Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 12/72/01. The contractual start date was in April 2013. The draft report began editorial review in August 2013 and was accepted for publication in December 2013. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
none
Note
this document and any associated economic model are protected by intellectual property rights, which are owned by the University of Southampton. Anyone wishing to modify, adapt, translate, reverse engineer, decompile, dismantle or create derivative work based on the economic model must first seek the agreement of the property owners.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2014. This work was produced by Frampton et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Background
Description of the underlying health problem
Introduction
The transparent ocular lens is enclosed in a membranous capsule and consists of two layers: a central ellipsoid, biconvex nucleus and a softer outer layer called the cortex. The lens contains epithelial cells that give rise to lens fibres throughout life, meaning that it becomes thicker and more compact with age and may lose optical clarity. Any loss of optical clarity in the lens is referred to as a cataract. Cataracts develop most often as a result of biological ageing, although there are numerous risk factors and some types of cataract are hereditary (see Cataract risk factors).
In the UK, one-quarter of the population will develop cataracts by the age of 75 years. 1 Cataracts lead to deterioration of vision, which may restrict daily activities and, in the elderly, independent living. Decreased visual function is associated with diminished quality of life,2 as well as a decrease in physical and mental health. 3 Poor vision related to cataracts is also a risk factor for falls and traffic accidents, which may lead to hospital admissions and limit independence. 4,5 The only effective treatment available to restore or maintain vision is the surgical removal of the cataract. 1 Cataract surgery is the most frequently conducted elective surgical procedure in the NHS, as well as in other Western countries. 6
Cataract types and classification
Cataracts are classified in a number of ways, primarily according to the part of the lens that is affected, and also according to their visual appearance and aetiology (e.g. some types of congenital cataract have a characteristic appearance). 7 The three most common types of age-related cataract are: nuclear sclerotic cataract, located in the lens nucleus; cortical cataract, located in the cortex; and posterior subcapsular cataract, located towards the back of the lens within the superficial posterior lens cortex. 7–9 Nuclear cataract is the most common type of age-related cataract. Posterior subcapsular cataract is more frequent among younger people.
Numerous clinical schemes have been developed for classifying the severity of the three main types of age-related cataract. Most of these schemes are based on slit lamp assessment of the eye (in which a narrow slit beam of light illuminates the eye) and comparison of the observations against standard cataract diagrams or photographs to determine a score. 10 The most popular classification schemes are the Oxford Clinical Cataract Classification and Grading System11 and the Lens Opacities Classification System III (LOCS III). 12 Alternative, simpler, schemes for recording cataract severity based on the area of the lens affected have also been used. 10
Prevalence and incidence of the condition
Recent data on the prevalence and incidence of cataracts in England and Wales are lacking. According to clinical experts, cataracts almost always develop bilaterally, i.e. patients with a cataract in one eye will already have signs of, or will develop, a cataract in their second eye. Estimates of the prevalence of people with cataracts in England have been made based on age- and sex-stratified regional population surveys,1 notably the North London Eye Study (1995–6), reported by Reidy and colleagues13 and Minassian and colleagues,14 and a study based on the Somerset and Avon survey of health (SASH) (1996–7), reported by Frost and colleagues,15 as well as other studies1 (described briefly below). These studies have produced markedly different estimates of prevalence, reflecting differences in their methodology, including different definitions of visual impairment and eligibility for cataract surgery.
The North London Eye Study randomly sampled people aged over 65 years from general practices in north London (1547/1840 people responded) and provides prevalence data specifically for visually impairing cataracts [i.e. Snellen visual acuity less than 6/12 that is attributable to a lens opacity, but not accounting for comorbidity or health-related quality of life (HRQoL)]. 13 The North London Eye Study found a prevalence of cataracts causing visual impairment (visual acuity in one or both eyes poorer than 6/12, attributable to lens opacity) of 30% [95% confidence interval (CI) 25.1% to 35.3%],13 and estimated the incidence of new cataract cases per annum in England and Wales to be around 224,000. 14 The prevalence of cataracts increased steadily with age from 16% in the 65–69 years age group, to 71% in people aged over 85 years. 13
The SASH-based study by Frost and colleagues15 randomly sampled 2783 people aged ≥ 55 years from 19 general practice registers in south-west England, from which data on 1078 people were available for analysis. Three definitions of eligibility for cataract were employed to reflect the likely range of eligibility criteria used in practice, and these included ocular comorbidity as well as HRQoL. 15 The estimated prevalence of cataract (in one or both eyes) requiring extraction was much lower than that from the North London Eye Study, ranging from 6 to 27 people per 1000 depending on the eligibility criteria. When adjusted according to the population profile of England (based on the 1991 census), the prevalent requirement for cataract surgery in England was estimated to range from 97,585 people (using the strictest eligibility criterion) to 384,000 people (using the least restrictive eligibility criterion), and was highest in patients aged over 74 years. 15
Recent data collected by the Royal National Institute of Blind People (RNIB)16 indicate that 269,636 people were treated for cataracts in England during 2012–13, which represents 0.48% of the population. This number of operations exceeds some of the cataract prevalence estimates from Frost and colleagues for England and Wales,15 indicating underestimation of the true prevalence if based on strict eligibility criteria for surgery. However, direct comparisons are difficult to make since the studies by Frost and colleagues15 and Reidy and colleagues13 were conducted over 15 years ago.
In a Medical Research Council (MRC) trial of assessment and management of older people in the community (1994–2001), nurses tested visual acuity in 14,403 people aged 75 years and older from 49 general practices in the UK. 17 Of 976 people with binocular visual impairment (binocular visual acuity < 6/18) excluding refractive error, 25% were classified as cataracts being the main or contributory cause of vision loss.
A study conducted in an urban population in England (the Newcastle 85+ cross-sectional study) based on family practice records of 839 patients aged 85 years and older in 2006–7 found that 36% had a previous history of cataract surgery in one or both eyes. 18 Surveys conducted both in the UK and the USA indicate that cataract prevalence is slightly higher in women,13,19 with 1.2 times as many women as men having cataracts in the North London Eye Study. 13 Prevalence also varies according to the type of cataract, with nuclear cataract being more common than posterior subcapsular cataract. 19
Assuming that it is reflective of the wider population case mix, the Cataract National Dataset, which reflects 55,567 cataract operations conducted in 12 NHS trusts during November 2001 to July 2006, would suggest that the ‘typical’ population in England presenting for cataract surgery in either eye would be 62% female and of a mean age of 75.4 years. 20 Pre-operative visual acuity was 6/12 or better in 55.3% of those patients surveyed who were attending second-eye cataract surgery. However, it should be borne in mind that visual acuity thresholds may have declined further since these data were collected. 20
Cataract risk factors
Although cataracts are more common in older people, the risk of developing cataracts may be associated with a wide range of factors. These include genetic factors,21 diet,22 metabolic and nutritional disorders (e.g. diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders), and treatment of ocular diseases (e.g. glaucoma) with steroids or vitreoretinal surgery with heavy gases or oil in the eye. Extrinsic risk factors include infections, smoking, alcohol and the use of systemic corticosteroids. 23 Exposure to radiation also increases the risk of developing cataracts, as the ocular lens is particularly sensitive to the effects of ionising radiation. Groups exposed to radiation that are at increased risk of developing cataracts include patients who have received radiotherapy, clinicians who frequently use X-ray procedures and airline pilots exposed to ultraviolet wavelengths. 24,25 As the prevalence data referred to above suggest, women appear to have a slightly higher risk of developing cataracts than men. 13,17,19,23
Symptoms and diagnosis
Generally, age-related cataracts are progressive8 although during the early stages of cataract development there may be minimal changes to an individual’s visual function. As cataracts develop further, they can affect vision in a number of ways, including increasing myopia (nearsightedness) and astigmatism, inducing monocular diplopia (double vision), reducing light transmission and/or changing colour perception. Visual loss from cataracts is principally as a result of the decreased transmission of light through the lens. Cataracts also increase scatter of intraocular light, which reduces the contrast of the retinal image, with the visual decrement being greatest in glare or bright light conditions. 10 During the later stages of opacity, vision may be limited to light and dark distinction. Cataract symptoms include blurred or reduced vision, and problems associated with glare or low-contrast conditions, ultimately leading to blindness if untreated, but symptoms do depend on the location and size of the cataract, and whether cataracts are present in one or both eyes. For example, glare may be a particular problem for people with posterior subcapsular cataracts, although they may see well in dim illumination, whereas people with nuclear cataracts may experience myopic refractive shift (improved near vision but worse distance vision), difficulty with night driving and loss of colour discrimination ability. 7
There is no single test to assess the effect of a cataract on a patient. Diagnosis usually involves examination of the eye by an ophthalmologist or optometrist using a slit lamp and assessment of one or more aspects of visual function, including visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and stereopsis (described in more detail in Clinical vision outcome measures). Clinical decisions concerning the need for cataract surgery also take into account the extent of symptoms and the impact of a cataract on the patient’s well-being and quality of life (see Current service provision).
Measurement of the condition
Approaches for measuring the impact of cataracts on patients can be divided into those that assess impacts on clinical vision and those that assess impacts on the way patients feel, for example how cataracts affect patients’ symptoms and quality of life. The main clinical vision measures that have been used for assessing effects of cataracts, both in clinical settings and as outcomes in clinical trials, are visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and stereopsis (other vision outcomes such as glare disability may be important to patients, but are less commonly reported in clinical trials of cataract surgery). A wide variety of validated patient-reported outcomes relating to symptoms and quality of life have been used in clinical trials but, unlike measures of clinical vision, they are not routinely employed in clinical decision-making practice for cataract surgery. The three main clinical visual outcomes and some of the most frequently used patient-reported outcomes that are used for assessing impacts of cataracts in clinical trials are described below.
Clinical vision outcome measures
For the outcome measures described below, assessments may be made with one eye covered (monocular assessment) or with both eyes open (binocular assessment). In addition, assessments may be made under specific conditions, for example to test for vision unaided or with spectacles, or to test for near or distance vision.
Visual acuity
Visual acuity refers to a person’s sharpness of vision, commonly measured using a Snellen chart. 26 Normal-distance visual acuity is defined as the ability of a person at a distance of 20 feet (or 6 metres) from the chart to separate lines that are one arc-minute apart (i.e. the ability to read the smallest line of letters on the chart). 27 Distance visual acuity is typically expressed as a ratio (comparing the closest distance that the person would need to be from the chart in order to read the smallest line with the closest distance a person with normal vision would need to be to read the same line). By definition, normal-distance visual acuity is 6/6 in metres or 20/20 in feet. Some studies report Snellen visual acuity as a decimal rather than a ratio (Table 1). Visual acuity can also be expressed as the minimum angle of resolution (MAR) in minutes of arc, usually converted to a logarithm (log-MAR), with larger values of log-MAR indicating worse visual acuity. 27,29 The clinical significance of changes in log-MAR visual acuity may be judged as those changes which exceed the 95% range of test–retest reliability. 30 However, published values vary according to the study and type of chart used, and individual clinicians may draw on their own experience concerning the repeatability of log-MAR test results when judging clinical importance of changes in vision. Published 95% ranges for log-MAR test–retest variance30 range from ± 0.07 to ± 0.19.
| Typical description | Snellen ratio for assessment at 6 m from chart | Snellen ratio for assessment at 20 feet from chart | Snellen decimal value | MAR (minutes of arc) | log-MAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Varying degrees of restricted visiona | 6/60 | 20/200 | 0.1 | 10.0 | 1.0 |
| 6/30 | 20/100 | 0.2 | 5.0 | 0.7 | |
| 6/15 | 20/50 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.4 | |
| Functional vision | 6/12 | 20/40 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 0.3 |
| Normal vision | 6/6 | 20/20 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Superlative vision | 6/3 | 20/10 | 2.0 | 0.5 | −0.3 |
Visual acuity is enhanced by binocular compared with monocular vision. 31 Binocular visual acuity reflects what a patient actually sees when using both eyes, but may give a misleading indication of the impact of a cataract, as the better-seeing eye can (depending on the extent of binocular summation or inhibition) compensate for visual deficits in the fellow eye. Indeed, people with no vision in one eye may still achieve normal or acceptable visual acuity with their functional eye. In many elderly patients, the monocular visual acuity of the better-seeing eye provides a reasonable approximation of their binocular visual acuity. However, in approximately one-fifth to one-third of elderly patients binocular vision is not well represented by monocular vision measures. 31
Visual acuity measures are often used to assess the need for cataract surgery, as well as for evaluating the success of the operation. However, visual acuity may be relatively unaffected by cataracts until they become severe, meaning that visual acuity may not be the most appropriate measurement tool. 32
Contrast sensitivity
Optical contrast is the difference in luminance and/or colour of an object that makes it distinguishable from the background and from other objects in the field of view. Contrast sensitivity refers to a person’s ability to distinguish between an object and its background or, more specifically, the ability to discern detail at low-contrast levels. People who can see details at very low contrast are said to have high-contrast sensitivity. Numerous charts are available for assessing contrast sensitivity, of which the Pelli–Robson chart is among the most widely used. 33,34 The chart consists of lines of equally sized triplets of letters which successively decrease in their contrast with the background and thus appear to gradually fade into it. 33,34 Contrast sensitivity is usually reported as a logarithmic value (1/contrast), and is determined as the logarithmic contrast sensitivity value of the last triplet for which at least two letters are correctly seen by the viewer. 33 The contrast sensitivity can also be expressed as a sensitivity on a dB scale (contrast sensitivity in dB = –20 log10 contrast, i.e. 0.05 log-units = 1 dB, 0.5 log-units = 10 dB, 1.0 log-units = 20 dB). ‘Normal’ values for logarithmic contrast sensitivity are higher for binocular assessments than for monocular assessments and decrease with age,33,35 although, according to clinical experts consulted during this project, age-adjusted reference values for contrast sensitivity are not used routinely in clinical practice.
Contrast sensitivity is enhanced by binocular compared with monocular vision. 36 Lens opacification can lead to a reduction in contrast sensitivity, with the reduction being greater as the extent of lens opacity increases. 37 When both eyes have equal contrast sensitivity, the binocular sensitivity is higher than the monocular sensitivity (known as binocular summation). However, unequal monocular contrast sensitivities can cause the binocular contrast sensitivity to decrease to a level below the monocular sensitivity of the better eye (known as binocular inhibition). This is similar to visual acuity summation and inhibition. 31 As a result, patients with a single cataract may complain of lower binocular contrast sensitivity compared with using one eye only and may prefer to shut the cataractous eye. 38 Binocular contrast sensitivity in cataract patients has been shown to correlate strongly with perceived visual disability. 35,39,40
Stereopsis
Stereopsis (also referred to as stereoacuity or depth perception) refers to a person’s ability to perceive the three-dimensional structure of the environment based on the different two-dimensional images captured by each eye. In normal vision, the brain is capable of measuring the disparity of vision between the two eyes and ‘fusing’ these into a single image to produce the sensation of depth. 41 If one eye is not functioning properly, the brain may struggle to accurately combine the two images, affecting a person’s ability to judge distances. Although some aspects of depth can be estimated using monocular cues, acute depth perception requires binocular vision. Cataract in one or both eyes may therefore compromise a person’s stereopsis. Suboptimal stereopsis has been shown to adversely affect motor skills,42 performance with everyday tasks,35 driving ability40 and risk of falls in the elderly. 43
Stereopsis is assessed by measuring the smallest lateral displacement (or ‘disparity’) of target images presented to each eye that can be perceived by a patient in a ‘stereotest’. 44,45 The results of a stereotest are usually expressed as the smallest image displacement discernible by the viewer, either in seconds of arc, or as logarithm units (e.g. 60 seconds of arc = 1.78 log-units). Unlike visual acuity and contrast sensitivity, stereopsis tends to remain constant until people are in their mid-70s and then declines rapidly. 35,46 In older people, values < 150 seconds of arc may be considered good stereopsis. People who cannot resolve images at high disparity are said to be ‘stereoblind’ (the threshold may vary but is often set at ≥ 3000 seconds of arc).
Patient-reported outcome measures
A variety of instruments have been employed in research studies for assessing the impacts of cataract surgery on patients’ symptoms, functional ability, well-being and HRQoL. 1 These can be divided into generic instruments which have been designed to apply across a range of different health conditions [e.g. the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) health survey and Short Form questionnaire-36 item health survey instrument (SF-36)] and instruments that focus specifically on vision-related conditions [e.g. the Visual Function Index (VF-14)]. Examples of vision-specific instruments are also provided by Khadka and colleagues47 and McAlinden and colleagues. 48
Impact on patients and the NHS
Without surgery, most types of cataract will progress with time, leading to loss of visual function, although the rapidity and severity of visual decline depends on the type and severity of cataract present as well as any ocular comorbidities (see Surgical and post-operative complications). Untreated cataracts may ultimately lead to blindness. Benefits of cataract surgery include improved visual acuity, with 85–90% of people having 6/12 best corrected vision as measured on a Snellen chart (i.e. meeting the driving requirements in the UK); improved clarity of vision; and improved colour vision. 9
Cataracts can affect patients directly by impairing their vision (e.g. visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and/or stereopsis) and indirectly by the deterioration in functional abilities and quality of life that can result from the visual impairment. In older people, deterioration of vision as a result of cataracts can have a range of consequences. People may have difficulty performing daily tasks, reading, using computers, or participating in games or social activities. Elderly women with cataracts are at an increased risk of having falls and fractures. 4
An issue of particular concern among drivers is that cataracts can affect their ability to drive safely. 16 Studies comparing populations of cataract patients who have or have not received cataract surgery suggest that cataracts contribute to self-reported driving difficulty49 and increase the frequency of motor vehicle collisions, as well as the financial costs associated with them. 50 It has been suggested that providing cataract surgery earlier, rather than after significant visual problems have become apparent, could reduce traffic accidents among older drivers. 5 Vision-related driving requirements are usually based only on visual acuity,51 although drivers who pass a visual acuity test may have poor contrast sensitivity or other visual defects which, although not tested, can impair their driving ability. 52,53 In the UK, people are required have a Snellen distance visual acuity of at least 6/12 (with spectacles if appropriate) in order to be allowed to hold a driving licence. 51 In addition, since 2001 the legal requirement for standards of vision for driving has been based on being able to read a car number plate from 20 metres. This may overestimate the driver’s functional vision in real-life motoring conditions, as many drivers with early cataracts experience problems with night vision. According to clinical experts consulted during this project, in cases where cataract surgery causes enough improvement in visual function for drivers to retain their eligibility to drive, this may impact positively on their quality of life. However, there do not appear to be any data on how many patients this would apply to, nor on the extent of the impact on quality of life.
Cataract surgery is the most common elective surgical procedure performed in the NHS,1 and cataracts place a direct financial burden on the NHS in terms of the cost of treatment. However, performing cataract surgery may lead to savings in health-care costs elsewhere, for example those associated with falls and traffic accidents, although it is uncertain how important second-eye cataract surgery would be compared with first-eye surgery in this respect.
According to a report by the RNIB published in 2013,16 there were 340,809 cataract operations in England during 2012–13 (up to 28 February 2013). The most recent data available on the proportions of first- and second-eye cataract surgery in England are from 2011–12 in the RNIB report,16 and indicate that cases of second-eye cataract surgery that were conducted within 1 year of the first-eye surgery accounted for 27% of all cataract operations. The National Schedule of Reference Costs54 puts the total cost of cataract surgery for 2011–12 at £240M. Assuming that 27% of cataract operations are on the second eye,16 an estimate of the cost per annum of second-eye surgery alone would be £64.8M. The burden of cataracts to the NHS will increase as the population ages and larger numbers of older people seek treatment. However, figures reported by the RNIB suggest that the frequency of second-eye cataract operations has decreased in England from 96,336 in 2009–10 to 91,959 in 2011–12. 16
Current service provision
Most cataract operations are performed on elderly patients, with 90% being on patients aged 60 years or over. 1 According to Cataract Surgery Guidelines published by the Royal College of Ophthalmologists in 2010,1 access to surgery is generally good, with NHS surgical waiting times under 3 months, although it was acknowledged that there is geographical variation and overprovision may have occurred in some areas. 1,55 The RNIB report published in July 201316 indicates that the average time to treatment (from first outpatient appointment to cataract surgery in either eye) during 2012–13 was 129 days (i.e. approximately 4 months), but with considerable regional variation among the Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCGs) in England, with a range from 44 days to 222 days. 16 In recent years, the clinical criteria which have been used for determining eligibility of patients for cataract surgery have become less stringent, with a lowering of the threshold of visual dysfunction. 56 This has led to concerns about whether or not there may be overprovision of cataract surgery55 and, if so, whether or not it would be cost-effective to treat cataract patients whose visual dysfunction is not so severe as to restrict their lifestyle. 56 However, as mentioned above, there has also been a decline in the frequency of second-eye operations,16 suggesting that access to second-eye surgery may have been restricted.
The rates of second-eye cataract surgery per annum were investigated in the RNIB report. 16 During the reporting period, primary care trusts (PCTs) in England were replaced by CCGs. In order to present data in a standard format, the RNIB report presents historical data under the name of the CCG that has responsibility for each area. Rates of second-eye cataract surgery in England varied geographically among the CCGs, ranging from 14.66 to 62.81 operations per 100,000 population during 2011 (the latest period for which these data were reported). There is no agreed figure for what a good rate of second-eye surgery should be, although data from 11 European countries suggests that 40% of patients who have a first-eye cataract are likely to require second-eye surgery. 16,57 Forty-four CCGs performed fewer than 30 second-eye cataract operations per 100,000 of population in 2011, while nine CCGs performed more than 50 second-eye cataract operations per 100,000 of population. A limitation of these data is that it is not possible to judge whether low surgery rates result from restrictive referral policies or from local population profiles. An online survey conducted by the Royal College of Ophthalmologists among its consultant ophthalmologist members in April 2011 (which did not distinguish between first- and second-eye surgery) found that 44.4% of consultants felt that local commissioners had placed restrictions on who could be listed for cataract surgery and 38.1% had encountered situations where they felt a patient had been disadvantaged by restrictions on cataract surgery. 58
Cataract management involves ophthalmologists, optometrists, nurses and technicians, with the ultimate responsibility for diagnosis and management resting with the ophthalmologist. The surgery itself is performed by an ophthalmic surgeon, although suitably trained non-medical members of the team may undertake much of the assessment and follow-up examinations. 1 People with cataracts may be referred to a consultant ophthalmologist by their general practitioner (GP) based on a visual assessment report from an optometrist, or may be referred directly by the optometrist. The actual surgery is usually undertaken as a day case, taking up to half a day. After the procedure, suitably trained practitioners will process the patient’s discharge and provide instructions for post-operative medication. Around 90% of cataract operations are uncomplicated and the final post-operative assessment is often deferred until 4–6 weeks after surgery. 59
Currently, there is no set level of vision in the NHS for which an operation is considered essential. 1,9,16,60 The survey conducted by the RNIB in February 2013 found wide variation in cataract commissioning policies (i.e. referral criteria) across the CCGs in England. Forty-nine per cent of the commissioning policies in England were found to have no arbitrary restrictions on vision or vision-related function; 33% had a visual acuity restriction but allowed for exemptions (e.g. if patients experience glare or need to drive), and 18% had strict criteria for visual acuity thresholds and limited or no exemptions. 16 Similar findings had been obtained from previous RNIB surveys in June 201158 and May 2012,61 and a survey of CCGs in England by academic researchers in May 2011. 60 The academic researchers concluded that almost all cataract surgery referral criteria employed in England (92%) were not evidence based, and some patients who would benefit from cataract surgery were being restricted in their access to surgery. 60 Two-thirds of the referral policies in England made provision for second-eye surgery. 60
The variation in service provision for second-eye surgery was not reported for all CCGs in England in the July 2013 RNIB report,61 but is illustrated in the May 2012 RNIB report, which suggested that patients in north-east England could have surgery as soon as they need it (i.e. they did not have to satisfy visual acuity criteria), whereas some patients in the south-east of England would have to lose three lines of visual acuity (Snellen 6/18) in order to be eligible to access second-eye surgery. 61 According to clinical experts consulted during this systematic review, most patients with bilateral cataracts prefer to have the second eye operated on.
Patients referred for second-eye cataract surgery are generally assessed for their second-eye surgery at the time of their first-eye surgery post-operation check (e.g. 4–6 weeks post operation). They may then wait up to a further 18 weeks for surgery unless there is an urgent reason to do it sooner, although, as noted above, there is considerable geographical variation in waiting times. One reason for expedited second-eye surgery would be where the difference in refraction between the two eyes is more than 2 dioptres (anisometropia) as this can cause considerable visual discomfort and double vision (diplopia), making vision with both eyes open worse than using the better eye alone in a small proportion of patients (around 5% according to clinical experts consulted during this systematic review). In some cases cataract surgery is justified on medical grounds (e.g. to prevent glaucoma, as large cataracts can increase intraocular pressure, or to allow assessment of retinal disorders). It is very uncommon for cataract extraction to take place in both eyes simultaneously because of the risk of associated complications, including bilateral infective endophthalmitis (inflammation of the inside of the eye) which may lead to blindness in both eyes and medico-legal concerns. Some cataract surgery referral policies in England allow simultaneous (same day) bilateral cataract extraction. 60 However, expert clinical opinion provided during this systematic review suggests that 1% or fewer bilateral cataract extractions are undertaken sequentially on the same day.
Relevant national guidelines
Current guidance on referral criteria for cataract surgery is given in the Department of Health report Action on Cataracts, which was published in 2000. 62 The report led to a number of improvements in NHS cataract care pathways during the 2000s, including enabling direct referral by optometrists, simplifying the number of consultations required, increasing the throughput of patients and reducing waiting times, and emphasising the need for care to be patient centred to prevent situations where people experience a reduction in their quality of life owing to treatable cataracts. 59,62 The most relevant current national guidelines are the Royal College of Ophthalmologists Cataract Surgery Guidelines (2010) (next due for review in 2015) which state that it is clinically and economically appropriate for second-eye surgery to be offered to those patients who want it. A 1b recommendation is given (a recommendation based on at least one randomised trial). 1 Similarly, the Scottish Health Technologies Group issued a statement in September 2012 advising that there is randomised controlled trial (RCT) evidence to support second-eye surgery and evidence from cost–utility analysis to demonstrate lifetime cost-effectiveness. 63 In England and Wales, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has not previously appraised second-eye cataract surgery. It is thought that such an appraisal is unlikely to be conducted by NICE until 2018, although the RNIB and Royal College of Ophthalmologists have requested this to be prioritised. 16
Description of the technology under assessment
An eye which retains its original crystalline lens is referred to as a phakic eye. The lens may or may not be cataractous. An eye which has undergone a cataract operation with a lens implant is referred to as a pseudophakic eye.
Routine cataract surgery consists of eight steps: (1) anaesthesia (with a local anaesthetic in around 96% of cases); (2) surgical entry (typically a small incision through the cornea or sclera); (3) capsulorhexis – creation of a small aperture in the lens capsule; (4) phacoemulsification – ultrasonic fragmentation of the cataractous lens nucleus using a device called a phaco probe and removal by suction of the resulting lens fragments; (5) removal by suction of the soft cortex which lies between the lens nucleus and the capsule; (6) insertion of the lens implant, sometimes followed by intracameral injection of antibiotics; (7) suturing of the eye if necessary; and (8) post-operative care, in which patients are given topical antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs typically for 4–6 weeks post operation.
Check-ups following cataract surgery include measurement of visual acuity, a slit lamp examination, measurement of intraocular pressure and ophthalmoscopy to evaluate the inside of the eye. The majority of patients who receive cataract surgery (around 86%20) do not experience any complications and require no further therapy or ongoing care after their post-surgery check-up.
Surgical and post-operative complications
The most frequent adverse consequence of cataract surgery is a clouding of the back of the lens capsule, known as posterior capsular opacification (PCO), which can lead to deterioration in vision months or years after the initial surgery. For the purposes of this report, we refer to PCO as a complication of cataract surgery, although strictly speaking PCO could be considered an expected consequence of phacoemulsification in a proportion of patients since phacoemulsification leaves the lens capsule intact but prone to opacification after cataract extraction. Clinical experts estimated that 20–30% of patients who have cataract surgery will experience PCO. Except in rare cases, PCO is easily treated with a procedure known as neodymium-doped yttrium–aluminium–garnet (Nd:YAG) laser lcapsulotomy in which a laser with a Nd:YAG crystal is used to cut a hole in the opacity of the lens capsule to allow light to pass through. 64 Laser capsulotomy is a painless outpatient surgical procedure that does not require anaesthesia. A single laser capsulotomy can provide lifelong recovery of good vision, although complications may occur in a minority of patients. 64
Serious surgical complications associated with cataract surgery (which may be sight-threatening, or increase the risk of sight-threatening sequelae) are posterior capsule rupture (PCR) during surgery65 and, post operatively, endophthalmitis,66 retinal detachment,67,68 cystoid macular oedema69 and retained lens fragments. 70,71 These complications are relatively uncommon, affecting fewer than 2% of cataract operations. 1,20,68,72–74 However, the occurrence of PCR during surgery increases the risk of cystoid macular oedema, endophthalmitis and retinal detachment. 65
Other complications that may arise from cataract surgery9 but which are usually not serious, except in rare cases, are uveitis, transient increase in intraocular pressure, bruising of the eye or eyelids after surgery which usually resolves without problems, refractive surprise (an unexpected need for a particular glasses prescription) and corneal decompensation (corneal oedema).
Identification of important subgroups
Important subgroups that may affect cataract surgery outcomes include patients’ age, pre-operative ocular comorbidities and the experience of surgeons conducting the procedure. Data from the UK Cataract National Dataset indicate that pre-operative risk factors for PCR and/or vitreous loss during cataract surgery include (among others) increasing age, male gender, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy and trainee surgeons performing operations. 75 Other pre- and peri-operative adverse risk factors for post-surgical monocular vision loss are age-related macular degeneration, amblyopia, corneal pathology, previous vitrectomy and posterior capsule rupture during surgery. 76 The UK Cataract National Dataset found that, during 2001–6, 28.5% of people presenting for cataract surgery (one or both eyes) had one or more ocular comorbidities. Post-operative visual acuity of 6/12 or better was achieved in 97% of patients who had no pre-operative comorbidities and 79.9% of patients with one or more ocular comorbidities (51% and 30%, respectively, achieved visual acuity 6/6 or better). 20
Chapter 2 Definition of the decision problem
Decision problem
Some patients with bilateral cataracts may have surgery on only one eye, but it is suggested that surgery on the second eye may have additional benefit for patients in terms of improving vision and being able to perform everyday activities (e.g. being able to drive). However, there is uncertainty about how cost-effective second-eye surgery would be, with no systematic reviews hitherto having addressed this question. The decision problem is relevant to current financial constraints faced by the NHS, with concerns having been raised about possible overprovision of cataract surgery55,56 and the need to ensure adequate patient access to cataract surgery. 58,77
Overall aims and objectives of the assessment
The aim of this systematic review was to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery. The objectives were:
-
to conduct a systematic review of studies assessing the clinical effectiveness of second-eye surgery
-
to conduct an economic evaluation comprising:
-
a systematic review of cost-effectiveness studies of second-eye surgery
-
a systematic review of relevant quality-of-life studies
-
an economic model, developed de novo or adapted from an existing one, to estimate cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery.
-
Chapter 3 Methods
The a priori methods for systematically reviewing the evidence of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness are described in the research protocol (see Appendix 1). The protocol was sent to our expert advisory group (AG) (see Acknowledgements) for comment and minor amendments were made as appropriate. None of the comments received identified specific problems with the methods of the review.
Identification of studies
Sensitive search strategies were developed and refined by an experienced information specialist (see Appendix 2).
Main searches for clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and HRQoL literature were undertaken from inception of databases to March/April 2013, with updated searches conducted in July 2013. Searches were limited to the English language.
The strategies were applied to the following databases:
-
Ovid MEDLINE (1946 to March 2013)
-
Ovid MEDLINE Daily Update (12 March 2013)
-
Ovid MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations (12 March 2013)
-
Ovid EMBASE (1974–March 2013)
-
Web of Science: Science Citation Index-Expanded (SCI-Expanded; 1970–March 2013); Conference Proceedings Citation Index – Science (CPCI-S; 1990–March 2013); Conference Proceedings Citation Index – Social Science and Humanities (CPCI-SSH)
-
BIOSIS Previews (Web of Science platform; 1956–March 2013)
-
The Cochrane Library: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials; Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
-
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD): Database of Abstracts and Reviews of Effectiveness; Health Technology Assessment (HTA) database.
In addition to the databases listed above, the searches of cost-effectiveness and HRQoL also included the following databases:
-
NHS Economic Evaluations Database (NHS EED) (cost-effectiveness searches)
-
The King’s Fund database (HRQoL searches).
For each of the systematic reviews of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and HRQoL, internet pages of the Cochrane Eyes and Vision Group, the Royal College of Ophthalmologists and NICE were searched. The reference lists of included primary studies were checked for additional references. If any relevant systematic reviews were identified, their reference lists were also checked for relevant references. Experts on the review AG were also asked to identify additional published and unpublished references. All search results were imported into a Reference Manager (Thomson ResearchSoft, San Francisco, CA, USA) database.
Study selection
Titles and abstracts of records identified by the bibliographic searches for clinical effectiveness literature were assessed independently by two reviewers for potential eligibility, using a standardised eligibility selection worksheet (see Appendix 3) containing the following pre-specified eligibility criteria:
-
Population: adults (aged 18 years and over) who have had one cataract operation already and still have or have developed a significant cataract causing visual impairment in the other eye.
-
Intervention(s): cataract surgery for the second eye. Studies reporting any surgical technique were included.
-
Comparator(s): cataract surgery in one eye only (can include a ‘waiting list control’ group in which the comparator population ultimately receives second-eye surgery, but not during the study period); and patients may receive additional supportive care if this is usual practice, such as prescription glasses.
-
Outcomes: any clinical visual measures (including measures of visual acuity; contrast sensitivity; stereopsis); patient-reported visual disability and symptoms (e.g. VF-14); patient satisfaction with surgery and vision; HRQoL (e.g. EQ-5D); and adverse events (including peri- and post-operative complications).
-
Study design: RCTs. If relevant systematic reviews were identified, these were only used as a source of references. Studies published as abstracts or conference presentations were only included if sufficient details were presented to allow an appraisal of the methodology and the assessment of results to be undertaken.
The systematic reviews of cost-effectiveness and HRQoL employed the inclusion criteria listed above, with the following modifications (which were reflected in the study selection worksheets):
-
Studies of any design were eligible for the cost-effectiveness review if they reported full economic evaluations (e.g. cost-effectiveness, cost–utility).
-
Studies of any design were eligible for the systematic review of HRQoL if they used generic preference-based HRQoL measures or generic preference valuation methods, and reported HRQoL outcomes. It was anticipated that there would be limited relevant literature on HRQoL in patients receiving second-eye cataract surgery. Therefore, the criteria were broader and could also include first-eye cataract surgery. While HRQoL data based on second-eye surgery were to be prioritised for use in the economic evaluation, data from studies of first-eye surgery could be included for context and to potentially inform sensitivity analysis.
Any disagreements between the reviewers regarding title and abstract screening using the above criteria were resolved by discussion or, if necessary, consultation with a third reviewer. Full-text records were then obtained for all titles and abstracts that met the inclusion criteria or remained unclear. The full-text records were assessed independently by two reviewers using the same criteria as for titles and abstracts. Any further disagreements between the reviewers were resolved through discussion and, if necessary, recourse to a third independent reviewer.
For the systematic review of HRQoL, the inclusion criteria were slightly revised for screening full papers, with the additional stipulation that to be included studies had to be primary research, and had to report utility values (i.e. patient preferences for a health outcome, commonly measured on an interval scale with 0 reflecting states of health equivalent to death and 1 reflecting perfect health) as opposed to, for example, reporting only HRQoL scores (i.e. not related to patient preferences).
Only articles published in English were eligible for the systematic reviews. Conference abstracts were not eligible for the systematic review of cost-effectiveness and HRQoL but were considered for the review of clinical effectiveness, subject to reporting adequate detail to enable an appraisal of the methodology.
Data extraction and critical appraisal
Standardised forms were used to collect data from the studies that were included in the systematic reviews (completed data extraction forms for the reviews of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and HRQoL are shown, see Appendices 4, 7 and 9, respectively). In each systematic review, data were extracted by one reviewer and then checked for accuracy by a second reviewer.
Randomised controlled trials included in the systematic review of clinical effectiveness were assessed in terms of their risk of bias (selection bias, detection bias, performance bias, attrition bias and selective reporting bias) using Cochrane Collaboration criteria. 78,79 Risk of bias was assessed independently by two reviewers who then met to compare their judgements. Disagreements were resolved through discussion and, if necessary, consultation with a third reviewer. Tables summarising and explaining the risk of bias judgements are included in the data extraction forms (see Appendix 4). Other aspects of study quality relating to statistical procedures, outcome measurement and generalisability were also assessed and recorded in the data extraction forms.
The methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of cost-effectiveness was assessed using accepted criteria for appraising economic evaluations. 80,81 Owing to the diverse types of study design eligible, the methodological quality of studies included in the systematic review of HRQoL was not formally assessed.
Method of data synthesis
As specified in the protocol (see Appendix 1), studies were synthesised narratively following a structured approach similar to one proposed by Rodgers and colleagues. 82 Quantitative pooling of outcomes across clinical effectiveness studies in a meta-analysis was not considered appropriate as the included studies differed in their methodological characteristics (see Chapter 4, Clinical effectiveness outcomes). Meta-analysis was also not possible for pooling outcomes in the systematic reviews of cost-effectiveness or HRQoL because of the different types of study design included (see Chapter 5, Economic analysis).
Chapter 4 Clinical effectiveness
Quantity and quality of research available
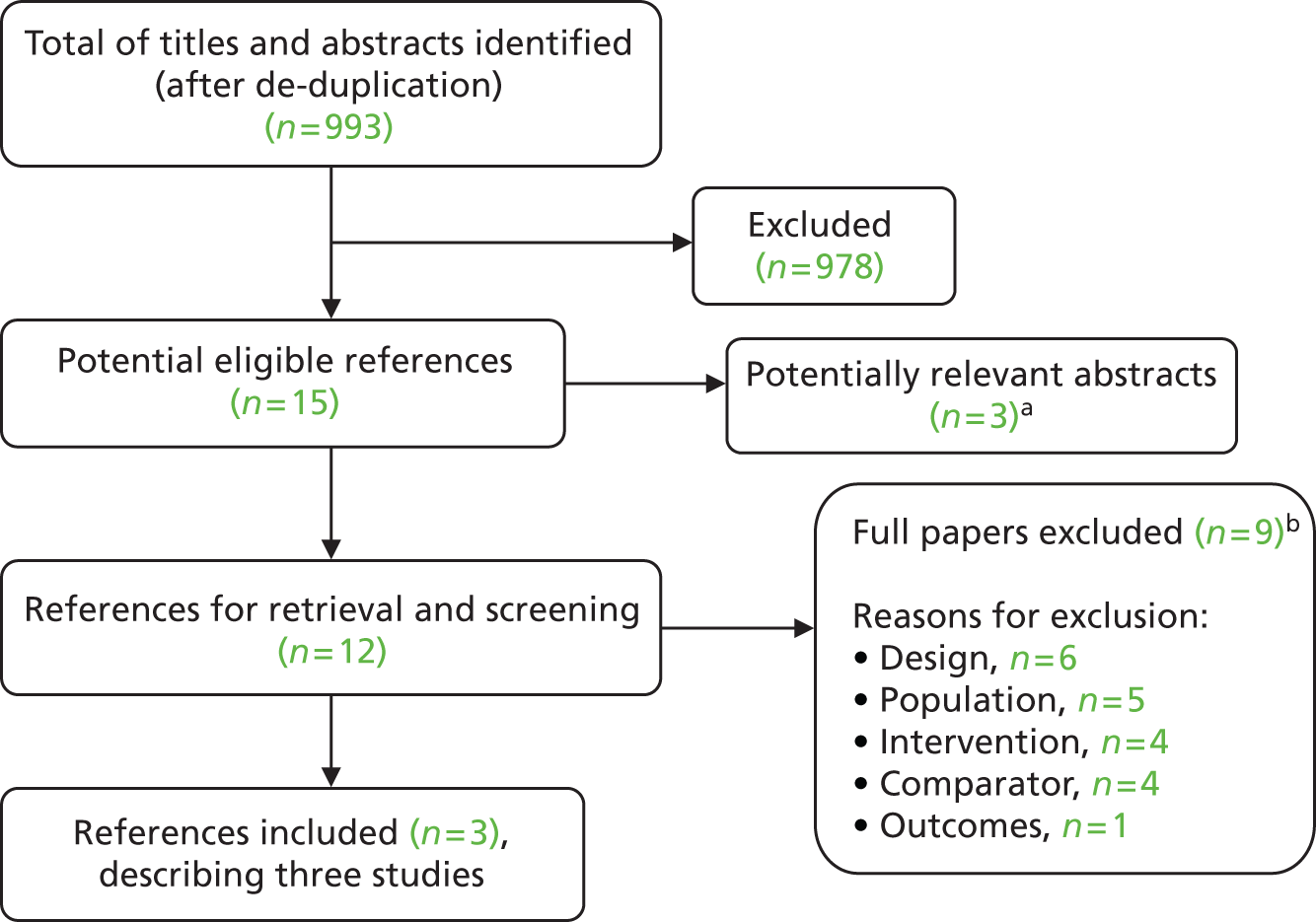
Searches identified a total of 993 references after de-duplication and full texts of 15 references were retrieved after screening titles and abstracts. Reviewer agreement at title and abstract screening was good, with both reviewers reaching the same decision in the study selection worksheet (see Appendix 3) for 99.2% of the titles and abstracts. The number of references excluded at each stage of the systematic review is shown in Figure 1. Nine of the 15 potentially eligible references were excluded (see Appendix 6). Three potentially relevant conference abstracts were identified but could not be appraised in detail because of a lack of methodological information (see Appendix 5). The remaining three full-text references met the inclusion criteria. These described three RCTs which we included in our systematic review. We did not identify any relevant existing systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery until after this report had been completed (see Relevant systematic reviews).
FIGURE 1.
Flow chart for the identification of studies. a, Listed in Appendix 5; and b, listed in Appendix 6.
Characteristics of the included studies
Two of the studies were set in the UK83,84 and one in Spain85 (Table 2). The publication date was 2006 for two of the studies83,85 and 1998 for the remaining study. 84 However, trials started as early as 1994. 84 Both the UK studies used only one centre, a hospital ophthalmology department83 and an eye hospital. 84 Castells and colleagues85 conducted their study in two ophthalmology departments in public teaching hospitals. Sample size ranged from 20884 to 296 randomised participants85 and the length of study follow-up was 485 to 12 months (see Table 2). 83 All three studies received only academic (non-commercial) funding.
| Parameter | Laidlaw et al. (1998)84 | Foss et al. (2006)83 | Castells et al. (2006)85 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | RCT | RCT | RCT |
| Country | UK | UK | Spain |
| Study dates | 1994–5 | 2000–4 | 1999–2000 |
| Intervention | Expedited second-eye surgery target within 6 weeks | Expedited second-eye surgery target within a month | Surgery in the first eye 1–2 months after enrolment, in the second eye 2–4 months after first-eye surgery |
| Comparator | Routine second-eye surgery (targeted 7–12 months) | Waiting list group, second-eye surgery within 13 months or the routine waiting time when this became less than 13 months | First-eye surgery 1–2 months after enrolling, second-eye surgery offered at end of study |
| Population: age (years) | Intervention: mean 76 (range 52–97) Comparator: mean 76 (range 41–93) |
Intervention: median 79.2 (range 70–90) Comparator: median 79.9 (range 70–92) |
Intervention: mean 71.70 (SD 9.07) Comparator: mean 72.03 (SD 8.87) |
| Population: sex, male, n (%) | Intervention: 40 (38) Comparator: 40 (39) |
0 (100% female for both groups) | Intervention: 57 (39) Comparator: 55 (37) |
| Country (no of centres and details) | UK (one centre – eye hospital) | UK (one centre – hospital ophthalmology department) | Spain (two centres – ophthalmology departments in public teaching hospitals) |
| Sample size (n randomised) | 208 (intervention: n = 105; comparator: n = 103) | 239 (intervention: n = 120; comparator: n = 119) | 296 (intervention: n = 148; comparator: n = 148) |
| Length of follow-up after surgery | Approximately 6 months (medians and interquartile ranges reported for each study group – see data extraction form in Appendix 4) | 6 and 12 months (visual and patient-reported outcomes 6 months; falls 12 months; complications 6 or 12 months) (assessments also at 3 and 9 months but results not reported) | 4–6 months after the last surgery (first-eye surgery for the comparator group and after second-eye surgery for the intervention group) |
| Losses to follow-up n/N (%) | Intervention: 7/105 (7) Comparator: 9/103 (9) |
Intervention: 5/120 (4) Comparator: 16/119 (13) |
Intervention: 9/148 (6) Comparator: 13/148 (9) |
| Key inclusion criteria | Awaiting second-eye surgery, a unilateral cataract and uncomplicated contralateral pseudophakia with corrected Snellen VA of at least 20/40 in the pseudophakic eye | Women age > 70 years, successful previous cataract operation, second operable cataract | Scheduled for first-eye cataract surgery, bilateral indication for cataract surgery (VA worse than 0.3 log-MAR in both eyes) |
| Comorbidities | NR | Non-ocular comorbiditiesa (intervention %, comparator %): heart problems (33, 30); chest problems (21, 19); arthritis (76, 78); stroke (8, 6); previous fracture (48, 48); postural dizziness (35, 24); postural hypotension (16; 12) | Ocular comorbidities (unspecified), n/N (%): intervention: 34/148 (23.0); comparator: 36/148 (24.3) |
| Type of lens | NR | Folding silicone intraocular lens | Foldable lens |
| Baseline visual acuity before second-eye surgery (log-MAR, mean) | 0.022 (binocular, corrected) | 0.09 (binocular, spectacles corrected), 0.22 (binocular, unaided) | 0.18 (binocular, corrected)b |
| Severity of cataract | NR | NR | NR |
| Type of surgery | NR | Small-incision cataract surgery (team A & C temporal clear cornea, team B superior clear cornea) | Ambulatory surgery using a phacoemulsification technique (3-mm corneal incision without suture) |
Participants had an average age of between 7185 and 79 years,83 with an age range of 41–97 years (see Table 2). Two studies had a higher percentage of female participants, ranging from 61%84 to 76%. 85 Foss and colleagues83 limited their study to female participants. Only two studies reported comorbidities. Foss and colleagues83 reported comorbidities relating to heart (31%), chest (20%) and arthritis (77%) problems, while Castells and colleagues85 reported ocular comorbidities (24%), but provided no further details. The key inclusion criteria for the Foss and colleagues83 study, apart from being female, was age > 70 years, a successful previous cataract operation and a second operable cataract (see Table 2). The study by Laidlaw and colleagues84 stipulated that participants had to be awaiting second-eye surgery, have a unilateral cataract and uncomplicated contralateral pseudophakia, with corrected Snellen visual acuity of at least 20/40 in the pseudophakic eye. Unlike the other two UK studies, the study by Castells and colleagues85 in Spain recruited participants who had not received any cataract surgery prior to enrolment, but were scheduled for first-eye cataract surgery and had a bilateral indication for cataract surgery (visual acuity worse than 0.3 log-MAR in both eyes). For this reason, the timing of baseline assessments differs between Castells and colleagues85 and the other two RCTs, and this should be borne in mind when interpreting any changes from baseline in the results of these studies. Castells and colleagues’85 baseline data were taken prior to first-eye surgery, whereas in the other two RCTs the baseline data were taken prior to second-eye surgery. Accordingly, changes from baseline in the RCTs by Laidlaw and colleagues84 and Foss and colleagues83 specifically refer to second-eye cataract surgery while changes from baseline in the RCT by Castells and colleagues85 refer to the combination of both first- and second-eye surgery. Binocular corrected visual acuity prior to second-eye surgery was good in each of the RCTs, ranging from 0.022 to 0.22 log-MAR (see Table 2), i.e. better than Snellen 6/10.
All three RCTs reported exclusion criteria. Laidlaw and colleagues84 excluded patients with ocular comorbidity or unsuccessful first-eye surgery. Foss and colleagues83 excluded participants with complex cataracts, those with severe comorbid eye disease affecting visual acuity or with visual field defects, and those with memory problems impacting on lengthy questionnaire completion or reliable recall of falls. Castells and colleagues85 excluded participants with severe ocular comorbidity that would contraindicate surgery in both eyes and those who were undergoing surgery combined with any other ophthalmological procedure or experiencing complications of first-eye surgery that would contraindicate surgery in the fellow eye. Overall, the participants in the three RCTs were similar in not having ocular comorbidities and being aged in their 70s, although mean patient age was 7–8 years higher in the RCT by Foss and colleagues83 than in the RCT by Castells and colleagues. 85 The most notable difference in the included populations was that Foss and colleagues83 included only women, in contrast to the other RCTs.
In the study by Laidlaw and colleagues,84 the intervention group received expedited large-incision second-eye cataract surgery, targeted to within 6 weeks, whereas the comparator group received routine second-eye cataract surgery after 7–12 months (i.e. a waiting list control group). Surgical details were not reported.
The study by Foss and colleagues83 employed small-incision phacoemulsification cataract surgery (temporal clear or superior clear cornea) conducted by three teams inserting a folding silicone intraocular lens under local anaesthetic. The intervention group received expedited second-eye surgery targeted to be within a month, whereas the comparator waiting list group received second-eye surgery within 13 months, or the routine waiting time when this became less than 13 months.
Castells and colleagues85 also used a phacoemulsification technique (3-mm corneal incision without suture), inserting a foldable lens under topical anaesthesia. The comparator group had cataract surgery on the first eye only between 1 and 2 months after enrolling, but were offered second-eye cataract surgery at the end of the study. The intervention group received second-eye surgery 2–4 months after first-eye surgery.
Losses to follow-up ranged from 4% to 13% of the randomised population (see Table 2). None of the RCTs fully described reasons for attrition. While the studies reported that analysis was performed on an intention-to-treat (ITT) basis, this was unsupported by data presented and there were inconsistencies in the reporting of the loss to follow-up of patients. In the RCTs of Laidlaw and colleagues84 and Castells and colleagues,85 rates of attrition were similar for the first- and second-eye study groups. In Foss and colleagues’ RCT, however,83 the rate of attrition was 9% higher in the waiting list comparator group. Of 16 patients lost to follow-up in this group, seven dropped out in order to receive non-trial surgery.
Risk of bias
Risk of bias varied between the studies (Table 3). All three studies were judged at high risk of bias on at least one domain. In four out of the six domains of bias, one or more of the studies provided insufficient information to allow for a conclusion about the risk to be reached and were therefore judged unclear. Explanations for risk of bias judgements are given in the data extraction forms (see Appendix 4).
| Domain of bias78 | Laidlaw et al. (1998)84 | Foss et al. (2006)83 | Castells et al. (2006)85 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selection bias: random sequence generation | Unclear | Unclear | Low |
| Selection bias: allocation concealment | Low | Low | Unclear |
| Detection bias: masking of outcome assessors | Unclear | High | Unclear |
| Performance bias: masking of participants on self-reported outcomes | High | High | High |
| Attrition bias: incomplete outcome data addressed | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear |
| Reporting bias: free of selective reporting | High | Unclear | Unclear |
The risk of selection bias relating to random sequence generation was low for the study by Castells and colleagues85 and unclear for the remaining two studies. 83,84
The risk of selection bias relating to allocation concealment was deemed low in two studies,83,84 but unclear in the third study by Castells and colleagues. 85
The risk of detection bias as a result of not masking outcome assessors was unclear for two of the studies,84,85 but considered high in the study by Castells and colleagues. 85
It was not feasible for any of the RCTs to mask their participants to the surgical interventions, and all were judged to be at high risk of performance bias through lack of masking of participants on self-reported outcomes (note that a high risk of performance bias does not necessarily imply poor quality of study design, given that masking may not be practically and/or ethically feasible79). Performance bias is less relevant to objective outcomes such as measures of clinical vision than subjective measures such as patient-reported questionnaires.
The risk of attrition bias was determined by considering whether or not the numbers of dropouts were balanced across the study groups, whether or not the reasons for attrition were reported and, if so, whether or not the reasons may have been influenced by the success or failure of the intervention. The three RCTs were all judged to be at unclear risk of attrition bias for different reasons. Each RCT reported that analysis was performed on an ITT basis but this was not supported by data presented as none of the RCTs fully reported reasons for attrition. In the RCT by Castells and colleagues,85 and Laidlaw and colleagues84 the rate of attrition was similar across the study groups. In the RCT by Foss and colleagues84 more dropouts occurred in the routine surgery group (13%) than the expedited surgery group (4%), with some of those leaving the routine surgery group switching to expedited surgery. Dissatisfaction with waiting is a plausible reason for patients in the routine surgery group switching to expedited surgery, which might mean that those remaining in the routine surgery group were those who were least dissatisfied with waiting; however, the picture may be more complex (e.g. elderly patients may feel dissatisfied with waiting, but may be reluctant to request a change). On balance, it is not possible to say with any certainty whether or not the imbalance of attrition reported by Foss and colleagues83 would have resulted in bias.
The risk of bias because of selective reporting (differences between reported and unreported findings) was considered to be high in the study by Laidlaw and colleagues84 because data relating to secondary outcomes were limited and because questions relating to vision in the right and left eye were recoded. It was deemed to be unclear for various reasons in the remaining two studies. 83,85
Overall, the assessment of study quality suggests that results of the three included RCTs should be interpreted with caution as their outcomes may not be unbiased.
Clinical effectiveness outcomes
The RCTs differed in their designated primary outcomes. Laidlaw and colleagues84 specified four primary outcomes: binocular distance visual acuity, near-reading visual acuity, stereopsis and selected questions from a newly developed and piloted questionnaire assessing the patients’ perspective of treatment on the second eye. Foss and colleagues83 specified one primary outcome: the number of patients experiencing a fall. Castells and colleagues85 had four primary outcomes: binocular visual acuity, binocular contrast sensitivity, stereopsis and patient-reported visual disability (assessed using the validated VF-14 instrument).
Secondary outcomes reported by Laidlaw and colleagues84 included reading speeds, general health status and the remaining selected questions from their self-designed patient questionnaire. Foss and colleagues’83 secondary outcomes included binocular visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, stereopsis, health status, cognitive function, activity, anxiety and depression, confidence, activities of daily living, visual disability, handicap and HRQoL, as well as a subjective vision question. Secondary outcomes in the study by Castells and colleagues85 were a cataract symptoms score, general health status, and two general questions about trouble and satisfaction with vision.
The three included RCTs had few outcomes in common, with only measures of visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and stereopsis being reported in all the RCTs, although the studies differed in how they measured and/or reported these outcomes (see Clinical vision outcomes). Only one other outcome, patient-reported visual disability using the VF-14, was reported consistently in two RCTs, but baseline VF-14 scores differed between these RCTs and the timing of the baseline assessments differed between the RCTs (before first-eye surgery in the RCT of Castells and colleagues,85 and before second-eye surgery in the RCT of Foss and colleagues;83 see Patient-reported outcomes).
As well as the heterogeneity of outcomes, the studies also had some notable differences in their methodological characteristics (e.g. one study was conducted before phacoemulsification was introduced,84 one included only women83 and, as mentioned above, the RCTs differed in the timing of their baseline assessments). Given this methodological heterogeneity and the relatively small number of studies included, we considered it inappropriate to pool outcomes across the RCTs in a meta-analysis. Instead, the results are synthesised narratively, as reported in the following sections.
Self-designed patient-reported outcomes which were reported by Laidlaw and colleagues84 and Castells and colleagues85 are not included in the narrative synthesis as the validity and clinical interpretation of these measures are unclear.
Clinical vision outcomes
None of the RCTs reported the severity, grade or type of cataract that their patients had. However, Foss and colleagues83 stated that cataracts in their study were less severe than those in the earlier trial by Laidaw and colleagues. 84
Visual acuity
Foss and colleagues83 and Castells and colleagues85 reported that visual acuity was measured using log-MAR-based Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) charts, whereas Laidlaw and colleagues84 did not specify the chart type. At baseline, the mean binocular visual acuity in log-MAR units for the intervention group ranged from 0.022 to 0.28 in the RCT by Laidlaw and colleagues84 and from 0.09 to 0.22 in the RCT by Foss and colleagues83 (see Table 4). These values indicate that the patients had only minor impairment of visual acuity before second-eye cataract surgery (reference values of log-MAR are given in Table 1). Foss and colleagues83 acknowledged that only 3% of patients in the routine surgery group and 8% in the expedited surgery group had poor vision (Snellen acuity worse than 6/12), with the median acuity at baseline being 6/7. The RCT by Castells and colleagues85 had baseline binocular visual acuity of 0.54 log-MAR units, indicating a greater degree of visual acuity impairment (equivalent to a Snellen acuity worse than 6/15 but better than 6/30). However, this was measured only prior to first-eye surgery and may not be representative of binocular visual acuity with one pseudophakic eye.
| Study; outcome | Intervention, mean (SD) | Comparator, mean (SD) | Mean difference between intervention and comparator (95% CI); p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laidlaw et al. (1998)84 | Expedited surgery | Routine surgery | At 6 monthsa | ||
| Baseline (n = 105) | 6 months (n = 98) | Baseline (n = 103) | 6 months (n = 94) | ||
| Binocular mean distance, log-MAR | 0.022 (0.101) | −0.027 (NR) | 0.063 (0.127) | 0.052 (NR) | 0.063 (0.035 to 0.090); p < 0.0001 |
| Binocular mean near-reading, log-MAR | 0.28 (0.13) | 0.23 (NR) | 0.29 (0.13) | 0.27 (NR) | 0.047 (0.017 to 0.077); p < 0.0029 |
| Monocular log-MAR for the initially pseudophakic (first) eye | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.025 (−0.004 to 0.054) |
| Monocular log-MAR for the initially cataractous (second) eye | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.756 (0.650 to 0.861) |
| Foss et al. (2006)83 | Expedited surgery (n = 120) | Routine surgery (n = 119) | At 6 monthsb | ||
| Baseline | 6 months | Baseline | 6 months | ||
| Unaided visual acuity (binocular), log-MAR | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.23 | −0.04 (−0.01 to −0.08); p = 0.001 |
| Spectacles visual acuity (binocular), log-MAR | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.09 | −0.04 (−0.01 to −0.06); p = 0.003 |
| Pinhole visual acuity (binocular), log-MAR | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.09 | −0.06 (−0.03 to −0.09); p < 0.0005 |
| Change in median visual acuity in the operated eye (i.e. monocular), log-MAR | 0.44 | −0.02 | 0.46c | ||
| Castells et al. (2006)85 mean (SD) | Both-eyes surgery (n = 139) | One-eye-only surgery (n = 135) | At 4–6 months | ||
| Baselined | 4–6 months | Baselined | 4–6 months | ||
| Binocular visual acuity, log-MAR | 0.54 (0.17) | 0.11 (0.10) | 0.56 (0.19) | 0.18 (0.17) | 0.07 (0.03 to 0.12); p < 0.001 |
| Decimal scale | 0.31 | 0.80 | 0.30 | 0.71 | NR |
| > 0.3 log-MAR (= 0.5 decimal), n (%) | NR | 3 (2.2) | NR | 20 (14.8) | NR; p < 0.001 |
| > 0.1 to ≤ 0.3 log-MAR, n (%) | NR | 72 (51.8) | NR | 79 (58.5) | NR |
| ≤ 0.1 log-MAR (= 0.8 decimal), n (%) | NR | 64 (46.0) | NR | 36 (26.7) | NR; p < 0.001 |
| Change from baselined (log-MAR) | −0.43 (0.18) | −0.38 (0.23) | 0.05 (−0.002 to 0.11) | ||
All three studies reported measures of corrected binocular visual acuity after surgery (adjusted statistically for baseline values in the RCTs of Laidlaw and colleagues84 and Foss and colleagues83), but they employed different measures (see Table 4). Two of the RCTs, by Laidlaw and colleagues84 and Foss and colleagues,83 also reported changes in monocular visual acuity in the second-eye surgery group. When interpreting log-MAR visual acuity, a common practice is to consider changes that exceed the 95% range of test–retest variance as being ‘real’ differences, i.e. as being clinically important. 30 Published 95% ranges for test–retest reliability span the range from ± 0.07 to ± 0.19. 30
Laidlaw and colleagues84 reported that 6 months after surgery, the differences in log-MAR binocular mean distance visual acuity and binocular mean near-reading visual acuity between patients who had received second-eye surgery and patients awaiting second-eye surgery was statistically significant, with lower log-MAR point estimates for both measures in patients with second-eye surgery (see Table 4). However, the authors acknowledged that the small difference in mean binocular log-MAR visual acuity would not be clinically significant (equivalent to half a Snellen line difference). This is in contrast to a marked improvement in mean monocular visual acuity after surgery in the first eye (log-MAR = 0.756, on average more than 4 Snellen line equivalents). 84 Laidlaw and colleagues84 also acknowledged that many of the visual acuity assessments were positively skewed, but suggested that numbers in the two treatment arms were large enough to allow parametric analyses for outcome comparisons.
Foss and colleagues83 reported that log-MAR point estimates 6 months after surgery were lower for binocular unaided visual acuity, spectacles visual acuity and pinhole visual acuity after expedited second-eye surgery compared with routine surgery (see Table 4). Differences in point estimates after 6 months were statistically significant for all three outcome measures. The median monocular visual acuity in the operated (second) eye improved by 0.44 log-MAR units compared with deterioration of −0.02 log-MAR units in the (second) eye awaiting routine surgery, but no statistical comparison was reported (see Table 4).
Castells and colleagues85 reported log-MAR for best corrected binocular visual acuity. Differences in point estimates between patients with surgery in both eyes and patients with surgery in one eye only were statistically significant 4–6 months after surgery and lower (better) in patients who had surgery in both eyes (change from baseline was also reported, but baseline measurements were taken before first-eye surgery so the change does not reflect effects of second-eye surgery alone). The binocular visual acuity decimal value was higher for patients who had received surgery in both eyes compared with those who had received surgery in one eye, but no statistical comparison was reported. The authors also reported the number of patients in three log-MAR classes of the decimal scale (see Table 4). The best (≤ 0.1 log-MAR) category contained significantly more patients who had received surgery in both eyes (46%) compared with the number of patients who had received one-eye surgery (26.7%) (p < 0.001). Conversely, the worst (> 0.3 log-MAR) category contained significantly fewer patients who had received surgery in both eyes (2.2%) compared with the number of patients who had surgery in one eye (14.8%) (p < 0.001). No statistical comparison for the middle category was reported. The change from baseline in log-units was reported (see Table 4), although all baseline measures were taken prior to first-eye surgery and, therefore, do not reflect effects of second-eye surgery alone.
Contrast sensitivity
Binocular contrast sensitivity assessed with a Pelli–Robson chart was reported after cataract surgery by all three RCTs, although the measurement units differed or were unclear (Table 5) and colour contrast sensitivity was not tested.
| Study; outcome | Intervention | Comparator | Mean difference between intervention and comparator (95% CI); p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laidlaw et al. (1998)84 | Expedited surgery | Routine surgery | At 6 monthsa | ||
| Baseline (n = 105) | 6 months (n = 98) | Baseline (n = 103) | 6 months (n = 94) | ||
| Binocular mean contrast sensitivity (scale unspecified), mean (SD) | 1.56 (0.15) | 1.76 (NR) | 1.53 (0.16) | 1.54 (NR) | −0.21 (−0.25 to −0.17); p < 0.0001 |
| Foss et al. (2006)83 | Expedited surgery (n = 120) | Routine surgery (n = 119) | At 6 monthsb | ||
| Baseline | 6 months | Baseline | 6 months | ||
| Binocular contrast sensitivity (dB), mean | 1.45 | 1.60 | 1.42 | 1.50 | 0.09 (0.06 to 0.13); p < 0.0005 |
| Castells et al. (2006)85 | Both-eyes surgery (n = 139) | One-eye-only surgery (n = 135) | At 4–6 months | ||
| Baselinec | 4–6 months | Baselinec | 4–6 months | ||
| Binocular contrast sensitivity, mean log-units (SD) | 1.14 (0.29) | 1.61 (0.1) | 1.13 (0.35) | 1.57 (0.18) | 0.04 (−0.002 to 0.09); stated not significant |
| < 1.30, n (%) | NR | 2 (1.4) | NR | 10 (7.4) | NR |
| ≥ 1.30 to < 1.70, n (%) | NR | 77 (55.4) | NR | 69 (51.1) | NR |
| ≥ 1.70, n (%) | NR | 60 (43.2) | NR | 56 (41.5) | NR |
| Change from baselinec (log-units) | 0.46 (0.32) | 0.44 (0.36) | 0.02 (−0.09 to 0.14) | ||
In Laidlaw and colleagues’ study,84 the mean difference in contrast sensitivity 6 months after surgery (reported on an unspecified scale, presumably log-contrast sensitivity or dB) between the routine surgery (1.54) and expedited surgery group (1.76) was statistically significant. However, the study authors stated that the clinical importance of the significant difference in binocular acuity measures was only slight, equivalent to four individual letters on the Pelli–Robson chart.
Foss and colleagues83 reported that at baseline contrast sensitivity was the best measurable (1.65 dB) in 44% of patients. Mean binocular contrast sensitivity on a dB scale increased more for those with expedited second-eye surgery compared with those waiting for routine surgery. The mean difference between the groups at 6 months was statistically significant. However, the difference was small, equivalent to less than 0.05 log-units. Experts consulted during the preparation of this report suggested that the interpretation of such a small change in contrast sensitivity is not fully clear but the change is probably of limited clinical importance.
Castells and colleagues85 reported a difference in log-units for binocular contrast sensitivity 4–6 months after surgery between those who had received surgery in both eyes (1.61 log-units) and those who had received surgery in one eye (1.57 log-units); however, the difference was not statistically significant. At follow-up, fewer patients who had surgery in both eyes (1.4%) were in the < 1.30 log-units category of binocular contrast sensitivity than those who had received surgery in one eye (7.4%), with differences between treatment groups less pronounced in the ≥ 1.30 to < 1.70 log-unit category (55.4 and 51.1 log-units, respectively) and the ≥ 1.70 log-unit category (43.2 and 41.5 log-units, respectively). However, no statistical testing for the differences between the treatment groups in any of the three categories was reported. The change from baseline in log-units was also reported (see Table 5), although baseline measures were taken prior to first-eye surgery and, therefore, do not reflect effects of second-eye surgery alone.
Stereopsis
All three RCTs reported measures for stereopsis, but the outcomes that were tested statistically were different in each study (Table 6). All the RCTs assessed stereopsis using combinations of stereotests that included the Wirt fly test44 to achieve a wide range of stereoscopic disparities (the tests employed in each RCT are listed in the data extraction forms, see Appendix 4).
| Study; outcome | Intervention | Comparator | Mean difference between intervention and comparator (95% CI); p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laidlaw et al. (1998)84 | Expedited surgery | Routine surgery | At 6 monthsa | ||
| Baseline (n = 105) | 6 months (n = 98) | Baseline (n = 103) | 6 months (n = 94) | ||
| Stereoacuity, 3000 seconds of arc or worse, n (%)b | 64 (61) | 12 (12) | 73 (71) | 66 (70) | 58% (47% to 69%); p < 0.0001 |
| Foss et al. (2006)83 | Expedited surgery | Routine surgery | At 6 monthsc | ||
| Baseline (n = 120) | 6 months (n = 115) | Baseline (n = 119) | 6 months (n = 113) | ||
| Depth perception, unspecified 5-point ordinal scale | 1.66 | 1.36 | 1.85 | 1.93 | −0.45 (−0.22 to −0.69); p < 0.0005 |
| Stereopsis (seconds of arc), n (%) | |||||
| 150 | 76 (63) | 100 (87) | 65 (55) | 67 (59) | NR |
| 300 | 22 (18) | 9 (8) | 27 (23) | 23 (20) | NR |
| 600 | 11 (9) | 4 (4) | 11 (9) | 10 (9) | NR |
| > 600 Wirt abled | 9 (8) | 2 (2) | 12 (10) | 8 (7) | NR |
| > 600 Wirt unabled | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | 4 (3) | 5 (4) | NR |
| Castells et al. (2006)85 | Both-eyes surgery (n = 139) | One-eye-only surgery (n = 135) | At 4–6 months | ||
| Baselinee | 4–6 months | Baselinee | 4–6 months | ||
| Stereopsis, mean log-units (SD) | 2.86 (0.66) | 1.75 (0.24) | 2.89 (0.70) | 2.37 (0.69) | 0.62 (0.45 to 0.79); p < 0.001 |
| ≥ 3.48 (≥ 3000 seconds of arc), n (%) | NR | 0 | NR | 25 (18.5) | p < 0.001 |
| > 1.78 to < 3.48, n (%) | NR | 42 (30.4) | NR | 84 (62.2) | NR |
| ≤ 1.78 (≤ 60 seconds of arc), n (%) | NR | 96 (69.6) | NR | 26 (19.3) | p < 0.001 |
| Change from baselined (log-units) | −1.11 (0.69) | −0.51 (0.79) | 0.60 (0.36 to 0.85); p < 0.001 | ||
Baseline stereopsis was poor in the RCT by Laidlaw and colleagues,84 with 61–71% of patients having loss of stereopsis (3000 seconds of arc or worse). In contrast, in the RCT by Foss and colleagues,83 65–76% of patients were in the best stereopsis class (150 seconds of arc) at baseline. Castells and colleagues’ baseline data on stereopsis were collected before first-eye surgery, but data collected after first-eye surgery in the one-eye-surgery group (as a proxy for baseline data in the second-eye surgery group) indicate moderate stereopsis (2.37 log-units or approximately 230 seconds of arc) (see Table 6). 85
In the study by Laidlaw and colleagues,84 the percentage of patients with stereopsis of 3000 seconds arc or worse (indicating total loss of stereo vision) at 6 months in the expedited surgery group (12%) was far lower compared with the routine surgery group (70%), indicating that second-eye surgery substantially improved stereopsis. The difference was statistically significant (58%, 95% CI −47% to 69%; p < 0.0001; see Table 6).
Foss and colleagues83 reported data for stereopsis in five classes ranging from 150 seconds of arc (best) to > 600 seconds of arc and unable to see a ‘Wirt’ image (worst), but did not provide any statistical comparisons (see Table 6). Six months after surgery, the best stereopsis class contained a higher proportion of patients from the expedited surgery group (87%) than from the routine surgery group (59%). In addition, Foss and colleagues83 recorded depth perception on an unspecified 5-point ordinal scale. Six months after surgery, the scores were lower for expedited surgery patients (1.36) than for routine surgery patients (1.93), with the difference being statistically significant (−0.45 ordinal scale units, 95% CI −0.22 to −0.69; p < 0.0005).
In the study by Castells and colleagues,85 the mean stereopsis in log-units 4–6 months after surgery was significantly lower (i.e. better) in patients who had received surgery in both eyes (1.75 log-units) compared with those who received surgery in one eye only (2.37 log-units) (mean difference 0.62 log-units, 95% CI 0.45 to 0.79 log-units; p < 0.001). Castells and colleagues85 also reported the proportions of patients in each of the study groups that were in each of three classes of stereopsis (see Table 6). Significantly more patients who had received surgery in both eyes (69.6%) than those who had received surgery in one eye only (19.3%) were in the best stereopsis class (≤ 1.78 log-units, ≤ 60 seconds of arc; p < 0.001). Conversely, significantly fewer patients who had received surgery in both eyes (0%) than those who had received surgery in one eye only (18.5%) were in the worst stereopsis class (≥ 3.48 log-units, ≥ 3000 seconds of arc; p < 0.001). The change from baseline in log-units was also reported (see Table 6), although baseline measures were taken prior to first-eye surgery and, therefore, do not reflect effects of second-eye surgery alone.
Overall, the results from all three RCTs, although presented in different ways, show that improvements in stereopsis occurred after second-eye surgery compared with single-eye surgery. Changes in the proportions of patients in the worst and best stereopsis classes indicate that a proportion of patients would have experienced a clinically meaningful change in stereopsis, i.e. they regained functional stereoscopic vision following second-eye surgery. The improvement was most pronounced in the RCT by Laidlaw and colleagues84 which had the lowest proportion of patients with functional stereopsis at baseline.
Patient-reported outcomes
There was a large variation in patient-reported outcomes between the studies, with few outcome measures common to more than one RCT. Although general health status was reported by all three studies, Laidlaw and colleagues84 utilised the SF-36, Foss and colleagues83 reported using the EQ-5D, and Castells and colleagues85 the Short Form questionnaire-12 item health survey instrument (SF-12). Both Foss and colleagues83 and Castells and colleagues85 assessed patient-reported visual disability as an outcome using the VF-14 instrument.
Generic instruments assessing general health status
Laidlaw and colleagues84 administered the SF-36 6 months after surgery, but did not report any data for the treatment groups, stating only that group differences were non-significant. The authors stated that after Bonferroni corrections, Mann–Whitney U-tests found statistically significant differences in favour of the expedited surgery group in five out of seven of the quality-of-life questions, but provided no further details. It is unclear whether or not the stated differences would be clinically significant.
Foss and colleagues83 employed the EQ-5D 6 months after surgery and found that the mean difference between the treatment arms at 6 months (0.02) was not statistically significant (p = 0.36) (Table 7).
| Study; outcome | Intervention, mean (SD) | Comparator, mean (SD) | Mean difference between intervention and comparator (95% CI); p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foss et al. (2006)83 | Expedited surgery (n = 120) | Routine surgery (n = 119) | At 6 monthsa | ||
| Baseline | 6 months | Baseline | 6 months | ||
| EuroQoL – EQ-5D | |||||
| Mean score (0 to 1.0/worst–best) | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.02 (−0.03 to 0.08); p = 0.36 |
| Castells et al. (2006)85 | Both-eyes surgery (n = 139) | One-eye-only surgery (n = 135) | At 4–6 months | ||
| Baselineb | 4–6 months | Baselineb | 4–6 months | ||
| SF-12 | |||||
| Physical, Mean score (0–100/worst–best) | 45.57 (9.79) | 47.5 (9.3) | 44.82 (10.89) | 46.2 (9.3) | 1.30 (1.85 to 4.40) |
| Change from baselineb | 1.76 (10.6) | 1.40 (9.2) | 0.36 (−3.04 to 3.56) | ||
| Mental, Mean score (0–100/worst–best) | 48.51 (9.36) | 53.1 (4.9) | 48.23 (10.38) | 51.2 (6.6) | 1.90 (0.03 to 3.79); p < 0.05 |
| Change from baselineb | 4.27 (10.2) | 2.96 (10.5) | 1.31 (−2.16 to 4.71) | ||
Castells and colleagues85 utilised the SF-12 4–6 months after surgery, reporting results for the physical and mental component summary (see Table 7). Scores for the physical component summary were marginally higher in patients who had been given surgery in both eyes compared with patients who had been given surgery in one eye (mean difference 1.30, 95% CI 1.85 to 4.40), although statistical significance was not reported. For the mental component summary, cataract surgery in both eyes resulted in marginally higher scores (53.1) than cataract surgery in one eye (51.2). Although relatively small, the point difference (1.90, 95% CI 0.03 to 3.79; p < 0.05) exceeds the threshold change of 0.03 units which is considered to be clinically important for preference-based measures including the SF-12. 86
Generic instruments assessing specific domains of quality of life or psychological distress
Foss and colleagues83 reported the scores from the Barthel Index (assessing activities of daily living), the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), the Falls Efficacy Scale (confidence) and the London Handicap Scale as outcome measures. The mean differences between treatment groups after 6 months on three of these scales were mostly small and not statistically significant: 0.1 for the Barthel Index (p = 0.61), 0.2 for the HADS – Anxiety (p = 0.54), and 0.5 for the HADS – Depression (p = 0.47) (Table 8). The mean differences between treatment groups after 6 months were statistically significant for confidence in avoiding falls, measured by the Falls Efficacy Scale and perceived functional disability measured by the London Handicap Scale. The mean difference between groups in the Falls Efficacy Scale was 3.6 points (p = 0.008) and indicated, counterintuitively, that patients in the expedited surgery group had lower confidence in avoiding falls, although both groups had relatively high scores overall, indicating a general lack of confidence in avoiding falls among all the patients. The authors83 claimed that second-eye surgery significantly improved confidence about falling, but this contradicts the published results, as higher scores in this measure are associated with lower falls self-efficacy (see Table 8). The mean difference between groups in the London Handicap Scale was 4.4 points (p < 0.0005) and indicated that patients in the expedited surgery group had a lower degree of perceived functional disadvantage (see Table 8). As far as we are aware, the minimal detectable change (MDC – the threshold for distinguishing actual change from measurement error) and minimal clinically important difference (MCID – the minimum change in score necessary for a patient to experience a clinically important improvement) have not been established for these two patient-reported measures. Foss and colleagues83 did not specify whether or not they considered these changes in falls efficacy and perceived handicap to be clinically meaningful.
| Outcomes – all data are from Foss et al. (2006)83 | Expedited surgery (n = 120) | Routine surgery (n = 119) | Mean difference between intervention and comparator at 6 months (95% CI); p-valuea | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 6 months | Baseline | 6 months | ||
| Barthel Index (activities of daily living scale; 0–20/worst–best) | 18.7 | 18.7 | 18.9 | 18.8 | −0.1 (−0.2 to 0.3); p = 0.61 |
| Confidence – Falls Efficacy Scale (10–100/best–worst)b | 85.5 | 86.1 | 84.4 | 81.7 | 3.6 (0.9 to 6.2); p = 0.008 |
| London Handicap Scale (0–100/worst–best) | 82.3 | 85.2 | 82.2 | 80.8 | 4.4 (2.2 to 6.5); p < 0.0005 |
| HADS (0–28/best–worst) | |||||
| Anxiety | 6.4 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 7.1 | −0.2 (−1.0 to 0.5); p = 0.54 |
| Depression | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.5 | 4.7 | −0.5 (−0.7 to 0.3); p = 0.47 |
Instruments assessing visual disability and symptoms
Patient-reported visual disability assessed using the VF-14 (rated from 0 to 100, where higher scores indicate less functional impairment) was reported by two RCTs. 83,85 Thresholds for the VF-14 for the MDC and MCID have been proposed as 10.81 and 15.57 units, respectively, on the VF-14 scale. 87
Both RCTs found less functional impairment was reported by those who had received second-eye surgery (Table 9).
| Study; outcome | Intervention | Comparator | Mean difference between intervention and comparator (95% CI); p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foss et al. (2006)83 | Expedited surgery (n = 120) | Routine surgerya (n = 119) | At 6 monthsb | ||
| Baseline | 6 months | Baseline | 6 months | ||
| VF-14, mean score (0 to 100/worst–best) | 87.5 | 94.7 | 87.5 | 87.2 | 7.5 (5.1 to 9.9); p < 0.0005 |
| Castells et al. (2006)85 | Both-eyes surgery (n = 139) | One-eye-only surgery (n = 135) | At 4–6 months | ||
| Baselinec | 4–6 months | Baselinec | 4–6 months | ||
| VF-14, mean score (SD) (0 to 100/worst–best) | 58.08 (20.59) | 97.7 (7.1) | 61.01 (22.28) | 89.5 (15.9) | 8.24 (4.35 to 12.36); p < 0.001 |
| Score ≤ 80, n (%) | NR | 5 (3.6) | NR | 26 (19.3) | NR; p < 0.001 |
| Score > 80 to < 100, n (%) | NR | 31 (22.3) | NR | 51 (37.8) | NR |
| Score = 100, n (%) | NR | 103 (74.1) | NR | 58 (43.0) | NR; p < 0.001 |
| Change in score from baseline, mean (SD)c | 39.9 (20.7) | 28.3 (20.4) | 11.57 (4.79 to 18.12); p < 0.001 |
||
Foss and colleagues83 reported that the mean VF-14 score difference (7.5 points) between the expedited surgery group and the routine surgery group at 6 months was statistically significant (see Table 9). However, this difference in mean scores is smaller than both the MDC and MCID for the VF-14, suggesting that a large proportion of the participants may not have experienced meaningful improvement in vision-related function, which was already very good before second-eye surgery.
Castells and colleagues85 found that, 4–6 months after surgery patients who had received surgery in both eyes reported less visual impairment than those who had received surgery in one eye (mean scores 97.7 vs. 89.5 points), with the mean difference in VF-14 score (8.24 points) being statistically significant. However, being smaller than the MDC and MCID, this difference suggests that for the majority of participants visual function may not have improved substantially after surgery in both eyes. In the best (100 points) score category 74.1% of patients had received surgery in both eyes, compared with 43.0% who had received surgery in one eye. In the worst (≤ 80 points) score category, only 3.6% had received surgery in both eyes, compared with 19.3% who had one-eye surgery. Differences in point estimates were statistically significant for both categories. No statistical comparison for the > 80 to < 100 points category was reported (22.3% had surgery in both eyes; 37.8% had surgery in one eye) (see Table 9).
In both RCTs, VF-14 scores were already high after first-eye surgery. In the RCT of Foss and colleagues,83 50% of scores were above 90% of the scale maximum, whereas in the RCT of Castells and colleagues85 the mean score in the single-eye surgery was 89.5 points out of a possible maximum of 100 points. Vision-related function was therefore already very good before second-eye surgery, with relatively limited improvement possible on the assessment scale due to ceiling effects.
Falls and fractures
Only Foss and colleagues83 reported falling (in a female population) as an outcome (Table 10). A fall was defined as unintentionally coming to rest on the ground or at a lower level with or without loss of consciousness. The proportion of women experiencing falling during the 12-month follow-up period was higher in the expedited surgery group (40%) than in the routine surgery group (34%). However, the authors did not report a statistical comparison between the treatment groups. The hazard ratio for women experiencing a first fall was 1.06 at 6 months follow-up, but not statistically significant, equating to a non-significantly higher rate of first falls in those who had received second-eye surgery (22%) than in women awaiting second-eye surgery (16%), whereas the number of women experiencing more than one fall was the same in both groups (18%). The rate of falling per 1000 patient-days was also non-significant. Fractures were experienced in 4% of women who had received second-eye surgery and in 3% of women awaiting second-eye surgery.
| Outcomes measured during 12 months after surgery | Expedited surgery (n = 120) | Routine surgery (n = 119) | Hazard or risk ratio (95% CI); p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total no. of patients experiencing falling, n (%) | 48 (40) | 41 (34) | NR |
| Number of patients experiencing first fall | 26 (22)a | 19 (16)a | Hazard ratio 1.06 (95% CI 0.69 to 1.61); log-rank test 0.06, 1df, p = 0.80 |
| Number of patients experiencing > 1 fall | 22 (18) | 22 (18) | Hazard ratio 0.85 (95% CI 0.49 to 1.56); log-rank test 0.26, 1df, p = 0.61 |
| Rate of falling per 1000 patient-days (range) | 2.9 (0 to 31) | 4.3 (0 to 120) | Rate ratio 0.68 (95% CI 0.39 to 1.19); p = 0.18b |
| Fractures | 5 (4%) | 3 (3%) | Risk ratio 2.5 (95% CI 0.5 to 12.5); Fisher’s exact test, p = 0.45 |
Surgical complications
Two of the studies reported surgical complications. 83,84 It should be noted that extracapsular cataract extraction, which was the method employed by Laidlaw and colleagues,84 has historically been associated with more problematic complications than the phacoemulsification approach to cataract surgery employed in the more recent study by Foss and colleagues. 83
Laidlaw and colleagues84 reported six types of surgical complication which were either sight-threatening or necessitated further surgery. In total, 11 complications occurred in nine patients (9%) in the expedited surgery group (Table 11). The most common complications were cystoid macular oedema (three events) and iris prolapse (three events).
| Study name, outcomes | Expedited surgery |
|---|---|
| Laidlaw et al. (1998)84 | n = 9/98 (9%), total of 11 complications |
| Vitreous loss | 2 |
| Retinal detachment | 1 |
| Cystoid macular oedema | 3 |
| Iris prolapse | 3 |
| Corneal oedema | 1 |
| Implant failure with subsequent secondary lens implantation | 1 |
| Foss et al. (2006)83 | n/N (%) |
| Iris damage | 1/115 (0.9) |
| Endophthalmitis | 0/115 (0) |
| Anterior vitrectomy performed | 4/115 (3) |
| Posterior capsular opacification noted at 6 months | 12/115 (10) |
| YAG capsulotomy performed during study period | 10/115 (9) |
Foss and colleagues,83 reported seven types of surgical complications, although two (section stitched and iris hooks) are surgical procedures rather than complications and we have not extracted these. The most frequent complication in the expedited surgery group was PCO at 6 months (10%), with Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy (to treat PCO) being performed at any time during the study period in 9% of the patients (see Table 11).
A limitation of these data is that it is not clear how complete the reporting of complications was, since follow-up differed between the RCTs and different complications were listed in each RCT. Foss and colleagues83 had a 12-month follow-up for most clinical outcomes but, as noted above, assessed only incidence of PCO 6 months after surgery, whereas Laidlaw and colleagues84 had a 6-month follow-up. The frequencies of complications such as PCO and retinal detachment, which may occur more than a year after cataract surgery, might therefore have been underestimated in both RCTs. It is unclear whether Laidlaw and colleagues84 had no cases of PCO up to 6 months after surgery or whether they did not record this complication. The RCT of Laidlaw and colleagues84 was conducted before phacoemulsification was introduced, and the complications they reported with extracapsular cataract surgery might not be reflective of current practice, as the safety of cataract surgery has improved since the introduction of phacoemulsification. 88 Among the complications reported in these RCTs, the most serious are retinal detachment and those involving vitreous loss or vitrectomy.
Castells and colleagues85 reported the number of post-randomisation exclusions that were due to complications of first-eye surgery. There were two exclusions from the second-eye surgery group and one from the single-eye surgery group.
Adverse events
Other than surgical complications, the only other adverse event that was reported in the RCTs was mortality. A patient flow chart presented by Laidlaw and colleagues84 suggests that no mortality occurred during their RCT. Foss and colleagues83 reported that three patients died during their RCT: one in the expedited surgery group and two in the routine practice group. Castells and colleagues85 also reported that three patients died during their RCT, of whom one was in the single-eye surgery group and two of whom were in the second-eye surgery group. Causes of mortality were not reported in any of the studies.
Ongoing studies
No ongoing studies were identified up to 10 July 2013.
Relevant systematic reviews
No relevant systematic reviews were identified in the study protocol (see Appendix 1) or during bibliographic searches conducted up to July 2013. However, after data synthesis had been completed, we identified a systematic review, published in October 2013, of the benefits of second-eye cataract surgery in the elderly. 89 Ishikawa and colleagues’89 inclusion criteria did not limit studies to RCTs, although their searches were limited to English-language publications. They included 10 primary studies, of which three were the RCTs that we report above,83–85 five were cohort studies, and two were before-and-after studies (no other RCTs were identified). One of the cohort studies they included, by Räsänen and colleagues,90 also investigated cost-effectiveness and HRQoL and is included in our systematic reviews of cost-effectiveness and HRQoL (see Systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence and Systematic review of health related quality-of-life studies).
Ishikawa and colleagues89 concluded that second-eye surgery led to improvement in visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, stereopsis, and self-reported visual functioning, supported by moderate-quality evidence. They also concluded that there was improvement in HRQoL based on mixed-quality evidence, but no improvement in falls reduction, based on limited-quality evidence. Interpretation of these findings is not straightforward, however, since the assessment of evidence quality was based on ‘best evidence synthesis guidelines’ which assessed only whether or not an improvement in outcomes occurred and did not consider the magnitude and variance of any observed improvements. Moreover, no quantitative results were presented and it was not specified whether the reported improvements in outcomes were based on clinical importance, statistical significance or other criteria. 89
Summary of clinical effectiveness
Study characteristics
Three parallel-group RCTs conducted from 1994 to 2006, each randomising 208–296 elderly participants (mean age 71.1–79.9 years), met the selection criteria and were included in the systematic review of clinical effectiveness. 83–85 The RCTs varied in quality, with all three being deemed at high risk of performance bias (patients could not be masked to the treatment group).
One RCT was conducted before phacoemulsification was introduced in the UK84 and one RCT included only women;83 the RCTs also differed in the timing of their baseline assessments. Owing to this methodological heterogeneity, quantitative pooling of outcomes in a meta-analysis was deemed inappropriate. Instead we synthesised outcomes narratively.
Effects on vision
All three RCTs reported measures of visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and stereopsis, but they did not report any other measures of clinical vision (e.g. glare disability). The three RCTs all indicated statistically significant slight improvements in binocular visual acuity (ranging from 0.04 to 0.063 log-MAR) after second-eye surgery compared with surgery in one eye alone. However, these differences (less than 1 Snellen line equivalent) would not be considered clinically important. Changes in monocular visual acuity in the second eye after surgery were reported in two RCTs and were relatively large (0.46 log-MAR83 and 0.75 log-MAR84), although neither RCT stated whether or not the changes were statistically significant.
Binocular contrast sensitivity was higher after second-eye surgery in all three RCTs, with the difference statistically significant in two RCTs. 83,84 However, the differences were clinically small, equivalent to 0.09 dB (less than 0.05 log-units)83 or no more than four letters on a Pelli–Robson chart. 84
Baseline stereopsis differed among the RCTs, being notably poor in the RCT by Laidlaw and colleagues,84 with 61–71% of patients having no functional stereopsis (3000 seconds of arc or worse). In contrast, in the RCT by Foss and colleagues83 65–76% of patients were in the best stereopsis class (150 seconds of arc) at baseline. Castells and colleagues85 did not collect baseline data immediately before second-eye surgery, but their data collected after first-eye surgery (a proxy for baseline data in the second-eye surgery group) indicate moderate stereopsis (mean approximately 230 seconds of arc). Stereopsis significantly improved after second-eye surgery in all three RCTs, although different ways of presenting and analysing these data were used in each RCT. These improvements would be of clinical benefit to patients’ vision and were largest in the RCT by Laidlaw and colleagues84 whose patients had the worst baseline stereopsis.
Effects on patient-reported outcomes
Three RCTs measured patient-reported outcomes for general HRQoL, but each used a different preference-based instrument (SF-12, SF-36 or EQ-5D). 83–85 Of these, the mental health component summary of the SF-12 indicated a statistically significant and clinically relevant improvement after second-eye surgery. 85 However, differences in the other measures between first- and second-eye surgery were not statistically significant (EQ-5D, SF-36)83,84 or the statistical significance was not reported (physical health component summary of the SF-12). 85 One RCT, which focused specifically on elderly women,83 employed generic instruments to assess specific domains of HRQoL and psychological distress. No statistically significant differences were found between first- and second-eye cataract surgery for activities of daily living, anxiety or depression. Statistically significant differences between the study groups were found for falls efficacy and handicap, although the differences in scores (3.6 on the Falls Efficacy Scale and 4.4 on the London Handicap Scale) were modest in comparison with already high baseline scores. The clinical importance of these findings is unclear, as the MCID has not been established for these patient-reported outcome measures and the authors of the RCT did not discuss clinical interpretation. 83
The only validated vision-specific instrument used was the VF-14, which assesses the impact on 14 vision-dependent activities. Two RCTs that employed this instrument recorded significantly higher (better) scores in the group who had received second-eye surgery, with mean differences of 7.5 points83 and 8.24 points. 85 However, these differences are smaller than the proposed MCD and MCID for the VF-14,87 suggesting that they did not reach clinical significance.
In summary, the majority of patient-reported outcome measures employed by the three RCTs did not demonstrate convincing effects of second-eye cataract surgery on patients’ HRQoL. This might reflect relatively good visual acuity and HRQoL that many patients had before second-eye surgery (i.e. ceiling effects of these outcomes) and/or limitations of the assessment instruments that were employed (see Chapter 7).
Effects on falls and fractures
Falls and fractures were assessed only in one RCT. 83 Compared with first-eye cataract surgery, second-eye surgery did not reduce the number of falls or fractures significantly.
Surgical complications
Two RCTs reported surgical complications, although one84 was conducted before phacoemulsification was introduced in the UK. In the more recent RCT, more relevant to current practice,83 the reported complications were typical of those associated with phacoemulsification, the most frequent being PCO (10% at 6 months).
Chapter 5 Economic analysis
Systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence
A systematic review of the literature was conducted to identify economic evaluations of second-eye cataract surgery, following the methods reported in Chapter 3. The purpose was to assess the current evidence base for cost-effectiveness evaluations and whether or not there is a need for further economic modelling, since any further modelling required would be informed by the methods used in previous cost-effectiveness studies.
A total of 190 potentially relevant references were found in the cost-effectiveness searches. Of these, the full texts of five papers were retrieved and four papers met all of the a priori inclusion criteria. 90–93 A summary of the selection process and the reasons for exclusion is presented in Figure 2. One study was excluded as a result of having a non-relevant intervention94 (see Appendix 8 for the list of excluded studies). Of the four papers included, two were linked. 92,93 For the purposes of this report, we refer to the main publication by Busbee and colleagues. 92 Characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 12 and discussed in more detail subsequently. The full data extraction forms for all included studies are provided (see Appendix 7).
FIGURE 2.
Flow chart of identification of studies for inclusion in the review of cost-effectiveness.
| Author | Busbee et al. (2003)92 | Räsänen et al. (2006)90 | Sach et al. (2010)91 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | USA | Finland | UK |
| Funding source | Retina Research and Development Fund, the Principals Initiative Research Award, Premier’s Award for Research Excellence | Research grants from the Helsinki and Uusimaa Hospital Group | Trent Regional NHS Research and Development Scheme and the PPP Foundation (now the Health Foundation) |
| Study type | Decision tree model (cost–utility analysis) | Prospective HRQoL study (cost–utility analysis) | Within-trial cost–utility analysis |
| Perspective | Third-party insurer | Secondary health-care provider | UK NHS and PSS (and carers) |
| Study population | Patients from the US National Cataract Patient Outcomes Research Team (PORT) study (722 individuals), who were undergoing a cataract extraction (median age 73 years) | Patients scheduled for routine cataract operation (386 individuals, of whom 219 were available for final analysis). Mean age varied from 69 to 75 years across three subgroups | Women over 70 years of age, without other visual comorbidities, who previously had a successful first-eye cataract surgery and had a second operable cataract |
| Baseline visual acuity | Mean VA Snellen 0.24 (decimal) | Mean best corrected VA in surgical eye Snellen 0.24 (decimal), (0.76 log-MAR) | Mean VA 0.09 log-MAR (spectacles corrected), binocular vision |
| Intervention(s) | Second-eye cataract surgery | Second-eye cataract surgery (group C); only one eye was operated (group A); both eyes were operated (group B) | Second-eye cataract surgery |
| Comparator | Unilateral pseudophakia | No treatment | Waiting list controls |
| Intervention effect: visual acuity | Mean VA Snellen 0.74 | NR | Mean VA 0.04 log-MAR binocular vision 6 months after surgery |
| Intervention effect: quality of life | Mean change in QoL before-and-after second-eye surgery of 0.109, using TTO valuation | Mean change in QoL between 6 months post surgery and baseline was −0.01, using 15D | Mean change in QoL before-and-after second-eye surgery of −0.01, using EQ-5D |
| Currency base, price year | US$, 2001 | Euro, 2002–3 | UK £, 2004 |
| Time horizon | Lifetime | Lifetime | 1 year/lifetime |
| Base case results | Second-eye cataract surgery had cost–utility of US$2495 per QALY gained | Mean hospital costs at 6 months, €1323, mean QALYs gained −0.0219; ICERs not reported | The ICER for surgery in the 1-year base case was £44,263. The long-term ICER was £17,299 |
Critical appraisal of the studies
The cost-effectiveness studies were assessed against a critical appraisal checklist (Table 13). This checklist assessed the quality of the studies and their generalisability to the UK and was adapted by the review authors from checklists by Philips and colleagues,80 Drummond and colleagues81 and the NICE reference case requirements. 95
| Item | Busbee et al. (2003)92 | Räsänen et al. (2006)90 | Sach et al. (2010)91 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Is there a clear statement of the decision problem? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2 | Is the comparator routinely used in UK NHS? | Yes | No | Yes |
| 3 | Is the patient group in the study similar to those of interest in UK NHS? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 4 | Is the health-care system comparable to UK? | ? | ? | Yes |
| 5 | Is the setting comparable to the UK? | ? | Yes | Yes |
| 6 | Is the perspective of the analysis clearly stated? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 7 | Is the study type appropriate? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 8 | Is the economic evaluation methodology appropriate? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 9 | Is the structure of the analysis described and does it reflect the disease process? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 10 | Are assumptions of the analysis listed and justified? | Yes | ? | Yes |
| 11 | Are the data inputs for the analysis described and justified? | Yes | ? | Yes |
| 12 | Is the effectiveness of the intervention established based on a systematic review? | No | N/Aa | N/Aa |
| 13 | Are health benefits measured in QALYs? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 14 | Are health benefits measured using a standardised and validated generic instrument? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 15 | Are the resource costs described and justified? | Yes | ? | Yes |
| 16 | Have the costs and outcomes been discounted? | Yes | Nob | Yes |
| 17 | Has uncertainty been assessed? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 18 | Has model validation been reported? | No | N/Aa | N/Aa |
Two of the cost-effectiveness studies by Räsänen and colleagues90 and Sach and colleagues,91 were also included in our systematic review of HRQoL (see Systematic review of health-related quality-of-life studies for a more detailed consideration of their HRQoL results).
All studies clearly defined the study question and explained the competing alternative. Two studies used a relevant comparator,91,92 whereas the other used a comparator that would be unlikely to be used in the UK (a hypothetical no-treatment group). 90 Each study clearly stated the patient group of interest and the study perspective. One of the studies was conducted in the UK,91 and the other studies were conducted in the USA92 and Finland,90 and it is unclear how generalisable these studies are to the UK NHS. The study type and methodology are appropriate for the decision problem in this report (see Chapter 2).
Reported descriptions of the parameters and assumptions varied between studies. Räsänen and colleagues90 provided limited information on assumptions and costs in their analysis, whereas the other two studies91,92 provided more complete information on their inputs and assumptions.
Busbee and colleagues92 based the effectiveness of the intervention on a single study, rather than a systematic review. They also included HRQoL, using standardised and generic instruments and reported the health benefits in terms of QALYs. Two studies91,92 discounted costs and benefits. The other study90 only discounted costs, as all costs were incurred in the first 6 months. All three studies assessed uncertainty through sensitivity analyses. Busbee and colleagues92 did not give any details of whether or not their model was validated.
Overall, the studies were found to vary in methodology quality. The studies by Busbee and colleagues92 and Sach and colleagues91 were of reasonable methodological quality, whereas Räsänen and colleagues’ study90 had limitations in its reporting and assumptions. The study by Sach and colleagues was of most relevance to the UK NHS91 (see Table 13).
Busbee and colleagues
Study approach
Busbee and colleagues92 developed a decision tree model in TreeAge software (TreeAge Software Inc., Williamstown, MA, USA). The model incorporated costs and consequences associated with second-eye cataract surgery compared with unilateral pseudophakia, including complications associated with cataract surgery. The model was based on one developed by the same authors for initial (first-eye) cataract surgery. 96 Costs and benefits were discounted at 3% per annum. Costs were in US dollars and the price year was 2001. In a linked study by Brown and colleagues,93 the price year was 2003. The model had a lifetime horizon.
The theoretical patient in the model presented with visual acuity in the pseudophakic eye equal to the mean post-operative visual acuity reported from the US National Cataract Patient Outcomes Research Team (PORT)97 (which included patients with mean age 73 years), and the post-operative visual acuity for the second-eye surgery was equal to that of the first-eye surgery (20/27). Complication rates associated with cataract extraction were taken from a previous study for first-eye cataract surgery96. Complications included in the model were PCO, endophthalmitis, cystoid macular oedema, lost lens fragments, intraocular lens dislocation, pseudophakic bullous keratopathy and PCO with subsequent retinal detachment.
Estimation of quality-adjusted life-years
Utility values were based on data from a large study of patients with ophthalmic disease98 and derived from patient preferences by using a time trade-off (TTO) model. Utility values associated with subsequent good visual acuity in both eyes after uneventful cataract extraction were based on a study that compared the utility change from unilateral good vision (i.e. 20/25 or better in one eye) compared with bilateral good vision (i.e. 20/25 or better vision in both eyes). 99 The utility value corresponding to unilateral pseudophakia was 0.858 and the reference case utility value for an ocular health state after second-eye cataract surgery was 0.967. These visual outcomes for each complication after treatment, with the exception of PCO, were assigned a utility value of 0.858. For PCO without retinal detachment, it was assumed that visual acuity returned to 20/27 in the operated eye, and had a utility value of 0.97.
Estimation of costs
The model included costs for cataract surgery, ambulatory and surgical procedures and retinal procedures. It also included drug expenditure costs associated with cataract surgery for medical and post-operative management. The cost of cataract surgery and management of endophthalmitis, intraocular lens dislocation, cystoid macular oedema and lost lens fragments was assumed to occur close to the initiation of cataract management. Other complications incurred costs at the mean time of treatment after surgery, i.e. 2 years for PCO, and 1 year for retinal detachment and pseudophakic bullous keratopathy.
Cost-effectiveness results
Second-eye cataract surgery resulted in 1.308 quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) gained. Discounting the QALYs gained by an annual 3% rate resulted in 0.92 QALYs gained over 12 years. Second-eye cataract surgery resulted in a total discounted health-care cost of US$2509. No costs were presented for unilateral pseudophakia. The cost–utility of second-eye cataract surgery was US$2727 per QALY gained. In the linked study by Brown and colleagues,99 the cost–utility of second-eye cataract surgery was US$2495 per QALY.
Räsänen and colleagues
Study approach
Räsänen and colleagues90 conducted a prospective HRQoL study to evaluate the cost–utility of routine cataract surgery in a real-world setting. They compared three groups: group A, in which only one eye was operated on; group B, in which both eyes were operated on during the follow-up; and group C, in which the first eye had been operated on earlier and the second eye was to be operated on. Group C is the group of most relevance to this review and is referred to as the intervention group. All groups were compared with a hypothetical situation of no treatment using age- and sex-matched controls from the general population based on data from a nationwide survey. The analysis included the costs of cataract surgery only, and the time horizon was lifetime, with health benefits discounted at 5% per annum.
The analysis used data from 386 patients scheduled for routine cataract operation (219 were available for final analysis) in the Helsinki University Eye Hospital (group A, n = 87; group B, n = 73; group C, n = 59). The mean age varied from 69 to 75 years across the three subgroups. The best decimal corrected visual acuity in the operated eye prior to cataract surgery was 0.19, 0.17, 0.24 in groups A, B and C, respectively, and in the non-operated eye was 0.58, 0.28 and 0.63, respectively. The visual acuity after surgery was not reported.
Estimation of quality-adjusted life-years
The 15D generic HRQoL instrument was used to estimate HRQoL. 100 The 15D HRQoL questionnaire is a 15-dimension standardised and self-administered instrument (covering moving, seeing, hearing, breathing, sleeping, eating, speech, excretion, usual activities, mental function, discomfort and symptoms, depression, distress, vitality and sexual activity). Patients completed the 15D at baseline and then again approximately 6 months after the cataract operation. The HRQoL gain was assumed to last until the end of the remaining statistical life expectancy of each patient based on life tables from 2002 from Statistics Finland. The utility gain from cataract surgery was negative for group C (−0.01) and small for the other two groups (group A, 0.0; group B, 0.03).
Estimation of costs
Direct health-care costs were obtained from the Ecomed® clinical patient administration system (Datawell Ltd, Espoo, Finland). Costing covered all relevant specialty-related costs including pre- and post-operative outpatient visits to the eye hospital. However, the costs of the visits to the referring ophthalmologists who were usually also responsible for the post-operative re-examination of the patients and prescription of eyeglasses, was not included in the analysis. Indirect costs, such as period of disability, were not included.
Cost-effectiveness results
The mean hospital costs at 6 months for groups A, B and C were €1318, €2289 and €1323, respectively. The QALY gain was 0.1605, 0.4464 and −0.0219 for groups A, B and C respectively. The mean cost per QALY gained was €8212 in group A and €5128 in group B. The study did not estimate the cost-effectiveness for group C (i.e. second-eye surgery), as there was a negative utility change.
Sach and colleagues
Study approach
Sach and colleagues91 developed a cost–utility analysis alongside a RCT of second-eye cataract surgery in secondary care ophthalmology clinics in UK. [The RCT, by Foss and colleagues,83 is included in our systematic review of clinical effectiveness (see Chapter 4, Clinical effectiveness)]. The costs and health benefits were measured for the operated group and a waiting list control group. These costs and benefits were extrapolated from the trial period to the lifetime of the patients. Costs were in UK pounds and the price year was 2004. Costs and benefits were discounted at 3.5% per annum.
Eligible women either received immediate second-eye surgery or were allocated to a waiting list control group (12-month wait). The trial consisted of 229 women, with 116 in the intervention group (mean age 79 years) and 113 in the control group (mean age 80 years). More details of the patient characteristics are shown in Table 2. Patients were followed up for 1 year. The trial provided data for HRQoL for the economic evaluation. The authors describe the patients as having minimal visual dysfunction in the eye to be operated on (86% had Snellen binocular visual acuity of 6/12 or better).
Estimation of quality-adjusted life-years
Patients’ HRQoL was estimated using the EuroQoL EQ-5D administered at baseline and at 6 months from the Foss and colleagues’ trial. 83 Area under the curve analysis was performed to take account of the baseline in estimating the number of QALYs for a 1-year period. In the base case, it was assumed that patient utility values at 1 month after surgery would be the same as the 6-month utility value. It was assumed that utility remained constant over the remaining lifetime for both groups.
The authors discuss the potential limitations of using the EQ-5D to assess cataract surgery, including possible lack of precision and responsiveness making it hard to detect small changes (the EQ-5D does not incorporate sensory function in its descriptive system). The authors also suggest their results are conservative because of their assumption that the difference in HRQoL between intervention and control groups is constant over the patients’ lifetime, whereas one would expect some deterioration in the control group in utility over time (mean utility declined from 0.72 to 0.69 in the 6-month period used to measure utility in the study).
Estimation of costs
Costs were derived from Foss and colleagues’ RCT. 83 Patient diaries were used to collect individual patient-level data on all contacts with health and social services, including care home admissions, informal care, and equipment and home modifications. No costs were included for treating adverse events from the cataract surgery. Data were collected at 3 and 9 months through telephone interviews and at 6 and 12 months through face-to-face interviews.
Patient life expectancy was estimated using UK government life tables. Annual costs for the control group were assumed to remain constant in subsequent years, assuming that future costs were similar to those seen during the trial period. For the intervention group, costs in the final three-quarters of the year were rescaled to better reflect costs over a full year. As with the control group, these costs were assumed to remain constant over the remaining lifespan.
Cost-effectiveness results
Over 1 year, the mean difference per patient in the base case was 0.015 QALYs. For the lifetime analysis, the mean difference was 0.074 QALYs. The mean total cost per patient (excluding carer time cost) in the operated group was £2139, compared with £1492 in the control group. The mean total cost per patient for the lifetime analysis was £12,171 and £10,887 in the operated and the control group, respectively. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) for surgery in the base case was £44,263 per QALY gained. The lifetime ICER was £17,299 per QALY gained.
Comparison of studies
Cost-effectiveness results varied across the studies. Busbee and colleagues92 reported an ICER of US$2495 per QALY,92 and Sach and colleagues91 reported an ICER of £44,263. However, in the latter study the ICER was reduced to £17,299 per QALY when a lifetime horizon was used. Räsänen and colleagues90 did not report an ICER, as second-eye cataract surgery was associated with negative QALYs.
The cost-effectiveness results were driven by the changes in utility in the studies. Each study used a different HRQoL instrument (EQ-5D, TTO or 15D). Post-surgical changes in HRQoL varied between the studies, with a utility gain of 0.109 in one study92 and a utility loss of 0.01 in two studies. 90,91 Räsänen and colleagues90 suggested that the reason for the lack of impact on HRQoL could be that two-thirds of the patients reported only minimal pre-operative subjective seeing problems despite objective evidence of poor visual acuity in the surgical eye, and one-third of patients had a secondary ophthalmic diagnosis which might have reduced the benefit of cataract surgery.
There was variation between the studies in the degree of pre-surgical visual impairment in the second eye. For Busbee and colleagues92 and group C of Räsänen and colleagues (second-eye patients),90 the mean pre-surgical visual acuity was 0.24 decimal (equivalent to around 6/24 metres), whereas in the Sach and colleagues’ study91 pre-surgical visual acuity was 0.09 decimal (or 6/7 metres).
The studies differed in their approaches to measuring the costs of second-eye surgery. Busbee and colleagues’92 report was the only study to assess the costs associated with treating post-operative complications, although the other studies collected hospital costs after surgery. Sach and colleagues91 conducted the only study to include the post-surgery costs associated with social services, such as residential care costs. Two of the studies extrapolated the short-term costs to a lifetime horizon by assuming future costs to be similar to those seen during the trial period, whereas Räsänen and colleagues90 used only the costs of the cataract procedure and hospitalisation and did not consider further costs.
In summary, there was variability across the three studies in terms of modelling approaches, patient characteristics, assumptions and parameter values, and this led to substantial differences in the estimated cost-effectiveness of the second-eye surgery. Therefore, no existing model was considered appropriate for this HTA and a de novo model was developed (see Methods for economic analysis).
Systematic review of health-related quality-of-life studies
A systematic review of studies reporting HRQoL in patients undergoing cataract surgery was conducted following the methods previously reported (see Chapter 3). The aim of this review was to identify HRQoL utility estimates that potentially could be included in our economic evaluation of second-eye cataract surgery (see Methods for economic analysis). The intention was to identify studies evaluating changes in HRQoL from cataract surgery which used generic preference-based HRQoL measures to value health utility [e.g. standard gamble (SG) or TTO]. These measures are favoured by NICE and other health-care organisations as they permit comparison of cost-effectiveness (e.g. in terms of QALYs) with other health-care interventions to inform decisions about recommended treatments. 95 Figure 3 presents the flow of studies through the inclusion/exclusion process in a flow chart.
FIGURE 3.
Flow chart for the systematic review of HRQoL studies.
A literature search identified a total of 860 references, the majority of which (96%) were excluded based on titles and abstracts. Of the full papers retrieved for further screening, 21 were excluded. The main reason for exclusion was the absence of reported utility values.
A total of 10 studies, reported in a total of 11 publications, were included in the review. 40,86,90,91,94,101–106 The included studies were diverse in terms of their aims, comparisons made, study designs, patient characteristics and locations. The full data extraction forms for all included studies are provided (see Appendix 9).
Characteristics of the included studies
Half of the studies (Table 14) were conducted in Europe,40,90,91,101,106 of which two were from the UK. 40,91 One of the UK studies, by Sach and colleagues,91 was a cost-effectiveness study conducted alongside a RCT and was included in our systematic review of cost-effectiveness (see Systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence), with the RCT itself (Foss and colleagues83) included in our systematic review of clinical effectiveness (see Chapter 4). Of the remaining studies, two were from the USA,102,104 one from Japan94,103 and one from Australia. 105
| Study | Design | Country | Number of patients | Clinical indication | Age | Baseline clinical vision status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Studies in which a comparison between first- and second-eye cataract surgery is possible | ||||||
| Dolders et al. (2004)101 | RCT with economic evaluation | The Netherlands | 143 | Bilateral senile cataract | Mean = 72 years | VA (log-MAR), mean (SD); monofocal/multifocal IOL: first eye: 0.46 (0.27)/0.49 (0.27) second eye: 0.31 (0.22)/0.28 (0.19) |
| Hiratsuka et al. (2011)94 | Prospective multicentre observational study | Japan | 549 (NB, numbers of patients available for analysis varied according to different HRQoL instruments) | First-eye, second-eye or bilateral cataract surgery | Mean (SD) = 71.0 years (7.9 years) | VA (log-MAR), mean (SD): better eye = 0.16 (0.28) worse eye = 0.51 (0.52) |
| Räsänen et al. (2006)90 | Single cohort pre and post study (with three subgroups) | Finland | 219 Group A – only one eye operated: n = 87 Group B – both eyes operated on during follow-up: n = 73 Group C – first eye operated on earlier, now second eye operated: n = 59 |
Scheduled for cataract surgery | Mean (SD): Group A = 69 years (12 years) Group B = 70 years (12 years) Group C = 75 years (10 years) |
Groups A, B and C, respectively: surgical eye: Snellen 0.19 (0.14)/0.17 (0.12)/0.24 (0.14), log-MAR 0.98 (0.66)/0.94 (0.49)/ 0.76 (0.48) non-surgical eye: Snellen 0.5 (0.23)/0.28 (0.16)/0.63 (0.25), log-MAR 0.29 (0.22)/0.65 (0.37)/ 0.25 (0.21) |
| Sach et al. (2010)91 | RCT with economic evaluation | UK | 229 Intervention = expedited second-eye surgery Control = unoperated second eye |
Previous successful first-eye cataract surgery with a second operable cataract | Aged over 70 years old | Mean log-MAR VA: 0.09 (binocular, spectacles corrected), 0.22 (binocular, unaided). Described as having minimal visual dysfunction in the eye to be operated on |
| Non-second-eye cataract surgery comparisons | ||||||
| Datta et al. (2008)40 | RCT | UK | 306 Randomised expedited first-eye surgery, n = 148 Unoperated first eye, n = 140 |
Patients with bilateral cataracts | Median = 78 years | Expedited first-eye surgery, log-MAR: unaided VA = 0.51 spectacles VA = 0.30 Unoperated first eye: unaided VA = 0.56 spectacles VA = 0.29 |
| Feeny et al. (2012)86,102 | Prospective single cohort study | USA | 210 | Patients undergoing cataract extraction surgery with lens replacement. No further information given | 35–44 years: n = 3 (1%) 45–64 years: n = 71 (34%) 65–91 years: n = 136 (65%) |
NR |
| Kishimoto (2012)103 | Single cohort retrospective analysis | Japan | 50: unilateral, n = 21 bilateral, n = 29 |
Patients with cataracts, glaucoma, or comitant strabismus (NB Only cataract patients reported here) | Mean (SD): 70.9 years (10.9 years)/74.5 years (5.8 years) (unilateral/bilateral) |
VA in better eye, mean (SD), decimal: unilateral n = 0.9 (0.5) bilateral n = 0.7 (0.3) VA in worse eye, mean (SD), decimal: unilateral n = 0.3 (0.3) bilateral n = 0.4 (0.3) |
| Naeim et al. (2006)104 | RCT with economic evaluation | USA | 250 First-eye surgery, n = 133 Watchful waiting, n = 177 |
Bilateral age-related cataracts | Mean 78 years | NR |
| Studies assessing cataract surgery complications | ||||||
| Clark et al. (2008)105 | Prospective case–control study | Australia | 49 | Patients developing post-operative endophthalmitis within 1 month following cataract surgery (cases). Controls were patients with uncomplicated cataract surgery, randomly selected | Mean (SD)a: cases = 81.2 years (8.5 years) controls = 76.60 years (11.5 years) |
NR |
| de Juan-Marcos et al. (2012)106 | Single cohort before-and-after study | Spain | 150 | Patients with posterior capsule opacification (PCO) following cataract surgery | Mean = 72 years | Mean VA in PCO eye, decimal before capsulotomy 0.4 (0.39 log-MAR) Mean VA in fellow eye, decimal 0.68 (0.16 log-MAR) Mean (SD) binocular VA (BVA), log-MAR 0.28 (0.16) |
Study designs included RCTs with economic evaluations,91,101,104 and RCTs with HRQoL evaluations,40 with the remainder of the studies being observational. The observational designs comprised single cohorts of patients;86,103,106 single cohorts of patients with subgroups based on whether patients received first-eye, second-eye or bilateral surgery;90,94 and a case–control study. 105
Mean ages, in years, in the studies were generally in the early 70s, but ranged from 69 to 81 years. The majority of the patient populations studied were mixed sex, with the exception of two studies in which all patients were female. 40,91 In the majority of the studies in which baseline clinical vision status was reported, the patients could be classed as having poor visual acuity. The mean visual acuity (generally in the eye to be operated on) was most often below Snellen 6/12, indicating visually impairing cataracts. 107 One study was an exception,91 with patients described as having minimal visual dysfunction in the eye to be operated on (86% had a baseline visual acuity of 6/12 or better).
A range of HRQoL instruments were used by the studies, the most common being the EQ-5D (seven studies). 40,86,91,94,101,105,106 Four studies used the TTO method with patients to elicit utility values,94,101,103,105 three studies used the Health Utilities Index 3 (HUI-3)86,94,103 and two studies asked patients to rate their HRQoL using a visual analogue scale (VAS) [in one case the EuroQol-visual analogue scales (EQ-VAS);106 in the other study101 the VAS instrument was not specified].
The studies were classified into three groups based on the comparisons it is possible to make (Table 15): studies in which a comparison between first- and second-eye cataract surgery is possible;90,91,94,101 non-second-eye cataract surgery comparisons (including, but not restricted to, studies assessing only first-eye surgery);40,86,103,104 and studies assessing the impact of cataract surgery complications on HRQoL. 105,106
| Study | HRQoL instruments used | Timing of measurements | Utility results | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Studies in which a comparison between first- and second-eye cataract surgery is possible | ||||||||
| Dolders et al. (2004)101 | EQ-5Da; VAS; TTO; SG | T1: 1–2 weeks pre-first-eye surgery T2: 3 months post first-eye surgery T3: 3 months post second-eye surgery |
Mean (SD) | Monofocal IOL (0) (n = 75) | ||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T3–T2b | |||||
| VAS | 0.78 (0.19) | 0.80 (0.19) | 0.79 (0.17) | −0.01 | ||||
| TTO | 0.68 (0.28) | 0.74 (0.28) | 0.67 (0.29) | −0.07 | ||||
| SG | 0.94 (0.06) | 0.95 (0.06) | 0.94 (0.05) | −0.01 | ||||
| Multifocal IOL (1) (n = 68) | ||||||||
| VAS | 0.66 (0.22) | 0.76 (0.22) | 0.70 (0.24) | −0.06 | ||||
| TTO | 0.70 (0.26) | 0.70 (0.30) | 0.62 (0.28) | −0.08 | ||||
| SG | 0.95 (0.06) | 0.94 (0.06) | 0.93 (0.07) | −0.01 | ||||
| VAS odds ratios 0.08 (0.01 to 0.56) between T2 and T1 (first eye); 0.10 (0.02 to 0.64) between T3 and T1 (both eyes); T1: 1–2 weeks before first-eye surgery; T2: 3 months after first-eye surgery; T3: 3 months post operatively after second-eye surgery | ||||||||
| Hiratsuka et al. (2011)94 | TTO; EQ-5Dc; HUI-3c | Baseline and 3 months post surgery | Mean (SD) | First-eye surgery (n = 157) | Second-eye surgery (n = 60) | Bilateral surgery (n = 312) | ||
| TTO | n = 109 | n = 38 | n = 234 | |||||
| Utility (before surgery) | 0.66 (0.25) | 0.64 (0.29) | 0.58 (0.29) | |||||
| Utility (after surgery) | 0.84 (0.28) | 0.88 (0.23) | 0.85 (0.25) | |||||
| Utility change | 0.18 (0.27) | 0.24 (0.30) | 0.27 (0.33) | |||||
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |||||
| EQ-5D | n = 138 | n = 52 | n = 292 | |||||
| Utility (before surgery) | 0.85 (0.16) | 0.83 (0.16) | 0.84 (0.15) | |||||
| Utility (after surgery) | 0.89 (0.15) | 0.92 (0.13) | 0.90 (0.15) | |||||
| Utility change | 0.05 (0.15) | 0.09 (0.17) | 0.06 (0.16) | |||||
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |||||
| HUI-3 | n = 131 | n = 47 | n = 256 | |||||
| Utility (before surgery) | 0.71 (0.25) | 0.70 (0.20) | 0.62 (0.24) | |||||
| Utility (after surgery) | 0.79 (0.18) | 0.79 (0.22) | 0.76 (0.25) | |||||
| Utility change | 0.08 (0.21) | 0.08 (0.25) | 0.14 (0.25) | |||||
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.05 | < 0.001 | |||||
| Räsänen et al. (2006)90 | 15D | Baseline and approximately 6 months post surgery | Mean (SD) | All patients | Group A (first-eye surgery) | Group B (bilateral surgery) | Group C (second-eye surgery) | |
| Baseline | 0.82 (0.13) | 0.85 (0.13) | 0.80 (0.13) | 0.82 (0.11) | ||||
| 6 months follow-up | 0.83 (0.14) | 0.85 (0.14) | 0.83 (0.14) | 0.81 (0.13) | ||||
| Change from baseline | 0.01 | 0.00 (0.14) | 0.03 (0.14) | −0.01 (0.07) | ||||
| p-value | NR | 0.852 | < 0.001 | 0.279 | ||||
| NR = not reported, but stated to be statistically insignificant | ||||||||
| Sach et al. (2010)91 | EQ-5D | Baseline and 6 months | EQ-5D, mean | Baseline | 6 months | Difference | ||
| Expedited second eye | 0.74 | 0.73 | −0.01 | |||||
| Unoperated second eye (control) | 0.72 | 0.69 | −0.03 | |||||
| Utility difference between expedited and control (adjusted for baseline values) = 0.02 (95% CI 0.03 to 0.08); p = 0.36 | ||||||||
| Non-second-eye cataract surgery comparisons | ||||||||
| Datta et al. (2008)40 | EQ-5D; London Handicap Scaled; VF-14d; activities of daily living (Barthel Index)d | Baseline and 6 months | Mean | Expedited first-eye surgery | Unoperated first eye | Mean difference | 95% CI | p-value |
| EQ-5D | 0.73 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.11 | 0.02 | |||
| Feeny et al. (2012)86,102 | EQ-5D; HUI-2 – overall; HUI-2 – sensation; HUI-3 – overall; HUI-3 – vision; QWB–SA; SF-6D | Baseline and 6 months (NB: only 1-month post-surgery data extracted here) | Mean (SD) | 1 month post-operation | Utility change from baseline | |||
| EQ-5D | 0.84 (0.16) | 0.02 (0.13) | ||||||
| HUI-2 overall score | 0.81 (0.19) | 0.02 (0.14) | ||||||
| HUI-2 sensation score | 0.84 (0.17) | 0.08 (0.19) | ||||||
| HUI-3 overall score | 0.72 (0.28) | 0.05 (0.21) | ||||||
| HUI-3 vision score | 0.91 (0.15) | 0.12 (0.22) | ||||||
| QWB–SA | 0.60 (0.14) | 0.01 (0.13) | ||||||
| SF-6D | 0.73 (0.12) | −0.01 (0.09) | ||||||
| Kishimoto (2012)103 | TTO | 2–3 months post-operatively (retrospectively) | Mean (SD) | Unilateral | Bilateral | |||
| Post-operative utility values | 0.894 (0.228) | 0.909 (0.155) | ||||||
| Post-operative utility change | 0.167 (0.237) | 0.245 (0.167) | ||||||
| Difference in gain between unilateral and bilateral = 0.078 | ||||||||
| Naeim et al. (2006)104 | HUI-3; Activities of Daily Vision Scale (ADVS)d; SF-12d; Charlson comorbidity scaled | Baseline and 6 months | HUI-3, mean | Surgery | Watchful waiting | |||
| Baseline | 0.744 | 0.754 | ||||||
| 6-month follow-up | 0.760 | 0.723 | ||||||
| Utility change from baseline | 0.016 | −0.031 | ||||||
| Adjusted impact of surgerye – mean (SD) = 0.041 (0.029); p = 0.156 | ||||||||
| Visual utility,f mean | Surgery | Watchful waiting | ||||||
| Baseline | 0.927 | 0.92 | ||||||
| 6-month follow-up | 0.954 | 0.92 | ||||||
| Change from baseline | 0.027 | 0 | ||||||
| Adjusted impact of surgerye – mean (SD) = 0.031 (0.014); p = 0.035 | ||||||||
| Studies assessing cataract surgery complications | ||||||||
| Clark et al. (2008)105 | EQ-5D; TTO; VFQ-25d | 12 months post surgery | EQ-5D summary score, mean (SD): cases = 0.66 (0.32); controls = 0.81 (0.25); mean difference = 0.15; p = 0.08 TTO, mean: cases = 0.90; controls = 0.96; mean difference = 0.06; p = 0.12 |
|||||
| de Juan-Marcos et al. (2012)106 | EQ-5D and EQ-VAS; VF-14 (data not extracted here) | Before surgery and 3 weeks after capsulotomy | Post-capsulotomy, mean (SD) EQ-VAS = 72.4 (17.3); mean change from baseline = 13.5; p-value = < 0.01 | |||||
The following instruments were used in one study each: HUI-286, Short Form questionnaire-6 Dimensions (SF-6D),86 the Quality of Well-Being – Self-Administered (QWB-SA) questionnaire86 and the 15D. 90 It was common for studies to use more than one instrument, for purposes of comparison. For example, Feeny and colleagues86 compared agreement among five generic preference-based measures of HRQoL in a cohort of patients undergoing cataract surgery. Some of the studies used other instruments to assess patient symptoms and HRQoL but data are not presented for them here (in line with our inclusion criteria) as they were vision-specific rather than generic health instruments and/or they were generic health instruments that did not yield health utilities. These included the VF-14,40 the Visual Function Questionnaire-25 item (VFQ-25),105 the Activities of Daily Vision Scale,104 the SF-12,104 Charlson Comorbidity Index104 and the London Handicap Scale40 (see Table 15).
Results of the included studies
This section focuses on the results of the four studies which provided second-eye cataract surgery comparisons, as these are most relevant to the decision problem of this report. The results of these and the other six studies are summarised in Table 15.
Dolders and colleagues101 reported a cost–utility analysis comparing monofocal and multifocal intraocular lenses (IOLs) in cataract surgery in the Netherlands. Patients were randomised to receive surgery with either a monofocal or a multifocal IOL (n = 143 analysed). The patients were interviewed to assess HRQoL and all other outcomes at three time points: T1 (1–2 weeks before first-eye surgery), T2 (3 months after first-eye surgery) and T3 (3 months post operatively after second-eye surgery). Although not an intention of the authors, it is possible to examine changes in utility values from T2 to T3 in both randomised arms, analogous to assessing the effect of second-eye surgery. Utility values were elicited through use of VAS, TTO and SG (the EQ-5D was used, but utility values were not reported in the study publication). Although there was a general increase in utility from baseline (T1) to post-first-eye surgery (T2), utility values declined (in both trial arms) between first- (T2) and second-eye surgery (T3). This decline was common to all three utility instruments used.
Hiratsuka and colleagues94 assessed HRQoL using the TTO, the EQ-5D and the HUI-3 prior to, and 3 months after, cataract surgery. Patients were recruited from Japanese hospital ophthalmological clinics and private surgical clinics, with the aim of reflecting a real-world setting. Patients were classified using three subgroups: first-eye surgery (n = 157), second-eye surgery (n = 60) and bilateral eye surgery (n = 312). For second-eye surgery patients, increases in utility values ranged from 0.08 (HUI-3) to 0.24 (TTO) and were statistically significant for all instruments. Generally, utility gains were slightly higher for second-eye cataract surgery patients compared with first-eye patients (except on the HUI-3), and utility gains for bilateral eye surgery were slightly higher compared with first- and second-eye cataract surgery (except on the EQ-5D) (see Table 15). However, differences between these subgroups were not tested statistically. The authors suggest that the TTO method, when used to measure ophthalmic treatment, is more sensitive to small changes in utility than generic survey questionnaires such as the EQ-5D and HUI-3. However, they note that even the relatively smaller utility gains for EQ-5D and HUI-3 were statistically significant.
The study by Räsänen and colleagues90 was similar in design to that of Hiratsuka and colleagues,94 comprising three subgroups of Finnish patients: first-eye surgery (group A, n = 87); bilateral eye surgery (group B, n = 73), and second-eye surgery (group C, n = 59). HRQoL was measured using the 15D instrument, at baseline and at the 6-month follow-up. There was no change in utility for first-eye surgery patients, a slight increase of 0.03 for bilateral eye surgery patients, and a reduction of 0.01 for second-eye surgery patients. The only statistically significant result was for the bilateral surgery group. The authors propose a number of explanations for lack of improvement in HRQoL, including the fact that two-thirds of patients reported only minimal pre-operative subjective seeing problems, despite objective evidence of poor visual acuity in the surgical eye (though at baseline there was poor correlation between 15D score and visual acuity in the surgical eye); the real-world setting of a university clinic and its mixed sample; that one-third of patients had a secondary ophthalmic diagnosis (which might reduce the benefit of surgery); and potential insensitivity of the 15D to measure changes in HRQoL (it includes only one question relating to sight).
Sach and colleagues,91 as reported earlier, conducted a cost-effectiveness study alongside a RCT in the UK comparing expedited second-eye surgery (n = 116, target within 1 month) with a waiting list control group (n = 113, described as routine surgery, target within 13 months). All patients were female and described as having minimal visual dysfunction in the eye to be operated on (approximately 86% of participants had baseline visual acuity of 6/12). There was a reduction in utility in both arms following surgery: −0.01 and −0.03 for expedited second-eye and unoperated second-eye surgery patients, respectively (representing a 0.02 gain for second-eye cataract surgery patients). The difference between arms was reported to be not statistically significant. The authors discuss the potential limitations of using EQ-5D to assess the benefits of cataract surgery, noting that it does not incorporate sensory function in its descriptive system and, therefore, may lack precision and responsiveness to changes in HRQoL.
Discussion
There was variation in the utility estimates across the studies included in the review. Räsänen and colleagues90 reported a decrease in utility of 0.01 following second-eye surgery compared with no change for patients undergoing first-eye surgery. Sach and colleagues91 also reported a decrease of 0.01 for second-eye surgery compared with a slightly bigger decrease of 0.03 for patients not undergoing second-eye surgery, representing a net 0.02 utility gain. Dolders and colleagues101 reported decreases in utility of 0.01 to 0.08 from completion of first-eye surgery to completion of second-eye surgery, with estimates varying according to which HRQoL instrument was used. In their study, for first-eye cataract surgery there was an increase in utility for some instruments, no change for other instruments and for some instruments there was a slight decrease.
Hiratsuka and colleagues94 reported statistically significant increases in utility following second-eye surgery, with the magnitude of the increase varying according to which instrument was used. The EQ-5D and the HUI-3 both yielded gains of 0.09, whereas the TTO yielded a larger value of 0.24. The TTO estimates were derived directly from preferences valued by cataract surgery patients themselves, while the EQ-5D and HUI-3, though completed by patients, use preferences valued by samples of the general public. The EQ-5D does not include a sensory function and may not always be sensitive to improvements in clinical vision following cataract surgery. 90,91,108 However, the HUI-3 does contain a visual utility subscale and may be more responsive to change. For example, the study by Feeny and colleagues86 (presumed to include first-eye cataract surgery patients, though not explicitly stated) compared a number of generic HRQoL instruments and found that the largest increases in utility were for the HUI-3 and for subscales for sensation (HUI-2 sensation) and vision (HUI-3 vision) (see Table 14). Feeny and colleagues86 suggest that a change of 0.03 or more in the utility score for preference-based measures is interpreted as a clinically important change for cataract surgery. They also propose that for the single-attribute utility scores for HUI-2 sensation (which includes vision) and HUI-3 vision, the guideline for a clinically important difference is 0.05. The utility estimates reported by Hiratsuka and colleagues94 therefore exceed these thresholds for clinically important differences and may be suitable for inclusion in cost-effectiveness analysis.
Of the four studies, those by Sach and colleagues91 and Hiratsuka and colleagues94 are considered to be the most appropriate for informing the assessment of cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery in this HTA, based on methodological quality. Each study has advantages and disadvantages. To summarise, Sach and colleagues91 benefited from a RCT design directly comparing patients receiving second-eye surgery with patients on a waiting list. The study was conducted in the UK and the utility estimates could therefore be considered more relevant to the NHS. However, the patient population was exclusively female, and had mild visual impairment, so in this respect is less typical than the UK patient population where visual impairment is greater. 20 Furthermore, the authors report patients’ binocular rather than monocular visual acuity at baseline, prohibiting an assessment of the degree of visual impairment in the eye to be operated on (the second eye). The study also assessed HRQoL using the EQ-5D which, as discussed above, does not include a sensory function. Similarly, Hiratsuka and colleagues94 employed the EQ-5D but also used the TTO method and the HUI-3, which has a visual utility subscale and is therefore potentially more sensitive to improvements in vision following cataract surgery. Hiratsuka and colleagues94 also reported baseline monocular visual acuity for both eyes, allowing an assessment of the degree of visual impairment in the eye to be operated on. However, the study was observational in design, and patients undergoing second-eye cataract surgery were a relatively small subgroup of a wider group of patients having first-eye or bilateral cataract surgery. Therefore, reported visual acuity is not specific to second-eye cataract surgery patients. Furthermore, this was a Japanese study and applicability to the UK patient population is questionable. Given that expert clinical advice sought in the production of this report suggests that use of a HRQoL instrument that is sensitive to changes in clinical vision is a key consideration, on balance Hiratsuka and colleagues94 would be the most appropriate study for informing the assessment of cost-effectiveness in this report, as will be described in the next section.
The remaining two studies which reported changes in HRQoL following first- and second-eye surgery (see Table 14) were not considered appropriate for informing the base case of our cost-effectiveness analysis. Räsänen and colleagues90 used a HRQoL utility measure, 15D, not commonly used outside Scandinavia. The utility loss for second-eye surgery was small and there was no statistical difference between the utility at baseline and at 6 months. Furthermore, it is unclear whether or not this utility loss was due to other factors such as general health utility decline for an old population, as the study was for a single cohort. Dolders and colleagues101 employed several preference-based instruments (see Table 14) which provide relevant utility estimates but it is unclear whether the study could reliably detect changes in utilities since no statistical tests of differences in relation to first- and second-eye surgery were reported. This may reflect that the aim of the study was to compare two different types of IOL, not to compare first- and second-eye surgery. Nevertheless, the study by Dolders and colleagues101 does provide information on utility changes in relation to first- and second-eye surgery within each of the IOL comparison groups (albeit of uncertain reliability) and the results suggest that second-eye surgery was consistently associated with a decline in utility values compared with first-eye surgery. For this reason we have explored the impact of this study on the economic analysis results in a scenario analysis (see Results of the economic analysis).
Methods for economic analysis
Overview
As no existing published cost-effectiveness model was considered appropriate owing to methodological limitations and non-relevance to the NHS, we developed an economic model to estimate the cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery in patients with bilateral cataracts, compared with patients with bilateral cataracts who receive only first-eye cataract surgery. The modelling was conducted following accepted standards for economic evaluation. 80,81,95
The model was structured to include outcomes proposed in the research protocol (see Appendix 1). Model data input parameters were identified from our systematic reviews of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and HRQoL, and from the wider literature where necessary. Second-eye cataract surgery is associated with a change in visual acuity and a corresponding change in HRQoL, assumed to last the patient’s lifetime. Patients undergoing surgery either experience post-surgical complications or do not. Complications are associated with a health disutility and require additional treatment and/or monitoring.
The model evaluates costs (in UK pounds using a 2012 price base) from the perspective of the NHS and Personal Social Services (PSS). Outcomes in the model are expressed as QALYs and cost-effectiveness is expressed in terms of ICERs. Uncertainty with regard to model input parameters is investigated through deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses, and scenario analyses. Both costs and outcomes are discounted using a 3.5% annual discount rate in line with current guidance. 95,109
Description of the model
The conceptualisation and design of the model was informed by the assessment of the models included in our systematic review of cost-effectiveness (see Systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence). The modelling structure was similar to that developed by Busbee and colleagues,92 with some modifications to allow patients to experience long-term complications in any subsequent year.
The UK Cataract National Dataset20 has been used to supply some of the assumptions and input parameters for the economic model, as it provides a large set of routinely collected data (55,567 cataract operations from 12 NHS trusts between 2001 and 2006), with an unselected case mix of patients considered representative of routine practice in the NHS. It reports characteristics of surgical procedures, patient demographic information and comorbidities, pre- and post-operative data on visual acuity for both first and second eyes, and intraoperative and post-operative complications. Although there are data limitations, such as the percentage of various post-operative complications being available for only 30% of all operations, the study nonetheless provides the most comprehensive published data available which is relevant to the UK and is regarded to be ‘fit for purpose’. 20
Figure 4 shows a schematic of the model. A hypothetical cohort of patients that receives second-eye cataract surgery is compared with a cohort which receives no second-eye surgery (not shown). Patients receiving surgery may experience short-term post-operative complications (endophthalmitis, cystoid macular oedema and retained lens fragments). They may also experience longer-term post-surgical complications and consequences (PCO or retinal detachment). These post-surgical complications and consequences are associated with additional outpatient visits and additional remedial procedures. Patients remain in the short- or long-term complications health states (including PCO or retinal detachment) for one cycle and then are assumed to be successfully treated. Patients may die in any model cycle (based on general population mortality rates). The model has a lifetime (25-year) horizon, with a cycle length of 1 year.
FIGURE 4.
Schematic representation of the economic model. a, post-operative complication: endophthalmitis, cystoid macular oedema, retained lens fragments; and b, long-term complications: PCO, retinal detachment.
The patient cohort starting age is 75 years based on the mean age at surgery of patients in the UK Cataract National Dataset. 20 Pre-operative visual acuity in the surgical (second) eye in the cohort was assumed to be 6/12 or better, and this was based on the UK Cataract National Dataset which reported that 55% of patients undergoing second-eye cataract surgery had a mean visual acuity of 6/12 or better in the operated eye. 20
Mean life expectancy for all patients in the model was calculated to be 9.7 years, based on UK mortality tables. 110
The model included the following assumptions:
-
Utility values for the second-eye cataract surgery are assumed to remain constant over patient lifetimes, unless patients have complications from the surgery. Utility values for the no second-eye surgery group are assumed to decline over time owing to unoperated cataract progression and age-related visual acuity decline.
-
Post-surgical complications are assumed to incur a disutility for 1 year.
-
The model does not consider intraoperative complications as these are assumed to manifest as post-operative complications.
-
It was assumed that the incidence of post-surgical complications would not differ between first- or second-eye cataract surgery and, hence, the rates used were not specific to studies of second-eye surgical patients.
-
With the exception of costs for long-term post-surgical complications, the costs for outpatient visits and further procedures were assumed to be the same after the first year for the second-eye cataract surgery and no-surgery groups.
Evaluation of uncertainty
The evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery is subject to uncertainties about variables such as clinical effectiveness, HRQoL and resource use. This is the result of data limitations in current published studies. Uncertainty was assessed using deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses (PSA). One-way deterministic sensitivity analyses were conducted to evaluate the influence of individual parameters on the model results and test the robustness of the cost-effectiveness results to variations in the structural assumptions and parameter inputs (see Results of the economic analysis). Multiparameter uncertainty in the model was addressed using PSA. 111 In the PSA, probability distributions were assigned to the point estimates used in the base case analysis. The model was run for 1000 iterations, with a different set of parameter values for each iteration, by sampling parameter values at random from their probability distributions. The uncertainty surrounding the cost-effectiveness of the treatment is represented on a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC) according to the probability that the intervention will be cost-effective at a particular willingness-to-pay threshold.
Model validation
The model was validated by checking the model structure, calculations and data inputs for technical correctness. The structure was reviewed by clinical experts from our AG to establish that it was appropriate for the disease and its treatment. The robustness of the model to changes in input values was tested using sensitivity analyses to ensure that any changes to the input values produced changes to the results of the expected direction and magnitude. To establish its external consistency, the model results were compared with outcomes reported in clinical trials and other economic evaluations.
Data sources
Post-surgical complications and consequences
Of the three economic evaluations in our systematic review of cost-effectiveness, only the study by Busbee and colleagues92 included surgical complications and consequences (see Systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence). However, it is important that complications are included in economic evaluations of cataract surgery as many require treatment which will incur additional costs. Furthermore, some complications affect vision and have a consequent adverse effect on HRQoL.
In our model, we have included a range of post-surgical complications and consequences, but have not directly included intraoperative complications. Many post-surgical complications are associated with intraoperative complications (e.g. retinal detachment may be caused by PCR during surgery) and we have therefore assumed that the occurrence of intraoperative complications is reflected by rates of post-operative complications. Post-operative complications included in the model are classified as short-term (endophthalmitis, cystoid macula oedema, retained lens fragments) or longer-term expected consequences (PCO, retinal detachment). The complications were included following expert clinical advice and all were also included in the economic evaluation reported by Busbee and colleagues. 92 Other potential complications were considered to be rare or to have minimal costs or adverse effects on patients’ utility. We assumed that the incidence of post-surgical complications would not differ between first- or second-eye cataract surgery and, hence, the rates used were not specific to studies of second-eye surgical patients.
It was assumed that short-term post-surgical complications occurred within the first year of surgery and, hence, in the first model cycle. The UK National Cataract Survey73 reported a 0.1% rate of endophthalmitis in its sample of 18,454 patients (77% of whom had surgery performed by phacoemulsification) 3 months post surgery. Similarly, the British Ophthalmological Surveillance Unit72 reported a rate of 0.14% in its sample of 211 patients, 92% of whom had phacoemulsification. The incidence rate chosen for our model was therefore 0.1% (Table 16). This compares with a rate of acute endophthalmitis of 0.128% from a systematic review of 215 international studies. 74 The incidence of cystoid macular oedema (CMO) used in the model was 1.62%, taken from the UK Cataract National Dataset. 20 Estimates of the occurrence of lost lens fragments vary from 0.1% to 1.6% in the international literature. 70 The rate of lost lens fragments reported by the UK Cataract National Dataset20 was 0.45%, and this value was included in our model (see Table 16).
| Parameter | Base case | Upper estimate | Lower estimate | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Costs | ||||
| Cataract surgery (weighted average day case and inpatient) | £862.66 | £1121.46 | £603.86 | NHS reference costs 2011–12 (HRG code BZ02Z)54 |
| Ophthalmology outpatient visit | £85.12 | £110.66 | £59.58 | NHS reference costs 2011–12 (service code 130)54 |
| GP visits | £43.00 | £55.90 | £30.10 | PSSRU 2012112 |
| PCO (YAG laser posterior capsulotomy) | £506.42 | £658.35 | £354.49 | NHS reference costs 2011–12 (HRG code BZ04Z lens capsulotomy)54 |
| Retinal detachment (vitrectomy) | £1615.65 | £2100.35 | £1130.96 | NHS reference costs 2011–12 (HRG code BZ21Z major vitreous retinal procedures)54 |
| Endophthalmitis (vitreous tap; vitrectomy) | £760.11 | £988.14 | £532.08 | NHS reference costs 2011–12 (HRG codes BZ21Z and BZ23Z)54 |
| CMO (fluorescein angiography and OCT) | £313.30a | £407.29 | £219.31 | Colquitt et al. (2008)113 |
| Lost lens fragments (vitrectomy) | £451.69 | £587.20 | £316.18 | NHS reference costs 2011–12 (HRG code BZ23Z minor vitreous retinal procedures)54 |
| Resources | ||||
| Outpatient visits surgery | 6.94 | 7.98 | 5.90 | Sach et al. (2010)91 |
| Outpatient visits no surgery | 2.81 | Sach et al. (2010)91 | ||
| GP visits surgery | 4.40 | 5.21 | 3.59 | Sach et al. (2010)91 |
| GP visits no surgery | 4.00 | Sach et al. (2010)91 | ||
| Incidence of complications | ||||
| PCO year 1 | 3.49% | 5.24% | 1.75% | ECCERT114 |
| PCO year 2 | 9.49% | 14.24% | 4.75% | ECCERT114 |
| PCO year 3 | 5.06% | 7.59% | 2.53% | ECCERT114 |
| Retinal detachment year 1 | 0.26% | 0.39% | 0.13% | Erie et al. (2006)67 |
| Retinal detachment year 2+ | 0.14% | 0.21% | 0.07% | Erie et al. (2006)67 |
| Endophthalmitis | 0.10% | 0.15% | 0.05% | UK National Cataract Survey73 |
| CMO | 1.62% | 2.43% | 0.81% | UK Cataract National Dataset20 |
| Lost lens fragments | 0.45% | 0.68% | 0.23% | UK Cataract National Dataset20 |
| Utilities | ||||
| Utility no surgery | 0.70 | Hiratsuka et al. (2011)94 | ||
| Utility gain for surgical group | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.017 | Hiratsuka et al. (2011)94 |
| Reduction in utility for non-second-eye surgery group, per year | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.0001 | ECCERT114 |
| Other parameters | ||||
| VA decimal (pre-second-eye surgery) | 0.50 | UK Cataract National Dataset20 | ||
| VA decimal (post-second-eye surgery) | 0.80 | 1.20 | 0.67 | UK Cataract National Dataset20 |
| Discount rate, benefits/costs | 3.50% | 6.00% | 1.5% | NICE reference case95 |
Longer-term post-surgical complications and consequences were assumed to occur in only the first three successive model cycles for PCO and in any model cycle for retinal detachment. Incidence of PCO and retinal detachment were likely to be underestimated in the UK Cataract National Dataset20 (which had short-term follow-up) and were instead based on estimates from a meta-analysis of Japanese clinical studies, as reported in an economic evaluation by the Eye Care Comparative Effectiveness Research Team (ECCERT). 114 Probabilities of PCO in surgical patients were: 3.49%, 9.49% and 5.06% for years 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The probability of retinal detachment was 0.26% in year 1, and 0.14% in year 2 and all following years (see Table 16). 67
We did not model secondary complications arising from the treatment of primary post-surgical complications. We modelled only the risk of complications arising from the second-eye cataract surgery itself, as these secondary complications will probably have a negligible effect on the model results.
Costs
Costs for cataract surgery (phacoemulsification) were taken from 2011–12 NHS reference costs. 54 The vast majority of operations (98.7%) are day-case procedures, at a cost of £851 each. 54 The remaining 1.3% were inpatient operations, at a cost of £1748 each. A weighted average for the cost of surgery was estimated as £862.66. A mean of 6.94 outpatient visits for cataract surgery patients and 2.81 visits for non-surgery patients was assumed based on the number reported in the UK economic evaluation by Sach and colleagues. 91 A mean of 4.4 GP visits for cataract surgery patients and four visits for non-surgery patients was assumed. 91 Ophthalmic outpatient visits were costed at £85 per visit54 and GP visits at £43 per consultation. 112
The costs of procedures for treating post-surgical complications and consequences were estimated using 2011–12 NHS reference costs. 54 We did not include the cost of any prescribed pharmaceutical treatments as these are not thought to significantly impact on costs. For treatment of all post-surgical complications we assumed an additional two ophthalmic outpatient appointments would be required. Longer-term complication costs for PCO are incurred within the first three years, and retinal detachment may occur in any year.
We assumed that 80% of patients with endophthalmitis would receive a vitreous tap (biopsy). 54 Patients with severe cases may require vitrectomy. The British Ophthalmological Surveillance Unit72 reported that 18% of patients with endophthalmitis in its study required a vitrectomy, and this percentage was used in our economic model. 54
Lost lens fragments in the post-operative period may need to be removed by vitrectomy, but a small number of fragments may dissolve spontaneously. Patients may be prescribed topical anti-inflammatory drops and intraocular pressure, CMO and retinal detachment monitored. We assumed that the majority of cases will require a day-case vitrectomy and chose an arbitrary rate of 70%, at a mean total cost of £451.69 per case. 54 No surgical treatment was assumed to be necessary for CMO; however, patients would undergo fluorescein angiography and optical coherence tomography, at a cost of £84.79 and £58.27, respectively [costs were taken from a previous HTA on the treatment for macular degeneration113 and inflated to current prices using the Personal Social Services Research Unit (PSSRU)112 inflation indices]. PCO is most commonly treated using Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy,1 costing a total of £506.42 per case, assumed to be a day-case operation. 54 Retinal detachment was assumed to be treated via day-case vitrectomy, at a total cost of £1615.65 per case (see Table 16). 54
It is unclear whether there are differences in PSS costs for patients who have second-eye cataract surgery and those who do not. The study by Sach and colleagues91 found a reduction in PSS costs of £339 per person for patients with second-eye surgery compared with the no-surgery group. However, this difference was not statistically significant and contrasted with their earlier study of first-eye surgery, which found an increase in PSS costs of £560 per person for those who had surgery. 115 In the base case, we have assumed there is no difference in PSS costs for patients who have second-eye surgery and those who do not, and have tested this assumption in a scenario analysis (see Scenario analyses with unadjusted utility gain).
Health-related quality of life
Health-related quality of life utility estimates were taken from the Japanese economic evaluation by Hiratsuka and colleagues94 which was included in our systematic review of HRQoL (see Systematic review of health-related quality-of-life studies). As discussed earlier (see Systematic review of health-related quality-of-life studies), the rationale for using this study was because it estimated health utility using a generic preference-based HRQoL instrument (HUI-3) that included a visual utility subscale. The gain in utility (0.08) was assumed to last the patient’s lifetime, as assumed by other economic evaluations,92 and is in accord with clinical consensus of a permanent improvement in clinical vision from cataract surgery. As noted earlier (see Systematic review of health-related quality-of-life studies), Hiratsuka and colleagues94 found a bigger utility increase of 0.24 using the TTO approach. The estimate chosen for our model, based on HUI-3, may therefore be regarded as conservative. To account for a potentially bigger improvement in HRQoL, the 0.24 estimate was included in a scenario analysis (see Scenario analyses with unadjusted utility gain).
In the base case, we assumed that the utility gain from the Hiratsuka and colleagues study94 was generalisable to our UK NHS cohort, although there are likely to be differences in the population characteristics.
Hiratsuka and colleagues’ study94 was chosen in preference to the economic evaluation by Sach and colleagues,91 which estimated utility using the EQ-5D. As noted, the EQ-5D does not include any sensory-related dimensions and may not be sensitive to improvements in vision following cataract surgery. However, in recognition of some of the merits of the Sach and colleagues91 study (e.g. it was based on a RCT conducted in UK patients) we have included its utility estimates in a scenario analysis (see Scenario analyses with unadjusted utility gain).
In the base case, we have assumed that visual acuity declines with unoperated cataract progression and age for the non-second-eye surgery group. The decline was estimated using data from the Japanese ECCERT study,114 which estimated that, for those with visual acuity between 0.5 and 0.9 (decimal), there is a 2.27% probability of a decline in visual acuity to between 0.1 and 0.4 (decimal) in each successive year. We calculated that this would be equivalent to an annual mean visual acuity decline per patient of 0.01 and, thus, a mean utility decline of 0.002.
We assumed that second-eye cataract surgery patients experiencing post-surgical complications and consequences retain their baseline HRQoL for the duration of the complication, and once successfully treated they would experience the same gain in utility as patients with uncomplicated surgery. These complications are known to impair visual acuity and therefore are likely to reduce HRQoL. The study by Clark and colleagues,105 included in our systematic review of HRQoL studies (see Systematic review of health-related quality-of-life studies), assessed HRQoL at 12 months post surgery to ensure that results reflected the long-term impact of endophthalmitis rather than just its acute effect. We therefore assumed that the disutility associated with endophthalmitis, and also with CMO and retained lens fragments, lasted for one model cycle, i.e. 1 year. As these are short-term complications, this may be considered a conservative assumption, and we have therefore explored the effect of shorter periods of disutility in scenario analysis (see Scenario analyses with unadjusted utility gain). Similarly, the duration of the disutility associated with PCO and retinal detachment is assumed to be for 1 year.
A summary of all the parameter values included in the economic model is given in Table 16.
Results of the economic analysis
This section reports the cost-effectiveness results for second-eye cataract surgery compared with no second-eye cataract surgery. Results in terms of costs and QALYs are presented for each group, with costs and benefits discounted at 3.5%. 95 The summary results are shown in Table 17 for one average hypothetical patient. In the base case analysis, patients receiving second-eye cataract surgery had an additional cost of £1341, an additional 0.68 QALY, and an ICER of £1964 per QALY gained compared with no second-eye cataract surgery. The results indicate that second-eye cataract surgery is likely to be cost-effective at conventional willingness-to-pay thresholds. 95
| Parameter | QALYs | Costs | ICER (cost/QALY) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No second-eye cataract surgery | 5.29 | £411 | |
| Second-eye cataract surgery | 5.97 | £1752 | |
| Incremental | 0.68 | £1341 | £1964 |
Sensitivity analysis
A one-way deterministic sensitivity analysis (DSA) was performed, by varying one parameter at a time from its base case value and leaving all other variables unchanged. All parameters were varied between the high and low estimates in Table 16. The estimates used for the sensitivity analysis were based on the uncertainty of these data, and where data were available these were based on the 95% CI ranges for these parameters (e.g. resources). Where these data were not available, an alternative suitable range was chosen, based on ranges commonly used in other economic evaluations, as follows: cataract surgery costs (± 30%), post-surgical complication incidence rates (± 50%), costs for treating post-surgical complications (± 30%) and the discount rate for costs (2–5%).
Table 18 shows the results of the DSA for the model parameters. The cost-effectiveness results are robust to changes in these parameters. The model results are most sensitive to the utility gain, where the ICER varies between £1185 and £6342 per QALY. This reflects the uncertainty around the utility gain estimate from the Hiratsuka and colleagues94 study which had a 95% CI between 0.017 and 0.14. The model results are also sensitive to the cost of the cataract operation. The model results are insensitive to changes in the parameter values for the complications associated with cataract surgery.
| Parameter | Baseline value | Higher Estimate | Lower estimate | ICER (cost/QALY) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher estimate | Lower estimate | Range | ||||
| Utility gain second-eye surgery | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.017 | £1185 | £6342 | £5157 |
| Cataract operation cost | £862.66 | £1121.46 | £603.86 | £2343 | £1585 | £758 |
| Discount rate benefits | 3.5% | 6.0% | 1.5% | £2310 | £1702 | £608 |
| Non-operated eye utility decline | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.0001 | £1748 | £2225 | £476 |
| Cataract outpatient appointment cost | £85.12 | £110.66 | £59.58 | £2118 | £1809 | £309 |
| Mean number of outpatient appointments, surgery group | 6.94 | 7.98 | 5.9 | £2094 | £1834 | £259 |
| Mean number of GP visits, surgery group | 4.4 | 5.21 | 3.6 | £2015 | £1914 | £101 |
| PCO incidence year 2 | 9.49% | 14.24% | 4.75% | £2005 | £1923 | £82 |
| PCO cost | £506.42 | £658.35 | £354.49 | £2000 | £1928 | £71 |
| PCO incidence year 3 | 5.06% | 7.59% | 2.53% | £1984 | £1944 | £40 |
| PCO incidence year 1 | 3.49% | 5.24% | 1.75% | £1980 | £1948 | £33 |
| Retinal detachment incidence year 2+ | 0.14% | 0.21% | 0.07% | £1977 | £1950 | £27 |
| Discount rate costs | 3.5% | 6.0% | 1.5% | £1954 | £1973 | £19 |
| Retinal detachment cost | £1615.65 | £2100.35 | £1130.96 | £1973 | £1955 | £18 |
| GP visit cost | £43.00 | £55.90 | £30.10 | £1971 | £1956 | £15 |
| CMO incidence | 1.62% | 2.43% | 0.81% | £1969 | £1958 | £11 |
| Retinal detachment incidence year 1 | 0.26% | 0.39% | 0.13% | £1967 | £1961 | £7 |
| Lost lens fragments incidence | 0.45% | 0.68% | 0.23% | £1966 | £1962 | £4 |
| CMO cost | £313.30 | £407.29 | £219.31 | £1966 | £1962 | £4 |
| Lost lens fragments cost | £451.69 | £587.20 | £316.18 | £1965 | £1963 | £2 |
| Endophthalmitis incidence | 0.10% | 0.15% | 0.05% | £1965 | £1963 | £1 |
| Endophthalmitis cost | £760.11 | £988.14 | £532.08 | £1964 | £1964 | £1 |
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis
In the PSA, all parameters were sampled probabilistically from an appropriate distribution using similar ranges as used in the DSA. The parameters included in the PSA, the form of distribution used for sampling each parameter, and the upper and lower limits assumed for each variable are provided (see Appendix 10).
One thousand simulations were run. The PSA results are presented in Table 19 and are similar to the results of the deterministic analysis, with an ICER of £1970. The scatterplot for cost and QALYs for the PSA is shown in Figure 5. The CEAC is shown in Figure 6 and indicates that, at the £20,000 willingness-to-pay threshold, second-eye surgery has the highest probability of being cost-effective of 100%. The cost-effectiveness estimate was less than £10,000 per QALY in 100% of the simulations.
| Parameter | QALYs | Costs | ICER (Cost/QALY) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No second-eye cataract surgery | 5.29 | £412 | |
| Second-eye cataract surgery | 5.97 | £1747 | |
| Incremental | 0.68 | £1335 | £1970 |
FIGURE 5.
Scatterplot of the additional costs and QALYs for second-eye surgery compared with no surgery.
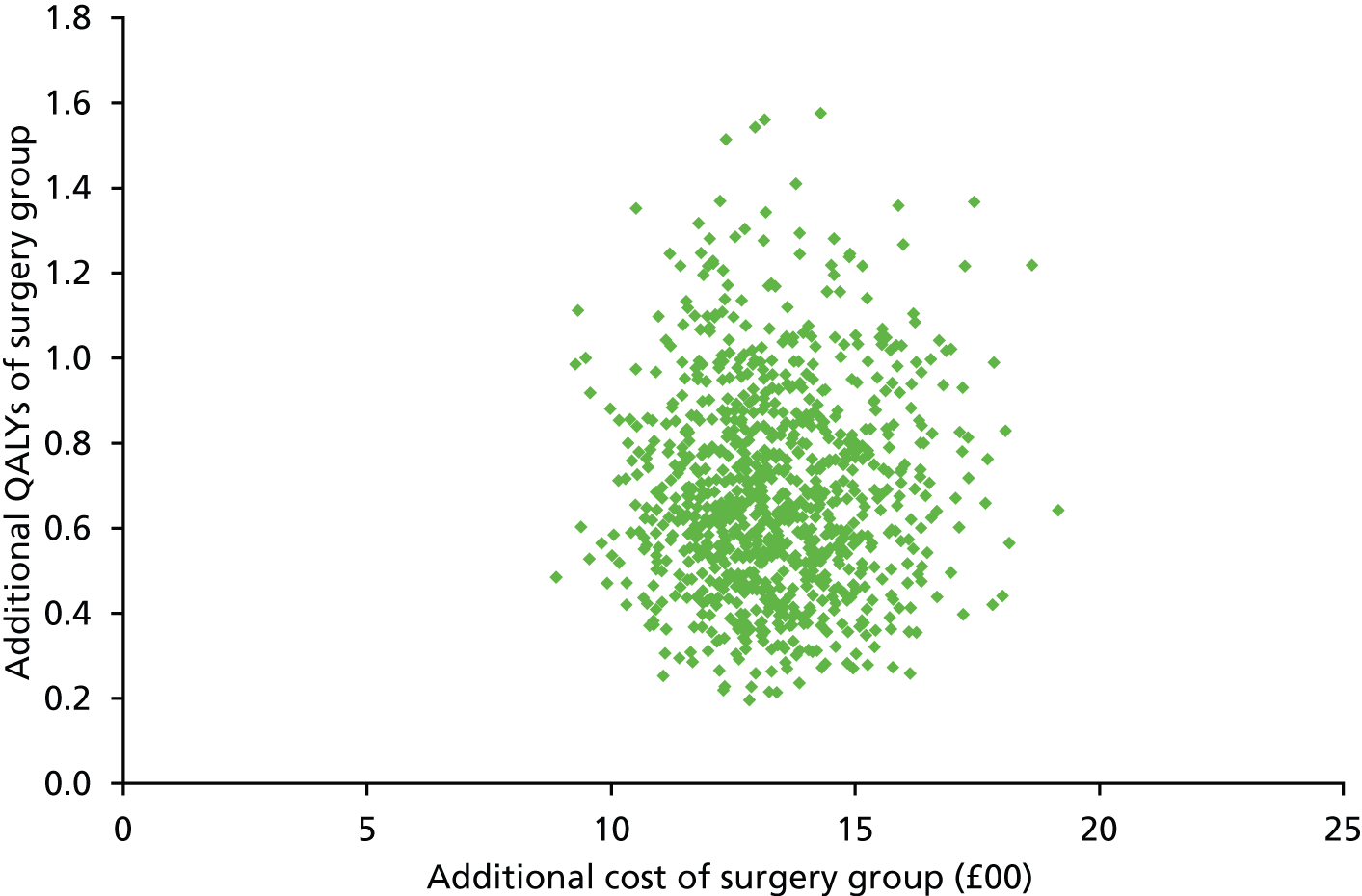
FIGURE 6.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve from the PSA.
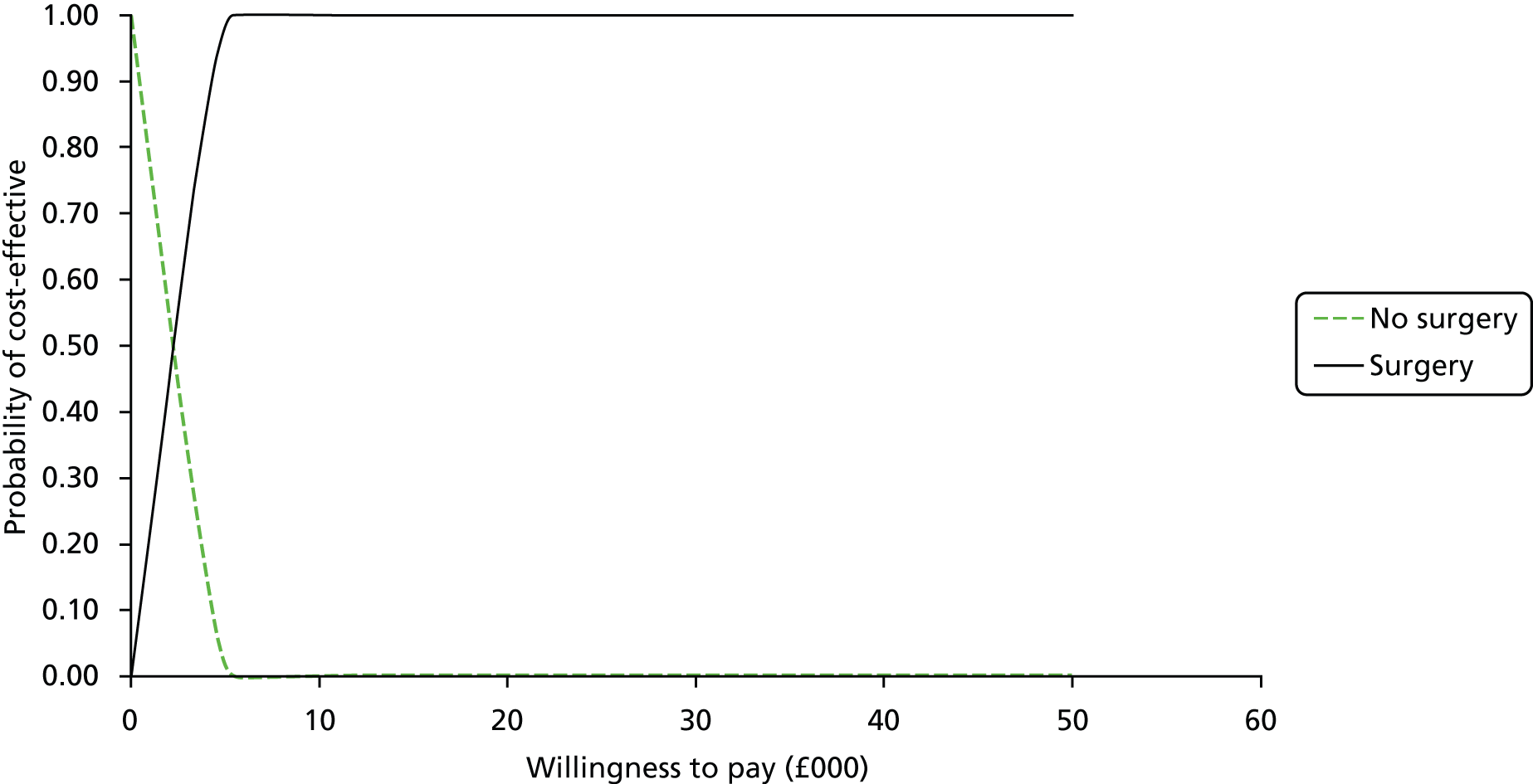
Scenario analyses with unadjusted utility gain
In addition to the sensitivity analyses, six scenario analyses were undertaken to investigate the uncertainty around structural model assumptions and input parameter values (scenarios A to F) (Table 20). A further three scenario analyses to explore the effect of adjusting utility values (scenarios G and H) and the impact of varying pre-operative visual acuity (scenario I) are described below (see Scenario analyses with adjusted utility gain).
| Scenario | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICERs (cost/QALY) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base case | 0.68 | £1341 | £1964 | |
| A | Using EQ-5D utility gain (0.02) from Sach et al. (2010)91 | 0.23 | £1341 | £5734 |
| Using TTO utility (0.24) gain from Hiratsuka et al. (2011)94 | 1.88 | £1341 | £713 | |
| Using TTO utility loss (−0.08) from Dolders et al. (2004)101 | −0.51 | £1341 | −£2607a | |
| B | No post-surgical complications included | 0.70 | £1231 | £1763 |
| Double frequency of post-surgical complications | 0.67 | £1451 | £2174 | |
| C | Duration of disutility for post-surgical complications, 6 months | 0.69 | £1341 | £1942 |
| Duration of disutility for post-surgical complications, 2 years | 0.66 | £1341 | £2022 | |
| D | Time horizon 5 years | 0.31 | £1332 | £4271 |
| Time horizon 10 years | 0.53 | £1337 | £2544 | |
| E | PSS costs | 0.68 | £1002 | £1467 |
| F | Utility loss from Dolders et al. (2004)101 and double frequency of post-surgical complications | 0.5 | £1451 | −£2908a |
Scenario A: health-related quality-of-life measures
Scenario A investigates the impact of different utility gains from second-eye cataract surgery. For our base case we have used the utility gain from the HUI-3 HRQoL measure (0.08) from the Hiratsuka and colleagues94 study. The rationale for choosing this study is discussed (see Methods for economic analysis). In this scenario, we investigated the impact of using other more and less favourable HRQoL estimates. The utility difference (the difference between second-eye surgery and unoperated second-eye patients) from the study by Sach and colleagues91 was 0.02 (based on the EQ-5D). For this scenario, the results gave a less favourable ICER of £5734. Using the TTO utility gain (0.24) from the Hiratsuka and colleagues94 study gave a more favourable ICER of £713 per QALY gained. Using the TTO utility loss (0.08) from second-eye surgery (multifocal IOL group) from the Dolders and colleagues study101 results in a reduction in QALYs for second-eye surgery, and so it is dominated by (i.e. more costly and less effective than) not having second-eye surgery.
Scenario B: frequency of surgical complications
Scenario B investigates the effect of varying the frequency of post-surgical complications, as there was uncertainty around some of these parameter estimates. We took extreme values and varied the frequency of complications from zero to double that used in the base case analysis. The frequency of complications only had a small impact on the model results, with the ICER varying from £1763 per QALY to £2174 per QALY, respectively.
Scenario C: duration of disutility for post-surgical complications and consequences
In the base case, patients with complications are assumed to retain the pre-surgery utility values for 1 year following surgery. However, some complications may last less than a year, whereas others may last longer. We tested the sensitivity of this assumption by varying the duration of disutility between 6 months and 2 years. This scenario also had minimal impact on the model results, with the ICER varying between £1942 per QALY and £2022 per QALY.
Scenario D: time horizon
The time horizon used in the model for the base case was 25 years. Each of the three economic evaluations in our systematic review of cost-effectiveness employed a lifetime horizon, though one of them91 also included a 1-year horizon. We investigated the effect of choosing shorter, more conservative, time horizons on the model results. Scenario D used time horizons of 5 and 10 years, with increases in ICERs of £4271 per QALY and £2544 per QALY, respectively.
Scenario E: Personal Social Services costs
As discussed earlier, it is unclear how PSS costs for patients who have second-eye cataract surgery differ from those who do not. In the base case, we have assumed that there is no difference in PSS costs for patients who have second-eye surgery and those who do not. In scenario E, this assumption was tested using the differences in PSS costs from the study by Sach and colleagues. 91 In that study there was a reduction in PSS costs for patients with second-eye surgery (£411) compared with the no second-eye surgery group (£750). Using these costs for the first year gave a more favourable ICER of £1467 per QALY.
Scenario F: worst-case scenario
We investigated the effect of a worst-case scenario on the model results. Scenario F presents the combination of scenarios A and B, i.e. using the lower utility gain from the Dolders and colleagues study101 and double the frequency of post-surgical complications than in the base case. In this scenario, not performing second-eye surgery is the preferred option with an ICER of −£2908 per QALY.
In general, the model results were robust to changes in assumptions and model structure, and the results are within conventional cost-effectiveness ranges, varying between £713 and £5734 per QALY, except for the analyses using the utility loss from the Dolders and colleagues study,101 in which second-eye cataract surgery was dominated (i.e. was less effective and more costly) (scenarios A and F).
Scenario analyses with adjusted utility gain
In the base case analysis we assumed that the utility gain estimated by Hiratsuka and colleagues94 was generalisable to the UK patient population. However, the baseline visual acuity of the patient population in Hiratsuka and colleagues’ study94 may not reflect that of UK patients. Therefore, we conducted further scenario analyses in which we adjusted the utility gain to account for this disparity in visual acuity.
We assumed that the utility gain from second-eye surgery is proportional to the improvement in visual acuity, and therefore developed a method to link visual acuity gain to utility gain. Using this method we were able to calculate the estimated utility gain according to the baseline and post-operative visual acuity.
The visual acuity of the study populations in Hiratsuka and colleagues’ study94 and in the UK Cataract National Dataset20 are shown in Table 21. Hiratsuka and colleagues94 reported their results using the log-MAR scale, whereas the UK Cataract National Dataset20 has used the Snellen scale. For the purposes of the model, we have converted the values from these studies to the decimal scale. All values shown are the visual acuity for monocular vision.
| Study | Log-MAR | Snellen | Decimal | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hiratsuka et al. (2011)94 | ||||
| Better-eye pre-operative VA | 0.16 | 0.7 | ||
| Better-eye post-operative VA | −0.05 | 1.1 | 0.4 | |
| Worse-eye pre-operative VA | 0.51 | 0.3 | ||
| Worse-eye post-operative VA | 0.03 | 1 | 0.7 | |
| UK Cataract National Dataset20 | ||||
| Median pre-operative VA | 6/12 | 0.5 | ||
| Median post-operative VA | 6/7.5 | 0.8 | 0.3 | |
There was some uncertainty around the visual acuity gain for the second-eye cataract surgery in the Hiratsuka and colleagues study. 94 The values given in Table 21 for pre- and post-operative visual acuity are for the whole study sample, which also included patients undergoing first-eye cataract surgery and patients receiving bilateral cataract surgery. It is unclear what the post-surgical visual acuity would be if it was restricted to the subgroup of patients undergoing second-eye cataract surgery. Furthermore, we assume, for the subgroup of patients in the study undergoing second-eye surgery, that the ‘better eye’ is the eye to be operated on. This was because the study also included patients receiving first-eye surgery and we assumed that the first-eye surgery would be on the ‘worse eye’.
The mean baseline visual acuity of patients in the study by Hiratsuka and colleagues94 was log-MAR 0.16 (decimal 0.7) in the better eye. For the better eye, utility values from Hiratsuka and colleagues94 are associated with a post-surgery mean visual acuity of −0.05 log-MAR (approximate to decimal visual acuity 1.1). There was therefore an estimated visual acuity gain of 0.4 on the decimal scale.
We then calculated the expected utility gain for our modelled cohort, which represents a hypothetical cohort treated in the UK. The median baseline visual acuity of patients in the UK Cataract National Dataset20 (UKNCD) was 6/12 (decimal 0.5) and the median post-operative visual acuity for this group was 6/7.5 (decimal 0.8) and, therefore, the estimated visual acuity gain is 0.3 on the decimal scale.
The adjusted utility gain was as follows:
and the adjusted utility gain is 0.08 × 0.3/0.4 = 0.06.
Scenario G: adjusted utility gain
Scenario G shows the results using the adjusted utility gain of 0.06 for second-eye surgery. In this scenario, the results are slightly less favourable with an ICER of £2515 per QALY (Table 22).
| Scenario | Incremental QALYs | Incremental costs | ICERs (cost/QALY) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base case | 0.68 | £1341 | £1964 | |
| G | Adjusted utility gain of 0.06 | 0.53 | £1341 | £2515 |
| H | Worse eye VA from Hiratsuka et al. (2011)94 study, utility gain of 0.034 | 0.34 | £1341 | £3935 |
| I | Pre-surgical VA 6/15, post-surgical VA 6/7.5 (0.8) | 0.68 | £1341 | £1964 |
| Pre-surgical VA 6/18, post-surgical VA 6/7.5 (0.8) | 0.78 | £1341 | £1714 | |
| Pre-surgical VA 6/9, post-surgical VA 6/6.5 (0.9) | 0.47 | £1341 | £2866 | |
| Pre-surgical VA 6/7.5, post-surgical VA ≈ 6/6 (0.95) | 0.31 | £1341 | £4344 |
Scenario H: assumption on adjusted utility gain
As described earlier, we assumed that the subgroup of second-eye cataract surgery patients from Hiratsuka and colleagues94 underwent surgery on what the authors refer to as the better eye, as the study population predominantly comprised patients undergoing first-eye cataract surgery. However, it may be that patients from this study underwent second-eye surgery on what the authors refer to as the worse eye. The worse-eye pre- and post-operative visual acuity was 0.51 and 0.03 log-MAR, respectively, equivalent to a visual acuity gain of log-MAR 0.48 (decimal 0.7) (see Table 21). Thus, the visual acuity gain would be almost double the gain from surgery on the better eye. Using this assumption, the utility gain, adjusted for our modelled cohort based on the UK National Cataract Dataset using the formula above,20 would therefore be 0.034 (compared with 0.06 in the base case). For this scenario, the ICER increases to £3935 per QALY and would still be considered cost-effective at conventional willingness-to-pay thresholds.
Scenario I – baseline visual acuity
Scenario I investigates the effect of different baseline visual acuity estimates in the operated eye, for the ranges 6/18 to 6/7.5 (the base case assumed 6/12 or better). The purpose was to explore changes in cost-effectiveness given that second-eye cataract surgery has been suggested to be more beneficial to patients when the degree of visual impairment in the operated eye is greater. 107 The mean post-operative visual acuity gain for each group was calculated from the UK Cataract National Dataset. 20 (The calculated mean post-operative visual acuity is shown as a decimal, and does not always correspond exactly to whole number ratios on the Snellen scale reported in the publication.)20 The scenario analysis indicates that the mean visual acuity gain would be higher in patients with lower baseline visual acuity. For example, the visual acuity gain for the group with baseline visual acuity of 6/15 would be 0.46, compared with 0.24 for the group with baseline visual acuity of 6/9. The ICERs for patients with poorer baseline visual acuity of 6/15 and 6/18 are £1964 per QALY and £1714 per QALY and for better baseline visual acuity of 6/9 and 6/7.5 are £2866 per QALY and £4344 per QALY, respectively.
Summary of cost-effectiveness
A systematic search of the literature found three economic evaluations of second-eye cataract surgery and one additional linked publication. One of the studies was conducted in the UK91 and the other studies were conducted in the USA92 and Finland. 90 The cost-effectiveness estimates varied widely between the studies, depending on the assumed improvement of HRQoL associated with the procedure. All three economic evaluations had methodological limitations, such as not reporting all modelling assumptions, and none was wholly relevant to the NHS.
A systematic review of HRQoL studies for patients with second-eye cataract surgery identified a total of 10 studies, reported in a total of 11 publications. 40,86,90,91,94,101–106 Half of the studies were conducted in Europe,40,90,91,101,106 of which two were from the UK. 40,91 One of the UK studies, by Sach and colleagues,91 was also in our systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence (see Systematic review of cost-effectiveness evidence) and the RCT on which it was based was included in our systematic review of clinical effectiveness (see Chapter 4). Four studies allowed comparisons to be made between second-eye cataract surgery and no second-eye cataract surgery. 90,91,94,101 There was variation between these studies in utility change, with some reporting utility loss following second-eye cataract surgery, and some reporting gain. One study showed variations in the magnitude of the increase according to which assessment instrument was used. 94 The HUI-3 yielded a utility gain of 0.08, whereas the TTO yielded a larger utility gain of 0.24, giving large variation in the estimates from this study.
We developed a de novo economic model, designed to overcome the limitations of the existing published models. The decision analytical model included short- and long-term complications associated with second-eye cataract surgery. Patients who had surgery showed improvement in HRQoL proportionate to their gain in visual acuity. Costs included in the model were for the surgery and associated hospital visits, and the costs associated with treating complications from surgery. The model base case results for second-eye surgery showed increased QALYs at an increased cost compared with no surgery. The incremental cost-effectiveness estimate was £1964 per QALY gained. The effect of varying the parameter values in the economic model was assessed in sensitivity and scenario analyses. The model results were most sensitive to changes in the utility gain associated with second-eye surgery, but otherwise were robust to changes in the parameter values. The PSA estimated the probability that surgery would be cost-effective at the £20,000 and £10,000 willingness-to-pay thresholds as 100%.
Chapter 6 Assessment of factors relevant to the NHS and other parties
Increased provision of second-eye cataract surgery will have health service budget implications, although it is uncertain exactly how many additional operations will be required. As mentioned in Chapter 1, there were 340,809 cataract operations in England during 2012–13. The total cost of cataract surgery for 2011–12 was estimated to be £240M. 54 Based on estimates that 27% of cataract operations are in the second eye,16 the cost per annum of second-eye surgery would be around £64.8M. Therefore, if provision of second-eye surgery is to increase, costs will exceed this figure.
We assume that little investment would be required in new infrastructure, equipment or training as this would be an extension of an existing service, rather than scaling-up of a new service (an exception would be if additional patient assessments such as for stereopsis are to be performed, which would require additional staff training and equipment costs). However, provision of additional cataract surgery may place further demands on operating theatres/clinics and ophthalmologist time. On the other hand, it may potentially fill any spare capacity and lead to efficiencies, though this is unlikely to be widespread.
Our systematic review of clinical effectiveness found only limited evidence that second-eye cataract surgery improved patients’ quality of life. It was not clear whether or not patients experienced meaningful improvement in visual acuity which was already very good before second-eye surgery, although stereopsis was consistently improved in all the RCTs. A possible explanation for the lack of evidence that second-eye surgery affected HRQoL could be that the patient-reported measures of HRQoL administered do not specifically assess visual function. 91 It is possible that for some patients, particularly those with greater cataract-related visual impairment, second-eye surgery may provide a marked improvement in their activities of daily living and general HRQoL. Consequently, they may become less dependent on family and carers to assist them in activities such as reading, shopping, cooking and transport. They may be less at risk of falls and accidents, and may be able to participate more in recreation and physical activity, with consequent improvements in physical health and psychological health and well-being.
Chapter 7 Discussion
Statement of principal findings
Clinical effectiveness
Our systematic review demonstrates that the evidence base for the clinical effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery is limited, with only three RCTs having met the inclusion criteria. 83–85 These RCTs appear relevant to a rather specific population group, namely elderly people in their 70s who had bilateral cataracts and had good binocular visual acuity after their first cataract operation. Although this population is relevant to the NHS, it is unclear whether it would also be representative of population groups such as those younger or older than their 70s who are eligible for second-eye cataract surgery or those with poorer visual acuity after first-eye surgery. The included RCTs are also now relatively old, having been conducted between 9 and 19 years prior to our systematic review, and it may be questioned whether or not they remain fully relevant to current clinical practice. The oldest of the RCTs was conducted by Laidlaw and colleagues84 during 1994–5, before the introduction of phacoemulsification in the UK. Compared with extracapsular cataract surgery, which was previously the standard approach, phacoemulsification has been associated with improvements in the safety of cataract surgery. 88
The RCTs83–85 all assessed effects of second-eye cataract surgery on measures of visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and stereopsis, but did not measure other vision outcomes that are affected by cataracts, such as glare disability. According to the Royal College of Ophthalmologists, glare, contrast sensitivity and patient-reported visual disability are outcomes that are increasingly being considered when making recommendations for cataract surgery. 1 A range of patient-reported outcomes covering general health and quality of life, symptoms, psychological distress and vision-related disability were reported in the included RCTs. However, several of the instruments were self-developed ad hoc by the RCT investigators without wider validation. As their clinical interpretation and reliability are unclear, we did not include these study-specific instruments in data synthesis. Where validated patient-reported measures were employed in the RCTs, there are a number of limitations and uncertainties about their interpretation (see Uncertainties).
Results of the RCTs83–85 should be interpreted with caution as they were judged to be at high risk of performance bias (although it was not practicable to mask patients to their allocated study group, so this source of potential bias was not avoidable). Assuming that the outcomes were reliable, improvements in binocular visual acuity following second-eye compared with first-eye cataract surgery would be less than 1 Snellen line equivalent, which is smaller than would normally be regarded as clinically important. However, on average, patients already had near-normal visual acuity after first-eye surgery (0.02–0.22 log-MAR, or Snellen 6/6 to 6/9.5), limiting the degree to which the second-eye surgery could have further improved their visual acuity. This ceiling effect was also evident for other outcomes reported in the RCTs, with relatively high proportions of patients also having good contrast sensitivity as well as relatively high scores for falls efficacy, handicap and vision-related disability before second-eye surgery (see Clinical effectiveness outcomes).
Among the visual outcomes assessed in the RCTs, notable improvements in stereopsis occurred following second-eye surgery, with the changes likely to be clinically meaningful to patients. Good stereopsis is important for everyday tasks that involve judging distances,35 including driving. 40 Deterioration of stereopsis can adversely affect motor skills (e.g. threading a needle, climbing stairs)42 and increases the risk of accidents such as falls,43 negatively affecting quality of life. 40 Although the evidence base is limited, stereopsis may be a more sensitive than binocular visual acuity as an indicator of patients’ vision before and after second-eye cataract surgery. However, stereopsis is unlikely to be assessed routinely in clinical practice as the stereotests required are more complex than tests of visual acuity.
The severity and type of cataract were not explicitly reported in the RCTs, but patients would appear to have had relatively mild cataracts, according to the vision parameters reported prior to second-eye surgery. A study in Singapore has suggested that the benefits of second-eye cataract surgery are related to the difference in vision between the pseudophakic and phakic eyes. 107 People who have more severe bilateral cataracts might show a greater incremental benefit from having second-eye surgery than the included RCTs suggest, as treatment of the first cataract may create a vision imbalance (e.g. anisometropia or binocular inhibition) (see Description of the underlying health problem).
Cost-effectiveness
There is a limited evidence base for the cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery. We identified only three published full economic evaluations, which varied in their study methods, patient characteristics and findings. Of these evaluations, one was a modelling study, one was a within-trial analysis and the other was an analysis alongside a prospective HRQoL study. All three had limitations, for example only one study included post-surgical complications. None was based on a systematic review of the evidence (though one was conducted alongside a RCT) or were considered wholly relevant to the NHS. For this reason it was considered necessary to develop a de novo economic model to assess cost-effectiveness.
The findings show that second-eye cataract surgery is cost-effective under conventional willingness-to-pay thresholds. The ICER in the base case analysis was £1964 per QALY gained, which is comparable with a number of other health-care interventions regarded to be cost-effective. Our results are comparable to those from the Busbee and colleagues92 study, which reported an ICER of US$2495 per QALY, but differ significantly from the other two cost-effectiveness studies. 90,91 The reason for these differences is largely driven by the utility gain for second-eye surgery assumed in the studies, and the assumptions used for long-term utility for non-second-eye cataract surgery patients. The patient cohort modelled in this study reflected the characteristics of the UK Cataract National Dataset,20 specifically the degree of visual impairment, whereas patients in the Sach and colleagues91 study were selected for inclusion in a RCT and had good vision prior to surgery.
Varying the input parameter values in the sensitivity analyses and considering alternative model scenarios did not significantly change this finding, except for one scenario varying utility values using a study that found a utility loss associated with second-eye surgery. Although there was some uncertainty around the utility change associated with second-eye surgery, with some studies in our review finding a utility gain while other a utility loss, our critical assessment of the studies found that the most appropriate HRQoL studies reported a utility gain associated with second-eye surgery.
Strengths and limitations of the assessment
This HTA was conducted by an independent academic team with extensive experience in the methods of systematic reviews and economic evaluations. We employed standard, rigorous and transparent methods for evidence synthesis and economic decision modelling, based on criteria set out a priori in a peer-reviewed research protocol. Sets of evidence for clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and HRQoL were sought, appraised, synthesised and checked systematically by a minimum of two reviewers.
The economic model was informed by previously published models and their limitations were taken into account, where possible. The model structure and data inputs are clearly presented in this report, to facilitate replication and testing of our model assumptions.
Experts in ophthalmology and patient care have been consulted for input throughout the project and the current report was subjected to independent peer review by the National Institute for Health Research HTA programme.
Inevitably, this HTA has some potential limitations, although these appear unlikely to substantially alter our conclusions. For pragmatic reasons, searches were limited to studies published in English; however, none of the clinical experts we contacted identified any additional relevant RCTs to those obtained in our searches.
Given the possibility of introducing recall bias owing to the age of the primary studies, we did not contact authors of the primary studies for additional information. This is unlikely to have influenced our conclusions, as the decision not to quantitatively pool outcomes in a meta-analysis was based on heterogeneity of the study characteristics rather than on the availability of quantitative data.
We also took a pragmatic decision to limit the systematic review of clinical effectiveness to RCTs because well-conducted RCTs are at lower risk of bias than non-randomised studies (especially selection bias, which can only be controlled through randomisation), and initial scoping work indicated that RCT evidence for clinical vision outcomes would be available. However, RCTs may not always capture long-term or rare outcomes, such as adverse events. To ensure that adverse events parameters for the economic model were as up to date and complete as possible, we conducted targeted searches for the specific parameters (e.g. rates of retinal detachment) as well as asking clinical experts for their opinions and for sources of data; these sources have been transparently reported (see Methods for economic analysis).
As is common in many economic evaluations, certain assumptions have been made regarding resources, costs, surgical complications, patient characteristics and outcomes. These have all been explicitly reported and tested in sensitivity and scenario analyses. For example, it would have been desirable to stratify our base case analyses by age or baseline visual acuity, as these factors may predict outcome of surgery. However, this was not possible because of limited availability of data that would have been required for all of the model parameters. Instead we accounted for these variables in a scenario analysis.
Finally, our cost-effectiveness analysis focuses on the costs and benefits for patients attending hospital ophthalmology departments and does not include the wider benefits to the NHS and to society that would be made by the prevention of accidents and their sequelae that result from poor vision related to cataracts.
Uncertainties
There are a number of uncertainties around the use and interpretation of the patient-reported outcomes.
The VF-14 appears to be commonly used in research assessing vision-related functional ability after cataract surgery, and was employed in two of our three included RCTs. However, there are uncertainties about the validity and interpretation of VF-14 scores. The MCID for the VF-14 was originally considered to be 5.0 points116 (as quoted by Castells and colleagues85 in their RCT) but, more recently, has been proposed as being higher, at 15.57 points. 87 The differences in VF-14 scores between first- and second-eye surgery groups in the RCTs by Foss and colleagues83 and by Castells and colleagues85 would be considered clinically important at the lower MCID, but not if the more recently proposed higher MCID is applied. The relevance of the VF-14 for cataract referral pathways in the NHS is also being called into question56 and ceiling effects appear common,117 with more than half of NHS patients who were sampled presenting VF-14 scores of 90 or more points (out of 100 points) before second-eye surgery. 56 As a result, the VF-14 is not supported by the UK Department of Health for use as a standard tool in the assessment of eligibility for cataract surgery referral. 1,56 So, although patient-reported visual disability may be considered in cataract surgery referral recommendations,1 it is unclear which assessment instrument(s) should be employed. The clinical interpretation of some generic patient-reported outcomes assessing specific domains of HRQoL and psychological distress would also benefit from clarification. We are not aware of a relevant MDC or MCID for the Falls Efficacy Scale or the London Handicap Scale when these instruments are applied in surgical ophthalmology. The authors of primary studies which employ these instruments did not provide justification for their choice of outcome measures or explain their clinical interpretation.
Our systematic review of HRQoL found that very small gains (and in some cases losses) were associated with second-eye surgery compared with no second-eye surgery. A potential explanation is that generic patient-reported outcome instruments may not be sensitive to effects of changes in vision, as they do not include sensory domains, although the evidence for their responsiveness following cataract surgery appears to be mixed. 56,86,90,91 However, even where studies used the same preference-based utility assessment (e.g. TTO), results varied, with indication of utility gains94 and losses101 after second-eye surgery.
The EQ-5D is important as a generic tool for enabling comparisons of utilities across health conditions, but only one of the RCTs included in our systematic review of clinical effectiveness employed the EQ-5D, finding no significant difference in scores between the first- and second-eye cataract surgery groups. Utility estimates for our economic model were obtained instead from other published studies and tested in sensitivity and scenario analyses (see Results of the economic analysis). The EQ-5D, like other generic instruments, has been criticised for being insensitive to visual function (it does not contain questions related specifically to vision);90,91 however, the evidence is mixed, with some studies reporting changes in EQ-5D scores following cataract surgery. 108,118 It is unclear, therefore, whether the absence of effects of second-eye cataract surgery on EQ-5D scores in the included RCT can be attributed to limitations of the EQ-5D instrument or an actual lack of effects of the surgery on patients’ HRQoL. These uncertainties around the relevance of the EQ-5D suggest that a preference-based measure that includes a visual sensation domain (such as, for example, the HUI-3) may be more appropriate for estimating utility changes in relation to cataract surgery. 94,108
The explanation for heterogeneity among the studies in utility changes is unclear. In particular, a study by Dolders and colleagues appeared to indicate a consistent utility decline after second-eye surgery for several preference-based measures. The study101 was somewhat unique among the studies we included in not being designed specifically to test for differences between first- and second-eye surgery and confidence in its ability to detect utility changes is uncertain since no statistical testing was reported. A possible explanation for variation in utility changes among the included studies could be variation in the time that patients had to wait for second-eye surgery,119 although this was not explicitly investigated by any of the primary study authors and may be only one of various contributory factors (e.g. also differences between the study designs and their population characteristics).
Other relevant factors
As mentioned above (see Current service provision), there is considerable regional variation in the criteria employed by NHS CCGs in their cataract referral pathways. Ideally, referral pathways for both first- and second-eye cataract surgery should be evidence based. 60 A number of ways of assessing vision and vision-related functional ability could be considered when making recommendations for cataract surgery referral. 1 Binocular visual acuity is commonly assessed, but visual acuity thresholds for first- and second-eye surgery have fallen in recent years. 55 Other measures, such as contrast sensitivity and stereopsis, may be more important than visual acuity for functional tasks, especially in elderly people,40,106 although they may be less straightforward to assess than visual acuity and may therefore require additional resources if routine tests are to be implemented in clinical practice. The RCTs suggested that stereopsis was more sensitive than visual acuity for indicating changes in vision following second-eye cataract surgery, although they did not indicate any major changes in contrast sensitivity. Another measure of visual function which might be important to patients, especially drivers, is glare disability, but this was not assessed in any of the RCTs. Future research to improve the cataract surgery referral guidelines should consider which of the vision outcomes (binocular and monocular visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, stereopsis, glare disability) should be routinely assessed, what the clinical thresholds of these outcomes should be for decision-making, and how feasible any additional testing would be in clinical practice.
The published economic evaluations included in our systematic review of cost-effectiveness favoured visual acuity as a measure of clinical vision rather than stereopsis. Consequently, there are no published methods linking changes in stereopsis to health utilities. Current generic preference-based utility instruments are unlikely to reflect changes in stereopsis. For example, the visual subscale of the HUI-3 (which has been used to inform this economic evaluation) appears to refer predominantly to clearness of vision (e.g. ability to read ordinary newsprint and recognise a friend on the other side of the street), rather than depth perception. It would therefore be useful for future economic evaluations of cataract surgery to consider methods to link health utilities to other measures of clinical vision, to provide a more comprehensive assessment of HRQoL.
Chapter 8 Conclusions
The evidence base for the clinical effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery in patents with bilateral cataracts is relatively limited. Three RCTs were identified, all of which were conducted more than 9 years ago, and one of which was conducted before the current practice of phacoemulsification was introduced in the UK. Each was judged to be at high risk of performance bias on patient-reported outcomes, as it was not possible to mask patients to the study group. Populations in the RCTs were in their 70s and had relatively good visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and HRQoL at baseline, limiting room for improvement after surgery, with changes mostly small and not clinically important. However, stereopsis was suboptimal in many patients at baseline and improved to a clinically meaningful degree when second-eye surgery was compared with surgery in the first eye alone. The mental health component of HRQoL (assessed with the SF-12 instrument in one RCT) appeared to show benefit from second-eye surgery, but other measures of HRQoL and vision-related functional ability did not differ to a clinically meaningful extent before and after second-eye surgery. Interpretation of several patient-reported outcomes is uncertain because of a lack of clearly established MCIDs or other limitations. Although the populations included in the RCTs were broadly reflective of cataract surgery patients in the NHS, it is questionable whether the results of the RCTs can be extrapolated reliably to current practice, given changes in surgical techniques. A more up-to-date RCT that stratifies patients according to the range of baseline (pre-surgery) vision currently found in the UK and which is planned a priori to include an economic evaluation would enable more precise estimation of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery in the NHS. There is a need for clarification as to which clinical vision and vision-related patient-reported outcomes are most appropriate for assessing the effectiveness of cataract surgery in the NHS, and for guidance on their clinical interpretation.
Based on economic modelling, second-eye surgery is generally considered cost-effective under conventional willingness-to-pay thresholds used in the NHS, tested under a range of scenarios and assumptions and using the best available evidence. In the base case analysis, second-eye cataract surgery generated 0.68 incremental QALYs at an additional cost of £1341 compared with cataract surgery in one eye only. The ICER was £1964. The base case results did not change significantly when input parameters and assumptions were varied in deterministic sensitivity analyses and scenario analyses. Notable exceptions were the utility changes associated with second-eye surgery where ICERs ranged between −£2908 and £5734 per QALY in sensitivity analyses. In the probabilistic analysis, the mean ICER was £1970 and the probability that second-eye cataract surgery was cost-effective at willingness-to-pay thresholds of £10,000 and £20,000, respectively, was 100%.
Implications for service provision
Our findings suggest that second-eye cataract surgery would likely be cost-effective if implemented routinely in the NHS. Although the mean visual acuity gain would be higher in patients who have lower pre-operative visual acuity, second-eye surgery appears to be cost-effective even in those with a relatively small deficiency of pre-operative binocular visual acuity (the base case assumed 6/12 or better). However, measuring visual acuity alone does not reflect patients’ functional disability resulting from a cataract. Therefore, careful consideration should be given to ensure that appropriate evidence-based measures are applied consistently for assessing patients’ eligibility for surgery (e.g. binocular and monocular visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, stereopsis, glare disability, vision-related functional ability and/or other aspects of HRQoL) and that clinically meaningful reference values for these measures are established.
Suggested research priorities
To determine the clinical effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery, a well-designed RCT would be appropriate, to overcome the lack of recent RCTs in this area and to improve on the methodological limitations of the previous RCTs. In order to design such a RCT it may be necessary first to clarify which outcomes are most appropriate for NHS cataract surgery pathways. Currently, the outcomes which are used in clinical practice to make referral decisions vary among the NHS CCGs and there is no recommended patient-reported outcome for assessing effects of cataracts on vision-related functional ability. 56 Specific limitations of previous RCTs that should be addressed in any future RCTs in this area are as follows:
-
Patient-reported outcomes should employ validated instruments, with accepted MCID, and should be scaled in such a way that they are not limited by ceiling effects when applied to people with bilateral cataracts in the UK (this may be challenging56).
-
To fully capture the effects of cataracts and cataract surgery on patients’ clinical vision, HRQoL and visual disability, a ‘core’ set of outcome measures may be appropriate, including specified tests of vision (e.g. including stereopsis, glare disability) as well as the aforementioned patient-reported outcome(s), and these may benefit from being developed in consultation with patients to ensure that all functional domains of importance to patients can be considered.
-
The study population should capture the range of age groups and cataract severity classes relevant to age-related cataract in the UK; it may be appropriate to stratify a RCT population according to cataract severity (or pre-operative vision measures) so as to enable effects of cataract severity on second-eye surgical outcomes to be explored.
-
Cataract severity should ideally be reported for both eyes, using an agreed classification system; monocular assessments of visual acuity and other vision measures such as stereopsis should be reported for both eyes, as this may identify patients more likely to benefit from second-eye surgery. 107
-
An a priori planned economic evaluation should be included, so as to improve precision of the estimates of cost-effectiveness in NHS settings.
-
To inform the economic evaluation, utilities should be estimated using a preference-based measure (e.g. TTO) to ensure direct relevance of utility estimates to the NHS cataract surgery population; it may be appropriate to compare several preference-based measures (e.g. including the EQ-5D because it is widely used for comparisons across health conditions) and a preference-based measure with a vision subscale (e.g. the HUI-3) to ensure adequate sensitivity to the effects of cataract surgery).
Measures of vision that require a high-quality retinal image in each eye, notably stereopsis, would be expected to be more sensitive than binocular visual acuity as an indicator of the effects of cataracts and cataract surgery, and this was demonstrated by the improvements in stereopsis seen after second-eye surgery in the included RCTs. However, stereopsis is not routinely monitored in cataract surgery patients and, although stereopsis affects HRQoL, it is not clear how this would translate into utility estimates. Research to clarify how changes in stereopsis influence utilities would be helpful to inform future economic evaluations and to clarify whether or not assessment of stereopsis should be made routinely in cataract surgery patients as part of the surgery referral decision process.
Acknowledgements
We thank Karen Welch (Information Specialist, SHTAC) for developing the search strategies, conducting bibliographic searches and acquiring and de-duplicating bibliographic references; and Andrew Clegg (Professor of Health Services Research, SHTAC) and Jeremy Jones (Principal Research Fellow, SHTAC) for their contributions to developing the project protocol.
We also thank the AG for their input throughout the course of the work and for commenting on the research protocol and on a draft of this report. Members of the AG were:
-
Dr Ewen Cummins, Health Economist, McMDC Ltd.
-
Parul Desai, Consultant in Ophthalmology and Public Health, Moorfields Eye Hospital (invited to the AG after the protocol was finalised, therefore did not comment on the protocol).
-
Simon Kelly, Member of the Quality and Safety subcommittee of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists, Ophthalmic Department, Royal Bolton Hospital.
-
Professor Janet Marsden, Professor of Ophthalmology and Emergency Care, Faculty of Health, Psychology and Social Care, Manchester Metropolitan University.
-
Professor John Sparrow, Honorary Professor and Consultant Ophthalmologist, Bristol Eye Hospital.
Contributions of authors
Geoff Frampton (Senior Research Fellow, SHTAC) was the project co-ordinator and chaired the project meetings. He contributed to the systematic review of clinical effectiveness by: screening studies for inclusion; extracting data from the included studies; assessing the quality of the included studies; and conducting the synthesis of outcomes data. He also contributed to writing the final report.
Petra Harris (Research Fellow, SHTAC) contributed to the systematic review of clinical effectiveness by: screening studies for inclusion; extracting data from the included studies; assessing the quality of the included studies; and conducting the synthesis of outcomes data. She also contributed to writing the final report.
Keith Cooper (Senior Research Fellow, Health Economics, SHTAC) contributed to the systematic reviews of cost-effectiveness and quality of life by: screening studies for inclusion; extracting data from the included studies; assessing the quality of the included studies; and conducting the synthesis of outcomes data. He also developed the economic model, conducted cost-effectiveness analyses, and contributed to writing the final report.
Andrew Lotery (Professor of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Southampton) commented on the draft protocol and on the clinical relevance of the draft economic model; responded to clinical questions from the research team; and contributed to writing the final report.
Jonathan Shepherd (Principal Research Fellow, SHTAC) was the project guarantor. He drafted the research protocol and revised it following peer review. He contributed to the systematic reviews of cost-effectiveness and quality of life by screening studies for inclusion; extracting data from the included studies; assessing the quality of the included studies; and conducting the synthesis of outcomes data. He also assisted with developing the economic model and conducting the cost-effectiveness analysis, and contributed to writing the final report.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Cataract Surgery Guidelines. London: Scientific Department, Royal College of Ophthalmologists; 2010.
- Knudtson MD, Klein BE, Klein R, Cruickshanks KJ, Lee KE. Age-related eye disease, quality of life, and functional activity. Arch Ophthalmol 2005;123:807-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archopht.123.6.807.
- Lee PP, Cunningham WE, Nakazono TT, Hays RD. Associations of eye diseases and symptoms with self-reported physical and mental health. Am J Ophthalmol 2009;148:804-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2009.06.021.
- Harwood RH, Foss AJ, Osborn F, Gregson RM, Zaman A, Masud T. Falls and health status in elderly women following first eye cataract surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Ophthalmol 2005;89:53-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2004.049478.
- Mennemeyer ST, Owsley C, McGwin G. Reducing older driver vehicle collisions via earlier cataract surgery. Accid Anal Prev 2013;61:203-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2013.01.002.
- Prokofyeva E, Wegener A, Zrenner E. Cataract prevalence and prevention in Europe: a literature review. Acta Ophthalmol 2013;91:395-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-3768.2012.02444.x.
- Edward S, Airiani S, Braunstein RE, Chang S, Barile G, Cheung P, et al. Digital Reference of Opthalmology. New York, NY: Edward S Harkness Eye Institute, Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center; 2003.
- American Academy of Ophthalmology . Cataract in the Adult Eye. Preferred Practice Pattern Guidelines n.d. http://one.aao.org/CE/PracticeGuidelines/PPP_Content.aspx?cid=a80a87ce-9042–4677–85d7–4b876deed276 (accessed 29 August 2013).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Clinical Knowledge Summaries: Cataracts n.d. http://cks.nice.org.uk/cataracts#azTab (accessed 29 August 2013).
- Pseudovs K, Elliott DB. Cataract morphology, classification, assessment and referral. CE Optometry 2001;42:55-60.
- Sparrow JM, Frost NA, Pantilidis E, Laidlaw DAH. Decimalizartion of the Oxford Clinical Cataract Classification and Grading System: approach and performance. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2000;7:49-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1076/0928-6586(200003)7:1;1-2;FT049.
- Chylack LT, Wolfe JK, Singer DM, Leske MC, Bullimore MA, Bailey IL, et al. The lens opacities classification system III. Arch Ophthalmol 1993;111:831-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archopht.1993.01090060119035.
- Reidy A, Minassian DC, Vafidis G, Joseph J, Farrow S, Wu J, et al. Prevalence of serious eye disease and visual impairment in a north London population: population based, cross sectional study. BMJ 1998;316:1643-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.316.7145.1643.
- Minassian DC, Reidy A, Desai P, Farrow S, Vafidis G, MInassian A. The deficit in cataract surgery in England and Wales and the escalating problem of visual impairment: epidemiological modelling of the population dynamics of cataract. Br J Ophthalmol 2000;84:4-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.84.1.4.
- Frost A, Hopper C, Frankel S, Peters TJ, Durant J, Sparrow J. The population requirement for cataract extraction: a cross-sectional study. Eye 2001;15:745-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/eye.2001.242.
- Sight Denied. Variation in Cataract Surgery Provision Across England. London: Royal National Institute for Blind People; 2013.
- Evans JR, Fletcher AE, Wormald RP. MRC trial of assessment and management of older people in the community. Causes of visual impairment in people aged 75 years and older in Britain: an add-on study to the MRC Trial of Assessment and Management of Older People in the Community. Br J Ophthalmol 2004;88:365-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2003.019927.
- Jefferis JM, Taylor J-P, Collerton J, Jagger C, Kingston A, Davies K, et al. The association between diagnosed glaucoma and cataract and cognitive performance in very old people: cross-sectional findings from the Newcastle 85+ study. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2013;20:82-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09286586.2012.757626.
- Koo E, Chang JR, Agrón E, Clemons TE, Sperduto RD, Ferris FL, et al. Ten-year incidence rates of age-related cataract in the Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS): AREDS Report No. 33. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2013;20:71-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09286586.2012.759598.
- Jaycock P, Johnston RL, Taylor H, Adams M, Tole DM, Galloway P, et al. The Cataract National Dataset electronic multi-centre audit of 55,567 operations: updating benchmark standards of care in the United Kingdom and internationally. Eye 2009;23:38-49. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6703015.
- Hammond CJ, Duncan DD, Snieder H, de Lange M, West SK, Spector TD, et al. The heritability of age-related cataract: the twin eye study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2001;42:601-5.
- Appleby PN, Allen NE, Key TJ. Diet, vegetarianism and cataract risk. Am J Clin Nutr 2011;93:1128-35. http://dx.doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.110.004028.
- Asbell PA, Dualan I, Mindel J, Brocks D, Ahmad M, Epstein S. Age-related cataract. Lancet 2005;365:599-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17911-2.
- Ainsbury EA, Bouffler SD, Dorr W, Graw J, Muirhead CR, Edwards AA, et al. Radiation cataractogenesis: a review of recent studies. Radiation Res 2009;172:1-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1667/RR1688.1.
- McCarty CA, Taylor HR. A review of the epidemiologic evidence linking ultraviolet radiation and cataracts. Dev Ophthalmol 2002;35:21-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000060807.
- Rosser DA, Laidlaw DA, Murdoch IE. The development of a ‘reduced logMAR’ visual acuity chart for use in routine clinical practice. Br J Ophthalmol 2001;85:432-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.85.4.432.
- Bailey IL, Lovie-Kitchin JE. Visual acuity testing: from the laboratory to the clinic. Vision Res 2013;90:2-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.visres.2013.05.004.
- Department of Work and Pensions: . Registration of Blindness Partially Sighted n.d. www.dwp.gov.uk/publications/specialist-guides/medical-conditions/a-z-of-medical-conditions/vision/reg-blind-partial-sight-vision.shtml (accessed 29 August 2013).
- Holladay JT. Proper method for calculating average visual acuity. J Refract Surg 1997;13:388-91.
- Rosser DA, Cousens SN, Murdoch IE, Fitzke FW, Laidlaw DAH. How sensitive to clinical change are ETDRS logMAR visual acuity measurements?. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003;44:3278-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.02-1100.
- Schneck ME, Haegerstrõm-Portnoy G, Lott LA, Brabyn JA. Monocular vs. binocular measurement of spatial vision in elders. Optom Vis Sci 2010;87:526-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181e61a88.
- Charalampidou S, Loughman J, Nolan J, Stack J, Cassidy L, Pesudovs K, et al. Prognostic indicators and outcome measures for surgical removal of symptomatic nonadvanced cataract. Arch Ophthalmol 2011;129:1155-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archophthalmol.2011.111.
- Mäntyjärvi M, Laitinen T. Normal values for the Pelli–Robson contrast sensitivity test. J Cataract Refrac Surg 2001;27:261-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0886-3350(00)00562-9.
- Rubin GS, West SK, Muñoz B, Bandeen-Roche K, Zeger S, Schein O, et al. A comparative assessment of visual impairment in a population of older Americans: The SEE Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1997;38:557-68.
- Rubin GS, Bandeen-Roche K, Huang G-H, Muñoz B, Schein OD, Fried LP, et al. The association of multiple visual impairments with self-reported visual disability: SEE Project. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2001;42:64-72.
- Rabin J. Two eyes are better than one: binocular enhancement in the contrast domain. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 1995;15:45-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1475-1313.1995.9592791.x.
- Cheng Y, Shi X, Cao XG, Li XX, Bao YZ. Correlation between contrast sensitivity and the lens opacities classification system III in age-related nuclear and cortical cataracts. Chinese Med J 2013;126:1430-5.
- Pardhan S, Gilchrist J. The importance of measuring binocular contrast sensitivity in unilateral cataract. Eye 2013;5.
- Elliott D, Hurst M, Weatherill J. Comparing tests of visual function in cataract with the patient’s perceived visual disability. Eye 1990;4:712-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/eye.1990.100.
- Datta S, Foss AJ, Grainge MJ, Gregson RM, Zaman A, Masud T, et al. The importance of acuity, stereopsis, and contrast sensitivity for health-related quality of life in elderly women with cataracts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008;49:1-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.06-1073.
- Poggio GF, Poggio T. The analysis of stereopsis. Ann Rev Neurosci 1984;7:379-412. http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.002115.
- O’Connor AR, Birch EE, Anderson S, Draper H. The functional significance of stereopsis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010;51:2019-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.09-4434.
- Nevitt MC, Cummings SR, Kidd S, Black D. Stereoacuity has been found to be a significant risk factor for falls in the elderly. JAMA 1989;261:2663-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.1989.03420180087036.
- Fricke TR, Siderov J. Stereopsis, stereotests, and their relation to vision screening and clinical practice. Clin Exp Optom 1997;80:165-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-0938.1997.tb04876.x.
- Hirai T, Ito Y, Arai M, Ota Y, Kojima T, Sato M, et al. Loss of stereopsis with optical chiasmal lesions and stereoscopic tests as a differential test. Ophthalmology 2002;109:1692-702. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0161-6420(02)01171-5.
- Schneck ME, Hagerström-Portnoy G, Lott LA, Brabyn JA. Ocular contributions to age-related loss in coarse stereopsis. Optom Vis Sci 2013;77:531-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006324-200010000-00007.
- Khadka J, Gothwal VK, McAlinden C, Lamoureux EL, Pseudovs K. The importance of rating scales in measuring patient-reported outcomes. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2012;10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-10-80.
- McAlinden C, Gothwal VK, Khadka J, Wright TA, Lamoureux EL, Pseudovs K. A head-to-head comparison of 16 cataract surgery outcome questionnaires. Ophthalmology 2011;118:2374-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.06.008.
- Fraser ML, Meuleners LB, Lee AH, Ng JQ, Morlet N. Which visual measures affect change in driving difficulty after first eye cataract surgery?. Accid Anal Prev 2013;58:10-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2013.04.015.
- Meuleners LB, Hendrie D, Lee AH, Ng JQ, Morlet N. The effectiveness of cataract surgery in reducing motor vehicle crashes: a whole population study using linked data. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2012;19:23-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09286586.2011.628776.
- GOV.UK. Driving Eyesight Rules n.d. www.gov.uk/driving-eyesight-rules (accessed 29 August 2013).
- Wood JM, Tyrrell RA, Chaparro A, Marszalek RP, Carberry TP, Chu BS. Even moderate visual impairments degrade drivers’ ability to see pedestrians at night. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012;53:2586-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.11-9083.
- Bal T, Coeckelbergh T, Van Looveren J, Rozema JJ, Tassignon M-J. Influence of cataract morphology on straylight and contrast sensitivity and its relevance to fitness to drive. Opthalmologica 2011;225:105-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000317076.
- Department of Health . NHS Reference Costs 2011 2012 n.d. www.gov.uk/government/publications/reference-costs-guidance-for-2011–12 (accessed 29 August 2013).
- Sparrow JM. Cataract surgical rates: is there overprovision in certain areas?. Br J Ophthalmol 2007;91:852-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2006.111211.
- Black N, Browne J, van der Meulen J, Jamieson L, Copley L, Lewsey J. Is there overutilisation of cataract surgery in England?. Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93:13-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2007.136150.
- Lundström M, Barry P, Henry Y, Rosen P, Stenevi U. Evidence-based guidelines for cataract surgery: guidelines based on data in the European Registry of Quality Outcomes for Cataract and Refractive Surgery database. J Cataract Refract Surg 2012;38:1086-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrs.2012.03.006.
- Don’t Turn Back the Clock. Cataract Surgery – The Need for Patient-Centred Care. London: Royal National Institute for Blind People and Royal College of Ophthalmologists; 2011.
- Steele C. Shared care and referral pathways Part 3: See through cataract referral. Optometry Today 2013:53-7.
- Coronini-Cronberg S, Lee H, Darzi A, Smith P. Evaluation of clinical threshold policies for cataract surgery among English commissioners. J Health Serv Res Policy 2012;17:241-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/jhsrp.2012.012023.
- Save Our Sight Campaign Report. RNIB Campaign Report, May 2012. London: Royal National Institute for Blind People; 2012.
- Action on Cataracts. Good Practice Guidance. London: Department of Health; 2000.
- Healthcare Improvement Scotland . Is It Clinically and Cost Effective to Perform Second-Eye Cataract Surgery in the Absence of Other Ocular Co-Morbidities in Patients Who Have Already Had First-Eye Surgery? n.d. www.healthcareimprovementscotland.org/our_work/technologies_and_medicines/shtg_advice_statements/advice_statement_008–12.aspx (accessed 29 August 2013).
- Aslam TM, Devlin H, Dhillon B. Use of Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy. Surv Opthalmol 2003;48:594-612. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.survophthal.2003.08.002.
- Trinavarat A, Neerucha V. Visual outcome after cataract surgery complicated by posterior capsule rupture. J Med Assoc Thai 2012;95:S30-5.
- Kresloff MS, Castellarin AA, Zarbin MA. Endophthalmitis. Surv Ophthalmol 1998;43:193-224. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6257(98)00036-8.
- Erie JC, Raecker ME, Baratz KH, Schleck CD, Robertson DM. Risk of retinal detachment after cataract extraction, 1980–2004: a population-based study. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 2006;104:167-75.
- Lois N, Wong D. Pseudophakic retinal detachment. Surv Ophthalmol 2003;48:467-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6257(03)00083-3.
- Rotsos TG, Moschos MM. Cystoid macular edema. Clin Ophthalmol 2008;2:919-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S4033.
- Vanner EA, Stewart MW. Vitrectomy timing for retained lens fragments after surgery for age-related cataracts: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Ophthalmol 2011;152:345-57. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2011.02.010.
- Chakrabarti M, Stephen V, Rani John S, Chakrabarti A. Managing retained lens fragments after cataract surgery. Keral J Ophthalmol 2013;XX:269-77.
- Kamalarajah S, Silvestri G, Sharma N, Khan A, Foot B, Ling R, et al. Surveillance of endophthalmitis following cataract surgery in the UK. Eye 2004;18:580-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6700645.
- Desai P, Minassian DC, Reidy A. National cataract surgery survey 1997–8: a report of the results of the clinical outcomes. Br J Ophthalmol 1999;83:1336-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.83.12.1336.
- Taban M, Behrens A, Newcomb RL, Nobe MY, Saedi G, Sweet PM, et al. Acute endophthalmitis following cataract surgery. A systematic review of the literature. Arch Ophthalmol 2005;123:613-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archopht.123.5.613.
- Narendran N, Jaycock P, Johnston RL, Taylor H, Adams M, Tole DM, et al. The Cataract National Dataset: electronic multicentre audit of 55 567 operations: risk stratification for posterior capsule rupture and vitreous loss. Eye 2009;23:31-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6703049.
- Sparrow JM, Taylor H, Qureshi K, Smith R, Birnie K, Johnston RL. The Cataract National Dataset electronic multi-centre audit of 55 567 operations: risk indicators for monocular visual acuity outcomes. Eye 2012;26:821-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/eye.2012.51.
- The Press Association . Cataracts surgery restricted by unnecessary eye test thresholds. Nurs Times 2012;108.
- Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011.
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343.
- Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al. Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment. Health Technol Assess 2004;8.
- Drummond M, Sculpher M, Torrance G, O’Brien B, Stoddart G. Methods for the Economic Evaluation of Health Care Programmes. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2005.
- Rodgers M, Sowden A, Petticrew M, Arai L, Roberts H, Britten N, et al. Testing methodological guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. Evaluation 2009;15:47-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1356389008097871.
- Foss AJ, Harwood RH, Osborn F, Gregson RM, Zaman A, Masud T. Falls and health status in elderly women following second eye cataract surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 2006;35:66-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afj005.
- Laidlaw DA, Harrad RA, Hopper CD, Whitaker A, Donovan JL, Brookes ST, et al. Randomised trial of effectiveness of second eye cataract surgery. Lancet 1998;352:925-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(97)12536-3.
- Castells X, Comas M, Alonso J, Espallargues M, Martinez V, Garcia-Arumi J, et al. In a randomized controlled trial, cataract surgery in both eyes increased benefits compared to surgery in one eye only. J Clin Epidemiol 2006;59:201-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.06.007.
- Feeny D, Spritzer K, Hays RD, Liu H, Ganiats TG, Kaplan RM, et al. Agreement about identifying patients who change over time: cautionary results in cataract and heart failure patients. Med Decis Making 2012;32:273-86. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0272989X11418671.
- Bilbao A, Quintana JM, Escobar A, García S, Andradas E, Baré M, et al. Responsiveness and clinically important differences for the VF-14 Index, SF-36, and visual acuity in patients undergoing cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 2009;116:418-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.11.020.
- Riaz Y, Mehta JS, Wormald R, Evans JR, Foster A, Ravilla T, et al. Surgical interventions for age-related cataract. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;18.
- Ishikawa T, Desapriya E, Puri M, Kerr JM, Hewapathirane DS, Pike I. Evaluating the benefits of second-eye cataract surgery among the elderly. J Cataract Refract Surg 2013;39:1593-603. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrs.2013.08.033.
- Räsänen P, Krootila K, Sintonen H, Leivo T, Koivisto AM, Ryynanen OP, et al. Cost-utility of routine cataract surgery. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2006;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-4-74.
- Sach TH, Foss AJ, Gregson RM, Zaman A, Osborn F, Masud T, et al. Second-eye cataract surgery in elderly women: a cost-utility analysis conducted alongside a randomized controlled trial. Eye 2010;24:276-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/eye.2009.112.
- Busbee BG, Brown MM, Brown GC, Sharma S. Cost-utility analysis of cataract surgery in the second eye. Ophthalmology 2003;110:2310-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00796-6.
- Brown GC, Brown MM. Cost-utility analysis: the foundation of value-based medicine-cataract surgery in the second eye. Evidence-Based Eye Care 2004;5:112-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00132578-200404000-00025.
- Hiratsuka Y, Yamada M, Murakami A, Okada AA, Yamashita H, Ohashi Y, et al. Cost-effectiveness of cataract surgery in Japan. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2011;55:333-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10384-011-0041-3.
- Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal. London: NICE; 2013.
- Busbee BG, Brown MM, Brown GC, Sharma S. Incremental cost-effectiveness of initial cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 2002;109:606-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0161-6420(01)00971-X.
- Norregaard JC, Hindsberger C, Alonso J, Bellan L, Bernth-Petersen P, Black C, et al. Visual Outcomes of cataract surgery in the United States, Canada, Denmark, and Spain. Report From the International Cataract Surgery Outcomes Study. Arch Ophthalmol 1998;116:1095-100. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archopht.116.8.1095.
- Brown GC. Vision and quality-of-life. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1999;97:473-511.
- Brown MM, Brown GC, Sharma S, Busbee B, Brown H. Quality of life associated with unilateral and bilateral good vision. Ophthalmology 2001;108:643-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0161-6420(00)00635-7.
- Sintonen H. The 15D instrument of health-related quality of life: properties and applications. Ann Med 2001;33:328-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/07853890109002086.
- Dolders MG, Nijkamp MD, Nuijts RM, van den Borne B, Hendrikse F, Ament A, et al. Cost effectiveness of foldable multifocal intraocular lenses compared to foldable monofocal intraocular lenses for cataract surgery. Br J Ophthalmol 2004;88:1163-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2003.035527.
- Kaplan RM, Tally S, Hays RD, Feeny D, Ganiats TG, Palta M, et al. Five preference-based indexes in cataract and heart failure patients were not equally responsive to change. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:497-506. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.010.
- Kishimoto F, Naito T, Hasebe S, Ohtsuki H. Time trade-off utility analysis for surgical intervention in comitant strabismus, glaucoma, and cataract. Acta Med Okayama 2012;66:191-20.
- Naeim A, Keeler EB, Gutierrez PR, Wilson MR, Reuben D, Mangione CM. Is cataract surgery cost-effective among older patients with a low predicted probability for improvement in reported visual functioning?. Med Care 2006;44:982-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.mlr.0000228216.18270.3e.
- Clark A, Ng JQ, Morlet N, Tropiano E, Mahendran P, Spilsbury K, et al. Quality of life after postoperative endophthalmitis. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2008;36:526-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9071.2008.01827.x.
- de Juan-Marcos L, Blanco-Blanco JF, Hernandez-Galilea E. Visual function and quality of life in pseudophakic patients before and after capsulotomy. Eur J Ophthalmol 2012;22:943-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.5301/ejo.5000146.
- Tan ACS, Tay WT, Zheng YF, Tan AG, Wang JJ, Mitchell P, et al. The impact of bilateral or unilateral cataract surgery on visual functioning: when does second eye cataract surgery benefit patients?. Br J Ophthalmol 2012;96:846-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2011-301233.
- Tosh J, Brazier J, Evans P, Longworth L. A review of generic preference-based measures of health-related quality of life in visual disorders. Value Health 2012;15:118-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2011.08.002.
- Her Majesty’s Treasury . The Green Book. Appraisal and Evaluation in Central Government n.d. www.hm-treasury.gov.uk/data_greenbook_index.htm (accessed 29 August 2013).
- Office of National Statistics . Death Registrations by Single Year of Age, United Kingdom 2010 n.d. www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/vsob1/death-registrations-by-single-year-of-age/index.html (accessed 29 August 2013).
- Briggs A, Sculpher M, Claxton K. Decision Modelling for Health Economic Evaluation. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2006.
- Curtis L. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2012 n.d. www.pssru.ac.uk/project-pages/unit-costs/2012/ (accessed 29 August 2013).
- Colquitt JL, Jones J, Tan SC, Takeda AL, Clegg AJ, Price A. Ranibizumab and pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2008;12.
- Eye Care Comparative Effectiveness Research Team (ECCERT) . Cost-utility analysis of cataract surgery in Japan: a probabilistic Markov modeling study. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2013:1-11.
- Sach TH, Foss AJ, Gregson RM, Zaman A, Osborn F, Masud T, et al. Falls and health status in elderly women following first eye cataract surgery: an economic evaluation conducted alongside a randomised controlled trial. Br J Ophthalmol 2007;91:1675-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2007.118687.
- Javitt JC, Steinberg EP, Sharkey P, Schein OD, Tielsch JM, Diener M, et al. Cataract surgery in one eye or both. A billion dollar per year issue. Ophthalmology 1995;102:1583-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0161-6420(95)30824-X.
- Davis JC, McNeill H, Wasdell M, Chunick S, Bryan S. Focussing both eyes on healthy outcomes: revisiting cataract surgery. BMC Geriatr 2012;12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2318-12-50.
- Ang M, Fenwick E, Wong TY, Lamoureux E, Luo N. Utility of EQ-5D to assess patients undergoing cataract surgery. Optom Vis Sci 2013;90:861-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/OPX.0000000000000004.
- Hodge W, Horsley T, Albiani D, Baryla J, Belliveau M, Buhrmann R, et al. The consequences of waiting for cataract surgery. CMAJ 2007;176:1285-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.060962.
- Cohen HE. Drug Topics Red Book. Montvale, NJ: Medical Economics Company; 2001.
Appendix 1 Protocol
1. Cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery
2. Name of TAR team and project ‘lead’
Southampton Health Technology Assessments Centre (SHTAC)
University of Southampton
First Floor, Epsilon House
Enterprise Road
Southampton Science Park
Southampton
SO16 7NS
Project lead:
Dr Geoff Frampton, Senior Research Fellow, SHTAC
Tel: +44 (0) 23 80 599299 Fax: +44 (0) 23 80 595662 Email: gkf1@soton.ac.uk
Other members of the team:
Ms Petra Harris, Research Fellow, SHTAC
Dr Keith Cooper, Senior Research Fellow (Health Economics), SHTAC
Professor Andrew Lotery, Professor of Ophthalmology and Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist, University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust
Dr Jonathan Shepherd, Principal Research Fellow, SHTAC
3. Plain English Summary
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the lens of the eye which results in symptoms such as blurred or reduced vision. Cataracts are linked to ageing and are more common in people over 65. Other risk factors include smoking, alcohol, diabetes, and use of medical drugs such as corticosteroids. The main treatment for cataracts is surgical extraction. Surgery involves removal of the natural (crystalline) lens of the eye that has developed an opacification (cataract) and replacement with an artificial lens to restore clarity of vision. Cataract extraction is a common procedure and is beneficial to patients in improving their vision and ability to perform daily activities. Cataract is generally a bilateral condition (i.e. affecting both eyes) and surgery is generally performed on one eye at a time. It is currently standard practice for surgeons to offer surgery where a second-eye cataract exists and the patient is symptomatic and wishes to proceed. Cataract extraction in the first eye is known to be cost-effective for health services, however, there is uncertainty about how cost-effective second-eye cataract surgery is.
We propose to summarise the most up-to-date and highest quality evidence on the benefits, harms and costs of second-eye cataract surgery in adults. We will search for, review and assess the quality of trials that examine how effective second-eye cataract surgery is, compared with single eye cataract extraction. The review will be undertaken following a recognised, systematic and transparent approach, allowing people to understand and judge the process and methods we have used. We will summarise the findings of the review through a discussion and, if appropriate, by combining results statistically.
We will develop an economic model either through adapting an existing model or developing a new economic model to examine the costs and benefits of second-eye cataract surgery within the UK. The model will use data from our review of trials, and data from recognised sources (e.g. national published data, data from local hospitals’ finance departments), as well as advice from experts in the field. We will also identify the areas where further research is needed. The results of this study will be used to inform health policy and practice.
4. Decision problem
4.1 Research aim and objectives
The aim of this project is to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery. The objectives are:
-
To conduct a systematic review of studies assessing the clinical effectiveness of second-eye surgery.
-
To conduct an economic evaluation comprising: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness studies of second-eye surgery; and to develop/adapt an economic model to estimate cost-effectiveness.
Cataract removal surgery is a common procedure in the UK and has been shown to be cost-effective in the initial eye. 1 Some patients with bilateral cataract may only have surgery on one eye, but it is suggested that surgery on the second eye may have additional benefit for patients in terms of improving vision and being able to perform everyday activities (e.g. being able to drive). However, there is debate about how cost-effective second-eye surgery would be.
Scoping searches for this protocol have identified three published randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of second-eye cataract surgery compared with first-eye surgery. 2–4 All of these trials reported varying degrees of benefit associated with second-eye surgery, in terms of improved visual acuity, visual symptoms, and quality of life. No published systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery have been identified. Three published economic evaluations have been identified5–7 (one of which was a trial-based evaluation conducted in the UK5) which have used divergent methods and generated mixed results (see section 6). An evidence synthesis and economic evaluation would therefore be useful to inform health service policy and practice in this area.
4.2 Background
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye which results in symptoms such as blurred or reduced vision, and problems associated with glare or low-contrast conditions. Formation of cataracts is linked to ageing, with the gradual accumulation of yellow-brown pigment within the lens reducing light transmission. Cataracts can also be congenital or secondary to other causes (e.g. chronic uveitis). Other, extrinsic, risk factors include smoking, alcohol diabetes, and use of systemic corticosteroids. In developing countries malnutrition and acute dehydrating diseases are also associated with cataract development. 8
Cataracts are a common cause of visual impairment worldwide, and are more common in older people. The North London Eye Study randomly sampled people aged over 65 years from general practices in north London (1547/1840 responding), and found a prevalence of cataract causing visual impairment (visual acuity in one or both eyes poorer than 6/12, attributable to lens opacity) of 30%. 9 The prevalence of cataract increased steadily with age from 16% in the 65 to 69 age group, to 71% in people aged over 85 years. In the MRC Trial of Assessment and Management of Older People in the Community, nurses tested visual acuity in 14,403 people aged 75 years and older from 49 general practices in Britain. 10 Of 976 people with binocular visual impairment (binocular acuity <6/18) excluding refractive error, 36% were classified as having cataract.
4.3 Definition of the intervention
Cataract extraction surgery is considered to be the only curative intervention available. First-eye cataract surgery refers to removal of the cataract in only one eye. Second-eye cataract surgery is performed in patients with bilateral cataract at a point in time following first-eye surgery. Surgery involves removal of the natural (crystalline) lens of the eye that has developed an opacification (cataract) and replacement with a synthetic lens to restore clarity of vision.
Phacoemulsification is the standard method of cataract removal in the NHS and is associated with better visual outcome than conventional extracapsular surgery. 11 It involves making small incisions (e.g. 3 mm in width) where the clear front covering (cornea) meets the white of the eye (sclera). A circular opening is created on the lens surface (capsule). A small surgical instrument (phaco probe) is inserted into the eye and ultrasound waves are used to break the cataract into small pieces. The cataract and lens pieces are removed from the eye using suction and an intraocular lens implant may then be placed inside the lens capsule. The procedure is usually carried out under local anaesthetic as day surgery.
4.4 Place of the intervention in the treatment pathway(s)
People with cataracts may be referred to an ophthalmologist by a GP or optometrist. Referral criteria include clinically significant visual symptoms related to the cataract (e.g. reduced visual acuity, functional impairment), negative effects on the patient’s lifestyle by the cataract, and patient’s wish to undergo surgery.
Cataract extraction is one of the most common elective surgical procedures in the UK. In 2009–10 there were 334,142 cataract extractions performed in England. 12 It is estimated that over a one-third of NHS cataract operations are performed in the second eye. 13 Patients are generally assessed for their second-eye surgery at their first-eye surgery post-operation check (e.g. 4 weeks post-operation). They then may wait up to a further 18 weeks for surgery unless there is an urgent reason to do it sooner. It is very uncommon for cataract extraction to take place in both eyes simultaneously due to the risk of associated complications including bilateral infective endophthalmitis (inflammation of the inside of the eye) which may lead to blindness in both eyes. Expert clinical opinion suggests that 1% or fewer extractions are simultaneous.
The indication for second-eye surgery is based on whether the patient has a cataract in the second eye, is symptomatic and wishes to undergo surgery. Patients would have a glasses check so that they can assess the full benefit of the first-eye surgery, in order to correctly judge their level of symptoms and visual rehabilitation with a change in glasses. The threshold for impairment to visual acuity would be the same as for initial cataract extraction surgery, and expert clinical opinion suggests that thresholds may vary between health trusts. A proportion of patients choose not to undergo second-eye surgery and some die before they develop a second cataract.
The Royal College of Ophthalmologists cataract surgery guidelines (2010) state that it is clinically and economically appropriate for second-eye surgery to be offered to those patients who want it. A 1b recommendation is given (recommendation based on at least one randomised trial). 13 Similarly, the Scottish Health Technologies Group issued an advice statement in September 2012 advising that there is RCT evidence to support second-eye surgery and evidence from cost–utility analysis to demonstrate lifetime cost-effectiveness. 14 In England and Wales, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has not appraised second-eye cataract surgery.
4.5 Relevant comparators
Single eye cataract surgery can be considered a relevant comparator in patients with bilateral cataracts not currently scheduled for second-eye surgery. They may receive additional supportive care such as prescription glasses.
4.5 Outcomes
The clinical effectiveness of cataract surgery can be measured in a variety of ways. Commonly used clinical visual measures include: visual acuity (clearness of vision measured via, for example, a Snellen chart); stereopsis (depth perception); contrast sensitivity (the ability to see objects that may not be outlined clearly or that do not stand out from their background) and stereoacuity (the smallest detectable depth difference that can be seen in binocular vision).
Functional status is measured using assessment tools including the visual functioning index (VF-14), a well-established patient questionnaire designed to measure functional impairment caused by cataracts. In the VF-14 patients rate their ability to undertake activities such as reading a newspaper or a book, driving and reading traffic signs or taking part in games, and a total score is computed representing the degree of visual function. 15 It is suggested, however, that the VF-14 is not sensitive to all cataract symptoms and therefore a new instrument to assess the impact of cataract surgery in terms of visual function and quality of life is needed. 16
The health-related quality of life of people with cataracts has been assessed in clinical trials using generic instruments such as the SF-362 and the EuroQoL EQ-5D. 5 The EQ-5D has five dimensions (mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression) with three possible levels of severity for each.
Like all forms of surgery, cataract removal is associated with adverse events. These can include: endophthalmitis; retinal detachment; bullous keratopathy (swelling of the cornea); and intraocular lens dislocation.
4.6 Population and relevant subgroups
As discussed earlier, cataracts mainly affect older people, with increasing prevalence with age. Some people may have eye comorbidities such as age-related macular degeneration or glaucoma.
5. Report methods for synthesis of evidence of clinical effectiveness
A review of the evidence for clinical effectiveness will be undertaken systematically following the general principles outlined in Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) report ‘Undertaking Systematic Reviews of Research on Effectiveness’ (Third edition)17 and the PRISMA statement (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) (formally QUOROM statement). 18
5.1 Search strategy
A comprehensive search strategy will be developed, tested and refined by an experienced information scientist (see Appendix for draft MEDLINE search strategy). Separate searches will be conducted to identify studies of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, Health Related Quality of Life (HRQoL), resource use and costs, and epidemiology.
The search strategy will comprise the following main elements:
-
Searching of electronic databases
-
Contact with experts in the field
-
Scrutiny of bibliographies of retrieved papers
Electronic databases to be searched will include:
-
General health and biomedical databases – MEDLINE (Ovid); PreMedline In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations; EMBASE; the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials; and the Science Citation Index.
-
Specialist databases – the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effectiveness (DARE); Health Technology Assessment database; EconLit; NHS Economic Evaluation Database.
-
Grey literature and research in progress – UK Clinical Research Network Portfolio Database; and Conference Proceedings Citation Index –Science (Web of Science); Current Controlled Trials; Clinical Trials.gov; BIOSIS; NIHR Clinical Research Network Portfolio; CenterWatch; Health Services Research Projects in Progress and Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects (CRISP).
All databases will be searched from inception to the current date and searches will be limited to English language.
5.2 Inclusion/exclusion criteria
-
Population: adults (aged 18 or over) who have had one cataract operation already and still have or develop significant cataract causing visual impairment in the other eye.
-
Interventions: cataract surgery for the second eye. Studies reporting any surgical technique will be included.
-
Comparators: cataract extraction surgery in one eye only.
-
Outcomes: clinical visual measures (visual acuity; stereoacuity; contrast sensitivity); patient-reported visual disability and symptoms (e.g. VF-14); patient satisfaction with surgery and vision; health-related quality of life (e.g. EQ-5D); adverse events.
-
Types of studies: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) will be included. If necessary non-RCT data will be sought to inform the cost-effectiveness analysis (e.g. on safety). Any systematic reviews identified will be used only as a source of references.
-
Studies published as abstracts or conference presentations will only be included if sufficient details are presented to allow an appraisal of the methodology and the assessment of results to be undertaken.
5.3 Inclusion, data extraction and quality assessment process
Studies will be selected for inclusion through a two-stage process using the predefined and explicit criteria (as specified in section 5.2). The literature search results will be screened by two reviewers to identify all citations that may meet the inclusion criteria. Full manuscripts of relevant studies will be retrieved and assessed by two reviewers using a standardised eligibility form.
Data extraction and quality assessment will be undertaken by one reviewer and checked by a second reviewer using a pre-designed and piloted data extraction form to avoid any errors. At each stage, any disagreements between reviewers will be resolved by consensus or if necessary by arbitration by a third reviewer.
5.4 Quality assessment
Included trials will be assessed in terms of their risk of bias (e.g. selection bias, detection bias, performance bias, attrition bias, and selective reporting bias) using Cochrane Collaboration criteria. 19,20 Aspects of study quality including statistical procedures, outcome measurement and generalisability will also be assessed.
5.5 Methods of analysis/synthesis
Studies will be synthesised through a structured narrative review with tabulation of results of included studies. Where appropriate and where suitable data are available, meta-analysis will be employed to estimate a summary measure of effect on relevant outcomes. The specific methods for meta-analysis and for the detection and investigation of heterogeneity will depend upon the summary measure selected and will used standard procedures recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration. 19 Cochrane Review Manager (RevMan) software will be used to perform any meta-analysis. Heterogeneity will be explored through consideration of the study populations, methods and interventions, by visualisation of results and, in statistical terms, by the χ2 test for homogeneity and the I2 statistic.
6. Report methods for synthesising evidence of cost-effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery will be assessed through two stages: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness studies and the development of a decision analytic economic model.
6.1 Review of published cost-effectiveness studies
The sources detailed in section 5.1 will be used to identify studies of the cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery. Studies will be included in the systematic review of cost-effectiveness if they are full economic evaluations (cost-effectiveness, cost–utility or cost–benefit analyses) that report both measures of costs and consequences. The methodological quality of included studies will be assessed using accepted criteria for appraising economic evaluations. 21 Where relevant this will be supplemented with additional criteria for critical appraisal of model-based evaluations. 22 Studies will be synthesised through a narrative review that includes a clear explanation of the assessment process, detailed critical appraisal of study methods, critical assessment of data used in any economic models and tabulation of the results of included studies.
Published studies conducted in the UK and adopting an NHS and Personal Social Services (PSS) perspective will be examined in more detail. Stand alone cost analyses based in the UK NHS will also be searched for – these will not be included in the systematic review, but will be retained as sources of information on resource use and cost associated with second-eye cataract surgery (including short-term and longer-term adverse events).
Scoping searches have identified two published cost–utility studies of second-eye cataract surgery,5,7 in addition to the one study identified in the NIHR HTA programme commissioning brief, by Busbee and colleagues. 6 One of the additional studies was conducted in the UK and has an NHS and Personal Social Services (PSS) perspective. 5 Neither of the additional studies is a model-based evaluation – one was a study of ‘routine’ cataract surgery (of 219 patients, 73 had both eyes operated on and 59 had a second-eye operation, the first eye having been operated earlier)7, the other was conducted alongside a RCT. 5
6.2 Evaluation of costs and cost-effectiveness
Existing economic models developed to estimate the cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery, identified in the systematic review of economic evaluations, will be assessed for their quality, relevance and suitability for adoption in the current review. If considered relevant and valid the models will be adapted (if required) and populated with updated (and UK-practice-relevant) clinical and cost parameter values using data identified in our clinical and cost-effectiveness reviews.
The decision tree model presented by Busbee and colleagues,6 will be considered for adaptation in this economic evaluation. Key assumptions of this study will be discussed with our clinical and methodological advisors for their appropriateness. These include:
-
the inclusion and timing of adverse events: endophthalmitis; cystoid macular oedema; lost lens fragments (each occurring within 4 months of surgery); posterior capsular opacification (occurring at rate of 28% over 5 years, with treatment occurring on average 2 years after surgery); retinal detachment (in 0.81% of cases, with treatment on average 1 year after surgery); intraocular lens dislocation (in 1.1% of cases); and pseudophakic bullous keratopathy (in 0.3% of cases, with treatment on average 1 year after surgery). Retinal detachment following posterior capsular opacification was assumed to occur in 3% of cases.
-
the most appropriate measure of outcome. The model uses assumed levels of bilateral visual acuity which are then mapped to utility values derived using the time-trade-off technique. However, it is recognised that bilateral visual acuity may have limitations and other measures, including patient-reported visual dysfunction, may be more informative.
Current guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling and the general principles outlined in the NICE ‘reference case’ will be followed. 22–24 Development of the structure and parameters of the model will be informed by several sources including previous models identified in the systematic review of cost-effectiveness, evidence from our systematic review of clinical effectiveness, as well as guidance from clinical and methodological advisors. The model will be validated through discussion with expert advisors. Additional targeted literature searches will be required to populate other parameters in the model as necessary.
The model will adopt a UK NHS and PSS perspective with cost and outcomes discounted at an annual rate of 3.5%. The model will present estimates of the cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery, in terms of incremental cost per quality adjusted life-year (QALY) gained, compared with first-eye surgery only.
Resource use for second-eye cataract surgery, including management of adverse events, will be estimated from studies included in the systematic review of clinical effectiveness, published costing studies identified by our searches, any relevant clinical guidelines and from discussion with expert advisors.
As far as is possible, costings developed for the model will proceed by first identifying and quantifying resource use and then applying appropriate unit costs. Where resource use data from published literature is insufficient we would use estimates from relevant clinical experts and this will be clearly identified in the final report. To develop unit cost estimates we will assess official, nationally representative sources (NHS Reference Costs,25 Unit Costs of Health and Social Care,26 British National Formulary27) for applicability and level of detail, as well as unit cost estimates applied in studies included in the systematic review of cost-effectiveness and in costing studies identified by our searches. If these sources are inadequate we would develop unit cost estimates in collaboration with the costing unit at Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust. Costs will be inflated to current prices using the Hospital and Community Health Services Pay and Prices Index, where necessary. 26
Health-related quality-of-life (HRQoL) data, where available, will be extracted from studies included in the clinical- and cost-effectiveness systematic reviews. Where available, the impact of treatment adverse effects on patients will also be incorporated. Where QoL data are insufficient to calculate utility estimates, data will be derived from the broader literature or estimated from other sources. In accordance with the NICE methodological guide for technology appraisals,24 the utility values used in the model will be elicited where possible from the general population using a preference-based method. Where these are not available, utility estimates will be derived from alternative sources and the assumptions made will be explicitly stated.
The cost–utility studies identified in our preliminary searches vary in the approaches used to estimate the utility gain associated with second-eye cataract surgery. Busbee and colleagues6 estimated levels of bilateral visual acuity (they assumed the same utility values based on VA outcomes for patients having first-eye surgery) and mapped these to previously estimated utility values associated with given levels of bilateral visual acuity. This yielded comparatively large utility gains of 0.109. In contrast, the other studies based their utility estimates on patient responses to generic HRQoL instruments (EQ-5D5 and 15D7) valued using population-derived tariffs. These both estimated substantially lower utility gains following second-eye surgery [a small QALY gain of 0.015 for a 12 month time horizon (difference in EQ-5D utility at post-surgery follow-up not reported) in one study6 and a statistically non-significant decrease of −0.01 in the other7]. Both studies using patient-reported QoL measures included patients with limited vision loss (Sach and colleagues5 report that 86% of trial participants had baseline visual acuity of 6/12 or better, while Rasanen and colleagues7 noted that 17% of patients reported having no pre-operative difficulty in seeing and 47% only minor difficulties). It is not clear how far differences in patient populations studied may have given rise to divergent results in these studies, although baseline visual dysfunction (in the eye to be operated on) is likely to be an important factor in determining the potential gain from second-eye surgery. Current Cataract Surgery Guidelines published by the Royal College of Ophthalmologists13 note potential benefits from second-eye surgery, but do not indicate the degree of visual dysfunction in the second eye at which it would be appropriate to undertake second-eye surgery.
Sensitivity analyses and scenario analyses will be conducted with respect to variables over which there is greatest uncertainty. For the deterministic analyses this will be oriented towards variables with the greatest uncertainty over their methods of derivation or where choices/judgments have had to be made between alternative sources. The key variables to be explored in sensitivity/scenario analyses are likely to be the clinical benefit (for example gain in bilateral visual acuity) from second-eye cataract surgery and the utility associated with such benefits. However the robustness of model results to other clinical variables (including incidence and timing of adverse events) and to resource use assumptions will also be considered. The importance of the underlying model assumptions will be assessed through an analysis of different scenarios, particularly where evidence to populate the model is inadequate or conflicting (for example where the model uses data derived using expert opinion).
The results of the probabilistic sensitivity analysis will be presented using cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEACs).
7. Expertise in this TAR team
SHTAC is one of nine academic research teams in the UK contracted to the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA) programme to assess the clinical and cost-effectiveness of health technologies. Our research supports several key decision-making bodies within the UK, including the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). With expertise in evidence synthesis, health economics, statistical modelling and epidemiology, SHTAC is involved in research addressing major policy questions on the use of drugs, devices, procedures, screening programmes, health promotion and public health, and other interventions. SHTAC has previously conducted research into eye diseases, including a systematic review and economic evaluation of ranibizumab and pegaptanib for age-related macular degeneration. 28,29
Advisory group
An AG has been recruited comprising clinical experts in ophthalmology, experts in health technology assessment methodology (including health economics) and representatives from patient organisations. The group will has commented on the draft protocol and will comment on the draft final report. The group will be consulted during the course of the project for advice as necessary. The current members of the group are:
-
Professor Janet Marsden, Professor of Ophthalmology and Emergency Care & Chair of the RCN Ophthalmic Nursing Forum, Research Institute for Health and Social Change (Health Care Studies Department), Manchester Metropolitan University.
-
Professor John Sparrow, Consultant Ophthalmologist, University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust, & Honorary Professor of Ophthalmic Health Services Research and Applied Epidemiology, University of Bristol.
-
Mr Simon P Kelly, Chair of Quality & Safety subcommittee of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists, & Consultant Ophthalmic Surgeon at Royal Bolton Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Dr Ewen Cummins, Health Economist, McMaster Development Consultants
Additional members may be recruited to the group during the course of the project, as required.
8. Competing interests of authors
None.
9. Timetable/milestones
To follow.
10. Appendices
10.1. Draft Medline (Ovid) search strategy
-
exp cataract extraction/ (26,455)
-
(cataract* adj5 (surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis*)).tw. (19,067)
-
phacoemulsification.tw. (5253)
-
(PKE or PCIOL or ECCE or ICCE or MSICS or MISICS or SICS).tw. (931)
-
(pseudoaphakia or pseudoaphakic or phakectomy or phakectomies or “enzymatic zonulolysis” or “zonulolyses enzymatic” or “enzymatic zonulolyses” or “zonulolysis enzymatic”).tw. (107)
-
lens implantation, intraocular/ or lenses intraocular/ (16,135)
-
“cataract patient*”.tw. (1092)
-
or/1-7 (36,944)
-
(“single eye*” or “right eye*” or “left eye*” or “one eye” or “dominant eye*” or “better seeing eye*” or “either eye” or “unilateral cataract*” or “first eye*”).tw. (22,936)
-
(“fellow eye*” or “second eye*” or “both eyes” or “other eye*” or “two eyes” or “next eye*”).tw. (16,331)
-
(eye* adj5 (sequential* or simultaneous* or serial*)).tw. (1275)
-
(bilateral* adj5 cataract*).tw. (1369)
-
8 and (9 or 10 or 11 or 12) (3749)
-
Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic/ (83,981)
-
randomized controlled trial.pt. (339,605)
-
controlled clinical trial.pt. (85,425)
-
Controlled Clinical Trial/ (85,425)
-
placebos/ (31,477)
-
random allocation/ (76,252)
-
Double-Blind Method/ (117,819)
-
Single-Blind Method/ (16,898)
-
(random* adj2 allocat*).tw. (18,020)
-
placebo*.tw. (140,190)
-
((singl* or doubl* or trebl* or tripl*) adj (blind* or mask*)).tw. (115,464)
-
crossover studies/ (30,752)
-
(crossover* or (cross adj over*)).tw. (51,975)
-
Research Design/ (68,167)
-
((random* or control*) adj5 (trial* or stud*)).tw. (452,653)
-
Clinical Trials as Topic/ (163,152)
-
random*.ab. (567,167)
-
or/14-30 (1,175,731)
-
13 and 31 (612)
References
- Busbee BG, Brown MM, Brown GC, Sharma S. Incremental cost-effectiveness of initial cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 2002;109:606-12.
- Laidlaw DA, Harrad RA, Hopper CD, Whitaker A, Donovan JL, Brookes ST, et al. Randomised trial of effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery. Lancet 1998;352:925-9.
- Foss AJ, Harwood RH, Osborn F, Gregson RM, Zaman A, Masud T. Falls and health status in elderly women following second-eye cataract surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2006;35:66-71.
- Castells X, Alonso J, Ribó C, Casado A, Buil JA, Badia M, et al. Comparison of the results of first and second cataract eye surgery. Ophthalmology 1999;106:676-82.
- Sach TH, Foss AJ, Gregson RM, Zaman A, Osborn F, Masud T, et al. Second-eye cataract surgery in elderly women: a cost-utility analysis conducted alongside a randomized controlled trial. Eye 2010;24:276-83.
- Busbee BG, Brown MM, Brown GC, Sharma S. Cost-utility analysis of cataract surgery in the second eye. Ophthalmology 2003;110:2310-7.
- Rasenen P, Krootila K, Sintonen H, Leivo T, Koivisto A-M, Ryynanen O-P, et al. Cost-utility of routine cataract surgery. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2006;4.
- Allen D, Vasavada A. Cataract and surgery for cataract. BMJ 2006;333:128-32.
- Reidy A, Minassian DC, Vafidis G, Joseph J, Farrow S, Wu J, et al. Prevalence of serious eye disease and visual impairment in a north London population: population based, cross sectional study. BMJ 1998;316:1643-6.
- Evans JR, Fletcher AE, Wormald RP. Causes of visual impairment in people aged 75 years and older in Britain: an add-on study to the MRC Trial of Assessment and Management of Older People in the Community. Br J Ophthalmol 2004;88:365-70.
- Riaz Y, Mehta JS, Wormald R, Evans JR, Foster A, Ravilla T, et al. Surgical interventions for age-related cataract. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006.
- Hospital Episode Statistics . Hospital Episode Statistics: Total Procedures and Interventions 2009-10 2012. URL: www hesonline nhs uk (accessed 22/10/12).
- Cataract Surgery Guidelines, September 2010. London: The Royal College of Opthalmologists.; 2010.
- Healthcare Improvement Scotland . Is It Clinically and Cost Effective to Perform Second-Eye Cataract Surgery in the Absence of Other Ocular Co-Morbidities in Patients Who Have Already Had First-Eye Surgery? Advice Statement 008 12 n.d. URL: http://www.healthcareimprovementscotland.org/our_work/technologies_and_medicines/shtg_advice_statements/advice_statement_008-12.aspx.
- Steinberg EP, Tielsch JM, Schein OD, Javitt JC, Sharkey P, Cassard SD, et al. The VF-14. An index of functional impairment in patients with cataract. Arch Ophthalmol 1994;112:630-8.
- Black N, Browne J, van der Meulen J, Jamieson L, Copley L, Lewsey J. Is there overutilisation of cataract surgery in England?. Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93:13-7.
- Systematic Reviews: CRD’s Guidance for Undertaking Reviews in Health Care. York: CRD; 2009.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 2009;6.
- Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011.
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011.
- Drummond MF, Sculpher MJ, Torrance GW, O’Brien BJ, Stoddart GL. Methods for the Economic Evaluation of Health Care Programmes. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2005.
- Philips Z, Ginnelly L, Sculpher M, Claxton K, Golder S, Riemsma R, et al. Review of guidelines for good practice in decision-analytic modelling in health technology assessment. Health Technology Assessment 2004;8:1-158.
- Caro JJ, Briggs AH, Seibert U, Kuntz KM. Modeling Good Research Practices-Overview: A Report of the ISPOR-SMDM Modeling Good Research Practices Task Force-1. Value in Health 2012;15:796-803.
- London: NICE; 2004.
- NHS Reference Costs 2010-2011. UK: Department of Health; n.d.
- Curtis L. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2011. University of Kent; 2012.
- British National Formulary. British Medical Association and Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain; 2012.
- Colquitt JL, Jones J, Tan SC, Takeda AL, Clegg AJ, Price A. Ranibizumab and pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technology Assessment 2008;12.
- Takeda A, Colquitt J, Clegg AJ, Jones J. Pegaptanib and ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review. Br J Ophthalmol 2007;91:1177-82.
Appendix 2 Search strategies
Ovid MEDLINE(R); Ovid MEDLINE (R) Daily Update; Ovid MEDLINE(R) In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations
Search: 1946 to February week 4 2013; 12 March 2013; 12 March 2013.
Date of search: 13 March 2013.
Search strategy
-
exp cataract extraction/ (26,480)
-
exp cataract/ (21,988)
-
(surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis* or implant*).tw. (2,884,239)
-
2 and 3 (7602)
-
(cataract* adj5 (surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis* or implant*)).tw. (19,222)
-
(pha?oemulsif* or capsulor?hexis).tw. (5916)
-
(PKE or PCIOL or ECCE or ICCE or MSICS or MISICS or SICS).tw. (941)
-
(pseudophaki* or pseudoaphaki* or phakectomy or phakectomies or “enzymatic zonulolysis” or “zonulolyses enzymatic” or “enzymatic zonulolyses” or “zonulolysis enzymatic”).tw. (2658)
-
lens implantation, intraocular/ or lenses intraocular/ (16,139)
-
(cataract* and (IOL* or “intraocula* lens*” or “intra ocula* lens*”)).tw. (5879)
-
(cataract* adj5 patient*).tw. (7222)
-
(cataract* and (endocapsula* or “endo capsula”* or extracapsula* or “extra capsula*” or capsulor* or capsulot*)).tw. (3664)
-
1 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 (40,118)
-
(“single eye*” or “right eye*” or “left eye*” or “one eye” or “dominant eye*” or “better seeing eye*” or “either eye” or “unilateral cataract*” or “first eye*” or “initial eye”).tw. (23,081)
-
(“fellow eye*” or “second eye*” or “both eyes” or “other eye*” or “two eyes” or “next eye*”).tw. (16,323)
-
(eye* adj5 (sequential* or simultaneous* or serial*)).tw. (1280)
-
(bilateral* adj5 cataract*).tw. (1361)
-
13 and (14 or 15 or 16 or 17) (4160)
-
Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic/ (83,796)
-
randomized controlled trial.pt. (342,617)
-
controlled clinical trial.pt. (85,357)
-
Controlled Clinical Trial/ (85,357)
-
placebos/ (31,395)
-
random allocation/ (76,571)
-
Double-Blind Method/ (118,451)
-
Single-Blind Method/ (17,153)
-
(random* adj2 allocat*).tw. (18,091)
-
placebo*.tw. (140,578)
-
((singl* or doubl* or trebl* or tripl*) adj (blind* or mask*)).tw. (115,971)
-
crossover studies/ (31,186)
-
(crossover* or (cross adj over*)).tw. (52,412)
-
Research Design/ (72,908)
-
((random* or control*) adj5 (trial* or stud*)).tw. (456,444)
-
Clinical Trials as Topic/ (162,983)
-
random*.ab. (572,735)
-
or/19-35 (1,187,578)
-
18 and 36 (665)
-
limit 37 to humans (612)
-
limit 38 to (“all infant (birth to 23 months)” or “newborn infant (birth to 1 month)” or “infant (1 to 23 months)” or “preschool child (2 to 5 years)” or “child (6 to 12 years)”) (60)
-
38 not 39 (552)
-
(child* or infant* or newborn* or paediatric* or pediatric* or toddler*).tw. (1,218,343)
-
40 not 41 (550)
-
“second-eye cataract surgery”.tw. (41)
-
42 or 43 (582)
-
limit 44 to english language (538)
EMBASE (Ovid)
Search: 1974 to 12 March 2014.
Date of search: 13 March 2013.
Search strategy
-
Randomized Controlled Trial/ (341,060)
-
Randomization/ (60,956)
-
Single Blind Procedure/ (17,104)
-
Double Blind Procedure/ (116,041)
-
((single or doubl* or trebl* or tripl*) adj (mask* or blind*)).tw. (156,621)
-
(placebo* and control* and trial*).tw. (66,289)
-
randomi?ed control* trial*.tw. (87,684)
-
(random* adj2 allocat*).tw. (23,594)
-
(placebo* and random* and (trial* or study or studies)).tw. (106,340)
-
(randomized or randomised).tw. (440,771)
-
Controlled Clinical Trial/ (394,901)
-
Meta Analysis/ (69,502)
-
(meta-analys* or meta analys* or metaanalys*).tw. (64,286)
-
(systematic* adj3 review*).tw. (57,534)
-
health technology assessment*.ti,ab,in. (3383)
-
biomedical technology assessment/ (11,452)
-
or/1-16 (895,494)
-
exp cataract extraction/ (35,068)
-
lens implantation/ (5183)
-
exp cataract/ (43,214)
-
(surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis* or implant*).tw. (3,900,922)
-
20 and 21 (15,788)
-
(cataract* adj5 (surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis* or implant*)).tw. (24,554)
-
(pha?oemulsif* or capsulor?hexis).tw. (7825)
-
(PKE or PCIOL or ECCE or ICCE or MSICS or MISICS or SICS).tw. (1259)
-
(pseudophaki* or pseudoaphaki* or phakectomy or phakectomies or “enzymatic zonulolysis” or “zonulolyses enzymatic” or “enzymatic zonulolyses” or “zonulolysis enzymatic”).tw. (3166)
-
(cataract* and (IOL* or “intraocula* lens*” or “intra ocula* lens*”)).tw. (7704)
-
(cataract* adj5 patient*).tw. (9283)
-
(cataract* and (endocapsula* or “endo capsula*” or extracapsula* or “extra capsula*” or capsulor* or capsulot*)).tw. (4513)
-
or/18-19,22-29 (48,985)
-
(“single eye*” or “right eye*” or “left eye*” or “one eye” or “dominant eye*” or “better seeing eye*” or “either eye” or “unilateral cataract*” or “first eye*” or “initial eye”).tw. (31,441)
-
(“fellow eye*” or “second eye*” or “both eyes” or “other eye*” or “two eyes” or “next eye*”).tw. (21,105)
-
(eye* adj5 (sequential* or simultaneous* or serial*)).tw. (1586)
-
(bilateral* adj5 cataract*).tw. (1792)
-
or/31-34 (47356)
-
17 and 30 and 35 (571)
-
limit 36 to english language (507)
-
limit 37 to (infant <to one year> or child <unspecified age> or preschool child <1 to 6 years> or school child <7 to 12 years> or adolescent <13 to 17 years>) (39)
-
37 not 38 (468)
-
(infant* or newborn* or toddler* or child* or paediatric* or pediatric* or schoolchild* or preschool or adolesc*).tw. (1,571,707)
-
39 not 40 (457)
-
limit 41 to human (437)
-
41 not 42 (20)
-
from 43 keep 3,18 (2)
-
42 or 44 (439)
Web of Science Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Conference Proceedings Citation Index- Science (CPCI-S) – 1990–present; Conference Proceedings Citation Index – Social Science & Humanities (CPCI-SSH); BIOSIS Previews on Web of Science platform 1956–2013.
Search: 1970–present.
Date of search: 13 March 2013.
Search strategy
# 1 (TS=(cataract* NEAR (surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis* or implant*))) (14,211)
# 2 (TS=(cataract* NEAR (pha?oemulsif* or capsulor?hexis))) (2150)
# 3 (TS=(cataract* NEAR (PKE or PCIOL or ECCE or ICCE or MSICS or MISICS or SICS))) (328)
# 4 (TS=(pseudophaki* or pseudoaphaki* or phakectomy or phakectomies or “enzymatic zonulolysis” or “zonulolyses enzymatic” or “enzymatic zonulolyses” or “zonulolysis enzymatic”)) (2077)
# 5 (TS=(intraocula* NEAR ("lens* implant*”))) (3053)
# 6 (TS=(cataract* and (IOL* or “intraocula* lens*” or “intra ocula* lens*”))) (5509)
# 7 (TS=(cataract* NEAR patient*)) (7086)
# 8 (TS=(cataract* NEAR (endocapsula* or “endo capsula”* or extracapsula* or “extra capsula*” or capsulor* or capsulot*))) (2149)
# 9 #8 OR #7 OR #6 OR #5 OR #4 OR #3 OR #2 OR #1 (18,158)
# 10 (TS=(“single eye*” or “right eye*” or “left eye*” or “one eye” or “dominant eye*” or “better seeing eye*” or “either eye” or “unilateral cataract*” or “first eye*” or “initial eye”)) (15,249)
# 11 (TS=(“fellow eye*” or “second eye*” or “both eyes” or “other eye*” or “two eyes” or “next eye*”)) (11,121)
# 12 (TS=(eye* NEAR (sequential* or simultaneous* or serial*))) (2525)
# 13 (TS=(bilateral* NEAR cataract*)) (1121)
# 14 (#13 OR #12 OR #11 OR #10) (25,184)
# 15 #14 AND #9 (2957)
# 16 151 (TS=(cataract and “second eye*”)) (151)
# 17 #16 OR #15 (2959)
# 18 (TS=(random* NEAR (trial* or study or studies or allocat*))) (355,822)
# 19 (TS=(randomized or randomised)) (352,591)
# 20 (TS=((single or doubl* or trebl* or tripl*) NEAR (mask* or blind*))) AND Language=(English) (137,950)
# 21 (TS=(placebo* and control* and trial*)) (59,613)
# 22 (TS=(placebo* and control* and stud*)) (65,141)
# 23 #22 OR #21 OR #20 OR #19 OR #18 (490,189)
# 24 #23 AND #17 (397)
# 25 (TS=(child* or infant* or newborn* or paediatric* or pediatric* or toddler)) (689,724)
# 26 (#24 NOT #25) (355)
# 27 (TS=(animal* or monkey* or rabbit* or rat* or mouse or mice or cat or cats or dog or dogs)) (5,387,399)
# 28 (#26 NOT #27) (231)
# 29 (TS=(randomi?ed and cataract* and second and eye*)) (119)
# 30 (#29 NOT #27) (80)
# 31 (#30 NOT #25) (78)
# 32 (#28 or #31) (279)
The Cochrane Library Central; Health Technology Assessment; Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects
Search: Issue 2 of 12; Issue 1 of 4; Issue 2 of 12; Issue 1 of 4.
Date of search: 20 March 2013.
Also searched Cochrane Eyes and Vision Group (lens disease and cataract topic).
Search strategy
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Cataract Extraction] explode all trees
#2 MeSH descriptor: [Cataract] explode all trees
#3 (surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis* or implant*)
#4 #2 and #3
#5 (cataract* near (surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis* or implant*))
#6 (pha?oemulsif* or capsulor?hexis)
#7 (PKE or PCIOL or ECCE or ICCE or MSICS or MISICS or SICS)
#8 (pseudophaki* or pseudoaphaki* or phakectomy or phakectomies or “enzymatic zonulolysis” or “zonulolyses enzymatic” or “enzymatic zonulolyses” or “zonulolysis enzymatic”)
#9 MeSH descriptor: [Lens Implantation, Intraocular] explode all trees
#10 MeSH descriptor: [Lenses, Intraocular] explode all trees
#11 (cataract* and (IOL* or “intraocula* lens*” or “intra ocula* lens*”))
#12 (cataract near patient*)
#13 (cataract* and (endocapsula* or “endo capsula*” or extracapsula* or “extra capsula*” or capsulor* or capsulot*))
#14 #1 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13
#15 (“single eye*” or “right eye*” or “left eye*” or “one eye” or “dominant eye*” or “better seeing eye*” or “either eye” or “unilateral cataract*” or “first eye*” or “initial eye”)
#16 (“fellow eye*” or “second eye*” or “both eyes” or “other eye*” or “two eyes” or “next eye*”)
#17 (eye* near (sequential* or simultaneous* or serial*))
#18 (bilateral* adj5 cataract*)
#19 #15 or #16 or #17 or #18
#20 #14 and #19
#21 (child* or infant* or newborn* or paediatric* or pediatric* or toddler* or schoolchild* or “school child*”)
#22 #20 not #21
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects Health Technology Assessment
Date of search: 20 March 2013.
Search strategy
-
(phacoemulsif* or phakoemulsif* or capsulorhexis) (30)
-
(cataract* near (surg* or remov* or extract* or procedure* or operat* or excis* or aspirat* or incis* or implant*)) (165)
-
(pseudophaki* or pseudoaphaki* or phakectomy or phakectomies or “enzymatic zonulolysis” or “zonulolyses enzymatic” or “enzymatic zonulolyses” or “zonulolysis enzymatic”) (10)
-
(cataract* and (IOL* or “intraocula* lens*” or “intra ocula* lens*”)) (52)
-
(cataract near patient*) (35)
-
(cataract* and (endocapsula* or “endo capsula*” or extracapsula* or “extra capsula*” or capsulor* or capsulot*)) (20)
-
(PKE or PCIOL or ECCE or ICCE or MSICS or MISICS or SICS) (12)
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Cataract Extraction EXPLODE ALL TREES (80)
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Lens Implantation, Intraocular EXPLODE ALL TREES (32)
-
(#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9) (188)
-
(“second eye*”) (13)
-
(“fellow eye”) (8)
-
(#12 or #13) (18)
-
(#11 and #14) (9)
Appendix 3 Clinical effectiveness study selection worksheet
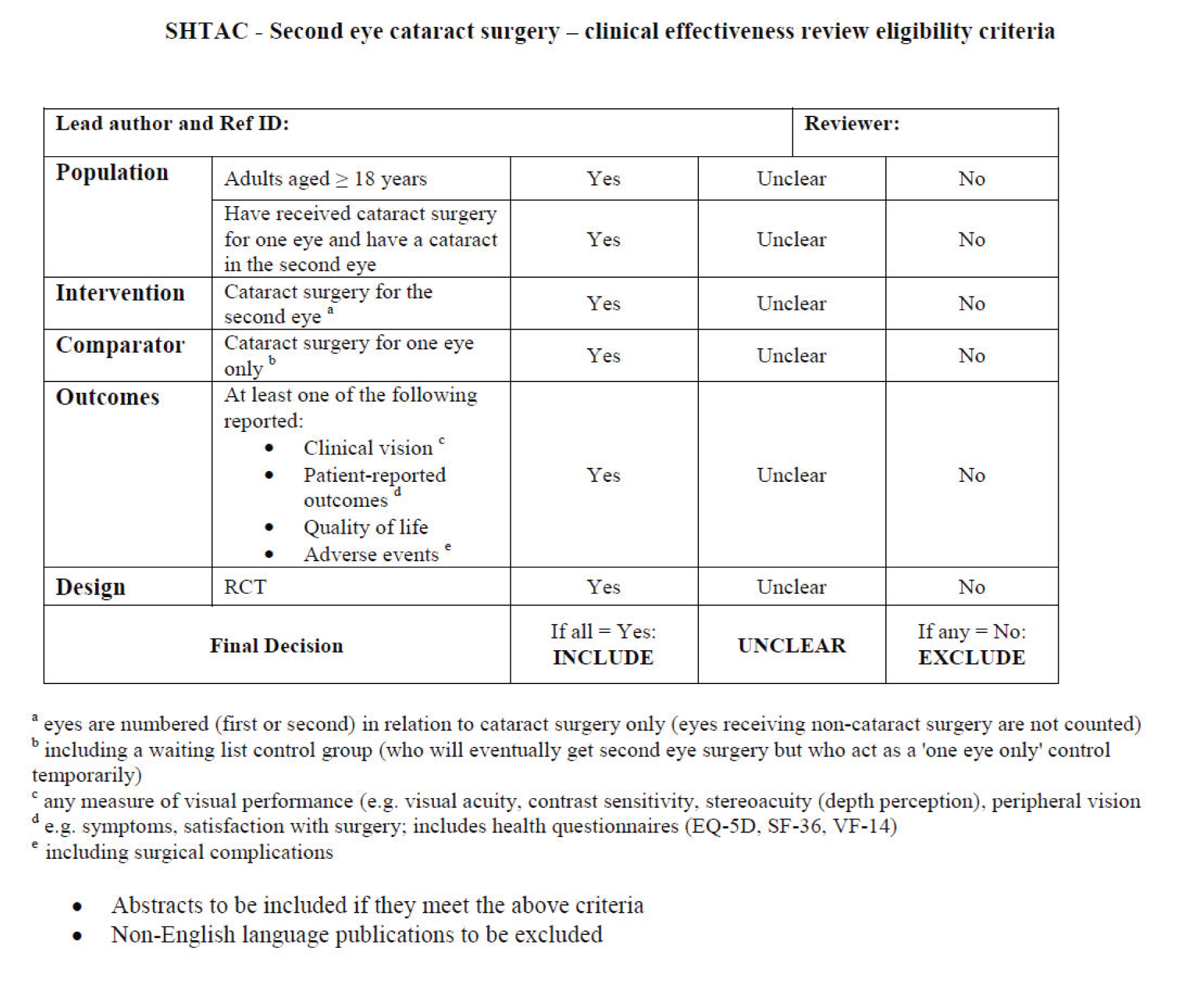
Appendix 4 Data extraction forms for clinical effectiveness studies
| Reviewer 1: PH | Reviewer 2: GF | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference and design | Technology | Participants | Outcome measures |
| Author: Castells et al.85 Publication year: 2006 Study year(s): 7/1999 – 7/2000 Study design: RCT Number of centres: 2 Country: Spain Sponsor: Catalan Agency for Health Technology Assessment and Research (CAHTAR) and the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (FIS) Trial name: none reported |
Intervention group: Both-eyes surgery (surgery in the first eye 1 to 2 months after enrolment and surgery in the second eye 2 to 4 months after first-eye surgery) (n = 148) Type of surgery: ambulatory surgery using a phacoemulsification technique (3-mm corneal incision without suture) – same procedure in both hospitals Duration of surgery: not reported Type(s) of lens: foldable lens Type(s) of anaesthetic: topical anaesthesia Number of surgeons/teams: not reported Comparator group: One-eye-only surgery (control, surgery to first eye only between 1 and 2 months after enrolling, offered second-eye surgery at end of study) (n = 148) Length of experience/training of surgeon(s): not reported Setting: ophthalmology departments in public teaching hospitals |
Number of participants: Eligible: not reported Randomised: 296 Pre-, peri- and post-operative therapy: not reported Inclusion criteria: scheduled for first-eye cataract surgery and presented bilateral indication for cataract surgery (visual acuity worse than 0.3 log-MAR in both eyes) Exclusion criteria: severe ocular comorbidity that would contraindicate surgery in both eyes (e.g. terminal glaucoma, amblyopia or prior strabismus surgery); undergoing surgery combined with any other ophthalmologic procedure (e.g. glaucoma or keratoplasty); experiencing complications of first-eye surgery that would contraindicate surgery in the fellow eye Baseline measurements: Gender male, n (%): Intervention: 57 (39) Comparator: 55 (37) Age (years), mean (SD): Intervention: 71.70 (9.07) Comparator: 72.03 (8.87) Ethnicity, n (%): not reported Weight (kg): not reportedCataract classification status: not reported Ocular comorbidities (not specified), n (%): Intervention: 34 (23.0) Comparator: 36 (24.3) Other comorbidities: not reported Losses to follow-up: Intervention: n = 9 (five withdrawals, four post-randomisation exclusions) Control: n = 13 (eight withdrawals, five post-randomisation exclusions) |
Primary outcomes:
|
| Outcome, mean (SD) | Intervention (n = 139) | Comparator (n = 135) | Difference (95% CI); p-valuep ≥ 0.05 unless specified | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baselinea | Follow-up | Baselinea | Follow-up | ||
| Primary clinical visual outcomes | |||||
| Binocular visual acuity, log-MAR | 0.54 (0.17) | 0.11 (0.10) | 0.56 (0.19) | 0.18 (0.17) | 0.07 (0.03 to 0.12); p < 0.001 |
| Decimal scale | 0.31 | 0.80 | 0.30 | 0.71 | |
| > 0.3 (= 0.5 decimal), n (%) | 3 (2.2) | 20 (14.8) | p < 0.001 | ||
| > 0.1 to ≤ 0.3, n (%) | 72 (51.8) | 79 (58.5) | |||
| ≤ 0.1 (= 0.8 decimal), n (%) | 64 (46.0) | 36 (26.7) | p < 0.001 | ||
| Change from baselinea (log-MAR) | −0.43 (0.18) | −0.38 (0.23) | 0.05 (−0.002 to 0.11) | ||
| Binocular contrast sensitivity, log-units | 1.14 (0.29) | 1.61 (0.1) | 1.13 (0.35) | 1.57 (0.18) | 0.04 (−0.002 to 0.09) |
| < 1.30, n (%) | 2 (1.4) | 10 (7.4) | |||
| ≥ 1.30 to < 1.70, n (%) | 77 (55.4) | 69 (51.1) | |||
| ≥ 1.70, n (%) | 60 (43.2) | 56 (41.5) | |||
| Change from baselinea (log-units) | 0.46 (0.32) | 0.44 (0.36) | 0.02 (−0.09 to 0.14) | ||
| Stereopsis, log-units | 2.86 (0.66) | 1.75 (0.24) | 2.89 (0.70) | 2.37 (0.69) | 0.62 (0.45 to 0.79); p < 0.001 |
| ≥ 3.48 (= 3000 seconds of arc), n (%) | 0 | 25 (18.5) | p < 0.001 | ||
| > 1.78 to < 3.48, n (%) | 42 (30.4) | 84 (62.2) | |||
| ≤ 1.78 (= 60 seconds of arc), n (%) | 96 (69.6) | 26 (19.3) | p < 0.001 | ||
| Change from baselinea (log-units) | −1.11 (0.69) | −0.51 (0.79) | 0.60 (0.36 to 0.85); p < 0.001 | ||
| Health-related quality of life | |||||
| Primary visual disability (VF-14), units | 58.08 (20.59) | 97.7 (7.1) | 61.01 (22.28) | 89.5 (15.9) | 8.24 (4.35 to 12.36); p < 0.001 |
| ≤ 80, n (%) | 5 (3.6) | 26 (19.3) | p < 0.001 | ||
| > 80 to < 100, n (%) | 31 (22.3) | 51 (37.8) | |||
| 100, n (%) | 103 (74.1) | 58 (43.0) | p < 0.001 | ||
| Change from baselinea | 39.9 (20.7) | 28.3 (20.4) | 11.57 (4.79 to 18.12); p < 0.001 | ||
| Other self-reported outcomes | |||||
| Trouble with vision score | 3.11 (0.89) | 1.17 (0.48) | 3.11 (0.91) | 1.58 (0.86) | 0.41 (0.17 to 0.64); p < 0.001 |
| Change in score from baselinea | −1.96 (1.03) | –1.53 (1.3) | 0.43 (0.06 to 0.81); p < 0.05 | ||
| No trouble with vision, n (%) | 120 (86.3) | 83 (61.5) | p < 0.001 | ||
| Satisfaction with vision score | 3.72 (0.53) | 1.13 (0.38) | 3.64 (0.60) | 1.53 (0.81) | 0.40 (0.20 to 0.61); p < 0.001 |
| Change in score from baselinea | −2.61 (0.62) | −2.10 (1.02) | 0.51 (0.23 to 0.79); p < 0.001 | ||
| Very satisfied, n (%) | 123 (88.5) | 84 (62.2) | p < 0.001 | ||
| Cataract Symptoms Score | 3.85 (3.14) | 0.12 (0.45) | 3.84 (3.43) | 0.78 (1.9) | 0.66 (0.21 to 1.11); p < 0.001 |
| Change in score from baselinea | −3.83 (3.13) | −3.17 (3.81) | 0.66 (−0.49 to 1.86) | ||
| General health status (SF-12) | |||||
| Physical | 45.57 (9.79) | 47.5 (9.3) | 44.82 (10.89) | 46.2 (9.3) | −1.30 (−4.40 to 1.85) |
| Change from baselinea | 1.76 (10.6) | 1.40 (9.2) | −0.36 (−3.56 to 3.04) | ||
| Mental | 48.51 (9.36) | 53.1 (4.9) | 48.23 (10.38) | 51.2 (6.6) | −1.90 (−3.79 to −0.03); p < 0.05 |
| Change from baselinea | 4.27 (10.2) | 2.96 (10.5) | −1.31 (−4.71 to 2.16) | ||
| Complications, adverse events and comorbidities | |||||
| Surgical complications | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | |
| Adverse events | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | |
| Ocular comorbidities, n (%) | 34 (23.0) | Not reported | 36 (24.3) | Not reported | |
| Other comorbidities | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | |
Allocation to treatment groups: randomised after first-eye surgery using a computerised minimisation algorithm with stratification by hospital, age (< 65 or ≥ 65 years) and pre-operative visual acuity (> 1 or ≤ 1 log-MAR).
Allocation concealment: patients were centrally randomised in a research unit (no further details).
Masking: masking for data analyst only.
Analysis by intention to treat: stated that final outcomes analysis performed on an ITT basis, however follow-up results reported without post-randomisation exclusions or drop-outs.
Comparability of treatment groups at baseline: groups similar on age, gender,% living alone, education achievement and % employed (no statistical comparison reported).
Method of data analysis: a subgroup analysis was planned according to age groups. Sociodemographic factors and primary outcome variables were compared at baseline. The final outcomes analysis compared 4–6 months post-operative visits between groups (after the second-eye surgery for the intervention group and after the first-eye surgery for the control group) on means of the final measure and on the change from baseline, as well as on three category groupings of the main outcome variables. Cut-off points were set at 0.3 and 0.1 log-MAR for visual acuity; at 1.30 and 1.70 for log-contrast sensitivity; at 3000 and 60 seconds of arc for stereopsis; and at 80 and 100 points for VF-14 scores. Non-parametric Mann–Whitney U-tests for quantitative variables and chi-squared tests for qualitative variables were used for comparisons. Non-parametric CIs for the differences in means between groups were calculated using the bootstrap method. A secondary analysis was performed upon post-operative VF-14 and binocular visual acuity of patients in the control group (surgery in one eye only – not data extracted).
Sample size/power analysis: sample size was calculated separately for patients aged < 65 and ≥ 65 years to detect clinically relevant differences in VF-14 and binocular visual acuity. With 296 patients (148 per treatment group; 36 younger and 112 older), the trial was able to detect a minimum relevant difference of 5 points (SD = 8 for younger and SD = 14 for older patients) in mean post-operative VF-14 and a minimum clinically relevant difference in post-operative visual acuity of one Snellen line (SD = 0.16 for younger and SD = 0.22 for older patients). The sample sizes took into account a significance level of 5%, a power of 80%, and an expected proportion of withdrawals of 15%.
Attrition/drop-out: intervention n = 5 (three lost to follow-up, two died), plus four post-randomisation exclusions (two developed comorbidity, two complication in the first-eye surgery); control n = 8 (two lost to follow-up, three expedited second-eye surgery, two switched to private sector and one died) plus five post-randomisation exclusions (two developed comorbidity, two complications in first-eye surgery and one developed senile dementia).
General commentsGeneralisability: limited to those with bilateral cataracts and only moderate refractive errors, majority aged > 65 years and of low education status.
Inter-centre variability: not reported.
Conflict of interests: not reported.
SD, standard deviation.
Risk of bias assessment (for guidance, refer to chapter 8 of the Cochrane Handbook)
| Domain | Judgement | Support for judgement |
|---|---|---|
| Random sequence generation? (Is the method used to generate the allocation sequence described in sufficient detail to allow an assessment of whether or not it should produce comparable groups?) | Low |
|
| Allocation concealment? (Is the method used to conceal the allocation sequence described in sufficient detail to determine whether intervention allocations could have been foreseen in advance of, or during, recruitment?) | Unclear | Comment: no information provided |
| Detection bias: masking of outcome assessors? (Which measures, if any, were used to mask outcome assessors from knowledge of which intervention a participant received? Was any information provided relating to whether or not the intended masking was effective?) | Unclear |
|
| Performance bias: masking of participants on self-reported outcomes? (Which measures, if any, were used to mask participants from knowledge of which intervention they received? Was any information provided relating to whether or not the intended masking was effective?) | High |
|
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? (How complete was the reporting of outcome data for each main outcome, including the numbers and reasons for attrition and exclusions from the analysis?) | Unclear | Comment: not all the reasons why patients were lost to follow-up were reported. The number of patients included in the review assessment excluded drop-out and additional post-randomisation exclusions. No statistical comparisons for results with and without drop-outs were reported. Authors stated that the final outcomes analysis was performed on an ITT basis, but the data do not support this |
| Free of selective reporting? (Is there any evidence that outcomes were measured but not reported, or were reported incompletely, or in an inappropriate format?) | Unclear | Comment: it is unclear if outcomes for the three category groupings, proportion of change due to surgery in one eye only and the second analysis of visual acuity by patient-reported visual disability post operatively (first-eye surgery) were planned a priori. Also, not stated whether the control and intervention groups were equally distributed between the two hospitals (i.e. whether different staff assessed each group) |
| Reviewer 1: PH | Reviewer 2: GF | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference and Design | Technology | Participants | Outcome measures |
| Author: Foss et al.83 Publication year: 2006 Study year(s): 2000–4 Study design: RCT Number of centres: 1 Country: UK Sponsor: The Health Foundation and former Trent Regional Health Authority Trial name: none reported |
Intervention group: Expedited surgery (target within a month) (n = 120) Type of surgery: small-incision cataract surgery (team A and C temporal clear cornea, team B superior clear cornea) Duration of surgery, mean phacoemulsification time: 56–87 seconds (team A 56 seconds, team B 87 seconds, team C 66 seconds) Type(s) of lens: folding silicone intraocular lens Type(s) of anaesthetic: local anaesthetic Number of surgeons/teams: three teams Comparator group: routine surgery (n = 119) (a ‘waiting list’ control group, target surgery within 13 months or the routine waiting time when this became less than 13 months) Length of experience/training of surgeon(s): not reported Setting: hospital ophthalmology department |
Number of participants: Eligible: 302 Randomised: 239 Pre-, peri- and post-operative therapy: none reported Inclusion criteria: women age > 70 years, had one successful cataract operation and a second operable cataract Exclusion criteria: complex cataracts (Fuchs corneal dystrophy, active intraocular inflammation, lens zonule dehiscence or lens instability), visual field defects, severe comorbid eye disease affecting visual acuity, those with memory problems preventing the completion of the lengthy questionnaires or reliable recall of falls Baseline measurements: Gender, n (%): 100% female Age (years), median: Intervention: surgery: 79.2 (range 70 to 90) Comparator: 79.9 (range 70 to 92) Ethnicity, n (%): not reported Weight (kg): not reported Cataract classification status: not reported Mini-mental state, mean (range): Intervention: 27 (range 10–30) Control: 27 (range 10–30) Ocular comorbidities: not reportedOther comorbidities, n/N (%): Heart problems Intervention: 39/120 (33) Control: 36/119 (30) Chest problems Intervention: 25/120 (21) Control: 23/119 (19) Arthritis Intervention: 91/120 (76) Control: 93/119 (78) Stroke Intervention: 10/120 (8) Control: 7/119 (6) Pervious fracture (any) Intervention: 57/120 (48) Control: 57/119 (48) Postural dizziness Intervention: 42/120 (35) Control: 28/119 (24) Postural hypotension Intervention: 19/120 (16) Control: 14/119 (12) Losses to follow-up, n/N (%): Intervention: = 5/120 (4.2) Comparator: = 16/119 (13.4) |
Primary outcome: number of patients experiencing a falla Secondary outcomes:
Methods of assessing outcomes:
|
| Outcome | Expedited surgery | Routine surgerya | Mean differenceb between groups at 6 months (95% CI); p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome: no. of patients with falls, n/N (%):Total no. of patients experiencing falling | 48/120 (40) | 41/119 (34) | Not reported | ||
| Number of patients experiencing first fall | 26/120 (22)c | 19/119 (16)c | Hazard ratio 1.06 (95% CI, 0.69 to 1.61), log rank test 0.06, 1 df; p = 0.80 | ||
| Number of patients experiencing > 1 fall | 22/120 (18) | 22/119 (18) | Hazard ratio 0.85 (95% CI, 0.49 to 1.56), log rank test 0.26, 1 df; p = 0.61 | ||
| Rate of falling per 1000 patient-days (range) | 2.9 (0 to 31) | 4.3 (0 to 120) | Rate ratio 0.68 (95% CI, 0.39 to 1.19); p = 0.18d | ||
| Fractures | 5/120 (4%) | 3/119 (3%) | Risk ratio 2.5 (95% CI, 0.5 to 12.5); Fisher’s exact test; p = 0.45 | ||
| Outcome | Expedited surgery | Routine surgerya | Mean differenceb between groups at 6 months (95% CI); p-value | ||
| Baseline | 6 months | Baseline | 6 months | ||
| Clinical visual outcomes (binocular), mean | |||||
| Unaided visual acuity (log-MAR) | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.23 | −0.04 (−0.01 to −0.08); p = 0.001 |
| Spectacles visual acuity (log-MAR) | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.09 | −0.04 (−0.01 to −0.06); p = 0.003 |
| Pinhole visual acuity (log-MAR) | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.09 | −0.06 (−0.03 to −0.09); p < 0.0005 |
| Change in median visual acuity in the operated eye (i.e. monocular), log-MAR | 0.44 | −0.02 | Not reported | ||
| Contrast sensitivity (Pelli–Robson, dB) | 1.45 | 1.60 | 1.42 | 1.50 | 0.09 (0.06 to 0.13); p < 0.0005 |
| Depth perception/5-point scale | 1.66 | 1.36 | 1.85 | 1.93 | −0.45 (−0.22 to −0.69); p < 0.0005 |
| Stereopsis (seconds of arc), n/N (%) | |||||
| 150 | 76/120 (63) | 100/115 (87) | 65/119 (55) | 67/113 (59) | |
| 300 | 22/120 (18) | 9/115 (8) | 27/119 (23) | 23/113 (20) | |
| 600 | 11/120 (9) | 4/115 (4) | 11/119 (9) | 10/113 (9) | |
| > 600 Wirt able | 9/120 (8) | 2/115 (2) | 12/119 (10) | 8/113 (7) | |
| > 600 Wirt unable | 2/120 (2) | 0/115 (0) | 4/119 (3) | 5/113 (4) | |
| health-related quality of life, mean | |||||
| Activity scale | 7.4 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 0.4 (−0.8 to 1.5); p = 0.53 |
| Confidence – Falls Efficacy Scale/100 | 85.5 | 86.1 | 84.4 | 81.7 | 3.6 (0.9 to 6.2); p = 0.008 |
| HADS – anxiety/28 | 6.4 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 7.1 | −0.2 (−1.0 to 0.5); p = 0.54 |
| HADS – depression/28 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.5 | 4.7 | −0.5 (−0.7 to 0.3); p = 0.47 |
| Barthel Index/20 | 18.7 | 18.7 | 18.9 | 18.8 | −0.1 (−0.2 to 0.3); p = 0.61 |
| VF-14 visual disability/100 | 87.5 | 94.7 | 87.5 | 87.2 | 7.5 (5.1 to 9.9); p < 0.0005 |
| London Handicap Scale/100 | 82.3 | 85.2 | 82.2 | 80.8 | 4.4 (2.2 to 6.5); p < 0.0005 |
| EuroQoL (EQ-5D)/1.0 | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.02 (−0.03 to 0.08); p = 0.36 |
| Other self-reported outcomes | |||||
| Surgical complications, n/N (%) | Expedited surgery | Routine surgerya | Mean differenceb (95% CI); p-value | ||
| Section stitched | 4/115 (3) | Not reported | |||
| Iris hooks | 1/115 (0.9) | Not reported | |||
| Iris damage | 1/115 (0.9) | Not reported | |||
| Endophthalmitis | 0/115 (0) | Not reported | |||
| Anterior vitrectomy performed | 4/115 (3) | Not reported | |||
| Posterior capsular opacification noted at 6 months | 12/115 (10) | Not reported | |||
| YAG capsulotomy performed during study period | 10/115 (9) | Not reported | |||
| Surgical complications by surgical approach, n/N (%) | Team A: temporal clear cornea | Team B: superior clear cornea | Team C: temporal clear cornea | ||
| Section stitched | 1/63 (1.6) | 3/38 (7.9) | 0/19 (0) | ||
| Iris hooks | 0/63 (0) | 0/38 (0) | 1/19 (5.3) | ||
| Iris damage | 0/63 (0) | 1/38 (2.6) | 0/19 (0) | ||
| Anterior vitrectomy performed | 1/63 (1.6) | 2/38 (5.3) | 1/19 (5.3) | ||
| Posterior capsular opacification at 6 months | 2/63 (3.2) | 8/38 (21.1) | 2/19 (10.5) | ||
| YAG capsulotomy performed during study period | 4/63 (6.4) | 4/38 (10.5) | 2/19 (10.5) | ||
| Expedited surgery | Routine surgerya | Mean differenceb (95% CI); p-value | |||
| Adverse events | Not reported | Not reported | |||
| Ocular comorbidities | Not reported | Not reported | |||
| Other comorbidities | Baseline data only | ||||
Surgical teams had different workloads, team A completed 63 cases, team B 38 cases and team C 19 cases (temporal clear cornea cases n = 82, superior clear cornea cases n = 38).
While no cataract classification was reported, authors suggest that the cataracts operated on were less severe than those of a comparable study. 84
Authors suggest that as a result of high baseline ratings for some measures (30% of scores on the London Handicap Scale, 50% on the Falls Efficacy Scale and VF-14 visual disability scale were above 90% of the scale maximum), there was limited scope for measuring further improvements. Similarly binocular visual acuity and contrast sensitivity were already good at baseline: limited scope for improvement.
Methodological commentsAllocation to treatment groups: randomisation was from lists prepared by one of the authors from random numbers, in variably sized, permuted blocks to maintain approximate equality in the size of the groups.
Allocation concealment: allocation was concealed in sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes that were opened after consent was obtained and baseline assessment made.
Masking: assessment (after baseline) was not masked to allocation.
Analysis by intention to treat: stated that all analyses were ITT, but ITT not defined in terms of sample size.
Comparability of treatment groups at baseline: groups were reported to be well matched at baseline (no statistical comparison reported), although poor vision (proportion with Snellen acuity worse than 6/12) was higher in the expedited surgery group (8%) compared with the routine surgery group (3%). However, frequency of postural dizziness was more than 10% higher in the expedited surgery group compared with the routine surgery group (n = 42/120 vs. 28/119, respectively).
Method of data analysis: primary analysis was a comparison of the rate of falling (total number of falls/number of days in the trial). Negative binomial regression was used for statistical testing and to generate CIs around the rate ratio as falls in the same patient are not statistically independent events. Observation time for routine surgery patients was up to a final assessment, scheduled about a week before surgery (including surgery performed before 12 months of follow-up was complete). For both first and second falls, a Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was used to compare the proportions of participants falling (regardless of the number of falls they have) and to estimate relative risk. Participants reaching the end of observation without experiencing a fall, and those withdrawing or having out-of-trial early surgery, were censored. The proportions of participants experiencing fractures were also compared. Health gains were assessed by comparing changes in visual functions, activity, anxiety, depression, confidence, disability, handicap and quality-of-life measures between operated and control groups using linear regression to adjust for baseline imbalances. The relative size of differences in health status measures was compared using the effect size (mean change/initial SD).
Sample size/power analysis: the expected prevalence of falls was 50%. A one-third reduction in participants falling, giving a difference of 16% between the two groups, was taken to be clinically significant. To have an 80% chance of detecting this at 95% confidence required 160 patients in each arm, giving a trial size of 320. Authors state that due to a reduction in waiting time to less than 6 months for routine surgery, it was impractical and unethical for the trial to continue and leaving it under-powered (n = 239).
Attrition/drop-out: expedited surgery n = 5. At: 3 months n = 2 (one ill health, one other), 6 months n = 1 (withdrew), 9 months n = 2 (one died, one withdrew) and 12 months n = 0.
Routine surgery: n = 16. At: 3 months n = 3 (1 withdrew, 2 non-trial surgery), 6 months n = 3 (1 died, 2 withdrew), 9 months n = 2 (1 died, 1 non-trial surgery) and 12 months n = 8 (4 withdrew, 4 non-trial surgery)
General commentsGeneralisability: limited to women aged over 70 years with age-associated comorbidities and bilateral cataracts.
Inter-centre variability: not applicable.
Conflict of interests: reported as none.
SD, standard deviation.
Risk of bias assessment (for guidance refer to chapter 8 of the Cochrane Handbook)
| Domain | Judgement | Support for judgement |
|---|---|---|
| Random sequence generation? (Is the method used to generate the allocation sequence described in sufficient detail to allow an assessment of whether or not it should produce comparable groups?) | Unclear |
|
| Allocation concealment? (Is the method used to conceal the allocation sequence described in sufficient detail to determine whether intervention allocations could have been foreseen in advance of, or during, recruitment?) | Low |
|
| Detection bias: masking of outcome assessors? (Which measures, if any, were used to mask outcome assessors from knowledge of which intervention a participant received? Was any information provided relating to whether or not the intended masking was effective?) | High | Comment: stated ‘assessment (after baseline) was not masked to allocation’ |
| Performance bias: masking of participants on self-reported outcomes? (Which measures, if any, were used to mask participants from knowledge of which intervention they received? Was any information provided relating to whether or not the intended masking was effective?) | High | Comment: stated ‘assessment (after baseline) was not masked to allocation’ |
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? (How complete was the reporting of outcome data for each main outcome, including the numbers and reasons for attrition and exclusions from the analysis?) | Unclear |
Attrition rates differed between groups (expedited surgery n = 5, 4%; routine surgery n = 16, 13%); reasons incompletely reported but stated that seven of the 16 drop-outs from routine surgery went on to receive non-trial surgery (not defined but assumed by reviewers to mean second-eye cataract surgery). Unclear whether this would have led to a prognostic imbalance between the study groups |
| Free of selective reporting? (Is there any evidence that outcomes were measured but not reported, or were reported incompletely, or in an inappropriate format?) | Unclear | Comment: unable to establish without a protocol. Unclear whether list of surgical complications complete |
| Reviewer 1: PH | Reviewer 2: GF | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference and design | Technology | Participants | Outcome measures |
| Author: Laidlaw et al.84 Publication year: 1998 Study year(s): 1994–1995 Study design: RCT Number of centres: 1 Country: UK Sponsor: Wellcome Trust Trial name: none reported |
Intervention group: Expedited surgery (target within 6 weeks) (n = 105) Type of surgery: not reported Duration of surgery: not reported Type(s) of lens: not reported Type(s) of anaesthetic: not reported Number of surgeons/teams: not reported Comparator group: routine surgery (target 7–12 months) (n = 103) Length of experience/training of surgeon(s): not reported Setting: eye hospital |
Number of participants: Eligible: 350 Randomised: 208 Pre-, peri- and post-operative therapy: post-operative rehabilitation based on a treatment schedule (no further details) Inclusion criteria: awaiting second-eye cataract surgery, unilateral cataract and uncomplicated contralateral pseudophakia with corrected Snellen visual acuity of at least 20/40 in the pseudophakic eye, absence of other visually significant ophthalmic pathology affecting either eye, ability to understand questionnaires Exclusion criteria: patients with ocular comorbidities were excluded Baseline measurements: Gender male, n (%): Intervention: 40 (38) Comparator: 40 (39) Age (years), mean (range): Intervention: 76 (52–97) Comparator: 76 (41–93) Ethnicity, n (%): not reported Weight (kg): not reported Cataract classification status: not reported Ocular comorbidities: not reported Other comorbidities: not reported Losses to follow-up: Intervention: n = 7 Comparator: n = 9 |
Primary outcomes:
Methods of assessing outcomes:
|
| Outcome | Expedited surgery | Routine surgery | Difference (control – expedited surgery; 95% CI); p-valuea | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline(n = 105) | 6 months(n = 98) | Baseline(n = 103) | 6 months(n = 94) | ||
| Primary clinical visual outcomes, mean (SD) | |||||
| Binocular mean distance log-MARb | 0.022 (0.101) | −0.027 | 0.063 (0.127) | 0.052 | 0.063 (0.035 to 0.090)c; p < 0.0001 |
| Binocular mean near-reading log-MARc | 0.28 (0.13) | 0.23 | 0.29 (0.13) | 0.27 | 0.047 (0.017 to 0.077)b; p < 0.0029 |
| Binocular mean Pelli–Robson contrast sensitivityc | 1.56 (0.15) | 176 | 1.53 (0.16) | 1.54 | −0.21 (−0.25 to −0.17)b; p < 0.0001 |
| Stereoacuity, 3000 seconds of arc or worse,d n/N (%) | 64/105 (61) | 12/98 (12) | 73/103 (71) | 66/94 (70) | 58% (47 to 69%); p < 0.0001 |
| Monocular log-MAR acuity, mean difference (control – expedited surgery). Analysis of covariance adjusting for baseline differences (unspecified) | |||||
| Initially pseudophakic eye | Not reported | Not reported | 0.025 (−0.004 to 0.054) | ||
| Initially cataractous eye | Not reported | Not reported | 0.756 (0.650 to 0.861) | ||
| health-related quality of life | |||||
| HRQoL | Not reported | Not reported | |||
| Primary self-reported outcomes, n/N (%) | |||||
| Q2 – at least some difficulty reading normal print | 36/105 (35) | 6/98 (6) | 34/103 (34) | 33/94 (36) | 30% (19 to 41%); p < 0.0001 |
| Q5 – eyesight preventing activities most or all of the time | 11/105 (10) | 0 | 9/103 (9) | 10/94 (11) | 11% (4.4 to17%); p < 0.0001 |
| Q11 – below average overall vision | 15/105 (14) | 0 | 17/103 (17) | 17/94 (18) | 18% (10 to 26%); p < 0.0001 |
| Q30 – eyesight interfering with life quite a lot or a great deal | 27/105 (26) | 1/98 (1) | 26/103 (25) | 24/94 (26) | 25% (15 to 34%); p < 0.0001 |
| Complications, adverse events and comorbidities | |||||
| Surgical complications, sight threatening or requiring further surgery | n = 9/98 (9%), 11 complications | Not reported | |||
| Vitreous loss | 2 | Not reported | |||
| Retinal detachment | 1 | Not reported | |||
| Cystoid macular oedema | 3 | Not reported | |||
| Iris prolapse | 3 | Not reported | |||
| Corneal oedema | 1 | Not reported | |||
| Implant failure with subsequent secondary lens implantation | 1 | Not reported | |||
| Adverse events | Not reported | Not reported | |||
| Ocular comorbidities | Not reported | Not reported | |||
| Other comorbidities | Not reported | Not reported | |||
Allocation to treatment groups: random allocation was on a 1/1 basis in blocks of 20. Method of generating random sequence not stated.
Allocation concealment: used numbered sealed opaque envelopes produced by members of the research team not in contact with patients.
Masking: none reported.
Analysis by ITT: authors state that groups were compared at review on an ITT basis. Results were reported without drop-outs.
Comparability of treatment groups at baseline: sociodemographic (only age and gender reported) and primary outcomes were broadly similar between groups apart from mean binocular distance log-MAR. Authors state that the difference of mean binocular distance log-MAR is equivalent to less than half a Snellen line (no statistical comparison reported). There were also some baseline differences in subjective vision between the groups. Baseline data for other secondary outcomes were not reported.
Method of data analysis: the distributions of several variables (sociodemographic factors, monocular visual acuity and primary outcome variables) were compared at randomisation. Simple comparisons of the variables at the time of the review were done with chi-squared, Mann-Whitney U-, and t-tests as appropriate, together with relevant 95% CI for differences between the groups. For the quantitative outcomes, analyses of covariance were used to adjust for baseline differences. For the (ordinal) questionnaire items, simple differences (review-baseline) between the two groups were compared by the Mann-Whitney U-test. No correction for multiple testing was applied to the eight primary outcomes. For the 39 secondary outcomes a Bonferroni correction, which maintains a 5% overall significance level, would indicate that test-wise p-values should only be regarded as significant if they fell below 0.0013. Authors reported that many of the visual-acuity assessments were positively skewed, but suggested that numbers in the two groups were large enough to allow parametric analyses for outcome comparisons.
Sample size/power analysis: stated only that with sample sizes of about 100 in each group, the trial was able to detect differences of 15–20% in the proportions reporting various symptoms between the two groups, with 80% power and a two-sided 5% significance level.
Attrition/drop-out: expedited surgery – one did not receive as allocated (did not receive early eye surgery due to an administrative error), seven lost to follow-up (reasons not reported); routine surgery – one did not receive as allocated (underwent second-eye surgery), nine lost to follow-up (reasons not reported).
General commentsGeneralisability: limited to those with bilateral cataracts who had undergone successful cataract surgery in one eye and had no other visually significant ocular pathology in either eye.
Inter-centre variability: not applicable.
Conflict of interests: not reported.
Risk of bias assessment (for guidance refer to chapter 8 of the Cochrane Handbook)
| Domain | Judgement | Support for judgement |
|---|---|---|
| Random sequence generation? (Is the method used to generate the allocation sequence described in sufficient detail to allow an assessment of whether or not it should produce comparable groups?) | Unclear |
|
| Allocation concealment? (Is the method used to conceal the allocation sequence described in sufficient detail to determine whether intervention allocations could have been foreseen in advance of, or during, recruitment?) | Low |
|
| Detection bias: masking of outcome assessors? (Which measures, if any, were used to mask outcome assessors from knowledge of which intervention a participant received? Was any information provided relating to whether or not the intended masking was effective?) | Unclear | Comment: none reported |
| Performance bias: masking of participants on self-reported outcomes? (Which measures, if any, were used to mask participants from knowledge of which intervention they received? Was any information provided relating to whether or not the intended masking was effective?) | High |
|
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? (How complete was the reporting of outcome data for each main outcome, including the numbers and reasons for attrition and exclusions from the analysis?) | Unclear | Comment: reasons why patients were lost to follow-up were not reported. Authors state that the two patients that did not receive the allocated treatment (one in each group) had a review assessment, but do not explain how the data were dealt with, as one patient in the control group received surgery and one in the expedited group did not. The number of patients included in the review assessment excluded drop-out. No statistical comparisons for results with and without drop-outs were reported. Authors stated that results were compared at review on an ITT basis, but ITT was not defined |
| Free of selective reporting? (Is there any evidence that outcomes were measured but not reported, or were reported incompletely, or in an inappropriate format?) | High | Comment: subjective vision questionnaire not mentioned in the method section, limited data for secondary outcomes reported and responses to two questions related to vision in the right and left eyes were recoded. Stated no difference between groups in change in primary questions scores from baseline but data were not reported |
Appendix 5 List of potentially relevant clinical effectiveness abstracts
Castells X, Comas M, Espallargues M, Castilla M, Garcia-Arumi J, Alonso J. Benefits of cataract surgery in both eyes compared to surgery only in the first eye. A randomized controlled trial. International Society of Technology Assessment in Health Care, 17th Annual Meeting; Building Bridges Between Policy, Providers, Patients and Industry, 3–6 June 2001, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Laidlaw D, Whitaker A, Hopper C, Marsh G, Donovan J, Peters T, et al. Results of a multi disciplinary randomised controlled trial of the benefits of second-eye cataract surgery: Changes in visual symptoms and function. Invest Opthalmol Vis Sci 1996;37:ARVO.
Whitaker A, Laidlaw D, Hopper C, Donovan J, Sparrow J, Harrad R. Improvement in stereoacuity after second-eye cataract extraction: Subjective and objective assessment in a randomised controlled trial. Invest Opthalmol Vis Sci 1996;37:ARVO.
Appendix 6 List of excluded full-text clinical effectiveness papers
| Reference | Reason(s) for exclusiona |
|---|---|
| Anstey KJ, Lord SR, Hennessy M, Mitchell P, Mill K, von Sanden C. The effect of cataract surgery on neuropsychological test performance: a randomized controlled trial. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2006;12:632–9 | P, I, C |
| Bardocci A, Ciucci F, Lofoco G, Perdicaro S, Lischetti A. Pain during second-eye cataract surgery under topical anesthesia: an intraindividual study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2011;249:1511–14 | P, D |
| Bellucci R, Pucci V, Morselli S, Bonomi L. Secondary implantation of angle-supported anterior chamber and scleral-fixated posterior chamber intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg 1996;22:247–52 | P, I, C, D |
| Boezaart A, Berry R, Nell M. Topical anesthesia versus retrobulbar block for cataract surgery: the patients’ perspective. J Clin Anesth 2000;12:58–60 | P, I, C |
| Lane SS, Javitt JC, Nethery DA, Waycaster C. Improvements in patient-reported outcomes and visual acuity after bilateral implantation of multifocal intraocular lenses with +3.0 diopter addition: multicenter clinical trial. J Cataract Refract Surg 2010;36:1887–96 | P, I, C, D |
| Mitsonis CI, Mitropoulos PA, Dimopoulos NP, Mitsonis MI, Andriotis NM, Gitsa OE, et al. Anxiety and depression in cataract surgery: a pilot study in the elderly. Psychol Reports 2006;99:257–65 | D |
| Sach TH, Foss AJ, Gregson RM, Zaman A, Osborn F, Masud T, et al. Second-eye cataract surgery in elderly women: a cost-utility analysis conducted alongside a randomized controlled trial. Eye 2010;24:276–83 | O |
| Talbot EM, Perkins A. The benefit of second-eye cataract surgery. Eye 1998;12:983–9 | D |
| Wormald R. Second-eye cataract surgery was beneficial in otherwise healthy patients. Evidence-Based Med 1999;4:86 | D |
Appendix 7 Data extraction forms for cost-effectiveness studies
1 Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
1.1 Health technology
Second-eye cataract surgery.
1.2 Interventions and comparators
What interventions/strategies were included?
Second-eye cataract surgery.
Was a no treatment/supportive care strategy included?
Yes. Unilateral pseudophakia.
Describe interventions/strategies
As above.
1.3 Research question
What are the stated objectives of the evaluation?
To perform a reference case cost–utility analysis of second-eye cataract surgery.
1.4 Study type
Cost-effectiveness/cost–utility/cost–benefit analysis?
Cost–utility.
1.5 Study population
What definition was used for [condition]? What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
722 patients from the US National Cataract PORT study, who were undergoing a cataract extraction (median age 73 years).
1.6 Institutional setting
Where is/are the intervention(s) being evaluated usually provided?
Not reported, but assumed to be secondary care.
1.7 Country/currency
Has a country setting been provided for the evaluation? What currency are costs expressed in and does the publication give the base year to which those costs relate?
1.8 Funding source
Supported in part by the Retina Research and Development Fund, Philadelphia (PA), USA, the Principals Initiative Research Award, Kingston, Canada, and the Premier’s Award for Research Excellence, Kingston, Canada.
1.9 Analytical perspective
What is the perspective adopted for the evaluation (health service, health and Personal Social Services, third-party payer, societal (i.e. including costs borne by individuals and lost productivity)?
The analysis was performed from the perspective of a third-party insurer.
2 Effectiveness
Were the effectiveness data derived from: a single study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion? Give the definition of treatment effect used in the evaluation. Give the size of the treatment effect used in the evaluation.
Visual acuity data for patients undergoing cataract extraction were taken from the report of the US National Cataract PORT. The post-operative visual acuity of the second-eye surgery was assumed to be equal to that of the first eye, i.e. 20/27.
Complication rates associated with cataract extraction were taken from a previous study for initial cataract surgery. 96 Complications included in the model were PCO, endophthalmitis, cystoid macular oedema, lost lens fragments, intraocular lens dislocation, pseudophakic bullous keratopathy, and PCO with subsequent retinal detachment.
3 Intervention costs
Were the cost data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion? Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)? List the direct intervention costs and other direct costs used in the evaluation – include resource estimates (and sources for these estimates, if appropriate) as well as sources for unit costs used.
The health-care costs associated with each of the primary costs of cataract surgery and the costs of defined cataract complications were derived from multiple sources.
The costs of ambulatory procedures and surgical procedures were obtained from US Medicare statistics for 2001 (reference no longer available). Drug expenditure costs associated with cataract surgery, including the medical and post-operative managements, were obtained from the 2001 Drug Topics Red Book. 120 When multiple evidence-based treatment options were available for management of complications associated with cataract surgery, an estimate of the costs for a certain complication was derived from the weighted average of the costs relating to each treatment option.
3.1 Indirect costs (costs due to lost productivity, unpaid inputs to patient care)
Were indirect costs included?
No.
4 Health state valuations/utilities (if study uses quality-of-life adjustments to outcomes)
Were the utility data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion. Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Utility values were based on data from a large study of patients with ophthalmic disease. 98 Utility values were derived from patient preferences by using a TTO model. Utility values associated with subsequent good visual acuity in both eyes after uneventful cataract extraction were based on a study that compared the utility change from unilateral good vision (i.e. 20/25 or better in one eye) vs. bilateral good vision (i.e. 20/25 or better vision in both eyes). 99
4.1 List the utility values used in the evaluation
For the Busbee study,92 the utility value corresponding to unilateral pseudophakia was 0.858. The reference case utility value for an ocular health state after second-eye cataract surgery was 0.967. These visual outcomes for each complication after treatment, with the exception of PCO, were assigned a utility value of 0.858. For PCO without retinal detachment, it was assumed that visual acuity returned to 20/27 in the operated eye, and had a utility value of 0.97.
The Brown study93 uses slightly different utility values to those in Busbee and colleagues. 92 The mean utility associated with cataract surgery and 20/27 vision in one eye (with vision ≤ 20/40 in the second eye) is 0.86. The mean utility when the visual acuity is 20/27 in both eyes is 0.97.
5 Modelling
If a model was used, describe the type of model used (e.g. Markov state transition model, discrete event simulation). Was this a newly developed model or was it adapted from a previously reported model? If an adaptation, give the source of the original. What was the purpose of the model (i.e. why was a model required in this evaluation)? What are the main components of the model (e.g. health states within a Markov model)? Are sources for assumptions over model structure (e.g. allowable transitions) reported – list them if reported.
A decision tree model was developed in TreeAge (TreeAge Software, Inc., Williamstown, MA, USA). The model incorporated costs and consequences associated with second-eye cataract surgery compared with unilateral pseudophakia (20/27), including complications associated with cataract surgery (over 4 months).
It was assumed that the theoretical patient presented with visual acuity in the pseudophakia eye equal to the mean post-operative visual acuity reported by the PORT study, and that the post-operative visual acuity for the second-eye surgery was equal to that of the first-eye surgery (20/27).
5.1 Extract transition probabilities for [natural history/disease progression] model and show sources (or refer to table in text)
Posterior capsule opacification occurs at a rate of 28% over a five year post-operative period. The mean time of treatment after surgery was assumed to be 2 years. Retinal detachment was assumed to occur at a rate of 0.81% after cataract surgery, at a mean time of 1 year after surgery. Retinal detachment repair after treatment of PCO occurred three years after cataract surgery. Intraocular lens dislocation was assumed to occur at a rate of 1.1% after cataract extraction.
Pseudophakic bullous keratopathy was assumed to occur at a rate of 0.3%, with a mean time to post-operative treatment of 1 year after cataract extraction. PCO with subsequent retinal detachment was assumed to occur at a 3.9-fold increase from the cumulative retinal detachment rate of 0.81%.
5.2 What is the model time horizon?
Lifetime.
5.3 What, if any, discount rates have been applied in the model? Same rate for costs and outcomes?
An annual discount rate of 3% was used for costs and benefits.
6 Results/analysis
What measure(s) of benefit were reported in the evaluation?
QALYs.
6.1 Provide a summary of the clinical outcome/benefits estimated for each intervention/strategy assessed in the evaluation
In the Busbee study,92 second-eye cataract surgery resulted in 1.308 QALYs gained. Discounting the QALYs gained by an annual 3% rate resulted in 0.92 QALYs gained over 12 years.
In the Brown study,93 second-eye cataract surgery resulted in 1.2 QALYs gained. Discounting the QALYs gained by an annual 3% rate resulted in 0.9954 QALYs gained over 12 years.
6.2 Provide a summary of the costs estimated for each intervention/strategy assessed in the evaluation
6.3 Synthesis of costs and benefits – are the costs and outcomes reported together (e.g. as cost-effectiveness ratios)? If so, provide a summary of the results
6.4 Give results of any statistical analysis of the results of the evaluation
Not applicable.
6.5 Was any sensitivity analysis performed – if yes, what type(s) [i.e. deterministic (one-way, two-way, etc.) or probabilistic]
One-way sensitivity analysis. 92
6.6 What scenarios were tested in the sensitivity analysis? How do these relate to structural uncertainty (testing assumptions over model structure such as relationships between health states), methodological uncertainty (such as choices of discount rate or inclusion of indirect costs) or parameter uncertainty (assumptions over values of parameters in the model, such as costs, quality of life or disease progression rates)?
One-way sensitivity analysis was performed by varying utility values, costs, and discounting rates. 92
6.7 Give a summary of the results of the sensitivity analysis – did they differ substantially from the base case analysis. If so, what were the suggested causes?
Increasing discounted costs by 25% resulted in $3408 per QALY gained (Busbee and colleagues, 2003),92 whereas decreasing the costs by 25% resulted in $2045 per QALY gained. When all utility values were increased by 25%, the cost-effectiveness was $2182 per QALY gained. By decreasing all utility values by 25%, the cost-effectiveness was $3646 per QALY gained. Varying the annual discount rate resulted in $1918 per QALY gained for a 0% rate, $3445 per QALY gained for a 5% rate, and $5964 per QALY gained for a 10% rate.
7 Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
The authors concluded that second-eye cataract surgery is an extremely cost-effective procedure.
7.1 What are the implications of the evaluation for practice?
Not reported.
8 SHTAC commentary
Selection of comparators:
Appropriate, based upon a US cataract study.
Validity of estimate of measure of benefit:
Appropriate, although not based upon systematic review. Utility values taken from a study of patients with ophthalmic disease not specifically just cataracts. They also assume the same visual acuity benefit from the second-eye surgery as for the first eye, and it is unclear how valid this assumption is.
Validity of estimate of costs:
Appropriate, all costs appear to have been included (US health care).
1 Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Räsänen and colleagues (2006). 90
1.1 Health technology
Second-eye cataract surgery.
1.2 Interventions and comparators
What interventions/strategies were included?
Cataract surgery.
Was a no treatment/supportive care strategy included?
Yes – described as a ‘hypothetical situation of no treatment’ using age and sex matched controls from the general population based on data from a nation-wide survey.
Describe interventions/strategies.
Group A – only one eye was operated (n = 87).
Group B – both eyes were operated during the follow-up (n = 73).
Group C – first eye had been operated earlier, now the second eye was operated (n = 59).
Group C is of most relevance to this HTA as it allows a comparison between first and second-eye surgery. Data for all groups are extracted here for completeness.
1.3 Research question
What are the stated objectives of the evaluation?
To evaluate the cost-utility of cataract surgery compared with a hypothetical situation of no treatment by studying unselected patients referred by practicing ophthalmologists for a routine cataract operation to a large university clinic because of objective signs of poor visual acuity.
1.4 Study type cost-effectiveness/cost–utility/cost–benefit analysis?
Cost–utility.
1.5 Study population
What definition was used for [condition]? What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
386 patients scheduled for routine cataract operation (219 available for final analysis). Mean age varied from 69 to 75 years across the three subgroups. Percentage female varied from 56 to 71 years across the groups.
Patients with no or only minor subjective pre-operative seeing problems at baseline (levels 1 and 2 of the seeing dimension of the 15D): n = 140 (64%).
Patients with significant subjective pre-operative seeing problems at baseline (levels 3 to 5 of the seeing dimension of the 15D): n = 79 (36%).
Compared with age- and gender-matched general population based on data from a nationwide survey, cataract patients were pre-operatively statistically significantly worse off on the dimensions seeing, moving, sleeping, usual activities, depression and distress, but better off on the dimension of mental function.
Best corrected visual acuity in the surgical eye and the non-surgical eye prior to cataract surgery in groups A–C: group A, group B, group C, respectively.
Mean (SD) best corrected visual acuity in the surgical eye:
Snellen 0.19 (0.14); 0.17 (0.12); 0.24 (0.14)
Log-MAR 0.98 (0.66); 0.94 (0.49); 0.76 (0.48)
Differences between the groups (A, B, C) not statistically significant.
Mean (SD) best corrected visual acuity in the non-surgical eye:
Snellen 0.58 (0.23); 0.28 (0.16); 0.63 (0.25)
Log-MAR 0.29 (0.22); 0.65 (0.37); 0.25 (0.21)
A versus B p < 0.001
B versus C p < 0.001.
SD, standard deviation.
1.6 Institutional setting where is/are the intervention(s) being evaluated usually provided?
Helsinki University Eye Hospital.
1.7 Country/currency
Has a country setting been provided for the evaluation? What currency are costs expressed in and does the publication give the base year to which those costs relate?
Finland is the country where the study was set. The currency is euros and the cost data were from 2002–3 (to coincide with when effectiveness data were collected).
1.8 Funding source
Funded by research grants from the Helsinki and Uusimaa Hospital Group.
1.9 Analytical perspective
What is the perspective adopted for the evaluation (health service, health and personal social services, third-party payer, societal (i.e. including costs borne by individuals and lost productivity)?
Perspective of the secondary health-care provider.
2 Effectiveness
Were effectiveness data derived from: a single study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion? Give the definition of treatment effect used in the evaluation. Give the size of the treatment effect used in the evaluation.
Effectiveness was estimated from the 15D generic 15-dimensional, standardised HRQoL instrument. Patients completed the 15D at baseline and then again approximately 6 months after the cataract operation.
Best corrected visual acuity was measured before the operation in both eyes by Snellen notation at 6 metres. Best corrected visual acuity was not measured after surgery but the authors suggest that they have no reason to doubt it would have improved in most of the patients.
The only statistically significant increase in the individual dimensions of the 15D was for ‘seeing’, observed across all three subgroups.
Changes in utility scores for the individual domains are presented according to severity of HRQoL (levels 1 and 2 vs. levels 3 to 5 of the scoring dimension). They are given for the whole study rather than the three subgroups and, therefore, data have not been extracted.
3 Intervention costs
Were the cost data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion? Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)? List the direct intervention costs and other direct costs used in the evaluation – include resource estimates (and sources for these estimates, if appropriate) as well as sources for unit costs used.
Direct health-care costs were obtained from the Ecomed® clinical patient administration system (Datawell Ltd, Espoo, Finland), where all costs of treatment of individual patients in the hospital are routinely stored. Costing covered all relevant specialty-related costs including pre- and post-operative outpatient visits to the eye hospital. However, the costs of the visits to the referring ophthalmologists who were usually also responsible for the post-operative re-examination of the patients and prescription of eyeglasses, was not included in the analysis. Indirect costs, like period of disability, were not included.
Mean (SD) hospital costs at 6 months:
Group A = €1318 (184)
Group B = €2289 (266)
Group C = €1323 (361)
Whole sample = €1261 (246).
No other cost or resource estimates reported.
SD, standard deviation.
Indicate the source for individual cost values (if appropriate).
3.1 Indirect costs (costs due to lost productivity, unpaid inputs to patient care)
Were indirect costs included:
Not included.
4 Health state valuations/utilities (if study uses quality-of-life adjustments to outcomes)
Were the utility data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion. Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
As above under ‘2 Effectiveness’, HRQoL was estimated directly through patients completing the 15D questionnaire before and after surgery.
The generic, 15-dimensional, standardised, self-administered HRQoL instrument can be used both as a profile and a single index utility score measure. The 15D questionnaire consists of 15 dimensions: moving, seeing, hearing, breathing, sleeping, eating, speech, eliminating, usual activities, mental function, discomfort and symptoms, depression, distress, vitality and sexual activity. For each dimension, the respondent must choose one of the five levels that best describes his/her state of health at the moment (the best level = 1; the worst level = 5). The valuation system of the 15D is based on an application of the multiattribute utility theory. A set of utility or preference weights, elicited from the general public through a three-stage valuation procedure, is used in an additive aggregation formula to generate the utility score, i.e. the 15D score (single index number) over all the dimensions. The maximum score is 1 (no problems on any dimension), and minimum score 0 (equal to being dead). In most of the important properties the 15D compares favourably with other instruments of that kind (references given).
The HRQoL gain was assumed to last till the end of the remaining statistical life expectancy of each patient based on life tables from 2002 from Statistics Finland.
4.1 List the utility values used in the evaluation
Whole sample, mean (SD)
HRQoL baseline = 0.82 (0.13)
HRQoL 6 months = 0.83 (0.14)
HRQoL difference = 0.01
p-value not stated, but reported to be statistically insignificant.
Group A, mean (SD)
HRQoL baseline = 0.85 (0.13)
HRQoL 6 months = 0.85 (0.14)
HRQoL difference = 0.00 (0.14); p = 0.852.
Group B, mean (SD)
HRQoL baseline = 0.80 (0.13)
HRQoL 6 months = 0.83 (0.14)
HRQoL difference = 0.03 (0.14); p = < 0.001.
Group C, mean (SD)
HRQoL baseline = 0.82 (0.11)
HRQoL 6 months = 0.81 (0.13)
HRQoL difference = –0.01 (0.07); p = 0.279.
SD, standard deviation.
Indicate the source for individual cost values (if appropriate).
5 Modelling
If a model was used, describe the type of model used (e.g. Markov state transition model, discrete event simulation). Was this a newly developed model or was it adapted from a previously reported model? If an adaptation, give the source of the original. What was the purpose of the model (i.e. why was a model required in this evaluation)? What are the main components of the model (e.g. health states within a Markov model)? Are sources for assumptions over model structure (e.g. allowable transitions) reported – list them if reported.
Analysis of a prospective HRQoL study, rather than a model.
5.1 Extract transition probabilities for [natural history/disease progression] model and show sources (or refer to table in text)
Not applicable.
5.2 What is the model time horizon?
Lifetime.
5.3 What, if any, discount rates have been applied in the model? Same rate for costs and outcomes?
5% for outcomes.
6 Results/analysis
What measure(s) of benefit were reported in the evaluation?
QALYs.
6.1 Provide a summary of the clinical outcome/benefits estimated for each intervention/strategy assessed in the evaluation
Mean (SD) QALYs gained
Group A = 0.1605 (0.9421)
Group B = 0.4464 (1.1966)
Group C = –0.0219 (0.7424).
SD, standard deviation.
6.2 Provide a summary of the costs estimated for each intervention/strategy assessed in the evaluation
See ‘3 Intervention costs’ above.
6.3 Synthesis of costs and benefits – are the costs and outcomes reported together (e.g. as cost-effectiveness ratios)? If so, provide a summary of the results
Mean cost per QALY gained
Group A = €8212
Group B = €5128
Group C = not estimated (negative utility change)
Whole cohort = €7947.
6.4 Give results of any statistical analysis of the results of the evaluation
10,000 re-samples from the original stochastic cost–utility data set were simulated using a bootstrapping technique.
6.5 Was any sensitivity analysis performed – if yes, what type(s) (i.e. deterministic (one-way, two-way, etc.) or probabilistic)
Deterministic one-way sensitivity analyses.
6.6 What scenarios were tested in the sensitivity analysis? How do these relate to structural uncertainty (testing assumptions over model structure such as relationships between health states), methodological uncertainty (such as choices of discount rate or inclusion of indirect costs) or parameter uncertainty (assumptions over values of parameters in the model, such as costs, quality of life or disease progression rates)?
Base case analysis using median values:
Discount rate variation (5%, 3%, 1%)
Upper and lower 95% CI of the QALY gain
Upper and lower 95% CI of the treatment costs.
6.7 Give a summary of the results of the sensitivity analysis – did they differ substantially from the base case analysis. If so, what were the suggested causes?
Authors state that the results of the one-way sensitivity analysis were relatively robust when varying costs and treatment effectiveness, but use of median values substantially increased the cost/QALY in the group of patients whose first eye had been operated on earlier (presume this is a mistake as the group mentioned – group C – did not have a cost per QALY estimated due to negative change in HRQoL. Presume they mean group A where cost per QALY increased from €8212 to €39,188).
Bootstrap simulation suggested that compared with no treatment, surgery was more costly and less effective in 46.4% of simulated cases, and more costly and more effective in 53.6% of simulated cases in subgroup A (quadrant I vs. quadrant II in figure 7). The corresponding percentages were 37.9% and 62.1% in subgroup B (figure 8), and 51.1% and 48.9% in subgroup C (figure 9), respectively. Bootstrap sensitivity analysis also suggested that at a willingness to pay threshold of €20,000 per QALY gained, the probability of cataract surgery being acceptable was 51.7% in subgroup A, 59. 0% in subgroup B and 46. 4% in subgroup C (figure 10).
7 Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
The utility gain from cataract surgery was small and confined to an improvement in seeing only. Possible explanations: two-thirds of patients reported only minimal pre-operative subjective seeing problems despite objective evidence of poor visual acuity in the surgical eye; the ‘real-world’ setting of a university clinic and its ‘mixed sample’; one-third of patients had a secondary ophthalmic diagnosis (which might reduce the benefit of surgery); potential insensitivity of the 15D to measure changes in HRQoL (it includes only one question relating to sight).
7.1 What are the implications of the evaluation for practice?
The authors do not explicitly state practice implications. From the results it would seem that single eye or bilateral eye cataract surgery is cost-effective (according to current willingness to pay thresholds). Second-eye surgery does not appear to be cost-effective due to an apparent reduction in quality of life following second-eye surgery.
8 Southampton Health Technology Assessments Centre commentary
Selection of comparators:
Comparison of first- and second-eye surgery in this study comes from a single group of patients (group C), rather than comparing one group who only had first-eye surgery with a separate group who had second-eye surgery. It could be that their subjective assessment of HRQoL following second-eye surgery was confounded by the benefit they derived from the first operation, such that the independent effect of second-eye surgery cannot be estimated.
Validity of estimate of measure of benefit:
The authors acknowledge the limitations of translating measured visual acuity into utility values, and justify why measuring HRQoL from patients directly might better reflect utility gain from cataract surgery. The 15D generic HRQoL instrument is described by the authors, but they do not state whether or not it has been validated. It’s potential insensitivity to changes in HRQoL related to eye conditions are acknowledged by the authors (discussed above).
Validity of estimate of costs:
Relatively little detail is given on cost estimation.
1 Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Sach and colleagues (2010). 91
1.1 Health technology
Second-eye cataract surgery.
1.2 Interventions and comparators
What interventions/strategies were included?
Second-eye cataract surgery.
Was a no treatment/supportive care strategy included?
Yes, waiting list controls.
Describe interventions/strategies.
Patients were randomised to immediate second-eye cataract surgery (median time to surgery 30 days) or no surgery (‘waiting list controls’ median time to surgery 216 days; range 37–527 days).
1.3 Research question
What are the stated objectives of the evaluation?
To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery for older women with minimal dysfunction in the eye to be operated on, compared with waiting list controls who had already undergone first-eye cataract surgery.
1.4 Study type cost-effectiveness/cost–utility/cost–benefit analysis?
Cost–utility.
1.5 Study population
What definition was used for [condition]? What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
Women over 70 years of age who had previously had successful first-eye cataract surgery and who had a second operable cataract. Women were excluded if they had complex cataracts or other visual comorbidities. Most participants (86%) had good vision in the eye to be operated upon (baseline Snellen acuity of 6/12 or better).
1.6 Institutional setting where is/are the intervention(s) being evaluated usually provided?
Secondary care (ophthalmology clinic).
1.7 Country/currency
Has a country setting been provided for the evaluation? What currency are costs expressed in and does the publication give the base year to which those costs relate?
UK, all costs were UK pounds and the price year was 2004 (inflated using the Hospital and Community Health Services Inflation Index, where necessary).
1.8 Funding source
Trent Regional NHS Research and Development Scheme and the Public – Private Partnerships Foundation (now the Health Foundation).
1.9 Analytical perspective
What is the perspective adopted for the evaluation (health service, health and PSS, third-party payer, societal (i.e. including costs borne by individuals and lost productivity)?
UK NHS and PSS. (Carer costs were included in a separate analysis).
2 Effectiveness
Were the effectiveness data derived from: a single study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion? Give the definition of treatment effect used in the evaluation. Give the size of the treatment effect used in the evaluation.
The clinical evidence was from a published RCT. 83 The trial consisted of 229 women, with 116 in the intervention group and 113 in the control group. Patients were followed up for 1 year. The trial provided data for quality of life for the economic evaluation. Other trial outcomes such as improvements in visual function were not included in the model.
3 Intervention costs
Were the cost data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion? Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)? List the direct intervention costs and other direct costs used in the evaluation – include resource estimates (and sources for these estimates, if appropriate) as well as sources for unit costs used.
Costs were derived from the Foss and colleagues RCT. 83 Patient diaries were used to collect individual patient level data on all contacts with health and social services, including care home admission, informal care, equipment and home modifications. Data were collected at 3 and 9 months through telephone interviews and at 6 and 12 months through face-to-face interviews.
Lifetime costs were estimated by using a life expectancy from UK government life tables. Annual costs for the control group were assumed to remain constant in subsequent years as that observed in the trial period. Costs in the final three-quarters of the year were rescaled to better reflect costs over a full year without a cataract operation for the intervention group. As with the control group, these costs were assumed to remain constant over the remaining lifespan.
3.1 Indirect costs (costs due to lost productivity, unpaid inputs to patient care)
Were indirect costs included:
Carer costs were excluded from the base case.
Table shows mean cost (£) per patient over 12 months for second-eye cataract surgery and no second-eye cataract surgery.
4 Health state valuations/utilities (if study uses quality-of-life adjustments to outcomes)
Were the utility data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis of previous studies or expert opinion. Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Patients’ quality of life was estimated using the EuroQoL EQ-5D administered at baseline and at 6 months from the Foss and colleagues’ trial. 83 Area under the curve analysis was performed to take account of the baseline in estimating the number of QALYs for a single year period. It was assumed that utility remained constant over the remaining lifetime for both groups.
4.1 List the utility values used in the evaluation
| EuroQoL EQ-5D, Foss et al. (2006)83 | Baseline | 6 months |
|---|---|---|
| Expedited second eye | 0.74 | 0.73 |
| Unoperated second eye (control) | 0.72 | 0.69 |
| Difference | + 0.02 | + 0.04 |
5 Modelling
If a model was used, describe the type of model used (e.g. Markov state transition model, discrete event simulation). Was this a newly developed model or was it adapted from a previously reported model? If an adaptation, give the source of the original. What was the purpose of the model (i.e. why was a model required in this evaluation)? What are the main components of the model (e.g. health states within a Markov model)? Are sources for assumptions over model structure (e.g. allowable transitions) reported – list them if reported.
Trial-based economic analysis rather than a model.
5.1 Extract transition probabilities for [natural history/disease progression] model and show sources (or refer to table in text)
Not applicable.
5.2 What is the model time horizon?
One year and lifetime.
5.3 What, if any, discount rates have been applied in the model? Same rate for costs and outcomes?
3.5% for benefits and costs in the lifetime analysis only.
6 Results/Analysis
What measure(s) of benefit were reported in the evaluation?
QALYs.
6.1 Provide a summary of the clinical outcome/benefits estimated for each intervention/strategy assessed in the evaluation
Over 1 year, the mean difference in QALYs per patient in the base case was 0.015. For the lifetime analysis, the mean difference in QALYs was 0.074.
6.2 Provide a summary of the costs estimated for each intervention/strategy assessed in the evaluation
The mean total cost per patient (excluding carer time cost) in the operated group was £2139 compared with £1492 in the control group. The mean total cost per patient for the lifetime analysis was £12,171 and £10,887 for the operated and control group, respectively.
6.3 Synthesis of costs and benefits – are the costs and outcomes reported together (e.g. as cost-effectiveness ratios)? If so, provide a summary of the results
The ICER for surgery in the base case was £44,263 per QALY gained. The long-term ICER was £17,299 per QALY gained.
6.4 Give results of any statistical analysis of the results of the evaluation
Non-parametric bootstrap analysis was undertaken to produce CEACs.
6.5 Was any sensitivity analysis performed – if yes, what type(s) (i.e. deterministic (one-way, two-way, etc.) or probabilistic)
Deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses. Threshold analyses also conducted.
6.6 What scenarios were tested in the sensitivity analysis? How do these relate to structural uncertainty (testing assumptions over model structure such as relationships between health states), methodological uncertainty (such as choices of discount rate or inclusion of indirect costs) or parameter uncertainty (assumptions over values of parameters in the model, such as costs, quality of life or disease progression rates)?
Assumptions were tested regarding the time to quality of life improvement after surgery (immediately after surgery to gradually over 6 months), discount rates (0 and 5%) and whether carer costs were included.
6.7 Give a summary of the results of the sensitivity analysis – did they differ substantially from the base case analysis. If so, what were the suggested causes?
Changing the assumptions about the time course of quality of life improvement after surgery, or the discount rate, had little effect on conclusions. The unit cost threshold for the cataract operation itself, at which the ICER fell beneath £30,000 was £454 (68% of the actual cost) for the trial period analysis.
7 Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
Although second-eye cataract surgery improves visual disability and general status, it is not likely to be cost-effective in the short-term for those with mild visual dysfunction pre-operation. In the long term, second-eye cataract surgery appears to be cost-effective unless carer costs are included.
7.1 What are the implications of the evaluation for practice?
Second-eye surgery appears to be a cost-effective treatment on the basis of the lifetime analysis.
8 SHTAC commentary
Selection of comparators:
Appropriate.
Validity of estimate of measure of benefit:
Appropriate, based upon EQ-5D elicited from cataract patients directly in a RCT. The authors discuss the potential limitations of using EQ-5D to assess cataract surgery, including possible lack of precision and responsiveness making it hard to detect small changes. EQ-5D does not incorporate sensory function in its descriptive system.
The authors also suggest their results are conservative due to the assumption that the difference in quality of life between intervention and control being constant over the lifetime whereas one would expect some deterioration in the control group in utility over time (mean utility declined from 0.72 to 0.69 in the 6-month period used to measure utility in the study).
Validity of estimate of costs:
Appropriate and based upon UK patients. The costs of treating adverse events are not included.
Appendix 8 List of excluded full-text cost-effectiveness papers
Excluded study
Hiratsuka Y, Yamada M, Murakami A, et al. Cost-effectiveness of cataract surgery in Japan. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2011;55:333–42.
Appendix 9 Data extraction forms for HRQoL studies
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Clark and colleagues (2008). 105
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To determine if post-operative endophthalmitis adversely affects quality of life after cataract surgery.
Describe the type of study and study design.
Case–control study (prospective).
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, and (iv) other?
Cataract patients who developed post-operative endophthalmitis.
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Years, mean (SD)a: Cases = 81.2 (8.5) Controls = 76.60 (11.5) |
|---|---|
| Sex | Male, N (%)a: Cases = 6 (32) Controls = 8 (27) |
| Race (if appropriate) | Not stated |
| Indication/disease (e.g. presence or absence of comorbidities) | Cataract patients who developed post-operative endophthalmitis within 1 month following cataract surgery (cases). The controls were patients with uncomplicated cataract surgery, randomly selected |
| Baseline clinical vision | Not reported |
| Other characteristics (sample size) | Cases = 19 Controls = 30 |
| QoL instrument (state when administered) | EQ-5D TTO VFQ-25 Instruments administered 12 months post surgery. Cases were interviewed, controls received questionnaires |
| Utility values | Baseline values not collected |
| Treatment effect, if reported (e.g. clinical vision measures) | The proportion of cases with post-operative VA < 6/12 in their operated eye was significantly more than the comparison group (p = 0.01) (authors consider VA < 6/12 to indicate vision impairment) Degree of vision loss, n (%): No visual impairment: Cases = 9 (47) Controls = 25 (83) Unilateral visual impairment: Cases = 9 (47) Controls = 3 (10) Bilateral visual impairment: Cases = 1 (6) Controls = 2 (7) p = 0.009 (Fisher’s exact test) |
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
Australia.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were the quality of life data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
Case–control study, as above.
Results
Summarise the results
EQ-5D summary score, mean (SD):
Cases = 0.66 (0.32)
Controls = 0.81 (0.25).
Mean difference = 0.15.
p = 0.08.
Of the five EQ-5D subscales, the only statistically significant difference between cases and controls was for the mobility subscale (p = 0.03) (further detail on EQ-5D sub-scales reported but not extracted here).
TTO, mean (SD):
Cases = 0.90
Controls = 0.96.
Mean difference = 0.06.
p = 0.12.
VFQ-25: cases generally had a statistically significant lower composite score than controls (p = 0.01), and a statistically significant lower score for 5 of the 11 subscales after adjusting for age, sex and visual acuity in the better eye (full data not extracted here).
SD, standard deviation.
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
Post-operative endophthalmitis following cataract surgery results in poorer patient perceived vision-related quality of life compared with uncomplicated cataract surgery, irrespective of visual acuity. However, no statistically significant effect upon general HRQoL was found. The authors suggest this is due to a combination of a small sample size and the relative insensitivity of the EQ-5D and TTO for detecting more subtle vision-related impacts on quality of life as detected by the VFQ-25.
What are the implications of the study for the model?
The difference in utility between patients with post-operative endophthalmitis and patients with uncomplicated surgery (ranging from 0.06 to 0.15 TTO and EQ-5D, respectively) can be potentially used in the model to take account of adverse events on HRQoL following treatment. However, it should be noted that the EQ-5D and the TTO may be insensitive to changes in QoL following cataract surgery.
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Datta and colleagues (2008). 40
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To determine which factors contribute most to quality of life among elderly women patients with pre-operative bilateral cataracts, and which visual factors best explain change in quality of life over time.
Describe the type of study and study design.
RCT.
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
Patients with bilateral cataracts.
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Years Median = 78 Minimum = 70 Maximum = 94 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 100% female | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race (if appropriate) | Not stated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication/disease (e.g. presence or absence of comorbidities) | Comorbid diagnoses, n Median = 8 Minimum = 4 Maximum = 11 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline clinical vision | Entire sample (n = 306 randomised)Spectacle-corrected visual acuity (log-MAR)Contrast sensitivity (Pelli–Robson)/log-contrastStereopsis (1–5)aMedian0.281.351Minimum−0.080.051Maximum0.961.955 Randomised study groupsb (subset of patients completing baseline and 6-month assessments)Expedited first-eye surgery (n = 148)Unoperated first eye (n = 140)MeanUnaided VA0.510.56Spectacles VA0.300.29Pinhole VA0.210.22Contrast sensitivity (dB)1.371.39Depth perception (5-point scale)1.712.03VA, visual acuity. VA reported in log-MAR units. |
Spectacle-corrected visual acuity (log-MAR) | Contrast sensitivity (Pelli–Robson)/log-contrast | Stereopsis (1–5)a | Median | 0.28 | 1.35 | 1 | Minimum | −0.08 | 0.05 | 1 | Maximum | 0.96 | 1.95 | 5 | Expedited first-eye surgery (n = 148) | Unoperated first eye (n = 140) | Mean | Unaided VA | 0.51 | 0.56 | Spectacles VA | 0.30 | 0.29 | Pinhole VA | 0.21 | 0.22 | Contrast sensitivity (dB) | 1.37 | 1.39 | Depth perception (5-point scale) | 1.71 | 2.03 | VA, visual acuity. VA reported in log-MAR units. | ||||||||||
| Spectacle-corrected visual acuity (log-MAR) | Contrast sensitivity (Pelli–Robson)/log-contrast | Stereopsis (1–5)a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median | 0.28 | 1.35 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum | −0.08 | 0.05 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum | 0.96 | 1.95 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expedited first-eye surgery (n = 148) | Unoperated first eye (n = 140) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unaided VA | 0.51 | 0.56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectacles VA | 0.30 | 0.29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pinhole VA | 0.21 | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contrast sensitivity (dB) | 1.37 | 1.39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depth perception (5-point scale) | 1.71 | 2.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA, visual acuity. VA reported in log-MAR units. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other characteristics (sample size) | 306 women randomised – 154 allocated to expedited (within a month of randomisation) first-eye surgery, 152 allocated to routine (12-month wait) surgery (control) Authors describe the study population as moderately frail, and half had fallen in the year before randomisation. Heart problems were reported by 31%, chest problems by 20%, arthritis by 76% and history of stroke by 7% |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL instrument (state when administered) | EQ-5D London Handicap Scale (data not extracted here) VF-14 (data not extracted here) Activities of daily living (Barthel Index) (data not extracted here) Administered at baseline and 6 months after randomisation |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility values | EQ-5D Entire sample Median (0–1.0) (transformed) = 0.73 (0.26) Minimum = –0.08 (0.0) Maximum = 1.0 (0.32) (The EuroQoL scores varied from –0.08 to 1.0, and they were transformed by the equation: transformed EuroQoL = log10 (Baseline EuroQoL + 1.08), 1.08 being a constant added to give positive scores for logarithmic function. This substantially improved kurtosis and skew) Expedited first-eye surgeryb Mean = 0.70 Unoperated first eyeb Mean = 0.70 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment effect, if reported (e.g. clinical vision measures) | Expedited first-eye surgery (n = 148)Unoperated first eye (n = 140)Mean difference95% CIp-valueMeanUnaided VA0.220.56−0.32−0.27 to –0.36< 0.0005Spectacles VA0.100.35−0.25−0.22 to –0.29< 0.0005Pinhole VA0.090.26−0.17−0.14 to –0.19< 0.0005Contrast sensitivity (dB)1.551.330.230.18 to 0.27< 0.0005Depth perception (5-point scale)1.472.240.620.41 to 0.83< 0.0005VA, visual acuity. Mean difference adjusted for baseline values. | Expedited first-eye surgery (n = 148) | Unoperated first eye (n = 140) | Mean difference | 95% CI | p-value | Mean | Unaided VA | 0.22 | 0.56 | −0.32 | −0.27 to –0.36 | < 0.0005 | Spectacles VA | 0.10 | 0.35 | −0.25 | −0.22 to –0.29 | < 0.0005 | Pinhole VA | 0.09 | 0.26 | −0.17 | −0.14 to –0.19 | < 0.0005 | Contrast sensitivity (dB) | 1.55 | 1.33 | 0.23 | 0.18 to 0.27 | < 0.0005 | Depth perception (5-point scale) | 1.47 | 2.24 | 0.62 | 0.41 to 0.83 | < 0.0005 | VA, visual acuity. Mean difference adjusted for baseline values. | |||||||
| Expedited first-eye surgery (n = 148) | Unoperated first eye (n = 140) | Mean difference | 95% CI | p-value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unaided VA | 0.22 | 0.56 | −0.32 | −0.27 to –0.36 | < 0.0005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectacles VA | 0.10 | 0.35 | −0.25 | −0.22 to –0.29 | < 0.0005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pinhole VA | 0.09 | 0.26 | −0.17 | −0.14 to –0.19 | < 0.0005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contrast sensitivity (dB) | 1.55 | 1.33 | 0.23 | 0.18 to 0.27 | < 0.0005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depth perception (5-point scale) | 1.47 | 2.24 | 0.62 | 0.41 to 0.83 | < 0.0005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA, visual acuity. Mean difference adjusted for baseline values. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
UK.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were quality of life data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
RCT, as above.
Results
Summarise the results
| EQ-5D at 6 months. Entire sample: Median (0–1.0) (transformed) = 0.73 (0.26) Minimum = −0.24 (0.08) Maximum = 1.0 (0.32). (NB: The above figures appear to be based on the whole trial population, half of which were patients who had not yet received their cataract surgery. They are also near identical to baseline values. For this reason they are not very useful for estimating change in quality of life following surgery, but have been reported here for completeness). Authors report that no visual variables were significantly associated with EuroQoL, based on univariate and multivariate linear regression. Expedited first-eye surgeryUnoperated first eyeMean difference95% CIp-valueMeanEQ-5D0.730.670.060.01 to 0.110.02 |
Expedited first-eye surgery | Unoperated first eye | Mean difference | 95% CI | p-value | Mean | EQ-5D | 0.73 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.11 | 0.02 | ||
| Expedited first-eye surgery | Unoperated first eye | Mean difference | 95% CI | p-value | ||||||||||
| Mean | ||||||||||||||
| EQ-5D | 0.73 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.11 | 0.02 | |||||||||
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
Authors describe a ‘weak and inconsistent effect of visual factors on EuroQoL’. They suggest that the lack of responsiveness of the EuroQoL to clinically significant changes in vision make it an inadequate instrument for measurement of vision-related quality of life.
From the main results of the RCT4 the authors suggest that first-eye surgery is associated with ‘large’ gains in visual function and these changes are accompanied by improvements in quality of life. Referring specifically to the EQ-5D they go on to say that ‘although we did demonstrate changes on this scale, they were small in magnitude, and suggest that this scale is insufficiently sensitive to change for this intervention (by virtue of its content)’ [p. 58 of Hartwell et al. (2005)]. 4
What are the implications of the study for the model?
The statistically significant mean EQ-5D difference between operated and unoperated patients (0.06) (which is accompanied by an improvement in visual acuity) could be used in the economic evaluation. The authors consider the changes in vision to be large, but note that the changes in utility were small. Therefore, this is likely to be an underestimate. The estimate is not necessarily representative of the difference in utility that might be observed between first- and second-eye patients either. Furthermore, the study comprised only women, who were fairly elderly and with comorbidities, and therefore is not likely to be generalisable to the general cataract surgical population.
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Dolders and colleagues (2004). 101
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To conduct a cost–utility analysis of monofocal and multifocal IOLs in cataract surgery, following a societal perspective.
Describe the type of study and study design
A cost-effectiveness analysis conducted alongside a RCT.
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
Patients awaiting cataract surgery.
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Years, mean (SD) Monofocal IOL = 72.2 (7.9) Multifocal IOL = 72.9 (7.0) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female-to-male ratio Monofocal IOL = 56.0 : 44.0 Multifocal IOL = 64.7 : 35.3 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race (if appropriate) | Not stated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication/disease (e.g. presence or absence of comorbidities) | Patients with bilateral senile cataract. Ocular comorbidity was an exclusion criterion General comorbidity (%) Monofocal IOL No = 41.3 Yes = 58.7 Multifocal Iol No = 42.6 Yes = 57.4 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline clinical vision | T1 (1–2 weeks before first-eye surgery), mean (SD) Monofocal IOLMultifocal IOLVA (first eye)0.46 (0.27)0.49 (0.27)VA (second eye)0.31 (0.22)0.28 (0.19)VA, visual acuity. (log-MAR).Refraction error in spherical equivalent reported but not extracted. |
Monofocal IOL | Multifocal IOL | VA (first eye) | 0.46 (0.27) | 0.49 (0.27) | VA (second eye) | 0.31 (0.22) | 0.28 (0.19) | VA, visual acuity. (log-MAR). Refraction error in spherical equivalent reported but not extracted. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monofocal IOL | Multifocal IOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA (first eye) | 0.46 (0.27) | 0.49 (0.27) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA (second eye) | 0.31 (0.22) | 0.28 (0.19) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA, visual acuity. (log-MAR). Refraction error in spherical equivalent reported but not extracted. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other characteristics (sample size) | Monofocal IOL n = 75 Multifocal IOL n = 68 General health status EQ-5D (%)Monofocal IOLMultifocal IOLHealthy36.026.5(Very) mild60.047.0(Very) severe4.026.5 |
General health status EQ-5D (%) | Monofocal IOL | Multifocal IOL | Healthy | 36.0 | 26.5 | (Very) mild | 60.0 | 47.0 | (Very) severe | 4.0 | 26.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General health status EQ-5D (%) | Monofocal IOL | Multifocal IOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Healthy | 36.0 | 26.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Very) mild | 60.0 | 47.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Very) severe | 4.0 | 26.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL instrument (state when administered) | Patients were interviewed to assess quality of life and all other outcomes at three time points: T1: 1 to 2 weeks before first-eye surgery T2: 3 months after first-eye surgery T3: 3 months post operatively after second-eye surgery EQ-5D VAS* TTO SG *It is not specified if this was the EQ-VAS or another instrument |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility values | See below under ‘Results’ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment effect, if reported (e.g. clinical vision measures) | Monofocal IOL (0) (n = 75)T1T2T3VA (first eye)0.46 (0.27)0.12 (0.22)NAVA (second eye)0.31 (0.22)NA0.07 (0.14)Multifocal IOL (1) (n = 68)T1T2T3VA (first eye)0.49 (0.27)0.13 (0.17)NAVA (second eye)0.28 (0.19)NA0.09 (0.16)Differences between monofocal and multifocal IOL at T2 or T3 reported as not statistically significant.Refraction error in spherical equivalent reported but not extracted. | Monofocal IOL (0) (n = 75) | T1 | T2 | T3 | VA (first eye) | 0.46 (0.27) | 0.12 (0.22) | NA | VA (second eye) | 0.31 (0.22) | NA | 0.07 (0.14) | Multifocal IOL (1) (n = 68) | T1 | T2 | T3 | VA (first eye) | 0.49 (0.27) | 0.13 (0.17) | NA | VA (second eye) | 0.28 (0.19) | NA | 0.09 (0.16) | Differences between monofocal and multifocal IOL at T2 or T3 reported as not statistically significant. Refraction error in spherical equivalent reported but not extracted. |
|||||||||
| Monofocal IOL (0) (n = 75) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA (first eye) | 0.46 (0.27) | 0.12 (0.22) | NA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA (second eye) | 0.31 (0.22) | NA | 0.07 (0.14) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multifocal IOL (1) (n = 68) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA (first eye) | 0.49 (0.27) | 0.13 (0.17) | NA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VA (second eye) | 0.28 (0.19) | NA | 0.09 (0.16) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Differences between monofocal and multifocal IOL at T2 or T3 reported as not statistically significant. Refraction error in spherical equivalent reported but not extracted. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
The Netherlands.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were quality of life data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
Derived from patients in a RCT, as described above.
Results
Summarise the results
| Utility values, mean (SD). Monofocal IOL (0) (n = 75)T3–T2*Multifocal IOL (1) (n = 68)T3–T2*T1T2T3T1T2T3VAS0.78 (0.19)0.80 (0.19)0.79 (0.17)−0.010.66 (0.22)0.76 (0.22)0.70 (0.24)−0.06TTO0.68 (0.28)0.74 (0.28)0.67 (0.29)−0.070.70 (0.26)0.70 (0.30)0.62 (0.28)−0.08SG0.94 (0.06)0.95 (0.06)0.94 (0.05)−0.010.95 (0.06)0.94 (0.06)0.93 (0.07)−0.01SD, standard deviation.Odds ratio (95% CI).*Calculated by reviewers.VAS.0.08** (0.01 to 0.56) between T2 and T1 (first eye).0.10** (0.02 to 0.64) between T3 and T1 (both eyes).**p < 0.05 (authors suggest that the significant difference between trial arms for the VAS was due to baseline significant differences between arms).TTO and SG stated as not significant.VAS, TTO and SG correlated significantly (p < 0.01). Correlations varied from 0.40 to 0.43, indicating that the underlying construct is similar. |
Monofocal IOL (0) (n = 75) | T3–T2* | Multifocal IOL (1) (n = 68) | T3–T2* | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | VAS | 0.78 (0.19) | 0.80 (0.19) | 0.79 (0.17) | −0.01 | 0.66 (0.22) | 0.76 (0.22) | 0.70 (0.24) | −0.06 | TTO | 0.68 (0.28) | 0.74 (0.28) | 0.67 (0.29) | −0.07 | 0.70 (0.26) | 0.70 (0.30) | 0.62 (0.28) | −0.08 | SG | 0.94 (0.06) | 0.95 (0.06) | 0.94 (0.05) | −0.01 | 0.95 (0.06) | 0.94 (0.06) | 0.93 (0.07) | −0.01 | SD, standard deviation. Odds ratio (95% CI). *Calculated by reviewers. VAS. 0.08** (0.01 to 0.56) between T2 and T1 (first eye). 0.10** (0.02 to 0.64) between T3 and T1 (both eyes). **p < 0.05 (authors suggest that the significant difference between trial arms for the VAS was due to baseline significant differences between arms). TTO and SG stated as not significant. VAS, TTO and SG correlated significantly (p < 0.01). Correlations varied from 0.40 to 0.43, indicating that the underlying construct is similar. |
|||||||||||||
| Monofocal IOL (0) (n = 75) | T3–T2* | Multifocal IOL (1) (n = 68) | T3–T2* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAS | 0.78 (0.19) | 0.80 (0.19) | 0.79 (0.17) | −0.01 | 0.66 (0.22) | 0.76 (0.22) | 0.70 (0.24) | −0.06 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TTO | 0.68 (0.28) | 0.74 (0.28) | 0.67 (0.29) | −0.07 | 0.70 (0.26) | 0.70 (0.30) | 0.62 (0.28) | −0.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SG | 0.94 (0.06) | 0.95 (0.06) | 0.94 (0.05) | −0.01 | 0.95 (0.06) | 0.94 (0.06) | 0.93 (0.07) | −0.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SD, standard deviation. Odds ratio (95% CI). *Calculated by reviewers. VAS. 0.08** (0.01 to 0.56) between T2 and T1 (first eye). 0.10** (0.02 to 0.64) between T3 and T1 (both eyes). **p < 0.05 (authors suggest that the significant difference between trial arms for the VAS was due to baseline significant differences between arms). TTO and SG stated as not significant. VAS, TTO and SG correlated significantly (p < 0.01). Correlations varied from 0.40 to 0.43, indicating that the underlying construct is similar. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
Cataract surgery implanting a monofocal or a multifocal IOL is equally cost-effective.
What are the implications of the study for the model?
Although the aim of this study was to compare monofocal or a multifocal IOL in cataract surgery patients, it appears that patients underwent first-eye surgery and then 3 months later had second-eye surgery (as opposed to just single-eye surgery, or both eyes simultaneously). Patients were assessed before first-eye surgery, after first- and second-eye surgery, therefore, permitting comparison of changes in quality of life between first- and second-eye surgery in both trial arms. However, whilst there was an increase in utility from baseline (T1) to post-first-eye surgery (T2), between first-eye surgery (T2) and second-eye surgery (T3) utility values declined (in both trial arms). It may have been that patients perceived to have benefited most from first-eye surgery, and pre-surgical visual impairment in the second eye may have been mild [in both trial arms the eye with the highest visual impairment (in terms of log-MAR visual acuity) was prioritised for first-eye surgery]. Also, the TTO and SG instruments may not have been sensitive enough to capture changes in quality of life following second-eye surgery.
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
De Juan-Marcos and colleagues (2012). 106
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To assess the correlation between visual acuity, visual function, and health-related quality of life before-and-after Nd:YAG laser posterior capsulotomy in patients with posterior capsule opacification (PCO).
Describe the type of study and study design.
Single cohort before-and-after study.
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
Patients with PCO following cataract surgery.
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Mean = 72 years Range = 40–87 years |
|---|---|
| Sex | n (%) Male 51 (34) |
| Race (if appropriate) | Not stated |
| Indication/disease (e.g. presence or absence of comorbidities) | Patients with posterior capsule opacification (PCO) Comorbidities n (%) Systemic 120 (80) Ocular 107 (71.3) |
| Baseline clinical vision | Mean VA in PCO eye, decimal Before capsulotomy 0.4 (0.39 log-MAR) After capsulotomy 0.7 (0.15 log-MAR) Mean VA in fellow eye, decimal 0.68 (0.16 log-MAR) Mean (SD) binocular visual acuity (BVA), log-MAR 0.28 (0.16) |
| Other characteristics (sample size) | 150 patients, with a total of 175 PCO eyes included |
| QoL instrument (state when administered) | EuroQoL EQ-5D and EQ-VAS VF-14 (data not extracted here) Before surgery and 3 weeks after capsulotomy |
| Utility values | EQ-VAS 58.8 (SD 14.5) The authors note a celling effect for EQ-5D and EQ-VAS in 11 (8.5%) and 2 (1.5%) of the patients, respectively, at baseline |
| Treatment effect, if reported (e.g. clinical vision measures) | Post-capsulotomy Mean (SD) BVA log-MAR 0.08 (0.1) Mean difference = 0.2 p < 0.01 |
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
Spain.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were qualiy of life data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
Single cohort before-and-after study, as above.
Results
Summarise the results
| BVA, log-MARNumber of patientsPost-capsulotomy, mean (SD) EQ-VASMean change from baselinep-valueAll patients15072.4 (17.3)13.5< 0.01≤ 0.524467.5 (19.2)15.5< 0.010.51–0.165870.5 (17.2)10.8< 0.01≥ 0.154879.2 (11.5)14.2< 0.01BVA, binocular visual acuity; SD, standard deviation. Authors report that the EQ-VAS improvement did not demonstrate relationship to binocular visual acuity at baseline. They found significant mean changes in the VAS scores when patients were categorised in BVA groups at baseline; however, the analysis of variance did not reflect a significant (p = 0.084) linear trend in the mean EQ-VAS across the three binocular visual acuity groups (table). The authors measured the MCID (the smallest difference in a score that is considered to be worthwhile or clinically important and which would lead the clinician to consider a change in the patient’s management). The MCID after capsulotomy was 0.28 for binocular visual acuity, and 11.8 for EQ-VAS. The EQ-VAS score improvement had a weak relationship to the binocular visual acuity improvement (r = 0.21, p < 0.01). The correlation coefficients between EQ-VAS score improvement and changes in satisfaction with vision and changes in VF-14 scores were 0.41 (p < 0.01) and 0.61 (p < 0.01), respectively. The percentage of patients reporting problems on the 5 dimensions of the EQ-5D before-and-after capsulotomy is reported (data not extracted here). |
BVA, log-MAR | Number of patients | Post-capsulotomy, mean (SD) EQ-VAS | Mean change from baseline | p-value | All patients | 150 | 72.4 (17.3) | 13.5 | < 0.01 | ≤ 0.52 | 44 | 67.5 (19.2) | 15.5 | < 0.01 | 0.51–0.16 | 58 | 70.5 (17.2) | 10.8 | < 0.01 | ≥ 0.15 | 48 | 79.2 (11.5) | 14.2 | < 0.01 | BVA, binocular visual acuity; SD, standard deviation. | ||||
| BVA, log-MAR | Number of patients | Post-capsulotomy, mean (SD) EQ-VAS | Mean change from baseline | p-value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All patients | 150 | 72.4 (17.3) | 13.5 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ≤ 0.52 | 44 | 67.5 (19.2) | 15.5 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.51–0.16 | 58 | 70.5 (17.2) | 10.8 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ≥ 0.15 | 48 | 79.2 (11.5) | 14.2 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BVA, binocular visual acuity; SD, standard deviation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
There was a substantial improvement in visual acuity after Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy. The study also shows that treatment of PCO leads to noticeable changes for the patient in everyday life; there is a reduction in patients’ perceived difficulties performing activities of daily living.
Measuring the outcomes of capsulotomy by clinical indicators alone may underestimate the overall benefits of treatment. Visual acuity in conjunction with visual function and HRQoL questionnaires will likely prove to be better indicators of the need for and outcome of capsulotomy.
What are the implications of the study for the model
The pre-capsulotomy EQ-VAS utility value [58.8 (SD 14.5)] could be used to estimate the disutility associated with PCO in the modelled cohort. The post-capsulotomy utility value could be used for patients successfully treated for PCO (NB PCO treatment led to adverse events in 11 eyes).
SD, standard deviation.
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To examine agreement among generic preference-based measures of HRQoL and vision-specific measures in classifying patients into the same categories of change – better, stable or worse.
Describe the type of study and study design.
Prospective single cohort study. (NB The study included a cohort of cataract patients, and a cohort of heart disease patients, but only the cataract cohort is reported here).
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
A cohort of patients undergoing cataract extraction surgery with lens replacement. No detail given on whether first, second or bilateral eye surgery.
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation? [NB These data have been extracted from the subset of patients with complete baseline and 1 month follow-up data for all measures (n = 210) reported in the Feeny paper. The Kaplan paper reports baseline data for all enrolled patients (n = 376).]
| Age | N (%) 35–44 years, n = 3 (1) 45–64 years, n = 71 (34) 65–91 years, n = 136 (65) |
|---|---|
| Sex | Female n = 124 (59%) |
| Race (if appropriate) | n (%) White = 184 (88) Black = 7 (3) Asian = 13 (6) Other = 2 (1) Missing = 4 (2) |
| Indication/disease | Cataract patients undergoing cataract extraction surgery with lens replacement. Patients were excluded if undergoing simultaneous glaucoma, corneal or vitreoretinal procedures |
| Baseline clinical visual (e.g. visual acuity) | Not reported |
| Other characteristics (sample size) | Enrolled n = 376 Complete data n = 210 |
| QoL instrument | Generic instruments: EQ-5D HUI-2 HUI-2 sensation HUI-3 HUI-3 vision QWB–SA SF-6D Disease-specific instruments: VFt VFQui SRH Mostly self-completed (93% reported that no one helped them to complete the questionnaires) Administered at baseline, 1 and 6 months post-operation. In the Feeny et al. (2012)86 publication data are reported only for the 1 month follow-up as the authors note that changes are most common during the first month following surgery and then stabilise thereafter. The Kaplan et al. (2011)102 paper does report 6-month data, but these are not extracted here The authors suggest that a change of 0.03 or more in the overall preference score for each of the preference-based measures is interpreted as a clinically important change. Empirical estimates of clinically important change for the 5 preference-based measures vary from 0.01 to 0.08. For the single-attribute utility scores for HUI-2 sensation (which includes vision) and HUI vision the guideline for a clinically important difference is 0.05 |
| Utility values | Yes |
| Treatment effect, if reported | Not reported |
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
USA.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were quality of life data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
Prospective single cohort study.
Results
Summarise the results
| Generic instrument | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| EQ-5D | ||
| Baseline | 0.83 | 0.17 |
| 1 month post-operation | 0.84 | 0.16 |
| Change from baseline | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| HUI-2 | ||
| Baseline | 0.79 | 0.17 |
| 1 month post-operation | 0.81 | 0.19 |
| Change from baseline | 0.02 | 0.14 |
| HUI-2 sensation | ||
| Baseline | 0.76 | 0.14 |
| 1 month post-operation | 0.84 | 0.17 |
| Change from baseline | 0.08 | 0.19 |
| HUI-3 | ||
| Baseline | 0.66 | 0.27 |
| 1 month post-operation | 0.72 | 0.28 |
| Change from baseline | 0.05 | 0.21 |
| HUI-3 vision | ||
| Baseline | 0.80 | 0.22 |
| 1 month post-operation | 0.91 | 0.15 |
| Change from baseline | 0.12 | 0.22 |
| QWB–SA | ||
| Baseline | 0.59 | 0.14 |
| 1 month post-operation | 0.60 | 0.14 |
| Change from baseline | 0.01 | 0.13 |
| SF-6D | ||
| Baseline | 0.74 | 0.12 |
| 1 month post-operation | 0.73 | 0.12 |
| Change from baseline | −0.01 | 0.09 |
NB The values provided by Kaplan and colleagues102 differ slightly from those in the above table. This appears to be due to Kaplan and colleagues102 reporting data for all patients who completed each instrument at both baseline and at the 1-month follow-up. In contrast, Feeny and collaegues86 report only the subset of 210 patients who completed baseline and the 1-month follow-up and all instruments. Values do not differ markedly and should not affect interpretation.
NB Kaplan and colleagues102 report that at 1 month, differences were statistically significant for all the indices except the SF-6D (for their dataset). Feeny and collaegues86 do not mention statistical significance.
NB Data in agreement between the different instruments were reported by Feeny and collaegues86 but have not been extracted here.
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
The mean change in HUI-3 vision score and HUI-2 sensation score exceed the 0.03 clinically important difference guideline. The mean changes in scores for EQ-5D, QWB-SA, SF-6D and self-rated health (questionnaire) (SRH) are less than the guidelines for a clinically important difference (0.03).
There was very little pair-wise agreement between the disease-targeted measures and the five preference-based measures about which patients improved, were stable or deteriorated. The instruments must be regarded as not interchangeable.
What are the implications of the study for the model?
It is not clear whether patients received first-eye, second-eye or bilateral cataract surgery. It is therefore difficult to extrapolate the utility values to patients undergoing second-eye surgery. The severity of patients’ baseline clinical vision impairment is also not stated, making it difficult to generalise to the modelled patient cohort.
The EQ-5D and SF-6D are not responsive to changes in quality of life following cataract surgery. The HUI-2 and HUI-3 would appear to be more sensitive to changes in quality of life following cataract surgery.
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Hiratsuka and colleagues (2011). 94
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of cataract surgery through measurement of the cost per QALY in Japan. To confirm the generalisability of the cost–utility of cataract surgery in the real-world setting in Japan.
Describe the type of study and study design.
Authors define it as a prospective multicentre observational study (conducted by the ECCERT). The study can also be classed as a full economic evaluation as cost per QALYs are reported (though not extracted here).
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
Patients scheduled for first-eye, second-eye or bilateral cataract surgery.
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Years, mean (SD) 71.0 (7.9) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Women n = 335 (61%); men = 214 (39%) | |||||||||||||||
| Race (if appropriate) | Not stated, presume Japanese | |||||||||||||||
| Indication/disease | Scheduled for first-eye, second-eye or bilateral cataract surgery. Patients were excluded if surgery was combined with glaucoma, corneal, or vitreoretinal surgery, or if significant ocular comorbidity | |||||||||||||||
| Baseline clinical vision | VA (log-MAR), mean (SD): Better eye = 0.16 (0.28) Worse eye = 0.51 (0.52) |
|||||||||||||||
| Other characteristics (sample size) | 549 patients enrolled. Numbers of patients available for analysis vary according to different measures BaselinePost surgeryVA549529TTO440381EQ-5D541482HUI-3496434 |
Baseline | Post surgery | VA | 549 | 529 | TTO | 440 | 381 | EQ-5D | 541 | 482 | HUI-3 | 496 | 434 | |
| Baseline | Post surgery | |||||||||||||||
| VA | 549 | 529 | ||||||||||||||
| TTO | 440 | 381 | ||||||||||||||
| EQ-5D | 541 | 482 | ||||||||||||||
| HUI-3 | 496 | 434 | ||||||||||||||
| QoL instrument | TTO EQ-5D (Japanese version) HUI-3 (Japanese version) Administered at baseline and 3 months post surgery |
|||||||||||||||
| Utility values | Baseline utility values, mean (SD) TTO (n = 440 patients) = 0.60 (0.28) EQ-5D (n = 541 patients) = 0.84 (0.15) HUI-3 (n = 496 patients) = 0.65 (0.24) |
|||||||||||||||
| Treatment effect, if reported | The mean better VA (log-MAR) and worse VA (log-MAR) improved to –0.05 ± 10 and 0.03 ± 0.25, respectively (no further information given). (presume ‘better’ and ‘worse’ means better eye/worse eye VA, respectively) |
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
Twelve clinical sites in Japan. Seven ophthalmologic departments in university hospitals, three ophthalmologic departments in public hospitals, and two private surgical clinics.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were quality of life data derived from a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
A single (observational) study, as described above.
Results
Summarise the results
| Post-operative utility values, mean (± SD). First-eye surgery (N = 157)Second-eye surgery (N = 60)Bilateral surgery (N = 312)TTOn = 109n = 38n = 234Utility (before surgery)0.66 ± 0.250.64 ± 0.290.58 ± 0.29Utility (after surgery)0.84 ± 0.280.88 ± 0.230.85 ± 0.25Utility gain0.18 ± 0.270.24 ± 0.300.27 ± 0.33p-value< 0.001< 0.001< 0.001EQ-5Dn = 138n = 52n = 292Utility (before surgery)0.85 ± 0.160.83 ± 0.160.84 ± 0.15Utility (after surgery)0.89 ± 0.150.92 ± 0.130.90 ± 0.15Utility gain0.05 ± 0.150.09 ± 0.170.06 ± 0.16p-value< 0.001< 0.001< 0.001HUI-3n = 131n = 47n = 256Utility (before surgery)0.71 ± 0.250.70 ± 0.200.62 ± 0.24Utility (after surgery)0.79 ± 0.180.79 ± 0.220.76 ± 0.25Utility gain0.08 ± 0.210.08 ± 0.250.14 ± 0.25p-value< 0.001< 0.05< 0.001 In the entire group of 381 patients (i.e. all three subgroups together) the overall TTO utility showed a statistically significant improvement from 0.60 to 0.85 3 months after cataract surgery. Pre-surgery TTO utilities were stratified according to the corrected distance VA (decimal) in the better seeing eye. The utilities were correlated with six different visual stratifications. As the VA in the better seeing eye decreased, the corresponding TTO utilities decreased at every stratification level (data not extracted, see table 2 in the publication). In a multiple linear regression model the better VA (log-MAR) showed a significant correlation with TTO utilities. Utility changed by 0.21 for each change in VA of one (log-MAR) (p < 0.001). |
First-eye surgery (N = 157) | Second-eye surgery (N = 60) | Bilateral surgery (N = 312) | TTO | n = 109 | n = 38 | n = 234 | Utility (before surgery) | 0.66 ± 0.25 | 0.64 ± 0.29 | 0.58 ± 0.29 | Utility (after surgery) | 0.84 ± 0.28 | 0.88 ± 0.23 | 0.85 ± 0.25 | Utility gain | 0.18 ± 0.27 | 0.24 ± 0.30 | 0.27 ± 0.33 | p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | EQ-5D | n = 138 | n = 52 | n = 292 | Utility (before surgery) | 0.85 ± 0.16 | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 0.84 ± 0.15 | Utility (after surgery) | 0.89 ± 0.15 | 0.92 ± 0.13 | 0.90 ± 0.15 | Utility gain | 0.05 ± 0.15 | 0.09 ± 0.17 | 0.06 ± 0.16 | p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | HUI-3 | n = 131 | n = 47 | n = 256 | Utility (before surgery) | 0.71 ± 0.25 | 0.70 ± 0.20 | 0.62 ± 0.24 | Utility (after surgery) | 0.79 ± 0.18 | 0.79 ± 0.22 | 0.76 ± 0.25 | Utility gain | 0.08 ± 0.21 | 0.08 ± 0.25 | 0.14 ± 0.25 | p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.05 | < 0.001 | |
| First-eye surgery (N = 157) | Second-eye surgery (N = 60) | Bilateral surgery (N = 312) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TTO | n = 109 | n = 38 | n = 234 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility (before surgery) | 0.66 ± 0.25 | 0.64 ± 0.29 | 0.58 ± 0.29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility (after surgery) | 0.84 ± 0.28 | 0.88 ± 0.23 | 0.85 ± 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility gain | 0.18 ± 0.27 | 0.24 ± 0.30 | 0.27 ± 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EQ-5D | n = 138 | n = 52 | n = 292 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility (before surgery) | 0.85 ± 0.16 | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 0.84 ± 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility (after surgery) | 0.89 ± 0.15 | 0.92 ± 0.13 | 0.90 ± 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility gain | 0.05 ± 0.15 | 0.09 ± 0.17 | 0.06 ± 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUI-3 | n = 131 | n = 47 | n = 256 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility (before surgery) | 0.71 ± 0.25 | 0.70 ± 0.20 | 0.62 ± 0.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility (after surgery) | 0.79 ± 0.18 | 0.79 ± 0.22 | 0.76 ± 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility gain | 0.08 ± 0.21 | 0.08 ± 0.25 | 0.14 ± 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.05 | < 0.001 |
SD, standard deviation; VA, visual acuity.
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
The TTO method is more sensitive to small changes in utility than generic survey questionnaires such as the EQ-5D and HUI-3. However, even the relatively smaller utility gains for EQ-5D and HUI-3 were statistically significant.
What are the implications of the study for the model?
The difference between the post-surgery utility gains from the first- and second-eye surgery subgroups can be estimated from this study for the three instruments used, as follows:
TTO = 0.06
EQ-5D = 0.04
HUI-3 = 0.
[NB This study was screened for inclusion in our cost-effectiveness systematic review. However, it did not meet the criteria as cost-effectiveness outcomes were not reported for second-eye surgery (the first- and second-eye cataract surgery groups were merged into one overall group ‘one eye’ and compared with bilateral cataract surgery).]
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Kishimoto and colleagues (2012). 103
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To calculate and evaluate the utility value of surgical treatment in patients with cataract, glaucoma, and comitant strabismus, and to compare their changes using TTO analysis. The validity of TTO analysis was assessed by correlating the TTO value with the VF-14.
Describe the type of study and study design.
Single cohort retrospective analysis.
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
Patients with cataract, glaucoma, and comitant strabismus. The cataract patients were stratified by unilateral or bilateral cataract surgery (only the cataract subgroup are extracted here).
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Mean (SD) 70.9 (10.9)/74.5 (5.8) (unilateral/bilateral) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male, n (%) 14 (67)/17 (59) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Race (if appropriate) | Not stated but presume Japanese | |||||||||||||||||||
| Indication/disease | Unilateral and bilateral cataracts | |||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline clinical vision | VA in better eye, mean (SD), decimal: Unilateral n = 0.9 (0.5) Bilateral n = 0.7 (0.3) VA in worse eye, Mean (SD), decimal: Unilateral n = 0.3 (0.3) Bilateral n = 0.4 (0.3) |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Other characteristics (sample size) | Number of cataract patients responding to the questionnaire: Unilateral n = 21 Bilateral n = 29 (NB On p. 196, it is stated that only 44 cataract patients completed the TTO questionnaire) |
|||||||||||||||||||
| QoL instrument | TTO measurement sheet (self-completed). Patients were told to assume there was a surgical treatment that would offer them perfect vision if successful, and asked whether they would be willing to trade-off some of their expected remaining years for perfect vision. The expected remaining years were based on data from the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of 2008. The utility value was calculated using the following equation: utility value = 1 – time traded/expected remaining years VF-14 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Utility values | Baseline, mean (SD): Unilateral = 0.727 (0.279) Bilateral = 0.663 (0.196) |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment effect, if reported | VA, mean (SD), decimal: Better eyeWorse eyeBaselinePost surgeryBaselinePost surgeryUnilateral0.9 (0.5)0.9 (0.4)0.3 (0.3)0.6 (0.4)Bilateral0.7 (0.3)1.1 (0.4)0.4 (0.3)0.7 (0.4) |
Better eye | Worse eye | Baseline | Post surgery | Baseline | Post surgery | Unilateral | 0.9 (0.5) | 0.9 (0.4) | 0.3 (0.3) | 0.6 (0.4) | Bilateral | 0.7 (0.3) | 1.1 (0.4) | 0.4 (0.3) | 0.7 (0.4) | |||
| Better eye | Worse eye | |||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | Post surgery | Baseline | Post surgery | |||||||||||||||||
| Unilateral | 0.9 (0.5) | 0.9 (0.4) | 0.3 (0.3) | 0.6 (0.4) | ||||||||||||||||
| Bilateral | 0.7 (0.3) | 1.1 (0.4) | 0.4 (0.3) | 0.7 (0.4) | ||||||||||||||||
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
Japan.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were quality of life data derived from a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
Single observational study. The publication says utility was assessed retrospectively via questionnaires completed 2–3 months post operatively. However, pre- and post-operative values are given, so it is therefore assumed that patients assessed their pre-operative quality of life retrospectively.
Results
Summarise the results
Post-operative utility values, mean (SD):
Unilateral = 0.894 (0.228)
Bilateral = 0.909 (0.155).
Post-operative utility gain, mean (SD):
Unilateral = 0.167 (0.237)
Bilateral = 0.245 (0.167).
Difference in gain between unilateral and bilateral = 0.078.
The TTO utility value improved significantly post operatively in all four patient groups.
SD, standard deviation.
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes, though it is not clear how baseline utility values were assessed if patients only completed the questionnaire post operatively.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
None.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
The TTO utility value improved significantly compared with that before surgery in all four treatment groups. The gain was larger for bilateral than unilateral surgery.
Statistically significant correlation was observed between post-operative bilateral cataracts TTO utility and the VF-14, but not for unilateral cataracts.
Significant negative correlations were noted between the utility value and corrected visual acuity of the better eye of the post-operative unilateral cataract.
What are the implications of the study for the model?
The difference in post-operative utility gain between unilateral and bilateral surgery (0.078) cannot be assumed to be analogous to the difference between first- and second-eye surgery. However, it could be indicative of this if the VA of the worst eye (0.6) post surgery in unilateral cataract patients is considered to be similar to the VA of an unoperated bilateral cataract.
VA, visual acuity.
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Naeim and colleagues (2006). 104
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of first-eye surgery in persons with cataracts who had < 30% predicted probability of benefiting from the procedure, and to determine whether any subgroup based on the Cataract Surgery Index could be identified for whom the costs of surgery would outweigh the health benefits.
Describe the type of study and study design.
Randomised trial (first-eye surgery vs. watchful waiting) accompanied by an economic evaluation.
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
People with bilateral cataracts.
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Mean age 78 years |
|---|---|
| Sex | 62% women |
| Race (if appropriate) | 87% white |
| Indication/disease (e.g. presence or absence of comorbidities) | Patients (older than 64) with bilateral age-related cataracts, with or without other chronic eye diseases, with a CSI score equal to or greater than 10 (representing < 30% predicted probability of reporting improvement in visual function after surgery) (NB A higher CSI score = lower predicted probability of improvement). The severity of cataracts was not graded Patients were classified into CSI categories = 10, = 11, > 11. The scoring system is based on ADVS score, amongst other factors (see p. 983 of publication) |
| Baseline clinical vision | Best corrected Snellen acuity and pinhole acuity for vision worse than 20/100 was assessed, but results not reported in the publication |
| Other characteristics (sample size) | 250 patients randomised, 133 assigned to surgery, 117 assigned to watchful waiting. After withdrawals the sample sizes at 6 months were 117 and 100, respectively |
| QoL instrument (state when administered) | HUI-3, administered at baseline (pre surgery) and at 6 months post surgery ADVS (data not extracted here) SF-12 (data not extracted here) Charlson Comorbidity Index (data not extracted here) |
| Utility values | HUI-3 (n = 209) All patients = 0.74 (SD 0.26) See below for baseline utility values for HUI-3 (CSI > 11) and for visual utility subscale |
| Treatment effect, if reported (e.g. clinical vision measures) | Clinical vision measures not reported. ADVS scores are given, showing a statistically significant benefit for surgery compared with watchful waiting (data not extracted here) |
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
USA.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were quality of life data derived from a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
RCT.
Results
Summarise the results.
| 6-month follow-up. SurgeryWatchful waitingHUI-3Baseline0.7440.7546-month follow-up0.7600.723Change from baseline0.016−0.031Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.041 (0.029), p = 0.156HUI-3 (CSI > 11)Baseline0.7830.7886-month follow-up0.7330.710Change from baseline−0.05−0.078Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.024 (0.053), p = 0.657Visual utilitybBaseline0.9270.926-month follow-up0.9540.92Change from baseline0.0270Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.031 (0.014), p = 0.035SD, standard deviation.a Mean difference between the control arm and the cataract surgery arm. General linear multivariate regression model analysis controlling for baseline HUI, age, diabetes, Physical Component Summary Score (PCS 12) age-related macular degeneration (AMD), gender, baseline PCS 12, baseline Mental Composite Score (MCS 12), and medical comorbidities.b Not explicitly stated but presume this refers to the vision subscale of the HUI-3. |
Surgery | Watchful waiting | HUI-3 | Baseline | 0.744 | 0.754 | 6-month follow-up | 0.760 | 0.723 | Change from baseline | 0.016 | −0.031 | Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.041 (0.029), p = 0.156 | HUI-3 (CSI > 11) | Baseline | 0.783 | 0.788 | 6-month follow-up | 0.733 | 0.710 | Change from baseline | −0.05 | −0.078 | Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.024 (0.053), p = 0.657 | Visual utilityb | Baseline | 0.927 | 0.92 | 6-month follow-up | 0.954 | 0.92 | Change from baseline | 0.027 | 0 | Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.031 (0.014), p = 0.035 | SD, standard deviation. a Mean difference between the control arm and the cataract surgery arm. General linear multivariate regression model analysis controlling for baseline HUI, age, diabetes, Physical Component Summary Score (PCS 12) age-related macular degeneration (AMD), gender, baseline PCS 12, baseline Mental Composite Score (MCS 12), and medical comorbidities. b Not explicitly stated but presume this refers to the vision subscale of the HUI-3. |
|||||||||||||||
| Surgery | Watchful waiting | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUI-3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 0.744 | 0.754 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-month follow-up | 0.760 | 0.723 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change from baseline | 0.016 | −0.031 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.041 (0.029), p = 0.156 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUI-3 (CSI > 11) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 0.783 | 0.788 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-month follow-up | 0.733 | 0.710 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change from baseline | −0.05 | −0.078 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.024 (0.053), p = 0.657 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Visual utilityb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 0.927 | 0.92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-month follow-up | 0.954 | 0.92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change from baseline | 0.027 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted impact of surgerya – mean (SD) = 0.031 (0.014), p = 0.035 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SD, standard deviation. a Mean difference between the control arm and the cataract surgery arm. General linear multivariate regression model analysis controlling for baseline HUI, age, diabetes, Physical Component Summary Score (PCS 12) age-related macular degeneration (AMD), gender, baseline PCS 12, baseline Mental Composite Score (MCS 12), and medical comorbidities. b Not explicitly stated but presume this refers to the vision subscale of the HUI-3. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
It is cost-effective for 75% of patients who were previously estimated to have a small probability (< 30%) of benefiting from the procedure. There is a subgroup (those with CSI > 11) for whom the costs would exceed $50,000 per QALY.
CSI, Cataract Surgery Index.
What are the implications of the study for the model?
The HUI-3 utility gains for the surgery group could potentially inform the economic evaluation, though as these were patients undergoing first-eye surgery they cannot necessarily be assumed to apply to second-eye surgery. Furthermore, the patients enrolled in this study cannot be considered representative of the general surgical population as they were chosen to reflect a subgroup less likely to benefit, on the basis of comorbidities, symptoms and age. Clinical benefit was measured in terms of favourable changes in ADVS scores for surgery patients, though changes in post-surgical VA were not reported.
ADVS, Activities of Daily Vision Scale; VA, visual acuity.
Reference (lead author, year, ref ID)
Räsänen and colleagues (2006). 90
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
The aim was to evaluate the cost–utility of cataract surgery, compared with a hypothetical situation of no treatment by studying unselected patients referred by practising ophthalmologists for a routine cataract operation to a large university clinic because of objective signs of poor visual acuity due to cataract.
Describe the type of study and study design.
Single cohort (with three subgroups) pre- and post-study. The authors state that these data were collected in the framework of a large trial.
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
Patients with cataracts:
Group A – only one eye was operated (n = 87)
Group B – both eyes were operated during the follow-up (n = 73)
Group C – first eye had been operated earlier, now the second eye was operated (n = 59).
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Mean (SD): Group A = 69 (12) Group B = 70 (12) Group C = 75 (10) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female, n (%): Group A = 49 (56%) Group B = 52 (71%) Group C = 53 (71%) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race (if appropriate) | Not stated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication/disease (e.g. presence or absence of comorbidities) | Patients scheduled for cataract surgery. Presence of comorbidities not reported other than around a one-third of patients had secondary ophthalmic diagnosis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline clinical vision | Mean (SD) best corrected visual acuity in the surgical eye prior to cataract surgery (all patients) Group AGroup BGroup CSignificanceSurgical eyeSnellen0.19 (0.14)0.17 (0.12)0.24 (0.14)Not statistically significantLog-MAR0.98 (0.66)0.94 (0.49)0.76 (0.48)Not statistically significantNon-surgical eyeSnellen0.58 (0.23)0.28 (0.16)0.63 (0.25)Not statistically significantLog-MAR0.29 (0.22)0.65 (0.37)0.25 (0.21)A vs. B p < 0.001B vs. C p < 0.001A vs. C not statistically significant Mean (SD) best corrected visual acuity in the surgical eye prior to cataract surgery in patients reporting minor or significant pre-operative seeing problems Patients with no or only minor subjective pre-operative seeing problems at baseline (levels 1 and 2 of the seeing dimension of the 15D). N = 140 (64%)Patients with significant subjective pre-operative seeing problems at baseline (levels 3 to 5 of the seeing dimension of the 15D). N = 79 (36%)SignificanceSurgical eyeSnellen0.21 (0.14)0.17 (0.12)Not statistically significantLog-MAR0.88 (0.59)0.94 (0.52)Not statistically significantNon-surgical eyeSnellen0.57 (0.24)0.35 (0.24)Not statistically significantLog-MAR0.30 (0.23)0.58 (0.39)p < 0.001 |
Group A | Group B | Group C | Significance | Surgical eye | Snellen | 0.19 (0.14) | 0.17 (0.12) | 0.24 (0.14) | Not statistically significant | Log-MAR | 0.98 (0.66) | 0.94 (0.49) | 0.76 (0.48) | Not statistically significant | Non-surgical eye | Snellen | 0.58 (0.23) | 0.28 (0.16) | 0.63 (0.25) | Not statistically significant | Log-MAR | 0.29 (0.22) | 0.65 (0.37) | 0.25 (0.21) | A vs. B p < 0.001 B vs. C p < 0.001 A vs. C not statistically significant |
Patients with no or only minor subjective pre-operative seeing problems at baseline (levels 1 and 2 of the seeing dimension of the 15D). N = 140 (64%) | Patients with significant subjective pre-operative seeing problems at baseline (levels 3 to 5 of the seeing dimension of the 15D). N = 79 (36%) | Significance | Surgical eye | Snellen | 0.21 (0.14) | 0.17 (0.12) | Not statistically significant | Log-MAR | 0.88 (0.59) | 0.94 (0.52) | Not statistically significant | Non-surgical eye | Snellen | 0.57 (0.24) | 0.35 (0.24) | Not statistically significant | Log-MAR | 0.30 (0.23) | 0.58 (0.39) | p < 0.001 | ||||||||||||||||
| Group A | Group B | Group C | Significance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surgical eye | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Snellen | 0.19 (0.14) | 0.17 (0.12) | 0.24 (0.14) | Not statistically significant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Log-MAR | 0.98 (0.66) | 0.94 (0.49) | 0.76 (0.48) | Not statistically significant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-surgical eye | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Snellen | 0.58 (0.23) | 0.28 (0.16) | 0.63 (0.25) | Not statistically significant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Log-MAR | 0.29 (0.22) | 0.65 (0.37) | 0.25 (0.21) | A vs. B p < 0.001 B vs. C p < 0.001 A vs. C not statistically significant |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with no or only minor subjective pre-operative seeing problems at baseline (levels 1 and 2 of the seeing dimension of the 15D). N = 140 (64%) | Patients with significant subjective pre-operative seeing problems at baseline (levels 3 to 5 of the seeing dimension of the 15D). N = 79 (36%) | Significance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surgical eye | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Snellen | 0.21 (0.14) | 0.17 (0.12) | Not statistically significant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Log-MAR | 0.88 (0.59) | 0.94 (0.52) | Not statistically significant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-surgical eye | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Snellen | 0.57 (0.24) | 0.35 (0.24) | Not statistically significant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Log-MAR | 0.30 (0.23) | 0.58 (0.39) | p < 0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other characteristics (sample size) | 386 patients scheduled for routine cataract operation (219 available for final analysis) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QoL instrument (state when administered) | 15D generic 15-dimensional, standardised HRQoL instrument. Patients completed the 15D at baseline and then again approximately 6 months after the cataract operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utility values | See below The correlation between the best corrected visual acuity (expressed in log-MAR units) in the surgical eye and the subjective level of seeing (the seeing dimension of the HRQoL-instrument) was poor (r = 0.17, p = 0.013). However, the visual acuity of the non-surgical eye correlated fairly well with the seeing dimension of the 15D instrument (r = 0.503, p < 0.001) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment effect, if reported (e.g. clinical vision measures) | Not reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
Finland.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were quality of life data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
Single cohort of patients, as above.
Results
Summarise the results.
| Mean (SD) utility values. All patientsGroup AGroup BGroup CBaseline0.82 (0.13)0.85 (0.13)0.80 (0.13)0.82 (0.11)6-month follow-up0.83 (0.14)0.85 (0.14)0.83 (0.14)0.81 (0.13)Change from baseline0.010.00 (0.14)0.03 (0.14)−0.01 (0.07)p-valueNRp = 0.852p = < 0.001p = 0.279NR, not reported, but stated to be statistically insignificant. The only statistically significant increase in the individual dimensions of the 15D was for ‘seeing’, observed across all three subgroups. Changes in utility scores for the individual domains are presented according to severity of HRQoL (levels 1 and 2 vs. levels 3 to 5 of the scoring dimension). They are given for the whole study rather than the three subgroups and therefore data have not been extracted. |
All patients | Group A | Group B | Group C | Baseline | 0.82 (0.13) | 0.85 (0.13) | 0.80 (0.13) | 0.82 (0.11) | 6-month follow-up | 0.83 (0.14) | 0.85 (0.14) | 0.83 (0.14) | 0.81 (0.13) | Change from baseline | 0.01 | 0.00 (0.14) | 0.03 (0.14) | −0.01 (0.07) | p-value | NR | p = 0.852 | p = < 0.001 | p = 0.279 | NR, not reported, but stated to be statistically insignificant. | |||||
| All patients | Group A | Group B | Group C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baseline | 0.82 (0.13) | 0.85 (0.13) | 0.80 (0.13) | 0.82 (0.11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-month follow-up | 0.83 (0.14) | 0.85 (0.14) | 0.83 (0.14) | 0.81 (0.13) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change from baseline | 0.01 | 0.00 (0.14) | 0.03 (0.14) | −0.01 (0.07) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-value | NR | p = 0.852 | p = < 0.001 | p = 0.279 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NR, not reported, but stated to be statistically insignificant. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SD, standard deviation.
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
Mean utility gain after routine cataract surgery in a real-world setting was relatively small and confined mostly to patients whose both eyes were operated. Possible explanations: two-thirds of patients reported only minimal pre-operative subjective seeing problems despite objective evidence of poor visual acuity in the surgical eye; the ‘real-world’ setting of a university clinic and its ‘mixed sample’; one-third of patients had a secondary ophthalmic diagnosis (which might reduce the benefit of surgery); potential insensitivity of the 15D to measure changes in HRQoL (it includes only one question relating to sight).
What are the implications of the study for the model.
Group C is most relevant to this study as it evaluates the change in quality of life for second-eye cataract surgery. However, there is a statistically significant decrease in quality of life after second-eye surgery which is counterintuitive. The study sample could be seen to reflect a typical patient population, though around two-thirds of patients were classified (by the 15D) as having no or only minor subjective seeing problems (NB Baseline Snellen visual acuity and 15D correlated poorly in the surgical eye).
Reference (Lead author, year, ref ID)
Sach and colleagues (2010). 91
Study characteristics
Research question
What are the stated objectives of the study?
To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of second-eye cataract surgery for older women with minimal visual dysfunction in the eye to be operated on from a health and PSS perspective, compared with waiting list controls who had already undergone first-eye cataract surgery.
Describe the type of study and study design.
Cost–utility analysis conducted alongside a RCT.
Was the sample from (i) the general population, (ii) patients with the disease of interest, (iii) individuals with knowledge of the disease, (iv) other?
Patients with a second operable cataract.
What are the characteristics of the baseline cohort for the evaluation?
| Age | Aged over 70 years old |
|---|---|
| Sex | 100% female |
| Race (if appropriate) | Not reported |
| Indication/disease (e.g. presence or absence of comorbidities) | Previous successful first-eye cataract surgery with a second operable cataract. Exclusion criteria included complex cataracts, visual field defects, severe comorbid eye disease |
| Baseline clinical vision | Described as having minimal visual dysfunction in the eye to be operated on (86% had VA 6/12 or better) |
| Other characteristics (sample size) | 239 women randomised. 229 women were included in the economic analysis (116 intervention; 113 control) |
| QoL instrument (state when administered) | EuroQoL EQ-5D, administered at baseline and 6 months |
| Utility values | See below |
| Treatment effect, if reported (e.g. clinical vision measures) | Visual function, especially stereopsis, improved slightly after second-eye cataract surgery, compared with unoperated controls (see Foss and colleagues83) |
Country/setting
What is the country and setting for the evaluation?
UK, secondary care ophthalmology clinics.
Data sources
Effectiveness
Were quality of life data derived from: a single (observational) study, a review/synthesis or combination of previous studies, expert opinion?
Quality of life data were collected as part of a RCT.
Results
Summarise the results.
| From Foss and colleagues (2006).83 EuroQoL EQ-5DBaseline6 monthsDifferenceExpedited second eye0.740.73−0.01Unoperated second eye (control)0.720.69−0.03Difference between expedited and control (adjusted for baseline values) = 0.02 95% CI −0.03 to 0.08); p = 0.36. |
EuroQoL EQ-5D | Baseline | 6 months | Difference | Expedited second eye | 0.74 | 0.73 | −0.01 | Unoperated second eye (control) | 0.72 | 0.69 | −0.03 | Difference between expedited and control (adjusted for baseline values) = 0.02 95% CI −0.03 to 0.08); p = 0.36. | |||
| EuroQoL EQ-5D | Baseline | 6 months | Difference | |||||||||||||
| Expedited second eye | 0.74 | 0.73 | −0.01 | |||||||||||||
| Unoperated second eye (control) | 0.72 | 0.69 | −0.03 | |||||||||||||
| Difference between expedited and control (adjusted for baseline values) = 0.02 95% CI −0.03 to 0.08); p = 0.36. | ||||||||||||||||
Were the methods for deriving these data adequately described (give sources if using data from other published studies)?
Yes.
Mapping
If a model was used, describe the type of model (e.g. regression) or other conversion algorithm.
Not applicable.
Conclusions/implications
Give a brief summary of the author’s conclusions from their analysis.
Second-eye cataract surgery is not likely to be cost-effective in the short-term for those with mild visual dysfunction pre-operation. In the long term, second-eye cataract surgery appears to be cost-effective unless carer costs are included.
What are the implications of the study for the model?
The utility data comes from a generic preference-based instrument (EQ-5D) and can therefore be used to estimate QALYs. However, the difference between treatments at 6 months is slight and unlikely to be clinically significant. The authors discuss the potential limitations of using EQ-5D to assess cataract surgery, including possible lack of precision and responsiveness making it hard to detect small changes. EQ-5D does not incorporate sensory function in its descriptive system. The fact that the study population was all female, and had only mild visual impairment needs to be taken into account if using the utility data from this study for a typical patient cohort in the model.
Appendix 10 Parameters included in probabilistic sensitivity analyses
| Name | Deterministic | Higher CI | Lower CI | Standard error | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discount rate costs | 3.5% | 6.0% | 1.5% | ||
| Discount rate benefits | 3.5% | 6.0% | 1.5% | ||
| Visual acuity | |||||
| Pre surgery | 0.50 | ||||
| Post surgery | 0.8 | 1.20 | 0.67 | 0.068 | Beta |
| Costs | |||||
| Cataract operation | 862.66 | £1121 | £604 | 132.04 | Gamma |
| Cataract OP | 85.12 | £111 | £60 | 13.03 | Gamma |
| GP visits | 43 | £56 | £30 | 6.58 | Gamma |
| PCO | £506.42 | £658.35 | £354.49 | 77.51 | Gamma |
| Retinal detachment | £1615.65 | £2100.35 | £1130.96 | 247.29 | Gamma |
| Endophthalmitis | £760.11 | £988.14 | £532.08 | 116.34 | Gamma |
| CMO | £313.30 | £407.29 | £219.31 | 47.95 | Gamma |
| Lost lens fragments | £451.69 | £587.20 | £316.18 | 69.14 | Gamma |
| Resources | |||||
| OP surgery | 6.94 | 7.98 | 5.9 | 0.53 | Log normal |
| OP no surgery | 2.81 | Fixed | |||
| GP visits surgery | 4.40 | 5.21 | 3.6 | 0.41 | Log normal |
| GP visits no surgery | 4.00 | Fixed | |||
| Complications | |||||
| PCO year 1 | 3.49% | 5.24% | 1.75% | 0.009 | Beta |
| PCO year 2 | 9.49% | 14.24% | 4.75% | 0.024 | Beta |
| PCO year 3 | 5.06% | 7.59% | 2.53% | 0.013 | Beta |
| Retinal detachment year 1 | 0.26% | 0.39% | 0.13% | 0.001 | Beta |
| Retinal detachment year 2+ | 0.14% | 0.21% | 0.07% | 0.000 | Beta |
| Endophthalmitis | 0.10% | 0.15% | 0.05% | 0.000 | Beta |
| CMO | 1.62% | 2.43% | 0.81% | 0.004 | Beta |
| Lost lens fragments | 0.45% | 0.68% | 0.23% | 0.001 | Beta |
| Utilities | |||||
| No surgery | 0.70 | Fixed | |||
| Utility gain | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.031 | Beta |
| Age (years) | 75 | Fixed | |||
List of abbreviations
- AG
- advisory group
- CCG
- Clinical Commissioning Group
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CI
- confidence interval
- CMO
- cystoid macular oedema
- DSA
- deterministic sensitivity analysis
- ECCERT
- Eye Care Comparative Effectiveness Research Team
- EQ-5D
- European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions health survey
- EQ-VAS
- European Quality of Life-visual analogue scale
- ETDRS
- Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study
- GP
- general practitioner
- HADS
- Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
- HRQoL
- health-related quality of life
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- HUI
- Health Utilities Index
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IOL
- intraocular lens
- ITT
- intention to treat
- log-MAR
- logarithm of minimum angle of resolution
- MAR
- minimum angle of resolution
- MCID
- minimal clinically important difference
- MDC
- minimal detectable change
- Nd:YAG
- neodymium-doped yttrium–aluminium garnet
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- PCO
- posterior capsule opacification
- PCR
- posterior capsule rupture
- PCT
- primary care trust
- PORT
- US National Cataract Patient Outcomes Research Team
- PSA
- probabilistic sensitivity analysis
- PSS
- Personal Social Services
- PSSRU
- Personal Social Services Research Unit
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- QWB–SA
- Quality of Well-Being – Self-Administered questionnaire
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RNIB
- Royal National Institute of Blind People
- SASH
- Somerset and Avon Survey of Health
- SF-12
- Short Form questionnaire-12 item health survey instrument
- SF-36
- Short Form questionnaire-36 item health survey instrument
- SF-6D
- Short Form questionnaire-6 Dimensions
- SG
- standard gamble
- TTO
- time trade-off
- VAS
- visual analogue scale
- VF-14
- Visual Function Index-14
- VFQ-25
- Visual Function Questionnaire-25-item