Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned and funded by the HTA programme on behalf of NICE as project number 11/75/01. The protocol was agreed in December 2011. The assessment report began editorial review in May 2012 and was accepted for publication in November 2012. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
R Riemsma is a member of the NIHR Journals Library Board.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2013. This work was produced by Riemsma et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Background and definition of the decision problem(s)
Conditions and aetiologies
Bile acid malabsorption
The principal diagnosis/indication for this assessment is chronic diarrhoea due to bile acid malabsorption (BAM). Diarrhoea can be defined as the abnormal passage of loose or liquid stools more than three times daily and/or a daily stool weight greater than 200 g per day and is considered to be chronic if it persists for more than 4 weeks. 1 The cause of chronic diarrhoea in adults is often difficult to ascertain and patients may undergo several investigations without a definitive cause being identified. 2 Chronic diarrhoea is one of the most common reasons for referral to a gastrointestinal clinic,3 and could account for as many as 1 in 20 referrals. Estimates of the prevalence of chronic diarrhoea in a Western population are 4–5%. 4 Some of the causes of chronic diarrhoea are given in Box 1 .
-
Colonic neoplasia.
-
Ulcerative and Crohn’s colitis.
-
Microscopic colitis.
-
Coeliac disease.
-
Crohn’s disease.
-
Other small bowel enteropathies (e.g. Whipple’s disease, tropical spruce, amyloid, intestinal lymphangiectasia).
-
Bile acid malabsorption.
-
Disaccharidase deficiency.
-
Small bowel bacterial overgrowth.
-
Mesenteric ischaemia.
-
Radiation enteritis.
-
Lymphoma.
-
Giardiasis (and other chronic infections).
-
Chronic pancreatitis.
-
Pancreatic carcinoma.
-
Cystic fibrosis.
-
Hyperthyroidism.
-
Diabetes.
-
Hypoparathyroidism.
-
Addison’s disease.
-
Hormone-secreting tumours (VIPoma, gastrinoma, carcinoid).
-
Factitious diarrhoea.
-
‘Surgical’ causes (e.g. small bowel resection, internal fistulae).
-
Drugs.
-
Alcohol.
-
Autonomic neuropathy.
Bile acid malabsorption is one of several causes of chronic diarrhoea (see Box 1 ) and results from failure to absorb bile acids (which are required for the absorption of dietary fats and sterols in the intestine) in the distal ileum. Normally, more than 90% of the acids are reabsorbed in the distal ileum. BAM results in excess bile acids in the colon where they cause diarrhoea by various mechanisms. These mechanisms include:
-
inducing secretion of sodium and water, particularly at a concentration above 3 mmol/l
-
increase colonic motility
-
stimulating defecation
-
inducing mucus secretion
-
causing damage to mucosa, thereby increasing mucosal permeability.
Bile acid malabsorption has been divided into three types depending on aetiology:
-
type 1: following ileal resection, disease or bypass of the terminal ileum
-
type 2: primary idiopathic malabsorption
-
type 3: associated with cholecystectomy, peptic ulcer surgery, chronic pancreatitis, coeliac disease and diabetes mellitus.
Irritable bowel syndrome
People with chronic diarrhoea are often diagnosed as having diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) if a definitive cause has not been identified. There is evidence that suggests a high prevalence of BAM (up to one-third) in patients previously diagnosed with IBS-D. 3,5 On this basis, approximately half a million patients in the NHS who are currently treated for IBS-D actually have BAM, for which potential diagnosis and effective treatment are available. 6
Irritable bowel syndrome is one of the most common functional gastrointestinal disorders. It is a chronic, relapsing and often life-long disorder, characterised by the presence of abdominal pain/discomfort associated with defecation, a change in bowel habit together with disordered defecation (constipation or diarrhoea or both), the sensation of abdominal distension, and can include associated non-colonic symptoms. These morbidities can cause dehydration, lack of sleep, anxiety and lethargy, with consequences such as time taken off work, avoidance of stressful or social situations and significant reduction in quality of life. 7
Irritable bowel syndrome most commonly affects people between the ages of 20 and 30 years and is twice as common in women as in men. People with IBS are the largest group of patients seen in a general gastroenterology clinic (1 in 20 referrals). The prevalence of the condition in the general population is estimated at between 10% and 20%. 7 Recent trends indicate that there is also a significant prevalence of IBS in older people, and therefore IBS diagnosis should be a consideration when an older person presents with unexplained abdominal symptoms. The true prevalence of IBS in the whole population may be higher than estimated, because it is thought that many people with IBS symptoms do not seek medical advice; NHS Direct online data suggest that 75% of people using this service who have IBS symptoms rely on self-care. In England and Wales, the number of people consulting for IBS is extrapolated to between 1.6 million and 3.9 million. 7
Inflammatory bowel disease
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are the two most common forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Together these long-term conditions are estimated to affect about 240,000 people in the UK: approximately 400 per 100,000 population. 8 Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease directly cause chronic diarrhoea.
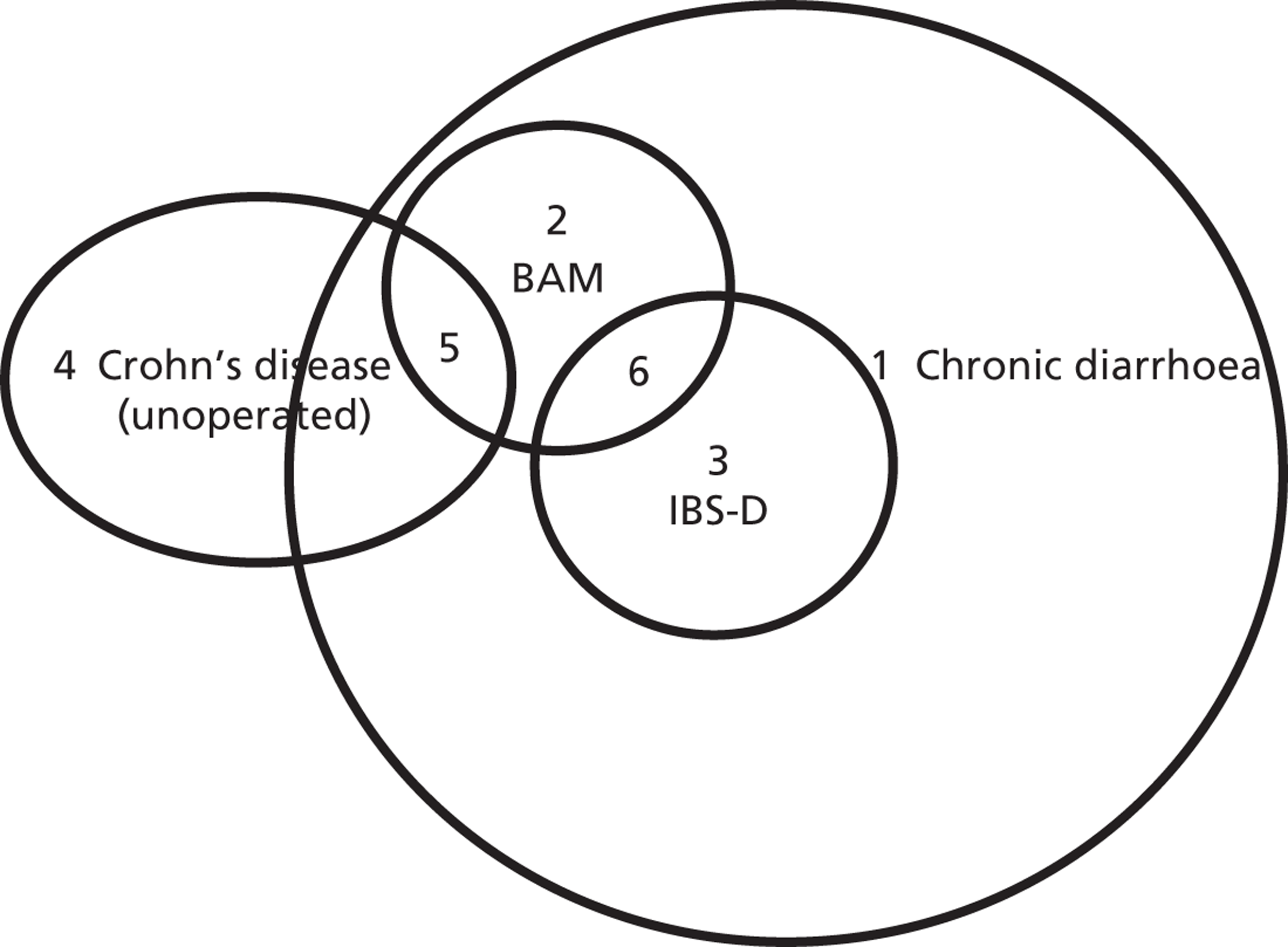
Crohn’s disease is a chronic severe condition characterised by inflammation, ulcers and bleeding which may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract but mostly the terminal ileum. There are approximately 60,000 people in the UK with this condition ( Figure 1 ). 9 Crohn’s disease is sometimes treated by ileal resection. In a study carried out by Smith et al. 3 BAM was found in 97% of people with Crohn’s disease with ileal resection who were in clinical remission and in 54% of people in clinical remission with unoperated Crohn’s disease.
FIGURE 1.
Venn diagram with approximate population sizes in the UK. 1, 3 million in the UK (prevalence of chronic diarrhoea in a Western population: 4–5%);1 2, unknown; 3, 1.3 million in the UK (there are up to 3.9 million adults in the UK being treated for IBS, with one-third of these having IBS-D);10 4, unknown (there are approximately 60,000 people in the UK with Crohn’s disease);9 5, unknown (BAM was found in 54% of people in clinical remission with unoperated Crohn’s disease);3 6, 500,000 in the UK. 10
Description of technologies under assessment (selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine)
Selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine (SeHCAT) (GE Healthcare) is a radiopharmaceutical that is licensed for use in the investigation of BAM and measurement of bile acid pool loss. It may also be used in assessing ileal function, in the investigation of IBD and chronic diarrhoea and in the study of enterohepatic circulation.
SeHCAT product information lists its applications as follows:
Tauroselcholic acid is a bile acid analogue which shows identical physiological behaviour with naturally occurring bile acid conjugates. Following oral administration in normal subjects, approximately 95% of the labelled bile acid is absorbed, mainly by the terminal ileum during each enterohepatic cycle. The distribution of activity is almost entirely confined to the lumen of the biliary ducts, gut and liver. Whole body retention data from normal subjects showed 97 to 100% of [75Se]tauroselcholic was excreted with a biological half-life of 2.6 days and that, in most cases, a small component of about 3% was eliminated with a mean half time of 62 days. GE Healthcare Ltd. 11
p. 3
Comparators
There is no direct comparator for this diagnostic test. Current diagnostic options include analysis of a patient’s history, investigations to exclude ‘red flag’ symptoms and a variety of other diagnostic tests such as blood tests and lactose tolerance tests. Trial of treatment is used, with mixed results, to diagnose BAM. It is, however, not widely used in current practice. 12
The main comparator for the assessment will be tests and clinical observations contained in the British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) guidelines for the investigation of chronic diarrhoea (see Care pathways). 1
Care pathways
Diagnosis
Patients with undiagnosed BAM are likely to present with chronic diarrhoea. The BSG guideline states that bile salt malabsorption occurs when normal active uptake from the ileum is disrupted by ileal inflammation or resection. It also states that the degree of malabsorption depends on the length of ileal involvement or resection. According to the BSG guidelines, diagnosis of BAM can be made via SeHCAT scanning.
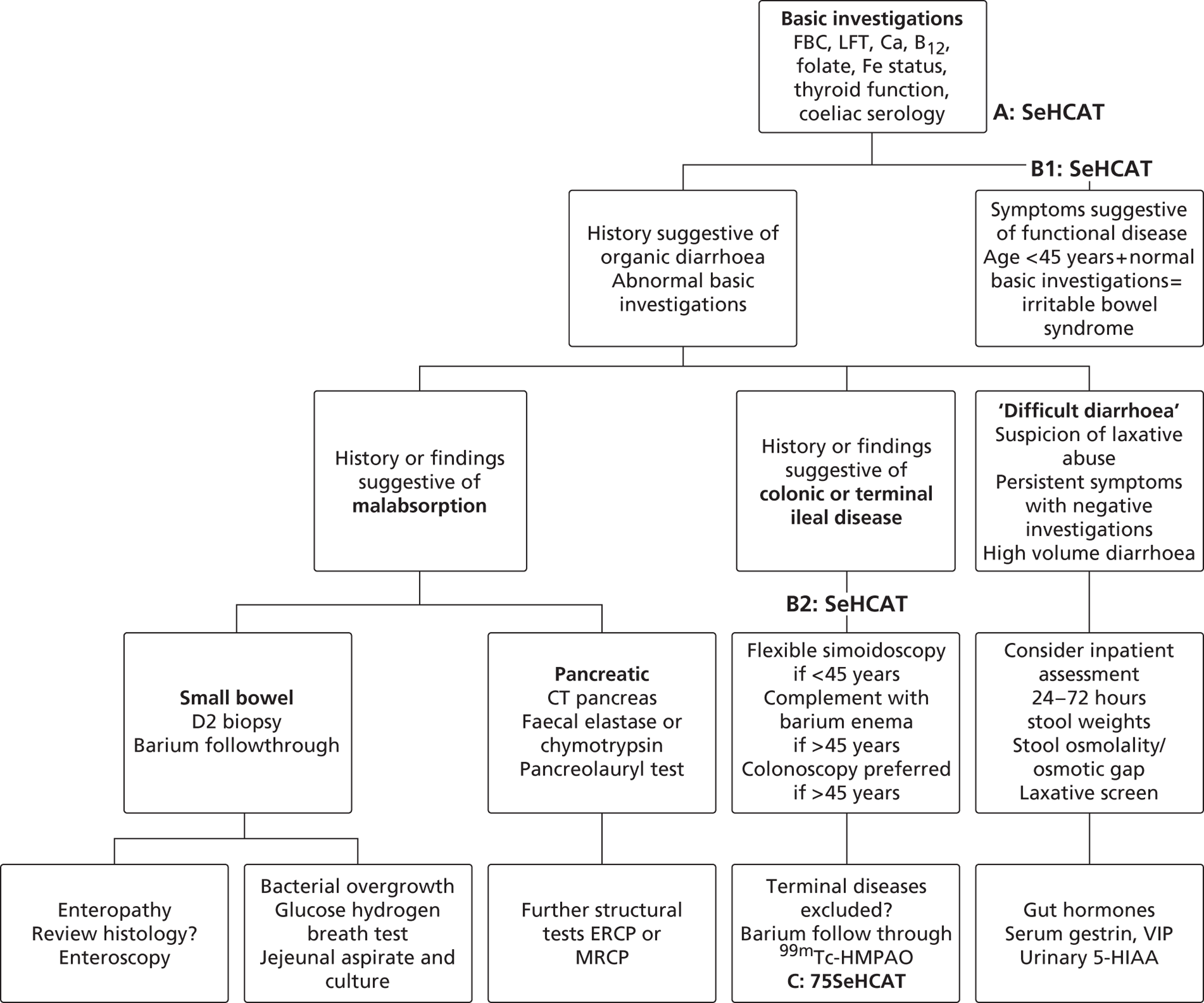
During early scoping, two issues arose regarding the BSG pathway. First, all experts agreed that SeHCAT needs to be placed earlier in the pathway to help patients gain a firm diagnosis at an earlier stage. However, expert opinion varied as to where SeHCAT should be placed on the pathway. Some felt that it should be available to general practitioners (GPs) for use in all patients with chronic, erratic bowels with a tendency to diarrhoea, while others felt that it is more appropriate for use in secondary care. Second, the BSG guideline does not take into account the prevalence of BAM in people diagnosed with IBS. The BSG guideline place SeHCAT at the end of the diagnostic algorithm (position C in Figure 2 ). Possible alternatives are:
-
SeHCAT as part of the basic investigations for all patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea (position A in Figure 2 )
-
SeHCAT for all patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea and symptoms suggestive of functional disease (i.e. age < 45 and normal basic investigations) (position B1 in Figure 2 ); and also for patients with a history of findings suggestive of colonic or terminal ileal disease (position B2 in Figure 2 ).
FIGURE 2.
British Society of Gastroenterology’s guideline for the investigation of chronic diarrhoea (adapted from Thomas et al. 1). B12, vitamin B12; Ca, calcium; FBC, full blood count; LFT, liner function tests.
Selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine as part of the basic investigations (position A in Figure 2 ) means that all patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea will be tested with SeHCAT. However, during the scoping workshop clinical experts advised that a positive SeHCAT test at this stage does not rule out the possibility of organic disease. As no subsequent tests for organic disease are made redundant, it is unlikely that SeHCAT in position A will be more cost-effective than in position B1. Therefore, this assessment will focus on position B1.
The same applies to SeHCAT in position B2. A positive SeHCAT test in position B2 is not thought likely to stop clinicians from doing subsequent tests such as sigmoidoscopy, barium enema or colonoscopy. Therefore, in the assessment, using SeHCAT in position B2 and in position C will be considered as having the same effect on the care pathway.
This leaves two possible populations for investigation:
-
people presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease
-
people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection of the terminal ileum).
Treatment
Following a definitive diagnosis, patients may be treated with bile acid sequestrants (BASs), which can cause significant reduction in bowel frequency and therefore a better quality of life. 13 There are currently two types of BAS available:
-
Bile binding resins (cholestyramine and colestipol): although they are tolerated by some, most people dislike these treatments because of side effects and the difficulty of administration, but take them in the long term because they can help in managing the condition. One in four patients cannot take more than a single dose.
-
Colesevelam (Cholestagel,® Genzyme) (gel matrix): two-thirds of patients take this treatment for at least 4 years and most of those who stop do so because they found no benefit initially.
The response to BAS therapy varies among people with bile acid diarrhoea. For those with Crohn’s disease with ileal resection and BAM (assessed with SeHCAT), the response to BAS was 60%; response was 40% in those with Crohn’s disease without ileal resection and BAM and 70% in those with a diagnosis of IBS-D and BAM. 3
Chapter 2 Objective
The objective of this project is to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of SeHCAT, a bile acid analogue which is used as a test for investigating BAM and the measurement of bile acid pool loss in patients referred to a gastrointestinal clinic for investigation and diagnosis of BAM.
This can be translated in the following research questions. For people with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and in people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection):
-
What are the effects of SeHCAT compared with no SeHCAT in terms of chronic diarrhoea, other health outcomes and costs?
-
What are the effects of BASs compared with no BASs in people with a positive or negative SeHCAT test?
-
Does a positive or negative SeHCAT test predict improvement in terms of chronic diarrhoea, other health outcomes and costs?
Chapter 3 Assessment of clinical effectiveness
A systematic review was conducted to summarise the evidence on the clinical effectiveness of SeHCAT for the assessment of BAM and the measurement of bile acid pool loss. Systematic review methods will follow the principles outlined in the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) guidance for undertaking reviews in health care,14 and National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Diagnostic Assessment Programme interim methods statement. 15
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Participants
Study populations eligible for inclusion will be all patients (including children) referred to a gastrointestinal clinic for investigation and diagnosis of BAM which is a common underlying cause of chronic diarrhoea and the measurement of bile acid pool loss. 3,5
As explained above, this report will focus on two specific populations:
-
people presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease
-
people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection of the terminal ileum).
Setting
The relevant setting is secondary care.
Interventions
The intervention is SeHCAT.
Comparators
The comparator will be no SeHCAT test (the current situation).
Outcomes
The following outcomes are considered:
-
effect of testing on treatment plan (e.g. surgical or medical management), where information on the appropriateness of the final treatment plan is also reported
-
effect of testing on clinical outcome (e.g. morbidity and adverse events)
-
prognosis – the ability of test result to predict clinical outcome (e.g. response to treatment).
For included studies reporting any of the above outcome measures, the following outcomes will also be considered if reported:
-
acceptability of tests to patients or surrogate measures of acceptability (e.g. waiting time and associated anxiety)
-
adverse events associated with testing (e.g. pain/discomfort experienced during the procedure and waiting times before results).
Study design
The following study designs were eligible for inclusion:
-
Randomised or non-randomised controlled trials, where participants are assigned to the intervention or comparator tests, for treatment planning, and outcomes are compared at follow-up.
-
Observational studies which report the results of multivariable regression modelling with clinical outcome as the dependent variable and index test result as an independent variable. Included studies should control adequately for potential confounders (e.g. age, sex, disease, etc.).
The following study/publication types were excluded:
-
pre-clinical and animal
-
reviews, editorials, and opinion pieces
-
case reports
-
studies reporting only technical aspects of the test, or image quality
-
studies with < 10 participants.
As no studies were found with either of the above-mentioned study designs, it was decided to broaden the inclusion criteria by allowing lower levels of evidence (change to protocol). Therefore, observational studies reporting data to calculate the accuracy of SeHCAT in predicting treatment response and studies reporting data on the clinical effectiveness of treatment given a positive and/or negative SeHCAT test will also be included.
Search strategy
Search strategies were based on principal diagnosis and intervention, as recommended in the CRD guidance for undertaking reviews in health care and the Cochrane Handbook for Diagnostic Test Accuracy Reviews. 14,16,17
The following databases were searched for relevant studies. No date limit was used and searches were limited to remove animal studies:
-
MEDLINE (1946–week 1 April 2012) (OvidSP)
-
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily Update (up to 17 April 2012) (OvidSP)
-
EMBASE (1980–week 15 2012) (OvidSP)
-
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) (The Cochrane Library Issue 3:2012) (Wiley Online Library)
-
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library Issue 4:2012) (Wiley Online Library)
-
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) (up to 19 April 2012) (CRD website)
-
Health Technology Assessment Database (HTA) (up to 19 April 2012) (CRD website)
-
Science Citation Index (SCI) (1970–18 April 2012) (Web of Science)
-
NIHR HTA (up to 19 April 2012) (internet).
Supplementary searches were undertaken on the following resources to identify grey literature, completed and ongoing trials:
-
National Institutes of Health (NIH) Clinicaltrials.gov (internet) www.clinicaltrials.gov
-
Current Controlled Trials (internet) www.controlled-trials.com
-
WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (internet) www.who.int/ictrp/en
-
EU Clinical Trials Register (EU CTR) (internet) www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu.
Original clinical effectiveness and trials searches undertaken between 9th and 16th January 2012 retrieved 5142 records. Update searches undertaken between 17th and 20th April 2012 found an additional 82 records (after deduplication), but no new includes.
Searches were undertaken to identify studies of SeHCAT in the diagnosis of BAM. The main EMBASE strategy for each set of searches was independently peer reviewed by a second information specialist, using the PRESS-EBC checklist. 18 Search strategies were developed specifically for each database and the keywords associated with BAM were adapted according to the configuration of each database. Searches took into account generic and other product names for the intervention. No restrictions on language or publication status were applied. Limits were applied to remove animal studies. Full search strategies are reported in Appendix 1 .
Electronic searches were undertaken for the following conference abstracts:
-
British Society of Gastroenterology Annual Meetings 2008–2011: www.bsg.org.uk/education/meeting/index.html
-
Advances in Clinical Oesophageal Investigation Conference (ASCONA ESSENTIALS 2011). Online Learning in Gastroenterology (OLGa): http://olga.uegf.org/portal/documents-explore.html#solr0
-
Eighth Summer School of Gastroenterology (ASNEMGE-SS-PRAGUE2011). Online Learning in Gastroenterology (OLGa): http://olga.uegf.org/portal/documents-explore.html#solr0
-
GASTRO2009. Online Learning in Gastroenterology (OLGa): http://olga.uegf.org/portal/documents-explore.html#solr0
-
18th United European Gastroenterology Week (UEGW2010). Online Learning in Gastroenterology (OLGa): http://olga.uegf.org/portal/documents-explore.html#solr0
-
19th United European Gastroenterology Week (UEGW2011). Online Learning in Gastroenterology (OLGa): http://olga.uegf.org/portal/documents-explore.html#solr0
-
Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Science (CPCI-S) (1990–2012/04/18) (Web of Knowledge).
Identified references were downloaded in EndNote X4 software (Thomson Reuters, CA, USA) for further assessment and handling.
References in retrieved articles were checked for additional studies. The final list of included papers was also checked on PubMed for retractions and errata. 19–21
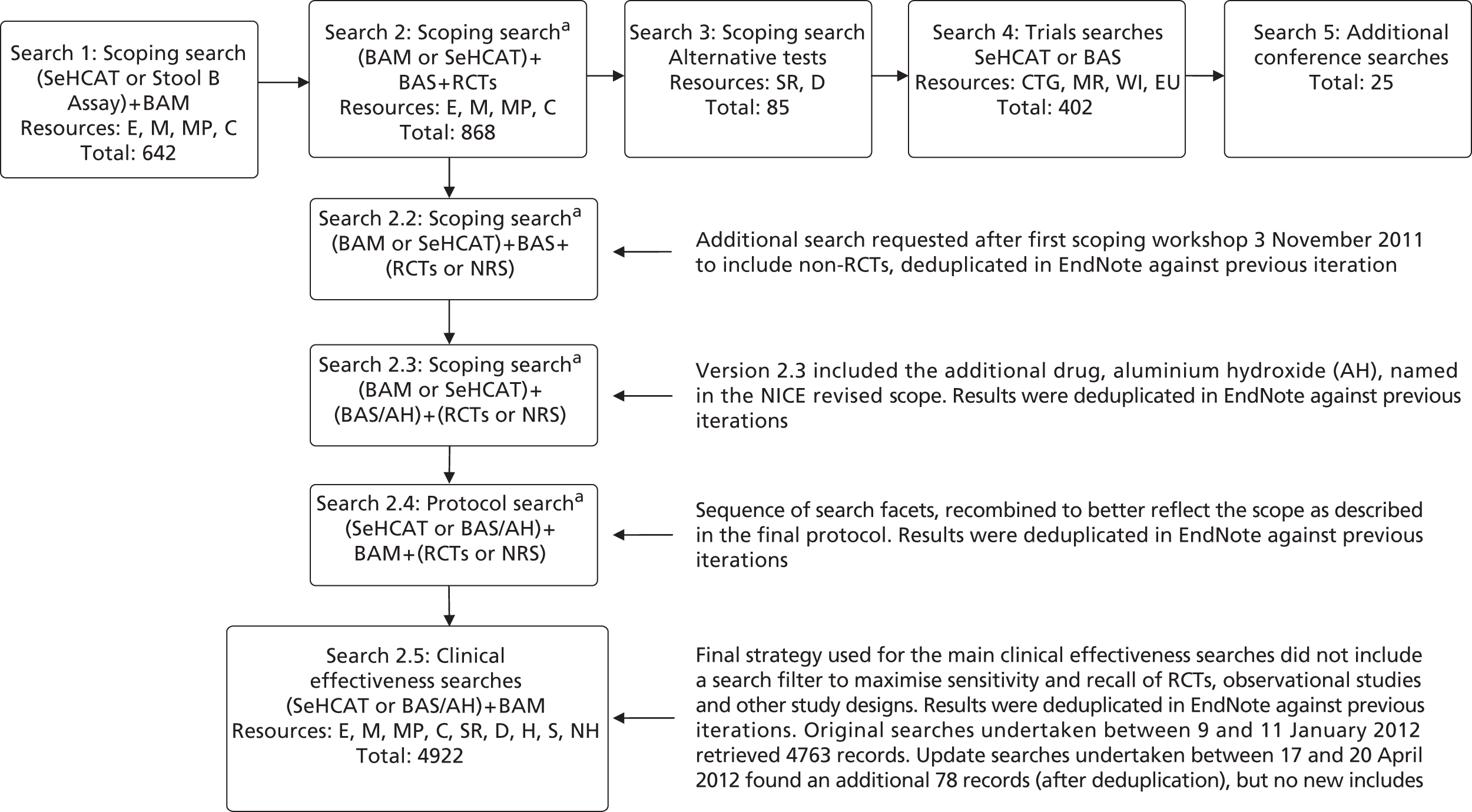
Figure 3 depicts the flow of searches for clinical effectiveness.
FIGURE 3.
Flow of searches developed for SeHCAT clinical effectiveness. Records retrieved – 6944 prior to deduplication; total was 4240 after deduplication. Resources: E, EMBASE; C, CENTRAL; CTG, ClinicalTrials.gov; D, DARE; EU, EU Clinical Trials Register; H, HTA; M, MEDLINE; MP, MEDLINE In Process and Daily Update; MR, metaRegister of Current Controlled Trials; NH, NIHR HTA; S, SCI; SR, CDSR; WI, WHO ICTRP. For the full search strategies please see Appendix 1 . a, Please note: these early iterations of the final clinical effectiveness searches are not included in Appendix 1 . For further information please contact the authors.
Inclusion screening and data extraction
Two reviewers independently screened the titles and abstracts of all reports identified by searches and any discrepancies were discussed and resolved by consensus. Full copies of all studies deemed potentially relevant, after discussion, were obtained and the same two reviewers independently assessed these for inclusion; any disagreements were resolved by consensus. Details of studies excluded at the full paper screening stage are presented in Appendix 5 .
Data relating to study details, participants, intervention and comparator tests, reference standard, and outcome measures were extracted by one reviewer, using a piloted, standard data extraction form. A second reviewer checked data extraction and any disagreements were resolved by consensus.
Quality assessment
The evidence-based Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS) tool22–24 is recommended for assessing the methodological quality of test accuracy studies. 14,17 A revised version of QUADAS (QUADAS-2) has recently been published (www.QUADAS.org). 25 QUADAS-2 more closely resembles the approach and structure of the Cochrane risk of bias tool. It is divided into four key domains covering participant selection, index test, reference standard, and the flow of patients through the study (including timing of tests). Each domain is rated for risk of bias (low, high or unclear) and the tool provides signalling questions, in each domain, to aid reviewers in reaching a judgement. The participant selection, index test and reference standard domains are also, separately, rated for concerns regarding the applicability of the study to the review question (low, high or unclear). Thus, QUADAS-2 separates bias from external validity (applicability) and does not include any items that assess only reporting quality. The QUADAS-2 tool does not currently include domains specific to the assessment of studies comparing multiple index tests, such as those included in this assessment. Further development of QUADAS-2 in this area is planned. A modified version of the QUADAS-2 tool, which includes an additional domain for the comparator test and additional signalling questions in the ‘flow and timing’ domain, has been used in this assessment. Review-specific guidance was produced for the use of the modified version of QUADAS-2 and is reported in Appendix 2 .
The results of the quality assessment are summarised and presented in tables and graphs in the results of the systematic review (see Chapter 4, Results) and are presented in full, by study, in Appendix 3 . No diagnostic accuracy data set included in this assessment was of sufficient size to allow statistical exploration of between-study heterogeneity based on aspects of risk of bias. The findings of the quality assessment were used to inform recommendations for future research.
The risk of bias in the controlled clinical trial was assessed using a table based on the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias. 16
The methodological quality of included effectiveness studies was assessed using standard tools. 14 The Cochrane Collaboration quality assessment checklist was used to assess the methodological quality of each included study as detailed in Table 1 . 16
| Domain | Item | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence generation | Was the allocation sequence adequately generated? | The method used to generate the allocation sequence should be described in sufficient detail to allow an assessment of whether it should produce comparable groups |
| Allocation concealment | Was allocation adequately concealed? | The method used to conceal the allocation sequence should be described in sufficient detail to determine whether intervention allocations could have been foreseen in advance of, or during, enrolment |
| Blinding of participants, personnel and outcome assessors | Was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study? | All measures used, if any, to blind study participants and personnel from knowledge of which intervention a participant received, should be described. Any information relating to whether the intended blinding was effective should also be reported |
| Assessments will be made for each main outcome (or class of outcomes) | ||
| Incomplete outcome data | Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed? | The completeness of outcome data for each main outcome should be described, including attrition and exclusions from the analysis. The authors should report any attrition and exclusions, the numbers in each intervention group (compared with total randomised participants), reasons for attrition/exclusions and any re-inclusions in analyses |
| Assessments will be made for each main outcome (or class of outcomes) | ||
| Selective outcome reporting | Are reports of the study free of suggestion of selective outcome reporting? | The study should be free of the possibility of selective outcome reporting |
| Other sources of bias | Was the study apparently free of other problems that could put it at a high risk of bias? | Overall, the study should be free from any important concerns about bias (i.e. bias from other sources not previously addressed by the other items) |
Each study was awarded a ‘yes’, ‘no’ or ‘unclear/unknown’ rating for each individual item in the checklist. Any additional clarifications or comments were also recorded.
The quality of case–control and cohort studies was assessed using specific checklists for the methodological quality assessment of these studies. In addition, we used an adapted version of the quality assessment checklist by Wedlake et al. 6 (see Appendix 2 ).
Quality assessment was carried out independently by two reviewers. Any disagreements were resolved by consensus. The results of the quality assessment were used for descriptive purposes to provide an evaluation of the overall quality of the included studies and to provide a transparent method of recommendation for design of any future studies. In addition, where enough data were available from the included studies, each of the quality components were included as explanatory variables in a meta-regression analysis to investigate the association of each of these components with study results as a way of explaining possible heterogeneity. Based on the findings of the quality assessment, recommendations are made for the conduct of future studies.
Methods of analysis/synthesis
Meta-analysis was considered inappropriate, owing to the small number of test accuracy studies with varying diagnostic thresholds and between-study heterogeneity in other study design categories (principal diagnosis, treatment dose, definition of response, follow-up period and SeHCAT administration); we therefore employed a narrative synthesis. Typically, this involved the use of text and tables to summarise data. Studies were organised by clinical application (diagnosis of BAM in those with chronic diarrhoea and those with Crohn’s disease) and study design (DTAs, observational studies of treatment effect in SeHCAT-positive patients, and RCT of BAS treatment in patients without SeHCAT testing). Text summaries were supported by tables and figures as appropriate.
Test accuracy
The results of DTA studies included in this review were summarised by clinical indication (chronic diarrhoea only). For all included studies, the absolute numbers of true-positive (TP), false-negative (FN), false-positive (FP) and true-negative (TN) test results of SeHCAT compared with the reference standard of treatment response, as well as sensitivity and specificity values, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were presented in results tables. The results of individual studies were plotted in the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) plane, with the diagnostic threshold used for the SeHCAT test indicated.
As no studies were found for the assessment of SeHCAT’s test accuracy and very few studies for the accuracy of SeHCAT to predict treatment response, it was decided to include studies reporting response to BAS given a positive test to estimate the probability of a positive BAS response at different SeHCAT cut-off points. Based on the data retrieved, a random-effects meta-analysis was performed to find a pooled estimate for each of the three cut-off values.
Dichotomous outcomes
Dichotomous data were analysed by calculating the relative risk (RR) for each trial using the random-effects DerSimonian and Laird method and the corresponding 95% CIs. 26
Continuous outcomes
Continuous data were analysed by calculating the standardised mean difference (SMD) between groups and the corresponding 95% CI, due to the different types of outcome measures. Where the standard deviations and means were not determinable, they were estimated from the data that were provided or from a representative value from other studies.
Systematic differences between studies (heterogeneity) are likely; therefore, the random-effects model was used for the calculation of RRs or SMDs. Heterogeneity was initially to be assessed by measuring the degree of inconsistency in the studies’ results (I 2). This measure (I 2) describes the percentage of total variation across studies that were due to heterogeneity rather than the play of chance. The value of I 2 can lie between 0% and 100%. Low, moderate and high I 2 values correspond to 25%, 50% and 75%.
Where important heterogeneity was identified, we planned to formally investigate this using meta-regression. In addition, a funnel plot (plots of logarithm of the RR for efficacy against the precision of the logarithm of the RR) was planned to be generated in order to estimate potential asymmetry, which is indicative of small study effects. In addition, we wanted to use the Egger regression asymmetry test in order to facilitate the prediction of potential publication biases. This test detects funnel plot asymmetry by determining whether or not the intercept deviates significantly from zero in a regression of the standardised effect estimates against their precision. However, due to the lack of data this was not possible.
Statistical analyses were performed using the following software: RevMan (version 5, The Cochrane Collaboration, The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen, Denmark), Comprehensive Meta-Analyses (CMA version 2, Biostat, Englewood, NJ, USA: www.meta-analysis.com/pages/about_us.html) and Stata (version 10, StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
A detailed commentary on the major methodological problems or biases that affected the studies was also included, together with a description of how this may have affected the individual study results. Recommendations for further research were made based on any gaps in the evidence or methodological flaws.
Results
The literature searches of bibliographic databases identified 4240 references. After initial screening of titles and abstracts, 185 were considered to be potentially relevant and ordered for full-paper screening. Five additional papers were ordered based on information from the manufacturer; one of these studies had already been identified by bibliographic database searches (see Appendix 6 ). One additional study was identified from searches of clinical trials registries. Of the total of 191 publications considered potentially relevant, three could not be obtained within the time scale of this assessment: two possibly because the reference details were not correct27,28 and one was held in British Library stacks which are currently closed for asbestos removal. 29 Figure 4 shows the flow of studies through the review process, and Appendix 5 provides details, with reasons for exclusions, of all publications excluded at the full-paper screening stage.
FIGURE 4.
Flow of studies through the review process.
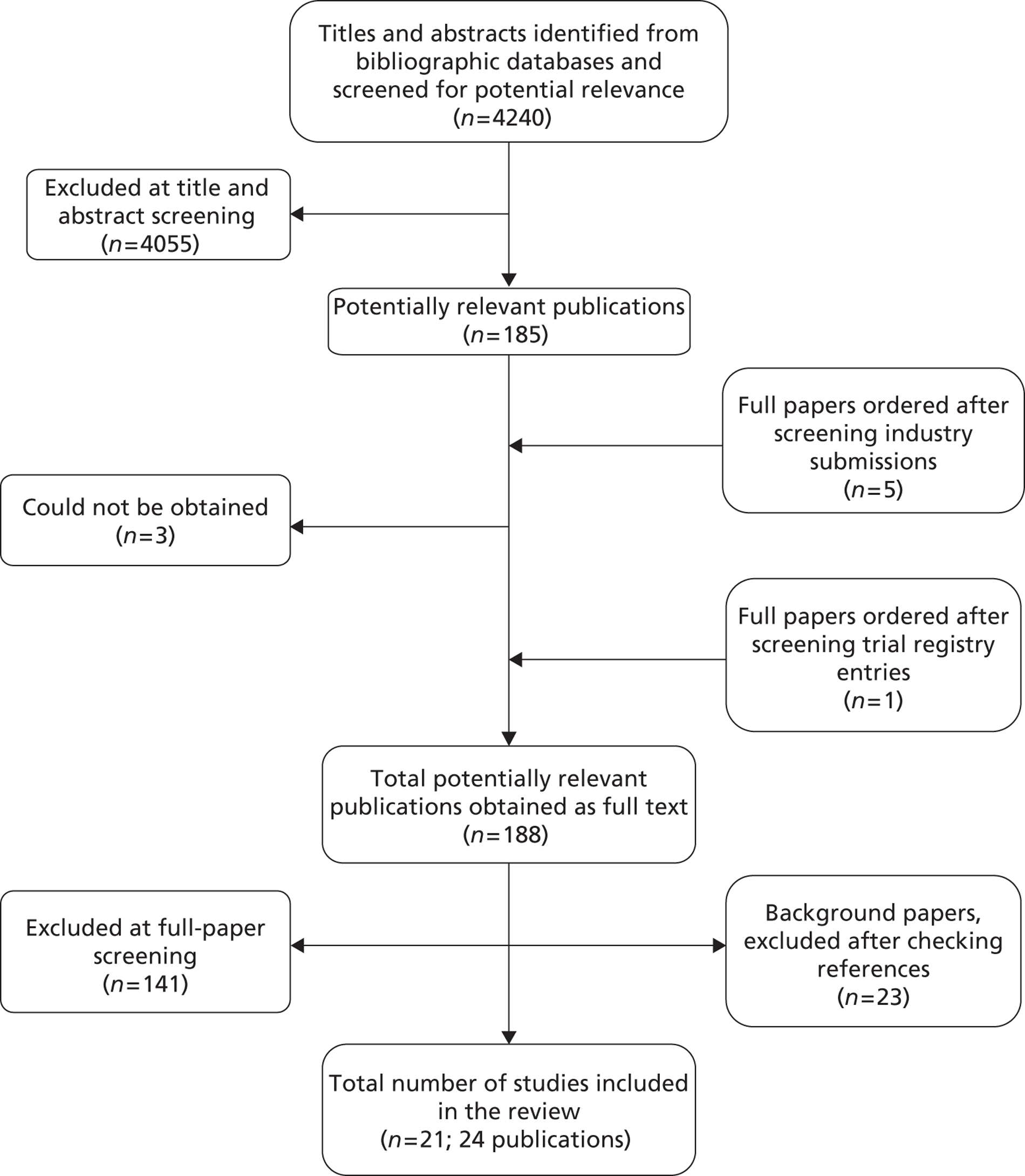
Based on the searches and inclusion screening described above, 24 publications of 21 studies were included in the review. One of the included studies was reported as a conference abstract,30,31 and another included study was reported as a student’s project under supervision of Professor McLaughlin at the University of Manchester. 32
All but one of the included studies were studies providing data on the accuracy of SeHCAT in predicting treatment response (where treatment response is treated as the reference standard), or studies providing data on treatment effects in SeHCAT-positive and -negative patient groups. Out of the 20 SeHCAT studies, 19 included people with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause2,3,5,31–45 and two studies included people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea. 3,46 The remaining study was a RCT which compared treatment with BAS (colesevelam) with placebo for patients with IBS-D. 47 This study reported the following patient-relevant outcomes: colonic transit, bowel function, colonic mucosal permeability and adverse events.
Three included studies were published between 1985 and 1987, nine studies were published in the 1990s, four in 2000, 2001, 2003 and 2007 and five in 2010 and 2011. Twenty of the 21 included studies were conducted in Europe (eight in the UK, five in Scandinavia, three in Spain and Italy each, and one in France) and the remaining study was conducted in the USA. Nineteen of the 21 included studies were single-centre studies and two were multicentre studies. Funding was not reported in most studies, and in one study Amersham International supplied SeHCAT. 39
Table 2 shows the details of included studies. Further details of the characteristics of study participants and the technical details of the conduct of the index test (SeHCAT), comparator test(s) and reference standard (where applicable) and their interpretation are reported in the data extraction tables presented in Appendix 4 .
In the following sections we will discuss the results we found for the accuracy of SeHCAT for the detection of BAM, the accuracy of SeHCAT for the assessment of response to treatment in people with chronic diarrhoea and in people with Crohn’s disease; and the effectiveness of BAS for the treatment of BAM in people with chronic diarrhoea and in people with Crohn’s disease.
| Study ID | Study design | Objective | Chronic diarrhoea | IBS | Crohn’s disease | Study design and outcome extracted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede 201133 | Retrospective study in 298 patients Groups: type I: Crohn’s disease in terminal ileum (n = 29); type I: other (n = 58); type II: diarrhoea unknown cause (n = 14); type III: known cause (n = 97) Recruitment: not described Single centre Country: Denmark Funded by: Not reported/no conflicts |
To investigate the frequency of BAM and treatment responses to cholestyramine with 75SeHCAT scanning among patients suffering from chronic watery diarrhoea | ✓ | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
|
| Dyson 201131 (abstract only) | Retrospective study in 109 patients who underwent SeHCAT test, followed by a questionnaire among 59 patients with a positive test Groups: normal: IBS/no cause found (n = 34), neurological (n = 1), collagenous colitis (n = 2), Crohn’s/colitis (n = 7), drug side effect (n = 1), records unavailable (n = 1) Abnormal: type 1 (ileal disease) (n = 12); type 2 (primary BSD) (n = 33); type 3 (post cholecystectomy) (n=11); not acted on (n = 2); not clinically relevant (no diarrhoea) (n = 1) Recruitment: not described Single centre Country: UK Funded by: not reported |
A review of the indication and result for each SeHCAT test and the final diagnoses reached since introduction of the test in 2007 and a questionnaire to all patients with a positive SeHCAT test, examining treatment received, symptom response, any side effects, satisfaction with their care and effect of their treatment on quality of life | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Eusufzai 199334 | Study in 24 patients, unclear if it is prospective or retrospective Groups: chronic diarrhoea unknown cause despite extensive investigations Single centre Country: Sweden Funded by: Axel Ax:son Johnson Foundation and the Swedish Medical Research Council |
To determine the prevalence of BAM in chronic diarrhoea patients with unknown cause by using the SeHCAT test | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Eusufzai 199335 | Prospective study in 28 patients (four patients had a known ileal dysfunction, of whom one could be traced and removed from the 2 × 2 table but the others had been mixed in the population) and 29 healthy controls Recruitment: patients with diarrhoea who have undergone extensive investigation to evaluate their intestinal function were consecutively referred for the SeHCAT test Single centre Country: Sweden Funded by: Axel Ax:son Johnson Foundation, the Swedish Medical Research Council and the Karolinska Institute |
To determine whether or not there is any correlation between the serum concentration of 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one and results of the SeHCAT test | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Fellous 199436 | Prospective study in 129 patients (23 healthy volunteers of average age 33 years and 106 sick patients of average age 48 years) Group 1: patients with diarrhoea and ileal involvement (n = 33); group 2: patients with organic diarrhoea, without ileal involvement (n = 20); group 3: patients with functional diarrhoea (n = 53) Single centre Country: France Funding: NR |
To determine the performance and the clinical significance of a simplified version of 75 SeHCAT test which measures ileal absorption of bile salt | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Fernandez-Banares 2001;37 related publication48 | Prospective study in 83 patients Group 1: patients with microscopic colitis (n = 51). Forty were consecutive patients newly diagnosed between January 1996 and June 1998. Eleven had already diagnosed but had persistent diarrhoea in spite of treatment with either mesalazine (500 mg three times a day; nine patients) or mesalazine plus oral prednisone (1 mg/kg per day; two patients) Group 2: patients with unexplained functional chronic diarrhoea. Thirty-two consecutive patients were prospectively included between 1996 and 1999. All had unexplained watery diarrhoea Single centre Country: Spain Funding: grant of the ‘Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias’, Ministry of Health, Spain |
(1) To prospectively assess the frequency and severity of BAM in patients with collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis as well as in patients unexplained functional chronic diarrhoea; (2) to evaluate if BAM might be related to the severity of histological changes in microscopic colitis; (3) to investigate the potential therapeutic benefit of cholestyramine in microscopic colitis patients with or without BAM and in patients with previously unexplained chronic diarrhoea and BAM | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Fernandez-Banares 200749 | Study in 62 consecutive patients prospectively selected Group: patients with chronic watery diarrhoea of origin previously unexplained fulfilling Rome II criteria of functional disease Single centre Country: Spain Funding: grant of the Fundacio Banc de Sabadell (Barcelona, Spain) |
(1) To assess prospectively the presence of gluten-sensitive enteropathy, BAM, and sugar malabsorption in consecutive patients with chronic watery diarrhoea of obscure origin fulfilling Rome II criteria of functional disease; and (2) to evaluate the long-term response to specific therapy | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Ford 199238 | Study in 166 undergoing SeHCAT test was retrospectively reviewed Groups: (1) Possible type I BAM: ileal resection (n = 7); previous radiotherapy (n = 12); known Crohn’s disease (n = 4); suspected Crohn’s disease (n = 5) (2) Possible type II BAM (n = 74) (3) Possible type III BAM: post cholecystectomy (n = 30); post vagotomy (n = 11); post cholecystectomy and vagotomy (n = 4) (4) Diabetics (n = 19) Single centre Country: UK Funding: NR |
To report experience of using the SeHCAT test to assess BAM in the investigation if diarrhoea in 166 patients during a 3-year period | ✓ | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
|
| Galatola 19925 | Open prospective trial in 98 consecutive patients fulfilling the selection criteria Groups: IBS patients complaining of diarrhoea Multicentre Country: Italy Funding: NR |
To assess the prevalence of BAM and the efficacy of cholestyramine therapy in improving symptoms associated with this condition in patients with diarrhoeic-type IBS | ✓ | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
|
| Merrick 198539 | Prospective study in 106 patients and 63 controls Four groups: (1) normal controls (n = 63); (2) previously undergone small bowel resection (n = 26); (3) persistent diarrhoea after previous vagotomy or surgery for peptic ulcer (n = 29); (4) chronic diarrhoea of non-inflammatory origin, namely IBS in 43, coeliac disease in 2, small bowel ischaemia in 2, and other miscellaneous conditions in 4 (n = 51) Recruitment: not described Single centre Country: Scotland Funded by Amersham International (supplies of SeHCAT) |
To assess the value of measuring absorption of SeHCAT as a test for the presence of BAM | ✓ | Cohort Accuracy to predict BAM (defined as response to BAS) and response to BAS in SeHCAT-positive and SeHCAT-negative groups separately |
||
| Notta 201140 | Prospective study of 37 patients with diarrhoea syndrome (within 1 month of diagnosis) Recruitment: May 2009 to February 2010 Single centre Country: Spain Funding: NR |
To evaluate the utility of the quantification of abdominal retention of SeHCAT as a first-line diagnostic test in the early pathophysiological diagnosis of patients with chronic diarrhoea | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Nyhlin 199446 | Retrospective study in 53 patients with Crohn’s disease [25 had unoperated Crohn’s disease and their symptoms had failed to respond adequately to conventional treatment, 26 had previously undergone bowel resection for their Crohn’s disease (22 ileocaecal, 3 colonic, and 1 limited ileal resection). Treatment response presented for 22 patients, unclear which] Recruitment: Between 1983 and 1989 Two centres (hospitals) Country: Scotland Funding: NR |
To explore the clinical indications for referring patients with Crohn’s disease for bile acid assessment and the extent of BAM in this selected group of patients | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Odunsi-Shiyanbade 201047, related publications50,51 | Prospective randomised controlled clinical trial of colesevelam vs. placebo in patients with IBS-D Recruitment: 2009, no details Single centre Country: USA Funding: Mayo Clinic |
To measure the effects of the bile acid binder, colesevelam hydrochloride, on gastrointestinal and colonic transit, bowel function, and colonic permeability in IBS-D | ✓ | RCT Response to BAS in an unselected (no SeHCAT testing) population of patients with IBS-D |
||
| Rudberg 199641 | Prospective study of 20 patients with chronic or recurrent diarrhoea of unknown cause Recruitment: consecutive patients (no dates reported) Single centre Country: Sweden Funding: NR |
To investigate the usefulness of SeHCAT in patients suffering from functional diarrhoea and to disclose earlier radiological investigation performed in course of disease | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Sciaretta 198642 | Prospective study of 23 healthy volunteers and 66 patients [resected ileum (n = 36), intestinal problems (n = 17) and chronic diarrhoea (n = 13)] Recruitment: not described Single centre Country: Italy Funding: NR |
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the 75SeHCAT test in patients with pathology or resections of various lengths of terminal 100 cm of the ileum. Group D was excluded from this assessment | ✓ | Cohort Accuracy to predict BAM (defined as response to BAS) and response to BAS in SeHCAT-positive and -negative groups separately |
||
| Sciaretta 198743 | Study of 23 healthy volunteers and 46 patients [IBS-D (n = 38) and cholecystectomy with chronic diarrhoea (n = 8); unclear if prospective] Recruitment: not described Single centre Country: Italy Funding: NR |
To evaluate whether or not BAM assessed by the 75SeHCAT test, had a pathogenetic role in functional chronic diarrhoea and to ascertain whether or not the small bowel transit time (SBTT) could be correlated with the 75SeHCAT test results | ✓ | Cohort Accuracy to predict BAM (defined as response to BAS) and response to BAS in SeHCAT-positive and -negative groups separately |
||
| Sinha 19986 | Retrospective study in 298 patients Recruitment: the records of all patients referred to the department with chronic diarrhoea over a 2-year period were examined retrospectively. IBAM was considered in patients with chronic diarrhoea, a history suggestive of IBS (based on the Manning criteria), and with no other obvious cause of diarrhoea. Seventeen patients were selected to undergo the SeHCAT and they were included in the study if their SeHCATs were positive (n = 9) (no dates reported) Single centre Country: UK Funding: NR |
To identify patients with idiopathic BAM, to describe their clinical features, both qualitatively and quantitatively, and to assess the response to cholestyramine | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Smith 20003 | Retrospective study in 304 patients Recruitment: NR Single centre Country: UK Funding: NR |
To investigate BAM and its response to treatment in patients seen in a district general hospital with chronic continuous or recurrent diarrhoea | ✓ | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
|
| Tunney 201132 | Retrospective study in 276 patients Recruitment: Patients who underwent SeHCAT scanning between April 2005 and January 2011, using a database compiled by the Nuclear Medicine Department of the Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust Single centre Country: UK Funding: NR |
To determine how useful the BSG guidelines are for the investigation of chronic diarrhoea. This focused on the question of whether or not SeHCAT should be prioritised in the investigation of chronic diarrhoea, rather than considered as a second-line option | ✓ | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
|
| Wildt 200344 | Retrospective study in 135 patients Recruitment: during a 5-year period (1997–2001) the SeHCAT test was performed in 135 patients with chronic diarrhoea from the Department of Gastroenterology, H:S Hvidovre Hospital, in whom a primary programme for diagnostic evaluation of chronic diarrhoea had not revealed a cause Single centre Country: Denmark Funding: NR |
To evaluate the usefulness of SeHCAT testing by assessing the extent of BAM and describing the clinical characteristics in a group of patients with chronic diarrhoea. Clinical outcome after treatment with cholestyramine was also evaluated | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
||
| Williams 199145 | Retrospective study in 181 patients Recruitment: patients referred for measurement of 75SeHCAT retention because of unexplained diarrhoea between 1982 and 1989 and entered into a departmental database which recorded the a priori diagnosis and relevant diagnostic information Single centre Country: Scotland Funding: NR |
To determine the clinical characteristics of patients with idiopathic BAM and to identify their response to treatment | ✓ | Cohort Response to BAS given a positive test result |
Accuracy of selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine for the detection of bile acid malabsorption
As mentioned in the NICE scope, there is no direct comparator for SeHCAT. Current diagnostic options include analysis of a patient’s history, investigations to exclude ‘red flag’ symptoms and a variety of other diagnostic tests such as blood tests and lactose tolerance tests. Trial of treatment and measurement of faecal bile acids are two methods used, with mixed results, to diagnose BAM. They are, however, not widely used in current practice.
In addition, the clinical effectiveness of BASs in people with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and in people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause is not known. Therefore, this assessment will focus on the value of a SEHCAT test in predicting the response to treatment with BASs.
Any studies described in the literature as accuracy studies (Sciaretta42 in Johnston et al. ;52 Merrick39 and Sciaretta42 in Kurien et al. ;53 and Sciaretta42 in Wedlake et al. 6), will be included in this review under studies predicting the response to BAS, if treatment response was assessed.
None of the studies evaluated in this report, including the studies described in the literature as accuracy studies, was included in this review as diagnostic test accuracy (DTA) studies, because they either do not use an acceptable reference standard or they include a population not in line with the scope (i.e. healthy volunteers or people with ileal resection).
Accuracy of selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine for the assessment of response to treatment in people with chronic diarrhoea
Nineteen of the 20 studies with information on the relationship between SeHCAT and response to treatment were in patients with chronic diarrhoea. These can be divided in different groups, depending on the reliability of the results.
Most studies (12 out of 19) have no information about respondents with a negative SeHCAT test. 2,3,5,31–33,37,38,40,44,45,49 Therefore, these studies should be regarded as flawed design for the purposes of this review and cannot be used to reliably asesess the relationship between SeHCAT and response to treatment. Another three studies34,35,41 have very limited data for respondents with a negative SeHCAT test.
Four studies36,39,42,43 have data for all respondents with a negative SeHCAT test. However, in two of these studies36,39 it is unclear why certain patients are treated and others not. In Fellous et al. ,36 16 out of 53 patients with functional diarrhoea were treated with cholestyramine; 11 of these had a positive SeHCAT test and 5 a negative SeHCAT test. It is not clear why the other 37 patients with functional diarrhoea did not receive cholestyramine.
This leaves three studies to assess the relationship between the SeHCAT test and treatment with cholestyramine:
-
Merrick et al. 39 estimated the sensitivity of SeHCAT in predicting a positive response as 0.667 (95% CI 0.223 to 0.957), and the specificity as 0.971 (95% CI 0.847 to 0.999) using a cut-off of 8% for the test. Using a cut-off of 15%, the sensitivity is 1.000 (95% CI 0.541 to 1.000) and the specificity is 0.912 (95% CI 0.763 to 0.981).
-
Sciaretta et al. 42 estimated the sensitivity of SeHCAT in predicting a positive response as 0.857 (95% CI 0.421 to 0.996), and the specificity as 1.000 (95% CI 0.541 to 1.000) using a cut-off of 5% for the test. However, only 13 patients were included in this analysis.
-
Sciaretta et al. 43 estimated the sensitivity of SeHCAT in predicting a positive response as 0.950 (95% CI 0.751 to 0.999), and the specificity as 0.962 (95% CI 0.804 to 0.999) using a cut-off of 8% for the test.
It should be noted here that in the study by Merrick et al. ,39 31 patients were considered TNs. This assessment was based on long-term follow-up: ‘None of the 31 patients with irritable bowel disease who retained more than 15% at seven days showed any evidence of small bowel disease, and none appeared during a follow-up of at least 12 months, and in some up to 24 months. Simple conservative treatment resolved or eased most symptoms’ (p. 266). The remaining nine patients were treated with cholestyramine; five of these had a SeHCAT test result < 8%, one of whom did not respond to treatment and four had an equivocal (between 8% and 15%) SeHCAT test result; two of these patients responded to cholestyramine and two did not.
In the study by Sciaretta et al. ,43 the cut-off for a positive SeHCAT was 8% based on a 7-day SeHCAT retention measurement. However, in the study by Sciaretta et al. ,42 the cut-off for a positive SeHCAT was most likely based on a 3-day retention measurement, which was according to the authors equivalent to 5% at 7 days. These issues and possible overlap in populations in both Sciaretta papers are discussed in more detail in the quality assessment (QUADAS-2, see Appendix 3 ) of these studies.
As can be seen in Figure 5 , the sensitivity is highest with a cut-off of 15% and decreases with lower cut-offs; while the specificity is less clearly related to the cut-off used.
FIGURE 5.
‘Accuracy’ of SeHCAT to predict a response to treatment at different cut-offs. The centre dots represent the point estimates for sensitivity and specificity of SeHCAT in predicting response to treatment in the three studies at different cut offs (5%, 8% and 15%). The vertical and horizontal lines represent the 95% CIs for sensitivity and specificity respectively; see data in Table 4 .
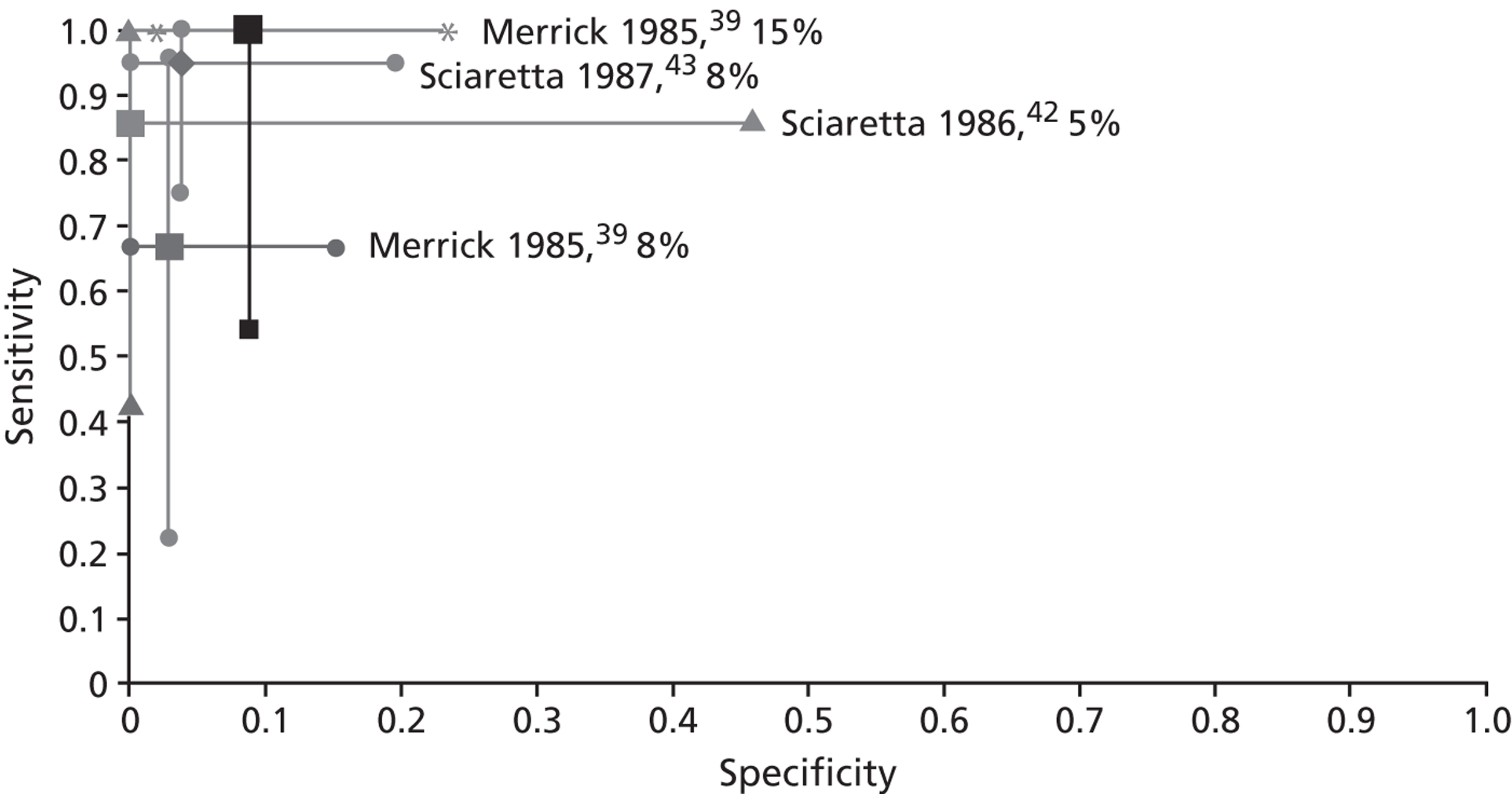
The between-study heterogeneity in these three studies is considerable. The principal diagnosis, treatment dose, the definition of response, follow-up period and SeHCAT administration was different between trials. Most of these differences were between Merrick and the two Italian studies, but even the two Italian studies were not completely similar (see Appendices 3 and 4 for details).
Three studies were included in the QUADAS-2 assessment; all three studies were rated as ‘unclear’ risk of bias for the patient selection domain. Merrick et al. 39 was rated ‘high’ risk of bias for the ‘flow and timing’ domain of QUADAS-2 because only test positive and equivocal patients received the reference treatment. The test-negative patients were followed up and hence all patients did not receive the same reference standard. Sciaretta et al. 42 was rated ‘high’ risk of bias for the ‘index test’ domain of QUADAS-2 because a threshold was not prespecified. Sciaretta et al. 43 was rated as ‘low’ risk of bias for all the QUADAS-2 domains in this assessment except for ‘patient selection’ domain, where it was rated ‘unclear’ risk of bias because the study did not clearly state whether the patient enrolment was prospective or retrospective. The applicability concerns were high in two studies for the ‘patient selection’ domain because some patients had cholecystectomy and < 90% of patients had unknown-cause diarrhoea. 42,43 Merrick et al. 39 had low applicability concerns for the ‘patient selection’ domain.
Table 3 provides a summary of the quality assessments for studies in this section and Table 4 summarises individual study results.
| Study ID | Risk of bias | Applicability concerns | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient selection | Index test | Reference standard | Flow and timing | Patient selection | |
| Merrick 198539 | ? | ☺ | ? | ☹ | ☺ |
| Sciaretta 198642 | ? | ☹ | ? | ? | ☹ |
| Sciaretta 198743 | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ |
| Study ID | Patient data, n | Index test or comparator | Reference standard | TP | FN | FP | TN | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Tested/treated, n patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria: chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause/IBS | ||||||||||
| Merrick 198539 | 43 IBS patients | SeHCAT; 8% cut-off | Responsea | 4 | 2 | 1 | 33b | 0.667 (0.223 to 0.957) | 0.971 (0.847 to 0.999) | Three patients not treated |
| 43 IBS patients | SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | Responsea | 6 | 0 | 3 | 31b | 1.000 (0.541 to 1.000) | 0.912 (0.763 to 0.981) | Three patients not treated | |
| Sciaretta 198642 | 13 patients (group D only) | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Responsec | 6 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0.857 (0.421 to 0.996) | 1.000 (0.541 to 1.000) | All treated |
| Sciaretta 198743 | 46 patients (group B only) | SeHCAT; 8% cut-off | Responsed | 19 | 1 | 1 | 25 | 0.950 (0.751 to 0.999) | 0.962 (0.804 to 0.999) | All treated |
Accuracy of selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine for the assessment of response to treatment in people with Crohn’s disease
None of the studies looking specifically at people with Crohn’s disease presented reliable data for the prediction of response to treatment with BAS. Only two studies looked at this population. 3,46 Neither of these studies presented data for people with a negative SeHCAT test. In addition, it was not clear why certain people were treated and others not. In the study by Nyhlin et al. ,46 34 out of 51 patients had a positive SeHCAT test at a 10% cut-off, while 22 patients were treated, of whom one had a negative SeHCAT (at 10%). In the study by Smith et al. ,3 24 out of 44 patients had a positive SeHCAT test at a 10% cut-off; 11 of these were successfully treated with conventional treatment (prednisolone with or without 5-ASA) and a further nine patients were treated with BAS after conventional treatment had failed. Finally, Nyhlin et al. 46 included patients with or without resection.
Effectiveness of bile acid sequestrants for the treatment of bile acid malabsorption in patients with chronic diarrhoea
One controlled clinical trial compared colesevelam with placebo for patients with IBS-D. 47,50,51 All participants had fasting plasma 7α-C4 (C4) measured to assess for underlying BAM and had serum FGF-19 measured. However, it is not certain whether or not this was used as an inclusion criterion. SeHCAT was not used in this trial.
No controlled trials were found to assess the clinical effectiveness of cholestyramine in terms of bowel function in patients with chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause, nor were any such trials found for other BASs.
This randomised trial was considered to have ‘risk of bias’ in a number of areas: sequence generation was described as independently generated by a statistician at the Mayo Clinic, no further details were reported, allocation concealment was not described, and results for some of the outcomes were not reported.
According to the authors, ‘colesevelam modestly affected overall colonic transit (24 hours, p = 0.22). Emptying of the ascending colon took an average four hours longer in patients given colesevelam compared with placebo. Colesevelam was associated with greater ease of stool passage (p = 0.048) and somewhat firmer stool consistency (p = 0.12). No effects on mucosal permeability or safety were identified’ (p. 160). 47 Our analyses using Cochrane’s Review Manager software identified no significant differences between colesevelam and placebo for all outcomes.
Table 5 provides a summary of the risk of bias assessment for this study and Table 6 summarises results.
| Items | Judgement | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Adequate sequence generation? | Unclear | ‘An independent Mayo Clinic statistician generated the randomisation codes. Mayo Research Pharmacy maintained the randomisation schedule in case of emergency.’ No further details reported |
| Allocation concealment? | No | No details reported |
| Blinding? | Yes | Double blind. ‘All clinical and laboratory study personnel were blinded throughout the study until all data were locked and analysed’ |
| Were patient characteristics comparable at baseline? | Yes | See table 1 in paper |
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? | Yes | All outcomes assessed appear to be reported for all patients |
| Free of selective reporting? | No | Some outcomes assessed were not reported [HAD and SCL-90 (somatisation)] |
| Free of other bias? | Yes |
| Study ID | Population | Intervention (n) | Comparator (n) | Outcome | n with outcome (I) | n with outcome (C) | OR (95% CI) | Mean ± SEM (I) | Mean ± SEM (C) | Mean difference (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odunsi-Shiyanbade 2010;47 related publications50,51 | Patients with IBS-D | Colesevelam (1.875 g, twice daily) for 12–14 days (n = 12) | Matching placebo (n = 12) | Transit | ||||||
| GE t ½ (minutes) | 12 | 12 | 156.1 ± 17.36 | 119.6 ± 7.69 | 36.50 (–0.72 to 73.72) | |||||
| CF 6 (%) | 12 | 12 | 58.5 ± 8.72 | 64.5 ± 8.17 | –6.00 (–29.42 to 17.42) | |||||
| GC 4 (hours) | 12 | 12 | 0.42 ± 0.16 | 0.81 ± 0.19 | –0.39 (–0.88 to 0.10) | |||||
| GC 24 (hours) | 12 | 12 | 2.68 ± 0.32 | 3.30 ± 0.33 | –0.62 (–1.52 to 0.28) | |||||
| GC 48 (hours) | 12 | 12 | 4.65 ± 0.13 | 4.47 ± 0.20 | 0.18 (–0.29 to 0.65) | |||||
| AC t ½ (hours) | 12 | 12 | 18.85 ± 2.88 | 14.9 ± 3.58 | 3.95 (–5.06 to 12.96) | |||||
| Bowel function | ||||||||||
| Stool frequency per day | 12 | 12 | 2.14 ± 0.31 | 2.25 ± 0.34 | –0.11 (–1.01 to 0.79) | |||||
| Stool consistency by BSFS | 12 | 12 | 3.78 ± 0.27 | 4.57 ± 0.35 | –0.79 (–1.66 to 0.08) | |||||
| Ease of passage (scale 1–7) | 12 | 12 | 4.18 ± 0.14 | 4.39 ± 0.11 | –0.21 (–0.56 to 0.14) | |||||
| Mucosal permeability | ||||||||||
| Urinary excretion of mannitol 8–24 hours, mg | 12 | 12 | 64.3± 13.3 | 45.8 ± 8.8 | 18.50 (–12.75 to 49.75) | |||||
| Urinary excretion of lactulose 8–24 hours, mg | 12 | 12 | 28.5 ± 5.9 | 19.9 ± 3.12 | 8.60 (–4.48 to 21.68) | |||||
| L/M ratio 8–24 hours | 12 | 12 | 0.59 ± 0.19 | 0.49 ± 0.05 | 0.10 (–0.29 to 0.49) | |||||
| HADS | NR | |||||||||
| SCL-90 (somatisation) | NR | |||||||||
| Adverse eventsa | ||||||||||
| Uterine cramps | 1/12 | 2/12 | 0.45 (0.04 to 5.81) | |||||||
| Headache | 5/12 | 4/12 | 1.43 (0.27 to 7.52) | |||||||
| URI | 1/12 | 4/12 | 0.18 (0.02 to 1.95) | |||||||
| Lower abdominal cramps | 2/12 | 0/12 | 5.95 (0.26 to 138.25) | |||||||
| Flatulence | 3/12 | 1/12 | 3.67 (0.32 to 41.59) | |||||||
| Green-coloured stools | 2/12 | 2/12 | 1.00 (0.12 to 8.56) | |||||||
| Nausea | 2/12 | 3/12 | 0.60 (0.08 to 4.45) | |||||||
In addition to the RCT reported above, information about the clinical effectiveness of BAS for the treatment of BAM can be derived from the 19 studies reported in Chapter 4 (see Accuracy of SeHCAT for the assessment of response to treatment in people with chronic diarrhoea). All 19 studies provide data on the clinical effectiveness of BAS given a positive SeHCAT test; three studies39,42,43 also provide data on the effectiveness of BAS given a negative SeHCAT test. Table 7 provides a summary of the risk of bias assessment for these studies; the results are reported in Tables 8 and 9 . In these tables we have used data for the population defined in the scope where we could find them and we have included only patients who were actually treated, ignoring those with a positive SeHCAT test who were not treated.
| Study ID | Q1: prospective | Q2: diarrhoea | Q3: known cause | Q4: SeHCAT test | Q5: cut-off | Q6: reason treatment | Q7: neg. test | Q8: treatment | Q9: response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede 201133 | R | N | N (57), Y (298) | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y |
| Dyson 201131 (abstract only) | R | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y |
| Eusufzai 199334 | Unclear | Y | N | Y | Y | N | Y: 2/15 | Y | Y |
| Eusufzai 199335 | P | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y: 1/13 | N | N |
| Fellous 199436 | P | Y | N (36), Y (53) | Y | Y | N | Y: all | Y | Y |
| Fernandez-Banares 200137 | P | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
| Fernandez-Banares 200749 | P | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y |
| Ford 199238 | R | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
| Galatola 19925 | P | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
| Merrick 198539 | P | Y | N (43), Y (106) | Y | Y | N | Y: all | N | Y |
| Notta 201140 | P | N | Unclear | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y |
| Rudberg 199641 | P | Y | N | Y | Y | N | Y: 4/10 | Y | Y |
| Sciaretta 198642 | P | Y | N (13) | Y | Y | Y | Y: all | N | Y |
| Sciaretta 198743 | Unclear | Y | Y (46) | Y | Y | Y | Y: all | Y | Y |
| Sinha 19982 | R | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
| Smith 20003 | R | N | Unclear | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y |
| Tunney 201132 | R | N | N (136) | Y | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Wildt 200344 | R | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
| Williams 199145 | R | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y |
| Study ID | Patient data (n) | Index test or comparator | Reference standard | Total N | Number treated | Number with positive/negative test | Number of responders given a positive SeHCAT test | Number of responders given a negative SeHCAT test | Tested/treated (n patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria: chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause/IBS | |||||||||
| Merrick 198539 | 43 IBS patients | SeHCAT; 8% cut-off | Response | 43 | 40 | 5/35 | 4a out of 5 (80%) | 2 out of 35 (5%)b | 3 patients not treated |
| 43 IBS patients | SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | Response | 43 | 40 | 9/31 | 6a out of 9 (67%) | 0 out of 31 (0%)b | 3 patients not treated | |
| Sciaretta 198642 | 13 patients (group D only) | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Response | 13 | 13 | 6/7 | 6c out of 6 (100%) | 1 out of 7 (14%) | All treated |
| Sciaretta 198743 | 46 patients (group B only) | SeHCAT; 8% cut-off | Response | 46 | 46 | 20/26 | 19d out of 20 (95%) | 1 out of 26 (4%) | All treated (8/46 patients had cholecystectomy) |
| Study ID | Patient data (n) | Index test or comparator | Reference standard | Total N | Number treated | Number with positive/negative test | Number of responders given a positive SeHCAT test | Number of responders given a negative SeHCAT test | Tested/treated (n patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria: Chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause/IBS | |||||||||
| Borghede 201133 | 298 patients | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Response | 298 | 171 | 129/42 | 89a out of 129 (69%) | Not reliableb | 30 patients not treated |
| SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | 298 | 171 | 157/14 | 111a out of 157 (71%) | Not reliable | ||||
| SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | 298 | 171 | 171/0 | 119a out of 171 (70%) | No patients treated | ||||
| 114 Type II BAM | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Response | 114 | 57 | 39/18 | 29a out of 39 (74%) | Not reliable | x patients not treated | |
| SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | 114 | 57 | 53/4 | 41a out of 53 (77%) | Not reliable | ||||
| SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | 114 | 57 | 57/0 | 43a out of 57 (75%) | No patients treated | ||||
| Dyson 201131 (abstract only) | 109 patients (all); 59 positive test only | SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | Response | 109 | 27 | 27/0 | 18c out of 27 (67%) | No patients treated | 59 positive test; response data for 27/59 |
| Eusufzai 199334 | 24 patients | SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 24 | 8 | 6/2 | 2d out of 6 (33%) | Not reliable | 13 not treated; three treated had cholecystectomy |
| Eusufzai 199335 | 28 patients | SeHCAT; cut-off unclear | Response | 28 | 11 | 10/1 | 8e out of 10 (80%) | Not reliable | 16 patients not treated; one patient treated had extensive ileal resection |
| Fellous 199436 | 53 patients with functional diarrhoea | SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 53 | 16 | 11/5 | 8f out of 11 (73%) | Not reliable | 16/53 patients treated; unclear why these treated |
| Fernandez-Banares 200137 | 32 patients (chronic diarrhoea only) | SeHCAT; 11% cut-off | Response | 32 | 20 | 20/0 | 20g out of 20 (100%) | No patients treated | 24/32 positive SeHCAT; 11 patients not treated; one unclear response ignored. 9/32 patients had cholecystectomy |
| 83 patients (all) | SeHCAT; 11% cut-off | Response | 83 | 50 | 42/8 | 39g out of 42 (93%) | Not reliable | 46/83 positive SeHCAT; 29 not treated; four unclear responses ignored | |
| Fernandez-Banares 200749 | 62 patients | SeHCAT; 11% cut-off | Response | 62 | 37 | 37/0 | 28h out of 37 (76%) | No patients treated | 25 patients not treated |
| Ford 199238 | 166 patients [no separate data for possible type II BAM (n = 74)] | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Complete response | 166 | 84 | 40/44 | 37i out of 40 (93%) | Not reliable | 82 patients not treated |
| SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | 166 | 84 | 69/15 | 49i out of 69 (71%) | Not reliable | ||||
| SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | 166 | 84 | 84/0 | 49i out of 84 (58%) | No patients treated | ||||
| SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Partial response | 166 | 84 | 40/44 | 37i out of 40 (93%) | Not reliable | |||
| SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | 166 | 84 | 69/15 | 59i out of 69 (86%) | Not reliable | ||||
| SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | 166 | 84 | 84/0 | 66i out of 84 (79%) | No patients treated | ||||
| Galatola 19925 | 98 patients | SeHCAT 11.7% cut-off | Response | 98 | 41 | 41/0 | 39j out of 41 (95%) | No patients treated | 42/56 followed up; one unclear |
| Best case | 98 | 56 | 42/14 | 39j out of 42 (93%) | 14 out of 14 (100%) | 42 patients not treated | |||
| Worst case | 98 | 56 | 42/14 | 39j out of 42 (93%) | 0 out of 14 (0%) | 42 patients not treated | |||
| Notta 201140 | 37 patients | SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 37 | 16 | 16/0 | 8k out of 16 (50%) | No patients treated | 21 patients not treated |
| Rudberg 199641 | 20 patients | SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 20 | 11 | 3/8 | 2l out of 3 (67%) | Not reliable | Seven patients not treated; 2/13 patients had cholecystectomy |
| SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | Response | 20 | 11 | 7/4 | 6l out of 7 (86%) | Not reliable | |||
| Sinha 19982 | 17 patients | SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | Response | 17 | 9 | 9/0 | 6m out of 9 (67%) | No patients treated | 17 patients selected for SeHCAT, nine had a positive test |
| Smith 20003 | 197 IBS-D patients | SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 197 | 34 | 34/0 | 28n out of 34 (82%) | No patients treated | 65/197 positive SeHCAT; 40/65 treated and followed up; six conventional success |
| Tunney 201132 | 276 in total. 136 chronic diarrhoea, no known risk factors | SeHCAT; 8% cut-off | Response | 136 | 22 | 15/7 | 10e out of 15 (67%) | Not reliable | 33/136 positive SeHCAT; 32 analysed for response (two not treated, eight lost to follow-up). Unclear which patients treated |
| SeHCAT;15% cut-off | Response | 136 | 22 | 22/0 | 12e out of 22 (55%) | No patients treated | |||
| Wildt 200344 | 135 patients (all) | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Response | 135 | 54 | 31/23 | 23o out of 31 (74%) | Not reliable | 2/135 lost to follow-up; 74/133 positive SeHCAT; 61/74 treated (13 not treated); 54/61 followed up |
| SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 135 | 54 | 47/7 | 33o out of 47 (70%) | Not reliable | |||
| SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | Response | 135 | 54 | 54/0 | 38o out of 54 (70%) | No patients treated | |||
| 56 patients with type 2 BAM | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Response | 56 | 17 | 13/4 | 11o out of 13 (85%) | Not reliable | ||
| SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 56 | 17 | – | Not reported | ||||
| SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | Response | 56 | 17 | 17/0 | 14o out of 17 (82%) | No patients treated | |||
| Williams 199145 | 181 patients | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Response | 181 | 42 | 21/21 | 21p out of 21 (100%) | Not reliable | 60/181 positive SeHCAT; 42/60 treated (18 not treated). Five treated with aluminium hydroxide excluded |
| SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 181 | 42 | 34/8 | 24p out of 31 (77%) | Not reliable | |||
| SeHCAT; 15% cut-off | Response | 181 | 42 | 42/0 | 24p out of 39 (62%) | No patients treated | |||
Meta-analysis of test accuracy studies was considered inappropriate, owing to the small number of studies with varying diagnostic thresholds and between-study heterogeneity in other study design categories (principal diagnosis, treatment dose, definition of response, follow-up period and SeHCAT administration); therefore, we employed a narrative synthesis in Chapter 4 (see Accuracy of selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine for the assessment of response to treatment in people with Crohn’s disease). As mentioned previously, the between-study heterogeneity in the 19 studies included in this section is also considerable. The principal diagnosis, treatment dose, the definition of response, follow-up period and SeHCAT administration were different between trials (see Appendix 4 for details). However, for the economic model we need estimates for the probability of a positive SeHCAT test in people with IBS-D or Crohn’s disease and the probability of a positive BAS response given a positive test result (see Chapter 5 , Model parameters). These probabilities can be derived from the data in these studies. Despite the heterogeneity between studies, we decided to combine the results from different studies to derive an estimate for these probabilities. As no studies could be classified as superior based on risk of bias, we decided to include all studies in the meta-analysis. We chose a random-effects model, as this would ensure that the CI would be wide enough to capture most uncertainties. However, given the large heterogeneity, these results should be treated with appropriate caution.
For those with a positive SeHCAT test response rates ranged from 74% to 100% at a cut-off of 5% and from 62% to 86% at a cut-off of 15%. For those with a negative SeHCAT test the response rate was 14% at a cut-off of 5% and 0% at a cut-off of 15%.
Table 10 shows the average response rates given a positive or negative SeHCAT test at all different cut-offs using all available data for patients with unknown cause chronic diarrhoea. This analysis combines results from different studies weighted by population size.
| Cut-off | Positive SeHCAT test | Negative SeHCAT test |
|---|---|---|
| Response rate, % (n, N) | ||
| 5% | 85 (79, 4) | 14 (7, 1) |
| 8% | 80 (5, 1) | 5 (51, 2) |
| 10% | 73 (143, 6) | |
| 11% | 76 (37, 1) | |
| 11.7% | 95 (41, 1) | |
| 15% | 72 (138, 6) | 0 (31, 1) |
| Unclear | 80 (10, 1) | |
Using the random-effects analysis,26 the results are very similar ( Table 11 ). Data are now grouped in cut-off bands of 5%, 10%, and 15% plus or minus 2% points. These are the data used in the economic model.
| Cut-off bands | Positive SeHCAT test |
|---|---|
| Response rate, % (n, N) | |
| 5% | 88, 95% CI 75 to 100 (79, 4) |
| 10% | 76, 95% CI 65 to 86 (226, 9) |
| 15% | 73, 95% CI 66 to 81 (138, 6) |
Effectiveness of bile acid sequestrant for the treatment of bile acid malabsorption inpatients with Crohn’s disease
As reported earlier in this chapter (see Accuracy of selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine for the assessment of response to treatment in people with Crohn’s disease), none of the studies looking specifically at people with Crohn’s disease presented reliable data for the prediction of response to treatment with BAS. Only two studies looked at this population. 3,46 Neither of these studies presented data for people with a negative SeHCAT test. In addition, it was not clear why certain people were treated and others not. In Nyhlin et al. ,46 34 out of 51 patients had a positive SeHCAT test at a 10% cut-off, while 22 patients were treated, of whom one had a negative SeHCAT (at 10%). In Smith et al. ,3 24 out of 44 patients had a positive SeHCAT test at a 10% cut-off; 11 of these were successfully treated with conventional treatment (prednisolone with or without 5-ASA) and a further nine patients were treated with BAS after conventional treatment had failed. Finally, Nyhlin et al. 46 included patients with or without resection. Nevertheless, information about the effectiveness of BAS for the treatment of BAM given a positive SeHCAT test can be obtained from the two studies.
Table 12 provides a summary of the quality assessments for studies in this section and Table 13 summarises individual study results.
| Study ID | Q1: prospective | Q2: diarrhoea | Q3: known cause | Q4: SeHCAT test | Q5: cut-off | Q6: reason treatment | Q7: negative test | Q8: treatment | Q9: response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nyhlin 199446 | R | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Smith 20003 | R | N | Unclear | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y |
| Study ID | Patient data (n) | Index test or comparator | Reference standard | Total N | Number treated | Number with positive/negative test | Number of responders given a positive SeHCAT test | Number of responders given a negative SeHCAT test | Tested/treated (n patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria: Crohn’s disease without resection | |||||||||
| Nyhlin 199446 | 53 patients (± resection) | SeHCAT; 5% cut-off | Response | 53 | 22 | 19/3 | 18a out of 19 (95%) | Not reliableb | Two patients not analysed; 29 not treated |
| SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 53 | 22 | 21/1 | 18a out of 21 (86%) | Not reliable | |||
| Smith 20003 | 44 patients (without resection) | SeHCAT; 10% cut-off | Response | 44 | 9 | 9/0 | 8c out of 9 (89%) | No patients treated | 24 positive SeHCAT; 20/24 treated and followed up; 11 conventional success |
For those with a positive SeHCAT test the response rate was 95% at a cut-off of 5% and 86% or 89% at a cut-off of 15%.
Table 14 shows the average response rates given a positive SeHCAT test at two different cut-offs using all available data.
| Cut-off | Positive SeHCAT test |
|---|---|
| Response rate (n) | |
| 5% | 95% (19) |
| 10% | 87% (30) |
Summary
Twenty of the 21 included studies in the systematic review were considered for the assessment of the value of SeHCAT in predicting the response to BAS. Of these 20 SeHCAT studies, 19 included people with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause2,3,5,31–45 and two studies included people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea. 3,46
Three studies were reasonably reliable in assessing the relationship between the SeHCAT test and treatment with cholestyramine. 39,42,43 However, the studies had small numbers of patients with unknown cause chronic diarrhoea, they used different cut-offs for the assessment of BAM and between-study heterogeneity was considerable.
Sensitivity ranged from 0.67 (at a cut-off of 8%) to 1.00 (at a cut-off of 15%) and specificity ranged from 0.91 (at a cut-off of 15%) to 1.00 (at a cut-off of 5%) ( Table 15 ).
| Study ID | Cut-off bands | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Merrick 198539 (n = 40) | 8% | 0.667 (0.223 to 0.957) | 0.971 (0.847 to 0.999) |
| 15% | 1.000 (0.541 to 1.000) | 0.912 (0.763 to 0.981) | |
| Sciaretta 198642 (n = 13) | 5% | 0.857 (0.421 to 0.996) | 1.000 (0.541 to 1.000) |
| Sciaretta 198743 (n = 46a) | 8% | 0.950 (0.751 to 0.999) | 0.962 (0.804 to 0.999) |
None of the studies looking specifically at people with Crohn’s disease presented reliable data for the prediction of response to treatment with BAS because no data were presented for people with a negative SeHCAT test in the two studies.
One randomised controlled trial in patients with IBS-D which compared treatment with BAS (colesevelam) with placebo showed no significant differences in terms of colonic transit [e.g. geometric centre at 48 hours: mean difference (MD) = 0.18 (95% CI –0.29 to 0.65)], bowel function [e.g. stool frequency per day: MD = –0.11 (95% CI –1.01 to 0.79)] or adverse events [e.g. uterine cramps: OR = 0.45 (95% CI 0.04 to 5.81)]. However, randomisation (sequence generation and allocation concealment) was not adequately reported and groups were small (n = 12 in both arms).
For people with chronic diarrhoea, 19 studies provided data on the clinical effectiveness of BAS given a positive SeHCAT test; three studies also provided data on the effectiveness of BAS given a negative SeHCAT test. For those with a positive SeHCAT test response rates were on average 85%, 73% and 72% for cut-offs at 5%, 10% and 15%, respectively. For those with a negative SeHCAT test the response rate was 14% at a cut-off of 5% and 0% at a cut-off of 15%. For people with Crohn’s disease and a positive SeHCAT test the response rate was 95% at a cut-off of 5% and 86% or 89% at a cut-off of 15%.
Chapter 4 Assessment of cost-effectiveness
Search strategy
Searches were undertaken to identify cost-effectiveness studies of SeHCAT in the diagnosis of BAM and BASs used to treat BAM. As with the clinical effectiveness searching, the main EMBASE strategy for each set of searches was independently peer reviewed by a second information specialist, using the PRESS-EBC checklist. 18 Search strategies were developed specifically for each database and searches took into account generic and other product names for the BASs and SeHCAT. No restrictions on language or publication status were applied. Limits were applied to remove animal studies. Full search strategies are reported in Appendix 1 .
The following databases were searched for relevant studies with no date limits:
-
MEDLINE (1946–week 1 January 2012) (OvidSP)
-
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily Update (up to 13 January 2012) (OvidSP)
-
EMBASE (1980–week 2 2012) (OvidSP)
-
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (EED) (up to 16 January 2012) (CRD website)
-
Health Economic Evaluation Database (HEED) (Wiley Online Library) (up to 6 March 2012) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/book/10.1002/9780470510933
-
EconLit (1886–16 January 2012) (EBSCOhost)
-
SCI (1970–12 January 2012) (Web of Science).
Supplementary searches on SeHCAT, BAM, IBS, Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea were undertaken on the following resources to identify guidelines and guidance:
-
National Guidelines Clearinghouse (NGC) (up to 28 November 2011) (internet) www.guideline.gov
-
International Guidelines Library (GIN) (up to 28 November 2011) www.g-i-n.net
-
NICE Guidance (up to 28 November 2011) (internet) http://guidance.nice.org.uk
-
Turning Research Into Practice (TRIP) database (limited to Guidelines) (up to 28 November 2011) (internet) www.tripdatabase.com
-
HTA Database (up to 28 November 2011) (CRD website)
-
NIHR HTA (up to 9 December 2011) (internet).
Owing to the lack of studies found that matched all the criteria, an additional keyword search of the Clinical Effectiveness EndNote Library was performed to identify potentially relevant cost/economic studies. After deduplication, 121 records were identified (see Appendix 1 ).
As described by the NICE Methods Guide, the information process that supports the development of a model is ‘a process of assembling evidence and this reflects an iterative, emergent process of information gathering’. 54 The following additional searches were requested by the health economists as part of this process:
-
Searches for utility weights for BAM, IBS, Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea were conducted on the CEA Registry: https://research.tufts-nemc.org/cear4/Home.aspx.
-
Additional searches were also requested for health-related quality of life and cost-effectiveness for both Crohn’s disease and IBS on the following resources:
-
NHS EED (CRD website)
-
MEDLINE (OvidSP).
-
These searches were targeted to find results to inform the inputs of a model and were not intended to be used for a comprehensive systematic literature review.
The final list of included papers was also checked on PubMed for retractions and errata. 19–21
Figure 6 depicts the flow of searches for cost-effectiveness.
FIGURE 6.
Flow of searches developed for SeHCAT health economics. Records retrieved 3292 prior to deduplication; total 2975 after deduplication. AH, aluminium hydroxide. Resources: E, EMBASE; EC, EconLit; C, CENTRAL; CEA, Tufts CEA register; D, DARE; G, GIN; H, HTA; HE, HEED; M, MEDLINE; MP, MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily Update; NE, NHS EED; NG, National Guidelines Clearing House; NH, NIHR HTA; SR, CDSR. For the full search strategies please see Appendix 1 .
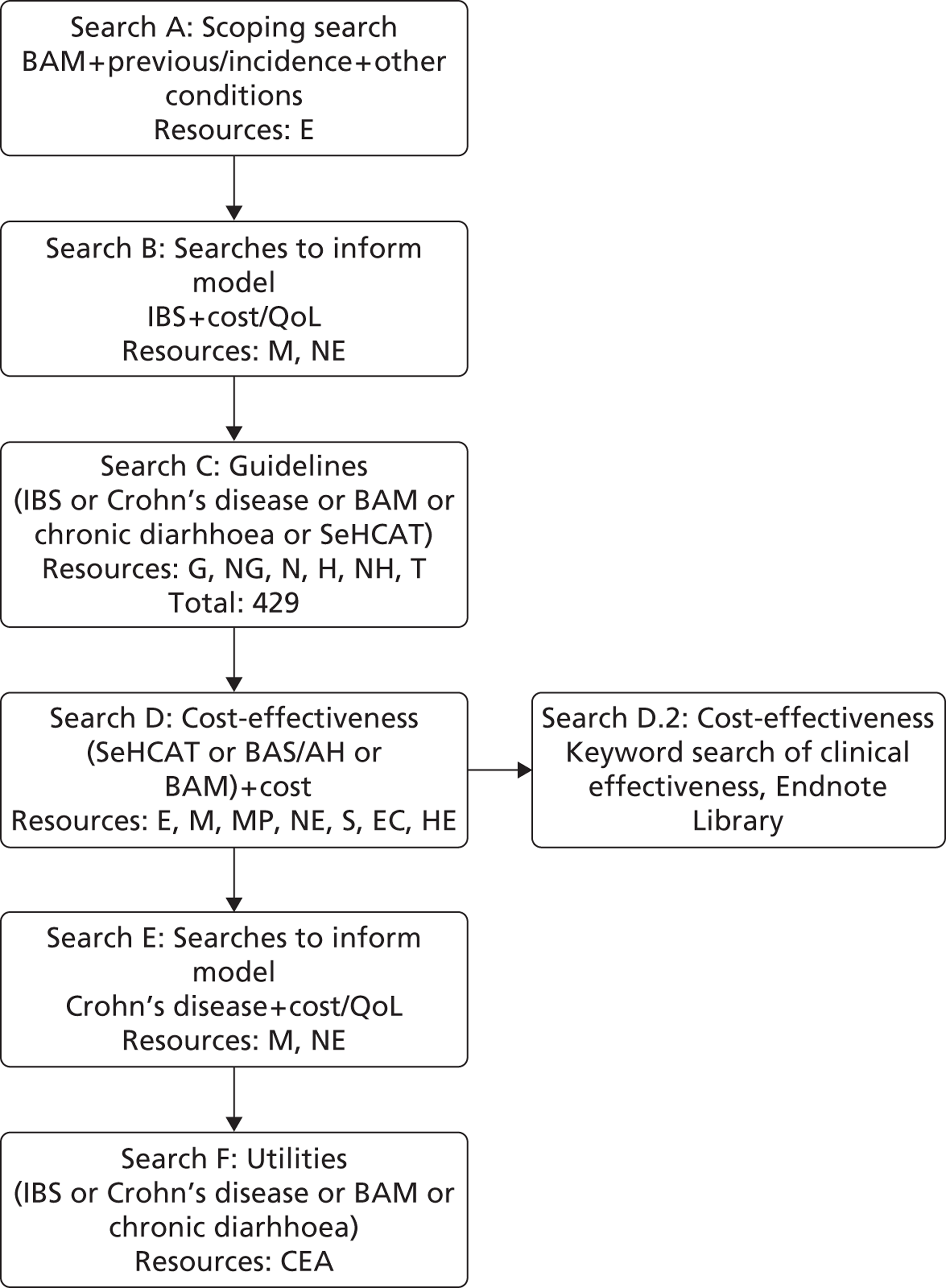
Search B identified three existing health economic models for IBS. Additionally, various other health economic evaluations were found but they all assessed costs and effects alongside clinical trials.
The first model, by Suleiman et al. ,55 assesses the cost-effectiveness of endoscopy in IBS. The model considers only the diagnostic phase, and thus does not consider long-term costs and effects. The reported outcome was test costs divided by increment in diagnostic certainty. No relevant information could be extracted from this paper.
The second model was developed by Mein and Ladabaum56 and investigates the cost-effectiveness of coeliac screening in patients with IBS symptoms. This model consists of a diagnostic part until final diagnosis and a long-term part where life expectancy of patients is multiplied with overall annual costs for IBS treatment and with a utility value for either IBS or coeliac disease with gluten-free diet. In this paper, a utility of 0.689 was applied to IBS patients, which is slightly lower than the value we derived from the utility studies we identified (see Diagnostic and initial treatment model IBS-D).
The final model, by Spiegel et al. ,57 also considers the cost-effectiveness of testing for coeliac disease in patients with IBS-D symptoms. This model consists of a diagnostic part and a Markov model. The Markov model consists of two health states: ‘symptoms improve’ and ‘symptoms recur’. The model does not include utilities; the main outcome measure is incremental costs per additional symptomatic improvement. We carefully considered both the cost of IBS treatment included in this model and the initial therapeutic benefit of IBS-D treatment that was included. The model applied a cost estimate of US$45 per month for IBS-D treatment. No details were presented to explain this estimate other than the remark that this estimate represents the monthly costs in the USA for therapies such as loperamide, fiber supplements or antispasmodics. As we will see later in this chapter (see Diagnostic and initial treatment model for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome), based on expert opinion the costs of medication in the UK are estimated to be much lower at approximately £5 per month. The estimate for the initial therapeutic response that was included in the study was based on data from studies with alosetron, yielding an estimate of 75%. However, they also reported a range from a study by Brandt et al. 58 from 35% to 75%. This latter study presents the probability of response for the various treatment options for IBS per treatment. However, it does not present the probability that a patient will eventually be responsive (after trying several treatments).
Additionally, we also considered how this model estimates long-term transition probabilities. The authors indicate a lack of data to support these estimates and then describe how data from patients receiving tegaserod reveal that up to 85% develop symptomatic recurrence after discontinuing a successful therapeutic course, of whom 80% achieve symptomatic remission following a second therapeutic course. Although these data apply to patients with constipation-predominant IBS, Speigel et al. 57 adopted these favourable results to their population of IBD-D patients. To bias the model against CS testing, they assumed that only 50% (instead of 85%) of IBS-D patients developed symptomatic recurrence following successful therapy and adopted the tegaserod data of 80% remission following a second therapeutic course.
In addition to health economic models, search B also provided the literature for the utility estimates used in the models (see Diagnostic and initial treatment model for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and Diagnostic and initial treatment model for Crohn’s disease without ileal resection for further details).
The guidelines search (search C) provided mainly general information about diagnosis, treatments and prognosis in IBS and Crohn’s disease. The most relevant document was the clinical practice guideline for IBS in adults in primary care from the National Collaborating Centre for Nursing and Supportive Care. 59 This report included various health economic searches on, for example, utilities and long-term prognosis, some of which have been used in this report.
Search D did not lead to any relevant papers; no economic evaluations of SeHCAT or treatment of BAM were found.
Search E did not yield any papers assessing costs or utility of chronic diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients. Some health economic models for medical treatment of Crohn’s disease were found, especially relating to treatment with anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). However, none of these models considered diarrhoea as a health state and no useful data could be extracted from these studies.
Finally, search F did not reveal any new relevant studies on utilities for our models.
Model structure and methodology
In this section, we describe the models used for the economic evaluation. As no relevant models were identified in the searches, a de novo model was developed for each population. This model consists of two parts: a decision model reflecting the diagnostic and initial treatment phase and a Markov model to estimate long-term costs and effects. We compare various strategies.
The scoping document clearly defined SeHCAT and no SeHCAT as strategies. The option of trial of treatment was also mentioned without specifically including it as a comparator. According to the clinical experts at the scoping meeting, trial of treatment is rarely used as a treatment strategy and was thus not considered relevant. However, trial of treatment can also not be completely excluded as an option. Thus, in this report we will present two sets of results: one where trial of treatment is not considered as a comparator and one where it is.
For the IBS-D population we compare first the SeHCAT strategy using three different cut-off points (absorption < 5%, < 10% and < 15%) with no SeHCAT testing, that is to say treating patients as IBS-D patients. In the second set of results, trial of treatment is added as a strategy.
For the Crohn’s disease population, we include the same strategies, with the exception of SeHCAT 5% as no data were available for this strategy. In this population, no SeHCAT entails treatment for chronic diarrhoea (which may or may not be a direct result of a disease relapse).
The models used in the analyses are described, in detail, below. The stochastic analyses are based on cohort simulations. To investigate decision uncertainty, second-order uncertainty microsimulations were run. All costs and effects were discounted by 3.5%. The model incorporated a lifetime time horizon to estimate outcomes in terms of quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) and costs from the perspective of the NHS. Only health effects of patients were included.
Diagnostic and initial treatment model for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome
Given the fact that no data are available on the accuracy of SeHCAT, the model uses response to treatment, dependent on the test outcome (see also Chapter 3 , Accuracy of selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine for the detection of bile acid malabsorption). We compare two no SeHCAT strategies with three SeHCAT strategies. Figure 7 presents the decision tree used.
FIGURE 7.
Decision tree for IBS-D population.
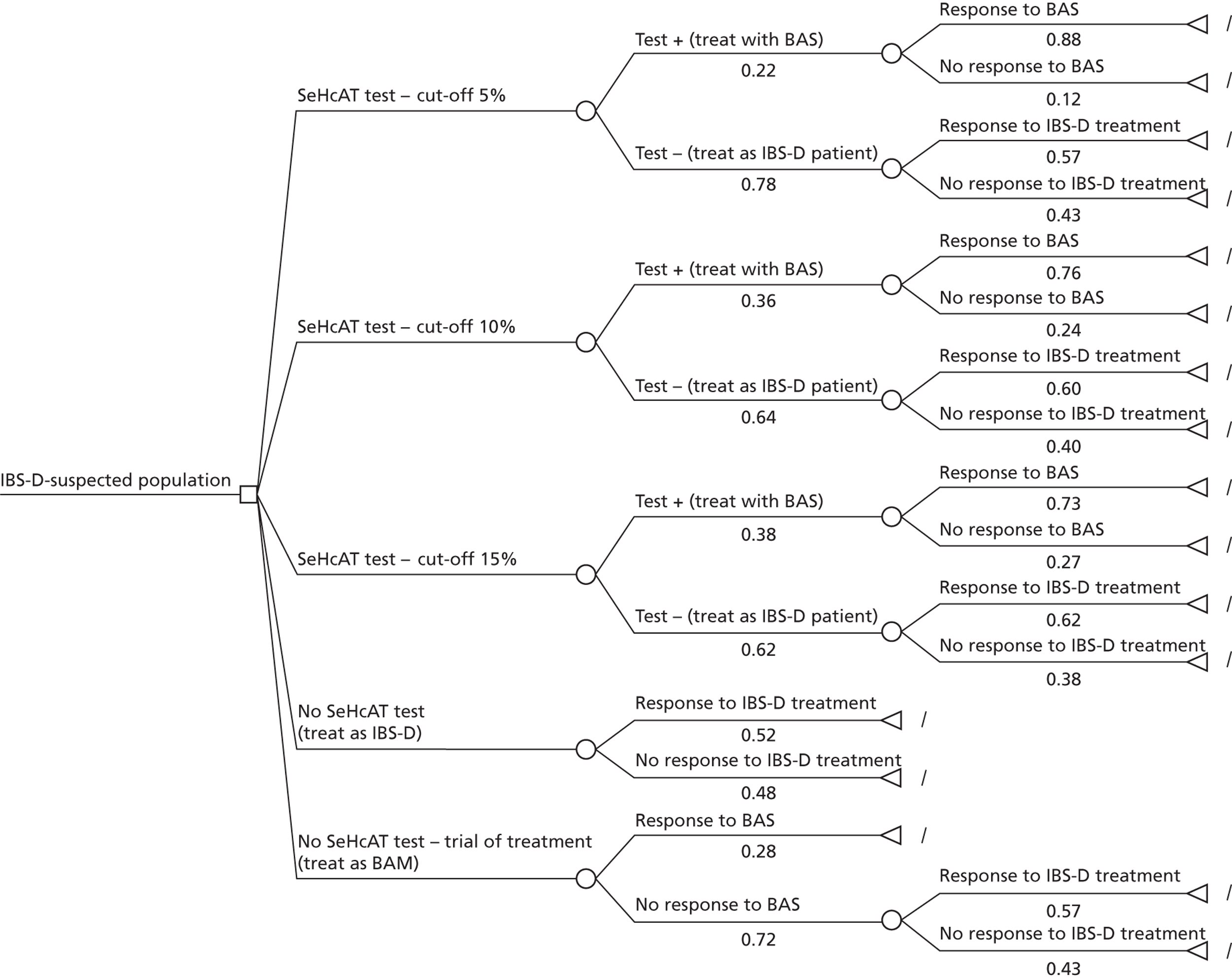
In the SeHCAT strategies, patients may have a positive or negative test result. If the test is positive, that is to say the percentage resorption of bile acids is below a certain cut-off, patients are treated with cholestyramine (a BAS) and they may or may not respond to that treatment. If the test is negative, the patient is diagnosed as IBS-D and treated accordingly. Again, patients may or may not respond to that treatment. The first no SeHCAT strategy assumes that all patients are treated with IBS-D treatment and patients may or may not respond to that treatment. Finally, in the trial of treatment, all patients receive cholestyramine. If patients do not respond to this, they receive IBS-D treatment and again, patients may respond or not respond to this treatment.
Diagnostic and initial treatment model for Crohn’s disease without ileal resection
For the Crohn’s disease population, the outline of the model is in essence the same as for the IBS-D population ( Figure 8 ). However, here, if no SeHCAT test is used, if the test result is negative or if patients do not respond to a trial of cholestyramine, patients will receive treatment for diarrhoea. This treatment can vary between patients, as the diarrhoea may be a result/symptom of a relapse of the disease, and thus focus could be on treating the relapse, but it may also occur in patients who are in remission. 3 Chronic diarrhoea in patients in remission has been suggested to be the result of repeated relapses, which have led to fibrosis. 46 For these patients, treatment is targeted at controlling the diarrhoea.
FIGURE 8.
Decision tree for Crohn’s disease population.
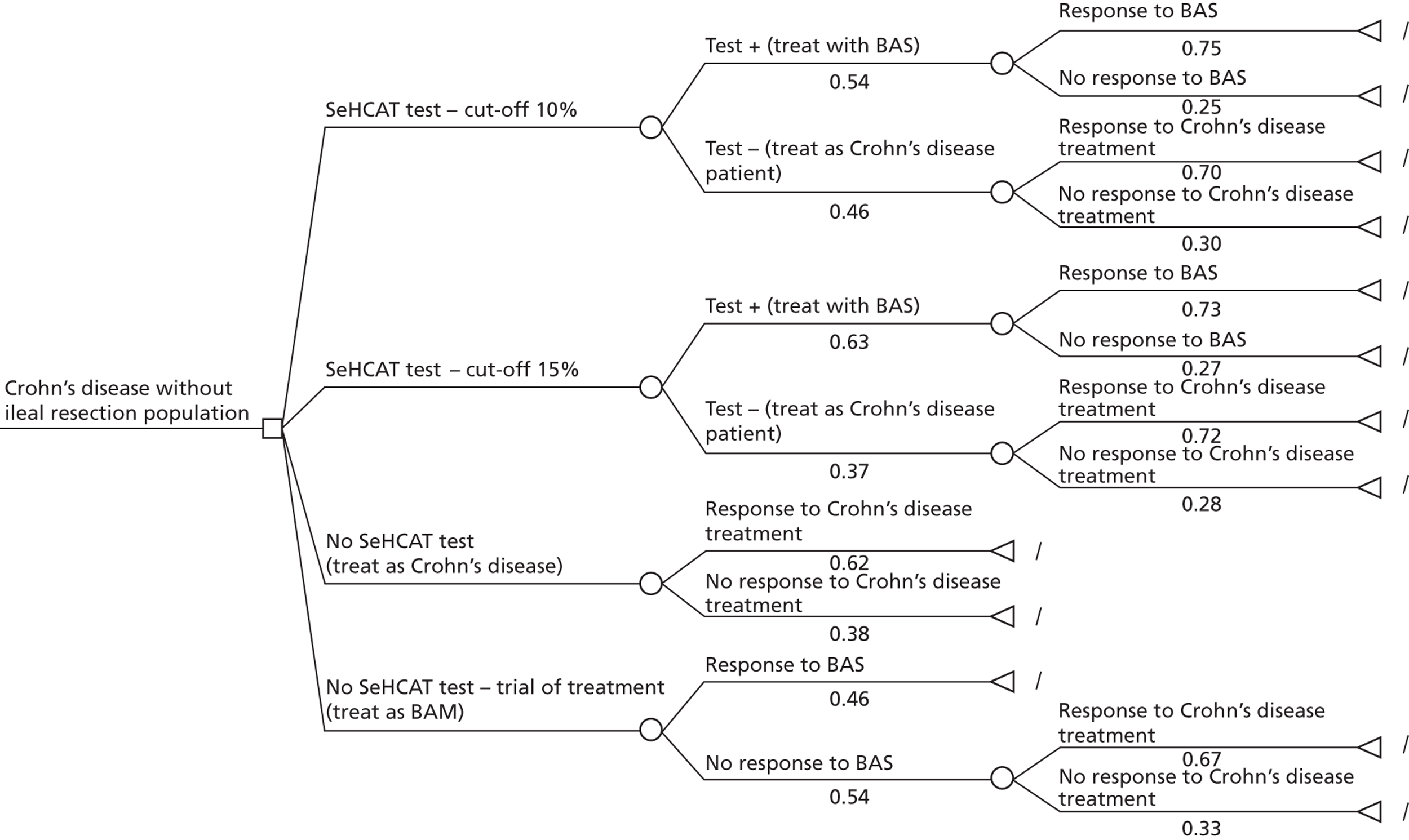
This model assesses only two SeHCAT strategies; no data on the probability of a positive test result were available for a cut-off absorption of < 5%, and so this strategy was not evaluated in this assessment.
Markov model
To assess the long-term costs and effects of the various strategies, patients enter into a three-state Markov model ( Figure 9 ). Patients who had a treatment response enter the Markov model into the ‘no diarrhoea’ state and patients who did not respond enter into the ‘diarrhoea’ state. As the model has a lifetime time horizon, the third state included is death.
FIGURE 9.
Outline Markov model.
In theory, patients can either move between the ‘no diarrhoea’ state and the ‘diarrhoea’ state from one cycle to another, stay in the same state or die. The cycle length used is 6 months. The general Markov model is parameterised according to treatment; that is to say, in the IBS-D population, patients who receive(d) BAS enter the BAS Markov model and patients who receive(d) IBS-D treatment enter the IBS-D Markov model. Likewise, in the Crohn’s disease population, patients who receive(d) BAS enter the BAS Markov model and patients who receive(d) treatment for Crohn’s disease with chronic diarrhoea (non-BAM diarrhoea) enter the Crohn’s disease Markov model.
Model parameters
This section describes the parameters used in the decision trees and the Markov models and how their values were estimated.
Diagnostic and initial treatment model for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome
The diagnostic model estimates the initial costs of diagnosis and initial treatment. We assume that the diagnostic model reflects the first 6 months after the moment the patient is seen by a specialist.
Probabilities
The first probability encountered in the decision tree (see Figure 7 ) is that of a positive SeHCAT test. To estimate this we used the studies listed in Tables 9 and 10 . Based on the data retrieved, a random-effects meta-analysis was performed to find a pooled estimate for each of the three cut-off values ( Tables 16 – 18 ). 26 Note that studies with cut-off points between 8% and 12% have all been grouped as 10%. In some studies, patients with a history of cholecystectomy were included in the ‘IBS-D-like’ population. As we are interested in patients with idiopathic BAM, we excluded the patients with a cholecystectomy from the calculations.
| Study | n | Number SeHCAT positive | Probability SeHCAT positive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede33 | 114 | 41 | 0.36 |
| Ford38 | 74 | 3 | 0.04 |
| Sciaretta42 | 13 | 6 | 0.46 |
| Wildt44 | 56 | 13 | 0.23 |
| Williams45 | 181 | 23 | 0.13 |
| RE mean | 0.22 | ||
| SD | 0.06 |
| Study | n | Number SeHCAT positive | Probability SeHCAT positive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede33 | 114 | 55 | 0.48 |
| aEusufzai34 | 17 | 10 | 0.59 |
| aFellous36 | 36 | 10 | 0.28 |
| aFernandez-Banares37 | 23 | b | 0.65 |
| Fernandez-Banares49 | 62 | 37 | 0.60 |
| Ford38 | 74 | 15 | 0.20 |
| Galatola5 | 98 | 56 | 0.57 |
| Kurien53 | 102 | 37 | 0.36 |
| Merrick39 | 43 | 5 | 0.12 |
| Notta40 | 37 | 16 | 0.43 |
| aRudberg41 | 18 | 3 | 0.17 |
| aSciaretta43 | 38 | 13 | 0.34 |
| Smith3 | 197 | 65 | 0.33 |
| Tunney32 | 136 | 33 | 0.24 |
| Wildt44 | 56 | 21 | 0.38 |
| Williams45 | 181 | 39 | 0.22 |
| RE mean | 0.36 | ||
| SD | 0.04 |
| Study | n | Number SeHCAT positive | Probability SeHCAT positive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede33 | 114 | 68 | 0.60 |
| Ford38 | 74 | 20 | 0.27 |
| Merrick39 | 43 | 12 | 0.28 |
| Rossel60 | 150 | 30 | 0.20 |
| aRudberg41 | 18 | 8 | 0.44 |
| Sinha2 | 17 | 9 | 0.53 |
| Tunney32 | 136 | 59 | 0.43 |
| Wildt44 | 56 | 24 | 0.43 |
| Williams45 | 181 | 60 | 0.33 |
| RE mean | 0.38 | ||
| SD | 0.05 |
Patients with a positive SeHCAT test result, that is to say those who are classified as having idiopathic BAM, are assumed to be treated with BASs (cholestyramine). The response rate to BASs differs between the various cut-off points. Again, using the studies described in Chapter 3 , we have estimated the response rate to BASs using random-effects meta-analysis ( Tables 19 – 21 ). It is important to note that it is a well-known fact that compliance is usually not optimal when patients are treated with cholestyramine. We studied the various papers included into Tables 19 – 21 to see if compliance or drop-out were reported. Most studies do not report any information about these issues. The study by Borghede et al. 33 reports (at 15% cut-off) 43 out of 57 patients responding to treatment. They also report that 49 out of 57 patients used cholestyramine continuously, indicating that the response rate is already based on a less-than-100% compliance. Additionally, the study by Notta et al. 40 reports that many patients used cholestyramine on demand after achieving an initial response to counteract side effects. Thus, again this study reports a response rate that is already based on reduced compliance. As other studies did not report anything about compliance, we will assume that they also implicitly include the impact of reduced compliance on the response rate. The drop-out of treatment is only considered in the Markov model after the initial phase.
| Study | n | Number positive response | Probability positive response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede33 | 39 | 29 | 0.74 |
| Sciaretta43 | 6 + 1 | 6 + 0.5a | 0.93 |
| Wildt44 | 13 | 11 | 0.85 |
| Williams45 | 21 + 1 | 21 + 0.5a | 0.98 |
| RE mean | 0.88 | ||
| SD | 0.06 |
| Study | n | Number positive response | Probability positive response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede33 | 53 | 41 | 0.77 |
| aEusufzai34 | 6 | 2 | 0.33 |
| Fernandez Banares49 | 37 | 28 | 0.76 |
| Galatola5 | 41 | 39 | 0.95 |
| Merrick39 | 5 | 4 | 0.80 |
| Notta40 | 16 | 8 | 0.50 |
| aRudberg41 | 3 | 2 | 0.67 |
| Smith3 | 34 | 28 | 0.82 |
| Williams45 | 31 | 24 | 0.77 |
| RE mean | 0.76 | ||
| SD | 0.05 |
| Study | n | Number positive response | Probability positive response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede33 | 57 | 43 | 0.75 |
| Merrick39 | 9 | 6 | 0.67 |
| Rudberg41 | 7 | 6 | 0.86 |
| Sinha2 | 9 | 6 | 0.67 |
| Wildt44 | 17 | 14 | 0.82 |
| Williams45 | 39 | 24 | 0.62 |
| RE mean | 0.73 | ||
| SD | 0.04 |
The next important probability is that of a positive response to IBS-D treatment in patients with no SeHCAT test (i.e. the whole initial population is receiving this treatment). IBS-D treatment varies greatly between patients. Patients may receive a variety of drugs, diet advice or even psychological treatment. Owing to the large array of treatment options and the various orders in which they are attempted, we could not find clear data from the literature regarding how many IBS-D patients will eventually, after trying various options, respond to treatment. We therefore sent out a questionnaire to approximately 20 specialists, seven of whom returned it. In the questionnaire we asked what percentage of patients would eventually be successfully treated with the usual IBS-D treatment options, and the plausible range for this percentage. We have included the full questionnaire in Appendix 9 . The responses are presented in Table 22 .
| Expert | Patients successfully treated (%) | Lowest | Highest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 10 | 60 |
| 2 | 50 | 25 | 75 |
| 3 | 40 | 30 | 50 |
| 4 | 40 | 0 | 50 |
| 5 | 90 | 70 | 95 |
| 6 | 80 | 20 | 100 |
| 7 | 50 | 40 | 80 |
| Mean | 52 | ||
| SD | 10 |
We assume that the percentage of IBS-D patients considered successfully treated follows a triangular distribution with the point estimate given by the experts representing the mode of the distribution. For example, for the data provided by expert 1, 0.4 is the mode, and the associated mean and standard deviation are 0.366 and 0.102, respectively. By simulating from these triangular distributions we estimated the pooled mean and standard deviation of the probability of responding to IBS-D medication when no SeHCAT test is available, which is assumed to have a beta distribution. We found a mean of 52% and a standard deviation of 10%.
In the strategies where a SeHCAT test is performed, only patients with a negative SeHCAT test receive IBS-D treatment. This means that most patients who actually have BAM are no longer part of the group receiving IBS-D treatment. Thus, the response rate to IBS-D treatment in the SeHCAT-negative population may be higher than in the ‘no SeHCAT testing’ population, especially as IBS-D treatment also includes antidepressants, psychological therapy and other treatments unlikely to benefit BAM patients.
Unfortunately, no data were available to give any indication of whether or not this assumption is correct and, if so, how much higher the response rate should be. In the base-case analysis we will make the rather subjective assumption that at a cut-off point of 15% (when the maximum number of BAM patients have been removed from the IBS-D-treated population) the response rate to IBS-D treatment in the SeHCAT negative population is 10 percentage points higher than in the ‘no SeHCAT’ population. For SeHCAT cut-off points of 5% and 10%, these increases are assumed to be 5 percentage points and 8 percentage points respectively.
For the trial of treatment strategy, where again the maximum number of BAM patients have been removed from the IBS-D-treated population, we assume the same response rate as in the SeHCAT 15% strategy.
Because of the subjective nature of this estimate, we have explored its impact on the outcomes through scenario analyses.
Finally, the model required a response rate for BAS treatment given as a trial (trial of treatment) to all patients. Theoretically, data from the two studies by Sciaretta42,43 might be used to inform this input parameter. When we look at those results [i.e. 54% (7/13) in one study and 44% (20/46) in the other] we find that, on average, 46% of all patients would respond to BAS treatment regardless of test status. In the SeHCAT 15% strategy, the percentage who test positive AND respond to treatment is only 28% (38% × 73%). If one then assumes that the 46% is applicable to all studies then the remaining 18% (46% – 28%) would be FNs (i.e. test negative AND would have responded to treatment if it had been tried) (18/62). However, in the two Sciaretta studies,42,43 almost none of the SeHCAT-negative patients responded to BAS, so using just these data for the trial of treatment strategy while using pooled data from a much larger group of studies to inform the SeHCAT strategies leads to inconsistencies.
To avoid these inconsistencies in input values, we have chosen to assume that the 28% of patients who responded to BAS in the SeHCAT 15% strategy is the percentage of responders that would be found when giving all patients a trial of BAS. On the one hand, this might be a slight underestimation, as there may be patients in the SeHCAT 15% strategy with a negative test result who might have responded to BAS, either because they were FNs or because they showed a placebo response to BAS treatment. But, at the same time, it may also be an overestimation as it is possible that patients receiving a trial of BAS are less compliant than patients with a definite diagnosis of BAM or that a lack of patience prevents the right dose of BAS being achieved. Thus, as a base-case estimate we have assumed a response rate of 28%, and this estimate was varied to 21% in scenario analyses. This value of 21% was chosen because it is the threshold value for which trial of treatment and SeHCAT 15% result in the same proportion of responders.
Quality of life
The searches B and F, as outlined in Figure 6 , formed the base from which we tried to derive utility values for both responders (no diarrhoea) and non-responders (diarrhoea) in the model. Based on a review of titles and abstracts, papers presenting utility values in IBS patients were retrieved. This resulted in six papers, of which four presented utility values for unspecified health states. The paper by Spiegel et al. 61 described utilities (EQ-5D) for patients with IBS who showed either ‘considerable relief’ after 3 months of usual care or ‘no considerable relief’ ( Table 23). This study found no significant difference between the subtypes of IBS. The second paper with health-state-specific utilities (Mearin et al. 62) presented utility scores for high and low severity symptoms. We aggregated these across IBS subtypes for patients with high-frequency symptoms (present > 50% of the time) (see Table 23 ). We assumed that the utility gain associated with response to treatment was equivalent to an improvement in symptom severity from high to low.
| Study | Mean | SE |
|---|---|---|
| Non-responders/diarrhoea | ||
| Mearin62 | 0.704 | 0.026 |
| Spiegel61 | 0.730 | 0.037 |
| RE estimate | 0.712 | 0.021 |
| IBS-D responders/no diarrhoea | ||
| Mearin62 | 0.775 | 0.014 |
| Spiegel61 | 0.780 | 0.037 |
| RE estimate | 0.776 | 0.013 |
| BAS responders/no diarrhoea | ||
| Assumption | 0.760 | 0.020 |
For the BAS responders, we considered two scenarios: one where BAS responders have the same utility gain as IBS-D treatment responders and one where we assume that the utility gain is lower, due to the generally cited unpleasantness of cholestyramine. As we have no data to support this smaller increment, we have assumed that BAS responders have 75% of the utility increment observed in IBS-D treatment.
Costs
The costs considered in the model can be distinguished into three groups: (1) the costs of a SeHCAT test, (2) the costs of treatment of BAM and (3) the costs of treatment of IBS-D.
For the cost of the SeHCAT test, we used information provided by the manufacturer. SeHCAT capsules cost £195 per patient (and therefore per treatment). The tariff for administering this diagnostic test in the NHS is £186 (HRG RA36Z nuclear medicine cat 2, OPCS code – U172, non-mandatory national tariff 2011–12). 63 Thus, we would arrive at a total cost of £381. In the scoping document it was suggested, however, that the tariff for administration might not contain all costs associated with maintenance and service costs. A range from £55 to £105 was suggested for these costs. In the model, we have applied the cost estimate of £381 as a base-case value, and in scenario analyses we have explored a total cost estimate of £55 or £105 higher.
Patients with a positive test for BAM all receive treatment with BAS. These costs were based on the unit price for cholestyramine from the British National Formulary (BNF) 63 and the actual use observed in the studies with SeHCAT. 64
Most studies present the dosage as it could be used (see Appendix 4 ) but only a few present information on the actual dosage used in the study. In the study by Fernandez-Banares,37 a median dosage of 8 g per day was recorded, with an interquartile range of 4–12 g per day. Wildt44 reported that the most common dosage was 5–12 g per day. Finally, Williams45 reported a mean dosage of 12 g per day. We have based our cost estimate for BAS treatment on this latter value, as it presents a mean. Thus, we arrive at costs of 12 mg = 3 sachets = 3 × £0.21 = £0.63 per day.
For the treatment of IBS-D, we distinguish three main types of resource use: (1) medication, (2) dietitian visits and (3) counselling and psychological therapy. All of these were estimated based on expert opinion. To find an overall estimate, we calculated a simple mean and standard deviation of the expert’s individual estimates. We did assess whether or not the range represented by the standard deviation did cover most of the individual responses (including the range suggested by the experts). As these data were not collected in a formal sample (i.e. each expert gave a subjective estimate), we opted not to use formal meta-analysis to find an overall estimate.
Patients treated for IBS-D may use a wide variety of medication. The experts consulted listed, for example, loperamide, codeine, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), mebeverine and BAS. Table 24 presents the costs of medication per expert, based on their estimates of use of the various medications. The prices of the medications were derived from the BNF. 64 Exact details on medication use, dosage and fraction of patients receiving the treatment are presented in Appendix 10 , including the ranges suggested by the experts. The experts’ responses ranged from £0.02 to £0.64 per day. Given this skewed range around the point estimate we will assume a gamma distribution for this estimate in the probabilistic sensitivity analysis.
| Patients receiving medication (%) | Average cost per treated patient per day (£) | Average cost per patient per day (£) |
|---|---|---|
| 60 | 0.45 | 0.27 |
| 100 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| 75 | 0.23 | 0.17 |
| 80 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| 100 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| 80 | 0.29 | 0.24 |
| 100 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Mean | 0.17 | |
| SD | 0.068 | |
Table 25 presents the responses of the experts to the question of how many patients would visit a dietitian and how many visits would be involved. The cost price of one visit to a dietitian was £67. 63
| Patients who visit dietitian (%) | Number of visits | Average cost per patient (£) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1 | 67 |
| 40 | 5 | 134 |
| 2.5 | 1 | 2 |
| 10 | 1 | 7 |
| 40 | 1.5 | 40 |
| 10 | 2 | 13 |
| 30 | 3 | 60 |
| Mean | 46 | |
| SD | 56.54 | |
Table 26 presents the response of the experts to the question of how many patients would receive some form of psychological therapy and how many visits would be involved. The cost price of cognitive behavioural therapy and cognitive analytical therapy is £121 per visit, of counselling is £60 per visit and of hypnotherapy is £88 per visit. 63
| Expert | Type of therapy | Patients who receive therapy (%) | Number of visits | Average cost per patient (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | CAT/CBT | 10 | 30 | 363 |
| B | CBT | 2 | 15a | 36 |
| C | Counselling | 20b | 7c | 84 |
| C | CBT | 8b | 15c | 145 |
| C | Hypnotherapy | 2b | 12c | 21 |
| C | Total | 250 | ||
| D | Counselling | 15 | 7 | 63 |
| D | CBT | 5 | 12 | 73 |
| D | CAT | 3 | 12 | 44 |
| D | Total | 179 | ||
| E | CBT | 1.5 | 18 | 33 |
| E | Hypnotherapy | 0.5 | 12 | 5 |
| E | Total | 38 | ||
| F | Counselling | 10 | 7 | 42 |
| Mean | 130 | |||
| SD | 137.28 | |||
Markov model for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome population
Probabilities
As mentioned in Markov model, patients who receive(d) BAS in the decision tree enter the BAS Markov model and patients who receive(d) IBS-D treatment enter the IBS-D Markov model.
Each Markov model consists of six transition probabilities: from diarrhoea to no diarrhoea and vice versa, from diarrhoea (D) to death, from no diarrhoea (ND) to death and to stay in diarrhoea or no diarrhoea.
Regarding the probability of death, we have assumed that only overall mortality in the UK population is relevant, as no excess mortality is associated with IBS-D and BAM. 65 This also implies that both of these transition probabilities are the same. We derived these from England and Wales Interim Life Tables 1980–82 to 2008–10. 66 Using the studies listed in Appendix 4 , we found that the average age in the IBS-D population in the various SeHCAT studies was 47 years, and the ratio of male to female was 0.71. Our model cohort was assumed to have the same age and sex distribution.
For the estimation of the transition probabilities in BAM responders two long-term follow-up studies were available. 60,67 In the study by Luman et al. , the mean follow-up duration was 99.2 months. Out of 12 patients, seven were in remission, as defined by a stool frequency of < 2 per day in the absence of BAS or anti-diarrhoeal drugs. The duration of BAS treatment in these patients ranged from 2 to 3 years. Five patients had ‘symptomatic’ diarrhoea that was controlled by BAS or loperamide.
The study by Rossel60 has a median follow-up time of 88 months. In total 16 patients were included, of whom only three patients had normalised SeHCAT test and stool frequency (i.e. fewer than two per day). The remaining 13 patients still had a non-normal SeHCAT test at follow-up despite treatment with BAS (seven patients) and symptomatic treatment (four patients). Two of the 13 patients chose to be without any treatment despite symptoms. Their symptoms had also not normalised, but patients treated with BAS did show a significant improvement in stool frequency (8.7 per day before treatment, 3.6 per day at follow-up, p < 0.05).
It is difficult to correctly interpret these findings. The study by Luman et al. 67 suggests a relatively high probability of spontaneous remission after a few years of BAS treatment. This study also suggests that if no remission occurs patients show little improvement over their baseline stool frequency even with treatment. The study by Rossel60 shows a much lower probability of remission, but also shows a significant improvement in stool frequency in seven patients treated with BAS.
Overall, it is difficult to derive from this the transition probabilities from ND to D and from D to ND for the BAS Markov model. It is possible, given the above information, that patients move from D to ND due to remission; however, in the studies by Luman67 and Rossel,60 remission took place after a period of BAS treatment, and it may not be possible to extrapolate this to patients not responding to BAS treatment. At the same time, it is also possible that patients move from ND to D, for example due to lack of compliance. For example, the study by Rossel60 showed six patients who had an initial response to BAS treatment who had to discontinue treatment due to adverse effects or other compliance problems.
For patients receiving IBS-D treatment entering the IBS-D Markov model, we searched through guidelines and previous health economic studies to find long-term data. One IBS guideline68 cited only a study by Agreus et al. 69 to show that a large group of IBS patients experience spontaneous remission. However, several difficulties exist with this study. The study comprised a random sample from the inhabitants of a specific Swedish region. They were sent a questionnaire where they were asked to indicate which (if any) of a list of 24 symptoms had troubled them in the last 3 months and also to indicate the type and location of pain. Based on their answers people were classified into one of six symptom groups or as ‘symptom free’. One of these symptom groups was IBS. The same questionnaire was sent to these people 1 year after baseline and again 7 years after baseline. Of the 75 patients classified as IBS at baseline, 55% were still classified as IBS after 1 year and after 7 years. Note that as a cross-section of the population was given the questionnaire, patients ‘diagnosed’ as having IBS could have had complaints for years, or only for a few months.
The results of this study seem to indicate that after 1 year a large group of patients showed remission; however, between year 1 and year 7 after the first questionnaire, no such remission occurred at the group level. The fact that this population was a cross-section of a general population makes it difficult to extrapolate these results to an IBS-D population referred for specialist care. It is not unlikely that the spontaneous remissions are more likely to occur in patients under GP care, and the fact that symptoms persist over a longer period may well be the reason why patients are referred to a specialist.
Additionally, we identified a clinical practice guideline which also contained a literature review of long-term stability of IBS diagnosis and symptoms. 59 In total, 14 papers were identified as relevant, most of which were also included in a systematic review by El-Serag et al. 70 The length of follow-up ranged from 2 months to up to 32 years and the percentage of the original cohort with follow-up data available also varied widely, from 38% to 100%. Of these 14 studies, four reported whether symptoms were worse, unchanged or improved over the follow-up period. 71–74
In these studies, between 48% and 65% of patients reported improvement, 30–50% reported no change, and 2–14% said their symptoms were worse. Seven studies reported resolution of symptoms, yielding widely differing estimates ranging from 7% to 48%. 71,72,74–78
Overall, we must conclude that there are clear indications that patients may move from ND to D and vice versa. However, from the data available, these transition probabilities are impossible to quantify. We will therefore present a range of equally plausible scenarios with various values, without actually selecting one as a base case, to show the impact of the assumptions on the outcomes.
Quality of life
The IBS Markov model uses the same utility estimates as reported in Diagnostic and initial treatment model for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome for the decision tree.
Costs
There are four relevant health states for which a cost estimate is required: ND-IBS, D-IBS, ND-BAM and D-BAM. The ND states are the states where the treatment responders start the Markov model. Hence, for BAS responders we have assumed that the costs per cycle are equal to the costs used in the decision tree (i.e. 182.5 × £0.63 = £115 per cycle), and for IBS responders we have assumed that the cost per cycle are equal to the medication costs used in the decision tree (£31.70 per cycle, see Table 24 ). For the ND costs for IBS and BAM, we assume a gradual decline in costs due to patients no longer needing the treatment, stopping treatment due to various compliance issues or entering this health state from the diarrhoea state as a result of spontaneous remission. This decline in the cost per cycle was rather arbitrarily set at approximately 2% per cycle (i.e. 2% decrease of the remaining costs). For patients who did not respond to BAM treatment or IBS-D treatment in the initial phase, that is to say the patients entering the Markov model in the D health state, both for IBS-D and BAM, we assumed that patients use some loperamide to at least reduce the stool frequency somewhat (£10.90 per cycle).
Diagnostic and initial treatment model for Crohn’s disease without ileal resection
Probabilities
Again, the first probability encountered in the decision tree (see Figure 8 ) is that of a positive SeHCAT test. To estimate this we used the studies by Smith3 and Tunney32 as they were the only studies reporting results specifically for patients without ileal resection. We derived pooled estimates for a 10% and a 15% cut-off ( Tables 27 and 28 ). No studies were available with a 5% cut-off.
| Study | n | Number SeHCAT positive | Probability SeHCAT positive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smith3 | 44 | 24 | 0.55 |
| Tunney32 | 30 | 16 | 0.53 |
| RE meana | 0.54 | ||
| SD | 0.06 | ||
| Study | n | Number SeHCAT positive | Probability SeHCAT positive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tunney32 | 30 | 19 | 0.63 |
| Mean | 0.63 | ||
| SD | 0.09 | ||
No data were available on the response to BAS in patients with a positive SeHCAT test. We therefore assumed that this response rate would be the same as in patients with idiopathic BAM, that is to say 76% and 73% for 10% and 15% cut-off, respectively (see Tables 21 and 22 ).
For the probability of a positive response to treatment of diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients with no SeHCAT test (i.e. the whole initial population is receiving this treatment), again no literature was available. The approach to diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients varies greatly between patients, mostly because the diarrhoea may occur as a symptom of relapse but it also may occur while the patient is in remission. In the first case, treatment may be targeted at treating the relapse, assuming that this will decrease the diarrhoea. In the second case, more diarrhoea-specific treatments such as the use of loperamide or codeine may be considered. So, owing to the large range of treatment options and the various orders in which they are attempted, we could not find data from the literature as to how many Crohn’s patients with diarrhoea without ileal resection will eventually, after trying various options, respond to treatment. We have therefore asked the experts what percentage of patients would eventually be successfully treated with the usual treatment options in this Crohn’s disease population, and the plausible range for this percentage. The responses are presented in Table 29 .
| Expert | Patients successfully treated (%) | Lowest | Highest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70 | 50 | 90 |
| 2 | 70 | 60 | 90 |
| 3 | 50 | 40 | 80 |
| 4 | 70 | 20 | 80 |
| 5 | 60 | 30 | 70 |
| Mean | 62 | ||
| SD | 9 | ||
We assume that the percentage of Crohn’s patients considered successfully treated follows a triangular distribution with the point estimate given by the experts representing the mode of the distribution. Based on these triangular distributions we derived the pooled mean and standard deviation of the probability of responding to medication for diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients when no SeHCAT test is available, which is assumed to have a beta distribution. We found a mean of 62% and a standard deviation of 9%.
As in the IBS-D population, we may expect that the response rate to diarrhoea treatment in the SeHCAT negative Crohn’s patients may be higher than in the ‘no SeHCAT’ population. Again, no data were available to give any indication of whether or not this assumption is correct and, if so, how much higher the response rate should be. We will therefore assume the same increase as in the IBS-D population, that is to say 10 percentage points higher than in the ‘no SeHCAT’ population for a cut-off of 15% and 8 percentage points higher for a cut-off of 10%.
For the trial of treatment strategy we assume the same response rate as in the SeHCAT 15% strategy.
Because of the subjective nature of this estimate, we have explored its impact on the outcomes through scenario analyses.
Finally, for the response rate for BAS treatment given as a trial to all patients we use the same approach as in the IBS-D population. That is, we have chosen to assume that the 46% patients who respond to BAS in the SeHCAT 15% strategy is the percentage of responders that would be found when giving all patients a trial of BAS. This estimate was varied in scenario analyses.
Quality of life
No studies were identified that specifically address the issue of diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients. We have thus assumed that the utility decrement due to diarrhoea in this patient population is the same as for the IBS-D population. In order to calculate QALYs, we have taken the utility estimate from Buxton et al. ,79 where EQ-5D utilities were estimated in a group of 3672 patients with moderate to severe active Crohn’s disease. A mean of 0.7 was found with a standard deviation of 0.25. We have assumed that this utility reflects the quality of life in the diarrhoea health state, and thus the utility for the no-diarrhoea health state is 0.75.
Costs
As in the IBS-D model, the costs considered in this model can be distinguished into three groups: (1) the costs of a SeHCAT test, (2) the costs of treatment with BAS and (3) the costs of treatment of diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients.
The costs of the SeHCAT test and of treatment with BAS are the same as for the IBS-D model. Thus, the total cost of the SeHCAT test is £381 as a base-case value, and in scenario analyses we have explored a total cost estimate of £55 or £105 higher. Treatment with BAS is assumed to be £0.63 per day.
For the treatment of chronic diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients without ileal resection, a large variety of medication was suggested by the experts. This variety is explained by the fact that the diarrhoea can be a result of relapsing disease, in which case drugs to treat the relapse may be prescribed (such as mesalazine, azathioprine, corticosteroids or adalimumab), or it can occur while the patient is in remission, in which case anti-diarrhoeal drugs such as loperamide will more often be prescribed. Table 30 presents the costs of medication per expert, based on their estimates of use of the various medications. The prices of the medications were derived from the BNF. 64 Exact details on medication use, dosage and fraction of patients receiving the treatment are presented in Appendix 10 . The experts’ responses ranged from £0.11 to £5.63. Given this skewed range around the point estimate we will assume a gamma distribution for this estimate in the probabilistic sensitivity analysis.
| Patients receiving medication (%) | Average cost per treated patient per day | Average cost per patient per day |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2.42 | 2.42 |
| 100 | 4.01 | 4.01 |
| 50 | 0.14 | 0.07 |
| 95 | 0.25 | 0.24 |
| 100 | 1.44 | 1.44 |
| Mean | 1.64 | |
| SD | 1.63 | |
Markov model for Crohn’s disease without ileal resection
Probabilities
No reports were found in the literature that chronic diarrhoea itself in Crohn’s patients would lead to excess mortality. However, patients with Crohn’s disease have a shorter life expectancy compared with that of the general population. A meta-analysis by Canavan et al. 80 showed a pooled estimate of the standardised mortality ratio (SMR) of 1.52 (95% CI 1.32 to 1.74). Thus, we have applied this SMR to the overall mortality in the UK population, for which we used again the England and Wales Interim Life Tables 1980–82 to 2008–10. 66 Using the study by Nyhlin et al. ,46 we found an average age of 39 years and a ratio of male to female of 0.61. Our model cohort was assumed to have the same age and sex distribution.
For the transitions between ND and D, both in the BAS Markov model and the Crohn’s Markov model, no data were available. As in IBS-D, it seems likely that patients will transfer between these health states over time for various reasons, especially in patients where the relapse becomes so severe that eventually an ileal resection becomes necessary. These patients will almost certainly develop BAM if they did not have it before. 38,44
All in all, as no evidence exists to formulate base-case values for these transition probabilities, we have defined a range of equally plausible scenarios for the long-term analysis.
Quality of life
The same utility estimates were used as in the decision tree for Crohn’s disease.
Costs
Again for four health states a cost estimate is required: ND-no BAM, D-no BAM, ND-BAM and D-BAM. The ND states are the states where the treatment responders start the Markov model; hence, for BAS responders we have assumed that the costs per cycle are equal to the costs used in the decision tree, that is to say £115 per cycle (i.e. 182.5 × £0.63). For non-BAM responders we have assumed that the cost per cycle are equal to the medication costs used in the decision tree minus the costs of anti-TNF-α as it appears unlikely that these would be continued for life. Thus, we arrive at an estimate of £197 per cycle. We defined two different scenarios related to these ND costs for non-BAM and BAM responders, one where the costs per cycle remain the same for the full time horizon and another where we assume a gradual decline in costs due to patients no longer needing the treatment or stopping treatment owing to various compliance issues. This decline in the cost per cycle was rather arbitrarily set at approximately 2% per cycle (i.e. 2% decrease of the remaining costs). For the D health state, both for non-BAM and BAM, again we assumed that patients use some loperamide to at least reduce the stool frequency somewhat (£10.90 per cycle).
Uncertainty analysis
In the model many uncertainties exist with regard to the input data. The impact of these uncertainties was explored through probabilistic sensitivity analysis. Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEACs) have been used to describe which strategy has the highest probability of being considered cost-effective given a threshold incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER). All values used are listed in Tables 31 and 32 .
| Categories | Descriptions | Mean values | Distributions | Distribution parameters | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Branch probability (for decision tree only) | Probability of having a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 5% | 0.22 | Beta | α = 9.10; β = 33.18 | L |
| Probability of responding to BAS given a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 5% | 0.88 | Beta | α = 21.27; β = 2.98 | L | |
| Probability increase (%) of responding to IBS-D treatment given a negative SeHCAT test – cut-off value 5% | 0.05 | Uniform | a = 0.025; b = 0.075 | A | |
| Probability of having a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 10% | 0.36 | Beta | α = 50.49; β = 88.53 | L | |
| Probability of responding to BAS given a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 10% | 0.76 | Beta | α = 48.00; β = 15.27 | L | |
| Probability increase (%) of responding to IBS-D treatment given a negative SeHCAT test – cut-off value 10% | 0.03 | Uniform | a = 0.01; b = 0.05 | A | |
| Probability of having a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 15% | 0.38 | Beta | α = 37.25; β = 60.51 | L | |
| Probability of responding to BAS given a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 15% | 0.73 | Beta | α = 101.64; β = 36.91 | L | |
| Probability increase (%) of responding to IBS-D treatment given a negative SeHCAT test – cut-off value 15% | 0.02 | Uniform | a = 0.01; b = 0.03 | A | |
| Probability of responding to IBS-D treatment when no SeHCAT is available | 0.52 | Beta | α = 13.14; β = 12.04 | E | |
| Probability of responding to BAS – trial of treatment | 0.28 | Beta | α = 22.29; β = 57.34 | A | |
| Probability increase (%) of responding to IBS-D treatment when response to BAS is negative in trial of treatment | 0.05 | Uniform | a = 0.025; b = 0.075 | A | |
| Transition probability (for Markov model only) | Transition probability from ‘diarrhoea’ to ‘no diarrhoea’ | 0.05 | Triangular | a = 0.02; b = 0.08; c = 0.05 | A |
| Transition probability from ‘no diarrhoea’ to ‘diarrhoea’ | 0.05 | Triangular | a = 0.02; b = 0.08; c = 0.05 | A | |
| Cost | Cost per day of IBS-D medication | 0.17 | Gamma | Shape = 6.57; scale = 0.02 | E |
| Diet costs per 6 months associated with IBS-D | 46.05 | Gamma | Shape = 46.89; scale = 0.98 | E | |
| Psychological costs per 6 months associated with IBS-D | 129.81 | Gamma | Shape = 145.17; scale = 0.89 | E | |
| Cost per day of BAS medication | 0.63 | Triangular | a = 0.42; b = 0.84; c = 0.63 | E | |
| Cost SeHCAT capsule | 195 | Fixed | – | ||
| Cost for administering SeHCAT test | 186 | Fixed | – | ||
| Maintenance and service costs of SeHCAT test | 0 | Fixed | – | ||
| Cost per day associated with health state ‘diarrhoea’ | 0.06 | Triangular | a = 0.03; b = 0.09; c = 0.06 | A | |
| IBS-D medication cost per day associated with health state ‘no diarrhoea’ | 0.17 | Gamma | Shape = 6.57; scale = 0.02 | E | |
| BAS cost per day associated with health state ‘no diarrhoea’ | 0.63 | Triangular | a = 0.42; b = 0.84; c = 0.63 | E | |
| Utility | Utility associated with health state ‘diarrhoea’ | 0.71 | Beta | α = 317.95; β = 128.40 | L |
| Utility associated with health state ‘no diarrhoea’ (IBS-D) | 0.78 | Beta | α = 781.54; β = 226.15 | L | |
| Utility associated with health state ‘no diarrhoea’ (BAM) | 0.76 | Beta | α = 345.92; β = 109.38 | A |
| Categories | Descriptions | Mean values | Distributions | Distribution parameters | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Branch probability (for decision tree only) | Probability of having a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 10% | 0.54 | Beta | α = 39.46; β = 33.54 | L |
| Probability of responding to BAS given a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 10% | 0.76 | Beta | α = 48.00; β = 15.27 | A | |
| Probability increase (%) of responding to Crohn’s treatment given a negative SeHCAT test – cut-off value 10% | 0.08 | Uniform | a = 0.04; b = 0.12 | A | |
| Probability of having a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 15% | 0.63 | Beta | α = 18.36; β = 10.64 | L | |
| Probability of responding to BAS given a positive SeHCAT test – cut-off value 15% | 0.73 | Beta | α = 101.64; β = 36.91 | A | |
| Probability increase (%) of responding to Crohn’s treatment given a negative SeHCAT test – cut-off value 15% | 0.02 | Uniform | a = 0.01; b = 0.03 | A | |
| Probability of responding to Crohn’s treatment when no SeHCAT is available | 0.62 | Beta | α = 15.77; β = 9.60 | E | |
| Probability of responding to BAS – trial of treatment | 0.46 | Beta | α = 45.24; β = 53.11 | A | |
| Probability increase (%) of responding to Crohn’s treatment when response to BAS is negative in trial of treatment | 0.05 | Uniform | a = 0.03; b = 0.07 | A | |
| Transition probability (for Markov model only) | Transition probability from ‘diarrhoea’ to ‘no diarrhoea’ | 0.05 | Triangular | a = 0.02; b = 0.08; c = 0.05 | A |
| Transition probability from ‘no diarrhoea’ to ‘diarrhoea’ | 0.05 | Triangular | a = 0.02; b = 0.08; c = 0.05 | A | |
| Cost | Cost per day of Crohn’s medication | 1.78 | Gamma | Shape = 2.55; scale = 0.69 | E |
| Cost per day of BAS medication | 0.63 | Triangular | a = 0.42 b = 0.84 c = 0.63 |
E | |
| Cost SeHCAT capsule | 195 | Fixed | – | ||
| Cost for administering SeHCAT test | 186 | Fixed | – | ||
| Maintenance and service costs of SeHCAT test | 0 | Fixed | – | ||
| Cost per day associated with health state ‘diarrhoea’ | 0.06 | Triangular | a = 0.03; b = 0.09; c = 0.06 | A | |
| Crohn’s medication cost per day associated with health state ‘no diarrhoea’ | 1.08 | Gamma | Shape = 2.00; scale = 0.54 | E | |
| BAS cost per day associated with health state ‘no diarrhoea’ | 0.63 | Triangular | a = 0.42; b = 0.84; c = 0.63 | E | |
| Utility | Utility associated with health state ‘diarrhoea’ | 0.70 | Beta | α =320.21; β = 137.23 | L |
| Utility associated with health state ‘no diarrhoea’ (Crohn’s) | 0.76 | Beta | α = 802.58; β = 253.44 | L | |
| Utility associated with health state ‘no diarrhoea’ (BAM) | 0.74 | Beta | α = 353.08; β = 120.85 | L |
We also explore the value of information associated with the model uncertainty by estimating the expected value of perfect information (EVPI), which is the amount the decision-maker should be willing to pay to eliminate all uncertainty in the decision. For the IBS-D model we assumed a potential population of 1.3 million in the UK (see Figure 1 ). For the Crohn’s disease model, we do not know the size of the population and present, therefore, the EVPI per patient.
In addition, extensive scenario analyses were performed for all those input parameters where, due to lack of published data, assumptions had to be made.
Model assumptions
Diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome population decision tree (first 6 months)
-
A positive SeHCAT test result depends on a cut-off threshold; from literature three main cut-off points are considered: 5%, 10% and 15%.
-
Studies with cut-off points between 8% and 12% have all been grouped as 10% (see Chapter 3 , Effectiveness of bile acid sequestrants for thetreatment of bile acid absorption in patients with chronic diarrhoea).
-
Response to BAS treatment for positive SeHCAT test is estimated (depending on the cut-off value) from literature.
-
Response to BAS in the trial of treatment strategy is assumed to be 28%, which is equivalent to the percentage of BAS responders in the SeHCAT 15% strategy.
-
Response to IBS-D treatment for no SeHCAT test patients is derived from experts’ answers (question 11 – no SeHCAT available).
-
For the response to IBS-D treatment when SeHCAT test (15%) is negative we assume a 10-percentage-point higher response rate, as a large group of patients with BAM (who would be less respondent to IBS treatment) has been excluded because they have a positive SeHCAT result.
-
In line with this, for SeHCAT 5% and 10% we assume a 5-percentage-point and 8-percentage-point higher response rate.
-
SeHCAT is assumed not to be associated with any adverse effects.
-
We assumed that the utility gain for IBS-D treatment would be larger than for BAS treatment, due to side effects caused by BAS. In the Markov models, it may lead to declining costs and transitions from ND to D.
-
We assumed that reduced compliance with BAS or IBS-D treatment in the decision tree was already implicitly included in the response rates.
-
The SeHCAT test lasts 1 week. The decision tree is assumed to cover 6 months (same as Markov cycle).
-
We assume no difference in number of gastroenterologists visits between the various strategies.
-
IBS-D treatment costs (no SeHCAT and SeHCAT negative) consist of medication, diet and psychological therapy costs.
-
Resource use IBS-D was based on expert opinion.
-
BAM treatment (SeHCAT positive) consists of medication costs only.
-
The cost estimate for the BAS treatment is based on the reported dosage of Williams. 45
Crohn’s population decision tree (first 6 months)
-
Response rate to BAS in patients with a positive SeHCAT would be the same as in patients with idiopathic BAM.
-
Percentage of Crohn’s patients considered successfully treated for their chronic diarrhoea based on expert opinion.
-
For the response to diarrhoea/Crohn’s disease treatment when SeHCAT test (15%) is negative we assume a 10-percentage-point higher response rate, as a large group of patients with BAM (who would be less respondent to diarrhoea/Crohn’s disease treatment) has been excluded because they have a positive SeHCAT result, and 8 percentage points higher for a cut-off of 10%. This is similar to the assumption in the IBS-D population.
-
Response to BAS in the trial of treatment strategy is assumed to be 46%, which is equivalent to the percentage of BAS responders in the SeHCAT 15% strategy.
-
We assume that the quality of life in the diarrhoea health state is 0.7.
-
We assume that the utility decrement due to diarrhoea in the Crohn’s patient population is the same as for the IBS-D population.
Markov model
-
Cycle length: 6 months.
-
Time horizon: lifetime = 50 years = 100 cycles.
-
Initial distribution of patients (from decision tree): we assume that patients responding to treatment are in no diarrhoea and those not responding are in diarrhoea.
-
No excess mortality due to chronic diarrhoea is assumed.
-
Our model cohort was assumed to have the same age and sex distribution as those found in the studies used for the probability of a positive SeHCAT test.
-
In the diarrhoea state patients are assumed to use loperamide.
-
Patients treated as IBS-D in the no diarrhoea state are assumed to only incur medication cost (per cycle) as in decision tree.
-
Patients treated with BAS are assumed to continue their medication.
-
Patients treated as Crohn’s with chronic diarrhoea in the no diarrhoea state are assumed to only incur medication cost (per cycle) without anti-TNF-α.
Results
In this section we discuss the costs, effects and the cost-effectiveness of the various strategies per population. First, the full results are given for the IBS-D population: both short-term and long-term results. These are first presented without trial of treatment as a comparator and then with trial of treatment as a comparator. The results are then presented for the Crohn’s population again both short-term and long-term results and again these are first presented without trial of treatment as comparator and then with trial of treatment as a comparator. ICERs were estimated as additional cost per additional responder in the short term (first 6 months) and per additional QALY in the long term (lifetime).
Costs, effects and cost-effectiveness for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome
Short-term results for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (decision tree)
Table 33 presents the probabilistic outcomes of the base-case decision tree for the IBS-D population. Results are presented in order of increasing number of responders. From this, it becomes clear that the SeHCAT 15% strategy dominates the other SeHCAT strategies. Also, SeHCAT 15% is more expensive while also generating more responders.
| Strategy | Percentage of responders | Costs (per patient) | Incremental responders | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test – treat IBS-D | 0.5145 | 208 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 0.632 | 569 | Dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 0.654 | 555 | Dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 0.6596 | 553 | 0.1451 | 345 | 2378 |
To investigate what the impact is of the various (statistical) uncertainties in the model, we also present the CEAC ( Figure 10 ). It should be noted that the outcome here is cost per responder; we cannot judge the curve using the usual threshold, which relates to cost per QALY.
FIGURE 10.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve short-term (cost per responder) results for IBS-D population, base case (scenario A1).
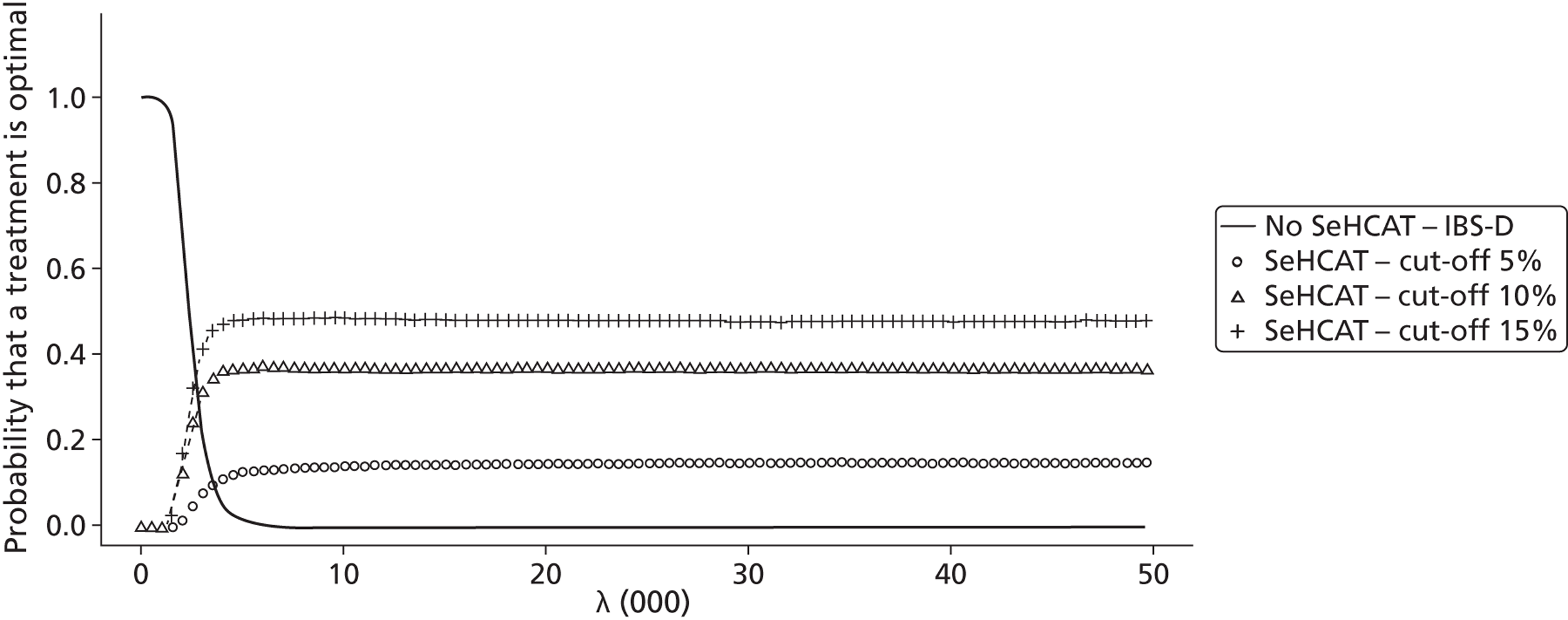
As mentioned in the methods section, various assumptions regarding probabilities had to be made where neither literature nor expert opinion was available. Additionally, the costs of IBS-D treatment are very uncertain, as the experts had very differing responses, and some uncertainty exists about the total costs of SeHCAT.
Thus, we formulated several scenarios, which are listed in Table 34 . We varied the percentage point change in the response rate to IBS-D treatment for SeHCAT-negative and BAS trial-negative patients from 10% (i.e. response rate 62%) to both 0% and 25%; we increased IBS-D treatment costs by 100% and decreased these costs by 50%; and finally we increased SeHCAT cost by £55 and £105 and decreased it by £95.
| Scenarios | SeHCAT service cost (£) | Probability response to IBS-D treatment in SeHCAT-negative patients | Costs IBS-D treatment | Cost SeHCAT capsule (£) | Results presented? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0 | 0.62 | 195 | Yes | |
| A2 | 55 | 0.62 | 195 | No | |
| A3 | 105 | 0.62 | 195 | No | |
| A4 | 0 | 0.52 | 195 | Yes | |
| A5 | 0 | 0.87 | 195 | No | |
| A6 | 0 | 0.62 | × 2 | 195 | No |
| A7 | 0 | 0.62 | /2 | 195 | No |
| A8 | 0 | 0.52 | /2 | 195 | Yes |
| A9 | 0 | 0.62 | 100 | Yes | |
| A10 | 0 | 0.52 | 100 | No | |
| A11 | 0 | 0.87 | 100 | No |
We found that increasing SeHCAT costs has no impact on the conclusions from the base case. This is intuitively clear, as in the base case, the SeHCAT strategies are already the most expensive, and these only become slightly more expensive. When we change the probability of IBS-D treatment response in SeHCAT-negative and BAS trial-negative patients to the same value as when all patients receive IBS-D treatment (52% response rate), we see that the number of responders in the SeHCAT strategies decreases ( Table 35 ). The CEAC ( Figure 11 ) shows that now SeHCAT 10% dominates the other SeHCAT strategies for all larger threshold ICERs.
| Strategy | Percentage of responders | Costs (per patient) | Incremental responders | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 0.5202 | 207 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 0.5971 | 568 | Dominated by SeHCAT 10% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 0.6014 | 553 | Extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 10% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 0.6068 | 555 | 0.0865 | 348 | 4019 |
FIGURE 11.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve short-term (cost per responder) results for IBS-D population, response to IBS-D treatment in SeHCAT-negative patients 52% (scenario A4).
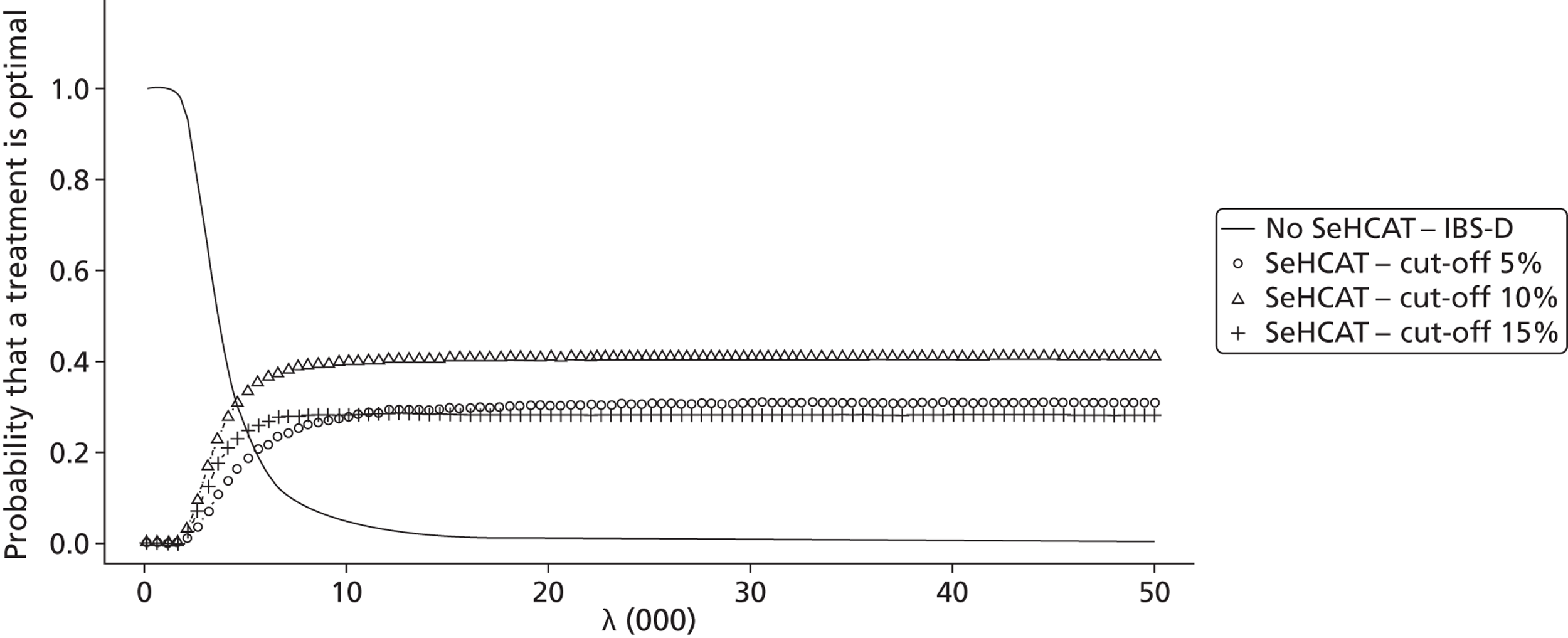
When we also decrease the cost of IBS-D treatment to 50% of the base case we see costs per strategy decrease while the incremental costs stay approximately the same ( Table 36 ). Thus, the CEAC ( Figure 12 ) is similar to the previous. Clearly, the impact of the treatment costs for IBS-D for the short term is limited.
| Strategy | Percentage of responders | Costs (per patient) | Incremental responders | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test – treat IBS-D | 0.5272 | 104 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 0.6024 | 487 | Extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 10% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 0.6058 | 489 | Dominated by SeHCAT 10% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 0.6111 | 489 | 0.0839 | 385 | 4591 |
FIGURE 12.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve short-term (cost per responder) results for IBS-D population, response to IBS-D treatment in SeHCAT-negative patients 52% and cost of IBS-D treatment 50% of base case (scenario A8).
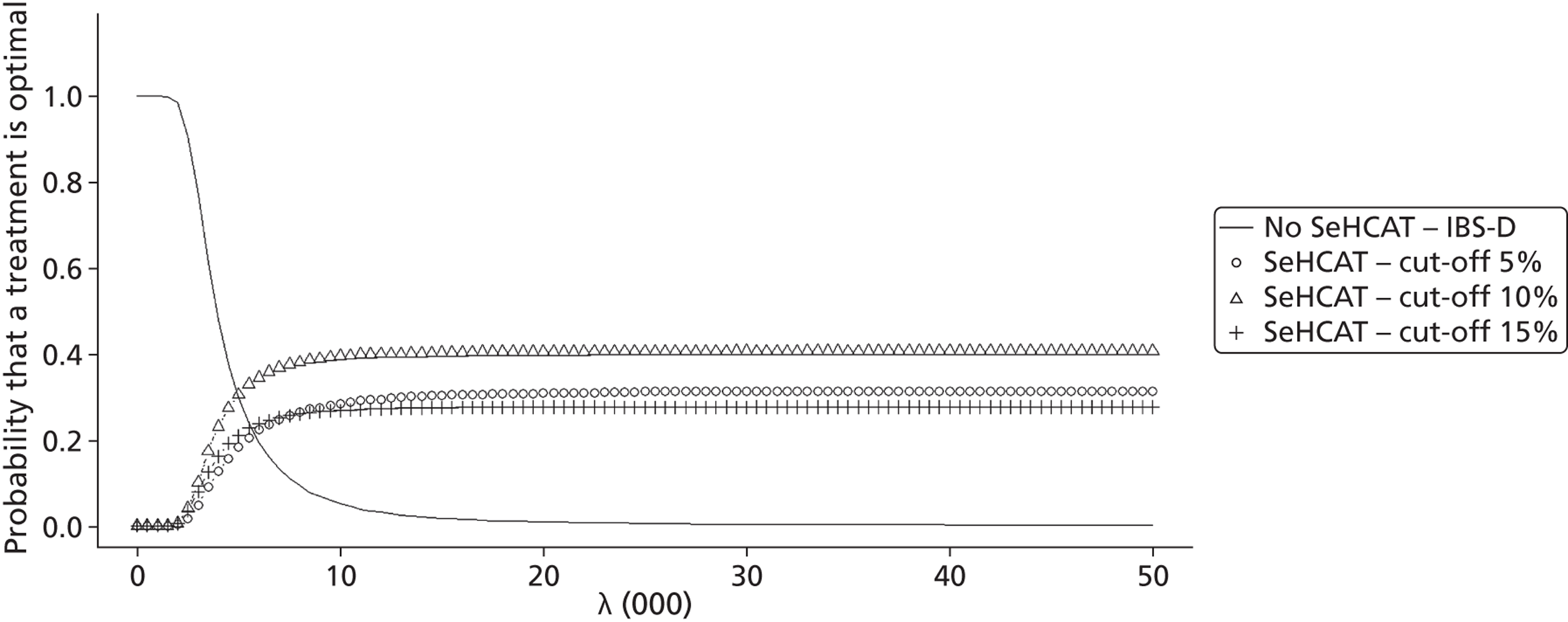
When we reduce the cost of the SeHCAT test we observe that now SeHCAT 15% again dominates the other SeHCAT strategies ( Table 37 ), but overall the impact is limited. This is confirmed by the CEAC where we still find that trial of treatment is dominant. The CEAC ( Figure 13 ) is very similar to the base-case curve, indicating that the impact of lowering the cost of SeHCAT has little impact on the results.
| Strategy | Percentage of responders | Costs (per patient) | Incremental responders | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test – treat IBS-D | 0.5275 | 208 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 0.6421 | 474 | Dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 0.6627 | 460 | Dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 0.668 | 459 | 0.1405 | 251 | 1784 |
FIGURE 13.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve short-term (cost per responder) results for IBS-D population, costs of SeHCAT reduced to £100 (scenario A9).
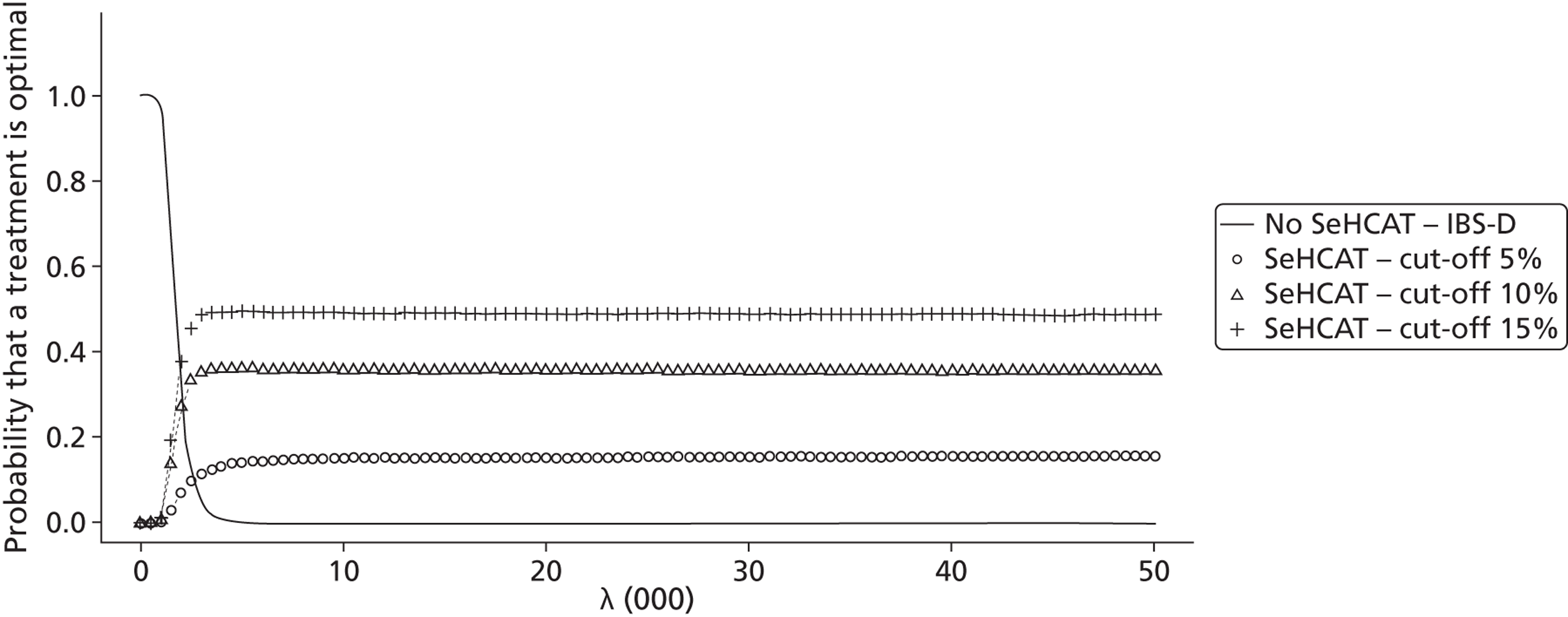
Lifetime results for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome
As mentioned in the methods section, no information was available to estimate the transition probabilities in the Markov models other than the all-cause mortality rates. Thus, we formulated various scenarios with different transition probabilities for ND-BAM → D-BAM, D-BAM → ND-BAM, ND-IBS → D-IBS and D-IBS → ND-IBS. Additionally, we have two scenarios regarding the utility in the no diarrhoea health state; either this is the same for BAS and IBS-D or utility of BAS responders is lower than for IBS-D responders. Table 38 presents an overview of all scenarios we explored. As many yielded the same results, we only present a selection of the scenarios, as indicated in the table.
| Scenario | IBS-D P(ND→D) | IBS-D P(D→ND) | BAM P(ND→D) | BAM P(D→ND) | Utility BAS no diarrhoea | Results presented? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | BAS < IBS | Yes |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS < IBS | Yes |
| 3 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS < IBS | Yes |
| 4 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS < IBS | Yes |
| 5 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | BAS < IBS | No, same as 1 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS < IBS | No, same as 1 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | BAS < IBS | No, same as 4 |
| 8 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | BAS = IBS | Yes |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 2 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 3 |
| 11 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 4 |
| 12 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | BAS = IBS | Yes |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 6 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 7 |
Below are the results for scenario 1. Scenario 1 assumes that all four transition probabilities are 5% per cycle. We observe that all SeHCAT strategies are dominated by no SeHCAT ( Table 39 ). When we look at the CEACs ( Figure 14 ), we notice that no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being cost-effective for the whole range of thresholds.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.273 | 1624 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.2744 | 1611 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.2925 | 1462 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| No SeHCAT test | 15.3006 | 818 | |||
FIGURE 14.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 1.
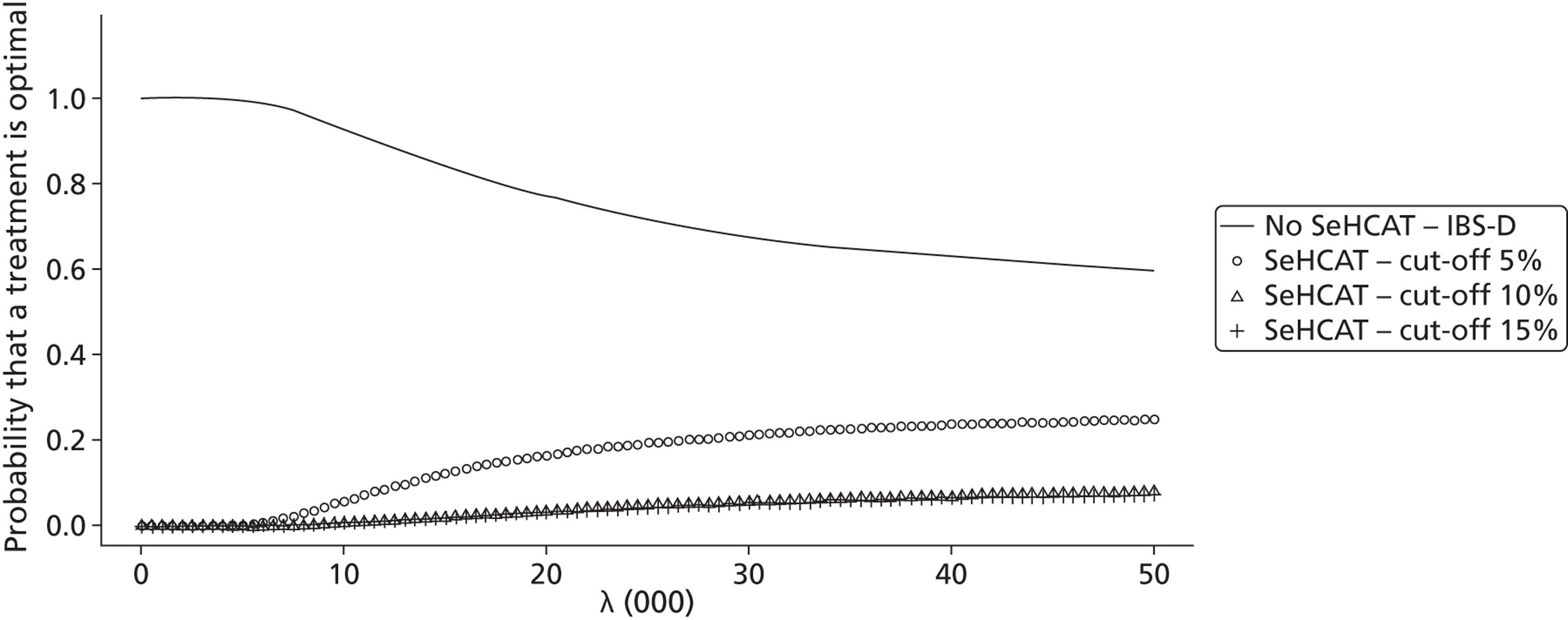
Figure 15 shows the population EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000, the value of perfect information amounts to £10,000M.
FIGURE 15.
Population EVPI for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 1.
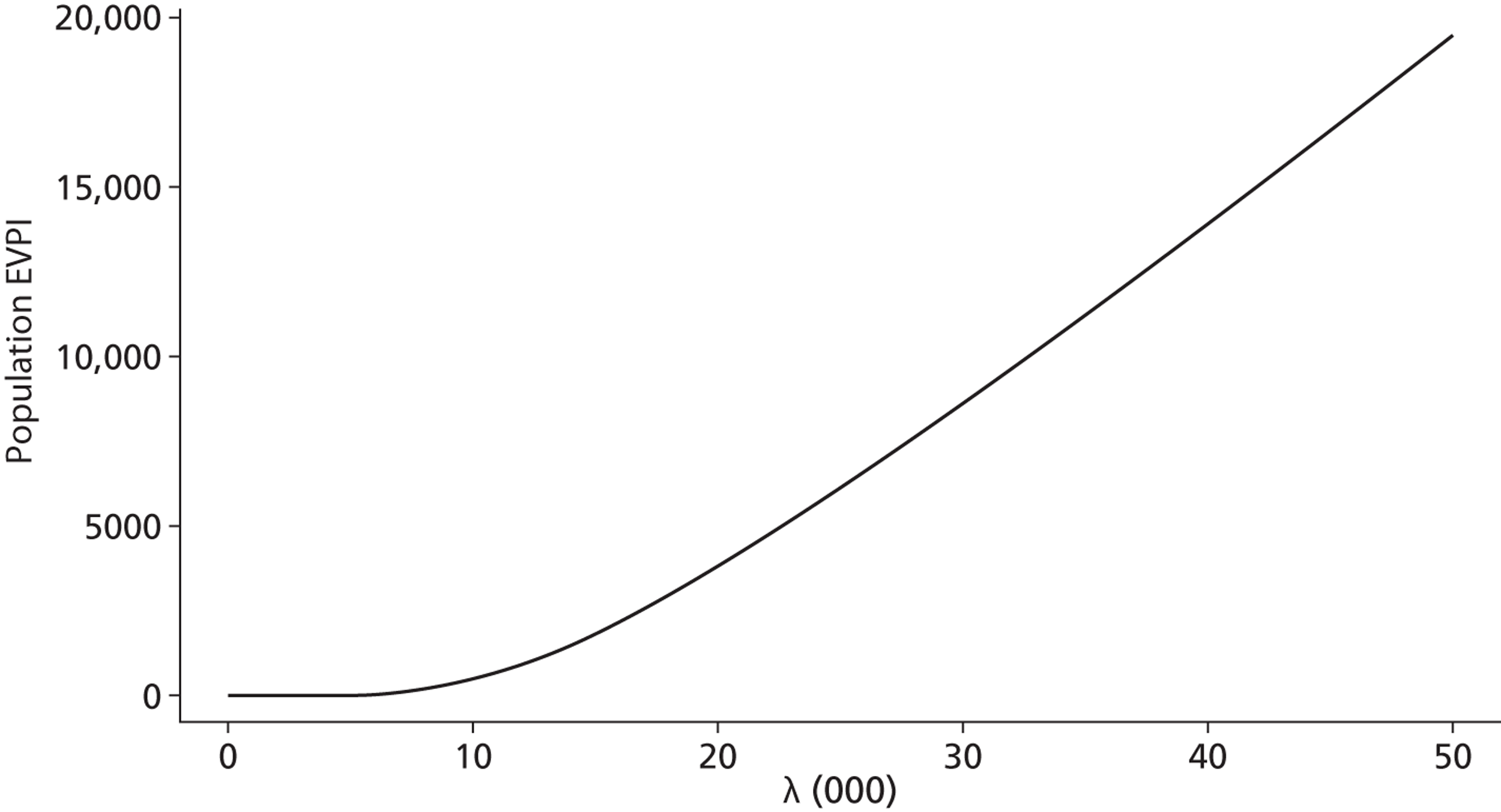
Scenario 2 assumes that all four transition probabilities are 0% per cycle. We now observe ( Table 40 ) that the ICER of SeHCAT 5% compared with no SeHCAT falls well below the commonly used £30,000 threshold. The ICER of SeHCAT 15% compared with SeHCAT 5% is approximately equivalent to this threshold. When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 16 ), we notice that, for small thresholds, no SeHCAT – treat IBS-D has the highest probability of being cost-effective while for larger thresholds (around £10,000) SeHCAT 5% has the highest probability of being cost-effective.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 15.3244 | 823 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.4127 | 1783 | Dominated by SeHCAT 5% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.4133 | 1613 | 0.0889 | 790 | 8886 |
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.4191 | 1793 | 0.0058 | 180 | 31031 |
FIGURE 16.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 2.
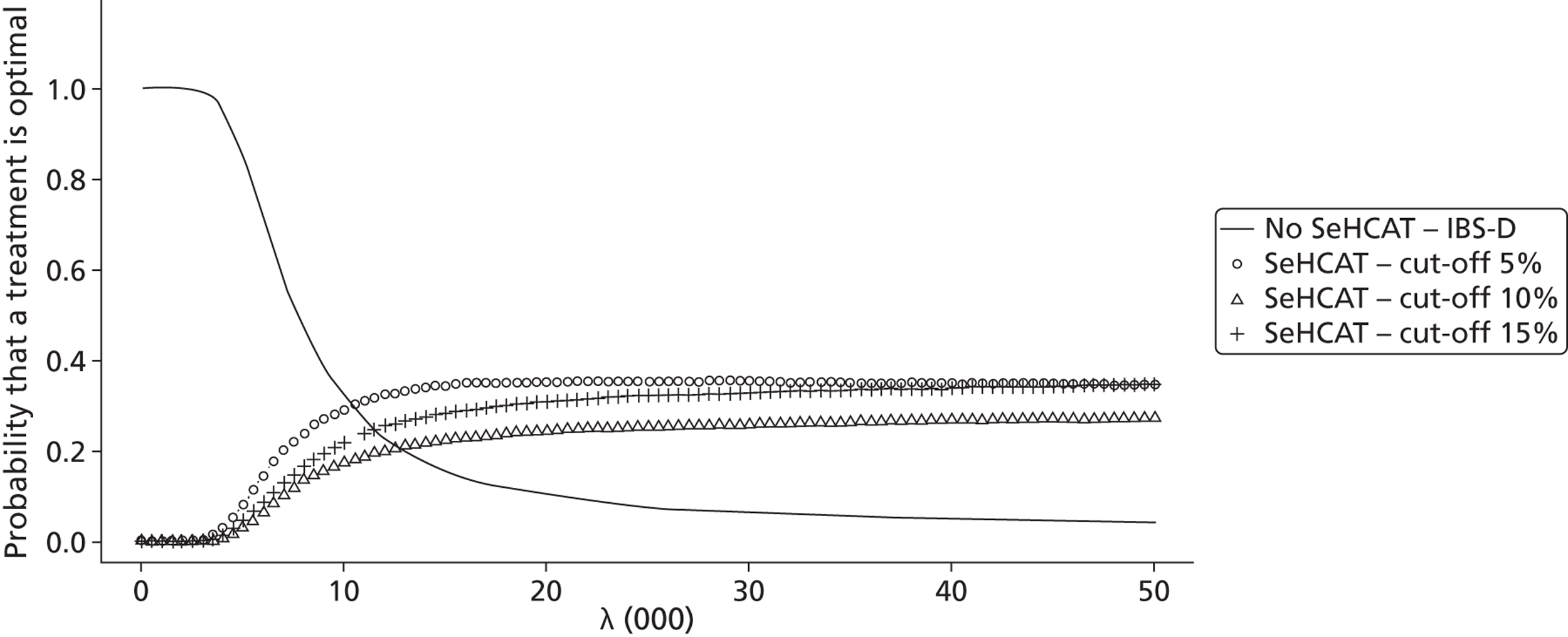
Scenario 3 assumed that the two transition probabilities from ND to D are 5% per cycle while the other two are 0. As can be seen in Table 41 , SeHCAT 5% has a favourable ICER compared with no SeHCAT, and the subsequent ICER of SeHCAT 15% versus SeHCAT 5% may also be considered acceptable given a threshold of £30,000. The CEAC presented in Figure 17 shows that for lower threshold values (< £20,000) no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being cost-effective while for higher threshold values (> £30,000), all three SeHCAT strategies have a higher probability of being cost-effective than no SeHCAT.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 14.8964 | 751 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 14.9272 | 1307 | 0.0308 | 557 | 18077 |
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.9275 | 1379 | Extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.93 | 1382 | 0.0028 | 75 | 26786 |
FIGURE 17.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 3.
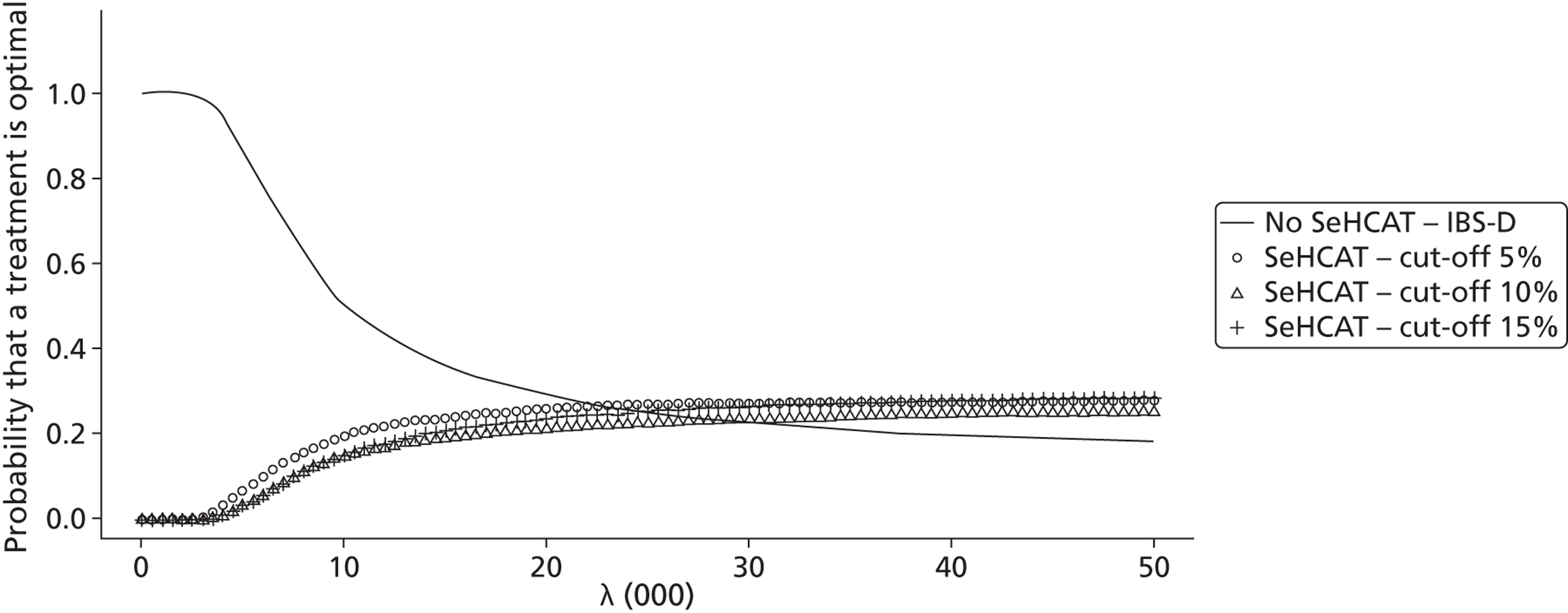
Figure 18 shows the population EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000 the value of perfect information amounts to £30,000M. This is three times higher than in scenario 1, which is explained by the fact that at that threshold value all four strategies have approximately the same probability of being the most cost-effective.
FIGURE 18.
Population EVPI for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 3.
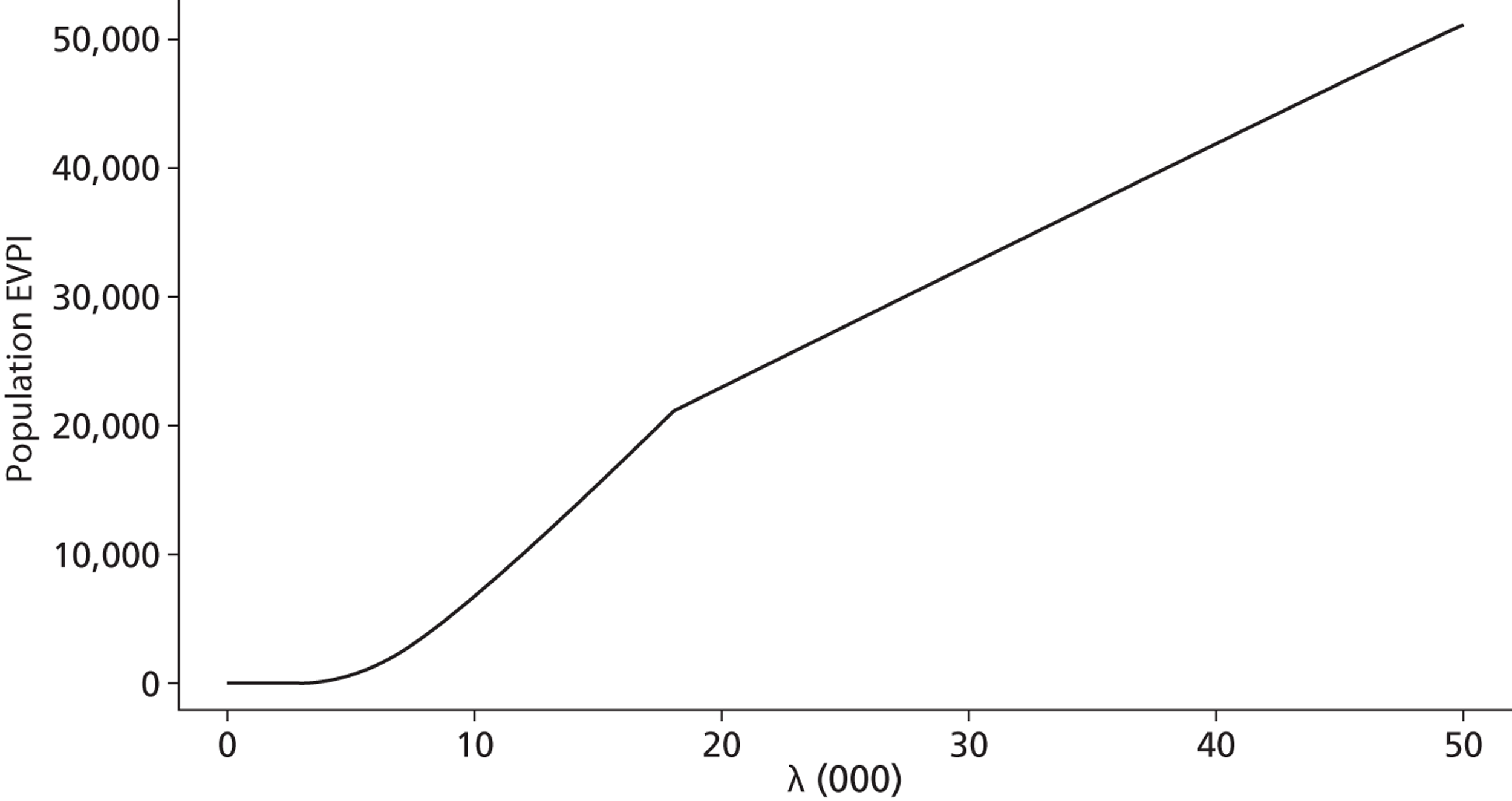
Scenario 4 assumes that the transition probability from ND to D in the IBS model is 5% per cycle while all others are 0. We observe that SeHCAT 15% compared with no SeHCAT yields an ICER well below the common threshold of £30,000, while the other two SeHCAT strategies are extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 15% ( Table 42 ). When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 19 ), we again observe that, for small thresholds, no SeHCAT – treat IBS-D has the highest probability of being cost-effective while for larger thresholds (around £5000) SeHCAT 15% has the highest probability of being cost-effective.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 14.8939 | 749 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.0432 | 1548 | Extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.0965 | 1727 | Extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.1003 | 1736 | 0.2064 | 987 | 4782 |
FIGURE 19.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 4.
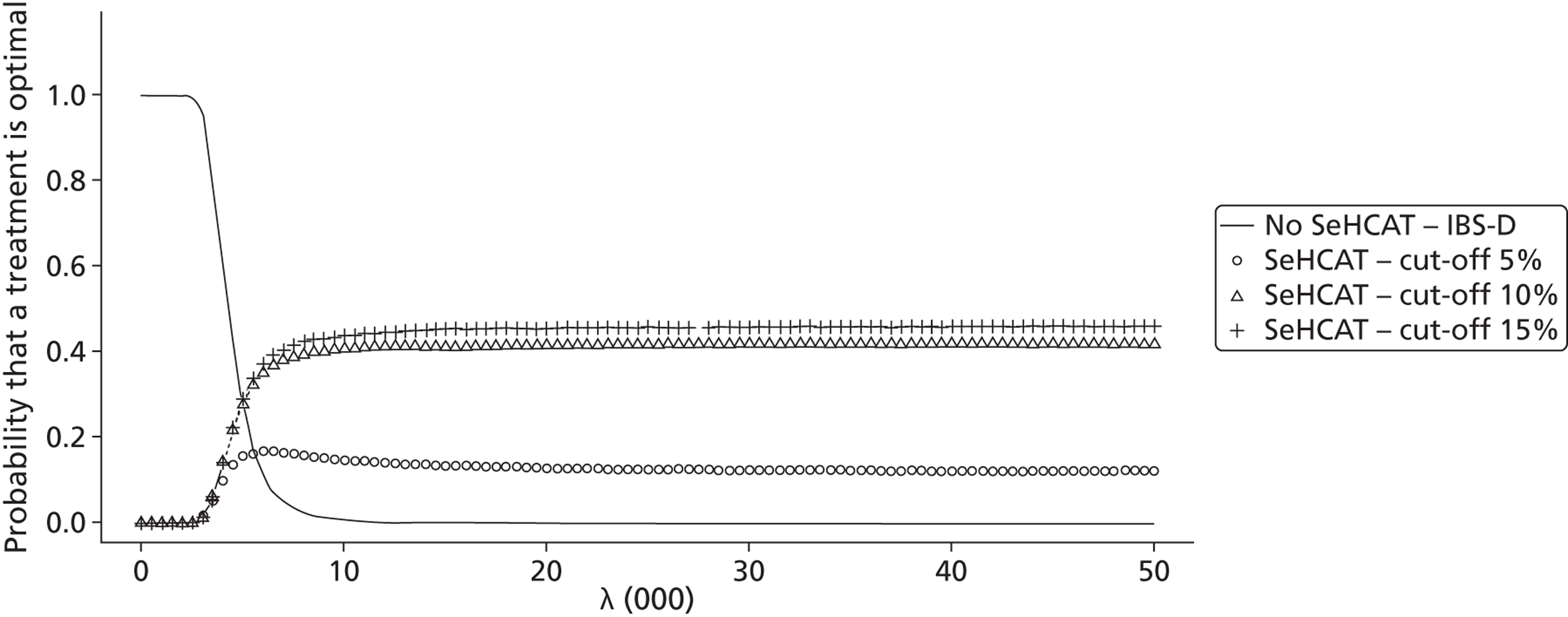
Scenario 8 is the same as scenario 1, but now with utilities for IBS-D and BAM the same. As can be seen in Table 43 , SeHCAT 5% has a favourable ICER compared with no SeHCAT, and the ICER of SeHCAT 15% versus SeHCAT 5% may also be considered acceptable given a threshold of £30,000. The CEAC presented in Figure 20 shows that for lower threshold values no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being optimal while at a threshold of between £20,000 and £30,000, the three SeHCAT strategies have approximately the same probability of being optimal.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 15.3034 | 819 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.334 | 1460 | 0.0306 | 642 | 20,976 |
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.3388 | 1610 | Extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.3408 | 1625 | 0.0068 | 165 | 24,265 |
FIGURE 20.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 8.
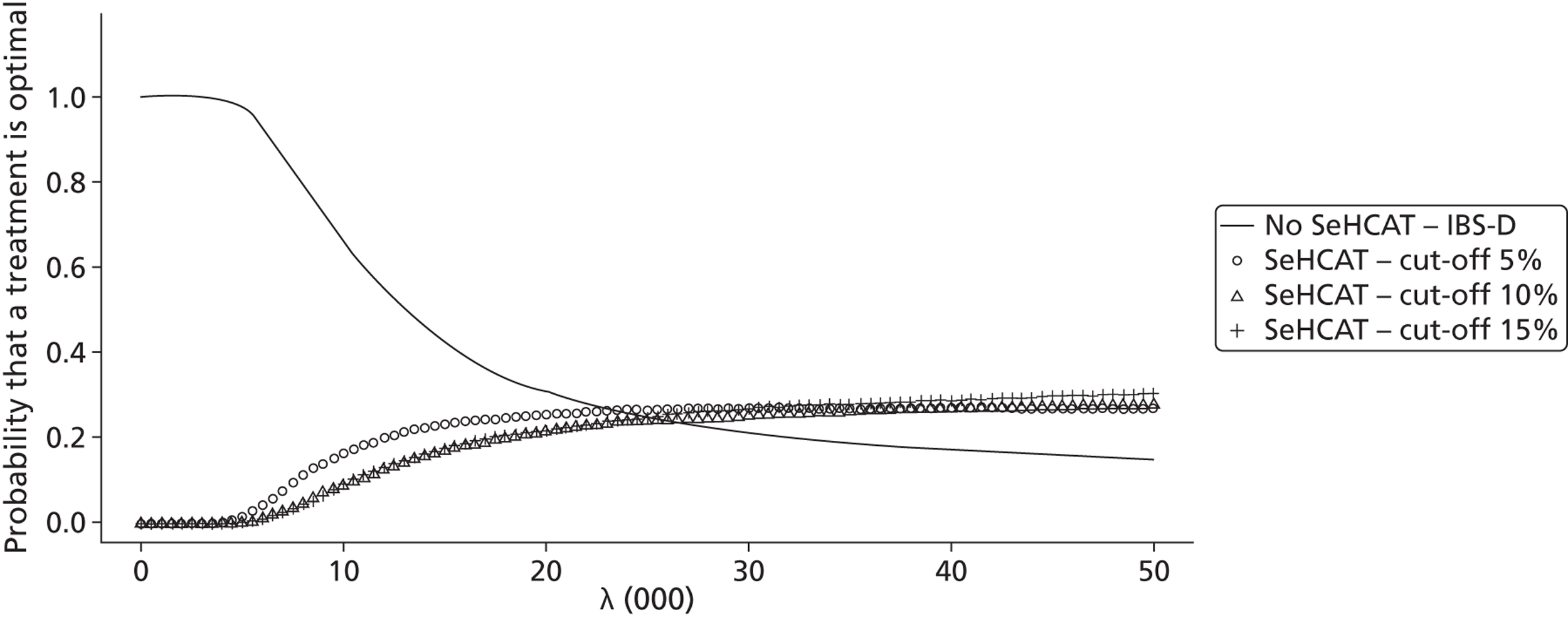
Figure 21 shows the population EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000, the value of perfect information amounts to £20,000M.
FIGURE 21.
Population EVPI for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 8.
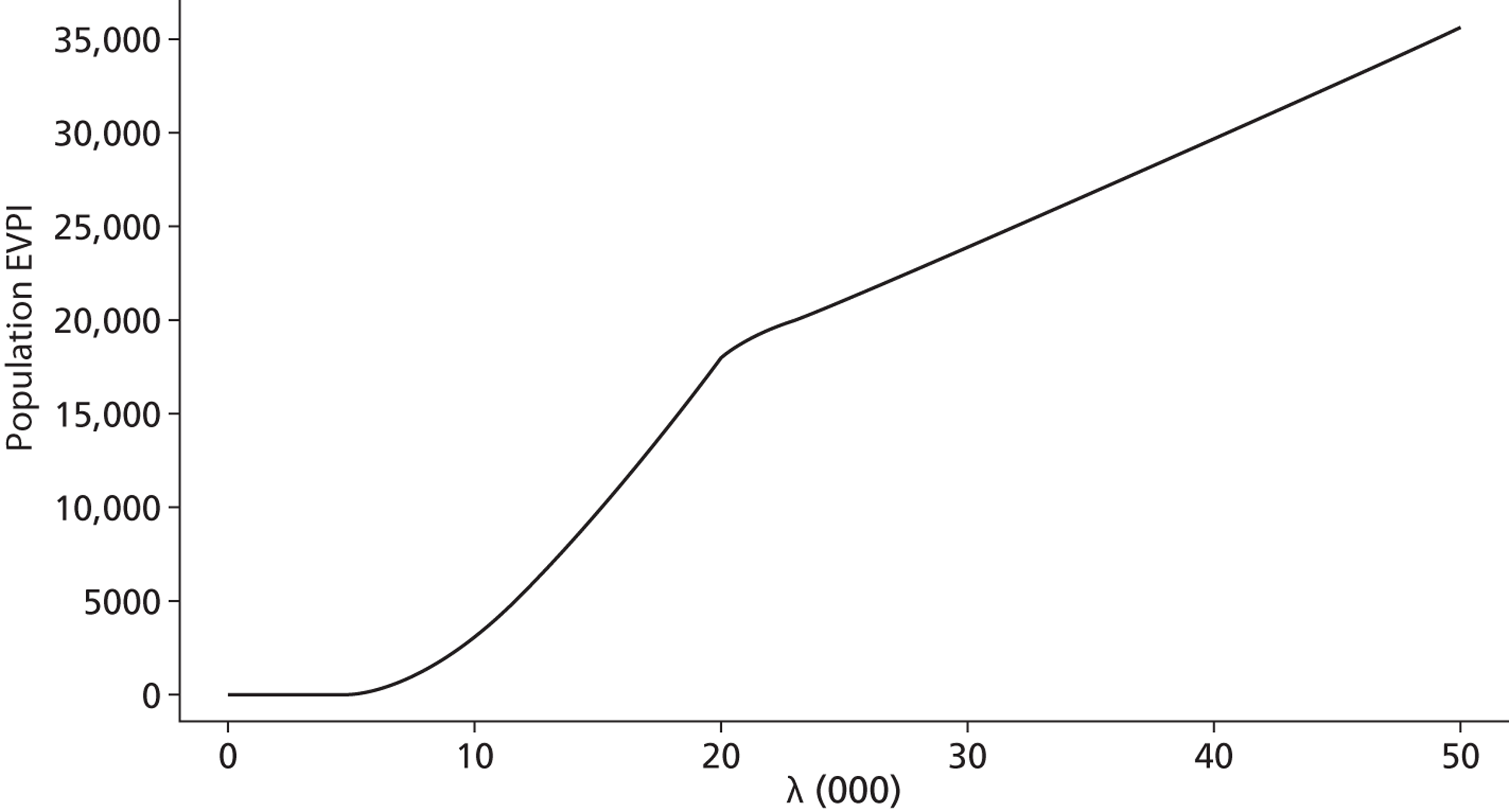
Finally, scenario 12 is the same as scenario 5, but now with utilities for IBS-D and BAM the same. As can be seen in Table 44 , due to the higher utility for BAM responders, now SeHCAT 5% has a favourable ICER compared with no SeHCAT given a threshold of £30,000. The CEAC presented in Figure 22 shows that for lower threshold values no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being optimal while at a threshold of between £20,000 and £30,000, SeHCAT 5% has the highest probability of being optimal.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.7042 | 1823 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.7136 | 1820 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| No SeHCAT test | 15.7239 | 893 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.7539 | 1660 | 0.03 | 767 | 25,567 |
FIGURE 22.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 12.
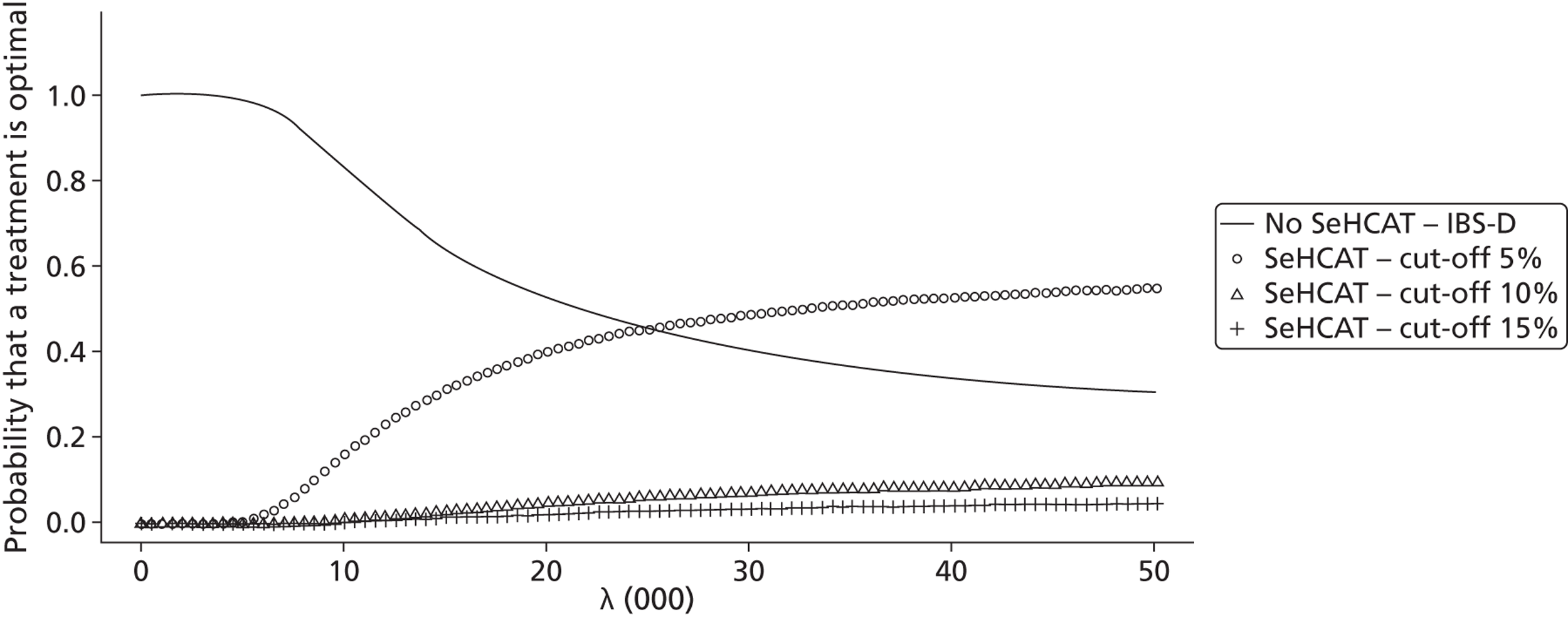
Costs, effects and cost-effectiveness diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome with trial of treatment included
Short-term results (decision tree) for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome with trial of treatment
Table 45 presents the probabilistic outcomes of the base-case decision tree for the IBS-D population when trial of treatment is also considered as comparator. Results are presented in order of increasing number of responders. From this, it becomes clear that the trial of treatment strategy dominates all other strategies: it leads to the highest number of responders for the lowest costs. Thus, no ICERs should be calculated. From the table we also notice that of the three SeHCAT scenarios, the 15% cut-off dominates the other two cut-offs.
| Strategy | Percentage of responders | Costs (per patient) | Incremental responders | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 0.5145 | 208 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 0.632 | 569 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 0.654 | 555 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 0.6596 | 553 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 0.6862 | 148 | |||
To investigate what the impact is of the various (statistical) uncertainties in the model, we also present the CEAC ( Figure 23 ). We notice that the trial of treatment strategy has the highest probability of being considered cost-effective over the whole range of possible threshold ICERs.
FIGURE 23.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for short-term (cost per responder) results for IBS-D population, base case with trial of treatment.
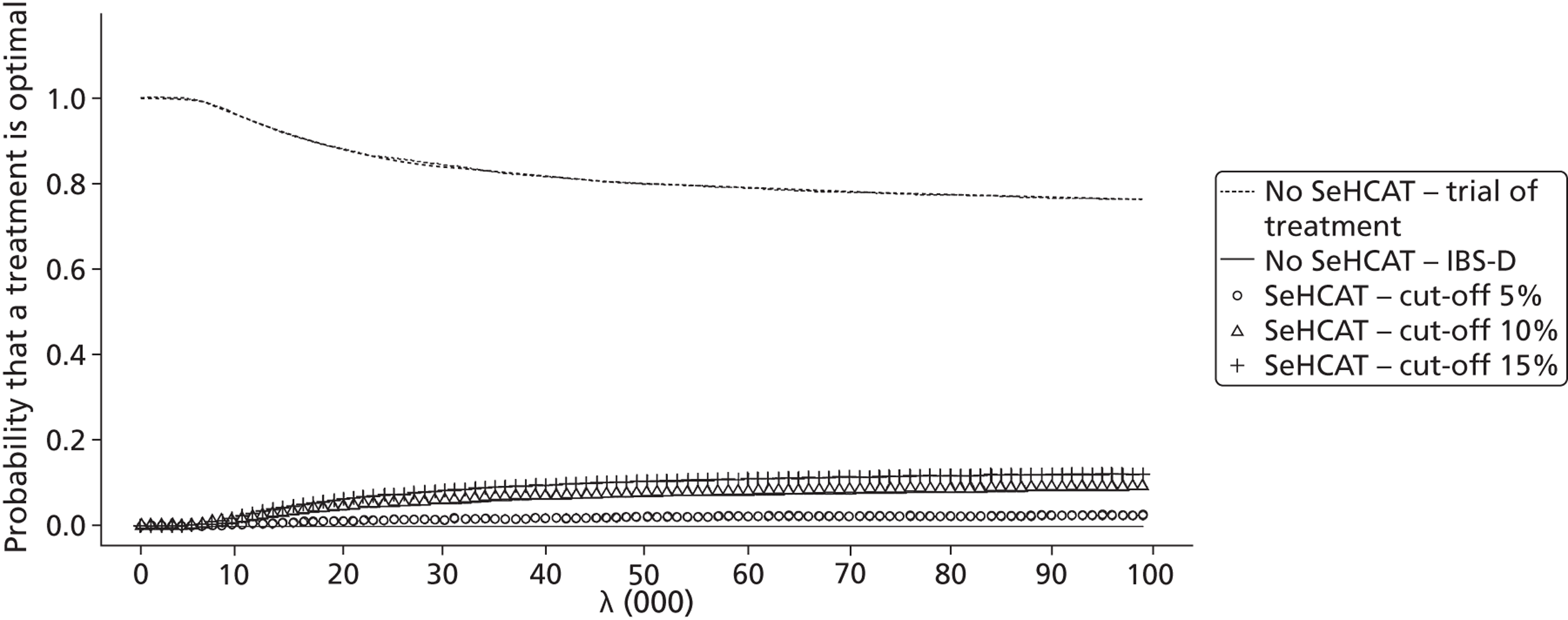
As mentioned in the methods section, various assumptions regarding probabilities had to be made where neither literature nor expert opinion was available. Additionally, the costs of IBS-D treatment are very uncertain, as the experts had very differing responses and some uncertainty exists about the total costs of SeHCAT. Thus, we formulated several scenarios, which are listed in Table 46 . However, none of these scenarios led to any results different from the base case; in all cases trial of treatment was the dominant strategy. For all scenarios trial of treatment had the highest probability of being cost-effective; this probability was for most scenarios around 90%, decreasing for some scenarios to 50%.
| Scenario | SeHCAT service cost | Probability response to BAS with trial of treatment | Probability response to IBS-D treatment in SeHCAT-negative patients | Costs IBS-D treatment | Cost SeHCAT capsule | Results presented? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 195 | Yes | |
| B2 | 55 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| B3 | 105 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| B4 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.52 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| B5 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| B6 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.62 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| B7 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.52 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| B8 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.87 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| B9 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.62 | × 2 | 195 | No, same as 1 |
| B10 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.62 | /2 | 195 | No, same as 1 |
| B11 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.52 | /2 | 195 | No |
| B12 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.52 | /2 | 195 | No, same as 1 |
| B13 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| B14 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.52 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| B15 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| B16 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.62 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| B17 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.52 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| B18 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.87 | 100 | No, same as 1 |
Lifetime results for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome with trial of treatment
As in Lifetime results for diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome, above, we have again explored a list of 14 scenarios regarding transition probabilities of the Markov models and the utility of the no diarrhoea health state. Again, we present only a limited number of these scenarios ( Table 47 ).
| Scenario | IBS-D P(ND→D) | IBS-D P(D→ND) | BAM P(ND→D) | BAM P(D→ND) | Utility BAS no diarrhoea | Results presented? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | BAS < IBS | Yes |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS < IBS | Yes |
| 3 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS < IBS | No, same as 2 |
| 4 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS < IBS | No, same as 2 |
| 5 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | BAS < IBS | No, same as 1 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS < IBS | No, same as 1 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | BAS < IBS | Yes |
| 8 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | BAS = IBS | Yes |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 2 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 3 |
| 11 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 4 |
| 12 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | BAS = IBS | Yes |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 6 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | BAS = IBS | No, same as 7 |
Below are the results for scenario 1. Scenario 1 assumes that all four transition probabilities are 5% per cycle. We observe that all SeHCAT strategies are dominated by no SeHCAT ( Table 48 ). When we look at the CEACs ( Figure 24 ), we notice that no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being cost-effective for the whole range of thresholds.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.273 | 1624 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.2744 | 1611 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 15.2863 | 1211 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.2925 | 1462 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| No SeHCAT test | 15.3006 | 818 | |||
FIGURE 24.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 1 with trial of treatment.
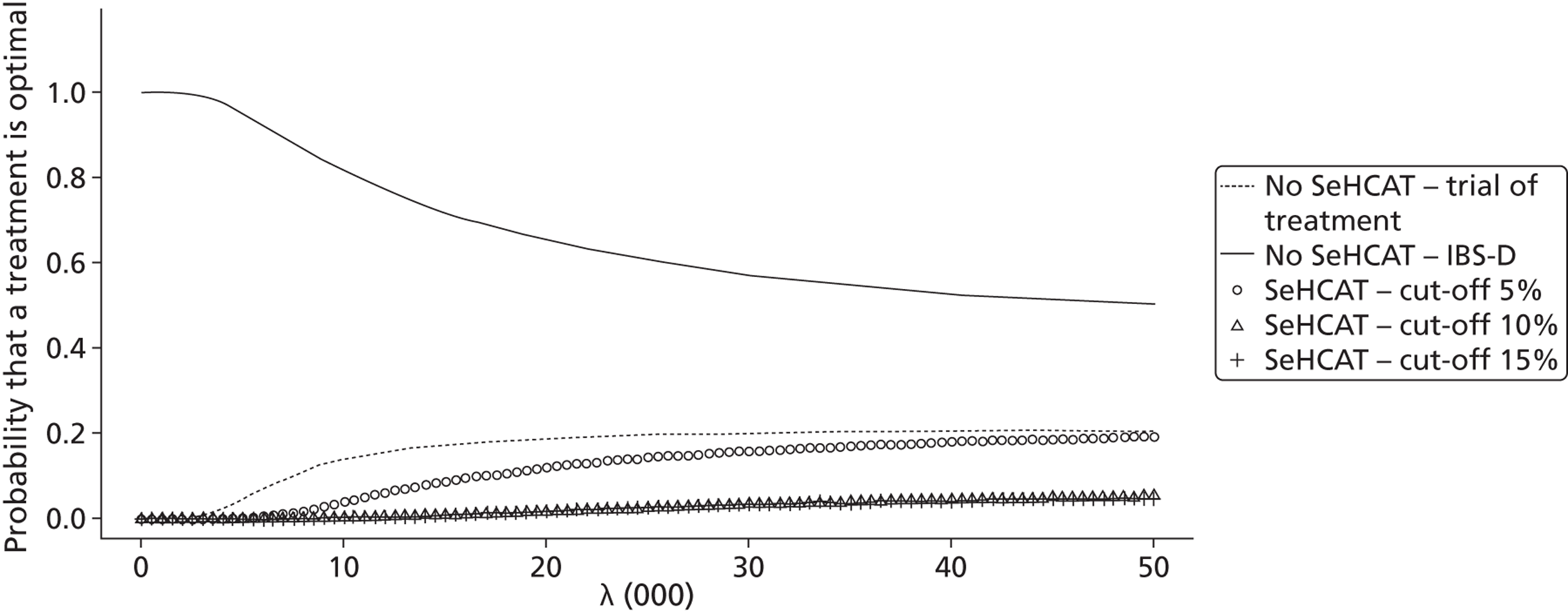
Figure 25 shows the population EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000, the value of perfect information amounts to £10,000M.
FIGURE 25.
Population EVPI for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 1 with trial of treatment.
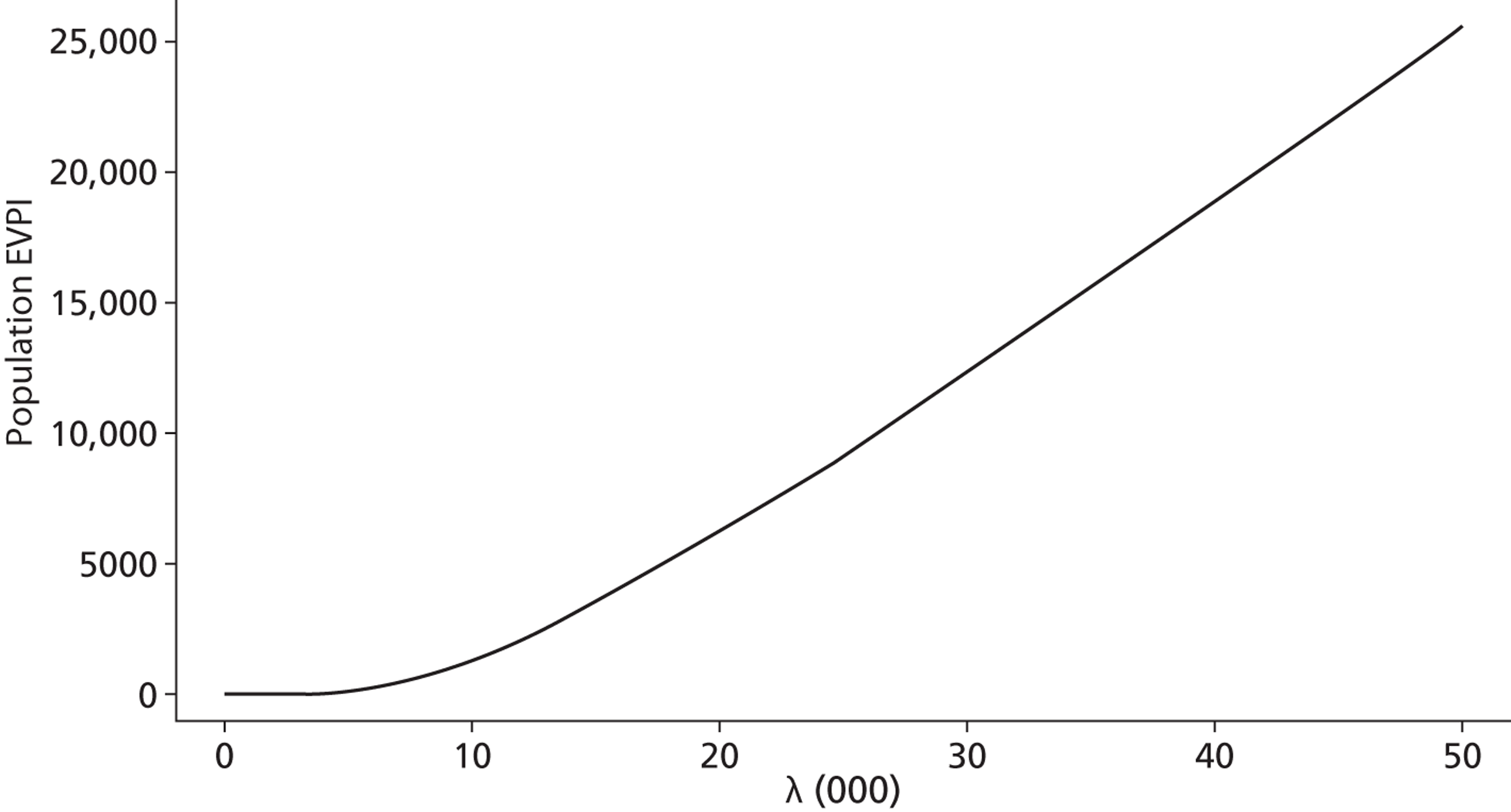
Scenario 2 assumes that all four transition probabilities are 0% per cycle. We now observe ( Table 49 ) that the ICER of trial of treatment compared with no SeHCAT falls well below the commonly used £30,000 threshold, while all SeHCAT strategies are dominated by trial of treatment. When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 26 ), we notice that for small thresholds no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being cost-effective while for larger thresholds (around £5000) trial of treatment has the highest probability of being cost-effective.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 15.3244 | 823 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.4127 | 1783 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.4133 | 1613 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.4191 | 1793 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 15.45 | 1459 | 0.1256 | 636 | 5064 |
FIGURE 26.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 2 with trial of treatment.
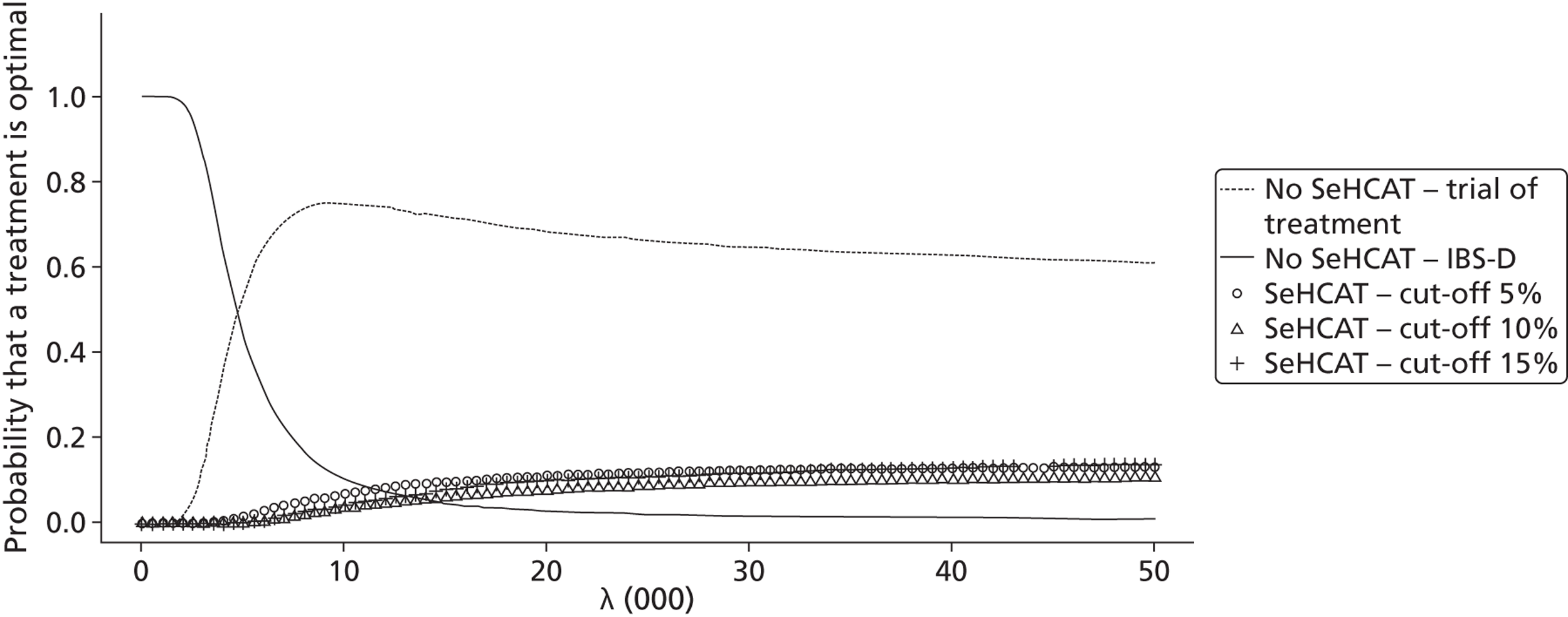
Scenario 7 assumes that the transition probability from D to ND in the BAM model is 5% per cycle while all others are 0. We observe that trial of treatment compared with no SeHCAT yields an ICER well below the common threshold of £30,000, as is the ICER of SeHCAT 15% compared with trial of treatment ( Table 50 ). When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 27 ), we again observe that for small thresholds no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being cost-effective, for thresholds between £5000 and £15,000 trial of treatment is optimal and for thresholds higher than £15,000 SeHCAT 15% has the highest probability of being cost-effective.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 15.3192 | 822 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.4264 | 1643 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 15.4451 | 1459 | 0.1259 | 637 | 5060 |
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.4653 | 1894 | Extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.4797 | 1919 | 0.0346 | 460 | 13,295 |
FIGURE 27.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 7 with trial of treatment.
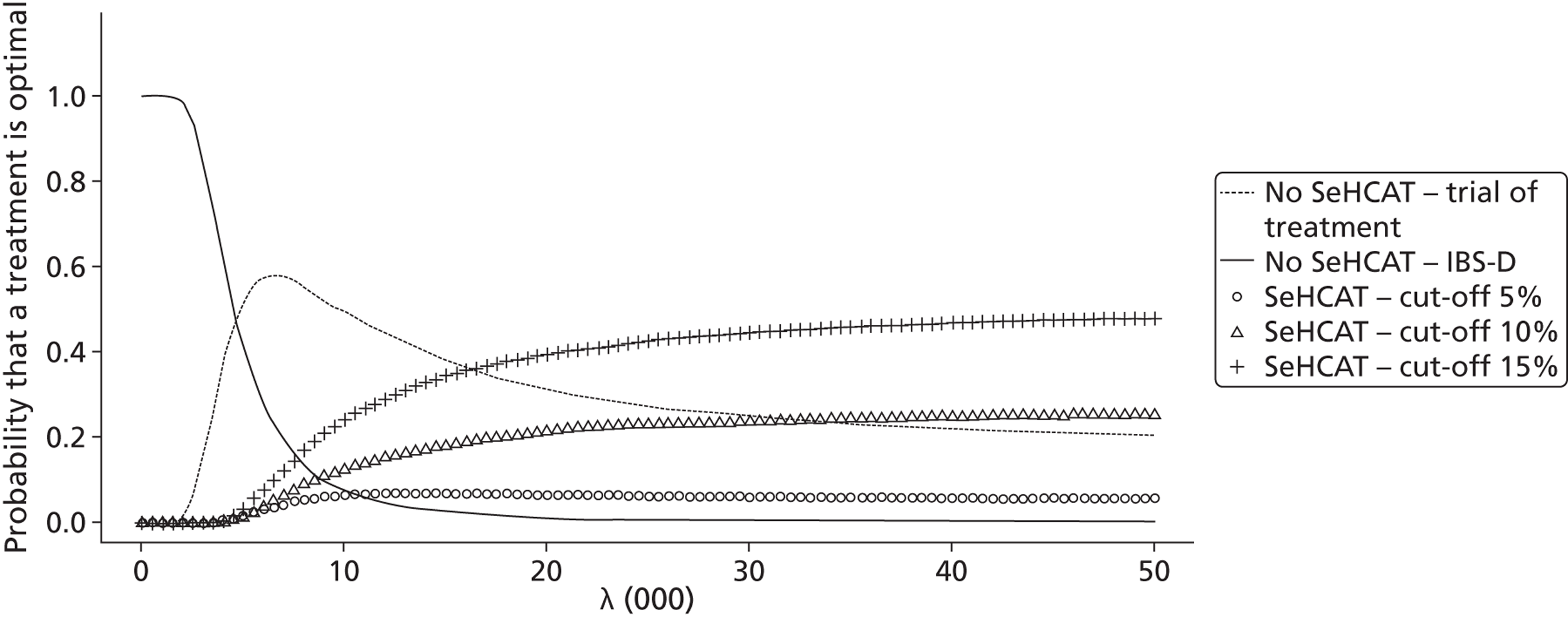
Figure 28 shows the population EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000, the value of perfect information amounts to £15,000M.
FIGURE 28.
Population EVPI for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 7 with trial of treatment.
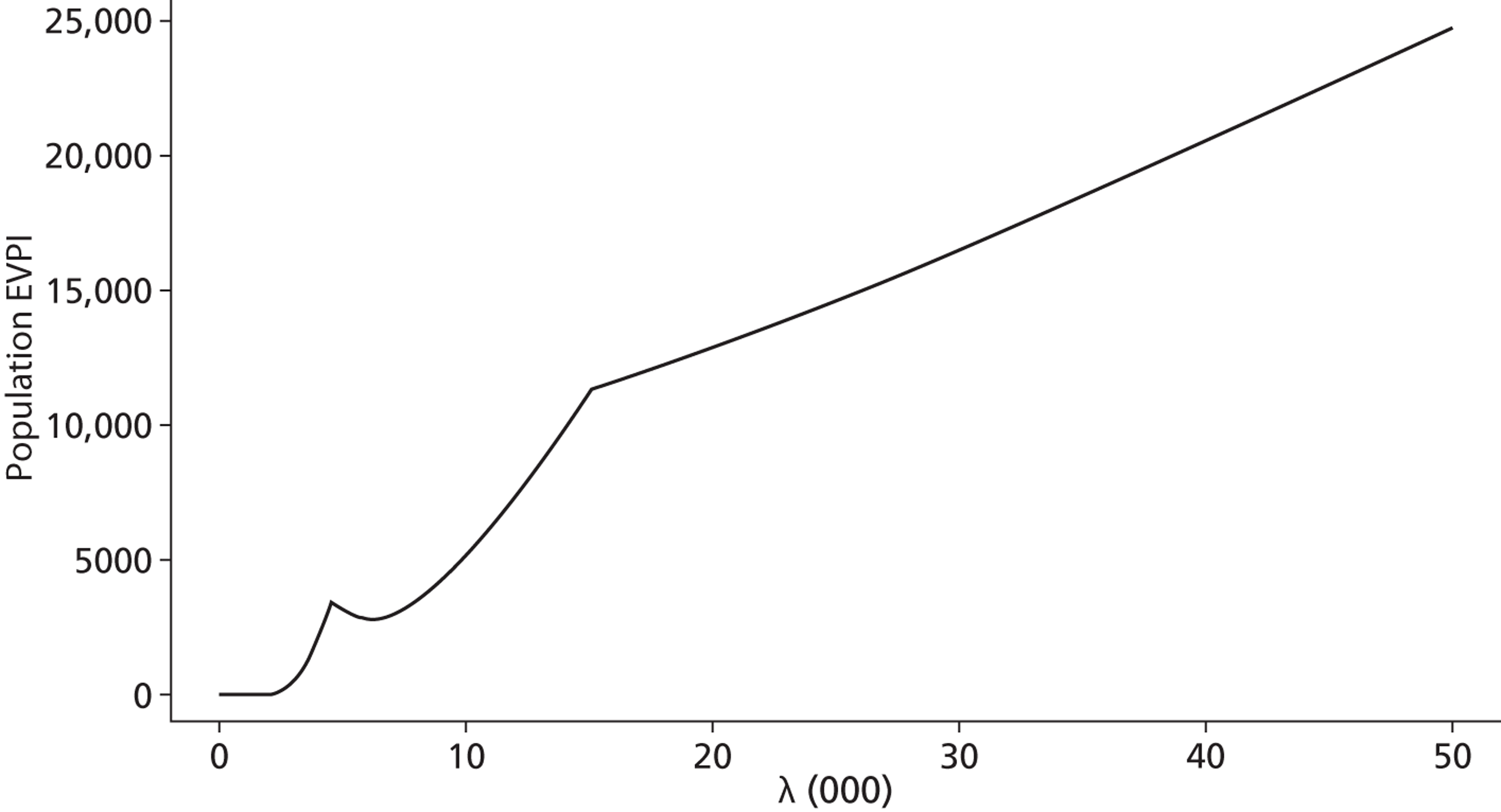
Scenario 8 is the same as scenario 1, but now with utilities for IBS-D and BAM the same. As can be seen in Table 51 , now trial of treatment has a favourable ICER compared with no SeHCAT, while all the SeHCAT strategies are dominated by trial of treatment. The CEAC presented in Figure 29 shows that for lower threshold values no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being optimal while for thresholds above £10,000 trial of treatment has the highest probability of being optimal.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 15.3034 | 819 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.334 | 1460 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.3388 | 1610 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.3408 | 1625 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 15.3412 | 1210 | 0.0378 | 391 | 10,344 |
FIGURE 29.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 8 with trial of treatment.
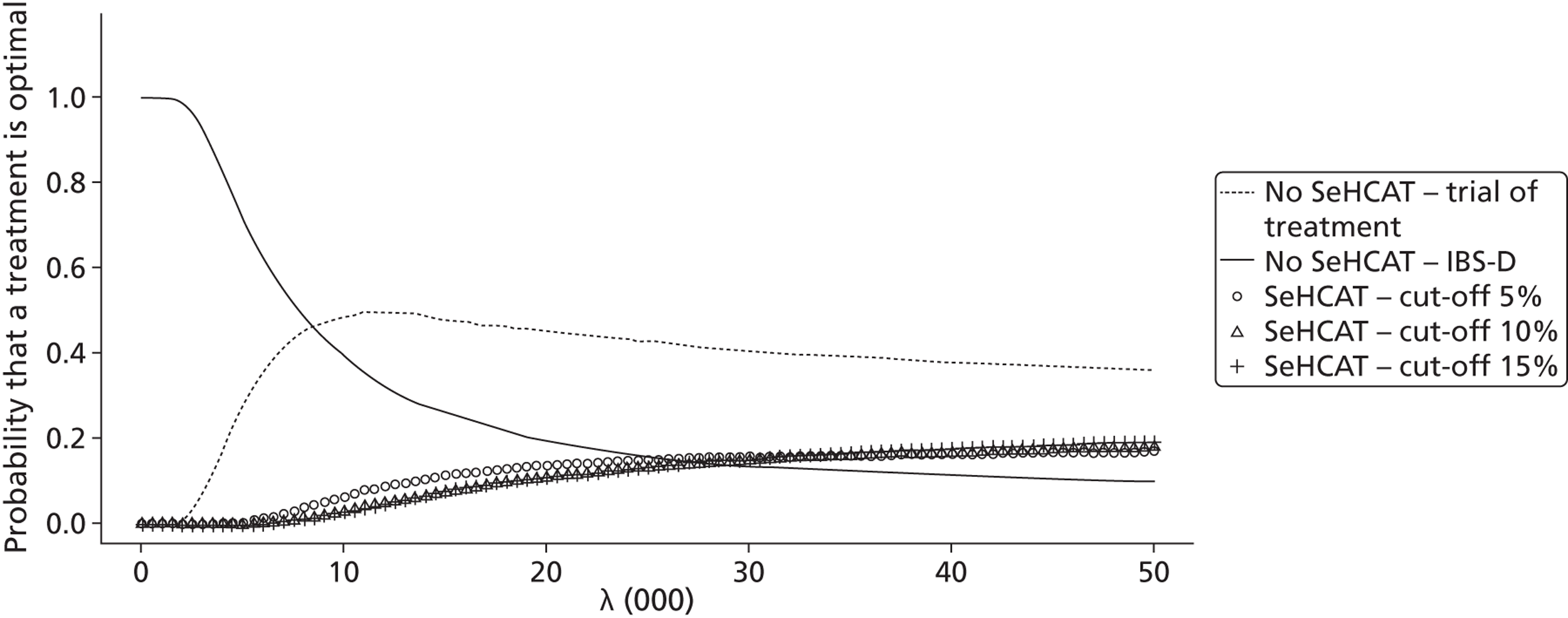
Figure 30 shows the population EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000, the value of perfect information amounts to £15,000M.
FIGURE 30.
Population EVPI for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 8 with trial of treatment.
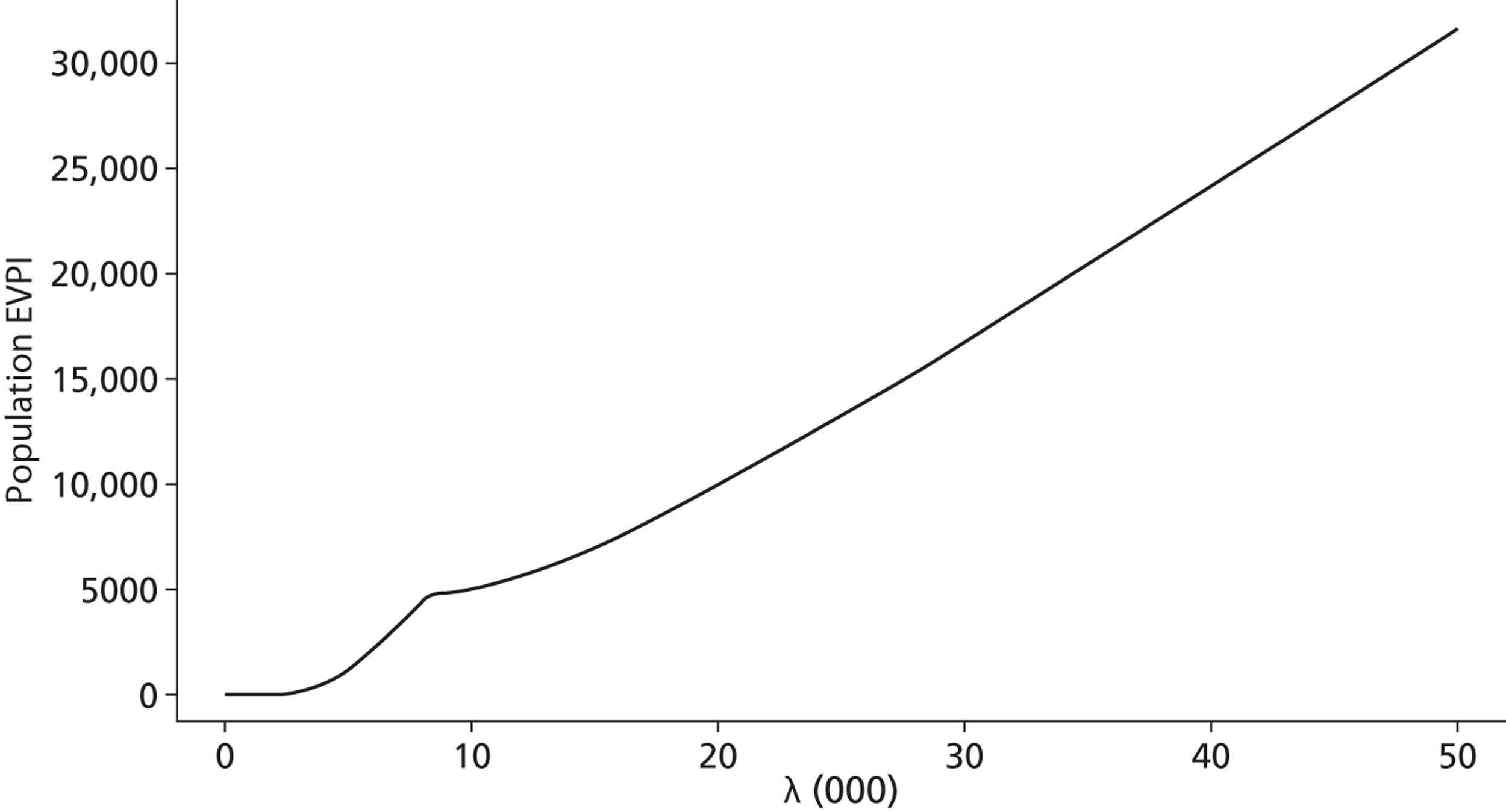
Finally, scenario 12 is the same as scenario 5, but now with utilities for IBS-D and BAM the same. As can be seen in Table 52 , due to the higher utility for BAM responders, now trial of treatment has a favourable ICER compared with no SeHCAT given a threshold of £30,000. The CEAC presented in Figure 31 shows that for lower threshold values no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being optimal while for thresholds above £10,000 trial of treatment has the highest probability of being optimal.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 15.7042 | 1823 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 15.7136 | 1820 | Dominated by no SeHCAT | ||
| No SeHCAT test | 15.7239 | 893 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 5% cut-off | 15.7539 | 1660 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 15.7956 | 1508 | 0.0717 | 615 | 8577 |
FIGURE 31.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime IBS-D population, scenario 12 with trial of treatment.
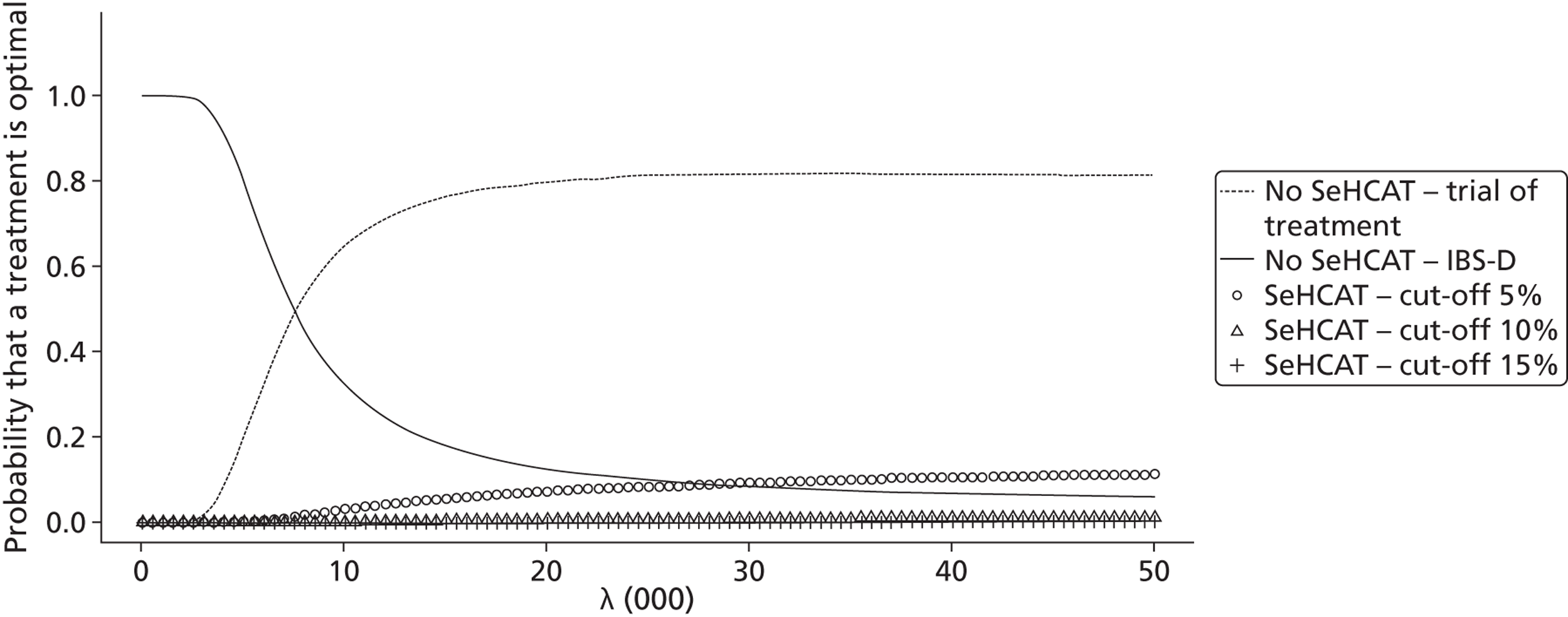
Costs, effects and cost-effectiveness Crohn’s without ileal resection
Short-term results for Crohn’s disease (decision tree)
Table 53 presents the probabilistic outcomes of the decision tree for the Crohn’s disease population. Results are presented in order of increasing number of responders. From this, it becomes clear that testing with SeHCAT leads to more costs and more responders. Note that the ICER is in costs per additional responder and, thus, we cannot compare it with the usual threshold.
| Strategy | Percentageof responders | Expected costs | Incremental responders | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test – treat Crohn’s | 0.6226 | 327 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 0.7296 | 573 | 0.1069 | 245 | 2293 |
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 0.7343 | 592 | 0.0046 | 19 | 4134 |
Figure 32 presents the CEACs. We notice that for smaller thresholds no SeHCAT is the strategy with the highest probability of being cost-effective whereas for larger thresholds, both SeHCAT strategies are equally likely to have the highest probability of being cost-effective.
FIGURE 32.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for short-term (cost per responder) results for Crohn’s population, base case (scenario C1).
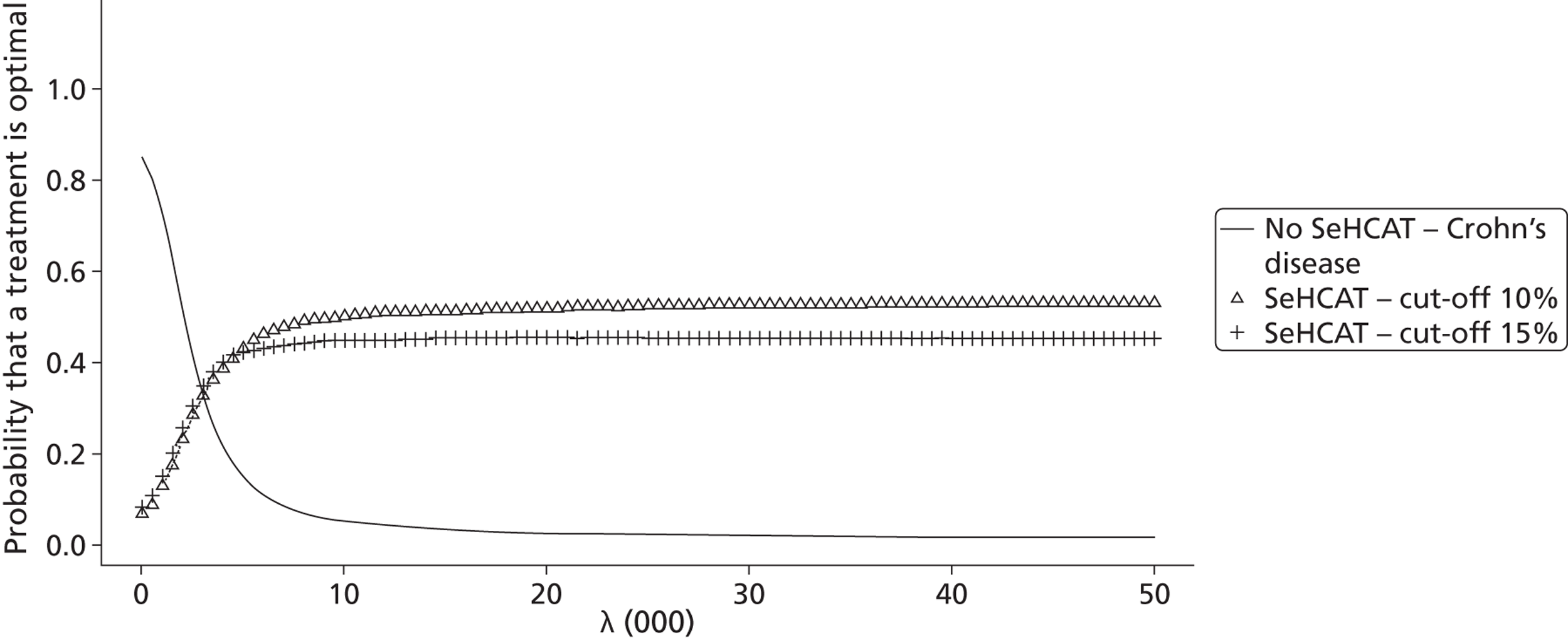
As for the IBS-D population we had to make various assumptions regarding probabilities where neither literature nor expert opinion was available. Additionally, the costs of treating Crohn’s patients with chronic diarrhoea are very uncertain, as the experts had very differing responses and some uncertainty exists about the total costs of SeHCAT.
These assumptions were explored through scenario analysis. The list of scenarios analysed is presented in Table 54 .
| Scenario | SeHCAT service cost | Probability response to Crohn’s treatment in SeHCAT-negative patients | Costs Crohn’s treatment | Cost SeHCAT capsule | Results presented? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0 | 0.72 | 195 | Yes | |
| C2 | 55 | 0.72 | 195 | No | |
| C3 | 105 | 0.72 | 195 | No | |
| C4 | 0 | 0.62 | 195 | No | |
| C5 | 0 | 0.97 | 195 | Yes | |
| C6 | 0 | 0.72 | × 2 | 195 | No |
| C7 | 0 | 0.72 | /2 | 195 | No |
| C8 | 0 | 0.62 | /2 | 195 | No |
| C9 | 0 | 0.72 | 100 | No | |
| C10 | 0 | 0.62 | 100 | No | |
| C11 | 0 | 0.97 | 100 | No |
We found that increasing or decreasing costs related to SeHCAT did not alter the results. For most scenarios, the CEACs were close to the base-case CEAC, except for scenarios C5 and C11. These scenarios have a near-perfect response to Crohn’s treatment in SeHCAT-negative patients. The main difference that is observed in the CEAC for that scenario ( Figure 33 ) is that SeHCAT 15% and SeHCAT 10% are no longer equally likely to be the most cost-effective strategy. This is explained by the fact that in SeHCAT 10% more patients have a negative test result and then receive Crohn’s treatment, with a 97% response rate; thus, this strategy becomes more favourable ( Table 55 ).
| Strategy | Percentage of responders | Expected costs | Incremental responders | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test – treat Crohn’s | 0.6144 | 324 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 0.8108 | 574 | Extendedly dominated by SeHCAT 10% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 0.8366 | 593 | 0.2222 | 268 | 1208 |
FIGURE 33.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for short-term (cost per responder) results for Crohn’s population, response to Crohn’s treatment in SeHCAT-negative patients 97% (scenario C5).
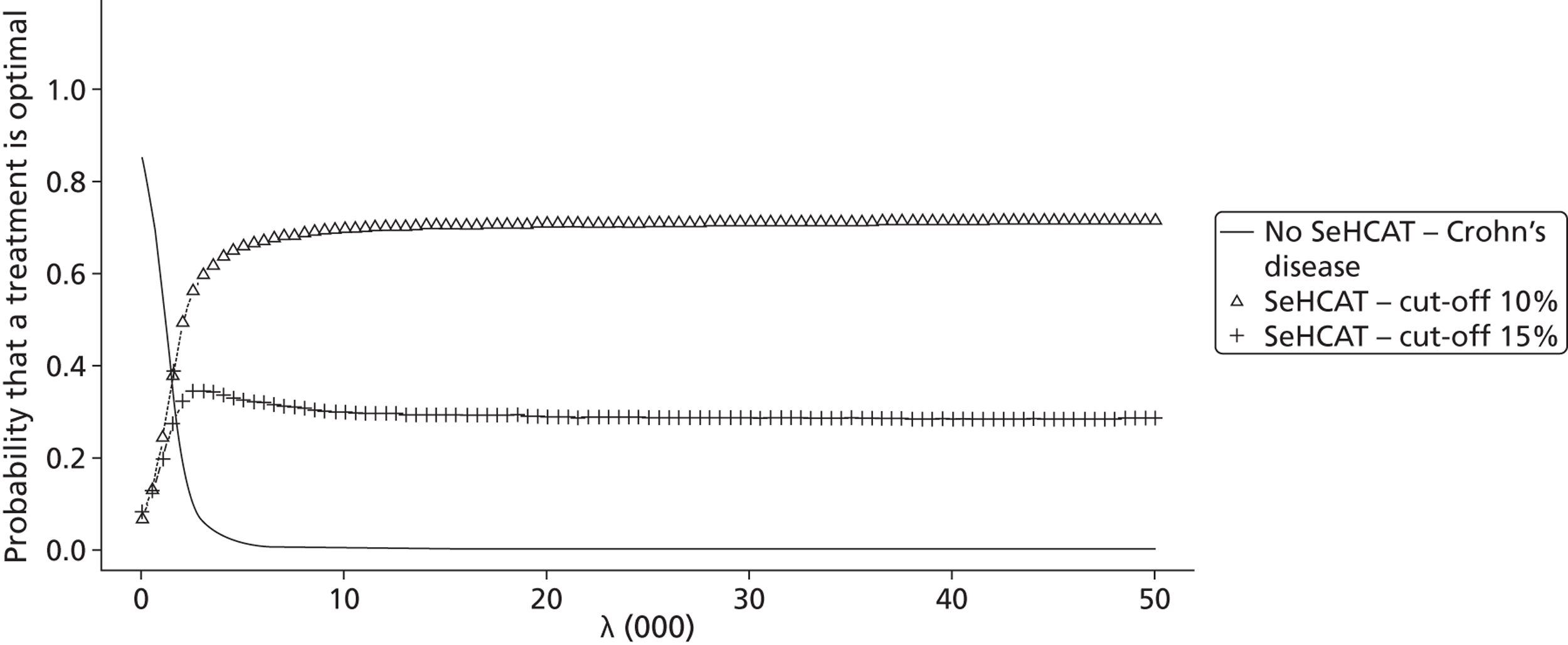
Lifetime results for Crohn’s population
As mentioned in the methods section, no information was available to estimate the transition probabilities in the Markov models other than the all-cause mortality rates. Thus, we formulated various scenarios with different transition probabilities for ND-BAM → D-BAM, D-BAM → ND-BAM, ND-Crohn → D-Crohn, D-Crohn → ND-Crohn. Additionally, we have two scenarios regarding the utility in the no diarrhoea health state; either this is the same for BAS and Crohn’s or utility of BAS responders is lower than for Crohn’s responders. Table 56 presents an overview of all scenarios we explored. As many yielded the same results, we only present a selection of the scenarios, as indicated in the table.
| Scenario | Crohn P(ND → D) | Crohn P(D → ND) | BAM P(ND → D) | BAM P(D → ND) | Utility BAS no diarrhoea | Results presented? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | BAS < Crohn | Yes |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | Yes |
| 3 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | No, same as 2 |
| 4 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | Yes |
| 5 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | No, same as 1 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | No, same as 1 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | BAS < Crohn | No, same as 4 |
| 8 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | BAS = Crohn | Yes |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 8 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 8 |
| 11 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 4 |
| 12 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | Yes |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 6 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 4 |
Below are the results for scenario 1. Scenario 1 assumes that all four transition probabilities are 5% per cycle. We observe that no SeHCAT is the most favourable strategy, with not only the highest costs but also the highest effect ( Table 57 ). When we look at the CEACs ( Figure 34 ), we notice that no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being cost-effective for thresholds above £5000.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.0847 | 2710 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.0994 | 2828 | Extendedly dominated by no SeHCAT test | ||
| No SeHCAT test | 14.1571 | 3023 | 0.0724 | 313 | 4323 |
FIGURE 34.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 1.
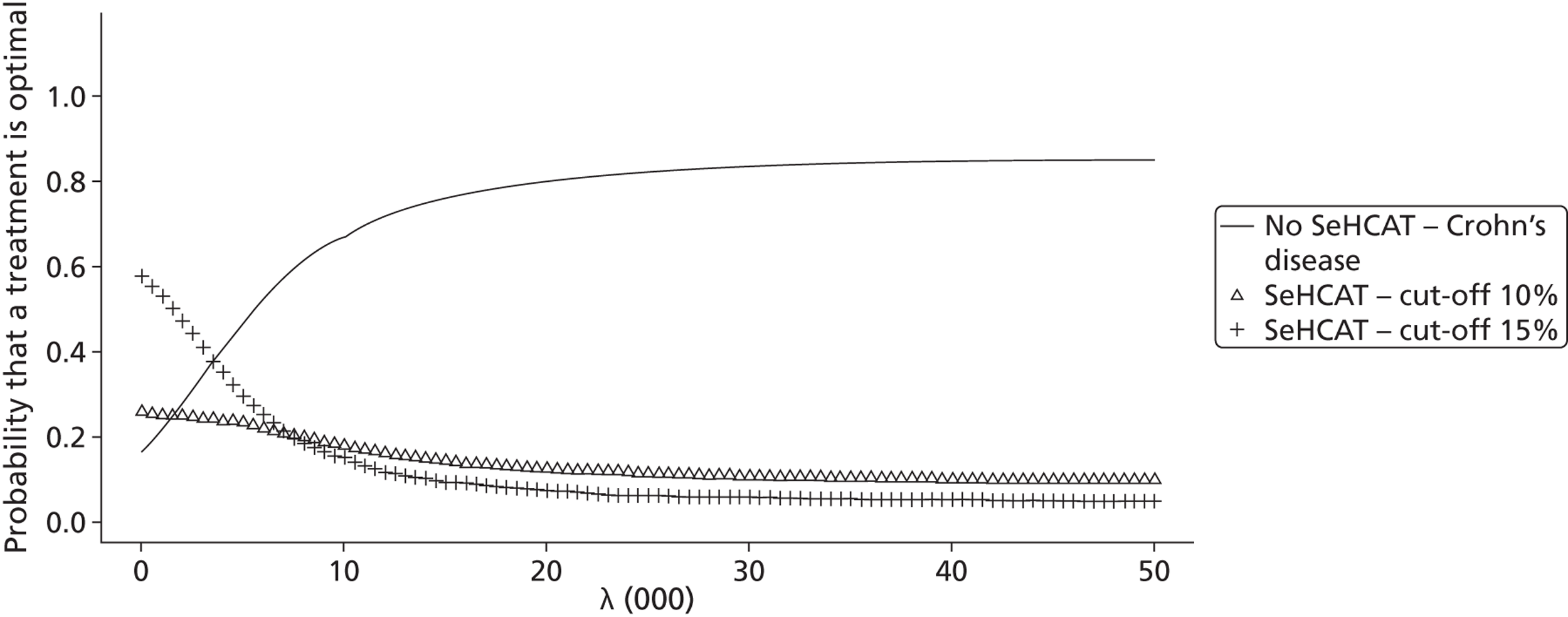
Figure 35 shows the patient EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000, the value of perfect information amounts to £100.
FIGURE 35.
Patient EVPI for Crohn’s population, scenario 1.
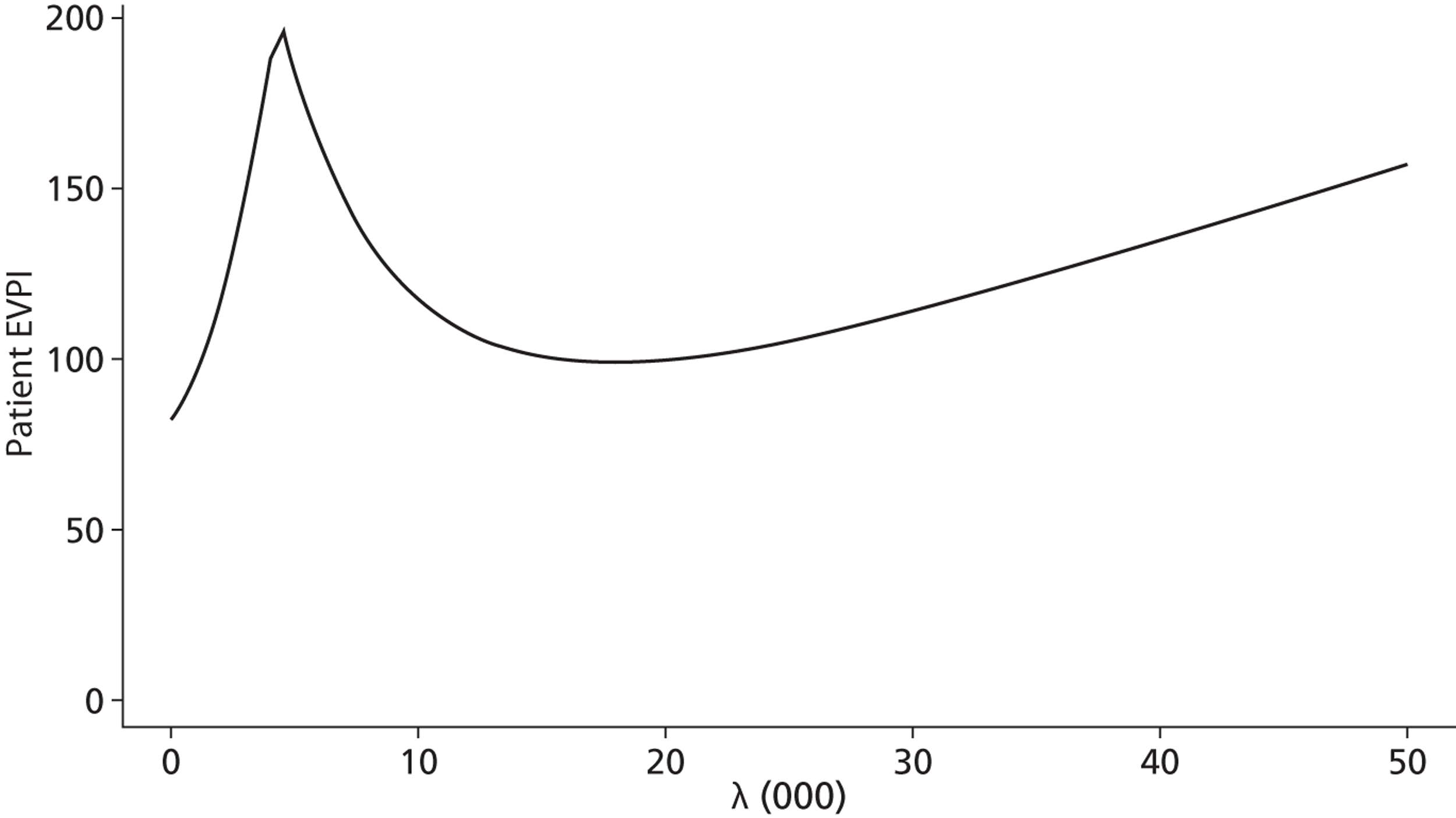
Scenario 2 assumes that all four transition probabilities are 0% per cycle. We now observe ( Table 58 ) that the ICER of SeHCAT 10% compared with SeHCAT 15% falls well below the commonly used £30,000 threshold and that SeHCAT 10% dominates no SeHCAT. When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 36 ), we notice that for small thresholds SeHCAT 15% has the highest probability of being cost-effective while for larger thresholds (above £8000) SeHCAT 10% has the highest probability of being cost-effective. However, for no SeHCAT this probability is almost the same as for SeHCAT 10%.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.2517 | 3196 | |||
| No SeHCAT test | 14.2635 | 3400 | Dominated by SeHCAT 10% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.2712 | 3336 | 0.0195 | 140 | 7179 |
FIGURE 36.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 2.
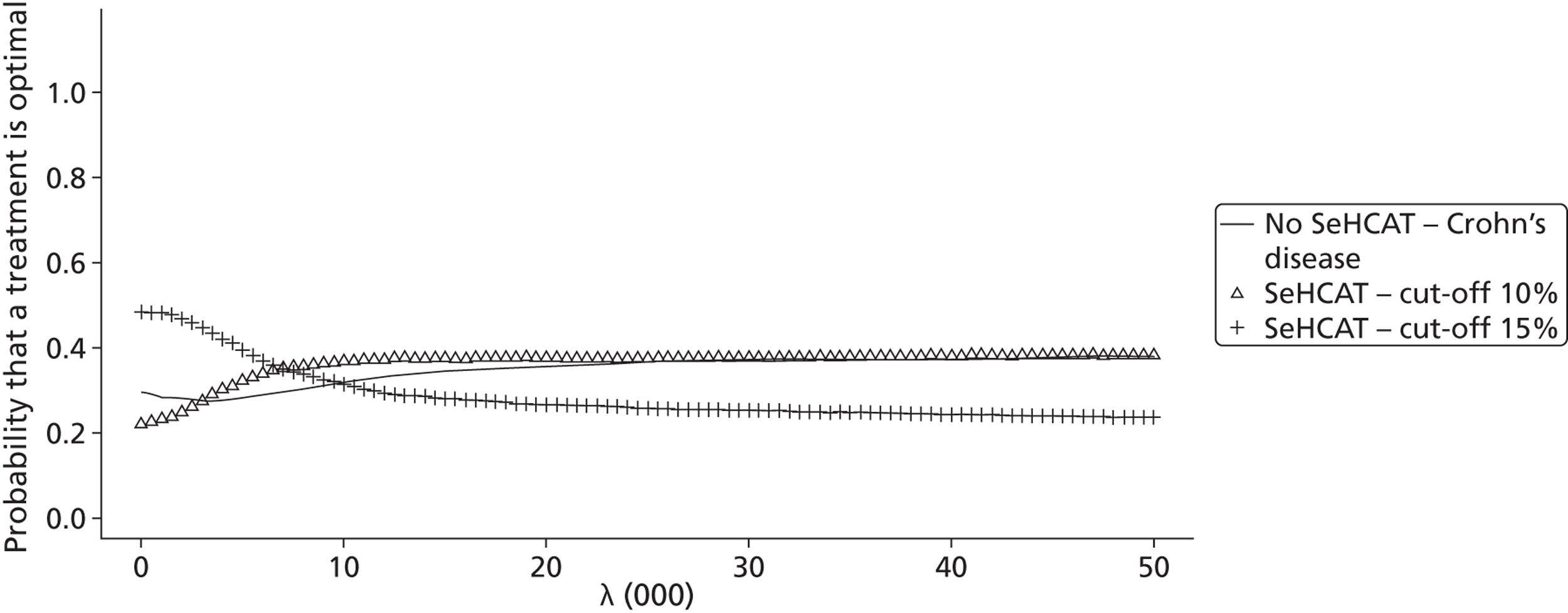
Scenario 4 assumes that the transition probability from ND to D in the Crohn’s model is 5% per cycle while all others are 0. We observe that SeHCAT 15% compared with no SeHCAT yields an ICER well below the common threshold of £30,000, while SeHCAT 10% is dominated by SeHCAT 15% ( Table 59 ). When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 37 ), we observe that for small thresholds no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being cost-effective while for larger thresholds (around £5000) SeHCAT 15% has the highest probability of being cost-effective.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 13.8169 | 1972 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.042 | 2596 | Dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.0657 | 2595 | 0.2488 | 623 | 2504 |
FIGURE 37.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 4.
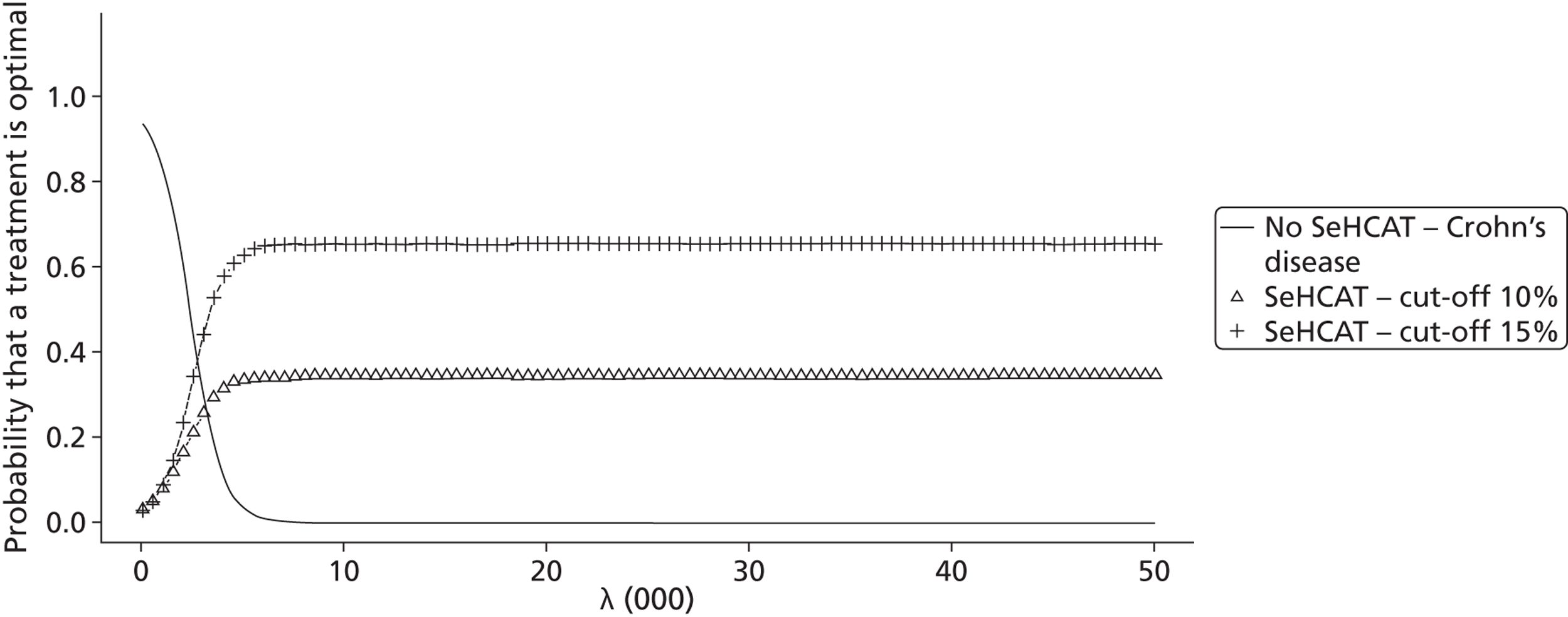
Scenario 8 is the same as scenario 1, but now with utilities for Crohn’s and BAM the same. As can be seen in Table 60 , SeHCAT 15% dominates no SeHCAT, and the ICER of SeHCAT 10% versus SeHCAT 15% would be considered too high given a threshold of £30,000. The CEAC presented in Figure 38 shows that SeHCAT 15% has the highest probability of being optimal over the whole range of thresholds. However, the curves of SeHCAT 15% and SeHCAT 10% are quite close, thus leading to more decision uncertainty. This is reflected in the EVPI ( Figure 39 ), which at a threshold of £30,000 amounts to £400 per patient.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 14.1592 | 3031 | Dominated by SeHCAT 15% | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.1865 | 2708 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.1876 | 2828 | 0.0011 | 119 | 108,412 |
FIGURE 38.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 8.
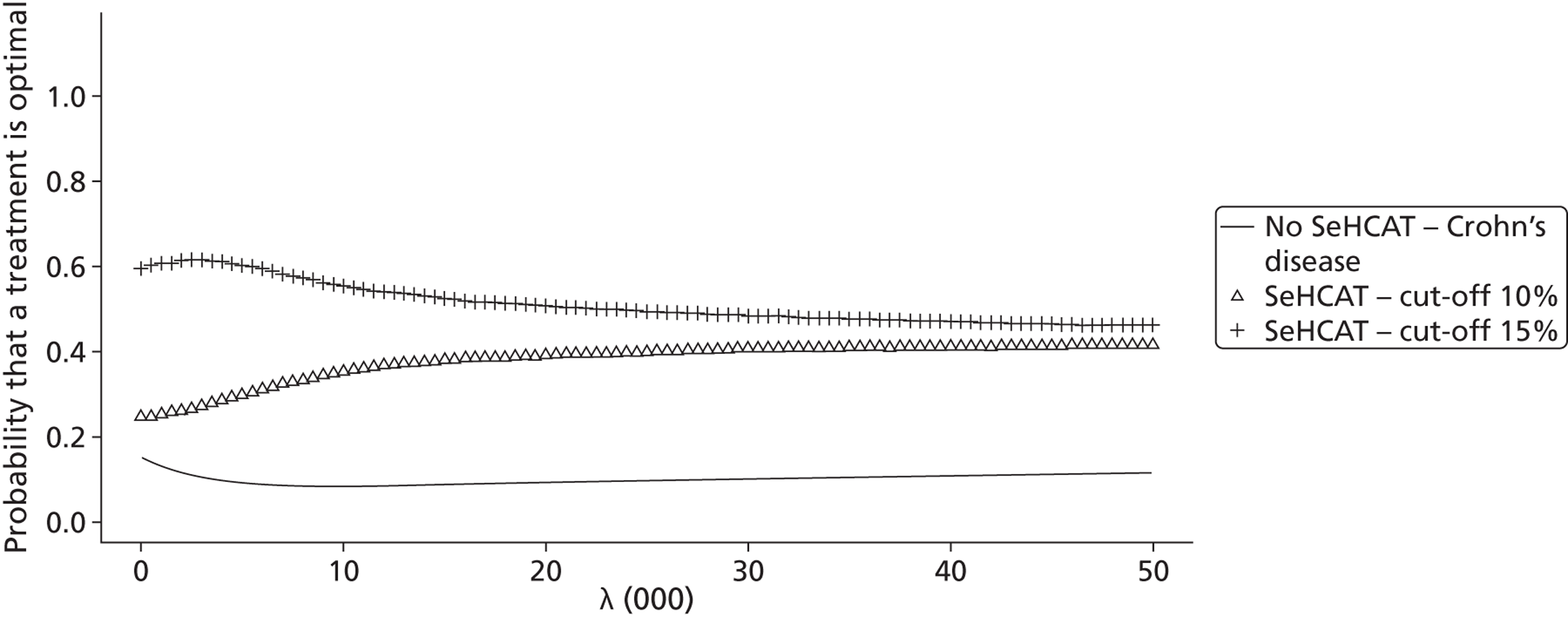
FIGURE 39.
Patient EVPI for Crohn’s population, scenario 8.
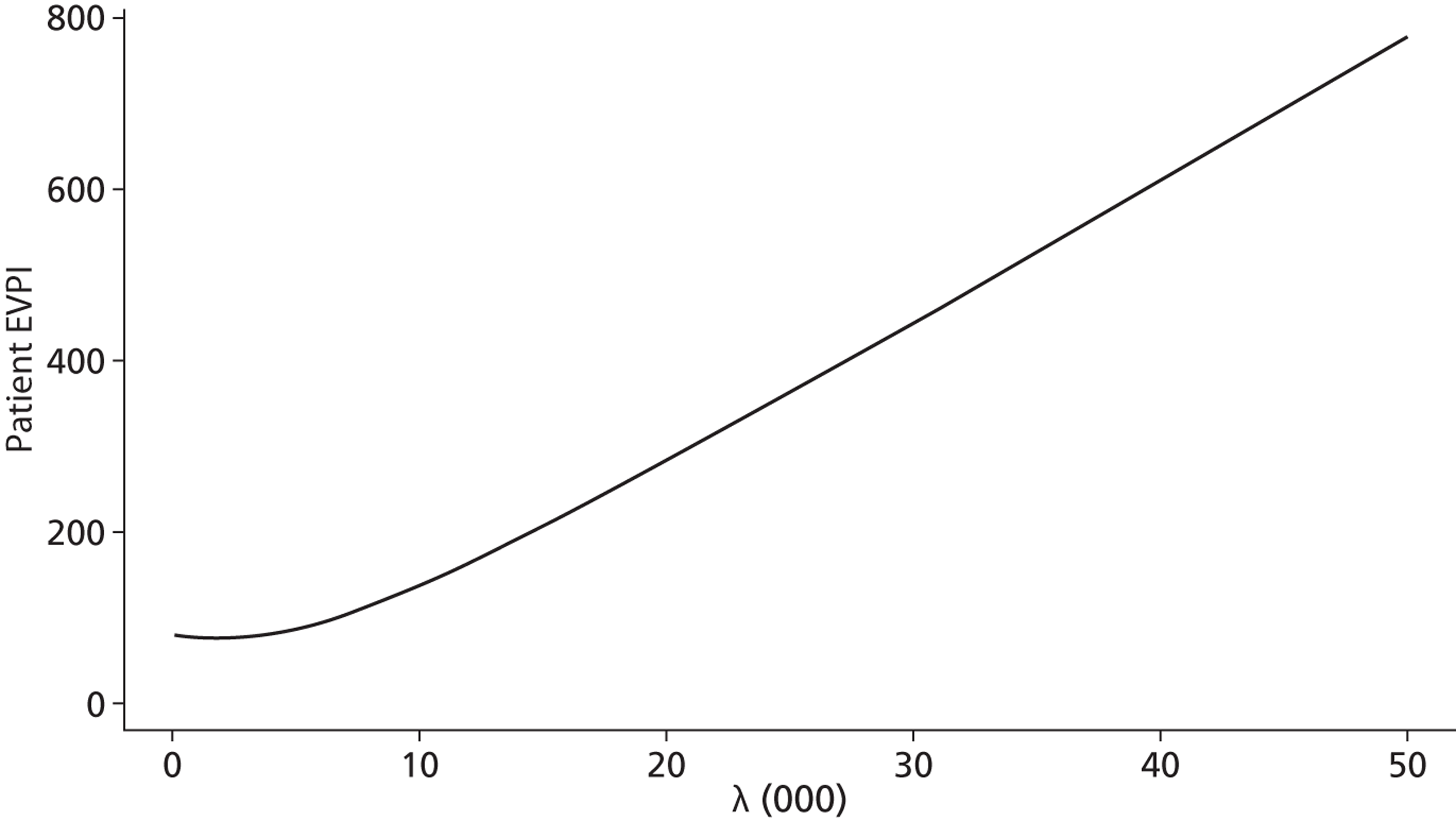
Finally, scenario 12 assumes that the transition probability from D to ND in the Crohn’s model is 5% per cycle while all others are 0 and that the utilities for IBS-D and BAM are the same. As can be seen in Table 61 , here no SeHCAT can be considered the most favourable strategy given a threshold of £30,000. The CEAC presented in Figure 40 shows that for lower threshold values (below £7000) SeHCAT 15% has the highest probability of being optimal, for thresholds between £7000 and £14,000 SeHCAT 10% has the highest probability while for thresholds above £14,000 no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being optimal.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.4624 | 3426 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.4917 | 3639 | 0.0293 | 213 | 7282 |
| No SeHCAT test | 14.5362 | 4246 | 0.0445 | 606 | 13,621 |
FIGURE 40.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 12.
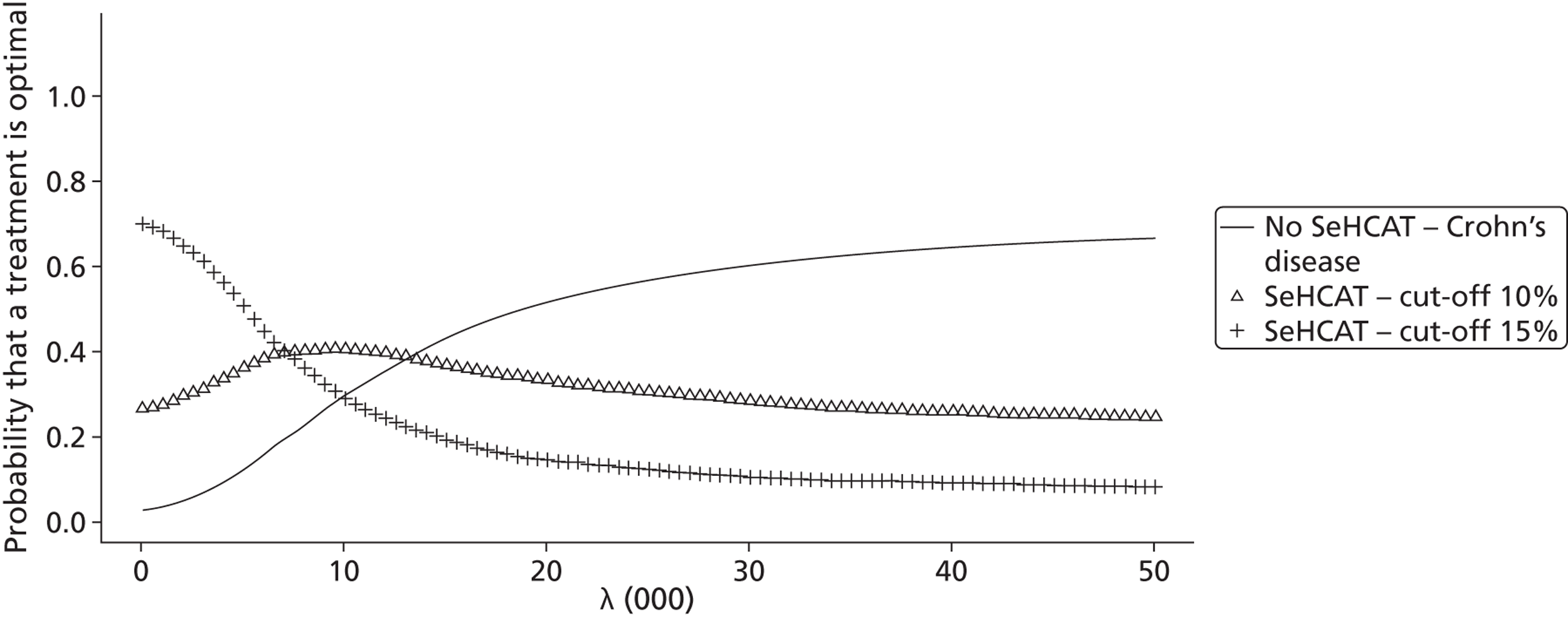
Figure 41 shows the patient EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000, the value of perfect information amounts to £400.
FIGURE 41.
Patient EVPI for Crohn’s population, scenario 12.
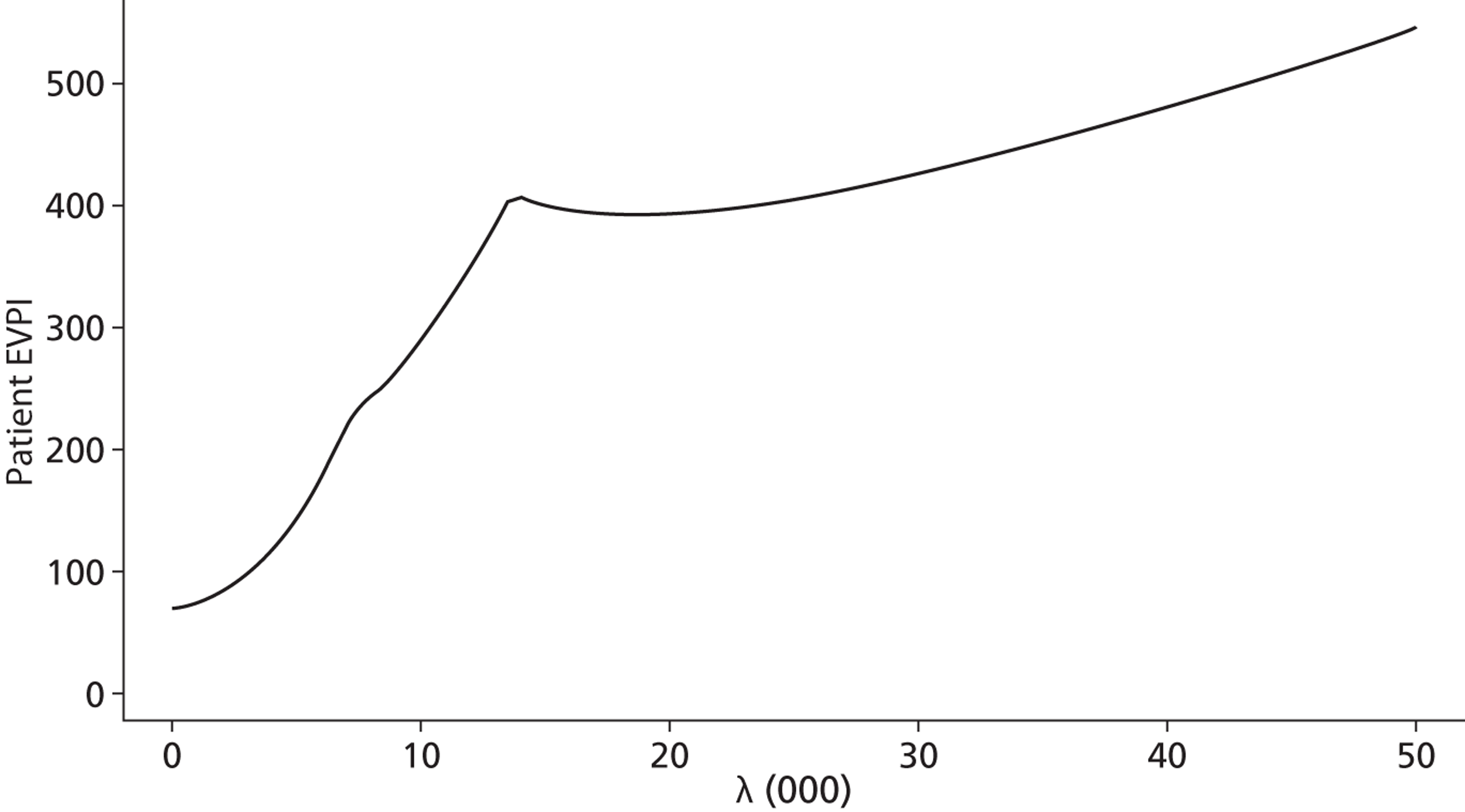
Costs, effects and cost-effectiveness for Crohn’s disease without ileal resection with trial of treatment included
Short-term results for Crohn’s disease (decision tree) with trial of treatment
Table 62 presents the probabilistic outcomes of the base-case decision tree for the Crohn’s population when trial of treatment is also considered as comparator. Results are presented in order of increasing number of responders. From this, it becomes clear that the trial of treatment strategy dominates all other strategies: it leads to the highest number of responders for the lowest costs. Thus, no ICERs should be calculated.
| Strategy | Percentage of responders | Expected costs | Incremental responders | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test – treat Crohn’s | 0.6226 | 327 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 0.7296 | 573 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 0.7343 | 592 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 0.8232 | 171 | |||
To investigate what the impact is of the various (statistical) uncertainties in the model, we also present the CEAC ( Figure 42 ). We notice that the trial of treatment strategy has the highest probability of being considered cost-effective over the whole range of possible threshold ICERs.
FIGURE 42.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for short-term (cost per responder) results for Crohn’s population, base case with trial of treatment (scenario D1).
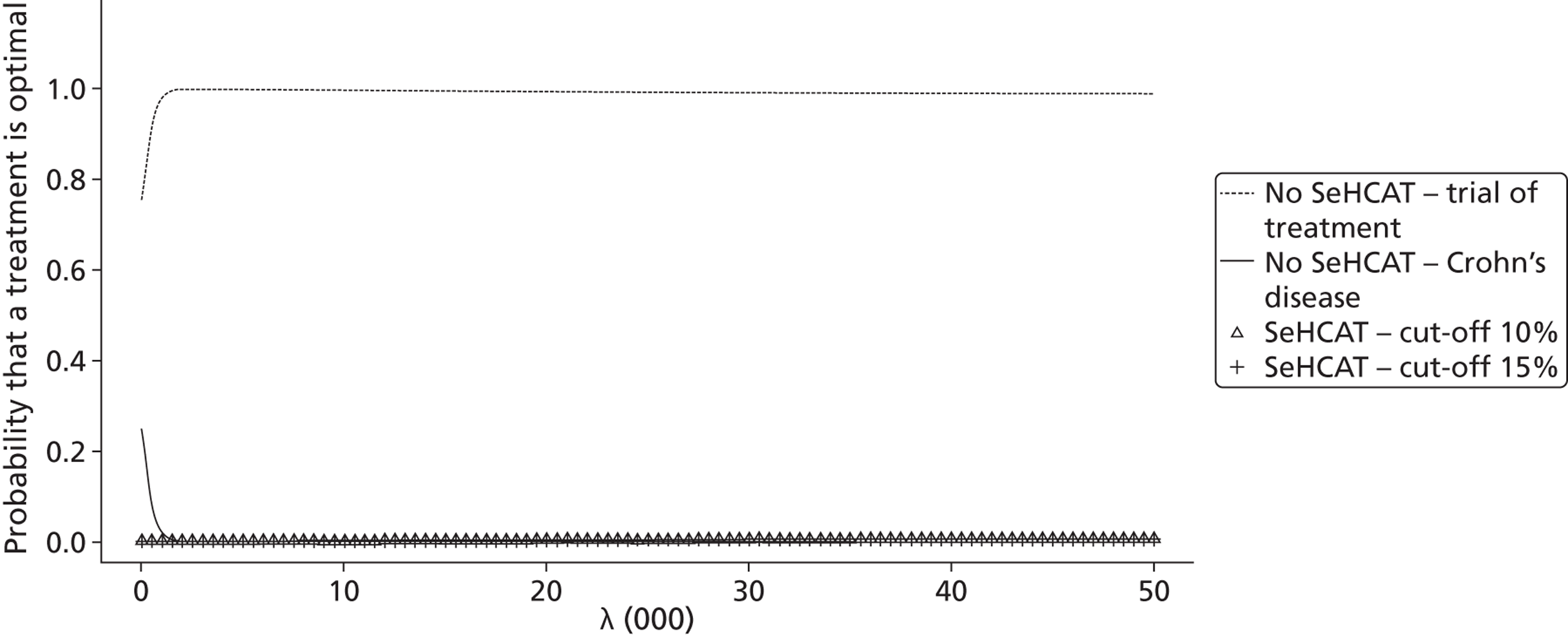
As for the IBS-D population, we formulated several scenarios to explore the sensitivity of the model for various major assumptions we made. The scenarios are listed in Table 63 . None of these scenarios led to any result other than the base case; in all cases trial of treatment was the dominant strategy.
| Strategy | SeHCAT service cost | Probability response to BAS with trial of treatment | Probability response to Crohn’s treatment in SeHCAT-negative patients | Costs Crohn’s treatment | Cost SeHCAT capsule | Results presented? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.72 | 195 | Yes | |
| D2 | 55 | 0.46 | 0.72 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| D3 | 105 | 0.46 | 0.72 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| D4 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.62 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| D5 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.87 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| D6 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.72 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| D7 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| D8 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 195 | No, same as 1 | |
| D9 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.72 | × 2 | 195 | No, same as 1 |
| D10 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.72 | /2 | 195 | No, same as 1 |
| D11 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.62 | /2 | 195 | No, same as 1 |
| D12 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.62 | /2 | 195 | No, same as 1 |
| D13 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.72 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| D14 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.62 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| D15 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.87 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| D16 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.72 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| D17 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 100 | No, same as 1 | |
| D18 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 100 | No, same as 1 |
Lifetime results for Crohn’s with trial of treatment
As above (see Lifetime results for Crohn’s), we have again explored a list of 14 scenarios regarding transition probabilities of the Markov models and the utility of the no diarrhoea health state. Again, we present only a limited number of these scenarios ( Table 64 ).
| Scenario | Crohn P(ND→D) | Crohn P(D→ND) | BAM P(ND→D) | BAM P(D→ND) | Utility BAS no diarrhoea | Results presented? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | BAS < Crohn | Yes |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | Yes |
| 3 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | No, same as 2 |
| 4 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | No, same as 2 |
| 5 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | Yes |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS < Crohn | No, same as 5 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | BAS < Crohn | No, same as 3 |
| 8 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 2 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 2 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 3 |
| 11 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 4 |
| 12 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 2 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | BAS = Crohn | No, same as 6 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | BAS = Crohn | Yes |
Below are the results for scenario 1. Scenario 1 assumes that all four transition probabilities are 5% per cycle. We observe that both SeHCAT strategies are dominated by trial of treatment, while no SeHCAT can be considered cost-effective compared with trial of treatment for thresholds above £14,000 ( Table 65 ). The CEAC confirms this assessment ( Figure 43 ).
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.0847 | 2710 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.0994 | 2828 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 14.1227 | 2545 | |||
| No SeHCAT test | 14.1571 | 3023 | 0.0343 | 477 | 13,889 |
FIGURE 43.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 1 with trial of treatment.
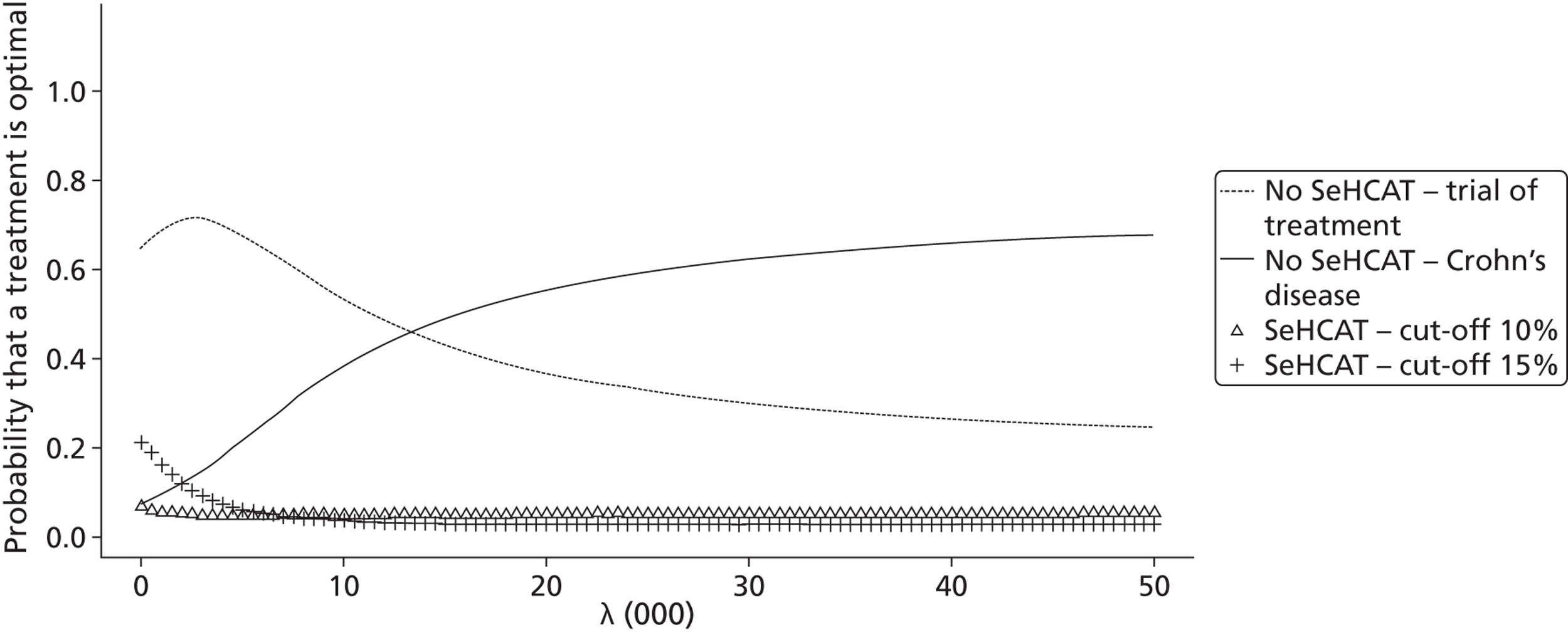
Figure 44 shows the patient EVPI; from this we see that at a threshold of £30,000, the value of perfect information amounts to £300.
FIGURE 44.
Patient EVPI for Crohn’s population, scenario 1 with trial of treatment.
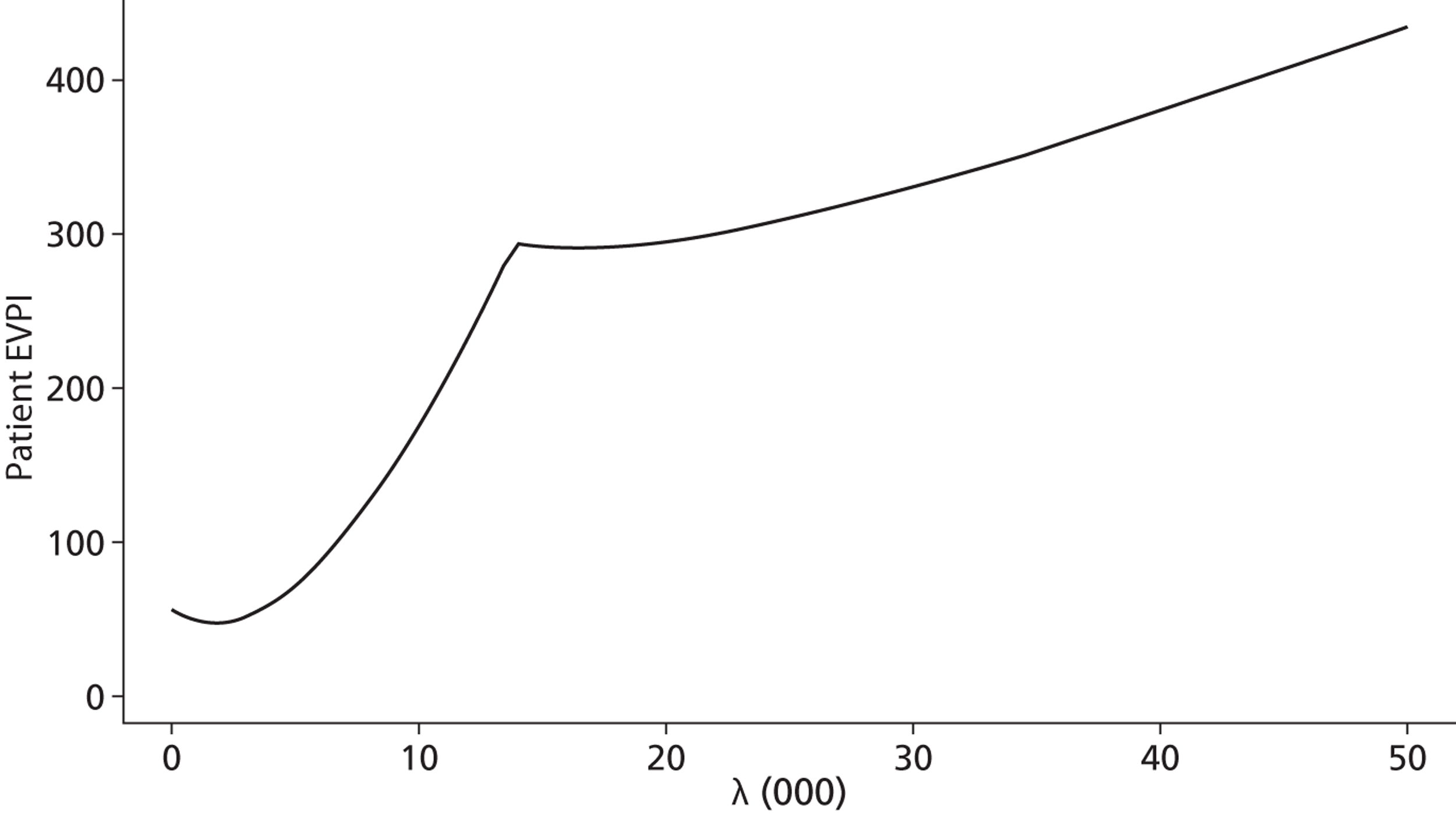
Scenario 2 assumes that all four transition probabilities are 0% per cycle. We now observe ( Table 66 ) that no SeHCAT and SeHCAT 10% are dominated by trial of treatment and the ICER of trial of treatment compared with SeHCAT 15% falls well below the commonly used £30,000 threshold. When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 45 ), we notice that for almost the whole range of thresholds trial of treatment has the highest probability of being cost-effective, up to even 90% for thresholds above £10,000.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.2517 | 3196 | |||
| No SeHCAT test | 14.2635 | 3400 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.2712 | 3336 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 14.3572 | 3213 | 0.1055 | 17 | 161 |
FIGURE 45.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 2 with trial of treatment.
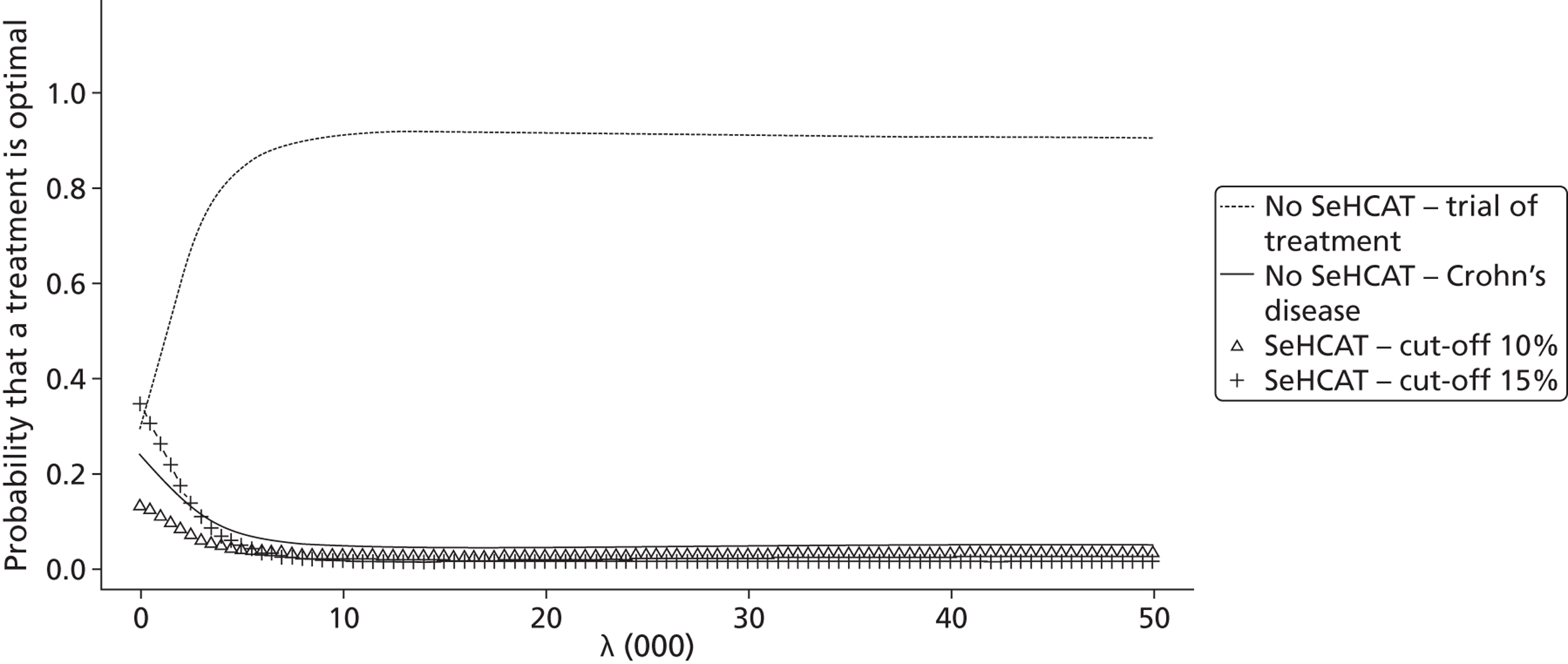
Scenario 5 assumes that the transition probability from D to ND in the Crohn’s model is 5% per cycle while all others are 0. We observe that SeHCAT 15% compared with no SeHCAT yields an ICER well below the common threshold of £30,000, while SeHCAT 10% is dominated by SeHCAT 15% ( Table 67 ). When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 46 ), we observe that for lower threshold values (below approximately £1000) SeHCAT 15% has the highest probability of being optimal, for thresholds between £1000 and £13,000 trial of treatment has the highest probability while for thresholds above £13,000 no SeHCAT has the highest probability of being optimal.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.326 | 3434 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.3689 | 3646 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 14.4834 | 3612 | 0.1574 | 178 | 1131 |
| No SeHCAT test | 14.5341 | 4250 | 0.0506 | 637 | 12,581 |
FIGURE 46.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 5 with trial of treatment.
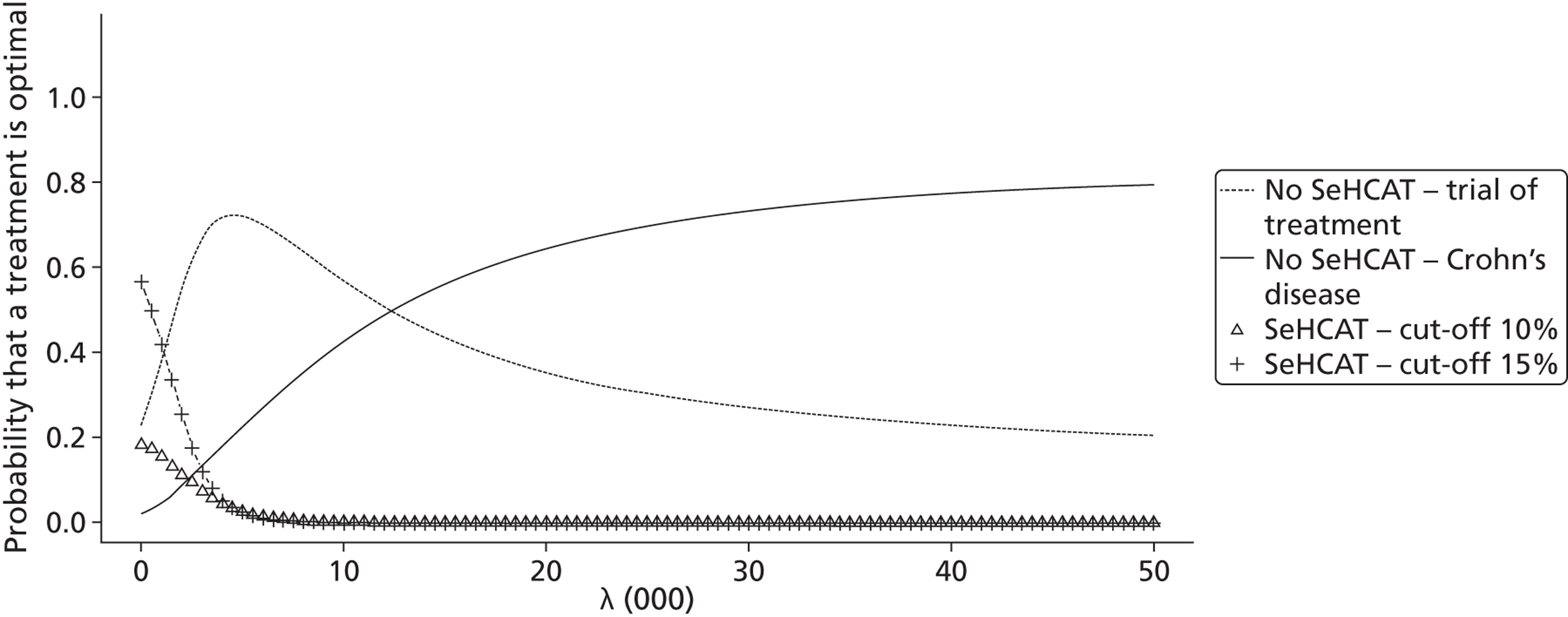
Scenario 14 assumes that the transition probability from D to ND in the BAM model is 5% per cycle while all others are 0 and that utilities per health state are the same in the Crohn’s model and the BAM model. In this scenario we observe ( Table 68 ) that no SeHCAT and SeHCAT 10% are dominated by trial of treatment and the ICER of SeHCAT 15% compared with trial of treatment falls well below the commonly used £30,000 threshold. When we look at the CEAC ( Figure 47 ), we notice that for thresholds up to £10,000 trial of treatment has the highest probability of being cost-effective, whereas for higher thresholds SeHCAT 15% has the highest probability of being cost-effective, up to 50% for thresholds above £20,000.
| Strategy | Expected QALYs | Expected costs | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No SeHCAT test | 14.2627 | 3379 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| SeHCAT test – 10% cut-off | 14.4892 | 3490 | Dominated by trial of treatment | ||
| No SeHCAT test – trial of treatment | 14.4943 | 3197 | |||
| SeHCAT test – 15% cut-off | 14.5145 | 3399 | 0.0201 | 202 | 10,020 |
FIGURE 47.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for lifetime Crohn’s population, scenario 14 with trial of treatment.
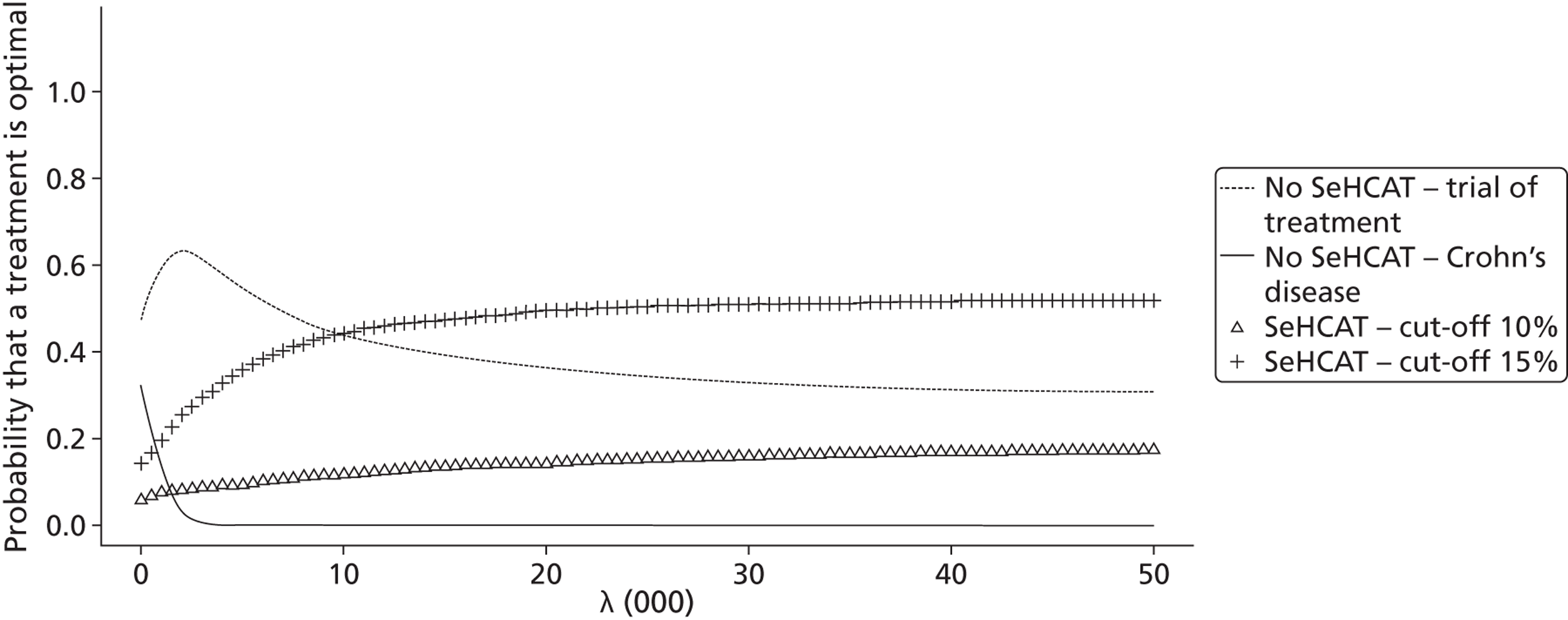
Summary
In this chapter we assessed the cost-effectiveness of SeHCAT in two different populations. The first is the population of patients with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of IBS-D and the second population concerns patients with Crohn’s disease without ileal resection with chronic diarrhoea.
For both populations the cost-effectiveness of SeHCAT compared with no SeHCAT was assessed. For the SeHCAT option we defined various strategies based on the test cut-off points used to classify patients. For the IBS-D patient population data were available to be able to distinguish between cut-off points of 5%, 10% and 15%. For the Crohn’s patient population, only data on a 10% and 15% SeHCAT test cut-off were available. For the no SeHCAT strategy all patients received regular treatment for either IBS-D or chronic diarrhoea in Crohn’s. Additionally, in the scoping document, trial of treatment with BAS was mentioned as another possible strategy without specifically including it as a comparator. According to the clinical experts at the scoping meeting, trial of treatment is rarely used as a treatment strategy and was thus not considered relevant. However, trial of treatment could also not be completely excluded as an option. Thus, in this report, for both populations we have presented two sets of results: one where trial of treatment is not considered as a comparator and one where it is. In the trial of treatment strategy, patients first receive a BAS and when patients do not respond they receive regular treatment for either IBS-D or chronic diarrhoea in Crohn’s.
For each population, three models were combined
-
a short-term decision tree that models the diagnostic pathway and initial response to treatment (first 6 months)
-
a long-term Markov model that estimates the lifetime costs and effects for patients initially receiving BAS
-
a long-term Markov model that estimates the lifetime costs and effects for patients initially receiving regular treatment (IBS-D treatment in the first population and Crohn’s treatment in the second population).
In the decision tree the 6-month number of responders and the expected costs were calculated for each comparator while for the Markov models lifetime expected QALYs and expected costs per patient were calculated for each comparator.
Where possible, input for the model was based on our SeHCAT systematic review, other published literature and UK databases. When such evidence was not available, expert opinion was used. The impact of uncertainty about the various input parameters on the outcomes was explored through probabilistic sensitivity analyses and scenario analyses.
ICERs were estimated as additional cost per additional responder in the short term (first 6 months) and per additional QALY in the long term (lifetime).
When trial of treatment is not considered as a comparator, the evaluation for the IBS-D population showed for the short term that the optimal choice depends on the willingness to pay for an additional responder. For lower values (base case £2400, scenarios between £1800 and £4600) the choice will be no SeHCAT in all scenarios; for higher values either SeHCAT 10% or SeHCAT 15% becomes cost-effective.
For the lifetime perspective, we did not define a base case, as we had no information of any kind to inform the transition probabilities between the health states diarrhoea and no diarrhoea and vice versa. Thus, only scenario analysis was performed. The various scenarios showed widely differing results. Depending on the scenario, in the threshold range of £20,000–30,000 per QALY gained, we found as optimal choice either no SeHCAT, SeHCAT 5% or SeHCAT 15%; only SeHCAT 10% never had the highest probability of being cost-effective.
When trial of treatment is considered a comparator, the analysis showed for the IBS-D population that for the short term, trial of treatment is the optimal choice across a range of scenarios. In the base-case scenario, trial of treatment dominated all other strategies and had a 95% probability of being the most cost-effective option. In the various scenarios, trial of treatment was dominant compared with all strategies. For all scenarios trial of treatment had the highest probability of being cost-effective; this probability was for most scenarios around 90%, decreasing for some scenarios to 50%.
For the lifetime perspective, for all but two scenarios, trial of treatment was the strategy with the highest probability of being cost-effective for thresholds above £5000 to £15,000, with no SeHCAT the most favourable strategy for lower threshold ICERs. In the two scenarios where the transition probability from diarrhoea to no diarrhoea in the BAM model was 5% per cycle while all others were 0, we observed that for thresholds higher than £15,000 SeHCAT 15% had the highest probability of being cost-effective.
For the Crohn’s population, the short-term evaluation without trial of treatment as comparator showed for the short term that the optimal choice depends on the willingness to pay for an additional responder. For lower values (base case £2300, scenarios between £1500 and £4000) the choice will be no SeHCAT in all scenarios; for higher values SeHCAT 10% becomes cost-effective.
For the long term, the various scenarios show widely differing results. Depending on the scenario, in the threshold range of £20,000–30,000 per QALY gained, we found as optimal choice either no SeHCAT or SeHCAT 15% while some scenarios found that all three strategies had the same probability of being cost-effective.
When trial of treatment is considered a comparator, the analysis showed for the Crohn’s population that for the short term, trial of treatment dominated all other strategies (in terms of number of responders) and had an almost 100% probability of being the most cost-effective option. In the various scenarios, trial of treatment was dominant compared with all strategies. For all scenarios trial of treatment had the highest probability of being cost-effective; for most scenarios this probability was around 90%.
For the lifetime perspective in Crohn’s with trial of treatment, again the various scenarios show widely differing results. Depending on the scenario, in the threshold range of £20,000–30,000 per QALY gained, we found as optimal choice either trial of treatment, no SeHCAT or SeHCAT 15%.
In conclusion, the various analyses have shown that, for both populations, considerable decision uncertainty exists, and that no firm conclusions can be formulated as to which strategy is optimal.
Chapter 5 Discussion
Statement of principal findings
Clinical effectiveness
Three studies were reasonably reliable in assessing the relationship between the SeHCAT test and treatment with cholestyramine. 39,42,43 However, the studies had small numbers of patients with unknown cause chronic diarrhoea, they used different cut-offs for the assessment of BAM and between-study heterogeneity was considerable.
Sensitivity ranged from 0.67 (at a cut-off of 8%) to 1.00 (at a cut-off of 15%) and specificity ranged from 0.91 (at a cut-off of 15%) to 1.00 (at a cut-off of 5%) ( Table 69 ).
| Study | Cut-off | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Merrick 198539 (n = 40) | 8% | 0.667 (0.223 to 0.957) | 0.971 (0.847 to 0.999) |
| 15% | 1.000 (0.541 to 1.000) | 0.912 (0.763 to 0.981) | |
| Sciaretta 198642 (n = 13) | 5% | 0.857 (0.421 to 0.996) | 1.000 (0.541 to 1.000) |
| Sciaretta 198743 (n = 46a) | 8% | 0.950 (0.751 to 0.999) | 0.962 (0.804 to 0.999) |
None of the studies looking specifically at people with Crohn’s disease presented reliable data for the prediction of response to treatment with BAS because no data were presented for people with a negative SeHCAT test in the two studies.
One RCT in patients with IBS-D which compared treatment with BAS (colesevelam) with placebo showed no significant differences in terms of colonic transit [e.g. geometric centre at 48 hours: MD = 0.18 (95% CI –0.29 to 0.65)] bowel function [e.g. stool frequency per day: MD = –0.11 (95% CI –1.01 to 0.79)] or adverse events [e.g. uterine cramps: OR = 0.45 (95% CI 0.04 to 5.81)]. However, randomisation (sequence generation and allocation concealment) was not adequately reported and groups were small (n = 12 in both arms).
For people with chronic diarrhoea, 19 studies provide data on the clinical effectiveness of BAS given a positive SeHCAT test; three studies also provide data on the effectiveness of BAS given a negative SeHCAT test. For those with a positive SeHCAT test response rates were on average 85%, 73% and 72% for cut-offs at 5%, 10% and 15%, respectively. For those with a negative SeHCAT test the response rate was 14% at a cut-off of 5% and 0% at a cut-off of 15%. For people with Crohn’s disease and a positive SeHCAT test the response rate was 95% at a cut-off of 5% and 86% or 89% at a cut-off of 15%.
Several studies reported data on the accuracy of SeHCAT for the detection of BAM in people with chronic diarrhoea ( Table 70 ). However, all of these studies are flawed because they either do not use an acceptable reference standard or include a population not in line with the scope (healthy volunteers or people with ileal resection). Therefore, these data are not used in this review.
| Study | Sensitivity | Specificity | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Balzer 199381 | 80% | 98% | Study itself |
| Balzer 199582 | 60–85% | 84–100% | Kruis 1987,28 Balzer 1988,83 Singe 1987,27 Merrick 198539 |
| Brydon 199684 | 100% | 96% | Study itself |
| Ferraris 199285 | 72% | 96% | Study itself |
| Johnston 201152 | 100% | 94% | Sciaretta 198642 |
| Kurien 201186 | 80–90% | ∼100% | Merrick 1985,39 Sciaretta 198642 |
| Merrick 198539 | 97% | 80–99% | Study itself |
| Pattni 200913 | 80–90% | 70–100% | Not reported |
| Sciaretta 198642 | 100% | 94% | Study itself |
| Wedlake 20096 | 89% | 100% | Sciaretta 198642 |
Cost-effectiveness
In Chapter 4 we assessed the cost-effectiveness of SeHCAT in two different populations. The first is the population of patients with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of IBS-D and the second population concerns patients with Crohn’s disease without ileal resection with chronic diarrhoea.
For both populations the cost-effectiveness of SeHCAT compared with no SeHCAT was assessed. For the SeHCAT option we defined various strategies based on the test cut-off points used to classify patients. For the IBS-D patient population data were available to be able to distinguish between cut-off points of 5%, 10% and 15%. For the Crohn’s patient population, only data on a 10% and 15% SeHCAT test cut-off were available. For the no SeHCAT strategy all patients received regular treatment for either IBS-D or chronic diarrhoea in Crohn’s. Additionally, in the scoping document, trial of treatment with BAS was mentioned as another possible strategy without specifically including it as a comparator. According to the clinical experts at the scoping meeting, trial of treatment is rarely used as a treatment strategy and was thus not considered relevant. However, trial of treatment could also not be completely excluded as an option. Thus, in this report, for both populations we presented two sets of results: one where trial of treatment is not considered as a comparator and one where it is. In the trial of treatment strategy, patients first receive a BAS and when patients do not respond they receive regular treatment for either IBS-D or chronic diarrhoea in Crohn’s.
For each population, three models were combined:
-
a short-term decision tree that models the diagnostic pathway and initial response to treatment (first 6 months)
-
a long-term Markov model that estimates the life time costs and effects for patients initially receiving BAS
-
a long-term Markov model that estimates the life time costs and effects for patients initially receiving regular treatment (IBS-D treatment in the first population and Crohn’s treatment in the second population).
In the decision tree the 6-month number of responders and the expected costs were calculated for each comparator while for the Markov models lifetime expected QALYs and expected costs per patient were calculated for each comparator.
Where possible, input for the model was based on our SeHCAT systematic review, other published literature and UK databases. When such evidence was not available, expert opinion was used. The impact of uncertainty about the various input parameters on the outcomes was explored through probabilistic sensitivity analyses and scenario analyses.
Incremental cost-effectiveness ratios were estimated as additional cost per additional responder in the short term (first 6 months) and per additional QALY in the long term (lifetime).
When trial of treatment is not considered as a comparator, the evaluation for the IBS-D population showed, for the short term, that the optimal choice depends on the willingness to pay for an additional responder. For lower values (base case £2400, scenarios between £1800 and £4600) the choice will be no SeHCAT in all scenarios; for higher values either SeHCAT 10% or SeHCAT 15% becomes cost-effective.
For the lifetime perspective, we did not define a base case, as we had no information of any kind to inform the transition probabilities between the health states diarrhoea and no diarrhoea and vice versa. Thus, only scenario analysis was performed. The various scenarios showed widely differing results. Depending on the scenario, in the threshold range of £20,000–30,000 per QALY gained, we found as optimal choice either no SeHCAT, SeHCAT 5% or SeHCAT 15%; only SeHCAT 10% never had the highest probability of being cost-effective.
When trial of treatment is considered a comparator, the analysis showed for the IBS-D population that for the short term, trial of treatment is the optimal choice across a range of scenarios. In the base-case scenario, trial of treatment dominated all other strategies and had a 95% probability of being the most cost-effective option. In the various scenarios, trial of treatment was dominant compared with all strategies. For all scenarios trial of treatment had the highest probability of being cost-effective; this probability was for most scenarios around 90%, decreasing for some scenarios to 50%.
For the lifetime perspective, for all but two scenarios, trial of treatment was the strategy with the highest probability of being cost-effective for thresholds above £5000 to £15,000, with no SeHCAT the most favourable strategy for lower threshold ICERs. In the two scenarios where the transition probability from diarrhoea to no diarrhoea in the BAM model was 5% per cycle while all others were 0, we observed that for thresholds higher than £15,000 SeHCAT 15% had the highest probability of being cost-effective.
For the Crohn’s population, the short-term evaluation without trial of treatment as comparator showed for the short term that the optimal choice depends on the willingness to pay for an additional responder. For lower values (base case £2300, scenarios between £1500 and £4000) the choice will be no SeHCAT in all scenarios, for higher values SeHCAT 10% becomes cost-effective.
For the long term, the various scenarios show widely differing results. Depending on the scenario, in the threshold range of £20,000–30,000 per QALY gained, we found as optimal choice either no SeHCAT or SeHCAT 15% while some scenarios found that all three strategies had the same probability of being cost-effective.
When trial of treatment is considered a comparator, the analysis showed for the Crohn’s population that for the short term, trial of treatment dominated all other strategies (in terms of number of responders) and had an almost 100% probability of being the most cost-effective option. In the various scenarios, trial of treatment was dominant compared with all strategies. For all scenarios trial of treatment had the highest probability of being cost-effective; for most scenarios this probability was around 90%.
For the lifetime perspective in Crohn’s with trial of treatment, again the various scenarios show widely differing results. Depending on the scenario, in the threshold range of £20,000–30,000 per QALY gained, we found as optimal choice either trial of treatment, no SeHCAT or SeHCAT 15%.
In conclusion, the various analyses have shown that for both populations considerable decision uncertainty exists, and that no firm conclusions can be formulated as to which strategy is optimal.
Strengths and limitations of assessment
Clinical effectiveness
A main strength for this assessment is the fact that the SeHCAT test has been long established; it has been used for over 25 years in clinical practice. The adverse events profile of the test seems favourable. Unfortunately, there are no published data to support this statement.
Extensive literature searches were conducted in an attempt to maximise retrieval of relevant studies. These included electronic searches of a variety of bibliographic databases, as well as screening of clinical trials registers and conference abstracts to identify unpublished studies. Because of the known difficulties in identifying test accuracy studies using study design-related search terms,87 no study design filters were used in order to maximise sensitivity at the expense of reduced specificity. Thus, large numbers of citations were identified and screened, many of which did not meet the inclusion criteria of the review.
The possibility of publication bias remains a potential problem for all systematic reviews. Considerations may differ for systematic reviews of test accuracy studies. It is relatively simple to define a positive result for studies of treatment, e.g. a significant difference between the treatment and control groups that favours treatment. This is not the case for test accuracy studies, which measure agreement between index test and reference standard. It would seem likely that studies finding greater agreement (high estimates of sensitivity and specificity) will be published more often. In addition, test accuracy data are often collected as part of routine clinical practice, or by retrospective review of records; test accuracy studies are not subject to the formal registration procedures applied to RCTs and are therefore more easily discarded when results appear unfavourable. The extent to which publication bias occurs in studies of test accuracy remains unclear; however, simulation studies have indicated that the effect of publication bias on meta-analytic estimates of test accuracy is minimal. 88 Formal assessment of publication bias in systematic reviews of test accuracy studies remains problematic and reliability is limited. 88 We did not undertake a statistical assessment of publication bias in this review. However, our search strategy included a variety of routes to identify unpublished studies and resulted in the inclusion of a number of conference abstracts.
Clear inclusion criteria were specified in the protocol for this review and the one protocol modification that occurred during the assessment has been documented in the methods section (see Chapter 3, Assessment of clinical effectiveness, Methods) of this report. The eligibility of studies for inclusion is therefore transparent. In addition, we have provided specific reasons for excluding all of the studies considered potentially relevant at initial citation screening (see Appendix 5 ). The review process followed recommended methods to minimise the potential for error and/or bias;14 studies were independently screened for inclusion by two reviewers and data extraction and quality assessment were done by one reviewer and checked by a second (RR and SD). Any disagreements were resolved by consensus. The only French-language study was extracted by one reviewer and checked by a second (Shona Lang and RR).
Three studies included in the review were test accuracy studies. The methodological quality of these studies was assessed using a modification of the QUADAS-2 tool. 25 The QUADAS tool has been recommended for assessing the methodological quality of test accuracy studies,14,17 and has been widely adopted by researchers and key organisations such as the Cochrane Collaboration, NICE in the UK, and Institut für Qualität und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesundheitswesen (IQWiG) in Germany. It has been mentioned in more than 200 abstracts on the DARE database and has been cited more than 500 times. The revised version of QUADAS (QUADAS-2) has recently been published. 25 QUADAS-2 more closely resembles the approach and structure of the Cochrane risk of bias tool. It is structured into four key domains covering participant selection, index test, reference standard, and the flow of patients through the study (including timing of tests). Each domain is rated for risk of bias (low, high or unclear) and the tool provides signalling questions, in each domain, to help reviewers in reaching a judgement. The participant selection, index test and reference standard domain are also, separately, rated for concerns regarding the applicability of the study to the review question (low, high or unclear). However, the QUADAS-2 tool does not currently include domains specific to the assessment of studies comparing multiple index tests; further development of QUADAS-2 in this area is planned. This assessment used a modified version of the QUADAS-2 tool, which includes an additional domain for the comparator test and additional signalling questions in the ‘flow and timing’ domain. It should be noted, however, that these components of the tool were not developed using the same rigorous evidence-based approach as the core QUADAS-2 tool. The inclusion criteria for this review were considered to largely match the review question and questions of applicability were, therefore, only relevant to the ‘patient selection’ domain. The review-specific guidance used in our QUADAS-2 assessment is reported in Appendix 2 . The results of the risk of bias assessment are reported, in full, for all included studies (see Appendix 3 ) and in summary in the results section (see Chapter 3, Assessment of clinical effectiveness, Results). However, the usefulness of this assessment was limited by poor reporting of primary study methods, particularly with respect to how the index and comparator tests and the reference standard were applied.
The main limitations for this assessment are the lack of data, differences between studies included in the review, and the generally poor quality of included papers. As reported in Chapter 3 (see Assessment of clinical effectiveness,Results), most studies did not report information on the probability of a response to treatment with BAS for people with a negative SeHCAT test. Therefore, information on the accuracy of the SeHCAT test to predict a treatment response is largely missing. In addition, there were considerable differences between studies; the principal diagnosis, treatment dose, the definition of response, follow-up period and SeHCAT administration were different between trials (see Appendix 4 for details).
Three studies were included for the assessment of the accuracy of a SeHCAT test to predict a response to treatment. All three studies were published between 1985 and 1987; two were Italian studies and one was a UK study. It is unclear whether or not there was any overlap in study populations included in the two Italian studies, which were performed by the same group.
Cost-effectiveness
Searching the literature, no economic evaluation studies were found regarding the use of SeHCAT-testing in chronic diarrhoea patients. This report therefore presents, as far as we are aware, the first full economic evaluation study, both in (a) patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease (IBS-D) and (b) people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. without resection of the terminal ileum) assessing the short- and long-term consequences both in costs and effects of using SeHCAT. For this purpose, for each of these patient populations, a linked evidence approach was used in modelling cost and consequences, combining outcomes of the diagnostic test and the related changes in treatment decisions and final health outcomes. A clear distinction was made between the initial diagnostic phase (treatment responder vs. non-responder at 6 months) and the long-term projection of this intermediate outcome of the diagnostic phase into final health outcomes (lifetime costs and consequences, the latter presented in QALYs).
The available evidence regarding the cut-off values defining a positive and negative SeHCAT test shows that various cut-off values are used, which influences test-accuracy estimates expressed in BAS treatment response. In our approach we assessed the impact of different cut-off values explicitly by making a distinction between SeHCAT test strategies based on three levels: 5%; 10% and 15%. Furthermore, current clinical practice shows that no-SeHCAT testing implies different clinical approaches. Two major approaches were explicitly modelled: first, IBS-D treatment in all patients involved, and secondly, the trial of treatment approach, in which all patients initially receive BAS and within the first period of 6 months (the time horizon of the diagnostic decision tree) non-responders will switch from BAS to IBS-D treatment. Our methods made it possible to analyse and present the cost-effectiveness of all competing five strategies simultaneously.
We included the impact of using SeHCAT in terms of BAS-treatment response as reported in peer reviewed papers and selected for this purpose only those papers that fulfilled our quality criteria as presented in Chapter 3 . In all models presented (both the decision trees that represented the diagnostic phase and the Markov models represented the subsequent life-years of patients) we have used evidence to inform parameters that was UK relevant and as up to date and high quality as possible. Where evidence was not available through published studies or databases, we used the most likely and plausible values and ranges as reported by clinical experts. However, given the time constraints, no formal expert solicitation process could be conducted and instead a questionnaire was sent out. The seven experts who filled out the questionnaire showed a wide variation in their responses, highlighting the uncertainty about important input parameters.
The remaining lack of evidence of certain parameters was handled by performing extensive uncertainty analyses, both using probabilistic sensitivity analyses and running a wide range of scenario analyses. For the latter, because the plausibility of one of the scenarios was not larger over any other, we did not judge about the likelihood of any of them. Additionally, given the discussion on the acceptability of trial of treatment with BAS as a comparator, we also ran all analyses once with trial of treatment as comparator and once without.
One of the main limitations of the study is that the studies used to estimate the probability of a positive SeHCAT test and the probability of a BAS response were based on other populations than the ones defined in this evaluation. Most, if not all, IBS-D studies included patients in whom various tests had been performed and where no organic cause of the diarrhoea could be found. This is in contrast with the population defined here, which is patients with symptoms suggestive of functional disease in whom only basic blood tests have been performed. It is not unlikely that in our population the prevalence of BAM is lower than that observed in the published studies.
For the Crohn’s population, we combined the estimates from Tunney et al. 32 and Smith et al. 3 The Tunney paper does not provide much detail on the population of surgically naïve Crohn’s patients, so it is unclear whether or not this group would be representative of the population under investigation here. The study by Smith was specifically in patients who were in clinical remission, thus excluding patients having a relapse. It is unclear how this would impact the results.
Another limitation concerns the modelling of the IBS-D population. It is assumed in the model that patients not responding to IBS-D treatment will only use loperamide for some symptomatic relief. It is, however, not unlikely that in our IBS-D population (i.e. patients in whom no diagnostic testing other than initial blood work has been performed) some non-responders will be referred for diagnostic testing to check for organic causes of the chronic diarrhoea. However, the discussion among the experts during the scoping meeting suggested that SeHCAT testing would not make subsequent tests for organic disease redundant in which case these costs would be the same in all strategies.
We also did not incorporate patients switching from treatment with cholestyramine to colesevelam because of non-response or intolerability, as no data on response rates for colesevelam were available. Including that option would most likely lead to a higher response rate, a smaller percentage of patients moving from the ‘no diarrhoea’ health state to the ‘diarrhoea’ health state over time (due to increased persistence) and to higher treatment costs since colesevelam is more expensive than cholestyramine.
However, the most important limitation is the lack of data on various important parameters, and thus the necessity to rely on expert opinion for the short term and to rely on scenario analysis for the long term.
Uncertainties
Clinical effectiveness
The main uncertainties regarding clinical effectiveness are both the accuracy of the SeHCAT test in predicting either BAM or response to treatment and the effectiveness of BAS for the treatment of chronic diarrhoea caused by BAM.
For the assessment of the accuracy of the SeHCAT test in predicting BAM there was no evidence, mainly because there is not an appropriate reference standard for this assessment. For the assessment of the accuracy of the SeHCAT test in predicting a response to treatment, we found three studies. However, the studies had small numbers of patients with unknown cause chronic diarrhoea, they used different cut-offs for the assessment of BAM and between-study heterogeneity was considerable. One study was included for the assessment of the clinical effectiveness of BAS for the treatment of chronic diarrhoea caused by BAM. This study looked at colesevelam versus placebo and included 24 patients: 12 in each arm. All other included studies used cholestyramine.
We found no data on the accuracy of the SeHCAT test in predicting either BAM or response to treatment, or the clinical effectiveness of BAS for the treatment of chronic diarrhoea caused by BAM in patients with Crohn’s disease.
Cost-effectiveness
The main uncertainties in the cost-effectiveness analyses are caused by lack of essential data. Several assumptions had to be made to make it possible to perform the cost-effectiveness analyses.
The lack of evidence of the accuracy of SeHCAT based on a reference test meant that in the diagnostic decision trees the conventional way of modelling test accuracy using sensitivity and specificity of testing was not feasible. Therefore, it remained impossible to indicate FP and FN probabilities of testing. The accuracy of SeHCAT testing was necessarily based on test result in combination with response to BAS treatment. Logically, this response after testing is an unknown function of actual test accuracy and BAS efficacy. In other words, patients responding to BAS may be TP patients with a true response but may also be FP patients with a placebo response.
The limited number of papers was heterogeneous regarding cut-off value of SeHCAT test results. Given the variety of cut-off values between 8% and 12% and the small number of studies, these studies were considered one group. Of course it is not possible to make a distinction between these grouped cut-off values. The 5% and 15% cut-off values based date are more homogenous in this respect.
The parameter value for BAS treatment response given a positive SeHCAT test was derived from the literature. However, for the SeHCAT-negative patients the model assumed IBS-D treatment and for this specific response parameter only a subjective assumption could be made with what was only indirectly related expert opinion: the expert opinion on IBS-D treatment response without testing (52%) was increased by 10 percentage points for this purpose. This was motivated by the idea that a positive SeHCAT test would have selected potential IBS-D non-responders to be treated by BAS.
Important uncertainties exist about the trial of treatment strategy. No data were available to inform the response rate to BAS, and so we made assumptions based on the total number of BAS responders in the SeHCAT 15% strategy. One question is to what extent it is reasonable to choose this strategy rather than SeHCAT 10% to base the response rate on, as resorption values between 10% and 15% are often seen as subnormal. However, we found in our model that the combination of first a positive SeHCAT test and then a positive response to BAS occurs almost as often in the SeHCAT 10% strategy as in the SeHCAT 15% strategy. Thus, this choice does not influence the results. Other issues regarding the trial of treatment strategy relate to the placebo response that may be expected in the true IBS-D patients receiving BAS. It is a well-known fact that patients with IBS-D tend to show high placebo responses to treatment. 68 One of the clinical experts pointed out that long-term inappropriate treatment with BAS may have implications for instance absorption of other drugs and vitamins. Ideally, such long-term consequences would need to be included when modelling the trial of treatment strategy. Additionally, long-term transitions between ‘diarrhoea’ and ‘no diarrhoea’ may not be the same for BAS patients having a positive SeHCAT result and patients responding to a trial of treatment, as patients without a positive diagnosis may be less inclined to accept the side effects of BAS.
In the long-term Markov model, the state of having diarrhoea was valued by cost and utilities irrespective of the cause of the symptom, being either BAM or IBS-D. It remains to be seen whether or not this is fact. For the increase in utility when patients become responders (i.e. are in the ‘no diarrhoea’ health state) we made two assumptions; one where this increase is the same for BAM and IBS-D patients and one where the increase in BAM patients is only 75% of the increase seen for IBS-D patients. This latter scenario reflects the idea that BAS is usually not well tolerated by patients with side effects leading to a smaller utility gain. To what extent this assumption of 75% is realistic is unknown.
The lifetime transition probabilities between the Markov states diarrhoea and non-diarrhoea could not be based on reliable evidence. For this reason, several equally plausible scenarios were used. Furthermore, it turned out to be impossible to include a health state constipation in the long-term Markov model because data on this issue were lacking and the impact on the results was estimated to be negligible.
In the protocol of the study, it was suggested that in patients who tested positive for BAM despite in fact not having BAM (FPs) an important question would be whether or not (some of) these patients will be detected at some point as having IBS-D. Likewise, patients who tested negative for BAM despite in fact having BAM (FNs) are assumed to receive treatment for IBS-D. Again, an important question is whether or not (some of) these patients will be detected at some point as having BAM. Experts indicated that in the latter situation, patients most likely would not be diagnosed as BAM with some delay. For the first situation the lack of essential data made it impossible to incorporate the impact of a possible delay in efficacious treatment in the cost-effectiveness analyses.
As stated, for the Crohn’s disease population no evidence regarding essential parameters could be found to be used in the model calculations. This raises the question if modelling should have even been attempted. However, as the NICE diagnostic assessments may also be used to formulate which, if any, additional research is required, it was felt useful to make all the uncertainties for the Crohn’s population explicit. Thus, for various parameters the assumption was made that the data defined for the population of patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease were considered to be generalisable to the Crohn’s population. Expert inputs did not state to do otherwise.
The cost-effectiveness analyses are based on adult patient data only. Whether or not the findings hold for children and adolescents is unknown.
Chapter 6 Conclusions
Implications for service provision
The results of our systematic review suggest that the accuracy of the SeHCAT test in predicting either BAM or response to treatment, and the clinical effectiveness of BAS for the treatment of chronic diarrhoea caused by BAM, are uncertain. Additionally, the results of our economic evaluation showed that for both populations studied, the lifetime perspective gave different results for different scenarios meaning that all strategies may potentially be the most cost-effective. Therefore, the implications for service provision of SeHCAT are equally uncertain. The main reason for this uncertainty is the lack of good-quality evidence.
Suggested research priorities
Standardisation of the definition of a positive SeHCAT test should be the first step in assessing the usefulness of this test. As there is no reference standard for the diagnosis of BAM and SeHCAT testing provides a continuous measure of metabolic function, DTA studies are not the most appropriate study design. However, in studies where all patients are tested with SeHCAT and all patients are treated with BAS (see Chapter 4 , Results, Accuracy of selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine for the assessment of responses to treatment in people with chronic diarrhoea), response to treatment can provide a surrogate reference standard; further DTA studies of this type may provide information on the ability of SeHCAT to predict response to BAS. A potentially more informative option would be multivariate regression modelling of treatment response (dependent variable), with SeHCAT result and other candidate clinical predictors as covariates. Such a study design could also inform the definition of a positive SeHCAT result.
The limited evidence identified means that the effectiveness of BAS, both in unselected patients with chronic diarrhoea and where treatment decisions are based on SeHCAT test results, remains uncertain. Two possible randomised controlled designs are, therefore, potentially useful:
-
Patients with chronic diarrhoea receive SeHCAT testing and all patients are then randomised to treatment with BAS or placebo. This study design can provide information on the effectiveness of BAS in all patients with relevant symptoms. If the analysis is then stratified by test result, information can be obtained on any difference in effectiveness between SeHCAT positive and SeHCAT-negative patients, or variation in the effectiveness of BAS with levels of SeHCAT absorption.
-
Patients with chronic diarrhoea receive SeHCAT testing and only patients with a positive SeHCAT test are randomised to treatment with BAS or placebo. This study design can provide information on the effectiveness of BAS in SeHCAT-positive patients. This design might be considered more ethical if it is believed that current evidence is sufficient to indicate no, or minimal, effectiveness of BAS in SeHCAT-negative patients.
The inclusion criteria for such a trial are important to make sure that patients are not unnecessarily subjected to BAS treatment and, at the same time, that all patients suitable for a SeHCAT test are included. Treatment strategies should be clearly described in the study protocol. Long-term follow-up is needed to fully assess the effectiveness of BAS in all relevant patient groups. Outcomes should include all relevant bowel function and transit outcomes, as well as quality of life and adverse events of testing and treatment. Additionally, such a trial would enable the collection of resource use data related to the chronic diarrhoea problems.
Moreover, the large variation in outcomes between the scenarios considered for the Markov models make it clear that long-term data is important for patients with IBS-D, patients identified as having BAM and Crohn’s patients with chronic diarrhoea. These data do not necessarily need to come from a RCT; it might be possible to set up a retrospective study using existing databases, patient records, etc. to find relevant long-term data. If those sources of information do not provide enough information, prospective observational studies could collect data on treatment and treatment switches and resource use.
It was also shown in the various scenarios that the assumption about utility values for BAM health states have an important impact on the results. For reliable utility estimates for the various health states, a cross-sectional study in the relevant patient populations would be a relatively easy way to inform these important parameters.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the clinical advice and expert opinion provided by:
Professor Julian RF Walters, Professor of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Imperial College London, London UK.
Dr Michael Glynn, Consultant Physician and Gastroenterologist/Hepatologist, Barts and the London NHS Trust, London UK.
Dr Stephen Middleton, Spire Cambridge Lea Hospital, Cambridge, UK.
Professor David Rampton, Consultant Gastroenterologist, Barts and the London NHS Trust, London, UK.
Dr Mark Fox, Clinical Associate Professor and Honorary Consultant Gastroenterologist at the NIHR Biomedical Research Unit and Nottingham Digestive Diseases Centre, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK.
Professor KD Bardhan, Consultant Physician and Gastroenterologist, Rotherham General Hospital, Rotherham, UK.
And the following specialist DAC members for providing their advice and expert opinion:
Dr Nick Read, Chairperson and Medical Advisor Lay IBS Network.
Dr Matthew Brookes, Consultant Gastroenterologist, The Royal Wolverhampton Hospital NHS Trust.
Professor John McLaughlin, Gastroenterologist, Salford Royal Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
The views expressed in this report are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR HTA Programme. Any errors are the responsibility of the authors.
Contributions of authors
Rob Riemsma and Sohan N Deshpande planned and performed the systematic review and interpretation of evidence.
Maiwenn Al, Isaac Corro Ramos and Hans Severens planned and performed the cost-effectiveness analyses and interpreted results.
Nigel Armstrong, Kelly Lee and Steve Ryder contributed to planning and interpretation of cost-effectiveness analyses and acquisition of input data for modelling.
Caro Noake devised and performed the literature searches and provided information support to the project.
Marieke Krol contributed to the acquisition of input data for modelling.
Mark Oppe assisted in performing the cost-effectiveness analyses.
Jos Kleijnen provided senior advice and support to the assessment. All parties were involved in drafting and/or commenting on the report.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Thomas PD, Forbes A, Green J, Howdle P, Long R, Playford R, et al. Guidelines for the investigation of chronic diarrhoea. Gut 2003;52:v1-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.52.suppl_5.v1.
- Sinha L, Liston R, Testa HJ, Moriarty KJ. Idiopathic bile acid malabsorption: qualitative and quantitative clinical features and response to cholestyramine. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1998;12:839-44. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.1998.00388.x.
- Smith MJ, Cherian P, Raju GS, Dawson BF, Mahon S, Bardhan KD. Bile acid malabsorption in persistent diarrhoea. J R Coll Physicians Lond 2000;34:448-51.
- Patient UK. Chronic Diarrhoea in Adults. Leeds: EMIS (Egton Medical Information Systems); 2009.
- Galatola G, Ferraris R, Pellerito R, Barlotta A, Umberto OM, Sciaretta TG, et al. The prevalence of bile acid malabsorption in irritable bowel syndrome and the effect of cholestyramine: an uncontrolled open multicentre study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1992;4:533-7.
- Wedlake L, A’Hern R, Russell D, Thomas K, Walters JRF, Andreyev HJN. Systematic review: the prevalence of idiopathic bile acid malabsorption as diagnosed by SeHCAT scanning in patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009;30:707-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04081.x.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence . Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Adults: Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Primary Care [CG61] 2008. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG61 (accessed 19 December 2011).
- Rubin GP, Hungin AP, Kelly PJ, Ling J. Inflammatory bowel disease: epidemiology and management in an English general practice population. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000;14:1553-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00886.x.
- Crohn’s Disease. Leeds: EMIS (Egton Medical Information Systems); 2011.
- Walters JRF, Pattni SS. Managing bile acid diarrhoea. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2010;3:349-57. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1756283X10377126.
- GE Healthcare Limited . Summary of Product Characteristics: SeHCAT 370 KBq Capsules 2001. www.mhra.gov.uk/home/groups/spcpil/documents/spcpil/con1362371060280.pdf (accessed 17 September 2013).
- Diagnostics Assessment Programme: SeHCAT (tauroselcholic [75selenium] acid) for the investigation of diarrhoea due to bile acid malabsorption: final scope. London: NICE; 2011.
- Pattni S, Walters JRF. Recent advances in the understanding of bile acid malabsorption. Br Med Bull 2009;92:79-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldp032.
- Systematic Reviews: CRD’s Guidance for Undertaking Reviews in Health Care. York: University of York; 2009.
- Diagnostics Assessment Programme: interim methods statement (version 2). London: NICE; 2010.
- Higgins JPT, Green S. The Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org/ (accessed 23 March 2011).
- Cochrane Diagnostic Test Accuracy Working Group . The Cochrane Collaboration. Handbook for DTA Reviews. 2009. http://srdta.cochrane.org/handbook-dta-reviews (accessed 23 March 2011).
- McGowan J, Sampson M, Lefebvre C. An evidence based checklist for the peer review of electronic search strategies (PRESS EBC). EBLIP 2010;5:1-6.
- Wright K, McDaid C. Reporting of article retractions in bibliographic databases and online journals. J Med Libr Assoc 2011;99:164-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.99.2.010.
- Royle P, Waugh N. Should systematic reviews include searches for published errata?. Health Info Libr J 2004;21:14-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2004.00459.x.
- Wright K, McDaid C. Is the Retraction of Journal Articles in Electronic Journals and Databases Consistent and Timely? n.d.
- Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J. The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 2003;3.
- Whiting P, Rutjes AWS, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PMM, Kleijnen J. A systematic review of sources of variation and bias in studies of diagnostic accuracy. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:189-202. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.05.014.
- Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Dinnes J, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J. A systematic review finds that diagnostic reviews fail to incorporate quality despite available tools. J Clin Epidemiol 2005;58:1-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.04.008.
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 2011;155:529-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009.
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 1986;7:177-88. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2.
- Singe CC, Karbach U, Biederlack S, Ewe K. 75-SeHCAT-retentionstest bei ileitis crohn: korrelation mit befallslange und postprandialen serumanstieg von cholylglycin. Z Gastroenterol 1987;22:166-70.
- Kruis W, Scheurlen C, Moser E, Paumgartner G. Spezifitat und sensitivitat des SeHCAT-testes fur die diagnose einer ileumdysfunktion bei patienten mit morbus crohn. Z Gastroenterol 1987;22:159-63.
- Scheurlen C, Kruis W, Bull U, Stellaard F, Kalek HD, Lang P, et al. Comparison between total-body retention of SE-75-homotaurocholic acid and faecal bile-acid excretion in patients with disordered ileum function. Z Gastroenterol 1983;21:419-20.
- Dyson J, Barbour J. Use of SeHCAT Testing: Investigation of Diarrhoea and Patient Satisfaction n.d. http://uegw.congress-online.com/uegw2011/guest/AbstractView?ABSID=12003 (accessed 7 February 2012).
- Dyson J, Bartholomew P, Barbour J. Use of SeHCAT Testing: Investigation of Diarrhoea and Patient Satisfaction n.d.
- Tunney R. The Clinical Value of SeHCAT in the Diagnosis of Bile Acid Malabsorption: An Evaluation of The British Society of Gastroenterology Guidelines for the Investigation of Chronic Diarrhoea. Manchester: University of Manchester; 2011.
- Borghede MK, Schlutter JM, Agnholt JS, Christensen LA, Gormsen LC, Dahlerup JF. Bile acid malabsorption investigated by selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine ((75)SeHCAT) scans: causes and treatment responses to cholestyramine in 298 patients with chronic watery diarrhoea. Eur J Intern Med 2011;22:E137-40.
- Eusufzai S. Bile acid malabsorption in patients with chronic diarrhoea. Scand J Gastroenterol 1993;28:865-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00365529309103126.
- Eusufzai S, Axelson M, Angelin B, Einarsson K. Serum 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one concentrations in the evaluation of bile acid malabsorption in patients with diarrhoea: correlation to SeHCAT test. Gut 1993;34:698-701.
- Fellous K, Jian R, Haniche M, Marteau P, Messing B, Rain JD, et al. Measurement of ileal absorption of bile salts with the selenium 75 labelled homotaurocholic acid test. Validation and clinical significance. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 1994;18:865-72.
- Fernandez-Banares F, Esteve M, Salas A, Forne M, Espinos JC, Martin-Comin J, et al. Bile acid malabsorption in microscopic colitis and in previously unexplained functional chronic diarrhoea. Dig Dis Sci 2001;46:2231-8.
- Ford GA, Preece JD, Davies IH, Wilkinson SP. Use of the SeHCAT test in the investigation of diarrhoea. Postgrad Med J 1992;68:272-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/pgmj.68.798.272.
- Merrick MV, Eastwood MA, Ford MJ. Is bile acid malabsorption underdiagnosed? An evaluation of accuracy of diagnosis by measurement of SeHCAT retention. Br Med J 1985;290:665-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.290.6469.665.
- Notta PC, Ramal D, Maisterra S, Gasen AR, Maymo S, Sabate A, et al. Measurement of 75Se-SeHCAT abdominal retention in the initial diagnosis of bile acid absorption (BAM). Rev Esp Med Nucl 2011;30:297-300. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.remngl.2011.03.005.
- Rudberg U, Nylander B. Radiological bile acid absorption test 75SeHCAT in patients with diarrhoea of unknown cause. Acta Radiol 1996;37:672-5.
- Sciarretta G, Vicini G, Fagioli G. Use of 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine to detect bile acid malabsorption in patients with ileal dysfunction or diarrhoea. Gastroenterology 1986;91:1-9.
- Sciarretta G, Fagioli G, Furno A, Vicini G, Cecchetti L, Grigolo B, et al. 75Se HCAT test in the detection of bile acid malabsorption in functional diarrhoea and its correlation with small bowel transit. Gut 1987;28:970-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.28.8.970.
- Wildt S, Norby Rasmussen S, Lysgard Madsen J, Rumessen JJ. Bile acid malabsorption in patients with chronic diarrhoea: clinical value of SeHCAT test. Scand J Gastroenterol 2003;38:826-30.
- Williams AJ, Merrick MV, Eastwood MA. Idiopathic bile acid malabsorption: a review of clinical presentation, diagnosis, and response to treatment. Gut 1991;32:1004-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.32.9.1004.
- Nyhlin H, Merrick MV, Eastwood MA. Bile acid malabsorption in crohn’s disease and indications for its assessment using SeHCAT. Gut 1994;35:90-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.35.1.90.
- Odunsi-Shiyanbade ST, Camilleri M, McKinzie S, Burton D, Carlson P, Busciglio IA, et al. Effects of chenodeoxycholate and a bile acid sequestrant, colesevelam, on intestinal transit and bowel function. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;8:159-65. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2009.10.020.
- Fernandez-Banares F, Esteve M, Espinos JC, Forne M, Martin-Comin J, Viver JM. Bile acid malabsorption (BAM) in patients with functional chronic diarrhoea: response to cholestyramine. Gastroenterology 2000;118.
- Fernandez-Banares F, Esteve M, Salas A, Alsina M, Farre C, Gonzalez C, et al. Systematic evaluation of the causes of chronic watery diarrhoea with functional characteristics. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:2520-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01438.x.
- Rao AS, Wong BS, Odunsi-Shiyanbade ST, Burton D, McKinzie S, Zinsmeister AR, et al. The bile salt chenodeoxycholate and the bile acid sequestrant colesevelam both retard gastric emptying despite opposite effects on colonic transit in IBS patients. Paper presented at 2010 Joint International Neurogastroenterology and Motility Meeting, 26–29 August 2010, Boston, MA. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2010;22.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2009.
- Johnston I, Nolan J, Pattni SS, Walters JRF. New insights into bile acid malabsorption. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2011;13:418-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11894-011-0219-3.
- Kurien M, Evans KE, Leeds JS, Hopper AD, Harris A, Sanders DS. Bile acid malabsorption: an under-investigated differential diagnosis in patients presenting with diarrhoea predominant irritable bowel syndrome type symptoms. Scand J Gastroenterol 2011;46:818-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2011.574728.
- Kaltenthaler E, Tappenden P, Paisley S, Squires H. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 13: Identifying and Reviewing Evidence to Inform the Conceptualisation and Population of Cost-Effectiveness Models. 2011. www.nicedsu.org.uk (accessed 22 February 2012).
- Suleiman S, Sonnenberg A. Cost-effectiveness of endoscopy in irritable bowel syndrome. Arch Intern Med 2001;161:369-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archinte.161.3.369.
- Mein SM, Ladabaum U. Serological testing for coeliac disease in patients with symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004;19:1199-210. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01958.x.
- Spiegel BMR, DeRosa VP, Gralnek IM, Wang V, Dulai GS. Testing for coeliac sprue in irritable bowel syndrome with predominant diarrhoea: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1721-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2004.03.012.
- Brandt LJ, Bjorkman D, Fennerty MB, Locke GR, Olden K, Peterson W, et al. Systematic review on the management of irritable bowel syndrome in North America. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97:S7-26.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Adults: Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Primary Care. London: Royal College of Nursing; 2008.
- Rossel P, Sortsoe Jensen H, Qvist P, Arveschoug A. Prognosis of adult-onset idiopathic bile acid malabsorption. Scand J Gastroenterol 1999;34:587-90.
- Spiegel B, Harris L, Lucak S, Mayer E, Naliboff B, Bolus R, et al. Developing valid and reliable health utilities in irritable bowel syndrome: results from the IBS PROOF Cohort. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:1984-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2009.232.
- Mearin F, Baro E, Roset M, Badia X, Zarate N, Perez I. Clinical patterns over time in irritable bowel syndrome: symptom instability and severity variability. Am J Gastroenterol 2004;99:113-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1572-0241.2003.04023.x.
- NHS Reference Costs 2010–2011. London: Department of Health; 2011.
- British National Formulary. London: BMA and RPS; 2012.
- Owens DM, Nelson DK, Talley NJ. The irritable bowel syndrome: long-term prognosis and the physician–patient interaction. Ann Intern Med 1995;122:107-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-122-2-199501150-00005.
- England and Wales Interim Lifetables. London: Office for National Statistics; 2011.
- Luman W, Williams AJ, Merrick MV, Eastwood MA. Idiopathic bile acid malabsorption: long-term outcome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1995;7:641-5.
- Spiller R, Aziz Q, Creed F, Emmanuel A, Houghton L, Hungin P, et al. Guidelines on the irritable bowel syndrome: mechanisms and practical management. Gut 2007;56:1770-98. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.2007.119446.
- Agreus L, Svardsudd K, Talley NJ, Jones MP, Tibblin G. Natural history of gastroesophageal reflux disease and functional abdominal disorders: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:2905-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9270(01)03242-7.
- El-Serag HB, Pilgrim P, Schoenfeld P. Systemic review: natural history of irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004;19:861-70.
- Waller S, Misiewicz J. Prognosis in the irritable-bowel syndrome: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 1997;81:529-31.
- Hillman LC, Stace NH, Pomare EW. Irritable bowel patients and their long-term response to a high fibre diet. Am J Gastroenterol 1984;79:1-7.
- Fowlie S, Eastwood MA, Ford MJ. Irritable bowel syndrome: the influence of psychological factors on the symptom complex. J Psychosom Res 1992;36:169-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0022-3999(92)90025-W.
- Adeniji OA, Barnett CB, Di Palma JA. Durability of the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome based on clinical criteria. Dig Dis Sci 2004;49:572-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000026300.47363.3b.
- Chaudhary NA, Truelove SC. The irritable colon syndrome: a study of the clinical features, predisposing causes, and prognosis in 130 cases. Q J Med 1962;31:307-22.
- Hawkins CF, Cockel R. The prognosis and risk of missing malignant disease in patients with unexplained and functional diarrhoea. Gut 1971;12:208-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.12.3.208.
- Holmes KM, Salter RH. Irritable bowel syndrome: a safe diagnosis?. Br Med J 1982;285:1533-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.285.6354.1533.
- Prior A, Whorwell PJ. Gynaecological consultation in patients with the irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 1989;30:996-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.30.7.996.
- Buxton MJ, Lacey LA, Feagan BG, Niecko T, Miller DW, Townsend RJ. Mapping from disease-specific measures to utility: an analysis of the relationships between the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire and Crohn’s Disease Activity Index in Crohn’s disease and measures of utility. Value Health 2007;10:214-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00171.x.
- Canavan C, Abrams KR, Mayberry JF. Meta-analysis: mortality in Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007;25:861-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03276.x.
- Balzer K, Breuer N, Quebe-Fehling E. Postprandial serum bile acid level and 75SeHCAT retention in diagnosis of bile acid malabsorption syndrome. a comparative study. Med Klin 1993;88:23-8.
- Balzer K. The 75SeHCAT test: methodology and clinical application possibilities. Med Klin 1995;90:35-9.
- Balzer K, Dirks E, Brueuer N, Goebell H, Goebell H, Peskar BM, et al. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Basic Research and Clinical Implications. Lancaster: MTP Press; 1988.
- Brydon WG, Nyhlin H, Eastwood MA, Merrick MV. Serum 7 alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one and selenohomocholyltaurine (SeHCAT) whole body retention in the assessment of bile acid induced diarrhoea. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1996;8:117-23.
- Ferraris R, Galatola G, Barlotta A, Pellerito R, Fracchia M, Cottino F, et al. Measurement of bile acid half-life using [75Se]HCAT in health and intestinal diseases: comparison with [75Se]HCAT abdominal retention methods. Dig Dis Sci 1992;37:225-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01308176.
- Kurien M, Evans KE, Leeds JS, Hopper AD, Harris A, Hanney M, et al. Bile acid malabsorption a differential diagnosis for patients presenting with diarrhoea predominant irritable bowel syndrome type symptoms? [PWE-077]. Paper presented at Annual General Meeting of the British Society of Gastroenterology, 14–17 March 2011, Birmingham, UK. Gut 2011;60:A160-1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.2011.239301.340.
- Whiting P, Westwood M, Beynon R, Burke M, Sterne JA, Glanville J. Inclusion of methodological filters in searches for diagnostic test accuracy studies misses relevant studies. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:602-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.006.
- Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J Clin Epidemiol 2005;58:882-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.01.016.
- Thaysen EH, Orholm M, Arnfred T, Carl J, Rodbro P. Assessment of ileal function by abdominal counting of the retention of a gamma emitting bile acid analogue. Gut 1982;23:862-5.
- Delhez H, van den Berg JWO, van Blankenstein M, Meerwaldt JH. New method for the determination of bile acid turnover using 77Se-homocholic acid taurine. Eur J Nucl Med 1982;7:269-71.
- Warner GT, Oliver R, Schoenfeld P. A whole-body counter for clinical measurements utilizing the ‘shadow-field‘ technique. Phys Med Biol 1966;11:83-94.
Appendix 1 Literature search strategies
Clinical effectiveness search strategies
Search 1: scoping search
(SeHCAT or Stool B Assay) + bile acid malabsorption
Scoping search to identify background literature on this topic prior to NICE scoping meeting.
EMBASE (OvidSP): 1980 to week 40 2011
Searched 11 October 2011.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).mp. (150)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75).mp. (711)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid).mp. (18)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").mp. (480)
-
or/1-4 (1095)
-
((Stool$ or f?ecal or f?eces) adj3 (bile salt$ or bile acid$ or BA) adj3 (assay$ or measure$ or test$ or analy$ or check$ or assess$)).mp. (111)
-
((stool$ or f?ecal or f?eces) adj3 (mass spectro$ or mass spectrum analy$ or gas chromatog$ or flame ioni?ation or mass fragmentography or GC or Gas-Liquid chromatography or GLC)).mp. (952)
-
or/6-7 (1047)
-
5 or 8 (2139)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).mp. (1937)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.mp. (4)
-
chronic diarrhea/ (2468)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protracted) adj2 diarrh?e$).mp. (11,457)
-
malabsorption.mp. (15,720)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).mp. (31,082)
-
bile acid/ (17,139)
-
or/10-16 (58,203)
-
9 and 17 (439)
-
limit 18 to embase (326)
MEDLINE (OvidSP): 1948 to week 4 September 2011
Searched 11 October 2011.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).ti,ab,ot,hw. (2)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75).ti,ab,ot,hw. (220)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid).ti,ab,ot,hw. (314)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").ti,ab,ot,hw. (143)
-
or/1-4 (582)
-
((Stool$ or f?ecal or f?eces) adj3 (bile salt$ or bile acid$ or BA) adj3 (assay$ or measure$ or test$ or analy$ or check$ or assess$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (100)
-
((stool$ or f?ecal or f?eces) adj3 (mass spectro$ or mass spectrum analy$ or gas chromatog$ or flame ioni?ation or mass fragmentography or GC or Gas-Liquid chromatography or GLC)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (128)
-
or/6-7 (223)
-
5 or 8 (803)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).mp. (1664)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.mp. (3)
-
diarrhea/ (35,419)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protracted) adj2 diarrh?e$).mp. (6619)
-
"Bile Acids and Salts"/ (18,279)
-
malabsorption.mp. (13,123)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).mp. (28,188)
-
or/10-16 (79,009)
-
9 and 17 (256)
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations (OvidSP): up to 10 October 2011
MEDLINE Daily Update (OvidSP): up to 10 October 2011
Searched 11 October 2011.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75).ti,ab,ot,hw. (7)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").ti,ab,ot,hw. (3)
-
or/1-4 (9)
-
((Stool$ or f?ecal or f?eces) adj3 (bile salt$ or bile acid$ or BA) adj3 (assay$ or measure$ or test$ or analy$ or check$ or assess$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (2)
-
((stool$ or f?ecal or f?eces) adj3 (mass spectro$ or mass spectrum analy$ or gas chromatog$ or flame ioni?ation or mass fragmentography or GC or Gas-Liquid chromatography or GLC)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (6)
-
or/6-7 (8)
-
5 or 8 (17)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).mp. (209)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.mp. (1)
-
diarrhea/ (32)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protracted) adj2 diarrh?e$).mp. (206)
-
"Bile Acids and Salts"/ (9)
-
malabsorption.mp. (197)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).mp. (568)
-
or/10-16 (1181)
-
9 and 17 (7)
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (Wiley Online Library): Issue 4: 2011
Searched 12 October 2011.
#1 tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2 3
#2 SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 7
#3 23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid 6
#4 selenium near "75" 13
#5 (#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4) 26
#6 (Stool* or faecal or fecal or feces or faeces) near (bile salt* or bile acid* or BA) near (assay* or measure* or test* or analy* or check* or assess*) 43
#7 (Stool* or faecal or fecal or feces or faeces) near (mass spectro* or mass spectrum analy* or gas chromatog* or flame ionization or flame ionisation or mass fragmentography or GC or Gas-Liquid chromatography or GLC) 27
#8 (#6 OR #7) 67
#9 (#5 OR #8) 93
#10 BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM 43
#11 primary near bile acid near (diarrhoe* or diarrhe*) 1
#12 (chronic or watery or recur* or persist* or protracted) near (diarrhoe* or diarrhe*) 548
#13 malabsorption 463
#14 (bile or biliary) near (acid* or salt*) 1242
#15 Medical subject heading (MeSH) descriptor Bile Acids and Salts explode all trees 806
#16 MeSH descriptor Diarrhea, this term only 1856
#17 (#10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16) 4048
#18 (#9 AND #17) 56
The CENTRAL search retrieved 53 records.
Search 2.5: clinical effectiveness searches
(SeHCAT or bile acid sequestrant/aluminium hydroxide) + bile acid malabsorption
The searches detailed below are the final iteration of a series of strategies and supersede strategies 2 to 2.4 illustrated in Figure 3 (see Chapter 3 ). The earlier iterations of these strategies are not included below; for further information please contact the authors. All results were collated and deduplicated in the Clinical Effectiveness EndNote Library. Original searches undertaken between 9 and 11 January 2012 retrieved 4763 records. Update searches undertaken between 17 and 20 April 2012 found an additional 78 records (after deduplication), but no new includes.
EMBASE search: Facet 1 combined terms for SeHCAT (lines #1–5) and Bile Acid Sequestrants (lines #6–12) using OR in line #13 (n = 33005). Facet 2 for Bile Acid Malabsorption (lines #14–20) was then combined with facet 1 using AND in line #21 (n = 3190). Line #21 was limited to remove animal studies. The final set was then limited to EMBASE records only in line #33 (n = 2359). For the full strategy please see below.
EMBASE (OvidSP): 1980 to week 15 2012
Searched 18 April 2012.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).mp. (155)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75).mp. (781)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid or 75Se-homotaurocholate).mp. (22)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").mp. (494)
-
or/1-4 (1172)
-
bile acid sequestrant/ (671)
-
((bile adj3 (acid or salt) adj3 sequestra$) or BAS).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (14,757)
-
Colestipol/ or (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2514)
-
Colestyramine/ or (colestyramine or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (9165)
-
Colesevelam/ or (Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (744)
-
aluminum hydroxide/ or (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel or 21645-51-2 or brasivil or rocgel or alugel or hydrated alumina or basalgel or dialume or nephrox).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (7652)
-
or/6-11 (31,903)
-
5 or 12 (33,005)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or BSM).mp. (2760)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.mp. (5)
-
chronic diarrhea/ or bile acid/ or bile salt/ (23,708)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protract$ or continual$ or continuous$ or sustain$ or constant$ or relentless$ or unrelent$ or functional or aggressive) adj2 (diarrh?e$ or diarrea$)).mp. (15,363)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).mp. (17,122)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).mp. (32,898)
-
or/14-19 (65,965)
-
13 and 20 (3190)
-
animal/ (1,767,504)
-
animal experiment/ (1,500,644)
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or murine or rodent or rodents or hamster or hamsters or pig or pigs or porcine or rabbit or rabbits or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or cow or bovine or sheep or ovine or monkey or monkeys).mp. (505,4056)
-
or/22-24 (5,054,056)
-
exp human/ (13,75,388)
-
human experiment/ (299,549)
-
or/26-27 (13,376,780)
-
25 not (25 and 28) (4,017,276)
-
21 not 29 (2684)
-
limit 30 to embase (2359)
MEDLINE (OvidSP): 1946 to week 1 April 2012
Searched 18 April 2012.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (3)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (277)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid or 75Se-homotaurocholate).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (321)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").ti,ab,ot,hw. (145)
-
or/1-4 (641)
-
((bile adj3 (acid or salt) adj3 sequestra$) or BAS).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2637)
-
Colestipol/ or (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (504)
-
Cholestyramine Resin/ or (colestyramine$ or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine$ or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid$ or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran$ or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0 or mk 135 or mk135).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (3239)
-
(Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (155)
-
Aluminum Hydroxide/ or (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (4378)
-
or/6-10 (10,414)
-
5 or 11 (11,017)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or BSM).ti,ab,ot,hw. (2205)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (4)
-
diarrhea/ (35,612)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protracted or continual$ or continuous$ or sustain$ or constant$ or relentless$ or unrelent$ or functional or aggressive) adj2 (diarrh?e$ or diarrea$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (6803)
-
"Bile Acids and Salts"/ (18,212)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (13,540)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (28,118)
-
or/13-19 (80,116)
-
12 and 20 (1769)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (3,607,371)
-
21 not 22 (1312)
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations (OvidSP): up to 17 April 2012
MEDLINE Daily Update (OvidSP): up to 17 April 2012
Searched 18 April 2012.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (0)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (6)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid or 75Se-homotaurocholate).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (0)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").ti,ab,ot,hw. (1)
-
or/1-4 (7)
-
((bile adj3 (acid or salt) adj3 sequestra$) or BAS).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (172)
-
Colestipol/ or (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2)
-
Cholestyramine Resin/ or (colestyramine$ or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine$ or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid$ or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran$ or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0 or mk 135 or mk135).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (28)
-
(Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (18)
-
Aluminum Hydroxide/ or (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (152)
-
or/6-10 (357)
-
5 or 11 (363)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or BSM).ti,ab,ot,hw. (261)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
diarrhea/ (24)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protracted or continual$ or continuous$ or sustain$ or constant$ or relentless$ or unrelent$ or functional or aggressive) adj2 (diarrh?e$ or diarrea$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (222)
-
"Bile Acids and Salts"/ (12)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (254)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (627)
-
or/13-19 (1367)
-
12 and 20 (50)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (3162)
-
21 not 22 (49)
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (Wiley Online Library): Issue 4: 2012
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) (Wiley Online Library): Issue 3: 2012
Searched 18 April 2012.
#1 tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2 3
#2 SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75 10
#3 23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid or 75Se-homotaurocholate 7
#4 selenium near "75" 16
#5 (#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4) 33
#6 ((bile near (acid or salt) near sequestra*) or BAS) 342
#7 MeSH descriptor Colestipol, this term only 90
#8 (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6) 190
#9 MeSH descriptor Cholestyramine Resin, this term only 250
#10 (colestyramine or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0) 462
#11 (Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7) 49
#12 MeSH descriptor Aluminum Hydroxide, this term only 350
#13 (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel or 21645-51-2 or brasivil or rocgel or alugel or hydrated alumina or basalgel or dialume or nephrox) 3393
#14 (#6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13) 4263
#15 (#5 OR #14) 4287
#16 primary near bile acid near (diarrhoe* or diarrhe* or diarrea*) 1
#17 (chronic or watery or recur* or persist* or protract* or continual* or continuous* or sustain* or constant* or relentless* or unrelent* or functional or aggressive) near (diarrhoe* or diarrhe* or diarrea*) 653
#18 (malabsorb* or mal-absorb* or malabsorp* or mal-absorp*) 577
#19 BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or BSM 71
#20 (bile or biliary) near (acid* or salt*) 1269
#21 MeSH descriptor Bile Acids and Salts explode all trees 813
#22 MeSH descriptor Diarrhea, this term only 1907
#23 (#16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20 OR #21 OR #22) 4306
#24 (#15 AND #23) 305
The CENTRAL search retrieved 168 records.
The CDSR search retrieved 130 records.
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) (internet): up to 19 April 2012
Health Technology Assessment Database (HTA) (internet): up to 19 April 2012
www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/
Searched 19 April 2012.
-
((tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2)) 0
-
((SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75)) 0
-
((23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid opr 75Se-homotaurocholate)) 0
-
((selenium near "75")) 1
-
#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 1
-
(((bile near (acid or salt) near sequestra*) or BAS)) 18
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Colestipol 3
-
((Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6) ) 21
-
((colestyramine or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0)) 32
-
((Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7)) 3
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Aluminum Hydroxide 2
-
((aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel or 21645-51-2 or brasivil or rocgel or alugel or hydrated alumina or basalgel or dialume or nephrox)) 7
-
#6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 65
-
((primary near bile acid near (diarrhoe* or diarrhe* or diarrea*))) 0
-
((chronic or watery or recur* or persist* or protract* or continual* or continuous* or sustain* or constant* or relentless* or unrelent* or functional or aggressive) near (diarrhoe* or diarrhe* or diarrea*))) 55
-
((malabsorb* or mal-absorb* or malabsorp* or mal-absorp*)) 28
-
((BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or BSM)) 3
-
((bile or biliary) near (acid* or salt*)) 26
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Diarrhea EXPLODE ALL TREES 130
-
#14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 221
-
#5 OR #13 66
-
#20 AND #21 11
-
#22 IN DARE 9
-
#22 IN HTA 0
The DARE search retrieved nine records.
The HTA search retrieved no records.
Science Citation Index (SCI) (Web of Knowledge): 1970 to 18 April 2012
Searched 19 April 2012.
Databases=SCI-EXPANDED Timespan=All Years
Lemmatization=On
#21 892 #19 not #20
#20 3,083,864 TS=(cat or cats or dog or dogs or animal or animals or rat or rats or hamster or hamster or feline or ovine or canine or bovine or sheep or mice)
#19 1,350 #12 and #18
#18 50,168 #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17
#17 35,208 TS= ((bile or biliary) SAME (acid* or salt*))
#16 8,288 TS= (malabsorb* or mal-absorb* or malabsorp* or mal-absorp*)
#15 3,716 TS= ((chronic or watery or recur* or persist* or protracted or continual* or continuous* or sustain* or constant* or relentless* or unrelent* or functional or aggressive) SAME (diarrh?e* or diarrea*))
#14 23 TS= primary bile acid diarrh?ea*
#13 3,908 TS= (BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or BSM)
#12 26,883 #5 or #11
#11 24,843 #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10
#10 18,785 TS= (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel)
#9 227 TS= (Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7)
#8 2,201 TS= (colestyramine* or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine* or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid* or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran* or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0 or mk 135 or mk135)
#7 653 TS= (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6)
#6 3,444 TS= ((bile SAME (acid or salt) SAME sequestra*) or BAS)
#5 2,084 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4
#4 1,208 TS= (selenium SAME "75")
#3 48 TS= (23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid or 75Se-homotaurocholate)
#2 1,161 TS= (SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75)
#1 2 TS=(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2)
NIHR Health Technology Assessment (HTA) (internet): up to 19 April 2012
http://www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk
Searched 19 April 2012.
Browsed by relevant terms, found three references.
Search 3: scoping search alternative tests
Scoping search to identify background literature on this topic prior to NICE scoping meeting.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) (Wiley Online Library): Issue 10: 2011
Searched 27 October 2011
#1 (barium follow-through or barium follow through):ti,ab,kw 23
#2 (barium enema or lower gastrointestinal series or barium-examination):ti,ab,kw 257
#3 MeSH descriptor Barium Sulfate explode all trees 253
#4 (Barium-Sulfate or Barium Sulfate or alubar or anatrast or artificial-barite or artificial-heavy-spar or astrabaryt or bakontal or bar-test or baridol or bariform or barite or barium- compound-bas-16 or barium-sulfate-suspension or baro-cat or barolac or baropaque or barosperse or barotrast or barytcontrast or bear-e-yum-gi or blanc-fixe or citobaryum or colloidal-barium-sulfate or e-z-cat or e-z-em or e- z-em or eneset-2 or entero-h or esophotrast or ez-hd or ezem or falibaryt or fotogel or gelobarin or hd-85 or intestibar or kinetrast or microbar or microfanox-enema or micropaque or microtrast or mixobar or neobar or notopacol or nov-umbrose or oratrast or polibar or prontobario or pulvobarin or raybar or rayso or shadoform or skiabaryt or skiabaryum or steripaque* or stomagnost or synthetic-barytes or tixobar or tonojug or tonopaque or unibaryt):ti,ab,kw 314
#5 MeSH descriptor Sigmoidoscopy, this term only 269
#6 Sigmoidoscopy:ti,ab,kw 433
#7 MeSH descriptor Colonoscopy explode all trees 1194
#8 (Colonoscopy or colonscopy or coloscopy or fiber-colonoscopy):ti,ab,kw 1425
#9 99mTc-HMPAO:ti,ab,kw 39
#10 (#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9) 2102
The CDSR search retrieved 19 records.
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) (CRD): up to 27 October 2011
www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/
Searched 29 October 2011.
-
((barium follow-through or barium follow through)) 3
-
((barium enema or lower gastrointestinal series or barium-examination)) 51
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Sigmoidoscopy WITH QUALIFIER undefined 39
-
(Sigmoidoscopy) 120
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Colonoscopy EXPLODE ALL TREES WITH QUALIFIER undefined 148
-
(Colonoscopy or colonscopy or coloscopy or fiber-colonoscopy) 303
-
(99mTc-HMPAO) 1
-
#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 337
-
(#8) IN DARE FROM 2006 TO 2011 66
The DARE search retrieved 66 records.
Search 4: trials searches
SeHCAT or bile acid sequestrant
Original searches undertaken between 9 and 16 January 2012 retrieved 379 records. Update searches undertaken between 17 and 20 April 2012 found an additional 4 records (after deduplication), but no new includes.
Clinicaltrials.gov (internet)
http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/search/advanced
Searched 19 April 2012.
Advanced search option – search terms box:
| Search terms | Results |
|---|---|
| SeHCAT OR Se-HCAT OR 75SeHCAT OR Se-75 OR 75-SeHCAT OR SE75 | 0 |
| tauroselcholic OR selenohomocholyltaurine OR selenium homocholic acid taurine OR tauroselenocholic acid OR 75Se-homotaurocholate | 0 |
| (Colestipol OR cholestabyl OR cholestipol OR colestid OR flavored-colestid OR lestid OR u-26,597a OR u-26597-a OR u-26597a OR u-26,597a OR 25085-17-0 OR 37296-80-3 OR 50925-79-6) | 4 |
| (colestyramine OR chol-less OR choles OR cholesthexal OR cholestyramin OR cholestyramine OR cholybar OR cholytar OR colestepril OR colestiramina OR colestran OR colestrol OR colestyramin OR cuemid OR lipocol-merz OR questran) | 14 |
| (Colesevelam OR cholestagel OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR gt31-104 OR gt31-104hb OR gt31-104 OR gt31-104hb OR welchol OR 182815-43-6 OR 182815-44-7) | 35 |
| aluminum hydroxide OR Ageldrate OR al u creme OR alcid OR aldrox OR algeldraat OR algeldrate OR algelox OR alhydrogel OR alkagel OR alocol OR alokreem OR alterna gel OR alu cap OR hycolal OR hydracoll OR hydrated alumina OR hydrolum OR hydronal OR hydroxal OR lactalumina OR neutroxide | 123 |
| TOTAL | 176 |
mRCT – metaRegister of Current Controlled Trials (internet)
www.controlled-trials.com/
Searched 19 April 2012.
Advanced search option – search terms box:
| Search terms | Results |
|---|---|
| SeHCAT OR Se-HCAT | 1 |
| 75SeHCAT OR Se-75 | 0 |
| 75-SeHCAT OR SE75 | 0 |
| tauroselcholic OR selenohomocholyltaurine OR 75Se-homotaurocholate | 0 |
| selenium homocholic acid taurine | 0 |
| tauroselenocholic acid | 0 |
| (Colestipol OR cholestabyl OR cholestipol OR colestid OR flavored-colestid OR lestid ) AND (diarrhea* OR diarrhoea* OR diarrea* OR bile acid* OR bile salt* OR BAM) | 14 |
| (colestyramine OR cholesthexal OR cholestyramin OR cholestyramine OR cholybar OR colestepril OR colestiramina OR colestran OR colestrol OR colestyramin OR cuemid OR questran) AND (diarrhea* OR diarrhoea* OR diarrea* OR bile acid* OR bile salt* OR BAM) | 36 |
| (Colesevelam OR cholestagel OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR welchol OR 182815-43-6 OR 182815-44-7)AND (diarrhea* OR diarrhoea* OR diarrea* OR bile acid* OR bile salt* OR BAM) | 22 |
| (aluminum hydroxide OR Ageldrate OR al u creme OR alcid OR aldrox OR algeldraat OR algeldrate OR alu cap OR hycolal OR hydracoll OR hydrated alumina)AND (diarrhea* OR diarrhoea* OR diarrea* OR bile acid* OR bile salt* OR BAM) | 1 |
| TOTAL | 74 |
WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (internet)
www.who.int/ictrp/en/
Searched 20 April 2012.
Advanced search option – search terms box:
| Search terms | Results |
|---|---|
| SeHCAT OR Se-HCAT OR 75SeHCAT OR Se-75 OR 75-SeHCAT OR SE75 | 0 |
| tauroselcholic OR selenohomocholyltaurine OR selenium homocholic acid taurine OR tauroselenocholic acid OR 75Se-homotaurocholate | 0 |
| (Colestipol OR cholestabyl OR cholestipol OR colestid OR flavored-colestid OR lestid OR u-26,597a OR u-26597-a OR u-26597a OR u-26,597a OR 25085-17-0 OR 37296-80-3 OR 50925-79-6) | 4 |
| (colestyramine OR chol-less OR choles OR cholesthexal OR cholestyramin OR cholestyramine OR cholybar OR cholytar OR colestepril OR colestiramina OR colestran OR colestrol OR colestyramin OR cuemid OR lipocol-merz OR questran) | 3/13 |
| (Colesevelam OR cholestagel OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR gt31-104 OR gt31-104hb OR gt31-104 OR gt31-104hb OR welchol OR 182815-43-6 OR 182815-44-7) | 3/47 |
| aluminum hydroxide OR Ageldrate OR al u creme OR alcid OR aldrox OR algeldraat OR algeldrate OR algelox OR alhydrogel OR alkagel OR alocol OR alokreem OR alterna gel OR alu cap OR hycolal OR hydracoll OR hydrated alumina OR hydrolum OR hydronal OR hydroxal OR lactalumina OR neutroxide | 7/56 |
| TOTAL | 120 |
EU Clinical Trials Registry (EU CTR) (internet)
www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/
Searched 20 April 2012.
Advanced search option – search terms box:
| Search terms | Results |
|---|---|
| SeHCAT OR Se-HCAT OR 75SeHCAT OR Se-75 OR 75-SeHCAT OR SE75 | 2 |
| tauroselcholic OR selenohomocholyltaurine OR selenium homocholic acid taurine OR tauroselenocholic acid OR 75Se-homotaurocholate | 0 |
| (Colestipol OR cholestabyl OR cholestipol OR colestid OR flavored-colestid OR lestid OR u-26,597a OR u-26597-a OR u-26597a OR u-26,597a OR 25085-17-0 OR 37296-80-3 OR 50925-79-6) | 0 |
| (colestyramine OR chol-less OR choles OR cholesthexal OR cholestyramin OR cholestyramine OR cholybar OR cholytar OR colestepril OR colestiramina OR colestran OR colestrol OR colestyramin OR cuemid OR lipocol-merz OR questran) | 27 |
| (Colesevelam OR cholestagel OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR gt31-104 OR gt31-104hb OR gt31-104 OR gt31-104hb OR welchol OR 182815-43-6 OR 182815-44-7) | 3 |
| aluminum hydroxide OR Ageldrate OR al u creme OR alcid OR aldrox OR algeldraat OR algeldrate OR algelox OR alhydrogel OR alkagel OR alocol OR alokreem OR alterna gel OR alu cap OR hycolal OR hydracoll OR hydrated alumina OR hydrolum OR hydronal OR hydroxal OR lactalumina OR neutroxide | 0 |
| TOTAL | 32 |
Search 5: conference abstract searches
Online Learning in Gastroenterology (OLGa) (internet)
http://olga.uegf.org/portal/documents-explore.html#solr0
Searched 10 February 2012.
Documents search:
| Keyword | Results |
|---|---|
| "SeHCAT" | 5 |
| "Se-HCAT" | 5 (duplicates) |
| "75SeHCAT" | 0 |
| "75-SeHCAT" | 0 |
| TOTAL | 5 |
OLGa contains the following conferences:
-
Advances in Clinical Oesophageal Investigation Conference (ASCONA ESSENTIALS 2011)
-
Eighth Summer School of Gastroenterology (ASNEMGE-SS-PRAGUE2011)
-
GASTRO2009
-
18th United European Gastroenterology Week (UEGW2010)
-
19th United European Gastroenterology Week (UEGW2011).
British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) Annual Meetings (internet)
www.bsg.org.uk/education/meeting/index.html
Searched 10 February 2012.
| Terms | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeHCAT | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Se-HCAT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 75SeHCAT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 75-SeHCAT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 8 | |||
Conference Proceedings Citation Index: Science (CPCI-S) (Web of Knowledge): 1990 to 18 April 2012
Searched 19 April 2012.
#14 12 #12 or #13
#13 11 TS=(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or 75-SeHCAT)
#12 11 #5 and #11
#11 4,584 #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10
#10 2,975 TS= ((bile or biliary) SAME (acid* or salt*))
#9 564 TS= (malabsorb* or mal-absorb* or malabsorp* or mal-absorp*)
#8 243 TS= ((chronic or watery or recur* or persist* or protracted or continual* or continuous* or sustain* or constant* or relentless* or unrelent* or functional or aggressive) SAME (diarrh?e* or diarrea*))
#7 1 TS= primary bile acid diarrh?ea*
#6 894 TS= (BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or BSM)
#5 190 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4
#4 122 TS= (selenium SAME "75")
#3 5 TS= (23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid or 75Se-homotaurocholate)
#2 106 TS= (SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75)
#1 0 TS=(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2)
Cost-effectiveness search strategies
Search A: scoping search
Bile acid malabsorption + (prevalence/incidence) + other conditions
Scoping search to identify background literature on this topic prior to NICE Scoping meeting.
EMBASE (OvidSP): 1980 to week 43 2011
Searched 1 November 2011.
-
chronic diarrhea/ (2481)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protract$ or continual$ or continuous$ or sustain$ or constant$ or relentless$ or unrelent$) adj2 diarrh?e$).mp. (14,305)
-
or/1-2 (14,305)
-
(Irritable bowel syndrome or IBS or spastic colon).mp. [mp=title, abstract, subject headings, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword] (10,347)
-
inflammatory bowel disease/ (35,062)
-
(inflammat$ adj3 (bowel disease$ or intestinal or intestine)).mp. (33,511)
-
(inflammatory bowel disease or inflammatory enteropathy or granulomatous enteritis or acute hemorrhagic necrotizing enteritis or IBD).mp. (28,794)
-
or/5-7 (50,644)
-
Crohn disease/ (43,017)
-
((cleron or Crohn’s or Crohns) adj3 disease).mp. (31,200)
-
morbus crohn.mp. (1119)
-
((regional or regionalis) adj3 (enteritis or enterocolitis)).mp. (893)
-
or/9-12 (47,518)
-
ulcerative colitis/ (36,695)
-
((colitis or colorectitis or proctocolitis) adj3 (ulcerative or ulcerosa or mucosal or ulcerous)).mp. (40249)
-
or/14-15 (40,249)
-
Incidence/ (172,688)
-
Prevalence/ (266,293)
-
exp morbidity/ (154,454)
-
(morbidit$ or frequency or frequencies or occurrence$ or incidence$ or prevalence$ or number$ or times or rate or rates or episode$ or recurren$ or reoccur$ or re-occur$ or distributed or distribution$).mp. (5,600,176)
-
or/17-20 (5,600,176)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).mp. (1948)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.mp. (4)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).mp. (16,265)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).mp. (31,172)
-
bile acid/ (17,182)
-
or/25-26 (31,172)
-
24 and 27 (960)
-
22 or 23 or 28 (2870)
-
3 or 4 or 8 or 13 or 16 (121,285)
-
21 and 29 and 30 (98)
-
limit 31 to embase (87)
Search B: searches to inform model
Irritable bowel syndrome + cost/quality of life
The health economists requested a search to identify literature on health-related quality of life and cost-effectiveness for IBS. These searches were conducted to inform the model and were not intended to be exhaustive.
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED) (CRD) (internet): up to 18 November 2011
www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd
Searched: 18 November 2011.
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR irritable bowel syndrome EXPLODE ALL TREES IN NHSEED 5
-
((Irritable bowel syndrome* or IBS or IBS-D) ) IN NHSEED 21
-
(((spastic or irritable or spasm or unstable) NEAR colon)) IN NHSEED 0
-
((Colitis or colitides) NEAR (spastic or mucous or mucomembraneous or mucomembranous)) IN NHSEED 0
-
(colonospasm) IN NHSEED 0
-
#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 21
NHS EED search retrieved 21 records.
MEDLINE (OvidSP): 1948 to week 2 November 2011
Searched 21 November 2011.
-
Irritable bowel syndrome/ (3197)
-
(Irritable bowel syndrome$ or IBS or IBS-D).ti,ab,ot,hw. (7638)
-
((spastic or irritable or spasm or unstable) adj2 colon).ti,ab,ot,hw. (493)
-
((Colitis or colitides) adj2 (spastic or mucous or mucomembraneous or mucomembranous)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (30)
-
colonospasm.ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
or/1-5 (8061)
-
economics/ (26,484)
-
exp "costs and cost analysis"/ (161,477)
-
economics, dental/ (1888)
-
exp "economics, hospital"/ (17,725)
-
economics, medical/ (8761)
-
economics, nursing/ (3855)
-
economics, pharmaceutical/ (2303)
-
(economic$ or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic$).ti,ab. (351,771)
-
(expenditure$ not energy).ti,ab. (14,848)
-
(value adj1 money).ti,ab. (20)
-
budget$.ti,ab. (14,945)
-
or/7-17 (467,125)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj cost).ti,ab. (2391)
-
(metabolic adj cost).ti,ab. (629)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj expenditure).ti,ab. (13,784)
-
or/19-21 (16,171)
-
18 not 22 (463,461)
-
letter.pt. (732,976)
-
editorial.pt. (288,333)
-
historical article.pt. (284,321)
-
or/24-26 (1,292,390)
-
23 not 27 (438,432)
-
(sf36 or sf 36 or short form 36 or shortform 36).ti,ab. (11,834)
-
(sf thirtysix or sf thirty six or shortform thirtysix or shortform thirty six or short form thirty six or short form thirtysix or short form thirty six).ti,ab. (1)
-
(sf6 or sf 6 or short form 6 or shortform 6 or sf six or sfsix or shortform six or short form six).ti,ab. (879)
-
(euroqol or euro qol or eq5d or eq 5d).ti,ab. (2414)
-
(hql or hrql or hqol or h qol or hrqol or hr qol).ti,ab. (7060)
-
(hye or hyes).ti,ab. (50)
-
health$ year$ equivalent$.ti,ab. (36)
-
(hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3 or hui4 or hui-4 or hui-1 or hui-2 or hui-3).ti,ab. (677)
-
(quality of well being or quality of wellbeing or qwb).ti,ab. (306)
-
(Disability adjusted life year$ or Disability-adjusted life year$ or health adjusted life year$ or health-adjusted life year$ or years of healthy life or healthy years equivalent or years of potential life lost or years of health life lost or quality adjusted life year$).ti,ab. (5185)
-
(QALY$ or HRQOL or HRQL or DALY$ or HALY$ or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL).ti,ab. (11,277)
-
(Irritable Bowel Syndrome adj Quality Of Life).ti,ab,ot,hw. (26)
-
(Quality of Life Questionnaire for Functional Digestive Disorders or Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale).ti,ab,ot,hw. (165)
-
(FDDQL or GSRS-self or GSRS or IBS-36 or IBS-QOL).ti,ab,ot,hw. (245)
-
or/29-42 (26,151)
-
28 or 43 (457,578)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (3,623,263)
-
44 not 45 (431,745)
-
6 and 46 (475)
-
(2000$ or 2001$ or 2002$ or 2003$ or 2004$ or 2005$ or 2006$ or 2007$ or 2008$ or 2009$ or 2010$ or 2011$).ed. (8,439,370)
-
47 and 48 (410)
Economics filter
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. NHS EED Economics Filter: Medline (Ovid) monthly search. York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2010 (cited 28 September 2010). URL: www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/intertasc/nhs_eed_strategies.html.
Patient-Reported Outcome and Quality of Life Instruments Database (PROQOLID)
www.proqolid.org
Searched 21 November 2011.
Browsed for relevant QoL instruments to inform MEDLINE search.
Search C: guidelines
(IBS or Crohn’s or BAM or chronic diarrhoea or SeHCAT)
International Guidelines Library (GIN) (internet): up to 28 November 2011
www.g-i-n.net
Searched 28 November 2011.
| Terms searched | Hits |
|---|---|
| Free-text: Irritable bowel syndrome* or IBS or IBS-D or spastic colon | 7 |
| Free-text: BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or Bile acid malabsorption | 0 |
| Bile and acid* | 0 |
| Free-text: SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75 | 0 |
| Free-text: Crohn* disease | 10 |
| Free-text: chronic diarrhea* or chronic diarrhoea* or functional diarrhea* or functional diarrhoea* | 0 |
| Free-text: diarrhea* or diarrhoea* | 14 |
| Total (prior to deduplication) | 31 |
Update search undertaken 1 May 2012; no new relevant references were retrieved.
National Guidelines Clearinghouse (internet): up to 28 November 2011
www.guideline.gov
Searched 28 November 2011.
Advanced search:
| Terms searched | Hits |
|---|---|
| Irritable bowel syndrome* or IBS or IBS-D or spastic colon | 23 |
| BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or Bile acid malabsorption | 2 |
| SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75 | 0 |
| Crohn* disease | 48 |
| “chronic diarrhea” or “chronic diarrhoea” or “functional diarrhea” or “functional diarrhoea*” | 11 |
| Total (prior to deduplication) | 84 |
Update search undertaken 1 May 2012, no new relevant references were retrieved.
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) Guidance (internet): up to 2012/05/01
http://guidance.nice.org.uk/
Searched 1 May 2012.
Advanced search:
| Terms searched | Hits |
|---|---|
| Irritable bowel syndrome OR IBS OR IBS-D | 13/52 |
| BAM OR I-BAM OR IBAM OR PBAM OR Bile acid malabsorption | 1 |
| SeHCAT OR Se-HCAT OR 75SeHCAT OR Se-75 OR 75-SeHCAT OR SE75 | 1 |
| Crohn disease OR crohns disease OR crohn’s disease | 26/69 |
| chronic diarrhea OR chronic diarrhoea OR functional diarrhea OR functional diarrhoea | 12/55 |
| Total | 53/178 |
Original search undertaken 28 November 2011 retrieved 31/146 results. An issue with the search interface resulted in only being able to search for single terms, at the time of the update search (see above) this had been rectified. An additional 22 references were retrieved, but no new includes were identified.
Turning Research into Practice (TRIP database) (internet): up to 2011/12/08
http://www.tripdatabase.com/
Searched 9 December 2011.
Limited to guidelines only.
| Terms searched | Hits |
|---|---|
| “Irritable bowel syndrome” or “Irritable bowel syndromes” or IBS or IBS-D or “spastic colon” | 74 |
| BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM or “Bile acid malabsorption” | 7 |
| SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75 | 4 |
| Crohns disease OR Crohn disease | 94 |
| "chronic diarrhea" or "chronic diarrhoea" or "functional diarrhea" or "functional diarrhoea" | 29 |
| Total (prior to deduplication) | 208 |
Update search undertaken 1.5.12, Total 0/212 no new relevant references were retrieved.
Health Technology Assessment Database (HTA) (internet): up to 28 November 2011
www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd
Searched 28 November 2011.
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Irritable bowel syndrome IN HTA 2
-
((Irritable bowel syndrome* or IBS or IBS-D or spastic colon)) IN HTA 12
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM ) IN HTA 0
-
((Bile near acid*) OR (Biliary near acid*) OR (Bile near salt*) OR (Biliary near salt*)) IN HTA 3
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Crohn disease IN HTA 25
-
((Crohn* near disease)) IN HTA 43
-
(((chronic near diarrhoea*) or (chronic near diarrhea*))) IN HTA 2
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR diarrhea IN HTA 8
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75) IN HTA 0
-
#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 64
Update search undertaken 2 May 2012; no new relevant references were retrieved.
HTA search retrieved 64 records.
NIHR Health Technology Assessment (HTA) (internet): up to 9 December 2011
www.hta.ac.uk
Searched 9 December 2011.
Browsed by relevant terms found three references.
Update search undertaken 2 May 2012; no new relevant references were retrieved.
Search D: cost-effectiveness
(SeHCAT or bile acid sequestrant/aluminium hydroxide or bile acid malabsorption) + cost
MEDLINE search: Facet 1 combined terms for SeHCAT (lines #1–5) and Bile Acid Sequestrants (lines #6–11) and BAM (lines #12–19) using OR in line #20 (n = 13,148). Facet 2 contained an economics filter and was limited to remove animal studies (lines #21–44). Facet 2 was then combined with facet 1 using AND in line #45 (n = 209). For the full strategy please see below.
MEDLINE (OvidSP): 1946 to week 1 January 2012
Searched 16 January 2012.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (273)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (317)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").ti,ab,ot,hw. (144)
-
or/1-4 (636)
-
((bile adj3 acid adj3 sequestra$) or BAS).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2524)
-
Colestipol/ or (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (503)
-
Cholestyramine Resin/ or (colestyramine$ or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine$ or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid$ or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran$ or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0 or mk 135 or mk135).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (3217)
-
(Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (152)
-
Aluminum Hydroxide/ or (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (4308)
-
or/6-10 (10226)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1659)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (3)
-
"Bile Acids and Salts"/ (17,977)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (27,677)
-
14 or 15 (27,677)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (13,415)
-
16 and 17 (852)
-
12 or 13 or 18 (2487)
-
5 or 11 or 19 (13,148)
-
economics/ (26,137)
-
exp "costs and cost analysis"/ (160,072)
-
economics, dental/ (1833)
-
exp "economics, hospital"/ (17,561)
-
economics, medical/ (8422)
-
economics, nursing/ (3852)
-
economics, pharmaceutical/ (2278)
-
(economic$ or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic$).ti,ab. (347,246)
-
(expenditure$ not energy).ti,ab. (14,604)
-
(value adj1 money).ti,ab. (17)
-
budget$.ti,ab. (14,875)
-
or/21-31 (461,486)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj cost).ti,ab. (2356)
-
(metabolic adj cost).ti,ab. (618)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj expenditure).ti,ab. (13,458)
-
or/33-35 (15,805)
-
32 not 36 (457,877)
-
letter.pt. (727,126)
-
editorial.pt. (286,075)
-
historical article.pt. (278,564)
-
or/38-40 (1,278,705)
-
37 not 41 (433,012)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (3,550,250)
-
42 not 43 (407,938)
-
20 and 44 (209)
Economics filter
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. NHS EED Economics Filter: Medline (Ovid) monthly search. York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2010 (cited 28.9.10). URL: www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/intertasc/nhs_eed_strategies.html.
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations (OvidSP): up to 13 January 2012
MEDLINE Daily Update (OvidSP): up to 13 January 2012
Searched 16 January 2012.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (1)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (5)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (0)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").ti,ab,ot,hw. (2)
-
or/1-4 (6)
-
((bile adj3 acid adj3 sequestra$) or BAS).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (154)
-
Colestipol/ or (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (3)
-
Cholestyramine Resin/ or (colestyramine$ or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine$ or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid$ or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran$ or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0 or mk 135 or mk135).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (28)
-
(Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (17)
-
Aluminum Hydroxide/ or (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (146)
-
or/6-10 (332)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).ti,ab,ot,hw. (204)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (1)
-
"Bile Acids and Salts"/ (7)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (601)
-
14 or 15 (601)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (247)
-
16 and 17 (8)
-
12 or 13 or 18 (211)
-
5 or 11 or 19 (542)
-
economics/ (0)
-
exp "costs and cost analysis"/ (134)
-
economics, dental/ (0)
-
exp "economics, hospital"/ (13)
-
economics, medical/ (0)
-
economics, nursing/ (1)
-
economics, pharmaceutical/ (1)
-
(economic$ or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic$).ti,ab. (26398)
-
(expenditure$ not energy).ti,ab. (746)
-
(value adj1 money).ti,ab. (3)
-
budget$.ti,ab. (1394)
-
or/21-31 (27873)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj cost).ti,ab. (146)
-
(metabolic adj cost).ti,ab. (40)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj expenditure).ti,ab. (614)
-
or/33-35 (783)
-
32 not 36 (27,665)
-
letter.pt. (17,895)
-
editorial.pt. (11,256)
-
historical article.pt. (107)
-
or/38-40 (29,247)
-
37 not 41 (27,328)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (1960)
-
42 not 43 (27,296)
-
20 and 44 (17)
Economics filter
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. NHS EED Economics Filter: Medline (Ovid) monthly search. York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2010 (cited 28 September 2010). URL: www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/intertasc/nhs_eed_strategies.html.
EMBASE (OvidSP): 1980 to week 2 2012
Searched 16 January 2012.
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).mp. (154)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75).mp. (769)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid).mp. (19)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").mp. (485)
-
or/1-4 (1154)
-
bile acid sequestrant/ (651)
-
((bile adj3 acid adj3 sequestra$) or BAS).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (16,068)
-
Colestipol/ or (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2501)
-
Colestyramine/ or (colestyramine or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (9054)
-
Colesevelam/ or (Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (715)
-
aluminum hydroxide/ or (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel or 21645-51-2 or brasivil or rocgel or alugel or hydrated alumina or basalgel or dialume or nephrox).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (7448)
-
or/6-11 (32,909)
-
5 or 12 (33,993)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).mp. (1964)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.mp. (5)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).mp. (16,434)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).mp. (31,558)
-
bile acid/ or bile salt/ (20,540)
-
or/17-18 (31,558)
-
16 and 19 (968)
-
14 or 15 or 20 (2893)
-
5 or 12 or 21 (36,610)
-
health-economics/ (30,837)
-
exp economic-evaluation/ (176,160)
-
exp health-care-cost/ (168,886)
-
exp pharmacoeconomics/ (142,771)
-
or/23-26 (402,578)
-
(econom$ or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic$).ti,ab. (460,397)
-
(expenditure$ not energy).ti,ab. (18,296)
-
(value adj2 money).ti,ab. (1018)
-
budget$.ti,ab. (19,324)
-
or/28-31 (479,792)
-
27 or 32 (716,473)
-
letter.pt. (752,514)
-
editorial.pt. (389,343)
-
note.pt. (462,400)
-
or/34-36 (1,604,257)
-
33 not 37 (642,745)
-
(metabolic adj cost).ti,ab. (679)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj cost).ti,ab. (2622)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj expenditure).ti,ab. (15,921)
-
or/39-41 (18,536)
-
38 not 42 (638,607)
-
exp animal/ (1,665,824)
-
exp animal-experiment/ (1,486,602)
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or murine or rodent or rodents or hamster or hamsters or pig or pigs or porcine or rabbit or rabbits or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or cow or bovine or sheep or ovine or monkey or monkeys).mp. (4,860,767)
-
or/44-46 (4,861,129)
-
exp human/ (12,846,204)
-
exp human-experiment/ (296,685)
-
or/48-49 (12,847,588)
-
47 not (47 and 50) (3,891,410)
-
43 not 51 (610,079)
-
22 and 52 (1164)
-
limit 53 to embase (1102)
Economics filter
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. NHS EED Economics Filter: Embase (Ovid) weekly search. York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2010 (cited 17 March 2011). URL: www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/intertasc/nhs_eed_strategies.html.
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED) (CRD) (internet): up to 16 January 2012
www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd
Searched 16 January 2012.
-
((tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2)) 0
-
((SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75)) 0
-
((23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid)) 0
-
((selenium near "75")) 1
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 1
-
(((bile near acid near sequestra*) or BAS) ) 18
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Colestipol EXPLODE ALL TREES 3
-
((Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6)) 21
-
((colestyramine or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0)) 32
-
((Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7)) 3
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Aluminum Hydroxide EXPLODE ALL TREES 2
-
((aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel or 21645-51-2 or brasivil or rocgel or alugel or hydrated alumina or basalgel or dialume or nephrox)) 7
-
#6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 65
-
(primary near bile acid near (diarrhoe* or diarrhe* or diarrea*)) 0
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM)) 0
-
((bile or biliary) near (acid* or salt*)) 26
-
((malabsorb* or mal-absorb* or malabsorp* or mal-absorp*)) 28
-
#14 or #15 or #16 or #17 54
-
#5 or #13 or #18 111
-
#19 and NHS EED 19
NHS EED search retrieved 19 records.
Health Economics Evaluation Database (HEED) (internet): up to 6 March 2012
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/book/10.1002/9780470510933
Searched 6 March 2012.
Compound search, (all data), unable to limit by date:
tauroselcholic OR selenohomocholyltaurine OR 75018-71-2
OR
SeHCAT OR Se-HCAT OR 75SeHCAT OR Se-75 OR 75-SeHCAT OR SE75
OR
23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid OR selenium homocholic acid taurine OR 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine OR 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate OR 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid OR selenium radioisotopes OR tauroselenocholic acid OR 75Se-homotaurocholate
OR
bile acid sequestrant OR bile acid sequestrants OR BAS
OR
Colestipol OR cholestabyl OR cholestipol OR colestid OR flavored-colestid OR lestid OR u-26,597a OR u-26597-a OR u-26597a OR u-26,597a OR 25085-17-0 OR 37296-80-3 OR 50925-79-6
OR
colestyramine OR chol-less OR choles OR cholesthexal OR cholestyramin OR cholestyramine OR cholybar OR cholytar OR colestepril OR colestiramina OR colestran OR colestrol OR colestyramin OR cuemid OR lipocol-merz OR questran
OR
Colesevelam OR cholestagel OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR gt-31-104 OR gt-31-104hb OR gt31-104 OR gt31-104hb OR gt31-104 OR gt31-104hb OR welchol OR 182815-43-6 OR 182815-44-7
OR
aluminum hydroxide OR Ageldrate OR alcid OR aldrox OR algeldraat OR algeldrate OR algelox OR alhydrogel OR alkagel OR alocol OR alokreem OR alterna gel OR alu cap OR hycolal OR hydracoll OR hydrated alumina OR hydrolum OR hydronal OR hydroxal OR lactalumina OR neutroxide
OR
BAM OR I-BAM OR IBAM OR PBAM OR BSM
OR
Bile acid OR bile salt OR Bile acids OR bile salts
Heed search retrieved 85 records.
Science Citation Index (Web of Science): 1970 to 12 January 2012
Searched 17 January 2012.
Databases=SCI-EXPANDED Timespan=All Years
Lemmatization=On
#31 65 #19 and #30
#30 617,715 #24 not #29
#29 2,436,639 #25 or #26 or #27 or #28
#28 2,376,074 TS=(cat or cats or dog or dogs or animal or animals or rat or rats or hamster or hamster or feline or ovine or canine or bovine or sheep)
#27 22,447 TS=((energy or oxygen) SAME expenditure)
#26 6,234 TS=(metabolic SAME cost)
#25 44,234 TS=((energy or oxygen) SAME cost)
#24 691,819 #20 or #21 or #22 or #23
#23 44,677 TS=(budget*)
#22 798 TS=(value NEAR/1 money)
#21 13,786 TS=(expenditure* not energy)
#20 648,500 TS=(economic* or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic*)
#19 5,706 #5 or #17 or #18
#18 99 #11 and #17
#17 3,756 #12 or #13 or #16
#16 684 #14 and #15
#15 34,726 TS= ((bile or biliary) SAME (acid* or salt*))
#14 8,188 TS= (malabsorb* or mal-absorb* or malabsorp* or mal-absorp*)
#13 23 TS= primary bile acid diarrh?ea*
#12 3,094 TS= (BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM)
#11 24,351 #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10
#10 18,388 TS= (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel)
#9 215 TS= (Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7)
#8 2,190 TS= (colestyramine* or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine* or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid* or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran* or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0 or mk 135 or mk135)
#7 652 TS= (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6)
#6 3,356 TS= ((bile SAME acid SAME sequestra*) or BAS)
#5 2,055 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4
#4 1,185 TS= (selenium SAME "75")
#3 47 TS= (23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid)
#2 1,156 TS= (SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75)
#1 2 TS=(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2)
EconLit (EBSCOhost) 1886 to 3 February 2012
Searched 3 February 2012.
Search modes – Boolean/Phrase:
S17 S5 or S11 or S16 (22)
S16 S12 or S13 or S14 or S1 (19)
S15 TX(malabsorb* or mal-absorb* or malabsorp* or mal-absorp*) (0)
S14 (bile N4 acid*) or (biliary N4 acid*) or (bile N4 salt*) (0)
S13 TX(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM) (19)
S12 TX(primary N4 bile acid N4 diarrhoe*) or (primary N4 bile acid N4 diarrhe*) or (primary N4 bile acid N4 diarrea*) (0)
S11 S6 or S7 or S8 or S9 or S10 (3)
S10 TX(“aluminum hydroxide” or Ageldrate or “al u crème” or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or “alterna gel” or “alu cap” or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or “alumina gel” or “alumina trihydrate” or “aluminium hydroxide” or aluminoid or aluminox or “aluminum hydrate” or “aluminum hydroxide gel” or “aluminum oxide trihydrate” or “aluminum trihydrate” or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel or 21645-51-2 or brasivil or rocgel or alugel or hydrated alumina or basalgel or dialume or nephrox) (0)
S9 TX(colestyramine or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0) (3)
S8 TX(Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7) (0)
S7 TX(Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6)(0)
S6 TX(bile N4 acid N4 sequestra*) (0)
S5 S1 or S2 or S3 or S4 (0)
S4 TX(selenium N4 "75") (0)
S3 TX(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid or 75Se-homotaurocholate ) (0)
S2 TX(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75) (0)
S1 TX(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2) (0)
Subset search of clinical effectiveness EndNote Library
Searched 31 January 2012.
An EndNote Library containing 4010 references, identified by the search undertaken for the evidence of effectiveness review, was searched to identify potentially relevant cost/economic studies. After deduplication 121 records were identified.
The following terms were entered line by line (_indicates a space):
#1 _cost_ (46)
#2 _costs_ (39)
#3 _cost-_ (0)
#4 _costly (8)
#5 _costing (0)
#6 _econom (40)
#7 _budget (2)
#8 _price (6)
#9 _pricing (2)
#10 _expenditure (27)
#11 value for money. (0)
Total of 121 references were retrieved and scanned for relevance.
Search E: searches to inform model
Crohn’s + cost/quality of life
The health economists requested a search to identify literature on health-related quality of life and cost-effectiveness for Crohn’s disease. These searches were conducted to inform the model and were not intended to be exhaustive.
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED) (CRD) (internet): up to 6 January 2012
www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd
Searched 6 January 2012.
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR crohn disease EXPLODE ALL TREES IN NHSEED 22
-
(((cleron or Crohn*) NEAR disease)) IN NHSEED 40
-
(morbus crohn) IN NHSEED 0
-
(((regional or regionalis or granulomatous) NEAR (enteritis or enterocolitis))) IN NHSEED 0
-
(Ileocolitis) IN NHSEED 0
-
((ileitis NEAR (terminal or regional))) IN NHSEED 0
-
(colitis granulomatous) IN NHSEED 0
-
#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 40
NHS EED search retrieved 40 records.
MEDLINE (OvidSP): 1946 to week 3 January 2012
Searched 27 January 2012.
-
Crohn Disease/ (26,810)
-
((cleron or Crohn$) adj3 disease).ti,ab,ot,hw. (32,722)
-
morbus crohn.ti,ab,ot,hw. (769)
-
((regional or regionalis or granulomatous) adj3 (enteritis or enterocolitis)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (997)
-
Ileocolitis.ti,ab,ot,hw. (344)
-
(ileitis adj3 (terminal or regional)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (536)
-
colitis granulomatous.ti,ab,ot,hw. (6)
-
or/1-7 (33,051)
-
economics/ (26,139)
-
exp "costs and cost analysis"/ (160,362)
-
economics, dental/ (1833)
-
exp "economics, hospital"/ (17,587)
-
economics, medical/ (8423)
-
economics, nursing/ (3853)
-
economics, pharmaceutical/ (2280)
-
(economic$ or cost or costs or costly or costing or price or prices or pricing or pharmacoeconomic$).ti,ab. (348,214)
-
(expenditure$ not energy).ti,ab. (14,640)
-
(value adj1 money).ti,ab. (17)
-
budget$.ti,ab. (14,893)
-
or/9-19 (462,563)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj cost).ti,ab. (2360)
-
(metabolic adj cost).ti,ab. (623)
-
((energy or oxygen) adj expenditure).ti,ab. (13491)
-
or/21-23 (15,846)
-
20 not 24 (45,8945)
-
letter.pt. (728,276)
-
editorial.pt. (286,848)
-
historical article.pt. (278,816)
-
or/26-28 (1,280,851)
-
25 not 29 (434,045)
-
(sf36 or sf 36 or short form 36 or shortform 36).ti,ab. (11,765)
-
(sf thirtysix or sf thirty six or shortform thirtysix or shortform thirty six or short form thirty six or short form thirtysix or short form thirty six).ti,ab. (1)
-
(sf6 or sf 6 or short form 6 or shortform 6 or sf six or sfsix or shortform six or short form six).ti,ab. (868)
-
(euroqol or euro qol or eq5d or eq 5d).ti,ab. (2454)
-
(hql or hrql or hqol or h qol or hrqol or hr qol).ti,ab. (6944)
-
(hye or hyes).ti,ab. (50)
-
health$ year$ equivalent$.ti,ab. (36)
-
(hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3 or hui4 or hui-4 or hui-1 or hui-2 or hui-3).ti,ab. (668)
-
(quality of well being or quality of wellbeing or qwb).ti,ab. (303)
-
(Disability adjusted life year$ or Disability-adjusted life year$ or health adjusted life year$ or health-adjusted life year$ or years of healthy life or healthy years equivalent or years of potential life lost or years of health life lost or quality adjusted life year$).ti,ab. (5122)
-
(QALY$ or HRQOL or HRQL or DALY$ or HALY$ or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL).ti,ab. (11,115)
-
(Crohn$ adj3 Quality Of Life).ti,ab,ot,hw. (24)
-
(Gastrointestinal Quality of Life index or Digestive Health Status Instrument).ti,ab,ot,hw. (194)
-
(GIQLI or DHSI).ti,ab,ot,hw. (165)
-
or/31-44 (25,863)
-
30 or 45 (453,004)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (3,554,274)
-
46 not 47 (427,393)
-
8 and 48 (587)
-
(2000$ or 2001$ or 2002$ or 2003$ or 2004$ or 2005$ or 2006$ or 2007$ or 2008$ or 2009$ or 2010$ or 2011$ or 2012$).ed. (8,244,633)
-
49 and 50 (472)
Economics filter:
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. NHS EED Economics Filter: Medline (Ovid) monthly search. York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2010 (cited 28 September 2010). URL: http://www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/intertasc/nhs_eed_strategies.html.
Patient-Reported Outcome and Quality of Life Instruments Database (PROQOLID)
www.proqolid.org
Searched 27 January 2012.
Browsed for relevant quality of life instruments to inform MEDLINE search.
Search F: utilities
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Registry (CEA) (internet): up to 6 February 2012
https://research.tufts-nemc.org/cear4/Home.aspx
Searched 6 February 2012.
| Terms searched | Utility weights |
|---|---|
| #1 Irritable bowel syndrome | 13 |
| #2 IBS | 64 |
| #3 BAM | 0 |
| #4 Bile acid malabsorption | 0 |
| #5 Crohn | 69 |
| #6 diarrhea | 29 |
| #7 diarrhoea | 18 |
| Total | 193 |
Appendix 2 Quality assessment checklists
Appendix 2a: Study specific guide to completion of QUADAS-2
The version of QUADAS-2 used in this assesses only applicability for the ‘patient selection’ domain, as it was considered that the inclusion criteria matched the review question for the ‘index test’ and ‘reference standard’ domains. All risk of bias domains are included.
Before starting the risk of bias assessment, we considered the relevance of each signalling question to our review, as well as the potential need for additional questions. Further criteria were then defined, as needed, to ensure consistent application of signalling questions and to help in the judgement of the risk of bias. Many signalling questions were not further specified and the answer was judged to be ‘yes’ if it was clearly reported in the study. If the answer to a signalling question was not clearly reported the question was judged as ‘unclear’ unless specified differently. ‘No’ was answered if it was clear from the reporting that an aspect was not fulfilled. Details of the assessment criteria used are reported below.
Domain 1: patient selection
Risk of bias
Question 1: Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled?
-
‘Yes’ → low risk of bias.
-
‘Unclear’ → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ → high risk of bias.
Question 2: Was a case–control design avoided?
-
‘Yes’ → low risk of bias.
-
‘Unclear’ → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ → high risk of bias.
Question 3: Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions?
-
‘Yes’ or < 10% of patients excluded → low risk of bias.
-
‘Unclear’ → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ or ≥ 10% of patients excluded → high risk of bias.
Concerns regarding applicability
-
If ≥ 90% of included patients were people with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease → low concern.
-
If ≥ 90% of included patients were people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (before resection of terminal ileum) → low concern.
-
If ≤ 90% included patients were people with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause or people with Crohn’s disease with chronic diarrhoea with known cause or with unknown cause after resection of terminal ileum → high concern.
Domain 2: index test
Risk of bias
Question 1: Were the index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard?
Question 2: Did the study pre-specify the threshold for a positive result?
The same criteria applied to each of the two signalling questions:
-
‘Yes’ → low risk of bias.
-
‘Unclear’ → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ → high risk of bias.
Domain 3: reference standard
Risk of bias
Question 1: Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition?
-
‘Yes’ if ≥ 90% of test results were confirmed using the reference standard (response to treatment, where response is defined as no symptoms of diarrhoea) → low risk of bias.
-
‘Unclear’ → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ if < 90% of test results were confirmed using the reference standard (response to treatment, where response is defined as no symptoms of diarrhoea) → high risk of bias.
Question 2: Were the reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test?
-
‘Yes’ → low risk of bias.
-
‘Unclear’ → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ → high risk of bias.
Domain 4: flow and timing
Question 1: Was response to treatment assessed over an adequate period?
Follow-up had to be ≥ 6 months in order to be judged as ‘adequate’.
-
‘No’ but for < 10% of patients or ‘Yes’ → low risk of bias.
-
The answer was judged to be ‘unclear’ if the follow-up period was not reported or if it was unclear what proportion of patients had an inadequate follow-up → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ for ≥ 10% of patients → high risk of bias.
Question 2: Did all patients receive a reference standard?
-
‘No’ but for < 10% of patients or ‘Yes’ → low risk of bias.
-
‘Unclear’ → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ for ≥ 10% of patients → high risk of bias.
Question 3: Were all patients included in the analysis?
-
‘No’ but for < 10% of patients or ‘Yes’ → low risk of bias.
-
‘Unclear’ → unclear risk of bias.
-
‘No’ for ≥ 10% of patients → high risk of bias.
The following criteria were used to reach a per-domain judgement of risk of bias:
-
If at least one of the signalling questions of a domain had an answer associated with a high risk of bias the domain was judged to have a high risk of bias.
-
If the answer to any of the signalling questions was ‘unclear’ and the answers to the remaining questions were ‘yes’, the risk of bias was judged to be unclear.
-
The answer to all the signalling questions had to be ‘yes’ in order for the domain to be judged as having a low risk of bias.
Appendix 2b: Checklists for the methodological quality assessment of included effectiveness studies
A. Case–control studies
-
Is the case definition explicit?
-
Has the disease state of the cases been reliably assessed and validated?
-
Were the controls randomly selected from the source of population of the cases?
-
Were interventions and other exposures assessed in the same way for cases and controls?
-
How was the response rate defined?
-
Were the non-response rates and reasons for non-response the same in both groups?
-
Is it possible that overmatching has occurred in that cases and controls were matched on factors related to exposure?
-
Was an appropriate statistical analysis used (matched or unmatched)?
B. Cohort studies
-
Is there sufficient description of the groups and the distribution of prognostic factors?
-
Are the groups assembled at a similar point in their disease progression?
-
Is the intervention/treatment reliably ascertained?
-
Were the groups comparable on all important confounding factors?
-
Was there adequate adjustment for the effects of these confounding variables?
-
Was a dose–response relationship between intervention and outcome demonstrated?
-
Was outcome assessment blind to exposure status?
-
Was follow-up long enough for the outcomes to occur?
-
What proportion of the cohort was followed-up?
-
Were drop-out rates and reasons for drop-out similar across intervention and unexposed groups?
C. Other observational studies
-
Does the study have a retrospective ‘R’ or prospective ‘P’ study design? (R/P/Unclear)
-
Has a clear definition of diarrhoea in the presenting population been given or a validated tool for assessing chronic diarrhoea been used? (Y/N)
-
Does the population include people with known causes of chronic diarrhoea? (Y/N/Unclear)
-
Has an adequate description of the SeHCAT test procedures been provided? (Y/N)
-
Are the cut-off values used for establishing severity of BAM clearly reported? (Y/N)
-
Are the reasons for treating people clearly described (e.g. ‘all with a positive test’)? (Y/N)
-
Are data provided for people with a negative SeHCAT test (> 15%)? (Y-all/Y-some/N)
-
Is the treatment clearly described, including dose and duration of treatment and follow-up? (Y/N)
-
Has an objective measure of response to treatment been provided? (Y/N)
Appendix 3 Quality assessment: QUADAS-2 results
Completed QUADAS-2 assessments for all included studies.
Study ID: Merrick 198539
Domain 1: patient selection
A. Risk of bias
B. Concerns regarding applicability
Domain 2: index test
A. Risk of bias
Domain 3: reference standard
A. Risk of bias
Domain 4: flow and timing
A. Risk of bias
Study ID: Sciaretta 198642
Domain 1: patient selection
A. Risk of bias
B. Concerns regarding applicability
Domain 2: index test
A. Risk of bias
Domain 3: reference standard
A. Risk of bias
Domain 4: flow and timing
A. Risk of bias
Study ID: Sciaretta 198743
Domain 1: patient selection
A. Risk of bias
B. Concerns regarding applicability
Domain 2: index test
A. Risk of bias
Domain 3: reference standard
A. Risk of bias
Domain 4: flow and timing
A. Risk of bias
Appendix 4 Data extraction tables
Details of the methods and interpretation of the index test (assessed technology) and reference standard used in included studies.
| Study ID | SeHCAT details | Comparator details | Treatment details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede 201133 | SeHCAT Administrated after an overnight fast as an oral capsule (GE Healthcare, UK) containing 0.37 MBq. Basal activity was measured over the abdomen 3 hours after swallowing the capsule using a high-resolution collimator. The measurement was repeated after 7 days and a fraction was calculated by dividing the 7-day activity by the basal activity. Retention <15% was considered abnormal. No further details 7-day retention; cut-off: 5%, 10% and 15% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: NR Response: ‘positive effect on their bowel habits’. Response to treatment was defined as a lowered frequency of stools per day and/or a firmer consistency. A normal bowel habit was defined as one to two formed stools per day Follow-up: no details reported Duration of treatment: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: In 21/171 treatment was stopped due to AEs. No alternative treatment Alternative treatment due to non-response: 63/171 did not respond. No alternative treatment |
|
| Dyson 201131 (abstract only) | SeHCAT No details reported Background section states: SeHCAT is a nuclear medicine test to assess the enterohepatic circulation of bile salts. Patients swallow the SeHCAT-containing tablet and undergo a baseline scan and repeat scan at 7 days. Less than 15% retention of SeHCAT signifies BSM and likely response to treatment with bile salt sequestrants 7-day retention; cut-off: 15% |
Treatment: cholestyramine or colesevelam Dose: cholestyramine, one sachet alternate days to four per day; colesevelam, one tablet as needed to six tablets daily Response: ‘symptoms unchanged’, ‘symptoms improved’ or ‘no longer have diarrhoea’ Follow-up: no details reported Duration of treatment: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR [four stopped treatment due to AEs; eight unable to tolerate cholestyramine, three stopped taking colesevelam (one due to rash)] Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Eusufzai 199334 | SeHCAT A capsule of SeHCAT (10 µCi, Amersham International) was given with a drink of water, using the technique described by Thaysen 198289 and Delhez et al. 1982.90 The initial count rate (100% value) was measured 3 hours after the intake of isotope (day 0), with an uncollimated gamma camera (Porta Camera, General Electric Nuclear Medical ApS, Denmark). The gamma camera crystal was centred over the middle of the xiphoidoumbilical line. The count rate in a 25% window centred between the 265- and 280-keV photon peaks of 75Se was measured. The measurements were repeated on days 2, 4 and 7 after the administration of the capsule. The counts were plotted in a logarithmic–linear graph. The t½ – that is the time when the abdominal retention of the SeHCAT was reduced to 50% of initial – was calculated from the curve, as well as the fractional catabolic rate defined as ln(2/T½). In addition, the 7-day retention was calculated from the curve 7-day retention; cut-off: 10% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: starting dose 2 g b.i.d., before breakfast and supper. If no effect, gradual increase to 4 g t.i.d. before meals Response: ‘Frequency of diarrhoea decreased with more formed stools’ Follow up: no details reported Duration of treatment: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Eusufzai 199335 | SeHCAT On the morning of the SeHCAT test the patients had been fasting overnight. A capsule of SeHCAT (10 µCi, Amersham International) was given orally with a drink of water and the initial count rate (100% value) was measured 3 hours after intake of isotope (day 0), by an uncollimated gamma camera (Porta Camera, General Electric Nuclear Medical ApS, Horsholm, Denmark). The measurements were repeated on days 2, 4 and 7 after the administration of the capsule and the fractional carbolic rate (FCR) of the SeHCAT was calculated. Further details of the methods have been given in Eusufzai 1991:a ‘SeHCAT (10 [tCi, Amersham International) was given orally with a drink of water following the technique described by Thaysen 198289 and Delhez et al. 1982.90 The initial count rate (100% value) was measured three hours after the intake of isotope (day 0), with the subject lying in supine and prone position under an uncollimated gamma camera (Porta Camera, General Electric. Nuclear Medical ApS, Denmark). The distance from the bed to the gamma camera crystal was maintained at 75 cm and the crystal (Na I) was centred over the middle of the xiphoidoumbilical line. The count rate in a 25% window centred around the 265 and 280-keV-photon peaks of 7Se was measured. The measurements, which took 10 minutes (5 minutes each position), were repeated on days 2, 4, and 7 after the administration of the capsule. The background activity was subtracted and correction was made for the decay of the isotope. The geometric means of the counts measured in the anterior and posterior positions were plotted in a logarithmic-linear graph. An exponential function was fitted to the data points using the method of least squares. The T½ – that is the time when the abdominal retention of the SeHCAT was reduced to 50% of initial, was calculated from the curve, as well as the fractional catabolic rate defined as ln2/T½. After completing the SeHCAT test the subjects were given ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk, Dr Falk GmbH & Co, Germany, purity > 99%) in a dose of 15 mg/kg/day for three weeks. Fasting blood samples (obtained 12–14 hours after intake) were then collected again, and the SeHCAT test was repeated. The treatment was continued during the studies. After completing the second SeHCAT test, five of the subjects increased the dose of ursodeoxycholic acid to 30 mg/kg/day in order to load further the bile acid transport system. Fasting blood samples were collected after week, and the SeHCAT test was repeated during continued ‘high dose’ treatment 7-day retention; cut-off: not reported |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: NR Response: NR Follow up: no details reported Duration of treatment: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Fellous 199436 | SeHCAT The patients fasted for 4 hours before ingesting the 10 µCi (370 Bq) 75SeHCAT capsules (Amersham Int. Ltd) at mealtime. Radioactivity emitted by the body was measured according to the technique of Thaysen et al.,a with an uncollimated gamma camera (Philips Grand-Champ) and placed 70 cm from the patient lying down. Posterior and anterior detection was carried out successively for 5 minutes, with photoelectric peaks of 75Se (220–300 keV). Background was measured in the absence of the patient using the same conditions, and was subtracted from the radioactivity measure. Measures were made at 1 to 3 hours (J0) and 7 days (J7) after ingestion of the capsule. The percentage of retained 75SeHCAT was calculated using the formula (radioactivity at J7/radioactivity at J0) × 100, for the geometric mean of the anterior and posterior measurements. The physical decay of 75Se was negligible for the duration of the test. The half-life of 75SeHCAT was 2.6 ± 0.7 days for 96% of patients, and 62 ± 17 days for the remaining 4% subjects. The dosimetry maximum test was 132 mrad for the gall bladder, 121 mrad for the terminal ilium and 11 mrad for the whole body 7-day retention; cut-off: 10% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: 8–12 g per day for at least 15 days Response: the test was judged positive when the treatment permitted the return to a normal transit (one or two stools per day) with normal consistency or pasty-ish Follow-up: NR Duration of treatment: at least 15 days Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Fernandez-Banares 200137 | SeHCAT After an overnight fast 10 µCi of 75Se homotaurocholate (Radiochemical Centre, Amersham) was administered orally. 75Se activity was measured with a large field-of-view gamma camera equipped with a high-sensitivity collimator. The initial count rate (100% value) was measured 3 hours (day 0) after administration of the isotope. Retention was then measured after 4 and 7 days. Abdominal retention < 11% on day 7 was considered abnormal. Values lower than 5% on day 7 were considered as severe BAM 7-day retention; cut-off: 11% (< 5% severe BAM) |
Treatment: cholestyramine (Resincolestiramina, 4-g sachets, Rubio Laboratories, Spain) Dose: starting dose 4 g per day. Patients visited weekly and the drug dose was increased or decreased according to clinical response ranging from 2 g to 12 g per day Response: when complete resolution of diarrhoea was achieved (passage of two or less formed or semiformed stools per day) Follow-up: after achieving remission patients were followed up for every 3 months or sooner if diarrhoea recurred Duration of treatment: same as follow-up (patients ‘were maintained with the same dose of cholestyramine’) Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Fernandez-Banares 200749 | SeHCAT 10 µCi of 75Se homotaurocholate (Radiochemical Centre, Amersham) were administered orally after overnight fast 75Se activities were measured with a large field-of-view gamma camera equipped with a high-sensitivity collimator. The initial count rate (100% value) was measured 3 hours (day 0) after administration of the isotope 7-day retention; cut-off: < 11% on day 7 was considered abnormal |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: variable dose the median dose required was 8 g per day (IQR, 4–12) Response: the relief of the diarrhoea (passage of two or fewer formed or semiformed stools per day), and absence of clinical relapse after 12-month follow-up. No response was defined as non-improvement in diarrhoea or diarrhoea relapse during follow-up Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Ford 199238 | SeHCAT 75-selenium-labelled taurohomocholic acid, an analogue of the naturally occurring taurocholic acid, was administered orally with a single dose of 370 kBq. The absorbed radiation from this dose of SeHCAT has been estimated to be low, being less than skin doses received during gastrointestinal fluoroscopy. Retained activity was measured at day 0 and day 7 using an uncollimated gamma counter, a technique shown to correlate well with whole body counting. Using the results of previous groups, retention of less than 15% of the isotope at day 7 was considered abnormal 7-day retention; cut-offs: < 5%, < 10%, < 15% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: range (1–8 g per day) depending on increase or decrease in response Response: stool frequency returned to normal (formed stools once or twice daily) was recorded as a complete response. Patients who did not demonstrate a complete response but reported a reduction in average stool frequency were recorded as showing a partial response Follow up: assessment after 1 month of treatment Duration of treatment: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: 13/49 patients who responded well to cholestyramine found it unpalatable and did not wish to continue with treatment. They were prescribed aluminium hydroxide which was equally effective in 10 Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Galatola 19925 | SeHCAT 10 µCi of 75Se homotaurocholate (Amersham Ltd, Poole, UK) were administered orally in the fasting state together with a Lundh meal at lunch time; 3 hours (t = 0) and 171 hours (t = 1) later abdominal scans were performed for 300 seconds using a non-collimated γ-camera placed 70 cm from the couch surface, with a 35% window at 280 keV 7-day retention; cut-off: < 11.7% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: 2 g before breakfast and was increased in a stepwise manner every 5 days of therapy if no effect was reported by the patient in improving bowel frequency (the dose was increased to 2 g twice daily, then three times daily, then 2 g were added before breakfast) Response: reduction in bowel frequency and symptoms Follow up: first assessment after a month. Then treatment stopped for 2–3 weeks and restarted if required Duration of treatment: until efficacy was achieved Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Merrick 198539 | SeHCAT The methods of measuring retention of SeHCAT and vitamin Bl,2 have been described elsewhere (see Ludgate 1985a and Nyhlin 1983a). A tracer dose of less than 100 µg SeHCAT was administered labelled with 40 kBq (1 µCi) selenium-75 Ludgate 1985:a ‘The patients attended the Department of Nuclear Medicine in the morning after an overnight fast. A whole-body count was obtained before administering any tracer, using a shadow shield whole body counter (Warner and Oliver, 196691) to measure the patient’s background radiation level. 40 kBq of 58Co B12 was given orally in liquid form with water. A second count was made 30 minutes later to measure both the count rate in the cobalt peak and the scatter from the 58Co in the selenium window. A single capsule containing 40 kBq of SeHCAT was then administered orally and 30 minutes later a recount was done. We previously demonstrated that our shadow shield counter is sufficiently insensitive to changes in distribution of the radioactivity and that it is not necessary to wait several hours until the activity has equilibrated in the liver and small intestine Seven days later the patients reattended and a further whole-body count was obtained. On each occasion the count rate from the patient was compared with that in a standard. The percentage of the initial activity retained at 7 days was calculated for both 58Co and 75Se by comparison with the initial value and the standards. We have previously demonstrated that in normal subjects the retention of 75SeHCAT at 7 days is greater than 15%, while in subjects with ileal disease it is less than 8% (Merrick et al., 198539). Intermediate values are equivocal. The lower limit for normal whole-body retention of 58Co B12 has previously been established in this department as 23%.’ Nyhlin 1983:a ‘One microcurie (40 kBq) SeHCAT at a specific activity of 68.5 mCi/mmol was administered orally as an aqueous solution to each subject. Whole-body retention of selenium radioactivity was measured on three occasions using a shadow-shield whole-body counter equipped with four 100-mm-thick × 150-mm diameter Nal (TI) detectors, immediately after ingestion (designated 0 h), and 96 and 168 hours later. Several of the patients spontaneously commented on the unpleasant, faintly metallic taste, which persisted for a few minutes after drinking the solution. Two were transiently nauseated. No other side effects were noted. Each measurement took 10 minutes on each occasion’ 7-day retention; cut-off: 8% and 15% |
Treatment: simple conservative treatment (cholestyramine) Dose: NR Response: ‘asymptomatic’ or ‘free of small bowel disease’ Follow up of at least 12 months, and in some up to 24 months Duration of treatment: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Notta 201140 | SeHCAT The examination consisted in the oral administration after 4 hours of fasting of a capsule containing 0.01 mCi (0.37 MBq) 75SeHCAT. The patient had to continue fasting for 3 hours more after the test, after which the abdominal activity was recorded. This registry considered the initial activity or zero time (ACT0). The registry of the abdominal activity was repeated at 4 and 7 days of administration (ACT4 and ACT7). All the measurements were performed with the patient in decubitus supine position with the detector centred on the abdominal region, maintaining a constant patient-collimator distance (15 cm) and a 5-minute acquisition was made. A dual-headed gamma camera with low energy general-purpose collimator (LEGP) was used. The following measurements were recorded: preacquisition background (B), anterior abdomen (AP), posterior abdomen (PA) and post-acquisition background (B). After, the percentage of abdomen retention (AR) was calculated at 4 and 7 days. The formulas used are shown in the following: Actn = {[(AP − B) + (PA − B)]/2} Abd Ret4 : (Act4/Act0) × 100 Abd Ret7 : (Act7/Act0) × 100 In normal subjects, the AR should be greater than 25% at the fourth day and than 10% on the seventh day. The dosimeter received by the patient is of 0.3–5.7 mGy/MBq for the whole body and 3.2–11.3 mGy/MBq in the gall bladder 7-day retention; cut-off: 10% |
Treatment: resin cholestyramine Dose: NR Response: (a) complete response: normalisation of stool rhythm and consistency; (b) partial response: decrease of frequency and/or consistency; and (c) no response, without changes or increase in stool rhythm Follow-up: clinical follow-up at 3 and 6 months (data for only 3 months reported) Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Nyhlin 199446 | SeHCAT SeHCAT retention 7 days after oral administration was measured using a shadow shield, whole-body gamma counter, as previously described. Patients attended in the morning, having fasted overnight. After measurement of their background radioactivity levels (principally to ensure that they had not received other radioactive tracers), 40 kBq of 58CoB12 was administered orally with a drink of water. Thirty minutes later the patient’s radioactivity level was counted again to obtain the 100% count rate value and also an estimate of the scattered counts from the cobalt in the selenium window. A total of 40 kBq of 75SeHCAT was then administered orally, and after a further wait of half an hour a second measurement was made. The contribution of the scatter from 58Co in the 75Se window was calculated and subtracted. The patients returned 1 week later, when a further measurement was made of the radioactivity in both selenium and cobalt windows. The retention of each was expressed as a percentage of the initial administered activity 7-day retention; cut-off: 5% and 10% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: NR Response: NR Follow-up: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Odunsi-Shiyanbade 2010,47 related publications50,51 | Intervention: colesevelam (1.875 g, twice daily) for 12–14 days. The drug was purchased as Welchol® (Colesevelam HCl) from Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Parsippany, NJ as 625-mg tablets. The tablets were prepared as 312.5-mg capsules with matching placebo by Mayo Research Pharmacy | Comparator: placebo. The tablets were prepared as 312.5-mg capsules with matching placebo by Mayo Research Pharmacy | Reference standard: NA (not a test accuracy study) Outcomes of treatment were: transit, daily bowel frequency and consistency (stool diaries), and colonic mucosal permeability. Participants also completed the following questionnaires: HADS, SCL-90 (somatisation), and bowel function by validated daily diaries including BSFS scores |
| Rudberg 199641 | SeHCAT One capsule of 370-kBq 75SeHCAT (Amersham International) was swallowed with water by the patient after an overnight fast. Three hours later the patient was placed supine 70 cm beneath the face of the uncollimated gamma camera, which was centred at mid-abdomen. Counts were acquired in a 20% window at 265 keV utilising the central peak of the 75Se energy distribution. The same registration was then performed with the patient in the prone position. Background counts were collected before and after each registration. A geometric mean value was then calculated. The same registration and calculations were performed after 7 days and corrected for the gamma decay 7-day retention; cut-off: 10% and 15% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: 2–4 g three times a day for 10 days Response: ‘complete relief’ – no details reported Follow-up: at least 6 months Duration of treatment: from 10 days to 6 months, depending on effectiveness Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Sciaretta 198642 | SeHCAT For the test, 370 kBq (10 µCi) of 75SeHCAT (provided by Amersham Radiochemical Centre) in capsule form, containing < 100 µg of active ingredient absorbed on inert carrier, was orally administered following the technique of Thaysen et al. to patients who had been fasting for at least 4 hours. Whole-body absorbed dose was ∼0.2 µGy/kBq (1 mrad/µCi); the absorbed dose from the critical organ-gallbladder wall was 3.2 µGy/kBq (12 mrad/µCi). The 75Se activity was measured with a small field-of-view uncollimated γ-camera (Pho-Gamma IV, Searle Consumer Products, Chicago, IL). To minimise the effects due to geometric variations, the crystal was kept 70 cm away from the bed where the patient lay in a supine position, and the crystal was centred in the middle of the xiphoid umbilical line. For γ-counting, a 35% window centred at 260 keV was experimentally chosen, which allows energies from 214 to 305 keV to be detected with low background interference. Counting time was set at 5 minutes. In this condition, the initial count rate (time zero) was about 6 × 104 c.p.m. and the background count rate was always about 5 × 103 c.p.m. Measurements were carried out 3 hours after the administration of the isotope (1.5 hours in cases of severe diarrhoea) and at 1, 3, 5 and 7 days after the administration of the isotope; background activity was always subtracted. A standard source of 75Se (∼370 kBq) was also measured using the identical technique in order to monitor possible fluctuations in system stability. Correction for radioactive decay was not found to be necessary. Using the least–squares fit, a single exponential activity vs. time curve was obtained from which the percentages of 75SeHCAT retained in the abdomen on the third day were determined. The curve was obtained whenever at least three 75SeHCAT retention values were different from zero. The percentage activities at days 3, 5 and 7 were also evaluated by direct measurements with the γ-camera 3- or 7-day retention (unclear, see fig 2 in paper); cut-off: 5% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: 2–8 g per day Response: ‘disappearance of diarrhoea’ – no further details reported Follow-up: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Sciaretta 198743 | SeHCAT The 75SeHCAT test was carried out in all patients using the method we described elsewhere and the control group consisted of the same 23 subjects (see Sciaretta 198642). Results are expressed as percentage retention values calculated by the exponential time activity curve on day 3. Measurements of abdominal radioactivity were taken by gamma camera counting on the day of administration of 370 kBq 75Se-homocholyltaurine (75SeHCAT, Amersham Radiochemical Centre, England) (time zero) and on days 1, 3, 5 and 7. An abdominal retention of 34% or more on day 3 is considered normal by our method. The percentage abdominal retention on day 7, measured directly by gamma camera for both the control and the functional diarrhoea groups, was considered. An abdominal retention of less than 8% (the lowest value in a normal subject) is considered pathologic 3- or 7-day retention (unclear); cut-off: ≤ 8% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: twice daily, 2–8 g per day Response: the test was considered positive when diarrhoea stopped with cholestyramine administration, and recurred without it Follow-up: NR; treatment duration at least 10 days Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Sinha 19982 | SeHCAT Abdominal radioactivity is measured on day 7 following a capsule of SeHCAT given orally on day 1. A retention of < 15% of 23-selena-25-homotaurocholic acid confirms the presence of BAM. Possible secondary causes of BAM were excluded by performing the following investigations in all patients: routine blood tests, random glucose, haematinic screen, stool microscopy and culture, small bowel enema to exclude structural ileal disease, gastroscopy and duodenal biopsy to exclude coeliac disease, para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) test to exclude pancreatic insufficiency, hydrogen and 14C-glycocholate breath tests to exclude bacterial overgrowth and barium enema and colonoscopy (six out of nine patients) to exclude large bowel disease 7-day retention; cut-off: 15% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: initial dose: 1–2 sachets t.i.d.; titrated accordingly. Adjunctive therapy with loperamide was used initially because it was felt this would give the best chance of therapeutic success. Once an effect had been achieved, the loperamide was gradually withdrawn Response: response to therapy was assessed in an outpatient setting based on the patient’s overall assessment since their last appointment by monitoring: (i) the average stool frequency of bowel motions pre and post treatment; (ii) the consistency of stools pre and post treatment; and (iii) whether or not symptomatic improvement occurred within the first 24 hours Follow-up: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Smith 20003 | SeHCAT The SeHCAT retention test was carried out in a standard manner according to the manufacturers’ instructions. Patients swallowed a single capsule containing 370 kBq SeHCAT (Nycomed-Amersham, UK). After 3 hours for physiological equilibration, baseline counts were measured over the abdomen using an uncollimated gamma camera. Background-corrected counts were obtained in both antero–posterior and postero–anterior views, and the geometric mean of these counts recorded. The percentage of the baseline value retained on the seventh day was calculated 7-day retention; cut-off: 10% |
Treatment: patients were initially given conventional therapy (prednisolone ± ASA drugs in Crohn’s disease and anti-diarrhoeals in the others); if this failed, BAS (cholestyramine or colestipol) Dose: treatment with either drug was started at a low dose, one sachet (5 g) daily, and gradually built up to a maximum of one sachet t.i.d., titrating the dose against clinical response Response: the definition of successful response was based on the patient’s perception of improvement Follow-up: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Tunney 201132 | SeHCAT In this centre a cut-off of < 8% is used to diagnose BAM, with results 8–15% being equivocal and > 15% being normal. The amount of 75Se being administered was always 370 kBq, and patients were scanned at 3 hours and 7 days post ingestion using an uncollimated gamma camera 7-day retention; cut-off: 8 and 15% |
Treatment: BASs (no details reported) Dose: NR Response: NR Follow-up: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Wildt 200344 | SeHCAT The SeHCAT test was performed as a measurement of the 7-day retention, modified from descriptions in Thaysen et al.a and Nyhlin et al.a No further details 7-day retention; cut-off: 5%, 10% and 15% |
Treatment: cholestyramine Dose: 2–4 g per day; patients were recommended to increase or decrease dose according to response. Most common dosage: 5–12 mg per day Response: the definition of treatment response was: > 25% reduction in bowel frequency, or file data reporting excellent or moderate response to treatment. Patients with no response to treatment were defined as having < 25% reduction in bowel frequency or file data reporting no response Follow-up: NR (‘Several weeks after commencing treatment, the patients returned to the clinic reporting dose, response and perhaps further adjustment of dosage’) Alternative treatment due to AEs: NR Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
|
| Williams 199145 | SeHCAT 75SeHCAT absorption was assessed as previously described, by administering one capsule containing 40 kBq (1 µCi) 75SeHCAT after an overnight fast. The 100% value for whole-body retention was obtained at 30 minutes and the measurement was repeated at 7 days using a shadow shield whole-body counter. During the initial evaluation of 75SeHCAT a lower limit of 15% retention at 7 days was established on the basis of comparison with normal controls 7-day retention; cut-off: 5%, 10% and 15% |
Treatment: cholestyramine or aluminium hydroxide Dose: cholestyramine was administered in divided doses in powder form (4-g sachets) during the day. The mean dose was 12 g. Four patients required doses greater than 12 g per day to control their symptoms Response: a therapeutic response was defined as a reduction in stool frequency to ≤ 2 bowel actions/day with a concomitant increase in stool consistency occurring within 48 hours of beginning treatment Follow-up: NR Alternative treatment due to AEs: one patient was intolerant of cholestyramine but responded to aluminium hydroxide. Another patient responded to aluminium hydroxide as the initial treatment Alternative treatment due to non-response: NR |
Inclusion/exclusion criteria and participant characteristics of included studies
| Study ID | Participant number | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Participant characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borghede 201133 | Total patients (n = 298): Type II BAM (n = 114), Type I Crohn’s (n = 29) | All patients who received a 75SeHCAT scan during a 5-year period (2004–9) | None reported | Median age: 42 years (range 16–82 years) 198 female, 100 male Type I Crohn’s: 29 without resection Type II BAM: diarrhoea with unknown cause |
| Dyson 201131 (abstract only) | Total patients (n = 109), 59 with positive test | All patients who received a SeHCAT test since introduction in 2007 | None reported | Mean age: NR Male/female: NR Resection: NR Indication: positive test (n = 59): Type 1 (ileal disease) (n = 12), Type 2 (primary BSD) (n = 33), Type 3 (post cholecystectomy) (n = 11), not acted on (n = 2), not clinically relevant (no diarrhoea) (n = 1) |
| Eusufzai 199334 | Total patients (n = 24) All: chronic diarrhoea without known cause |
Chronic diarrhoea without known cause after extensive investigations of intestinal function | Patients with ileal resection, gastric resection, chronic IBD, bacterial overgrowth, fat malabsorption, or a history of abdominal radiation were excluded | Mean age: 48 years (range 24–76 years) Male/female: 20 female, four male Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (7 × cholecystectomy, 4 × lactose intolerant, 1 diabetes) |
| Eusufzai 199335 | Total patients (n = 28) All: patients with diarrhoea in some cases for longer duration |
Not reported specifically but consisted of patients with diarrhoea who had undergone extensive investigation to evaluate their intestinal function | Not reported specifically but excluded patients with heart, kidney and liver disease | Mean age: 60.7 years (range 24–76 years) Male/female: 20 female, eight male Resection: one villous atrophy of ileum, one ileocaecal resection, one villous adenoma of ileum, one extensive ileal resection Indication: all with chronic diarrhoea (10 × cholecystectomy, 1 × lactose intolerant, 3 × radiation therapy, 2 × partial gastrectomy) |
| Fellous 199436 | Total patients (n = 106): healthy volunteers (n = 23); group 1, diarrhoea with ileal involvement (n = 33); group 2, organic diarrhoea without ileal involvement (n = 20); group 3, functional diarrhoea (n = 53) | Patients with chronic diarrhoea referred to the hospital between 1990 and 1992 for a SeHCAT test to explore the cause of diarrhoea. Diarrhoea was defined as at least three soft stools or liquid diarrhoea per day for more than 6 months. Normal hepatic balance | Insufficient clinical/biological information (n = 63) | Group 1: average age: 46 ± 16 years (range 11–75 years) Male/female: 17 male, 16 female Resection: 20 × resection between 10 cm and 3 m Indication: diarrhoea with ileal involvement (6 × Crohn’s disease) Group 2: average age: 55 ± 16 years (range 24–74 years) Male/female: five male, 15 female Resection: NA Indication: organic diarrhoea without ileal involvement Group 3: average age: 47 ± 14 years (range 23–77) Male/female: 23 male, 30 female Resection: NA Indication: functional diarrhoea (36 × unknown cause) |
| Fernandez-Banares 200137 | Total patients (n = 83): (1) microscopic colitis (n = 51); (2) diarrhoea, unknown cause (n = 32) | (1) Clinical criteria included chronic or recurrent watery diarrhoea of at least 1 month’s duration and grossly normal full colonoscopy; and (2) diarrhoea, unknown cause: patients with previously unexplained chronic and recurrent watery diarrhoea of at least 3 months’ duration and fulfilled the Rome II criteria for functional diarrhoea. No detectable digestive or extra-digestive cause was found | None reported | Age: (1) Mean age in years (SD): 60.7 (± 2.2); (2) Mean age in years (SD): 52.7 (± 2.1) Male/female: (1) 41 female, 10 male; (2) 21 female, 11 male Resection: NA Indication: (1) 51 × microscopic colitis (7 × cholecystectomy); (2) 32 × diarrhoea, unknown cause (9 × cholecystectomy) |
| Fernandez-Banares 200749 | Total patients (n = 62): all: chronic watery diarrhoea and fulfilling Rome II criteria of functional diarrhoea | All above 18 years of age (1) Presence of non-bloody chronic watery diarrhoea, defined as more than three loose or liquid bowel movements a day for at least 4 weeks and a stool weight > 200 g per day; (2) to fulfil the Rome II criteria of either functional diarrhoea or diarrhoea-predominant IBS; (3) normal physical examination and blood analysis, including routine blood biochemistry and haematological counts, C-reactive protein, serum T4-TSH, and serum IgA-antiendomysial and IgA-human anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies; (4) negative faecal bacterial cultures and exam for ova and parasites; and (5) normal full colonoscopy with multiple biopsies |
The exclusion criteria were the presence of either post-cholecystectomy or post-vagotomy diarrhoea | Mean age in years (SD): 52.2 (± 2) 47 female, 15 male Chronic diarrhoea of predominant IBS 32 x Rome II criteria of functional diarrhoea 30 x |
| Ford 199238 | Total (166) Groups: (1) Possible type I BAM: ileal resection (n = 7) previous radiotherapy (n = 12); known Crohn’s disease (n = 4); suspected Crohn’s disease (n = 5) (2) Possible type II BAM (n = 74) (3) Possible type III BAM: post cholecystectomy (n = 30); post vagotomy (n = 11); post cholecystectomy and vagotomy (n = 4) (4) Diabetics (n = 19) |
All patients had diarrhoea as their main complaint, defined by at least two loose stools daily | NR | Total age range: 18–79 years 89 female, 77 male 1. Possible type 1 BAM 28 x 2. Possible type II BAM 74 x 3. Possible type III BAM 45 x 4. Diabetics 19 x |
| Galatola 19925 | Patients with IBS (n = 98) | Patients referred to gastroenterological problems by their GP because of abdominal pain distress, who gave a history of increased bowel frequency (> 3 per day) lasting for at least 3 months; negative results for routine biochemical, haematological, endoscopic, radiological and histological examinations implemented according to the clinical indications in order to search for an organic cause of their symptoms. Patients with cholecystectomy | Patients who underwent major abdominal surgical operations, liver disease patients, and patients in whom an organic cause of their symptoms was found were excluded from the study | Mean age in years (range): 43 (14–76) 53 female, 45 male Patients with IBS 98 x |
| Merrick 198539 | Patients (n = 106), normal controls (n = 63) | Four groups: (1) Normal controls (n = 63); (2) previously undergone small bowel resection (n = 26); (3) persistent diarrhoea after previous vagotomy or surgery for peptic ulcer (n = 29); (4) chronic diarrhoea of non-inflammatory origin – namely, IBS in 43, coeliac disease in two, small bowel ischaemia in two, and other miscellaneous conditions in four (n = 51) |
None reported | 1. Mean age in years (range): 52 (24–72) 2. Mean age in years (range): 48 (17–74) 3. Mean age in years (range): 54 (28–72) 4. Not reported 1. 56 female/7 male 2. 16 female/10 male 3. 10 female/19 male 4. Not reported 1. No 2. 18 partly/1 entire/7 unknown 3. No 4. Not reported 1. Normal, healthy 2. 15 Crohn’s disease 3. Post vagotomy 4. IBS, coeliac disease, etc. |
| Notta 201140 | Patients (n = 37) | Having chronic diarrhoea of more than 1 month’s duration and absence of previous treatment | Aged under 18 years, pregnancy and breastfeeding | Age (years): NR Male/female: 26 female/11 male Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause |
| Nyhlin 199446 | Patients (n = 53) | Patients with Crohn’s disease from two hospitals in Edinburgh that have specialist gastrointestinal facilities | None reported | Mean age in females: 39.8 years (range 16–72 years). Mean age in males: 37.9 years (range 16–60 years) Male/female: 20 male, 31 female Resection: 26 had previously undergone bowel resection for their Crohn’s disease (22 ileocaecal, 3 colonic and 1 limited ileal resection Indication: Crohn’s disease (with/without resection) |
| Odunsi-Shiyanbade 2010,47 related publications50,51 | 31 IBS-D patients were recruited and signed consent; 24 were randomised and completed the study. One withdrew consent prior to the start of the study; 2 had concomitant illness and were advised not to participate by their primary physicians; and 4 did not qualify based on baseline transit eligibility criteria (GC 24 hours < 2.3) | Patients with IBS-D. Aged 18–65 years. HADS score < 8. No abdominal surgery (except appendectomy or cholecystectomy as long as patient’s IBS-diarrhoea symptoms preceded the cholecystectomy) (n = 12) | Participants with known chronic liver disease or AST/ALT > 2.0 × upper limit of normal. Hypertriglyceridemia and pancreatitis by history. Diabetes or hypoglycaemia; significant coagulation disorder. History of bowel obstruction (n = 12) | Mean age: COL: 42.1 (± 4.0); PLA: 43.3 (± 3.7) years Male/female: all 24 female Resection: NA Indication: IBS-D |
| Rudberg 199641 | Patients (n = 20); 13 were treated with cholestyramine | Patients with chronic or recurrent diarrhoea of unknown cause. Lactose-restricted diet, loperamide or anticholinergic agents had not relieved their symptoms | Patients with periods of constipation, dominating abdominal pain or fragmented mucous stools. Clinical, endoscopic and radiological examinations were performed, as well as laboratory tests to exclude IBD, lactose intolerance, coeliac disease, abuse of laxative or other forms of diarrhoea | Mean age (n = 13): 49.5 years (range 27–82 years) Male/female: three male, 10 female Resection: NA Indication: chronic or recurrent diarrhoea of unknown cause |
| Sciaretta 198642 | Patients (n = 66), normal controls (n = 23) | Four groups: (A) healthy volunteers (n = 23); (B) distal ileum resection (n = 33) or Crohn’s disease of the ileum (n = 3); (C) various intestinal diseases (normal ileum) (n = 17); and (D) chronic diarrhoea syndrome but without evident intestinal or extra-intestinal pathology (n = 13) | None reported | Group D: Mean age (n = 13): 51 years (range 28–70 years) Male/female: three male, 10 female Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause |
| Sciaretta 198743 | Patients (n = 46), normal controls (n = 23) | Two groups: (A) healthy volunteers (n = 23); and (B) IBS-D (n = 38) or cholecystectomy with chronic diarrhoea (n = 8) | None reported | Group B: Mean age (n = 46): 41 years (range 17–73 years) Male/female: 20 male, 26 female Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause or cholecystectomy |
| Sinha 19982 | Patients (n = 9) | Patients with chronic diarrhoea referred to the department and selected to undergo the SeHCAT and a positive test result | None reported | Mean age (n = 9): 50.2 years (range 43–57 years) Male/female: NR Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea |
| Smith 20003 | Patients (n = 304) | Patients with persistent diarrhoea Four groups: (1) Crohn’s disease with ileal resection (n = 37); (2) Crohn’s disease, unoperated and in clinical remission (n = 44); (3) vagotomy and pyloroplasty, with/without cholecystectomy (n =26); and (4) IBS-D (n = 197) |
None reported | Mean age: NR Male/female: NR Resection: NA Indication: Crohn’s disease (without resection) and IBS-D |
| Tunney 201132 | Patients who underwent SeHCAT scanning. Thirteen groups, among which: (1) Chronic diarrhoea, no known risk factors (n = 136); and (2) Crohn’s disease, surgically naive (n = 30, no treatment details for these patients) | Patients referred from and managed by trusts other than Salford Royal and patients seen on a private basis. Patients who did not have a SeHCAT scan at 7 days. A patient with technically void results as declared by the staff due to retention of 100% of the isotope and no evidence in the notes that this patient had a repeated test. Patients taking a trial of BASs during investigation, which may have influenced their results. Patients with no information in their electronic records | Mean age (n = 276): 46 years (range 16–90 years) Male/female: 87 male, 189 female Resection: 30 patients with Crohn’s disease and surgically naive (no treatment details for these patients) Indication: chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause |
|
| Wildt 200344 | Patients (n = 135) | Patients with chronic diarrhoea (defined by subjective reports of > 3 weeks’ change in stool frequency and/or consistency) who were investigated for BAM using the SeHCAT test. The SeHCAT test was generally carried out when a first-line standard programme for diagnostic evaluation of chronic diarrhoea had failed to account adequately for the condition. First-line diagnostic evaluation at minimum included sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy with mucosal biopsies, faecal examination for parasites and bacteria and biochemistry (haemoglobin, white blood cell count, C-reactive protein, electrolytes, renal parameters, liver function tests and thyroid stimulating hormone). Often tests for coeliac disease, lactose malabsorption, stool volume and stool lipid concentration were included in the first-line diagnostic evaluation as well | None reported | All patients (n = 135) Mean age (n = 135): NR Male/female: 48 male, 87 female Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause Patients with BAM (i.e. positive SeHCAT): Median age females (n = 46): 52 years (range 24–83 years); median age males (n = 28): 48 years (range 27–78 years) Male/female: 28 male, 46 female Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause and BAM |
| Williams 199145 | Patients (n = 181) | Patients referred for measurement of 75SeHCAT retention because of unexplained diarrhoea between 1982 and 1989 | Patients with IBD who had undergone previous radiotherapy to the abdomen, any form of bowel resection, or other abdominal surgery were excluded | Patients with severe BAM (< 5%) (n = 23): Mean age (n = 23): 45 years (range 17–77 years) Male/female: 10 male, 13 female Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause and BAM Patients with moderate BAM (5–10%) (n = 13): Mean age (n = 13): 44 years (range 25–64 years) Male/female: nine male, four female Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause and BAM Patients with mild BAM (10–15%) (n = 21): Mean age (n = 21): 30 years (range 13–72 years) Male/female: 18 male, 13 female Resection: NA Indication: chronic diarrhoea of unknown cause and BAM |
Appendix 5 List of excluded studies with rationale
The following is a list of studies excluded at the full-paper screening stage of the review, along with the reasons for their exclusion (n = 141), along with the studies that could not be found (n = 3).
The reasons for study exclusion are coded as follows:
Population – the study did not consider the relevant populations for this assessment: people presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease or people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection of the terminal ileum).
Index test –the study did not assess the effectiveness of SeHCAT.
Reference standard – for test accuracy studies, the study did not use an acceptable reference standard.
Outcomes – the study did not report any of the outcomes specified in Chapter 3 , OR, for DTA studies, insufficient data were reported to allow the construction of 2 × 2 contingency tables (numbers of TP, FN, FP and TN test results).
Study design – the study design was not one of those specified in Chapter 3 , Inclusion and exclusion criteria, OR the study included < 10 participants in the relevant patient groups.
Duplicate – the study was a duplicate publication.
Authors contacted – the study did not report sufficient information for inclusion assessment and authors were contacted for additional information, but no response was received.
1. Allan JG, Russell RI. Proceedings: double-blind controlled trial of cholestyramine in the treatment of post-vagotomy diarrhoea. Gut 1975;16:830. Population.
2. Allan JG, Russell RI. Cholestyramine in treatment of postvagotomy diarrhoea: double-blind controlled trial. Br Med J 1977;1:674–6. Population.
3. Bajor A, Kilander A, Fae A, Galman C, Jonsson O, Ohman L, et al. Normal or increased bile acid uptake in isolated mucosa from patients with bile acid malabsorption. [Erratum appears in Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;19:185]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;18:397–403. Outcomes.
4. Bajor A, Rudling M, Ung KA, Wallin J, Simren M. Effects of the bile acid load to the intestine on IBS symptoms. Paper presented at 2010 Joint International Neurogastroenterology and Motility Meeting, 26–29 August 2010, Boston, MA. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2010;22:7. Study design.
5. Bajor A, Rudling M, Ung KA, Wallin J, Simren M. Impact of bile acids on IBS symptoms and the effects of resin treatment. Paper presented at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2011, 7–10 May 2011, Chicago, IL. Gastroenterology 2011;140(Suppl. 1):S3. Study design.
6. Bajor A, Wallin J, Strid H, Abrahamsson H, Ung K-A, Simren M. Overweight, high age and the presence of loose and frequent stools are suggestive of bile acid malabsorption in patients with the irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). [AGA Institute Abstracts: W1201]. Gastroenterology 2007;32:A682. Outcomes.
7. Balzer K, Breuer N, Quebe-Fehling E. [Postprandial serum bile acid level and 75SeHCAT retention in diagnosis of bile acid malabsorption syndrome. a comparative study.] Med Klin 1993;88(Suppl. 1):23–8. Population.
8. Balzer K, Dirks E, Brueuer N, Goebell H. 75SeHCAT test for characterization of ileal involvement in Crohn’s disease. In Goebell H, Peskar BM, Malchow H, editors. Inflammatory bowel diseases: basic research and clinical implications. Lancaster: MTP Press; 1988. pp. 398–9. Outcomes.
9. Balzer K, Goebell H. Bile-acid loss syndrome: an often overlooked diagnosis: experiences with the 75-SeHCAT retention test in 200 cases. Z Gastroenterol 1986;24:448. Outcomes.
10. Balzer K, Schmitt G, Reiners C, Goebell H. [Results of the 75selenium homotaurocholic acid retention test (SeHCAT test) in diagnosis of diarrhoea.] Med Klin 1995;90:27–32. Study design.
11. Benson GM, Hickey DMB. Bile acid sequestrants. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 1994;3:493–500. Study design.
12. Brown SR, Baraza W. Chromoscopy versus conventional endoscopy for the detection of polyps in the colon and rectum. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010;10:CD006439. Study design.
13. Bruck R, Chamovitz DL, Federico C, Bar-Meir S. Does the 75SeHCAT test diagnose bile acid malabsorption? J Clin Gastroenterol 1991;13:115–16. Study design.
14. Brydon G, Culbert P, Lacucci M, Ghosh S. An evaluation of the clinical use of serum 7 alpha hydroxycholestenone as a test of bile acid malabsorption [M1071]. Paper presented at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2010, 1–6 May 2010, New Orleans, LA. Gastroenterology 2010;138(5 Suppl. 1):S325. Index test.
15. Brydon WG, Culbert P, Kingstone K, Jarvie A, Iacucci M, Tenhage M, et al. An evaluation of the use of serum 7-alpha-hydroxycholestenone as a diagnostic test of bile acid malabsorption causing watery diarrhea. Can J Gastroenterol 2011;25:319–23. Outcomes.
16. Brydon WG, Nyhlin H, Eastwood MA, Merrick MV. Serum 7 alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one and selenohomocholyltaurine (SeHCAT) whole body retention in the assessment of bile acid induced diarrhoea. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1996;8:117–23. Outcomes.
17. Camilleri M, Nadeau A, Tremaine WJ, Lamsam J, Burton D, Odunsi S, et al. Measurement of serum 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (or 7alphaC4), a surrogate test for bile acid malabsorption in health, ileal disease and irritable bowel syndrome using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2009;21:734–e43. Index test.
18. Campbell S, Chandra N, Lisa G, Anthony M. Serum 7alpha - Hydroxycholestenone in patients with idiopathic bile salt malabsorption: a detailed comparison with conventional SeHCAT testing. Gastroenterology 2006;130:A319. Outcomes.
19. Capron JP, Dupas JL, Boulard A. [Effect of cholestyramine in the treatment of diarrhea resistant to common drugs.] Med Chir Dig 1977;6:165–6. Study design.
20. Caspary WF. [Diagnosis of bile acid malabsorption: evaluation of the new 75SeHCAT-test.] Inn Med 1986;13:248–51. Study design.
21. Centi-Colella A, Di Rocco E, Liberatore MF. Retention of 75Se-homotaurocholic acid measured by a low-background whole-body counter. J Nucl Med Allied Sci 1983;27:309–12. Population.
22. Chaparro M, Gisbert JP, del Campo L, Cantero J, Mate J. Accuracy of computed tomographic colonography for the detection of polyps and colorectal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Digestion 2009;80:1–17. Study design.
23. Clayden GS, Lawrence R, Glazer G. SE-75 HCAT a new radiolabeled bile-salt for studying the enterohepatic bile-salt circulation: a preliminary-study in normal subjects: Paper presented at Winter Meeting of the Surgical Research Society, 6–7 January 1983, Cambridge, UK. Br J Surg 1983;70:306. Population.
24. Collins PD, Mpofu C, Watson AJ, Rhodes JM. Strategies for detecting colon cancer and/or dysplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;2:CD000279. Study design.
25. Dalhez H, Van Den Berg JWO, Van Blankenstein M, Meerwaldt JH. New method for the determination of bile acid turnover using 75-Se-homocholic acid taurine. Eur J Nucl Med 1982;7:269–71. Population.
26. Danielsson A, Nyhlin H, Suhr O. [SeHCAT--a gamma-radiating bile acid isotope for the diagnosis of dysfunction of the terminal ileum.] Lakartidningen 1987;84:1266–70. Study design.
27. D’Arienzo A, Maurelli L, Di Siervi P, Panarese A, Giannattasio F, Scuotto A, et al. [The 75-seleno-homocholic acid-taurine test (SeHCAT): a useful method for detecting the idiopathic malabsorption of bile salts in chronic functional diarrhea]. Clin Ter 1989;130:11–16. Study design.
28. Darienzo A, Scuotto A, Maurelli L, Disiervi P, Squame G, Mazzacca G. Comparison between SeHCAT and fecal recovery of C-14 after oral-administration of cholylglycine-C-14 in the diagnosis of bile-salt malabsorption-syndrome. Ital J Gastroenterol 1986;18:50. Outcomes.
29. Davidson MH. A systematic review of bile acid sequestrant therapy in children with familial hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Lipidol 2011;5:76–81. Population.
30. De Lima Ramos PA, Martin-Comin J, Xiol X, Roca M, Castell M, Cervantes X, et al. [Diarrhoeic syndrome management using abdominal retention of 75Se-homo-tauro-colic acid (75Se-SeHCAT) measurement.] Rev Esp Med Nucl 1996;15:21–5. Population.
31. Del Vecchio Blanco G, Pallone F. [Malabsorbtion syndrome and chronic diarrhoea.] Giornale Italiano di Endoscopia Digestiva 2006;29:315–22. Study design.
32. Dionisio PM, Gurudu SR, Leighton JA, Leontiadis GI, Fleischer DE, Hara AK, et al. Capsule endoscopy has a significantly higher diagnostic yield in patients with suspected and established small-bowel Crohn’s disease: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2010;105:1240–8. Study design.
33. Dumaswala R, Heubi JE. Differential effect of cholestyramine (CHOL) on ileal and hepatic bile-acid (BA) transport. FASEB J 1995;9:A368. Population.
34. Duncombe VM, Bolin TD, Davis AE. Double-blind trial of cholestyramine in post-vagotomy diarrhoea. Gut 1977;18:531–5. Population.
35. Eusufzai S, Lofberg R, Veress B, Einarsson K, Angelin B. Studies on bile acid metabolism in collagenous colitis: no evidence of bile acid malabsorption as determined by the SeHCAT test. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1992;4:317–21. Outcomes.
36. Fagan EA, Chadwick VS, McLean Baird I. SeHCAT absorption: a simple test of ileal dysfunction. Digestion 1983;26:159–65. Population.
37. Farkkila MA, Kairemo KJ, Taavitsainen MJ, Strandberg TA, Miettinen TA. Plasma lathosterol as a screening test for bile acid malabsorption due to ileal resection: correlation with 75SeHCAT test and faecal bile acid excretion. Clin Sci 1996;90:315–19. Population.
38. Ferraris R, Barlotta A, Galatola G, Pellerito R, Cottino F, Delapierre M. Bile-acid malabsorption by 75-selenium homocholic acid taurine (SeHCAT) gallbladder retention, in ileal disease and obscure diarrhea. Ital J Gastroenterol 1988;20:33. Outcomes.
39. Ferraris R, Fracchia M, Galatola G. [The clinical importance of physiopathological studies of the bile salts performed using the gamma-emitting bile acid SeHCAT.] Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 1992;38:197–206. Study design.
40. Ferraris R, Galatola G, Barlotta A, Pellerito R, Fracchia M, Cottino F, et al. Measurement of bile acid half-life using [75Se]HCAT in health and intestinal diseases: comparison with [75Se]HCAT abdominal retention methods. Dig Dis Sci 1992;37:225–32. Outcomes.
41. Ferraris R, Galatola G, Barlotta A, Rolfo P, Scassa R, Cottino F, et al. SE-75 taurohomocholic acid (SeHCAT) T 1/2 as non invasive estimate of bile-acids turnover in intestinal-diseases: Paper presented at European Nuclear Medicine Congress, 3–6 September 1985, London, UK. Eur J Nucl Med 1985;11:A35. Outcomes.
42. Ferraris R, Jazrawi R, Bridges C, Northfield TC. Use of a labeled bile acid (75SeHCAT) as a test of ileal function: methods of improving accuracy. Gastroenterology 1986;90:1129–36. Study design.
43. Ferraris R, Jazrawi RP, Bridges C, Northfield TC. Can SeHCAT provide a non-invasive measurement of bile-acid kinetics and ileal absorption in man. Gastroenterology 1985;88:1658. Population.
44. Florin TH, Fong W. SeHCAT tests for determination of bile acid malabsorption. Aust N Z J Med 1997;27:344. Population.
45. Fracchia M, Pellegrino S, Secreto P, Pera A, Galatola G. Biliary lipid composition in idiopathic bile acid malabsorption. Gut 1998;43:812–16. Outcomes.
46. Freundlieb O, Szy D, Balzer K, Strotges MW. [Comparative study of various methods of measuring bile acid loss using 75Se-HCAT.] Nuklearmedizin 1983;22:258–61. Outcomes.
47. Galatola G, Jazrawi R, Bridges C, Joseph AEA, Northfield TC. Serum and hepatic kinetics of synthetic bile-acid 75SE-homocholic acid taurine (SeHCAT) in man. Ital J Gastroenterol 1988;20:34–5. Population.
48. Garnica AD, Rennert OM, Rodgers BM. Cholestyramine therapy in children with chronic diarrhea: evidence for inhibition of amino-acid absorption by bile-salts. Pediatr Res 1976;10:354. Population.
49. Gillen D, Neithercut WD, McColl KEL, Bercik P, Armstrong D, Blum AL. Cholestyramine for treatment of chronic diarrhea [3] (multiple letters). Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:599–601. Study design.
50. Grebe SF, Sattler EL, Rinkenberger C, Bodenmuller D, Grebe SKG, Muller KD, et al. [Studies of Se-75 labelled bile acid analogue absorption in different forms of gastrointestinal diseases using a whole body counter.] Nuklearmedizin 1996;35:86–93. Outcomes.
51. Gunnarsson J, Simren M. Efficient diagnosis of suspected functional bowel disorders. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;5:498–507. Study design.
52. Hames TK, Condon BR, Fleming JS, Phillips G, Holdstock G, Smith CL, et al. A comparison between the use of a shadow shield whole body counter and an uncollimated gamma camera ain the assessment of the seven-day retention of SeHCAT. Br J Radiol 1984;57:581–4. Study design.
53. Heaton KW. Staying cool with a hot test: gastroenterologists and 75SeHCAT. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986;292:1480–1. Study design.
54. Hewitson P, Glasziou PP, Irwig L, Towler B, Watson E. Screening for colorectal cancer using the faecal occult blood test, hemoccult. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;1:CD001216. Population.
55. Hofmann AF. Progress in idiopathic bile acid malabsorption. Gut 1998;43:738–9. Study design.
56. Hofmann AF. Chronic diarrhea caused by idiopathic bile acid malabsorption: an explanation at last. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;3:461–4. Study design.
57. Hofmann AF, Bolder U. Detection of bile acid malabsorption by the SeHCAT test. Principles, problems, and clinical utility. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 1994;18:847–51. Study design.
58. Hofmann AF, Poley JR. Cholestyramine treatment of diarrhea associated with ileal resection. N Engl J Med 1969;281:397–402. Population.
59. Højgaard L, et al. Bile acid induced diarrhoea treated with cholestyramine released from a newly developed enterocoating in colon or distal ileum: a double-blind, cross-over study on patients with ileal resection [abstract]. Eur J Clin Invest 1984;14:9. Population.
60. Isolauri E, Vahasarja V, Vesikari T. Effect of cholestyramine on acute diarrhoea in children receiving rapid oral rehydration and full feedings. Ann Clin Res 1986;18:99–102. Population.
61. Isolauri E, Vesikari T. Oral rehydration, rapid feeding, and cholestyramine for treatment of acute diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1985;4:366–74. Population.
62. Iwanczak F. [Results of cholestyramine treatment of chronic infantile diarrhea.] Polski Tygodnik Lekarski 1981;36:525–8. Population.
63. Jacobsen O, Hojgaard L, Hylander Moller E, Wielandt TO, Thale M, Jarnum S, et al. Effect of enterocoated cholestyramine on bowel habit after ileal resection: a double blind crossover study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985;290:1315–8.
64. Jacyna MR, Boyd EJ, Wormsley KG. Comparative study of four antacids. Postgrad Med J 1984;60:592–6. Population.
65. Javitt NB, Morrissey KP, Siegel E, Goldberg H, Gartner LM, Hollander M, et al. Cholestatic syndromes in infancy: diagnostic value of serum bile acid pattern and cholestyramine administration. Pediatr Res 1973;7:119–25. Population.
66. Jewkes AJ, Windsor CW, Ward RS, Timmins AE. Relationship between bile acid malabsorption using the 75Se homocholic acid taurine scanning method and diarrhoea following right hemicolectomy. Br J Surg 1989;76:707–8. Population.
67. Karbach U, Singe CC, Mahtricht M, Ewe K. Comparison of maximal postprandial serum cholylglycine concentration with the retention of 75Se-homotaurocholic acid in ileal dysfunction. Z Gastroenterol 1989;27:258–62. Outcomes.
68. Khalid U, Lalji A, Stafferton R, Andreyev J. Bile acid malabsoption: a forgotten diagnosis? Clin Med 2010;10:124–6. Study design.
69. Knox JF, Rose D, Emmons J, Podoll J, Seaian K, Attila T, et al. Colesevelam for the treatment of bile acid-induced diarrhea in crohn’s disease patients intolerant of cholestyramine. Gastroenterology 2004;126:A628. Population.
70. Kostic K, Popovic O, Janosevic S. [Measurement of 75Se labeled bile acid analogue abdominal retention (SeHCAT) for investigation of ileal function.] Radiologia Iugoslavica 1987;21(Suppl. 4):73–6. Study design.
71. Kruis W. [The 75Se homotaurocholic acid test in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases.] Z Gastroenterol Verh 1989;24:38–9. Study design.
72. Kruis W, Scheurlen C, Moser E, Paumgartner G. Spezifitat und sensitivitat des SeHCAT-testes fur die diagnose einer ileumdysfunktion bei patienten mit morbus crohn. Z Gastroent 1987;22:159–63. Not found.
73. Kurien M, Evans KE, Leeds JS, Hopper AD, Harris A, Hanney M, et al. Bile acid malabsorption a differential diagnosis for patients presenting with diarrhoea predominant irritable bowel syndrome type symptoms? [PWE-077]. Paper presented at Annual General Meeting of the British Society of Gastroenterology, 14–17 March 2011, Birmingham, UK. Gut 2011;60(Suppl. 1):A160–1. Outcomes.
74. Kurien M, Evans KE, Leeds JS, Hopper AD, Harris A, Sanders DS. Bile acid malabsorption: an under-investigated differential diagnosis in patients presenting with diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome type symptoms. Scand J Gastroenterol 2011;46:818–22. Study design.
75. Lankisch PG. Secretion and absorption (methods and functions). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2009;23:325–35. Study design.
76. Laudanna AA, Germ:an JC, Gama Rodriques JJ, Mekler M, Gama AH, Bertarello A. [Cholestyramine in the treatment of severe diarrhea and diarrhea of the diabetic patient.] Rev Fac Cienc Med Cordoba 1985;43:3–6. Index test.
77. Ludgate SM, Merrick MV. The pathogenesis of post-irradiation chronic diarrhoea: measurement of SeHCAT and B12 absorption for differential diagnosis determines treatment. Clin Radiol 1985;36:275–8. Population.
78. Luman W, Williams AJ, Merrick MV, Eastwood MA. Idiopathic bile acid malabsorption: long-term outcome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1995;7:641–5. Study design.
79. Maurelli L, D’Arienzo A, Di Siervi P, Scuotto A, Panarese A, Maurano A, et al. [Comparison of the 75SeHCAT test and the cholylglycine C-14 breath test associated with fecal recovery of C-14 in the assessment of ileal malabsorption of bile salts.] Italian Curr Radiol 1988;7:47–50. Study design.
80. Mehta G, Pavan M, Taslaq S, Dhesi E, Bansi DS, Thillainayagam AV. Idiopathic bile acid malabsorption is a common cause of chronic diarrhea with functional characteristics [S2061]. Paper presented at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2009, 30 May–4 June 2009, Chicago, IL. Gastroenterology 2009;136(5 Suppl. 1):A322. Outcomes.
81. Menon S, Jones BJM. Postinfective bile acid malabsorption: is this a long-term condition? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;23:308–10. Study design.
82. Merrick MV. Bile acid malabsorption: clinical presentations and diagnosis. Dig Dis 1988;6:159–69. Study design.
83. Miettinen TA. The role of bile salts in diarrhoea of patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 1971;12:632–5. Population.
84. Money ME, Hofmann AF, Hagey LR, Walkowiak J, Talley NJ. Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome-diarrhea with pancrealipase or colesevelam and association with steatorrhea. Pancreas 2009;38:232–3. Study design.
85. Morgan I, Morris AI, Stockdale HR, Brownless S. SeHCAT in the newborn. Br J Radiol 1985;58:273. Study design.
86. Moylan FM. Aluminum hydroxide in the symptomatic treatment of infants with chronic diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1983;2:295–8. Population.
87. Muller M, Willen R, Stotzer P-O. Colonoscopy and SeHCAT for investigation of chronic diarrhea. Digestion 2004;69:211–18. Outcomes.
88. Niaz SK, Sandrasegaran K, Renny FH, Jones BJ. Postinfective diarrhoea and bile acid malabsorption. J R Coll Physicians Lond 1997;31:53–6. Population.
89. Notta PC, Ramal D, Maisterra S, Roca M, Ricart Y, Mora J, et al. Biliary acids absorption measurement with 75Se-SEHCAT in the initial diagnosis of the chronic diarrhea. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37(Suppl. 2):S454. Outcomes.
90. Nyhlin H, Brydon G, Danielsson A, Westman S. Clinical application of a selenium (75Se)-labelled bile acid for the investigation of terminal ileal function. Hepatogastroenterology 1984;31:187–91. Population.
91. Nyhlin H, Merrick MV, Eastwood MA, Brydon WG. Evaluation of ileal function using 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate, a-gamma-labeled conjugated bile acid. Initial clinical assessment. Gastroenterology 1983;84:63–8. Outcomes.
92. Olmos RV, den Hartog Jager F, Hoefnagel C, Taal B. Imaging and retention measurements of selenium 75 homocholic acid conjugated with taurine, and the carbon 14 glycochol breath test to document ileal dysfunction due to late radiation damage. Eur J Nucl Med 1991;18:124–8. Study design.
93. Orholm M, Pedersen JO, Arnfred T, Rodbro P, Thaysen EH. Evaluation of the applicability of the SeHCAT test in the investigation of patients with diarrhoea. Scand J Gastroenterol 1988;23:113–17. Outcomes.
94. Pattni S, Dew T, Srinivas M, Basumani P, Bardhan KD, Walters JRF. Evaluation of fibroblast growth factor 19 in the diagnosis of bile acid diarrhoea [PTU-054]. Paper presented at Annual General Meeting of the British Society of Gastroenterology, 14–17 March 2011, Birmingham, UK. Gut 2011;60(Suppl. 1):A88. Outcomes.
95. Pattni SS, Brydon G, Dew T, Walters JR. Evaluation of fibroblast growth factor 19 and 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one in the diagnosis of bile acid diarrhea [770]. Paper presented at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2010, 1–6 May 2010, New Orleans, LA. Gastroenterology 2010;138(5 Suppl. 1):S107. Study design.
96. Pattni SS, Dew T, Srinivas M, Basumani P, Bardhan KD, Walters JR. Evaluation of fibroblast growth factor 19 in the diagnosis of bile acid diarrhea [Sa1337]. Paper presented at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2011, 7–10 May 2011, Chicago, IL. Gastroenterology 2011;140(5 Suppl. 1):S284. Outcomes.
97. Popovic O, Milovic V, Kostic K, Necic D, Jojic N, Durdevic D, et al. [Colestipol hydrochloride in the treatment of bile acid-induced diarrhoea.] Gastroenterohepatoloski Arhiv 1991;10:46–52. Population.
98. Puleston J, Morgan H, Andreyev J. New treatment for bile salt malabsorption [6]. Gut 2005;54:441–2. Population.
99. Radic Z, Golubovic S, Radosavljevic R, Zigic B. [The use of SeHCAT in diagnostics of terminal ileal disease.] Radiologia Iugoslavica 1987;21(Suppl. 4):77–9. Study design.
100. Rao AS, Wong BS, Odunsi-Shiyanbade ST, Burton D, McKinzie S, Zinsmeister AR, et al. The bile salt chenodeoxycholate and the bile acid sequestrant colesevelam both retard gastric emptying despite opposite effects on colonic transit in IBS patients. Paper presented at 2010 Joint International Neurogastroenterology and Motility Meeting, 26–29 August 2010, Boston, MA. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2010;22(Suppl. 1):66. Index test.
101. Rossel P, Sortsoe Jensen H, Qvist P, Arveschoug A. Prognosis of adult-onset idiopathic bile acid malabsorption. Scand J Gastroenterol 1999;34:587–90. Study design.
102. Rowe GG. Control of diarrhea by cholestyramine administration. Am J Med Sci 1968;255:84–8. Population.
103. Rust C, Sauter GB, Oswald M, Kullak-Ublick GA, Paumgartner G, Beuers U. [Effect of cholestyramin on bile acid profile and bile acid synthesis under treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid.] Z Gastroenterol 1998;36:100. Population.
104. Sali A, Murray WR, Mackay C. Aluminum hydroxide in bile-salt diarrhea. Lancet 1977;310:1051–3. Population.
105. Sali A, Watkinson G, Mackay C. Management of bile-salt diarrhea with aluminum hydroxide. Paper presented at British Society of Gastroenterology Spring Meeting, 1–2 April 1977, Cambridge, UK. Gut 1977;18:A419. Population.
106. Sauter GH, Munzing W, von Ritter C, Paumgartner G. Bile acid malabsorption as a cause of chronic diarrhea: diagnostic value of 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one in serum. Dig Dis Sci 1999;44:14–19. Population.
107. Scheurlen C, Kruis W, Bull U, Stellaard F, Kalek HD, Lang P, et al. Comparison between total-body retention of SE-75-homotaurocholic acid and fecal bile-acid excretion in patients with disordered ileum function. Z Gastroenterol 1983;21:419–20. Not found.
108. Scheurlen C, Kruis W, Bull U, Stellaard F, Lang P, Paumgartner G. Comparison of 75SeHCAT retention half-life and fecal content of individual bile acids in patients with chronic diarrheal disorders. Digestion 1986;35:102–8. Outcomes.
109. Scheurlen C, Kruis W, Moser E, Paumgartner G. Accuracy of the whole body retention half-life of 75SeHCAT in the diagnosis of ileal dysfunction in patients with Crohn’s disease. Hepatogastroenterology 1988;35:136–9. Population.
110. Schiller LR, Bilhartz LE, Santa Ana CA, Fordtran JS. Comparison of endogenous and radiolabeled bile acid excretion in patients with idiopathic chronic diarrhea. Gastroenterology 1990;98:1036–43. Outcomes.
111. Schiller LR, Hogan RB, Morawski SG, Santa Ana CA, Bern MJ, Norgaard RP, et al. Studies of the prevalence and significance of radiolabeled bile acid malabsorption in a group of patients with idiopathic chronic diarrhea. Gastroenterology 1987;92:151–60. Outcomes.
112. Sciarretta G, Furno A, Fagioli G, Vicini G, Lo Cuoco D, Ginevra A, et al. The SeHCAT test: a new radioisotopic diagnostic tool for bile acid malabsorption. Ital J Gastroenterol 1988;20:83–7. Study design.
113. Sciarretta G, Furno A, Mazzoni M, Malaguti P. Post-cholecystectomy diarrhea: evidence of bile acid malabsorption assessed by SeHCAT test. Am J Gastroenterol 1992;87:1852–4. Population.
114. Sciarretta G, Furno A, Morrone B, Malaguti P. Absence of histopathological changes of ileum and colon in functional chronic diarrhea associated with bile acid malabsorption, assessed by SeHCAT test: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 1994;89:1058–61. Study design.
115. Seaman MCE, Williams NR. SeHCAT acquisitions: beware outside influences. Paper presented at 39th Annual Meeting of the British Nuclear Medicine Society, 9–11 May 2011, Brighton, UK. Nucl Med Commun 2011;32:440. Outcomes.
116. Singe CC, Karbach U, Biederlack S, Ewe K. 75-SeHCAT-retentionstest bei ileitis crohn: korrelation mit befallslange und postprandialen serumanstieg von cholylglycin. Z Gastroent 1987;22:166–70. Not found.
117. Soeparto P, Subiyanto MS, Noerasid H. Cholestyramine in the management of recurrent diarrhoea in infancy. Paediatr Indones 1982;22:104–10. Index test.
118. Spada C, Hassan C, Marmo R, Petruzziello L, Riccioni ME, Zullo A, et al. Meta-analysis shows colon capsule endoscopy is effective in detecting colorectal polyps. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;8:516–22. Study design.
119. Stotzer PO, Sadik R, Sjovall H, Abrahamsson H. Effects of cholestyramine on gastrointestinal transit in idiopathic bile acid malabsorption (IBAM). Gastroenterology 2005;128:A452. Outcomes.
120. Suhr O, Danielsson A, Horstedt P, Stenling R. Bacterial contamination of the small bowel evaluated by breath tests, 75Se-labelled homocholic-tauro acid, and scanning electron microscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol 1990;25:841–52. Study design.
121. Suhr O, Danielsson A, Nyhlin H, Truedsson H. Bile acid malabsorption demonstrated by SeHCAT in chronic diarrhoea, with special reference to the impact of cholecystectomy. Scand J Gastroenterol 1988;23:1187–94. Outcomes.
122. Suhr O, Danielsson A, Steen L. Bile acid malabsorption caused by gastrointestinal motility dysfunction? an investigation of gastrointestinal disturbances in familial amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. Scand J Gastroenterol 1992;27:201–7. Study design.
123. Thaysen EH. Idiopathic bile acid diarrhoea reconsidered. Scand J Gastroenterol 1985;20:452–6. Study design.
124. Thaysen EH, Orholm M, Arnfred T, Carl J, Rodbro P. Assessment of ileal function by abdominal counting of the retention of a gamma emitting bile acid analogue. Gut 1982;23:862–5. Outcomes.
125. Thomas PD, Forbes A, Green J, Howdle P, Long R, Playford R, et al. Guidelines for the investigation of chronic diarrhoea, 2nd edn. Gut 2003;52(Suppl. 5):v1–15. Study design.
126. Thomsen LH, Arveschough AK, Gustenhoff P, Qvist P. [SeHCAT scanning in bile acid malabsorption.] Ugeskr Laeger 1998;160:5362–5. Study design.
127. Ung KA, Gillberg R, Kilander A, Abrahamsson H. Role of bile acids and bile acid binding agents in patients with collagenous colitis. Gut 2000;46:170–5. Outcomes.
128. Ung KA, Kilander AF, Lindgren A, Abrahamsson H. Impact of bile acid malabsorption on steatorrhoea and symptoms in patients with chronic diarrhoea. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2000;12:541–7. Outcomes.
129. Valdes Olmos R, Den Hartog Jager F, Hoefnagel C, Taal B. Effect of loperamide and delay of bowel motility on bile acid malabsorption caused by late radiation damage and ileal resection. Eur J Nucl Med 1991;18:346–50. Population.
130. Valdes Olmos R, Den Hartog Jager F, Hoefnagel C, Taal B. Imaging and retention measurements of selenium 75 homocholic acid conjugated with taurine, and the carbon 14 glycochol breath test to document ileal dysfunction due to late radiation damage. Eur J Nucl Med 1991;18:124–8. Index test.
131. Valdes Olmos RA, Taal BG, Hoefnagel CA, Boot H. 75SeHCAT in the assessment of improved bile acid absorption in patients with ileal damage by delaying bowel motility with loperamide. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1993;5:941–5. Population.
132. Valdes Olmos RA, Taal BG, Hoefnagel CA, Boot H. Sequential 75SeHCAT imaging in addition to the conventional 75SeHCAT test: a necessity. Eur J Nucl Med 1995;22:181–2. Study design.
133. van den Berg JW, de Rooij FW, Bosman-Jacobs EP. [75Se]-selenohomotaurocholic acid degradation by bacterial enzymes in vitro and in vivo: is it still a specific indicator for active ileal bile acid uptake? Digestion 1990;47:95–104. Outcomes.
134. Vantilburg AJP, Vanblankenstein M, Derooij FWM, Vandenberg JWO. Use of SeHCAT as a marker of fecal bile-acid loss in non-ileal disease. Gastroenterology 1987;92:1681. Index test.
135. Vesikari T, Isolauri E. A comparative trial of cholestyramine and loperamide for acute diarrhoea in infants treated as outpatients. Acta Paediatr Scand 1985;74:650–4. Population.
136. Vesikari T, Isolauri E, Maki M. Efficacy of cholestyramine in acute infantile diarrhoea: placebo-controlled double-blind trial in hospitalized children and in outpatients. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res 1984;2:151–8. Population.
137. Walters JRF, Tasleem AM, Omer OS, Brydon WG, Dew T, le Roux CW. A new mechanism for bile acid diarrhea: defective feedback inhibition of bile acid biosynthesis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;7:1189–94. Population.
138. Wedlake L, A’Hern R, Russell D, Thomas K, Walters JRF, Andreyev J. Idiopathic bile acid malabsorption is an important cause of symptoms frequently misdiagnosed as diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome [O-17]. Paper presented at Annual Meeting of the British Society of Gastroenterology, 23–26 March 2009, Glasgow, UK. Gut 2009;58(Suppl. 1):A6–7. Study design.
139. Wong BS, Camilleri M, Carlson P, Odunsi-Shiyanbade S, McKinzie S, Busciglio IA, et al. Pharmacogenetics of the effects of colesevelam on colonic transit in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea [Su1978]. Paper presented at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2011, 7–10 May 2011, Chicago, IL. Gastroenterology 2011;140(5 Suppl. 1):S524–5. Outcomes.
140. Worobetz L, Wilkinson A, Chmielowiec C, Tan L. Evaluation of SeHCAT test in determining ileal involvement and dysfunction in Cronn’s disease. Can J Gastroenterol 1993;7:597–601. Population.
141. Yarze JC. Cholestyramine for treatment of chronic diarrhea. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:599–601. Study design.
142. Zaniboni MG, Fagioli G, Lambertini A, Romeo N, Vicini G. [Use of the 75-SeHCAT (23-seleno-25-homotaurocholic acid) test in the diagnosis of chronic diarrhea in children: preliminary studies.] Minerva Pediatr 1987;39:19–23. Index test.
143. Zavoral JH, Laine DC, Bale LK, Wellik DL, Ellefson RD, Kuba K, et al. Cholesterol excretion studies in familial hypercholesterolemic children and their normolipidemic siblings. Am J Clin Nutr 1982;35:1360–7. Population.
144. Zijta FM, Bipat S, Stoker J. Magnetic resonance (MR) colonography in the detection of colorectal lesions: a systematic review of prospective studies. Eur Radiol 2010;20:1031–46. Study design.
Appendix 6 Studies provided by National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and/or the manufacturer
The following is a list of studies provided by NICE and/or the manufacturer of SeHCAT, along with the decision for inclusion or exclusion and reasons for exclusion:
1. Dyson J, Bartholomew P, Barbour J. Use of SeHCAT testing: investigation of diarrhoea and patient satisfaction. Poster presented at 19th United European Gastroenterology Week (UEGW), 22–26 October 2011, Stockholm, Sweden. INCLUDED.
2. International Commision on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Radiation dose to patients from radiopharmaceuticals (Addendum to ICRP Publication 53). ICRP Publication 80. Ann ICRP 1998;28:1–126. EXCLUDED – outcomes.
3. Morgan I, Morris AI, Stockdale HR, Brownless S. SeHCAT in the newborn. Br J Radiol 1985;58:273. EXCLUDED – study design.
4. Tunney R. The clinical value of SeHCAT in the diagnosis of bile acid malabsorption: an evaluation of the British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines for the investigation of chronic diarrhoea [report]. Manchester: University of Manchester; 2011. INCLUDED.
5. Zaniboni MG, Fagioli G, Lambertini A, Romeo N, Vicini G. [Use of the 75-SeHCAT (23-seleno-25-homotaurocholic acid) test in the diagnosis of chronic diarrhea in children: preliminary studies.] Minerva Pediatr 1987;39:19–23. EXCLUDED – index test.
Appendix 7 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance relevant to the treatment of chronic diarrhoea
None.
Other relevant guidelines:
-
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: diagnosis and management of irritable bowel syndrome in primary care. February 2008. URL: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG61
-
Mowat C, Cole A, Windsor A, Ahmad T, Arnott I, Driscoll R, et al. Guidelines for the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut 2011;60:571–607.
Appendix 8 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses checklist
| Section/topic | # | Checklist item | Reported on page # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Title | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both | Front page |
| Abstract | |||
| Structured summary | 2 | Provide a structured summary including, as applicable: background; objectives; data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, and interventions; study appraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions and implications of key findings; systematic review registration number | Scientific summary, pp. xiii–xviii |
| Introduction | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known | Chapter 1 , pp. 1–5 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of questions being addressed with reference to participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design (PICOS) | Chapter 2 , p. 7 |
| Methods | |||
| Protocol and registration | 5 | Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (e.g. Web address), and, if available, provide registration information including registration number | PROSPERO CRD42012001911; www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero |
| Eligibility criteria | 6 | Specify study characteristics (e.g. PICOS, length of follow-up) and report characteristics (e.g. years considered, language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale | Chapter 3 , pp. 9–10 |
| Information sources | 7 | Describe all information sources (e.g. databases with dates of coverage, contact with study authors to identify additional studies) in the search and date last searched | Chapter 3 , pp. 10–12, Figure 3 |
| Search | 8 | Present full electronic search strategy for at least one database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated | Appendix 1 |
| Study selection | 9 | State the process for selecting studies (i.e. screening, eligibility, included in systematic review, and, if applicable, included in the meta-analysis) | Chapter 3 , p. 11 |
| Data collection process | 10 | Describe method of data extraction from reports (e.g. piloted forms, independently, in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators | Chapter 3 , p. 11 |
| Data items | 11 | List and define all variables for which data were sought (e.g. PICOS, funding sources) and any assumptions and simplifications made | Chapter 3 , p. 9–10 |
| Risk of bias in individual studies | 12 | Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias of individual studies (including specification of whether this was done at the study or outcome level), and how this information is to be used in any data synthesis | Chapter 3 , pp. 11–14 |
| Summary measures | 13 | State the principal summary measures (e.g. risk ratio, difference in means) | Chapter 3 , pp. 13–15 |
| Synthesis of results | 14 | Describe the methods of handling data and combining results of studies, if done, including measures of consistency (e.g. I 2) for each meta-analysis | Chapter 3 , pp. 13–15 |
| Risk of bias across studies | 15 | Specify any assessment of risk of bias that may affect the cumulative evidence (e.g. publication bias, selective reporting within studies) | NA |
| Additional analyses | 16 | Describe methods of additional analyses (e.g. sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done, indicating which were pre-specified | NA |
| Results | |||
| Study selection | 17 | Give numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram | Chapter 3 , pp. 15–16, Figure 4, Appendix 5 and 6 |
| Study characteristics | 18 | For each study, present characteristics for which data were extracted (e.g. study size, PICOS, follow-up period) and provide the citations | Chapter 3 , pp. 17–32, Tables 2 and 6 , Appendix 4 |
| Risk of bias within studies | 19 | Present data on risk of bias of each study and, if available, any outcome level assessment (see item 12) |
Chapter 3
, pp. 26–28,
Table 3, Appendix 2
and
3
Chapter 3 , pp. 30–33, Tables 5 and 7 Chapter 3 , pp. 40–41, Table 12 |
| Results of individual studies | 20 | For all outcomes considered (benefits or harms), present, for each study: (a) simple summary data for each intervention group (b) effect estimates and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest plot |
Chapter 3
, p. 26 Chapter 3 , pp. 26–28, Table 4 Chapter 3, p. 28 Chapter 3, pp. 28–40, Tables 6, 8 and 9 Chapter 3 , pp. 40–41, Table 13 |
| Synthesis of results | 21 | Present results of each meta-analysis done, including confidence intervals and measures of consistency | Chapter 3 , pp. 41–43 |
| Risk of bias across studies | 22 | Present results of any assessment of risk of bias across studies (see Item 15) | NA |
| Additional analysis | 23 | Give results of additional analyses, if done (e.g. sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression [see Item 16]) | NA |
| Discussion | |||
| Summary of evidence | 24 | Summarize the main findings including the strength of evidence for each main outcome; consider their relevance to key groups (e.g. healthcare providers, users, and policy makers) | Chapter 5 , pp. 99–101 |
| Limitations | 25 | Discuss limitations at study and outcome level (e.g. risk of bias), and at review-level (e.g. incomplete retrieval of identified research, reporting bias) |
Chapter 5
, pp.102–103 Chapter 5 , p.104–106 |
| Conclusions | 26 | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence, and implications for future research | Chapter 6 , pp.107–108 |
| Funding | |||
| Funding | 27 | Describe sources of funding for the systematic review and other support (e.g. supply of data); role of funders for the systematic review | p. xviii |
Appendix 9 Questionnaire
Appendix 10 Details on estimation medication costs for IBS-D and diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients without ileal resection
| Expert | Drug | Per cent of patients (lowest–highest) | Dosage/frequency | Total dosage per day (expert) | Dosage per day (model) | Price per unit (£) | Costs per day (£) | Weighted cost per day (lowest–highest) (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Loperamide | 0.2 (0.1–0.25) | 2–4 mg t.i.d. | 6–12 mg | 9 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.135 | 0.03 (0.01–0.03) |
| A | Questran® (Bristol-Myers Squibb) | 0.55 (0.4–0.8) | 4–8 g OD–t.i.d. | 4–24 mg | 14 mg | 0.21 per 4 mg | 0.735 | 0.40 (0.3–0.6) |
| A | Antidepressant (assume TCA) | 0.2 (0.15–0.25 | Lowest recommended dose | 0.06 | 0.01 (0.01–0.02) | |||
| A | Total | 0.45 (0.32–0.64) | ||||||
| B | Loperamide | 0.9 (0.6–1) | 2–16 mg | 2–16 mg | 9 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.135 | 0.12 (0.08–0.14) |
| B | Codeine phosphate | 0.25 (0.05–0.4) | 30–60 mg | 30–60 mg | 45 mg | 0.04 per 15 mg | 0.12 | 0.03 (0.01–0.05) |
| B | Colestryramine | 0.1 (0–0.4) | 2–12 g | 2–12 g | 7 mg | 0.21 per 4 mg | 0.368 | 0.04 (0–0.15) |
| B | Amitriptyline | 0.05 (0–0.5) | 10–30 mg | 10–30 mg | 20 mg | 0.03 per 10 mg | 0.06 | 0.00 (0–0.01) |
| B | Total | 0.19 (0.09–0.34) | ||||||
| C | Loperamide | 0.9 (0.8–1) | 2 mg | As needed (assume 2/3 of the time) | 66.7% × 2 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.020 | 0.02 (0.02–0.02) |
| C | Codeine phosphate | 0.3 (0–0.4) | 30–60 mg | As needed (assume 2/3 of the time) | 66.7% × 45 mg | 0.04 per 15 mg | 0.080 | 0.02 (0–0.03) |
| C | Cholestyramine | 0.3 (0–0.5) | 4 mg q.i.d. | As needed (assume 2/3 of the time) | 66.7% × 16 mg | 0.21 per 4 mg | 0.560 | 0.17 (0–0.3) |
| C | Mebeverine | 0.3 (0–0.5) | 100 mg t.i.d. | As needed (assume 2/3 of the time) | 66.7% × 300 mg | 0.037 per 100 mg | 0.074 | 0.02 (0–0.04) |
| C | Total | 0.23 (0.02–0.37) | ||||||
| D | Opiate (assume loperamide) | 0.75 (0.7–0.9) | Assume average A and B | 9 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.135 | 0.10 (0.09–0.12) | |
| D | Cholestyramine | 0.15 (0–0.3) | Assume average A and B | 12 mg | 0.21 per 4 mg | 0.63 | 0.09 (0–0.19) | |
| D | Total | 0.20 (0.09–0.31) | ||||||
| E | Antispasmodic (assume mebeverine) | 0.8 (0.6–0.9) | Assume 100 mg t.i.d. | 300 mg | 300 mg | 0.037 per 100 mg | 0.111 | 0.09 (0.07–0.1) |
| E | SSRI | 0.1 (0.05–0.2) | Once per day | Assume same as B | 0.03 per 10 mg | 0.06 | 0.01 (0–0.01) | |
| E | TCA | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | Every night | Assume same as A | 0.03 per 10 mg | 0.06 | 0.01 (0.01–0.02) | |
| E | Anti-diarrhoeal (assume loperamide) | 0.15 (0.1–0.2) | As needed (average one per day) | 2 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.03 | 0.00 (0–0.01) | |
| E | Total | 0.11 (0.08–0.14) | ||||||
| F | Loperamide | 0.75 (0.5–0.9) | 1–8 mg | 1–8 mg | 4.5 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.068 | 0.05 (0.03–0.06) |
| F | Codeine phosphate | 0.25 (0.1–0.4) | 30–120 mg | 30–120 mg | 75 mg | 0.04 per 15 mg | 0.2 | 0.05 (0.02–0.08) |
| F | TCA | 0.5 (0.25–0.75) | Assume same as A | 0.03 per 10 mg | 0.06 | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | ||
| F | Questran® | 0.25 (0.25–0.75) | 1–2 sachets 2 × per day | 8–16 mg | 12 mg | 0.21 per 4 mg | 0.63 | 0.16 (0.06–0.25) |
| F | Total | 0.29 (0.13–0.44) | ||||||
| G | Loperamide | 1 (0.75–1) | 2–8 mg | 2–8 mg | 5 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.075 | 0.08 (0.06–0.08) |
| G | Total | 0.08 (0.06–0.08) |
| Expert | Drug | Per cent of patients (lowest–highest) | Dosage/frequency | Total dosage per day (expert) | Dosage per day (model) | Price per unit (£) | Costs per day (£) | Weighted cost per day (lowest–highest) (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | Loperamide | 0.8 (0.5–1) | 2–16 mg | 9 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.135 | 0.11 (0.07–0.14) | |
| Q | Codeine | 0.2 (0–0.5) | 30–120 mg | 75 mg | 0.04 per 15 mg | 0.2 | 0.04 (0–0.1) | |
| Q | Corticosteroids | 0.7 (0.5–1) | 40 mg prednisolone/9 mg budesonide | 40 mg prednisolone/9 mg budesonide | Prednisolone: 0.04 per 5 mg; budesonide: 0.75 per 3 mg | 1.285 (assume average prednisolone and budesonide) | 0.90 (0.64–1.29) | |
| Q | Anti-TNF-α adalimumab | 0.1 (0–0.3) | 160–40 mg | Assume 160 mg once plus 40 mg at weeks 2, 4, 6 | 352.14 per 40 mg | 13.69 | 1.37 (0–4.11) | |
| Q | Total | 2.42 (0.71–5.63) | ||||||
| R | Pentasa® (Ferring) | 0.6 (0.4–0.7) | 4 g per day | 4 g | 2.4 per 4 mg | 2.4 | 1.44 (0.96–1.68) | |
| R | Azathioprine | 0.5 (0.2–0.7) | 2 mg/kg per day | 156 mg (assume average weight 78) | 0.08 per 50 mg | 0.2496 | 0.12 (0.05–0.17) | |
| R | Corticosteroids | 0.8 (0.6–1) | 40 mg prednisolone/9 mg budesonide | 40 mg prednisolone/9 mg budesonide | Prednisolone: 0.04 per 5 mg; budesonide: 0.75 per 3 mg | 1.285 (assume average prednisolone and budesonide) | 1.03 (0.77–1.29) | |
| R | Anti-TNF-αα adalimumab | 0.1 (0–0.15) | 160–40 mg | Assume 160 mg once plus 40 mg at weeks 2, 4, 6 | 352.14 per 40 mg | 13.69 | 1.37 (0–2.05) | |
| R | BAS | 0.2 (0.05–0.4) | 2–8 g OD–t.i.d. | 2–24 mg | 13 mg | 0.21 per 4 mg | 0.6825 | 0.14 (0.03–0.28) |
| R | Antibiotics (small bowel over growth) | 0.2 (0.05–0.3) | Not included as it would be a short course, costs negligible | |||||
| R | Total | 4.10 (1.82–5.47) | ||||||
| S | Codeine | 0.5 (0.4–0.8) | 30–120 mg | 75 mg | 0.04 per 15 mg | 0.2 | 0.10 (0.08–0.16) | |
| S | Loperamide | 0.5 (0.4–0.8) | 2–8 mg | 5 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.075 | 0.04 (0.03–0.06) | |
| S | Total | 0.14 (0.11–0.22) | ||||||
| T | BAS | 0.8 (0.7–0.9) | 2–8 g OD–t.i.d. | 2–24 mg | 13 mg | 0.21 per 4 mg | 0.6825 | 0.55 (0.48–0.62) |
| T | Loperamide | 0.3 (0.25–0.35) | 2–4 mg OD–t.i.d. | 2–12 mg | 7 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.105 | 0.03 (0.03–0.04) |
| T | Total | 0.58 (0.51–0.66) | ||||||
| Ua | Codeine | 0.5 (0.4–0.8) | 30–120 mg | 75 mg | 0.04 per 15 mg | 0.2 | 0.10 (0.08–0.16) | |
| Ua | Loperamide | 0.8 (0.5–1) | 2–4 mg OD–t.i.d. | 2–12 mg | 7 mg | 0.03 per 2 mg | 0.105 | 0.08 (0.05–0.12) |
| Ua | Corticosteroids | 0.8 (0.6–1) | 40 mg prednisolone/9 mg budesonide | 40 mg prednisolone/9 mg budesonide | Prednisolone: 0.04 per 5 mg; budesonide: 0.75 per 3 mg | 1.285 (assume average prednisolone and budesonide) | 1.03 (0.77–1.29) | |
| Ua | BAS | 0.8 (0.7–0.9) | 2–8G OD–t.i.d. | 2–24 mg | 13 mg | 0.21 per 4 mg | 0.6825 | 0.55 (0.48–0.62) |
| U | Total | 1.76 (1.38–2.17) | ||||||
Appendix 11 Final protocol
DIAGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT REPORT COMMISSIONED BY THE NIHR HTA PROGRAMME ON BEHALF OF THE NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE – PROTOCOL
1 Title of project
A systematic review and economic evaluation of SeHCAT (Tauroselcholic [75Selenium] acid) for the investigation of bile acid malabsorption (BAM) and measurement of bile acid pool loss.
2 Name of External Assessment Group (EAG) and project lead
Kleijnen Systematic Reviews Ltd.
Project lead:
Rob Riemsma
Kleijnen Systematic Reviews Ltd
Unit 6, Escrick Business Park
Riccall Road
Escrick
York YO19 6FD
Tel: 01904 727986
Email: rob@systematic-reviews.com
Second contact:
Jos Kleijnen
Kleijnen Systematic Reviews Ltd
Unit 6, Escrick Business Park
Riccall Road
Escrick
York YO19 6FD
Tel: 01904 727981
Email: jos@systematic-reviews.com
Health economics lead:
Maiwenn Al
Institute for Medical Technology Assessment (iMTA)
Erasmus University
P.O. Box 1738
3000 DR Rotterdam
The Netherlands
Tel: +31-10-4088565
Email: al@bmg.eur.nl
3 Plain English Summary
Bile acids are produced in the liver, secreted into the biliary system, stored in the gall-bladder and are released after meals. They are important for the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine. Usually over 95% of the bile acids are absorbed in the terminal ileum and are taken up by the liver and resecreted. When larger amounts of bile acids enter the large intestine, they stimulate water secretion and intestinal motility in the colon, which causes symptoms of chronic diarrhoea. This is called bile acid malabsorption (BAM).
A SeHCAT scan is a diagnostic procedure, which looks at the function of the bowel. It involves swallowing a capsule containing a very slightly radioactive tracer and imaging with a special camera shortly after swallowing the capsule and after a week. This then shows which percentage of bile acid was absorbed, and thus whether the patient has BAM.
The purpose of this project is to assess the benefits, risks and cost-effectiveness of [75Se] tauroselcholic acid (SeHCAT), a bile acid analogue which is used as a test for investigating bile acid malabsorption (BAM) and the measurement of bile acid pool loss in patients with chronic diarrhoea referred to a GI clinic for investigation and diagnosis of BAM. Patients with Crohn’s disease with chronic diarrhoea will be assessed separately.
4 Decision problem
4.1 Objectives
The objective of this project is to evaluate the clinical and cost effectiveness of [75Se] tauroselcholic acid (SeHCAT), a bile acid analogue which is used as a test for investigating bile acid malabsorption (BAM) and the measurement of bile acid pool loss in patients referred to a GI clinic for investigation and diagnosis of BAM.
This can be translated in the following research questions. For people with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and in people with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection):
-
What are the effects of SeHCAT compared to no SeHCAT in terms of chronic diarrhoea, other health outcomes and costs?
-
What are the effects of bile acid sequestrants (BAS) compared to no BAS in people with a positive or negative SeHCAT test?
-
Does a positive or negative SeHCAT test predict improvement in terms of chronic diarrhoea, other health outcomes and costs?
4.2. Intervention technologies
For questions 1 and 3, SeHCAT is the intervention.
SeHCAT (GE Healthcare) is a radiopharmaceutical that is licensed for use in the investigation of bile acid malabsorption (BAM) and measurement of bile acid pool loss. It may also be used in assessing ileal function, in the investigation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and chronic diarrhoea and in the study of enterohepatic circulation.
SeHCAT product information lists its applications as:
Tauroselcholic acid is a bile acid analogue which shows identical physiological behaviour with naturally occurring bile acid conjugates. Following oral administration in normal subjects, approximately 95% of the labelled bile acid is absorbed, mainly by the terminal ileum during each enterohepatic cycle. The distribution of activity is almost entirely confined to the lumen of the biliary ducts, gut and liver. Whole body retention data from normal subjects showed 97 to 100% of [75Se]tauroselcholic was excreted with a biological half-life of 2.6 days and that, in most cases, a small component of about 3% was eliminated with a mean half time of 62 days. 1
For question 2 bile acid sequestrants are the relevant interventions. There are currently three bile acid sequestrants available: colestyramine, colestipol, and colesevelam. Where evidence is available, the effectiveness of fat restrictions and other dietary modifications will also be assessed.
4.3. Population
The populations for this evaluation are:
-
People presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause;
-
People with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection of the terminal ileum).
4.4. Relevant comparators
There is no direct comparator for this diagnostic test. Current diagnostic options include analysis of a patient’s history, investigations to exclude ‘red flag’ symptoms and a variety of other diagnostic tests such as blood tests and lactose tolerance tests. Trial of treatment and measurement of faecal bile acids are two methods used, with mixed results, to diagnose BAM. They are however, not widely used in current practice.
The current BSG guideline for chronic diarrhoea places SeHCAT at the end of the diagnostic algorithm (position C in Figure 1). Possible alternatives are:
-
SeHCAT as part of the basic investigations for all patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea (position A in Figure 1);
-
SeHCAT for all patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea and symptoms suggestive of functional disease (i.e. age < 45 and normal basic investigations) (position B1 in Figure 1); and also for patients with a history of findings suggestive of colonic or terminal ileal disease (position B2 in Figure 1).
SeHCAT as part of the basic investigations (position A in Figure 1), means that all patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea will be tested with SeHCAT. However, during the scoping workshop clinical experts advised that a positive SeHCAT test at this stage does not rule out the possibility of organic disease. As no subsequent tests for organic disease are made redundant, it is unlikely that SeHCAT in position A will be more cost-effective than in position B1. Therefore, this protocol will focus on position B1.
The same applies to SeHCAT in position B2. A positive SeHCAT test in position B2 will most likely not stop clinicians from doing subsequent tests (e.g. simoisdoscopy, barium enema or colonoscopy). Therefore, position B2 will be treated the same as position C in this report.
This leaves two possible populations for investigation:
-
People presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease;
-
People with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection of the terminal ileum)
For both populations, the intervention will be SeHCAT followed by the appropriate treatment (see figures 2 and 3); and the comparator will be appropriate treatment without SeHCAT.
5. Report methods for assessing clinical effectiveness
A systematic review will be conducted to summarise the evidence on the clinical effectiveness of SeHCAT for the assessment of bile acid malabsorption (BAM) and the measurement of bile acid pool loss. Systematic review methods will follow the principles outlined in the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) guidance for undertaking reviews in health care3 and NICE Diagnostic Assessment Programme interim methods statement. 4
5.1. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Participants
Study populations eligible for inclusion will be:
All patients (including children) referred to a GI clinic for investigation and diagnosis of BAM which is a common underlying cause of chronic diarrhoea and the measurement of bile acid pool loss. 5,6
As explained above, this report will focus on two specific populations:
-
People presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease;
-
People with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection of the terminal ileum).
Setting
Relevant settings are primary or secondary care.
Interventions (index test(s))
For population 1 the intervention is SeHCAT as the first test in people with symptoms suggestive of functional disease (position B1 in Figure 1).
For population 2 the intervention is SeHCAT.
Comparators
In the economic model the comparator will be no SeHCAT test (the current situation).
Outcomes
The following outcomes will be considered:
-
Effect of testing on treatment plan (e.g. surgical or medical management), where information on the appropriateness of the final treatment plan is also reported
-
Effect of testing on clinical outcome, (e.g. morbidity and adverse events)
-
Prognosis- the ability of test result to predict clinical outcome (e.g. response to treatment).
For included studies reporting any of the above outcome measures, the following outcomes will also be considered if reported:
-
Acceptability of tests to patients or surrogate measures of acceptability (e.g. waiting time and associated anxiety).
-
Adverse events associated with testing (e.g. pain/discomfort experienced during the procedure and waiting times before results).
Study design
The following types of studies will be included:
-
Randomised or non-randomised controlled trials, where participants are assigned to the intervention or comparator tests, for treatment planning, and outcomes are compared at follow-up.
-
Observational studies which report the results of multi-variable regression modelling with clinical outcome as the dependent variable and index test result as an independent variable. Included studies should control adequately for potential confounders (e.g. age, gender, disease, etc.).
The following study/publication types will be excluded:
-
Pre-clinical and animal.
-
Reviews, editorials, and opinion pieces.
-
Case reports.
-
Studies reporting only technical aspects of the test, or image quality.
-
Studies with < 10 participants.
5.2. Search strategy
Search strategies will be based on target condition and intervention, as recommended in the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) guidance for undertaking reviews in health care and the Cochrane Handbook for Diagnostic Test Accuracy Reviews. 7 – 9
Additional supplementary searches will be carried out as necessary. Searches for studies for cost and quality of life will also be included, see Section 6 for further detail.
The following databases will be searched for relevant studies from inception to the present:
-
MEDLINE (OvidSP)
-
MEDLINE In-Process Citations and Daily Update (OvidSP)
-
EMBASE (OvidSP)
-
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) (internet)
-
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (internet)
-
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) (internet)
-
Health Technology Assessment Database (HTA) (internet)
-
Science Citation Index (SCI) (Web of Science)
-
NIHR Health Technology Assessment Programme (internet)
Completed and ongoing trials will be identified by searches of the following resources (up to 2011):
-
NIH ClinicalTrials.gov (http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/)
-
Current Controlled Trials (http://www.controlled-trials.com/)
-
WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (http://www.who.int/ictrp/en/)
-
EU Clinical Trials Register (https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/)
Key conference proceedings, to be identified in consultation with clinical experts, will be screened for the last five years. These may include the European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology (EFSUMB) EUROSON congress.
Identified references will be downloaded in Endnote X4 software for further assessment and handling.
References in retrieved articles and relevant systematic reviews will be checked.
Search strategies will be developed specifically for each database and the keywords associated with BAM shall be adapted according to the configuration of each database. The main Embase search strategy for each set of searches will be independently peer reviewed by a second Information Specialist, using the PRESS-EBC checklist. 10
No restrictions on language or publication status will be applied. Limits will be applied to remove animal and phantom studies. Searches will take into account generic and other product names for the intervention. Examples of the search strategies to be used are presented in Appendix 1; these will be adapted as necessary following consultation with clinical experts.
5.3. Data extraction strategy
Two reviewers will independently screen titles and abstracts of all reports identified by searches and discrepancies will be discussed. Full copies of all studies deemed potentially relevant, after discussion, will be obtained and two reviewers will independently assess these for inclusion; any disagreements will be resolved by consensus or discussion with a third reviewer.
Data relating to study details, participants, intervention and comparator tests, reference standard, and outcome measures will be extracted by one reviewer, using a piloted, standard data extraction form. A second reviewer will check data extraction and any disagreements will be resolved by consensus or discussion with a third reviewer.
5.4. Quality assessment strategy
The methodological quality of included studies will be assessed using standard tools. 7 The Cochrane Collaboration quality assessment checklist will be used to assess the methodological quality of each included study as detailed in Table 1. 11
| Domain | Item | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence Generation | Was the allocation sequence adequately generated? | The method used to generate the allocation sequence should be described in sufficient detail to allow an assessment of whether it should produce comparable groups. |
| Allocation Concealment | Was allocation adequately concealed? | The method used to conceal the allocation sequence should be described in sufficient detail to determine whether intervention allocations could have been foreseen in advance of, or during, enrolment. |
| Blinding of participants, personnel and outcome assessors Assessments will be made for each main outcome (or class of outcomes). | Was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study? | All measures used, if any, to blind study participants and personnel from knowledge of which intervention a participant received, should be described. Any information relating to whether the intended blinding was effective should also be reported. |
| Incomplete outcome data Assessments will be made for each main outcome (or class of outcomes). |
Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed? | The completeness of outcome data for each main outcome should be described, including attrition and exclusions from the analysis. The authors should report any attrition and exclusions, the numbers in each intervention group (compared with total randomized participants), reasons for attrition/exclusions and any re-inclusions in analyses. |
| Selective outcome reporting | Are reports of the study free of suggestion of selective outcome reporting? | The study should be free of the possibility of selective outcome reporting. |
| Other sources of bias | Was the study apparently free of other problems that could put it at a high risk of bias? | Overall, the study should be free from any important concerns about bias (i.e. bias from other sources not previously addressed by the other items). |
Each study will be awarded a ‘yes’, ‘no’ or ‘unclear/unknown’ rating for each individual item in the checklist. Any additional clarifications or comments will also be recorded.
The quality of case–control and cohort studies will be assessed using specific checklists for the methodological quality assessment of these studies (see Appendix 2).
Quality assessment will be carried out independently by two reviewers. Any disagreements will be resolved by consensus. The results of the quality assessment will be used for descriptive purposes to provide an evaluation of the overall quality of the included studies and to provide a transparent method of recommendation for design of any future studies. In addition, if enough data are available from the included studies, each of the quality components will be included as explanatory variables in a meta-regression analysis to investigate the association of each of these components with study results as a way of explaining possible heterogeneity. Based on the findings of the quality assessment, recommendations will be made for the conduct of future studies.
5.5. Methods of analysis/synthesis
The results of initial scoping searches suggest that trial data and prognostic data are likely to be sparse or non-existent. This section therefore focuses on the synthesis of data from test accuracy studies. If other studies are identified, we anticipate that these will be summarised in a narrative synthesis.
Where meta-analysis is considered unsuitable for some or all of the data identified (e.g. due to the heterogeneity and/or small numbers of studies), we will employ a narrative synthesis. Typically, this will involve the use of text and tables to summarise data. These will allow the reader to consider any outcomes in the light of differences in study designs and potential sources of bias for each of the studies being reviewed. Studies will be organised by clinical application (diagnosis of BAM in those with chronic diarrhoea and those with Crohn’s disease).
Any data included on the following outcome measures: effects of testing on treatment planning and/or clinical outcome; adverse events associated with testing; acceptability to patients will be summarized according to the size and range of the outcomes reported.
The methods used to synthesis the data will be dependent on the types of outcome data included and the clinical and statistical similarity of the studies. Possible methods include the following types of analysis.
Dichotomous outcomes
Dichotomous data will be analysed by calculating the relative risk (RR) for each trial using the random-effects DerSimonian and Laird method and the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs). 12
Continuous outcomes
Continuous data will be analysed by calculating the standardised mean difference (SMD) between groups and the corresponding 95% CI, due to the different types of outcome measures. If the standard deviations and means are not determinable, they will be estimated from the data that is provided or from a representative value from other studies.
Systematic differences between studies (heterogeneity) are likely; therefore, the random-effects model will be used for the calculation of relative risks or standardised mean differences. Heterogeneity will initially be assessed by measuring the degree of inconsistency in the studies’ results (I2). This measure (I2) describes the percentage of total variation across studies that were due to heterogeneity rather than the play of chance. The value of I2 can lie between 0% and 100%. Low, moderate and high I2 values correspond to 25%, 50%, and 75%.
If important heterogeneity is identified, this will be formally investigated using meta-regression. In particular, a model will be used to explore the possible modifying effects of the following pre-specified factors: methodological quality of the primary studies, underlying illness, duration of pain, different age groups, and gender. The coefficient describing the predictive value of each factor and the overall effect on the main outcome will be modelled, using a fixed-effect model.
A funnel plot (plots of logarithm of the RR for efficacy against the precision of the logarithm of the RR) will be generated in order to estimate potential asymmetry, which will be indicative of small study effects. Treatment discontinuations will be chosen as an outcome since they are likely to be reported by the majority of included studies. In addition, the Egger regression asymmetry test will be used in order to facilitate the prediction of potential publication biases. This test detects funnel plot asymmetry by determining whether the intercept deviates significantly from zero in a regression of the standardised effect estimates against their precision.
Statistical analyses will be performed using the following software: RevMan (version 5), Comprehensive Meta-Analyses (CMA version 2), and STATA (STATA™ for Windows, version 10, Stata Corp; College Station, TX).
A detailed commentary on the major methodological problems or biases that affected the studies will also be included, together with a description of how this may have affected the individual study results. Recommendations for further research will be made based on any gaps in the evidence or methodological flaws.
6. Report methods for synthesising evidence of cost-effectiveness
6.1 Identifying and reviewing published cost-effectiveness studies
Exploration of the literature regarding published economic evaluations, utility studies and cost studies will be performed in the literature databases listed above. In addition, specific health economic databases will be searched (e.g. NHSEED (NHS Economic Evaluation Database), and HEED (Health Economic Evaluation Database). Searches will focus on original papers that report on cost, cost-accuracy, cost-effectiveness or cost-utility analyses, either studying the diagnostic phase (test accuracy in terms of detecting BAM of patients with chronic diarrhoea), therapeutic phase (patients with BAM), or a combination. For our assessment cost studies, utility studies and full economic evaluations, i.e. those that explicitly compare different decision options will selected. Clinical trials as well as modelling studies and cohort studies will be relevant within the frame of our project. The intention is not to perform a systematic review, but to use the studies identified to support the development of an economic model and estimation of model input parameters that will aim to answer the research questions of this project.
The results and the methodological quality of the studies selected will be summarised. Assessment of methodological quality will follow the criteria for economic evaluations in health care as described in the NICE methodological guidance. 4 Data extraction will focus on technologies compared, indicated population, main results in terms of costs and consequences of the alternatives compared, and the incremental cost-effectiveness, but also on methods of modelling used (if applicable), analytical methods and robustness of the study findings.
6.2 Evaluation of costs, quality of life and cost-effectiveness
Since this project aims to assess the value of SeHCAT in two different patient populations (see section 4.3 and 4.4), two separate economics models will be defined, constructed, analysed, and reported independently. Both models will evaluate the cost-effectiveness of SeHCAT compared to no SeHCAT as described in section 5.1. The perspective will be that of the NHS and the timeframe used will be life time. Consequences will be expressed as number of correct diagnoses for the diagnostic phase, and (quality adjusted) life years to also include the therapeutic phase. Any assumption used in the models and any parameter value will be based on literature if possible and supplemented by clinical expert opinion as required.
Model structure
Published studies that measure the clinical utility of SeHCAT from initial diagnosis through to final health outcomes have not been identified during the scoping phase. Consequently, it is likely that a linked evidence approach will need to be used in the modelling. That is, outcomes of the diagnostic tests to be assessed will need to be related to changes in treatment decisions, any delays in diagnosis and final heath outcomes.
An outline of the proposed models is presented in Figure 2 and 3.
FIGURE 2.
Outline of model for patients presenting with chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause and symptoms suggestive of functional disease.
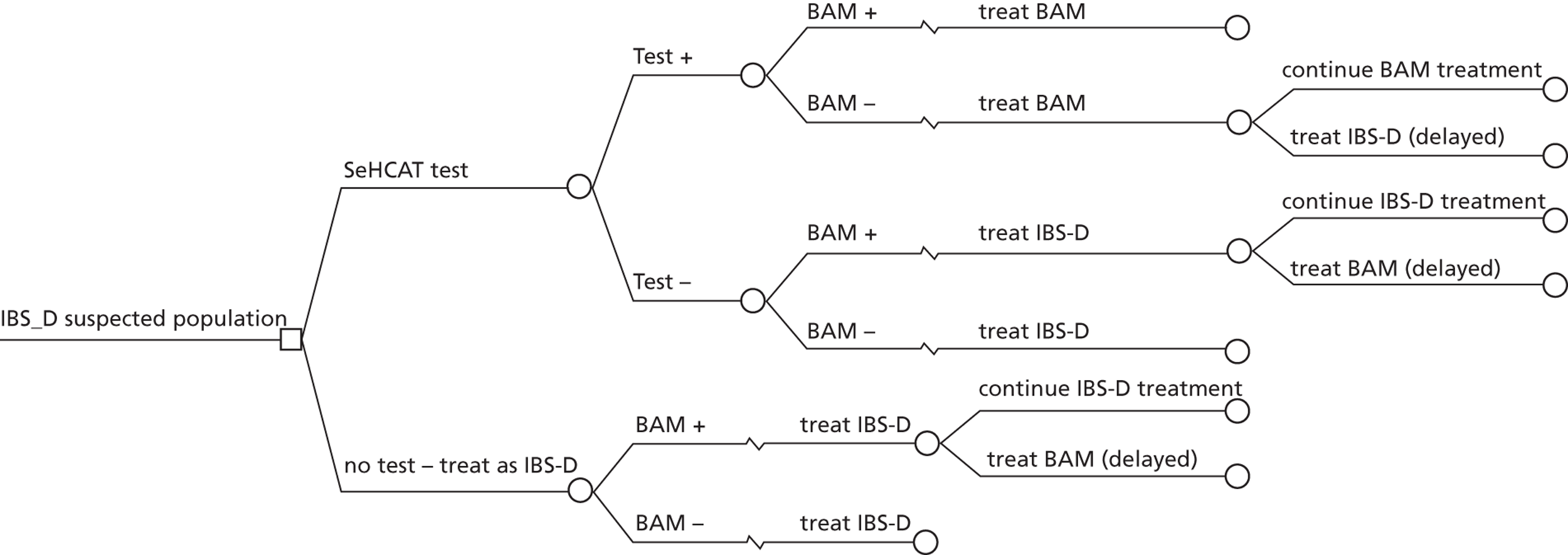
The diagnostic part of the model for population 1 is straightforward, including the outcome of SeHCAT (positive or negative) and the true disease status (BAM positive of negative). Both true positives and true negatives are treated according to usual management of BAM and IBS-D. Patients who tested positive for BAM while in fact not having BAM (false positives) are assumed to receive treatment for BAM. The important question that needs to be addressed in this study, most likely using expert opinion, is whether (some of) these patients will be detected at some point as having IBS-D, and how long this delay will last. Likewise, patients who tested negative for BAM while in fact having BAM (false negatives) are assumed to receive treatment for IBS-D. Again, an important question is whether (some of) these patients will be detected at some point as having BAM, and how long this delay will last. Also interesting in this situation is whether some parts of IBS-D management may also be helpful to some extent in patients with BAM, such as changes in diet.
Whether wrongly diagnosed patients will eventually receive a correct diagnosis and the duration of the delay until correct diagnosis is expected to have an important influence on the cost-effectiveness of SeHCAT.
If relevant, this part of the model will also take complications due to the SeHCAT test and the short and long-term consequences into account
The therapeutic part of the model requires modelling the life-long costs and effects of treating BAM and IBS-D. For this, a Markov model will be developed. Until now, no modelling studies in IBS and BAM have been identified that may be used in this study. Given the lack of data in this area, we anticipate a simple model structure for the Markov models, using health states defined based on whether the chronic diarrhoea is resolved or not and possibly including a health state for constipation.
For the treatment of BAM, the treatment of choice is medication with BAS. However, few published trials exist looking at the efficacy of BAS in BAM. It has been suggested that data on efficacy of BAS in other disease areas, such as hyperlipedemia, might be used. However, the endpoints by which the efficacy of BAS is measured will differ between disease areas. Another issue relates to one of the important problems of BAS treatment, i.e. tolerability. It is not unlikely that patients with a high cholesterol level (which does not lead to any symptoms in patients) are less willing to tolerate the side effects of BAS, merely to avoid future cardiovascular problems. For patients with BAM, the relief from a decrease in bowel movements might well outweigh the side effects. Thus, it is reasonable to expect that little to no data exist to meaningful model the costs and effects of treatment of BAM.
If relevant, the impact of untreated and treated BAM and IBS-D on mortality will be taken into account.
For the treatment of IBS-D, we anticipate that more information is available on the efficacy of (some of) the treatment options. So far, we have performed a search to obtain estimates of costs (of treatments) and utilities in IBS-D, which retrieved 401 references, of which 27 were selected from screening title and abstract. Some of these appear to be useful in terms of being UK based and relatively recent, although full papers are yet to be retrieved. We also intend to perform a similar search for the Crohn’s disease population.
For the trial-by-treatment comparator, the model may use data on effectiveness of BAS for those in the model with BAM and assuming that those without BAM have no improvement in symptoms and the same adverse event profiles as those with BAM.
For the second population, we will follow the same model structure. The analysis for this population is about the efficiency of BAS causing symptom relief and avoidance of unnecessary anti-inflammatory treatment (e.g. systemic cortico-steroids).
FIGURE 3.
Outline of model for patients with Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea with unknown cause (i.e. before resection of the terminal ileum).
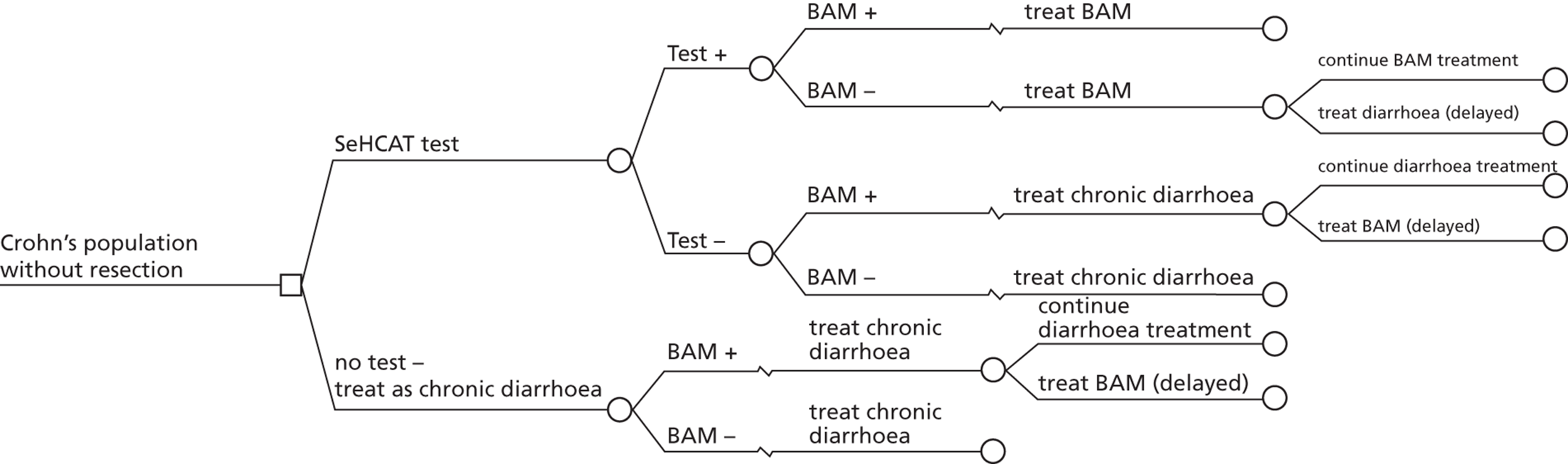
For this model, more information about the diagnostic part of the model needs to be collected (most importantly from experts) in order to establish what the current approach is to chronic diarrhoea in Crohn’s patients. And here the same questions arise as in the first population, i.e. whether (some of the) wrongly diagnosed patients are detected and what the delay in detection will be.
The therapeutic part of the model requires modelling the life-long costs and effects of treating BAM or chronic diarrhoea with non-BAM cause through a Markov model. Again, data on efficacy of treatments in this population will be scarce. Although assumptions can be made, and varied in sensitivity analysis and threshold analysis, the question is whether this will lead to any useful conclusions.
Final choices and definitions regarding the structure of the model will depend on the findings from the literature review and consultation with clinical experts. In addition, the existence/availability of any other electronic models that reflect the cost-effectiveness of treatment pathways for these patients, and are representative of current care within the NHS, will be determined.
Issues relevant to analyses:
-
Longer term costs and consequences will be discounted using the UK discount rates of 3.5% of both costs and effects.
-
One way sensitivity analyses will be performed for all key parameters, especially for parameters in the models which are based on expert opinion.
-
Probabilistic sensitivity analyses will be performed using parameter distributions instead of fixed values.
-
Decision uncertainty regarding mutually exclusive alternatives will be reflected using cost-effectiveness planes and cost-effectiveness acceptability curves.
Health outcomes
Utility values, based on literature or other sources, will be incorporated in the economic model. When utility values specific for BAM are not available, values for general chronic diarrhoea will be used. QALYs will be calculated from the economic modelling.
Costs
Resource utilisation will be estimated for the diagnostic tests and treatments. Data for the cost analyses will be drawn from routine NHS sources (e.g. NHS reference costs, Personal Social Services Research Unit (PSSRU), British National Formulary (BNF)), discussions with individual hospitals and with the manufacturers of the comparators.
7. Handling of information from the companies
All data submitted by the manufacturers/sponsors will be considered if received by the EAG no later than 05/03/2012. Data arriving after this date will not be considered. If the data meet the inclusion criteria for the review they will be extracted and quality assessed in accordance with the procedures outlined in this protocol.
Any ‘commercial in confidence’ data provided by manufacturers, and specified as such, will be highlighted in blue and underlined in the assessment report (followed by company name in parentheses). Any ‘academic in confidence’ data provided by manufacturers, and specified as such, will be highlighted in yellow and underlined in the assessment report. Any confidential data used in the cost-effectiveness models will also be highlighted.
8. Competing interests of authors
None
9. Timetable/milestones
10. References
- GE Healthcare Limited . Summary of product characteristics: SeHCAT 370 kBq capsules 2001.
- Thomas PD, Forbes A, Green J, Howdle P, Long R, Playford R, et al. Guidelines for the investigation of chronic diarrhoea. Gut 2003;52:v1-v15.
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination . Systematic Reviews: CRD’s guidance for undertaking reviews in health care [internet] 2009. URL: http://www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/SysRev/!SSL!/WebHelp/SysRev3.htm (accessed 23.11.11).
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence . Diagnostics Assessment Programme: interim methods statement (version 2) [internet] 2010. URL: http://www.nice.org.uk/media/164/3C/DAPInterimMethodsStatementProgramme.pdf (accessed 12.1.11).
- Galatola G, Ferraris R, Pellerito R, Barlotta A, Umberto OM, Sciaretta TG, et al. The prevalence of bile acid malabsorption in irritable bowel syndrome and the effect of cholestyramine: An uncontrolled open multicentre study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1992;4:533-7.
- Smith MJ, Cherian P, Raju GS, Dawson BF, Mahon S, Bardhan KD. Bile acid malabsorption in persistent diarrhoea. J R Coll Physicians Lond 2000;34:448-51.
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination . Systematic reviews: CRD’s guidance for undertaking reviews in health care [internet] n.d. URL: http://www.york.ac.uk/inst/crd/systematic_reviews_book.htm (accessed 7.6.11).
- Cochrane Diagnostic Test Accuracy Working Group . Handbook for DTA Reviews [internet]: Cochrane Collaboration 2011. URL: http://srdta.cochrane.org/handbook-dta-reviews (accessed 12.1.11).
- Whiting P, Westwood M, Beynon R, Burke M, Sterne JA, Glanville J. Inclusion of methodological filters in searches for diagnostic test accuracy studies misses relevant studies. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:602-7.
- McGowan J, Sampson M, Lefebvre C. An evidence based checklist for the peer review of electronic search strategies (PRESS EBC). Evidence Based Library and Information Practice 2010;5:1-6.
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions [internet]. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011. URL: http://www.cochrane-handbook.org/ (accessed 23.03.11).
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 1986;7:177-88.
Appendix 1
Clinical effectiveness search
Embase search: Facet 1 combined terms for SeHCAT (lines #1-5) and Bile Acid Sequestrants (lines #6-12) using OR in line #13 (n=33829). Facet 2 for Bile Acid Malabsorption (lines #14-20) was then combined with facet 1 using AND in line #21 (n=3044). Line #21 was then combined with both an RCT filter and Non-randomised studies filter and limited to remove animal studies. The final set was then limited to Embase records only in line #37 (n=1172). For the full strategy please see below.
Embase (OvidSP): 1980 to 2011 Week 46
Searched: 25.11.11
-----------------------------------------------
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).mp. (151)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75).mp. (765)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid).mp. (19)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").mp. (483)
-
or/1-4 (1150)
-
bile acid sequestrant/ (629)
-
((bile adj3 acid adj3 sequestra$) or BAS).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (15990)
-
Colestipol/ or (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2486)
-
Colestyramine/ or (colestyramine or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (9021)
-
Colesevelam/ or (Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (693)
-
aluminum hydroxide/ or (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel or 21645-51-2 or brasivil or rocgel or alugel or hydrated alumina or basalgel or dialume or nephrox).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (7408)
-
or/6-11 (32747)
-
5 or 12 (33829)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).mp. (1952)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.mp. (4)
-
chronic diarrhea/ (2492)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protract$ or continual$ or continuous$ or sustain$ or constant$ or relentless$ or unrelent$ or functional or aggressive) adj2 diarrh?e$).mp. (14493)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).mp. (16312)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).mp. (31246)
-
or/14-19 (61945)
-
13 and 20 (3044)
-
Random$.tw. or placebo$.mp. or double-blind$.tw. (835216)
-
"clinical trial (topic)"/ or "controlled clinical trial (topic)"/ or "multicenter study (topic)"/ or "phase 1 clinical trial (topic)"/ or "phase 2 clinical trial (topic)"/ or "phase 3 clinical trial (topic)"/ or "phase 4 clinical trial (topic)"/ (11859)
-
Clinical article/ or controlled study/ or major clinical study/ or prospective study/ (5272269)
-
(Cohort or compar$ or groups or multivariate).mp. (4685280)
-
or/22-25 (8026182)
-
animal/ (1661955)
-
animal experiment/ (1473625)
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or murine or rodent or rodents or hamster or hamsters or pig or pigs or porcine or rabbit or rabbits or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or cow or bovine or sheep or ovine or monkey or monkeys).mp. (4826714)
-
or/27-29 (4826714)
-
exp human/ (12719767)
-
human experiment/ (295041)
-
or/31-32 (12721151)
-
30 not (30 and 33) (3868516)
-
26 not 34 (6217248)
-
21 and 35 (1231)
-
limit 36 to embase (1172)
Based on Trials filter:
Wong SS, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically sound treatment studies in EMBASE. Journal of the Medical Library Association 2006;94(1):41-7.
&
Based on Non-randomised studies filter: Fixed method B for Embase:
Furlan AD, Irvin E, Bombardier C. Limited search strategies were effective in finding relevant nonrandomized studies. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1303-11. [Ovid]
MEDLINE (Ovid SP): 1948 to November Week 3 2011
Searched 25.11.11
-
(tauroselcholic or selenohomocholyltaurine or 75018-71-2).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2)
-
(SeHCAT or Se-HCAT or 75SeHCAT or Se-75 or 75-SeHCAT or SE75).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (274)
-
(23-seleno-25-homo-tauro-cholic acid or selenium homocholic acid taurine or 23-selena-25-homocholyltaurine or 23-selena-25-homotaurocholate or 23- selena-25-homotaurocholic-acid or selenium radioisotopes or tauroselenocholic acid).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (317)
-
(selenium adj3 "75").ti,ab,ot,hw. (143)
-
or/1-4 (639)
-
((bile adj3 acid adj3 sequestra$) or BAS).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2567)
-
Colestipol/ or (Colestipol or cholestabyl or cholestipol or colestid or diethylenetriamine-epichlorohydrin-copolymer or diethylenetriamine-polymer-with-1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane or epichlorohydrin-copolymer-with-diethylenetriamine or flavored-colestid or lestid or u-26,597a or u-26597-a or u-26597a or u-26,597a or 25085-17-0 or 37296-80-3 or 50925-79-6).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (503)
-
Cholestyramine Resin/ or (colestyramine$ or chol-less or choles or cholesthexal or cholestyramin or cholestyramine$ or cholybar or cholytar or colestepril or colestiramina or colestran or colestrol or colestyramin or cuemid$ or lipocol-merz or lismol or locholest or prevalite or quantalan or questran$ or resincoles-tiramina or resincolestiramina or vasosan-p-granulat or vasosan-s-granulat or 11041-12-6 or 58391-37-0 or mk 135 or mk135).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (3234)
-
(Colesevelam or cholestagel or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt-31-104 or gt-31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or gt31-104 or gt31-104hb or welchol or 182815-43-6 or 182815-44-7).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (155)
-
Aluminum Hydroxide/ or (aluminum hydroxide or Ageldrate or al u creme or alcid or aldrox or algeldraat or algeldrate or algelox or alhydrogel or alkagel or alocol or alokreem or alterna gel or alu cap or alu-cap or alu-tab or alucol or aludrox or alugelibys or alumigel or alumina gel or alumina trihydrate or aluminium hydroxide or aluminium hydroxide or aluminoid or aluminox or aluminum hydrate or aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum oxide trihydrate or aluminum trihydrate or alutab or amphogel or amphojel or amphotabs or antiphos or bayerite or chefarox or collumina or collumol or colodral or colugel or creamalin or cremorin or diplogel or f 1000 or f1000 or fluagel or gastracol or gastrosetarderm or gelumina or hoemigel or hycolal or hydracoll or hydrated alumina or hydrolum or hydronal or hydroxal or lactalumina or neutroxide or palliacol or pepsamar or ulcerin-p or vanogel).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (4374)
-
or/6-10 (10353)
-
5 or 11 (10957)
-
(BAM or I-BAM or IBAM or PBAM).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1657)
-
primary bile acid diarrh?ea$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (3)
-
diarrhea/ (35622)
-
((chronic or watery or recur$ or persist$ or protracted or continual$ or continuous$ or sustain$ or constant$ or relentless$ or unrelent$ or functional or aggressive) adj2 diarrh?e$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (6806)
-
"Bile Acids and Salts"/ (18352)
-
(malabsorb$ or mal-absorb$ or malabsorp$ or mal-absorp$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (13612)
-
((bile or biliary) adj3 (acid$ or salt$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (28246)
-
or/13-19 (79804)
-
12 and 20 (1746)
-
randomized controlled trial.pt. (322599)
-
controlled clinical trial.pt. (84057)
-
randomized.ab. (227373)
-
placebo.ab. (130354)
-
randomly.ab. (163568)
-
trial.ab. (235465)
-
groups.ab. (1082545)
-
or/22-28 (1586402)
-
Clinical Trials as Topic/ or Clinical Trials, Phase I as Topic/ or Clinical Trials, Phase II as Topic/ or Clinical Trials, Phase III as Topic/ or Clinical Trials, Phase IV as Topic/ or Controlled Clinical Trials as Topic/ (173991)
-
Cohort studies/ or comparative study/ or follow-up studies/ or prospective studies/ (2204429)
-
(Cohort or compar$ or groups or multivariate).ti,ab,ot,hw. (4454648)
-
or/30-32 (4921469)
-
29 or 33 (5121407)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (3630436)
-
34 not 35 (4030238)
-
21 and 36 (532)
Based on Trials filter:
Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: searching for studies. Box 6.4.c: Cochrane Highly sensitive search strategy for identifying randomized controlled trials in Medline: Sensitivity-maximizing version (2008 version); OVID format. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 [updated September 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org
&
Based on Non-randomised studies filter: Fixed method B:
Furlan AD, Irvin E, Bombardier C. Limited search strategies were effective in finding relevant nonrandomized studies. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1303-11. [Ovid]
Appendix 2
Checklists for the methodological quality assessment of case–control and cohort studies:
A. Case–control studies
-
Is the case definition explicit?
-
Has the disease state of the cases been reliably assessed and validated?
-
Were the controls randomly selected from the source of population of the cases?
-
Were interventions and other exposures assessed in the same way for cases and controls?
-
How was the response rate defined?
-
Were the non-response rates and reasons for non-response the same in both groups?
-
Is it possible that over-matching has occurred in that cases and controls were matched on factors related to exposure?
-
Was an appropriate statistical analysis used (matched or unmatched)?
B. Cohort studies
-
Is there sufficient description of the groups and the distribution of prognostic factors?
-
Are the groups assembled at a similar point in their disease progression?
-
Is the intervention/treatment reliably ascertained?
-
Were the groups comparable on all important confounding factors?
-
Was there adequate adjustment for the effects of these confounding variables?
-
Was a dose-response relationship between intervention and outcome demonstrated?
-
Was outcome assessment blind to exposure status?
-
Was follow-up long enough for the outcomes to occur?
-
What proportion of the cohort was followed-up?
-
Were drop-out rates and reasons for drop-out similar across intervention and unexposed groups?
Appendix 3
NICE guidelines on interventions for the treatment of chronic diarrhoea:
None.
Other relevant guidelines:
-
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: Diagnosis and management of irritable bowel syndrome in primary care. February 2008. Available from http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG61
-
Mowat et al. (2011) Guidelines for the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut;60:571–607.
Glossary
- Bile acid malabsorption
- One of several causes of chronic diarrhoea, resulting from failure to absorb bile acids (which are required for the absorption of dietary fats and sterols in the intestine) in the distal ileum.
- Bile acid sequestrant
- Intervention for the treatment of BAM, which can cause significant reduction in bowel frequency and therefore a better quality of life. There are currently three bile acid sequestrants available: cholestyramine, colestipol and colesevelam.
- Cost-effectiveness analysis
- An economic analysis that converts effects into health terms and describes the costs for additional health gain.
- Crohn’s disease
- A chronic, severe condition characterised by inflammation, ulcers and bleeding which may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, mostly the terminal ileum.
- Decision modeling
- A mathematical construct that allows the comparison of the relationship between costs and outcomes of alternative health-care interventions.
- False-negative
- Incorrect negative test result: number of diseased persons with a negative test result.
- False-positive
- Incorrect positive test result: number of non-diseased persons with a positive test result.
- Geometric centre
- The geometric centre analysis is often used for evaluating colonic transit data obtained by scintigraphy.
- Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- The difference in the mean costs of two interventions in the population of interest divided by the difference in the mean outcomes in the population of interest.
- Index test
- The test whose performance is being evaluated.
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- The most common types of IBD are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease directly cause chronic diarrhoea.
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- One of the most common functional gastrointestinal disorders, characterised by the presence of abdominal pain/discomfort associated with defecation, a change in bowel habit together with disordered defecation (constipation or diarrhoea or both), the sensation of abdominal distension, and can include associated non-colonic symptoms.
- Markov model
- An analytic method particularly suited to modelling repeated events, or the progression of a chronic disease over time.
- Meta-analysis
- Statistical techniques used to combine the results of two or more studies and obtain a combined estimate of effect.
- Meta-regression
- Statistical technique used to explore the relationship between study characteristics and study results.
- Opportunity costs
- The cost of forgone outcomes that could have been achieved through alternative investments.
- Publication bias
- Bias arising from the preferential publication of studies with statistically significant results.
- Quality-adjusted life-year
- A measure of health gain, used in economic evaluations, in which survival duration is weighted or adjusted by the patient’s quality of life during the survival period.
- Quality of life
- An individual’s emotional, social and physical well-being, and their ability to perform the ordinary tasks of living.
- Receiver operating characteristic curve
- A graph which illustrates the trade-offs between sensitivity and specificity which result from varying the diagnostic threshold.
- Reference standard
- The best currently available diagnostic test, against which the index test is compared.
- SeHCAT
- A radiopharmaceutical that is licensed for use in the investigation of BAM and measurement of bile acid pool loss.
- Sensitivity
- Proportion of people with the target disorder who have a positive test result.
- Specificity
- Proportion of people without the target disorder who have a negative test result.
- True-negative
- Correct negative test result: number of non-diseased persons with a negative test result.
- True-positive
- Correct positive test result: number of diseased persons with a positive test result.
List of abbreviations
- BAM
- bile acid malabsorption
- BAS
- bile acid sequestrant
- BNF
- British National Formulary
- BSG
- British Society of Gastroenterology
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CI
- confidence interval
- CRD
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination
- D
- diarrhoea
- DARE
- Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects
- DTA
- diagnostic test accuracy
- EAG
- External Assessment Group
- EVPI
- expected value of perfect information
- FN
- false-negative
- FP
- false-positive
- GE
- gastric emptying
- GP
- general practitioner
- HEED
- Health Economic Evaluations Database
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- IBD
- inflammatory bowel disease
- IBS
- irritable bowel syndrome
- IBS-D
- diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- KSR
- Kleijnen Systematic Reviews Ltd
- MD
- mean difference
- MeSH
- medical subject heading
- NA
- not applicable
- ND
- no diarrhoea
- NHS EED
- NHS Economic Evaluation Database
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NR
- not reported
- OR
- odds ratio
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- RE
- random effects
- ROC
- receiver operating characteristic
- RR
- relative risk
- SCI
- Science Citation Index
- SD
- standard deviation
- SeHCAT
- selenium-75-homocholic acid taurine
- SMD
- standardised mean difference
- SMR
- standardised mortality ratio
- SSRI
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
- TCA
- tricyclic antidepressant
- TN
- true-negative
- TNF-α
- tumour necrosis factor alpha
- TP
- true-positive