identify the times when blood glucose is too high. It can also be used to check on when the level might be going too low – hypoglycaemia or hypoglycaemic episodes.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose
Nowadays, patients can measure their blood glucose level by putting a drop of blood on to a test strip, and using a meter to read colour changes in that. This is painful as patients are required to prick their finger with a lancet to obtain a blood sample. The strips are cumulatively expensive, with the average cost2 being £14.57 for a 50-strip pack. The meters are inexpensive at an average cost of £14.68 (2009 price) [and the NHS requires manufacturers to provide them free of charge for distribution to patients as considered appropriate by health-care professionals (HCPs)]. Knowledge of high blood glucose levels may cause anxiety, and fear of the long-term complications. However, it can also give patients information that they can use to improve control of their blood glucose. They can also measure the amount of glucose in their urine, which is a guide to blood glucose level. Urine glucose tests only detect glucose in the urine once blood levels are above the renal threshold (around 10 mmol/l), so hypoglycaemia cannot be detected. Similarly, urine tests cannot detect the degree of hyperglycaemia.
A number of assumptions are made when proposing self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) as an effective tool for blood glucose control, as outlined by McAndrew et al. (2007). 3 The authors suggest that the efficacy of SMBG would depend on whether the interventions created a patient-centred behavioural control system that would address the patient’s skills in:
-
taking a blood glucose reading
-
interpreting the reading as a target for action
-
perceiving linkages between specific behaviours (diet, exercise) and the reading (i.e. which behaviours lower an above-target reading and which raise a below-target reading) – ideally, the linkage would also act as a motivator to change behaviour
-
implementing action plans (i.e. behavioural and treatment adjustments) in response to SMBG
-
giving less weight to subjective symptoms that are the basis for commonsense decisions that one is sick or well, as these cues are invalid guides for the regulation of blood glucose levels
-
incorporating the behavioural system into the patient’s ongoing daily behavioural patterns to eventually become automatic
-
viewing difficulties in achieving control as issues of adjusting the behavioural treatment, not deficits in personal motivation or competence for self-management.
Table 1 suggests possible facilitators and barriers to SMBG as an effective diabetes management tool.
| Facilitators | Barriers | Consequences | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | Health-care providers | ||
|
Instruction in SMBG use Accuracy checks and adherence checks Integrated into patient education so that patients can understand and use SMBG information in a wider context Positive messages Made easy for patient – ease of access and convenient regimen Feedback on self-monitoring and clear messages regarding treatment/behaviour changes as a consequence of readings |
Negative message: internal (failure of self) or external Lack of instruction/education – lack of understanding Lack of integration into management People don’t like pricking fingers – and ‘dose’ of SMBG may be inappropriate cost |
Direct feedback of effects of certain lifestyle behaviours on glucose values – learning effects of physiological consequences of, for example, eating certain foods Improved short- and long-term clinical outcomes if readings are adequately acted upon Improved control/empowerment – patients have more possibilities to make changes to influence disease positively |
Readings facilitate individualised treatment of patient/treatment adjustments |
The volume and costs of prescriptions for blood glucose monitoring in England has risen steadily over the last 6 years. The last figures available4 are for the quarter July–September 2008, when the cost was £34M, which gives a projected annual cost of almost £140M. This compares with ∼£107M in 2002. 5 However, one would expect that much of this will be for people with type 1 diabetes (T1DM).
The SMBG controversy
There have been several recent trials and systematic reviews to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of SMBG, but it still remains a controversial area. So, the first question may be – why is there still a question?
There are (at least) five possible answers to that.
Firstly, the evidence is to some extent conflicting, with different types of study design giving different results. There is also the issue of what harm it may do. Studies have shown that SMBG can increase anxiety.
Secondly, as with other diagnostic interventions, there is a hierarchy of questions;
-
The technical level – does it accurately measure what it is supposed to?
-
The treatment level – does SMBG lead to changes in treatment?
-
The outcomes level – does SMBG reduce the risk of heart disease, visual loss, etc.?
Thirdly, SMBG is not an end in itself, but only an aid to management, and another question is ‘who uses the results?’. Do the patients record the results and bring them to the clinic or surgery to discuss the implications, so that the doctor or nurse can adjust treatment accordingly? Or do the patients use the information themselves and self-adjust diet, or doses of oral drugs or insulin?
Fourthly, if patients are going to self-adjust management, are they given sufficient education with which to do that?
Fifthly, knowledge alone does not always lead to action. Education might have two strands – knowledge of how to adjust treatment, but also ‘motivational knowledge’ that makes people understand the importance of good control.
Also, is there a relationship between adherence to medication, and likelihood of SMBG improving HbA1c level? If people are not adhering to a diet, exercise regimen or oral medication as prescribed (one study reported that only 35% of people adhere to any medication regimen on average6) then what effect will SMBG have on patient perception of disease severity and/or importance of adherence generally? Some patients report in the qualitative studies7–9 that low SMBG readings give them the impression that they are fine. What impact does this have on adherence to therapy, diet and exercise? It is also not clear whether patients are instructed to monitor because they were in poor control initially or because they are given a tool to assist self-management.
The NICE clinical guideline1 on the management of T2DM, which was written before the two recent trials [DiGEM10–12 (Diabetes Glycaemic Education and Monitoring) and ESMON13 (Efficacy of Self MONitoring of blood glucose in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes trial)] had reported, supported SMBG in certain circumstances. It recommended that SMGB should be available to newly diagnosed patients (recommendation 22), and to those on insulin and oral agents (recommendation 23).
The evidence base for these recommendations was based mainly on two observational studies, from the Kaiser Permanente14 study and the ROSSO (RetrOlective Study: Self-monitoring of blood glucose and Outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes) study. 15 Two other observational studies by Wen et al. 16 and Davis et al. 17–19 were also mentioned, as were two randomised controlled trials (RCTs). 20,21 The evidence cut-off date was before the DiGEM study was published, and well before the ESMON one. However, the NICE Guideline Development Group was clearly aware of the DiGEM study, and discounted it because ‘a study which viewed self-monitoring as a stand-alone intervention, and not as an element of a full educational programme, could not properly inform the appropriate use of self-monitoring’. This seems curious, as the third arm of the DIGEM study included patient education and motivation.
The NICE evidence review mentions only one economic study of SMBG – that by Palmer et al. 22 – but did not mention that it was funded by the manufacturers of meters. As discussed in Chapter 3, it may be unduly favourable to SMBG. The cost-effectiveness results from the DiGEM trial came out too late to be included in the NICE review. It is not clear why other economics studies were not included.
The guideline commented that past research had failed ‘to address the complicated issue of its integration into patient education and self-management behaviours’.
Questions for this review
Primary question
Is SMBG worthwhile in patients, or selected patients, with T2DM:
-
on diet alone
-
on metformin monotherapy
-
on combination oral therapy
-
on combinations of oral therapy and basal insulin?
By ‘worthwhile’, we mean whether it provides clinical benefits, such as improved glycaemic control, fewer hypoglycaemic episodes or quality of life (QoL), at a cost that makes it cost-effective.
For the purposes of this review, we have assumed that, in line with NICE guidance,9 SMBG is worthwhile in those on more complicated insulin regimens, such as basal + mealtimes or twice-daily mixed insulin, and the evidence on that was not examined.
Additional questions
-
Which sub-groups of patients benefit most from SMBG?
-
Which are harmed?
-
What education is required to enable the patients, and their HCPs, to use the SMBG results to improve their diabetes control?
-
How do we motivate those groups of patients that could benefit from SMBG to use it to improve their diabetes control?
-
For those patients for whom SMBG is shown to be worthwhile, a subsidiary question might be how to best deliver SMBG (in terms of frequency and quality of testing, education, use of results, costs)?
Chapter 2 Clinical effectiveness of self-blood glucose monitoring
Methods
A protocol was produced and approved by the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) programme before the start of this review. It is available on the HTA programme website (www.ncchta.org/protocols/200900190001).
Criteria considered for synthesis of evidence of clinical effectiveness
Intervention
Self-testing of blood glucose with a meter and test strips.
Relevant comparators
The comparators were:
-
self-monitoring of urine glucose (SMUG)
-
monitoring with HbA1c
-
a combination of the above
-
comparisons of SMBG of different intensities (either in terms of frequency or additional education, feedback or similar).
A review of the evidence for clinical effectiveness was undertaken systematically following the general principles recommended in the QUOROM (Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses) statement. 23
Population
-
Inclusion criteria:
-
– studies including adult patients with T2DM on any oral treatment or combination of regimens, including lifestyle, oral agents or once-daily basal insulin
-
– minimum duration of study was 12 weeks (as it may take longer for people using SMBG to assess the effects of changes and fine tune their treatment, a trial giving a positive result at 12 weeks would give useful information. However, a negative result at 12 weeks would not be regarded as proof that SMBG was ineffective)
-
-
Exclusion criteria:
-
– pregnant women with diabetes
-
– studies in which some patients had T1DM and results were not given separately
-
– studies in people on complex insulin regimens.
-
Place of self-monitoring of blood glucose
Evidence from existing reviews suggests that not all groups of patients benefit.
Patients could be grouped by:
-
type of treatment, i.e. diet alone, metformin monotherapy, dual therapy (metformin + sulphonylurea), triple oral therapy, the combination of once-daily basal insulin + oral therapy
-
baseline HbA1c level
-
duration of diabetes
-
age
-
patient preference (patients who feel that SMBG will benefit and empower them might do better than patients who are reluctant to use SMBG – determined by patient self-report)
-
previous use of SMBG
-
levels of education
-
motivation for self-care (e.g. as determined using instruments related to an information-motivation-behavioural skills model of diabetes self-care).
Outcomes
-
HbA1c level.
-
Hypoglycaemia.
-
Quality of life, anxiety, depression.
-
Costs.
-
Treatment satisfaction.
-
Weight.
-
Treatment change in response to measurement (insulin dose, oral drug use, diet, exercise).
-
Lipids (patients who adjust their diet in order to control hyperglycaemia may improve cholesterol levels as a by-product).
-
Blood pressure.
-
In theory, complications such as retinopathy would be reported, but, realistically, very few studies would be long enough.
Technical issues related to SMBG were considered, but based only on reports in existing systematic reviews.
Study type
-
Inclusion criteria:
-
– For the review of clinical effectiveness, only systematic reviews and RCTs were included.
-
– Large observational studies (500 participants or more) of adequate duration and published as full text articles were included for information on adverse events, longer-term outcomes (e.g. cardiovascular events, retinopathy) and qualitative issues (motivation, adherence and QoL, patient preferences).
-
– Editorials, letters in journals, and small observational studies would be discussed if they threw light on the reasons for controversy.
-
– Titles and abstracts were examined for inclusion by two reviewers independently. Disagreement was resolved by consensus.
-
-
Exclusion criteria:
-
– non-English language papers
-
– papers published pre-1996
-
– reports published as meeting abstracts only, where insufficient methodological details were reported to allow critical appraisal of study quality.
-
Search strategy
The search strategy comprised the following searches:
-
electronic databases: including The Cochrane Library (all sections) (Issue 2, 2009), MEDLINE (1996–April 2009), EMBASE (1996–April 2009), PsycINFO (1996–April 2009), Web of Science – limited to meeting abstracts (1996–April 2009)
-
websites of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Diabetes UK searched for meeting abstracts in April 2009.
-
websites of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), SMBG International Working Group, Current Controlled Trials, ClinicalTrials.gov
-
contact with experts in the field
-
scrutiny of bibliographies of retrieved papers.
The searches were limited to the English language and to articles published since 1996 (due to the number of recent good quality systematic reviews) and in order to reflect current meter technologies.
The search strategy did not include limits for study design, as all types of studies were screened manually for potential inclusion. Selection was carried out independently by two reviewers.
A separate search strategy for cost-effectiveness studies was performed and comprised searches of the following electronic databases: MEDLINE (1996–June 2009), EMBASE (1996–June 2009), Web of Science with Conference Proceedings – limited to meeting abstracts (1996–June 2009), Cochrane Library (Issue 2, 2009).
Appendix 1 gives details of the search strategies and flow of studies.
Quality assessment strategy
Consideration of study quality for systematic reviews and trials included the following factors [based on key criteria of the QUOROM and CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) statements].
Systematic reviews
-
Were inclusion/exclusion criteria that addressed the review question reported?
-
Were details of the literature search given?
-
Was study selection described and study flow shown?
-
Was data extraction described?
-
Was the validity of the included studies assessed?
-
Were sufficient details about the individual included studies presented (characteristics, quality and results)?
-
Was the statistical analysis appropriate?
Quality was rated as ‘high’ if no more than one of the quality criteria was not clearly fulfilled. Quality was rated as ‘moderate’ if two of the quality criteria were not clearly fulfilled (or three including study flow), and as ‘poor’ if more than two quality criteria were not fulfilled.
Randomised controlled trials
-
Adequate description of trial design and participants.
-
Method of randomisation.
-
Allocation concealment.
-
Blinding of outcome assessment.
-
Adequate power.
-
Numbers of participants randomised, excluded and lost to follow-up reported.
-
Intention-to-treat analysis performed, methods for handling missing data given.
-
Appropriateness of statistical analysis.
-
Baseline characteristics similar.
-
Funding of study.
Quality was rated as ‘high’ if no more than one of the quality criteria was not clearly fulfilled. Quality was rated as ‘moderate’ if two or three of the quality criteria were not clearly fulfilled, and as ‘poor’ if more than three quality criteria were not fulfilled.
Methods of analysis/synthesis
Initially, existing systematic reviews of SMBG were summarised and results compared. Reasons for differences between the reviews were investigated and possible reasons for conflicting results were investigated in a narrative review. Any RCTs and observational studies that were not included in the existing systematic reviews were data extracted and included. Details of any RCTs and observational studies included in the reviews were tabulated as far as reported in the reviews. Where there were doubts regarding the accuracy of the information in the reviews or where there was missing information, data were verified using the original papers.
Evidence synthesis of all of the studies meeting our inclusion criteria was carried out using a narrative review. Data were to be analysed by outcome and subgroups as outlined above. HbA1c data from RCTs were summarised using a meta-analysis (weighted mean differences, random effects model, inverse variance method). Heterogeneity was calculated using the chi-squared and I2 methods.
The following analyses were carried out: SMBG compared to SMUG, SMBG versus no SMBG (in studies, where different intensities of SMBG were compared to no SMBG, this comparison included the less intensive SMBG intervention), more intensive SMBG (e.g. more frequent, enhanced by special education elements, etc.) versus less intensive SMBG, and more intensive SMBG versus no SMBG.
Relevant studies were examined with respect to the following aspects:
-
Did patients receive education about SMBG:
-
– about how to do SMBG (use of equipment, etc.)
-
– about how to interpret results and how to respond
-
– who carried out the education?
-
-
Were the accuracy and frequency of monitoring (i.e. adherence) checked? (and by whom?)
-
How the monitoring results were used:
-
– for behaviour change by the patient
-
– for treatment (medication) adjustment by the patient
-
– for treatment (medication) adjustment by a doctor (or nurse)
-
– was feedback on monitoring results given? (if so, what kind?)
-
-
What message did the patients receive?
-
– For example, that monitoring helped people gain control of their disease and that there was no reason to feel guilty about off-range values or that off-range values were a bad thing
-
– Did patients get the impression that their doctor/nurse thought monitoring was a good thing and took note of the values?
-
-
How does benefit of SMBG vary by:
-
– starting HbA1c level (or stable/well controlled versus poor control)
-
– frequency of monitoring
-
– (type of) education
-
– susceptibility to (unnoticed) hypoglycaemia
-
– treatment (sulphonylureas versus other)
-
– age
-
– time point during the course of the disease (e.g. after diagnosis, during treatment change, at other times)?
-
Results
Functionality issues
Technical issues were discussed in the HTA report by Coster et al. :24
-
They evaluated a sample of studies on device validation, which suggested that issues of observer training, interdevice variability, effects of long-term use and patient acceptability were not usually addressed.
-
Some evidence [Brunner et al. (1998)]25 suggests that meter performance may be less satisfactory in the low glycaemic range and that there is some variation in the size and direction of measurement bias in different parts of the glycaemic range.
-
Development of memory meters showed that patients often make incomplete and incorrect recordings of blood glucose values in their diary records; sources of inaccurate readings include rounding values to the nearest whole number, omission of outlying values, reporting results when no test was recorded by the meter; over- and under-reporting often occurred together and was associated with higher HbA1c values and poor testing technique; occurrence of hypo- and hyperglycaemia was often obscured; informing patients of memory function of the meter led to correct readings. 26
-
In some patients readings may be inaccurate because wide variations in blood glucose values between readings go unnoticed.
-
Evidence that more accurate blood glucose readings may be obtained if patients are given sufficient training – need for formal training and updating of skills in the use of meters, especially in people with special needs.
-
Further work should be done to develop standard packages to train patients in the use of self-monitoring devices and to provide them with the information needed to adjust their therapy in accordance with self-monitoring results.
No more recent systematic reviews were found. There is some indication that devices are becoming more reliable. 27
Systematic reviews and included RCTs
There were 112,24,28–38 mostly high-quality reviews. The number of RCTs included ranged from 3 to 13 out of a total of 20 referenced RCTs (of which two were not strictly RCTs), as shown in Table 2. Our searches identified six additional RCTs (also shown in Table 2), of which two were published as abstracts only. 42,53
| RCTs | Systematic reviews | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHRQ (2007)28 | Faas (1997)30 | Coster (2000) (NHS HTA)24,29 | Sarol (2005)34,39 | Welschen (2005)36,37 | Jansen (2006)31 | McAndrew (2007)2 | McGeoch (2007)32 | Poolsup (2008)33 | Towfigh (2008)35 | St John (2009)38 | Additional | |
| Allen (1990)40 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||||
| Barnett (2008)41 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Bonomo (2006)42 (abstract) | Yes | |||||||||||
| Brown (2002)43 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Cho (2006)44 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Davidson (2005)45 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Estey (1990)46 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
| Farmer (2007)10,11 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
| Fontbonne (1989)47 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Gallichan (1994)48 | Yes | Yes | ||||||||||
| Guerci (2003)49 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Jaber (1996)50 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
| Johnson (2006)51 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Jones (2003)52 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Joy (2003)53 (abstract) | Yes | |||||||||||
| Kibriya (1999)54 | Yes | Yes | ||||||||||
| Kwon (2004)55 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
| Miles (1997)56 | Yes (but judged to be non-randomised) | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
| Moreland (2006)20 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Muchmore (1994)57 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| O’Kane (2008)13 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Rutten (1990)58 | Yes (but judged to be non-randomised) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Scherbaum (2008)59,60 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Schwedes (2002)61 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Seaton (1996)62 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Wing (1986)63 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
Four of the reviews also included a range of 6–18 non-randomised/observational studies. [Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ; 2007),28 McAndrew et al. (2007),2 McGeoch et al. (2007)32 and St John et al. (2009)38]. Appendix 2 gives the characteristics of the systematic reviews.
Table 3 shows 31 observational or pseudoexperimental studies included in four of the systematic reviews,2,28,32,38 and another five relevant studies67,82,88,92,94 were identified which were not included in any of the reviews (three published as abstracts only). Table 4 shows the conclusions of the reviews, and Table 5 shows the results of any meta-analyses reported in the reviews.
| Observational study | Systematic reviews | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHRQ (2007)a,28 | McGeoch (2007)32 | McAndrew (2007)2 | St John (2009)38 | Additional | |
| Bajakowska-Fiedziukiewicz (2008)64 | Yes | ||||
| Banister (2004)65 | Yes | ||||
| Blonde (2002)66 | Yes | Yes | |||
| Capelson (2006)67 (abstract) | Yes | ||||
| Chan (2000)68 | Yes | ||||
| Davis (2006)18,19 | Yes | Yes | |||
| Evans (1999)69 | Yes | ||||
| Franciosi (2001)70 | Yes | Yes | |||
| Franciosi (2005)71 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Hanninen (2001)72 | Yes | ||||
| Harris (2001)73 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Jaworska (2004)74 | Yes | ||||
| Karter (2001)75 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Karter (2005)76 | Yes | ||||
| Karter (2006)14 | Yes | Yes | |||
| Klein (1993)77 | Yes | ||||
| Martin (2006)15,78 | Yes | ||||
| Meier (2002)79 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Mitchell (2004)80 | Yes | ||||
| Murata (2003)81 | Yes | ||||
| Murata (2009)82 | Yes | ||||
| Newman (1990)83 | Yes | ||||
| Oki (1997)84 | Yes | ||||
| Ozmen (2003)85 | Yes | ||||
| Patrick (1994)86 | Yes | ||||
| Rindone (1997)87 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Roblin (2001)88 (abstract) | Yes | ||||
| Rost (1990)89 | Yes | ||||
| Schiel (1999)90 | Yes | ||||
| Schütt (2006)91 | Yes | Yes | |||
| Secnik (2007)92 | Yes | ||||
| Soumerai (2004)93 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Stiptzarov (2003)94 (abstract) | Yes | ||||
| Tengblad (2007)95 | Yes | ||||
| Wen (2004)16 | Yes | Yes | |||
| Wieland (1997)96 | Yes | Yes | |||
| Study | Conclusions (medical effectiveness) | Recommendations for research | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faas (1997)30 |
HbA1c: efficacy of SMBG in non-insulin dependent patients with T2DM is questionable Hypoglycaemia (frequency and severity): not reported QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? not reported Treatment change in response to measurements (insulin dose, oral drug dose, etc.): not reported Behaviour change in response to measurements (diet, exercise etc.): not reported Weight: limited evidence Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported |
|
|
| Coster (2000) (NHS HTA)29 |
HbA1c: there is no evidence to show that SMBG or SMUG improves glucose control measured using GHb or FPG; there is no evidence that glucose monitoring is more effective than urine glucose monitoring in improving glucose control Hypoglycaemia (frequency and severity): not reported by trials QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? patients’ perceptions of monitoring were neither completely nor rigorously studied and further work is need in this area; urine testing is preferred by some patients Treatment change in response to measurements (insulin dose, oral drug dose, etc.): not reported Behaviour change in response to measurements (diet, exercise, etc.): not reported Weight: no significant effect of SMBG vs control or SMUG Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: urine testing is less costly than blood testing General: the studies reviewed had low statistical power and were poorly reported and conducted; small but clinically relevant changes might not have been detectable |
|
|
| Sarol (2005)34,39 | HbA1c: in the short term and when integrated with educational advice, SMBG as an adjunct to standard therapy may contribute to improving glycaemic control among non-insulin-requiring patients with T2DM; SMBG does not improve glycaemic control in isolation; proper use of SMBG data can guide clinical decisions and improve control only if SMBG results are used to modify behaviour, diet, exercise and medications |
|
|
| Welschen (2005)36,37 |
HbA1c: SMGB might be effective in improving glycaemic control in patients with T2DM not using insulin; meta-analysis resulted in a statistically significant and clinically relevant reduction of HbA1c (–0.39%) Hypoglycaemia (frequency and severity): not reported QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? not enough information in trials for conclusive results Behaviour change in response to measurements (diet, exercise, etc.): not reported Weight: not reported Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported |
|
|
| Jansen (2006)31 |
HbA1c: SMBG is effective in reducing HbA1c in T2DM – regular feedback is important; SMBG is likely to be more effective than SMUG Hypoglycaemia (frequency and severity): not reported QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? not reported Treatment change in response to measurements (insulin dose, oral drug dose, etc.): not reported Behaviour change in response to measurements (diet, exercise, etc.): not reported Weight: not reported Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported |
|
|
| AHRQ (2007)28 |
HbA1c: the studies may suggest small but possibly clinically non-significant reductions in HbA1c with SMBG; but overall studies are inconclusive; uncontrolled and cohort studies agreed with RCTs in finding small reductions in HbA1c; no conclusions regarding the frequency of SMBG and HbA1c Hypoglycaemia: considered three cohort studies investigating SMBG and hypoglycaemia, but all patients were insulin treated and large proportions were patients with T1DM – effect of SMBG on hypoglycaemia unclear QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? not reported Treatment change in response to measurements: not reported Weight: not reported Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported |
|
|
| McAndrew (2007)2 |
HbA1c: SMBG may be effective in controlling glucose for patients with T2DM Hypoglycaemia: not reported QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? One study found SMBG to be associated with higher depression but QoL unchanged in another two studies and improved in the SMBG group in one trial Treatment change in response to measurements: not reported Weight: not reported Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported |
Steps required for SMBG to be effective – patients must:
|
|
| McGeoch (2007)32 |
HbA1c: neither RCTs nor observational studies provided conclusive evidence for or against SMBG; larger observational studies showed better results in patients with higher initial HbA1c levels Hypoglycaemia: not reported QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? not reported Treatment change in response to measurements: not reported Weight: not reported Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported SMBG use: data suggests that fewer than 60% of patients with T2DM using diet and/or hypoglycaemic agents practice SMBG on a regular basis Other: observational study with the longest FU (6.5 years) had significantly lower mortality and morbidity in SMBG group than in non-SMBG group |
|
None of the studies examined how SMBG is used to modify patients’ lifestyles (which is also dependent on context of carrying out SMBG and incentives provided, e.g. free strips/monitors); none of the evidence addresses SMBG in terms of consistent guidance relating to when and how to monitor, and how to interpret and act on the results; frequent monitoring is meaningless unless the results are acted upon to prevent long-term diabetes complications Question may not be whether SMBG confers benefits on average, but for which particular patients, and how can they be identified? SMBG may not be helpful or economically justified in all cases, but it seems likely that individuals would benefit if: |
| Poolsup (2008)33 |
HbA1c: The evidence suggests that SMBG is beneficial in improving HbA1c, especially when used to adjust therapeutic regimens Hypoglycaemia: not reported QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? not reported Treatment change in response to measurements: not reported Weight: not reported Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported |
|
|
| Towfigh (2008)35 |
HbA1c: modest but statistically significant improvement in HbA1c at 6 months in patients with T2DM not requiring insulin when SMBG and education were added to management (–0.21%, 95% CI –0.38 to –0.04); 12-month result not significant; meta-regression suggested that effects may be lower with higher baseline HbA1c Hypoglycaemia: limited evidence of three trials suggests that SMBG may increase the frequency of recognised hypoglycaemia QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? not reported Treatment change in response to measurements: not reported Weight: not reported hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported |
|
|
| St John (2009)38 |
HbA1c: modest but statistically significant improvement in HbA1c in patients with T2DM not requiring insulin when using SMBG for up to 12 months (seven RCTs, –0.22% (95% CI –0.34 to –0.11)); finding consistent with most observational studies of similarly treated patients Hypoglycaemia: not reported QoL/measure of empowerment – self-efficacy? not reported Treatment change in response to measurements: not reported Weight: not reported Hospital admissions: not reported Costs: not reported |
|
Comments on potential modifiers:
|
| Outcome | Results of meta-analysis (for SBMG minus comparator, so negative value = better on SMBG) |
|---|---|
| Coster (2000)29 | |
| HbA1c | |
| Effect of blood or urine monitoring on GHb vs control | –0.25% (95% CI –0.61 to 0.10; p = NS) (four studies) |
| SMBG vs SMUG | –0.03% (95% CI –0.52 to 0.47; p = NS) |
| Weight | |
| Effect of blood or urine monitoring on weight vs control | –0.28 kg (95% CI –1.48 to 0.98; p = NS) (four studies) |
| SMBG vs SMUG | 0.36 kg (95% CI –1.93 to 2.65; p = NS) |
| Sarol (2005)34,39 | |
| HbA1c | |
| SMBG vs non-SMBG (random effects) | –0.42% (95% CI –0.63 to –0.21; p < 0.05) (eight studies) |
| Welschen (2005)36,37 | |
| HbA1c | |
| SMBG vs control | –0.39% (95% CI –0.56 to –0.21; p < 0.05) (five studies) |
| SMBG vs SMUG | –0.17% (95% CI –0.96 to 0.61; p = NS) (two studies) |
| Jansen (2006)31 | |
| HbA1c (adjusted for baseline HbA1c to all T2DM patients) | |
| No self-monitoring | –0.47% (95% CrI: –0.66 to –0.28) |
| SMUG | –0.61% (95% CrI: –1.20 to –0.05) |
| SMBG | –0.87% (95% CrI: –1.14 to –0.58) |
| SMUG vs control | –0.19% (95% CrI: –0.80 to 0.44; Pr = 74%) |
| SMBG vs control | –0.41% (95% CrI: –0.72 to –0.06; Pr = 98%) |
| SMBG + FB vs control | –1.13% (95% CrI: –1.87 to –0.35; Pr = 99%) |
| SMBG vs SMUG | –0.21% (95% CrI: –0.82 to 0.39; Pr = 78%) |
| SMBG + FB vs SMUG | –0.95% (95% CrI: –1.78 to –0.09; Pr = 98%) |
| SMBG + FB vs SMBG | –0.73% (95% CrI: –1.41 to –0.04; Pr = 98%) |
| Subgroups | Results similar for non-insulin-requiring patients with T2DM |
| Poolsup (2008)33 | |
| HbA1c | |
| SMBG vs no SMBG | –0.24% (95% CI –0.37 to –0.12; p = 0.0002) (seven trials) |
| SMBG vs no SMBG – SMBG results used to modify therapy | –0.27% (95% CI –0.41 to –0.14; p = 0.0001) (six trials) |
| SMBG vs no SMBG – SMBG results not used to modify therapy | –0.12% (95% CI –0.32 to 0.08; p = NS) (six trials) |
| Towfigh (2008)35 | |
| HbA1c | |
| SMBG vs no SMBG ≥ 1 year | –0.16% (95% CI –0.38 to 0.05; p = NS) (five trials) |
| SMBG vs no SMBG 6 months | –0.21% (95% CI –0.38 to –0.04; p < 0.05) (six trials) |
| St John (2009)38 | |
| HbA1c | |
| SMBG vs no SMBG | –0.22% (95% CI –0.34 to –0.11; p < 0.05) (seven trials) |
| SMBG vs no SMBG to duration < 1 year | –0.26% (95% CI –0.40 to –0.11; p = 0.001) (five trials) |
| SMBG vs no SMBG to duration ≥ 1 year | –0.17% (95% CI –0.36 to + 0.02; p = 0.072) (two trials – DiGEM to ESMON) |
Only two reviews were not of high or moderate quality. 28,30 Six reviews24,29,31,34,36,38 included a meta-analysis of RCTs, of which several performed subgroup analyses, for example based on trial duration of whether patients received feedback on their SMBG results or not. Most reviews focused on T2DM, with some excluding trials in insulin-treated patients. The trials included mostly compared SMBG with no SMBG. Three trials40,47,56 compared SMBG with SMUG (urine monitoring), and nine trials10,11,42–44,46,50,55,59–61 compared a more intensive SMBG intervention with a less intensive one.
The systematic reviews provided evidence both in support of the benefits of SMBG and evidence that it can be associated with increased anxiety and levels of depression in users. However, the size of benefit was often very small and below the change in HbA1c level that is usually considered clinically significant (0.5% – although this is a somewhat arbitrary figure). There is a lack of evidence on why SMBG clearly does not work for some patients, and on which patients are most likely to benefit from the technology. Results are presented addressing outcome measures such as HbA1c level, rather than exploring issues predicting success or failure, and there is little exploration of either accuracy of results or whether behaviour/therapy changes are made based on those results. Furthermore, there is little evidence in the literature regarding the way in which HCPs collaborate with patients regarding how to interpret and act on readings.
Mixed results were reported among systematic reviews in terms of improvements in HbA1c level with SMBG compared to no monitoring. Five reviews include a meta-analysis,24,29,31,34,37 with the newer ones all showing some significant reduction of HbA1c level in the SMBG groups versus control (between –0.21% and –0.42%). Towfigh et al. (2008),35 however, found only a short-term significant reduction of HbA1c at 6 months but this was not sustained after a year or more. The Bayesian meta-analysis (including indirect comparisons) by Jansen et al. (2006)31 found a reduction of –1.13% with SMBG plus feedback given to patients versus no self-monitoring. This difference is much larger than those from other reviews, and may be due to the use of indirect comparisons. Poolsup et al. (2008)33 found a significant difference in HbA1c level overall (–0.24% SMBG versus no SMBG), but, when comparing trials where SMBG results were used to modify therapeutic regimens with those that did not, only the results for the former were statistically significant and the difference (–0.27%) was not clinically significant. There was no significant difference between SMBG and urine monitoring. Some of the reviews reported results on weight and showed that there was no significant effect of SMBG versus no monitoring on weight.
Reviews tended to focus on comparisons between SMBG and no SMBG and on trials reporting HbA1c level as an outcome. There was less consideration of studies looking at different modes of using SMBG, for example frequency, duration of monitoring, purpose, etc. This could potentially highlight why some of the important components of a successful SMBG intervention are not fully explored. Features predicting success/failure include:
-
The SMBG regimens used in the trials were very different, ranging from 6 times per day for 6 days per week, to less frequent regimens or no fixed regimen, i.e. at patient’s discretion.
-
Most trials did not give any details on changes made to therapy or lifestyle based on SMBG results;32 in some trials, therapy changes were made by physician/nurse but the patient was not allowed to change anything. No trials reported patients being actively encouraged to make behaviour/lifestyle changes based on results of SMBG.
-
No feedback on results was given to patients. There appears to be difference in expectation between HCPs and patients, in that patients expect HCPs to make decisions based on the readings they provide, whereas HCPs see SMBG as a tool for patients to make behaviour/lifestyle changes.
-
SMBG readings were taken at inappropriate times and so it was impossible to gain meaningful results. 38
-
Efficacy of SMBG may be lower when baseline HbA1c level is higher, i.e. SMBG may be least effective for those who need it most. 35 This could be because at higher levels they have little scope to alter treatment or perhaps because those with higher levels are less willing to self manage.
-
While several trials included an educational/counselling component, this was not widespread across all trials and the detail of education was not provided. In some cases, interventions were incomparable between cohorts, thus contributing to possible confounding variables.
-
SMBG accuracy checks were not carried out in the majority of trials therefore it cannot be known whether readings represented an accurate reflection of blood glucose. Furthermore, McGeoch et al. (2007)32 raises questions about whether some participants are sufficiently literate and numerate to be able to take advantage of the intervention.
-
Only a very limited range of outcomes was reported – mainly HbA1c level, with few reviews reporting weight, hypoglycaemia, QoL or adverse effects. Behaviour change was acknowledged; however, the extent to which behaviour was adjusted or specific adjustments remains unclear.
-
Many included trials were of poor quality, i.e. sample sizes were often small and many trials had short follow-up times. Randomisation techniques were not described in many studies. 24,29,34 The study by Worth et al. ,97 as reported in a review by Coster et al. ,24,29 suggests that the main benefit of self-monitoring was an educational modality, leading to increased contact time with diabetes care staff and greater motivation. Any effects were short-lived and future research should focus on long-term results.
None of the systematic reviews addressed variations in benefit from SMBG by frequency of monitoring, type of education, susceptibility to hypoglycaemia, treatment, age, starting HbA1c level or time points during the course of diabetes (for example after diagnosis, during treatment change, etc.). One review noted that SMBG had no clear benefit on HbA1c level in a number of observational studies but did have some in RCTs. 2 Furthermore, in one study,40 reported in a review by McAndrew et al. ,2 there was a trend towards younger and better-educated participants improving more with SMBG. The prevalence of T2DM in ever younger patients needs to be explored in terms of use and effectiveness of SMBG because if there are no apparent benefits, yet individuals are encouraged to continue testing, the long-term financial costs are going to be enormous.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose does not improve glycaemic control in isolation,34 but proper use of SMBG data can guide clinical decisions and improve control if results are used only to modify behaviour, diet, exercise and medications. Optimal and realistic testing frequencies need to be explored, i.e. is it achievable by patients, do patients need to perform SBMG indefinitely or would time-limited periods be sufficient to address specific questions? One could suggest that testing 6 days per week before and after meals places an unnecessary burden on patients who are treated using diet and exercise alone.
Randomised controlled trials
Appendix 3 shows details of the 26 relevant RCTs identified from the reviews and from our additional searches.
Trial duration/follow-up ranged from 12 weeks to 30 months. Participant numbers varied from less than 30 to over 800, with over 100 participants in the majority of trials. Some trials included only non-insulin-treated patients, whereas others specified no medication restrictions. Trials generally provided no details of oral anti-hyperglycaemic treatment received and no details of subgroups of patients (e.g. those taking sulphonylureas or those susceptible to hypoglycaemia), therefore separate assessments by treatment type could not be carried out. A few trials included small numbers of patients also taking insulin, but no details were provided of subgroups taking insulin. Primary outcome measures were mainly HbA1c level, but trials also assessed a range of additional outcomes such as HbA1c level fluctuations, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), fructosamine, episodes of hypoglycaemia, weight/body mass index (BMI), diabetes self-care activities, adverse effects, frequency of SMBG, QoL, medication use, health-care utilisation and lipid parameters.
No adequate data for meta-analysis were available for outcomes other than HbA1c level, and no data on relevant subgroups could be identified (neither for narrative nor for statistical analysis).
Due to the limitations of the data, most of the original questions of this review could not be answered, as not enough data on relevant subgroups by treatment or patient characteristics were presented.
Most trials had serious quality deficits (see Appendix 3). Only four of the trials [Barnett et al. (2008),41 Farmer et al. (2007)10 (DiGEM), O’Kane et al. (2008)13 (ESMON) and Scherbaum et al. (2008)60] could clearly be classified as high quality, while more than half of the studies were classified as clearly being of poor quality. Randomisation and allocation concealment was often not described, sample sizes were often small, and some trials had substantial losses to follow-up. Additionally, important aspects of the SMBG intervention were not clearly described by many of the trials (e.g. what kind of instructions and education was received, how and if feedback was given, whether SMBG technique was checked, whether monitoring frequency was checked (and how frequently people were monitored, etc.).
Two of the high-quality trials, O’Kane et al. (2008 – ESMON)13 and Barnett et al. (2008 – DINAMIC; Diamicron MR in NIDDM: assessing management and improving control),41 have been criticised on the grounds that they were both in recently diagnosed patients whose control was poor, and was going to improve with treatment and intensive education whether SMBG was used or not. 98 In the control groups, HbA1c level improved from 8.6% to 6.9% (ESMON) and from 8.1% to 7.2% (DINAMIC), hence leaving little scope to show benefit from SMBG.
The DiGEM trial has been criticised on similar grounds because control was quite good at baseline (mean HbA1c level = 7.5%), making further improvements difficult. 98
Table 6 presents an attempt to classify the studies by the moderators we identified as being potentially important. Overall, less than half the studies found better HbA1c values in the intervention group than in the control group. All the studies that did find more favourable results for the intervention included an education component and/or feedback on SMBG results.
| Study | Comparison | SMBG instruction | Education/counselling | Feedback given | Treatment adjustment | SMBG regimen | Starting HbA1c level | Age | Treatment | Diabetes duration | Hba1c results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allen (1990)40 | SMBG vs SMUG | Yes | Yes (both) | Yes | Doctor | Moderate | 12 | 58 | Diet, oral | 8 | NS |
| Barnett (2008)41 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (both) | Unclear | No | Moderate | 8 | 56 | Diet, MET/SU | 3 | SMBG better |
| Bonomo (2006)42 | SMBG profile once per month vs more detailed SMBG profile every 2 weeks | No | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Infrequent | 8 | 65 | Diet, oral | 11 | More frequent better |
| Brown (2002)43 | SMBG plus education vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (only intervention) | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | 12 | NR | Oral | NR | Unclear |
| Cho (2006)44 | Internet vs non-internet SMBG | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | 7.6 | 53 | Diet, oral, insulin | 7 | SMBG better |
| Davidson (2005)45 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Unclear | Yes (both) | Unclear | Doctor/nurse | Frequent | 8.5 | 50 | MET/SU | 6 | NS |
| Estey (1990)46 | SMBG + feedback vs SMBG no feedback | Yes | Yes (both) | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | 6.2 | 55 | Diet, oral | NR | NS |
| Farmer (2007)10 | SMBG intensive vs SMBG less intensive vs no SMBG | No | Yes | Yes | Patient (intensive) | Moderate | 7.5 | 66 | Diet, oral | 3 | NS |
| Fontbonne (1989)47 | SMBG vs SMUG vs no SMBG | Yes | Limited | Yes | Doctor | Moderate | 8.3 | 55 | Diet, oral | 12.5 | NS |
| Gallichan (1994)48 | SMBG vs SMUG | Yes | No | No | Unclear | Unclear | NR | 64 | Diet, oral | NR | NS |
| Guerci (2003)49 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Yes | No | Unclear | Doctor | Frequent | 9 | 62 | MET/SU | 8 | SMBG better |
| Jaber (1996)50 | SMBG plus education vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (only intervention) | Unclear | Doctor? | Moderate | 9.5 | 62 | Unclear | 6.8 | SMBG better |
| Johnson (2006)51 | Free blood glucose meter plus testing strips vs free blood glucose meter | Yes | No | No | No | Frequent | 7.4 | 68 | Diet, oral | 8 | NS |
| Jones (2003)52 | PTC plus SMBG vs PTC vs SMBG vs control | No | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | 8.5 | 55 | Oral, insulin | 10.5 | NS |
| Joy (2003)53 | Preprandial SMBG vs postprandial SMBG | NR | NR | NR | Doctor | Frequent | 8.4 | NR | Oral, insulin (?) | NR | NS |
| Kibriya (1999)54 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (both) | Unclear | Patient | Infrequent | NR | 50 | Oral, insulin | NR | SMBG better (?) |
| Kwon (2004)55 | Internet vs non-internet SMBG | Unclear | Yes (only intervention) | Yes | Patient | Moderate | 7.3 | 54 | NR | 5.6 | SMBG better |
| Miles (1997)56 | SMBG vs SMUG | Unclear | Yes (both) | Unclear | Unclear | Frequent | 10.3 | 65 | Oral, insulin | 0 | NS |
| Moreland (2006)20 | BG meter + manual vs BG meter vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (all) | Unclear | Unclear | NR | 9 | 48 | Oral, insulin | 10 | NS |
| Muchmore (1994)57 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (both) | Yes | Doctor | Frequent/moderate | 10.4 | 59 | NR | 5.5 | NS |
| O’Kane (2008)13 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (both) | Yes | Patient/doctor? | Moderate/frequent | 8.7 | 60 | Diet, oral | 0 | NS |
| Rutten (1990)58 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Yes | No | Yes | Doctor | Infrequent | 9.3 | 63 | Diet, oral | 8.8 | SMBG better |
| Scherbaum (2008)60 | High SMBG vs low SMBG vs no SMBG | Unclear | No | Yes | Doctor | Moderate/infrequent | 7.2 | 62 | Diet, MET/SU | 8 | NS |
| Schwedes (2002)61 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (different in two groups) | Unclear | Unclear | Moderate | 8.5 | 60 | Diet, oral | 5.3 | SMBG better |
| Seaton (1996)62 | SMBG vs no SMBG | NR | NR | NR | Doctor | NR | NR | NR | Oral | NR | Unclear |
| Wing (1986)63 | SMBG vs no SMBG | Yes | Yes (both) | Yes | Doctor | Frequent | 10.5 | 54 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | NS |
The following figures (Figures 1–4) show the results of our meta-analyses. In total, 10 RCTs were included in the meta-analysis of (‘simple’) SMBG versus no SMBG. Overall, there was a small but significant reduction of HbA1c level with SMBG of –0.21% (95% CI –0.31 to –0.10, p < 0.0001, no significant heterogeneity). None of the studies comparing SMBG with SMUG (three RCTs) found a significant difference, and there was no significant difference overall (–0.06%, 95% CI –0.69 to 0.56, no significant heterogeneity).
FIGURE 1.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) versus no SMBG – HbA1c.
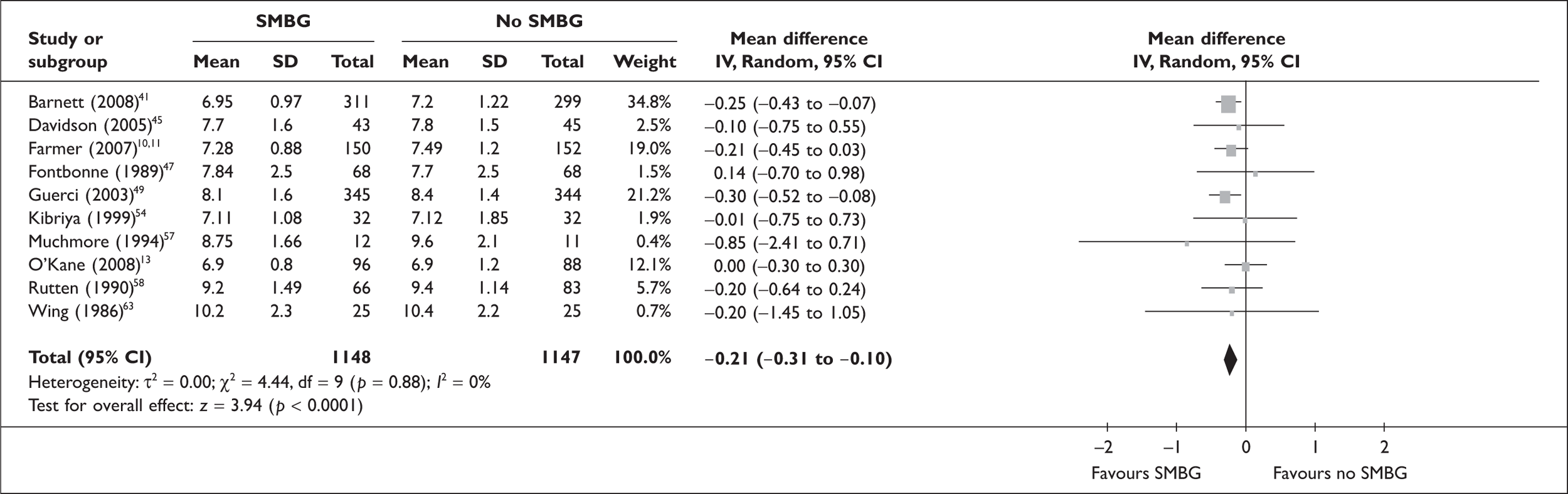
FIGURE 2.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) versus SMUG – HbA1c.
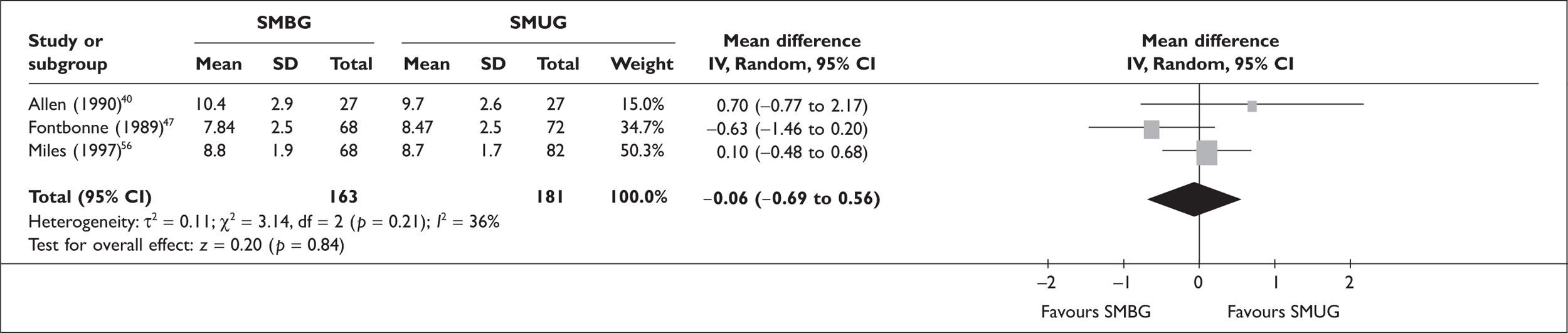
FIGURE 3.
Enhanced/more frequent SMBG versus only/less frequent SMBG – HbA1c.
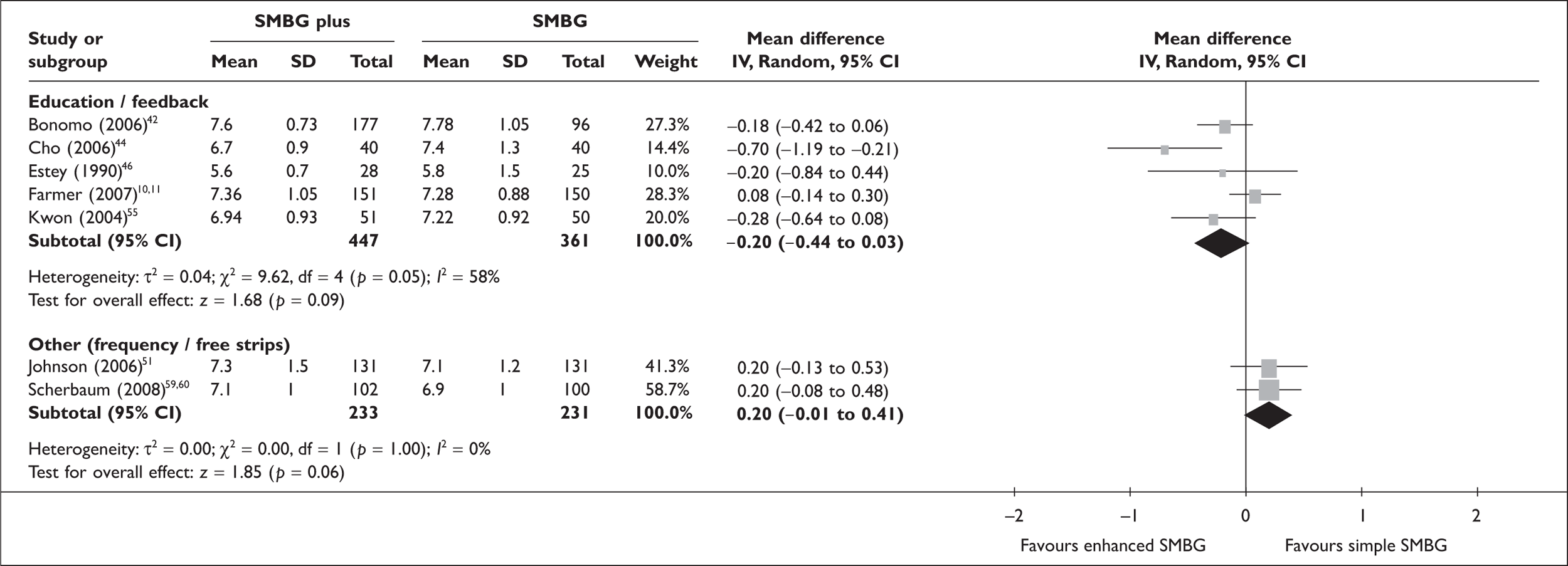
FIGURE 4.
Enhanced SMBG versus no SMBG – HbA1c.
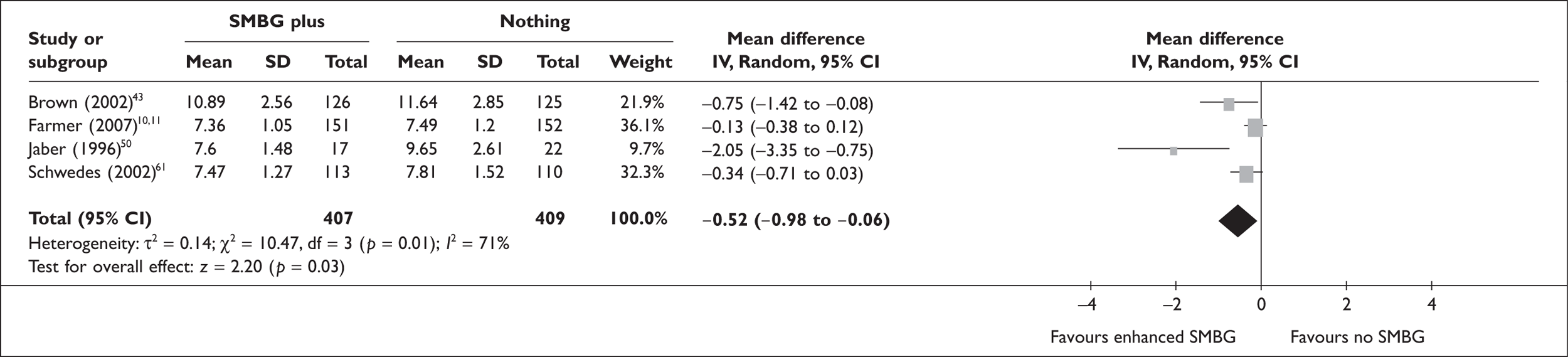
For the meta-analysis of ‘enhanced’ SMBG versus ‘simple’ SMBG, ‘enhanced’ SMBG was subdivided into those studies with a component of education and/or feedback and those using other methods (higher versus lower frequency of monitoring, free provision of strips versus no free provisions of strips). HbA1c level reduction when comparing SMBG with an educational/feedback component with ‘simple’ SMBG was in the same order of magnitude as when comparing ‘simple’ SMBG with no SMBG; however, the difference was not quite significant: –0.2% (95% CI –0.44 to 0.03; p = 0.09), with significant heterogeneity. There was no significant effect of providing free strips on HbA1c, or of decreasing the frequency of monitoring. For comparisons between enhanced SMBG and no SMBG (four RCTs), there was a significant difference in favour of enhanced SMBG of –0.52% (95% CI –0.98 to –0.06; p = 0.03). All studies in this group included some education or feedback component in the SMBG group only. There was significant heterogeneity, which was clearly due to an outlier study. 50
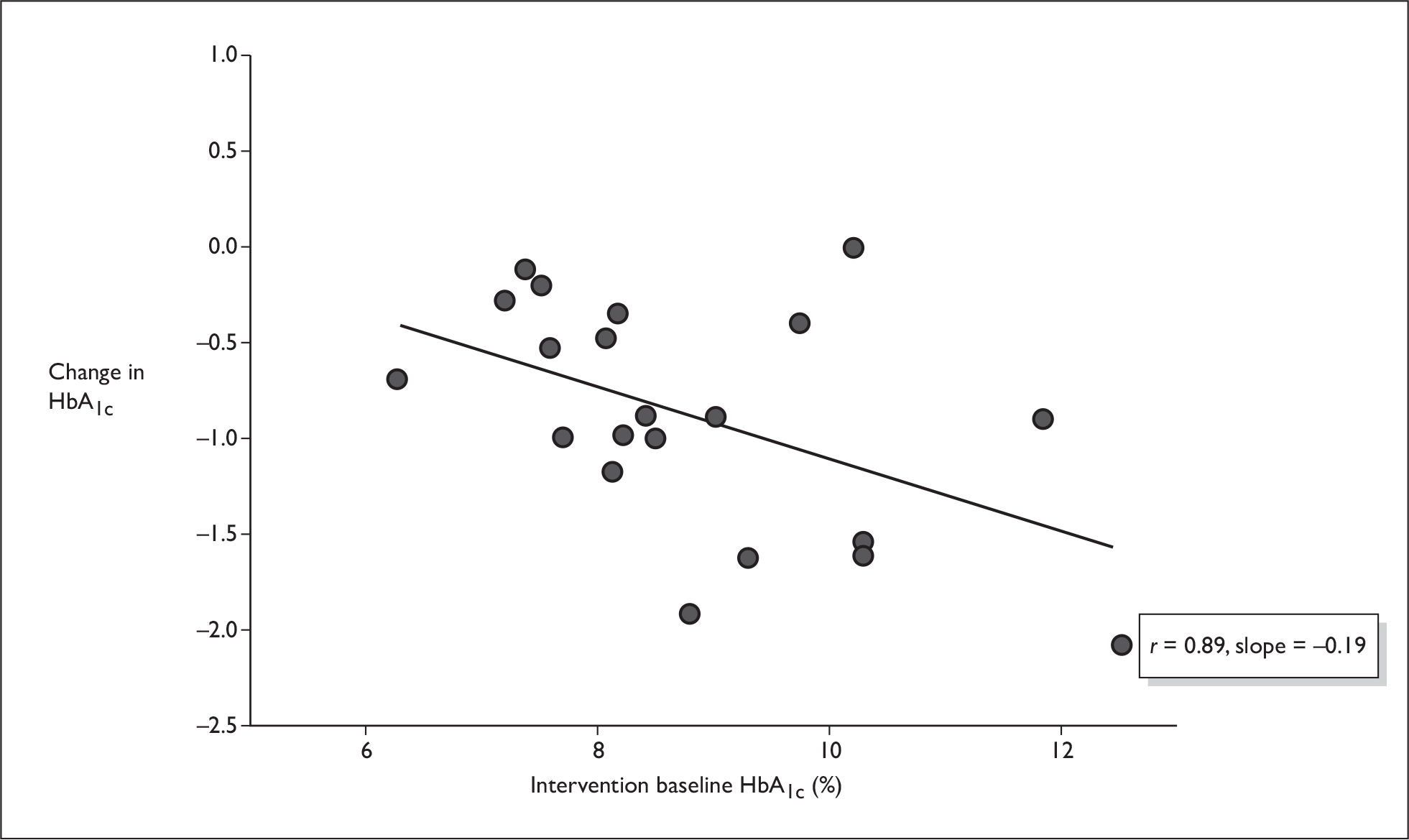
Figures 5–7 show some crude analyses of changes in HbA1c level dependent on baseline HbA1c level for all trials considered together. The graphs suggest that while both control groups and intervention groups showed a decrease in HbA1c level, which was larger with high baseline HbA1c values than with low baseline HbA1c values (Figures 6 and 7), the difference between the change in the control group and the change in the intervention group also increased with higher baseline HbA1c values (Figure 5).
FIGURE 5.
Treatment difference as a function of mean baseline HbA1c.
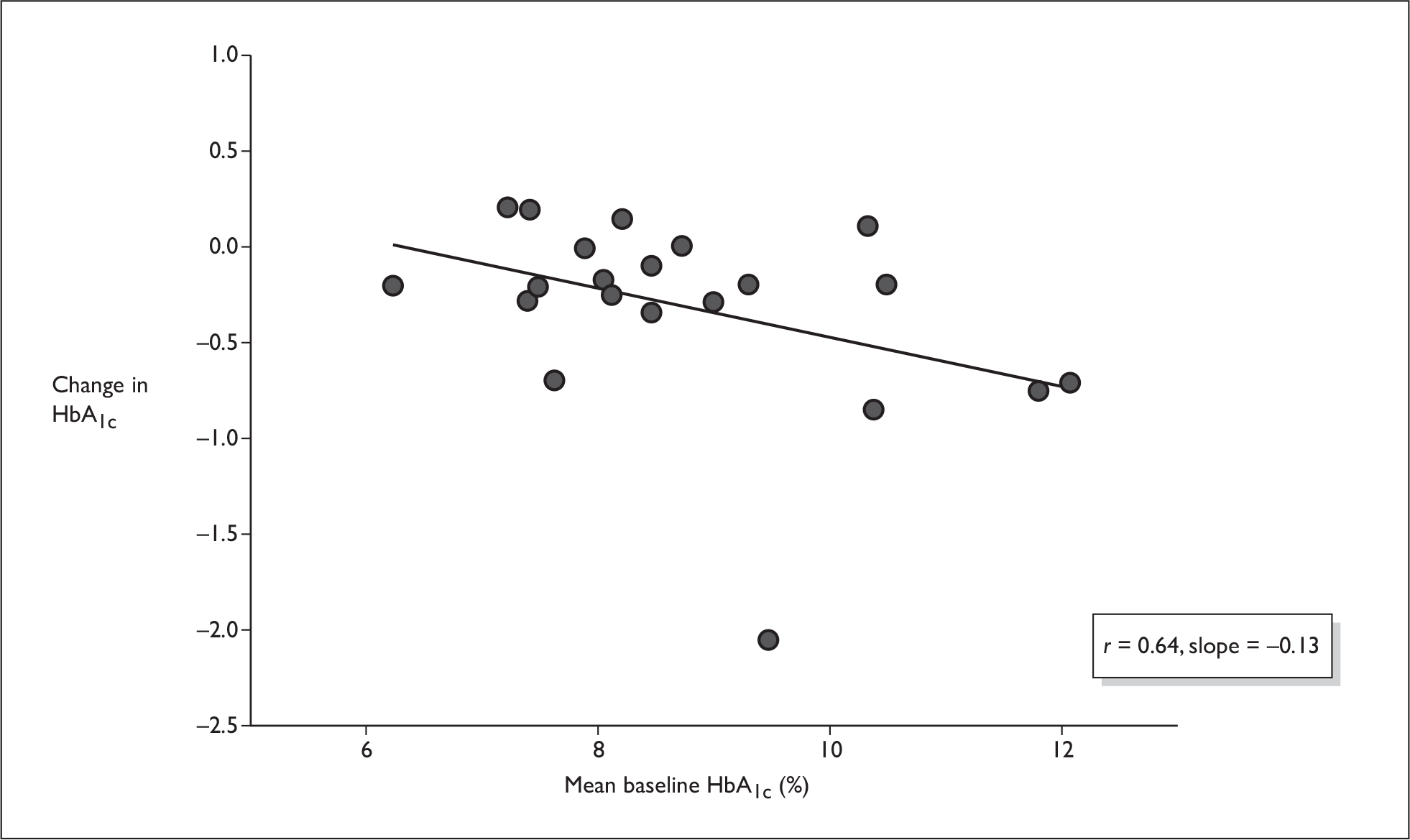
FIGURE 6.
Change from baseline as a function of baseline HbA1c (control group).
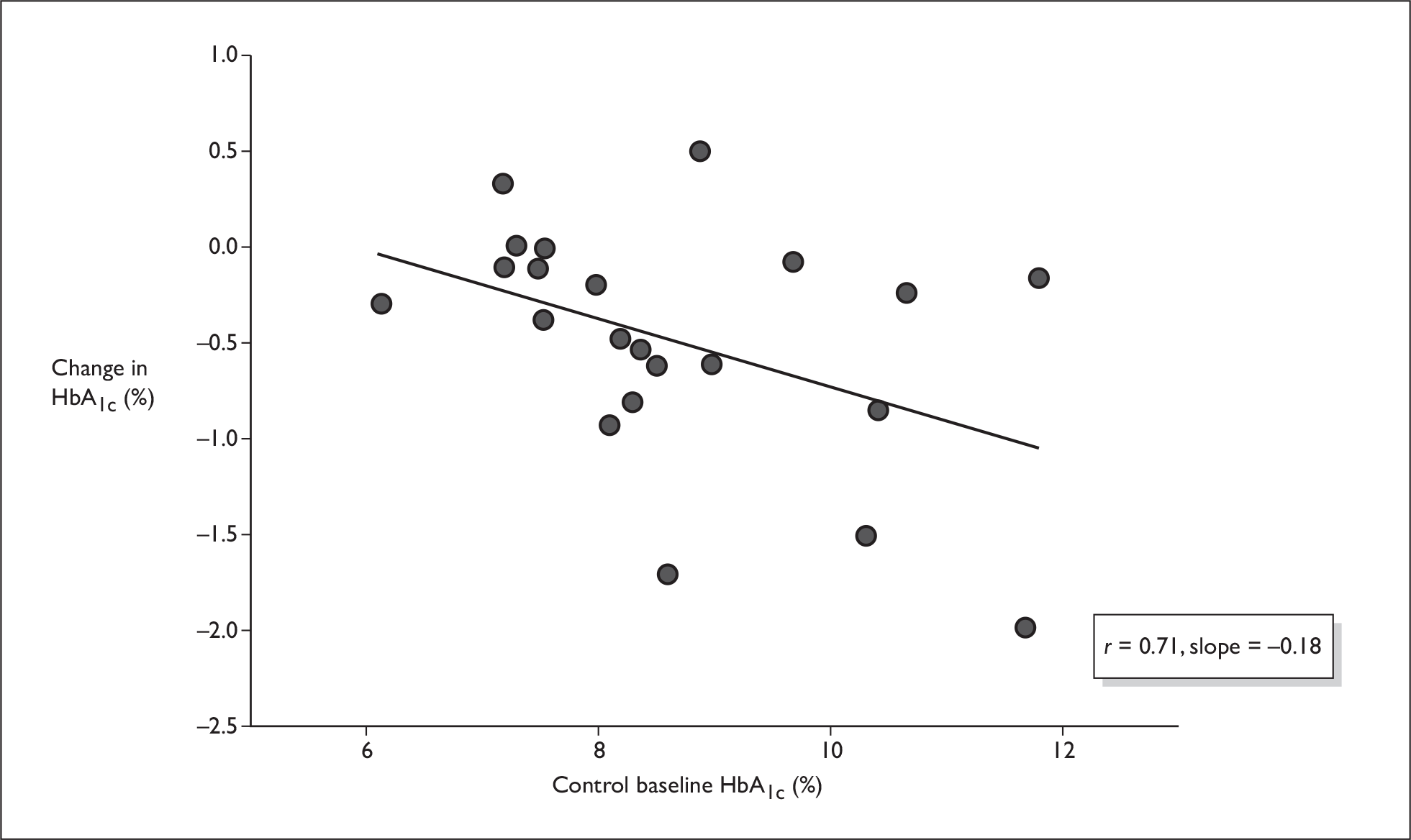
FIGURE 7.
Change from baseline as a function of baseline HbA1c (intervention group).
Details of other outcomes reported by the RCTs are shown in Appendix 4.
Hypoglycaemic events were reported by six RCTs. 10,13,41,49,54,60 Results for this outcome were inconsistent, although there was a suggestion that occurrence of (mild or moderate) hypoglycaemia was increased with more frequent self-monitoring.
Thirteen RCTs reported on weight or BMI and none found a significant difference between the intervention groups. Results on lipid parameters were reported by six RCTs and were inconsistent, with most studies finding no significant difference between groups. Similarly, no difference was found by a small number of studies reporting on blood pressure.
SMBG adherence was reported by eight RCTs. In most studies using a form of enhanced SMBG, adherence was greater in enhanced group – only the DiGEM trial10 reported reduced SMBG adherence in the more intensive group.
Data on medication changes were provided by seven RCTs. 10,45,49,55,61,63 None found a significant difference between groups (which could be a reason for the limited effectiveness of SMBG). Only two studies reported on behaviour changes (diet or physical activity) and one found improved dietary adherence in the SMBG group compared to the control group.
Seven studies reported on outcomes such as QoL, well-being, treatment satisfaction and depression. 10,13,20,56,57,61,63 For most measures, there was no significant difference between SMBG and no SMBG. However, both the DiGEM10 trial and the ESMON13 trial reported increased depression in the SMBG group (more intensive SMBG group for the DiGEM trial). The DiGEM trial found no significant difference between comparison groups for mobility, self-care, usual activities and pain; the ESMON trial found no significant differences for anxiety (p = 0.07), positive well-being and energy. On the other hand, two trials specifically including education/counselling components emphasising a positive attitude to SMBG20,61 found improved outcomes for negative affect with respect to SMBG and depression. In one study of SMBG versus SMUG, 70% of patients preferred SMUG to SMBG for ease of use (versus 15% preferring SMBG), 44% preferred SMUG for acceptability (versus 31% for SMBG), but 76% preferred SMBG for perceived accuracy (versus 11% SMUG) and 49% for usefulness (versus 21% SMUG).
Observational and non-randomised experimental studies
Appendix 5 shows details of the 36 observational and non-randomised studies identified (details for studies in reviews as far as provided by the reviews). Most studies only provided very limited details on SMBG methods and participants. Most studies examined the relationship between SMBG use and HbA1c level. An overview of the relevant parameters examined by the observational and non-randomised experimental studies is shown in Table 7.
| Study | Focus | SMBG method | Education/counselling | Starting HbA1c | Age | Treatment | Diabetes duration | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bajkowska-Fiedziukiewicz (2008)64 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | Reported | Yes | 7.5 | 63 | Oral, insulin | 11 | HbA1c: NS |
| Banister (2004)65 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | Reported | Yes | 9.7 | 49 | Unclear | NR | HbA1c: reduced |
| Blonde (2002)66 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 35–65 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | Higher % with HbA1c under 7% with more frequent SMBG |
| Capelson (2006)67 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 7.6 | 80 | Insulin | 21 | HbA1c: NS |
| Chan (2000)68 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 53 | NR | NR | HbA1c 0.7% lower with more frequent SMBG |
| Evans (1999)69 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | NR | Insulin | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Franciosi (2001)70 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 7.3 | 63 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | HbA1c higher with more SMBG, lower when insulin could be adjusted |
| Franciosi (2005)71 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 7–7.3 | 62 | Diet, oral | 9.1 | HbA1c: NS |
| Fremantle Diabetes Study [Davis (2007)17,19] | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 7.4 | 65 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR |
HbA1c: NS Mortality: NS SMBG: less retinopathy |
| Hanninen (2001)72 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 63 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | HbA1c higher with more SMBG |
| Harris (2001)73 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 7.6 | 63 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Jaworska (2004)74 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 62 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Karter (2001)75 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 8.4 | 60 | Diet, oral, insulin | 0 to > 10 | HbA1c 0.6% lower with more SMBG in those on oral drugs |
| Karter (2005)76 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 9.9 | 60 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | 5% more under 7% HbA1c with more SMBG |
| Karter (2006)14 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 6.4 | 60 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | Lower HbA1c with more SMBG |
| Klein (1993)77 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 62 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Meier (2002)79 | Reduced access test strips | NR | NR | NR | 64 | Diet, oral | NR | No change in HbA1c after SMBG reduction |
| Mitchell (2004)80 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 64 | Diet, oral | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Murata (2003)81 | Intensified SMBG | NR | NR | 8.1 | 48 | Insulin | NR | Lower HbA1c (by 0.3%) with more SMBG (depending on entry HbA1c) |
| Murata (2009)82 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c and medication change | NR | NR | NR | 59 | Oral | NR | HbA1c NS overall, lower HbA1c with more SMBG in specified treatment groups |
| Newman (1990)83 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 60 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Oki (1997)84 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 56 | Diet, oral, insulin | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Ozmen (2003)85 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | Yes | NR | 9.1 | 58 | Diet, oral, insulin | 8.6 | HbA1c reduced by 1.9% with SMBG |
| Patrick (1994)86 | Association between SMBG/SMUG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 65 | Sulphonylurea | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Rindone (1997)87 | Access strips vs no access | NR | NR | 8.1 | 68 | Sulphonylurea | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Roblin (2001)88 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 53 | Diet, oral, insulin | 12 | Lower HbA1c with SMBG in insulin-treated but not non-insulin treated |
| ROSSO study [Martin (2006)15] | Association between SMBG use and morbidity/mortality | NR | NR | 7.7 | 63 | Diet, oral, insulin | 0 | Morbidity and mortality lower with SMBG |
| Rost (1990)89 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c in insulin users and non-insulin users | NR | NR | NR | 56 | Oral, insulin | 0 | Lower HbA1c with SMBG |
| Schiel (1999)90 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | NR | Insulin | NR | Lower HbA1c with more SMBG |
| Schütt (2006)91 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 7.6 | NR | Diet, oral, insulin | 10 | Lower HbA1c with more SMBG |
| Secnik (2007)92 | Access-free blood glucose monitors | NR | NR | NR | 20 to > 65 | Oral, insulin | NR | Lower HbA1c with more SMBG only in insulin-treated patients, not with oral |
| Soumerai (2004)93 | Access-free blood glucose monitors | NR | NR | 8.4 | 56 | Oral, insulin | NR | Lower HbA1c with more SMBG only for those with higher initial HbA1c |
| Stiptzarov (2003)94 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | NR | 65 | NR | NR | Lower HbA1c with more SMBG |
| Tengblad (2007)95 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 5.4–6.9 | 69 | Diet, oral, insulin | 87%, > 4 | HbA1c: NS |
| Wen (2004)16 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 7.2 | 63 | Oral | NR | HbA1c: NS |
| Wieland (1997)96 | Association between SMBG use and HbA1c | NR | NR | 7.9 | 39–89 | Sulphonylurea | NR | HbA1c: NS |
Eighteen studies found no favourable changes in HbA1c level with SMBG, while 12 studies found a positive effect of SMBG on HbA1c level, whereas another six showed favourable effects of SMBG on HbA1c level, depending on treatment (especially in insulin-treated patients) or entry HbA1c level (especially with higher entry HbA1c level). Two studies reported on mortality and morbidity, with the ROSSO Study15,78,99 (Germany) finding that SMBG was associated with lower morbidity and mortality, while the Fremantle Diabetes Study17,19 (USA) found no changes in mortality in relation to SMBG, but SMBG use was associated with less retinopathy. These associations may be due to confounding factors – those who perform SMBG may be more motivated to self-manage in other ways.
Qualitative studies
A summary of studies including qualitative data in terms of study design, participants and brief results is presented in Appendix 6. Six qualitative studies were identified: Belsey et al. (2009),100 DiGEM RCT questionnaire and qualitative components,10,11 Lawton et al. (2004),6 Peel et al. (2004),101 Peel et al. (2007)102 and Zgibor and Simmons (2001). 103 These reported results from in-depth interview studies, repeated interviews, questionnaire and survey data. Numbers of participants ranged from n = 18 to n = 40 for interview studies, to n = 323 to n = 40,651 patient records examined for survey and questionnaire data. Key positive results showed increased awareness of diabetes and help with establishing relationship between physical symptoms and blood glucose readings; increased empowerment to take more control over their health care; and the ability to use SMBG to assess effects of behaviour and promotion of adherence to self-management as a result of SMBG. Negative results showed increased levels of depression and anxiety compared with patients who do not self-monitor, few patients use SMBG to guide and maintain change to behaviour or lifestyle; negative impact on patients’ self-management when readings are counterintuitive and lack of education on how to interpret and act on out of target readings. A summary of messages regarding advantages of SMBG and barriers to benefit of SMBG is shown in Table 8.
| Perceived advantages | Barriers |
|---|---|
|
Reassurance when blood glucose levels were normal Patients felt they could use SMBG to assess effects of behaviour Participants felt empowered to take more control over their health care and ability to contribute to physician’s evaluation of their status Convenience of taking measurements |
People tended not to act on their SMBG results SMBG associated with increased levels of depression and anxiety compared with patients who do not self-monitor SMBG as threat – constant reminder of illness Feeling of failure, self-blame when blood glucose levels were abnormal Health professionals were often perceived to show no interest in meter readings – lack of feedback Lack of specific instructions and education received |
Results from published qualitative studies have identified a number of reasons why SMBG may not be helping some individuals. Increased anxiety and depression have been reported,71,100 with individuals reporting feelings of obsession about results, paranoia, pain/discomfort, contradictory information, lack of knowledge/understanding of what results mean, monitoring fatigue, increased worry, distress and anxiety and self-blame and abandonment of regimen resulting in adverse effects on adherence, for example nihilistic attitudes. 101 Peel et al. (2007)102 reported that reasons for discontinuation of SBMG included self-chastisement, with SMBG seen as a proxy measure for ‘good and bad’ behaviour rather than an aid to better diabetes self-management. Women were particularly like to chastise themselves when readings were high, indicating specific gender differences.
Lack of education in how to interpret blood glucose results and what to do with that information, for example how to respond to high readings, was reported in a number of studies. 18,100,102,104 Peel et al. (2007)102 reported a lack of explicit and unified messages from health-care teams about if, when, and how, to self-monitor. None of the participants in this study reported receiving ongoing education about SMBG. It is unclear whether practice nurses provide sufficient (or any) training to patients, or indeed help patients to interpret results, and this is an area that requires further investigation. Anecdotal evidence suggests that practice nurses are unclear themselves about how to interpret blood glucose readings and how to use that information to direct behaviour changes. There is certainly a theme running through the qualitative literature that HCPs are disinterested in the results that patients take to them, resulting in disappointment and disinterest ultimately by patients. This may reflect a mismatch in expectations, with the professionals expecting patients to use SMBG to self-manage, and patients expecting the professionals to use the results to adjust treatment.
Individuals who simply purchase a blood glucose meter (which are widely available for sale in pharmacies, with basic instruction only on how to use the machine) will have received no education at all unless they have sought it from a HCP. There is perhaps an important role for pharmacists to ensure that anybody purchasing such a device is offered appropriate training on both how to use it and how to interpret the results. However, that assumes that the pharmacists have the necessary knowledge to do the training, or the ability to arrange for others to do it.
Failure to use SMBG to alter treatment dose or behaviour was reported. 100,102,104 In the UK, few patients use SMBG to guide and maintain changes to their behaviour and lifestyle,100 and this appears to be due, in part, to lack of education about interpreting and acting upon results. Indeed, some participants reported that reasons for continuing with SMBG included curiosity and reassurance102 rather than to guide diabetes self-care behaviours. Some individuals found that SMBG promoted a focus on the ‘here and now’, which could be detrimental to long-term health behaviours and decision-making. 102 Many were disappointed with HCPs’ disinterest in the results. 101 Song and Lipman (2008)8 reported that a patient who uses SMBG on a regular basis may believe the number on the glucose meter reflects ‘the truth’, even although it may not be consistent with what his/her body is telling him/her. This is particularly worrying in view of the lack of checking/calibrating of meters,104 which may result in inappropriate reliance on inaccurate results. Alternatively, other patients may not believe the number because they feel fine. Incorrectly interpreting a lack of symptoms (incorrect because blood glucose has to be well above normal to cause symptoms) as meaning that all is well could lead to SMBG results being ignored.
There was a lack of data in the studies (qualitative, systematic review or economic) about whether SMBG benefits vary by frequency of monitoring, type of education, susceptibility to hypoglycaemia, treatment, age, starting HbA1c level or time points during the course of diabetes, for example after diagnosis, during treatment change, etc. What was evident was that older and less well-educated patients were most interested in HCP attitudes to readings102 and that longer diabetes duration was associated with less SMBG. 18 Evans et al. (1999)69 reported a decreasing uptake of test strips which was associated with age, and Belsey et al. (2009)100 reported that participants on diet and exercise did least testing, with testing increasing as therapy intensifies. None of the studies reported monitoring results being used for treatment adjustment by the HCP, whilst Peel et al. (2007)102 were alone in reporting that most participants could counteract hypoglycaemia but not hyperglycaemia. Furthermore, they reported that inexplicable readings promoted nihilistic attitudes, whilst Lawton et al. (2004)6 reported that consistently normal results on self-monitoring of urine were interpreted as successful diabetes management/compliance. Highest SMBG frequency was reportedly conducted by participants who had attended diabetes education. 18
Interestingly, Peel et al. (2007)102 reported that participants felt they were monitoring for the benefit of their HCP, rather than their own benefit, despite the HCPs showing no interest in the readings. There is a clear incongruence between patient expectations of HCPs and vice versa. In fact, how the monitoring results were used for treatment adjustment by patients was not addressed in any of the qualitative studies. HCPs have an expectation that individuals are using SMBG as an aid to improved self-management of diabetes. If this assumption is not challenged then patients are needlessly burdened with an additional (not to mention painful) diabetes-related task for apparently no benefit. With the NHS spending almost as much on blood glucose testing materials as on oral hypoglycaemic agents,105 and 69% of participants on oral hypoglycaemic agents taking no action at all if a reading was beyond their target range, it is clear that patient education needs to be improved. Furthermore, the behaviours of HCPs in relation to how they issue blood glucose meters and help patients interpret the results, should be examined.
The simple act of how and whether a blood glucose meter was issued at all to a patient was associated with whether individuals felt their HCP was taking their diabetes seriously enough. 6 Failure to receive a blood glucose meter was associated with increased anxiety and undermining of confidence in HCPs.
The mode of obtaining meters or amounts of education received did not appear to differentially impact on patients’ views of glucose monitoring according to Peel et al. (2004). 101 Whether a patient had well-controlled diabetes or not affected satisfaction with SMBG, that is patients with well-controlled diabetes viewed SMBG positively, whereas poorly controlled patients voiced more concerns and experienced monitoring fatigue. 102
At a workshop at the Spring 2009 Diabetes UK conference (attended by two authors of this report), some patients and industry representatives said that some general practitioners (GPs) were now rationing test strips for individuals with diabetes, presumably because of rising costs and doubt about effectiveness. This can appear to be contrary to current guidelines, but these may not be sufficiently clear. For example, the NICE guideline CG669 says SMBG ‘should be available to those on oral glucose-lowering medications to provide information on hypoglycaemia’ but that is not relevant to those on metformin alone (because metformin does not cause hypoglycaemia). It also says that SMBG should be available to those on insulin treatment but does not say whether this should apply to those on a small once-daily dose of basal insulin. If individuals are not benefiting from SMBG, and indeed it is detrimental to their overall health, there is a clear need to cease SMBG. There is also a passionate argument from patient groups and the pharmaceutical industry that SMBG for individuals with T2DM should not be withdrawn. O’Kane and Pickup (2009)106 perhaps aptly declared that ‘present widespread use of SMBG in T2DM is a good example of a monitoring test that was adopted in advance of robust evidence of its clinical efficacy’. Thus identification of potential subgroups of those patients who would receive the most benefit from SMBG should be identified, perhaps by some qualitative work to identify characteristics of those most likely to benefit (which may be about patient attributes rather than treatment) followed by a RCT.
Most studies, including 18 out of the 36 observational studies, report that SMBG does not improve HbA1c level for most patients on diet and lifestyle change or oral hypoglycaemic agent (OHA) alone. There are repetitive themes throughout the literature on why SMBG is ineffective for many individuals. These include lack of education, lack of interest from HCPs in results, failure to make behaviour/lifestyle or therapy changes based on readings, failure to understand exactly what SMBG is (i.e. a tool to aid diabetes self-management), failure to calibrate or check accuracy of readings and failure to identify patients most likely to benefit from the technology. Consideration needs to be given to identifying those patients who would benefit from SMBG both biomedically in terms of glycaemic control and psychosocially in terms of improved QoL. However, the key may be to not only identify these patients, but also have a supportive HCP who supports them in self-management and the best use of SMBG data.
Funnel and Anderson (2004)107 developed the empowerment philosophy within which approaches to education incorporate interactive teaching strategies that are designed to involve patients in problem-solving and address their cultural and psychosocial needs. Key tenets of the empowerment philosophy include:
-
Empowering people with diabetes to make self-directed behaviour change.
-
It is not the HCP’s job to get patients to do what they consider ‘the right thing’, rather HCPs’ responsibilities include helping patients make informed decisions about diabetes and its self-management in the context of their own lives so that they are empowered to engage more effectively in self-care behaviours.
-
One of the biggest barriers to behaviour change is fear of failure, which grows each time we try unsuccessfully to achieve a goal. Being overwhelmed with information, but not given the tools to interpret it, can add to the burden, not reduce it. Emotions are important driving forces that require exploration.
-
Patients are already motivated to accomplish their own goals – their behaviours are often not irrational to them and underlying health beliefs should be explored. Collaboration between patients and HCPs is required to set goals and achieve targets.
-
Treatment needs to be personally meaningful to patients – i.e. what does it mean to me? What difference will doing this test make?
Chapter 3 Self-monitoring of blood glucose: economic literature review
In this literature review, a base year of 2008 has been applied for costs and prices, with sums converted being reported in square brackets: [£XX]. Where papers used an alternative base year, the Health and Community Services price index as reported within the Personal Social Services Research Unit (PSSRU) Costs of Health and Social Care108 has been applied. Where costs and prices were reported in a foreign currency these were converted to pounds sterling using the exchange rate prevailing on 5 April at the end of the base year of the paper, the Health and Community Services price index being subsequently applied to the resultant pounds sterling amount if required. Where the base year was not stated within the paper it was assumed to be the publication year.
Cost studies
Cost studies: full papers
Belsey et al. (2009)100 undertook a retrospective analysis of the IMS Disease Analyzer database of 40,651 patient records between March 2007 and February 2008. They identified those with T2DM who had received one or more prescriptions for oral glucose lowering drugs or insulin or had a clinical diagnosis of diabetes in the preceding 12 months. Among these patients 12.9% were estimated to be using diet and exercise alone, 34.1% were estimated to be on a single oral agent, 26.0% on multiple oral therapy, and 27% on oral therapy plus insulin.
Coprescription of test strips averaged 54%, but varied from a low of 26% among those on diet and exercise, between 36% and 44% among those on one oral agent, between 48% and 60% among those on multiple oral therapy, and between 87% and 89% for those receiving insulin. Given these rates of use, the annual average cost of tests strips was £9.83 [£10.16] for those on diet and exercise; between £15.95 [£16.48] and £23.50 [£24.28] for those on one oral therapy; between £23.87 [£24.67] and £37.91 [£39.18] for those on multiple oral therapy; and between £135.83 [£140.36] and £191.18 [£197.56] for those on insulin.
These costs were extrapolated to the UK as a whole by applying disease prevalence data of 3.7% to give an annual average cost per patient of £73.64 [£76.10] and a total UK cost of £165M [£171M]. The cost for England alone in 2006–7 was estimated to be £138M. The authors noted that what they describe as the UK consensus recommendations on monitoring, suggest that those using diet and exercise alone, or monotherapy metformin, monotherapy glitazone or metformin plus glitazone, should not be using SMBG. This resulted in an estimate of £13.42M [£13.87M] being spent unnecessarily on SMBG among these patients, which was only partially offset by a £610K [£630K] underspend among sulphonylurea monotherapy patients. In contrast, multiple oral agent patients were typically estimated as underutilising SMBG to the extent of £2.56M [£2.65M] per annum. Those using insulin plus an oral therapy were estimating as overutilising SMBG by £6.7M [£6.92M] per annum, to yield an estimate of the total overspend of £17.02M [£17.59M].
The authors acknowledged that individual circumstances will in some cases have correctly over-ridden the consensus guidelines and that, as a consequence, the estimated overspend will to some extent be an overestimate. However, they also note that the DiGEM trial showed no benefit to those on sulphonylurea alone, and avoiding SMBG in this group could double the potential savings.
Weber et al. (2007)109 used the results of the German ROSSO15 longitudinal observational study of SMBG versus non-SMBG between two groups of patients with T2DM: those using only oral drugs and those using oral drugs plus insulin. The ROSSO results included long-term outcomes in terms of micro- and macrovascular event rates over an average follow-up period of 6.5 years, which Weber et al. reported as being 7.2% among the SMBG group and 10.4% in the control group (p = 0.002). Similarly, fatal event rates were lower among the SMBG group at 2.7% compared with 4.6% with a p-value of 0.004. These event rates were associated with Swiss unit costs to determine the average cost per patient.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose was associated with an additional average annual direct cost for test strips and lancets of CHF90 (90 Swiss francs) [£39] among those using oral agents and CHF130 [£56] among those using oral agents in combination with insulin. But these additional direct costs were more than offset by the costs of reduced events with the total average annual costs of CHF5140 [£2219] among SMBG users compared with CHF5654 [£2441] for non-users among the oral agents group, and CHF8254 [£3564] among SMBG users compared with CHF11,776 [£5084] for non-users among the oral agents-plus-insulin group. However, the generalisability of the study is limited by the ROSSO source data being drawn from a longitudinal retrospective study, not a randomised trial. Tiley110 noted that SMBG could not be considered to be the sole source of the risk reduction. Other interventions would also have ‘played a part in the outcome; these including regular educational input, regular screening and more regular dietary advice and medical consultation’ among the SMBG group.
Meier et al. (2002)79 undertook a study of the effect of the frequency of SMBG on costs and HbA1c levels among a sample of patients with T2DM in the US Veterans Affairs study, who were being controlled on either diet or oral antidiabetic drugs. A retrospective analysis of prescription data provided the estimate of the pre-baseline frequency of SMBG, given an assumption of no wastage of test strips. A policy of reduced SMBG frequency was implemented by letter and by reducing the number of test strips per prescription.
The authors found that the frequency of SMBG among those on oral agents was 1.36 strips per day, with an average HbA1c level of 7.83%. Subsequent to implementation an average 0.74 strips were being used, with a non-statistically significant change in average HbA1c level to 7.86%. Among those being controlled on diet the average test frequency dropped from 1.07 strips per day to 0.51 strips per day, with HbA1c level again showing a non-significant change from 6.85% to 6.78%. The authors had to cope with a change of laboratory analyser between baseline and end of study, and used several methods to overcome this, which is slightly confusing. Despite these difficulties, the authors concluded that reduced SMBG could result in an average annual saving per patient of US$76.44 [£66.38] without affecting glycaemic control.
Cost studies: abstracts
Neeser et al. (2006)111 also report the results of the ROSSO15 study, but on the grounds of one group being 3.5 years older on average than the other group, they undertook a matched-pairs analysis based on age, gender, smoking status and blood glucose level at diagnosis. This resulted in 813 matched pairs being available for the comparison of SMBG with no-SMBG, with costs of 18 complications of diabetes being estimated in addition to the costs of SMBG. Among those treating their diabetes with oral antidiabetic drugs alone, Neeser et al. estimated that SMBG led a reduction of €214 [£162] per year, but this was not statistically significant. Among those using insulin in combination with oral antidiabetic drugs, SMBG was found to cause a significant reduction in costs of €1727 [£1310] per year. However, the caveats of Tiley (2002)110 still apply: the care for the SMBG group differed in other ways.
Quality of life
Quality of life: full papers
Farmer et al. (2009)11 reported the utility estimates derived from UK DiGEM10 trial. Within the trial period the QoL values, derived from the completed cases’ EuroQol-5D (EQ-5D) questionnaire data, showed no change between baseline and 12 months for the control group, the average increasing by an insignificant 0.002 (95% CI –0.034 to 0.038). There was some evidence of a fall among the less intensive SMBG group, –0.037 between baseline and 12 months, which, given a 95% CI of –0.080 to 0.005, was of borderline significance. The more intensive SMBG group recorded a larger fall of –0.056, which, given a 95% CI of –0.099 to –0.013, achieved significance. The differences between low-intensity SMBG and standardised care, and between more intensive SMBG and standardised care, exhibited a similar pattern, though neither quite reached statistical significance given respective central estimates and 95% CIs of –0.040 (–0.094 to 0.015) and –0.053 (–0.109 to 0.004), respectively. QoL values were also imputed for the full data set. These showed a similar pattern to that reported above, the main difference of note being that the difference between more intensive SMBG and standardised care was estimated to reach statistical significance given a central estimate and 95% confidence interval of –0.072 (–0.127 to –0.017). So SMBG may slightly reduce the QoL.
The 2005 Cochrane review of SMBG37 in patients with T2DM not using insulin found two relevant papers57,61 for assessing the QoL impacts of SMBG. Muchmore et al. (1994)57 was reported as finding identical results for QoL for those using SMBG compared with the control group across the dimensions assessed: satisfaction, impact and worry (social/vocational and diabetes related). Paralleling this, Schwedes et al. (2002)61 found that well-being and treatment satisfaction improved by the same amount across both groups. Neither study found any statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of QoL.
Franciosi et al. (2001)70 reported the results of a prospective study of 3567 Italian outpatients with T2DM, among whom there were 2855 patients with data on SMBG: 17% tested more than once per day, 31% tested more than once per week, 14% tested less than once per week and 38% did not perform SMBG. Among those not using insulin, and adjusting for baseline characteristics, SMBG of at least once per day was significantly associated with higher levels of distress, worries and depressive symptoms, and SMBG of at least once per week was still significantly associated with higher levels of distress and worries. In contrast, there was no association between QoL and SMBG among patients using insulin, with the exception of stress, which was lower for those patients performing SMBG at least once per week.
Could these differences relate to ability to self-adjust medication? People on insulin are able to, and indeed are encouraged to, adjust insulin dose according to blood glucose levels. However, those on oral agents are presumably dependent on their doctors to change prescribed doses.
Cost-effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness: full papers
Farmer et al. (2009)11 undertook a cost–utility study using the results of the UK DiGEM trial, comparing the costs and effects among the DiGEM10 trial population of patients with T2DM being controlled through either diet or oral drug therapy. This was an update of the Simon et al. (2008)12 paper, and, in line with this, considered the three comparators of:
-
more intensive SMBG, through which the average HbA1c level fall was –0.17%
-
less intensive SMBG, through which the average HbA1c level fall was –0.14%
-
standardised usual care, through which there was no impact on HbA1c level.
This analysis used only the results of the DiGEM trial, and the alternative of SMUG was not considered. Note that in addition to the HbA1c changes, clinical effects also were observed in terms of blood pressure and cholesterol. The direct QoL effects of SMBG are reported in the previous section.
The direct impact of SMBG on QoL was estimated through the baseline and 12-month EQ-5D responses, through the application of the standard UK tariff. Given the 12 months’ clinical results from the DiGEM trial, the risk factors for the complications of diabetes were extrapolated to lifetime costs, life expectancy and quality-adjusted life expectancy using the UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Outcomes Model. 112 Future health effects and costs were discounted at 3.5%.
The modelling assumed that patients were initially controlling their diabetes through diet alone or oral drug therapy. As the disease progresses and control worsens, patients will intensify their therapy, moving from controlling their diabetes using diet alone, to oral drug therapy, to basal insulin-plus-oral drug therapy to basal/bolus insulin-plus-oral drug therapy. It is unclear if, or how, these intensifications of therapy have been incorporated within the modelling.
During the 12 months’ period of the DiGEM trial a resource use questionnaire was also administered, which, together with patients’ SMBG diaries and nurse notes, provided data on the within trial resource utilisation – including nurse visits, medications, primary care, hospital care, and auxiliary medical resource use such as podiatry, optician and dietitian services. Where information was missing on SMBG and medication use, the last value carried forward technique was used, which could be misleading because those who do not return may have altered their behaviour. SMBG was typically associated with longer nurse visits than standardised care, with the more intensive SMBG typically also being associated with longer nurse visits than less intensive SMBG.
Resource use was valued by applying unit costs reported in the NHS reference costs 2005–06;113 the Annual financial returns of NHS trusts 2003–2004;114 and the PSSRU Costs of Health and Social Care 2002,115 with these being inflated to 2005–6 costs using the Department of Health Pay and Prices Inflation Indices. 113
Within the trial period, standardised care was estimated to cost £89 [£95] compared with £181 [£193] for the less intensive SMBG and £173 [£184] for the more intensive SMBG, giving cost increases of £92 [£98] and £84 [£90] for the SMBG groups, respectively. Given parallel QoL losses of –0.008 quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) and –0.036 QALYs from less intensive SMBG and more intensive SMBG, respectively, compared with standardised care, the within trial comparison estimated that standardised care dominated SMBG.
The above values are as per those reported in the Simon et al. (2009)12 paper, with Farmer et al. (2008)11 extending this through extrapolating the long-term effects by using the UKPDS Outcomes Model. 112 This marginally improved the situation for the SMBG: for the less intensive SMBG, the lifetime patient loss was estimated to be –0.004 QALYs, while the additional lifetime cost was £59 [£63]; and, for the more intensive SMBG the lifetime patient loss was estimated as –0.020 QALYs, while the additional lifetime cost was £56 [£60]. This did not change the overall conclusion that standardised care was both more effective and less costly than SMBG, and so dominated SMBG.
Similarly, a probabilistic analysis estimated that while the probability of SMBG being cost-effective would rise as the willingness to pay increased to around £10K per QALY, any increases in the probability of SMBG being cost-effective as the willingness to pay increased further were limited. At a willingness to pay of £30K per QALY, the probability of less intensive SMBG was a little under 40% and the probability of more intensive SMBG was around 15%, these probabilities showing little change as the willingness to pay was increase to £50K per QALY.
Tunis and Minshall (2008),116 in a study funded by LifeScan, a major manufacturer of glucose testing material, modelled the cost–utility of SMBG among patients with T2DM using oral antidiabetic drugs within the US Medicare setting, using the CORE Diabetes Model. 117 This compared:
-
three-times-daily SMBG, through which average HbA1c level was assumed to fall by 1.02%
-
once daily SMBG, through which average HbA1c level fell by 0.32%
-
no SMBG, through which average HbA1c level rose by 0.13%.
Clinical effectiveness estimates in terms of the HbA1c effect were drawn from the large 3-year Kaiser Permanente Healthcare Group observational study among 30,000 patients, with the HbA1c changes reported above relating to a subset of around 16,000 new users of SMBG as reported in Karter et al. (2001). 75
Medicare reimbursement unit costs were applied, with QoL values being drawn from the UKPDS study, but, crucially, it was assumed that there was no disutility associated with SMBG use.
The changes in HbA1c level were assumed to be maintained for the duration of the modelling. Patients had an average age of 63 years, with the model time horizon of 40 years consequently, and effectively, being a lifetime horizon. Costs were inflated to 2006 prices, with costs and benefits being discounted at 3%. It was assumed that after 5 years patients would switch to insulin.
For the comparison of ‘once-daily SMBG’ with ‘no SMBG’, the central estimate was that an additional 0.103 QALYs would accrue at an additional cost of US$808 [£493] to yield a cost-effectiveness estimate of US$7856 [£4789] per QALY. For the comparison of ‘three-times-daily SMBG’ with ‘no SMBG’ the central estimate was that an additional 0.327 QALYs would accrue at an additional cost of US$2161 [£1317] to yield a cost-effectiveness estimate of US$6601 [£4024] per QALY.
Results were particularly sensitive to the time horizon assumed. Reducing this to 5 years resulted in cost-effectiveness estimates for ‘once-daily SMBG’ and ‘three-times-daily SMBG’ compared with ‘no SMBG’ of $23,380 [£14,253] per QALY and $29,137 [£17,762] per QALY, respectively.
The Tunis and Minshall (2008)116 study needs to be interpreted with caution due to the clinical data being from an observational study, the observed differences in HbA1c level during the study being assumed to be maintained over the lifetime of the patient, and, most obviously, due to the assumption of SMBG not in itself being associated with any disutility. Aspinall and Glassman (2008)118 expressed additional concerns in a letter to the editors that not all patients would commence SMBG at the average HbA1c value assumed by Tunis and Minshall, and that the effect of SMBG would be, in all likelihood, different for different baseline levels of HbA1c. Note also that an abstract of a cost-effectiveness study, undertaken by Tunis,119 of SMBG among patients with T2DM, using the same clinical data source as her 2008116 paper, reported a considerably worse cost-effectiveness ratio than those reported above.
Palmer et al. (2006),22 also funded by LifeScan, modelled the cost–utility of SMBG among patients with T2DM controlling their diabetes with diet and exercise, or with oral antidiabetic drugs, or with insulin. This compared SMBG with non-SMBG among the three patient groups, with assumptions on HbA1c level as follows:
-
for those on:
-
– diet and exercise – SMBG resulted in a fall of 0.3%
-
– oral antidiabetic drugs – SMBG resulted in a fall of 0.4%
-
– insulin – SMBG resulted in a fall of 0.6%.
-
These clinical effectiveness estimates were drawn from the Karter et al. (2001)75 study, as reported above for the Tunis and Minshall (2008) paper,116 though within an alternative patient grouping. Palmer et al. (2006)22 also assumed that only 78% of patients would adhere to SMBG. The 22% not adhering to SMBG were assumed to be identical to the non-SMBG in terms of both costs and effects, and, as a consequence, the main effect of the inclusion of non-adherence is simply to dilute the SMBG arm.
The analysis was undertaken using the CORE model in the UK setting in terms of costs, with a base year of 2004. A lifetime horizon was adopted with costs and benefits being discounted at 3.5%.
In common with Tunis and Minshall (2008),116 Palmer et al. (2006)22 also assumed that the benefit in terms of improved HbA1c level would be maintained over patient lifetime and that there was no direct disutility from SMBG, although a sensitivity analysis was undertaken equalising this to the disutility from taking insulin.
The additional annual ongoing cost of SMBG varied between the patient groups, being £124 [£142] for those on diet and exercise, £247 [£283] for those on oral agents and £371 [£425] for those on insulin. The respective average lifetime patient gains were estimated as being 0.165 QALYs, 0.225 QALYs and 0.255 QALYs, respectively, while the respective additional lifetime costs were estimated to be £2564 [£2934], £1013 [£1160] and £1171 [£1340], respectively. This resulted in cost-effectiveness estimates for SMBG compared with non-SMBG of:
-
£15,515 [£17,760] per QALY for those on diet and exercise
-
£4508 [£5160] per QALY for those on oral antidiabetic drugs
-
£4593 [£5257] per QALY for those on insulin.
As in the Tunis and Minshall (2008) paper,116 Palmer et al. (2006)22 found results to be sensitive to a shorter time horizon. Reducing this to 10 years resulted in estimates of cost-effectiveness of £74,528 [£85,311] per QALY for those on diet and exercise; £33,742 [£38,624] per QALY for those on oral antidiabetic drugs; and £11,082 [£12,685] per QALY for those on insulin. An assumption of the HbA1c benefit only lasting for 5 years also worsened cost-effectiveness ratios among the three patient groups: £25,802 [£29,535] per QALY; £9141 [£10,464] per QALY; and, £9909 [£11,342] per QALY, respectively.
Applying the disutility of taking insulin to SMBG reduced the anticipated gains from SMBG. This particularly affected the diet and exercise group, among whom the anticipated gain fell from 0.165 to 0.077 QALYs, resulting in a cost-effectiveness estimate of £34,259 [£39,216] per QALY. The effect, while still large, was less dramatic for those taking oral antidiabetic drugs and those taking insulin, with the QALY gains falling from 0.225 to 0.140 QALYs and from 0.255 QALYs to 0.172 QALYs, respectively. As a consequence, their respective cost-effectiveness estimates worsened to £6985 [£7996] and £6586 [£7539] per QALY.
Cost-effectiveness: abstracts
Tunis (2009)119 reported the results of further cost-effectiveness modelling using data from the Kaiser Permanente Healthcare Group observational study as for her 2008 paper. 116 Compared with ‘no SMBG’, the results were as follows, the first and third being roughly one-half to one-third of the estimated gains of her 2008 paper. 116
-
Once-daily SMBG led to an additional 0.047 QALYs.
-
Twice-daily SMBG led to an additional 0.116 QALYs.
-
Three-times daily SMBG led to an additional 0.132 QALYs.
The difference may be because the 2008 study was of new users. As a consequence, cost-effectiveness estimates worsened considerably to US$26,206 [£17,706] per QALY, US$18,572 [£12,548] per QALY and US$25,436 [£17,186] per QALY, respectively.
Mataveli et al. (2008),120 in an abstract with few details, reported the results of a cost-effectiveness analysis of SMBG among patients with T2DM using oral glucose lowering drugs within the Brazilian setting. It was reported that daily use of SMBG was associated with a fall in HbA1c level of 0.6%, though details are sparse and other changes may have occurred. Over a 3-year period, once-daily SMBG was estimated to result in average cost savings across three Brazilian health maintenance organisations: R$3499 (Brazilian real) [£954], R$884 [£258] and R$649 [£190]. The source of funds is not given, but one author is from LifeScan.
Erny-Albrecht et al. (2007)121 reported the outcome of modelling of the cost-effectiveness of SMBG using the Kaiser Permanente Healthcare Group observational study. The estimated patient impacts of this modelling fell between those of the Tunis and Minshall (2008)116 full paper and the Tunis (2009)119 abstract above. Compared to ‘no SMBG’:
-
Once-daily SMBG led to an additional 0.083 QALYs.
-
Twice-daily SMBG led to an additional 0.216 QALYs.
-
Three-times-daily SMBG led to an additional 0.270 QALYs.
Given these estimates, the respective cost-effectiveness estimates were US$6530 [£3424] per QALY, US$5997 [£3145] per QALY and US$7784 [£4082] per QALY, respectively. The source of funding is not given but, from the authorship, it is likely to have been industry funded.
Weber et al. (2007)122 also reported the outcomes of modelling using the Kaiser Permanente Healthcare Group observational study. Few details were provided but the additional cost of treatment in the SMBG group was estimated as being €1524 [£1073] for testing of between every 2 days and once daily, and as being €3273 [£2304] for testing of between 2.5 and 3-times-daily. Additional life expectancies of 0.021 years and 0.222 were estimated, resulting in cost-effectiveness ratios of €70,199 [£49,419] and €14,710 [£10,356], respectively. Further modelling estimated the cost-effectiveness of testing between once and twice daily as between €33,607 [£23,659] and €34,211 [£24,084], respectively. The authors regarded this as being cost-effective.
In an earlier abstract, Weber et al. (2006)123 report the outcome of a Markov model looking at the cost-effectiveness of SMBG among patients with T2DM not using insulin. The impact of SMBG was limited to the change in HbA1c level reported in the Sarol meta-analysis. 34 Given a frequency of seven times per week, the impact on HbA1c level was reported as an improvement of 0.42%. This led to an estimate of the cost-effectiveness of SMBG alongside metformin treatment of €28,171 [£21,074] per life-year gained and alongside sulphonylurea of €27,062 [£20,245] per life-year gained. Applying the upper and lower 95% confidence limits reported in Sarol et al. 34,39 resulted in cost-effectiveness estimates of €63,404 [£47,433] per life-year gained and €19,351 [£14,477] per life-year gained, respectively.
Neeser et al. (2006),124 in a letter, reported undertaking a Markov modelling exercise of the cost-effectiveness within the German health-care system using a 0.39% HbA1c level reduction from SMBG among non-insulin-using patients with T2DM, the reduction being derived from the Welschen et al. (2005)36 meta-analysis. No other details are provided as to the modelling inputs or the model used, but they report an anticipated 0.083 years’ additional life expectancy and a cost per life-year of ∼€31,000 [£23,191]. Davidson (2006),125 in a response to this, highlighted the anticipated gain estimated by Neeser et al. (2006)124 being only 30 days, and that the estimate of a reduction in HbA1c level was significant in only two out of the six trials within the meta-analysis.
Summary
Reviewing cost-effectiveness was complicated by:
-
a lack of clarity as to the assumed duration of therapies and when or if intensification of therapy, such as switching to insulin, had been allowed for
-
a lack of clarity as to the assumed duration of an effect upon HbA1c level, though it appears likely that this was assumed to be lifetime, regardless of any intensification of therapy
-
with the exception of Farmer et al. ,10,11 typically assuming no direct QoL decrement from SMBG among those controlling their diabetes with diet or oral medication.
The cost of SMBG in people with T2DM in England is probably around £38M per year,100 of which about £17M could be saved by adhering to previous guidelines, and another similar amount by applying the findings of DiGEM in the sulphonylurea-only group.
The reported costs per annum of SMBG vary amongst studies, the lowest being the estimate by Belsey et al. (2009)100 of about £10 per year for infrequent testers on diet alone, to £259 in the Palmer et al. (2006) study. 22
Several studies assert that SMBG can lead to savings that offset testing costs, for example Weber et al. (2007)122 estimate the additional costs to be £39 annually but that taking avoided events into account gives an average annual saving of £222. Meier et al. (2002)79 estimate savings to be £66 per annum.
However, most of these studies fail to allow for the negative impact of SMBG on QoL, as reported by the DiGEM10 group and Franciosi et al. (2001). 70
The cost-effectiveness analyses vary in their assumptions, with those funded by industry being more optimistic in the size of gains in HbA1c level, and hence producing lower incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs). The best analysis to date is that of Farmer et al. (2009)11 (funded by the UK Health Technology Assessment programme), which, after taking into account all costs, gains and disutilities, concluded that SMBG was not cost-effective.
Chapter 4 Discussion
Problems with the evidence base
Some of the reasons for the controversy around the value of SMBG in people with T2DM are apparent from the literature. They include:
-
The evidence base did not allow us to answer our original primary or additional questions; the studies did not provide information on patient outcomes by treatment received (i.e. diet alone, metformin monotherapy, combination oral therapy, or combinations of oral therapy and insulin), with most studies not even providing a breakdown of the treatment patients were taking. Similarly, none of the studies provided enough information for making a judgement on any subgroups of patients that might benefit most, or that might be harmed. We also did not find any studies that investigated in detail the different aspects of education in relation to SMBG.
-
Most, if not all, RCTs have treated SMBG – which, in the first instance, is a diagnostic tool – as an intervention in its own right, rather than acknowledging that in order to be able to have a benefit on patient outcomes. SMBG needs to be linked to appropriate education, feedback, treatment and behaviour adjustment, as well as to an analysis of the types of patients and situations for which SMBG might be most helpful. In some studies there appeared to be a lack of provision of education and/or feedback, and in others there was a lack of detail about what education was offered. Most other potential modifiers of SMBG benefit were not assessed at all.
-
Differences in conclusions of the systematic reviews, with some reporting that results are inconclusive, while others reported that SMBG improves HbA1c level. However, it is notable that the latter usually find small differences in HbA1c level ranging from improvements of 0.16%35–0.42%. 34 It is also noteworthy that the effects sizes are smaller in the later reviews with more trials – for example 0.24%,33 0.16%35 and 0.22%38 compared with 0.42%,34 0.39%37 and 0.41%. 31
-
There is also lack of agreement on what is a clinically significant difference in HbA1c level. The consensus seems to be 0.5% or more but that appears to be an arbitrary number.
-
Differences in the use made of the data from SMBG. In some studies, no action was taken based on the results, so no benefit was likely. In others, drug treatment could be changed by doctors but not by patients. In some studies, patients were encouraged to adjust treatment themselves. However, there was little evidence for adjustment in what was most under their control – diet and exercise. There appears to be a disconnection between SMBG and diet/exercise, in that neither patients nor HCPs are actively checking SMBG in response to specific behaviour changes, such as a diet or starting an exercise regime. It’s almost as if patients don’t regard lifestyle change as an appropriate remedy. Kempf et al. (2008)126 suggest that ‘appropriate use of SMBG data by the patient may be improved by practical lessons that allow the patient to recognise the impact of high versus low glycaemic meals and of moderate physical activity such as 30 minutes of brisk walking’.
-
Some of the observational studies had too many confounders to provide useful data. For example, some reported higher HbA1c level in those undertaking SMBG but that may be because poor control was the reason for starting SMBG. In others, SMBG appeared to improve control but the improvements may have been in adherence to other aspects of self-care.
-
Some studies reported the results of SMBG where there was no education to empower patients in altering treatment. Some implied that SMBG was carried out to inform the doctor or nurse, rather than the patient.
-
The baseline HbA1c level may be relevant. It was sometimes too low to expect much improvement (but there could be improvements in other areas such as hypoglycaemic episodes). A simple regression analysis suggested that effects of SMBG were larger in patients with higher baseline HbA1c values.
Some common themes emerged. Use of SMBG in T2DM is clearly an international issue, with studies from the UK, Italy, New Zealand and Australia.
It may be that better targeted selection of patients for SMBG is required. McGeoch et al. (2007)32 concluded that SMBG may not be helpful or economically justified in all cases, but that individuals would benefit if:
-
their baseline HbA1c level is above 8%
-
they are properly educated in the use of SMBG and how to take appropriate action based on the results
-
they are sufficiently literate and numerate to take advantage of the intervention
-
they are receptive to the need for better metabolic control and are motivated to make the necessary changes
-
there are special circumstances – such as new diagnosis, initiation or change in medication, illness, gestational diabetes and lack of awareness of hypoglycaemia.
Davidson (2005)127 commented that possible explanations for lack of effect of SMBG in patients include:
-
patients receive little or no feedback on their results
-
they are not taught the self-management skills to lower blood glucose
-
(in his experience) the vast majority of patients monitor fasting or preprandial BG values, which neither serves to educate or motivate.
The type of education offered also seems to be of importance, with education emphasising a positive attitude and enhanced self-efficacy possibly being more effective than simple ‘information-based’ education. In one trial of both T1DM patients and T2DM patients,20 recruits in the intervention arm were given the Blood sugar monitoring owner’s manual, devised by Laffel et al. (available at US$5.25 from Joslin Diabetes Center, Boston, Massachusetts, USA),128 which emphasises a positive attitude. The control group was given meters, strips and instructions in use. While there was no significant difference in absolute HbA1c levels at the end of the 6-month trial (the difference was only 0.09%), significantly more patients in the intervention group managed to improve their HbA1c values (61% versus 44%) and fewer participants had a negative affect regarding SMBG than patients who were not receiving the manual (38% versus 65%).
In the trial by Schwedes et al. ,21,61 SMBG use in patients with T2DM (on diet and/or oral treatment) was combined with a short counselling algorithm focusing on promotion of self-perception (diary entries of eating, well-being and SMBG readings), self-reflection (what worked/did not work in experience with SMBG, what facilitated SMBG), and enhancement of self-regulation (ideas of how to use diary entries and SMBG to improve glycaemic control, assessment of probability of achieving goals). Compared with the non-SMBG control group, patients in the intervention group had a 0.46% greater reduction in HbA1c level, and depression was significantly reduced (no significant difference in treatment satisfaction, general well-being, anxiety, energy or positive well-being). This is in contrast with the results of the DiGEM and ESMON trials, which used more traditional educational strategies. It has been argued that the additional counselling strategy used in the SMBG group (but not in the control group) in the trial by Schwedes et al. meant that the effect of SMBG per se could not be distinguished from the effect of the counselling – but then as a diagnostic test rather than an intervention, SMBG cannot be expected to have a benefit without giving patients and HCPs optimal help in using the results.
Thus, education is required not only for patients, but also for professionals such as practice nurses so that they can advise on treatment changes – though this might require a change in prescription that the nurse could organise rather than provide. However, if the prescription was dietary, the nurse or the practice might not have access to sufficient dietetic help.
Another issue is that there seems to be an assumption across the literature that it is simply a case of ‘to test or not to test’, i.e. that SMBG is ongoing rather than episodic. There was little reference in the literature to suggest that HCPs are engaging patients in short bursts of targeted testing, for example to assess the effects of lifestyle changes (weight change, exercise, dietary changes, etc.). Such an episodic approach might be more effective and less costly. Testing could be at greater intensity initially, with routine testing then stopped pending HbA1c results. It is also unclear whether patients achieving ‘good’ diabetes control without SMBG might be actively discouraged from taking on the additional burden of it.
Selection might also be better if based more on patients’ personalities (some want to take control themselves, some do not) than on treatment group. It would be useful to split the insulin-treated group into those on single basal injections per day from those on more complex regimens.
There may also be unrealistic expectations of the value of SMBG, for example stimulated by advertising to HCPs and patients. Being a diagnostic tool, SMBG is only ever going to be as good as the context in which it is used and the actions taken in response to the readings.
There are psychological disbenefits from SMBG as used in current practice – anxiety, depression and self-chastisement. Adverse effects on QoL were not only seen in clinical trials, but also in a large Italian observational study on SMBG in T2DM (2855 respondents, of whom 2254 were not on insulin). 70 There was no association of SMBG frequency with HbA1c level in non-insulin-treated patients, but QoL (including diabetes-related distress, diabetes health distress, diabetes-related worries and depressive symptoms) was significantly decreased in those who were monitoring once or more per day (no significant difference for those monitoring less frequently). The authors suggest that the correlation with poorer psychological well-being could be related to the feeling of powerlessness caused by unsatisfactory results that patients are not able to improve, and they call for education and better guidance on how to use the results for treatment adjustment and/or behaviour change. In a recent study from the USA of attitudes and behaviours in 253 people with T2DM the following factors were found to be significant barriers for SMBG, and were associated with higher HbA1c levels: ‘costs too much’, ‘hassle’, ‘depression interferes’, ‘don’t understand’, ‘don’t like’, ‘it hurts’ and ‘don’t know how to use the results’. 129
The invasiveness of the SMBG procedure may also contribute to anxiety, as suggested by another American study of 339 diabetes patients (69.5% T2DM, 51.2% on diet and/or oral agents only), which showed that anxiety associated with SMBG invasiveness contributes to perceived burden and is negatively correlated with adherence to SMBG recommendations. 130
The question is whether the conclusion should be that because of these potential psychological disbenefits SMBG should not be used at all or whether these effects are just a warning sign that it should be used differently than used at present. There is a possibility – supported by some of the qualitative evidence – that depression and anxiety are due to the constant reminder of illness when monitoring (and this may be especially true in newly diagnosed patients, such as those in the ESMON trial, who may not yet have adapted to the disease). On the other hand, if the aim is increased self-efficacy then avoidance is probably not an appropriate strategy. In a study of 292 insulin-treated patients who had either T1DM or T2DM (48% T2DM) in the Netherlands, the coping style of diabetes avoidance was significantly associated with less frequent SMBG and perceiving SMBG as a burden. Participants with a low level of self-efficacy perceived all types of self-management activities as a burden. As also suggested by the data from the RCT by Schwedes et al. described above,21,61 increased self-efficacy may therefore lead to feeling more in control, less burdened and less depressed. 131
Clear, specific guidelines on who should use SMBG, and how frequently, are required – repeatedly articles cite ambiguity around current guidance for T2DM. Further research needs to address these factors, rather than just asking whether SMBG is useful per se.
The economics of SMBG
Belsey et al. (2009)100 estimated that in the UK SMBG varies from a low of 26% among those controlling their diabetes through diet and exercise alone, at an average annual cost of £10, rising as oral agents are added to peak at between 87% and 89% for those using insulin, at an average annual cost of between £140 and £198. Given this, the annual overall UK cost of SMBG was estimated as £171M, of which the authors estimated around £13M was unnecessary, given current guidelines. These results can be coupled with those of the US Veterans Affairs study of Meier et al. (2002),79 within which a policy of reducing test strip usage found that those using diet and exercise alone could approximately halve test strip usage, to one every other day with no impact upon HbA1c level. Similar results were reported for those using oral agents, though test strip usage was higher after the reduction, at around five per week.
Whether SMBG is cost-effective given its direct cost and its direct QoL impacts is not clear from the current literature. Farmer et al. 10,11 undertook what appears to be the most comprehensive study of the cost-effectiveness of SMBG in the UK setting. This applied the direct QoL effects and HbA1c levels effects of SMBG from the DiGEM study, assessing cost-effectiveness within the trial period and also extrapolating beyond this using the UKPDS Outcomes Model. Within the trial period, SMBG was estimated to result in additional costs and QALY losses and so be dominated by standard care. Extrapolation using the UKPDS Outcomes Model reduced both the additional costs and the QALY losses, due to some avoidance of downstream complications, but this did not affect the conclusion that SMBG was dominated by standard care. But the overall effects were small and subject to considerable uncertainty.
Other cost-effectiveness studies typically found minor QALY gains due to improvements in HbA1c level. This was typically at some additional cost, though some studies suggested the possibility of downstream cost savings outweighing the initial costs of SMBG. A key aspect of these studies was that SMBG was assumed not to be associated with any direct QoL loss, which appears unrealistic. There is the clear potential for the immediate direct QoL loss from SMBG to outweigh any downstream benefit in terms of reduced complications if the immediate impact of SMBG upon HbA1c level is minor or not sustained.
Other reviews
The IQWiG preliminary report on SMUG and SMBG in T2DM.
The German equivalent of NICE, the Institut für Qualität und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesundheitswesen (IQWiG), produced a report (in German, and not included in our clinical effectiveness partly because of language and partly because the preliminary report was published after ours was completed) assessing the effects of SMBG or SMUG as an integral part of any management strategy aimed at lowering blood glucose, compared with a strategy without self-measurement of glucose, or the comparison of a strategy involving SMBG with one involving SMUG in patients with T2DM who were not treated with insulin, with respect to patient-related outcomes. 132 Studies were included only if they also considered outcomes such as hypoglycaemia, QoL, mortality, diabetes-related morbidity, etc., but HbA1c level was also recorded. RCTs were considered, as well as epidemiological studies assessing mortality and morbidity. Minimum study duration was 6 months. Only full publications were included.
The findings of the IQWiG report are summarised in Box 1. The report placed most importance on assessment of hypoglycaemia. There was little emphasis on the issues of education and adjustment of therapy (other than using this as an outcome, but not in the sense of arguing that this is what should follow the SMBG measurement), and no discussion of behaviour changes.
The IQWiG report findings and conclusions were as follows:
The search identified 15 relevant papers describing 11 studies. However, five studies were excluded for the following reasons: three did not report relevant outcome measures other than HbA1c level (Allen 1990, Davidson 2005, Gallichan 1994) and two included relevant subgroups but the authors did not send the required data (Oria-Pino 2006, Wong 1986). The following five studies were included in the analysis: Guerci 2003, DiGEM 2007, Barnett 2008, ESMON 2008, Scherbaum 2008 and Schwedes 2002. Three studies were classified as having a low risk of bias, two as having a high risk of bias.
Data on hypoglycaemia were insufficiently reported: three studies reported data on severe hypoglycaemia but these were very rare. There was a statistically significant difference in HbA1c level in favour of SMBG (–0.23%), but this was judged not to be relevant as it was within the non-inferiority interval of 0.4%. There was no significant difference in therapy changes. Only one study reported other adverse events, and there was no significant difference between groups. There was no evidence of harm of SMBG compared with interventions without SMBG, but data were insufficient.
Four out of five studies reported on body weight and tended to show a slight reduction with SMBG, but overall the difference was non-significant.
Three studies reported on health-related QoL. The risk of bias for this measure was judged to be high for all three studies. In the DiGEM study, there was no significant difference for the W-BQ12 measure, and results on the EQ-5D were partially contradictory and could not be used. The ESMON study found increased depression in SMBG patients, whereas Schwedes 2002 found reduced depression in patients performing SMBG. Overall, there was no evidence for benefit or harm based in health-related QoL.
Three studies reported on patient satisfaction and there was no significant difference between groups. Two epidemiological studies were identified that reported on diabetes-related mortality and morbidity (ROSSO study and Fremantle diabetes study), but gave contradictory results.
Overall, there was no evidence for a benefit of self-measurement of blood or urinary glucose in patients with T2DM who were not being treated with insulin. There were no relevant and sufficiently clearly reported studies on measurement of urinary glucose. There was no evidence that measurement frequency had an influence on results. Epidemiological studies showed no evidence of an association between SMBG or SMUG and morbidity and mortality.
A review by O’Kane and Pickup (2009)106 comes to a similar conclusion as our review and ends with the comment that ‘The widespread use of SMBG (particularly in type-2 patients) is a good example of self-monitoring that was adopted in advance of robust evidence of it clinical efficacy’. Their review provides a useful history of SMBG and the technical aspects.
One issue raised by O’Kane and Pickup (2009)106 is that most previous RCTs have excluded patients who are already monitoring their blood glucose, and that this may cause a bias in that the excluded people may be the most successful.
The International Diabetes Federation issued its guidelines on SMBG in non-insulin-treated diabetes at the World Diabetes Congress in October 2009. 98 The summary noted ‘further studies are needed to better assess the benefits, optimal use and cost-effectiveness of SMBG’. The recommendations are given in Box 2.
SMBG should be used only when individuals with diabetes and/or their health-care providers have the knowledge, skills and willingness to incorporate SMBG monitoring and therapy adjustment into their diabetes care plans in order to attain agreed treatment goals
SMBG should be considered at the time of diagnosis to enhance the understanding of diabetes as part of individuals’ education and to facilitate timely treatment initiation and titration optimisation
SMBG should also be considered as part of ongoing diabetes self-management education to assist people with diabetes to better understand their disease and provide a means to actively and effectively participate in its control and treatment, modifying behavioural and pharmacological interventions as needed, in consultation with their health-care provider
SMBG protocols (intensity and frequency) should be individualised to address each individual’s specific educational/behavioural/clinical requirements (to identify/prevent/manage acute hyper- and hypoglycaemia) and provider requirements for data on glycaemic patterns and to monitor the impact of therapeutic decisions
The purpose(s) of performing SMBG and using SMBG data should be agreed between the person with diabetes and the health-care provider
Research needs
The top priority for research is to determine whether SMBG is ineffective in T2DM, or whether we have just not used it effectively in appropriately selected and empowered patients. Perhaps there has been too much focus on the technology end of the technology–human interface and not enough on the human end.
Research is required to:
-
determine characteristics of patients benefiting most from SMBG, in terms of psychological attributes, preferences, underlying treatment, baseline HbA1c level, duration of diabetes, age, level of education, previous use of SMBG, motivation for self-care, etc.
-
determine the optimal duration and frequency of SMBG for such individuals; specific time periods may occur at diagnosis, onset of behaviour change regimen (such as diet or exercise programme) or on progression of disease, for example when HbA1c level exceeds target on two or more consecutive measurements; there may be a particular benefit in patients on combination oral therapy who are being considered for the addition of insulin, as this is a group where intensive lifestyle intervention may avoid the need for insulin133 – it may be that motivation would be stronger at that stage; short, targeted bursts of SMBG may be more effective
-
assess the size and duration of the HbA1c effect in those in whom it does work
-
assess the impact of structured education on how to read and interpret results of SMBG
-
compare education containing empowerment techniques for patients with/without the aid of SMBG in patients treated with diet and/or oral glucose-lowering medication to determine the effective component, for example education, empowerment or SMBG
-
assess the effect of feedback in response to SMBG with respect to treatment changes (by HCP or patient) and behavioural/lifestyle changes and examine the interaction/communication between HCP and patient regarding SMBG readings and resulting action; this would include assessing the impact on intensification of treatment, such as whether SMBG can prolong the time on diet alone or on oral agents prior to insulin
-
assess the effects of SMBG on QoL and patient satisfaction, especially with respect to depression and anxiety and try to elicit the causes of depression/anxiety and the interaction between self-efficacy, depression/anxiety and clinical outcomes; if patients feel that SMBG can help them to improve their control, would that remove the depression and anxiety?
-
determine situations in which urinary glucose monitoring may be of value and whether it causes less anxiety (a trial is under way – see below)
-
assess the role pharmacists play in SMBG. If they are selling meters, are they providing education? What role could pharmacists play in delivering education? People usually have to go to the pharmacy to pick up their test strips
-
check as to whether newer devices with quicker results and memory for storing results are more effective.
Current or planned research
The Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose Trialists Collaboration is going to carry out an individual patient-based meta-analysis,134 which will, amongst other things, examine effectiveness amongst predefined subgroups, look for interactions with behavioural variables, assess the effect of co-intervention with psychosocial and educational interventions, and provide more detail on the interventions used in the trials.
A three-armed RCT of SMBG versus urine testing versus standard care is planned by Malanda et al. 135 from Amsterdam, the Netherlands: 600 patients will be recruited. The primary outcomes will be changes in diabetes-specific emotional distress and efficacy. Secondary outcomes include glycaemic control, patient satisfaction, physical activity, health status, depressive status, hypoglycaemia and cost–utility.
A trial funded by Diabetes UK is comparing SMBG with SMUG. 136 It is an extension of the DESMOND (Diabetes Education and Self-Management for On-going and Newly Diagnosed) study, and is measuring effects on glycaemic control (both HbA1c level and hypoglycaemia) and QoL, with an 18-month follow-up. If differences between the arms are seen then there will be a full economic assessment using the Sheffield Diabetes Model. It started early in 2007.
A German study is comparing once-weekly glucose profile self-monitoring with 3-monthly HbA1c to see which is better after 1 year. There are four arms: SMBG, HbA1c, both and neither, with all arms having urine glucose monitoring. The study duration is 5 years and it was expected to end by December 2008. 137
An Italian study called PRISMA (Prospective Randomised trial on Intensive Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Management Added Value in Non-insulin treated type 2 diabetes), funded by Hoffman-La Roche, has two arms, both with SMBG: one arm has standard care and the other arm provides patients with specific glycaemic targets and suggestions on how to achieve them by changes in diet or physical activity. 138
Another Dutch study in people with T2DM, not on insulin, is comparing SMBG (four times per day, 2 days per week) with standard care (not defined) with glycaemic control, QoL, treatment satisfaction, weight and need to start insulin as outcomes. It was due to end in 2008. It is funded by the Medical Research Foundation. 139
In the USA, Bergenstal et al. 140 are examining the effects of different frequencies and timing (SMBG three times per day versus only once-daily fasting) but with a control arm with no SMBG. The trial is due to end in 2009. It is supported by LifeScan.
Conclusions
Self-monitoring of blood glucose seems to provide only slight benefit in terms of glycaemic control, and it can have psychological disbenefits. There was a lack of evidence regarding the subgroups of patients who may benefit most from SMBG, and optimal frequency and timing. But SMBG clearly can yield benefits if used appropriately. One issue is that a number of studies showed that no changes in self-management or treatment were made as a result of SMBG – there is no point in collecting data on blood glucose levels if nothing is done with the data.
The current evidence on cost-effectiveness is mixed, but the best economics paper is from the DiGEM trial in the UK, which concluded that SMBG in patients with T2DM not on insulin was not cost-effective.
It may be that the key should be to identify those patients who will most benefit and divert some of the money currently allocated to SMBG to improved education for both HCPs and patients. SMBG might be more effective if associated with appropriate self-care plans developed between HCPs and patients to best meet patient needs and fit into their own lifestyle.
The prevalence and costs of T2DM are rising steadily at a time when NHS development funds are going to be very scarce. If we fund an increase in SMBG, funding will have to be taken from other aspects of care. The case for investing in SMBG for patients with T2DM not treated with insulin has to be regarded at present as ‘not proven’.
Acknowledgements
We thank the following for commenting on a near final draft of this report, but absolve them from any errors in the final report, responsibility for which rests with the review team:
-
Professor Simon Heller, Sheffield, UK
-
Dr Mark Houliston, general practitioner and lead clinician, Grampian Diabetes Managed Clinical Network
-
Dr Maurice O’Kane, Londonderry, Northern Ireland, UK.
We also thank the members of the Department of Health Working Group on self-monitoring of blood glucose, whose discussions and comments on both this research review and the drafts of the Working Group Report were very useful. The members of the working group included:
-
Simon Heller (Chair)
-
Eleanor Kennedy
-
Andrew Farmer
-
Adrian Griffin
-
Martin Gulliford
-
Julia Lawton
-
Maurice O’Kane
-
Mark Samuels
-
Grace Sweeney
-
Bridget Turner.
Contributions of authors
-
Christine Clar led the review of clinical effectiveness, commented on other sections, and edited the report after peer review and editorial comments.
-
Katharine Barnard led the review of qualitative studies and commented on other sections.
-
Ewen Cummins led the review of economic studies.
-
Pamela Royle did searches, quality assurance and editing, and commented on all sections.
-
Norman Waugh wrote Chapters 1 and 4, and undertook final editing.
About the Aberdeen HTA group
The Aberdeen Health Technology Assessment Group is part of the Institute of Applied Health Sciences (IAHS), which is part of the College of Medicine and Life Sciences of the University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK. The IAHS is made up of discrete but methodologically related research groups. The HTA Group is drawn mainly from the Health Services Research Unit, Public Health, and the Health Economics Research Unit.
The HTA Group produces independent health TARs for the UK HTA programme, which commissions TARs for NICE and other bodies, such as the National Screening Committee. It also carries out evidence reviews to support the NICE Single Technology Appraisal Programme.
Particular interests include evaluation of non-pharmacological technologies, screening and diabetes. Previous TARs from Aberdeen include:
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaled insulin in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2007;11(33).
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2009; in press.
-
Screening for type 2 diabetes: literature review and economic modelling. Health Technol Assess 2007;11(17).
-
Non-pharmacological prevention of diabetes in those with impaired glucose tolerance. In preparation.
-
Newer agents for blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes. Health Technol Assess 2010; in press.
We also do Cochrane reviews on diabetic topics.
Disclaimers
The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence . Type 2 Diabetes: The Management of Type 2 Diabetes (update) 2008. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG66.
- British Medical Association and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain . British National Formulary 57 n.d. www.bnf.org/bnf/bnf/current/104945.htm 2009 (accessed 21 July 2009).
- McAndrew L, Schneider SH, Burns E, Leventhal H. Does patient blood glucose monitoring improve diabetes control? A systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Educ 2007;33:991-1011.
- Yorkshire and Humber Public Health Observatory n.d. www.yhpho.org.uk/ (accessed August 2009).
- The Health and Social Care Information Centre PSUatYaHPHO . Prescribing for Diabetes in England. An Analysis of Volume, Expenditure and Trends 2009. www.yhpho.org.uk/resource/item.aspx?RID=9711 (accessed 21 July 2009).
- Chapman RH, Benner JS, Petrilla AA, Tierce JC, Collins SR, Battleman DS, et al. Predictors of adherence with antihypertensive and lipid-lowering therapy. Arch Intern Med 2005;165:1147-52.
- Lawton J, Peel E, Douglas M, Parry O. ‘Urine testing is a waste of time’: newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetes patients’ perceptions of self-monitoring. Diabet Med 2004;21:1045-8.
- Lawton J. Patients’ perceptions and experiences of taking oral glucose-lowering agents: a longitudinal qualitative study. Diabet Med 2008;25:491-5.
- Song M, Lipman TH. Concept analysis: self-monitoring in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Nurs Stud 2008;45:1700-10.
- Farmer A, Wade A, Goyder E, Yudkin P, French D, Craven A, et al. Impact of self monitoring of blood glucose in the management of patients with non-insulin treated diabetes: open parallel group randomised trial. BMJ 2007;335.
- Farmer AJ, Wade AN, French DP, Simon J, Yudkin P, Gray A, et al. Blood glucose self-monitoring in type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Health Technology Assessment 2009;13.
- Simon J, Gray A, Clarke P, Wade A, Neil A, Farmer A, et al. Cost-effectiveness of self monitoring of blood glucose in patients with non-insulin treated type 2 diabetes: economic evaluation of data from the DiGEM trial. BMJ 2008;336:1177-80.
- O’Kane MJ, Bunting B, Copeland M, Coates VE. ESMON study group . Efficacy of self monitoring of blood glucose in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (ESMON study): randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2008;336:1174-7.
- Karter AJ, Parker MM, Moffet HH, Spence MM, Chan J, Ettner SL, et al. Longitudinal study of new and prevalent use of self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1757-63.
- Martin S, Schneider B, Heinemann L, Lodwig V, Kurth HJ, Kolb H, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes and long-term outcome: an epidemiological cohort study. Diabetologia 2006;49:271-8.
- Wen L, Parchman ML, Linn WD, Lee S. Association between self-monitoring of blood glucose and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2004;61:2401-5.
- Davis TME, Van-Minnen K, Bruce DG, Davis WA. The relationship between self-monitoring of blood glucose results and glycosylated haemoglobin in type 2 diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetologia 2007;50.
- Davis WA, Bruce DG, Davis TM. Is self-monitoring of blood glucose appropriate for all type 2 diabetic patients? The Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1764-70.
- Davis WA, Bruce DG, Davis TM. Does self-monitoring of blood glucose improve outcome in type 2 diabetes? The Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetologia 2007;50:510-5.
- Moreland EC, Volkening LK, Lawlor MT, Chalmers KA, Anderson BJ, Laffel LM. Use of a blood glucose monitoring manual to enhance monitoring adherence in adults with diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med 2006;166:689-95.
- Siebolds M, Gaedeke O, Schwedes U. SMBG Study Group . Patient Educ Couns 2006;62:104-10.
- Palmer AJ, Dinneen S, Gavin JR, Gray A, Herman WH, Karter AJ. Cost-utility analysis in a UK setting of self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin 2006;22:861-72.
- Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses. Lancet 1999;354:1896-900.
- Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, Powrie JK, Swaminathan R. Monitoring blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess 2000;4.
- Brunner GA, Ellmerer M, Sendlhofer G, Wutte A, Trajanoski Z, Schaupp L, et al. Validation of home blood glucose meters with respect to clinical and analytical approaches. Diabetes Care 1998;21:585-90.
- Williams CD, Scobie IN, Till S, Crane R, Lowy C, Sonksen PH. Use of memory meters to measure reliability of self blood glucose monitoring. Diabet Med 1988;5:459-62.
- Arabadjief D, Nichols JH. Assessing glucose meter accuracy. Curr Med Res Opin 2006;22:2167-74.
- AHRQ . Applicability of the Evidence Regarding Intensive Glycemic Control and Self-Monitored Blood Glucose to Medicare Patients With Type 2 Diabetes 2007.
- Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, Powrie JK, Swaminathan R. Self-monitoring in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med 2000;17:755-61.
- Faas A, Schellevis FG, Van Eijk JT. The efficacy of self-monitoring of blood glucose in NIDDM subjects. A criteria-based literature review. Diabetes Care 1997;20:1482-6.
- Jansen JP. Self-monitoring of glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Bayesian meta-analysis of direct and indirect comparisons. Curr Med Res Opin 2006;22:671-81.
- McGeoch G, Derry S, Moore RA. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type-2 diabetes: what is the evidence?. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2007;23:423-40.
- Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Jiamsathit W. Systematic review of the benefits of self-monitoring of blood glucose on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Technol Ther 2008;10:S51-66.
- Sarol JN, Nicodemus NA, Tan KM, Grava MB. Self-monitoring of blood glucose as part of a multi-component therapy among non-insulin requiring type 2 diabetes patients: a meta-analysis (1966–2004). Curr Med Res Opin 2005;21:173-84.
- Towfigh A, Romanova M, Weinreb JE, Munjas B, Suttorp MJ, Zhou A, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus not taking insulin: a meta-analysis. Am J Manag Care 2008;14:468-75.
- Welschen LM, Bloemendal E, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, Stalman WA, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin: a systematic review. Diabetes Care 2005;28:1510-7.
- Welschen LM, Bloemendal E, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, Stalman WA, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005.
- St John A, Davis WA, Price CP, Davis TM. The value of self-monitoring of blood glucose: a review of recent evidence. J Diabetes Complications 2009.
- Sarol JN, Nicodemus NA, Tan KM, Flores JVPG. Self-monitoring of blood glucose as part of a multi-component treatment strategy in non-insulin requiring type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2004;53.
- Allen BT, DeLong ER, Feussner JR. Impact of glucose self-monitoring on non-insulin-treated patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Randomized controlled trial comparing blood and urine testing. Diabetes Care 1990;13:1044-50.
- Barnett AH, Krentz AJ, Strojek K, Sieradzki J, Azizi F, Embong M, et al. The efficacy of self-monitoring of blood glucose in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes treated with a gliclazide modified release-based regimen. A multicentre, randomized, parallel-group, 6-month evaluation (DINAMIC 1 study). Diabetes Obes Metab 2008;10:1239-47.
- Bonomo K, De Salve A, Pignatelli S, Fiora E, Mularoni E, Cavalot F, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetic patients not on insulin treatment: waist of money or tool to reach the glyeaemic targets?. Diabetologia 2006;49.
- Brown SA, Garcia AA, Kouzekanani K, Hanis CL. Culturally competent diabetes self-management education for Mexican Americans: the Starr County border health initiative. Diabetes Care 2002;25:259-68.
- Cho JH, Chang SA, Kwon HS, Choi YH, Ko SH, Moon SD, et al. Long-term effect of the Internet-based glucose monitoring system on HbA1c reduction and glucose stability: a 30-month follow-up study for diabetes management with a ubiquitous medical care system. Diabetes Care 2006;29:2625-31.
- Davidson MB, Castellanos M, Kain D, Duran P. The effect of self monitoring of blood glucose concentrations on glycated hemoglobin levels in diabetic patients not taking insulin: a blinded, randomized trial. Am J Med 2005;118:422-5.
- Estey AL, Tan MH, Mann K. Follow-up intervention: its effect on compliance behavior to a diabetes regimen. Diabetes Educ 1990;16:291-5.
- Fontbonne A, Billault B, Acosta M, Percheron C, Varenne P, Besse A, et al. Is glucose self-monitoring beneficial in non-insulin-treated diabetic patients? Results of a randomized comparative trial. Diabete Metab 1989;15:255-60.
- Gallichan MJ. Self-monitoring by patients receiving oral hypoglycemic agents: a survey and a comparative trial. Pract Diabetes 1994;11:28-30.
- Guerci B, Drouin P, Grange V, Bougneres P, Fontaine P, Kerlan V, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose significantly improves metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Auto-Surveillance Intervention Active (ASIA) study. Diabetes Metab 2003;29:587-94.
- Jaber LA, Halapy H, Fernet M, Tummalapalli S, Diwakaran H. Evaluation of a pharmaceutical care model on diabetes management. Ann Pharmacother 1996;30:238-43.
- Johnson JA, Majumdar SR, Bowker SL, Toth EL, Edwards A. Self-monitoring in Type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial of reimbursement policy. Diabet Med 2006;23:1247-51.
- Jones H, Edwards L, Vallis TM, Ruggiero L, Rossi SR, Rossi JS, et al. Changes in diabetes self-care behaviors make a difference in glycemic control: the Diabetes Stages of Change (DiSC) study. Diabetes Care 2003;26:732-7.
- Joy S, Rodgers P, Elmore L, Calvert S. Assessment of therapeutic interventions and degree of glycemic control for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using preprandial versus postprandial self blood glucose monitoring in a primary care setting. Diabetes 2003;52:A96-7.
- Kibriya MG, Ali L, Banik NG, Khan AK. Home monitoring of blood glucose (HMBG) in Type-2 diabetes mellitus in a developing country. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1999;46:253-7.
- Kwon HS, Cho JH, Kim HS, Song BR, Ko SH, Lee JM, et al. Establishment of blood glucose monitoring system using the internet. Diabetes Care 2004;27:478-83.
- Miles P, Everett J, Murphy J, Kerr D. Comparison of blood or urine testing by patients with newly diagnosed non-insulin dependent diabetes: patient survey after randomised crossover trial. BMJ 1997;315:348-9.
- Muchmore DB, Springer J, Miller M. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in overweight type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol 1994;31:215-19.
- Rutten G, van EJ, de NE, Beek M, van der Helden H. Feasibility and effects of a diabetes type II protocol with blood glucose self-monitoring in general practice. Fam Pract 1990;7:273-8.
- Scherbaum WA, Ohmann C, Abholz HH, Lankisch M. Evaluating the optimal frequency of self-monitoring blood glucose in type 2 diabetes at glycaemic target: a multi-centre, randomized controlled trial. Diabetes 2007;56.
- Scherbaum WA, Ohmann C, Abholz HH, Dragano N, Lankisch M. Effect of the frequency of self-monitoring blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with oral antidiabetic drugs-a multi-centre, randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2008;3.
- Schwedes U, Siebolds M, Mertes G. Meal-related structured self-monitoring of blood glucose: effect on diabetes control in non-insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2002;25:1928-32.
- Seaton TL. Benefit of self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with NIDDM receiving oral sulfonylureas [abstract]. Pharmacotherapy 1996;16.
- Wing RR, Epstein LH, Nowalk MP, Scott N, Koeske R, Hagg S. Does self-monitoring of blood glucose levels improve dietary compliance for obese patients with type II diabetes?. Am J Med 1986;81:830-6.
- Bajkowska-Fiedziukiewicz A, Cypryk K, Kozdraj T, Mikolajczyk-Swatko A, Kosinski M, Jozefowska M. Self-monitoring of blood glucose and treatment outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients. Polskie Archiwum Medycyny Wewnetrznej 2008;118:267-72.
- Banister NA, Jastrow ST, Hodges V, Loop R, Gillham MB. Diabetes self-management training program in a community clinic improves patient outcomes at modest cost. J Am Diet Assoc 2004;104:807-10.
- Blonde L, Ginsberg BH, Horn S. Frequency of blood glucose monitoring in relation to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;25:245-55.
- Capelson R, Principe A, Trey G, Hayes M, Suhl E, Ayres D, et al. Does increased home monitoring of blood glucose (HMBG) improve glycemic control in patients over 75?. Diabetes 2006;55.
- Chan WB, Chan JC, Chow CC, Yeung VT, So WY, Li JK, et al. Glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: the impact of body weight, beta-cell function and patient education. QJM 2000;93:183-90.
- Evans JM, Newton RW, Ruta DA, MacDonald TM, Stevenson RJ, Morris AD. Frequency of blood glucose monitoring in relation to glycaemic control: observational study with diabetes database. BMJ 1999;319:83-6.
- Franciosi M, Pellegrini F, De Berardis G, Belfiglio M, Cavaliere D, Di Nardo B, et al. The impact of blood glucose self-monitoring on metabolic control and quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients: an urgent need for better educational strategies. Diabetes Care 2001;24:1870-7.
- Franciosi M, Pellegrini F, De Berardis G, Belfiglio M, Di Nardo B, Greenfield S, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in non-insulin-treated diabetic patients: a longitudinal evaluation of its impact on metabolic control. Diabet Med 2005;22:900-6.
- Hanninen J, Takala J, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S. Good continuity of care may improve quality of life in Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2001;51:21-7.
- Harris MI. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) . Frequency of blood glucose monitoring in relation to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001;24:979-82.
- Jaworska J, Dziemidok P, Kulik TB, Rudnicka-Drozak E. Frequency of self-monitoring and its effect on metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med 2004;59:310-16.
- Karter AJ, Ackerson LM, Darbinian JA, D’Agostino RB, Ferrara A, Liu J, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose levels and glycemic control: the Northern California Kaiser Permanente Diabetes registry. Am J Med 2001;111:1-9.
- Karter AJ, Moffet HH, Liu J, Parker MM, Ahmed AT, Ferrara A, et al. Achieving good glycemic control: initiation of new antihyperglycemic therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes from the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Diabetes Registry. Am J Manag Care 2005;11:262-70.
- Klein CE, Oboler SK, Prochazka A, Oboler S, Frank M, Glugla M, et al. Home blood glucose monitoring: effectiveness in a general population of patients who have non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Gen Intern Med 1993;8:597-601.
- Martin S, Kolb H, Schneider B, Heinemann L, Weber C, Kocher S, et al. Myocardial infarction and stroke in early years after diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: risk factors and relation to self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Technol Ther 2009;11:234-41.
- Meier JL, Swislocki AL, Lopez JR, Noth RH, Bartlebaugh P, Siegel D. Reduction in self-monitoring of blood glucose in persons with type 2 diabetes results in cost savings and no change in glycemic control. Am J Manag Care 2002;8:557-65.
- Mitchell CG, Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Toth EL, Johnson JA. Lack of correlation between patient-reported outcomes and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes not managed by insulin. Can J Diabetes 2004;28:362-8.
- Murata GH, Shah JH, Hoffman RM, Wendel CS, Adam KD, Solvas PA, et al. Intensified blood glucose monitoring improves glycemic control in stable, insulin-treated veterans with type 2 diabetes: the Diabetes Outcomes in Veterans Study (DOVES). Diabetes Care 2003;26:1759-63.
- Murata GH, Duckworth WC, Shah JH, Wendel CS, Mohler MJ, Hoffman RM. Blood glucose monitoring is associated with better glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: a database study. J Gen Int Med 2009;24:48-52.
- Newman WP, Laqua D, Engelbrecht D. Impact of glucose self-monitoring on glycohemoglobin values in a veteran population. Arch Intern Med 1990;150:107-10.
- Oki JC, Flora DL, Isley WL. Frequency and impact of SMBG on glycemic control in patients with NIDDM in an urban teaching hospital clinic. Diabetes Educ 1997;23:419-24.
- Ozmen B, Boyvada S. The relationship between self-monitoring of blood glucose control and glycosylated haemoglobin in patients with type 2 diabetes with and without diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Complications 2003;17:128-34.
- Patrick AW, Gill GV, MacFarlane IA, Cullen A, Power E, Wallymahmed M. Home glucose monitoring in type 2 diabetes: is it a waste of time?. Diabet Med 1994;11:62-5.
- Rindone JP, Austin M, Luchesi J. Effect of home blood glucose monitoring on the management of patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in the primary care setting. American J Manag Care 1997;3:1335-8.
- Roblin DW, Barizlay JI. Self-monitoring of blood glucose: Variation in frequency of monitoring and its association with glycemic control. Diabetes 2001;50.
- Rost KM, Flavin KS, Schmidt LE, McGill JB. Self-care predictors of metabolic control in NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care 1990;13:1111-3.
- Schiel R, Muller UA, Rauchfub J, Sprott H, Muller R. Blood-glucose self-monitoring in insulin treated type 2 diabetes mellitus a cross-sectional study with an intervention group. Diabetes Metab 1999;25:334-40.
- Schütt M, Kern W, Krause U, Busch P, Dapp A, Grziwotz R, et al. Is the frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose related to long-term metabolic control? Multicenter analysis including 24,500 patients from 191 centers in Germany and Austria. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2006;114:384-8.
- Secnik K, Yurgin N, Lage MJ, Donald-Everett C. Patterns of blood glucose monitoring in relation to glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes in the UK. J Diabetes Complications 2007;21:181-6.
- Soumerai SB, Mah C, Zhang F, Adams A, Barton M, Fajtova V, et al. Effects of health maintenance organization coverage of self-monitoring devices on diabetes self-care and glycemic control. Arch Intern Med 2004;164:645-52.
- Stiptzarov N, Zhang Q, Pogach L. Increased utilization of self monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) is associated with decreased A1c levels. Diabetes 2003;52.
- Tengblad A, Grodzinsky E, Lindstrom K, Molstad S, Borgquist L, Ostgren CJ. Self-monitoring of blood glucose and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes. Scand J Prim Health Care 2007;25:140-6.
- Wieland LD, Vigil JM, Hoffman RM, Janis LW. Relationship between home glucose testing and hemoglobin Alc in type II diabetes patients. Am J Health Syst Pharm 1997;54:1062-5.
- Worth R, Home PD, Johnston DG, Anderson J, Ashworth L, Burrin JM, et al. Intensive attention improves glycaemic control in insulin-dependent diabetes without further advantage from home blood glucose monitoring: results of a controlled trial. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982;285:1233-40.
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Guideline on Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Non-Insulin Treated Type 2 Diabetes 2008. www.idf.org/idf-guideline-self-monitoring-blood-glucose-non-insulin-treated-type-2-diabetes (accessed 5 December 2009).
- Schneider B, Martin S, Heinemann L, Lodwig V, Kolb H. Interrelations between diabetes therapy, self-monitoring of blood glucose, blood glucose and non-fatal or fatal endpoints in patients with type 2 diabetes/results of a longitudinal cohort study (ROSSO 5). Arzneimittelforschung 2007;57:762-9.
- Belsey JD, Pittard JB, Rao S, Urdahl H, Jameson K, Dixon T. Self blood glucose monitoring in type 2 diabetes. A financial impact analysis based on UK primary care. Int J Clin Pract 2009;63:439-48.
- Peel E, Parry O, Douglas M, Lawton J. Blood glucose self-monitoring in non-insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a qualitative study of patients’ perspectives. Br J Gen Pract 2004;54:183-8.
- Peel E, Douglas M, Lawton J. Self monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: longitudinal qualitative study of patients’ perspectives. BMJ 2007;335.
- Zgibor JC, Simmons DS. Barriers to self glucose monitoring in a multi-ethnic community. Diabetes 2001;50:A500-1.
- Stewart D, McCaig D, Davie A, Juroszek L, Blackwood L, Findlay N, et al. Glucose self-monitoring in primary care: a survey of current practice. J Clin Pharm Ther 2004;29:273-7.
- National Prescribing Centre . When and How Should Patients With Diabetes Mellitus Test Blood Glucose? 2002. www.npc.co.uk/ebt/merec/cardio/diabetes1/resources/merec_bulletin_vol13_no1.pdf (accessed 21 July 2009).
- O’Kane MJ, Pickup J. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in diabetes: is it worth it?. Ann Clin Biochem 2009;46:273-82.
- Funnell M, Anderson RM. Empowerment and self-management of diabetes. Clin Diabetes 2004;22.
- Curtis L, Netten A. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2006 2006. www.pssru.ac.uk/pdf/uc/uc2006/uc2006.pdf (accessed August 2009).
- Weber C, Schneider B, Lodwig V, Holm MV, Neeser K. Cost impact of blood glucose self-monitoring on complications of type 2 diabetes: a Swiss perspective (ROSSO study No.11). Swiss Med Wkly 2007;137:545-50.
- Tiley S. Home blood glucose monitoring – What cost?. Pract Diabetes Int 2002;19:S1-4.
- Neeser K, Weber C, Wenzel H, Schneider B. Costs of self-measurement of blood glucose (SMBG) regarding morbidity and mortality in type 2 diabetes in a reality of care setting (The ROSSO study No. 6). Diabetologia 2006;49.
- Clarke PM, Gray AM, Briggs A, Farmer AJ, Fenn P, Stevens RJ, et al. A model to estimate the lifetime health outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Outcomes Model (UKPDS no. 68). Diabetologia 2004;47:1747-59.
- Department of Health . NHS Reference Costs 2005–06 n.d. www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAndGuidance/DH_062884 (accessed August 2009).
- National Health Service . Annual Financial Returns of NHS Trusts 2003–2004 2005.
- Netten A, Curtis L. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2002 n.d. www.pssru.ac.uk/UC2002.htm (accessed August 2009).
- Tunis SL, Minshall ME. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: cost-effectiveness in the united states. Am Journal Manag Care 2008;14:131-40.
- Palmer AJ, Roze S, Valentine WJ, Minshall ME, Foos V, Lurati FM, et al. The CORE Diabetes Model: projecting long-term clinical outcomes, costs and cost-effectiveness of interventions in diabetes mellitus (types 1 and 2) to support clinical and reimbursement decision-making. Curr Med Res Opin 2004;20:5-26.
- Aspinall SL, Glassman PA. Cost-effectiveness of blood glucose monitoring is controversial. Am J Manag Care 2008;14:398-9.
- Tunis SL. Cost-effectiveness of changing self-monitoring of blood glucose frequency. Diabetes 2009;58.
- Mataveli F, Turatti L, Pimazoni Netto A. Short-term economic benefits of self monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) in type 2 diabetes for health maintenance organisations (HMOs). Diabetologia 2008;51.
- Erny-Albrecht KM, Tunis SL, Minshall ME, Valentine W, Foos V, Palmer AJ. Frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: a cost-effectiveness modeling study in the US setting. Diabetes 2007;56:A308-9.
- Weber C, Neeser K, Schneider B, Heinemann L, Lodwig V, Scherbaum WA. Cost-effectiveness of self measurement of blood glucose (SMBG) in function of the testing frequency in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2007;56.
- Weber C, Erny-Albrecht K, Neeser K. Cost effectiveness of SMBG for the treatment of non insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2006;49.
- Neeser K, Erny-Albrecht K, Weber C. Cost-effectiveness of self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetic patients not receiving insulin [comment]. Diabetes Care 2006;29:480-1.
- Davidson MB, . Cost-effectiveness of self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetic patients not receiving insulin: Response to Neeser. Diabetes Care 2006;29:480-1.
- Kempf K, Neukirchen W, Martin S, Kolb H. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: a new look at published trials. Diabetologia 2008;51:686-8.
- Davidson MB. Counterpoint: Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetic patients not receiving insulin: a waste of money. Diabetes Care 2005;28:1531-3.
- Joslin Diabetes Center . Blood Sugar Monitoring owner’s Manual n.d. www.joslin.org/ (accessed August 2009).
- Daly JM, Hartz AJ, Xu Y, Levy BT, James PA, Merchant ML, et al. An assessment of attitudes, behaviors, and outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes. J Am Board Fam Med 2009;22:280-90.
- Wagner J, Malchoff C, Abbott G. Invasiveness as a barrier to self-monitoring of blood glucose in diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2005;7:612-9.
- Weijman I, Ros WJ, Rutten GE, Schaufeli WB, Schabracq MJ, Winnubst JA. The role of work-related and personal factors in diabetes self-management. Patient Educ Couns 2005;59:87-96.
- IQWiG (Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care) . Urine and Blood Glucose Self-Measurement in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 2009. www.iqwig.de/index.559.en.html (accessed 21 October 2009).
- Aas AM, Bergstad I, Thorsby PM, Johannesen O, Solberg M, Birkeland KI. An intensified lifestyle intervention programme may be superior to insulin treatment in poorly controlled Type 2 diabetic patients on oral hypoglycaemic agents: results of a feasibility study. Diabet Med 2005;22:316-22.
- Farmer AJ, Heneghan C, Barnett AH, Davidson MB, Guerci B, O’Kane M, et al. Individual patient data meta-analysis of trials of self-monitoring of blood glucose in non-insulin treated type 2 diabetes: Protocol for a systematic review. Prim Care Diabetes 2009;3:117-21.
- Malanda UL, Bot SDM, Kostense PJ, Snoek FJ, Dekker JM, Nijpels G. Effects of self-monitoring of glucose in non-insulin treated patients with type 2 diabetes: design of the IN CONTROL-trial. BMC Fam Pract 2009.
- Heller S. Does Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose As Opposed to Urinalysis Provide Additional Benefit to Newly Diagnosed Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Structured Education? n.d. http://public.ukcrn.org.uk/Search/StudyDetail.aspx?StudyID=3773 (accessed 13 August 2009).
- Deutsche Diabetes Gesellschaft . Blood Glucose Self Monitoring and HbA1c Effects on Glucose Control 2008. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00688363?term=NCT00688363%26rank=1 (accessed 13 August 2009).
- Hoffmann-La Roche . Intensive Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Management Added Value in Non-Insulin Treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients 2009. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00643474?term=NCT00643474%26rank=1 (accessed 13 August 2009).
- Medical Research Foundation, Langerhans Foundation . Effect of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Not Using Insulin 2008. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00287807 (accessed 13 August 2009).
- International Diabetes Center, Park Nicollet Institute, LifeScan . Impact of Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Frequency on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes 2009. www.parknicollet.com/diabetes/ (accessed 13 August 2009).
- Downs SH, Black N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised trials and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epid Community Health 1998;52:377-84.
- Franciosi M, De Berardis G, Cavaliere I, Valentini M, Nicolucci A. The impact of blood glucose self-monitoring on quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 2001;50.
Appendix 1 Search strategy and flow of studies
Search strategy for clinical effectiveness studies
The following MEDLINE search strategy was adapted as appropriate for other databases:
-
(self monitor* adj3 blood glucose).tw.
-
(home monitor* adj3 blood glucose).tw.
-
(HMBG or HBGM or SMBG or BGSM).tw.
-
exp Blood Glucose Self-Monitoring/
-
(glucose adj2 monitor* adj3 (self or home)).tw.
-
4 or 1 or 3 or 2 or 5
-
exp Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/
-
type 2 diabetes.tw.
-
8 or 7
-
6 and 9
-
((self or home) and monitor* and glucose).m_titl.
-
11 or 10
-
limit 12 to english language
Search strategy for a cost-effectiveness studies
The MEDLINE strategy below was used and adapted as appropriate for other databases:
-
(self monitor* adj3 blood glucose).tw.
-
(home monitor* adj3 blood glucose).tw.
-
(HMBG or HBGM or SMBG or BGSM).tw.
-
exp Blood Glucose Self-Monitoring/
-
(glucose adj2 monitor* adj3 (self or home)).tw.
-
4 or 1 or 3 or 2 or 5
-
exp Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/
-
type 2 diabetes.tw.
-
8 or 7
-
6 and 9
-
((self or home) and monitor* and glucose).m_titl.
-
11 or 10
-
limit 12 to english language
-
(cost* or economic or financial).mp. [mp=title, original title, abstract, name of substance word, subject heading word]
-
13 and 14
Flow of studies for SMBG general search
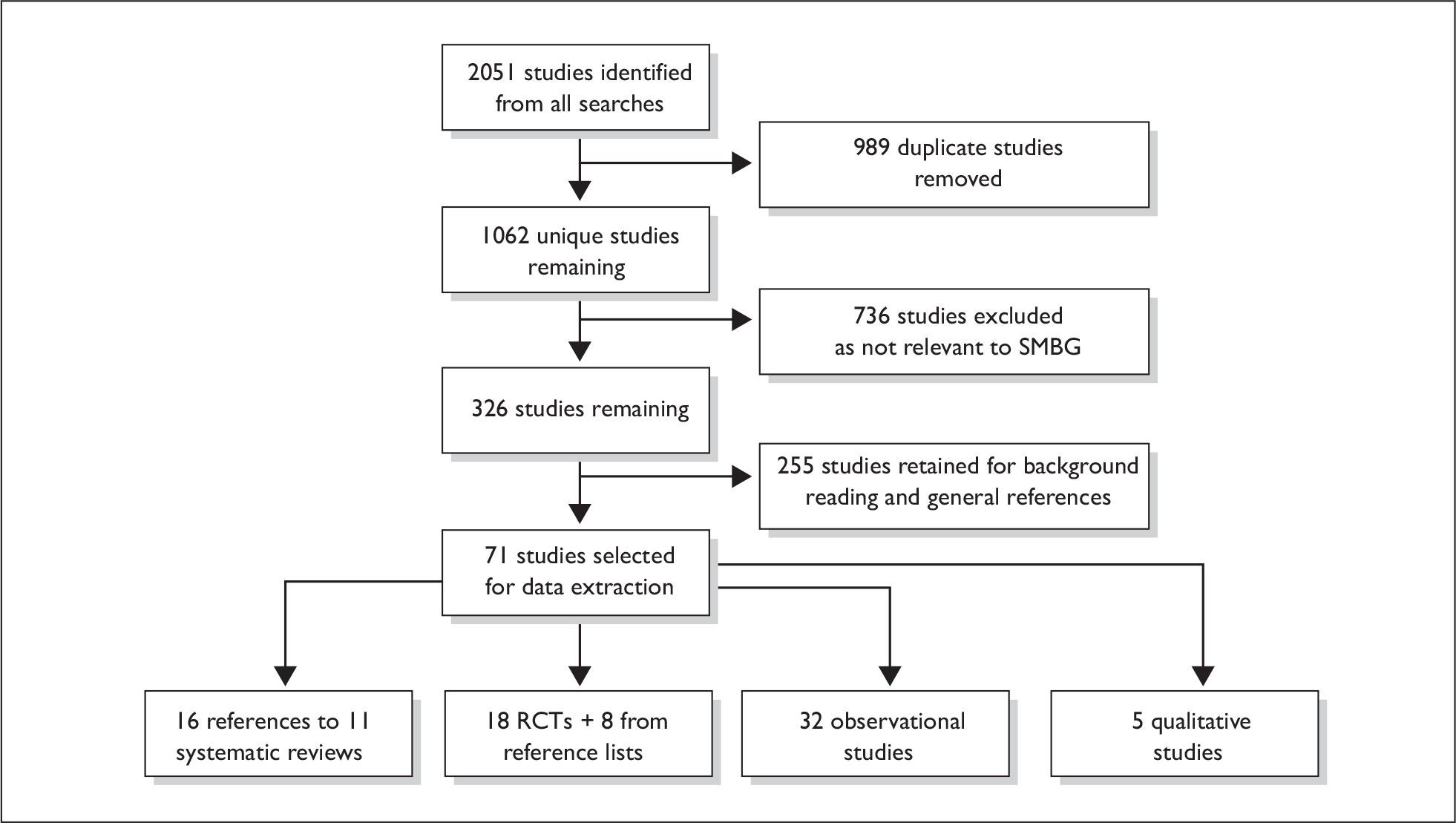
Flow of studies for SMBG cost-effectiveness search
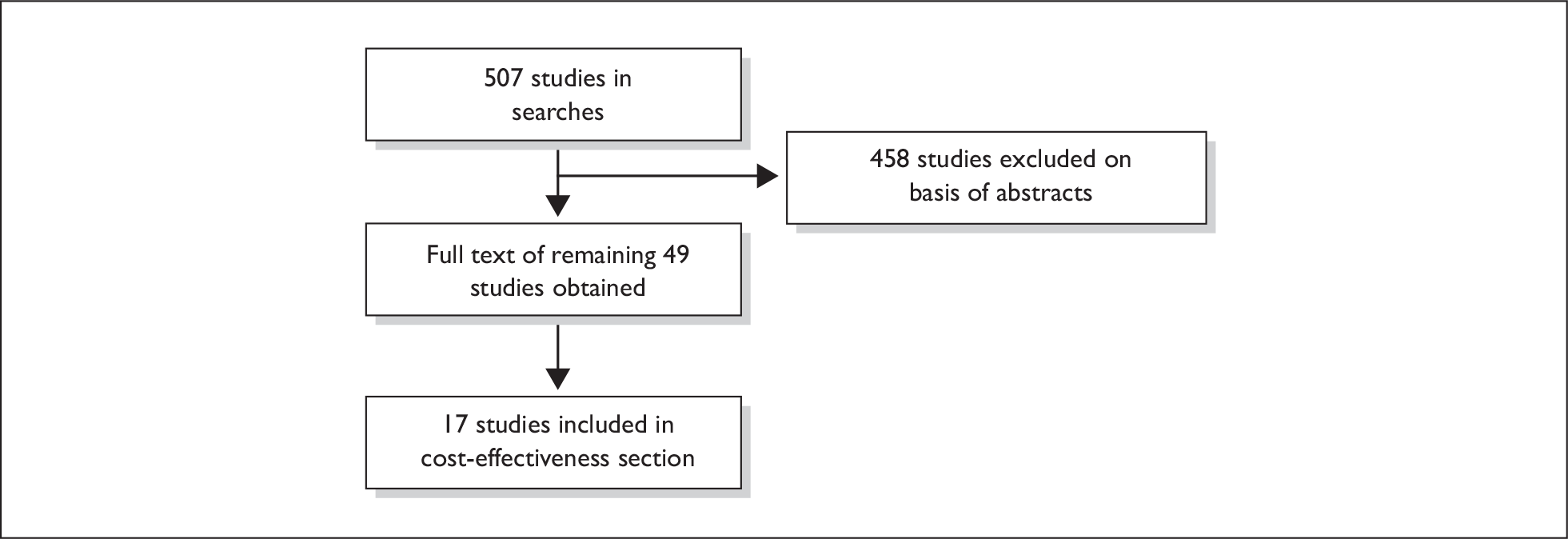
Appendix 2 Characteristics of systematic reviews
| Review | Inclusion criteria and methodology | Included studies | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Faas (1997) 30 Netherlands Focus: efficacy of self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Funding: not reported |
Inclusion criteria Study design: unclear; non-RCTs included initially, but only RCTs investigated in more detail Participants: T2DM; studies exclusively with patients using insulin excluded Interventions: SMBG; any comparison Outcomes: HbA1c; other outcomes as reported Methodology Search strategy: MEDLINE (1976–1996); keywords given; bibliographies searched Study selection: method not reported Quality assessment: criteria by Deyo and ter Riet Data extraction: method not reported Meta-analysis: no Data analysis: text and tables Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: none |
Number of included trials: 11; 6 RCTs, 5 non-RCTs not further evaluated Number of participants: 592 TRIALS: Design: only RCTs further evaluated Duration: 12–62 weeks Quality: 4 RCTs 7/7 points, rest 3/7 and 4/7 PARTICIPANTS: see trial descriptions INTERVENTIONS: 4 only SMBG, 4 vs no SMBG, 3 vs urine testing; some interventions including education OUTCOMES: HbA1c, weight, fasting glucose, lifestyle adherence, SMBG adherence, fructosamine |
OVERALL QUALITY: moderate – limited description of methods and of study characteristics COMMENT: investigated use of therapy decision scheme by the investigator, comparisons, nature of SMBG device; key points of patient instruction and education, self-monitoring regimen, assessment of self-monitoring frequency, feedback received from care provider |
|
Coster (2000) 29 UK – NHS HTA Focus: effectiveness of blood or urine glucose self-monitoring in T2DM Funding: NHS R&D HTA programme |
Inclusion criteria Study design: RCTs Participants: T2DM; independent of treatment type Interventions: SMBG vs SMUG or no monitoring Outcomes: HbA1c, weight, any other outcomes reported Methodology Search strategy: MEDLINE, EMBASE; Index and Bibliography of Social Science (IBSS), database of Diabetes Health Economic Study Group; search dates 1976–99 (MEDLINE); 1980–98 (EMBASE); keywords given; hand-searching Diabetic Medicine (1990–9) and Diabetes Care (1990–9); requests to British Diabetic Association and manufacturers of testing equipment (Bayer and Roche Diagnostics); reference lists; restriction to English language Study selection: method not reported Quality assessment: modified quality checklist by Downs and Black (1998);141 applied by two reviewers independently Data extraction: method not reported Meta-analysis: yes Data analysis: random effects model; heterogeneity assessed Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: sensitivity analyses used that did not change the overall results (based on study design and comparisons) |
Number of included trials: 8 Number of participants: 734 TRIALS: Design: RCTs Duration: 3–12 months Quality: mean quality score 15 of 27 PARTICIPANTS: see trial descriptions INTERVENTIONS: some interventions including education – see descriptions OUTCOMES: HbA1c, fasting blood glucose, fructosamine, body weight, QoL |
|
|
Philippines Focus: self-monitoring of blood glucose on HbA1c in non-insulin-requiring patients with T2DM Funding: Johnson & Johnson |
Inclusion criteria Study design: RCTs Participants: T2DM without insulin treatment Interventions: diabetes management strategy with SMBG component vs strategy without SMBG component Outcomes: HbA1c Methodology Search strategy: MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, CRD databases, Online ADA Index Journals, personal collections (up to 2004); keywords listed; reference lists searched; English or English translation Study selection: titles and abstracts independently assessed by two reviewers Quality assessment: Cochrane Collaboration criteria Data extraction: items extracted listed Meta-analysis: yes Data analysis: fixed and random effects; heterogeneity assessed |
Number of included trials: 8 Number of participants: 1307 TRIALS: Design: RCTs Duration: 12–44 weeks Quality: quality B for 5 studies and C for 3 studies PARTICIPANTS: see trial descriptions INTERVENTIONS: some interventions including education – see descriptions OUTCOMES: HbA1c |
|
|
Welschen (2005) 37 Netherlands Focus: effects of SMBG in patients with T2DM who are not using insulin Funding: non-commercial |
Inclusion criteria Study design: RCTs Participants: T2DM; non-insulin treated Interventions: SMBG vs SMUG or no monitoring Outcomes: HbA1c, FPG, QoL, patient satisfaction, hypoglycaemia, morbidity, adverse effects, costs Methodology Search strategy: MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, NHS Economic Evaluation database, EMBASE, ongoing trials, reference lists; search dates up to September 2004; electronic search strategy given; no language restriction Study selection: titles and abstracts independently assessed by two reviewers Quality assessment: Maastricht–Amsterdam score; assessed independently by two reviewers Data extraction: data extraction form; data extracted independently by two reviewers Meta-analysis: no for Cochrane review/yes for published paper Data analysis: random effects model, heterogeneity assessed Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: planned but not carried out |
Number of included trials: 6 Number of participants: 1285 TRIALS: Design: RCTs Duration: 6 months to 44 weeks Quality: 1 trial 7/11, 1 trial 6/11, 4 trials 5/11 PARTICIPANTS: see trial descriptions INTERVENTIONS: education on diet and lifestyle reported by one study OUTCOMES: glycaemic control – HbA1c and/or fasting glucose, QoL – SF-36, well-being, patient satisfaction – DTSQ, hypoglycaemic episodes, morbidity, adverse effects, costs, weight |
|
|
Jansen (2006) 31 Netherlands Focus: relative effectiveness of interventions with SMBG and SMUG vs interventions without self-monitoring in terms of HbA1c reductions in T2DM Funding: Roche Diagnostics |
Inclusion criteria Study design: RCTs (full, published reports) Participants: T2DM; independent of treatment type Interventions: self-monitoring of blood (SMBG) or urine glucose (SMUG); SMBG vs no SMBG; SMBG vs SMUG, SMBG with feedback vs SMBG without feedback Outcomes: HbA1c Methodology Search strategy: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library (1966–2005); keywords given; previous systematic reviews searched; English, German, French, Dutch Study selection: two reviewers independently checked identified studies against inclusion criteria Quality assessment: checklist by Downs and Black (1998);141 assessed independently by two reviewers Data extraction: data extraction sheet; data extracted by two reviewers independently Meta-analysis: yes Data analysis: Bayesian random effects model (simultaneous direct and indirect comparisons) Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: all T2DM and non-insulin-treated T2DM only |
Number of included trials: 13 Number of participants: 2092 TRIALS: Design: all RCTs Duration: 3 months to 62 weeks Quality: mean quality score 8.5 of 13 PARTICIPANTS: no demographic information on participants provided; 2 studies – mixed insulin and non-insulin patients; 11 studies – patients did not use insulin or there was no information on insulin use INTERVENTIONS: some, but not all, studies used education component OUTCOMES: HbA1c |
OVERALL QUALITY: high COMMENT: compares SMBG with feedback with SMBG without feedback; outcomes only HbA1c |
|
AHRQ (2007) 28 USA Focus: effect of frequency of glucose monitoring on clinical outcomes and HbA1c in patients with T2DM Funding: AHRQ |
Inclusion criteria Study design: prospective studies with at least 50 patients and 6 weeks FU Participants: T2DM of any duration; independent of treatment type; studies with more than 50% T1DM excluded Interventions: SMBG vs no monitoring Outcomes: HbA1c Methodology Search strategy: MEDLINE (up to April 2006); keywords given; reference lists of reviews and guidelines searched; English only Study selection: abstracts screened by two reviewers Quality assessment: quality not assessed Data extraction: data extraction into evidence tables by single reviewer Meta-analysis: no Data analysis: text and tables Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: none |
Number of included trials: 5 RCTs, 8 non-RCTs Number of participants: 2092 TRIALS: Design: RCTs and cohort studies (but some probably rather chart reviews etc.) Duration: RCTs 6–18 months, cohort up to 3 years Quality: not reported PARTICIPANTS: see trial details INTERVENTIONS: 1 out of 5 RCTs did not report on training on how to respond to readings OUTCOMES: HbA1c |
|
|
McAndrew (2007) 2 USA Focus: to perform a comprehensive review of relevant studies of SMBG on HbA1c levels in patients with T2DM and to explore mediators and moderators Funding: NIH |
Inclusion criteria Study design: RCT, cross-sectional and longitudinal studies Participants: T2DM; non-insulin treated Interventions: SMBG, comparator unclear Outcomes: HbA1c Methodology Search strategy: MEDLINE, PsycInfo, Cochrane Library, CINAHL (up to first quarter 2006); keywords given Study selection: unclear – by one reviewer only? Quality assessment: ADA evidence grading criteria, rated by one reviewer, if in doubt referring to other reviewers; only studies of ADA evidence grade A, B or C included Data extraction: data extracted by one reviewer, checked by a second one Meta-analysis: no Data analysis: text and tables Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: none |
Number of included trials: 29 (30, DiGEM added in addendum) Number of participants: 1759 RCTs, 36,091 non-RCTs TRIALS: Design: 9 cross-sectional, 9 longitudinal, 11 RCTs Duration: RCTs unclear, non-RCTs up to 3 years Quality: mean quality score 8.5 of 13 PARTICIPANTS: see trial descriptions INTERVENTIONS: some included education – see trial details OUTCOMES: depression, HbA1c, QoL |
|
|
McGeoch (2007) 32 UK Focus: effect of SMBG on HbA1c Funding: non-commercial |
Inclusion criteria Study design: RCTs and observational studies; at least 50 patients, FU at least 6 months Participants: T2DM; non-insulin treated Interventions: SMBG, comparator unclear Outcomes: HbA1c and diabetes-related morbidity Methodology Search strategy: PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, MEDLINE; search dates: Jan 1990–Nov 2006; Google and Google Scholar; keywords given; no language restrictions Study selection: no details of methods Quality assessment: 1–5 score quality scale Data extraction: two reviewers independently extracted information; items listed Meta-analysis: no Data analysis: text and tables Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: none |
Number of included trials: 16 Number of participants: 1000 in RCTs, > 60,000 in observational TRIALS: Design: 3 RCTs, 13 observational Duration: RCTs 6–12 months, observational up to 6.5 years Quality: RCTs 1 or 2 of 5 points PARTICIPANTS: see trial info INTERVENTIONS: interventions differed significantly in the amount of education given and in advised monitoring practice; control groups also received differing amounts of training in diabetes management OUTCOMES: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG, weight, BMI, medication use, adverse effects (including diabetic complications) |
|
|
Poolsup (2008) 33 Thailand Focus: effects of SMBG on glycaemic control in non-insulin-treated patients with T2DM Funding: not reported |
Inclusion criteria Study design: RCTs Participants: T2DM; non-insulin treated Interventions: SMBG vs no SMBG Outcomes: HbA1c reported as outcome measure Methodology Search strategy: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library; search dates: inception to September 2007; keywords given; reference lists of reviews and trials searched; no language restriction Study selection: studies selected by two reviewers, differences settled by consensus Quality assessment: quality assessed using Maastricht–Amsterdam score and the Delphi list; done independently by two reviewers Data extraction: items listed, extracted independently by two reviewers Meta-analysis: yes Data analysis: random and fixed-effects model; heterogeneity assessed, funnel plot Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: use of SMBG to modify treatment vs no use of SMBG to modify treatment |
Number of included trials: 7 RCTs Number of participants: 1625 TRIALS: Design: all RCTs Duration: 4–12 months Quality: 5/7 high quality, 2/7 low quality PARTICIPANTS: see trial details INTERVENTIONS: some including education/counselling – see trial details OUTCOMES: HbA1c, body weight, BMI, QoL score, FPG, blood pressure, serum creatinine, creatinine clearance, microalbumin–creatinine ratio, total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, LDL, well-being, treatment satisfaction, hypoglycaemic episodes |
|
|
Towfigh (2008) 35 USA Focus: effect of SMBG in patients withT2DM Funding: non-commercial |
Inclusion criteria Study design: RCTs and CCTs; FU at least 12 weeks Participants: T2DM Interventions: SMBG alone or as part of multicomponent intervention vs no SMBG Outcomes: HbA1c Methodology Search strategy: PubMed; Welschen search strategy updated to July 2007; keywords given; bibliographies/systematic reviews searched Study selection: titles independently assessed by two reviewers Quality assessment: Delphi list Data extraction: data extraction form; data extracted independently by two reviewers Meta-analysis: yes Data analysis: random effects mode; baseline HbA1c; heterogeneity assessed Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: meta-regression on treatment frequency, quality score |
Number of included trials: 9 Number of participants: 1862 TRIALS: Design: all RCTs Duration: 6 months to 62 weeks Quality: quality variable, most trials scored positively on less than half of the criteria of the Delphi list PARTICIPANTS: see trial details INTERVENTIONS: all patients with T2DM treated without insulin except one study OUTCOMES: HbA1c, hypoglycaemia, fasting glucose, BMI/weight loss, health-related QoL |
|
|
St John (2009) 38 Australia/UK Focus: reviewing literature relating to SMBG and glycaemic control in T1DM and T2DM Funding: not reported |
Inclusion criteria Study design: experimental (RCTs or pseudo-experimental) and observational (cross-sectional or cohort studies) Participants: adults and children with type 1 or T2DM (excluding pregnant women) Interventions: SMBG alone or education programmes including SMBG and HbA1c as primary outcome measure Outcomes: HbA1c, SMBG use Methodology Search strategy: EMBASE, MEDLINE; search dates: 1996–June 2008; keywords reported, checking of reference lists Study selection: not reported Quality assessment: not reported Data extraction: not reported Meta-analysis: yes Data analysis: fixed and random effects models; heterogeneity assessed Subgroups/sensitivity analyses: in/excluding studies of doubtful eligibility, excluding largest trial, robustness to fixed vs random effects, duration < 1 year or ≥ 1 year |
Number of included trials: in T2DM: 23 Number of participants: > 75,000 in observational studies, 3941 pseudo-experimental, 2573 in RCTs TRIALS: Design: 13 observational, 4 pseudo-experimental, 6 RCTs Duration: experimental and pseudo-experimental 6 months to 4 years Quality: not reported PARTICIPANTS: see trial details INTERVENTIONS: some including education – see details trial description OUTCOMES: HbA1c, SMBG frequency, blood pressure, weight, cholesterol, hypoglycaemia, depression |
|
Appendix 3 Characteristics of RCTS
| Trial – design | Participants | Intervention | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Allen (1990) 40 USA Follow-up: 6 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 54 (27/27) Inclusion criteria: FPG > 8.8 and < 22 mmol, no history of ketoacidosis, treatment with diet and/or oral hypoglycaemic agent, no active infection or serious concurrent illness, no physical or mental handicap, no prior knowledge of monitoring; poorly controlled; diet or oral agents only Age: 58 years; 100% male BMI: HbA1c: I: 12.4 ± 3.3%, C: 11.7 ± 3.0% Diabetes duration: SMBG: 6.8 years; SMUG: 9.0 years Treatment: diet, oral hypoglycaemic agents (details of oral treatment unclear) |
SMBG regimen: every other day SMBG before each meal SMBG other: SMBG method: Chemstrips bG, Accu-Chek 1; Tes-Tape (Eli Lilly) for urine Use of therapy decision scheme: yes SMBG instruction: yes; patients were instructed in use of prescribed testing technique, which they practised for 7–10 days SMBG accuracy checks: yes; were required to show proficiency in technique at initial visit; during study, physician, physician’s associate and diabetes teaching nurse reinforced proper use of the monitoring techniques Education: yes; instruction and exercise diary; instruction and food intake diary; diet instruction by a dietitian, based on weight and activity level; booklet with ADA’s exchange lists for food items with estimate of fibre content (both groups) Assessment of monitoring frequency: yes Feedback on SMBG: yes SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: patients not allowed to alter their own therapy, but encouraged to alter behavioural regimen or diet according to readings; urine and BG results and FPG were used to guide physician-initiated treatment alterations Control: urine glucose testing Adherence assessment: records submitted were complete on > 87% of visits in both groups Outcomes: GHb, weight, fasting glucose, lipids |
|
|
Barnett (2008) 41 DINAMIC 1 study, international Follow-up: 27 weeks Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: high |
Total number: 610 patients with T2DM Inclusion criteria: T2DM, not insulin treated Age: 56 years, men and women BMI: 30 kg/m2 HbA1c: 8.12% Diabetes duration: 2.8 years Treatment: 70–74% previously treated with oral glucose lowering agent (43% biguanide, 46–50% insulin secretagogue) (the rest diet only) |
SMBG (n = 311): patients instructed in self-monitoring their blood-glucose (approved devices listed); instruction on what to do in case of asymptomatic hypoglycaemia; appropriate use of glucose meter was checked at each visit by study investigator; patients assessed BG on 2 days per week (one working and one non-working day) before each meals and 2 hours after the main meal and before bedtime; once-a-month frequency was increased to measuring postprandial values after each meal; no specific information given to patients with respect to changing behaviour based on SMBG results Control (n = 299): no SMBG Both groups: all patients received diet and lifestyle advice, which was reinforced at each visit; oral antidiabetic therapy was standardised for all patients – those previously on insulin secretagogue were transferred to gliclazide MR following approved dosage recommendations; for other patients, gliclazide was added to their treatment at an initial dose of 30 mg once daily then up-titrated as necessary; all patients had patient’s diary for recording symptoms of hypoglycaemia and SMBG (for intervention group) Outcomes: HbA1c, hypoglycaemia, FPG, adverse events, weight |
After 6 months:
|
|
Bonomo (2006) 42 Italy (abstract) Follow-up: 6 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 273 Inclusion criteria: T2DM, stable HbA1c within last 6 months, already on SMBG, not on insulin Age: mean 63–66 years BMI: mean 28–29 kg/m2 HbA1c: 8.0–8.1% Diabetes duration: 10.6 years Treatment: not reported |
SMBG regimen: group A – one BG profile (fasting, 2 hours after breakfast, 2 hours after lunch, 2 hours after dinner) per month vs group B1: one BG profile (fasting, 2 hours after breakfast, before lunch, 2 hours after lunch, before dinner, 2 hours after dinner) every 2 weeks vs group B2: as B1 but with recommendation to call diabetes clinic when BG targets were not met SMBG other: stated that patients followed the same education and treatment protocol SMBG method: no other details given Education: yes – not specified SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: Control: see above – three modes of SMBG compared Adherence assessment: SMBG carried out as recommended by 73% of group A and 44% of groups B1 and B2; very few patients of group B2 called the clinic, so groups B1 and B2 were lumped together – only compliant patients assessed Outcomes: HbA1c, BG, therapeutic changes |
|
|
Brown (2002) 43 Follow-up: 12 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 252 Inclusion criteria: FBG 140 mg/dl; have taken glucose lowering agents > 1 year; poorly controlled; oral agents Age: 54 years BMI: NR HbA1c: I: 11.8 (SD 3.0), C: 11.8 (SD 3.0) Diabetes duration: 7.9 years Treatment: 7% diet only, 67% oral only, 20% insulin only, 6% oral plus insulin (no details on oral treatment) |
SMBG regimen: unclear SMBG other: culturally competent diabetes self-management intervention with SMBG education and support sessions; focused on success, designed to provide rapid frequent feedback SMBG method: no further details on SMBG given Education: yes (intervention only) Control: waiting list with usual care Adherence assessment: not reported Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Cho (2006) 44 Korea Follow-up: 30 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: moderate/poor |
Total number: 80 patients with T2DM Age: 51–55 years BMI: 23–24 kg/m2 (Asian population!) HbA1c: 7.5–7.7% Diabetes duration: 6.7–6.9 years Treatment: 18 patients were insulin treated (7 in intervention, 11 in control) (no details on oral treatment) |
Intervention: internet-based glucose monitoring system; patients logged onto a website at their convenience and uploaded their SMBG results; additional information also uploaded (current medication, blood pressure, weight, changes in lifestyle, questions patients wanted to discuss); 3 endocrinologists, a dietitian and a nurse participated in the online system, and logged on daily and sent appropriate recommendations (based in the patients’ SMBG data) every 2 weeks Control: standard SMBG; outpatient visits every 3 months; conventional note-keeping record system; usual recommendation about medications, dosage and lifestyle modification Both groups: patients were given glucometers; diabetes education programme; method and frequency of SMBG monitoring Outcomes: HbA1c, HbA1c fluctuation index |
After 30 months:
|
|
Davidson (2005) 45 USA Follow-up: 6 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: high/moderate |
Total number: 88 (43/45) Inclusion criteria: patients with T2DM on oral antidiabetic treatment Age: 50 years BMI: 32.2 kg/m2 HbA1c: I: 8.4 (SD 2.1), C: 8.5 (SD 2.2) Diabetes duration: 5.6 years Treatment: MET (27–28% MET alone, 51–53% in combination with SU), SU (0–9% SU alone, 51–53% in combination with MET), and/or thiazolidinedione (triple therapy with MET and SU, 7–21%) |
SMBG regimen (n = 43): SMBG 6 days per week before and after each meal (6 times per day) SMBG other: five dietitian visits SMBG method: NR Use of therapy decision scheme: yes SMBG instruction: NR SMBG accuracy checks: NR Education: dietitian visits; dietitian used glucose values and meal descriptions in nutritional counselling to educate the patient on the effects of meal components and portion sizes on the rise of postprandial glucose values (both groups) Assessment of monitoring frequency: Feedback on SMBG: SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: did not report training on how to respond to readings; nurse followed detailed algorithm to make therapeutic decisions (to achieve HbA1c goal of < 7.5%) Control (n = 45): regular HbA1c determination every 2 months by a physician; 5 dietitian visits Adherence assessment: patients performed an average of 45% of required tests Outcomes: HbA1c, BMI/weight loss |
|
|
Estey (1990) 46 Canada Follow-up: 4 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: moderate/poor |
Total number: 60 (controls 25 after dropouts/intervention 28) Inclusion criteria: T2DM; treatment with diet and/or oral hypoglycaemic agents; completion of the 3-day education programme provided at the Diabetes Centre; accessibility by telephone Age: I: 56 years, C: 54 years BMI: weight 85.6 kg; 36–46% > 115% ideal body weight HbA1c: I: 6.3 ± 1.1%, C: 6.1 ± 1.4% Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: diet, oral hypoglycaemic agents (no details on oral treatment) |
SMBG regimen: no details of protocols for SMBG SMBG other: 3-day education plus SMBG; intense FU and feedback on SMBG testing practices was given by series of telephone calls and one home visit from a registered nurse SMBG method: no description of device, diary Use of therapy decision scheme: SMBG instruction: yes SMBG accuracy checks: no Education: yes; 3-day education (both groups) Assessment of monitoring frequency: yes Feedback on SMBG: yes SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: no details on changes made to therapy or lifestyle Control: standard 3-day education plus SMBG Adherence assessment: patient data sheets or memory of meters consulted to compare number of tests conducted with number of tests requested Outcomes: HbA1c, weight, SMBG adherence |
|
|
DiGEM trial Follow-up: 12 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: high |
Total number: 453 patients with T2DM Inclusion criteria: T2DM, not insulin treated Age: 65.7 years BMI: 31–32 kg/m2 Diabetes duration: median 3 years HbA1c: 7.4–7.5% Treatment: diet only 26–29%, oral monotherapy 37.5–39%; combined oral therapy 34–35% (no details on oral treatment) |
SMBG less intensive: continued to use goal setting and review techniques introduced at assessment visit; were given a glucose meter and asked to record 3 values daily on 2 days per week (one after fasting and 2 before meals or 2 ours after meals) and to aim for glucose levels of 4–6 mmol/l after fasting and before meals and levels of 6–8 mmol/l 2 hours after meals; advised by nurse to contact doctor if readings were consistently high or low (defined); given no information on how to interpret BG readings SMBG intensive: as before, and were given training and support in timing, interpreting and using the results of SMBG to enhance motivation and to maintain adherence to diet, physical activity and drug regimens Control: standardised usual care, including the use of goal setting and review; asked not to use a glucose meter unless their doctor considered it essential for their clinical management Outcomes: HbA1c, hypoglycaemia, lipids, BMI, blood pressure |
After 12 months:
|
|
Fontbonne (1989) 47 France Follow-up: 6 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 208 (68/72/68) Inclusion criteria: treatment with diet and/or oral hypoglycaemic agents, FBG > 8.8 mmol/l or postprandial BG > 11 mmol/l 3 times within preceding year; at least occasional glucosuria; no rapidly progressing complications, no severe illness, DM > 3 years Age: SMBG 55; SMUG 55; C: 56 BMI: 27.1 kg/m2 HbA1c: I: 8.2 (SE 0.3), C1: 8.6 (SE 0.3), C2: 8.2 (SE 0.3) Diabetes duration: 12.5 years Treatment: diet, oral hypoglycaemic agents (details of oral treatment unclear) |
SMBG regimen: SMBG twice every other day, fasting and 2 hours after the evening meal, with an extra test 2 hours after lunch on Sunday SMBG other: not reported SMBG method: Dextrostix, Glucometer (Ames), diary; Ketodiastix for urine Use of therapy decision scheme: not reported SMBG instruction: yes SMBG accuracy checks: no Education: no; patients received individualised dietary recommendations, but no specific algorithms or predetermined strategy for behavioural changes Assessment of monitoring frequency: yes Feedback on SMBG: yes SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: no instructions on how to alter therapy according to SMBG readings (all changes made by physician) Control 1: urine glucose monitoring twice every other day, on the first urine voided in the morning and the first urine voided after the evening meal, with an extra test on the first urine voided after lunch on Sundays Control 2: no self-testing of urine or BG; HbA1c was determined every 2 months at the outpatient clinic visit; the results were sent to the patient with the physician’s comment on their metabolic control Adherence assessment: number of reactive strips that should have been used – urine group had used significantly less; poorer compliance than SMBG or control group Outcomes: HbA1c, weight, number of reactive strips reported |
|
|
Gallichan (1994) 48 UK Follow-up: 24 weeks Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: study not available for assessment; rated as follows by other reviews: Faas 1997:30 3/7; Coster 200029 4/11 reporting, 3/3 external validity, 3/7 bias, 3/6 confounding, 13/27 total (poor) |
Total number: 27 (15/12) Inclusion criteria: on oral hypoglycaemic agents Age: 64 years (47–80) BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: diet, oral hypoglycaemic agents (details of oral treatment unclear) |
SMBG regimen: no details of protocols for blood or urine monitoring SMBG other: FBG and after meals 2 days per week SMBG method: no description Use of therapy decision scheme: not reported SMBG instruction: yes SMBG accuracy checks: no Education: no Assessment of monitoring frequency: no Feedback on SMBG: no SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: no details on changes made to therapy or lifestyle Control: SMUG Adherence assessment: not reported Outcomes: fructosamine |
|
|
Guerci (2003) 49 France Follow-up: 24 weeks Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: moderate/poor |
Total number: 689 (345/344) Inclusion criteria: T2DM < 1 year, patients insufficiently controlled with oral glucose lowering treatment (HbA1c > 7.5 and < 11%), age 40–75 years and not previously treated with insulin (for more than 7 consecutive days) and not requiring insulin at inclusion, patients who did not previously receive SMBG but able to carry out SMBG Age: 62 (40–75) years BMI: 30 kg/m2 HbA1c: I: 9.0 ± 1.3%, C: 9.0 ± 1.3% Diabetes duration: 8.0 years Treatment: 99.5% on oral antidiabetic agents (80.8% on SUs, 61.1% on biguanides, 30% on alpha-glucosidase inhibitors), ~80% on fibrates, ACE I or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors |
SMBG regimen: (n = 345): patients received a conventional laboratory work-up based on laboratory measurement of HbA1c every 12 weeks and underwent SMBG (≥ 6 times per week) SMBG other: unclear SMBG method: unclear Use of therapy decision scheme: unclear SMBG instruction: yes; initial training given by GP SMBG accuracy checks: yes Education: no; at GP visits, patients were informed of their BG values, the necessity of good diabetes control, and importance of weight loss in combination with physical activity Assessment of monitoring frequency: unclear Feedback on SMBG: unclear SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: did not report training on how to respond to readings; GP could change treatment based on HbA1c Control (n = 344): conventional laboratory work-up only Adherence assessment: not reported Outcomes: HbA1c, hypoglycaemia, weight, blood pressure |
|
|
Jaber (1996) 50 Follow-up: 4 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: moderate/poor |
Total number: 39 (17/22) Inclusion criteria: urban African-American patients with T2DM who were currently attending a university-affiliated, internal medicine outpatient clinic Age: I: 59 years, C: 65 years BMI: 33 kg/m2 HbA1c: I: 9.2 (SD 2.0), C: 9.7 (SD 2.5) Diabetes duration: 6.8 years Treatment: details of treatment unclear |
SMBG regimen: 4 times per day for 2 days per week SMBG other: instruction on diabetes and diabetes regulation, medical counselling, exercise, SMBG SMBG method: unclear Use of therapy decision scheme: unclear SMBG instruction: yes SMBG accuracy checks: Education: yes (intervention only) Assessment of monitoring frequency: unclear Feedback on SMBG: unclear SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: yes Control: usual care Adherence assessment: unclear Outcomes: HbA1c, hypoglycaemia, HRQoL |
|
|
Johnson (2006) 51 Canada Follow-up: 6 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: moderate |
Total number: 262 Inclusion criteria: T2DM (> 1 year); not insulin treated Age: 68.4 years, men and women BMI: 29–32 kg/m2 HbA1c: 7.3–7.5% Diabetes duration: 7.7–8.6 years Treatment: 96–97% on oral agents (no details) |
Intervention: free BG meter, free 6-month supply of testing strips Control: free BG meter Both: all participants received free meter (Glucometer Elite XL); all received training at the pharmacy; study pharmacists recommended average testing of 7 times per week for patients on oral agents, and for those on diet only, once daily 3 or 4 times per week; FU visits at 3 and 6 months for reinforcement of testing procedures No information on therapy changes in response to SMBG Outcomes: HbA1c, diabetes self-care activities [Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities (SDSCA)] |
|
|
Jones (2003) 52 Diabetes Stages of Change Study (DiSC), Canada RCT stratified by diabetes treatment but no detailed separate reporting for T1DM and T2DM and insulin vs non-insulin Follow-up: 12 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 860 Inclusion criteria: patients with T1DM or T2DM for SMBG intervention (all in pre-action stage for SMBG (i.e. using less than recommended) (of a total of 1029 patients, 58.2% were enrolled for 2 behaviours, 89% of those for SMBG and healthy eating) Age: 55 years, men and women BMI: 32 kg/m2 HbA1c: 8.4–8.6% Diabetes duration: 10–11 years Treatment: about half of the patients were insulin-treated (no details of oral treatment); patients on diet only were not included |
Four comparison groups: PTC + SMBG: Pathways to Change (based on Transtheoretical Model of Change) plus free strips; PTC: multicomponent intervention programme; monthly mail or telephone contact for 12 months; focus on SMBG, and/or healthy eating, or smoking PTC: Pathways to Change, no free strips TAU (treatment as usual) + SMBG: treatment as usual plus free strips TAU: treatment as usual, no free strips Outcomes: stage of change, HbA1c, weight, behaviour (SMBG monitoring – and healthy eating, smoking for other parts of the study) |
|
|
Joy (2003) 53 USA (abstract) Follow-up: 4 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 57 Inclusion criteria: T2DM, using medication Age: NR BMI: NR HbA1c: 8.3–8.4% Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: NR |
SMBG regimen: twice-daily, preprandial SMBG SMBG other: SMBG method not reported SMBG method: NR Use of therapy decision scheme: NR SMBG instruction: NR SMBG accuracy checks: NR Education: NR Assessment of monitoring frequency: NR Feedback on SMBG: NR SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: physician could give treatment advice Control: twice-daily, postprandial SMBG Adherence assessment: NR Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Kibriya (1999) 54 Bangladesh Follow-up: 18 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 64 Inclusion criteria: T2DM, oral medication or insulin Age: 50 (35–65) years BMI: 23.9 kg/m2 (Asian population!) HbA1c: 7.55–8.2% Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: oral hypoglycaemic agents or insulin (not reported how many were using insulin, no details of oral medication) |
SMBG regimen: 2–3 times/day every 2 weeks (FPG and 2 hours after breakfast and/or lunch) SMBG other: not reported SMBG method: Glucostix Use of therapy decision scheme: unclear SMBG instruction: 2-day class on SMBG SMBG accuracy checks: yes Education: yes, both groups Assessment of monitoring frequency: unclear Feedback on SMBG: unclear SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: patients were advised how to act based on SMBG measurements; medications adjusted by patients based on SMBG, as necessary Control: no SMBG, monthly visits, doctor made medication changes Adherence assessment: unclear Outcomes: HbA1c, costs, hypoglycaemia |
|
|
Kwon (2004) 55 Korea Follow-up: 12 weeks Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 101 (50/51) Inclusion criteria: men and women diagnosed with T2DM for > 1 year; age > 30 years, no medication limits reported Age: 54 years BMI: 24 kg/m2 (Asian population!) HbA1c: I: 7.59% (SD 1.42), C: 7.19% (SD 1.17) Diabetes duration: 6.8 years Treatment: NR |
SMBG regimen (n = 40): SMBG pre and post meals; recommended to use SMBG ≥ 3 days per week 1–3 times per day including after meals SMBG other: SMBG with internet-assisted patient consultations without outpatient management visits; included recording SMBG values online, asking questions, receiving feedback (recommendations re diet, exercise, medication) SMBG method: not reported Use of therapy decision scheme: no SMBG instruction: NR SMBG accuracy checks: NR Education: intervention patients were taught how to use the internet system Assessment of monitoring frequency: yes Feedback on SMBG: recommendations received via the internet SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: internet recommendations included medication changes Control (n = 41): SMBG and usual care involved monthly visits with two or three visits with senior staff during 12-week period; control group also recommended to use SMBG ≥ 3 days per week 1–3 times per day including after meals Adherence assessment: yes Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Miles (1997) 56 UK Follow-up: 24 weeks Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 150 Inclusion criteria: newly diagnosed T2DM; oral agents or insulin Age: 65 (31–91) years BMI: 27.3 kg/m2 HbA1c: I: 10.3 (SD 2.6), C: 10.3 (SD 2.3) Diabetes duration: 0 (newly diagnosed) Treatment: no details of treatment |
SMBG regimen: SMBG once daily before a different meal or at bedtime, each day (target < 8 mmol/l) SMBG method: no details given SMBG accuracy checks: yes Education: 4 education sessions (both groups) NR SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: no details on changes made to therapy or lifestyle Control: test once daily for glucosuria, alternating before or 2 hours after different meals, or at bedtime (target = aglucosuria) Adherence assessment: NR Outcomes: GHb, QoL, weight |
|
|
Moreland (2006) 20 USA Follow-up: 6 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 199 patients with T1DM or T2DM (26–39% in each group had T1DM) Inclusion criteria: T1DM or T2DM Age: 46–50 years BMI: 30 kg/m2 Diabetes duration: 9.5–11 years HbA1c: 8.9–9.3% Treatment: 16–18% were not insulin-treated (no details of oral therapy) |
Three comparison groups: BGM+ (n = 50): BG meter and received blood sugar monitoring owner’s manual – includes practical information, but also information to help people overcome barriers to monitoring (e.g. emphasis on positive emotions, not self-blame, etc.) MT (n = 50): BG meter Both groups: BG meter received and 30-minute diabetes education session focusing on BG monitoring and support from certified diabetes educator; patients received new meters but no test strips; received prescriptions for monitoring supplies (covered by health insurance) SC (n = 99): standard care [individual or group standard diabetes education (ADA accredited)] No information on recommended SMBG regimen, no information on therapy adjustments in response to SMBG; no information on accuracy checks Outcomes: SMBG monitoring, HbA1c, affect |
After 6 months:
|
|
Muchmore (1994) 57 USA Follow-up: 44 weeks Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 29 Inclusion criteria: overweight patients with T2DM, age 40–75 years, T2DM > 1 year, no SMBG within the previous 3 months, not instructed to count dietary carbohydrate, HbA1c 9.5–13%, no serious underlying medical or psychiatric illness, drug abuse or alcoholism Age: I: 57 years, C: 60 years BMI: 34 kg/m2 HbA1c: I: 10.3 (SD 1.1), C: 10.5 (SD 1.5) Diabetes duration: I: 5.7 years, C: 5.2 years Treatment: 74% on oral agents (no details given), rest on diet |
SMBG regimen (n = 12): initially 6 times per day before and after meals then just one set of tests before and after meals per day SMBG other: proprietary behavioural weight control programme, one-on-one counselling by a diabetes nurse and dietitian during a run-in period of 8 weeks; SMBG, carbohydrate counting training, using the blood monitoring SMBG method: One touch (LifeScan) reflectance meters Use of therapy decision scheme: NR SMBG instruction: yes SMBG accuracy checks: yes Education: counselling (both groups) Assessment of monitoring frequency: Feedback on SMBG: NR SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: SMBG used to support dietary intervention based on caloric counting; patients not allowed to alter their own therapy (but could be altered by GP), but encouraged to alter behavioural regimen or diet according to readings Control (n = 11): proprietary behavioural weight control programme, one-on-one counselling by a diabetes nurse and dietitian during a run-in period of 8 weeks Adherence assessment: average SMBG frequency 4.67 times/week Outcomes: HbA1c, QoL, weight |
|
|
O’Kane (2008) 13 UK ESMON study Follow-up: 1 year Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: high |
Total number: 184 (96/88) Inclusion criteria: patients with newly diagnosed T2DM; not insulin treated Age: 58–61 years, men and women BMI: 32–34 kg/m2 HbA1c: 8.6–8.8% Diabetes duration: 0 Treatment: not reported |
SMBG: provided with glucose monitor (LifeScan OneTouch Ultra) and given instruction on monitoring; patients were asked to monitor 4 fasting and 4 postprandial capillary BG measurements per week; were advised on appropriate responses to high or low readings (including need for dietary review or suggestion of exercise in response to high readings); at each clinic visit, concordance with self-monitoring regimen was verified by downloading meter readings; ongoing advice and support in appropriate interpretation of and response to their BG results Control: no monitoring Both groups: identical structured core education programme involving diabetes nurse practitioners, dietitians, podiatrists, medical staff; all patients reviewed by doctor, diabetes nurse practitioner and dietitian at 3-monthly intervals; at each visit all aspects of diabetes care were reviewed; identical algorithm for dietary and pharmacological management of glycaemia for both groups based on HbA1c Outcomes: HbA1c, hypoglycaemia, BMI, use of oral hypoglycaemic drugs, well-being, treatment satisfaction, attitude |
No significant difference in HbA1c at 12 months: 6.9 ± 0.8% SMBG vs 6.9 ± 1.2% control Psychological variables: no significant difference in anxiety, positive well-being, energy, but patients receiving SMBG were significantly more depressed (scoring 6% higher on the depression subscale of the well-being questionnaire) |
|
Rutten (1990) 58 Netherlands Follow-up: 12 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor; SMBG confounded with further interventions |
Total number: 149 (66/83) Inclusion criteria: T2DM > 6 months, age 40–75 years, no insulin, no treatment by internist for diseases other than diabetes, obesity or hypertension Age: 63 (40–75) years BMI: 51% < 27 kg/m2, 21% 27–30 kg/m2, 27% > 30 kg/m2 HbA1c: I: 9.7 (SD 2.1), C: 8.9 (SD 1.9) Diabetes duration: 8.8 years Treatment: diet, oral hypoglycaemic agents (not details given) |
SMBG regimen: no fixed regimen; patients were told to monitor BG when they did not feel well or if they had taken part in unusually strenuous activity SMBG other: patients accepting opportunity of SMBG were given instructions; patients contacted practice nurse monthly to state level of FBG; patients under GP care (not practising SMBG) consulted their doctors at least 4 times per year, during which patients was informed of current BG level; for all patients in experimental group a therapeutic scheme was used with fixed targets for weight and regulation and with emphasis on loss of body weight SMBG method: Haemo-Glukotest 20–800 strips Use of therapy decision scheme: yes SMBG instruction: yes (2–5 sessions) SMBG accuracy checks: yes Education: 2–3 training visits Assessment of monitoring frequency: no Feedback on SMBG: no SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: no instructions on how to alter therapy according to SMBG readings (all changes made by physician); made appointment with GP when BG high Control: no fixed appointments; no instruction in SMBG Adherence assessment: adherence inferred by noting low number of trial dropouts Outcomes: HbA1c, weight, FPG |
|
|
Germany Follow-up: 12 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: high |
Total number: 202 Inclusion criteria: patients with T2DM; not insulin-treated Age: 61–62 years, men and women BMI: not reported HbA1c: 7.2% Diabetes duration: 7.8–8.2 years Treatment: 71–75% MET, ~50% SUs, and various others |
Low SMBG (n = 100): SMBG with one measurement per week and additional measurement in the event of suspected hypoglycaemia or severe hyperglycaemia High SMBG (n = 102): SMBG with four measurements per week on Tuesdays, Thursdays and one day of the weekend before dinner and one additional measurement before lunch – also additional measurement in the event of suspected hypoglycaemia or severe hyperglycaemia Both groups: case-management approach, all patients asked to report back to their doctor in the event of inappropriate diabetes control, based on the targets set between the patient and their doctor Outcomes: HbA1c, adherence, change in diabetes treatment, hypoglycaemia, QoL, satisfaction, adverse events |
|
|
Schwedes (2002)61/Siebolds (2006)21 Germany Follow-up: 12 months Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 223 Inclusion criteria: age 45–70 years, BMI > 25 kg/m2; with HbA1c values between 7.5% and 10%; treated either with diet alone or diet in combination with SUs or MET; diabetes known at least 3 months; participants in a diabetes educational programme within the previous 2 years Age: 60 (45–70) years BMI: 31.4 (> 25) kg/m2 HbA1c: I: 8.5 (SD 0.9), C: 8.4 (SD 0.8) Diabetes duration: 5.3 years Treatment: diet alone, with or without SU or MET (no details given) |
SMBG regimen (n = 113): patients requested to measure BG 6 times on 2 days per week (before and 1 hour after 3 meals; weekday and Sunday) SMBG other: patients undergoing SMBG were given instructions in use of BG device; patients requested to record values obtained in a diary where documentation of eating and state of well-being was also recorded; counselling designed to discuss problems/issues related to SMBG Use of therapy decision scheme: yes, SMBG counselling algorithm used by nurse SMBG instruction: yes SMBG accuracy checks: nurses assessed correct use of the monitoring device in the intervention group Education: SMBG instruction and standardised counselling vs non standardised counselling Assessment of monitoring frequency: checks by nurses at regular visits Feedback on SMBG: not applicable SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: did not report training on how to respond to readings Control (n = 110): non-standardised counselling with focus on diet and lifestyle Adherence assessment: after 6 months’ intervention, 87% of patients still monitored their BG Outcomes: HbA1c, QoL, BMI |
|
|
Seaton (1996) 62 USA (abstract) Follow-up: NR Quality: |
Total number: 10 Inclusion criteria: T2DM on oral medication Age: NR BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: NR |
SMBG regimen: NR SMBG other: NR SMBG method: no details reported Use of therapy decision scheme: yes, standardised treatment algorithm Control: no SMBG Adherence assessment: NR Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Wing (1986) 63 USA Follow-up: 62 weeks Quality:OVERALL QUALITY: poor |
Total number: 50 (25/25) Inclusion criteria: age 35–65 years; > 20% above ideal weight for height; use of oral hypoglycaemic medication or insulin for BG control; development of diabetes after the age of 30 Age: 54 years (35–65) BMI: weight 98 kg HbA1c: I: 10.19 (SD 2.51), C: 10.86 (SD 2.00) Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: diet, oral hypoglycaemic agents; about half of the patients used insulin |
SMBG regimen: fasting BG on 5 days per week and 2 postprandial glucose measurements per week; after 12 weeks only FBG on 5 days per week SMBG other: behavioural weight control treatment programme, SMBG and focusing on weight–BG relationship SMBG method: Chemstrips bG, diary Use of therapy decision scheme: yes SMBG instruction: yes SMBG accuracy checks: yes Education: behavioural weight control programme (both); 3 months, FU sessions over per year Assessment of monitoring frequency: yes Feedback on SMBG: yes SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: participants required to modify diet and exercise habits according to SMBG results; patients not allowed to change therapy Control: behavioural weight control treatment programme Adherence assessment: patient data sheets or memory of meters consulted to compare number of tests conducted with number of tests requested; marked item technique Outcomes: GHb, weight, fasting glucose, lifestyle adherence, medication changes, serum lipids |
|
Appendix 4 Results of RCTs (included in reviews and additional)
| Study | Outcome | Baseline | End of study | Difference | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c/glucose control | |||||
| Allen (1990)40 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 12.4% (SD 3.3) SMUG: 11.7% (SD 3.0) |
SMBG: 10.4% (SD 2.9) SMUG: 9.7% (SD 2.6) |
SMBG: –2.0% (SD 3.4) SMUG: –2.0% (SD 2.4) |
NS |
| Barnett (2008)41 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 8.12% (SD 0.89) C: 8.12% (SD 0.84) |
SMBG: 6.95% (SD 0.97) C: 7.2% (SD 1.22) |
||
| Bonomo (2006)42 | HbA1c |
More frequent SMBG: 8.08% (SD 0.84) Less frequent SMBG: 7.97% (SD 0.72) |
More frequent SMBG: 7.6% (SD 0.73) Less frequent SMBG: 7.78% (SD 1.05) |
Significant decrease in HbA1c in twice monthly SMBG monitoring group, no decrease in once monthly |
Difference between groups not reported |
| Cho (2006)44 | HbA1c |
SMBG internet: 7.7% (SD 1.5) SMBG: 7.5% (SD 1.3) |
SMBG internet: 6.7% (SD 0.9) SMBG: 7.4% (SD 1.3) |
p = 0.029 | |
| Brown (2002)43 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 11.8% (SD 3.0) C: 11.8% (SD 3.0) |
SMBG: 10.89% (SD 2.56) C: 11.64% (SD 2.85) |
p = 0.016 | |
| Davidson (2005)45 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 8.4% (SD 2.1) C: 8.5% (SD 2.2) |
SMBG: 7.53% (SE 0.236) C: 7.88% (SE 0.221) |
SMBG: –0.8% (SD 1.6) C: –0.6% (SD 2.1) |
NS |
| Estey (1990)46 | HbA1c |
SMBG + FB: 6.3% (SD 1.1) SMBG: 6.1% (SD 1.4) |
SMBG + FB: 5.6% (SD 0.7) SMBG: 5.8% (SD 1.5) |
SMBG + FB: –0.7% (SD 0.9) SMBG: –0.3% (SD 0.7) |
NS |
| Farmer (2007)10 | HbA1c |
SMBG intensive: 7.53% (SD 1.12) SMBG simple: 7.41% (SD 1.02) C: 7.49% (SD 1.09) |
SMBG intensive: –0.17% (SD 0.73) SMBG simple: –0.14% (SD 0.82) C: –0% (SD 1.02) |
||
| Fontbonne (1989)47 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 8.2% (SD 2.5) SMUG: 8.6% (SD 2.5) C: 8.2% (SD 2.5) |
SMBG: 7.84% SMUG: 8.47% C: 7.7% |
SMBG: –0.36% (SD 3.14) SMUG: –0.13% (SD 2.20) C: –0.5% (SD 1.54) |
NS |
| Gallichan (1994)48 | Fructosamine |
SMBG: 324 µmol/l SMUG: 343 µmol/l |
SMBG: 333 µmol/l SMUG: 322 µmol/l |
NS | |
| Guerci (2003)49 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 9.0% (SD 1.3) C: 9.0% (SD 1.3) |
SMBG: 8.1% (SD 1.6) C: 8.4% (SD 1.4) |
SMBG: –0.88% (SD 1.54) C: –0.6% (SD 1.54) |
0.012 |
| HbA1c improvement |
SMBG: 57.1% C: 46.8% |
0.007 | |||
| Jaber (1996)50 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 9.2% (SD 2.0) C: 9.7% (SD 2.5) |
SMBG: 7.6% (SD 1.48) C: 9.65% (SD 2.61) |
SMBG: –1.62% (SD 1.83) C: –0.07% (SD 2.12) |
|
| Johnson (2006)51 | HbA1c |
Free strips: 7.5% (SD 1.6) No free strips: 7.3% (SD 1.2) |
Free strips: 7.3% (SD 1.5) No free strips: 7.3% (SD 1.2) |
NS | |
| Joy (2003)53 | HbA1c |
Preprandial SMBG: 8.3% Postprandial SMBG: 8.4% |
Preprandial SMBG: –0.8% Postprandial SMBG: –0.9% |
NS | |
| Kibriya (1999)54 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 8.19% (SD 1.37) C: 7.55% (SD 1.62) |
SMBG: 7.11% (SD 1.0.8) C: 7.12% (SD 1.85) |
SMBG: –0.99% C: –0.38% |
NS |
| Kwon (2004)55 | HbA1c |
SMBG + FB: 7.59% (SD 1.42) SMBG: 7.19% (SD 1.17) |
SMBG + FB: 6.94% (SD 0.92) SMBG: 7.62% (SD 0.93) |
SMBG + FB: –0.54% SMBG: +0.33% |
p < 0.001 |
| HbA1c < 7% at baseline |
SMBG + FB: 6.38% (SE 0.22) SMBG: 6.99% (SE 0.18) |
0.046 | |||
| HbA1c ≥ 7% at baseline |
SMBG + FB: 7.38% (SE 0.16) SMBG: 8.12% (SE 0.19) |
< 0.001 | |||
| Miles (1997)56 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 10.3% (SD 2.6) SMUG: 10.3% (SD 2.3 |
SMBG: 8.8% (SD 1.9) SMUG: 8.7% (SD 1.7) |
SMBG: –1.5% (SD 2.1) SMUG: –1.6% (SD 1.9) |
NS |
| Moreland (2006)20 | HbA1c | BGM+: 9.3% (SD 1.2) | BGM+: 9.3% (SD 1.7) | BGM+: –0.13% (SD 1.28) | NS; no significant difference between T1DM and T2DM |
| MT: 9.1% (SD 1.2) | MT: 9.1% (SD 1.3) | MT: –0.04% (SD 1.31) | |||
| SC: 8.9% (SD 0.9) | SC: 9.0% (SD 1.5) | SC: +0.04% (SD 1.1) | |||
| Muchmore (1994)57 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 10.29% (SD 1.1) C: 10.45% (SD 1.5 |
SMBG: 8.75% (SD 1.66) C: 9.6% (SD 2.1) |
SMBG: –1.54% (SD 1.46) C: –0.85% (SD 1.87 |
NS |
| O’Kane (2008)13 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 8.8% (SD 2.1) C: 8.6% (SD 2.3) |
SMBG: 6.9% (SD 0.8) C: 6.9% (SD 1.2) |
NS | |
| Rutten (1990)58 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 9.7% (SD 2.1) C: 8.9% (SD 1.9) |
SMBG: 9.2% (SD 1.49) C: 9.4% (SD 1.14) |
SMBG: –0.4%) C: +0.5% |
< 0.05 |
| Scherbaum (2008)60 | HbA1c |
Low SMBG: 7.2% (SD 1.4) High SMBG: 7.2% (SD 1.0) |
Low SMBG: 6.9% (SD 1.0) High SMBG: 7.1% (SD 1.0) |
||
| Schwedes (2002)61 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 8.5% (SD 0.9) C: 8.4% (SD 0.8) |
SMBG: 7.47% (SD 1.27) C: 7.81% (SD 1.52) |
SMBG: –1.0% (SD 1.08) C: –0.54% (SD 1.41) |
0.009 |
| Wing (1986)63 | HbA1c |
SMBG: 10.2% (SD 2.5) C: 10.7% (SD 2.0) |
SMBG: 10.2% (SD 2.29) C: 10.4% (SD 2.16) |
SMBG: 0.0% (SD 2.16) C: –0.24% (SD 1.87) |
NS |
| Hypoglycaemia | |||||
| Barnett (2008)41 | Hypoglycaemic events |
SMBG: n = 27 (8.7%) with 51 hypoglycaemic events (27, symptomatic, 11 asymptomatic, 11 SMBG confirmed, 2 non-graded) C: n = 21 (7%) with 66 hypoglycaemic events (64, symptomatic, 2 non-graded) |
p-value not reported | ||
| Nocturnal hypoglycaemia |
SMBG: n = 3 patients C: n = 7 patients |
||||
| Farmer (2007)10 | Hypoglycaemic episodes |
SMBG more intensive: 43 SMBG less intensive: 33 C: 14 |
|||
| Guerci (2003)49 | Hypoglycaemic episodes (capillary BG < 3 mmol/l) | Significant difference in asymptomatic hypoglycaemia (10.4% of patients in SMBG and 5.2% of patients in control group), but based on capillary blood, which could not be determined by control group – probably invalid comparison; no serious hypoglycaemia | 0.003 | ||
| Kibriya (1999)54 | Hypoglycaemic episodes |
SMBG: 5 patients with 7 episodes; 0.172/patient-year C: 10 patients with 17 episodes; 0.354/patient-year |
0.03 | ||
| O’Kane (2008)13 | Hypoglycaemic episodes |
SMBG: 31 episodes C: 36 episodes |
NS | ||
| Scherbaum (2008)60 | Relevant hypoglycaemia |
Low SMBG: 5 patients (1 with 1 event, 4 with several events) High SMBG: 18 patients (9 with 1 event, 9 with several) |
Significantly more with 1 event in high group than low group | 0.02 | |
| Weight | |||||
| Allen (1990)40 | Weight |
SMBG: –2 kg SMUG: +0 kg |
NS | ||
| Barnett (2008)41 | Weight |
SMBG: –0.68 kg (SD 5.70) C: –0.50 kg (SD 4.01) |
NS | ||
| Brown (2002)43 | BMI |
SMBG: 32.33 kg/m2 (SD 5.97) C: 32.12 kg/m2 (SD 6.35) |
SMBG: 32.17 kg/m2 (SD 6.45) C: 32.28 kg/m2 (SD 6.52) |
NS | |
| Estey (1990)46 | Weight |
SMBG + FB: 84.2 kg (SD 15.8) SMBG: 86.1 kg (SD 17.3) |
SMBG + FB: 82.4 kg (SD 22.2) SMBG: 86.1 kg (SD 17.3) |
Difference SMBG vs control –1.10 kg (95% CI –2.95 to 0.75) | NS |
| Davidson (2005)45 | Weight |
SMBG: –0.7 kg (SD 6.3) C: –0.1 kg (SD 2.9) |
NS | ||
| BMI |
SMBG: –0.3 kg/m2 (SD 2.3) C: –0.1 kg/m2 (SD 1.6) |
NS | |||
| Farmer (2007)10 | Weight |
SMBG more intensive: 86.9 kg (SD 16.4) SMBG less intensive: 90.4 kg (SD 18.9) C: 86.7 kg (SD 18.9) |
SMBG more intensive: 86.1 kg (SD 15.7) SMBG less intensive: 89.9 kg (SD 19.0) C: 86.4 kg (SD 19.4) |
SMBG more intensive: –0.8 kg (SD 3.3) SMBG less intensive: –0.5 kg (SD 2.6) C: –0.3 kg (SD 2.7) |
NS |
| BMI |
SMBG more intensive: 31.0 kg/m2 (SD 5.3) SMBG less intensive: 31.9 kg/m2 (SD 6.2) C: 30.9 kg/m2 (SD 6.1) |
SMBG more intensive: 30.7 kg/m2 (SD 5.0) SMBG less intensive: 31.8 kg/m2 (SD 6.3) C: 30.8 kg/m2 (SD 6.3) |
SMBG more intensive: –0.3 kg/m2 (SD 1.2) SMBG less intensive: –0.2 kg/m2 (SD 0.9) C: –0.1 kg/m2 (SD 1.0) |
NS | |
| Fontbonne (1989)47 | Weight | Difference SMBG/SMUG vs control –0.22 kg (95% CI –1.36 to 0.93) | NS | ||
| Guerci (2003)49 | Weight |
SMBG: –0.93 ± 4.35 kg C: –0.83 ± 4.87 kg |
NS | ||
| Muchmore (1994)57 | Weight | Difference SMBG vs control –0.10 kg (95% CI –12.28 to 12.08) | NS | ||
| O’Kane (2008)13 | BMI |
SMBG: 34.0 kg/m2 (SD 7.0) C: 32.0 kg/m2 (SD 6.2; p = 0.04) |
SMBG: 33.1 kg/m2 (SD 6.4) C: 31.8 kg/m2 (SD 6.0) |
NS | |
| Rutten (1990)58 | Weight |
SMBG: –0.4 kg C: +0.1 kg |
NS | ||
| Schwedes (2002)61 | Weight |
SMBG: –1.96 ± 2.99 kg C: –1.62 ± 3.54 kg |
p-value not reported | ||
| Wing (1986)63 | Weight |
SMBG: 99.02 kg (SD 16.13) C: 96.35 kg (SD 23.57) |
SMBG: 94.92 kg (SD 16.50) C: 88.11 kg (SD 17.79) |
Difference SMBG vs control 4.10 kg (95% CI –1.07 to 9.27) | NS |
| Lipid parameters | |||||
| Brown (2002)43 | Cholesterol | No significant difference | |||
| Triglycerides | No significant difference | ||||
| Cho (2006)44 | Total cholesterol | Significantly lower in the intervention group | |||
| HDL cholesterol | No significant difference | ||||
| Triglycerides | No significant difference | ||||
| Farmer (2007)10 | Total cholesterol | Significantly more reduction in more intensive vs control | 0.01 | ||
| Total–HDL cholesterol ratio | Significantly more reduction in more intensive vs control | 0.013 | |||
| Kwon (2004)55 | Total cholesterol | No significant differences reported | |||
| HDL cholesterol | Significant increase from baseline in control group, but not significant differences between groups reported | ||||
| LDL cholesterol | No significant differences reported | ||||
| Triglycerides | No significant differences reported | ||||
| Schwedes (2002)61 | Total cholesterol | No significant difference | |||
| Triglycerides | No significant difference | ||||
| Wing (1986)63 | Lipid parameters (cholesterol, triglycerides) | No significant difference | |||
| Adherence | |||||
| Cho (2006)44 | SMBG frequency |
SMBG + internet: 34 ± 28 times per month SMBG: 22 ± 19 times per month |
0.024 | ||
| Estey (1990)46 | SMBG adherence | SMBG adherence greater in SMGB + FB group (no data shown) | < 0.0001 | ||
| Farmer (2007)10 | SMBG adherence |
SMBG more intensive: 52.3% continued to use meter at least twice weekly for 12 months SMBG less intensive: 66% continued to use meter at least twice weekly for 12 months |
0.012 | ||
| Number of readings in meter users | Significantly more in the more intensive group | 0.022 | |||
| Johnson (2006)51 | Days of testing | Patients receiving free strips tested and average of 0.64 days per week more often than patients not receiving free strips | 0.007 | ||
| Kwon (2004)55 | Frequency of SMBG during study (3 months) |
SMBG internet: 71.5 ± 36.2 SMBG: 38.1 ± 24.8 |
p-value not reported | ||
| Moreland (2006)20 | Frequency of SMBG |
BGM+: 2.8 (SD 1.5) MT: 2.0 (SD 1.3) SC: 2.1 (SD 1.7) |
< 0.05 BGM+ vs the other two groups | ||
| Scherbaum (2008)60 | Adherence assessed by investigator |
(at 6 months) Low SMBG: 73% High SMBG: 83% |
NS | ||
| Adherence assessed by patient |
(at 6 months) Low SMBG: 85–88% High SMBG: 84–88% |
||||
| Wing (1986)63 | Adherence with self-monitoring | SMBG: 89.1% of strips used during initial treatment, 70.2% during FU; 83% of patients interpreted results within 20% of actual level | |||
| Changes in treatment | |||||
| Davidson (2005)45 | Medication at end of study |
SMBG: 19% MET, 35% MET + SU, 37% triple oral therapy, 7% insulin + oral, 2% insulin alone C: 22% MET, 38% MET + SU, 27% triple oral therapy, 13% insulin + oral, 0 insulin alone |
NS | ||
| Farmer (2007)10 | Medication increase |
SMBG more intensive: increased in 31.8% of patients SMBG less intensive: increased in 28.7% of patients C: increased in 29.6% of patients |
NS | ||
| Guerci (2003)49 | Medication change | No significant difference | |||
| O’Kane (2008)13 | Medication use |
SMBG: no drugs n = 86, 1 drug n = 8, 2 drugs n = 0 C: no drugs n = 78, 1 drug n = 7, 2 drugs n = 2 |
SMBG: no drugs n = 34, 1 drug n = 44, 2 drugs n = 11 C: no drugs n = 29, 1 drug n = 40, 2 drugs n = 6 |
NS | |
| Rutten (1990)58 | Medication change |
SMBG: 64% unchanged C: 78% unchanged |
NS | ||
| Scherbaum (2008)60 | Change from oral agents to insulin | No significant difference | |||
| Wing (1986)63 | Change in medication |
SMBG: decrease in oral agents 73%, decrease in insulin 83% C: decrease in oral agents 64%, decrease in insulin 64% |
NS | ||
| QoL/preference | |||||
| Farmer (2007)10 | QoL (EQ-5D) | Significantly lower values on EQ-5D for more intensive group vs control, mainly due to increased anxiety/depression | |||
| Gallichan (1994)48 | Preference | 71% preferred urine testing to blood testing | |||
| Miles (1997)56 | Preference | 70% preferred urine testing, 15% preferred blood testing | |||
| Well-being questionnaire | No significant difference | ||||
| Moreland (2006)20 | Negative affect with respect to SMBG | BGM+: 38% MT: 65% SC: 57% | 0.03 | ||
| Satisfaction | No significant difference | ||||
| Muchmore (1994)57 | Quality-of-life inventory (satisfaction, impact, worry – social/vocational, worry –diabetes related) | No significant difference | |||
| O’Kane (2008)13 | Depression | Significantly worse in the SMBG group | 0.011 | ||
| Anxiety | Marginally worse in the SMBG group | 0.07 | |||
| Positive well-being | NS | ||||
| Energy | NS | ||||
| Schwedes (2002)61 | Well-being, treatment satisfaction | Similar improvement in both groups | |||
| Depression | Significantly less in the SMBG group | 0.032 | |||
| Wing (1986)63 | Mood | Significantly improved in both groups, no significant difference | |||
| Changes in behaviour | |||||
| Guerci (2003)49 | Diet and exercise behaviour | Significantly more patients in the SMBG group continued following dietary instructions than in the control group; no significant difference in exercise behaviour | |||
| Wing (1986)63 | Diet and exercise habits | No significant difference | |||
| Cost | |||||
| Allen (1990)40 | Cost | SMBG 12 times more in first year, 8 times more in later years | |||
| Other | |||||
| Farmer (2007)10 | Systolic blood pressure | No significant difference | |||
| Diastolic blood pressure | No significant difference | ||||
| Guerci (2003)49 | Systolic blood pressure | No significant difference | |||
| Diastolic blood pressure | No significant difference | ||||
| Scherbaum (2008)60 | Physician visits | No significant difference | |||
| Inpatient stay | No significant difference | ||||
| Incapacity to work | No significant difference | ||||
| Wing (1986)63 | Blood pressure | No significant difference | |||
| Adverse events | |||||
| Barnett (2008)41 | All-cause adverse events |
SMBG: 13.2% C: 15.1% |
|||
| Scherbaum (2008)60 | Adverse events (with details) | No significant difference | |||
Appendix 5 Observational and non-randomised studies (included in reviews and new)
| Study | Participants | Interventions | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Bajkowska-Fiedziukiewicz (2008) 64 Poland Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 600 Setting: diabetes clinic, Lódź Inclusion criteria: T2DM, insulin and/or oral treatment Age: 63.4 years BMI: NR HbA1c: 7.45% Diabetes duration: 11.4 years Treatment: insulin, oral glucose-lowering medication |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: maximum and minimum glucose levels during last week plus 8-point profile on freely selected day SMBG method: glucometer Education: standard diabetes education Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG |
|
|
Banister (2004) 65 USA Design: cohort, before and after Follow-up: 2–12 months |
Total number: 70 Setting: community clinic Inclusion criteria: T2DM Age: 49 years Ethnicity: most Hispanic or African-American BMI: 34 kg/m2 (90% > 25) HbA1c: 9.7% (range 5.2–16.2%) Diabetes duration: NR |
SMBG regimen: SMBG once per day SMBG method: glucometer Education: diabetes self-management training programme SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: did not report on how to respond to readings Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Blonde (2002) 66 USA Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 228 Setting: USA health clinics, chart review Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no medication limits Age: range 35–65 years BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: no details |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG |
|
|
Capelson (2006) 67 USA Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 808 Setting: chart review Joslin Clinic 2001–2005 Inclusion criteria: diabetes (type not specified), > 75 years, insulin use Age: 80.4 ± 4.5 years BMI: NR HbA1c: 7.5–7.7% Diabetes duration: 21.3 ± 14.9 years Treatment: insulin |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: divided into groups: (1) no SMBG; (2) SMBG 1–2 times per day; (3) SMBG 3–4 times per day; (4) SMBG > 4 times per day Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Chan (2000) 68 China Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 562 Setting: teaching hospital Inclusion criteria: T2DM Age: 53 years BMI: mean 2.4 HbA1c: 8.4% (SD 2.3%) Diabetes duration: 5 (SD 6) years Treatment: 63% OHA, 21% diet alone, 9% insulin, rest no treatment |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Evans (1999) 69 UK Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 790 with T2DM; 807 with T1DM Setting: UK diabetes database Inclusion criteria: diabetes mellitus, insulin treated Age: unclear BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: mean NR Treatment: all on insulin, some with OHAs in addition |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG (no. of strips dispensed) |
|
|
Part of QuED Study Italy Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: 3 years |
Total number: 2855 Setting: Italian diabetes clinics and GP practices Inclusion criteria: T2DM Age: 63 years BMI: NR HbA1c: ~7.3 ± 1.7% Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: diet only, oral antihyperglycaemic agents, insulin |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG, QoL |
|
|
Franciosi (2005) 71 Part of QuED Study Italy Design: longitudinal Follow-up: 3 years |
Total number: 1896 people with T2DM Setting: outpatient diabetes clinics Inclusion criteria: T2DM, users and non-users of SMBG; no insulin use Age: 62.4 years BMI: males 27, females 28 HbA1c: 7.0% (testing < once per week), 7.2% (testing ≥ once per week), 7.3% (testing ≥ once per day) Diabetes duration: 9.1 years Treatment: diet only (14.4–28.7%), SUs (23.6–27.9%), MET (6.6–9.3%), SU + MET (35.3–55.4%) |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols SMBG other: SMBG method: glucometer used by 99% of patients using SMBG at least once per day; by 95.8% of patients using SMBG at least once per week; by 20.8% of the rest Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Fremantle Diabetes Study [Davis (2007)17,19] Australia Design: cross-sectional and longitudinal Follow-up: 5 years |
Total number: 1286 patients with T2DM at entry, 531 followed up over 5 years (longitudinal cohort significantly younger, healthier, better glycaemic control) Setting: community-based Inclusion criteria: T2DM Age: 64 ± 11 years BMI: 29.6 ± 5.5 kg/m2 HbA1c: 7.4% (6.4–8.9) Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: NR |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Control: no use of SMBG Outcomes: HbA1c, morbidity |
|
|
Hanninen (2001) 72 Finland Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 260 Setting: Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no medication limits Age: 63 years BMI: 30 (SEM 0.5) HbA1c: 8.5% (SEM 0.2) Diabetes duration: some newly diagnosed Treatment: OHA or insulin |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Harris (2001) 73 USA Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 1480 people with T2DM Setting: NHANES III database Inclusion criteria: T2DM, users and non-users of SMBG Age: 62.5 years BMI: NR HbA1c: mean 7.64%, 6.37% (diet only), 8.04% (oral agents), 8.29% (insulin) Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: diet only (27.2%), oral hypoglycaemic agents (45.5%), insulin (27.3%) |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Jaworska (2001) 74 Poland Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 218 people with T2DM Setting: outpatient Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no medication limits reported Age: 62 years |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Karter (2001) 75 (Kaiser Permanente) USA Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 23,153 people with T2DM Setting: Kaiser Permanente database Inclusion criteria: T2DM, > 19 years, pharmacy benefits, single HbA1c measured during FU; on insulin, oral agents or diet only Age: 60 years BMI: NR HbA1c: ~8.4 ± 2.2% Diabetes duration: 75% 0–9 years; 25% ≥ 10 years Treatment: diet only (21%), oral hypoglycaemic agents (55%), insulin (24%) |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: ADA recommendations Control: no use of SMBG Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG |
|
|
Karter (2005) 76 (Kaiser Permanente) USA Design: retrospective database Follow-up: 1 year |
Total number: 4775 people with T2DM Setting: Kaiser Permanente database Inclusion criteria: T2DM, HbA1c >8%, initiating new therapies Age: 60 years BMI: NR HbA1c: 9.9 ± 1.5% Diabetes duration: ≥ 1 year Treatment: 74.2% not using insulin (pre-initiation) |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: not reported Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG |
|
|
Karter (2006) 14 (Kaiser Permanente) USA Design: longitudinal Follow-up: 3.5 years |
Total number: 16091 new users, 15347 prevalent users with T2DM Setting: Kaiser Permanente database Inclusion criteria: T2DM, insulin, oral therapy or diet Age: ~60 ± 10 years BMI: NR HbA1c: 6.4 ± 0.8% to 8.6 ± 2.0% (new user cohort higher HbA1c) Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: new users : n = 9264 no medication, n = 5867 oral only; prevalent users : n = 1622 no medication, n = 7409 oral only |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG |
|
|
Klein (1993) 77 USA Design: chart review Follow-up: |
Total number: 229 Setting: chart review at Veterans Affairs medical centre Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no medication limits; patients who received blood or urine monitoring supplies Age: 62 years; 97% male |
Comparison: association between SMBG/SMUG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG |
|
|
Meier (2002) 79 USA Design: before/after Follow-up: 6 months |
Total number: 471 patients with T2DM; chart review of 1467 patients Setting: Veterans Affairs chart review and before and after study Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no insulin Age: 64 years; 98% male BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: oral antihyperglycaemic agents (89%, most on SU), diet (11%) |
Intervention: reduced access to test strips Outcomes: HbA1c, strip use |
|
|
Mitchell (2004) 80 Canada Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 434 patients with T2DM Setting: community pharmacies Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no insulin Age: 64 years BMI: 30.7 (SD 6) HbA1c: 7.3% (SD 1.3%) Diabetes duration: 7.8 (SD 6.5) years Treatment: diet and OHA only |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Murata (2003) 81 USA Design: before/after Follow-up: 12 months |
Total number: 218 Setting: veterans’ administration Inclusion criteria: T2DM, stable Age: mean 65 years BMI: mean 31 (SD 5.7) HbA1c: 8.1% (SD 1.7%) Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: insulin, 35% on OHAs as well |
Intervention: intensified SMBG SMBG regimen: SMBG using an electronic BG meter before all meals and at bedtime for 8 weeks then usual monitoring resumed Outcomes: HbA1c Quality: 27.1% dropouts at 1 year |
|
|
Murata (2008) 82 USA Design: database study Follow-up: 24 months |
Total number: 5862 patients with T2DM Setting: Southwest Healthcare Network veterans Inclusion criteria: T2DM, taking oral antihyperglycaemic agents Age: NR BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: no details |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c and medication change SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Newman (1990) 83 USA Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: 3 years |
Total number: 38 patients with T1DM or T2DM Setting: Veteran Affairs chart review Inclusion criteria: T1DM or T2DM, no medication limits Age: 60 years BMI: NR HbA1c: 8.2% (from graph) Diabetes duration: 14 years Treatment: diet, OHA or insulin |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Oki (1997) 84 USA Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 98 patients with T2DM Setting: routine care Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no medication limits Age: 56 years BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: diet, OHAs, insulin |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Ozmen (2003) 85 Turkey Design: cohort Follow-up: 1 year |
Total number: 267 patients with T2DM Age: 58 years BMI: 29.1 kg/m2 HbA1c: 9.1% Diabetes duration: 8.6 years Treatment: 34% using insulin; diet alone, insulin ± SUs, acarbose or MET |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: month 1: 2–3 per week, during the following 11 months: as necessary to maintain normoglycaemia SMBG treatment adjustment/advice: clinicians evaluated SMBG readings to adjust treatment Control: none Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Patrick (1994) 86 UK Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 200 Setting: hospital diabetes clinic Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no insulin Age: 65 years BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: 6.4 years Treatment: diet oral hypoglycaemic agents |
Comparison: association between SMBG/SMUG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Rindone (1997) 87 USA Design: retrospective chart review Follow-up: 2 years |
Total number: 115 Setting: outpatient clinics Inclusion criteria: T2DM, SU therapy for > 2 years; no insulin or MET Age: 68 years BMI: weight 91 ± 20 kg HbA1c: 8.1 ± 1.5% Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: oral hypoglycaemic agents (SU) |
Comparison: access to strips vs no access SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols SMBG method: Chemstrips Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Roblin (2001) 88 (abstract) USA Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 955 Setting: 3 sites of an HMO Inclusion criteria: T2DM (95%), pharmacologically treated Age: 53 years BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: 12 years Treatment: 43% insulin, 52% oral agents |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c Outcomes: HbA1c, SMBG frequency |
|
|
ROSSO Study (Martin (2006) 15 /Schneider (2007) 99 /Martin (2009) 78 ) Germany Design: longitudinal study Follow-up: mean 6.5 years |
Total number: 3268 patients with T2DM Setting: 192 doctors’ practices Inclusion criteria: T2DM, followed from diagnosis Age: 62.4 years BMI: 29.8 kg/m2 HbA1c: 7.7% Diabetes duration: followed from diagnosis Treatment: n = 2515 not using insulin |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and morbidity/mortality SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c, diabetes-related morbidity (non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, foot amputation, blindness, haemodialysis), all-cause mortality |
|
|
Rost (1990) 89 USA Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 84 patients with T2DM Setting: inpatient Inclusion criteria: T2DM, no medication limitation Age: 56 years Diabetes duration: followed from diagnosis Treatment: insulin, oral medication |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c in insulin users and non-insulin users Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Schiel (1999) 90 Germany Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 842 Setting: hospital outpatient clinic Inclusion criteria: T2DM, insulin treatment > 1 year Age: 60 (SD 1.1) years Diabetes duration: 12.6 (SD 7) years Treatment: insulin |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c, frequency of SMBG |
|
|
Schütt (2006) 91 Germany/Austria Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 5009 people with T2DM Setting: German/Austrian DPV-Wiss database, 191 centres Inclusion criteria: T2DM Age: NR BMI: NR HbA1c: mean 7.64%, 6.37% (diet only), 8.04% (oral agents), 8.29% (insulin) Diabetes duration: 10 years Treatment: insulin, oral antihyperglycaemic agents, diet (n = 2988 not using insulin) |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: most recent frequency of SMBG, most recent HbA1c |
|
|
Secnik (2007) 92 UK Design: database study Follow-up: 12 months |
Total number: 2783 Setting: UK General Practice Research Database Inclusion criteria: T2DM, insulin or oral agent, 12-month postinitiation data Age: 8% 20–44 years, 45% 45–64 years, 47% ≥ 65 years BMI: > 80% overweight or obese HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: n = 347 insulin, n = 2436 oral agents |
Intervention: access to free BG monitors Outcomes: HbA1c, SMBG use |
|
|
Soumerai (2004) 93 USA Design: interrupted time series Follow-up: 4 years |
Total number: 3219 people with T1DM or T2DM Setting: database Inclusion criteria: T2DM, any treatment Age: 56 ± 12.3 years BMI: <25 kg/m2 11.8%, 25–30 kg/m2 24.6%, ≥ 30 kg/m2 44.5% HbA1c: 8.4 ± 1.7% Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: insulin, oral hypoglycaemic agents (57% on SUs) |
Intervention: access to free BG monitors SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c, SMBG use, medication use |
|
|
Stiptzarov (2003) 94 USA Design: cross-sectional, survey Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 14329 Setting: Veterans Affairs facilities Age: 65 years; 98% male BMI: NR HbA1c: NR Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: OHAs, insulin; no details given |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Tengblad (2007) 95 Sweden Design: cross-sectional Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 6495 people with T2DM, further exploration of medical records of 896, telephone interviews with 533 patients using SMBG on their opinions and SMBG habits Setting: 18 primary care health centres in Östergötland and Jönköping, Sweden Inclusion criteria: T2DM, users and non-users of SMBG Age: 69 years BMI: NR HbA1c: 5.4% to 6.9% Diabetes duration: < 2 years, 4–33%; 2–4 years, 9–35%; > 4 years, 32–87% Treatment: diet only (32%), oral hypoglycaemic agents (37%), insulin (31%) |
Comparison: association between SMBG use and HbA1c SMBG regimen: no details of SMBG use/protocols SMBG other: SMBG method: Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Wen (2004) 16 USA Design: chart review Follow-up: 3 years |
Total number: 976 people with T2DM Setting: Veteran Affairs Inclusion criteria: T2DM, prescribed oral medication Age: 63 years; 97% male BMI: 31 ± 6 kg/m2 HbA1c: 7–7.3% Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: OHAs only |
Comparison: no SMBG vs SMBG year 3 or SMBG years 2–3 or SMBG years 1–3 Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
|
Wieland (1997) 96 USA Design: retrospective chart review Follow-up: NA |
Total number: 216 people with T2DM Setting: Veteran Affairs Inclusion criteria: T2DM, prescribed glyburide Age: range 39–89 years; all male BMI: NR HbA1c: 7.9 ± 1.4% Diabetes duration: NR Treatment: OHAs only |
Comparison: no SMBG vs SMBG once per day vs SMBG ≥ twice per day Outcomes: HbA1c |
|
Appendix 6 Characteristics and results of qualitative studies
| Study, design | Participants/issues | Results |
|---|---|---|
|
Belsey (2009),100 UK Prevalence data assessed using Quality and Outcomes Framework |
|
SMBG value is less clear-cut for patients unlikely to alter their treatment dose/behaviour, or if they are using treatments that lack the potential to cause hypoglycaemia British people tend not to act on their SMBG results SMBG is associated with increased levels of depression and anxiety compared with that of patients who do not self-monitor Expenditure in the UK in 2006–7 was £164,648,000; mean annual test strip cost per patient was £62.06, with those taking oral antidiabetic treatment having a mean of £21.56 Patients who are on diet and exercise alone (mean 2.5 strips per week), MET/glitazones (2.6–3.3 mean per week). This group represents 22% of all patients testing, thus the absolute expenditure in these groups is high In the UK, few patients use SMBG to guide and maintain changes to their behaviour/lifestyle and this appears to be due in part to a lack of education about interpreting and acting upon result; could be considerable wastage due to inappropriate repeat prescriptions |
|
DiGEM RCT, UK 10 Qualitative component |
|
Several patients mentioned an increased awareness of having diabetes as a consequence of SMBG Presence of elevated BG level viewed by respondents as tangible evidence of abnormality, one participant felt threatened by constant reminder of illness Some participants noted SMBG helped them establish the relationship between their physical symptoms and their blood sugar – most who reported this used SMBG to confirm suspected hypoglycaemia rather than hyperglycaemia Awareness of blood sugar levels provided reassurance for several respondents when associated with normal readings; however, readings outside parameters were associated with feelings of failure Some participants felt they could use SMBG to assess effects of behaviour, for example timing of monitoring, effect of certain foods Promotion of adherence to self-management emerged as benefit of SMBG. Respondents used feedback on general diabetes control and on specific behaviours in both monitoring groups Other incentives might be needed to encourage maintenance of behaviour change in patients who did not recognise long-term benefits of behaviour change Two participants said they timed their SMBG to ensure they only got satisfactory readings Participants felt empowered to take more control over their health care and ability to contribute to physician’s evaluation of their status Several participants said convenience was a benefit of SMBG While SMBG may have enabled some participants to feel more in control of their diabetes, only 2 respondents expressed an absolute preference for SMBG over periodic clinic visits and HbA1c SMBG thought to be more accurate than SMUG, but participants expressed reservations about its accuracy when compared with HbA1c |
|
DiGEM RCT, UK Questionnaire study measuring patients’ beliefs about diabetes and self-monitoring |
|
Concerns about the consequences of diabetes increased in both self-monitoring groups, relative to control participants Beliefs about the importance of self-testing increased in both self-monitoring groups relative to usual care Changes in psychological well-being did not differ, but control patients reported greater increases in general and specific dietary adherence than patients in either self-monitoring groups Authors concluded that despite changes in some beliefs about diabetes differing between groups there was no corresponding change in self-reported health behaviours |
|
Lawton (2004),6 UK Qualitative study using in-depth interviews, study informed by grounded theory Patients were interviewed at 6-monthly intervals over 1 year (3 interviews) Patients were recruited from hospital clinics (n = 3) and general practices (n = 16) in Lothian, Scotland |
|
16 patients performed urine testing post diagnoses: of these, 6 had changed to SMBG by round 2, and 2 further had changed to SMBG by round 3; 3 had stopped monitoring altogether; 3 patients did not monitor at any point (SMBG mainly initiated after visiting hospital clinic, GPs generally advised urine testing or nothing) Patients expressed negative views about urine testing, especially when compared to subsequent use of SMBG – SMBG perceived to be more convenient, hygienic and accurate Most patients assumed that BG meters were given to those with more advanced or serious forms of diabetes; this could have implications on how they thought about their own disease Patients often interpreted negative urine results as indicating that they could not have diabetes |
|
Peel (2004),101 UK Qualitative study using repeat interviews; thematic analysis based in grounded theory Two interviews over 6 months Patients were recruited from hospital clinics (n = 3) and general practices (n = 16) in Lothian, Scotland |
|
In round 1 interviews, 37.5% of patients used glucose meters, 7 did not self-monitor; by round 2, 52.5% used glucose meters – most reported having been provided with meters by hospital clinics and had attended structured group-based education sessions including instructions on meter use Patients see both pros and cons in self-monitoring; can encourage self-regulation and regimen modifications; low readings can offer reassurance; glucose monitoring can heighten patients’ awareness of the impact of lifestyle, for example dietary choices, on BG levels; glucose monitoring amplifies a sense of ‘success’ or ‘failure’ about self-management, often resulting in anxiety and self-blame if glucose readings remain consistently high. Moreover, monitoring can negatively effect patients’ self-management when readings are counterintuitive Conclusions: Analysis highlights the importance of understanding the meanings that newly diagnosed patients attach to glucose self-monitoring. To maximise the positive effects of self-monitoring, health professionals should ensure that patients understand the purpose of monitoring and should clarify with patients how readings should be interpreted |
|
Peel (2007),102 UK Qualitative study as above, repeat interviews over 4 years after diagnosis |
|
Analysis revealed three main themes – the role of health professionals, interpreting readings and managing high values, and the ongoing role of BG self-monitoring. Self-monitoring decreased over time, and health professionals’ behaviour seemed crucial in this: participants interpreted doctors’ focus on levels of HbA1c, and lack of perceived interest in meter readings, as indicating that self-monitoring was not worth continuing. Some participants saw readings as a proxy measure of good and bad behaviour – with women, especially, chastising themselves when readings were high. Some participants continued to find readings difficult to interpret, with uncertainty about how to respond to high readings. Reassurance and habit were key reasons for continuing. There was little indication that participants were using self-monitoring to effect and maintain behaviour change Conclusions: Clinical uncertainty about the efficacy and role of BG self-monitoring in patients with T2DM is mirrored in patients’ own accounts. Patients tended not to act on their self-monitoring results, in part because of a lack of education about the appropriate response to readings. Health professionals should be explicit about whether and when such patients should self-monitor and how they should interpret and act upon the results, especially high readings |
|
Zgibor (2002),103 New Zealand Qualitative survey |
|
Patient-reported barriers to diabetes care associated with SMBG include financial, psychosocial and self-efficacy issues Characteristics associated with SMBG greater than or twice weekly were female sex, HbA1c > 8%, higher diabetes knowledge scores, insulin use; multivariate analyses demonstrated that those reporting external physical barriers (particularly financial), external psychological barriers, internal psychological barriers were less likely to perform SMBG independent of ethnicity, insulin use, age, sex, diabetes knowledge and glycaemic control Carriers need to be addressed to encourage increased participation in self-care Previous studies have shown lower SMBG in ethnic minorities, lower socioeconomic status and patients with lower diabetes knowledge Individuals reporting personal barriers to diabetes care – particularly relating to finance and access, community and family support and self-efficacy, motivation and health beliefs – were less likely to perform prescribed SMBG |
List of abbreviations
- ADA
- American Diabetes Association
- AHRQ
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
- BG
- blood glucose
- BMI
- body mass index
- CHF
- Swiss franc
- DiGEM
- Diabetes Glycaemic Education and Monitoring
- DTSQ
- Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire
- EASD
- European Association for the Study of Diabetes
- ESMON
- Efficacy of Self-MONitoring of blood glucose in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes trial
- EQ-5D
- EuroQol-5D questionnaire
- FBG
- fasting blood glucose
- FDA
- US Food and Drug Administration
- FPG
- fasting plasma glucose
- GPs
- general practitioners
- HbA1c
- glycosylated/glycated haemoglobin
- HCPs
- health-care professionals
- HDL
- high-density lipoprotein
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IQWiG
- Institut für Qualität und Wirtschaftlickeit im Gesundheitswesen
- LDL
- low-density lipoprotein
- MHRA
- Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
- NIH
- National Institutes of Health
- NR
- not reported
- NS
- not significant
- OHA
- oral hypoglycaemic agent
- PTC
- Pathways To Change
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- QoL
- quality of life
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- SF-36
- Short Form-36
- SMBG
- self-monitoring of blood glucose
- SMUG
- self-monitoring of urine glucose
- T1DM
- type 1 diabetes
- T2DM
- type 2 diabetes
- UKPDS
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study
All abbreviations that have been used in this report are listed here unless the abbreviation is well known (e.g. NHS), or it has been used only once, or it is a non-standard abbreviation used only in figures/tables/appendices, in which case the abbreviation is defined in the figure legend or in the notes at the end of the table.
Notes
Health Technology Assessment reports published to date
-
Home parenteral nutrition: a systematic review.
By Richards DM, Deeks JJ, Sheldon TA, Shaffer JL.
-
Diagnosis, management and screening of early localised prostate cancer.
A review by Selley S, Donovan J, Faulkner A, Coast J, Gillatt D.
-
The diagnosis, management, treatment and costs of prostate cancer in England and Wales.
A review by Chamberlain J, Melia J, Moss S, Brown J.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Hewison J.
-
A review of near patient testing in primary care.
By Hobbs FDR, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Wilson S, Hyde CJ, Thorpe GH, et al.
-
Systematic review of outpatient services for chronic pain control.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA, Eccleston C, Morley S, de C Williams AC.
-
Neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism: cost, yield and outcome.
A review by Pollitt RJ, Green A, McCabe CJ, Booth A, Cooper NJ, Leonard JV, et al.
-
Preschool vision screening.
A review by Snowdon SK, Stewart-Brown SL.
-
Implications of socio-cultural contexts for the ethics of clinical trials.
A review by Ashcroft RE, Chadwick DW, Clark SRL, Edwards RHT, Frith L, Hutton JL.
-
A critical review of the role of neonatal hearing screening in the detection of congenital hearing impairment.
By Davis A, Bamford J, Wilson I, Ramkalawan T, Forshaw M, Wright S.
-
Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism: a systematic review.
By Seymour CA, Thomason MJ, Chalmers RA, Addison GM, Bain MD, Cockburn F, et al.
-
Routine preoperative testing: a systematic review of the evidence.
By Munro J, Booth A, Nicholl J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of laxatives in the elderly.
By Petticrew M, Watt I, Sheldon T.
-
When and how to assess fast-changing technologies: a comparative study of medical applications of four generic technologies.
A review by Mowatt G, Bower DJ, Brebner JA, Cairns JA, Grant AM, McKee L.
-
Antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome.
A review by Wald NJ, Kennard A, Hackshaw A, McGuire A.
-
Screening for ovarian cancer: a systematic review.
By Bell R, Petticrew M, Luengo S, Sheldon TA.
-
Consensus development methods, and their use in clinical guideline development.
A review by Murphy MK, Black NA, Lamping DL, McKee CM, Sanderson CFB, Askham J, et al.
-
A cost–utility analysis of interferon beta for multiple sclerosis.
By Parkin D, McNamee P, Jacoby A, Miller P, Thomas S, Bates D.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of methods of dialysis therapy for end-stage renal disease: systematic reviews.
By MacLeod A, Grant A, Donaldson C, Khan I, Campbell M, Daly C, et al.
-
Effectiveness of hip prostheses in primary total hip replacement: a critical review of evidence and an economic model.
By Faulkner A, Kennedy LG, Baxter K, Donovan J, Wilkinson M, Bevan G.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in colorectal surgery: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials.
By Song F, Glenny AM.
-
Bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for malignancy.
A review by Johnson PWM, Simnett SJ, Sweetenham JW, Morgan GJ, Stewart LA.
-
Screening for speech and language delay: a systematic review of the literature.
By Law J, Boyle J, Harris F, Harkness A, Nye C.
-
Resource allocation for chronic stable angina: a systematic review of effectiveness, costs and cost-effectiveness of alternative interventions.
By Sculpher MJ, Petticrew M, Kelland JL, Elliott RA, Holdright DR, Buxton MJ.
-
Detection, adherence and control of hypertension for the prevention of stroke: a systematic review.
By Ebrahim S.
-
Postoperative analgesia and vomiting, with special reference to day-case surgery: a systematic review.
By McQuay HJ, Moore RA.
-
Choosing between randomised and nonrandomised studies: a systematic review.
By Britton A, McKee M, Black N, McPherson K, Sanderson C, Bain C.
-
Evaluating patient-based outcome measures for use in clinical trials.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Davey C, Buxton MJ, Jones DR.
-
Ethical issues in the design and conduct of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Edwards SJL, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Jackson JC, Hewison J, Thornton J.
-
Qualitative research methods in health technology assessment: a review of the literature.
By Murphy E, Dingwall R, Greatbatch D, Parker S, Watson P.
-
The costs and benefits of paramedic skills in pre-hospital trauma care.
By Nicholl J, Hughes S, Dixon S, Turner J, Yates D.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic ultrasound in gastro-oesophageal cancer.
By Harris KM, Kelly S, Berry E, Hutton J, Roderick P, Cullingworth J, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of trials and other studies.
By Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR, Sheldon TA, Song F.
-
Primary total hip replacement surgery: a systematic review of outcomes and modelling of cost-effectiveness associated with different prostheses.
A review by Fitzpatrick R, Shortall E, Sculpher M, Murray D, Morris R, Lodge M, et al.
-
Informed decision making: an annotated bibliography and systematic review.
By Bekker H, Thornton JG, Airey CM, Connelly JB, Hewison J, Robinson MB, et al.
-
Handling uncertainty when performing economic evaluation of healthcare interventions.
A review by Briggs AH, Gray AM.
-
The role of expectancies in the placebo effect and their use in the delivery of health care: a systematic review.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Thomas H.
-
A randomised controlled trial of different approaches to universal antenatal HIV testing: uptake and acceptability. Annex: Antenatal HIV testing – assessment of a routine voluntary approach.
By Simpson WM, Johnstone FD, Boyd FM, Goldberg DJ, Hart GJ, Gormley SM, et al.
-
Methods for evaluating area-wide and organisation-based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review.
By Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ.
-
Assessing the costs of healthcare technologies in clinical trials.
A review by Johnston K, Buxton MJ, Jones DR, Fitzpatrick R.
-
Cooperatives and their primary care emergency centres: organisation and impact.
By Hallam L, Henthorne K.
-
Screening for cystic fibrosis.
A review by Murray J, Cuckle H, Taylor G, Littlewood J, Hewison J.
-
A review of the use of health status measures in economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Deverill M, Green C, Harper R, Booth A.
-
Methods for the analysis of quality-of-life and survival data in health technology assessment.
A review by Billingham LJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR.
-
Antenatal and neonatal haemoglobinopathy screening in the UK: review and economic analysis.
By Zeuner D, Ades AE, Karnon J, Brown J, Dezateux C, Anionwu EN.
-
Assessing the quality of reports of randomised trials: implications for the conduct of meta-analyses.
A review by Moher D, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Tugwell P, Moher M, Jones A, et al.
-
‘Early warning systems’ for identifying new healthcare technologies.
By Robert G, Stevens A, Gabbay J.
-
A systematic review of the role of human papillomavirus testing within a cervical screening programme.
By Cuzick J, Sasieni P, Davies P, Adams J, Normand C, Frater A, et al.
-
Near patient testing in diabetes clinics: appraising the costs and outcomes.
By Grieve R, Beech R, Vincent J, Mazurkiewicz J.
-
Positron emission tomography: establishing priorities for health technology assessment.
A review by Robert G, Milne R.
-
The debridement of chronic wounds: a systematic review.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Sheldon T.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) Dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds.
By Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson EA, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D.
-
A systematic literature review of spiral and electron beam computed tomography: with particular reference to clinical applications in hepatic lesions, pulmonary embolus and coronary artery disease.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Harris KM, Roderick P, Boyce JC, et al.
-
What role for statins? A review and economic model.
By Ebrahim S, Davey Smith G, McCabe C, Payne N, Pickin M, Sheldon TA, et al.
-
Factors that limit the quality, number and progress of randomised controlled trials.
A review by Prescott RJ, Counsell CE, Gillespie WJ, Grant AM, Russell IT, Kiauka S, et al.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in total hip replacement: a systematic review.
By Glenny AM, Song F.
-
Health promoting schools and health promotion in schools: two systematic reviews.
By Lister-Sharp D, Chapman S, Stewart-Brown S, Sowden A.
-
Economic evaluation of a primary care-based education programme for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.
A review by Lord J, Victor C, Littlejohns P, Ross FM, Axford JS.
-
The estimation of marginal time preference in a UK-wide sample (TEMPUS) project.
A review by Cairns JA, van der Pol MM.
-
Geriatric rehabilitation following fractures in older people: a systematic review.
By Cameron I, Crotty M, Currie C, Finnegan T, Gillespie L, Gillespie W, et al.
-
Screening for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia: a systematic review with supplementary research.
By Davies SC, Cronin E, Gill M, Greengross P, Hickman M, Normand C.
-
Community provision of hearing aids and related audiology services.
A review by Reeves DJ, Alborz A, Hickson FS, Bamford JM.
-
False-negative results in screening programmes: systematic review of impact and implications.
By Petticrew MP, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D, Wright K.
-
Costs and benefits of community postnatal support workers: a randomised controlled trial.
By Morrell CJ, Spiby H, Stewart P, Walters S, Morgan A.
-
Implantable contraceptives (subdermal implants and hormonally impregnated intrauterine systems) versus other forms of reversible contraceptives: two systematic reviews to assess relative effectiveness, acceptability, tolerability and cost-effectiveness.
By French RS, Cowan FM, Mansour DJA, Morris S, Procter T, Hughes D, et al.
-
An introduction to statistical methods for health technology assessment.
A review by White SJ, Ashby D, Brown PJ.
-
Disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Publication and related biases.
A review by Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, Duley L, Sutton AJ.
-
Cost and outcome implications of the organisation of vascular services.
By Michaels J, Brazier J, Palfreyman S, Shackley P, Slack R.
-
Monitoring blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, Powrie JK, Swaminathan R.
-
The effectiveness of domiciliary health visiting: a systematic review of international studies and a selective review of the British literature.
By Elkan R, Kendrick D, Hewitt M, Robinson JJA, Tolley K, Blair M, et al.
-
The determinants of screening uptake and interventions for increasing uptake: a systematic review.
By Jepson R, Clegg A, Forbes C, Lewis R, Sowden A, Kleijnen J.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prophylactic removal of wisdom teeth.
A rapid review by Song F, O’Meara S, Wilson P, Golder S, Kleijnen J.
-
Ultrasound screening in pregnancy: a systematic review of the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and women’s views.
By Bricker L, Garcia J, Henderson J, Mugford M, Neilson J, Roberts T, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the taxanes used in the treatment of advanced breast and ovarian cancer.
By Lister-Sharp D, McDonagh MS, Khan KS, Kleijnen J.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: a rapid and systematic review.
By Payne N, Chilcott J, McGoogan E.
-
Randomised controlled trial of non-directive counselling, cognitive–behaviour therapy and usual general practitioner care in the management of depression as well as mixed anxiety and depression in primary care.
By King M, Sibbald B, Ward E, Bower P, Lloyd M, Gabbay M, et al.
-
Routine referral for radiography of patients presenting with low back pain: is patients’ outcome influenced by GPs’ referral for plain radiography?
By Kerry S, Hilton S, Patel S, Dundas D, Rink E, Lord J.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (3) antimicrobial agents for chronic wounds; (4) diabetic foot ulceration.
By O’Meara S, Cullum N, Majid M, Sheldon T.
-
Using routine data to complement and enhance the results of randomised controlled trials.
By Lewsey JD, Leyland AH, Murray GD, Boddy FA.
-
Coronary artery stents in the treatment of ischaemic heart disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Meads C, Cummins C, Jolly K, Stevens A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Outcome measures for adult critical care: a systematic review.
By Hayes JA, Black NA, Jenkinson C, Young JD, Rowan KM, Daly K, et al.
-
A systematic review to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions to promote the initiation of breastfeeding.
By Fairbank L, O’Meara S, Renfrew MJ, Woolridge M, Sowden AJ, Lister-Sharp D.
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators: arrhythmias. A rapid and systematic review.
By Parkes J, Bryant J, Milne R.
-
Treatments for fatigue in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By Brañas P, Jordan R, Fry-Smith A, Burls A, Hyde C.
-
Early asthma prophylaxis, natural history, skeletal development and economy (EASE): a pilot randomised controlled trial.
By Baxter-Jones ADG, Helms PJ, Russell G, Grant A, Ross S, Cairns JA, et al.
-
Screening for hypercholesterolaemia versus case finding for familial hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Marks D, Wonderling D, Thorogood M, Lambert H, Humphries SE, Neil HAW.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists in the medical management of unstable angina.
By McDonagh MS, Bachmann LM, Golder S, Kleijnen J, ter Riet G.
-
A randomised controlled trial of prehospital intravenous fluid replacement therapy in serious trauma.
By Turner J, Nicholl J, Webber L, Cox H, Dixon S, Yates D.
-
Intrathecal pumps for giving opioids in chronic pain: a systematic review.
By Williams JE, Louw G, Towlerton G.
-
Combination therapy (interferon alfa and ribavirin) in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a rapid and systematic review.
By Shepherd J, Waugh N, Hewitson P.
-
A systematic review of comparisons of effect sizes derived from randomised and non-randomised studies.
By MacLehose RR, Reeves BC, Harvey IM, Sheldon TA, Russell IT, Black AMS.
-
Intravascular ultrasound-guided interventions in coronary artery disease: a systematic literature review, with decision-analytic modelling, of outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Hutton J, Lindsay HSJ, Blaxill JM, Evans JA, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of counselling patients with chronic depression.
By Simpson S, Corney R, Fitzgerald P, Beecham J.
-
Systematic review of treatments for atopic eczema.
By Hoare C, Li Wan Po A, Williams H.
-
Bayesian methods in health technology assessment: a review.
By Spiegelhalter DJ, Myles JP, Jones DR, Abrams KR.
-
The management of dyspepsia: a systematic review.
By Delaney B, Moayyedi P, Deeks J, Innes M, Soo S, Barton P, et al.
-
A systematic review of treatments for severe psoriasis.
By Griffiths CEM, Clark CM, Chalmers RJG, Li Wan Po A, Williams HC.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Clegg A, Bryant J, Nicholson T, McIntyre L, De Broe S, Gerard K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of riluzole for motor neurone disease: a rapid and systematic review.
By Stewart A, Sandercock J, Bryan S, Hyde C, Barton PM, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Equity and the economic evaluation of healthcare.
By Sassi F, Archard L, Le Grand J.
-
Quality-of-life measures in chronic diseases of childhood.
By Eiser C, Morse R.
-
Eliciting public preferences for healthcare: a systematic review of techniques.
By Ryan M, Scott DA, Reeves C, Bate A, van Teijlingen ER, Russell EM, et al.
-
General health status measures for people with cognitive impairment: learning disability and acquired brain injury.
By Riemsma RP, Forbes CA, Glanville JM, Eastwood AJ, Kleijnen J.
-
An assessment of screening strategies for fragile X syndrome in the UK.
By Pembrey ME, Barnicoat AJ, Carmichael B, Bobrow M, Turner G.
-
Issues in methodological research: perspectives from researchers and commissioners.
By Lilford RJ, Richardson A, Stevens A, Fitzpatrick R, Edwards S, Rock F, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) beds; (6) compression; (7) laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy.
By Cullum N, Nelson EA, Flemming K, Sheldon T.
-
Effects of educational and psychosocial interventions for adolescents with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review.
By Hampson SE, Skinner TC, Hart J, Storey L, Gage H, Foxcroft D, et al.
-
Effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte transplantation for hyaline cartilage defects in knees: a rapid and systematic review.
By Jobanputra P, Parry D, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Statistical assessment of the learning curves of health technologies.
By Ramsay CR, Grant AM, Wallace SA, Garthwaite PH, Monk AF, Russell IT.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of temozolomide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma: a rapid and systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Cave C, Huang S, Major K, Milne R.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of debriding agents in treating surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.
By Lewis R, Whiting P, ter Riet G, O’Meara S, Glanville J.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.
By Burns T, Knapp M, Catty J, Healey A, Henderson J, Watt H, et al.
-
How to develop cost-conscious guidelines.
By Eccles M, Mason J.
-
The role of specialist nurses in multiple sclerosis: a rapid and systematic review.
By De Broe S, Christopher F, Waugh N.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of orlistat in the management of obesity.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a rapid and systematic review.
By Chilcott J, Wight J, Lloyd Jones M, Tappenden P.
-
Extended scope of nursing practice: a multicentre randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained nurses and preregistration house officers in preoperative assessment in elective general surgery.
By Kinley H, Czoski-Murray C, George S, McCabe C, Primrose J, Reilly C, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) Acute day hospital versus admission; (2) Vocational rehabilitation; (3) Day hospital versus outpatient care.
By Marshall M, Crowther R, Almaraz- Serrano A, Creed F, Sledge W, Kluiter H, et al.
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.
By Bruce J, Russell EM, Mollison J, Krukowski ZH.
-
Action research: a systematic review and guidance for assessment.
By Waterman H, Tillen D, Dickson R, de Koning K.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
By Ward S, Morris E, Bansback N, Calvert N, Crellin A, Forman D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the evidence for the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.
By Lloyd Jones M, Hummel S, Bansback N, Orr B, Seymour M.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.
By Brocklebank D, Ram F, Wright J, Barry P, Cates C, Davies L, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging for investigation of the knee joint.
By Bryan S, Weatherburn G, Bungay H, Hatrick C, Salas C, Parry D, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Shirran L, Bagnall A-M, Duffy S, ter Riet G.
-
Superseded by a report published in a later volume.
-
The role of radiography in primary care patients with low back pain of at least 6 weeks duration: a randomised (unblinded) controlled trial.
By Kendrick D, Fielding K, Bentley E, Miller P, Kerslake R, Pringle M.
-
Design and use of questionnaires: a review of best practice applicable to surveys of health service staff and patients.
By McColl E, Jacoby A, Thomas L, Soutter J, Bamford C, Steen N, et al.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.
By Clegg A, Scott DA, Sidhu M, Hewitson P, Waugh N.
-
Subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials: quantifying the risks of false-positives and false-negatives.
By Brookes ST, Whitley E, Peters TJ, Mulheran PA, Egger M, Davey Smith G.
-
Depot antipsychotic medication in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: (1) Meta-review; (2) Patient and nurse attitudes.
By David AS, Adams C.
-
A systematic review of controlled trials of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of brief psychological treatments for depression.
By Churchill R, Hunot V, Corney R, Knapp M, McGuire H, Tylee A, et al.
-
Cost analysis of child health surveillance.
By Sanderson D, Wright D, Acton C, Duree D.
-
A study of the methods used to select review criteria for clinical audit.
By Hearnshaw H, Harker R, Cheater F, Baker R, Grimshaw G.
-
Fludarabine as second-line therapy for B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a technology assessment.
By Hyde C, Wake B, Bryan S, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, et al.
-
Rituximab as third-line treatment for refractory or recurrent Stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wake B, Hyde C, Bryan S, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
A systematic review of discharge arrangements for older people.
By Parker SG, Peet SM, McPherson A, Cannaby AM, Baker R, Wilson A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaler devices used in the routine management of chronic asthma in older children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Peters J, Stevenson M, Beverley C, Lim J, Smith S.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of sibutramine in the management of obesity: a technology assessment.
By O’Meara S, Riemsma R, Shirran L, Mather L, ter Riet G.
-
The cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance angiography for carotid artery stenosis and peripheral vascular disease: a systematic review.
By Berry E, Kelly S, Westwood ME, Davies LM, Gough MJ, Bamford JM, et al.
-
Promoting physical activity in South Asian Muslim women through ‘exercise on prescription’.
By Carroll B, Ali N, Azam N.
-
Zanamivir for the treatment of influenza in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burls A, Clark W, Stewart T, Preston C, Bryan S, Jefferson T, et al.
-
A review of the natural history and epidemiology of multiple sclerosis: implications for resource allocation and health economic models.
By Richards RG, Sampson FC, Beard SM, Tappenden P.
-
Screening for gestational diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Scott DA, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of surgery for people with morbid obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Colquitt J, Sidhu MK, Royle P, Loveman E, Walker A.
-
The clinical effectiveness of trastuzumab for breast cancer: a systematic review.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, Forbes C, Shirran E, Duffy S, Kleijnen J, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of vinorelbine for breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Lewis R, Bagnall A-M, King S, Woolacott N, Forbes C, Shirran L, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty for treatment of hip disease.
By Vale L, Wyness L, McCormack K, McKenzie L, Brazzelli M, Stearns SC.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bupropion and nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott NF, Jones L, Forbes CA, Mather LC, Sowden AJ, Song FJ, et al.
-
A systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation of new drug treatments for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: etanercept.
By Cummins C, Connock M, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cave C, Mihaylova B, Chase D, McIntyre L, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of growth hormone in adults in relation to impact on quality of life: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Loveman E, Chase D, Mihaylova B, Cave C, Gerard K, et al.
-
Clinical medication review by a pharmacist of patients on repeat prescriptions in general practice: a randomised controlled trial.
By Zermansky AG, Petty DR, Raynor DK, Lowe CJ, Freementle N, Vail A.
-
The effectiveness of infliximab and etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety.
By Kaltenthaler E, Shackley P, Stevens K, Beverley C, Parry G, Chilcott J.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride for ovarian cancer.
By Forbes C, Wilby J, Richardson G, Sculpher M, Mather L, Reimsma R.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions based on a stages-of-change approach to promote individual behaviour change.
By Riemsma RP, Pattenden J, Bridle C, Sowden AJ, Mather L, Watt IS, et al.
-
A systematic review update of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists.
By Robinson M, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Jones L, Riemsma R, Palmer S, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and barriers to implementation of thrombolytic and neuroprotective therapy for acute ischaemic stroke in the NHS.
By Sandercock P, Berge E, Dennis M, Forbes J, Hand P, Kwan J, et al.
-
A randomised controlled crossover trial of nurse practitioner versus doctor-led outpatient care in a bronchiectasis clinic.
By Caine N, Sharples LD, Hollingworth W, French J, Keogan M, Exley A, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost – consequences of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of sex offenders.
By Adi Y, Ashcroft D, Browne K, Beech A, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Treatment of established osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Brazier JE, Stevenson M, Calvert NW, Lloyd Jones M.
-
Which anaesthetic agents are cost-effective in day surgery? Literature review, national survey of practice and randomised controlled trial.
By Elliott RA Payne K, Moore JK, Davies LM, Harper NJN, St Leger AS, et al.
-
Screening for hepatitis C among injecting drug users and in genitourinary medicine clinics: systematic reviews of effectiveness, modelling study and national survey of current practice.
By Stein K, Dalziel K, Walker A, McIntyre L, Jenkins B, Horne J, et al.
-
The measurement of satisfaction with healthcare: implications for practice from a systematic review of the literature.
By Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Storey L, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia: a systematic review.
By Garside R, Round A, Dalziel K, Stein K, Royle R.
-
A comparative study of hypertonic saline, daily and alternate-day rhDNase in children with cystic fibrosis.
By Suri R, Wallis C, Bush A, Thompson S, Normand C, Flather M, et al.
-
A systematic review of the costs and effectiveness of different models of paediatric home care.
By Parker G, Bhakta P, Lovett CA, Paisley S, Olsen R, Turner D, et al.
-
How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study.
By Egger M, Jüni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of home versus hospital or satellite unit haemodialysis for people with end-stage renal failure.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Perez J, Wyness L, Fraser C, MacLeod A, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of the effectiveness of infliximab for the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
By Clark W, Raftery J, Barton P, Song F, Fry-Smith A, Burls A.
-
A review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine anti-D prophylaxis for pregnant women who are rhesus negative.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wight J, Forman K, Wray J, Beverley C, et al.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of the use of tumour markers in paediatric oncology: Ewing’s sarcoma and neuroblastoma.
By Riley RD, Burchill SA, Abrams KR, Heney D, Lambert PC, Jones DR, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for Helicobacter pylori to reduce mortality and morbidity from gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease: a discrete-event simulation model.
By Roderick P, Davies R, Raftery J, Crabbe D, Pearce R, Bhandari P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of routine dental checks: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Davenport C, Elley K, Salas C, Taylor-Weetman CL, Fry-Smith A, Bryan S, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial assessing the costs and benefits of using structured information and analysis of women’s preferences in the management of menorrhagia.
By Kennedy ADM, Sculpher MJ, Coulter A, Dwyer N, Rees M, Horsley S, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost–utility of photodynamic therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Meads C, Salas C, Roberts T, Moore D, Fry-Smith A, Hyde C.
-
Evaluation of molecular tests for prenatal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities.
By Grimshaw GM, Szczepura A, Hultén M, MacDonald F, Nevin NC, Sutton F, et al.
-
First and second trimester antenatal screening for Down’s syndrome: the results of the Serum, Urine and Ultrasound Screening Study (SURUSS).
By Wald NJ, Rodeck C, Hackshaw AK, Walters J, Chitty L, Mackinson AM.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound locating devices for central venous access: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Calvert N, Hind D, McWilliams RG, Thomas SM, Beverley C, Davidson A.
-
A systematic review of atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenia.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Lewis R, Ginnelly L, Glanville J, Torgerson D, et al.
-
Prostate Testing for Cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) feasibility study.
By Donovan J, Hamdy F, Neal D, Peters T, Oliver S, Brindle L, et al.
-
Early thrombolysis for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Boland A, Dundar Y, Bagust A, Haycox A, Hill R, Mujica Mota R, et al.
-
Screening for fragile X syndrome: a literature review and modelling.
By Song FJ, Barton P, Sleightholme V, Yao GL, Fry-Smith A.
-
Systematic review of endoscopic sinus surgery for nasal polyps.
By Dalziel K, Stein K, Round A, Garside R, Royle P.
-
Towards efficient guidelines: how to monitor guideline use in primary care.
By Hutchinson A, McIntosh A, Cox S, Gilbert C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of acute hospital-based spinal cord injuries services: systematic review.
By Bagnall A-M, Jones L, Richardson G, Duffy S, Riemsma R.
-
Prioritisation of health technology assessment. The PATHS model: methods and case studies.
By Townsend J, Buxton M, Harper G.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tension-free vaginal tape for treatment of urinary stress incontinence.
By Cody J, Wyness L, Wallace S, Glazener C, Kilonzo M, Stearns S, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of patient education models for diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Loveman E, Cave C, Green C, Royle P, Dunn N, Waugh N.
-
The role of modelling in prioritising and planning clinical trials.
By Chilcott J, Brennan A, Booth A, Karnon J, Tappenden P.
-
Cost–benefit evaluation of routine influenza immunisation in people 65–74 years of age.
By Allsup S, Gosney M, Haycox A, Regan M.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulsatile machine perfusion versus cold storage of kidneys for transplantation retrieved from heart-beating and non-heart-beating donors.
By Wight J, Chilcott J, Holmes M, Brewer N.
-
Can randomised trials rely on existing electronic data? A feasibility study to explore the value of routine data in health technology assessment.
By Williams JG, Cheung WY, Cohen DR, Hutchings HA, Longo MF, Russell IT.
-
Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies.
By Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to assess the impact of a package comprising a patient-orientated, evidence-based self- help guidebook and patient-centred consultations on disease management and satisfaction in inflammatory bowel disease.
By Kennedy A, Nelson E, Reeves D, Richardson G, Roberts C, Robinson A, et al.
-
The effectiveness of diagnostic tests for the assessment of shoulder pain due to soft tissue disorders: a systematic review.
By Dinnes J, Loveman E, McIntyre L, Waugh N.
-
The value of digital imaging in diabetic retinopathy.
By Sharp PF, Olson J, Strachan F, Hipwell J, Ludbrook A, O’Donnell M, et al.
-
Lowering blood pressure to prevent myocardial infarction and stroke: a new preventive strategy.
By Law M, Wald N, Morris J.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine and tegafur with uracil for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Kaltenthaler E, Cowan J, Brewer N.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of new and emerging technologies for early localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Hummel S, Paisley S, Morgan A, Currie E, Brewer N.
-
Literature searching for clinical and cost-effectiveness studies used in health technology assessment reports carried out for the National Institute for Clinical Excellence appraisal system.
By Royle P, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic decision modelling for the prevention and treatment of influenza A and B.
By Turner D, Wailoo A, Nicholson K, Cooper N, Sutton A, Abrams K.
-
A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the clinical and cost-effectiveness of Hickman line insertions in adult cancer patients by nurses.
By Boland A, Haycox A, Bagust A, Fitzsimmons L.
-
Redesigning postnatal care: a randomised controlled trial of protocol-based midwifery-led care focused on individual women’s physical and psychological health needs.
By MacArthur C, Winter HR, Bick DE, Lilford RJ, Lancashire RJ, Knowles H, et al.
-
Estimating implied rates of discount in healthcare decision-making.
By West RR, McNabb R, Thompson AGH, Sheldon TA, Grimley Evans J.
-
Systematic review of isolation policies in the hospital management of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review of the literature with epidemiological and economic modelling.
By Cooper BS, Stone SP, Kibbler CC, Cookson BD, Roberts JA, Medley GF, et al.
-
Treatments for spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.
By Beard S, Hunn A, Wight J.
-
The inclusion of reports of randomised trials published in languages other than English in systematic reviews.
By Moher D, Pham B, Lawson ML, Klassen TP.
-
The impact of screening on future health-promoting behaviours and health beliefs: a systematic review.
By Bankhead CR, Brett J, Bukach C, Webster P, Stewart-Brown S, Munafo M, et al.
-
What is the best imaging strategy for acute stroke?
By Wardlaw JM, Keir SL, Seymour J, Lewis S, Sandercock PAG, Dennis MS, et al.
-
Systematic review and modelling of the investigation of acute and chronic chest pain presenting in primary care.
By Mant J, McManus RJ, Oakes RAL, Delaney BC, Barton PM, Deeks JJ, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of microwave and thermal balloon endometrial ablation for heavy menstrual bleeding: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Stein K, Wyatt K, Round A, Price A.
-
A systematic review of the role of bisphosphonates in metastatic disease.
By Ross JR, Saunders Y, Edmonds PM, Patel S, Wonderling D, Normand C, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of capecitabine (Xeloda®) for locally advanced and/or metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones L, Hawkins N, Westwood M, Wright K, Richardson G, Riemsma R.
-
Effectiveness and efficiency of guideline dissemination and implementation strategies.
By Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE, MacLennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay CR, Vale L, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and costs of the Sugarbaker procedure for the treatment of pseudomyxoma peritonei.
By Bryant J, Clegg AJ, Sidhu MK, Brodin H, Royle P, Davidson P.
-
Psychological treatment for insomnia in the regulation of long-term hypnotic drug use.
By Morgan K, Dixon S, Mathers N, Thompson J, Tomeny M.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: development of a patient-based measure of outcome.
By Hobart JC, Riazi A, Lamping DL, Fitzpatrick R, Thompson AJ.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography compared with diagnostic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
By Kaltenthaler E, Bravo Vergel Y, Chilcott J, Thomas S, Blakeborough T, Walters SJ, et al.
-
The use of modelling to evaluate new drugs for patients with a chronic condition: the case of antibodies against tumour necrosis factor in rheumatoid arthritis.
By Barton P, Jobanputra P, Wilson J, Bryan S, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: a systematic review.
By Pandor A, Eastham J, Beverley C, Chilcott J, Paisley S.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Czoski-Murray C, Warren E, Chilcott J, Beverley C, Psyllaki MA, Cowan J.
-
Routine examination of the newborn: the EMREN study. Evaluation of an extension of the midwife role including a randomised controlled trial of appropriately trained midwives and paediatric senior house officers.
By Townsend J, Wolke D, Hayes J, Davé S, Rogers C, Bloomfield L, et al.
-
Involving consumers in research and development agenda setting for the NHS: developing an evidence-based approach.
By Oliver S, Clarke-Jones L, Rees R, Milne R, Buchanan P, Gabbay J, et al.
-
A multi-centre randomised controlled trial of minimally invasive direct coronary bypass grafting versus percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting for proximal stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery.
By Reeves BC, Angelini GD, Bryan AJ, Taylor FC, Cripps T, Spyt TJ, et al.
-
Does early magnetic resonance imaging influence management or improve outcome in patients referred to secondary care with low back pain? A pragmatic randomised controlled trial.
By Gilbert FJ, Grant AM, Gillan MGC, Vale L, Scott NW, Campbell MK, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of anakinra for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Clark W, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Burls A.
-
A rapid and systematic review and economic evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for treatment of mania associated with bipolar affective disorder.
By Bridle C, Palmer S, Bagnall A-M, Darba J, Duffy S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Liquid-based cytology in cervical screening: an updated rapid and systematic review and economic analysis.
By Karnon J, Peters J, Platt J, Chilcott J, McGoogan E, Brewer N.
-
Systematic review of the long-term effects and economic consequences of treatments for obesity and implications for health improvement.
By Avenell A, Broom J, Brown TJ, Poobalan A, Aucott L, Stearns SC, et al.
-
Autoantibody testing in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus.
By Dretzke J, Cummins C, Sandercock J, Fry-Smith A, Barrett T, Burls A.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prehospital intravenous fluids in trauma patients.
By Dretzke J, Sandercock J, Bayliss S, Burls A.
-
Newer hypnotic drugs for the short-term management of insomnia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dündar Y, Boland A, Strobl J, Dodd S, Haycox A, Bagust A, et al.
-
Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies.
By Whiting P, Rutjes AWS, Dinnes J, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PMM, Kleijnen J.
-
EVALUATE hysterectomy trial: a multicentre randomised trial comparing abdominal, vaginal and laparoscopic methods of hysterectomy.
By Garry R, Fountain J, Brown J, Manca A, Mason S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Methods for expected value of information analysis in complex health economic models: developments on the health economics of interferon-β and glatiramer acetate for multiple sclerosis.
By Tappenden P, Chilcott JB, Eggington S, Oakley J, McCabe C.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib for first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Price A.
-
VenUS I: a randomised controlled trial of two types of bandage for treating venous leg ulcers.
By Iglesias C, Nelson EA, Cullum NA, Torgerson DJ, on behalf of the VenUS Team.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for the diagnosis and management of angina and myocardial infarction.
By Mowatt G, Vale L, Brazzelli M, Hernandez R, Murray A, Scott N, et al.
-
A pilot study on the use of decision theory and value of information analysis as part of the NHS Health Technology Assessment programme.
By Claxton K, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Palmer S.
-
The Social Support and Family Health Study: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of two alternative forms of postnatal support for mothers living in disadvantaged inner-city areas.
By Wiggins M, Oakley A, Roberts I, Turner H, Rajan L, Austerberry H, et al.
-
Psychosocial aspects of genetic screening of pregnant women and newborns: a systematic review.
By Green JM, Hewison J, Bekker HL, Bryant, Cuckle HS.
-
Evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: comparison of three outpatient procedures within cohorts defined by age and menopausal status.
By Critchley HOD, Warner P, Lee AJ, Brechin S, Guise J, Graham B.
-
Coronary artery stents: a rapid systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill R, Bagust A, Bakhai A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, et al.
-
Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment.
By Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al.
-
Rituximab (MabThera®) for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Knight C, Hind D, Brewer N, Abbott V.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of clopidogrel and modified-release dipyridamole in the secondary prevention of occlusive vascular events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones L, Griffin S, Palmer S, Main C, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Pegylated interferon α-2a and -2b in combination with ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Brodin H, Cave C, Waugh N, Price A, Gabbay J.
-
Clopidogrel used in combination with aspirin compared with aspirin alone in the treatment of non-ST-segment- elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Palmer S, Griffin S, Jones L, Orton V, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Provision, uptake and cost of cardiac rehabilitation programmes: improving services to under-represented groups.
By Beswick AD, Rees K, Griebsch I, Taylor FC, Burke M, West RR, et al.
-
Involving South Asian patients in clinical trials.
By Hussain-Gambles M, Leese B, Atkin K, Brown J, Mason S, Tovey P.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes.
By Colquitt JL, Green C, Sidhu MK, Hartwell D, Waugh N.
-
Identification and assessment of ongoing trials in health technology assessment reviews.
By Song FJ, Fry-Smith A, Davenport C, Bayliss S, Adi Y, Wilson JS, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of a long-acting insulin analogue, insulin glargine
By Warren E, Weatherley-Jones E, Chilcott J, Beverley C.
-
Supplementation of a home-based exercise programme with a class-based programme for people with osteoarthritis of the knees: a randomised controlled trial and health economic analysis.
By McCarthy CJ, Mills PM, Pullen R, Richardson G, Hawkins N, Roberts CR, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of once-daily versus more frequent use of same potency topical corticosteroids for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Davidson P, Payne E.
-
Acupuncture of chronic headache disorders in primary care: randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By Vickers AJ, Rees RW, Zollman CE, McCarney R, Smith CM, Ellis N, et al.
-
Generalisability in economic evaluation studies in healthcare: a review and case studies.
By Sculpher MJ, Pang FS, Manca A, Drummond MF, Golder S, Urdahl H, et al.
-
Virtual outreach: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of joint teleconferenced medical consultations.
By Wallace P, Barber J, Clayton W, Currell R, Fleming K, Garner P, et al.
-
Randomised controlled multiple treatment comparison to provide a cost-effectiveness rationale for the selection of antimicrobial therapy in acne.
By Ozolins M, Eady EA, Avery A, Cunliffe WJ, O’Neill C, Simpson NB, et al.
-
Do the findings of case series studies vary significantly according to methodological characteristics?
By Dalziel K, Round A, Stein K, Garside R, Castelnuovo E, Payne L.
-
Improving the referral process for familial breast cancer genetic counselling: findings of three randomised controlled trials of two interventions.
By Wilson BJ, Torrance N, Mollison J, Wordsworth S, Gray JR, Haites NE, et al.
-
Randomised evaluation of alternative electrosurgical modalities to treat bladder outflow obstruction in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
By Fowler C, McAllister W, Plail R, Karim O, Yang Q.
-
A pragmatic randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of palliative therapies for patients with inoperable oesophageal cancer.
By Shenfine J, McNamee P, Steen N, Bond J, Griffin SM.
-
Impact of computer-aided detection prompts on the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
By Taylor P, Champness J, Given- Wilson R, Johnston K, Potts H.
-
Issues in data monitoring and interim analysis of trials.
By Grant AM, Altman DG, Babiker AB, Campbell MK, Clemens FJ, Darbyshire JH, et al.
-
Lay public’s understanding of equipoise and randomisation in randomised controlled trials.
By Robinson EJ, Kerr CEP, Stevens AJ, Lilford RJ, Braunholtz DA, Edwards SJ, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of electroconvulsive therapy for depressive illness, schizophrenia, catatonia and mania: systematic reviews and economic modelling studies.
By Greenhalgh J, Knight C, Hind D, Beverley C, Walters S.
-
Measurement of health-related quality of life for people with dementia: development of a new instrument (DEMQOL) and an evaluation of current methodology.
By Smith SC, Lamping DL, Banerjee S, Harwood R, Foley B, Smith P, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of drotrecogin alfa (activated) (Xigris®) for the treatment of severe sepsis in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Green C, Dinnes J, Takeda A, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Cave C, et al.
-
A methodological review of how heterogeneity has been examined in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kirby J, Roderick P.
-
Cervical screening programmes: can automation help? Evidence from systematic reviews, an economic analysis and a simulation modelling exercise applied to the UK.
By Willis BH, Barton P, Pearmain P, Bryan S, Hyde C.
-
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair: systematic review of effectiveness and economic evaluation.
By McCormack K, Wake B, Perez J, Fraser C, Cook J, McIntosh E, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness, tolerability and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for epilepsy in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilby J, Kainth A, Hawkins N, Epstein D, McIntosh H, McDaid C, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare the cost-effectiveness of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and lofepramine.
By Peveler R, Kendrick T, Buxton M, Longworth L, Baldwin D, Moore M, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of immediate angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hartwell D, Colquitt J, Loveman E, Clegg AJ, Brodin H, Waugh N, et al.
-
A randomised controlled comparison of alternative strategies in stroke care.
By Kalra L, Evans A, Perez I, Knapp M, Swift C, Donaldson N.
-
The investigation and analysis of critical incidents and adverse events in healthcare.
By Woloshynowych M, Rogers S, Taylor-Adams S, Vincent C.
-
Potential use of routine databases in health technology assessment.
By Raftery J, Roderick P, Stevens A.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of newer immunosuppressive regimens in renal transplantation: a systematic review and modelling study.
By Woodroffe R, Yao GL, Meads C, Bayliss S, Ready A, Raftery J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd Jones M, De Nigris E, Brewer N, Davis S, Oakley J.
-
A systematic review to examine the impact of psycho-educational interventions on health outcomes and costs in adults and children with difficult asthma.
By Smith JR, Mugford M, Holland R, Candy B, Noble MJ, Harrison BDW, et al.
-
An evaluation of the costs, effectiveness and quality of renal replacement therapy provision in renal satellite units in England and Wales.
By Roderick P, Nicholson T, Armitage A, Mehta R, Mullee M, Gerard K, et al.
-
Imatinib for the treatment of patients with unresectable and/or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wilson J, Connock M, Song F, Yao G, Fry-Smith A, Raftery J, et al.
-
Indirect comparisons of competing interventions.
By Glenny AM, Altman DG, Song F, Sakarovitch C, Deeks JJ, D’Amico R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of alternative strategies for the initial medical management of non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: systematic review and decision-analytical modelling.
By Robinson M, Palmer S, Sculpher M, Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Bowens A, et al.
-
Outcomes of electrically stimulated gracilis neosphincter surgery.
By Tillin T, Chambers M, Feldman R.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of pimecrolimus and tacrolimus for atopic eczema: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Stein K, Castelnuovo E, Pitt M, Ashcroft D, Dimmock P, et al.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.
By Newman DJ, Mattock MB, Dawnay ABS, Kerry S, McGuire A, Yaqoob M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the cost-effectiveness of water-based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis.
By Cochrane T, Davey RC, Matthes Edwards SM.
-
Longer term clinical and economic benefits of offering acupuncture care to patients with chronic low back pain.
By Thomas KJ, MacPherson H, Ratcliffe J, Thorpe L, Brazier J, Campbell M, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness and safety of epidural steroids in the management of sciatica.
By Price C, Arden N, Coglan L, Rogers P.
-
The British Rheumatoid Outcome Study Group (BROSG) randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of aggressive versus symptomatic therapy in established rheumatoid arthritis.
By Symmons D, Tricker K, Roberts C, Davies L, Dawes P, Scott DL.
-
Conceptual framework and systematic review of the effects of participants’ and professionals’ preferences in randomised controlled trials.
By King M, Nazareth I, Lampe F, Bower P, Chandler M, Morou M, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of implantable cardioverter defibrillators: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Brodin H, Loveman E, Payne E, Clegg A.
-
A trial of problem-solving by community mental health nurses for anxiety, depression and life difficulties among general practice patients. The CPN-GP study.
By Kendrick T, Simons L, Mynors-Wallis L, Gray A, Lathlean J, Pickering R, et al.
-
The causes and effects of socio-demographic exclusions from clinical trials.
By Bartlett C, Doyal L, Ebrahim S, Davey P, Bachmann M, Egger M, et al.
-
Is hydrotherapy cost-effective? A randomised controlled trial of combined hydrotherapy programmes compared with physiotherapy land techniques in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
By Epps H, Ginnelly L, Utley M, Southwood T, Gallivan S, Sculpher M, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness study of systematic screening (targeted and total population screening) versus routine practice for the detection of atrial fibrillation in people aged 65 and over. The SAFE study.
By Hobbs FDR, Fitzmaurice DA, Mant J, Murray E, Jowett S, Bryan S, et al.
-
Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty.
By Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW, Forbes JF.
-
Long-term outcome of cognitive behaviour therapy clinical trials in central Scotland.
By Durham RC, Chambers JA, Power KG, Sharp DM, Macdonald RR, Major KA, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of dual-chamber pacemakers compared with single-chamber pacemakers for bradycardia due to atrioventricular block or sick sinus syndrome: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Castelnuovo E, Stein K, Pitt M, Garside R, Payne E.
-
Newborn screening for congenital heart defects: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Knowles R, Griebsch I, Dezateux C, Brown J, Bull C, Wren C.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of left ventricular assist devices for end-stage heart failure: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clegg AJ, Scott DA, Loveman E, Colquitt J, Hutchinson J, Royle P, et al.
-
The effectiveness of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph and laser diagnostic glaucoma scanning system (GDx) in detecting and monitoring glaucoma.
By Kwartz AJ, Henson DB, Harper RA, Spencer AF, McLeod D.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage defects in knee joints: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Clar C, Cummins E, McIntyre L, Thomas S, Lamb J, Bain L, et al.
-
Systematic review of effectiveness of different treatments for childhood retinoblastoma.
By McDaid C, Hartley S, Bagnall A-M, Ritchie G, Light K, Riemsma R.
-
Towards evidence-based guidelines for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: systematic reviews of mechanical methods, oral anticoagulation, dextran and regional anaesthesia as thromboprophylaxis.
By Roderick P, Ferris G, Wilson K, Halls H, Jackson D, Collins R, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of parent training/education programmes for the treatment of conduct disorder, including oppositional defiant disorder, in children.
By Dretzke J, Frew E, Davenport C, Barlow J, Stewart-Brown S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine for Alzheimer’s disease.
By Loveman E, Green C, Kirby J, Takeda A, Picot J, Payne E, et al.
-
FOOD: a multicentre randomised trial evaluating feeding policies in patients admitted to hospital with a recent stroke.
By Dennis M, Lewis S, Cranswick G, Forbes J.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for lung cancer: systematic reviews.
By Black C, Bagust A, Boland A, Walker S, McLeod C, De Verteuil R, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neuroimaging assessments used to visualise the seizure focus in people with refractory epilepsy being considered for surgery.
By Whiting P, Gupta R, Burch J, Mujica Mota RE, Wright K, Marson A, et al.
-
Comparison of conference abstracts and presentations with full-text articles in the health technology assessments of rapidly evolving technologies.
By Dundar Y, Dodd S, Dickson R, Walley T, Haycox A, Williamson PR.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of methods of assessing urinary incontinence.
By Martin JL, Williams KS, Abrams KR, Turner DA, Sutton AJ, Chapple C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for children with epilepsy. A systematic review.
By Connock M, Frew E, Evans B-W, Bryan S, Cummins C, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Surveillance of Barrett’s oesophagus: exploring the uncertainty through systematic review, expert workshop and economic modelling.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Somerville M, Stein K, Price A, Gilbert N.
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Main C, Bojke L, Griffin S, Norman G, Barbieri M, Mather L, et al.
-
Evaluation of molecular techniques in prediction and diagnosis of cytomegalovirus disease in immunocompromised patients.
By Szczepura A, Westmoreland D, Vinogradova Y, Fox J, Clark M.
-
Screening for thrombophilia in high-risk situations: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. The Thrombosis: Risk and Economic Assessment of Thrombophilia Screening (TREATS) study.
By Wu O, Robertson L, Twaddle S, Lowe GDO, Clark P, Greaves M, et al.
-
A series of systematic reviews to inform a decision analysis for sampling and treating infected diabetic foot ulcers.
By Nelson EA, O’Meara S, Craig D, Iglesias C, Golder S, Dalton J, et al.
-
Randomised clinical trial, observational study and assessment of cost-effectiveness of the treatment of varicose veins (REACTIV trial).
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, Brazier JE, MacIntyre JB, Palfreyman SJ, Ratcliffe J, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for oral cancer in primary care.
By Speight PM, Palmer S, Moles DR, Downer MC, Smith DH, Henriksson M, et al.
-
Measurement of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of non-invasive diagnostic testing strategies for deep vein thrombosis.
By Goodacre S, Sampson F, Stevenson M, Wailoo A, Sutton A, Thomas S, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of HealOzone® for the treatment of occlusal pit/fissure caries and root caries.
By Brazzelli M, McKenzie L, Fielding S, Fraser C, Clarkson J, Kilonzo M, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trials of conventional antipsychotic versus new atypical drugs, and new atypical drugs versus clozapine, in people with schizophrenia responding poorly to, or intolerant of, current drug treatment.
By Lewis SW, Davies L, Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Murray RM, Kerwin R, et al.
-
Diagnostic tests and algorithms used in the investigation of haematuria: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Nixon J, Hempel S, Aho T, Kelly J, Neal D, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in addition to antispasmodic therapy for irritable bowel syndrome in primary care: randomised controlled trial.
By Kennedy TM, Chalder T, McCrone P, Darnley S, Knapp M, Jones RH, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapies for Fabry’s disease and mucopolysaccharidosis type 1.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Frew E, Mans A, Dretzke J, Fry-Smith A, et al.
-
Health benefits of antiviral therapy for mild chronic hepatitis C: randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation.
By Wright M, Grieve R, Roberts J, Main J, Thomas HC, on behalf of the UK Mild Hepatitis C Trial Investigators.
-
Pressure relieving support surfaces: a randomised evaluation.
By Nixon J, Nelson EA, Cranny G, Iglesias CP, Hawkins K, Cullum NA, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methylphenidate, dexamfetamine and atomoxetine for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.
By King S, Griffin S, Hodges Z, Weatherly H, Asseburg C, Richardson G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher’s disease: a systematic review.
By Connock M, Burls A, Frew E, Fry-Smith A, Juarez-Garcia A, McCabe C, et al.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of salicylic acid and cryotherapy for cutaneous warts. An economic decision model.
By Thomas KS, Keogh-Brown MR, Chalmers JR, Fordham RJ, Holland RC, Armstrong SJ, et al.
-
A systematic literature review of the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to prevent wandering in dementia and evaluation of the ethical implications and acceptability of their use.
By Robinson L, Hutchings D, Corner L, Beyer F, Dickinson H, Vanoli A, et al.
-
A review of the evidence on the effects and costs of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in different patient groups, and modelling of cost-effectiveness and cost–utility for these groups in a UK context.
By Buxton M, Caine N, Chase D, Connelly D, Grace A, Jackson C, et al.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Takeda A, Davidson P, Price A.
-
An evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of pulmonary artery catheters in patient management in intensive care: a systematic review and a randomised controlled trial.
By Harvey S, Stevens K, Harrison D, Young D, Brampton W, McCabe C, et al.
-
Accurate, practical and cost-effective assessment of carotid stenosis in the UK.
By Wardlaw JM, Chappell FM, Stevenson M, De Nigris E, Thomas S, Gillard J, et al.
-
Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Woolacott N, Bravo Vergel Y, Hawkins N, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Misso K, et al.
-
The cost-effectiveness of testing for hepatitis C in former injecting drug users.
By Castelnuovo E, Thompson-Coon J, Pitt M, Cramp M, Siebert U, Price A, et al.
-
Computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for depression and anxiety update: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Kaltenthaler E, Brazier J, De Nigris E, Tumur I, Ferriter M, Beverley C, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.
By Williams C, Brunskill S, Altman D, Briggs A, Campbell H, Clarke M, et al.
-
Psychological therapies including dialectical behaviour therapy for borderline personality disorder: a systematic review and preliminary economic evaluation.
By Brazier J, Tumur I, Holmes M, Ferriter M, Parry G, Dent-Brown K, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tests for the diagnosis and investigation of urinary tract infection in children: a systematic review and economic model.
By Whiting P, Westwood M, Bojke L, Palmer S, Richardson G, Cooper J, et al.
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy in chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomised controlled trial of an outpatient group programme.
By O’Dowd H, Gladwell P, Rogers CA, Hollinghurst S, Gregory A.
-
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling.
By Brown TJ, Hooper L, Elliott RA, Payne K, Webb R, Roberts C, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for coronary artery disease: systematic review.
By Waugh N, Black C, Walker S, McIntyre L, Cummins E, Hillis G.
-
What are the clinical outcome and cost-effectiveness of endoscopy undertaken by nurses when compared with doctors? A Multi-Institution Nurse Endoscopy Trial (MINuET).
By Williams J, Russell I, Durai D, Cheung W-Y, Farrin A, Bloor K, et al.
-
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin and capecitabine for the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pandor A, Eggington S, Paisley S, Tappenden P, Sutcliffe P.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W, et al.
-
Telemedicine in dermatology: a randomised controlled trial.
By Bowns IR, Collins K, Walters SJ, McDonagh AJG.
-
Cost-effectiveness of cell salvage and alternative methods of minimising perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion: a systematic review and economic model.
By Davies L, Brown TJ, Haynes S, Payne K, Elliott RA, McCollum C.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.
By Murray A, Lourenco T, de Verteuil R, Hernandez R, Fraser C, McKinley A, et al.
-
Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review.
By Woolacott N, Hawkins N, Mason A, Kainth A, Khadjesari Z, Bravo Vergel Y, et al.
-
Systematic reviews of clinical decision tools for acute abdominal pain.
By Liu JLY, Wyatt JC, Deeks JJ, Clamp S, Keen J, Verde P, et al.
-
Evaluation of the ventricular assist device programme in the UK.
By Sharples L, Buxton M, Caine N, Cafferty F, Demiris N, Dyer M, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapy for renal transplantation in children.
By Yao G, Albon E, Adi Y, Milford D, Bayliss S, Ready A, et al.
-
Amniocentesis results: investigation of anxiety. The ARIA trial.
By Hewison J, Nixon J, Fountain J, Cocks K, Jones C, Mason G, et al.
-
Pemetrexed disodium for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Dickson R, Dodd S, Green J, Haycox A, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of docetaxel in combination with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer.
By Collins R, Fenwick E, Trowman R, Perard R, Norman G, Light K, et al.
-
A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection.
By Dinnes J, Deeks J, Kunst H, Gibson A, Cummins E, Waugh N, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women.
By Stevenson M, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M, Beverley C.
-
A systematic review of quantitative and qualitative research on the role and effectiveness of written information available to patients about individual medicines.
By Raynor DK, Blenkinsopp A, Knapp P, Grime J, Nicolson DJ, Pollock K, et al.
-
Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Adi Y, Juarez-Garcia A, Wang D, Jowett S, Frew E, Day E, et al.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost–utility analysis.
By Kanis JA, Stevenson M, McCloskey EV, Davis S, Lloyd-Jones M.
-
Epidemiological, social, diagnostic and economic evaluation of population screening for genital chlamydial infection.
By Low N, McCarthy A, Macleod J, Salisbury C, Campbell R, Roberts TE, et al.
-
Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Connock M, Juarez-Garcia A, Jowett S, Frew E, Liu Z, Taylor RJ, et al.
-
Exercise Evaluation Randomised Trial (EXERT): a randomised trial comparing GP referral for leisure centre-based exercise, community-based walking and advice only.
By Isaacs AJ, Critchley JA, See Tai S, Buckingham K, Westley D, Harridge SDR, et al.
-
Interferon alfa (pegylated and non-pegylated) and ribavirin for the treatment of mild chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Hartwell D, Davidson P, Price A, Waugh N.
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of bevacizumab and cetuximab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
By Tappenden P, Jones R, Paisley S, Carroll C.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of epoetin alfa, epoetin beta and darbepoetin alfa in anaemia associated with cancer, especially that attributable to cancer treatment.
By Wilson J, Yao GL, Raftery J, Bohlius J, Brunskill S, Sandercock J, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of statins for the prevention of coronary events.
By Ward S, Lloyd Jones M, Pandor A, Holmes M, Ara R, Ryan A, et al.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of community-based respite care for frail older people and their carers.
By Mason A, Weatherly H, Spilsbury K, Arksey H, Golder S, Adamson J, et al.
-
Additional therapy for young children with spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial.
By Weindling AM, Cunningham CC, Glenn SM, Edwards RT, Reeves DJ.
-
Screening for type 2 diabetes: literature review and economic modelling.
By Waugh N, Scotland G, McNamee P, Gillett M, Brennan A, Goyder E, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cinacalcet for secondary hyperparathyroidism in end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Mealing S, Roome C, Snaith A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Takeda AL, Jones J, Loveman E, Tan SC, Clegg AJ.
-
A systematic review of duplex ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease.
By Collins R, Cranny G, Burch J, Aguiar-Ibáñez R, Craig D, Wright K, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treatments for children with idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a systematic review.
By Colquitt JL, Kirby J, Green C, Cooper K, Trompeter RS.
-
A systematic review of the routine monitoring of growth in children of primary school age to identify growth-related conditions.
By Fayter D, Nixon J, Hartley S, Rithalia A, Butler G, Rudolf M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness of preventing and treating Staphylococcus aureus carriage in reducing peritoneal catheter-related infections.
By McCormack K, Rabindranath K, Kilonzo M, Vale L, Fraser C, McIntyre L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation versus electroconvulsive therapy in severe depression: a multicentre pragmatic randomised controlled trial and economic analysis.
By McLoughlin DM, Mogg A, Eranti S, Pluck G, Purvis R, Edwards D, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of direct versus indirect and individual versus group modes of speech and language therapy for children with primary language impairment.
By Boyle J, McCartney E, Forbes J, O’Hare A.
-
Hormonal therapies for early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Ward S, De Nigris E, Simpson E, Carroll C, Wyld L.
-
Cardioprotection against the toxic effects of anthracyclines given to children with cancer: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Picot J, Levitt G, Sullivan I, Baxter L, Clegg A.
-
Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Dagenais P, Dickson R, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Prenatal screening and treatment strategies to prevent group B streptococcal and other bacterial infections in early infancy: cost-effectiveness and expected value of information analyses.
By Colbourn T, Asseburg C, Bojke L, Philips Z, Claxton K, Ades AE, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bone morphogenetic proteins in the non-healing of fractures and spinal fusion: a systematic review.
By Garrison KR, Donell S, Ryder J, Shemilt I, Mugford M, Harvey I, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of postoperative radiotherapy following breast-conserving surgery in a minimum-risk older population. The PRIME trial.
By Prescott RJ, Kunkler IH, Williams LJ, King CC, Jack W, van der Pol M, et al.
-
Current practice, accuracy, effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the school entry hearing screen.
By Bamford J, Fortnum H, Bristow K, Smith J, Vamvakas G, Davies L, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of inhaled insulin in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Cummins E, Royle P, Philip S, Waugh N.
-
Surveillance of cirrhosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and economic analysis.
By Thompson Coon J, Rogers G, Hewson P, Wright D, Anderson R, Cramp M, et al.
-
The Birmingham Rehabilitation Uptake Maximisation Study (BRUM). Homebased compared with hospital-based cardiac rehabilitation in a multi-ethnic population: cost-effectiveness and patient adherence.
By Jolly K, Taylor R, Lip GYH, Greenfield S, Raftery J, Mant J, et al.
-
A systematic review of the clinical, public health and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection and identification of bacterial intestinal pathogens in faeces and food.
By Abubakar I, Irvine L, Aldus CF, Wyatt GM, Fordham R, Schelenz S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial examining the longer-term outcomes of standard versus new antiepileptic drugs. The SANAD trial.
By Marson AG, Appleton R, Baker GA, Chadwick DW, Doughty J, Eaton B, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different models of managing long-term oral anti-coagulation therapy: a systematic review and economic modelling.
By Connock M, Stevens C, Fry-Smith A, Jowett S, Fitzmaurice D, Moore D, et al.
-
A systematic review and economic model of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of interventions for preventing relapse in people with bipolar disorder.
By Soares-Weiser K, Bravo Vergel Y, Beynon S, Dunn G, Barbieri M, Duffy S, et al.
-
Taxanes for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ward S, Simpson E, Davis S, Hind D, Rees A, Wilkinson A.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening for open angle glaucoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burr JM, Mowatt G, Hernández R, Siddiqui MAR, Cook J, Lourenco T, et al.
-
Acceptability, benefit and costs of early screening for hearing disability: a study of potential screening tests and models.
By Davis A, Smith P, Ferguson M, Stephens D, Gianopoulos I.
-
Contamination in trials of educational interventions.
By Keogh-Brown MR, Bachmann MO, Shepstone L, Hewitt C, Howe A, Ramsay CR, et al.
-
Overview of the clinical effectiveness of positron emission tomography imaging in selected cancers.
By Facey K, Bradbury I, Laking G, Payne E.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Garside R, Pitt M, Anderson R, Rogers G, Dyer M, Mealing S, et al.
-
Drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hill RA, Boland A, Dickson R, Dündar Y, Haycox A, McLeod C, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cardiac resynchronisation (biventricular pacing) for heart failure: systematic review and economic model.
By Fox M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Dean J, Stein K, Price A, et al.
-
Recruitment to randomised trials: strategies for trial enrolment and participation study. The STEPS study.
By Campbell MK, Snowdon C, Francis D, Elbourne D, McDonald AM, Knight R, et al.
-
Cost-effectiveness of functional cardiac testing in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease: a randomised controlled trial. The CECaT trial.
By Sharples L, Hughes V, Crean A, Dyer M, Buxton M, Goldsmith K, et al.
-
Evaluation of diagnostic tests when there is no gold standard. A review of methods.
By Rutjes AWS, Reitsma JB, Coomarasamy A, Khan KS, Bossuyt PMM.
-
Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
By Leontiadis GI, Sreedharan A, Dorward S, Barton P, Delaney B, Howden CW, et al.
-
A review and critique of modelling in prioritising and designing screening programmes.
By Karnon J, Goyder E, Tappenden P, McPhie S, Towers I, Brazier J, et al.
-
An assessment of the impact of the NHS Health Technology Assessment Programme.
By Hanney S, Buxton M, Green C, Coulson D, Raftery J.
-
A systematic review and economic model of switching from nonglycopeptide to glycopeptide antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery.
By Cranny G, Elliott R, Weatherly H, Chambers D, Hawkins N, Myers L, et al.
-
‘Cut down to quit’ with nicotine replacement therapies in smoking cessation: a systematic review of effectiveness and economic analysis.
By Wang D, Connock M, Barton P, Fry-Smith A, Aveyard P, Moore D.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of strategies for reducing fracture risk in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis with additional data on long-term risk of fracture and cost of disease management.
By Thornton J, Ashcroft D, O’Neill T, Elliott R, Adams J, Roberts C, et al.
-
Does befriending by trained lay workers improve psychological well-being and quality of life for carers of people with dementia, and at what cost? A randomised controlled trial.
By Charlesworth G, Shepstone L, Wilson E, Thalanany M, Mugford M, Poland F.
-
A multi-centre retrospective cohort study comparing the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of hysterectomy and uterine artery embolisation for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids. The HOPEFUL study.
By Hirst A, Dutton S, Wu O, Briggs A, Edwards C, Waldenmaier L, et al.
-
Methods of prediction and prevention of pre-eclampsia: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Meads CA, Cnossen JS, Meher S, Juarez-Garcia A, ter Riet G, Duley L, et al.
-
The use of economic evaluations in NHS decision-making: a review and empirical investigation.
By Williams I, McIver S, Moore D, Bryan S.
-
Stapled haemorrhoidectomy (haemorrhoidopexy) for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Epstein D, Baba-Akbari A, Weatherly H, Fox D, Golder S, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of diabetes education models for Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.
By Loveman E, Frampton GK, Clegg AJ.
-
Payment to healthcare professionals for patient recruitment to trials: systematic review and qualitative study.
By Raftery J, Bryant J, Powell J, Kerr C, Hawker S.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Fry-Smith A, Harris G, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of central venous catheters treated with anti-infective agents in preventing bloodstream infections: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hockenhull JC, Dwan K, Boland A, Smith G, Bagust A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Stepped treatment of older adults on laxatives. The STOOL trial.
By Mihaylov S, Stark C, McColl E, Steen N, Vanoli A, Rubin G, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial of cognitive behaviour therapy in adolescents with major depression treated by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. The ADAPT trial.
By Goodyer IM, Dubicka B, Wilkinson P, Kelvin R, Roberts C, Byford S, et al.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Tumur I, Eggington E, Sutcliffe P, Ryan A.
-
Ranibizumab and pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Colquitt JL, Jones J, Tan SC, Takeda A, Clegg AJ, Price A.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of 64-slice or higher computed tomography angiography as an alternative to invasive coronary angiography in the investigation of coronary artery disease.
By Mowatt G, Cummins E, Waugh N, Walker S, Cook J, Jia X, et al.
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Albon E, Tsourapas A, Frew E, Davenport C, Oyebode F, Bayliss S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and over.
By Shepherd J, Rogers G, Anderson R, Main C, Thompson-Coon J, Hartwell D, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years.
By Main C, Shepherd J, Anderson R, Rogers G, Thompson-Coon J, Liu Z, et al.
-
Ezetimibe for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Tumur I, Pandor A, Duenas A, Williams R, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
Topical or oral ibuprofen for chronic knee pain in older people. The TOIB study.
By Underwood M, Ashby D, Carnes D, Castelnuovo E, Cross P, Harding G, et al.
-
A prospective randomised comparison of minor surgery in primary and secondary care. The MiSTIC trial.
By George S, Pockney P, Primrose J, Smith H, Little P, Kinley H, et al.
-
A review and critical appraisal of measures of therapist–patient interactions in mental health settings.
By Cahill J, Barkham M, Hardy G, Gilbody S, Richards D, Bower P, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of screening programmes for amblyopia and strabismus in children up to the age of 4–5 years: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Carlton J, Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith KJ, Marr J.
-
A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness and economic modelling of minimal incision total hip replacement approaches in the management of arthritic disease of the hip.
By de Verteuil R, Imamura M, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Munro N, et al.
-
A preliminary model-based assessment of the cost–utility of a screening programme for early age-related macular degeneration.
By Karnon J, Czoski-Murray C, Smith K, Brand C, Chakravarthy U, Davis S, et al.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Jones J, Frampton GK, Tanajewski L, Turner D, Price A.
-
Absorbent products for urinary/faecal incontinence: a comparative evaluation of key product categories.
By Fader M, Cottenden A, Getliffe K, Gage H, Clarke-O’Neill S, Jamieson K, et al.
-
A systematic review of repetitive functional task practice with modelling of resource use, costs and effectiveness.
By French B, Leathley M, Sutton C, McAdam J, Thomas L, Forster A, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectivness of minimal access surgery amongst people with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease – a UK collaborative study. The reflux trial.
By Grant A, Wileman S, Ramsay C, Bojke L, Epstein D, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Time to full publication of studies of anti-cancer medicines for breast cancer and the potential for publication bias: a short systematic review.
By Takeda A, Loveman E, Harris P, Hartwell D, Welch K.
-
Performance of screening tests for child physical abuse in accident and emergency departments.
By Woodman J, Pitt M, Wentz R, Taylor B, Hodes D, Gilbert RE.
-
Curative catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation and typical atrial flutter: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, McKenna C, Palmer S, Chambers D, Van Hout S, Golder S, et al.
-
Systematic review and economic modelling of effectiveness and cost utility of surgical treatments for men with benign prostatic enlargement.
By Lourenco T, Armstrong N, N’Dow J, Nabi G, Deverill M, Pickard R, et al.
-
Immunoprophylaxis against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) with palivizumab in children: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Wang D, Cummins C, Bayliss S, Sandercock J, Burls A.
-
Deferasirox for the treatment of iron overload associated with regular blood transfusions (transfusional haemosiderosis) in patients suffering with chronic anaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By McLeod C, Fleeman N, Kirkham J, Bagust A, Boland A, Chu P, et al.
-
Thrombophilia testing in people with venous thromboembolism: systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
By Simpson EL, Stevenson MD, Rawdin A, Papaioannou D.
-
Surgical procedures and non-surgical devices for the management of non-apnoeic snoring: a systematic review of clinical effects and associated treatment costs.
By Main C, Liu Z, Welch K, Weiner G, Quentin Jones S, Stein K.
-
Continuous positive airway pressure devices for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McDaid C, Griffin S, Weatherly H, Durée K, van der Burgt M, van Hout S, Akers J, et al.
-
Use of classical and novel biomarkers as prognostic risk factors for localised prostate cancer: a systematic review.
By Sutcliffe P, Hummel S, Simpson E, Young T, Rees A, Wilkinson A, et al.
-
The harmful health effects of recreational ecstasy: a systematic review of observational evidence.
By Rogers G, Elston J, Garside R, Roome C, Taylor R, Younger P, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of oesophageal Doppler monitoring in critically ill and high-risk surgical patients.
By Mowatt G, Houston G, Hernández R, de Verteuil R, Fraser C, Cuthbertson B, et al.
-
The use of surrogate outcomes in model-based cost-effectiveness analyses: a survey of UK Health Technology Assessment reports.
By Taylor RS, Elston J.
-
Controlling Hypertension and Hypotension Immediately Post Stroke (CHHIPS) – a randomised controlled trial.
By Potter J, Mistri A, Brodie F, Chernova J, Wilson E, Jagger C, et al.
-
Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis for RhD-negative women: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Pilgrim H, Lloyd-Jones M, Rees A.
-
Amantadine, oseltamivir and zanamivir for the prophylaxis of influenza (including a review of existing guidance no. 67): a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Tappenden P, Jackson R, Cooper K, Rees A, Simpson E, Read R, et al.
-
Improving the evaluation of therapeutic interventions in multiple sclerosis: the role of new psychometric methods.
By Hobart J, Cano S.
-
Treatment of severe ankle sprain: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial comparing the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of three types of mechanical ankle support with tubular bandage. The CAST trial.
By Cooke MW, Marsh JL, Clark M, Nakash R, Jarvis RM, Hutton JL, et al. , on behalf of the CAST trial group.
-
Non-occupational postexposure prophylaxis for HIV: a systematic review.
By Bryant J, Baxter L, Hird S.
-
Blood glucose self-monitoring in type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial.
By Farmer AJ, Wade AN, French DP, Simon J, Yudkin P, Gray A, et al.
-
How far does screening women for domestic (partner) violence in different health-care settings meet criteria for a screening programme? Systematic reviews of nine UK National Screening Committee criteria.
By Feder G, Ramsay J, Dunne D, Rose M, Arsene C, Norman R, et al.
-
Spinal cord stimulation for chronic pain of neuropathic or ischaemic origin: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Simpson, EL, Duenas A, Holmes MW, Papaioannou D, Chilcott J.
-
The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the identification of suspected acoustic neuroma: a systematic review of clinical and cost-effectiveness and natural history.
By Fortnum H, O’Neill C, Taylor R, Lenthall R, Nikolopoulos T, Lightfoot G, et al.
-
Dipsticks and diagnostic algorithms in urinary tract infection: development and validation, randomised trial, economic analysis, observational cohort and qualitative study.
By Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, Warner G, Moore M, Lowes JA, et al.
-
Systematic review of respite care in the frail elderly.
By Shaw C, McNamara R, Abrams K, Cannings-John R, Hood K, Longo M, et al.
-
Neuroleptics in the treatment of aggressive challenging behaviour for people with intellectual disabilities: a randomised controlled trial (NACHBID).
By Tyrer P, Oliver-Africano P, Romeo R, Knapp M, Dickens S, Bouras N, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial to determine the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors plus supportive care, versus supportive care alone, for mild to moderate depression with somatic symptoms in primary care: the THREAD (THREshold for AntiDepressant response) study.
By Kendrick T, Chatwin J, Dowrick C, Tylee A, Morriss R, Peveler R, et al.
-
Diagnostic strategies using DNA testing for hereditary haemochromatosis in at-risk populations: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Bryant J, Cooper K, Picot J, Clegg A, Roderick P, Rosenberg W, et al.
-
Enhanced external counterpulsation for the treatment of stable angina and heart failure: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By McKenna C, McDaid C, Suekarran S, Hawkins N, Claxton K, Light K, et al.
-
Development of a decision support tool for primary care management of patients with abnormal liver function tests without clinically apparent liver disease: a record-linkage population cohort study and decision analysis (ALFIE).
By Donnan PT, McLernon D, Dillon JF, Ryder S, Roderick P, Sullivan F, et al.
-
A systematic review of presumed consent systems for deceased organ donation.
By Rithalia A, McDaid C, Suekarran S, Norman G, Myers L, Sowden A.
-
Paracetamol and ibuprofen for the treatment of fever in children: the PITCH randomised controlled trial.
By Hay AD, Redmond NM, Costelloe C, Montgomery AA, Fletcher M, Hollinghurst S, et al.
-
A randomised controlled trial to compare minimally invasive glucose monitoring devices with conventional monitoring in the management of insulin-treated diabetes mellitus (MITRE).
By Newman SP, Cooke D, Casbard A, Walker S, Meredith S, Nunn A, et al.
-
Sensitivity analysis in economic evaluation: an audit of NICE current practice and a review of its use and value in decision-making.
By Andronis L, Barton P, Bryan S.
-
Trastuzumab for the treatment of primary breast cancer in HER2-positive women: a single technology appraisal.
By Ward S, Pilgrim H, Hind D.
-
Docetaxel for the adjuvant treatment of early node-positive breast cancer: a single technology appraisal.
By Chilcott J, Lloyd Jones M, Wilkinson A.
-
The use of paclitaxel in the management of early stage breast cancer.
By Griffin S, Dunn G, Palmer S, Macfarlane K, Brent S, Dyker A, et al.
-
Rituximab for the first-line treatment of stage III/IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
By Dundar Y, Bagust A, Hounsome J, McLeod C, Boland A, Davis H, et al.
-
Bortezomib for the treatment of multiple myeloma patients.
By Green C, Bryant J, Takeda A, Cooper K, Clegg A, Smith A, et al.
-
Fludarabine phosphate for the firstline treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
By Walker S, Palmer S, Erhorn S, Brent S, Dyker A, Ferrie L, et al.
-
Erlotinib for the treatment of relapsed non-small cell lung cancer.
By McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Hockenhull J, Dundar Y, Proudlove C, et al.
-
Cetuximab plus radiotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
By Griffin S, Walker S, Sculpher M, White S, Erhorn S, Brent S, et al.
-
Infliximab for the treatment of adults with psoriasis.
By Loveman E, Turner D, Hartwell D, Cooper K, Clegg A
-
Psychological interventions for postnatal depression: cluster randomised trial and economic evaluation. The PoNDER trial.
By Morrell CJ, Warner R, Slade P, Dixon S, Walters S, Paley G, et al.
-
The effect of different treatment durations of clopidogrel in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and value of information analysis.
By Rogowski R, Burch J, Palmer S, Craigs C, Golder S, Woolacott N.
-
Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of diagnosis of heart failure, with modelling of implications of different diagnostic strategies in primary care.
By Mant J, Doust J, Roalfe A, Barton P, Cowie MR, Glasziou P, et al.
-
A multicentre randomised controlled trial of the use of continuous positive airway pressure and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation in the early treatment of patients presenting to the emergency department with severe acute cardiogenic pulmonary oedema: the 3CPO trial.
By Gray AJ, Goodacre S, Newby DE, Masson MA, Sampson F, Dixon S, et al. , on behalf of the 3CPO study investigators.
-
Early high-dose lipid-lowering therapy to avoid cardiac events: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Ara R, Pandor A, Stevens J, Rees A, Rafia R.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alpha for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: an updated systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Jones J, Shepherd J, Baxter L, Gospodarevskaya E, Hartwell D, Harris P, et al.
-
Methods to identify postnatal depression in primary care: an integrated evidence synthesis and value of information analysis.
By Hewitt CE, Gilbody SM, Brealey S, Paulden M, Palmer S, Mann R, et al.
-
A double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial of topical intranasal corticosteroids in 4- to 11-year-old children with persistent bilateral otitis media with effusion in primary care.
By Williamson I, Benge S, Barton S, Petrou S, Letley L, Fasey N, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methods of storing donated kidneys from deceased donors: a systematic review and economic model.
By Bond M, Pitt M, Akoh J, Moxham T, Hoyle M, Anderson R.
-
Rehabilitation of older patients: day hospital compared with rehabilitation at home. A randomised controlled trial.
By Parker SG, Oliver P, Pennington M, Bond J, Jagger C, Enderby PM, et al.
-
Breastfeeding promotion for infants in neonatal units: a systematic review and economic analysis.
By Renfrew MJ, Craig D, Dyson L, McCormick F, Rice S, King SE, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Picot J, Jones J, Colquitt JL, Gospodarevskaya E, Loveman E, Baxter L, et al.
-
Rapid testing for group B streptococcus during labour: a test accuracy study with evaluation of acceptability and cost-effectiveness.
By Daniels J, Gray J, Pattison H, Roberts T, Edwards E, Milner P, et al.
-
Screening to prevent spontaneous preterm birth: systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling.
By Honest H, Forbes CA, Durée KH, Norman G, Duffy SB, Tsourapas A, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cochlear implants for severe to profound deafness in children and adults: a systematic review and economic model.
By Bond M, Mealing S, Anderson R, Elston J, Weiner G, Taylor RS, et al.
-
Gemcitabine for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
By Jones J, Takeda A, Tan SC, Cooper K, Loveman E, Clegg A.
-
Varenicline in the management of smoking cessation: a single technology appraisal.
By Hind D, Tappenden P, Peters J, Kenjegalieva K.
-
Alteplase for the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke: a single technology appraisal.
By Lloyd Jones M, Holmes M.
-
Rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
By Bagust A, Boland A, Hockenhull J, Fleeman N, Greenhalgh J, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Omalizumab for the treatment of severe persistent allergic asthma.
By Jones J, Shepherd J, Hartwell D, Harris P, Cooper K, Takeda A, et al.
-
Rituximab for the treatment of relapsed or refractory stage III or IV follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
By Boland A, Bagust A, Hockenhull J, Davis H, Chu P, Dickson R.
-
Adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis.
By Turner D, Picot J, Cooper K, Loveman E.
-
Dabigatran etexilate for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing elective hip and knee surgery: a single technology appraisal.
By Holmes M, C Carroll C, Papaioannou D.
-
Romiplostim for the treatment of chronic immune or idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a single technology appraisal.
By Mowatt G, Boachie C, Crowther M, Fraser C, Hernández R, Jia X, et al.
-
Sunitinib for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumours: a critique of the submission from Pfizer.
By Bond M, Hoyle M, Moxham T, Napier M, Anderson R.
-
Vitamin K to prevent fractures in older women: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Stevenson M, Lloyd-Jones M, Papaioannou D.
-
The effects of biofeedback for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review.
By Greenhalgh J, Dickson R, Dundar Y.
-
A randomised controlled trial of the use of aciclovir and/or prednisolone for the early treatment of Bell’s palsy: the BELLS study.
By Sullivan FM, Swan IRC, Donnan PT, Morrison JM, Smith BH, McKinstry B, et al.
-
Lapatinib for the treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
By Jones J, Takeda A, Picot J, von Keyserlingk C, Clegg A.
-
Infliximab for the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
By Hyde C, Bryan S, Juarez-Garcia A, Andronis L, Fry-Smith A.
-
Rimonabant for the treatment of overweight and obese people.
By Burch J, McKenna C, Palmer S, Norman G, Glanville J, Sculpher M, et al.
-
Telbivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.
By Hartwell D, Jones J, Harris P, Cooper K.
-
Entecavir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.
By Shepherd J, Gospodarevskaya E, Frampton G, Cooper, K.
-
Febuxostat for the treatment of hyperuricaemia in people with gout: a single technology appraisal.
By Stevenson M, Pandor A.
-
Rivaroxaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism: a single technology appraisal.
By Stevenson M, Scope A, Holmes M, Rees A, Kaltenthaler E.
-
Cetuximab for the treatment of recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
By Greenhalgh J, Bagust A, Boland A, Fleeman N, McLeod C, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Mifamurtide for the treatment of osteosarcoma: a single technology appraisal.
By Pandor A, Fitzgerald P, Stevenson M, Papaioannou D.
-
Ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis.
By Gospodarevskaya E, Picot J, Cooper K, Loveman E, Takeda A.
-
Endovascular stents for abdominal aortic aneurysms: a systematic review and economic model.
By Chambers D, Epstein D, Walker S, Fayter D, Paton F, Wright K, et al.
-
Clinical and cost-effectiveness of epoprostenol, iloprost, bosentan, sitaxentan and sildenafil for pulmonary arterial hypertension within their licensed indications: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Chen Y-F, Jowett S, Barton P, Malottki K, Hyde C, Gibbs JSR, et al.
-
Cessation of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder drugs in the young (CADDY) – a pharmacoepidemiological and qualitative study.
By Wong ICK, Asherson P, Bilbow A, Clifford S, Coghill D, R DeSoysa R, et al.
-
ARTISTIC: a randomised trial of human papillomavirus (HPV) testing in primary cervical screening.
By Kitchener HC, Almonte M, Gilham C, Dowie R, Stoykova B, Sargent A, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness of glucosamine and chondroitin supplements in slowing or arresting progression of osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Black C, Clar C, Henderson R, MacEachern C, McNamee P, Quayyum Z, et al.
-
Randomised preference trial of medical versus surgical termination of pregnancy less than 14 weeks’ gestation (TOPS).
By Robson SC, Kelly T, Howel D, Deverill M, Hewison J, Lie MLS, et al.
-
Randomised controlled trial of the use of three dressing preparations in the management of chronic ulceration of the foot in diabetes.
By Jeffcoate WJ, Price PE, Phillips CJ, Game FL, Mudge E, Davies S, et al.
-
VenUS II: a randomised controlled trial of larval therapy in the management of leg ulcers.
By Dumville JC, Worthy G, Soares MO, Bland JM, Cullum N, Dowson C, et al.
-
A prospective randomised controlled trial and economic modelling of antimicrobial silver dressings versus non-adherent control dressings for venous leg ulcers: the VULCAN trial
By Michaels JA, Campbell WB, King BM, MacIntyre J, Palfreyman SJ, Shackley P, et al.
-
Communication of carrier status information following universal newborn screening for sickle cell disorders and cystic fibrosis: qualitative study of experience and practice.
By Kai J, Ulph F, Cullinan T, Qureshi N.
-
Antiviral drugs for the treatment of influenza: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Burch J, Paulden M, Conti S, Stock C, Corbett M, Welton NJ, et al.
-
Development of a toolkit and glossary to aid in the adaptation of health technology assessment (HTA) reports for use in different contexts.
By Chase D, Rosten C, Turner S, Hicks N, Milne R.
-
Colour vision testing for diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review of diagnostic accuracy and economic evaluation.
By Rodgers M, Hodges R, Hawkins J, Hollingworth W, Duffy S, McKibbin M, et al.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of weight management schemes for the under fives: a short report.
By Bond M, Wyatt K, Lloyd J, Welch K, Taylor R.
-
Are adverse effects incorporated in economic models? An initial review of current practice.
By Craig D, McDaid C, Fonseca T, Stock C, Duffy S, Woolacott N.
-
Multicentre randomised controlled trial examining the cost-effectiveness of contrast-enhanced high field magnetic resonance imaging in women with primary breast cancer scheduled for wide local excision (COMICE).
By Turnbull LW, Brown SR, Olivier C, Harvey I, Brown J, Drew P, et al.
-
Bevacizumab, sorafenib tosylate, sunitinib and temsirolimus for renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Thompson Coon J, Hoyle M, Green C, Liu Z, Welch K, Moxham T, et al.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of testing for cytochrome P450 polymorphisms in patients with schizophrenia treated with antipsychotics: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Fleeman N, McLeod C, Bagust A, Beale S, Boland A, Dundar Y, et al.
-
Systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of photodynamic diagnosis and urine biomarkers (FISH, ImmunoCyt, NMP22) and cytology for the detection and follow-up of bladder cancer.
By Mowatt G, Zhu S, Kilonzo M, Boachie C, Fraser C, Griffiths TRL, et al.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of arthroscopic lavage in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a mixed methods study of the feasibility of conducting a surgical placebo-controlled trial (the KORAL study).
By Campbell MK, Skea ZC, Sutherland AG, Cuthbertson BH, Entwistle VA, McDonald AM, et al.
-
A randomised 2 × 2 trial of community versus hospital pulmonary rehabilitation for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease followed by telephone or conventional follow-up.
By Waterhouse JC, Walters SJ, Oluboyede Y, Lawson RA.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of behavioural interventions for the prevention of sexually transmitted infections in young people aged 13–19: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Shepherd J, Kavanagh J, Picot J, Cooper K, Harden A, Barnett-Page E, et al.
-
Dissemination and publication of research findings: an updated review of related biases.
By Song F, Parekh S, Hooper L, Loke YK, Ryder J, Sutton AJ, et al.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of biomarkers for the prioritisation of patients awaiting coronary revascularisation: a systematic review and decision model.
By Hemingway H, Henriksson M, Chen R, Damant J, Fitzpatrick N, Abrams K, et al.
-
Comparison of case note review methods for evaluating quality and safety in health care.
By Hutchinson A, Coster JE, Cooper KL, McIntosh A, Walters SJ, Bath PA, et al.
-
Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation.
By Cummins E, Royle P, Snaith A, Greene A, Robertson L, McIntyre L, et al.
Health Technology Assessment programme
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
Prioritisation Strategy Group
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Bob Coates, Consultant Advisor, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Andrew Cook, Consultant Advisor, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Peter Davidson, Director of Science Support, NETSCC, HTA
-
Professor Robin E Ferner, Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor Paul Glasziou, Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Dr Nick Hicks, Director of NHS Support, NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Edmund Jessop, Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), Department of Health, London
-
Ms Lynn Kerridge, Chief Executive Officer, NETSCC and NETSCC, HTA
-
Dr Ruairidh Milne, Director of Strategy and Development, NETSCC
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Ms Pamela Young, Specialist Programme Manager, NETSCC, HTA
HTA Commissioning Board
-
Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Director, Medical Care Research Unit, University of Sheffield
-
Senior Lecturer in General Practice, Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford
-
Professor Ann Ashburn, Professor of Rehabilitation and Head of Research, Southampton General Hospital
-
Professor Deborah Ashby, Professor of Medical Statistics, Queen Mary, University of London
-
Professor John Cairns, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Peter Croft, Director of Primary Care Sciences Research Centre, Keele University
-
Professor Nicky Cullum, Director of Centre for Evidence-Based Nursing, University of York
-
Professor Jenny Donovan, Professor of Social Medicine, University of Bristol
-
Professor Steve Halligan, Professor of Gastrointestinal Radiology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Freddie Hamdy, Professor of Urology, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Allan House, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, University of Leeds
-
Dr Martin J Landray, Reader in Epidemiology, Honorary Consultant Physician, Clinical Trial Service Unit, University of Oxford?
-
Professor Stuart Logan, Director of Health & Social Care Research, The Peninsula Medical School, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Dr Rafael Perera, Lecturer in Medical Statisitics, Department of Primary Health Care, Univeristy of Oxford
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology & Public Health, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Mark Sculpher, Professor of Health Economics, University of York
-
Professor Helen Smith, Professor of Primary Care, University of Brighton
-
Professor Kate Thomas, Professor of Complementary & Alternative Medicine Research, University of Leeds
-
Professor David John Torgerson, Director of York Trials Unit, University of York
-
Professor Hywel Williams, Professor of Dermato-Epidemiology, University of Nottingham
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
Diagnostic Technologies & Screening Panel
-
Professor of Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Lecturer, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London
-
Professor Judith E Adams, Consultant Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Central Manchester & Manchester Children’s University Hospitals NHS Trust, and Professor of Diagnostic Radiology, Imaging Science and Biomedical Engineering, Cancer & Imaging Sciences, University of Manchester
-
Ms Jane Bates, Consultant Ultrasound Practitioner, Ultrasound Department, Leeds Teaching Hospital NHS Trust
-
Dr Stephanie Dancer, Consultant Microbiologist, Hairmyres Hospital, East Kilbride
-
Professor Glyn Elwyn, Primary Medical Care Research Group, Swansea Clinical School, University of Wales
-
Dr Ron Gray, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, Department of Public Health, University of Oxford
-
Professor Paul D Griffiths, Professor of Radiology, University of Sheffield
-
Dr Jennifer J Kurinczuk, Consultant Clinical Epidemiologist, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Oxford
-
Dr Susanne M Ludgate, Medical Director, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, London
-
Dr Anne Mackie, Director of Programmes, UK National Screening Committee
-
Dr Michael Millar, Consultant Senior Lecturer in Microbiology, Barts and The London NHS Trust, Royal London Hospital
-
Mr Stephen Pilling, Director, Centre for Outcomes, Research & Effectiveness, Joint Director, National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health, University College London
-
Mrs Una Rennard, Service User Representative
-
Dr Phil Shackley, Senior Lecturer in Health Economics, School of Population and Health Sciences, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Dr W Stuart A Smellie, Consultant in Chemical Pathology, Bishop Auckland General Hospital
-
Dr Nicholas Summerton, Consultant Clinical and Public Health Advisor, NICE
-
Ms Dawn Talbot, Service User Representative
-
Dr Graham Taylor, Scientific Advisor, Regional DNA Laboratory, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Professor Lindsay Wilson Turnbull, Scientific Director of the Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations and YCR Professor of Radiology, Hull Royal Infirmary
-
Dr Tim Elliott, Team Leader, Cancer Screening, Department of Health
-
Dr Catherine Moody, Programme Manager, Neuroscience and Mental Health Board
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Pharmaceuticals Panel
-
Consultant Physician and Director, West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions, City Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor in Child Health, University of Nottingham
-
Mrs Nicola Carey, Senior Research Fellow, School of Health and Social Care, The University of Reading
-
Mr John Chapman, Service User Representative
-
Dr Peter Elton, Director of Public Health, Bury Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Ben Goldacre, Research Fellow, Division of Psychological Medicine and Psychiatry, King’s College London
-
Mrs Barbara Greggains, Service User Representative
-
Dr Bill Gutteridge, Medical Adviser, London Strategic Health Authority
-
Dr Dyfrig Hughes, Reader in Pharmacoeconomics and Deputy Director, Centre for Economics and Policy in Health, IMSCaR, Bangor University
-
Professor Jonathan Ledermann, Professor of Medical Oncology and Director of the Cancer Research UK and University College London Cancer Trials Centre
-
Dr Yoon K Loke, Senior Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacology, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Femi Oyebode, Consultant Psychiatrist and Head of Department, University of Birmingham
-
Dr Andrew Prentice, Senior Lecturer and Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, The Rosie Hospital, University of Cambridge
-
Dr Martin Shelly, General Practitioner, Leeds, and Associate Director, NHS Clinical Governance Support Team, Leicester
-
Dr Gillian Shepherd, Director, Health and Clinical Excellence, Merck Serono Ltd
-
Mrs Katrina Simister, Assistant Director New Medicines, National Prescribing Centre, Liverpool
-
Mr David Symes, Service User Representative
-
Dr Lesley Wise, Unit Manager, Pharmacoepidemiology Research Unit, VRMM, Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Mr Simon Reeve, Head of Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness, Medicines, Pharmacy and Industry Group, Department of Health
-
Dr Heike Weber, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Therapeutic Procedures Panel
-
Consultant Physician, North Bristol NHS Trust
-
Professor of Psychiatry, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Jane Barlow, Professor of Public Health in the Early Years, Health Sciences Research Institute, Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Maree Barnett, Acting Branch Head of Vascular Programme, Department of Health
-
Mrs Val Carlill, Service User Representative
-
Mrs Anthea De Barton-Watson, Service User Representative
-
Mr Mark Emberton, Senior Lecturer in Oncological Urology, Institute of Urology, University College Hospital, London
-
Professor Steve Goodacre, Professor of Emergency Medicine, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Christopher Griffiths, Professor of Primary Care, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Paul Hilton, Consultant Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist, Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Nicholas James, Professor of Clinical Oncology, University of Birmingham, and Consultant in Clinical Oncology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital
-
Dr Peter Martin, Consultant Neurologist, Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge
-
Dr Kate Radford, Senior Lecturer (Research), Clinical Practice Research Unit, University of Central Lancashire, Preston
-
Mr Jim Reece Service User Representative
-
Dr Karen Roberts, Nurse Consultant, Dunston Hill Hospital Cottages
-
Dr Phillip Leech, Principal Medical Officer for Primary Care, Department of Health
-
Ms Kay Pattison, Section Head, NHS R&D Programme, Department of Health
-
Dr Morven Roberts, Clinical Trials Manager, Medical Research Council
-
Professor Tom Walley, Director, NIHR HTA programme, Professor of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Liverpool
-
Dr Ursula Wells, Principal Research Officer, Department of Health
Disease Prevention Panel
-
Medical Adviser, National Specialist, National Commissioning Group (NCG), London
-
Director, NHS Sustainable Development Unit, Cambridge
-
Dr Elizabeth Fellow-Smith, Medical Director, West London Mental Health Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr John Jackson, General Practitioner, Parkway Medical Centre, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Mike Kelly, Director, Centre for Public Health Excellence, NICE, London
-
Dr Chris McCall, General Practitioner, The Hadleigh Practice, Corfe Mullen, Dorset
-
Ms Jeanett Martin, Director of Nursing, BarnDoc Limited, Lewisham Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Julie Mytton, Locum Consultant in Public Health Medicine, Bristol Primary Care Trust
-
Miss Nicky Mullany, Service User Representative
-
Professor Ian Roberts, Professor of Epidemiology and Public Health, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
-
Professor Ken Stein, Senior Clinical Lecturer in Public Health, University of Exeter
-
Dr Kieran Sweeney, Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer, Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth
-
Professor Carol Tannahill, Glasgow Centre for Population Health
-
Professor Margaret Thorogood, Professor of Epidemiology, University of Warwick Medical School, Coventry
-
Ms Christine McGuire, Research & Development, Department of Health
-
Dr Caroline Stone, Programme Manager, Medical Research Council
Expert Advisory Network
-
Professor Douglas Altman, Professor of Statistics in Medicine, Centre for Statistics in Medicine, University of Oxford
-
Professor John Bond, Professor of Social Gerontology & Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Andrew Bradbury, Professor of Vascular Surgery, Solihull Hospital, Birmingham
-
Mr Shaun Brogan, Chief Executive, Ridgeway Primary Care Group, Aylesbury
-
Mrs Stella Burnside OBE, Chief Executive, Regulation and Improvement Authority, Belfast
-
Ms Tracy Bury, Project Manager, World Confederation for Physical Therapy, London
-
Professor Iain T Cameron, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of the School of Medicine, University of Southampton
-
Dr Christine Clark, Medical Writer and Consultant Pharmacist, Rossendale
-
Professor Collette Clifford, Professor of Nursing and Head of Research, The Medical School, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Barry Cookson, Director, Laboratory of Hospital Infection, Public Health Laboratory Service, London
-
Dr Carl Counsell, Clinical Senior Lecturer in Neurology, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Howard Cuckle, Professor of Reproductive Epidemiology, Department of Paediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, University of Leeds
-
Dr Katherine Darton, Information Unit, MIND – The Mental Health Charity, London
-
Professor Carol Dezateux, Professor of Paediatric Epidemiology, Institute of Child Health, London
-
Mr John Dunning, Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Papworth Hospital NHS Trust, Cambridge
-
Mr Jonothan Earnshaw, Consultant Vascular Surgeon, Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Gloucester
-
Professor Martin Eccles, Professor of Clinical Effectiveness, Centre for Health Services Research, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Professor Pam Enderby, Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Institute of General Practice and Primary Care, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Gene Feder, Professor of Primary Care Research & Development, Centre for Health Sciences, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Mr Leonard R Fenwick, Chief Executive, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Mrs Gillian Fletcher, Antenatal Teacher and Tutor and President, National Childbirth Trust, Henfield
-
Professor Jayne Franklyn, Professor of Medicine, University of Birmingham
-
Mr Tam Fry, Honorary Chairman, Child Growth Foundation, London
-
Professor Fiona Gilbert, Consultant Radiologist and NCRN Member, University of Aberdeen
-
Professor Paul Gregg, Professor of Orthopaedic Surgical Science, South Tees Hospital NHS Trust
-
Bec Hanley, Co-director, TwoCan Associates, West Sussex
-
Dr Maryann L Hardy, Senior Lecturer, University of Bradford
-
Mrs Sharon Hart, Healthcare Management Consultant, Reading
-
Professor Robert E Hawkins, CRC Professor and Director of Medical Oncology, Christie CRC Research Centre, Christie Hospital NHS Trust, Manchester
-
Professor Richard Hobbs, Head of Department of Primary Care & General Practice, University of Birmingham
-
Professor Alan Horwich, Dean and Section Chairman, The Institute of Cancer Research, London
-
Professor Allen Hutchinson, Director of Public Health and Deputy Dean of ScHARR, University of Sheffield
-
Professor Peter Jones, Professor of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
-
Professor Stan Kaye, Cancer Research UK Professor of Medical Oncology, Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, Surrey
-
Dr Duncan Keeley, General Practitioner (Dr Burch & Ptnrs), The Health Centre, Thame
-
Dr Donna Lamping, Research Degrees Programme Director and Reader in Psychology, Health Services Research Unit, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London
-
Mr George Levvy, Chief Executive, Motor Neurone Disease Association, Northampton
-
Professor James Lindesay, Professor of Psychiatry for the Elderly, University of Leicester
-
Professor Julian Little, Professor of Human Genome Epidemiology, University of Ottawa
-
Professor Alistaire McGuire, Professor of Health Economics, London School of Economics
-
Professor Rajan Madhok, Medical Director and Director of Public Health, Directorate of Clinical Strategy & Public Health, North & East Yorkshire & Northern Lincolnshire Health Authority, York
-
Professor Alexander Markham, Director, Molecular Medicine Unit, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Peter Moore, Freelance Science Writer, Ashtead
-
Dr Andrew Mortimore, Public Health Director, Southampton City Primary Care Trust
-
Dr Sue Moss, Associate Director, Cancer Screening Evaluation Unit, Institute of Cancer Research, Sutton
-
Professor Miranda Mugford, Professor of Health Economics and Group Co-ordinator, University of East Anglia
-
Professor Jim Neilson, Head of School of Reproductive & Developmental Medicine and Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Liverpool
-
Mrs Julietta Patnick, National Co-ordinator, NHS Cancer Screening Programmes, Sheffield
-
Professor Robert Peveler, Professor of Liaison Psychiatry, Royal South Hants Hospital, Southampton
-
Professor Chris Price, Director of Clinical Research, Bayer Diagnostics Europe, Stoke Poges
-
Professor William Rosenberg, Professor of Hepatology and Consultant Physician, University of Southampton
-
Professor Peter Sandercock, Professor of Medical Neurology, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Edinburgh
-
Dr Susan Schonfield, Consultant in Public Health, Hillingdon Primary Care Trust, Middlesex
-
Dr Eamonn Sheridan, Consultant in Clinical Genetics, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds
-
Dr Margaret Somerville, Director of Public Health Learning, Peninsula Medical School, University of Plymouth
-
Professor Sarah Stewart-Brown, Professor of Public Health, Division of Health in the Community, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Professor Ala Szczepura, Professor of Health Service Research, Centre for Health Services Studies, University of Warwick, Coventry
-
Mrs Joan Webster, Consumer Member, Southern Derbyshire Community Health Council
-
Professor Martin Whittle, Clinical Co-director, National Co-ordinating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health, Lymington