Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 10/66/01. The contractual start date was in May 2012. The draft report began editorial review in December 2014 and was accepted for publication in May 2015. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Peter Scanlon has received fees from Bayer Plc (Newbury, UK), Allergan Ltd (Marlow, UK), Roche (F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Basel, Switzerland) and Boots Opticians Ltd (Nottingham, UK) for consultancy work or advisory board participation and part of his salary is supported by the NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme in Public Health England. Stephen Aldington has part of his salary supported by the NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme in Public Health England. Sobha Sivaprasad has received fees from Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd (Frimley, UK), Bayer, Allergan and Roche for travel grants and research grants and advisory board participation.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2015. This work was produced by Scanlon et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Background
Introduction
Diabetes affects over 3 million people in the UK. The treatment and complications of diabetes cost over 10% of the NHS budget. 1 The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) published data2 in 2006 which showed that diabetes affects 246 million people worldwide, with 46% of all those affected in the 40–59 years working age group. By 2009, IDF estimates showed that 285 million people were living with the disease, with 90% of the burden caused by type 2 diabetes. 3 According to the IDF, reasons for these rises were driven by increases in life expectancy combined with sedentary lifestyles and increasing levels of obesity. In England, quarterly returns to the Department of Health4 show that the number of people identified by general practitioner (GP) practices as having diabetes had risen from approximately 1.4 million people in 2003 to 2.4 million5 in the third quarter of 2011, the numbers having been rising by 120,000 per annum since accurate data from the screening services became available in 2008. The number in the UK as a whole exceeded 3 million in 20136 and, at the same time, a further 850,000 people were estimated to have undiagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) by the charity Diabetes UK. 6
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) results from damage to the small blood vessels in the back of the eye, which generally occurs after about 10 years of diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness in the working age population around the world,7,8 except in countries such as Iceland9 and England,10 where screening programmes have become established. Two recent studies11,12 have shown that since 1985 people with diabetes have experienced lower rates of progression to proliferative DR (PDR) and severe visual loss, probably reflecting improvements in diabetes care. It is practical and affordable to treat13,14 sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy (STDR) if detected early using screening with retinal photography. DR is treated effectively with laser photocoagulation, although this has been found to be cost-effective only if retinopathy is detected before irreversible damage takes place. 13,15,16 Therefore, in order for DR treatment to be cost-effective, diagnosis has to be timely. Published evidence has shown that screening for STDR is highly cost-effective. 17–20
Since 2003, when the English NHS screening programme for DR was introduced, cases of loss of sight have reduced. Offering annual DR screening to increasing numbers of patients puts immense strain on resources and may not be necessary. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommendations exist but there is no evidence-based consensus as to the optimal frequency of testing for DR. The Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN)21 reported that patients with diabetes with no detected retinopathy could be screened every 2 years, with all others being screened at least annually. There have been a number of studies22–25 that have modelled the possible effect of moving from annual to 2–3-year intervals in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes using incidence data from screening programmes in Iceland, Liverpool and Norwich. In 2007, Olafsdottir and Stefansson26 reported the 10-year experience of biennial eye screening in patients with diabetes without retinopathy from Iceland, concluding that this seems to be safe and effective.
In 2000, Vijan et al. 27 reported on a cost–utility analysis of screening intervals for DR in patients with type 2 DM in an American population and concluded that annual retinal screening for all patients with type 2 DM without previously detected retinopathy may not be cost-effective, and tailoring recommendations to individual circumstances may be preferable.
An alternative modelling approach by Mehlsen et al. 28 used clinical data from 5365 patients who had undergone 23,324 examinations at the Department of Ophthalmology, Aarhus University Hospital and concluded that a subset of known risk factors for development and progression of DR should be used to construct a decision model for optimising screening intervals for DR.
The current studies have not included factors such as the economic consequences of visual loss other than legal blindness, the effect in ethnic or racial minority groups (the studies had mostly been in patients of northern European extraction), and that long intervals between appointments may lead to difficulties in maintaining follow-up with patients. 29 A study30 in the Coventry area of the UK found that people of South Asian ethnicity with diabetes were diagnosed at a younger age, had higher glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and total cholesterol, and greater prevalence of DR and maculopathy. The Diabetic Retinopathy In Various Ethnic groups (DRIVE) UK study, comprising patients in screening programmes in West Yorkshire and South London, showed that DR and visual impairment were more prevalent in people of African-Carribean and South Asian origin. 31,32
In Gloucestershire, we have undertaken a preliminary analysis33 of screening data and know that we can produce accurate and quality-assured screening results from the system because data already transferred from GP practices have been of high quality. We have also been the pilot site for the national system development and roll-out of software [General Practice to Diabetic Retinopathy Screening (GP2DRS)] for transfer of demographic and risk factor data from GP practices to screening software systems. It is vital that any modelling uses data that can be obtained easily from routine clinical care.
Grading of retinal photographs is not an exact measurement and, hence, intraobserver and interobserver variability occurs in the grading. 34 Screening and monitoring programmes for chronic conditions generate both ‘false-positive’ (FP) tests and ‘false-negative’ (FN) tests. In the retinal screening programme, FP tests correspond to people detected by the retinopathy screening service as requiring referral to hospital, but who are subsequently found not to have retinopathy requiring treatment. FN tests correspond to people with retinopathy who are missed by the screening service. FP and FN tests are an inevitable consequence of inexact measurement.
Glasziou et al. 35 showed that, even when there is no reference standard to determine which positive tests in a database are FP, the proportion that are FP can be estimated from a model of the variability of the test; similarly, so can the proportion of negative tests that are FN be estimated. The model has been subsequently applied to blood pressure monitoring36 and it has been developed further for monitoring HbA1c37 and microalbuminuria in diabetes. 38 In general the model needs to allow for variation between people, for average rate of change and variation in rate of change between people, and for the error rate in any individual test; we have recently published full details of the methodology. 39 These previous papers used a normal distribution model for the error structure, but we have conducted pilot methodological work showing that a logistic error structure can also be used successfully to model dichotomous outcomes.
As described previously, there is currently a well-documented epidemic of diabetes both in the UK and worldwide. With the increase in diabetes, the economic burden that DR places on society is high. 40,41 In the UK, it was estimated in 2006 that the lifetime costs of dealing with retinopathy can be up to £237,000 per person in the working age group, and that up to 50% of these costs are accounted for by the loss of productivity as a result of blindness or vision impairment. 42 Therefore, if 1000 cases of DR could be avoided in the working age population, the potential savings to the government could be in excess of £237M. 43 These compelling statistics encouraged the government to include annual DR screening in the National Service Framework for diabetes. 44
Conservative estimates of the costs of screening a patient with diabetes have been made of £26 per patient (although costs may be higher if screening is carried out in GP surgeries, and the estimates ignore costs to the patient in terms of travel costs and time off work). Although this cost might appear small, there are about 2.6 million people with diabetes in England alone. Assuming an uptake of 71% of those on the screening register (80% of those offered), these costs are of the order of £44M annually, without taking into account the centralised costs of the management of the national programme. This is a very sizeable financial resource, especially with the number of diabetes patients currently increasing at a rate of over 100,000 cases a year,4 which will drive up screening costs even further. In addition, any improvement in uptake would, obviously, have a corresponding impact upon these costs.
The current study uses currently available data from screening software systems and GP systems. The English NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme (DESP) has contracts with all the major GP software suppliers, including Egton Medical Information Systems (EMIS) Ltd (Leeds, UK), In Practice Systems Ltd (London, UK), iSOFT (formerly Torex; CSC Ltd. London, UK) and Microtest Ltd (Bodmin, UK). The Health and Social Care Information Centre GP Systems of Choice contracts make available the demographic transfer of data to screening programmes to invite people with diabetes for screening and to transfer risk factor data. These contracts use a consent model that has been agreed with the Patient Information Advisory Group and the National Information Governance Board. 45 With the imminent availability of this data to screening programmes in England there is an opportunity to provide cost-effective screening to patients which takes into account their absolute risk of developing STDR.
If tailored screening intervals were found to be clinically effective and cost-effective through this research, the logistical difficulties of delivering a national screening programme at a time of an epidemic of diabetes would be reduced, without increasing risks for any individual patients of losing vision. In addition, any potential savings might also give an opportunity to concentrate resources on persuading those most at risk to attend.
In addition, the evidence on the cost-effectiveness of different screening frequencies has been shown to be mixed. 46 A recent systematic review on the economic evidence of DR screening found three studies addressing the issue of screening frequency,46 one performed in the USA and two in the UK.
Vijan et al. 27 examined the cost-effectiveness of differing DR screening intervals for type 2 diabetes patients in the USA. The authors employed a Markov model using quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) as the main outcome measure, with costs being assessed from a third-party payer perspective. Using the definition of $50,000 per QALY gained as a cost-effective intervention, the authors reported that annual retinal screening for all type 2 diabetes patients was not warranted on the basis of cost-effectiveness.
A UK study by Brailsford et al. 47 also found similar results to that of Vijan et al. 27 The study, which again used decision modelling techniques to assess the cost-effectiveness of screening intervals in diabetes patients (both types 1 and 2), found that a 30-month screening interval was the most cost-effective option. However, in contrast to these two studies, another UK study by Davies et al. 48 found that screening diabetic patients less than once a year would not be any more cost-effective than every year. Davies et al. 48 also based their study on a decision analytic model populated using results obtained from the published literature. A finding common in both UK studies was that screening of type 1 diabetes patients was more cost-effective than screening of type 2 diabetes patients.
There were, however, important limitations with both of the UK studies. Both studies used sight years saved as their main outcome measure rather than a more generalisable health outcome, such as QALYs, that can be readily compared across interventions and disease areas, aiding the decision process. 49 In addition, the use of QALYs captures the full impact of the disease, in this case sight loss or blindness, on patients’ lives. The two studies also failed to include in their models the additional costs to the health-care service of patients losing sight or going blind. Finally, data in these two studies were derived from a wide range of sources and diabetic populations. As a result, numerous assumptions had to be made as to how best to synthesise the available data.
Our research plan was divided into four phases
Phase 1: Risk factor approach (see Chapter 5).
Phase 2: Extension to ethnically diverse populations (see Chapter 6).
Phase 3: Monitoring interval approach (see Chapter 7).
Phase 4: Cost-effectiveness of differing screening intervals in DR screening (see Chapter 8).
Planned inclusion/exclusion criteria
The criteria for inclusion in these analyses were people with diabetes aged 12 years or above who have been screened by the participating programmes of the English NHS DESP. We included patients who had assessable retinal images from two or more screening episodes (SEs) and for whom we had sufficient clinical information. The exclusion criteria as set by the English NHS DESP50 include the following:
-
patients with no perception of light in each eye
-
patients with a terminal illness
-
patients with physical disabilities making photographic screening impossible
-
patients with learning or mental disabilities making photographic screening impossible
-
patients who are currently under the care of an ophthalmologist and for whom a report on retinal status has been provided to the screening service
-
patients who have chosen to opt out of screening.
Proposed outcome measures
To develop a risk-based algorithm for screening interval, cost-effectiveness and adverse events.
Other outcomes: key recommendations for further research
Approval by ethics committees
It had been agreed that risk factor data should be collected in the Department of Health-sponsored GP2DRS project by screening services in the English NHS DESP and a national consent model was agreed in England by the National Patient Information Advisory Group and subsequently by the National Information Governance Board. Hence, we were advised that for the pilot of GP2DRS in Gloucestershire comparing GP2DRS extracts with Morbidity Information Query and Export Syntax (MIQUEST) extracts, we would not need to seek ethical approval. However, when it became clear that there were delays with the roll-out of the GP2DRS system and that we would need to use MIQUEST extraction methods in other areas to complete the research, we applied to the National Research Ethics Service Committee East of England – Cambridge South and received a favourable opinion on 9 November 2012.
Research governance
The Nominated Sponsor of this research application is Gloucestershire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
A Project Advisory Group was formed to oversee the progress of the research, and included an independent chair (Professor John Sparrow), the lead researcher (Professor Peter Scanlon), the co-applicants (Mrs Irene Stratton and Mr Steve Aldington), an independent statistician (Ms Catey Bunce), an independent consultant ophthalmologist (Miss Clare Bailey), a lay representative (Mr Mike Whatmore), and the research and development lead (Dr Julie Hapeshi) for the host Trust. Four of the Advisory Group members (John Sparrow, Catey Bunce, Clare Bailey and Mike Whatmore) formed the Independent Trial Steering Committee.
Proposed time period for retention of relevant documentation
The data from this study are pseudo-anonymised and will be kept for 8 years. It is likely that if any data are required after that time then a new extraction would be required.
Patient and public involvement
Mike Whatmore, a lay member of the Diabetes Research Network writing group ‘Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy’, was involved in the original discussions on both reasons for non-attendance in DR screening and screening intervals for DR and commented on the original application. A Diabetes UK Gloucestershire lay member, Mike Larkin, read and commented on the application. Mike Larkin has had type 1 diabetes since 1977 and has had DR since 1988. Mike Larkin is currently a member of a professional and lay group within Diabetes UK, setting the research strategy for the charity for the next 5 years. Feedback on the original application was also obtained from the Thames Valley Diabetes Local Research Network Patient and Lay Involvement Group during the development of the application.
Mike Whatmore serves as a member of the Project Advisory Group and the Independent Trial Steering Committee. Two other Gloucestershire lay members have regularly provided help and advice to the project at the different stages.
In our proposal we sought the views of the Warwick Diabetes Research and Education User Group on the original application and we were hoping to continue to consult with them but, unfortunately, as the Coventry and Warwickshire Screening Programme were unable to continue with the research project, it was not appropriate to continue using the resources of that user group.
Lay members contributed to this study report (in particular Mike Whatmore and Mike Larkin) and to the dissemination of results both formally and in their multiple contacts with health professionals and Diabetes UK.
Chapter 2 How the project has changed since the outline proposal was accepted
The project has changed since the outline application in the following ways:
-
Gloucestershire continued to be the pilot for the GP2DRS pilot during the early phases of this project and MIQUEST extracts were used to compare data from GP systems with GP2DRS extracts. Unfortunately, further delays in the GP2DRS implementation meant that we had to use MIQUEST extractions to complete data extractions from other clinical partner areas working with us in this project.
-
Unfortunately, the Coventry and Warwickshire programme withdrew from the project in August 2013. This was as a result of unforeseen competing work pressures at their clinical site, unrelated to this project. Effectively, the central team received no data from this site prior to their withdrawal from the project, nor were there any project funds transferred to them.
-
In December 2013, the Health Technology Assessment programme approved Nottinghamshire replacing Coventry and Warwickshire as the third site in the project in order to obtain data from ethnic minority populations. The Nottingham Diabetic Retinopathy Screening service serves 28,000 people with diabetes: 12,000 patients in Nottingham City primary care trust (PCT) [ethnic mix: 4.7% black; 8.0% Asian; 4.3% DM) and 16,000 patients in the southern half of the Nottinghamshire County PCT (ethnic mix: 1.0% black; 2.1% Asian; 4.6% DM). Approval was received to transfer funding from the Coventry and Warwickshire allocation to Nottinghamshire, to support their collection and supply of additional data from further GP practices.
-
A no-cost incorporation of data from a new clinical site in the East of England provided us with data from approximately 70,000 (predominantly Caucasian) patients. This was provided by Health Intelligence Ltd, the company running the screening services in the East of England. Acceptance and incorporation of these data was approved by the HTA.
-
In February 2014, a no-cost time extension of 6 months for the project was approved by the HTA programme, to support continued data collection and analyses, with a revised end date of November 2014.
-
The HTA Commissioning Board asked to see further clarification and justification for the randomised splitting of the database that was in our original proposal and stated at the time of our application that the Board felt it would probably be more useful to split the database in a systematic way. Hence, we altered the method of splitting the database to a systematic method using the postcode of the GP to define two areas (Group A and Group B) using the population data from the Office for National Statistics for Local Government Districts. Group A includes the two more urban larger towns (Gloucester and Cheltenham) and the remaining areas that make up Group A and Group B are more rural.
Timeline changes
-
Phase 1: Gloucestershire risk factor approach analysis commenced on 1 May 2012 and completed on 31 October 2012 as planned (Figure 1).
-
Phase 2: extension to an ethnically diverse population commenced on 1 July 2012 in South London and the first data sets were received in May 2013 and further data sets received until 1 April 2014.
FIGURE 1.
Screening intervals for DR original study design.

Coventry and Warwickshire withdrew in August 2013.
The first DR screening data sets were successfully received from Nottinghamshire in August 2013 and further data sets were received until 1 April 2014.
Analysis continued until mid-November 2014.
-
Phase 3: the Oxford monitoring interval approach commenced on 1 November 2012 and was completed on 27 April 2013.
-
Phase 4: the health economic modelling commenced on 1 July 2012 and continued until mid-November 2014.
Chapter 3 On-going literature review conducted by the research team
The review of the literature relating to screening for DR has been ongoing by the first author (PHS) since March 2000. The methodology involves a search technique for articles relating to screening or management of DR utilising Zetoc, a co-operative venture between The British Library, Manchester Information and Associated Services (MIMAS) and the Joint Information Systems Committee (JISC) of the UK Higher Education Funding Council (see http://zetoc.mimas.ac.uk), which is available to universities; PHS has access through the University of Oxford. Zetoc provides access to over 29,000 journals and more than 52 million article citations and conference papers through The British Library ’s electronic table of contents. The database covers 1993 to the present day and is updated daily.
The following subject, title and keywords were used:
‘retinopathy’, ‘digital’ and ‘imaging’ and ‘eye’, ‘digital’ and ‘imaging’ and ‘ophthalm’, ‘digital’ and ‘imaging’ and ‘diabet’, ‘laser’ and ‘eye’, ‘laser’ and ‘ophthalm’, ‘laser’ and ‘diabet’, ‘visual’ and ‘acuity’, ‘visual’ and ‘impairment’, ‘blindness’ and ‘diabet’, ‘diabetic’ and ‘screening’, ‘uptake’ and ‘screening’ and ‘diabet’ in title, ‘attendance’ and ‘screening’ and ‘diabet’, and/or ‘vitrectomy’ and ‘diabet’ in title.
These keywords were taken from other reviews in this area and refined to be selective to the field of interest of the first author (screening or management of DR). In addition, the contents page lists of the following journals, considered to be those most likely to publish articles relevant to this topic, were reviewed each month:
Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavia, American Journal of Ophthalmology, Archives of Ophthalmology, British Journal of Ophthalmology, British Medical Journal, Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, Current Eye Research, Diabetes, Diabetes Care, Diabetes Metabolism Research and Reviews, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics, Diabetic Medicine, Diabetologia, European Journal of Ophthalmology, Eye, Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Journal of Diabetes and its Complications, Journal of Medical Screening, Journal of the Eye, The Lancet, Ophthalmic Surgery and Lasers, Ophthalmologica, Ophthalmology, Pediatric Diabetes, Retina and Survey of Ophthalmology.
Articles of interest identified with this search strategy were sourced from the local NHS host trust library or online from the electronic journal resource (Athens51) accessible in the host trust library.
Chapter 4 Added value: relevant work conducted by members of the research team prior to commencement of or during work on this Health Technology Assessment project
The following work from members of the research team has helped to inform this project:
-
The GP2DRS project. 52 Gloucestershire was the Phase 1 pilot site for the GP2DRS project. This project is the primary phase of the GP2DRS programme, the objective of which is to automate the transfer of relevant patient information between GP practices and NHS DR screening programmes. For the GP2DRS Phase 1 pilot in Gloucestershire, 14,919 patients from 54 GP practices were identified on 17 April 2009 as being within the criteria [C10 coded (read code: diabetes) and 12 years old or over] for DR screening. Within this group, 712 patients were not known to the Gloucestershire DESP. A detailed investigation was carried out into the reasons why these patients were not known to Gloucestershire DESP. 52
-
Over the subsequent 12 months, we sent out patient information leaflets to practices in Gloucestershire, and we obtained risk factor data by September 2010 on 4220 people with diabetes by means of a single letter sent after screening at a practice asking that practice to provide a consent code update. Irene Stratton undertook a preliminary analysis33 of these data to check that they were of sufficient quality for this grant proposal. Irene Stratton also analysed all the outputs from the Electronic Annual Reporting System for the 91 eye screening programmes in England, in order to try and improve data quality. A full-time administrator was appointed in January 2011 in Gloucestershire in order to communicate with GP practices to encourage them to update the consent codes during 2011 so that we could achieve our target of 15,000 people with both historic risk factor and retinopathy screening data by the end of 2011.
-
The risk factor data that were collected from transfer of data from GP systems in the GP2DRS data transfer or via MIQUEST extractions included age, sex, ethnicity, duration of diabetes, diabetes type, visual acuity, certified severely sight impaired or blind, certified sight impaired or partially sighted, body mass index (BMI), systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, HbA1c, serum creatinine.
-
Our research group developed a simple risk stratification model for time to development of STDR,39 which was based on categorising the digital photographic screening results from two consecutive annual digital photographic screenings.
-
Our research group also published a paper demonstrating the influence of background DR in the second eye on rates of progression of DR in our cohort of patients in Gloucestershire between 2005 and 2010. 53
-
IS was one of a team of researchers who were involved in a research report produced by the University of Warwick on behalf of the Four Nations Diabetic Retinopathy Study Group entitled ‘Rapid literature review: would changing diabetic eye screening intervals from the current annual recommendation lead to changed clinical outcomes?’54
-
There has been much debate over the years on the influence of one or both eyes on quality-of-life scores and, believing that work in this area would be useful for this HTA project, we undertook a retrospective analysis of data collected in 289 people with diabetic macular oedema at baseline in a randomised clinical trial with diabetic macular oedema, and we recommended that a weighted visual acuity measure from both eyes is considered in future diabetic macular oedema trials. 55
-
We studied the agreement between screening photographic and hospital biomicroscopy grading of DR in two separate published audits56,57 which has helped to inform Phase 3 of this project – the monitoring interval approach (see Chapter 7).
-
Measurement of severely sight impaired or blindness rates in Gloucestershire. Gloucestershire has had a DESP based on two-field digital photography since 1998 and the numbers of people registered sight impaired (previously termed ‘partially sighted’) and severely sight impaired (previously termed ‘blind’) are very low. Please note that this uses the UK definitions and not the World Health Organization definitions (see Glossary).
The numbers of people recorded as sight impaired and severely sight impaired in the last few years are shown in Table 1.
| Years | Annual incidence numbers registered severely sight impaired or blind | Percentage of the population with diabetes registered severely sight impaired or blind | Annual incidence numbers registered sight impaired or partially sighted | Percentage of the population with diabetes registered sight impaired or partially sighted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005–8 | 5.33 per annum | 0.024% | 8.7 per annum | 0.039% |
| 2010–13 | 1 per annum | 0.0034% | 4.3 per annum | 0.015% |
The previously reported58 lowest annual incidence of blindness was reported in Newcastle as having been reduced to 0.035% of the population with diabetes.
Chapter 5 Phase 1: risk factor approach
Rationale
Rates of incidence and progression of retinopathy are greater in people with a longer duration of diabetes and with poor glycaemic control (higher HbA1c) and may also vary with other factors such as blood pressure and diabetes type. It has been shown in Denmark that it is possible to identify those at higher absolute risk of STDR,59 and this suggests that it may be possible to identify subgroups of those with diabetes in whom the screening interval can be extended without risk of STDR developing before the next screening visit. This Danish model was constructed using published data from several clinical trials for which patients were recruited in the 1970s and 1980s and followed into the 1990s. The Danish model may not be optimal for patients diagnosed in the past decade as these patients tend to be more obese and to be diagnosed somewhat earlier in the disease process as opportunistic screening becomes more frequent.
Data set
The Gloucestershire Diabetic Eye Screening Programme (GDESP) includes 27,000 people aged 12 years or older with diabetes who are eligible for annual screening. Our database includes:
-
longitudinal data on photographs from 2005 to the present
-
digital photographs on two fields, with mydriasis (eyes dilated) to maximise image quality
-
consistent grading team
-
quality control, including repeat grading and external quality assurance
-
patients invited for screening annually but may attend less frequently
-
-
risk factor data through separately funded ‘GP2DRS’ project
-
risk factor data were available from GP electronic records (EMIS) on 4400 screened patients by September 2010
-
by the end of December 2011, we had received risk factor data on over 12,000 patients.
-
Given that this data set is much larger than needed for this project, we used a data-splitting approach. We had originally planned to randomly select 50% of patients for the model derivation data set (‘derivation data’) and to reserve the other 50% for model validation purposes (‘validation data’). However, the reviewers on our original application suggested that a non-random method might be used for constructing the samples for the risk model and then testing it. We therefore altered the method of splitting the database to a systematic method using the postcode of the GP to define two areas (Group A and Group B) with similar sized populations using the population data from the Office for National Statistics for Local Government Districts (Table 2). Group A includes three more urban larger towns (Gloucester, Tewkesbury and Cheltenham) and the remaining areas that make up Group B are more rural.
| Derivation and validation set | District Council areas of Gloucestershire | Population | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | Gloucester | 117,300 | |
| Cheltenham | 113,900 | ||
| Tewkesbury | 80,600 | ||
| Subtotal | 311, 800 | ||
| Group B | Cotswolds | 83,500 | |
| Forest of Dean | 82,800 | ||
| Stroud | 111,100 | ||
| Subtotal | 277,400 | ||
| Total | 589,200 | ||
Methods
Exploratory data analysis was used to look for outliers in all variables. The population was divided into derivation and validation sets based on the postcode of the GP practice. Screening data were used from 2005, the date at which retinal cameras were upgraded to modern camera backs and grading was stable. For each SE, the most recent clinical data items were identified and the baseline SE was defined as the first at which all required variables were present. Patients were included in the cohort if they had one of three categories of DR at initial eye screening: no DR in either eye; mild DR in only one eye; or mild DR in both eyes. Cox proportional hazard models were used with interval censoring to identify risk factors for progression. The parameter estimates from the derivation set were applied to the patients within the validation set and the risk of progression to referable DR is reported by centile of risk. In those patients with at least three SEs and clinical variables at the second of these visits we compared this model with our previously published risk model. 39
The multivariate modelling used the following parameters:
-
outcome (either of):
-
referable DR (grade R2 pre-proliferative or R3 proliferative)
-
referable diabetic maculopathy (grade M1)
-
-
exposures:
-
age, sex, smoking, BMI
-
previous retinal photographs
-
duration of diagnosed diabetes
-
type of diabetes
-
HbA1c
-
systolic and diastolic blood pressure
-
measurements of renal function (urine albumin, serum creatinine)
-
lipid measurements
-
-
analysis:
-
Cox proportional hazards model with interval-censoring (as retinopathy status can only be observed at screening visits not at the point at which STDR actually develops)
-
stepwise selection was used to develop a risk score for referable retinopathy/maculopathy at subsequent visits.
-
We also developed a model for risk of progression to maculopathy alone and the risk of progression to pre-proliferative DR and PDR alone.
Results
In total, 84,148 screening events were available, of which 75,491 were in 2005 or later. However, grading results were stored separately and once matching was carried out, and those with missing grading results omitted, there were 72,077 episodes and, of these, 15,410 had two or more SEs.
The data extraction from the GP practices yielded 3.3 million data items. Results recorded within the data set are shown in Tables 3 and 4.
| Clinical and biochemical measures | n | Median | 25–75th centile | Minimum, maximum | Median observations per patient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 311,405 | 55 | 46 to 66 | 20, 199 | 16 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 277,858 | 30.3 | 26.8 to 34.7 | 15.1, 69.9 | 11 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 523,712 | 80 | 72 to 88 | 30, 210 | 20 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 525,517 | 140 | 130 to 153 | 50, 290 | 20 |
| Serum creatinine (µmol/l) | 285,914 | 84 | 72 to 101 | 2.8, 1484 | 12 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/l) | 217,405 | 4.5 | 3.8 to 5.4 | 0.4, 20.0 | 10 |
| Urine albumin/ creatinine ratio (mg/mmol) | 89,984 | 0.9 | 0.5 to 2.6 | 0.0, 791.2 | 5 |
| Smoking status (n = 233,149) | Median observations per patient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current smoker | Ex-smoker | Never smoked | Unknown | |
| 45,200 | 101,152 | 86,766 | 31 | 10 |
In exploratory analyses, models were fitted using all variables from Table 3, but urine albumin was subsequently dropped as the data were not available for all patients, and its inclusion led to the overall loss of 12% of data from patients and 20% of the follow-up time.
The grading levels recorded by the programme are the same as those recorded in the NHS DESP in England and are shown in Table 5 with an approximate Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) grade.
| NHS DESP category | Approximate ETDRS equivalent(s) | Description/features |
|---|---|---|
| R0M0 | 10 | No detected DR |
| R1 | 14 to 35 | Background DR (mild NPDR): microaneurysm(s) and/or retinal haemorrhage, with or without exudate or cotton wool spots |
| R2 | 43 to 53 | Pre-proliferative (moderate to severe NPDR): multiple deep, round or blot haemorrhages and/or definite IRMA and/or venous beading and/or reduplication |
| R3 | 61 and greater | PDR: any new vessels, pre-retinal fibrosis, vitreous or pre-retinal haemorrhage with or without tractional detachment |
| M0 | No direct equivalent | Absence of any M1 features below |
| M1 (with any of R1, R2 or R3) | No direct equivalent | Maculopathy (presence of any two-dimensional photographic markers of diabetic maculopathy):
|
The model fitting was explored using patients for whom age, duration of diabetes, blood pressure, HbA1c, glomerular filtration rate, smoking status, diabetes type and BMI were available. In total, 7012 people with diabetes were included in the derivation set and 5778 people with diabetes were included in the validation set (Table 6).
| Risk factors | Derivation set | Validation set | p-value for difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 7012 | n = 5778 | ||
| Progressed to STDR events, n (%) | 606 (8.5) | 490 (8.5) | 0.74 |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 3932 (56.1) | 3328 (57.6) | 0.08 |
| Female | 3080 (43.9) | 2450 (42.4) | |
| Diabetes type, n (%) | |||
| Type 1 | 305 (4.4) | 296 (5.1) | 0.08 |
| Type 2 | 6707 (95.6) | 5482 (94.9) | |
| Ever smoked, n (%) | |||
| No | 3438 (49.0) | 2681 (46.4) | 0.003 |
| Yes | 3574 (51.0) | 3097 (53.6) | |
| Current smoker, n (%) | |||
| No | 6098 (87.0) | 5085 (88.0) | 0.077 |
| Yes | 914 (13.0) | 693 (12.0) | |
| DR status, n (%) | |||
| No DR | 4638 (66.1) | 3698 (64.0) | 0.017 |
| One eye mild NPDR | 1411 (20.1) | 1231 (21.3) | |
| Two eyes mild NPDR | 963 (13.7) | 849 (14.7) | |
| HbA1c (mol/mol), n (25–75th centile) | 50 (43 to 60) | 50 (43 to 60) | 0.06 |
| Total serum cholesterol, n (25–75th centile) | 4.3 (3.7 to 5.1) | 4.3 (3.7 to 5.0) | 0.51 |
| Glomerular filtration rate, n (25–75th centile) | 78 (66 to 91) | 78 (65 to 91) | 0.13 |
| Years since diagnosis of diabetes, n (25–75th centile) | 1.9 (0.6 to 5.9) | 2.2 (0.8 to 6.1) | < 0.0001 |
| Age at baseline screening (years), n (25–75th centile) | 65 (55 to 73) | 65 (57 to 72) | 0.025 |
| Systolic blood pressure, n (25–75th centile) | 134 (125 to 142) | 135 (127 to 142) | 0.0034 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, n (25–75th centile) | 79 (70 to 82) | 78 (70 to 82) | < 0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2), n (25–75th centile) | 29.9 (26.5 to 33.9) | 29.9 (26.7 to 33.8) | 0.484 |
We investigated the effect of clinical variables having adjusted for the number of eyes with mild, non-proliferative DR (NPDR) to look at the univariate effects (Table 7).
| HR for progression to STDR (95% CI) | HR for progression to maculopathy (95% CI) | HR for progression to R2 or R3 (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic blood pressure (per 10 mmHg) | 1.03 (0.98 to 1.08) | 1.01 (0.96 to 1.07) | 1.08 (1.01 to 1.17) |
| Diastolic blood pressure (per 10 mmHg) | 0.95 (0.87 to 1.03) | 0.95 (0.86 to 1.03) | 1.00 (0.88 to 1.14) |
| Type 2 vs. type 1 diabetes | 0.45 (0.38 to 0.58) | 0.54 (0.42 to 0.68) | 0.39 (0.29 to 0.53) |
| Smoking status | |||
| Ever smoked | 0.89 (0.75 to 1.05) | 0.94 (0.78 to 1.12) | 0.90 (0.69 to 1.19) |
| Current smoker | 0.99 (0.76 to 1.3) | 0.94 (0.70 to 1.25) | 1.16 (0.77 to 1.74) |
| Sex: female | 1.10 (0.95 to 1.28) | 1.16 (0.96 to 1.36) | 1.06 (0.83 to 1.36) |
| HbA1c (per 10 mmol/mol) | 1.31 (1.26 to 1.36) | 1.29 (1.24 to 1.35) | 1.47 (1.39 to 1.55) |
| Duration of diabetes (per 5 years) | 1.20 (1.17 to 1.24) | 1.18 (1.13 to 1.22) | 1.26 (1.20 to 1.32) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 0.99 (0.98 to 1.01) | 1.01 (0.99 to 1.03) |
| Serum creatinine (per 10 µmol/l) | 1.02 (0.99 to 1.05) | 1.02 (0.99 to 1.06) | 1.00 (0.94 to 1.05) |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/l) | 1.14 (1.07 to 1.22) | 1.16 (1.01 to 1.25) | 1.15 (1.03 to 1.28) |
| Urine albumin | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.015) | 1.01 (1.00 to 1.020) | 1.01 (1.006 to 1.02) |
| Explanatory information which links type of diabetes to diabetes duration and HbA1c | |||
| Type 1 diabetes | Type 2 diabetes | ||
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 64 (55 to 76) | 50 (43 to 60) | |
| Duration of diabetes | 17 (8 to 28) | 2.0 (0.7 to 5.7) | |
The results (Table 8) of the Cox proportional hazards model show that the presence of background DR in both eyes at a screening visit has the highest hazard ratio (HR) of 7.13 [95% confidence interval (CI 5.84 to 8.70)] with background DR in one eye having a HR of 2.56 (95% CI 2.05 to 3.20), and HbA1c of 1.28 (95% CI 1.23 to 1.34), and duration of diabetes (per 5 year increase), total serum cholesterol (per 1 mmol/l) and serum creatinine (per 10 µmol/l) all having lower HRs.
| Risk factors | Parameter estimate | HR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Background DR (mild NPDR) in both eyes at screening visit | 1.96 | 7.1 | 5.8 to 8.7 |
| HbA1c (per 10 mmol/mol increase) | 0.25 | 1.28 | 1.23 to 1.34 |
| Duration of diabetes (per 5 year increase) | 0.18 | 1.20 | 1.16 to 1.24 |
| Background DR (mild NPDR) in one eye at screening visit | 0.94 | 2.6 | 2.0 to 3.2 |
| Total serum cholesterol (per 1 mmol/l) | 0.11 | 1.12 | 1.05 to 1.19 |
| Serum creatinine (per 10 µmol/l) | 0.004 | 1.04 | 1.01 to 1.07 |
Hence, the risk score for a patient with mild NPDR in both eyes is given by:
The risk score for a patient with mild NPDR in one eye is given by:
The risk score for a patient with no retinopathy is given by:
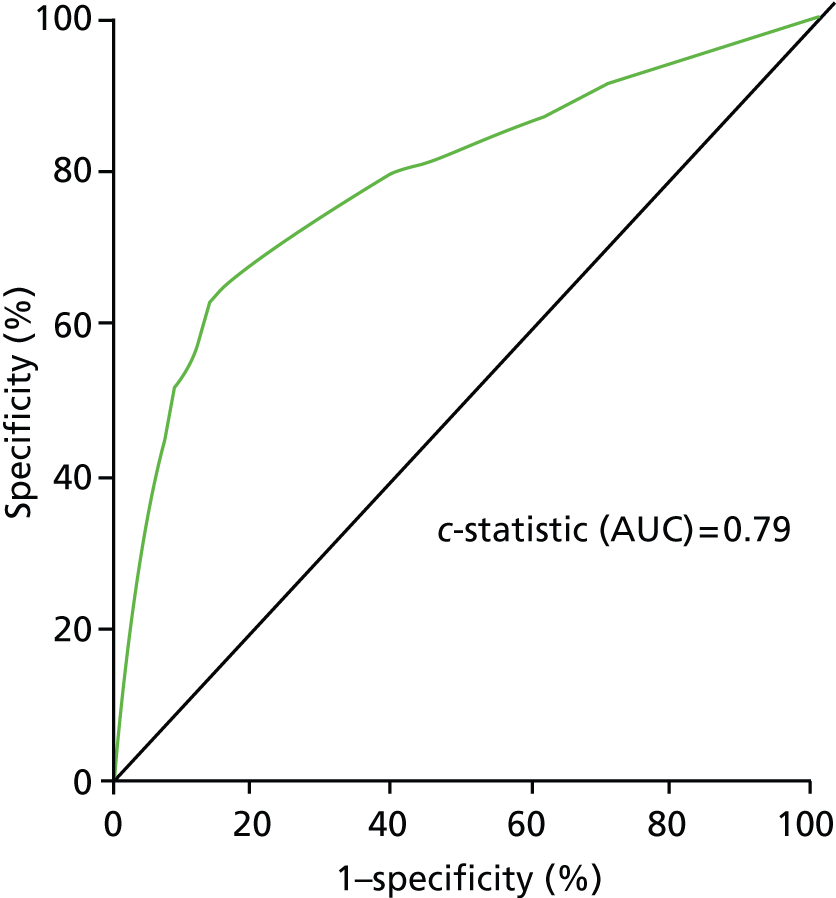
The model was built using these risk factors. The ROC curve for overall endpoints in the validation set is shown in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2.
Receiver operating characteristic curve for validation data set. AUC, area under the curve.
Estimates of the ROC curve at given time points were obtained using the SAS macro TDROC (time dependent receiver operating characteristic) written by Mithat Gönen of Memorial Sloan Kettring Cancer Centre60 which generates a time-dependent ROC curve at a given time point for a censored outcome and an ordinal or continuous predictor. CIs were obtained using boot-strapping. Figure 3 shows the Kaplan–Meier estimates of time to referral by quintile of risk in the validation data set. At 4 years, 25% of those in the top quintile have been referred and in the lowest quintile fewer than 2% have been referred.
FIGURE 3.
Validation data set: time to referable screening result by quintile of risk (i.e. Group 1 contains those whose risk score is 0–20th centile, Group 2 is 21–40th centile, Group 3 is 41–60th centile, Group 4 is 61–80th centile, Group 5 is 81–100th centile).

The characteristics that are included in the model of the highest and lowest risk groups in the validation set are shown in Table 9.
| Data items in risk model | Lowest quintile (n = 1071) | Highest quintile (n = 1195) |
|---|---|---|
| Mild NPDR at previous SE | ||
| Neither eye, n (%) | 1071 (100) | 53 (4.4) |
| One eye, n (%) | 0 (0) | 295 (24.7) |
| Both eyes, n (%) | 0 (0) | 847 (70.88) |
| HbA1c, mmol/mol (IQR) | 42 (39–44) | 58 (49–72) |
| Duration diabetes at baseline screen, years (IQR) | 0.9 (0.5–1.75) | 6.2 (1.3–13.25) |
| Serum total cholesterol, mmol/l (IQR) | 4.0 (3.5–4.6) | 4.3 (3.7–5.1) |
| Serum creatinine, µmol/l (IQR) | 78 (67–91) | 84 (72–100) |
The characteristics that are not included in the model of the highest and lowest risk groups in the validation set are shown in Table 10. There is very little difference in systolic and diastolic blood pressure between the highest and lowest risk groups in the validation set. Better control of blood pressure in the current era is likely to be the reason why blood pressure does not influence the model.
| Data items not in risk model | Lowest quintile (n = 1071) | Highest quintile (n = 1195) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 563 (52.6) | 726 (60.8) |
| Female | 508 (47.4) | 469 (39.2) |
| Type of diabetes, n (%) | ||
| Type 1 DM | 6 (0.56) | 183 (15.3) |
| Type 2 DM | 1065 (99.4) | 1012 (84.7) |
| Age at first screen, years (IQR) | 66 (58–73) | 64 (55–71) |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHG (IQR) | 134 (125–140) | 136 (127–144) |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHG (IQR) | 76 (70–80) | 77 (70–82) |
Figure 4 shows that almost all of the PDR is detected in the highest quintile of risk. The data are also shown in Table 11, which shows that no PDR is detected in the lowest two deciles of risk. The progression to STDR is shown in Table 12.
FIGURE 4.
First referable retinopathy detected by decile of risk in validation set.

| Decile | No referable DR | R1M1 | R2M0 | R2M1 | R3M0 | R3M1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 542 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 559 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 555 | 20 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 583 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 587 | 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 563 | 28 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 578 | 24 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 551 | 36 | 11 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 530 | 70 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 10 | 376 | 123 | 67 | 35 | 9 | 0 |
| Risk quintile | Number in risk group | Number of events | Rate of progression to STDR (per 1000 PYs) | Exposure time (PYs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1092 | 19 | 4.8 | 47,707 |
| 2 | 1190 | 42 | 9.1 | 55,690 |
| 3 | 1218 | 52 | 10.0 | 62,459 |
| 4 | 1218 | 88 | 18.4 | 57,404 |
| 5 | 1232 | 325 | 74.8 | 52,125 |
The risk estimates are demonstrated in Figure 5.
FIGURE 5.
Model fitting for risk of progression to STDR. (a) No DR, HR compared with patient with no DR, 5 years of diabetes, HbA1c = 50 mmol/mol; (b) mild NPDR in one eye, HR compared with patient with no DR, 5 years of diabetes, HbA1c = 50 mmol/mol; and (c) mild NPDR in both eyes, HR compared with patient with no DR, 5 years of diabetes, HbA1c = 50 mmol/mol.



Although the aim of the project was to examine the risk of progression to STDR for maculopathy M1 or for retinopathy (R2 or R3) collectively, we have examined the model fit for these endpoints separately.
These analyses (Tables 13 and 14) show that for progression to retinopathy R2 or R3, the presence of background retinopathy in both eyes or in just one eye is a more important risk factor than in progression to maculopathy M1. Cholesterol does not enter the model for progression to R2 or R3 but systolic blood pressure does enter the model. The inclusion of systolic blood pressure in the model of progression to R2 or R3 reflects results from earlier studies which analysed the progression of retinopathy alone (not including maculopathy) using scales such as the ETDRS scale.
| Risk factors | Parameter estimate | HR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Background DR (mild NPDR) in both eyes at screening visit | 1.81 | 6.1 | 4.9 to 7.5 |
| HbA1c (per 10 mmol/mol increase) | 0.22 | 1.25 | 1.20 to 1.31 |
| Duration of diabetes (per 5 year increase) | 0.17 | 1.18 | 1.13 to 1.23 |
| Background DR (mild NPDR) in one eye at screening visit | 0.88 | 2.4 | 1.9 to 3.0 |
| Total serum cholesterol (per 1 mmol/l) | 0.13 | 1.14 | 1.06 to 1.22 |
| Serum creatinine (per 10 µmol/l) | 0.05 | 1.05 | 1.01 to 1.08 |
| Risk factors | Parameter estimate | HR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Background DR (mild NPDR) in both eyes at screening visit | 2.6 | 14.1 | 10 to 21 |
| HbA1c (per 10 mmol/mol increase) | 0.39 | 1.5 | 1.4 to 1.6 |
| Duration of diabetes (per 5 year increase) | 0.24 | 1.27 | 1.21 to 1.33 |
| Background DR (mild NPDR) in one eye at screening visit | 1.2 | 3.4 | 2.2 to 5.5 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 0.09 | 1.09 | 1.01 to 1.17 |
Further analyses were carried out to assess the performance of the model proposed in our earlier paper based on the outcomes of two consecutive SEs. 39
The derivation data set for these analyses consisted of those patients who had two SEs with no referable DR and at least one further SE.
We looked at the performance of three models:
-
two baseline SEs and clinical risk factor (CRF) data
-
two baseline SEs
-
one SE and CRF data.
In the Tables 15a–15c we have calculated the parameter estimates and HRs for the different models in all patients who had at least three SEs and clinical data available. In the derivation set, there were 162 events in 5774 people, and in the validation set, there were 131 events in 4873 people.
| Retinopathy status and clinical variables at first screen’ | Retinopathy status and clinical variables at second screen’ | Clinical data and two screens | Clinical data and two screens |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter estimate | HR (95% CI) | ||
| First background two eyes | Second background two eyes | 2.7 | 13.8 (10.6 to 18.1) |
| First background one eye | Second background two eyes | 2.0 | 7.4 (5.2 to 10.7) |
| First no DR | Second background two eyes | 1.5 | 4.5 (3.1 to 6.5) |
| First background two eyes | Second background one eye | 1.1 | 3.1 (1.6 to 6.0) |
| First background one eye | Second background one eye | 1.3 | 3.6 (2.4 to 5.4) |
| First no DR | Second background one eye | 1.0 | 2.8 (2.0 to 3.0) |
| First background two eyes | Second no DR | Not in model | Not in model |
| First background one eye | Second no DR | Not in model | Not in model |
| First no DR | Second no DR | Reference | Reference |
| HbA1c (per 10 mmol/mol) | 0.3 | 1.35 (1.29 to 1.42) | |
| Total cholesterol | 0.16 | 1.17 (1.06 to 1.3) | |
| Retinopathy status at first screen | Retinopathy status at second screen’ | Two screens | Two screens |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter estimate | HR (95% CI) | ||
| First background two eyes | Second background two eyes | 2.8 | 16.7 (12.8 to 21.8) |
| First background one eye | Second background two eyes | 2.1 | 8.1 (5.7 to 11.6) |
| First no DR | Second background two eyes | 1.6 | 4.8 (3.3 to 6.9) |
| First background two eyes | Second background one eye | 1.17 | 3.2 (1.7 to 6.2) |
| First background one eye | Second background one eye | 1.25 | 3.5 (2.3 to 5.2) |
| First no DR | Second background one eye | 1.12 | 3.1 (2.2 to 4.3) |
| First background two eyes | Second no DR | Not in model | 1 |
| First background one eye | Second no DR | Not in model | 1 |
| First no DR | Second no DR | Reference | 1 |
| Retinopathy status and clinical variables at first screen | Clinical data and one screen | Clinical data and one screen |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter estimate | HR (95% CI) | |
| Both eyes with background DR | 2.1 | 8.1 (6.2 to 10.4) |
| HbA1c | 0.3 | 1.34 (1.27 to 1.42) |
| One eye with background DR | 1.1 | 3.0 (2.2 to 4.0) |
| Duration of diabetes per 5 years | 0.10 | 1.11 (1.05 to 1.17) |
| Total cholesterol | 0.16 | 1.12 (1.06 to 1.30) |
The following figures (Figures 6 and 7) show progression to referable DR by risk group. It is not possible to use quintiles of risk because most of the patients are in the low-risk group (no DR in each of two SEs). Hence, the groups have been defined to have the same number of patients as in the two SEs model.
FIGURE 6.
Progression to referable STDR by risk group in the three models. (a) Risk stratification in validation set using results of two SEs and clinical data; (b) risk stratification in validation set using results of two SEs; and (c) risk stratification in validation set using one SE and clinical information.


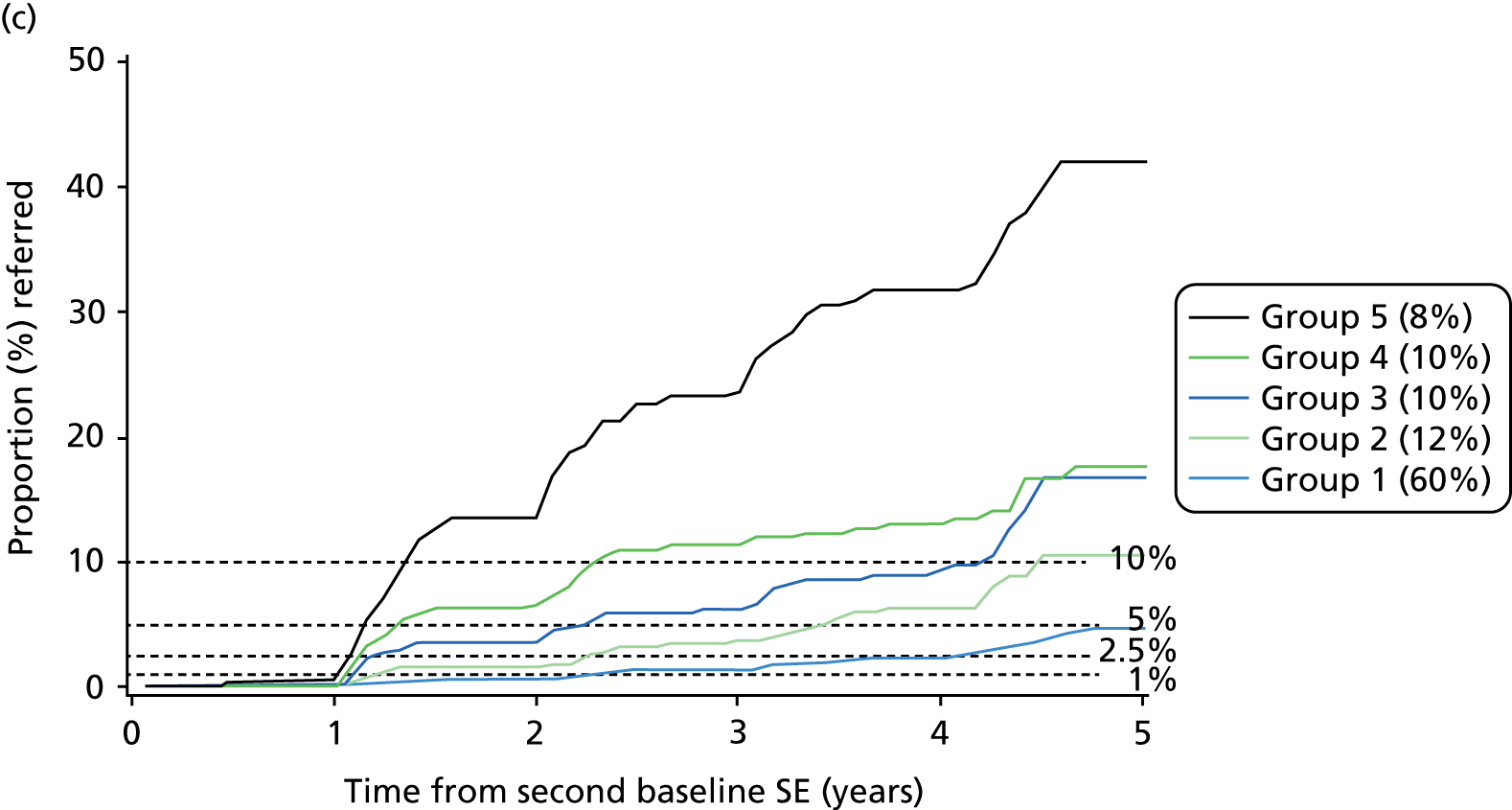
FIGURE 7.
The proportion of each grade of retinopathy by risk group in those found with referable retinopathy at the first SE where it was detected. (a) Referable retinopathy found by risk group: two screens plus clinical data; (b) referable retinopathy found by risk group: two screens; and (c) referable retinopathy found by risk group: one screen plus clinical data.



The bar charts in Figures 6 and 7 show the proportion of each grade of retinopathy by risk group in those found with referable retinopathy at the first SE where it was detected. There is no significant difference in the proportion of each grade of retinopathy between the three models.
Figure 8 and Table 16 show very little difference in the area under the curve (AUC) of the ROCs between the three models.
FIGURE 8.
Model comparison.
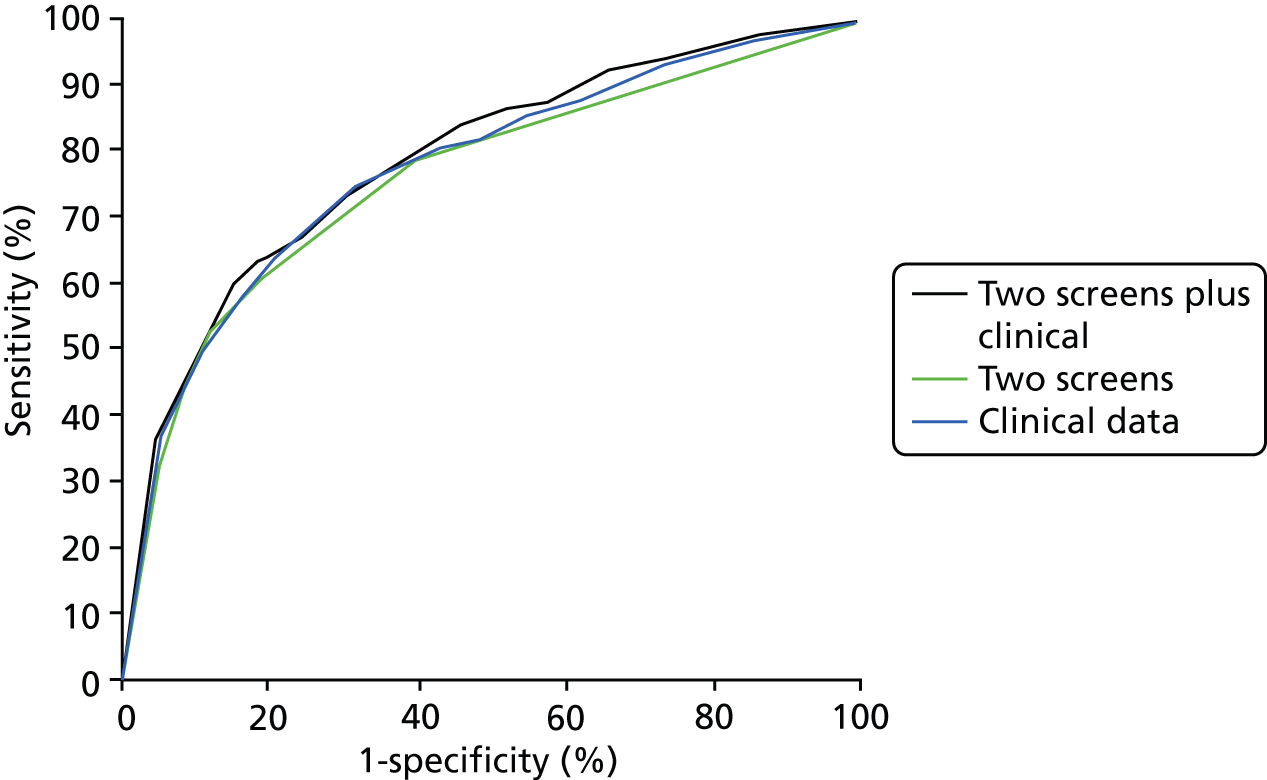
The AUC and 95% CI from boot-strapping are shown in Table 16.
| Model | AUC | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Two SEs plus clinical data | 0.786 | 0.759 to 0.813 |
| Two SEs | 0.759 | 0.732 to 0.788 |
| One SE plus clinical data | 0.774 | 0.748 to 0.800 |
Does the inclusion of cholesterol into the model improve the fit?
Although the addition of variables into the model may improve the fit using conventional estimations of fit, these may have little impact when it comes to defining groups for allocation of screening intervals. In order to examine this we have fitted the model including and excluding total cholesterol.
The distribution of risk for those who go on to develop STDR and those who do not develop STDR in the validation sets is shown in Figure 9.
FIGURE 9.
Ranked centile of linear risk predictor for those with and without STDR. Centile rank with cholesterol vs. centile rank without cholesterol. (a) With STDR; and (b) without STDR.


Reclassification among people who progressed to STDR and those who did not during follow-up is shown in Tables 17a–17d.
| Quintile of risk with cholesterol in the model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quintile of risk without cholesterol in the model | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Total | |
| 1 | 18 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23 | |
| 2 | 5 | 34 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 41 | |
| 3 | 0 | 3 | 46 | 3 | 0 | 52 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 79 | 2 | 89 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 318 | 321 | |
| Total | 23 | 42 | 56 | 85 | 320 | 526 | |
| Quintile of risk with cholesterol in the model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quintile of risk without cholesterol in the model | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Total | |
| 1 | 991 | 176 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1167 | |
| 2 | 170 | 853 | 126 | 0 | 0 | 1149 | |
| 3 | 6 | 118 | 930 | 84 | 0 | 1138 | |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 78 | 990 | 32 | 1101 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 838 | 869 | |
| Total | 1167 | 1148 | 1137 | 1105 | 870 | 5424 | |
We now sum groups 1 to 3 because these groups have very similar progression rates to STDR.
| Quintile of risk with cholesterol in the model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quintile of risk without cholesterol in the model | 1 to 3 | 4 | 5 | Total | |
| 1 to 3 | 113 | 3 | 0 | 116 | |
| 4 | 8 | 79 | 2 | 89 | |
| 5 | 0 | 3 | 318 | 321 | |
| Total | 121 | 85 | 320 | 526 | |
| Quintile of risk with cholesterol in the model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quintile of risk without cholesterol in the model | 1 to 3 | 4 | 5 | Total | |
| 1 to 3 | 3370 | 84 | 0 | 3454 | |
| 4 | 79 | 990 | 32 | 1101 | |
| 5 | 0 | 31 | 838 | 869 | |
| Total | 3449 | 1105 | 870 | 5424 | |
Reclassifications for subjects with and without events are summarised below.
When cholesterol is added to the model, those whose ranking does not change remain on the diagonal, those who move into a higher group are in shaded light green and those who move into a lower group are shaded dark green.
The net gain in reclassification proportion can be shown using the reclassification methods of Pencina et al. 61
For 12 subjects who progressed to STDR, classification improved using the model with high-density lipoprotein, and for 19 people it became worse. This may be estimated using formulae of Pencina et al. 61 with the net gain in reclassification proportion of 0.120, significantly greater than zero (p-value < 0.001). The net gain in reclassification proportion for subjects who did not experience an event was not significant; 174 individuals were reclassified down and 173 were reclassified up (p-value = 0.957). The net reclassification improvement (NRI) was estimated at 0.121 and was highly significant (p-value < 0.001).
The NRI is estimated as:
Looking at the changes in those with events:
And in those without events:
So, the addition of cholesterol to the model does not improve net reclassification.
Classical risk factors for progression of diabetic retinopathy
The model used in this study was intended to determine the risk of referable DR, which included the risk of developing maculopathy as well as the risk of development of pre-proliferative DR or PDR. Some classical risk factors did not enter the model (e.g. blood pressure) because, although they were significant for the development of pre-proliferative DR or PDR, blood pressure was not significant in the development of maculopathy and so did not have a significant influence on the development of referable retinopathy. A total of 68% of the referable events were for maculopathy. The overall blood pressure was also better controlled than in the era of the UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) study and the ETDRS study, and patients who attend regularly for screening do have better control than those who do not.
Chapter 6 Phase 2: extension to ethnically diverse populations
Rationale
It is good practice to verify statistical modelling results in external data, especially given that the Gloucestershire data are atypically high quality and collected on an ethnically homogenous population. 62 In this project we verified the results of Phase 1 modelling, described in Chapter 5, in external data sets of greater diversity.
Data
-
Data from the East Anglian Programme including risk factors and grading results.
-
Data from the South London screening service including risk factors and grading results.
-
Data from the Nottingham screening service including risk factors and grading results.
We tested the risk score and algorithm against outcome retinopathy grades in the data sets.
Expected outcome
To develop a validated algorithm for recalling patients of white, Asian or African-Caribbean ethnicities for retinopathy screening, for use by the NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme and the 84 individual screening programmes across England.
Potential limitations
The Gloucestershire programme has a well-established quality-assured screening service with a stable group of experienced graders. Hence, it may not be typical of all screening programmes. Even with controls in place, it is likely that some misgrading will have occurred. We have, therefore, estimated when this may have occurred in Chapter 5 and utilised this in Chapter 7.
Gloucestershire has a small ethnic minority population. The main ethnic minority groups in Gloucestershire are Indian/British Indian (0.7%), and black/black British (0.8%), although the percentage of people from an ethnic minority group in the population with diabetes in Gloucestershire is nearer 5% because of the higher prevalence of diabetes in these groups. East Anglia has a similar low prevalence of ethnic minority groups. However, the data from South London and Nottingham used data sources that include a higher ethnic minority population from UK Asian, African-Caribbean and other white (i.e. non-British) Caucasian groups.
Results
The minimal model includes the following parameters:
-
mild NPDR in both eyes at screening visit, HR 6.98 (95% CI 5.75 to 8.47)
-
mild NPDR in one eye at screening visit, HR 2.50 (95% CI 2.01 to 3.12)
-
HbA1c (per 10 mmol/mol increase), HR 1.30 (95% CI 1.25 to 1.35)
-
duration of diabetes (per 5 year increase), HR 1.20 (95% CI 1.16 to 1.24).
The model was validated in the following external data sets:
-
data from 17,634 people with diabetes in the East Anglian Programme (A) who have grading results from two SEs and risk factor data
-
data from 1223 people with diabetes in the South London Screening Service (B) who have grading results from two SEs and risk factor data
-
data from 1083 people with diabetes in the Nottingham Screening Service (C) who have grading results from two SEs and risk factor data.
Data from programmes A, B and C are shown in Table 18.
| Programme | A: n = 17,634 | B: n = 1223 | C: n = 1083 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (%) | |||
| Male | 56 | 50 | 52 |
| Female | 44 | 50 | 47 |
| Years since diagnosis of diabetes at baseline screen (IQR) | 4.5 (1.0–8.7) | 3.5 (1.3–6.7) | 2.9 (0.6–6.6) |
| Diabetes type (%) | |||
| Type 1 DM | 5 | 5 | 7 |
| Type 2 DM | 95 | 95 | 93 |
| Age at baseline screen, years (IQR) | 66 (57–74) | 59 (49–68) | 61 (52–69) |
| HbA1c, IFCC mmol/mol (IQR) | 55 (49–66) | 52 (45–64) | 53 (46–63) |
| HbA1c, DCCT % (IQR) | 7.2 (6.6–8.2) | 6.9 (6.3–8.0) | 7.0 (6.4–7.9) |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/l (IQR) | 4.3 (3.7–5.0) | 4.6 (4.0–5.3) | 4.4 (3.7–5.1) |
| First screen R0M0, n (%) | 13,121 (74.4) | 957 (78.3) | 823 (76.0) |
| First screen R1M0 in one eye, n (%) | 2372 (13.4) | 165 (13.5) | 141 (13.0) |
| First screen R1M0 in both eyes, n (%) | 2141 (12.2) | 101 (8.3) | 119 (11.0) |
| Ethnicity (%) | |||
| Caucasian | 98.0 | 46.9 | 81 |
| African or African-Caribbean | 0.4 | 31.4 | 18.5 |
| Asian | 1.0 | 11.3 | 1.5 |
| Mixed | 0.3 | 4.3 | 0 |
| Other | 0.3 | 5.9 | 0 |
| Median follow-up, years (IQR) | 2.7 (2.0–3.0) | 3.8 (2.0–6.8) | 4.2 (2.2–5.3) |
The validation was carried out using the three parameter model (baseline retinopathy, duration of diabetes and HbA1c), and the proportions progressing to STDR by quintiles of risk within each programme were estimated and are shown in Figure 10. Descriptions of the clinical information and rates of progression to STDR within each risk quintile by programme are shown in Table 19.
FIGURE 10.
Validation in three English programmes. (a) Programme A; (b) programme B; and (c) programme C. Patients grouped into quintiles of risk within each programme (i.e. Group 1 contains those whose risk score is 0–20th centile, Group 2 is 21–40th centile, Group 3 is 41–60th centile, Group 4 is 61–80th centile, Group 5 is 81–100th centile).



| Programme | A: n = 17,634 | B: n = 1223 | C: n = 1083 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC at 3 years (95% CI) | 0.782 (0.762 to 0.803) | 0.836 (0.78 to 0.884) | 0.815 (0.714 to 0.897) |
| PYs | 42,535 | 5046 | 4242 |
| Number of cases of STDR | 845 | 94 | 81 |
| Overall event rate | 20/1000 PYs | 19/1000 PYs | 19/1000 PYs |
| Proportion with DR in 0/1/2 eyes (%) | |||
| DR quintile 1 | 100/0/0 | 100/0/0 | 100/0/0 |
| DR quintile 2 | 100/0/0 | 100/0/0 | 100/0/0 |
| DR quintile 3 | 99.8/0.2/0 | 99.2/0.8/0 | 100/0/0 |
| DR quintile 4 | 79.9/20.1/0 | 66.9/33.1/0 | 64.5/35.5/0 |
| DR quintile 5 | 26.5/28.8/44.7 | 25/33.6/41.4 | 15.3/29.6/55.1 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol), median (IQR) | |||
| HbA1c quintile 1 | 45 (42–48) | 42 (39–44.5) | 43 (41–46) |
| HbA1c quintile 2 | 52 (49–54) | 50 (46–52) | 51 (47.5–53) |
| HbA1c quintile 3 | 58 (54–63) | 57 (52–61) | 58.5 (54–63) |
| HbA1c quintile 4 | 67 (56–76) | 66 (50–77) | 65 (51–79) |
| HbA1c quintile 5 | 67 (56–89) | 67.5 (55–92) | 65 (53–83) |
| Duration of diabetes (years), median (IQR) | |||
| Duration quintile 1 | 1.5 (0.35–3.34) | 1.7 (0.9–3.3) | 0.9 (0.3–2.1) |
| Duration quintile 2 | 3.8 (1.4–6.4) | 2.7 (1.2–4.8) | 2.2 (0.7–4.2) |
| Duration quintile 3 | 6.4 (3.4–9.2) | 4.8 (1.9–7.2) | 4.1 (1.1–6.9) |
| Duration quintile 4 | 6.8 (2.7–11.0) | 4.3 (1.4–7.9) | 4.8 (1.0–7.7) |
| Duration quintile 5 | 9.8 (5.1–15.8) | 7.2 (2.0–12.8) | 8.2 (1.5–14.7) |
| Event rate (per 1000 PYs) | |||
| Event rate quintile 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Event rate quintile 2 | 4 | 9 | 0 |
| Event rate quintile 3 | 7 | 6 | 7 |
| Event rate quintile 4 | 12 | 24 | 15 |
| Event rate quintile 5 | 74 | 55 | 79 |
The proportion of patients in these three programmes who developed STDR or had no STDR on the date of censoring is shown in Figure 11 by quintile of risk. The component levels of STDR are shown. This demonstrates that the severity of STDR is associated with risk estimation, as was seen in the Gloucestershire validation data set (see Figure 4 and Table 11).
FIGURE 11.
Severity of DR at event or censoring. (a) Programme A; (b) programme B; and (c) programme C.



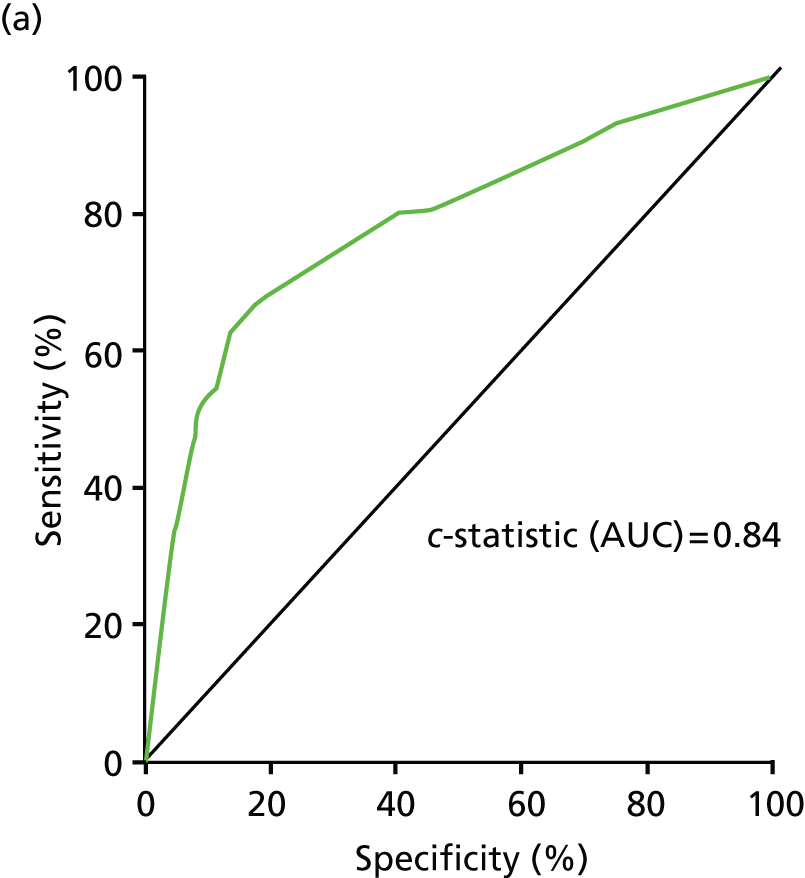
Model fit has been assessed using ROC curves and is shown in Figure 12.
FIGURE 12.
ROC for model with clinical information and one SE. (a) Programme A; (b) programme B; and(c) programme C.
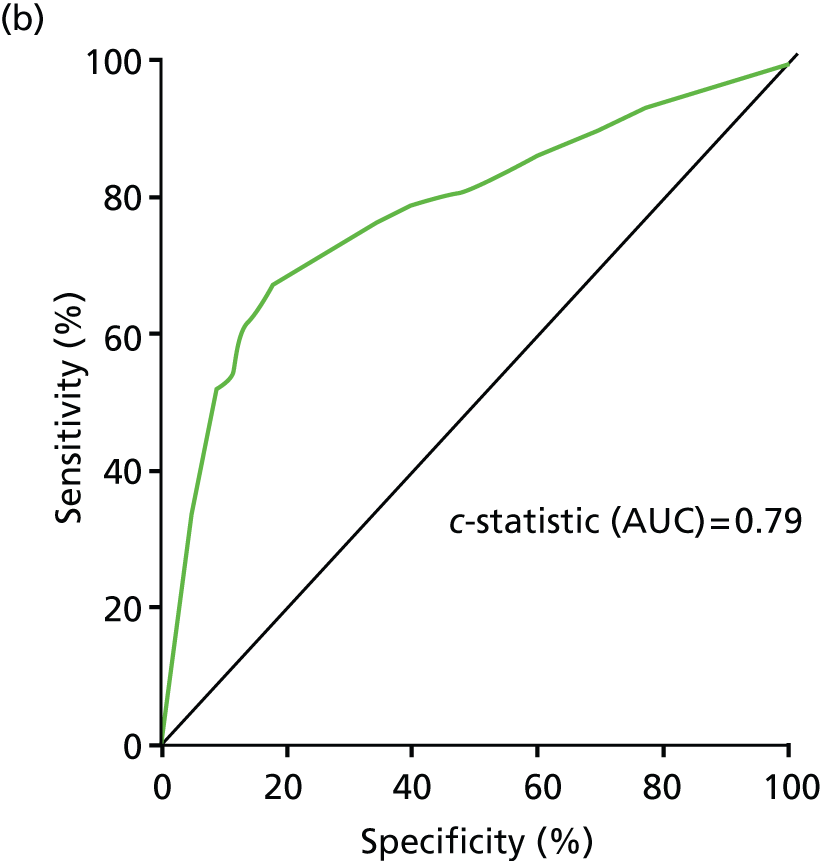

Validation of model by ethnic group
The participants in programme A are 98% Caucasian, and so this programme cannot be used to examine the effect of ethnicity.
Programme B had too few people with clinical information from primary care in the data set to fit the model with one SE and clinical information and so it was only possible to validate the model that uses two SEs to stratify patients by baseline risk. The risk estimator from this model was applied and ethnic group categories fitted in a Cox proportional hazards model. Results are shown in Figure 13 and Table 20.
FIGURE 13.
Validation in programme B using the risk stratification based on two SEs. Progression to STDR. (a) All risk groups; (b) high risk; (c) intermediate risk; and (d) low risk.

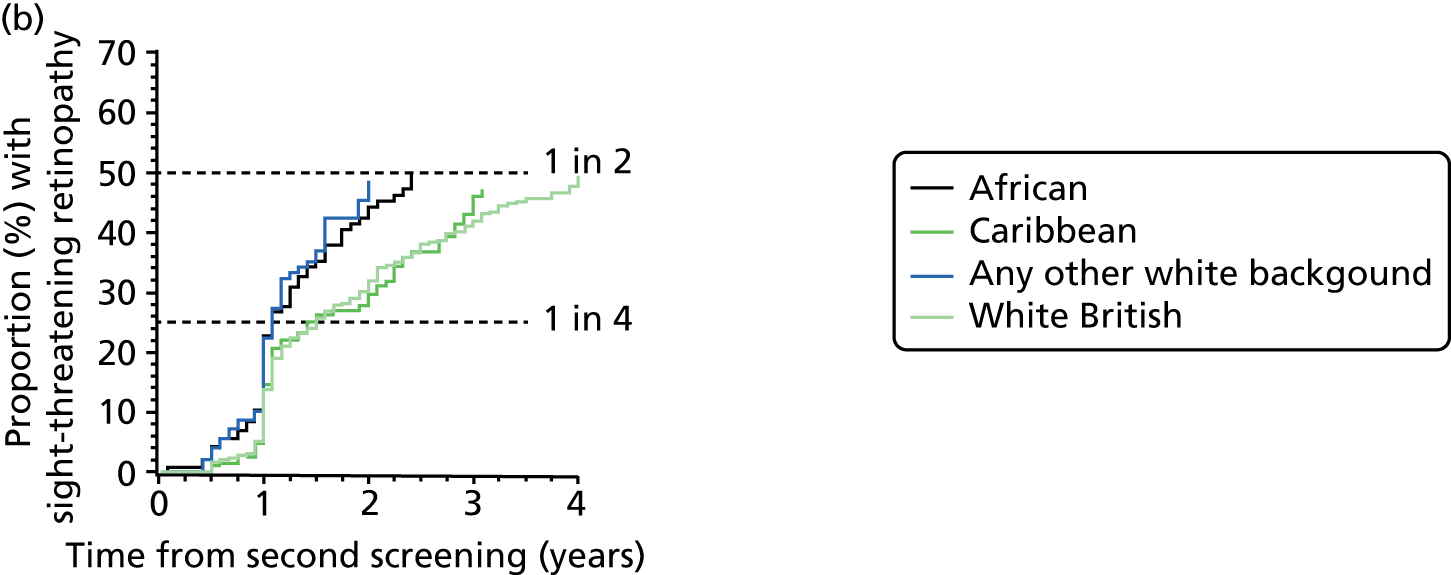
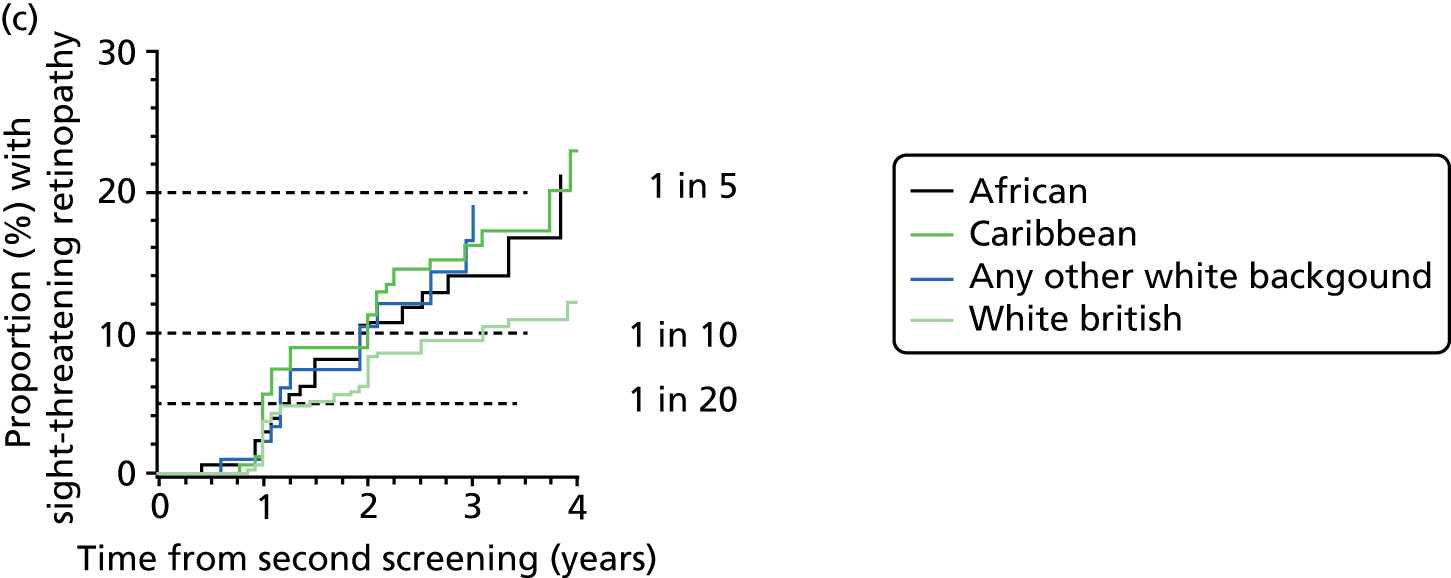
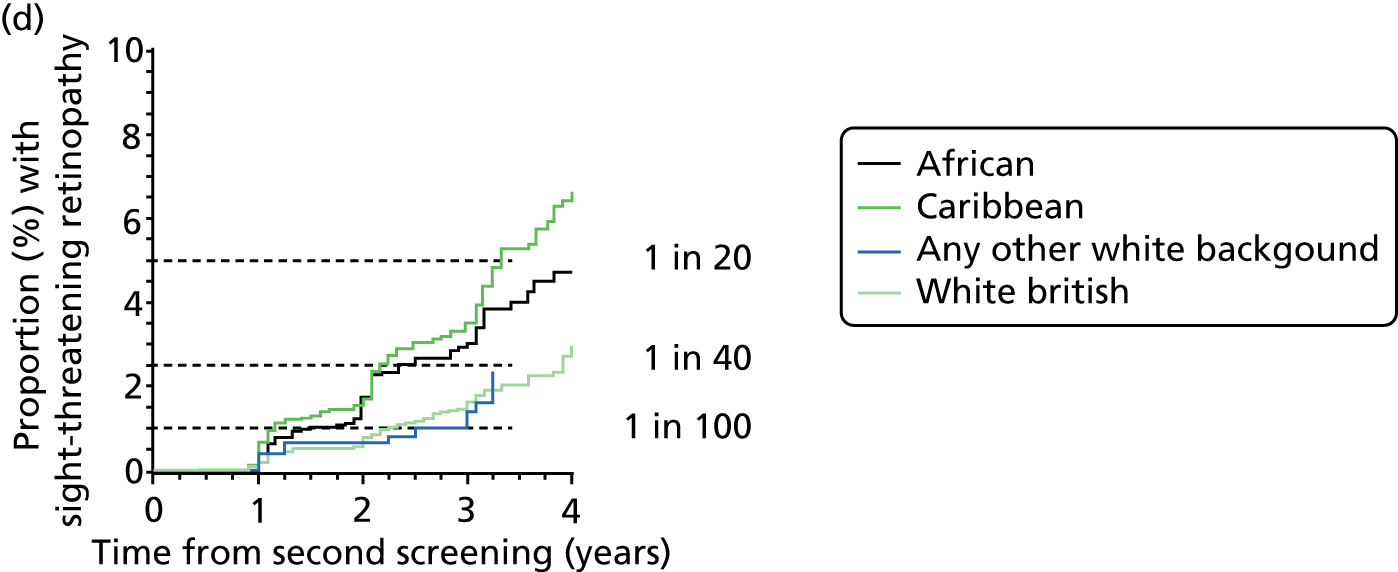
| Ethnic group | n | Sex (male/female), % | Type of diabetes (type 1/type 2/other), % | Duration of diabetes at second screening (years), median (IQR) | Age at diagnosis of diabetes (years), median (IQR) | Hazard ratio (95% CI) adjusted for risk category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| African | 3305 | 50.4/49.6 | 3.2/96.2/0.6 | 3 (1–6) | 47 (40–55) | 1.55 (1.33 to 1.80) |
| Caribbean | 3993 | 41.8/58.1 | 2.6/97.1/0.3 | 4 (1–9) | 57 (47–66) | 1.58 (1.38 to 1.81) |
| Other white | 1728 | 54.1/45.9 | 9.4/90.1/0.5 | 4 (1–9) | 55 (44–64) | 1.24 (1.03 to 1.48) |
| White British | 9478 | 54.8/45.2 | 9.6/90.1/0.3 | 4 (1–8) | 57 (46–66) | 1.0 |
Overall, the HR is over 50% higher for those of African or Caribbean ethnicity and 24% higher for those of other white ethnicity; in this category, many patients are Brazilian and Portuguese but the coding does not enable this to be broken down further.
The ethnicity coding in programme C is unreliable. The data for those with three SEs, with the first two episodes showing no referable retinopathy, are shown in Table 21. Over half the people in the cohort (54.8%) have no ethnic group recorded. There are 1257 people coded as African, yet the 2009 Office for National Statistics population estimates have 3100 people of African ethnicity in the whole area, and the African and Caribbean populations are about the same size. It appears that this coding may well be erroneous. Certainly, this level of uncertainty means that further analysis would be unreliable.
| Ethnic group | Code | n | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Null | Null | 5198 | 30.3 |
| Not stated | Z | 4195 | 24.5 |
| White British | A | 3596 | 21.0 |
| Any other | S | 2220 | 12.9 |
| African | N | 1257 | 7.3 |
| Other white | C | 236 | 1.4 |
| Pakistani | J | 163 | 1.0 |
| Caribbean | M | 82 | 0.5 |
| Indian | H | 81 | 0.5 |
| White Irish | B | 79 | 0.5 |
| Any other Asian | L | 14 | 0.1 |
| Any other black | P | 12 | 0.1 |
| Mixed race white: African-Caribbean | D | 8 | 0.05 |
| Bangladeshi | K | 8 | 0.05 |
| Any other mixed race | G | 4 | 0.02 |
| Mixed race white: African | E | 1 | 0.01 |
| Chinese | R | 1 | 0.01 |
| Total | 17,155 |
Conclusion
We have used data from three large, heterogeneous DESPs in England to validate the clinical model developed in Phase 1 (see Chapter 5).
-
Within each of these three English screening programmes, the risk model discriminates well between those at very low risk and those at very high risk of progression to STDR.
-
The model would be suitable for development of personalised screening intervals.
-
Further validation in other data sets with robust ethnicity information would be useful.
Chapter 7 Phase 3: monitoring interval approach
Rationale
The reasons for the current annual monitoring interval are unclear and may be more historical than evidence-based. In recent years, a statistical methodology has been developed for studying the time intervals in monitoring and screening programmes and their consequences for patients and service providers. In this project we extended that methodology to DR screening to confirm (or otherwise) the appropriateness of annual screening as the default for retinal photography.
Data set
We used the same longitudinal data on digital photographs and risk factor data as the risk-factor approach of Chapter 5.
Overview of method
We used a statistical method that has been used extensively to model the course of chronic diseases, including DR,63 and to evaluate screening programmes. 64 This project advances on the risk-factor approach of Chapter 5 (Phase 1) by allowing classification error in retinopathy grades by using a hidden (unobserved) Markov model to estimate simultaneously the progression of disease and the potential for screening to misclassify the true state of DR. The factors contributing to the risk score of Phase 1 were included as explanatory variables.
Retinal screening gives a composite categorical measure (retinopathy grade and presence or absence of maculopathy). We converted this into seven states or levels relating to the early stages of DR and degrees of sight-threatening or referable disease. We applied the modelling methods to the GDESP data to obtain estimates of disease progression and the probability of misclassification. We calibrated the rates of FP and FN tests to estimates reported in the literature.
We estimated rates of true- and false-positive and -negative tests under the following scenarios:
-
annual testing (base case)
-
at other fixed intervals including 6-monthly, and every 2, 3 and 5 years.
The impact of varying levels of non-attendance was considered based on estimated attendance rates from our data and, in sensitivity analyses, from the literature. Simulations were cross-checked against other calculation methods, and further checked against the observed data to verify the internal validity of the model.
Expected outcome
An evidence-base for the existing annual monitoring interval or a recommended alternative to annual monitoring as the default.
Introduction
Diabetic retinopathy and maculopathy are complications of diabetes that can lead to vision loss. Regular screening using fundus photography is recommended for all people with diabetes with referral to specialist care for optimal treatment. Recommendations for the frequency of screening for eye disease and subsequent monitoring for further progression in clinical guidelines are inconsistent. NICE recommends65 annual screening, whereas the American Diabetes Association recommend66 annual screening initially but suggest that less frequent examinations (2–3 years) may be considered following one or two normal eye examinations. The SIGN guidelines21 suggest annual screening in general but every 2 years for people with no evidence of retinopathy. Australian guidelines67 for the management of diabetes suggest 2-yearly screening in people with no retinopathy, but annual screening for higher-risk groups and more frequent monitoring after retinopathy has been detected. Canadian guidelines68 differentiate between diabetes type and suggest annual screening for people with type 1 diabetes and 1–2-yearly screening for those with type 2 diabetes. The IDF guidelines69 recommend 1–2-yearly intervals for those with no disease, yearly intervals for those with minimal unchanged retinopathy and 3–6-monthly intervals if there is worsening since the last examination.
Given that screening using digital photography is imperfect and subject to various sources of variation, there is potential for people to be over-referred to specialist ophthalmology services in the absence of sight-threatening disease, or under-referred, when screening fails to detect referable level disease. In addition, imperfect methods can give the impression of change over time (progression or deterioration) when, in fact, the condition is stable. The consequences of such errors are numerous and wide ranging. When people are over-referred to specialist eye clinics, health-care resources (time and money) are wasted that could be better used to treat people with consequential disease, and the extra appointments are inconvenient for patients and may cause unnecessary anxiety. Under-referrals may mean a window of opportunity is missed for optimal interventions and could result in a poorer prognosis. Finally, misclassification can lead to more frequent and unnecessary monitoring which subsequently increases the risk of over-referral or, conversely, less frequent monitoring and unnecessary delays in detection of true change.
The aim of this study was to use routinely collected screening data to model the natural history of DR and maculopathy and the rates of correct and incorrect assignments using a statistical model. These estimates of disease progression and rates of over- and under-referral can be used to compare different screening intervals in cost-effectiveness models (Chapter 8).
Methods
The criteria for screening and grading of digital photographs are as follows. At each screening assessment, visual acuity was assessed using logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution (logMAR) charts and two colour digital retinal photographs of two standard 45-degree fields (macula and disc centred) per eye after dilatation of the pupils. Photographs are then graded by trained assessors in a central location for the presence of maculopathy or DR and the severity of DR. The English screening programme grades retina images39 as R0 if there is no detectable DR and as M0 if there is no evidence of maculopathy. Images are graded R1 if there is at least one microaneurysm and/or retinal haemorrhage. R2 (pre-proliferative) identifies the presence of multiple haemorrhages and/or definite intraretinal microvascular abnormality (IRMA) and/or venous beading and/or reduplication. R3 level (PDR) indicates the presence of neovascularisation. M1 (maculopathy) identifies the presence of two-dimensional photographic markers of diabetic maculopathy, specifically an exudate within 1-disc diameter of the centre of the fovea, a group of exudates within the macula, or any microaneurysm or haemorrhage within 1-disc diameter of the centre of the fovea, but only if associated with a best visual acuity of worse than 0.3 logMAR (equivalent to Snellen 6/12). 39
For statistical analysis, we amalgamated retinopathy and maculopathy grades for both eyes into a univariate outcome with seven levels: (1) no DR in both eyes (R0M0 R0M0); (2) background in one eye, no detectable DR in the other eye (R1M0 R0M0); (3) background retinopathy in both eyes (R1M0 R1M0); (4) pre-proliferative DR or PDR in one eye, no detectable DR or background in the other (R2+M0 R0/1M0); (5) pre-proliferative DR or PDR in both eyes (R2+M0 R2+M0); (6) maculopathy in one eye and any DR (M0 M1); and (7) maculopathy in both eyes and any DR (M1 M1).
Model structure
We treat the seven levels of retinopathy and maculopathy described above as states in a Markov model. We used a continuous-time hidden Markov model to estimate simultaneously the transition rates (intensities) between states and the probabilities of misclassification. Markov models have been used extensively to model disease progression and to evaluate screening strategies. A hidden Markov model accounts for the fact that the true disease state is not always reflected by the test. In this context, the true disease state could be thought of as the potential grade determined by seven field stereo-photography or similar gold-standard tests for DR corresponding to each screening grade.
Model structure and assumptions were informed by what was known about DR, the evaluation needs and discussions with clinical experts, health economists, statisticians and epidemiologists involved in this project. This consisted of an iterative process as the conceptual framework was revisited following the analysis of data and the health economics evaluation. The following modelling assumptions about disease progression are required: (1) as there is good evidence to suggest that background retinopathy can develop and subsequently disappear,70 movement back and forth was permitted between the states corresponding to no detectable retinopathy and background retinopathy (levels 1, 2 and 3); (2) once disease has progressed to at least pre-proliferative retinopathy (level 4 upwards), remission to level 3 or below is assumed to be impossible; (3) we assumed that eyes cannot develop pre-proliferative retinopathy without first developing background retinopathy; hence, there is no direct link from state 1 to pre-proliferative retinopathy or proliferative retinopathy states (4 and 5); (5) for model parsimony, and because advanced retinopathy or maculopathy leads to treatment, we do not consider progressions from either level 5 (pre-proliferative or proliferative retinopathy in both eyes) or state 7 (maculopathy in both eyes). Figure 14 is a graphical representation of the model for underlying disease progression.
FIGURE 14.
Graphical representation of the model for progression of diabetic eye disease. Arrows from one state to another represent instantaneous transitions to be estimated. Absence of arrows indicates that instantaneous progression is not possible.

We did not impose modelling assumptions on the probabilities that any given state is misclassified, during retinopathy grading, as another. The model therefore estimates a 7 × 7 matrix of instantaneous transition probabilities with forced 0 entries representing the modelling assumptions listed above, and an unrestricted 7 × 7 matrix representing misclassification probabilities.
The model was fitted using the msm function71 in R version 3.0.1 (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). 72 The final model was derived by adding potentially explanatory variables separately and then together in turn in order to find the model with the lowest deviance (–2 log likelihood). The final model adjusted for duration of diabetes at the first SE, baseline HbA1c and serum cholesterol level. We explored adjusting the model for type of diabetes, but the low number of people with type 1 (≈900) in the screening cohort made the model too unstable. In the case of blood pressure, age and sex, these did not significantly improve the fit of the model and so were not included in the final model.
Estimated over- and under-referrals attributable to screening
We used the model to calculate the FP and FN rates for referable disease, defined as pre-proliferative or proliferative retinopathy or any maculopathy, at a screening visit. In a post-hoc secondary analysis, we also summarised these rates under varying assumptions about case mix to enable comparison with previously published studies.
We then considered the FP and FN rates over time in screening programmes with 6 months, 1 year, 3 years or 5 years between screening visits. Using the fitted intensity and error matrices, we calculated the expected number of people with referable eye disease, the number of over- and under-referrals and the ratio of false to true referrals at follow-up visit, stratified by observed state at baseline visit. Results are presented for two cohorts, one with risk factor levels (duration of diabetes, HbA1c, cholesterol) comparable to the Gloucester cohort, and a ‘high-risk’ cohort group with a longer (10 years) duration of diabetes, poorly controlled glycaemia (baseline HbA1c of 65 mmol/mol) and elevated cholesterol (6 mg/l). Results are presented in terms of screening 10,000 people to aid interpretation.
Results
From a total of 14,810 people, 68,992 examinations results were extracted from the screening service database. The modelling data set consisted of 65,839 grades from 14,187 people. Observations were excluded if retinopathy or maculopathy grade were missing from either eye or were obviously duplicate entries, and people were excluded if they only had one useable observation or did not have baseline HbA1c, serum cholesterol or duration of diabetes recorded. The median number of examinations was 5 [interquartile range (IQR) 3–6] and the median interval between examinations was 1.04 (IQR 0.99–1.17) years. Characteristics of the cohort at baseline are given in Table 22.
| Characteristic | Level | n = 14,187 |
|---|---|---|
| Retinopathy levels, n (%) | No detectable DR in either eye | 8571 (60.4) |
| Background DR in one eye | 2666 (18.8) | |
| Background DR in both eyes | 1835 (12.9) | |
| STDR in one eye and no maculopathy | 161 (1.1) | |
| STDR in both eyes and no maculopathy | 132 (0.9) | |
| Maculopathy in one eye | 563 (4.0) | |
| Maculopathy in both eyes | 259 (1.8) | |
| Sex, n (%) | Male | 8061 (56.8) |
| Female | 6126 (43.2) | |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 64 (56–72) | |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol), median (IQR) | 51.0 (43.5–61.0) | |
| Serum cholesterol (mmol/l), median (IQR) | 4.3 (3.7–5.0) | |
| Duration of diabetes (years), median (IQR) | 2.4 (0.75–7.2) |
Table 23 shows the raw unadjusted counts of transitions across all individuals in the cohort. These represent the number of times one grade has been followed by another. Row percentages are also given and can be interpreted as empirical probabilities of observing changes in consecutive examinations.
| From | To | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| States | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| Retinopathy levels, n (%) | No DR (R0) and no maculopathy (M0) | Background (R1) in one eye (R0 in other) | Background (R1) in both eyes | STDR (R2 or R3) in one eye (R0, R1 in other) | STDR (R2 or R3) in both eyes | Maculopathy (M1) in one eye, no maculopathy in other (M0) | Maculopathy (M1) in both eyes | |
| 1 | No DR | 21,127 (76) | 4694 (17) | 1723 (6) | 14 (0) | 5 (0) | 179 (1) | 12 (0) |
| 2 | Background in one eye | 4630 (45) | 3466 (34) | 1854 (18) | 34 (0) | 10 (0) | 203 (2) | 16 (0) |
| 3 | Background in both eyes | 1446 (16) | 1608 (18) | 4660 (53) | 196 (2) | 89 (1) | 645 (7) | 139 (2) |
| 4 | STDR in one eye | 18 (3) | 17 (3) | 138 (22) | 183 (29) | 105 (17) | 126 (20) | 39 (6) |
| 5 | STDR in both eyes | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 54 (8) | 71 (10) | 376 (54) | 137 (20) | 55 (8) |
| 6 | Maculopathy in one eye | 150 (6) | 172 (7) | 506 (21) | 103 (4) | 178 (7) | 932 (39) | 343 (14) |
| 7 | Maculopathy in both eyes | 12 (1) | 7 (1) | 76 (6) | 17 (1) | 51 (4) | 313 (26) | 721 (60) |
The estimated transition intensity matrix is shown in Table 24.
| From | To | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| States | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| Retinopathy levels, estimated transition intensities (95% CI) | No DR (R0) and no maculopathy (M0) | Background (R1) in one eye (R0 in other) | Background (R1) in both eyes | STDR (R2 or R3) in one eye (R0, R1 in other) | STDR (R2 or R3) in both eyes | Maculopathy (M1) in one eye, no maculopathy in other (M0) | Maculopathy (M1) in both eyes | |
| 1 | No DR | –0.11 (–0.12 to –0.10) | 0.11 (0.10 to 0.12) | – | – | – | 0.0005 (0 to 2.4) | – |
| 2 | Background in one eye | 0.12 (0.10 to 0.15) | –0.23 (–0.27 to –0.21) | 0.11 (0.09 to 0.12) | 0.0001 (0 to 0.07) | – | 0.004 (0.002 to 0.009) | 0.0003 (0 to 0.27) |
| 3 | Background in both eyes | 0.01 (0.003 to 0.04) | 0.12 (0.10 to 0.15) | –0.18 (–0.21 to –0.15) | 0.01 (0.01 to 0.02) | 0.001 (0 to 0.01) | 0.03 (0.02 to 0.03) | – |
| 4 | STDR in one eye | – | – | – | –0.08 (–0.11 to –0.06) | 0.08 (0.06 to 0.11) | – | – |
| 5 | STDR in both eyes | – | – | – | – | 0 | – | – |
| 6 | Maculopathy in one eye | – | – | – | – | – | –0.04 (–0.05 to –0.03) | 0.04 (0.03 to 0.05) |
| 7 | Maculopathy in both eyes | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 |
The matrix of estimated error probabilities is given in Table 25. Here, off-diagonal elements represent probabilities of grading errors, and diagonal elements probabilities of correct grading.
| True state | Observed grade | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| States | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| Retinopathy levels, estimated error matrix (95% CI) | No DR (R0) and no maculopathy (M0) | Background (R1) in one eye (R0 in other) | Background (R1) in both eyes | STDR (R2 or R3) in one eye (R0, R1 in other) | STDR (R2 or R3) in both eyes | Maculopathy (M1) in one eye, no maculopathy in other (M0) | Maculopathy (M1) in both eyes | |
| 1 | No DR | 0.87 (0 to 1) | 0.11 (0.10 to 0.12) | 0.018 (0.015 to 0.021) | 0a | 0a | 0.002 (0.0016 to 0.0035) | 0a |
| 2 | Background in one eye | 0.21 (0.17 to 0.24) | 0.56 (0 to 1) | 0.22 (0.19 to 0.24) | 0.002 (0.001 to 0.004) | 0a | 0.020 (0.016 to 0.025) | 0a |
| 3 | Background in both eyes | 0.007 (0.003 to 0.014) | 0.04 (0.03 to 0.05) | 0.86 (0.62 to 0.96) | 0.01 (0.0096 to 0.02) | 0.002 (0.001 to 0.004) | 0.07 (0.06 to 0.09) | 0.006 (0.004 to 0.01) |
| 4 | STDR in one eye | 0a | 0.01 (0.004 to 0.03) | 0.24 (0.14 to 0.37) | 0.49 (0 to 1) | 0.13 (0.08 to 0.21) | 0.12 (0.07 to 0.21) | 0a |
| 5 | STDR in both eyes | 0a | 0a | 0.04 (0.02 to 0.06) | 0.06 (0.04 to 0.10) | 0.59 (0.10 to 0.94) | 0.23 (0.17 to 0.30) | 0.08 (0.05 to 0.11) |
| 6 | Maculopathy in one eye | 0.003 (0.0009 to 0.011) | 0.01 (0.008 to 0.02) | 0.16 (0.12 to 0.21) | 0.06 (0.05 to 0.08) | 0.03 (0.02 to 0.05) | 0.60 (0.25 to 0.87) | 0.13 (0.10 to 0.17) |
| 7 | Maculopathy in both eyes | 0a | 0a | 0.02 (0.008 to 0.03) | 0.19 (0.14 to 0.24) | 0.75 (0.007 to 1.00) | ||
The duration of diabetes and baseline HbA1c and serum cholesterol were independent predictors of true progression of DR. To ensure model convergence, covariates effects were standardised and constrained to be equal for each of the 11 forward transition intensities and all three backward transition intensities. Table 26 shows the proportional HRs on forward and backward transition intensities for the three covariates.
| Covariate | Transitional | Estimated HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (equivalent to change in increments of 15 mmol/mol) | Progression | 1.46 (1.41 to 1.51) |
| Regression | 0.95 (0.86 to 1.04) | |
| Duration of diabetes (equivalent to change in increments of 7.8 years) | Progression | 1.21 (1.16 to 1.25) |
| Regression | 0.21 (0.16 to 0.27) | |
| Total cholesterol (equivalent to change in 1.1 mmol/l) | Progression | 1.0 (0.97 to 1.1) |
| Regression | 1.1 (1.04 to 1.2) |
The numbers of referrals (for maculopathy and retinopathy) and the numbers which represent true, over- and under-referrals and the ratio of false to true referrals were calculated using the estimated intensity and error matrices. Table 27 shows the results for people with no detectable retinopathy at baseline and the true and false referrals when the next screen occurs 6 months, 1, 3 or 5 years later. Table 28 shows the results for people with background retinopathy in one eye and Table 29 shows the results for people with background retinopathy in both eyes at intervals of 3, 6 and 12 months. Tables 30–32 show equivalent results for high-risk patients.
| Baseline screening result | Number with true referable disease | Referrals from screening that are correct | Referrals from screening which are false | Not referred by screening when referable disease is present | Ratio of over-referrals/true referrals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No detectable retinopathy, n per 10,000 screened | |||||
| Baseline | 2 | – | – | 2 | |
| 6 months | 5 | 4 | 54 | 1 | 12.1 |
| 1 year | 10 | 8 | 66 | 2 | 7.8 |
| 3 years | 50 | 41 | 111 | 9 | 2.7 |
| 5 years | 125 | 103 | 149 | 22 | 1.4 |
| Baseline screening result | Number with true referable disease | Referrals from screening that are correct | Referrals from screening which are false | Not referred by screening when referable disease is present | Ratio of over-referrals/true referrals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background retinopathy in one eye, n per 10,000 screened | |||||
| Baseline | 31 | – | – | 31 | |
| 6 months | 51 | 41 | 179 | 9 | 4.3 |
| 1 year | 75 | 61 | 193 | 14 | 3.1 |
| 3 years | 208 | 171 | 230 | 37 | 1.3 |
| 5 years | 373 | 309 | 247 | 64 | 0.8 |
| Baseline screening result | Number with true referable disease | Referrals from screening that are correct | Referrals from screening which are false | Not referred by screening when referable disease is present | Ratio of over-referrals/true referrals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background retinopathy in both eyes, n per 10,000 screened | |||||
| Baseline | 588 | – | – | 588 | |
| 6 months | 709 | 579 | 551 | 131 | 1.0 |
| 1 year | 825 | 675 | 526 | 150 | 0.8 |
| 3 years | 1234 | 1021 | 444 | 213 | 0.4 |
| 5 years | 1577 | 1319 | 383 | 258 | 0.3 |
Higher-risk patients
| Baseline screening result | Number with true referable disease | Referrals from screening that are correct | Referrals from screening which are false | Not referred by screening when referable disease is present | Ratio of over-referrals/true referrals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No detectable retinopathy, n per 10,000 screened | |||||
| Baseline | 2 | – | – | 2 | |
| 6 months | 7 | 6 | 61 | 1 | 9.9 |
| 1 year | 17 | 14 | 80 | 3 | 5.7 |
| 3 years | 111 | 91 | 159 | 20 | 1.7 |
| 5 years | 300 | 248 | 228 | 52 | 0.9 |
| Baseline screening result | Number with true referable disease | Referrals from screening that are correct | Referrals from screening which are false | Not referred by screening when referable disease is present | Ratio of over-referrals/true referrals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background retinopathy in one eye, n per 10,000 screened | |||||
| Baseline | 31 | – | – | 31 | |
| 6 months | 62 | 51 | 194 | 11 | 3.8 |
| 1 year | 105 | 86 | 222 | 19 | 2.6 |
| 3 years | 368 | 304 | 303 | 65 | 1.0 |
| 5 years | 730 | 607 | 347 | 123 | 0.6 |
| Baseline screening result | Number with true referable disease | Referrals from screening that are correct | Referrals from screening which are false | Not referred by screening when referable disease is present | Ratio of over-referrals/true referrals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background retinopathy in both eyes, n per 10,000 screened | |||||
| Baseline | 588 | – | – | 588 | |
| 6 months | 767 | 627 | 566 | 140 | 0.9 |
| 1 year | 942 | 773 | 553 | 170 | 0.7 |
| 3 years | 1606 | 1336 | 504 | 270 | 0.4 |
| 5 years | 2210 | 1863 | 460 | 347 | 0.2 |
Conclusion
Our results show that annual screening for DR is associated with a disproportionate number of FPs or over-referrals, and extending the interval of screening reduces the occurrence of over-referrals. The number of FPs far outweighs the number of FNs even though the specificity (1 – FP rate) of the screening test is high. This occurs because the population being screened consists largely of people with no detectable DR or background DR and, hence, FP error rates are ‘amplified’ by screening. 73 Waiting longer to rescreen reduces the number of errors as the balance of non-referable disease to referable-level disease starts to tilt towards the latter rather than the former. Screening less frequently is likely to reduce significantly the cost of screening and reduce the number of unnecessary referrals to specialist eye services. However, longer intervals of screening will mean inevitable delays in referring a small number of people with true STDR for either closer monitoring or therapy. Our modelling suggests that these FNs will mostly comprise people with pre-proliferative DR or maculopathy, and, although this requires referral to ophthalmology, it is not considered as urgent as PDR. The implications for such delays in people with pre-proliferative disease or maculopathy are not fully understood but could be detrimental.
Estimation of the rate of progression
Our approach to modelling the progression of DR takes into account misclassification (over- and under-referral) and hence is less susceptible to the bias associated with standard methods to calculate incidence in the presence of an imperfect test. 74 However, owing to the relatively low estimated error rates, our model produces similar estimates of the rates of progression of DR as reported elsewhere. For example, Liu et al. 75 used a multistate Markov model (not accounting for error in the test) to model the average sojourn time in states of DR using repeated examinations using fundus examination. They reported average dwelling time with no DR as 10.86 years and background DR as 8.33 years. 75 Estimated average sojourn time from our hidden Markov model in the no DR, background DR in one eye and background DR in both eyes states are 9.3 years (95% CI 8.5 years to 10.3 years), 4.3 years (95% CI 3.7 years to 4.9 years) and 5.6 years (95% CI 4.8 years to 6.6 years).
The risk of developing STDR as predicted by the model is also comparable to those risks reported in the UKPDS. 70 Our model suggests that the true incidence of any retinopathy after 6 years is 39% and 1.7% for STDR. In the UKPDS, the observed incidence of any retinopathy was 40.6% and 2.7% for STDR.
Estimation of misclassification rates
Our modelling results give valuable insights into the chance of correct or incorrect assignments (misclassifications) attributable to screening. As might be expected, it is common for screening to find background retinopathy in one eye when there is none (11 in 100), and for screening to miss background DR when it is present (21 in 100). At present, these errors will have little or no bearing on the management of such patients, as current recommendations for screening do not differ for those with no detectable DR or background DR.
False positives (over-referrals) are more likely when there is true background DR present in one or both eyes. We estimate that if 100 people with background DR in one eye undergo screening, two will be referred with suspected STDR (either M1, R2 or R3). When background DR affects both eyes, we expect nine in 100 to be referred in error.
Our modelling also suggests that a number of referrals are missed by screening. For 100 people with true STDR (but no maculopathy) in one eye, 25 will be undergraded and not referred; for 100 people with true STDR (no maculopathy) in both eyes, four are likely to be undergraded and not referred. For 100 people with true referable STDR and maculopathy present in one eye, we estimate that 16 will not be referred, and this drops to two in 100 when there is true STDR in both eyes (with maculopathy).
Comparison with external estimates
Direct comparison of our estimated misclassification rates with external and independent estimates is compromised by a lack of uniformity of grading systems, differences in screening methods and the varying case-mixes of people included in such studies. We found five diagnostic accuracy studies76–80 in which digital photography was compared with a reference test of either slit-lamp biomicroscopy or seven field stereo photography and used similar criteria to the DESP to define STDR. Four of these studies reported specificity from which we could calculate the false-positive rates (FPR). From the paper by Stellingwerf et al. 80 we derived an estimated FPR of 0.9%, from Scanlon et al. ,78 a FPR of 3.8%, from Scanlon et al. ,79 a FPR of 13.9%, and from Olson et al. ,77 a FPR of 12.7%. A direct comparison of these estimates of the FPR with our misclassification rates can only be made if the proportions of people with no DR or background DR in one or both eyes is known (case mix), so that we can derive an appropriate weighted estimate. However, we know that our model estimated FPR would be < 1% if all participants had no DR and would reach an upper bound of 9% if participants had background DR in both eyes. These estimates are within the FPRs reported by Stellingwerf et al. 80 and Scanlon et al. 78 but lower than those of Olson et al. 77 and Scanlon et al. 79
All five studies reported sensitivities from which we could derive the false-negative rate (FNR). The FNRs reported in the four studies using slit-lamp biomicroscopy as the reference test (4.8% in Stellingwerf et al. ,80 3.8% in Olson et al. ,77 8% in Kalm et al. 76 and 12.2% in Scanlon et al. 79) were considerably lower than the estimate of 19.7% in Scanlon et al. ,78 which used seven field stereo photography as a reference test. As with the FPR, we can only compare lower and upper bound estimates of the FNR. The FNR predicted by our model ranges from 2% to 25% depending on the relative mix of referable DR being studied. These estimates are comparable to the FNRs reported in the literature.
Empirical evidence for the probability of overgrading DR and diabetic maculopathy is rare. In the largest study we found, Healy et al. 56 regraded images from 1501 patients referred for STDR between 2008 and 2011. They reported that the most common source of error from the screening service was grading R1 as R2 (in 16% of all discrepant images) or grading R2 as R3 in the absence of new vessels (4%). After reviewing images that were referred for diabetic maculopathy, they found that the screening service misclassified 13% eyes as maculopathy in the absence of characteristics that warrant referral.
Evaluating different intervals of screening
Using our model we estimate that annual screening in people with no detectable retinopathy in either eye at baseline would lead to nearly eight times as many false referrals than true referrals. If the interval of screening were to be extended to 3 years then the ratio of false to true referrals is reduced to 2.7 and 1.44 after 5 years. When a previous screen has found background retinopathy in one eye then annual screening leads to 3.1 unnecessary referrals for every correct referral and this reduces to 1.3 referrals after 3 years and 0.8 referrals after 5 years. When background retinopathy has been detected in both eyes at baseline, screening at 6 months produces equal numbers of correct and unnecessary referrals (ratio = 1.0) and screening 1 year later yields more true than false referrals.
For people with elevated systemic risk factors, the ratio of false to true referrals is reduced for each initial grade of DR and as the interval of screening increases, but not to the extent that baseline DR status does. Therefore, higher levels of systemic risk factors in conjunction with evidence of background DR may warrant more frequent screening, leading to individualised screening intervals, a concept which has already been trialled in the Netherlands. 81
Discussion
Retinopathy screening is widely recommended, but guidelines for the frequency of screening are inconsistent. Evidence for these recommendations are largely based on consensus opinion and convenient timeframes rather than solid evidence. We have presented a model-based approach to evaluating screening programmes that can be used to construct evidence-based guidelines for the intervals of screening based upon the current screening grade and CRFs.
The significant advantage to a modelling approach is that it enables the comparison of a wide range of different screening strategies over long periods of time, which is infeasible in a controlled trial setting. Because all models make a number of assumptions, there are a number of inevitable limitations to such analyses. We could not adjust progression rates for type of diabetes (type 1 vs. type 2) and, hence, we were unable to evaluate screening strategies for this subgroup. However, diabetes type does not seem independently to affect the risk of progression over and above diabetes duration, HbA1c and status of DR (see Chapter 5). Another potential criticism of our evaluation of screening is that we have assumed that compliance to the screening programme is 100% and we have not attempted to adjust for varying take-up rates and sporadic attendance. This is likely to reduce the effectiveness of screening further, especially if attendance is associated with patients’ poorer control of their diabetes and subsequent greater risk of developing STDR. 82 However, the effect of non-attendance on screening effectiveness is addressed in the health economic analysis in Chapter 8.
We have shown that with a model-based approach it is possible to describe both the underlying progression of DR and the rates of misclassification attributable to screening using routinely collected screening data. Estimates from these models can be directly incorporated into cost-effectiveness models of different screening strategies and guide future recommendations for screening.
Chapter 8 Phase 4: cost-effectiveness of differing screening intervals in diabetic retinopathy screening
Introduction
No firm evidence or evidence-based consensus exists as to the optimal frequency of testing for DR. Although previous studies have assessed the cost-effectiveness of differing intervals for DR screening, the evidence is mixed. The aim of this work was to determine if assigning diabetic patients to differing DR screening intervals using a risk estimation model is cost-effective compared with the current English national screening programme (i.e. annual screening for all eligible people with diabetes aged 12 years and over).
Objective
Diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases, placing a great economic burden on society owing to its increased health-care expenditures and lost productivity. Although the treatment of diabetes on its own is costly, its complications are the major contributors to health-care costs. Among the main diabetes-related complications is DR, which has been shown to be, until recently, the leading cause of blindness in the working age population10 in the UK. DR is treated effectively with laser photocoagulation, although this has been found to be cost-effective only if retinopathy is detected before irreversible damages take place. 13,15,16 Therefore, in order for DR treatment to be cost-effective, diagnosis has to be timely, with published evidence showing that screening for STDR is highly cost-effective. 17–20,83 In the UK, results from published studies also highlight the cost-effectiveness of screening for DR,84 with James et al. 85 showing that a screening programme using retinal photography was cost-effective compared with opportunistic screening.
In 2003, a national screening programme was introduced in England, recommending digital imaging as the preferred method of retinal photography for screening and mandating that local programmes respond to local needs with different models of care,86 with eye screening to be performed at time of diabetes diagnosis and repeated annually thereafter. Annual DR screening was also recommended in NICE guidelines. 65,87
However, despite these recommendations, no firm evidence or evidence-based consensus exists as to the optimal frequency of testing for DR. SIGN reported that patients with diabetes with no detected retinopathy could be screened every 2 years, with all other patients being screened at least annually. 21 Given the rising numbers of people identified by primary care practices as having diabetes, a rise of over 100,000 people annually,5 and lower rates of progression to PDR and severe visual loss,11,12 reflecting in part improvements in general diabetes care, there is an argument for modifying DR screening recommendations. Therefore, the aim of this work is to determine whether assigning diabetic patients to differing DR screening intervals using a risk estimation model is cost-effective compared with the current English national screening programme (i.e. annual screening for all people with diabetes).
Existing research
A published systematic review assessing economic evidence surrounding differing DR screening frequencies showed that the evidence on cost-effectiveness was mixed. 46 The review only identified three studies, one performed in the USA and two in the UK.
The UK study by Brailsford et al. 88 found similar results to the US study. The study, which also used a decision analytic model to assess the cost-effectiveness of DR screening in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients, found that a 30-month screening interval was the most cost-effective option. However, in contrast to these two studies, Davies et al. 48 found that screening diabetic patients less than once a year would not be any more cost-effective than screening them every year. The study also based its work on a decision analytic model populated using results obtained from the published literature. A finding common in both UK studies was that screening type 1 diabetes patients was more cost-effective than screening type 2 diabetes patients.
There were, however, important limitations to both of the UK studies. Both studies used sight years saved as their main outcome measure, rather than a more generalisable health outcome, such as QALYs, that can be readily compared across intervention and disease areas, and for which willingness-to-pay thresholds exist to determine cost-effectiveness. The two studies also failed to include in their models the additional costs to the health-care service of patients losing sight or going blind, which have recently been shown to be considerable and non-negligible. 89 Finally, data in the two UK studies were derived from a wide range of sources and diabetic populations. As a result, both studies had to undertake numerous assumptions as to how best to synthesise the available data.
The US study examined the cost-effectiveness of differing DR screening intervals for type 2 diabetes patients in the USA. 27 The authors employed a Markov model using QALYs as the main outcome measure, with costs being assessed from a third-party payer perspective. Using a threshold of US$50,000 per QALY gained, or less, as an indication of a cost-effective intervention, the authors reported that annual screening for all type 2 diabetes patients was not warranted on the basis of cost-effectiveness.
An additional US study, published after the review by Jones and Edwards,46 found that annual screening was costly and added little benefit compared with biennial eye evaluation. 90 In addition, the authors found that the cost-effectiveness of biennial screening depended on the ability of the screening programme to detect other eye conditions. If a screening programme was unable to detect such conditions, then a simple telemedicine programme using acuity eye charts or screening questions became the most cost-effective alternative.
Methods
Interventions under study
For all the screening strategies under study, DR screening consisted of two digital photographs on two fields, with mydriasis (i.e. eye dilatation) to maximise image quality. We therefore modelled the cost-effectiveness of the following screening intervals for all patients with diabetes, including current practice in the English national screening programme, in which all patients with diabetes are screened annually:
-
DR screening every 6 months
-
DR screening every year (current practice)
-
DR screening every 2 years
-
DR screening every 3 years
-
DR screening every 5 years.
In addition, the cost-effectiveness of these screening intervals was assessed in patient subgroups at different risks of developing STDR or maculopathy. We used two different risk stratification models (see Chapter 5), one based on the results of two consecutive initial SEs and another based on the results of one SE in conjunction with CRF data (Table 33).
| Risk group | Initial screening results | Mean HbA1c (mmol/mol) | Mean cholesterol (mg/l) | Mean age (years) | Mean duration of diabetes (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two SEs | |||||
| Low | No DR in both eyes in two consecutive episodes (R0M0 R0M0) | 51.1 | 4.25 | 66.8 | 5.9 |
| Medium | Background in one eye, no detectable DR in the other eye (R1M0 R0M0) in two consecutive episodes | 53.8 | 4.17 | 66.77 | 7.3 |
| High | Background retinopathy in both eyes (R1M0 R1M0) in two consecutive episodes | 57.9 | 4.11 | 63.96 | 13.0 |
| One SE and CRF data | |||||
| Low | No DR in both eyes (R0M0 R0M0) or background in one eye, no detectable DR in the other eye (R1M0 R0M0) | 48.7 | 4.4 | 64.4 | 2.9 |
| Low-medium | No DR in both eyes (R0M0 R0M0) or background in one eye but no detectable DR in the other eye (R1M0 R0M0) or background retinopathy in both eyes (R1M0 R1M0) | 58.9 | 4.6 | 63.9 | 5.0 |
| Medium–high | Same as above | 58.3 | 4.5 | 63.5 | 5.4 |
| High | Same as above | 67.9 | 4.5 | 60.4 | 14.8 |
Common to all screening strategies, a diabetic patient was offered diabetic screening at the specified time intervals which could result in receiving screening or not, conditional on the screening uptake (Figure 15). Patients who were identified at screening to have pre-proliferative retinopathy (i.e. R2), PDR (i.e. R3) or diabetic maculopathy (M1) were referred to Hospital Eye Services (HES) for further tests and/or assessment by an ophthalmologist. Not all referred patients chose to attend their clinical appointment.
FIGURE 15.
Screening pathway for diabetic patients offered DR screening.
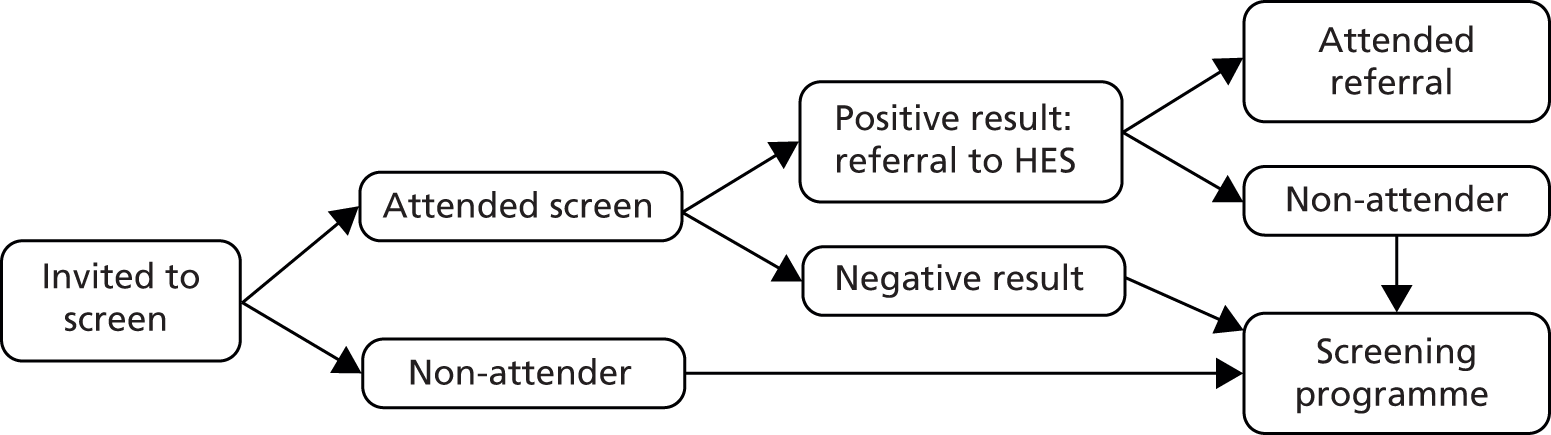
If diagnosis of DR (R2 or R3) or diabetic maculopathy (M1) was confirmed in at least one eye in the HES, then, depending on clinical need, patients would either be monitored by HES every 6 months, treated with either laser photocoagulation or antiangiogenic therapy, or referred back to the annual screening programme (Figure 16). Once treatment occurred the patient was referred back to the screening programme. Furthermore, patients who did not receive screening, patients who received screening but were not referred to the HES, and patients who were referred but did not attend their appointment were offered screening in the next time interval.
FIGURE 16.
Clinical pathways of confirmed cases of STDR (R2, R3 or M1) attending referral in HES.

Model structure
A decision analytic model was developed to evaluate the costs, (quality-adjusted) life expectancy and cost-effectiveness of the different DR screening strategies under evaluation. Given the natural history of DR progression with recursive events, the most appropriate type of model was judged to be a Markov model which was developed in Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). The model was used to simulate the natural history of the diabetic population across seven health states representing retinopathy and maculopathy grades for both eyes (Figure 17):
-
no DR in both eyes (R0M0 R0M0)
-
background in one eye, no detectable DR in the other eye (R1M0 R0M0)
-
background retinopathy in both eyes (R1M0 R1M0)
-
pre-proliferative or proliferative retinopathy in one eye, no detectable DR or background in the other (R2/3M0 R0/1M0)
-
pre-proliferative or proliferative retinopathy in both eyes (R2/3M0 R2/3M0)
-
diabetic maculopathy in one eye and any DR (M0 M1)
-
maculopathy in both eyes and any DR (M1 M1).
FIGURE 17.
Model structure capturing the natural history component.

Three absorbing states were defined: maculopathy in both eyes (M1 M1); pre-proliferative or proliferative retinopathy in both eyes (R2/3M0 R2/3M0); and death. We assumed that if patients progressed to these three states, they would remain in that health state for the rest of their lifetime. Model structure and assumptions were informed by what was known about DR, the evaluation needs and discussions with clinical experts, health economists, statisticians and epidemiologists involved in this project. Hence, the construction of the model consisted of an iterative process where the agreed conceptual framework was revisited given new findings in the data and published literature and validity of its outputs. Such discussions also helped to identify key uncertainties in the model structure to be explored in the sensitivity analyses.
The time horizon of the analysis was lifetime, and the population moved between health states according to defined transition probabilities. The transition probabilities between the seven DR health states were obtained from the work presented in Chapter 7. A cycle length of 6 months was considered appropriate given the natural history of diabetic patients and the screening strategies under evaluation. Half-cycle correction was performed and different cycle lengths were trialled (monthly, 3 months) to ascertain the potential impact on the relative costs and effects before deciding on the 6-month cycle.
The model simulated the transition of a cohort of diabetic patients through the health states over time, to estimate expected costs and outcomes. For example, at the start of a given cycle patients without DR in both eyes (R0M0 R0M0) could die, develop maculopathy in one eye (M1 M0) or, alternatively, develop background retinopathy in one eye (R1M0 R0M0). If the cycle coincided with a screening interval, the cohort could then attend screening or not (conditional on screening uptake), be referred or not to the HES (conditional on accuracy of the screening test), and attend or not the referral appointment (conditional on the uptake of assessment) (Figure 15). If patients attended the HES, they could either be monitored every 6 months, treated with either laser photocoagulation or antiangiogenic therapy, or referred back to the annual screening programme (Figure 16).
Given that slit lamp biomicroscopy is considered to be the ‘gold-standard’ for diagnosing DR, we assumed that HES would correctly identify the true state of DR and maculopathy (i.e. 100% sensitivity and specificity). Hence, only individuals with maculopathy (M1) or pre-proliferative/proliferative retinopathy (R2–3) were considered for treatment or monitoring by HES. The remaining individuals were referred back to the annual screening programme.
Patients monitored by the HES were allowed to continue progressing if they had not yet reached an absorbing state. Once patients were treated it was assumed that they would remain in the same retinopathy and maculopathy grades for the remainder of the simulation. This was based on evidence from clinical trials showing that the majority of patients remaining in the same grades despite improvements in visual acuity. 91 As discussed below (see Treatment effectiveness), the benefit of treatment was captured as changes to visual acuity.
Finally, the model adopted the perspective of the UK NHS and personal social services. All costs and effects were discounted beyond the first year of simulation using an annual discount rate of 3.5%, based on current UK government recommendations. The price year was 2012–13 and, when necessary, costs were inflated using the UK health sector pay and prices inflation factor. 92
Model inputs
Screening uptake rate
Information on the uptake of annual subsequent DR screening was obtained from 15,877 people with diabetes from the Gloucestershire Diabetic Eye Screening Service who attended an initial screen between January 2005 and May 2012. Of the 108,925 possible screens that these patients could have attended, after taking into account death and censoring (e.g. patients moving out of area), a total of 89,024 screening rounds were undertaken (82%).
To assess the characteristics independently predicting DR screening subsequent uptake rates, we performed a logistic regression, clustered at the patient level, controlling for age, sex, subsequent screen round attended and HbA1c and cholesterol as measured at baseline (i.e. shortly before the initial screen) (Table 34).
| Predictors | Coefficient | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.016 | < 0.001 | 0.014 to 0.019 |
| Sex: female | 0.024 | 0.398 | –0.032 to 0.081 |
| Subsequent year of screening | –0.135 | < 0.001 | –0.144 to –0.125 |
| HbA1c | –0.009 | < 0.001 | –0.011 to –0.007 |
| Cholesterol | –0.039 | 0.002 | –0.064 to –0.014 |
| Constant | 1.840 | < 0.001 | 1.619 to 2.061 |
| Number | 82,016 | ||
| Number of clusters | 13,910 | ||
| p > χ2 | < 0.001 |
Sensitivity and specificity of screening
The sensitivity and specificity of screening to detect the true states was obtained from the work presented in Chapter 7 (see Table 25). Sensitivity and specificity of screening given true state r was defined as the probability of being observed in state s given that the true state is r (Table 35). The error matrix presented in Table 25 was also used to convert true states to observed states and vice versa. This was used when data referred to observed (at screening) retinopathy grades rather than the desired true states.
| Sensitivity/specificity | Mean, % | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Specificity of screening relative to true state | ||
| R0M0 R0M0 | 99.7 | 99.6 to 99.8 |
| R1M0 R0M0 | 97.8 | 97.2 to 98.8 |
| R1M0 R1M0 | 90.6 | 89.1 to 91.8 |
| Sensitivity of screening relative to true state | ||
| RxM1 RxM0 | 82.2 | 77.9 to 85.5 |
| RxM1 RxM1 | 98.2 | 94.0 to 99.0 |
| R2–3M0 R0–1M0 | 75.0 | 71.5 to 79.5 |
| R2–3M0 R2–3M0 | 96.0 | 93.9 to 97.4 |
Assessment at Hospital Eye Services
Using linked data from patients in the Gloucestershire Diabetic Eye Screening service referred for suspected diagnosis of R2, R3 or M1 in any eye, and HES records, we estimated the probability of attending a HES assessment. For this we used a random-effects logistic regression controlling for age, sex and DR/maculopathy grade (Table 36).
| Predictors | Coefficient | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | –0.012 | < 0.001 | –0.018 to –0.005 |
| DR grade observed at screening | |||
| RxM1 RxM0 | Reference case | ||
| RxM1 RxM1 | 1.222 | < 0.001 | 1.005 to 1.440 |
| R2–3M0 R0–1M0 | 0.111 | 0.410 | –0.153 to 0.376 |
| R2–3M0 R2–3M0 | 0.667 | < 0.001 | 0.411 to 0.922 |
| Sex: female | –0.186 | 0.049 | –0.371 to –0.001 |
| Constant | 1.232 | < 0.001 | |
| Number | 4164 | ||
| Number of clusters | 2073 | ||
| p > χ2 | < 0.001 | ||
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy or maculopathy conditional on hospital eye service assessment
We used data from the Gloucestershire HES to assess the probability of being treated, after each assessment in the HES, given the true DR/maculopathy grade confirmed at the hospital (Table 37). For this we used a random-effects logistic model.
| Predictors | Coefficient | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| True DR grade diagnosed at HES | |||
| R2–3M0 R2–3M0 | Reference case | ||
| RxM1 RxM1 | 2.65 | < 0.001 | 2.22 to 3.07 |
| R2–3M0 R0–1M0 | 0.025 | 0.870 | –0.27 to 0.32 |
| RxM1 RxM0 | 1.85 | < 0.001 | 1.52 to 2.18 |
| Constant | –1.82 | < 0.001 | –2.10 to –1.54 |
| Number | 3926 | ||
| Number of clusters | 1145 | ||
| p > χ2 | < 0.001 | ||
Finally, we also used data from the Gloucestershire HES to assess which form of treatment patients received given the true DR/maculopathy grade confirmed at the hospital. Given that we found that over the past 5 years, the proportion of patients receiving antiangiogenic therapy has been increasing, we limited our results to patients who had been treated from 1 January 2013 to 31 May 2014. We performed a multinomial logit assessing the probability of the patient receiving antiangiogenic therapy or laser photocoagulation, given the DR/maculopathy grade confirmed at the hospital and the age of the patient (Table 38).
| Predictors | Coefficient | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antiangiogenic therapy | |||
| True DR grade diagnosed at HES | |||
| R2–3M0 R0–1M0 | Reference case | ||
| RxM1 RxM1 | –0.228 | 0.682 | –1.317 to 0.861 |
| R2–3M0 R2–3M0 | –3.142 | < 0.001 | –4.317 to –1.966 |
| RxM1 RxM0 | –1.174 | 0.032 | –2.250 to –0.098 |
| Constant | 0.693 | 0.160 | –0.274 to 1.660 |
| Both antiangiogenic therapy and laser photocoagulation | |||
| True DR grade diagnosed at HES | |||
| R2–3M0 R0–1M0 | Reference case | ||
| RxM1 RxM1 | 0.288 | 0.667 | –1.022 to 1.597 |
| R2–3M0 R2–3M0 | –3.008 | 0.001 | –4.843 to –1.174 |
| RxM1 RxM0 | –0.606 | 0.395 | –2.002 to 0.789 |
| Constant | –0.693 | 0.259 | –1.896 to 0.510 |
| Number | 310 | ||
| Number of clusters | 219 | ||
| p > χ2 | < 0.001 | ||
Treatment effectiveness
We assumed that the best eye in terms of visual acuity was always the first eye to be treated. We also assumed that improvements in visual acuity in the best eye were not cumulative with the number of treatments received and that the improvement would remain constant for the remainder of the simulation.
Effectiveness for diabetic maculopathy (M1)
To obtain estimates of treatment effectiveness of antiangiogenic therapy with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor and laser photocoagulation we examined the Cochrane meta-analysis undertaken by Virgili et al. 91
For the model, we focused our attention on the results of the meta-analysis comparing antiangiogenic therapy versus laser photocoagulation, with the outcome measured as difference in logMAR visual acuity at 1 year. The 1-year effectiveness of photocoagulation was estimated at –0.016 (95% CI –0.048 to 0.0016) improvements in logMAR visual acuity. When antiangiogenic therapy was compared with laser therapy the improvement in logMAR visual acuity at 1 year was –0.13 (95% CI –0.16 to –0.10).
Effectiveness for diabetic retinopathy (R2 and R3)
The annual probability of experiencing visual acuity loss for PDR and laser photocoagulation effectiveness (in terms of relative rate of the probability of acuity losses given treatment) were obtained from the modelling study by Rein et al. ,90 which obtained these probabilities based on data from the Diabetic Retinopathy Study and ETDRS.
Based on Rein et al. ,90 we assumed the annual probability of experiencing visual acuity loss with no treatment to be 0.141 (95% CI 0.127 to 0.155). Visual acuity loss was defined as a reduction of 18 letters in logMAR visual charts, which corresponds to a change in logMAR visual acuity of +0.36. Therefore, the annual mean logMAR visual acuity change, given no treatment, was 0.051 (95% CI 0.045 to 0.056). Conversely, the annual mean logMAR visual acuity change, given photocoagulation treatment, was 0.021. This was estimated by applying a relative of risk of 0.416 (95% CI 0.374 to 0.460). 90 Therefore, the annual change in logMAR visual acuity after laser photocoagulation was estimated at –0.030 (i.e. 0.021–0.051).
To assess the effectiveness of antiangiogenic therapy over laser photocoagulation we applied a risk ratio of 3.2 (95% CI 2.07 to 4.95). Therefore, logMAR visual acuity change after antiangiogenic therapy was estimated at –0.095 (i.e. –0.30 × 3.2).
Monitoring by Hospital Eye Services if true state is R2–3 or M1
If diagnosis of grade 2/3 DR (R2–3) or diabetic maculopathy (M1) was confirmed in at least one eye in the HES and patients were not treated, then, depending on clinical need, patients would either be monitored by the HES every 6 months or referred back to the annual screening programme (Figure 16). Based on clinical expert opinion, we assumed that 78% of patients not treated would be referred to be monitored every 6 months. We tested this assumption and time interval for monitoring in the sensitivity analysis.
Life expectancy
2013 English national life tables for the general population were obtained,93 to which we applied the relative risk of all-cause mortality in people with diabetes based on data from the Diabetes Epidemiology: Collaborative Analysis of Diagnostic Criteria in Europe (DECODE) study. 94
We did not apply any mortality decrement for visual loss, as data from the UKPDS95 found no significant independent impact of blindness, in at least one eye, on all-cause mortality.
Health utility and quality-adjusted life expectancy
We identified a systematic literature review assessing the impact of visual acuity on health status utility valuations in patients with DR, diabetic macular oedema or age-related macular degeneration. 96 This review identified four studies assessing utility in patients with DR.
For the model we used the results from the study by Lloyd et al. ,97 which assessed, using the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D™), the utility associated with visual acuity (as measured using the logMAR scale in the better seeing eye) in 49 patients with diabetes but no retinopathy and 122 patients with DR. The study identified, through multiple regression, that age, disease-specific quality of life (as measured using the National Eye Institute Visual Functioning Questionnaire) and visual acuity were all independent predictors of health utility.
To be able to use these estimates in the Markov model, we used the screening data from the Gloucestershire Diabetic Eye Screening service to assess the association between logMAR visual acuity in the best eye and DR/maculopathy grade observed at screening. For this, we performed an ordinary least squares regression adjusting for DR/maculopathy grade, age and HbA1c and cholesterol levels at baseline (Table 39). The logMAR visual acuity in the best eye by observed retinopathy grade was converted into logMAR in each true state using the estimated error probabilities given in Table 25.
| Predictors | Coefficient | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.004 | < 0.001 | 0.003 to 0.004 |
| Observed DR grade at screening | |||
| R0M0 R0M0 | Reference case | ||
| R1M0 R0M0 | –0.006 | < 0.001 | –0.009 to –0.003 |
| R1M0 R1M0 | –0.005 | 0.009 | –0.009 to –0.001 |
| R2–3M0 R0–1M0 | 0.030 | < 0.001 | 0.015 to 0.046 |
| R2–3M0 R2–3M0 | 0.039 | < 0.001 | 0.019 to 0.058 |
| M1 M0 | 0.053 | < 0.001 | 0.043 to 0.062 |
| M1 M1 | 0.125 | < 0.001 | 0.103 to 0.147 |
| HbA1c | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | 0.000 to 0.001 |
| Cholesterol | 0.002 | 0.020 | 0.000 to 0.004 |
| Constant | –0.202 | < 0.001 | –0.222 to –0.182 |
| Number | 86,004 | ||
| Number of clusters | 14,963 | ||
| p > χ2 | < 0.001 | ||
Health and social care resource use and costs
Screening costs
Costs of screening were obtained from 2009–10 NHS reference costs, which were then updated to 2012–13 prices, with a unit cost of £32 per person screened. 98
In addition, we also performed a microcosting study, to assess the unit costs of screening to local programmes. For this, a questionnaire was produced in which the local manager of a screening programme was asked to provide information on the staff time and costs devoted to: administration; staff time for screening; equipment; IT connections to upload, download and grade images; grading of images; and consumables. Using this approach we found the unit cost of screening to be £33 per person screened. Given that the costs of screening were virtually identical, we did not vary these estimates in one-way sensitivity analyses.
Health-care resource use costs
Information on health-care costs was obtained from 17,043 people with diabetes from the Gloucestershire Diabetic Eye Screening Service. For these patients, we obtained anonymised Hospital Episode Statistics records. Hospital Episode Statistics provide details of all admissions and contacts in English hospitals funded by the NHS, including information on:
-
admitted patient care: detailing all inpatient stays and day cases (including information on diagnoses, procedures and length of stay)
-
adult critical care: detailing information on all stays in intensive treatment and critical care units, including length of stay
-
renal care: detailing information of all the day cases in which patients underwent dialysis
-
outpatient care: detailing information on all outpatient contacts and specialties visited
-
accident and emergency care: detailing information on all accident and emergency contacts.
In England, NHS hospitals are reimbursed for the services they provide through a national tariff of prices reflecting the national average cost of providing a hospital service. Each hospital service is assigned to a Health Resource Group (HRG), which groups together similar clinical procedures that cost an equivalent amount to deliver. 99 Prices in the national tariff have been set on the basis of the average cost of providing a particular HRG using data gathered from NHS hospitals. In addition, hospitals receive additional funding for high-cost drugs, additional hospitalisation days past a certain threshold and provision of direct-access diagnostics and specialised rehabilitation.
Each hospital contact was valued using the 2012–13 HRG English tariff. To determine the HRG for each hospital contact, and any additional payments received for provision of additional services, each contact in Hospital Episode Statistics was coded using the HRG grouper (version 4+ 2012–13) software (The Health and Social Care Information Centre, Leeds, UK). HRGs were then linked to a series of elective, emergency and procedure reference costs obtained from the 2012–13 schedule of NHS reference costs. 100
For each patient in the Gloucestershire Diabetic Eye Screening Service, information on health-care resource use and costs obtained from Hospital Episode Statistics records was then linked with the information collected as part of the screening programme. This included: date of screening; the grading of the retina images; and the visual acuity as assessed using logMAR charts. Total costs were then evaluated on an annual basis from the date of first screen, with each subsequent year being linked to the subsequent screening rounds if they took place. Information from HES on referrals to the service, results of any assessments for confirmation of diagnosis and treatment received by patients was also linked to Hospital Episode Statistics and screening data. As before, these data were linked on annual basis from the date of the first screen.
In total, we obtained cost and screening data for 17,043 patients, representing a total of 101,482 patient-years (average of 5.95 years per patient). In 21,267 of these years (21%) screening did not occur. In these instances, the results of the previous screen were carried forward (i.e. last value carried forward).
To assess the main predictors of total annual care costs, a generalised linear model (GLM) with a gamma distribution, for the relationship between the variance and conditional mean, and a log link function, clustered at the patient level, was performed. Predictors included observed DR and maculopathy grading at screening; logMAR visual acuity as measured in the best seeing eye; whether the patient had attended an assessment at HES; whether the patient had received treatment for DR or maculopathy (either laser photocoagulation or antiangiogenic therapy); age; and HbA1c and cholesterol as measured at baseline (i.e. shortly before the initial screen) (Table 40). The annual costs by observed retinopathy grade were converted into costs by true retinopathy grade using the estimated error probabilities given in Table 25. An advantage of including logMAR visual acuity in the best eye as a predictor of annual costs was that it allowed modelling of the impact of treatment not only in terms of utility but also costs. Furthermore, the annual mean costs of assessment at the HES, £134 per patient assessed, and the annual mean costs of treatment (£307 and £382 per patient treated with laser photocoagulation and antiangiogenic therapy, respectively) were directly estimated using the GLM model.
| Predictors | Coefficient | Margins | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.014 | £17 | < 0.001 | 14 to 19 |
| DR grade observed at screening | ||||
| R0M0 R0M0 | Reference case | |||
| R1M0 R0M0 | 0.105 | £112 | 0.001 | £42 to £181 |
| R1M0 R1M0 | 0.269 | £310 | < 0.001 | £215 to £404 |
| R2–3M0 R0–1M0 | 0.487 | £629 | < 0.001 | £342 to £917 |
| R2–3M0 R2–3M0 | 0.625 | £871 | < 0.001 | £564 to £1,178 |
| RxM1 RxM0 | 0.444 | £560 | < 0.001 | £383 to £735 |
| RxM1 RxM1 | 0.423 | £528 | < 0.001 | £344 to £711 |
| Assessment at HES | 0.119 | £134 | 0.005 | £21 to £247 |
| Treatment with | ||||
| Photocoagulation | 0.271 | £307 | 0.005 | £92 to £521 |
| Antiangiogenic therapy | 0.337 | £382 | < 0.001 | £157 to £606 |
| LogMAR visual acuity (best eye) | 1.057 | £1,197 | < 0.001 | £914 to £1,479 |
| HbA1c | 0.003 | £4 | 0.001 | £2 to £6 |
| Cholesterol | –0.044 | –£50 | < 0.001 | –£79 to –£21 |
| Constant | 5.870 | |||
| Number | 86,004 | |||
| Number of clusters | 14,963 | |||
Social care costs: nursing/residential care home admission
A targeted literature review was undertaken in MEDLINE to identify studies assessing nursing/residential care home admission in patients with DR. The search was restricted to journals in the English language published between January 1990 and June 2013. Search terms included variations of keywords for retinopathy, diabetes, maculopathy, vision, visual loss, blind, institutionalisation, nursing home and residential home. Citations of identified studies were also reviewed.
No study was identified that evaluated the risk of nursing/residential care home admission and DR. As a result, we assessed studies evaluating the risk of nursing/residential care home admission and visual loss. In total, 11 relevant studies were identified. For the model, we used the results from Evans et al. ,101 which evaluated the risk of nursing home admission in over 14,000 older people living in the community and who were followed up for a mean of 4 years. The study found that after controlling for a number of characteristics including age, sex, marital status, DM and other co-morbidities, the adjusted risk ratio of being admitted was 1.14 (95% CI 0.97 and 1.34) for those with reduced vision (20/30 to 20/60) and 1.08 (95% CI 0.91 to 1.28) for those who were visually impaired (< 20/60) compared with those with good vision (> 20/30) (5.4% risk of a nursing home admission after a mean of 4 years of follow-up; 382 out of 7010 cases).
To be able to use these estimates in the Markov model, we used the screening data from the Gloucestershire Diabetic Eye Screening service to assess the probability of having good vision, reduced vision or visual impairment, as defined by Evans et al. 101 For this we performed an ordered logistic regression adjusting for DR/maculopathy grade, age and HbA1c and cholesterol levels at baseline (Table 41). Given that over 95% of residents living in nursing/residential care homes in the UK are aged 65 years and over,102 we assumed that patients with diabetes would only be at risk of a nursing home admission if aged 65 years or older. Furthermore, treatment for DR was assumed to shift all individuals with visual impairment to the reduced vision group, and those with reduced vision to the good vision group. In sensitivity analysis, this assumption was changed to: (1) shifting only 50% of cases from the worst to the better vision states; and (2) improvement in vision only occurred for those with reduced vision.
| Predictors | Coefficient | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.16 | < 0.001 | 0.15 to 0.17 |
| DR grade at screening | |||
| R0M0 R0M0 | Reference case | ||
| R1M0 R0M0 | –0.26 | < 0.001 | –0.36 to –0.16 |
| R1M0 R1M0 | –0.43 | < 0.001 | –0.56 to –0.31 |
| R2–3M0 R0–1M0 | 0.33 | 0.042 | 0.01 to 0.65 |
| R2–3M0 R2–3M0 | 0.12 | < 0.001 | –0.23 to 0.47 |
| RxM1 RxM0 | 0.89 | < 0.001 | 0.72 to 1.06 |
| RxM1 RxM1 | 1.62 | < 0.001 | 1.38 to 1.85 |
| HbA1c | 0.02 | < 0.001 | 0.02 to 0.03 |
| Cholesterol | 0.02 | 0.563 | –0.05 to 0.09 |
| Cut: reduced vision | 17.02 | < 0.001 | 16.29 to 17.76 |
| Cut: impaired vision | 22.15 | < 0.001 | 21.37 to 22.93 |
| Number | 86,004 | ||
| Number of clusters | 14,963 | ||
| p > χ2 | < 0.001 | ||
The annual costs of institutionalisation in a care home were obtained from data published by the Personal Social Services Research Unit,84 and estimated at £39,000 per year (£750 per week × 52 weeks).
Analysis
The value of £30,000 was adopted as the maximum willingness to pay for a QALY gained. The screening interval was deemed to be cost-effective if the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) was below this threshold. Model internal validity was checked using sensitivity analysis (extreme values) and comparing model outputs with the data used to build the model. Model comparison was performed by comparing the results of our model with similar previous work.
Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis
Model parameters and structural assumptions were evaluated in one-way and probabilistic sensitivity analysis. The distributions for the regression coefficients informing the several models described above were obtained by bootstrapping the sample and re-estimating the regression models. This allowed the correlation between coefficients to be captured fully. The joint distribution concerning the intensity matrix between the seven retinopathy states was obtained by simulating from the maximum likelihood estimation and hessian matrix of the parameters. The choice of distributions used for the remaining parameters was made according to recommended practice. 103
Relative effectiveness measures were modelled using a log-normal distribution. Incremental effectiveness measures were modelled using normal distributions. Parameters concerning proportions/probabilities were modelled using beta distributions. Coefficients of the regression model linking visual acuity and utility score were assumed to be independent and normally distributed. 89 Unit costs and resource use were modelled using gamma distributions.
A cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC) was constructed104 and analysis of covariance methods were used to determine the proportion of variance in the incremental costs and QALYs saved explained by parameter uncertainty. 103 Finally, the overall contribution of the model inputs to the decision uncertainty was explored using the expected value of perfect information (EVPI). The EVPI per patient was estimated non-parametrically. 103
The EVPI for the total population who stand to benefit from reducing the decision uncertainty was also estimated. This required information on the predicted lifetime of the screening technology and the period over which information about the decision will be useful, T (5, 10 and 15 year scenarios), and the number of diabetic patients eligible for screening in England (Pt):
where Pt was 2.2 million diabetic patients in England and the discount rate used (r), was 3.5%.
Results
Diabetic retinopathy screening for patients with diabetes
Table 42 presents the baseline characteristics of the simulated cohort of 1000 people with diabetes. In this cohort, 58% of patients had no DR in either eye, 23% had background retinopathy in one eye and a further 19% had background retinopathy in two eyes.
| True DR grade | Patients |
|---|---|
| R0M0 R0M0, n (%) | 580 (58) |
| R1M0 R0M0, n (%) | 230 (23) |
| R1M0 R1M0, n (%) | 190 (19) |
| Mean age, years | 66.6 |
| Sex: female, n (%) | 440 (44) |
| Mean duration of diabetes, years | 7.3 |
| Mean cholesterol, mg/l | 4.22 |
| Mean HbA1c, mmol/mol | 52.6 |
For our simulated cohort, screening every 2, 3 and 5 years would result in a reduction of 5375 (95% CI 5332 to 5411), 7166 (95% CI 7111 to 7213) and 8617 (95% CI 8552 to 8672) screens, respectively, compared with annual screening (Table 43). By screening every 2 years, as opposed to every year, a total of 143 (95% CI 120 to 162) fewer patients incorrectly diagnosed at screening as having R2–3 or M1 (i.e. true negatives) would be referred to HES. These reductions in numbers increase to 190 (95% CI 159 to 215) and 229 (95% CI 191 to 259) when screening every 3 or 5 years, respectively.
| Outcomes | Screening every 6 months | Annual screening | Screening every 2 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every 5 years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of screens | 21,990 | 11,253 | 5878 | 4087 | 2636 |
| Number of patients referred following screening | |||||
| True negatives | 584 | 298 | 155 | 108 | 69 |
| True positives | 303 | 277 | 234 | 203 | 157 |
| Number of patients assessed by HES following screening | 492 | 323 | 222 | 178 | 132 |
| Number of patients treated following screening | 70 | 65 | 57 | 50 | 40 |
| Number of patients treated over lifetime | 135 | 124 | 106 | 92 | 72 |
By contrast, screening every 2 years, as opposed to annually, would reduce the number of patients with true R2–3 or M1 grades (i.e. true positives) referred to HES, over the lifetime of the cohort, from 277 to 234 people, a reduction of 42 (95% CI 35 to 50) cases. Increasing the screening intervals to 3 years and 5 years would further reduce the number of true positives being referred by 74 (95% CI: 62 to 87) and 119 (95% CI: 100 to 139), respectively. This would result in 8 (95% CI 7 to 10), 15 (95% CI 12 to 17) and 25 (95% CI 21 to 29) fewer true cases of R2–3 or M1 being treated following screening if screening intervals were to be extended to 2, 3 and 5 years, respectively, compared with annual screening (Table 43). Over a lifetime, when compared with annual screening, there would be a reduction of 18 (95% CI 15 to 21), 32 (95% CI 27 to 37) and 52 (95% CI 44 to 59) true cases of R2–3 or M1 being treated if screening intervals were to be extended to 2, 3 and 5 years, respectively.
With annual screening, the average discounted screening cost per patient was £273 for annual screening, compared with £144, £101 and £67 for screening every 2, 3 and 5 years, respectively. Mean costs associated with assessment at HES of referral of R2–3 or M1 suspected cases was also higher, at £114, when screening annually than when screening at 2, 3 and 5 years (£70, £52 and £36, respectively), with a similar pattern of costs being observed for treatment of R2–3 and M1. However, as the screening interval increases, mean health-care costs (excluding screening, assessment and treatment) increase from £14,354 when screening every year to £14,377 at 2 years, £14,393 at 3 years and £14,413 at 5 years. Combining all health and social care costs included in the model, mean discounted costs are £20,672 when screening is performed annually, £20,490 when it is performed every 2 years, £20,433 when performed every 3 years, and £20,391 when performed every 5 years (Table 44). The discounted average QALYs gained by patients were 8.3710 when screening every year, 8.3692 when screening every 2 years, 8.3680 when screening every 3 years and 8.3663 when screening every 5 years.
| Costs and outcomes | Screening every 5 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every two years | Annual screening | Screening every 6 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs, £ (95% CI) | 20,391 (19,668 to 21,136) | 20,433 (19,707 to 21,176) | 20,490 (19,771 to 21,229) | 20,672 (19,947 to 21,405) | 21,050 (20,303 to 21,824) |
| Screening, £ | 67 | 101 | 144 | 273 | 529 |
| HES assessment, £ | 36 | 52 | 70 | 114 | 193 |
| Treatment of R2–3 or M1, £ | 24 | 35 | 48 | 81 | 141 |
| Other health-care costs, £ | 14,413 | 14,393 | 14,377 | 14,354 | 14,337 |
| Social care costs, £ | 5852 | 5851 | 5851 | 5850 | 5850 |
| Total QALYs (95% CI) | 8.3663 (4.3731 to 12.067) | 8.3680 (4.3743 to 12.070) | 8.3692 (4.3753 to 12.071) | 8.3710 (4.3768 to 12.074) | 8.3723 (4.3779 to 12.0755) |
After combining costs and outcomes in an incremental cost-effectiveness analysis, and at a £30,000 per QALY threshold, the most cost-effective screening interval was to screen patients every three years (Table 45). The probability of screening every 3 years being the most cost-effective option at £30,000/QALY was estimated to be 46%. Screening every 2 years was associated with an ICER of £45,684 per QALY gained compared with screening every 3 years. Screening every 6 months was estimated to cost an additional £288,497 per QALY gained compared with annual screening.
| Screening strategies | Difference in costs, £ (95% CI) | Difference in QALYs (95% CI) | ICER, £ | Probability that intervention is the most cost-effective at £30,000/QALY, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 5 years | – | – | – | 41 |
| Every 3 years | 42 (26 to 58) | 0.0019 (0.0004 to 0.0029) | 26,156 | 46 |
| Every 2 years | 57 (41 to 73) | 0.0012 (0.0003 to 0.0023) | 45,684 | 13 |
| Annually | 182 (141 to 226) | 0.0018 (0.0005 to 0.0034) | 98,085 | 0 |
| Every 6 months | 378 (306 to 457) | 0.0013 (0.0003 to 0.0024) | 288,497 | 0 |
Figure 18 reports the CEAC and EVPI per patient associated with the different screening options. The population EVPI over 5 years was estimated to be £86M at the £30,000 per QALY gained threshold. This suggests that undertaking additional major commissioned research work to reduce further decision uncertainty is likely to be of significant benefit given the large scale of the population affected by the decision.
FIGURE 18.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve and EVPI per patient.
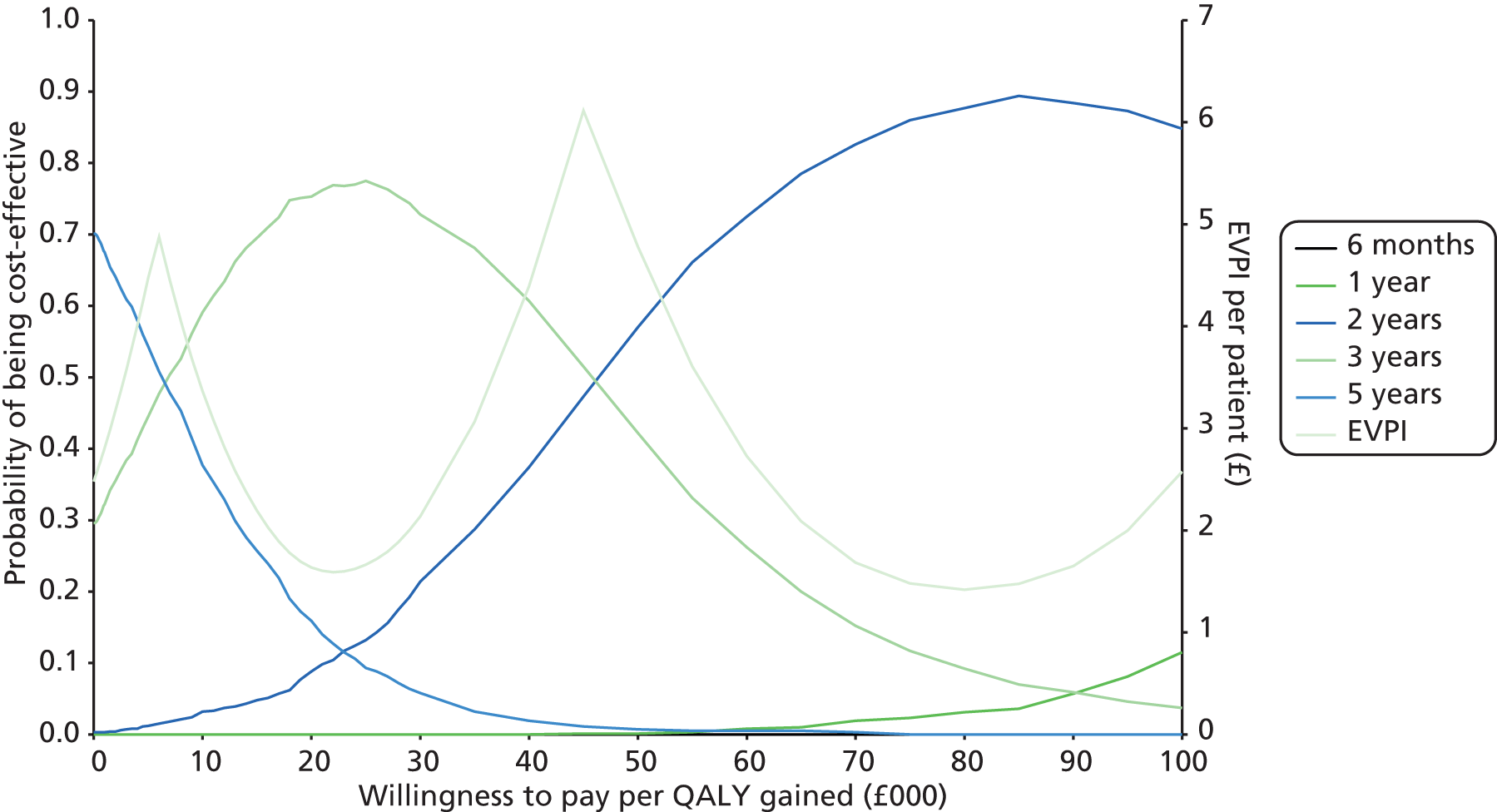
Figure 19 reports the parameters according to their impact on the variance of incremental costs and QALYs from the comparison of screening every 3 years with every 5 years. Variance in the estimated incremental costs was dominated by the variation in the following variables: costs of assessment following referral to HES; treatment costs; hospital costs; and effectiveness inputs. Variance in the incremental QALYs was dominated by the variance in the regression model associating utility with visual acuity, effectiveness inputs (mostly the effectiveness of laser/injection for M1) and natural history of progression.
FIGURE 19.
Analysis of covariance analysis of proportion of sum of squares for incremental QALYs saved and incremental costs explained by the uncertainty in the model inputs.

Table 46 reports the results of a range of other sensitivity analyses. Changes in the monitoring interval by HES from 6 months to 12 months did not alter the decision. The results were also robust to the proportion of individuals with M1 or R2–R3 that are referred to further monitoring every 6 months if assessed by HES but not treated. Given the difference in effectiveness across treatments, depending on which type of treatment was received there was a significant impact on the results. For example, increasing the proportion of M1 cases receiving injection rather than laser treatment among those treated resulted in screening every 2 years falling under the £30,000 per QALY threshold.
| Sensitivity analysis scenarios | Screening every 3 years vs. every 5 years | Screening every 2 years vs. every 3 years |
|---|---|---|
| Base case | £26,156 | £45,684 |
| Screening uptake: 81% | £27,060 | £47,805 |
| Screening uptake: 91% | £31,175 | £56,503 |
| Screening uptake: 71% | £23,305 | £40,008 |
| Hospital costs only (excluding social care costs) | £26,724 | £46,582 |
| 50% shift from visual impairment to reduced vision and from reduced vision to good vision (affects nursing home admission) | £26,296 | £46,194 |
| Only cases with reduced vision shift to good vision (affects nursing home admission) | £26,644 | £46,495 |
| Proportion of M1 cases treated with injection rather than laser: increase of 30% | £16,515 | £31,403 |
| All M1 cases are treated with injection or a combination of laser and injection | £12,438 | £24,624 |
| Probability of being referred to monitoring every 6 months of 0% instead of 78% | £29,796 | £45,566 |
| Probability of being referred to monitoring every 6 months of 50% instead of 78% | £26,539 | £44,520 |
| Probability of being referred to monitoring every 6 months of 100% instead of 78% | £25,880 | £47,635 |
| Monitoring interval by HES of 12 months instead of 6 months if R2–3 or M1 | £25,709 | £45,117 |
Cost-effectiveness of differing screening intervals by risk group as defined from the results from two consecutive screening episodes
We further assessed the cost-effectiveness of the different DR screening intervals in three groups at differing risks of developing R2–3 or M1 as defined in Table 33.
For the low-risk group (i.e. patients with no DR in either eye in two SEs), mean costs associated with assessment at HES of referral of R2–3 or M1 suspected cases was higher (£46) when screening annually than when screening at 2, 3 and 5 years (£27, £20 and £13, respectively), with a similar pattern of costs being observed for treatment of R2–3 and M1. However, as the screening interval increases, other health-care costs increase slightly from £13,378 when screening every year to £13,387 at 2 years, £13,392 at 3 years and £13,999 at 5 years. Combining all health and social care costs included in the model, mean discounted costs are £19,586 when screening is performed annually, £19,434 when performed every 2 years, £19,385 when performed every 3 years, and £19,346 when performed every 5 years (Table 47). The discounted average QALYs gained by patients were 8.3558 when screening every year, 8.3551 when screening every 2 years, 8.3547 when screening every 3 years and 8.3541 when screening every 5 years.
| Costs and outcomes | Screening every 5 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every 2 years | Annual screening | Screening every 6 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs, £ (95% CI) | 19,346 (18,714 to 20,018) | 19,385 (18,754 to 20,055) | 19,434 (18,805 to 20,103) | 19,586 (18,960 to 20,259) | 19,894 (19,253 to 20,572) |
| Screening, £ | 67 | 102 | 145 | 275 | 535 |
| HES assessment, £ | 13 | 20 | 27 | 46 | 81 |
| Treatment of R2–3 or M1, £ | 8 | 12 | 16 | 28 | 48 |
| Other health-care costs, £ | 13,399 | 13,392 | 13,387 | 13,378 | 13,372 |
| Social care costs, £ | 5864 | 5864 | 5863 | 5863 | 5863 |
| Total QALYs (95% CI) | 8.3541 (4.6933 to 12.2316) | 8.3547 (4.6940 to 12.2320) | 8.3551 (4.6945 to 12.2323) | 8.3558 (4.6952 to 12.2327) | 8.3563 (4.6958 to 12.2331) |
The most cost-effective screening intervention for the low-risk group was screening every 5 years (Table 48), with a probability of being the most cost-effective intervention of 99% at the £30,000 per QALY threshold. Other screening intervals for this patient group yielded considerably higher ICERs. For example, when screening every 3 years was compared with screening every 5 years the associated ICER was above £72,000 per QALY gained.
| Screening strategies | Difference in costs, £ (95% CI) | Difference in QALYs (95% CI) | ICER, £ | Probability that intervention is the most cost-effective at £30,000/QALY, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 5 years | – | – | – | 99 |
| Every 3 years | 39 (32 to 46) | 0.0005 (0.0001 to 0.0010) | 72,217 | 1 |
| Every 2 years | 49 (42 to 57) | 0.0004 (0.0001 to 0.0008) | 113,823 | 0 |
| Annually | 152 (131 to 171) | 0.0007 (0.0002 to 0.0013) | 225,004 | 0 |
| Every 6 months | 308 (279 to 344) | 0.0005 (0.0001 to 0.0010) | 615,664 | 0 |
For the medium-risk group (i.e. patients with background DR in one eye in two SEs), mean discounted costs were £21,180 when screening is performed annually, £20,992 when performed every 2 years, £20,933 when performed every 3 years, and £20,892 when performed every 5 years (Table 49). The discounted average QALYs gained by patients were 8.3314 when screening every year, 8.3292 when screening every 2 years, 8.3277 when screening every 3 years and 8.3258 when screening every 5 years.
| Costs and outcomes | Screening every 5 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every 2 years | Annual screening | Screening every 6 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs, £ (95% CI) | 20,892 (20,156 to 21,674) | 20,933 (20,201 to 21,722) | 20,992 (20,253 to 21,786) | 21,180 (20,415 to 21,990) | £21,573 (20,784 to 22,378) |
| Screening, £ | 67 | 101 | 144 | 272 | 526 |
| HES assessment, £ | 41 | 60 | 80 | 131 | 221 |
| Treatment of R2–3 or M1, £ | 27 | 41 | 55 | 93 | 162 |
| Other health-care costs, £ | 14,905 | 14,880 | 14,861 | 14,833 | 14,812 |
| Social care costs, £ | 5856 | 5856 | 5855 | 5855 | 5,854 |
| Total QALYs (95% CI) | 8.3258 (4.6654 to 12.1034) | 8.3277 (4.6680 to 12.1062) | 8.3292 (4.6700 to 12.1083) | 8.3314 (4.6731 to 12.1116) | 8.3329 (4.6754 to 12.1138) |
For the medium-risk group the most cost-effective screening intervention was screening every 3 years (Table 50). When screening for DR every 3 years was compared with screening every 5 years, the incremental cost per QALY gained was £22,266. By contrast, when screening for DR every 2 years was compared with screening every 3 years, the incremental cost per QALY gained was £39,829, with the probability of screening every 2 years being the most cost-effective at 25%.
| Screening strategies | Difference in costs, £ (95% CI) | Difference in QALYs (95% CI) | ICER, £ | Probability that intervention is the most cost-effective at £30,000/QALY, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 5 years | – | – | – | 31 |
| Every 3 years | 42 (22 to 60) | 0.0019 (0.0003 to 0.0036) | 22,266 | 43 |
| Every 2 years | 58 (38 to 77) | 0.0015 (0.0003 to 0.0028) | 39,829 | 25 |
| Annually | 188 (139 to 236) | 0.0022 (0.0004 to 0.0042) | 86,614 | 0 |
| Every 6 months | 394 (307 to 479) | 0.0015 (0.0003 to 0.0030) | 256,354 | 0 |
Of all the three risk groups assessed, high-risk patients (i.e. patients with background retinopathy in both eyes) had the highest mean discounted health and social care costs, regardless of screening strategy implemented. Mean discounted costs were £25,043 when screening is performed annually, £24,734 when performed every 2 years, £24,649 when performed every 3 years, and £24,600 when performed every 5 years (Table 51). The discounted average QALYs gained by patients were 9.2691 when screening every year, 9.2620 when screening every 2 years, 9.2570 when screening every 3 years and 9.2503 when screening annually.
| Costs and outcomes | Screening every 5 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every 2 years | Annual screening | Screening every 6 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs, £ (95% CI) | 24,600 (23,578 to 25,665) | 24,649 (23,633 to 25,710) | 24,734 (23,711 to 25,793) | 25,043 (23,991 to 26,147) | 25,728 (24,586 to 26,934) |
| Screening, £ | 71 | 107 | 152 | 286 | 551 |
| HES assessment, £ | 129 | 185 | 242 | 384 | 635 |
| Treatment of R2/3 or M1, £ | 96 | 142 | 191 | 321 | 557 |
| Other health-care costs, £ | 18,779 | 18,691 | 18,626 | 18,531 | 18,465 |
| Social care costs, £ | 5525 | 5523 | 5522 | 5521 | 5520 |
| Total QALYs (95% CI) | 9.2503 (5.4153 to 13.3784) | 9.2570 (5.4241 to 13.3874) | 9.2620 (5.4308 to 13.3939) | 9.2691 (5.4408 to 13.4034) | 9.2740 (5.4480 to 13.4074) |
For the high-risk group the most cost-effective screening intervention was screening every 2 years (Table 52). When screening for DR every 2 years was compared with screening every 3 years, the incremental cost per QALY gained was £16,926. The probability of screening every 2 years being the most cost-effective intervention was 59%. By contrast, when annual screening for DR was compared with screening every 2 years, the incremental cost per QALY gained was £43,156, with a probability of annual screening being the most cost-effective intervention of 21%.
| Screening strategies | Difference in costs, £ (95% CI) | Difference in QALYs (95% CI) | ICER, £ | Probability that intervention is the most cost-effective at £30,000/QALY, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 5 years | – | – | – | 3 |
| Every 3 years | 49 (–6 to 109) | 0.0067 (0.0016 to 0.0127) | 7197 | 16 |
| Every 2 years | 84 (32 to 144) | 0.0050 (0.0012 to 0.0095) | 16,962 | 59 |
| Annually | 309 (180 to 457) | 0.0071 (0.0017 to 0.0136) | 43,156 | 21 |
| Every 6 months | 685 (451 to 942) | 0.0049 (0.0009 to 0.0094) | 139,921 | 0 |
Cost-effectiveness of differing screening intervals by risk group as defined from the results of the initial screening episode and baseline clinical risk factors
We assessed the cost-effectiveness of the different DR screening intervals in four groups at differing risks of developing R2–3 or M1 conditional on baseline CRFs (Table 33).
For the low-risk group, mean costs associated with assessment at HES of referral of R2–3 or M1 suspected cases were higher (£35) when screening annually than when screening at 2, 3 and 5 years (£20, £15 and £10, respectively), with a similar pattern of costs being observed for treatment of R2–3 and M1. However, as the screening interval increases, other health-care costs increase slightly from £13,349 when screening every year to £13,354 at screening every 2 years, £13,358 at 3 years and £13,363 at 5 years. Combining all health and social care costs included in the model, mean discounted costs are £19,537 when screening is performed annually, £19,381 when performed every 2 years, £19,330 when performed every 3 years, and £19,290 when performed every 5 years (Table 53). The discounted average QALYs gained by patients were 9.0488 when screening every year, 9.0484 when screening every 2 years, 9.0480 when screening every 3 years and 9.0476 when screening every 5 years.
| Costs and outcomes | Screening every 5 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every 2 years | Annual screening | Screening every 6 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs, £ (95% CI) | 19,290 (18,623 to 20,018) | 19,330 (18,663 to 20,057) | 19,381 (18,715 to 20,108) | 19,537 (18,875 to 20,265) | 19,854 (19,186 to 20,582) |
| Screening, £ | 71 | 108 | 154 | 293 | 571 |
| HES assessment, £ | 10 | 15 | 20 | 35 | 61 |
| Treatment of R2/3 or M1, £ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 21 | 37 |
| Other health-care costs, £ | 13,363 | 13,358 | 13,354 | 13,349 | 13,344 |
| Social care costs, £ | 5840 | 5840 | 5840 | 5840 | 5840 |
| Total QALYs (95% CI) | 9.0476 (5.0056 to 13.0951) | 9.0480 (5.0062 to 13.0955) | 9.0484 (5.0067 to 13.0959) | 9.0488 (5.0074 to 13.0965) | 9.0492 (5.0079 to 13.0968) |
The most cost-effective screening intervention for the low-risk group was screening every 5 years (Table 54), with a probability of being the most cost-effective intervention of 100% at the £30,000 per QALY threshold. Other screening intervals for this patient group yielded considerably higher ICERs. For example, when screening every 3 years was compared with screening every 5 years, the associated ICER was above £90,000 per QALY gained.
| Screening strategies | Difference in costs, £ (95% CI) | Difference in QALYs (95% CI) | ICER, £ | Probability that intervention is the most cost-effective at £30,000/QALY, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 5 years | – | – | – | 100 |
| Every 3 years | 40 (35 to 45) | 0.0004 (0.0001 to 0.0008) | 97,059 | 0 |
| Every 2 years | 51 (46 to 56) | 0.0003 (0.0001 to 0.0006) | 158,008 | 0 |
| Annually | 156 (144 to 169) | 0.0005 (0.0001 to 0.0010) | 324,774 | 0 |
| Every 6 months | 316 (293 to 341) | 0.0003 (0.0001 to 0.0007) | 930,079 | 0 |
For the low- to medium-risk group, mean discounted costs were £21,194 when screening is performed annually, £21,004 when performed every 2 years, £20,946 when performed every 3 years, and £20,904 when performed every 5 years (Table 55). The discounted average QALYs gained by patients were 9.2588 when screening every year, 9.2569 when screening every two years, 9.2555 when screening every three years and 9.2538 when screening every 5 years.
| Costs and outcomes | Screening every 5 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every 2 years | Annual screening | Screening every 6 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs, £ (95% CI) | 20,904 (20,218 to 21,629) | 20,946 (20,257 to 21,677) | 21,004 (20,316 to 21,738) | 21,194 (20,474 to 21,938) | 21,590 (20,826 to 22,344) |
| Screening, £ | 71 | 108 | 154 | 293 | 569 |
| HES assessment, £ | 34 | 51 | 68 | 118 | 190 |
| Treatment of R2/3 or M1, £ | 24 | 36 | 49 | 83 | 145 |
| Other health-care costs, £ | 15,253 | 15,230 | 15,214 | 15,189 | 15,171 |
| Social care costs, £ | 5521 | 5521 | 5520 | 5520 | 5520 |
| Total QALYs (95%) | 9.2538 (5.2104 to 13.5974) | 9.2555 (5.2121 to 13.5980) | 9.2569 (5.2133 to 13.5984) | 9.2588 (5.2151 to 13.5991) | 9.2602 (5.2163 to 13.5996) |
The most cost-effective screening intervention for the low- to medium-risk group was screening every 3 years (Table 56), with an ICER of £23,893 per QALY gained when compared with screening every 5 years. The probability that screening every 3 years was the most cost-effective intervention was 48% at a £30,000 per QALY threshold.
| Screening strategies | Difference in costs, £ (95% CI) | Difference in QALYs (95% CI) | ICER, £ | Probability that intervention is the most cost-effective at £30,000/QALY, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 5 years | – | – | – | 35 |
| Every 3 years | 42 (26 to 59) | 0.0018 (0.0004 to 0.0035) | 23,893 | 48 |
| Every 2 years | 58 (42 to 76) | 0.0014 (0.0003 to 0.0027) | 43,597 | 17 |
| Annually | 189 (150 to 233) | 0.0020 (0.0004 to 0.0039) | 96,556 | 0 |
| Every 6 months | 396 (326 to 475) | 0.0014 (0.0003 to 0.0027) | 289,293 | 0 |
For the medium- to high-risk group, mean discounted costs were £22,525 when screening is performed annually, £22,288 when performed every 2 years, £22,218 when performed every 3 years, and £22,173 when performed every 5 years (Table 57). The discounted average QALYs gained by patients were 9.3956 when screening every year, 9.3919 when screening every 2 years, 9.3893 when screening every 3 years and 9.3857 when screening every 5 years.
| Costs and outcomes | Screening every 5 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every 2 years | Annual screening | Screening every 6 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs, £ | 22,173 | 22,218 | 22,288 | 22,525 | 23,036 |
| Screening, £ | 71 | 108 | 153 | 290 | 563 |
| HES assessment, £ | 71 | 101 | 133 | 212 | 354 |
| Treatment of R2/3 or M1, £ | 52 | 77 | 104 | 175 | 304 |
| Other health-care costs, £ | 16,447 | 16,402 | 16,368 | 16,319 | 16,286 |
| Social care costs, £ | 5532 | 5530 | 5530 | 5529 | 5529 |
| Total QALYs (95% CI) | 9.3857 (5.4478 to 13.7326) | 9.3893 (5.4541 to 13.7339) | 9.3919 (5.4586 to 13.7350) | 9.3956 (5.4649 to 13.7364) | 9.3982 (5.4691 to 13.7374) |
For the medium- to high-risk group, the most cost-effective screening intervention was screening every 2 years (Table 58), which was associated with an ICER of £26,406 per QALY gained when compared with screening every 3 years. The probability that screening every 2 years was the most cost-effective intervention was 57% at a £30,000 per QALY threshold.
| Screening strategies | Difference in costs, £ (95% CI) | Difference in QALYs (95% CI) | ICER, £ | Probability that intervention is the most cost-effective at £30,000/QALY, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 5 years | – | – | – | 10 |
| Every 3 years | 46 (14 to 76) | 0.0037 (0.0009 to 0.0069) | 12,823 | 30 |
| Every 2 years | 69 (38 to 100) | 0.0027 (0.0006 to 0.0051) | 26,406 | 57 |
| Annually | 238 (160 to 314) | 0.0039 (0.0009 to 0.0073) | 63,421 | 3 |
| Every 6 months | 511 (375 to 647) | 0.0026 (0.0006 to 0.0050) | 201,870 | 0 |
For the high-risk group, mean discounted costs were £26,212 when screening is performed annually, £25,863 when performed every 2 years, £25,773 when performed every 3 years, and £25,730 when performed every 5 years (Table 59). The discounted average QALYs gained by patients were 10.2733 when screening every year, 10.2637 when screening every two years, 10.2570 when screening every three years and 10.2477 when screening every 5 years.
| Costs and outcomes | Screening every 5 years | Screening every 3 years | Screening every 2 years | Annual screening | Screening every 6 months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs, £ | 25,730 | 25,773 | 25,863 | 26,212 | 27,003 |
| Screening, £ | 73 | 112 | 159 | 300 | 579 |
| HES assessment, £ | 162 | 232 | 303 | 478 | 786 |
| Treatment of R2/3 or M1, £ | 121 | 181 | 244 | 408 | 705 |
| Other health-care costs, £ | 20,620 | 20,498 | 20,409 | 20,280 | 20,187 |
| Social care costs, £ | 4752 | 4749 | 4747 | 4746 | 4745 |
| Total QALYs (95% CI) | 10.2477 (5.6241 to 14.7498) | 10.2570 (5.6345 to 14.7557) | 10.2637 (5.6422 to 14.7599) | 10.2733 (5.6535 to 14.7659) | 10.2799 (5.6616 to 14.7700) |
As with the two screening risk stratification model, screening patients deemed to be at high risk every 2 years was the most cost-effective screening intervention (Table 60). For this group of patients, screening every 2 years was associated with an ICER of £13,302 per QALY gained compared with screening every 3 years, and the probability that screening every 2 years was the most cost-effective intervention was 55%. Annual screening was associated with an ICER of £36,364 per QALY gained compared with screening every 2 years, with a probability of annual screening being cost-effective of 34%.
| Screening strategies | Difference in costs, £ (95% CI) | Difference in QALYs (95% CI) | ICER, £ | Probability that intervention is the most cost-effective at £30,000/QALY, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 5 years | – | – | – | 2 |
| Every 3 years | 43 (–36 to 125) | 0.0093 (0.0021 to 0.0170) | 4620 | 9 |
| Every 2 years | 89 (12 to 168) | 0.0068 (0.0016 to 0.0124) | 13,302 | 55 |
| Annually | 349 (166 to 542) | 0.0096 (0.0022 to 0.0177) | 36,364 | 34 |
| Every 6 months | 792 (469 to 1120) | 0.0066 (0.0014 to 0.0121) | 120,605 | 0 |
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy screening is widely recommended and has shown to be cost-effective compared with no screening. 9,10,12 However, a less clear understanding exists on the most appropriate screening interval, with published cost-effectiveness evidence showing conflicting results. 48
Our cost-effectiveness analysis shows that for patients with diabetes and no pre-proliferative DR or PDR or maculopathy, the current national screening programme of screening patients annually is not cost-effective. Results from our study show that for this group of patients, screening every 3 years would be the most cost-effective option. Annual screening, by contrast, was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of £98,085 compared with the next less effective DR screening strategy (i.e. screening every 2 years). At current NICE thresholds of £20,000 to £30,000 per QALY gained, annual screening would not be considered cost-effective. Our results are similar to those by Brailsford et al. ,88 which concluded that a 30-month screening interval was the most cost-effective option.
Irrespective of how patients were stratified in terms of their risk of developing STDR/maculopathy, our results suggest that the cost-effectiveness of the screening programme could be further improved by targeting patients using differing intervals for patients at different risks of developing STDR/maculopathy. Stratifying both based on the results from two consecutive SEs or based on the first single SE in conjunction with CRF data produced very similar results. In both risk stratification models, screening patients at low risk every 5 years, and those at high risk every 2 years would be the most cost-effective DR screening strategy.
There is, however, considerable uncertainty in the evidence informing the model, particularly the natural history of disease progression, association between utility scores and visual acuity and the effectiveness of treatment in diabetic maculopathy. There is also considerable uncertainty concerning the annual marginal costs attributable to treatment and assessments in the HES. This is reflected in the very large EVPI values of £86M to £458M, conditional on the expected lifetime of the current technology for screening. The EVPI gives the maximum amount of funding required for further research to reduce the decision uncertainty about which of the screening intervals is the most cost-effective option. The large population of diabetic patients that will be affected by making the wrong decision, together with considerable uncertainty in the evidence available, warrant caution about the model results. Hence, our results suggest undertaking additional major commissioned research work to further reduce the decision uncertainty.
There are several limitations to consider. First, there was very limited information concerning the proportion of patients with R2–3 or M1 grade that are referred for further monitoring by the HES. This led to assumptions being made concerning both the interval of monitoring and the proportion of patients being referred to it. However, sensitivity analyses showed the model results to be fairly robust to variations in these assumptions. The small number of patients in these health states also prevented the separation of R2 and R3 states. Hence, pre-proliferative and proliferative retinopathy were grouped together as both are grades prompting referral to the HES and are sight-threatening states. The absorbing states used, R2/R3 M0 and Rx M1 in both eyes, meant that no onwards state progression was explicitly modelled between and from these. However, such states lead to treatment, which seems to have limited effect on the retinopathy grade91 and, therefore, disease progression was implicitly modelled in terms of costs, visual acuity and utilities, which were found to increase with age/duration of diabetes. Furthermore, the lack of movements between the absorbing states is likely to have limited impact as few patients were identified as making such a transition.
Second, owing to the cohort nature of the model and the focus on simulating the progression of true states, it was not possible to evaluate strategies based on which states were observed at consecutive screening rounds. An alternative would have been to analyse the Markov model as an individual-based model (i.e. microsimulation) so that we could keep track of each individual’s history. 105 This would have allowed tailoring the frequency of screening during the lifetime of a cohort of patients conditional on the observed grades.
Although a great proportion of the data used were derived from patient-level data in patients with diabetes, we were not able to obtain all model parameters from this group of patients and, therefore, we had to obtain some of the model parameters from the literature. These included the risk of nursing home admission given losses in vision, health state utility values, and treatment effectiveness. As a result, the populations on which these studies based their results might be different from those in which the majority of the data were obtained (i.e. those attending the Gloucestershire DESP). For example, the data on the effectiveness of laser photocoagulation for treatment of STDR were obtained from evidence from the 1980s and early 1990s. In addition, the results are conditional on the model structure and the evidence used to inform it. For example, we used the results from the study by Lloyd et al. ,97 which assessed, using the EQ-5D, the utility associated with visual acuity. However, as with the other three studies identified, this association was only available for the best eye (in terms of visual acuity). Therefore, for modelling purposes, we assumed that the best seeing-eye was always the first to be treated. Internal validity was performed and was complemented by the exploration of different parameter and structural scenarios in the sensitivity analysis.
Routinely collected data were used to assess the impact of DR grade and visual acuity on health-care resource usage and costs. Therefore, it was not possible to determine whether use of health-care services was directly a result of vision loss or whether it was a result of other diabetes-related complications (such as stroke or heart attacks), given that poorly controlled diabetes is associated with both vision loss and other diabetes-related complications. 95 We performed additional analyses to assess whether the association between DR grade/visual acuity and annual care costs was confounded. Using the diagnoses codes included in patients’ HES records, we were able to estimate patients’ Charlson Co-morbidity Index (CCI) based on 22 clinical conditions present within a patient (including myocardial infarction, stroke, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and tumours). 106 When we adjusted for CCI, the significant and positive association between DR grade/visual acuity and annual care costs was still observed.
Finally, our analysis is from the perspective of the NHS and personal social services. As a result, other important cost categories not relevant to the perspective adopted were not included in the analysis. For example, we excluded some important economic considerations for people with visual loss, such as reductions in earnings through reduced or lost productivity, and the economic consequences of reduced mobility associated with vision loss (for example, people with moderate vision loss not being able to drive).
In conclusion, the work presented here suggests that it may be good value for money to use differing intervals for patients at different risks of developing STDR/maculopathy. Further research is needed to make more informed decisions.
Chapter 9 Other research using the same data set
-
This data set was used to demonstrate that the rate of detection of referable DR is elevated in those who were not screened promptly after diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. 107
-
The data set was also used to compare characteristics of those newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes between 2005 and 2012 with those recruited to UKPDS (1978–90). Patients in this screening programme have less DR and less referable DR and are less hyperglycaemic, more hypertensive and heavier than those newly diagnosed patients recruited to UKPDS.
Data were available for 2070 men and 1375 women, of whom 1403 (68%) men and 990 (72%) women had no retinopathy. Of those with DR, 20% had microaneurysms in one eye, 9% had microaneurysms in both eyes and 2% had referable retinopathy, and there was more retinopathy in men than in women (p-value = 0.0033). Patients were of similar ages to those in UKPDS and had lower HbA1c (mean difference –1.8%, –20 mmol/mol), higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure (+7 mmHg and +2 mmHg) and higher BMI (+4 kg/m2). Proportionately more participants in UKPDS had any DR (39% of men and 34% of women) and more had referable DR (15% of men and 11% of women, p-value < 0.0001).
Chapter 10 Lay perspective
Mike Whatmore’s contribution
I have been an independent member of the HTA Trial Steering Committee from its inception in October 2012, and actively involved at both live meetings and updated with all necessary interim documents by e-mail. Also, during this first meeting, a presentation was made of the data set information to be used for all areas involved in the study, and classification for reference for diabetic retinopathy.
In November 2012, I received an e-mail with the HTA Interim Progress Report attached, which included details of how the studies had been carried out to date and how problems encountered with the lack of data from one of the original expected sources, in South London, had been overcome and an alternative set of appropriate data had been accessed from the Nottingham Screening Service team.
At the second, live meeting, on 31 March 2014, the latest data obtained was presented, showing that progress was continuing to be made, and indicating the potential for considerations to be made to the current screening intervals. I made comments about showing the practical use of extending the screening intervals, and stated that I thought any changes would require good communication between all affected parties, viz. the Screening Service and G.P.’s, and, the G.P. and patient; supporting the reasons for making any changes to the current screening interval with accurate, precise results and providing examples to reinforce the justification.
In November 2014, I received a draft copy of the proposed HTA ‘Final’ Report, which asked for any comments I may wish to make, and I pointed out some minor errors within the text of the document.
I have read and understood the majority of the details contained in the Final Report (some of the statistical documentation, in chapter 5, I found confusing and did not fully understand) and accept the suggested recommendations to amend the intervals for diabetic eye screening. I would hope that monitoring of these changes, if applied, continues in the future and further safe, practical, outcomes are acted upon.
Mike Larkin’s contribution
Mike Larkin has met with the Lead Researcher regularly during the period of this research.
To date, my input has been reading and reviewing the drafts and providing a perspective on the work. I think my feedback covers two distinct areas:
Feedback on the report as a lay reader – here I have suggested a different plain English summary that attempts to take out the obvious and simplify the kernel of the research to help other non-researchers understand the project.
Patient view on the benefits of extending screening intervals. In a free to use system, patients don’t necessarily see benefit in less access. My comments are intended to acknowledge this and should be part of future discussion.
I think that overall the report moves a great way to better understanding suitable screening intervals – something that will be essential in the forthcoming years as we look to address the Type 2 epidemic.
Whilst there is acknowledgement that Type 1 patients are likely to receive closer monitoring (from the risk factor regarding length of condition) it’s dangerous to assume that both types of diabetes will affect the eyes the same. I feel that Type 1 as a condition is far more aggressive than Type 2 (for the same period of time). HbA1c levels are certainly good indicators for long term control, but are by their nature, averages. They don’t show if a person has had extreme highs over the 3 month period that the test is measuring. It’s for this reason that condition type should be differentiated in any recommendations on screening interval.
The reference to the lack of evidence around economic consequences of visual loss to the patient is important. It would be useful if this area could be considered in more depth. Before a person is able to officially register sight impairment, productivity and quality of life will, I believe, already have been significantly impacted. From a personal perspective, losing my sight to a point when I can no longer drive would have a substantial impact as mobility at home and work is restricted. Whilst, from a clinical sense, a person may have acceptable vision, the lack of personal mobility is economically and emotionally dramatic. The report sections centred on economics has focused entirely upon the costs to the NHS and not attributed any value to individual reduction of productivity.
Chapter 11 Conclusions
This project has demonstrated that:
-
Risk stratification can be used to identify low-risk groups. Risk estimation using either one SE plus clinical information or data from two sequential SEs in this quality-assured Gloucestershire programme are equally powerful for categorising risk. The risk model developed using results from one SE plus clinical information was then validated in three English screening programmes, two of which had a higher prevalence of people from ethnic minorities.
-
The model used in this study aimed to determine the risk of referable DR, which included the risk of developing maculopathy as well as the risk of development of pre-proliferative DR or PDR. The risk factors that were included in the model were duration of diabetes and HbA1c. Type of diabetes was not included because it could not be separated from duration of diabetes and HbA1c. Other risk factors that were considered but not included in the model because they did not have a significant impact were systolic and diastolic blood pressure, smoking status, sex, BMI, serum creatinine, total cholesterol, urine albumin and albumin : creatinine ratio.
-
Misclassification of a photograph to a more advanced stage (FP result) is more common than misclassification into a lower grade (FN result). The probability of misclassifying a photograph as a referable level from all lower grades is very small but this may be more reflective of the limitations of the method used.
-
A modelling approach to estimate misclassification rates is feasible using data from a screening programme but may be limited to progression up to, but no further than, referral.
-
The algorithms and approach developed in this project would be useful when deciding which of the local programmes should pilot and be early implementers of trialled risk-based extended screening intervals and which programmes need to look more closely at the grading of mild retinopathy before extension of screening intervals is considered. This should assist in reducing data variation between centres.
-
For all patients with diabetes and no presence of STDR, screening every 3 years was found to be the most cost-effective strategy using data from Gloucestershire.
-
Using a risk-based strategy, screening those at medium and high risk of developing STDR/maculopathy every 3 years and every 2 years, respectively, and those at low risk every 5 years, was the most cost-effective option using data from Gloucestershire.
-
The rate of detection of referable DR is elevated in those who were not screened promptly after diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
-
We have previously shown (outside this project) that there are patients with diabetes unknown to screening programmes and that some of these have referable DR. 52 This project has shown that GP2DRS or similar software to extract demographic and risk factor data from primary care is necessary.
-
We found different rates of progression to STDR between patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
-
We compared patients recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in the Gloucestershire screening programme with patients recruited to the UKPDS, a large, multicentre, randomised clinical trial in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients which reported in 1998. Fewer patients in this screening programme have DR and fewer have referable DR. Fewer are hyperglycaemic, more are hypertensive and they are heavier than newly diagnosed patients recruited to UKPDS.
-
Our study did have some difficulties because of the withdrawal of Coventry and Warwickshire and the fact that the ethnicity coding was incomplete in the other two screening programmes used to validate the data. Some GPs recorded no or very little ethnicity data. Because of this, there were not enough patients within each ethnic group to validate the models within the ethnic group. This is the reason for our recommendation that the models need to be validated in data from areas where ethnicity coding is accurate.
-
This study was undertaken before the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor Ranubizumab (Lucentis®, Novartis) and other novel agents were in widespread use. NICE approval for the use of Ranubizumab occurred in April 2013; treatment clinics were not set up in Gloucestershire until June 2013 and the cost-effectiveness data for treatment were collected between January 2013 and May 2014. These treatments were only just commencing towards the end of this period and if more maculopathy patients had received intravitreal VEGF inhibitor treatment, this would have had an impact on the results of the cost-effectiveness analysis.
In addition, the cost-effectiveness analysis was undertaken from data within the Gloucestershire DESP, which has a unique cohort of patients who are a stable population and who have had a long-standing screening programme and relatively well controlled HbA1c and blood pressure compared with some other parts of the UK; hence, the analysis does need to be confirmed in other areas.
Recommendations
This project recommends that:
-
software to identify patients with diabetes in primary care and to provide or extract promptly demographic and risk factor data to screening programmes is required
-
patient groups and stakeholders be consulted before any screening interval changes are introduced
-
all diabetic eye screening programmes record the date of diagnosis of diabetes and have access to recent HbA1c results, in addition to the result of grading from the previous SE. Ethnicity and type of diabetes should also be recorded
-
the risk stratification models should be validated in other eye screening programmes (inside and outside England) to identify risk groups
-
misclassification of photographic grading (i.e. grading error rates) needs to be evaluated in all local eye screening programmes
-
extended screening intervals should only be implemented by local programmes where grading misclassification rates have been evaluated and are shown to be acceptably low (once the threshold has been identified as outlined in Future work)
-
the knowledge arising from this project about progression and misgrading matrices are used to inform quality assurance processes in screening
-
data from patients with mild NPDR (R1M0) in just one eye are reported independently of patients with R1M0 in both eyes in DESP reports
-
the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of this model is tested in other populations.
Future work
This project has identified the following areas for future research:
-
investigate strategies to improve knowledge about risk of DR to the national programme, screening programmes, patients, HES, primary care and diabetes services. This would include investigating grading misclassification rates in local programmes and determining acceptable ranges
-
investigate strategies to increase uptake in those with a poor attendance record
-
determine whether extending the screening interval in patients in low-risk groups alters their behaviour over self-care of their diabetes or their attendance at subsequent screening events
-
investigate whether using the more granular information from feature-based grading (implemented in England from 2013) will enable better identification of those at risk of progression to STDR and improve the sensitivity and specificity of screening
-
data analysis and modelling to identify patients with diabetes who might safely be screened only once (‘screen once and forget’)
-
evaluate the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of this model in other populations outside Gloucestershire
-
evaluate the use of automated grading to reduce grading misclassifications and further improve the reliability of grading as a tool to provide personalised screening intervals.
Acknowledgements
Contributions of authors
Peter H Scanlon (Ophthalmologist and Clinical Lead, Gloucestershire) is the lead author for this publication and has written the first and subsequent drafts with input from other authors.
Stephen J Aldington (Research Manager, Gloucestershire Retinal Research Group) project-managed the data collection from the various sites, wrote project updates for submission and commented on various drafts of the publication.
Jose Leal (Senior Researcher, Health Economics Research Centre, University of Oxford) conducted the Markov modelling described in Chapter 8 and wrote Chapter 8 in conjunction with Ramon Luengo-Fernandez.
Ramon Luengo-Fernandez (Senior Researcher, Health Economics Research Centre, University of Oxford) conducted the health economic work and wrote Chapter 8 in conjunction with J Leal.
Jason Oke (Statistician, University of Oxford) conducted the statistical research using the Oxford Monitoring Interval Approach and wrote Chapter 7.
Sobha Sivaprasad (Ophthalmologist, King’s College London) commented on the drafts of the report.
Anastasios Gazis (Diabetologist and Clinical Lead, Nottingham) commented on the drafts of the report.
Irene M Stratton (Senior Statistician, Gloucestershire Retinal Research Group) conducted the statistical research involved in the Risk factor approach described in Chapter 5 and the Extension to an ethnically diverse population described in Chapter 6 and has contributed to various drafts of the report.
Acknowledgement to the Research Design Service
We have consulted the Research Design Service South West (Gloucester Office) at various stages of the application and conduct of this research and they have been extremely helpful.
Health economic support for the application has been provided by the Research Design Service South Central (Oxford Office).
Trial Steering Committee
We are particularly grateful to the members of the Independent Trial Steering Committee (Professor John Sparrow, Dr Catey Bunce, Miss Clare Bailey and Mike Whatmore) for their advice and guidance.
Acknowledgement to individuals who are not authors on this publication
We have very much appreciated the support of the following individuals:
-
Dr Richard Stevens and Professor Andrew Farmer from the Department of Primary Care, University of Oxford, contributed to the original application and gave advice during the conduct of the research but have not been able to contribute to the writing and editing of the report because of competing commitments.
-
Ms Clare Connor worked unceasingly to provide data from the South London Population from the Diabetic Eye Screening Programme based at St Thomas’ Hospital. Obtaining these data required a huge amount of effort from a very dedicated individual and our results in ethnic minority groups have been massively improved by her efforts. Clare also provided data for the health economic survey.
-
Mr Steve Chave for his efforts in obtaining the data set of risk factors in Gloucestershire when he managed the GP2DRS pilot in Gloucestershire and for organising the MIQUEST extractions from GP surgeries.
-
Mr Mike Olson for his support of the MIQUEST extractions in South London and Nottingham.
-
Mr Richard Cragg for his efforts in obtaining the data from the Nottingham Screening Programme.
-
Mr Andrew Tyrell, Data Warehouse Manager at Gloucestershire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, for providing the Hospital Episode Statistics records (including inpatient, outpatient and accident and emergency episodes for 12,790 patients identified through the GDESP).
-
Miss Sarah Cooper, Programme Manager in Nottingham, who provided data for the health economic survey.
-
Mr Malcolm Grey and Dr Andrew Brown, Programme Executive and Clinical Lead, respectively, for the Staffordshire Diabetic Eye Screening Programme, who provided data for the Health Economic Survey.
-
Mr Leon Gardner, Programme Manager for the Gloucestershire Diabetic Eye Screening Programme, who provided data for the Health Economic Survey.
-
Mrs Christel Jenkins and Mr Colin Jones, Eye Screening Programme Manager and Clinical Lead, respectively, for the Norfolk and Norwich Diabetic Eye Screening Programme, for the health economic survey.
-
Mr Phil Kirby and Mr Greg Russell from Health Intelligence for their generosity and efforts in providing the East Anglia data set for analysis in this study.
-
Mrs Kate Fenton, HTA Project Manager on behalf of the NIHR, for her constant support, guidance and encouragement.
Acknowledgement to lay members who have contributed to this research
We would like to thank Mr Mike Whatmore, who was involved in the original discussions on both reasons for non-attendance in DR screening and screening intervals for DR and who commented on the original application and the final report. Mike Whatmore has also served as a member of the Project Advisory Group and the independent Trial Steering Committee.
We would also like to thank another Gloucestershire lay member, Mr Mike Larkin, who read and commented on the application and on the final report.
We are grateful for the input into the original application from the Warwick Diabetes Research and Education User Group (WDREUG) and the Thames Valley Diabetes Local Research Network Patient and Lay Involvement Group.
Contributions to reports, posters, presentations and publications
The main output from this research will be data to inform decisions about the most appropriate DR screening intervals to be implemented across England.
Contribution to a Department of Health report to the UK National Screening Committee (November 2014)
We were contacted by the Health Improvement Analysis Team, Public Health Directorate, Department of Health, who are preparing a Health Economic Report that was being presented to the UK National Screening Committee on 28 November 2014 and we have provided data to inform an economic analysis of the diabetic eye screening programme, including estimating the impact of changes on the screening intervals based on risk levels for individuals. The report is expected to inform the UK NSC whether or not a policy change in screening intervals particularly for lower-risk groups and more frequent screening for higher-risk groups is cost-effective. Draft meeting minutes are available at http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20150525133544/http://screening.nhs.uk/meetings (accessed 26 November 2014).
Posters
Stratton IM, Adler AI, Aldington SJ, Histed M, Taylor D, Scanlon PH. A simple algorithm to estimate the time to development of sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy. American Diabetes Association Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, June 2012.
Stratton IM, Adler AI, Aldington SJ, Taylor D, Scanlon PH. A simple algorithm to estimate the time to development of sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy. Public Health Conference RSM, London, November 2012.
Stratton IM, Aldington SJ, Histed M, Scanlon PH. Twenty years on. More or Less Diabetic Retinopathy at Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes UK, Manchester, March 2013.
Aldington SJ, Stratton IM, Histed M, Scanlon PH. Relationship between time from diagnosis of diabetes to screening and grading outcome. European Association for the Study of Diabetic Eye Complications, Barcelona, May 2013.
Stratton IM, Aldington SJ, Histed M, Scanlon PJ. Retinopathy at diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes: more or less prevalent at older ages? European Association for the Study of Diabetes, Barcelona, September 2013.
Stratton IM, Aldington SJ, Farmer AJ, Scanlon PH. Personalised risk estimation for progression to sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy – how much does clinical information add to screening data? Lancet Public Health Meeting, London, November 2013.
Oke J, Stratton IM, Stevens R, Farmer A and Scanlon PH. Estimating the probability of grade misclassification using data from a national screening programme for diabetic retinopathy. Methods for Evaluating Medical Tests and Biomarkers Symposium, Birmingham, 2013.
Stratton IM, Sivaprasad S, Connor C, Aldington SJ, Scanlon PH. Do we need to consider ethnicity when estimating risk of progression to sight-threatening retinopathy? A retrospective cohort analysis of patients from an ethnically diverse diabetic eye screening programme with at least 3 screening episodes. Diabetes UK conference, Liverpool, March 2014.
Stratton IM, Aldington SJ, Farmer AJ, Scanlon PH. Personalised risk estimation for progression to sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy – how much does clinical information add to screening data? Diabetes UK conference, Liverpool, March 2014.
Aldington SJ, Stratton IM, Scanlon PH. Validation of a simple stratification algorithm for progression to sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy. European Association for the Study of Diabetes meeting, Vienna, September 2014.
Presentations
Scanlon PH. Research at the interface between screening and diabetic retinopathy management. Oxford Retinal Symposium, June 2013.
Scanlon PH. Screening of diabetic retinopathy: current concepts and future perspectives’. Presentation to two eye hospitals (Tan Tong Seng Hospital and Singapore Eye Research Institute), Singapore, March 2014.
Scanlon PH. Experience and outcome of the English Screening System. Euretina, September 2014.
Scanlon PH. The importance of early diagnosis and effective screening for diabetic retinopathy. Australian National Blindness Prevention Programme. Melbourne, October 2014
Scanlon PH. Screening and risk factors for progression of diabetic retinopathy. Australian National Blindness Prevention Programme. Melbourne, October 2014
Stratton IM. Risk models for progression to sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy – how do they perform? IDF, Melbourne, December 2013
Stratton IM. Precision or pragmatism? Fitting a risk model for progression to referable retinopathy in a cohort with missing data. European Association for the Study of Diabetes meeting, Vienna, September 2014.
Stratton IM, Aldington SJ, Cragg R, Gazis T, Russell G, Connor C, et al. Validation of a model to estimate risk of progression of diabetic retinopathy using screening and clinical data in 3 cohorts. European Association for the Study of Diabetes meeting, Vienna, September 2014.
Aldington SJ, Stratton IM, Connor C, Sivaprasad S, Fletcher E, Scanlon PH. Ethnicity and risk of progression to sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy in Type 2 diabetes – what’s the link? European Association for the Study of Diabetes meeting, Vienna, September 2014.
Publications
Scanlon PH, Aldington SJ, Stratton IM. Delay in diabetic retinopathy screening increases the rate of detection of referable diabetic retinopathy. Diabet Med 2014;31:439–42.
In addition to a closing HTA monograph, we anticipate publications in high-impact scientific and medical peer-reviewed journals on some or all of the following subjects:
-
Paper(s) on our risk score for retinopathy (from Phase 1) and its generalisation to other ethnic groups (from Phase 2)
-
Paper(s) on classification error and its implications for monitoring intervals (from Phase 3)
-
Paper(s) on the cost-effectiveness of assigning diabetic patients to differing diabetic retinopathy screening intervals (from Phases 4).
Data sharing statement
We are unable to share data owing to confidentiality restrictions.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Roberts S. Turning the Corner: Improving Diabetes Care. London: Department of Health; 2006.
- International Diabetes Federation . Diabetes Atlas 2006. www.idf.org/sites/default/files/Diabetes-Atlas-3rd-edition.pdf (accessed 7 July 2015).
- The Lancet . Type 2 diabetes epidemic: a global education. Lancet 2009;374. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61974-7.
- Vital Signs Monitoring 2011. London: Department of Health; 2011.
- Department of Health . Integrated Performance Measures Monitoring 2011 n.d. http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20130107105354/http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Statistics/Performancedataandstatistics/Integratedperfomancemeasuresmonitoring/DH_112536 (accessed 5 March 2012).
- Diabetes UK . Number of People Diagnosed With Diabetes Reaches Three Million n.d. www.diabetes.org.uk/About_us/News_Landing_Page/Number-of-people-diagnosed-with-diabetes-reaches-three-million/ (accessed 25 April 2014).
- Kocur I, Resnikoff S. Visual impairment and blindness in Europe and their prevention. Br J Ophthalmol 2002;86:716-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.86.7.716.
- Congdon N, Friedman DS, Lietman T. Important causes of visual impairment in the world today. JAMA 2003;290:2057-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.290.15.2057.
- Stefansson E, Bek T, Porta M, Larsen N, Kristinsson JK, Agardh E. Screening and prevention of diabetic blindness. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2000;78:374-85. http://dx.doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0420.2000.078004374.x.
- Liew G, Michaelides M, Bunce C. A comparison of the causes of blindness certifications in England and Wales in working age adults (16–64 years), 1999–2000 with 2009–2010. BMJ Open 2014;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004015.
- Wong TY, Mwamburi M, Klein R, Larsen M, Flynn H, Hernandez-Medina M, et al. Rates of progression in diabetic retinopathy during different time periods: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Care 2009;32:2307-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc09-0615.
- Klein R, Knudtson MD, Lee KE, Gangnon R, Klein BE. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: XXII the twenty-five-year progression of retinopathy in persons with type 1 diabetes. Ophthalmology 2008;115:1859-68. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.08.023.
- DRS . Photocoagulation treatment of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Clinical application of Diabetic Retinopathy Study (DRS) findings, DRS Report Number 8. The Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Ophthalmology 1981;88:583-600.
- ETDRS . Photocoagulation for diabetic macular edema. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study report number 1. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study research group. Arch Ophthalmol 1985;103:1796-806. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archopht.1985.01050120030015.
- Tu KL, Palimar P, Sen S, Mathew P, Khaleeli A. Comparison of optometry vs digital photography screening for diabetic retinopathy in a single district. Eye 2004;18:3-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6700497.
- Savolainen EA, Lee QP. Diabetic retinopathy - need and demand for photocoagulation and its cost-effectiveness: evaluation based on services in the United Kingdom. Diabetologia 1982;23:138-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01271176.
- Javitt JC, Aiello LP. Cost-effectiveness of detecting and treating diabetic retinopathy. Ann Intern Med 1996;124:164-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-124-1_Part_2-199601011-00017.
- Caro JJ, Ward AJ, O’Brien JA. Lifetime costs of complications resulting from type 2 diabetes in the U.S. Diabet Care 2002;25:476-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/diacare.25.3.476.
- Fendrick AM, Javitt JC, Chiang YP. Cost-effectiveness of the screening and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. What are the costs of underutilization?. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 1992;8:694-707. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0266462300002385.
- Nystrom L, Dahlquist G, Ostman J, Wall S, Arnqvist H, Blohme G, et al. Risk of developing insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) before 35 years of age: indications of climatological determinants for age at onset. Int J Epidemiol 1992;21:352-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ije/21.2.352.
- Management of Diabetes. A National Clinical Guideline. Edinburgh: Royal College of Physicians; 2010.
- Misra A, Bachmann MO, Greenwood RH, Jenkins C, Shaw A, Barakat O, et al. Trends in yield and effects of screening intervals during 17 years of a large UK community-based diabetic retinopathy screening programme. Diabet Med 2009;26:1040-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2009.02820.x.
- Kristinsson JK, Gudmundsson JR, Stefansson E, Jonasson F, Gislason I, Thorsson AV. Screening for diabetic retinopathy. Initiation and frequency. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 1995;73:525-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0420.1995.tb00329.x.
- Younis N, Broadbent DM, Harding SP, Vora JP. Incidence of sight-threatening retinopathy in Type 1 diabetes in a systematic screening programme. Diabet Med 2003;20:758-65. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.01035.x.
- Younis N, Broadbent DM, Vora JP, Harding SP. Incidence of sight-threatening retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes in the Liverpool Diabetic Eye Study: a cohort study. Lancet 2003;361:195-200. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12267-2.
- Olafsdottir E, Stefansson E. Biennial eye screening in patients with diabetes without retinopathy: 10-year experience. Br J Ophthalmol 2007;91:1599-601. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2007.123810.
- Vijan S, Hofer TP, Hayward RA. Cost-utility analysis of screening intervals for diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2000;283:889-96. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.283.7.889.
- Mehlsen J, Erlandsen M, Poulsen PL, Bek T. Individualized optimization of the screening interval for diabetic retinopathy: a new model. Acta Ophthalmol 2012;90:109-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-3768.2010.01882.x.
- Fong DS, Aiello LP, Ferris FL, Klein R. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabet Care 2004;27:2540-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.10.2540.
- Raymond NT, Varadhan L, Reynold DR, Bush K, Sankaranarayanan S, Bellary S, et al. Higher prevalence of retinopathy in diabetic patients of south Asian ethnicity compared to white Europeans in the community: a cross sectional study. Diabet Care 2009;32:410-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc08-1422.
- Sivaprasad S, Gupta B, Gulliford MC, Dodhia H, Mann S, Nagi D, et al. Ethnic variation in the prevalence of visual impairment in people attending diabetic retinopathy screening in the United Kingdom (DRIVE UK). PLOS ONE 2012;7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039608.
- Sivaprasad S, Gupta B, Gulliford MC, Dodhia H, Mohamed M, Nagi D, et al. Ethnic variations in the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in people with diabetes attending screening in the United Kingdom (DRIVE UK). PLOS ONE 2012;7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032182.
- Stratton IM, Provins E, Histed M, Chave S, Scanlon PH. Relationship of diabetic retinopathy levels with duration of diabetes and HbA1c in an English screening programme (poster 515 DUK Annual Conference). Diabet Med 2011;28.
- Milton RC, Ganley JP, Lynk RH. Variability in grading diabetic retinopathy from stereo fundus photographs: comparison of physician and lay readers. Br J Ophthalmol 1977;61:192-201. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.61.3.192.
- Glasziou P, Irwig L, Deeks JJ. When should a new test become the current reference standard?. Ann Intern Med 2008;149:816-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-149-11-200812020-00009.
- Keenan K, Hayen A, Neal BC, Irwig L. Long term monitoring in patients receiving treatment to lower blood pressure: analysis of data from placebo controlled randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2009;338. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b1492.
- Oke JL, Stevens RJ, Gaitskell K, Farmer AJ. Establishing an evidence base for frequency of monitoring glycated haemoglobin levels in patients with Type 2 diabetes: projections of effectiveness from a regression model. Diabet Med 2012;29:266-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03412.x.
- Farmer AJ, Stevens R, Hirst J, Lung T, Oke J, Clarke P, et al. Optimal strategies for identifying kidney disease in diabetes: properties of screening tests, progression of renal dysfunction and impact of treatment – systematic review and modelling of progression and cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess 2014;18. http://dx.doi.org/10.3310/hta18140.
- Stratton IM, Aldington SJ, Taylor DJ, Adler AI, Scanlon PH. A simple risk stratification for time to development of sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy. Diabet Care 2013;36:580-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc12-0625.
- Rein DB, Zhang P, Wirth KE, Lee PP, Hoerger TJ, McCall N, et al. The economic burden of major adult visual disorders in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol 2006;124:1754-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archopht.124.12.1754.
- Happich M, Reitberger U, Breitscheidel L, Ulbig M, Watkins J. The economic burden of diabetic retinopathy in Germany in 2002. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2008;246:151-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00417-007-0573-x.
- Baker M, Thornton P, Vernon A, Winyard A. The Costs of Blindness. Royal National Institute of Blind People Campaign Report. London: Royal National Institute for the Blind; 2000.
- Royal National Institute of Blind People and Diabetes UK . Don’t Turn a Blind Eye 2006. www.diabetes.org.uk/Documents/Reports/Dont_turn_a_blind_eye_0606.pdf.
- National Service Framework for Diabetes: Delivery Strategy. London: Department of Health; 2003.
- National Information Governance Board for Health and Social Care n.d. http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20130513181011/http://www.nigb.nhs.uk/.
- Jones S, Edwards RT. Diabetic retinopathy screening: a systematic review of the economic evidence. Diabet Med 2010;27:249-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2009.02870.x.
- Brailsford SC, Rauner MS, Gutjahr WJ, Zeppelzauer W. Combined discrete-event simulation and ant colony optimisation approach for selecting optimal screening policies for diabetic retinopathy. Comput Manage Sci 2007;4:59-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10287-006-0008-x.
- Davies R, Roderick P, Canning C, Brailsford S. The evaluation of screening policies for diabetic retinopathy using simulation. Diabet Med 2002;19:762-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00773.x.
- Updated guide to the methods of technology appraisal. London: NICE; 2008.
- ENSPDR . Excluding Patients from the NHS Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Temporarily or Permanently 2006.
- NICE . Open Athens Account 2014 n.d. www.evidence.nhs.uk/about-evidence-services/journals-and-databases (accessed 12 April 2014).
- Scanlon PH, Provins EK, Craske S, Chave SJ, Aldington SJ, Martin CN, et al. Updating diabetic retinopathy screening lists using automatic extraction from GP patient records. J Med Screen 2013;20:111-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0969141313505747.
- Scanlon PH, Stratton IM, Histed M, Chave SJ, Aldington SJ. The influence of background diabetic retinopathy in the second eye on rates of progression of diabetic retinopathy between 2005 and 2010. Acta Ophthalmol 2013;91:e335-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/aos.12074.
- Taylor-Phillips S, Mistry H, Leslie R, Todkill D, Tsertsvadze A, Connock M, et al. Extending the diabetic retinopathy screening interval beyond 1 year: systematic review [published online ahead of print 13 January 2015]. Br J Ophthalmol 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2014-305938.
- Scanlon PH, Loftus J, Starita C, Stratton IM. The use of weighted health-related Quality of Life scores in people with diabetic macular oedema at baseline in a randomized clinical trial. Diabet Med 2015;32:97-101. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dme.12593.
- Healy R, Sallam A, Jones V, Donachie PH, Scanlon PH, Stratton IM, et al. Agreement between photographic screening and hospital biomicroscopy grading of diabetic retinopathy and maculopathy. Eur J Ophthalmol 2014;24:550-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.5301/ejo.5000404.
- Sallam A, Scanlon PH, Stratton IM, Jones V, Martin CN, Brelen M, et al. Agreement and reasons for disagreement between photographic and hospital biomicroscopy grading of diabetic retinopathy. Diabet Med 2011;28:741-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03273.x.
- Arun CS, Ngugi N, Lovelock L, Taylor R. Effectiveness of screening in preventing blindness due to diabetic retinopathy. Diabet Med 2003;20:186-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.t01-1-00899.x.
- Aspelund T, Thornorisdottir O, Olafsdottir E, Gudmundsdottir A, Einarsdottir AB, Mehlsen J, et al. Individual risk assessment and information technology to optimise screening frequency for diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2011;54:2525-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2257-7.
- SAS . Analyzing Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves Using SAS 2007 n.d. www.sas.com/storefront/aux/en/spanlyrecop/60610_excerpt.pdf (accessed 29 October 2014).
- Pencina MJ, D’Agostino RB, D’Agostino RB, Vasan RS. Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: from area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Stat Med 2008;27:157-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.2929.
- Collins GS, de Groot JA, Dutton S, Omar O, Shanyinde M, Tajar A, et al. External validation of multivariable prediction models: a systematic review of methodological conduct and reporting. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014;14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-14-40.
- Marshall G, Jones RH. Multi-state models and diabetic retinopathy. Stat Med 1995;14:1975-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.4780141804.
- Chen AHH, Duffy SW, Tabar L. A Markov chain method to estimate the tumour progression rate from preclinical to clinical phase, sensitivity and positive predictive value for mammography in breast cancer screening. Statistician 1996;3:307-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/2988469.
- NICE . Type 2 Diabetes: National Clinical Guideline for Management in Primary and Secondary Care (Update): National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions (UK) 2008. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg66/resources/cg66-type-2-diabetes-full-guideline2 (accessed 28 October 2014).
- American Diabetes Association . American Diabetes Association: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2013. Diabet Care 2013;36:S11-66. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc13-S011.
- Australian Government: National Health and Medical Research Council . Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy 2008 n.d. www.nhmrc.gov.au/publications (accessed 28 October 2014).
- Canadian Diabetes Association . Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guideline Expert Committee. Can J Diabetes 2013;37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjd.2013.01.038.
- International Diabetes Federation . The Global IDF ISPAD Guideline for Diabetes in Childhood and Adolescence 2011 n.d. www.idf.org/global-idfispad-guideline-diabetes-childhood-and-adolescence (accessed 28 October 2014).
- Stratton IM, Kohner EM, Aldington SJ, Turner RC, Holman RR, Manley SE, et al. UKPDS 50: risk factors for incidence and progression of retinopathy in Type II diabetes over 6 years from diagnosis. Diabetologia 2001;44:156-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s001250051594.
- Jackson C. Multi-State Modelling With R: The Msm Package 2007 n.d. http://leg.ufpr.br/lib/exe/fetch.php/projetos:msc:msm-manual.pdf (accessed 28 October 2014).
- R CoreTeam . R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2012 n.d. www.r-project.org/ (accessed 28 October 2014).
- Shuster S. Malignant melanoma: how error amplification by screening creates spurious disease. Br J Dermatol 2009;161:977-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09399.x.
- Diggle PJ. Estimating prevalence using an imperfect test. Epidemiol Res Int n.d.:1-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2011/608719.
- Liu WJ, Lee LT, Yen MF, Tung TH, Williams R, Duffy SW, et al. Assessing progression and efficacy of treatment for diabetic retinopathy following the proliferative pathway to blindness: implication for diabetic retinopathy screening in Taiwan. Diabet Med 2003;20:727-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.01019.x.
- Kalm H, Egertsen R, Blohme G. Non-stereo fundus photography as a screening procedure for diabetic retinopathy among patients with type II diabetes. Compared with 60D enhanced slit-lamp examination. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1989;67:546-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-3768.1989.tb04106.x.
- Olson JA, Strachan FM, Hipwell JH, Goatman KA, McHardy KC, Forrester JV, et al. A comparative evaluation of digital imaging, retinal photography and optometrist examination in screening for diabetic retinopathy. Diabet Med 2003;20:528-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00969.x.
- Scanlon PH, Malhotra R, Greenwood RH, Aldington SJ, Foy C, Flatman M, et al. Comparison of two reference standards in validating two field mydriatic digital photography as a method of screening for diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2003;87:1258-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo.87.10.1258.
- Scanlon PH, Malhotra R, Thomas G, Foy C, Kirkpatrick JN, Lewis-Barned N, et al. The effectiveness of screening for diabetic retinopathy by digital imaging photography and technician ophthalmoscopy. Diabet Med 2003;20:467-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00954.x.
- Stellingwerf C, Hardus PL, Hooymans JM. Two-field photography can identify patients with vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy: a screening approach in the primary care setting. Diabetes Care 2001;24:2086-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/diacare.24.12.2086.
- van der Heijden AA, Walraven I, van’t Riet E, Aspelund T, Lund SH, Elders P, et al. Validation of a model to estimate personalised screening frequency to monitor diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2014;57:1332-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00125-014-3246-4.
- Sachdeva A, Stratton IM, Unwin J, Moreton R, Scanlon PH. Diabetic retinopathy screening: study to determine risk factors for non-attendance. Diabet Prim Care 2012;14:308-16.
- Dasbach EJ, Fryback DG, Newcomb PA, Klein R, Klein BE. Cost-effectiveness of strategies for detecting diabetic retinopathy. Med Care 1991;29:20-39. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00005650-199101000-00003.
- Bachmann M, Nelson SJ. Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy: A Quantitative Overview of the Evidence, Applied to the Populations of Health Authorities and Boards. Report. Bristol: Health Care Evaluation Unit, University of Bristol; 1996.
- James M, Turner DA, Broadbent DM, Vora J, Harding SP. Cost effectiveness analysis of screening for sight threatening diabetic eye disease. BMJ 2000;320:1627-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.320.7250.1627.
- Gillow JT, Gray JA. The National Screening Committee review of diabetic retinopathy screening. Eye 2001;15:1-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/eye.2001.1.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Diagnosis and Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Young People. London: NICE; 2004.
- Brailsford SC, Gutjahr WJ, Rauner MS, Zeppelzauer W. Combined discrete-event simulation and ant colony optimisation approach for selecting optimal screening policies for diabetic retinopathy. Computat Manag Sci 2007;4:59-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10287-006-0008-x.
- Royal National Institute of Blind People . Future Sight Loss UK: The Economic Impact of Partial Sight and Blindness in the UK Adult Population 2009 n.d. www.rnib.org.uk/sites/default/files/FSUK_Report.pdf (accessed 29 October 2014).
- Rein DB, Wittenborn JS, Zhang X, Allaire BA, Song MS, Klein R, et al. The cost-effectiveness of three screening alternatives for people with diabetes with no or early diabetic retinopathy. Health Serv Res 2011;46:1534-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6773.2011.01263.x.
- Virgili G, Parravano M, Menchini F, Brunetti M. Antiangiogenic therapy with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor modalities for diabetic macular oedema. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd007419.pub3.
- Curtis L. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2013. Canterbury: Personal Social Services Research Unit, University of Kent; 2013.
- Office for National Statistics . National Life Tables, England, 1980–82 to 2011–2013 2014. www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/lifetables/national-life-tables/2011-2013/rft-eng.xls (accessed 8 October 2014).
- Roglic G, Unwin N. Mortality attributable to diabetes: estimates for the year 2010. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2010;87:15-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2009.10.006.
- Hayes AJ, Leal J, Gray AM, Holman RR, Clarke PM. UKPDS outcomes model 2: a new version of a model to simulate lifetime health outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using data from the 30 year United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study: UKPDS 82. Diabetologia 2013;56:1925-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00125-013-2940-y.
- Poku E, Brazier J, Carlton J, Ferreira A. Health state utilities in patients with diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular oedema and age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review. BMC Ophthalmol 2013;13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2415-13-74.
- Lloyd A, Nafees B, Gavriel S, Rousculp MD, Boye KS, Ahmad A. Health utility values associated with diabetic retinopathy. Diabet Med 2008;25:618-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02430.x.
- Department of Health . NHS Reference Costs 2009–2010 2011. www.gov.uk/government/publications/nhs-reference-costs-2009-2010 (accessed 29 October 2014).
- Department of Health . National Tariff Payment System 2014 15 2013. www.gov.uk/government/publications/national-tariff-payment-system-2014-to-2015 (accessed 29 October 2014).
- Department of Health . NHS Reference Costs 2012 to 2013 2013. www.gov.uk/government/publications/nhs-reference-costs-2012-to-2013 (accessed 29 October 2014).
- Evans JR, Smeeth L, Fletcher AE. Risk of admission to a nursing home among older people with visual impairment in Great Britain. Arch Ophthalmol 2008;126:1428-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archopht.126.10.1428.
- Age UK. Later Life in the United Kingdom 2015. www.ageuk.org.uk/Documents/EN-GB/Factsheets/Later_Life_UK_factsheet.pdf?dtrk=true (accessed 20 March 2015).
- Briggs A, Sculpher M, Claxton K. Decision Modelling for Health Economic Evaluation. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2006.
- Fenwick E, Claxton K, Sculpher M. Representing uncertainty: the role of cost-effectiveness acceptability curves. Health Econ 2001;10:779-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hec.635.
- Siebert U, Alagoz O, Bayoumi AM, Jahn B, Owens DK, Cohen DJ, et al. State-transition modeling: a report of the ISPOR-SMDM Modeling Good Research Practices Task Force--3. Value Health 2012;15:812-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2012.06.014.
- Quan H, Li B, Couris CM, Fushimi K, Graham P, Hider P, et al. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am J Epidemiol 2011;173:676-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwq433.
- Scanlon PH, Aldington SJ, Stratton IM. Delay in diabetic retinopathy screening increases the rate of detection of referable diabetic retinopathy. Diabet Med 2014;31:439-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dme.12313.
Appendix 1 Patient Information Advisory Group approval of consent model
Patient Information Advisory Group approval of consent model
The National Screening Programme for Diabetic Retinopathy (‘NSC DR’) approached the Patient Information Advisory Group (PIAG) for advice on whether or not it was necessary to make a full application for Section 60 support. A decision was taken in December 2004 by PIAG and has been minuted as follows:
Diabetic retinopathy screening
The PIAG considered a request from the National Retinopathy Screening Programme for clarification about whether Section 60 support was required for the programme as information would need to be shared across several PCTs, hospital clinics and general practices. There had been reluctance on the part of some data controllers to release patient information to the screening programme because of confusion about this. The Advisory Group agreed that call and recall for retinopathy screening was part of the care pathway. As such, consent to sharing relevant data could be implied from information about how patient information is used by the retinopathy screening programme, being provided to patients, and by making it clear patients had the right to opt out. There was therefore no requirement to apply for Section 60 support.
The PIAG was also asked for their views on a consent model for the transfer of risk factor data within the GP2DRS project, a national project of electronic transfer of demographic and risk factor data between general practices and screening services in England.
The PIAG agreed that all patients should have the following letter sent to them prior to screening attendance, that there would be implied consent for risk factor data transfer if they attended for screening and did not inform the programme staff or general practice staff that they did not want risk factor data transferred.
The data used in this study will not identify individual patients. It will be pseudo-anonymised so that grading data can be matched with risk factor data and then the analysis will be anonymised to analytical staff.
Appendix 2 Health economic screening questionnaire
Appendix 3 Ethical Committee approval
Glossary
- 6/6 vision
- The ability to perceive correctly an object or letter of a designated size from a distance of 6 metres – classified as normal visual acuity. Called ‘20/20’ vision in the USA.
- Blindness (World Health Organization definition)
- Visual acuity that does not exceed 20/200 (6/60) in the better eye with correcting lens.
- Cotton wool spot
- Fluffy, white, opaque area caused by an accumulation of axoplasm in the nerve fibre layer of the retina.
- Diabetes mellitus
- The chronic condition in which there is an excess of glucose circulating in the blood stream.
- Diabetic retinopathy
- The microvascular complication of diabetes affecting the eye.
- Exudate (or hard exudate)
- Small white or yellowish-white deposit with sharp margins, located typically in the outer layers of the retina, but it may also be more superficial, particularly when retinal oedema is present.
- Focal (laser)
- Small treatment burn applied to defined localised areas of the retina to treat some eye conditions.
- Fovea
- A rod-free area at the centre of the retina, responsible for best central and colour vision.
- Haemorrhage
- A red spot or blot, with irregular margins and/or uneven density, particularly when surrounding a smaller central lesion considered to be a microaneurysm. Flame haemorrhages are superficial haemorrhages just under the nerve fibre layer and blot haemorrhages are deeper haemorrhages.
- Intraretinal microvascular abnormality
- Tortuous intraretinal vascular segments from dilated abnormal retinal capillaries.
- Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation (laser)
- Different types of laser are used in the imaging/diagnosis and treatment of many eye disorders. Low-powered laser instruments are used for ophthalmic imaging and diagnostic purposes, whereas higher-powered treatment lasers are used to apply retinal burns for focal, macular grid or pan-retinal photocoagulation retinal treatments.
- Logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution (logMAR)
- This is a modern method used for the measurement of visual acuity that has the same number of letters on each line, unlike the more common Snellen chart.
- Macula
- The area that surrounds the fovea, rich in neurosensory photoreceptor cones, responsible for central vision.
- Macular grid (laser)
- Small treatment burns applied in a grid pattern to the area around, but always avoiding, the fovea. Used to treat eye conditions, such as vascular leakage, affecting the macular region.
- Microaneurysm
- A red spot < 125 microns in diameter (approximately the width of a major vein at disc margin) and with sharp margins.
- New vessels at the disc
- New vessels at the optic disc or within 1-disc diameter of the optic disc margin.
- New vessels elsewhere
- New vessels greater than 1-disc diameter from the optic disc margin.
- Pan-retinal photocoagulation (laser)
- The type of scatter laser treatment that is given to patients with high-risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy, which usually involves 1200–2000 burns of 500-micron spot size to an oval area of retina defined by a line passing two disc diameters above, temporal to and below the centre of the macula and 500 microns from the nasal edge of the optic disc margin.
- Pupil
- The opening in the centre of the iris that appears as a black dot through which light enters the eye.
- Referable retinopathy
- The referable level in this study is when images in one or both eyes show the features of pre-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (R2) or proliferative diabetic retinopathy (R3) and/or maculopathy (M1) as defined by the grading form used in the English screening programme.
- Retina
- The innermost layer of the eye containing photoreceptor cells and fibres connecting with the brain through the optic nerve and nourished by a network of blood vessels.
- Severely sight impaired (blind; UK definition)
- Acuity below 3/60; acuity better than 3/60 but below 6/60 with a very restricted visual field.
- Sight impaired (partial sight; UK definition)
- From 3/60 to 6/60 with a full field; up to 6/24 with moderate restriction of visual field [e.g. glaucoma; 6/18 or better with a gross field defect (e.g. hemianopia) or a marked constriction of the field (e.g. retinitis pigmentosa)].
- Sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy (STDR)
- In this study, this is the same as the referable level, when images in one or both eyes show the features of pre-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (R2) or proliferative diabetic retinopathy (R3) and/or maculopathy (M1) as defined by the grading form used in the English screening programme.
- Slit lamp biomicroscopy
- Examination technique using a slit lamp biomicroscope to examine the anterior segment directly or posterior segment (retinal) detail through an indirect lens held between the slit lamp beam and the eye being examined.
- Type 1 diabetes
- Disease characterised by the absolute deficiency of insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes
- Disease characterised by the relative deficiency of insulin associated with insulin ‘resistance’.
- Venous loop
- An abrupt curving deviation of a vein from its normal path.
- Visual acuity
- Measurement of the ability of the eye to perceive the shape of objects in the direct line of vision and to distinguish detail; generally determined by finding the smallest symbol on an eye chart that can be recognised at a given distance.
List of abbreviations
- AUC
- area under the curve
- BMI
- body mass index
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CI
- confidence interval
- CRF
- clinical risk factor
- DESP
- Diabetic Eye Screening Programme
- DM
- diabetes mellitus
- DR
- diabetic retinopathy
- ETDRS
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study
- EVPI
- expected value of perfect information
- FN
- false negative
- FNR
- false-negative rate
- FP
- false positive
- FPR
- false-positive rate
- GP
- general practitioner
- GP2DRS
- General Practice to Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
- HbA1c
- glycated haemoglobin
- HES
- Hospital Eye Services
- HR
- hazard ratio
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IDF
- International Diabetes Federation
- IQR
- interquartile range
- IRMA
- intraretinal microvascular abnormality
- logMAR
- logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution
- MIQUEST
- Morbidity Information Query and Export Syntax
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NPDR
- non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- NRI
- net reclassification improvement
- PCT
- primary care trust
- PDR
- proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- PY
- person-year
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- ROC
- receiver operating characteristic
- SE
- screening episode
- SIGN
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
- STDR
- sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy
- UKPDS
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study