Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was commissioned and funded by the HTA programme on behalf of NICE as project number 14/18/01. The protocol was agreed in July 2014. The assessment report began editorial review in January 2015 and was accepted for publication in April 2015. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
none
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2015. This work was produced by Westwood et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Objectives
The overall objectives of this project are to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of adding procalcitonin (PCT) testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy in the following two populations:
-
adults and children with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in intensive care settings
-
adults or children presenting to the emergency department (ED) with suspected bacterial infection.
For each of these populations we defined the following research questions:
-
For adults and children with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis who are being treated in intensive care unit (ICU) settings, how does initiation of antibiotic therapy differ when PCT test results are added to the information available to treating clinicians?
-
How does duration of antibiotic therapy and length of hospital/ICU stay differ when PCT test results are added to the information available to treating clinicians?
-
How do clinical outcomes [e.g. septic shock, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores, in-hospital mortality] differ when PCT test results are added to the information available to treating clinicians?
-
Does the addition of PCT testing to current clinical practice, to determine whether or not to initiate and when to discontinue antibiotic therapy, represent a cost-effective use of UK NHS resources?
Chapter 2 Background and definition of the decision problem(s)
Population
This assessment is concerned with the value of PCT in managing antibiotic therapy in two distinct populations: adults and children with known or highly suspected sepsis, who are being treated in ICUs, and adults and children who present to the ED with suspected bacterial infection.
For the ICU setting, the assessment focuses primarily on people with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis; this is because sepsis is a common and serious problem amongst patients being treated in ICUs. 1 Sepsis is defined as probable or documented infection together with systemic manifestations of infection [sometimes described as systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)], severe sepsis is defined as sepsis plus sepsis-induced organ dysfunction, and septic shock is defined as severe sepsis with hypotension which is not reversed by fluid resuscitation. 2,3 Bacteria are the most common cause of sepsis; however, systemic viral and fungal infections can also occur. SIRS can also occur as a result of non-infectious challenge to the immune system and it is important for clinicians to be able to rapidly distinguish between infectious and non-infectious causes, as well as between different agents of infection, in order to guide appropriate therapy.
The most recent UK Hospital Episode Statistics (HES: 2012–13) recorded 69,036 finished consultant episodes related to sepsis. 4 In addition, a recently published analysis of the 2001–10 Office for National Statistics (ONS) mortality data found that, during this period, 4.7% of all deaths recorded in England were ‘definitely directly associated with sepsis’. 5 Ninety-nine per cent of deaths definitely associated with sepsis had at least one of the ICD-10 codes – A40 (sepsis due to pneumonia), A41 (other sepsis) or P36 (sepsis of newborn due to streptococcus group B) – on the death certificate; however, only 8.6% of deaths definitely associated with sepsis in 2010 had a sepsis-related condition as the underlying cause of death. 5 Only 7.0% of deaths definitely associated with sepsis did not occur in hospital. 5 Incidence of sepsis is particularly high in patients who are admitted to ICUs. A large retrospective analysis of 56,673 admissions of adult patients to ICUs in England Wales and Northern Ireland, between 1995 and 2000, found that 27.1% met the criteria for severe sepsis with the first 24 hours of admission. 1 Thirty-five per cent of these patients died before discharge from the ICU and 47% died in hospital. 1 Patients with severe sepsis accounted for 45% of intensive care bed-days and 33% of hospital bed-days used by all ICU admissions. 1 These data indicate that sepsis is a substantial health-care problem with a high mortality rate, representing a major clinical challenge and associated with high resource use. Improving the management of sepsis, in particular in ICU settings, is therefore an important health-care goal.
For the ED setting, the assessment considers a broader population, which includes people presenting with any suspected bacterial infection. This is because discussions at scoping suggested that inclusion of a broader population would be more clinically appropriate in this setting, and that presentation to the ED with symptoms consistent with sepsis would be relatively uncommon. The most recent UK HES (2012–13) recorded a first ED diagnosis of ‘infectious disease’ in 141,308 out of a total of 18.3 million ED presentations; ‘septicaemia’ was recorded as the first ED diagnosis for 24,850 presentations. 6 The most common type of suspected bacterial infection to present to the ED is respiratory tract infection. 7 A study of common medical presenting problems in the children’s ED department found that the two most common presenting problems were breathing difficulty (31%) and febrile illness (20%). 8 Lower respiratory tract infection [LRTI: acute bronchitis, acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma and pneumonia] is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in children and adults. Pneumonia is the main cause of childhood mortality worldwide and accounts for 9% of deaths in children aged < 5 years in Europe. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is diagnosed in 5–12% of adults presenting to the GP with LRTI, of whom 22–42% are admitted to hospital. Mortality in hospital is between 5% and 14%. 9 Many cases of pneumonia are caused by viruses and have a mild course, and so antibiotic treatment is inappropriate; a bacterial cause of pneumonia has been shown in 33–70% of cases. However, most children with pneumonia are treated with antibiotics without the causative agent being known. 10 LRTIs account for almost 10% of worldwide morbidity and mortality, and as much as 75% of all antibiotic prescriptions are for respiratory tract infections. 11 Rapid and accurate determination of the presence or absence of bacterial infection is important to guide appropriate therapy and to reduce unnecessary exposure to antibiotics. Reduction of antibiotic exposure is increasingly a priority for the NHS, in the context of efforts to conserve the effectiveness of existing drugs. The Department of Health has set out actions to slow the development and spread of antimicrobial resistance in the UK Five Year Antimicrobial Resistance Strategy 2013 to 2018. 12 One of the aims of the strategy is to conserve and steward the effectiveness of existing antimicrobials by ensuring that antibiotics are used responsibly and less often. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) public health guidance (PHG89) ‘Antimicrobial stewardship – changing risk-related behaviours‘ is currently under development. 13
Intervention technologies and comparator
Procalcitonin is a 116-amino-acid precursor to calcitonin. In normal metabolism, calcitonin is produced solely by the C cells of the thyroid medulla and neuroendocrine cells in the lungs. Normal serum or plasma levels of PCT in healthy adults are ≤ 0.05 ng/ml. 14 PCT can also be produced by a variety of cell types in response to inflammatory stimuli (including systemic infection) and can be very high (> 10 ng/ml) in sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock. 14 PCT modulates the immune response through induction of cytokine production and by affecting the migration of monocytes and parenchymal cells to the site of inflammation. A summary of the characteristics and clinical applications of PCT, produced by the Association for Clinical Biochemistry (ACB), lists the clinical uses of PCT measurement as follows, whilst cautioning that PCT can also be raised following surgery, trauma or severe burns, or, in cases of severe pancreatitis, severe liver damage, severe multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), and severe fungal or viral infections. 14 The ACB document also notes that particular care is needed when interpreting PCT levels in neonates, as PCT levels can exceed 10 ng/ml in neonates in the absence of infection:14
-
diagnosis of bacterial infections of the lower respiratory tract and sepsis
-
monitoring progression of sepsis and response to antibiotic treatment
-
informing initiation, change or discontinuation of antibiotic therapy for sepsis.
All methods for the quantification of PCT are based on immunoassay and there are currently a number of CE-marked automated assays available in the UK.
Thermo Fisher Scientific BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay
The BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), sometimes also referred to as the BRAHMS PCT Kryptor assay, is an automated immunofluorescent sandwich assay for the determination of PCT in human serum and plasma. It is indicated for use with the BRAHMS Kryptor, BRAHMS Kryptor compact and BRAHMS Kryptor compact PLUS analysers (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The assay has a measurement range of 0.02–5000 ng/ml, a functional assay sensitivity of 0.06 ng/ml, and an analytical sensitivity of 0.019 ng/ml. The time to result is 19 minutes. 15,16
A number of other companies have licensed the use of PCT and its antibodies from Thermo Fisher Scientific. The main difference between these assays is the mechanism of detection of the antibody–PCT–antibody complexes.
All of the commercial assays have been standardised using the BRAHMS PCT luminescence immunoassay (LIA) (the original manual PCT assay). This assay was designed to be used in conjunction with a luminometer, and results are calculated based on relative light units. The assay has a measurement range of 0.1–500 ng/ml, an analytical sensitivity of approximately 0.1 ng/ml, and a functional sensitivity of 0.3 ng/ml. The BRAHMS PCT LIA is not included in this assessment, as it is no longer in widespread use in the UK. A more sensitive version of the assay (BRAHMS PCT Ultrasensitive Kryptor, Thermo Fisher Scientific) is currently used for research purposes, not for sales. This version of the assay has a lower functional assay sensitivity than the BRAHMS Sensitive Kryptor assay, allowing measurement of very low PCT quantities in healthy individuals. The BRAHMS PCT Ultrasensitive Kryptor assay is also not included in this assessment, as it is not currently being marketed.
Roche Elecsys BRAHMS PCT
The Elecsys BRAHMS PCT assay (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) is an electrochemiluminescent immunoassay for the determination of PCT in human serum and plasma. The assay is indicated for use on the Elecsys, Modular and Cobas e analysers. It has a measurement range of 0.02–100 ng/ml, a functional sensitivity of 0.06 ng/ml and an analytical sensitivity of < 0.02 ng/ml. The time to result is 18 minutes. 16,17
Siemens ADVIA Centaur BRAHMS PCT
The ADVIA Centaur BRAHMS PCT assay (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Ltd, Camberley, UK) is a chemiluminescent assay for the determination of PCT in human serum and plasma. The assay is indicated for use with the ADVIA Centaur/XP and ADVIA Centaur CP analysers. It has a measurement range of 0.02–75.00 ng/ml, a functional sensitivity of < 0.05 ng/ml and an analytical sensitivity of < 0.02 ng/ml. The time to result is 26–29 minutes, depending on which analyser is used. 16
bioMérieux VIDAS BRAHMS PCT
The VIDAS BRAHMS PCT (bioMérieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France) is an enzyme-linked fluorescent assay for the determination of PCT in human serum and plasma. It is indicated for use with the VIDAS and miniVIDAS analysers. It has a measurement range of 0.05–200 ng/ml, a functional detection limit of 0.09 ng/ml and an analytical detection limit of 0.05 ng/ml. The time to result is 20 minutes. 18
DiaSorin LIAISON BRAHMS PCT
The LIAISON BRAHMS PCT assay (DiaSorin S.p.A., Saluggia, Italy) is a sandwich chemiluminescent immunoassay for the determination of PCT in human serum and plasma. The assay is indicated for use with the LIAISON analyser. It has a measurement range of 0.1–500 ng/ml, a functional sensitivity of < 0.24 ng/ml and an analytical sensitivity of < 0.032 ng/ml. This assay is not currently marketed in the NHS. However, it will be included in the assessment so that, should the marketing situation change, any relevant data will have been evaluated. 19
The ACB document states that PCT is not recommended as a routine screening test for infection, for example as part of an ED admission profile,14 i.e. it is not useful to rule out infection when there is a low pre-test probability. This proposition is supported by data from a randomised controlled trial (RCT), conducted in children (aged 1–36 months), presenting to the ED with fever of unknown origin, which compared diagnosis based on standard investigations, as directed by the attending physician, with and without information on the results of PCT testing. 20 This study found no difference in the overall rates of antibiotic use or hospitalisation between the groups. 20 When only patients without bacterial infection or neutropenia identified by other ED investigations [urinary tract infection (UTI), pneumonia, bacterial meningitis and neutropenia < 500 × 106/l excluded] were considered, there were still no differences between groups in either rate of antibiotic use or rate of hospitalisation; the researchers calculated that if all patients in this group with a PCT indicative of moderate risk of infection had been treated with antibiotics, the rate of antibiotic use would have increased by 24%. 20 An alternative diagnostic application would be in differentiating patients with sepsis from those who have SIRS without infection, i.e. diagnosing sepsis when there is a high pre-test probability. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis of 30 studies assessing PCT for the diagnosis of sepsis in critically ill patients reported summary estimates of sensitivity and specificity of 77% (95% CI 72% to 81%) and 79% (95% CI 74% to 84%). 21 The reference standard for determination of sepsis was defined as microbiological confirmation, or one or more of the following: white blood cells in a normally sterile body fluid; perforated viscus; radiographic evidence of pneumonia and production of purulent sputum; and syndrome associated with high risk of infection. 21 This level of sensitivity does not suggest that a negative PCT test results alone would be adequate to rule out bacterial infection in high-risk population; the study authors concluded that although ‘procalcitonin is a helpful biomarker for early diagnosis of sepsis in critically ill patients, the results of the test must be interpreted carefully in the context of medical history, physical examination, and microbiological assessment’. 21 This is in line with the ACB document, which states that ‘PCT results should be used to assist and guide clinicians towards a diagnosis or treatment strategy, but they should not be used to replace clinical judgement; treatment should not be withheld on the basis of PCT test results’. 14
In order to provide information on the effectiveness of PCT testing, when used in an appropriate context alongside other clinical information, this assessment summarises data from clinical trials comparing the management of patients with probable or confirmed sepsis (ICU setting) or infection (ED setting), based on standard practice plus PCT testing to management based on standard practice alone. Thus, the comparator for this assessment was antimicrobial management based on standard clinical practice, without PCT testing. Any multicomponent (i.e. not solely based on the results of a single biochemical or microbiological test) definition of standard clinical practice reported by the identified studies was considered relevant for inclusion.
Care pathway
Sepsis
Diagnosis and monitoring
There is currently no NICE clinical guideline covering the diagnosis and management of sepsis in general; NICE clinical guideline CG151 addresses the specific issue of prevention and management of neutropenic sepsis in cancer patients;22 neutropenic sepsis is outside the scope of this assessment. A new NICE guideline, ‘Sepsis: The recognition, diagnosis and management of severe sepsis’, is currently under development and publication is expected in July 2016. 23 There is also an ongoing study by the National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death (NCEPOD), commissioned by the Health Quality Improvement Partnership (HQIP), which aims to ‘identify and explore avoidable and remediable factors in the process of care for patients with known or suspected sepsis’. 24 This study will examine organisational issues, systems and processes, recognition or early signs of sepsis, appropriate management of established severe infection, communication with families and carers, and use of the ‘acute’ end-of-life pathway and ceilings of treatment; publication is expected in November 2015.
Comprehensive guidance on the diagnosis and management of sepsis is provided by the Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC), a joint collaboration of the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). 2 This guideline was last updated in 2012 and is currently undergoing revision. The guideline was developed following the principles of the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) system: the quality of evidence was rated as high (A) to very low (D), and recommendations were classified as strong (1) or weak (2). 25
The SSC guideline specifies the presence of some the following criteria, alongside the presence of proven or suspected infection, for the diagnosis of sepsis:2,3
-
Clinical criteria Fever or hypothermia, elevated heart, tachypnoea, altered mental status, significant oedema or positive fluid balance, hyperglycaemia in the absence of diabetes.
-
Inflammatory markers Abnormal white blood cell count, elevated plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) or PCT levels.
-
Haemodynamic status Arterial hypotension, or decrease in systolic blood pressure of > 40 mmHg in adults or < 2 SDs (standard deviations) below the age-specific normal range.
-
Organ dysfunction signs Arterial hypoxaemia, acute oliguria or elevated creatinine level, coagulation abnormalities, ileus (absent bowel sounds), thrombocytopenia, hyperbilirubinemia.
-
Tissue perfusion status Hyperlactatemia, decreased capillary refill or mottling.
Definitions of sepsis in children are similar to adult definitions but depend on age-specific heart rate, respiratory rate and white blood cell count cut-off values. Special considerations for managing sepsis in paediatric patients are described in the SSC guidelines. 2
The SSC guidelines include the specific recommendation (GRADE 1C – strong recommendation, low or very low quality evidence) that blood (and urine, cerebrospinal fluid, wounds, respiratory secretions, or other body fluids, as appropriate) cultures should be taken before initiating antimicrobial therapy, provided that this does not significantly delay (> 45 minutes) the start of antimicrobial therapy. 2 It should be noted that, although the guideline includes elevated PCT level in the list of criteria indicative of sepsis (see above), no specific recommendation is made for its use in the diagnosis of sepsis.
Treatment
The SSC guidelines provide the following recommendations on antimicrobial therapy:2
-
‘The administration of effective intravenous antimicrobials within the first hour of recognition of septic shock (GRADE 1B – strong recommendation, moderate quality evidence) and severe sepsis without septic shock (GRADE 1C – strong recommendation, low or very low quality evidence) should be a goal of therapy.’
-
‘Initial empiric anti-infective therapy should include one or more drugs that have activity against all likely pathogens (bacterial and/or fungal or viral) and that penetrate in adequate concentrations into the tissues presumed to be the source of sepsis.’ (GRADE 1B – strong recommendation, moderate quality evidence).
-
‘Combination empirical therapy for neutropenic patients with severe sepsis’ (GRADE 2B – weak recommendation, moderate quality evidence) ‘and for patients with difficult-to-treat, multidrug resistant bacterial pathogens such as Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas spp.’ (GRADE 2B – weak recommendation, moderate quality evidence). ‘For patients with severe infections associated with respiratory failure and septic shock, combination therapy with an extended spectrum beta-lactam and either an aminoglycoside or a fluoroquinolone is for P. aeruginosa bacteraemia’ (GRADE 2B – weak recommendation, moderate quality evidence). ‘A combination of beta-lactam and macrolide for patients with septic shock from bacteraemic Streptococcus pneumoniae infections’ (GRADE 2B – weak recommendation, moderate quality evidence).
-
‘Empiric combination therapy should not be administered for > 3–5 days. De-escalation to the most appropriate single therapy should be performed as soon as the susceptibility profile is known’ (GRADE 2B – weak recommendation, moderate quality evidence).
-
‘Duration of therapy typically 7–10 days; longer courses may be appropriate in patients who have a slow clinical response, undrainable foci of infection, bacteraemia with S. aureus; some fungal and viral infections or immunologic deficiencies, including neutropenia’ (GRADE 2B – weak recommendation, low or very low quality evidence).
-
‘Antiviral therapy initiated as early as possible in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock of viral origin’ (GRADE 2B – weak recommendation, low or very low quality evidence).
-
‘Antimicrobial agents should not be used in patients with severe inflammatory states determined to be of non-infectious cause’ (ungraded recommendation).
The SSC guidelines also include a recommendation (GRADE 2C – weak recommendation, low or very low quality evidence) for the use of PCT or similar biomarkers to aid the clinician in discontinuation of empiric antibiotics, when there is no subsequent evidence of infection. 2
Suspected bacterial infection in the emergency department
Diagnosis and monitoring
The NICE guideline on the diagnosis and management of community- and hospital-acquired pneumonia in adults9 includes elements that are relevant to the work-up of suspected bacterial infection in the ED.
These guidelines recommend the following:
-
Assess people with a clinical diagnosis of CAP at presentation to hospital to determine whether they are at low, intermediate or high risk of death using their CURB65 score26
-
Put in place processes to allow diagnosis and treatment of CAP within 4 hours of presentation to hospital.
The NICE clinical guideline CG160, on the assessment and management of feverish illness in children aged < 5 years,27 included a research recommendation for a UK study on the performance characteristics and cost-effectiveness of PCT versus CRP in identifying serious bacterial infection in children with fever of unknown origin. However, it should be noted that, although the guideline included a systematic review of studies assessing the diagnostic accuracy of these biomarkers, this review did not appear to have considered RCTs comparing the effectiveness of diagnostic strategies with and without PCT testing. Although the guideline cites later studies by the same authors, it does not include the RCT described above (p. 4, Index test section). 20
Treatment
The NICE guideline on pneumonia9 makes the following recommendations regarding antibiotic treatment:
-
Offer antibiotic therapy as soon as possible after diagnosis, and certainly within 4 hours, to all patients with CAP admitted to hospital.
Low-severity community-acquired pneumonia:
-
Offer a 5-day course of a single antibiotic to patients with low-severity CAP.
-
Consider amoxicillin in preference to a macrolide or tetracycline for patients with low-severity CAP; consider a macrolide or tetracycline for patients who are allergic to penicillin.
-
Consider extending the course of the antibiotic for > 5 days as a possible management strategy for patients with low-severity CAP, whose symptoms do not improve as expected after 3 days.
-
Explain to patients with low-severity CAP who are treated in the community, and, when appropriate, their families or carers, that they should seek further medical advice if their symptoms do not begin to improve within 3 days of starting the antibiotic, or earlier if their symptoms are worsening.
-
Do not routinely offer patients with low-severity CAP:
-
a fluoroquinolone
-
dual antibiotic therapy.
-
Moderate- and high-severity CAP:
-
Consider dual antibiotic therapy with amoxicillin and a macrolide (such as clarithromycin) for patients with moderate-severity CAP.
-
Consider dual antibiotic therapy with a beta-lactamase stable beta-lactam (such as co-amoxiclav) and a macrolide (such as clarithromycin) for patients with high-severity CAP.
-
Consider a 7- to 10-day course of antibiotic therapy for patients with moderate- or high-severity CAP.
Monitoring:
-
Consider measuring a baseline CRP concentration in patients with CAP on admission to hospital, and repeat the test if clinical progress is uncertain after 48–72 hours.
The guideline also includes the following research recommendation:
-
In patients hospitalised with moderate- to high-severity CAP, does using CRP monitoring in addition to clinical observation to guide antibiotic duration safely reduce the total duration of antibiotic therapy compared with a fixed empirical antibiotic course?
This assessment summarises the evidence on the use of PCT testing to determine whether or not to initiate antibiotics, and to guide the duration of therapy in patients who have been appropriately treated with antibiotics.
Note
This report contains reference to confidential information provided as part of the NICE appraisal process. This information has been removed from the report and the results, discussions and conclusions of the report do not include the confidential information. These sections are clearly marked in the report.
Chapter 3 Assessment of clinical effectiveness
A systematic review was conducted to summarise the evidence on the clinical effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy for the treatment of confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in ICU settings and the clinical effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy in people presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infection. Systematic review methods followed the principles outlined in the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) guidance for undertaking reviews in health care28 and the NICE Diagnostic Assessment Programme Manual. 29
Systematic review methods
Search strategy
Development of search strategies followed the recommendations of the CRD guidance for undertaking reviews in health care28 and the Cochrane Handbook for DTA Reviews. 30 Strategies were based on PCT assays and target conditions (sepsis or bacterial infection); initial searches included a sensitive filter for RCTs. 31 Because initial searches identified no RCTs for the paediatric intensive care unit (PICU) population and only one RCT for the paediatric ED population, searches were re-run without a study design filter and limited to the paediatric population.
Candidate search terms were identified from target references, browsing database thesauri [e.g. MEDLINE, MeSH (medical subject heading) and EMBASE Emtree], existing reviews identified during the rapid appraisal process and initial scoping searches. These scoping searches were used to generate test sets of target references, which informed text mining analysis of high-frequency subject indexing terms using EndNote reference management software version X6 (Thomson Reuters, CA, USA). Strategy development involved an iterative approach, testing candidate text and indexing terms across a sample of bibliographic databases, aiming to reach a satisfactory balance of sensitivity and specificity. Search dates were determined in consultation with clinical specialist members of the Assessment Subgroup.
No restrictions on language or publication status were applied. Date restrictions were determined in consultation with clinical specialist members of the Assessment Subgroup, based on expert advice on the earliest appearance of literature of PCT diagnostic testing. Searches took into account the generic and other product names for the intervention. The main EMBASE strategy for each set of searches was independently peer reviewed by a second information specialist, using the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH) Peer Review Checklist. 32 Search strategies were developed specifically for each database and keywords were adapted according to the configuration of each database.
Full search strategies are reported in Appendix 1.
Rapid appraisal searches
To assess the scope and scale of the literature, and to identify candidate search terms, a rapid appraisal of the literature was conducted.
The following databases were searched for relevant studies from database inception date to June 2014:
-
The Cochrane Library:
-
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR): up to Issue 4 of 12, April 2014
-
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE): up to Issue 1 of 4, January 2014
-
Health Technology Assessment (HTA) database: up to Issue 1 of 4, January 2014
-
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED): up to Issue 1 of 4, January 2014.
-
-
PROSPERO (internet): up to 9.4.14 (www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/).
-
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Guidance (internet): up to 8 April 2014 (www.nice.org.uk/).
-
National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA) programme (internet): up to 8 April 2014 (www.hta.ac.uk/).
-
US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (internet): up to 8 April 2014 (www.fda.gov/).
-
Guidelines International Network (G-I-N) (internet): up to 9 April 2014 (www.g-i-n.net/).
-
National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGCH) (internet): up to 9 April 2014 (www.guideline.gov/index.aspx).
-
Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) (internet): up to 9 April 2014 (www.mhra.gov.uk/index.htm).
-
The Medion database up to 2014/5/4 (internet): up to 9 April 2014 (www.mediondatabase.nl/).
Randomised controlled trial searches
The following databases were searched for relevant studies from 1995 to June 2014:
-
EMBASE (OvidSP): 1995 – 27 June 2014.
-
MEDLINE (OvidSP): 1995 – June Week 3 2014.
-
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily Update (OvidSP): 1995 – 27 June 2014.
-
PubMed (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed): 1995 – 14 July 2014.
-
CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature) (EBSCOhost): 1995 – 25 June 2014.
-
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (Wiley): 1995 – Issue 5 of 12, May 2014.
-
Science Citation Index (SCI) (Web of Science): 1995 – 27 June 2014.
-
Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (LILACS) (internet): 1995 – 1 July 2014 (http://regional.bvsalud.org/php/index.php?lang = en).
-
NIHR Health Technology Assessment Programme (internet): up to 1 July 2014 (www.nets.nihr.ac.uk/programmes/hta).
Completed and ongoing trials were identified by searches of the following resources (1995-present):
-
National Institutes of Health ClinicalTrials.gov: up to 14 July 2014 (www.clinicaltrials.gov/).
-
Current Controlled Trials (CCT): up to 14 July 2014 (www.controlled-trials.com/).
-
World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP): up to 14 July 2014 (www.who.int/ictrp/en/).
Paediatric population searches
The following databases were searched for relevant studies from 1995 to August/September 2014:
-
EMBASE (OvidSP): 1995 – 29 August 2014.
-
MEDLINE (OvidSP): 1995 – August Week 3 2014.
-
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily Update (OvidSP): 1995 – 29 August 2014.
-
PubMed (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed): 1995 – 2 September 2014.
-
CINAHL (EBSCOhost): 1995 – 27 August 2014.
-
SCI (Web of Science): 1995 – 29 August 2014.
-
LILACS (internet) (http://regional.bvsalud.org/php/index.php?lang = en): 1995 – 2 September 2014.
Electronic searches were undertaken for abstracts and poster presentations of studies of PCT from the following conferences:
-
Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health (RCPCH) meetings: 2009–14 (www.escmid.org/research_projects/eccmid/past_eccmids/).
-
European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID): 2009–14 (www.escmid.org/research_projects/eccmid/past_eccmids/.
-
International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine: 2009–14 (http://ccforum.com/supplements/).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Population
-
Adults and children with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis, in whom antibiotic therapy is indicated, who are being treated in ICUs.
-
Adults and children presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infection.
Studies of neonates or immunosuppressed neutropenic patients on chemotherapy, immunosuppressant drugs or transplant programmes were excluded.
Intervention/index test
Treatment decisions based on laboratory-based PCT testing, using any of the tests currently available to the NHS as described in Chapter 2 (see Intervention technologies and comparator), in addition to standard practice (as reported in individual studies).
Point-of-care tests, which do not provide a quantitative estimate of PCT levels, were excluded.
Comparator
Treatment decisions based on standard practice (as reported in individual studies), without PCT testing.
Outcomes
Antibiotic exposure (initiation/duration of antibiotic therapy), resource use (number of hospital admissions, length of hospital/ICU stay, costs), adverse clinical outcomes (e.g. SOFA scores, in-hospital mortality, condition-specific outcomes), antibiotic-related adverse events.
Study design
Randomised controlled trials, or controlled clinical trials (CCTs) when no RCTs were available. Where no controlled trials (RCTs or CCTs) were available for a specified population, studies assessing the change in diagnostic accuracy associated with the addition of PCT testing to standard diagnostic work-up were sought. On the advice of clinical specialist members of the Assessment Subgroup, such studies were required to use adjudication of infection by independent panel as the reference standard; microbiological testing alone was not considered adequate. Studies that assessed the diagnostic accuracy of PCT testing alone, or that used culture alone as the reference standard, were excluded.
Inclusion screening and data extraction
Two reviewers (MW and PW) independently screened the titles and abstracts of all reports identified by searches and any discrepancies were discussed and resolved by consensus. Full copies of all studies deemed potentially relevant were obtained and the same two reviewers independently assessed these for inclusion; any disagreements were resolved by consensus. Details of studies excluded at the full paper screening stage are presented in Appendix 5.
The principal investigators of completed trials (identified through searches of clinical trials registries) that appeared to meet our inclusion criteria but for which no publication was identified, were contacted and asked to provide publication details or unpublished data. Details of ongoing trials and trials for which data were requested are reported in Appendix 2.
Studies cited in materials provided by the manufacturers of PCT assays were first checked against the project reference database, in EndNote X6; any studies not already identified by our searches were screened for inclusion following the process described above.
Data were extracted on the following: setting (ICU or ED); age group (adults or children); study details; inclusion and exclusion criteria; participant characteristics (demographic characteristics, primary presentation and comorbidities); details of the PCT assay used; details of the intervention PCT algorithm (decision thresholds for PCT levels and any clinical criteria); details of the standard care comparator; outcome measures (measures of antibiotic exposure (e.g. initiation and/or duration of antibiotics), resource use (e.g. duration of hospital stay, duration of ICU stay, secondary presentations) and adverse clinical outcomes (e.g. mortality, relapse/re-infection, SOFA score). Data were extracted by one reviewer, using a piloted, standard data extraction form and checked by a second (MW and PW); any disagreements were resolved by consensus. One Chinese-language paper was extracted by PW in consultation with a native speaker. 33 Full data extraction tables are provided in Appendix 3.
Quality assessment
The methodological quality of included RCTs was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. 34 Risk of bias assessments were undertaken by one reviewer and checked by a second reviewer; any disagreements were resolved by consensus or discussion with a third reviewer. No studies of other designs were included in the review. The results of the risk of bias assessments are summarised and presented in tables and graphs in the results of the systematic review (see Study quality, below), and are presented in full, by study, in Appendix 4.
Methods of analysis/synthesis
The results of studies included in this review are summarised by population/setting (see Chapter 1), i.e. studies providing information on the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy for the treatment of confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in ICU settings and studies providing information on the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy in people presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infections. Within each section, studies on adults and children are described separately. In addition, results are structured to illustrate the effects of PCT algorithms on antibiotic exposure, resource use and costs, and adverse clinical outcomes.
When more than one study is reported, the same outcome measure for clinically similar populations, meta-analysis was used to calculate summary effect estimates [relative risk (RR) for dichotomous outcomes and weighted mean difference (WMD) for continuous outcomes] together with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), using DerSimonian and Laird random-effects models. 35 Forest plots are used to display results from individual studies and summary estimates to allow visual assessment of heterogeneity. Heterogeneity was assessed statistically using the I2 statistic. 36 Observed heterogeneity was explored using subgroup analyses.
Results of the assessment of clinical effectiveness assessment
The initial literature searches of bibliographic databases for RCTs identified 2919 references. After initial screening of titles and abstracts, 146 were considered to be potentially relevant and ordered for full paper screening; of these, 35 were included in the review. 33,37–68 Additional searches of bibliographic databases for non-RCTs conducted in paediatric populations yielded an additional 515 references. After initial screening of titles and abstracts, 14 were considered to be potentially relevant and ordered for full paper screening but none of these met the criteria for inclusion in the review (see Appendix 5). All potentially relevant studies cited in documents supplied by the test manufacturers had already been identified by bibliographic database searches. One additional publication was obtained through contact with the authors,69 after searches had identified the study protocol. 47 Figure 1 shows the flow of studies through the review process, and Appendix 4 provides details, with reasons for exclusions, of all publications excluded at the full paper screening stage.
FIGURE 1.
Flow of studies through the review process.

Overview of included studies
Based on the searches and inclusion screening described above (see Search strategy and Inclusion and exclusion criteria), 36 publications33,37–68 of 18 studies33,37,39,41,42,44,45,49,50,52,54–57,60–62,69 were included in the review; the results section of this report cites studies using the primary publication and, where this is different, the publication in which the referenced data were reported. Eight studies were conducted in ICU settings33,37,41,45,50,52,54,61 and all of these studies included only adult participants; we did not identify any studies conducted in paediatric ICU settings that met the inclusion criteria for this review. Ten studies39,42,44,49,55–57,60,62,69 were conducted in ED settings, of which eight included only adults42,44,55–57,60,62,69 and two included only children. 39,49
The majority (1237,39,41,42,44,49,52,57,60–62,69) of the included studies measured plasma/serum PCT levels using the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Two studies measured plasma/serum PCT levels using the VIDAS BRAHMS PCT. 45,50 The remaining four studies used quantitative PCT assays, but did not specify the assay manufacturer;33,54–56 two of these studies were published as conference abstracts only,55,56 and one was a Chinese-language publication. 33
Twelve37,39,41,42,44,49,50,52,57,60,61,69 of the 18 included studies were conducted in Europe (predominantly Switzerland), three studies33,54,62 were conducted in China, and one study45 was conducted in Brazil; no UK studies were identified. The two studies55,56 that were published as conference abstracts did not specify location. Nine37,39,41,42,44,52,57,60,61 of the 18 included studies reported receiving some support from assay manufacturers, including supply of assay platforms and/or kits; five studies33,49,54,62,69 were fully supported by public funding and four studies45,50,55,56 did not report any information on funding.
Full details of the characteristics of study participants, study inclusion and exclusion criteria, and intervention and comparator, and detailed results are reported in the data extraction tables presented in Appendix 3.
Study quality
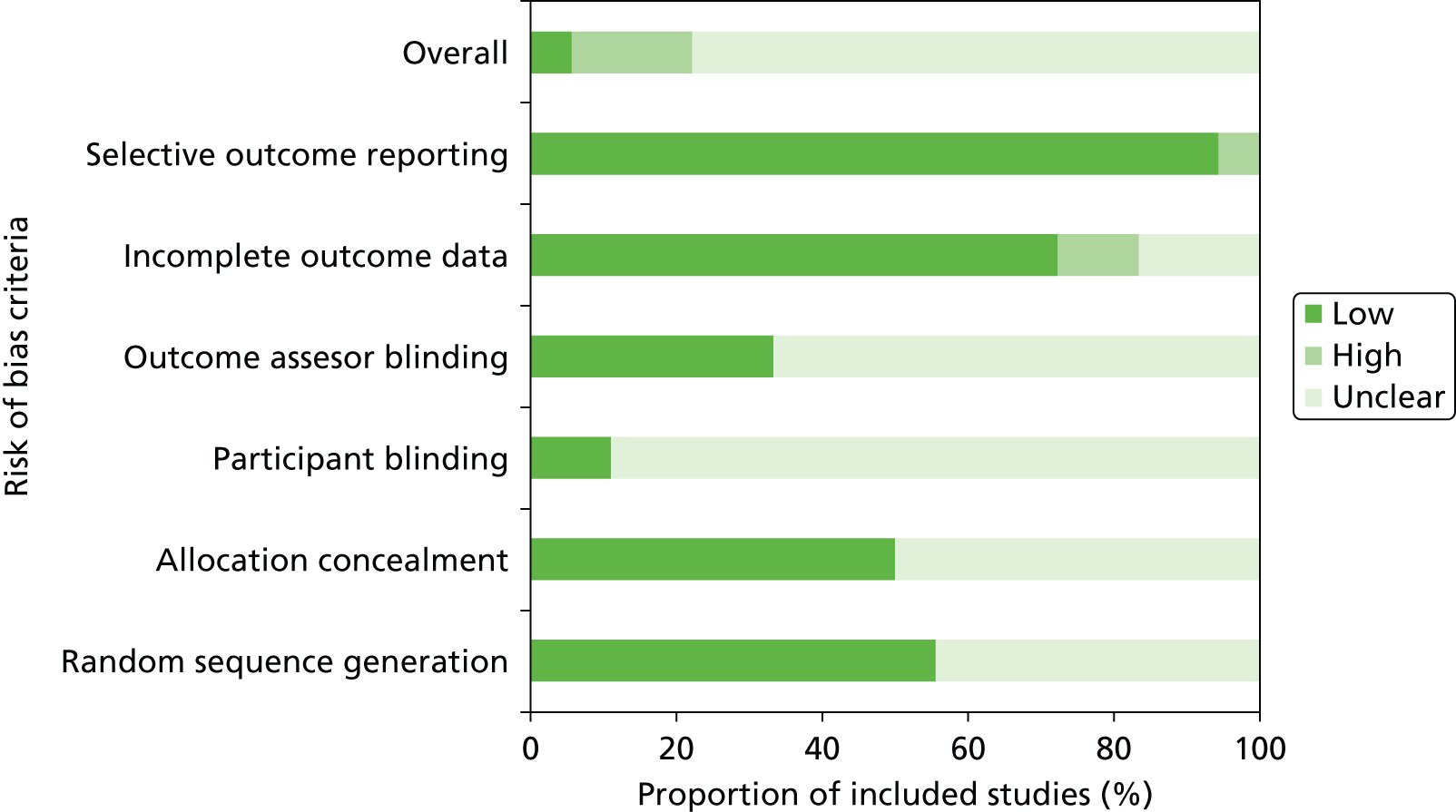
Studies were generally of unclear quality due to limitations in reporting. Three45,52,60 of the eighteen studies33,37,39,41,42,44,45,49,50,52,54–57,60–62,69 were judged at high risk of bias, one as low risk of bias,62 and all other studies were judged at unclear risk of bias, as insufficient information was reported to make a judgement on one or more bias domains (Figure 2 and Table 1).
FIGURE 2.
Risk of bias across included trials.
| Study details | Risk of bias | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random sequence generation | Allocation concealment | Participant blinding | Outcome assessor blinding | Incomplete outcome data | Selective outcome reporting | Overall | |
| Adults/ICU | |||||||
| Annane (2013)37 | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Bouadma (2010)41 | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | ? | ? | ? | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Layios (2012)50 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Liu (2013)33 | ✓ | ? | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Nobre (2008)52 | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ? | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Qu (2012)54 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ✓ | ? |
| Stolz (2009)61 | ? | ✓ | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Adults/ED | |||||||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | ✓ | ? | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | ? | ✓ | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Drozdov (2014)69 | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Roh (2013)56 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ✓ | ? |
| Roh (2010)55 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ✓ | ? |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Stolz (2007)60 | ? | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Tang (2013)62 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Children/ED | |||||||
| Baer (2013)39 | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
| Esposito (2011)49 | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? |
Two studies45,52 were judged at high risk of bias for incomplete outcome data. Both trials45,52 reported ITT and per-protocol analyses and showed considerable variation in results for the two analyses, suggesting that the relative large numbers of withdrawals (37% and 14%) may have introduced bias into the results. A further trial60 was judged at high risk of bias for selective outcome reporting as a single outcome (antibiotic exposure) was reported in multiple different formats, which could have resulted in confusion and a suggestion of a greater beneficial effect than was actually found. All other trials were judged at low risk of bias for selective outcome reporting. Where reported, methods used to randomise participants and conceal treatment allocation were appropriate; however, around half of the trials did not provide sufficient information on these processes. Given the nature of the intervention, it was not possible to blind study personnel. Very few studies provided details on participant blinding – only two studies37,62 provided this information; in both studies, this was judged to be appropriate. Details on outcome assessor blinding was also rarely reported. Six studies37,45,49,57,60,62 reported information on outcome assessor blinding, in all studies this was judged to be appropriate. There were no clear differences in study quality based on setting (ICU vs. ED) or population (adults vs. children). Full details of the risk of bias assessments for individual trials, including the support for judgements, are provided in Appendix 4.
Effectiveness of adding procalcitonin testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy for the treatment of confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in intensive care unit settings
Study details
Eight RCTs,33,37,41,45,50,52,54,61 reported in 12 publications,33,37,38,41,45,46,50–54,61 provided data on the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy in ICU settings. All studies33,37,41,45,50,52,54,61 were conducted in adult populations. Four studies33,37,45,52 fully matched the participant inclusion criteria for this review (adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis, in whom antibiotic therapy is indicated, who are being treated in ICUs). A further study41 included adults who were being treated in an ICU for suspected bacterial infection, or who developed sepsis during their ICU stay. Two additional studies54,61 that included adults being treated in ICU settings, who were considered to be at increased risk of developing sepsis, were also included: one study included adults with acute pancreatitis54 and the other included adults with ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). 61 The final study50 included adults who were being treated for suspected bacterial infections in ICU settings. This was the only study, conducted in an ICU setting, to assess the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the initiation of antibiotic treatment, reflecting the lower level of symptom severity in the included population;50 all of the other studies33,37,41,45,52,54,61 conducted in ICU settings assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment.
All studies33,37,41,45,50,52,54,61 used PCT algorithms with multiple decision thresholds to guide antibiotic treatment in the intervention arm, with final treatment decisions always remaining at the discretion of the treating clinician. The details of the PCT algorithm varied between studies; however, all discontinuation algorithms included a component that strongly encouraged/encouraged discontinuation of antibiotics when the PCT level was < 0.25 ng/ml,33,37,41,52,61 and/or encouraged discontinuation of antibiotics when the PCT level was < 0.5 ng/ml. 37,41,45,50,54,61 Discontinuation studies reported measuring PCT at baseline and daily33,41,52,54,61 or every 2 days37,45 until discontinuation, discharge or death. The study50 that assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the initiation of antibiotic treatment used similar thresholds; initiation of antibiotic treatment was strongly discouraged when PCT levels were < 0.25 ng/ml, less strongly discouraged when PCT levels were between 0.25 ng/ml and 0.5 ng/ml, less strongly recommended when PCT levels were between 0.5 and 1.0 ng/ml, and strongly recommended when PCT levels were > 1.0 ng/ml. This study50 stated that PCT levels were measured when infection was suspected. Full details of all PCT algorithms are reported in Appendix 3.2. All studies compared the intervention, a PCT algorithm combined with clinical decision-making, to decisions about antibiotic treatment based on standard clinical decision-making without PCT levels; full details of the standard clinical decision-making comparator are reported in Appendix 3.2.
Four of the studies37,41,52,61 conducted in ICU settings used the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay to measure PCT levels: two45,50 used the VIDAS BRAHMS PCT assay and two33,54 used an unspecified quantitative PCT assay.
Antibiotic exposure
The only study,50 conducted in an ICU setting, to assess the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the initiation of antibiotic treatment found no significant difference in the proportion of participants who were prescribed antibiotics (RR 1.24, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.71).
Four33,41,52,54 of the seven33,37,41,45,52,54,61 studies that assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment reported data to allow the calculation of mean difference in the duration of antibiotic therapy between study arms. Three of these studies33,41,54 found that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the clinical decision-making process resulted in a statistically significant reduction in the mean duration of antibiotic therapy; the fourth study52 found that the PCT algorithm was associated a trend towards reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy, which was not statistically significant (Table 2). The summary effect estimate, derived from these four studies,33,41,52,54 indicated that the addition of a PCT algorithm to the clinical decision-making process was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy (WMD –3.19 days, 95% CI –5.44 to –0.95 days); however, between-study heterogeneity was high (I2 = 95.2%) (Figure 3). The study with the largest effect size was conducted in adults with severe acute pancreatitis (mean difference –5.17 days, 95% CI –6.41 to –3.93 days; see Table 2 and Figure 3). 54 Of the remaining three studies33,41,52 included in the meta-analysis two33,52 conducted in populations with suspected or confirmed sepsis and one41 included both people with suspected bacterial infection and those who developed sepsis whilst in the ICU. When the meta-analysis was restricted to the two studies33,52 conducted in populations with suspected or confirmed sepsis, the summary effect estimate still indicated that the addition of a PCT algorithm to the clinical decision-making process was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy (WMD –1.20 days, 95% CI –1.33 to –1.07 days) (Figure 4). One of these studies used the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay52 and the other used the VIDAS BRAHMS PCT assay;33 there was no clear difference in effect between the two studies. Three further studies37,45,61 assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, but reported the outcome as median [interquartile range (IQR)] duration of antibiotic therapy, with p-values for the between-group comparison. Two of these studies37,45 were conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis and reported results indicating that adding a PCT algorithm to the clinical decision-making process had no statistically significant effect on the duration of antibiotic treatment (see Table 2). The remaining study61 was conducted in adults with VAP and found that, in these patients, inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the clinical decision-making process was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the median duration of antibiotic therapy from 15 to 10 days (see Table 2). 61
| Duration of antibiotics (days) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study details | Population | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement alone | Effect estimate |
| Median IQR or mean (SD) (no. of participants) | Median IQR or mean (SD) (no. of participants) | Mean difference at follow-up (CI) or p-value | ||
| Annane (2013)37 | Adults with apparent septic shock (SIRS and acute dysfunction of at least one organ) and no clear source of infection | 5 (2 to 5) (30) | 5 (3 to 5) (28) | p-value = 0.52 |
| Bouadma (2010)41 | Adults with suspected bacterial infection or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 6.1 (6) (307) | 9.9 (7.1) (314) | –3.80 (–4.83 to –2.77) |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | Adults with suspected or confirmed sepsis | 10 (3 to 39) (20) | 11 (2 to 45) (31) | p-value = 0.44 |
| Liu (2013)33 | Adults with suspected bacterial sepsis | 8.1 (0.3) (42) | 9.3 (0.3) (40) | –1.20 (–1.33 to –1.07) |
| Nobre (2008)52 | Adults with suspected severe sepsis or septic shock, or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 6 (2 to 33) (39) | 9.5 (3 to 34) (40) | –2.6 (–5.5 to 0.3) |
| Qu (2012)54 | Adults with severe acute pancreatitis | 10.89 (2.85) (35) | 16.06 (2.48) (36) | –5.17 (–6.41 to –3.93) |
| Stolz (2009)61 | Adults with VAP | 10 (6 to 16) (50) | 15 (10 to 23) (51) | p-value = 0.038 |
FIGURE 3.
Duration of antibiotic therapy.
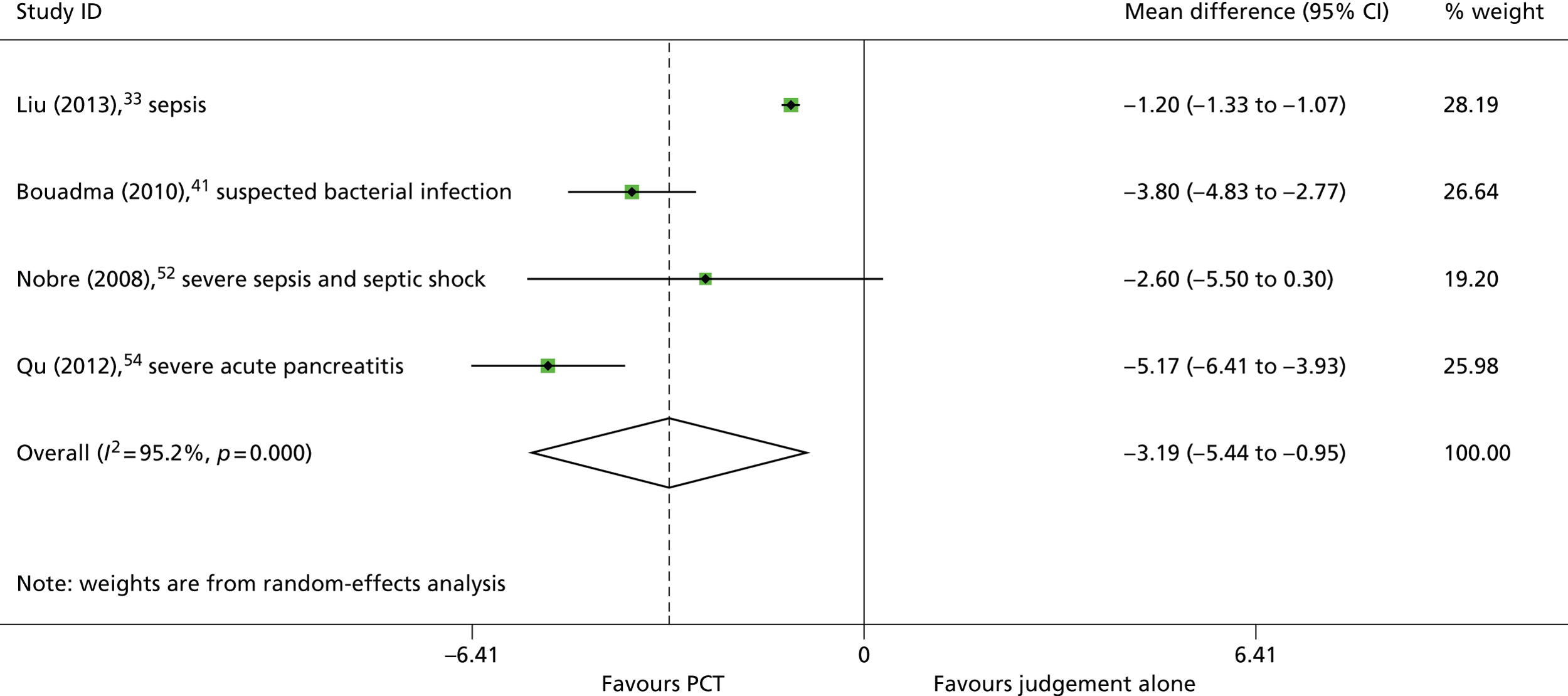
FIGURE 4.
Duration of antibiotic therapy (studies that included only people with suspected or confirmed sepsis).

The study by Bouadma et al.,41 which included both people with suspected bacterial infection and those who developed sepsis whilst in the ICU, was the only ICU study to report duration of antibiotic therapy stratified by clinical diagnosis (UTI, CAP, VAP, infection with positive blood culture, and intra-abdominal infection). The inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the clinical decision-making process was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy for people with UTI (mean difference –7.1 days, 95% CI –12.1 to –2.1 days), CAP (mean difference –5.0 days, 95% CI –6.5 to –3.5 days) or VAP (mean difference –2.1 days, 95% CI –3.9 to –0.3 days), but not for people with infection and positive blood cultures (mean difference –3.0 days, 95% CI –6.0 to 0.0 days) or intra-abdominal infections (mean difference –2.7 days, 95% CI –7.7 to 2.3 days). 41 Full results, including all clinical subgroup data are presented in Appendix 3.3 and 3.4.
Resource use and costs
Resource use and costs are illustrated in Table 3 and Figures 5–8. Seven of the studies33,37,41,45,52,54,61 conducted in ICU settings reported data on resource use and costs outcomes. All of these studies assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment. All seven studies33,37,41,45,52,54,61 reported information on both the duration of hospital stay and six studies33,37,41,45,52,54 reported data on the duration of ICU stay.
Four studies33,41,52,54 reported data to allow the calculation of mean difference in the duration of hospital stay between study arms. Two of these studies33,54 found that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the clinical decision-making process resulted in a statistically significant reduction in the mean duration of hospital stay, and one study52 found that the PCT algorithm was associated a trend towards reduction in the duration of hospital stay, which was not statistically significant (Table 3). The results of study by Bouadma et al.,41 which included both people with suspected bacterial infection and those who developed sepsis whilst in the ICU, indicated that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the clinical decision-making process did not reduce the duration of hospital stay for these patients (mean difference 0.3 days, 95% CI –3.26 to 2.66 days); this may be related to the less clinically severe spectrum of clinical presentations represented. The summary effect estimate, derived from these four studies,33,41,52,54 indicated that the PCT algorithm was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the duration of hospital stay (WMD –3.85 days, 95% CI –6.78 to –0.92 days); however, between-study heterogeneity was high (I2 = 75.2%) (Figure 5). As with duration of antibiotic therapy, the largest effect size was derived from the study54 conducted in adults with severe acute pancreatitis (mean difference –7.15 days, 95% CI –9.16 to –4.34 days) (see Table 3 and Figure 5). Two33,52 of the remaining three studies included in the meta-analysis were conducted in populations with suspected or confirmed sepsis, and one study41 included both people with suspected bacterial infection and those who developed sepsis whilst in the ICU. When the meta-analysis was restricted to studies conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis,33,52 the PCT algorithm appeared to be associated with a greater reduction in duration of hospital stay (WMD –4.32 days, 95% CI –6.50 to –2.14 days) (Figure 6). One of these studies52 used the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay and the other study33 used the VIDAS BRAHMS PCT assay; there was no clear difference in effect between the two studies. Three further studies37,45,61 assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, but reported duration of hospital stay as median (IQR), with p-values for the between-group comparison. Two37,45 of these studies were conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis and one study61 was conducted in people with VAP; all reported results indicating that the PCT algorithm had no statistically significant effect on the duration of hospital stay (see Table 3).
| Study details | Population | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement alone | Effect estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median IQR or mean (SD) (no. of participants) | Median IQR or mean (SD) (no. of participants) | Mean difference at follow-up (CI) or p-value | ||
| Duration of hospital stay (days) | ||||
| Annane (2013)37 | Adults with apparent septic shock (SIRS and acute dysfunction of at least one organ) and no clear source of infection | 27 (9 to 49) (30) | 33 (11 to 69) (28) | p-value = 0.22 |
| Bouadma (2010)41 | Adults with suspected bacterial infection or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 26.1 (19.3) (307) | 26.4 (18.3) (314) | –0.3 (–3.26 to 2.66) |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | Adults with suspected or confirmed sepsis | 11 (3 to 547) (20) | 11 (2, 228) (31) | p-value = 0.70 |
| Liu (2013)33 | Adults with suspected bacterial sepsis | 27 (4.9) (42) | 32 (5.4) (40) | –5.0 (–7.24 to –2.76) |
| Nobre (2008)52 | Adults with suspected severe sepsis or septic shock, or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 17 (3 to 96) (39) | 23.5 (5 to 44) (40) | –2.5 (–6.5 to 1.5) |
| Qu (2012)54 | Adults with severe acute pancreatitis | 16.66 (4.02) (35) | 23.81 (7.56) (36) | –7.15 (–9.16 to –4.34) |
| Stolz (2009)61 | Adults with VAP | 26 (7 to 21) (51) | 26 (16.8 to 22.3) (50) | p-value = 0.153 |
| Duration of ICU stay (days) | ||||
| Annane (2013)37 | Adults with apparent septic shock and no clear source of infection | 22 (8 to 42) (30) | 23 (10 to 60) (28) | p-value = 0.58 |
| Bouadma (2010)41 | Adults with suspected bacterial infection | 15.9 (16.1) | 14.4 (14.1) | 1.5 (–0.88 to 3.88) |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | Adults with suspected or confirmed sepsis | 3.5 (1 to 57) (20) | 3 (1 to 28) (31) | p-value = 0.60 |
| Liu (2013)33 | Adults with suspected bacterial sepsis | 12 (2.9) (42) | 14 (2.7) (40) | –2.0 (–3.21 to –0.79) |
| Nobre (2008)52 | Adults with suspected severe sepsis or septic shock, or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 4 (1 to 21) (39) | 7 (1 to 91) (40) | –4.6 (–8.2 to 1) |
| Qu (2012)54 | Adults with severe acute pancreatitis | 11.1 (2.94) (35) | 14.8 (2.49) (36) | –3.72 (–4.99 to –2.45) |
| Costs (total cost of hospitalisation in US dollars) | ||||
| Qu (2012)54 | Adult with severe acute pancreatitis | 24,401 (2631) (35) | 27,813 (2529) (36) | –3412 (–4613 to –2211) |
FIGURE 5.
Duration of hospital stay.
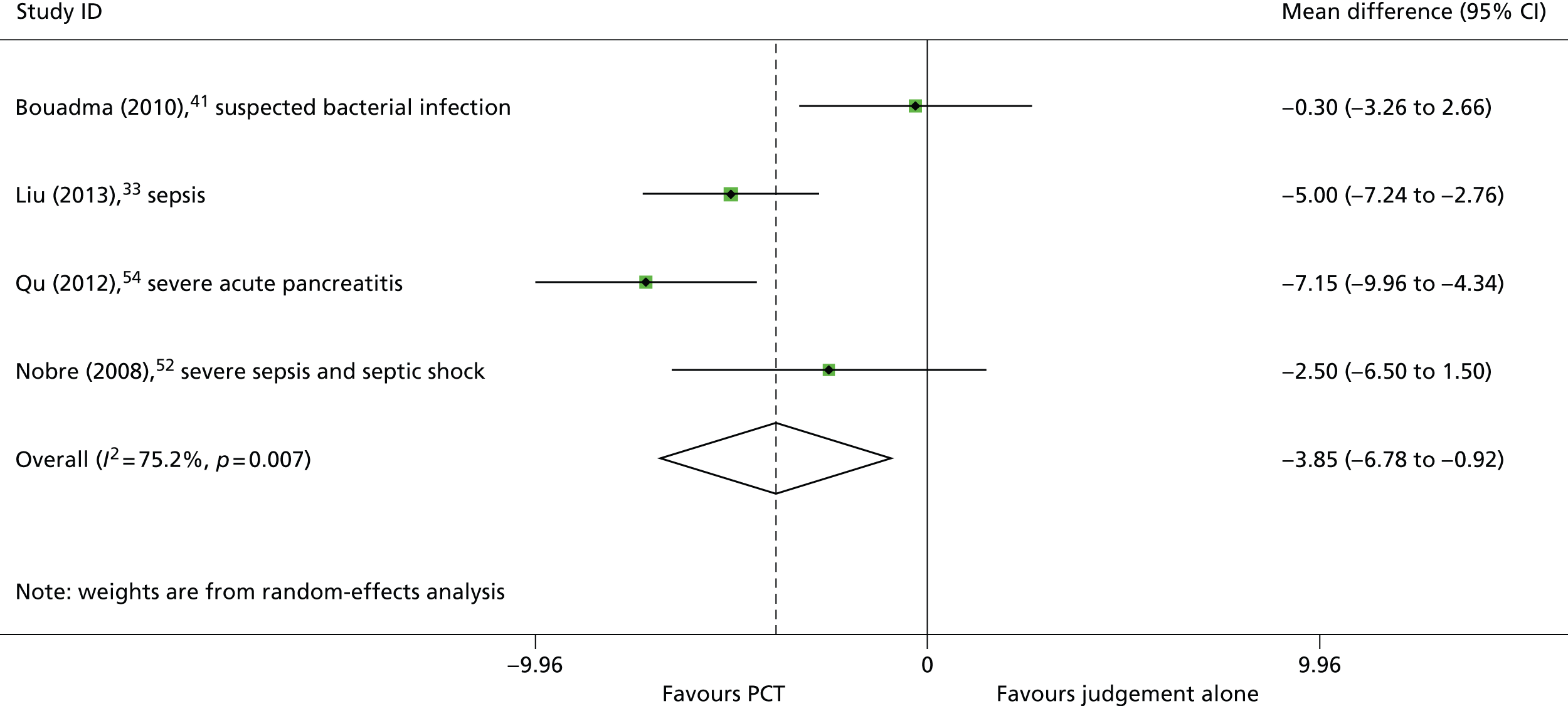
FIGURE 6.
Duration of hospital stay (studies that included only people with suspected or confirmed sepsis).

Four studies33,41,52,54 reported data to allow the calculation of mean difference in the duration of ICU stay between study arms. Two of these studies33,54 found that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the decision to discontinue antibiotics resulted in a statistically significant reduction in the mean duration of ICU stay, and one study52 found that the PCT algorithm was associated a trend towards reduction in the duration of hospital stay, which was not statistically significant (see Table 3). As with duration of hospital stay, the results of the study by Bouadma et al. 41 indicated that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the decision to discontinue antibiotics did not reduce the duration of ICU stay for these patients with a less severe spectrum of disease (mean difference 1.5 days, 95% CI –0.88 to 3.88 days). 41 The summary effect estimate, derived from these four studies,33,41,52,54 indicated that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the decision to discontinue antibiotics was associated with a trend towards decreased duration of ICU stay, which did not reach statistical significance (WMD –2.03 days, 95% CI –4.19 to 0.13 days); however, between-study heterogeneity was high (I2 = 81.0%) (Figure 7). The largest effect size was again derived from the study conducted in adults with severe acute pancreatitis (mean difference –3.72 days, 95% CI –4.99 to –2.45 days) (see Table 3 and Figure 6). 54 Two33,52 of the remaining three studies33,41,52 included in the meta-analysis were conducted in populations with suspected or confirmed sepsis, and one study41 included both people with suspected bacterial infection and those who developed sepsis whilst in the ICU. When the meta-analysis was restricted to studies conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis,33,52 the summary effect estimate indicated that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the decision to discontinue antibiotics was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the duration of ICU stay (WMD –2.31 days, 95% CI –3.97 to –0.65 days) (Figure 8). One52 of these studies used the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay and the other used the VIDAS BRAHMS PCT assay;33 there was no clear difference in effect between the two studies. Two further studies37,45 assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, but reported duration of ICU stay as median (IQR), with p-values for the between-group comparison. Both of these studies37,45 were conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis and both reported results indicating that adding the PCT algorithm had no statistically significant effect on the duration of ICU stay (see Table 3).
FIGURE 7.
Duration of ICU stay.
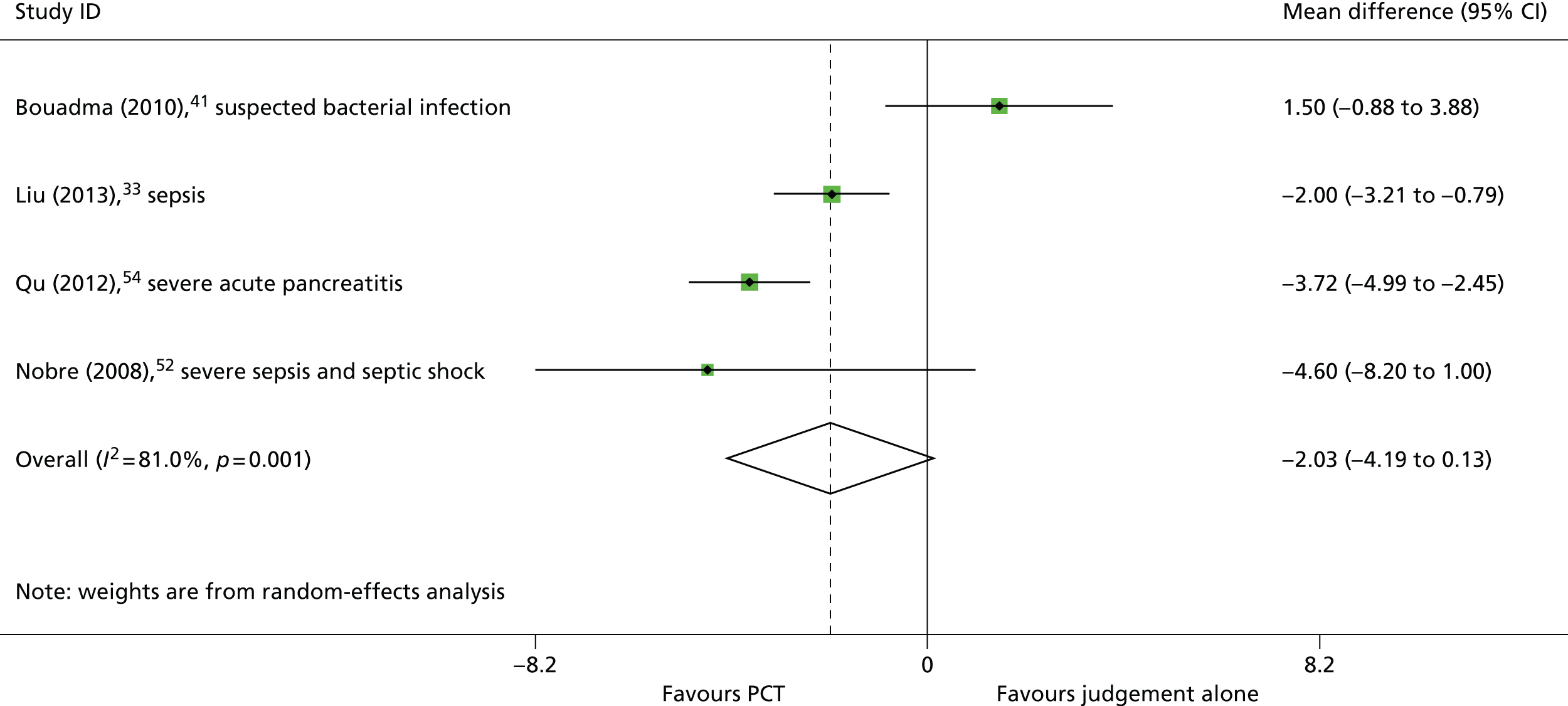
FIGURE 8.
Duration of ICU stay (studies that included only people with suspected or confirmed sepsis).

The study by Qu et al. 54 conducted in people with severe acute pancreatitis reported that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the decision to discontinue antibiotics was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the mean total cost of hospitalisation (mean difference –US$3412, 95% CI – US$4613 to –US$2211).
No study reported clinical subgroup data for resource use and costs outcomes.
Adverse clinical outcomes
Adverse clinical outcomes are illustrated in Table 4 and Figures 9–12. All eight studies33,37,41,45,50,52,54,61 conducted in ICU settings reported some data on adverse clinical outcomes. Three of these studies41,52,61 explicitly stated that they aimed to investigate whether the use of PCT in decision-making can reduce antibiotic exposure, without adversely affecting clinical outcomes, one41 of which specified a non-inferiority design for mortality and reported a Kaplan–Meyer survival curve.
Five studies33,41,52,54,61 reported 28-day all-cause mortality, and all reported no statistically significant difference in mortality rates between participants in the intervention group (decision to discontinue antibiotics based on PCT algorithm plus clinical judgement) and those in the control group (decision to discontinue antibiotics based on clinical judgement alone) (Table 4). The summary RR derived from these five studies33,41,52,54,61 was 0.98 (95% CI 0.76 to 1.27) (Figure 9). This finding was consistent when the meta-analysis was restricted to studies conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis33,52 (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.54 to 2.12). One study41 also reported mortality at 60 days and found no statistically significant difference between the intervention and control groups (RR 1.15, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.48). One further study,37 conducted in people with apparent septic shock, assessed mortality at 5 days and found no statistically significant difference between the intervention and control groups (RR 1.0, 95% CI 0.25 to 4.04).
| Study details | Population | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement alone | RR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients with event/no. of patients | No. of patients with event/no. of patients | |||
| All-cause mortality (28 day) | ||||
| Bouadma (2010)41 | Adults with suspected bacterial infection or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 65/307 | 64/314 | 1.04 (0.76 to 1.41) |
| Liu (2013)33 | Adults with suspected bacterial sepsis | 6/42 | 5/40 | 1.13 (0.39 to 3.22) |
| Nobre (2008)52 | Adults with suspected severe sepsis or septic shock, or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 8/39 | 8/40 | 1.03 (0.44 to 2.38) |
| Qu (2012)54 | Adults with severe acute pancreatitis | 7/35 | 8/36 | 0.91 (0.38 to 2.16) |
| Stolz (2009)61 | Adults with VAP | 8/51 | 12/50 | 0.67 (0.31 to 1.45) |
| In-hospital mortality | ||||
| Annane (2013)37 | Adults with apparent septic shock (SIRS and acute dysfunction of at least one organ) and no clear source of infection | 7/31 | 10/30 | 0.69 (0.31 to 1.53) |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | Adults with suspected or confirmed sepsis | 2/42 | 4/39 | 0.52 (0.12 to 2.28) |
| Nobre (2008)52 | Adults with suspected severe sepsis or septic shock, or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 9/39 | 9/40 | 1.03 (0.47 to 2.25) |
| Stolz (2009)61 | Adults with VAP | 10/51 | 14/50 | 0.71 (0.36 to 1.42) |
| ICU mortality | ||||
| Annane (2013)37 | Adults with apparent septic shock (SIRS and acute dysfunction of at least one organ) and no clear source of infection | 7/31 | 10/30 | 0.69 (0.31 to 1.53) |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | Adults with suspected or confirmed sepsis | 1/42 | 4/39 | 0.31 (0.05 to 1.87) |
| Layios (2012)50 | Adults with suspected bacterial infection | 56/258 | 53/251 | 1.03 (0.74 to 1.43) |
| Infection relapse/recurrence | ||||
| Bouadma (2010)41 | Adults with suspected bacterial infection or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 20/307 | 16/314 | 1.27 (0.68 to 2.38) |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | Adults with suspected or confirmed sepsis | 2/42 | 1/39 | 1.55 (0.21 to 11.19) |
| Liu (2013)33 | Adults with suspected bacterial sepsis | 3/42 | 1/40 | 2.22 (0.34 to 14.34) |
| Nobre (2008)52 | Adults with suspected severe sepsis or septic shock, or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 1/39 | 1/40 | 1.03 (0.11 to 9.44) |
| Other adverse clinical outcomes | ||||
| Annane (2013)37 Outcome definition All-cause mortality (5 day) |
Adults with apparent septic shock (SIRS and acute dysfunction of at least one organ) and no clear source of infection | 3/31 | 3/31 | 1 (0.25 to 4.04) |
| Bouadma (2010)41 Outcome definition All-cause mortality (60 day) |
Adults with suspected bacterial infection or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 92/307 | 82/314 | 1.15 (0.89 to 1.48) |
| Bouadma (2010)41 Outcome definition Multi-drug-resistant infection |
Adults with suspected bacterial infection or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 55/307 | 52/314 | 1.08 (0.77 to 1.52) |
| Nobre (2008)52 Outcome definition Sepsis-related mortality |
Adults with suspected severe sepsis or septic shock, or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 3/39 | 2/40 | 1.44 (0.3 to 6.85) |
| Qu (2012)54 Outcome definition Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome |
Adults with severe acute pancreatitis | 24/35 | 25/36 | 0.99 (0.73 to 1.34) |
| Stolz (2009)61 Outcome definition VAP-related clinical deterioration |
Adults with VAP | 5/51 | 7/50 | 0.72 (0.26 to 2.01) |
| Study details | Population | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement alone | Effect estimate |
| Median IQR or mean (SD) (CI) (no. of participants) | Mean difference at follow-up (CI) or p -value | |||
| Annane (2013)37 Outcome definition Mechanical ventilation (days) |
Adults with apparent septic shock (SIRS and acute dysfunction of at least one organ) and no clear source of infection | 11 (5 to 25) (30) | 1 4 (8 to 25) (28) | p-value = 0.56 |
| Layios (2012)50 Outcome definition Mechanical ventilation (days) |
Adults with suspected bacterial infection | 9.3 (4.9) (258) | 9.1 (5.4) (251) | p-value = 0.42 |
| Annane (2013)37 Outcome definition SOFA score (day 5) |
Adults with apparent septic shock and no clear source of infection | 8 (5 to 9) (30) | 8 (7 to 11) (28) | p-value = 0.61 |
| Bouadma (2010)41 Outcome definition SOFA score (day 28) |
Adults with suspected bacterial infection or who developed sepsis in the ICU | 1.5 (3) (307) | 0.9 (2.4) (314) | 0.6 (0 to 1.1) |
| Layios (2012)50 Outcome definition SOFA score (maximum during ICU stay) |
Adults with suspected bacterial infection | 9.3 (4.9) (258) | 9.1 (5.4) (251) | p-value = 0.42 |
FIGURE 9.
All-cause mortality (28 day).

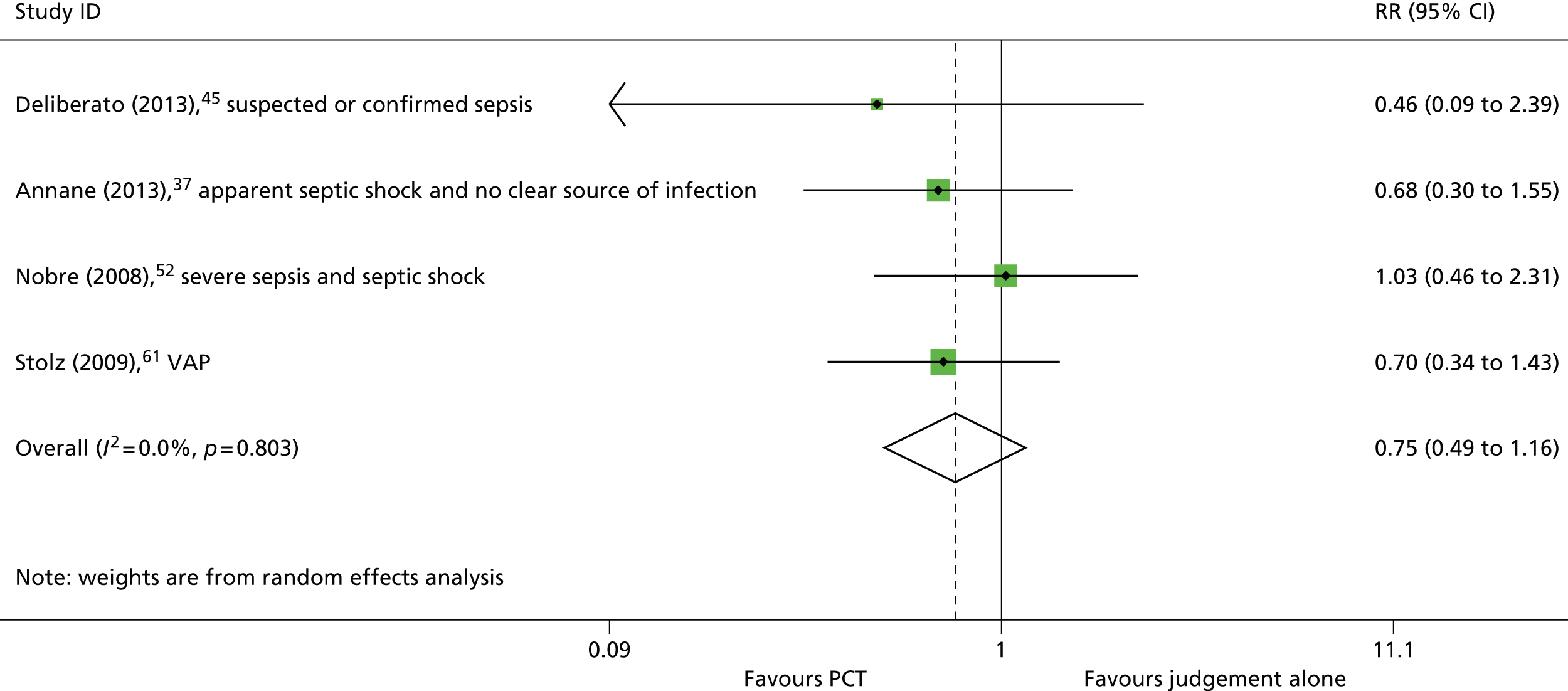
Four studies37,45,52,61 reported in-hospital mortality and, as with all-cause mortality, all reported no statistically significant difference in mortality rates between participants in the intervention and control groups (see Table 4). The summary RR derived from these four studies37,45,52,61 was 0.75 (95% CI 0.49 to 1.16) (Figure 10). This finding was consistent when the meta-analysis was restricted to studies conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis37,45,52 (RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.45 to 1.35).
FIGURE 10.
In-hospital mortality.
Three studies reported ICU mortality. 37,45,50 Two of these studies37,45 assessed the effects of the addition of a PCT algorithm to the information used to guide discontinuation of antibiotics, and were conducted in people with confirmed or suspected sepsis; both reported no statistically significant difference in the ICU-mortality rate between the intervention and control groups (see Table 4). The remaining study50 assessed the effects of adding a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and was conducted in people with suspected bacterial infection; this study also found no statistically significant difference in the ICU-mortality rate between the intervention and control groups (see Table 4). The summary RR derived from all three studies37,45,50 was 0.87 (95% CI 0.55 to 1.37) (Figure 11). This finding was consistent when the meta-analysis was restricted to studies conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis37,45 (RR 0.59, 95% CI 0.27 to 1.28).
FIGURE 11.
Intensive care unit mortality.

Four studies33,41,45,52 reported rates of infection relapse/recurrence, and all found no statistically significant difference in mortality rates between participants in the intervention group (decision to discontinue antibiotics based on PCT algorithm plus clinical judgement) and those in the control group (decision to discontinue antibiotics based on clinical judgement alone) (see Table 4). The summary RR derived from these four studies33,41,45,52 was 1.37 (95% CI 0.77 to 2.44) (Figure 12). This finding was consistent when the study by Bouadma et al.,41 which included both people with suspected bacterial infection and those who developed sepsis whilst in the ICU, was excluded from the meta-analysis (RR 1.89, 95% CI 0.47 to 7.59).
FIGURE 12.
Infection relapse/recurrence (ICU population). NR, not reported.

A variety of other general and disease-specific adverse clinical outcomes were reported by one or more studies (see Table 4). These included multidrug-resistant infection,41 sepsis-related mortality,52 MODS,54 VAP-related clinical deterioration,61 duration of mechanical ventilation,37,50 and SOFA score at various time points. 37,41,50 No study reported a statistically significant difference between the intervention and comparator groups for any adverse clinical outcome assessed. None of the included studies reported antibiotic-related adverse events.
No study reported clinical subgroup data for adverse clinical outcomes.
Effectiveness of adding procalcitonin testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy in people presenting to the emergency department with suspected bacterial infections
Study details
Ten RCTs,39,42,44,49,55–57,60,62,69 reported in 16 publications,39,40,42–44,47–49,55–59,62,69,70 provided data on the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy in ED settings. Two studies39,49 were conducted in children, and the remainder42,44,55–57,60,62,69 were conducted in all adult populations. The presenting characteristics of participants varied between studies; however, all but one study69 were conducted in people with respiratory presentations. Two of the adult studies44,57 were conducted in people with a primary diagnosis of LRTI, three studies42,55,56 were conducted in people with CAP, one study60 included people with COPD exacerbations, one study62 included people with suspected asthma exacerbations, and the final study71 was conducted in people with UTI. Of the two studies39,49 conducted in children, one study39 included children with LRTI (including CAP and non-CAP LRTI)39 and the other study49 included children with CAP. All but one of the studies39,42,44,49,55–57,60,62 conducted in ED settings assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the initiation of antibiotic treatment, and six of these studies39,42,49,55–57 also assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the discontinuation of antibiotic treatment. The study69 conducted in adults with UTI only considered the discontinuation application. This study69 divided participants into outpatients and those admitted to hospital; for the outpatient population the PCT algorithm informed an initial decision on the fixed length of antibiotic prescription, whereas for hospitalised participants the PCT algorithm informed the decision on when to discontinue antibiotics in a manner similar to other studies included in this assessment. Data reported in this section are unpublished subgroup data for the hospitalised participants and were supplied by a study author (Dr Werner Albrich, Division of Infectious Diseases and Hospital Epidemiology, Kantonsspital St Gallen, Switzerland, 22 October 2014, personal communication); results for the full study population are reported in Appendix 3.3 and 3.4. 69
With the exception of two studies published as abstracts,55,56 all studies used PCT algorithms with multiple decision thresholds to guide antibiotic treatment in the intervention arm, with final treatment decisions always remaining at the discretion of the treating clinician. The details of the PCT algorithm varied between studies; however, all algorithms (both initiation and discontinuation) discouraged antibiotic use when the PCT level was < 0.25 ng/ml; this decision threshold was also used by the two studies published as abstracts;55,56 these two studies did not report the timing of PCT measurements. Four studies39,42,44,57 used the same initiation algorithm: PCT < 0.1 ng/ml, antibiotics strongly discouraged; PCT 0.1–0.25 ng/ml, antibiotics discouraged; PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml, antibiotics encouraged; PCT > 0.5 ng/ml, antibiotics strongly encouraged, and three of these studies42,44,57 used the same thresholds to guide discontinuation decisions. Two further studies used a similar initiation algorithm,60,62 without the upper threshold (PCT > 0.5 ng/ml, antibiotics strongly encouraged). Reported timings for the measurement of PCT were similar; all studies39,42,44,57,60,62 that reported timings included a baseline measurement, three studies39,57,69 reported that repeat measurements were taken at days 3 and 539 or days 3, 5 and 7,57,69 and three studies42,44,49 reported that repeat measurements were taken at days 4, 6 and 842,44 or every 2 days until discontinuation. 49 Four studies42,44,57,62 noted that PCT measurements were repeated at between 6 and 24 hours if antibiotic treatment was initially withheld. Full details of all PCT algorithms are reported in Appendix 3.2. All studies compared the intervention, a PCT algorithm combined with clinical decision-making, to decisions about antibiotic treatment based on standard clinical decision-making without PCT levels; full details of the standard clinical decision-making comparator are reported in Appendix 3.2.
Eight of the studies39,42,44,49,57,60,62,69 conducted in ED settings used the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay to measure PCT levels, and two studies55,56 used an unspecified quantitative PCT assay.
Antibiotic exposure
Seven studies,42,44,55–57,60,62 conducted in adults presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infections, assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the initiation of antibiotic treatment; all of these studies reported the proportion of patients, in the intervention and control groups, who received antibiotic treatment, and all found that adding a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in antibiotic use (Table 5 and Figure 13). The summary RR, derived from these seven studies42,44,55–57,60,62 was 0.77 (95% CI 0.68 to 0.87) (see Figure 13). When studies reported data for clinical subgroups, a reduction in antibiotic use associated with the PCT algorithm was observed for all groups: severe acute exacerbations of COPD;44 COPD exacerbations; CAP and acute bronchitis;57 and differing severities of asthma62 (mild, moderate, severe and critical). One study62 reported data indicating that the reduction in antibiotic use associated with the PCT algorithm increased with decreasing severity of asthma (critical asthma RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.1; mild asthma RR 0.47, 95% CI 0.31 to 0.71) (see Appendix 3.3). Clinical subgroup data are reported in full in Appendix 3.3.
| Study details | Population | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement alone | RR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients with event/no. of patients | No. of patients with event/no. of patients | |||
| Initiation of antibiotics | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | Adults with suspected LRTI | 55/124 | 99/119 | 0.54 (0.43 to 0.66) |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | Adults with CAP | 128/151 | 149/151 | 0.86 (0.8 to 0.92) |
| Roh (2010)55 | Adults with CAP | 55/60 | 61/62 | 0.93 (0.86 to 1.01) |
| Roh (2013)56 | Elderly adults with CAP | 73/80 | 83/84 | 0.92 (0.86 to 0.99) |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | Adults with LRTI | 506/671 | 603/688 | 0.86 (0.82 to 0.91) |
| Stolz (2007)60 | Adults with exacerbations of COPD | 41/102 | 76/106 | 0.56 (0.43 to 0.73) |
| Tang (2013)62 | Adults with suspected acute exacerbation of asthma | 59/128 | 95/127 | 0.62 (0.5 to 0.76) |
| Baer (2013)39 | Children with LRTI | 104/168 | 93/169 | 1.12 (0.94 to 1.35) |
| Children with non-CAP LRTI | 27/60 | 10/62 | 2.71 (1.46 to 5.01) | |
| Children with CAP | 77/108 | 83/107 | 0.92 (0.79 to 1.08) | |
| Esposito (2011)49 | Children with CAP | 131/155 | 155/155 | 0.85 (0.79 to 0.9) |
| Duration of antibiotics | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | Adults with suspected LRTI | 10.9 (3.6) (124) | 12.8 (5.5) (119) | –1.90 (–3.07 to –0.73) |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | Adults with CAP | 5.8 (5.3) (151) | 12.9 (6.5) (151) | –7.10 (–8.44 to –5.76) |
| aDrozdov (2014)69 | Adults hospitalised with UTI | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed |
| Roh (2010)55 | Adults with CAP | 9.2 (60) | 14.6 (62) | p-value < 0.001 |
| Roh (2013)56 | Elderly adults with CAP | 11.2 (80) | 14.6 (84) | p-value < 0.05 |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | Adults with LRTI | 5 (1 to 8) (671) | 9 (6 to 11) (688) | NR |
| Baer (2013)39 | Children with LRTI | 4.5 (168) | 6.3 (169) | –1.8 (–3.1 to –0.5) |
FIGURE 13.
Initiation of antibiotics in adults.

Both of the two studies39,49 conducted in children presenting to the ED also reported the proportion of patients, in the intervention and control groups, who received antibiotic treatment. However, these two studies39,49 reported contradictory results. The study by Esposito et al.,49 conducted in children with CAP, found that adding a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment was associated with a statistically significant reduction in antibiotic use (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.79 to 0.91). Subgroup analyses, by severity of CAP, indicated that the PCT algorithm was associated with a greater reduction in antibiotic use for children with mild CAP (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.59 to 0.80) than was the case for children with severe CAP (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.92 to 1.01) (see Appendix 3.3). 49 In contrast, the study by Baer et al.,39 conducted in children with LRTI (including CAP and non-CAP LRTI), reported a trend towards increased antibiotic use when PCT levels were included in decision-making (RR 1.12, 95% CI 0.94 to 1.35) (see Table 5). The Baer et al. study39 also reported data on antibiotic initiation stratified by clinical subgroup (CAP and non-CAP LRTI). These data indicated that, for children presenting with non-CAP LRTI, adding a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment was associated with a statistically significant increase in antibiotic use (RR 2.71, 95% CI 1.46 to 5.01), whereas for children presenting with CAP the PCT algorithm was associated with a trend towards reduction in antibiotic use (RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.79 to 1.08) (see Table 5). 39 When data from the Esposito et al. study49 were combined with data from the CAP subgroup of the Baer et al. study39 the summary RR was 0.86 (95% CI 0.80 to 0.93) [Figure 14; pooling data for the whole population of both studies resulted in a summary RR of 0.97 (95% CI 0.67 to 1.40)].
FIGURE 14.
Initiation of antibiotics in children with CAP.

Six studies,42,44,55–57,69 conducted in adults presenting to the ED, assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment. However, only two studies42,44 reported data to allow the calculation of mean difference in the duration of antibiotic therapy between study arms. Both of these studies42,44 found that the inclusion of a PCT algorithm in the clinical decision-making process resulted in a statistically significant reduction in the mean duration of antibiotic therapy (see Table 5). The summary effect estimate, derived from these two studies,42,44 indicated that the addition of a PCT algorithm to the clinical decision-making process was associated with reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy, which did not reach statistical significance (WMD –4.49 days, 95% CI –9.59 to 0.61 days) (Figure 15). Four studies,55–57,69 conducted in adults, assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, but reported the outcome as median (IQR) duration of antibiotic therapy, with p-values for the between-group comparison57,69 or mean no estimate of variance. 55,56 The results of these studies55–57,69 were consistent with the two studies42,44 included in the meta-analysis – indicating that adding a PCT algorithm to the clinical decision making process was associated with a reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy in all populations considered (see Table 5). When studies reported data for clinical subgroups, the observed reduction in duration of antibiotic use associated with use of a PCT algorithm was generally consistent across groups (severe acute exacerbations of COPD,44 and COPD exacerbations, CAP and acute bronchitis);57 however, effects were less clear-cut owing to smaller numbers of patients (see Appendix 3.4). All studies that reported data on the duration of antibiotic treatment included patients with a zero duration (i.e. those who did not receive antibiotics) in their estimates of mean/median duration and hence are not strictly applicable to assessing the effectiveness of using PCT algorithms to inform the decision on when to discontinue antibiotics. We therefore conducted an additional meta-analysis, excluding participants who did not receive antibiotic treatment (see Appendix 8). The summary effect estimate for patients who received antibiotic treatment (i.e. WMD conditional upon receipt of antibiotics) was 1.48 days (95% CI –13.64 to 16.59 days), based on data from two studies. 42,44 The conditional data from one of these studies44 was consistent with PCT testing being associated with a decrease in the duration of antibiotic therapy (mean difference –6.23 days, 95% CI –7.54 to –4.92 days),44 whereas analysis of conditional data from the second study42 resulted in a reversal of the observed effect and indicated that PCT testing was associated with an increase in the duration of antibiotic therapy (mean difference 9.18 days, 95% CI 7.75 to 10.61 days).
FIGURE 15.
Duration of antibiotics in adults.

Only one of the studies39 conducted in children presenting to the ED reported data on duration of antibiotic therapy; this study found that adding a PCT algorithm to the clinical decision-making process was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy (mean difference –1.8 days, 95% CI–3.1 to –0.5 days). 39 Subgroup analyses from this study39 indicated that this reduction was apparent only for children with CAP (mean difference –3.4 days, 95% CI –4.9 to –1.7 days); for children with non-CAP LRTI, there was no apparent difference in the duration of antibiotic therapy when a PCT algorithm was used (mean difference was 0.8 days, 95% CI –0.5 to 2.0 days) (see Appendix 3.4).
Resource use and costs
All of the studies conducted in ED settings39,42,44,49,55–57,60,62,69 reported data on one or more resource use or costs outcome.
Six studies,42,44,55–57,60 conducted in adults presenting to the ED with various respiratory conditions, reported data on the effect on duration of hospital stay of adding a PCT algorithm to information used to guide antibiotic treatment (Table 6). The intervention arms of five of these studies42,44,55–57 used PCT algorithms in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, and in the remaining study60 only the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic therapy was considered. Only two studies42,44 reported data to allow the calculation of mean difference in the duration of hospital stay between study arms and neither found a statistically significant between-group difference. The summary effect estimate, derived from these two studies,42,44 indicated that the PCT algorithm was associated with a trend towards reduction in the duration of hospital stay (WMD –0.80 days, 95% CI –2.37 to 0.78 days) (Figure 16). Four further studies assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic treatment,55–57,60 but reported duration of hospital stay as mean number of days with no estimate of variance55,56 or median (IQR) with p-values for the between-group comparison. 57,60 Two of these studies,55,56 both conducted in people with CAP, reported results indicating that the PCT algorithm was associated with a reduction in the duration of hospital stay (mean duration 9.2 days in the PCT group and 14.6 days in the control group,55 and mean duration 14.6 days in the PCT group and 16 days in the control group56) (see Table 6). The remaining two studies,57,60 one conducted in people with LRTI57 and one conducted in people with COPD exacerbations,60 found that use of a PCT algorithm did not affect the median duration of hospital stay (see Table 6). This finding was consistent for all three clinical subgroups (COPD exacerbations, CAP and acute bronchitis) of the LRTI study (see Appendix 3.4). 57
| Study details | Population | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement alone | Effect estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median IQR or mean (SD) (no. of participants)a | Mean difference at follow-up (CI) or p-value | |||
| Duration of hospital stay (days) | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | Adults with suspected LRTI | 10.7 (8.9) (124) | 11.2 (10.6) (119) | –0.50 (–2.97 to 1.97) |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | Adults with CAP | 12 (9.1) (151) | 13 (9) (151) | –1.0 (–3.04 to 1.04) |
| Roh (2010)55 | Adults with CAP | 9.2 (60) | 14.6 (62) | p-value ≤ 0.001 |
| Roh (2013)56 | Elderly adults with CAP | 14.6 (80) | 16 (84) | p-value ≥ 0.05 |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | Adults with LRTI | 8 (4 to 12) (671) | 8 (4 to 12) (688) | NR |
| Stolz (2007)60 | Adults with COPD exacerbation | 9 (1 to 15) (102) | 10 (1 to 15) (106) | p-value = 0.960 |
| Baer (2013)39 | Children with LRTI | 2.6 (168) | 2.7 (169) | –0.1 (–0.8 to 0.5) |
| Baer (2013)39 | Children with non-CAP LRTI | 2.5 (60) | 2.3 (62) | 0.3 (–0.8 to 1.2) |
| Baer (2013)39 | Children with CAP | 2.6 (108) | 2.9 (107) | –0.3 (–1.1 to 0.5) |
| Esposito (2011)49 | Children with mild CAPb | 4.7 (2.88) (76) | 5.61 (1.99) (79) | –0.91 (–1.69 to –0.13) |
| Esposito (2011)49 | Children with severe CAPb | 5.01 (2.43) (79) | 5.93 (1.7) (76) | –0.92 (–1.58 to –0.26) |
| Duration of ICU stay (days) | ||||
| Stolz (2007)60 | Adults with COPD exacerbation | 3.3 (2.7) (102) | 3.7 (2.1) (106) | –0.40 (–1.06 to 0.26) |
| Hospital re-admission | ||||
| aDrozdov (2014)69 | Adults hospitalised with UTI | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed |
| Tang (2013)62 | Adults with suspected acute exacerbation of asthma | 5/128 | 8/127 | 0.64 (0.23 to 1.82) |
| Secondary ED visit | ||||
| Stolz (2007)60 | Adults with COPD exacerbation | 18/102 | 22/106 | 0.85 (0.49 to 1.48) |
| Tang (2013)62 | Adults with suspected acute exacerbation of asthma | 6/128 | 9/127 | 0.68 (0.26 to 1.79) |
| Antibiotic costs (US dollars) | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | Adults with suspected LRTI | 96.3 (172.8) (124) | 202.5 (250.6) (119) | –106.2 (–160.5 to –51.9) |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | Adults with CAP | 100 (33 to 186) (151) | 190 (133 to 337) (151) | NR |
FIGURE 16.
Duration of hospital stay for adults presenting to the ED.
Both of the studies39,49 conducted in children presenting to the ED with respiratory conditions assessed the effectiveness of including a PCT algorithm in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, and both reported data to allow the calculation of mean difference in the duration of hospital stay between study arms (see Table 6). When data from the subgroup of children with CAP from the Baer study39 were combined with the Esposito study49 the summary effect estimate indicated that the use of a PCT algorithm was associated with a small reduction in the duration of hospital stay (WMD –0.74 days, 95% CI –1.17 to –0.31 days) (Figure 17; this effect was reduced when a summary estimate was calculated using the whole population of both studies: WMD –0.62 days, 95% CI –1.18 to –0.07 days).
FIGURE 17.
Duration of hospital stay for children with CAP.

One ED study60 reported data on duration of ICU stay. 60 This study was conducted in adults with COPD exacerbations and assessed the effectiveness of adding a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment; there was no statistically significant difference in the mean duration of ICU stay between the study groups (mean difference –0.40, 95% CI –1.06 to 0.26).
Two studies,62,69 one assessing the effectiveness of adding a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment in adults with acute asthma exacerbations,62 and the other assessing the effectiveness of adding a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment in adults with UTI,69 reported hospital re-admission rates. Both studies62,69 found no statistically significant between-group difference in re-admission rates (see Table 6). Similarly, two studies,60,62 both assessing the effectiveness of adding a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment, in adults with acute asthma exacerbations62 and adults with COPD exacerbations,60 found no statistically significant between-group difference in the rate of secondary ED visits (see Table 6).
Two studies by Christ-Crain et al. ,42,44 both assessing the effectiveness including a PCT algorithm in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, reported that use of the PCT algorithm was associated with reductions in antibiotic costs (see Table 6). These findings are consistent with the reduced rate of antibiotic prescribing and mean duration of antibiotic therapy reported by these two studies, described above (see Antibiotic exposure).
Adverse clinical outcomes
All 10 studies conducted in ED settings39,42,44,49,55–57,60,62,69 reported data on at least one adverse clinical outcome. Five of these studies explicitly stated that they aimed to investigate whether the use of PCT in decision-making can reduce antibiotic exposure,39,42,57,60,69 and three studies further specified that they aimed to investigate whether a reduction in antibiotic exposures can be achieved without adversely affecting clinical outcomes. 42,57,60
Six studies reported all-cause mortality at various time points,42,44,55–57,60 ranging from 14 days to 6 months. The intervention arms of five of these studies42,44,55–57 used PCT algorithms in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, and in the remaining study60 only the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic therapy was considered. All studies42,44,55–57,60 reported no statistically significant difference in mortality rates between participants in the intervention group (antibiotic treatment decisions based on PCT algorithm plus clinical judgement) and those in the control group (antibiotic treatment decisions based on clinical judgement alone) (Table 7). When studies reported data for clinical subgroups (acute COPD exacerbations,44 and COPD exacerbations, CAP and acute bronchitis57), this finding was consistent across all subgroups (see Appendix 3.3). The summary RR derived from all six studies reporting mortality data42,44,55–57,60 was 0.95 (95% CI 0.71 to 1.27), I2 = 0% (Figure 18). When data from the two studies reporting follow-up (6 months) mortality56,60 were pooled the summary RR was 0.85 (95% CI 0.46 to 1.59).
| Study details | Population | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement alone | RR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients with event/no. of patients | No. of patients with event/no. of patients | |||
| All-cause mortality | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | Adults with suspected LRTI | 4/124 | 4/119 | 0.96 (0.27 to 3.46) |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | Adults with CAP | 18/151 | 20/151 | 0.9 (0.50 to 1.62) |
| Roh (2010)55 | Adults with CAP | 8/60 | 9/62 | 0.92 (0.39 to 2.17) |
| Roh (2013)56 | Elderly adults with CAP | 11/80 | 11/84 | 1.05 (0.49 to 2.24) |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | Adults with LTRI | 34/671 | 33/688 | 1.06 (0.66 to 1.68) |
| Stolz (2007)60 | Adults with COPD exacerbation | 5/102 | 9/106 | 0.6 (0.22 to 1.66) |
| ICU admission | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | Adults with suspected LRTI | 5/124 | 6/119 | 0.81 (0.27 to 2.46) |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | Adults with CAP | 20/151 | 21/151 | 0.95 (0.54 to 1.67) |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | Adults with LTRI | 43/671 | 60/688 | 0.74 (0.51 to 1.07) |
| Stolz (2007)60 | Adults with COPD exacerbation | 8/102 | 11/106 | 0.77 (0.33 to 1.79) |
| Infection relapse/recurrence | ||||
| aDrozdov (2014)69 | Adults hospitalised with UTI | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | Adults with LTRI | 25/671 | 45/688 | 0.57 (0.36 to 0.92) |
| Esposito (2011)49 | Children with CAP | 1/155 | 6/155 | 0.23 (0.04 to 1.34) |
| Antibiotic-related adverse events | ||||
| Schuetz (2009)57 | Adults with LTRI | 133/671 | 193/688 | 0.71 (0.58 to 0.86) |
| Baer (2013)39 | Children with LRTI | 56/168 | 57/169 | 0.99 (0.73 to 1.33) |
| Baer (2013)39 | Children with non-CAP LRTI | 14/60 | 6/62 | 2.30 (0.98 to 5.42) |
| Baer (2013)39 | Children with CAP | 42/60 | 51/62 | 0.85 (0.70 to 1.04) |
| Esposito (2011)49 | Children with CAP | 6/155 | 39/155 | 0.16 (0.07 to 0.37) |
| Other adverse clinical outcomes | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 Outcome definition Composite adverse outcome (death, recurrence, relapse, or persistence of clinical, laboratory, and radiological signs of CAP) |
Adults with CAP | 24/151 | 27/151 | 0.89 (0.54 to 1.46) |
| Schuetz (2009)57 Outcome definition Composite adverse outcome (death, ICU admission, recurrence, re-hospitalisation, or disease-specific complication) |
Adults with LTRI | 103/671 | 130/688 | 0.81 (0.64 to 1.03) |
| Stolz (2007)60 Outcome definition Need for steroids |
Adults with COPD exacerbation | 89/102 | 93/106 | 0.99 (0.9 to 1.1) |
| Tang (2013)62 Outcome definition Need for steroids (repeat need or dose increase) |
Adults with suspected acute exacerbation of asthma | 6/128 | 9/127 | 0.68 (0.26 to 1.79) |
| Tang (2013)62 Outcome definition Need for mechanical ventilation |
Adults with suspected acute exacerbation of asthma | 8/128 | 9/127 | 0.89 (0.36 to 2.17) |
| Baer (2013)39 Outcome definition Complications from pneumonia or other LRTI |
Children with LRTI | 38/168 | 33/169 | 1.16 (0.77 to 1.74) |
FIGURE 18.
All-cause mortality in adults presenting to the ED (any time point).
Neither of the two ED studies conducted in children39,49 reported mortality data.
Four studies42,44,57,60 reported data on rates of admission to the ICU. The intervention arms of three of these studies42,44,57 used PCT algorithms in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, and in the remaining study,60 only the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic therapy was considered. As was the case for all-cause mortality, all studies42,44,57,60 found no statistically significant between-group differences in ICU admissions (see Table 7) and this finding was consistent for clinical subgroups, when reported (see Appendix 3.3). 44 The summary RR derived from these four studies42,44,57,60 was 0.79 (95% CI 0.59 to 1.05) (Figure 19).
FIGURE 19.
Intensive care unit admission for adults presenting to the ED.
Neither of the two ED studies conducted in children39,49 reported any information on ICU admissions.
Two ED studies,57,69 conducted in adults, reported inconsistent results with respect to rates of infection relapse/recurrence. One study,69 conducted in adults hospitalised with UTI found no statistically significant difference in relapse/recurrence rates between participants in the intervention group (decision to discontinue antibiotics based on PCT algorithm plus clinical judgement) and those in the control group (decision to discontinue antibiotics based on clinical judgement alone) (see Table 7). The second study,57 conducted in adults with LRTI, found that inclusion of a PCT algorithm in both the information used to guide initiation and discontinuation of antibiotics was associated with a statistically significant reduction in infection relapse/recurrence rates (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.92) (see Table 7).
One ED study,49 conducted in children with CAP, reported very low rates of infection relapse/recurrence and a trend towards lower rates in the PCT group (RR 0.23, 95% CI 0.04 to 1.34) (see Table 7).
One ED study,57 conducted in adults with LRTI, reported numbers of participants experiencing antibiotic-related adverse events. This study57 found that including a PCT algorithm in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in antibiotic-related adverse events (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.58 to 0.86). This finding is consistent with the reduced rate of antibiotic prescribing and mean duration of antibiotic therapy reported by this study, described above (see Antibiotic exposure). 57
Both of the ED studies conducted in children reported numbers of participants experiencing antibiotic-related adverse events. 39,49 Results from the study by Esposito et al.,49 conducted in children with CAP, and from the subgroup of children with CAP from the study by Baer et al.,39 indicated that including a PCT algorithm in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in antibiotic-related adverse events (see Table 7). The summary RR derived from these two data sets was 0.37 (95% CI 0.04 to 3.49) (Figure 20; when data for all participants in both studies were included in the meta-analysis, the summary RR was 0.40 (95% CI 0.06 to 2.78).
FIGURE 20.
Antibiotic-related adverse events in children with CAP presenting to the ED.
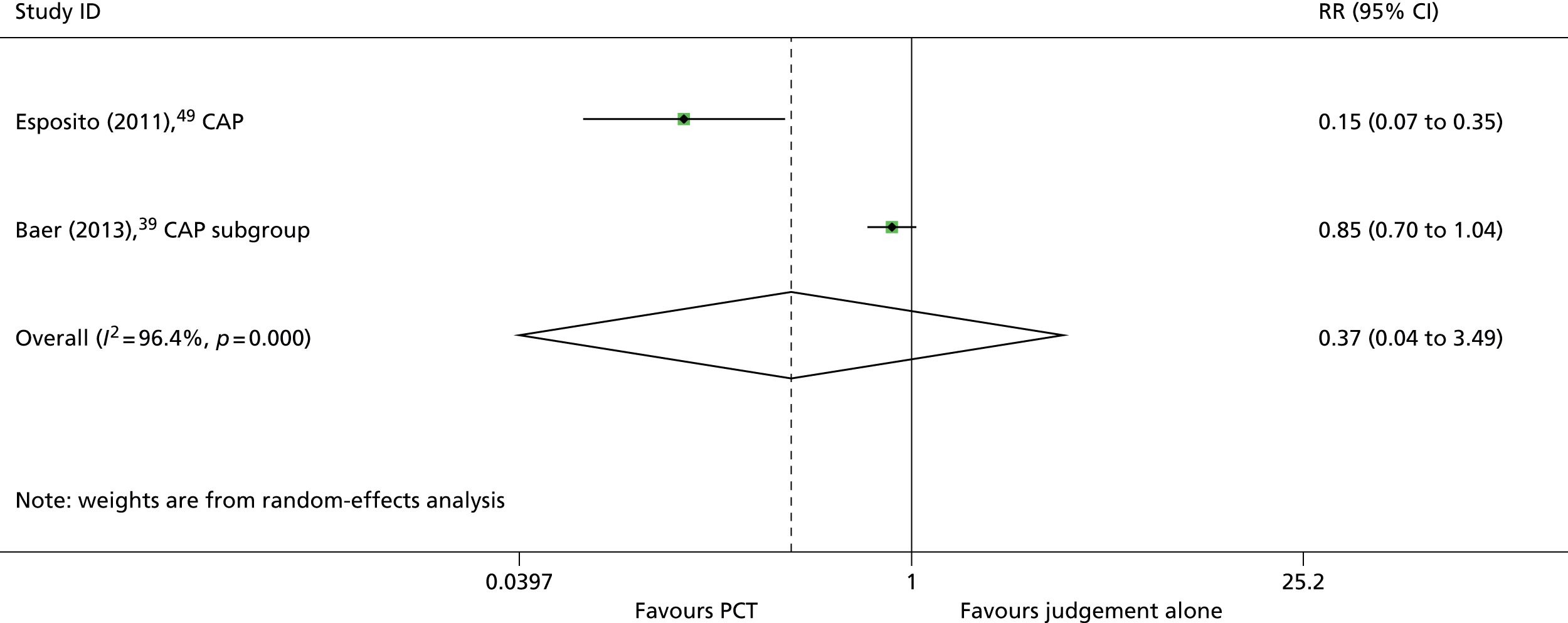
A variety of other general and disease-specific adverse clinical outcomes were reported by one or more studies (see Table 7). These included composite adverse outcome measures,42,57 need for steroids,57,62 need for mechanical ventilation,62 and complications from pneumonia. 39 No study reported a statistically significant difference between the intervention and comparator groups for any adverse clinical outcome assessed.
Chapter 4 Assessment of cost-effectiveness
This chapter explores the cost-effectiveness of adding PCT test results to the information available to clinicians treating (1) patients with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in intensive care settings and (2) patients presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infection. More specifically, the following research questions will be addressed:
-
In the ICU, does the addition of PCT testing to current clinical practice, to determine whether to initiate and when to discontinue antibiotic therapy, in adults and children with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis, who are being treated, represent a cost-effective use of NHS resources?
-
In the ED, does the addition of PCT testing to current clinical practice, to determine whether to initiate and when to discontinue antibiotic therapy, in adults and children presenting with suspected bacterial infection, represent a cost-effective use of NHS resources?
Review of economic analyses of procalcitonin assays
Search strategy
Searches were undertaken to locate relevant economic evaluations on adults and children presenting to or being treated at EDs and ICUs with sepsis or bacterial infection.
Economic evaluations
The following databases were searched for relevant studies from 2005 to August 2014:
-
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED) (Wiley): 2005 – Issue 3 of 4, July 2014.
-
Health Economic Evaluation Database (HEED) (Wiley): 2005 – 20 August 2014 (http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/book/10.1002/9780470510933).
-
IDEAS via Research Papers in Economics (REPEC) (internet): 2005 – 20 August 2014 (http://repec.org/).
-
EconLIT (EBSCOhost): 2005 – 20 August 2014.
Inclusion criteria
Studies reporting a full economic analysis, with (at least) one of the comparators including PCT testing and with survival and/or quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) as an outcome measure, were eligible for inclusion.
Quality assessment
Included studies were appraised using a quality checklist based on Drummond et al. 71
Results
The literature search identified 221 records from bibliographic database searches and supplementary searching (e.g. reference/citation checking, additional database searches including the database search for the assessment of clinical effectiveness). The studies identified through supplementary searching also included one potentially relevant unpublished paper sent by bioMérieux. After title and abstract screening, 21 records were considered to be potentially relevant and, after full text screening, two studies (three publications72–74) were considered eligible for inclusion (Figure 21). One study72,73 considered PCT testing for adult patients with acute respiratory tract infections (ARTIs) (outpatient setting) and one study74 considered PCT testing for adult patients with CAP (in-hospital setting). These studies are described in more detail below and summarised in Table 8. The results of the quality assessment are shown in Table 9.
FIGURE 21.
Flow chart (review of economic analyses). a, This includes one unpublished study (J Bagshaw, Clinical Strategic Marketing Manager bioMérieux UK Ltd, 2 October 2014, personal communication); b, reasons for exclusion: PCT-guided treatment was not considered as comparator (n = 9), PCT implementation study (n = 1), no comparison is performed (n = 1), cost-minimisation study (n = 6), cost-effectiveness study reporting other outcomes than QALYs and/or survival (n = 1).

| Michaelidis (2013)72,73 | Smith (2013)74 | |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Adult patients with ARTI | Patients with CAP (stratified for low- and high-risk patients) |
| Setting | Outpatient | In-hospital |
| Time horizon | ARTI treatment episode | Duration of the hospital stay |
| Objective | To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic therapy in outpatient management of ARTIs in adults | To estimate the cost-effectiveness of PCT protocols in CAP |
| Source of effectiveness information | Published literature | Published literature |
| Comparators | PCT-guided treatment vs. no PCT-guided treatment | PCT-guided treatment vs. no PCT-guided treatment |
| Unit costs | Antibiotic, PCT test and physician time costs | Antibiotic, PCT test and hospital stay costs |
| Main measure of benefit | Antibiotic prescriptions safely avoided and QALY | QALYs |
| Study type | Cost-effectiveness study (based on evidence synthesis) | Cost-effectiveness study (based on evidence synthesis) |
| Assumptions | It was assumed that patients with an elevated PCT were prescribed antibiotic. No differences in clinical outcomes between the strategies were assumed, as neither trial revealed significant differences in symptom duration, hospitalisation or death between usual care and PCT testing For the cost per QALY analysis, it was assumed that 15% of patients given antibiotic developed antibiotic-associated side effects (duration of 4 days) The utility values of the ARTI and antibiotic-associated side effect health states were assumed to be 1.0, 0.7 and 0.7, respectively |
No differences in-hospital length of stay, hospitalisation costs, or quality of life between PCT and no PCT were assumed |
| Perspective | Health care | Third-party payer |
| Discount rate | Not mentioned | Not mentioned |
| Uncertainty around cost-effectiveness ratio expressed | Yes, CEACs | Yes, CEACs |
| Sensitivity analysis | Yes, all parameter values are varied using one-way sensitivity analysis, and threshold analyses were performed | Yes, all parameter values are varied using one-way sensitivity analysis |
| Monetary outcomes | US$ | US$ |
| Outcomes per comparator | PCT vs. no PCT (analysis 1) Antibiotic prescriptions: 0.25 vs. 0.97 QALYs lost: 0.00746 vs. 0.00765 Costs: US$51 vs. US$29 PCT versus no PCT (analysis 2) Antibiotic prescriptions: 0.14 vs. 0.37 QALYs lost: 0.00743 vs. 0.00749 Costs: US$49 vs. US$15 |
PCT vs. no PCT QALYs: values not mentioned Costs: values not mentioned |
| Summary of incremental analysis | Analysis 1 PCT resulted in 0.72 less antibiotic prescriptions and additional costs of US$22 per patient, resulting in an ICER of US$31 per antibiotic prescription safely avoided. Moreover, PCT remained more expensive in all sensitivity analyses except when the antibiotic cost was > US$61 or the PCT testing cost was < US$17 (in which PCT became dominant). Furthermore, PCT resulted in 0.00019 QALYs gained leading into an ICER of US$118,828 per QALY gained Analysis 2 PCT resulted in 0.23 less antibiotic prescriptions and additional costs of US$34 per patient, resulting in an ICER of US$149 per antibiotic prescription safely avoided. Moreover, PCT remained more expensive in all sensitivity analyses except when the antibiotic cost was > US$61 or the PCT testing cost was < US$17 (in which PCT became dominant). Furthermore, PCT resulted in 0.00006 QALYs gained leading into an ICER of US$575,249 per QALY gained |
Estimated QALYs were not reported. Moreover, PCT-guided treatment was considered more costly (US$22 for low-risk patients using PCT for initiating antibiotic; US$10 for low-risk patients using PCT for antibiotic initiation and monitoring; and US$54 for high-risk patients using PCT for antibiotic initiation and monitoring). ICERs (calculated based on the PSAs) showed that PCT-guided antibiotic therapy is likely to be cost-effective for willingness-to-pay values of > US$90,000 per QALY for low-risk patients using PCT for initiating antibiotic only; US$40,000 per QALY when PCT is also used for monitoring antibiotic use for low-risk patients, and for high-risk patients this is US$170,000 per QALY (using PCT for both initiating antibiotic and monitoring antibiotic use). Results were most sensitive to variations in antibiotic cost, the likelihood that antibiotic therapy was initiated less frequently or over shorter durations, and the likelihood that physicians were non-adherent to PCT protocols |
| Michaelidis (2013)72,73 | Smith (2013)74 | |
|---|---|---|
| Study design | ||
| The research question is stated | ✓ | ✓ |
| The economic importance of the research question is stated | ✓ | ✓ |
| The viewpoint(s) of the analysis are clearly stated and justified | ✗ | ✗ |
| The rationale for choosing alternative programmes or interventions compared is stated | ✓ | ✓ |
| The alternatives being compared are clearly described | ✓ | ✓ |
| The form of economic evaluation used is stated | ✓ | ✓ |
| The choice of form of economic evaluation is justified in relation to the questions addressed | ✓ | ✓ |
| Data collection | ||
| The source(s) of effectiveness estimates used are stated | ✓ | ✓ |
| Details of the design and results of effectiveness study are given (if based on a single study) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Details of the methods of synthesis or meta-analysis of estimates are given (if based on a synthesis of a number of effectiveness studies) | NA | NA |
| The primary outcome measure(s) for the economic evaluation are clearly stated | ✓ | ✓ |
| Methods to value benefits are stated | ✗ | ✗ |
| Details of the subjects from whom valuations were obtained were given | ✗ | ✗ |
| Productivity changes (if included) are reported separately | NA | NA |
| The relevance of productivity changes to the study question is discussed | ✗ | ✗ |
| Quantities of resource use are reported separately from their unit costs | ✗ | ✓ |
| Methods for the estimation of quantities and unit costs are described | ✓ | ✓ |
| Currency and price data are recorded | ✓ | ✓ |
| Details of currency of price adjustments for inflation or currency conversion are given | NA | NA |
| Details of any model used are given | ✓ | ✓ |
| The choice of model used and the key parameters on which it is based are justified | ✗ | ✗ |
| Analysis and interpretation of results | ||
| Time horizon of costs and benefits is stated | ✓ | ✓ |
| The discount rate(s) is stated | NA | NA |
| The choice of discount rate(s) is justified | NA | NA |
| An explanation is given if costs and benefits are not discounted | ✗ | ✗ |
| Details of statistical tests and CIs are given for stochastic data | ✓ | ✓ |
| The approach to sensitivity analysis is given | ✓ | ✓ |
| The choice of variables for sensitivity analysis is justified | ✓ | ✓ |
| The ranges over which the variables are varied are justified | ✗ | ✓ |
| Relevant alternatives are compared | ✓ | ✓ |
| Incremental analysis is reported | ✓ | ✓ |
| Major outcomes are presented in a disaggregated as well as aggregated form | ✗ | ✗ |
| The answer to the study question is given | ✓ | ✓ |
| Conclusions follow from the data reported | ✓ | ✓ |
| Conclusions are accompanied by the appropriate caveats | ✗ | ✓ |
Michaelidis et al. 2013
The study by Michaelidis et al. 72,73 used a decision tree to analyse the cost-effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic therapy versus usual care for outpatient management of ARTIs in adults. Two separate analyses were performed using data from two European RCTs75,76 separately. The first analysis is based on a study published by Briel et al. ,75 which considered all adults presenting to an outpatient clinic with an ARTI and judged by their physicians to require an antibiotic prescription. The second analysis was based on a study published by Bukhardt et al. ,76 which included all adults presenting to an outpatient clinic with an ARTI prior to any decision to initiate antibiotic therapy. PCT-guided antibiotic therapy was both more costly and more effective than care as usual without PCT-guided treatment (see Table 8) leading to incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) of US$118,828 and US$575,249 per QALY gained for the first and second analyses, respectively.
Michaelidis et al. 73 also estimated the costs of antibiotic resistant infections attributable to an antibiotic prescription. It was estimated that these costs per antibiotic prescription (in the outpatient setting for management of ARTIs in adults) would range between US$0 and US$333 with a base-case value of US$43. These estimated costs of antibiotic resistance are not used in the economic evaluation. It is argued by the authors that these costs can be used as the willingness-to-pay per antibiotic prescription safely avoided and hence that PCT-guided antibiotic therapy would be cost-effective for adults presenting to an outpatient clinic with an ARTI and judged by their physicians to require an antibiotic prescription (probability of being cost-effective: 58%). Using this threshold PCT-guided antibiotic therapy would not be considered cost-effective for all adults presenting to an outpatient clinic with an ARTI prior to any decision to initiate antibiotic therapy (probability of being cost-effective: 3%).
Smith et al. 2013
The cost-effectiveness analysis by Smith et al. 74 (see Table 8) used a decision tree to estimate the cost-effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic therapy versus usual care in CAP. The analysis considered low-risk CAP patients [Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) risk class of ≤ 3, or a CURB-65 score of ≤ 2 (CURB-65 is an acronym for five risk factors: confusion of new onset; blood urea nitrogen; respiratory rate; blood pressure; and aged ≥ 65 years)] and high-risk CAP patients (PSI risk classes 4 or 5, or CURB-65 scores of ≥ 3). The base-case analysis assumed no differences in clinical outcomes or hospital length of stay between the treatment strategies. This assumption was relaxed in the probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) (using a disutility of 0.2 for hospitalisation). This analysis indicated that PCT-guided antibiotic therapy is both more costly and effective than care without PCT-guided treatment and is likely to be cost-effective for willingness-to-pay values of > US$90,000 per QALY for low-risk patients using PCT for initiating antibiotic only, US$40,000 per QALY when PCT is also used for monitoring antibiotic use for low-risk patients, and for high-risk patients this is US$170,000 per QALY (using PCT for both initiating antibiotic and monitoring antibiotic use).
Quality assessment and summary of studies in the cost-effectiveness review
Both studies72–74 used a short-term decision tree to assess the cost-effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic treatment compared with usual care for adults patients with ARTI (outpatient setting) and CAP (in-hospital setting), respectively. Quality assessment of the cost-effectiveness studies revealed caveats in justifications for choices that had been made (e.g. the viewpoint taken, choice of key parameters, exclusion of discounting and ranges for the PSA) and the description of the benefit valuation. Moreover, Smith et al. 74 did not report outcomes per comparator or incremental QALYs (see Table 9). The results of both cost-effectiveness studies indicated that PCT-guided treatment was more expensive than care as usual (incremental costs ranged between US$10 and US$54). Moreover, both analyses estimated higher QALYs for PCT-guided antibiotic treatment. For the study by Michaelidis et al. ,72,73 this was probably due to a difference in antibiotic treatment duration and hence a difference in the duration of the disutility for antibiotic-associated side effects (estimated based on the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions77). Although Smith et al. 74 did not report the estimated QALYs, their analyses were likely to have estimated a QALY gain for PCT-guided treatment (given that PCT-guided treatment was more expensive and the ICERs were positive) due to a shorter hospital stay for PCT-guided treatment (disutility during hospital stay was based on the Health and Activities Limitation Index; HALex78). In conclusion, depending on the setting, specific use of PCT tests (i.e. for initiating antibiotic and/or monitoring antibiotic use) and the patient population considered, the ICERs found in the literature ranged between US$40,000 and US$575,249 per QALY gained.
Overview of potentially relevant excluded studies
In addition to the included studies described above, seven potentially relevant studies42,45,79–83 that compared PCT testing with no PCT testing were excluded, as they were either cost-minimisation studies42,45,79–82 or a cost-effectiveness analysis83 using other outcomes than survival or QALYs. For completeness, an overview of these studies is provided in Table 10.
| Study details | Deliberato (2013)45 | Diez-Padrisa (2012)79 | Wilke (2011)80 | Heyland (2011)81 | Cleves (2010)83 | Christ-Cain (2006)42 | Schuetz (2015)82 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | Adult patients with microbiologically confirmed infections with sepsis, severe sepsis or septic shock | Hospitalised children with clinical severe pneumonia | Sepsis patients | Critically ill adult patients with infection | Adult patients admitted to the hospital with LRTI | Adult patients with suspected CAP | Patients with suspected ARTI |
| Setting | ICU | In-hospital | ICU | ICU | In-hospital | ED | Inpatient hospital setting (not in the ICU); ICU; outpatient clinic or ED |
| Time horizon | From 2 days before sepsis diagnosis until 14 days after, or after ICU discharge | Diagnosis only | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned (probably in-hospital period) | Up to 6 weeks | Based on the clinical studies included in the meta-analytic data, the costs and outcomes of each ARTI episode is assessed over a 30-day period Total costs and events are annualised based on the incidence of each condition and likelihood of treatment success and intensity |
| Objective | To assess whether a decrease in PCT levels could be used to reduce the duration of antibiotic therapy in ICU patients with a proven infection without risking a worse outcome | To evaluate the benefits of using PCT and CRP as prescreening tools to predict blood culture positivity among Mozambican children with clinical severe pneumonia | To determine possible savings in medication costs and costs for ICU treatment using DRG data and favourable effects of a PCT-based treatment algorithm in patients with sepsis | To evaluate the effect of a PCT-guided antibiotic strategy on clinical and economic outcomes | To analyse the cost-effectiveness of PCT to identify bacterial infection in LRTI | To assess PCT guidance for the initiation and duration of antibiotic therapy in CAP | To assess the economic impact of adopting PCT testing among patients with suspected ARTI |
| Source of effectiveness information | Prospective randomised trial conducted in the ICU of a tertiary care, private hospital in São Paulo, Brazil | Clinical trial | German national minimal basic data sets and published literature | Published literature | Published literature | Randomised, controlled, open intervention trial | Patient-level meta-analysis data of randomised trials |
| Comparators | PCT-guided treatment vs. no PCT-guided treatment | PCT-guided treatment vs. no PCT-guided treatment | PCT-guided treatment vs. no PCT-guided treatment | PCT-guided treatment vs. no PCT-guided treatment | PCT-guided treatment vs. no PCT-guided treatment | PCT-guided treatment (n = 151) vs. no PCT-guided treatment (n = 151) | PCT-guided treatment vs. no PCT-guided treatment |
| Unit costs | Antibiotic treatment and PCT costs | Blood cultures measurement and PCT costs | ICU costs, treatment on the regular ward, main treatment-related costs (e.g. surgery or cardiological interventions) All costs were based on DRGs |
Antibiotic treatment, intravenous administration and PCT test costs PCT costs (US$49.42 per test) include assay material, reagents, technician time, purchase, maintenance of a bench top analyser, and overhead |
Antibiotic and PCT test costs | Antibiotic treatment and PCT costs (including assay material, reagents, technicians’ time for processing specimens, and purchase and maintenance of durable laboratory equipment) | Antibiotic treatment, PCT costs and costs attributable to antibiotic resistance |
| Main measure of benefit | Duration of antibiotic therapy; ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay | No outcomes besides diagnostic accuracy | No benefits are considered | Duration of antibiotic utilisation, hospital mortality, 28-day mortality, ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, recurrent or relapsing infections | Correctly treated cases (with antibiotic) | Antibiotic use, measures of laboratory and clinical outcome recorded on days 4, 6 and 8 and at follow-up after 6 weeks | No benefits are considered |
| Study type | Cost-minimisation study [trial-based using the per-protocol analysis patient group (n = 51)] | Cost-minimisation study (trial based) | Cost-minimisation study (based on evidence synthesis) | Cost-minimisation study (based on evidence synthesis) | Cost-effectiveness study (based on evidence synthesis) | Cost-minimisation study (trial based) | Cost-minimisation study (based on evidence synthesis) |
| Assumptions | NA | NA | NA | NA | To use a single value (76%) for both sensitivity and specificity; moreover, it is assumed that doctors prescribe antibiotic based on the PCT test alone | NA | It was assumed that the mean baseline number of antibiotic days corresponds to the average length of stay for a typical hospitalisation Physician time associated with interpreting the PCT test was not included in the model because the associated costs have been found to be negligible |
| Perspective | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Hospital perspective | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | US payer perspective |
| Discount rate | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned |
| Uncertainty around cost-effectiveness ratio expressed | NA | NA | NA | NA | No | NA | NA |
| Sensitivity analysis | No | Yes, different costs for PCT testing | No | Yes, assuming different antibiotic costs | Yes, different sensitivity and specificity values, LRTI prevalence and antibiotic costs | Yes, assuming different antibiotic and PCT costs and assuming less than 3.5 PCT measures (base-case value) per patient | Yes, one-way sensitivity analyses (± 20% for key parameters) and lowering the antibiotic initiation rate |
| Monetary outcomes | US$ | US$ | € | CAN$ | £ | US$ (converted from CHF) | US$ |
| Outcomes per comparator | PCT vs. no PCT Duration of antibiotic therapy: 9.0 vs. 13.0 days ICU length of stay: 3.5 vs. 4.0 days Hospital length of stay: 10.5 vs. 14.0 days Costs: US$977.40 vs. US$1367.65 |
PCT vs. no PCT Costs: US$60–67 vs. US$72.5 (PCT test cost = US$30) Costs: US$40–47 vs. US$72.5 (PCT test cost = US$10) |
PCT vs. no PCT ICU costs: €17,940 vs. €18,826 Non-ICU costs: €6084 vs. €6220 |
PCT vs. no PCT Mean differences for duration of antibiotic utilisation, ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay are –2.14,a –1.50 and –1.86, respectively RRs for hospital mortality, 28-day mortality and recurrent or relapsing infections are 1.06, 0.98 and 1.26, respectively Costs: US$2597.94 vs. US$3068.56 |
PCT vs. no PCT Correctly treated: 76% vs. 34% Costs: £35.72 vs. £14.30 |
PCT vs. no PCT Antibiotic was withheld on admission for 15% vs. 1% The antibiotic discontinuation was higher in the PCT group (HR 3.2a) Antibiotic duration: 5 vs. 12 days Costs: US$290 vs. US$190 |
PCT vs. no PCT Costs: Inpatient hospital setting: US$416 vs. US$555 ICU: US$616 vs. US$755 Outpatient clinic and ED: US$105 vs. US$204 Weighted average: US$977 vs. US$1368 per patient (all calculated based on table 5 retrieved from this paper) |
| Summary of incremental analysis | PCT resulted in savings of US$388.25 per patient No incremental cost-effectiveness analyses are presented |
PCT lowered overall diagnosis costs by US$5.5–12.5 (PCT test cost = US$30) and US$25.5–32.5 (PCT test cost = US$10) per patient No incremental cost-effectiveness analyses are presented |
PCT resulted in savings of €886 (ICU) and €136 (non-ICU) per patient No incremental cost-effectiveness analyses are presented |
PCT resulted in savings of US$470.62 per patient. This was US$1134.86 if more expensive antibiotic would be used while cheaper antibiotic would result in PCT becoming US$193.64 more expensive than no PCT No incremental cost-effectiveness analyses are presentedb |
PCT resulted in additional costs of £21.42 per patient (despite lower antibiotic costs) and yielded 42% extra patients that are correctly treated with antibiotic. This resulted in an ICER of £51 per additional % of correctly treated patients. This varied between £45 and £120 in the sensitivity analyses | PCT resulted in additional costs of US$100 per patient (despite lower antibiotic costs); PCT would be cost-saving if the PCT costs are < US$25 No incremental cost-effectiveness analyses are presented |
PCT resulted in savings of US$103 per patient (weighted average calculated based on table 5 retrieved from this paper). PCT remained cost-saving in the sensitivity analyses (it was most sensitive to antibiotic costs) No incremental cost-effectiveness analyses are presented |
As was the case for the two cost-effectiveness analyses included in the review, the studies described in Table 10 were focused on short-term costs (and benefits). The comparison was PCT-guided treatment versus non PCT-guided treatment in all studies, and considered (adult) patients with sepsis in the ICU,45,80,81 hospitalised children with pneumonia,79 adult patients admitted to the hospital with LRTI,83 adult patients with suspected CAP admitted to the ED,42 and patients with suspected ARTI in three different settings. 82 In contrast with the two full economic evaluations included in the review, the cost-minimisation studies in the more severe populations (sepsis, ARTI and pneumonia) reported cost-savings when using PCT-guided treatment,45,79–82 whereas the two studies42,83 that focused on adult patients admitted to the hospital with LRTI83 and adult patients with suspected CAP presenting to the ED42 report additional costs when using PCT-guided treatment. The cost-effectiveness analysis by Cleves et al. 83 reported, for patients with LRTI, an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of £51 per additional percentage of correctly treated patients with antibiotics.
Review of health-related quality-of-life studies
Search strategy
Searches were undertaken to locate relevant utility value studies on adults and children with sepsis or bacterial infection presenting to, or being treated at, EDs and ICUs.
Utility values
The following databases were searched for relevant studies from database inception date to September 2014:
-
MEDLINE (OvidSP): 1946 – August Week 3 2014.
-
MEDLINE In-Process Citations & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily Update (OvidSP): up to 2 September 2014.
-
EMBASE (OvidSP): 1974 to 2 September 2014.
-
CENTRAL (Wiley): up to Issue 8 of 12, August 2014.
-
HTA database (Wiley): up to Issue 3 of 4, July 2014.
-
PubMed (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed): up to 3 September 2014.
-
PROQOLID (internet) (www.proqolid.org/): up to 3 September 2014.
Inclusion criteria
Studies reporting on health-related quality of life (HRQoL), in terms of utility scores, for patients with confirmed/highly suspected sepsis in intensive care settings or patients presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infection, were eligible for inclusion.
Results
The literature search identified 476 records (472 through database searches and four through supplementary searching). After title and abstract screening, 82 potentially relevant records were identified and after full text screening nine studies (10 papers84–93) were considered eligible for inclusion (Figure 22). This included one study84 conducted for paediatric patients at the ED, one study85 conducted in a paediatric ICU and six studies conducted in adult patients at the ICUs. 86–92 Moreover, for one study93 (abstract only) the specific setting (other than in-hospital) was not stated but the study was likely to have been conducted in an ICU setting, as it included patients with severe sepsis of presumed infectious origin; we have therefore assumed that this study was conducted in an ICU setting. The HRQoL studies are described in more detail below and summarised in Appendix 6.
FIGURE 22.
Flow chart (review of HRQoL studies). a, Reasons for exclusion: duplicate (n = 1), protocol (n = 1), no original/relevant utility data reported (n = 63), wrong setting/population (n = 7).

Adult intensive care unit
All seven studies86–93 that considered adult patients with sepsis, who were being treated in the ICU, used the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) to elicit utility scores. Only one93 of these studies (abstract only) reported short-term utility scores for a sepsis patient group (n = 93) that stayed in hospital (56% of the patients were in the hospital at day 30). This study93 reported utility values for 30, 60, 90 and 180 days after admission of 0.53, 0.62, 0.68 and 0.69, respectively. Long-term follow-up utility values found in the literature were 0.8489 and 0.6792 at 6 months, 0.7590 at 1.4 years, 0.7291 at 2 years, 0.6488 at 3.5 years and 0.6888 at 5 years. One study reported a utility value of 0.6886,87 for patients 1 year or later after discharge. The long-term utility values varied substantially between studies. These differences between the studies may be caused by context related factors (e.g. patient mix, countries and valuation functions). Studies with longitudinal data tended to show an increasing utility score over time (i.e. positive correlation between utility score and time since ICU admission). The Scottish study by Cuthbertson et al. 88 probably provides the most representative long-term utilities for the UK population (0.64 at 3.5 years and 0.68 at 5 years).
With regard to the long-term impact of sepsis ICU admission on HRQoL, the Finnish study by Karlsson et al. 90 concluded [based on the intention-to-treat (ITT) population] that there is a long-term utility decrement attributable to sepsis ICU admission, as the utility value at 17 months was lower than utility values measured before sepsis. It should be noted, however, that in most cases the first questionnaire (at the ICU considering HRQoL before acute critical illness) was filled out by a next of kin.
Paediatric intensive care unit
A Dutch study85 measured long-term HRQoL (median follow-up interval: 10 years) using the Health Utilities Index (HUI) in patients who experienced meningococcal septic shock and were admitted to the paediatric ICU (median age at admission: 3 years). The utility values reported by the respondents (n = 120) were 0.82 [Health Utilities Index Mark 3 (HUI3)] and 0.88 [Health Utilities Index Mark 2 (HUI2)], and were considered to be lower than those of a representative sample of 1435 Dutch school children aged between 5 and 13 years (HUI2 0.93 and HUI3 0.94).
Paediatric emergency department
In a study conducted in the USA,84 a total of 94 parents who presented at the paediatric ED with their children (aged between 3 and 36 months) were asked to elicit utility values to eight health state descriptions for their children using the standard gamble method. These health states and their valuations were death (0.02), meningitis with severe brain damage (0.39), meningitis with minor brain damage (0.74), meningitis with deafness (0.86), meningitis with recovery (0.98), hospitalisation for antibiotic (0.99), local infection (0.99), and blood drawn (1.00). It was concluded that extremely high utility values were found for health states without permanent sequelae (blood drawn, local infection, hospitalisation for antibiotic, and meningitis with recovery).
Model structure and methodology
Model structure
In a de novo health-economic analysis (in Microsoft Excel 2010), in accordance with the published protocol for this assessment (PROSPERO registration number CRD42014010822), PCT testing in addition to current clinical practice was compared with current clinical practice without PCT testing for: (1) adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in an ICU setting (2) adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED; (3) children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED. Children with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in an ICU setting were not considered because of the lack of data.
As shown in Figures 23 and 24, the structure of the decision tree starts with one decision node that denotes the use of PCT or current clinical practice without PCT. The key end points are (1) alive with antibiotic-related complications; (2) alive without antibiotic-related complications; and (3) death. It is important to notice that treatment initiation was explicitly incorporated in only the ED setting (see Figure 24). This is because PCT testing is mainly expected to be used to discontinue antibiotic therapy in the ICU setting (all patients with sepsis in the ICU are treated with antibiotics), whereas in the ED setting it is expected to be used to initiate antibiotics. This is reflected in the trials included in Chapter 3. What this means for parameter estimation is that, for the ED setting only, parameters are required to estimate both the probability of initiation and the duration of antibiotic use conditional on initiation. For the ICU setting, only parameters for duration of antibiotic use are required (see resource use and costs in Chapter 4, Model parameters).
FIGURE 23.
Decision tree for the ICU setting. a, Antibiotic-related complications are included in the model through a disutility for the duration of antibiotic treatment.

FIGURE 24.
Decision tree for the ED setting. a, Antibiotic-related complications are included through a disutility for the duration of antibiotic treatment.

The time horizon is 6 months (183 days), divided into an initial short-term (28 days) phase and a subsequent phase lasting 155 days (see Figures 23 and 24). The 6 months’ time horizon and the initial phase of 28 days were adopted to be consistent with the outcomes reported in the studies identified in Chapter 3 of this report. The mean expected costs, life-years (LYs), duration of antibiotic treatment and QALYs are calculated separately for both strategies.
Model parameters
Estimates for the input parameters were mainly retrieved through systematic literature searches and meta-analyses that are described in this assessment (see Results of the assessment of clinical effectiveness assessment, above, for mortality and resource-use parameters, and Chapter 4, Review of health-related quality of life studies, for utility values).
Given the variation within the patient groups of interest (see Results of the assessment of clinical effectiveness assessment/study details, above), a ‘lower clinical extreme’ and a ‘higher clinical extreme’ is specified for each population and setting (i.e. children in ED, adults in ED and adults in ICU). For these ‘clinical extremes’, different baseline values (based on selected studies) are used for mortality, duration of antibiotic therapy, probability of initiation of antibiotic treatment (ED setting only), length of hospital stay and/or length of ICU stay while applying the same RR or mean difference estimates for both clinical extremes (derived from the meta-analyses in Results of the assessment of clinical effectiveness assessment, above).
All-cause mortality
The assessment of clinical effectiveness (see Results of the assessment of clinical effectiveness assessment, above) was the primary input for the baseline probabilities and RRs used for the economic evaluation. Whenever a meta-analysis over the results of the identified studies was not possible, the most plausible source was chosen. This was based on two criteria: (1) compatibility with the population in the given scenario (low risk vs. high risk) and (2) availability of data for relevant outcomes.
Table 11 gives an overview of the selected sources used for the baseline mortality probabilities for each of the populations and the justifications for each of the choices. Table 12 gives an overview of the baseline mortality probabilities and mortality RRs used.
| Population | Clinical extremes | Study selected | Main population | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children ED population | Lower | National mortality rates94 | Children with LRTI | Mortality rates were not available from the identified studies. Personal communication with experts has indicated that mortality rates for children ED are close to zero (ref 5/11/2014) and therefore NATIONAL background mortality rates assumed. The average age was considered equal to that of control group in Baer (2013)39 (i.e. 3-year-old children) |
| Children ED population | Higher | National mortality rates94 | Children with CAP | Mortality rates were not available from the identified studies. Personal communication with experts (Enitan Caroll, Professor in Paediatric Infection, University of Liverpool, 5 November 2014) has indicated that indeed mortality rates for children ED are close to zero and therefore national background mortality rates assumed. The average age was considered equal to that of control group in Esposito (2011)49 (i.e. 5-year-old children) |
| Adults ED population | Lower | Christ-Crain (2004)44 for 28-day probability and Roh (2013)56 for baseline 6 months’ probability | Adults with suspected LRTI | Christ-Crain (2004)44 was selected among the least severe end of the range, given the availability of data on all parameters Roh (2013)56 was selected based on the fact that the data extend to 6 months and other 6-month follow-up studies such as Stolz (2007)60 seem inconsistent (i.e. too low 6-month probabilities) compared with the 28-day probabilities from Christ-Crain (2004)44 |
| Adults ED population | Higher | Christ-Crain (2006)42 for 28-day probability and Roh (2013)56 for baseline 6 months’ probability | Adults with CAP | Christ-Crain (2006)42 was selected among the most severe end of the range, given the availability of data on all parameters Roh (2013)56 was selected on the fact that the data extend to 6 months and other 6-month follow-up studies such as Stolz (2007)60 seem inconsistent (i.e. too low 6-month probabilities) compared with the 28-day probabilities from Christ-Crain (2006)42 |
| Adults ICU population | Lower | Bouadma (2010)41 for 28 days; 6 months’ conditional probability (after 28 days) assumed equal to ED probability | Adults with suspected bacterial infection | Bouadma (2010)41 was the only study available for 28 days’ follow-up The 6 months’ conditional (after being alive at 28 days) probability was assumed equal to the 6 months’ probability for ED conditional on being alive at 28 days |
| Adults ICU population | Higher | Qu (2012);54 6 months’ conditional probability (after 28 days) assumed equal to ED probability | Adults with suspected bacterial infection and no clear source of infection | Qu (2012)54 was chosen as it has a follow-up of 28 days, refers to patients with sepsis or septic shock, and has the highest mortality probabilities The 6 months’ conditional (after being alive at 28 days) probability was assumed equal to the 6 months’ probability for ED conditional on being alive at 28 days |
| Parameter | Period | Estimate | SE/(95%CI) | Distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline probability for all-cause mortality | |||||
| Children in ED Lower clinical extreme | 28 days | < 0.001 | – | Fixed | ONS (2014)94 |
| Children in ED Lower clinical extreme | 6 months | < 0.001 | – | Fixed | |
| Children in ED Higher clinical extreme | 28 days | < 0.001 | – | Fixed | |
| Children in ED Higher clinical extreme | 6 months | < 0.001 | – | Fixed | |
| Adults in ED Lower clinical extreme | 28 days | 0.062 | 0.015 | Beta | Christ-Crain (2004)44 |
| Adults in ED Lower clinical extreme | 6 months | 0.121 | 0.034 | Beta | Roh (2013)56 |
| Adults in ED Higher clinical extreme | 28 days | 0.072 | 0.543 | Beta | Christ-Crain (2006)42 |
| Adults in ED Higher clinical extreme | 6 months | 0.121 | 0.034 | Beta | Roh (2013)56 |
| Adults in ICU Lower clinical extreme | 28 days | 0.169 | 0.019 | Beta | Bouadma (2010)41 |
| Adults in ICU Lower clinical extremea | 6 months | 0.222 | 0.043 | Beta | Bouadma (2010),41 Christ-Crain (2004)44 Roh (2013)56 |
| Adults in ICU Higher clinical extreme | 28 days | 0.182 | 0.384 | Beta | Qu (2012)54 |
| Adults in ICU Higher clinical extremea | 6 months | 0.225 | 0.064 | Beta | Christ-Crain (2006),42 Qu (2012),54 Roh (2013)56 |
| RR for all-cause mortality | |||||
| Children in ED | 28 days | 0.950 | (0.710 to 1.270) | Log-normal | Meta-analysis |
| Children in ED | 6 months | 0.950 | (0.710 to 1.270) | Log-normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ED | 28 days | 0.980 | (0.710 to 1.360) | Log-normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ED | 6 months | 0.850 | (0.450 to 1.590) | Log-normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ICU | 28 days | 0.980 | (0.760 to 1.270) | Log-normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ICU | 6 months | 0.980 | (0.760 to 1.270) | Log-normal | Meta-analysis |
Adverse events
Antibiotic-related adverse events were incorporated through the time on antibiotic treatment (using a disutility for being on antibiotic treatment), as antibiotic-related adverse events were mostly reported as a compound end point instead of the individual adverse events. No differences in disease-specific complications were found between the intervention and comparator groups for any adverse clinical outcome assessed (see Effectiveness of adding procalcitonin testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy for the treatment of confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in intensive care unit settings, above). Moreover, disease-specific complications were also reported as a compound end point, making it difficult to incorporate these complications using complication-specific disutilities. Therefore, the disease-specific complications were not included and thus assumed to be equal for the comparators.
Health-state utilities
The systematic review of HRQoL studies (see Chapter 4, Review of health-related quality of life studies) was used as input for utility values for the economic evaluation (Table 13). For adults being treated in the ICU, a utility of score of 0.53 was used for the decision tree period, whereas a utility of 0.68 was used for the period thereafter (both retrieved from Drabinksi et al.,93 the only study with short-term utility values). In a scenario analysis the utility value of 0.68 was replaced with the 3.5-year utility value of 0.64 from Cuthbertson et al. ,88 which was judged to provide the most representative long-term utilities for the UK population.
| Estimate | Se | Distribution | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base utility up to 28 days | ||||
| Adults in the ICU | 0.53 | 0.01a | Beta | Drabinski (2001)93 |
| Adults in the ED (Wales) | 0.68 | 0.02 | Beta | Oppong (2013)77 |
| Adults in the ED (England) | 0.74 | 0.02 | Beta | Oppong (2013)77 |
| Adults in the ED (weighted) | 0.70 | b | ||
| Children on the ED | 0.99 | 0.00 | Beta | Bennett (2000)84 |
| Base utility up to 6 months | ||||
| Adults in the ICU | 0.68 | 0.01a | Beta | Drabinski (2001)93 |
| Adults in the ICU (sensitivity analysis) | 0.64 | 0.04 | Beta | Cuthbertson (2013)88 |
| Adults in the ED (Wales) | 0.83 | 0.02 | Beta | Oppong (2013)77 |
| Adults in the ED (England) | 0.89 | 0.02 | Beta | Oppong (2013)77 |
| Adults in the ED (weighted) | 0.86 | b | ||
| Children in the ED | 0.99 | 0.01a | Beta | Bennett (2000)84 |
| Disutility | ||||
| Disutility for antibiotic-related adverse events | 0.05 | 0.00a | Normal | Oppong (2013)77 |
No utility values for adults presenting to the ED with suspected infection were identified in the systematic review of HRQoL studies. Therefore, this utility value was retrieved from Oppong et al. ,77 which estimated a utility value (EQ-5D) for adults presenting to their primary care clinician with LRTI. The baseline and 4-week utility values reported in this study were used to calculate a weighted average (based on the number of patients per utility estimation) for England and Wales for the initial 28 days’ decision tree period (0.70) and thereafter (0.86).
For children presenting to the ED, a constant base utility of 0.99 was assumed (utility for local infection) from Bennett et al. 84 (only study available).
To incorporate antibiotic-related adverse events in adults being treated in the ICU, a disutility of 0.046 for being on antibiotic treatment was taken from Oppong et al. 77 (weighted average for England and Wales). Although this disutility might be higher for people being treated in the ICU, due to the intravenous route of administration, it was conservatively assumed that this disutility is equal for all settings and populations. Moreover, it was conservatively assumed that there is no disutility for staying in hospital.
Resource use and costs
Resource use consisted of duration of hospital stay (days), ICU stay (days) and antibiotic treatment duration (days). The estimates were retrieved from studies identified in the systematic review. The same criteria, as described above for the probabilities and RRs, are used to choose a study for a specific input parameter.
For the ED, antibiotic duration was calculated based on the probability of initiation of antibiotic treatment and the duration of antibiotic treatment conditional on that antibiotic treatment having been initiated, i.e. the mean from the studies excluding those patients with zero use. For the ICU, it was assumed that antibiotics were initiated for all patients and thus the antibiotic treatment duration mean for the whole sample from the studies was used.
The studies chosen for baseline resource use and the accompanying justification are given in Table 14. The resource-use parameters are given in Table 15.
| Population | Clinical extremes | Study selected | Main population | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children ED population | Lower | Baer (2013)39 except for length of ICU stay | Children with LRTI | Non-CAP LRTI subgroup from Baer (2013)39 selected as the low risk Length of ICU stay taken from Stolz (2007),60 as it is the only study reporting this |
| Children ED population | Higher | Esposito (2011)49 except for antibiotic duration and length of ICU stay | Children with CAP | Esposito (2011)49 selected as a study representing the high risk population The CAP subgroup from Baer (2013)39 was selected for antibiotic duration and antibiotic treatment initiation (not provided in Esposito 201149) Length of ICU stay taken from Stolz (2007)60 as it is the only study reporting this |
| Adults ED population | Lower | Christ-Crain (2004)44 except for length of ICU stay | Adults with suspected LRTI | Christ-Crain (2004)44 was selected among the least severe end of the range given the availability of data on all parameters Stolz (2007)60 was chosen length of ICU stay as it is the only study available |
| Adults ED population | Higher | Christ-Crain (2006)42 except for length of ICU stay | Adults with CAP | Christ-Crain (2006)42 was selected among the most severe end of the range, given the availability of data on all parameters Stolz (2007)60 was chosen for length of ICU stay, as it is the only study available |
| Adults ICU population | Lower | Bouadma (2010)41 | Adults with suspected bacterial infection | Bouadma (2010)41 was the only study available for 28 days’ follow-up |
| Adults ICU population | Higher | Qu (2012)54 and Annane (2013)37 | Adults with suspected bacterial infection and no clear source of infection | Qu (2013)54 was chosen as the study reporting the highest duration of antibiotic therapy Annane (2013)37 was chosen based on availability of parameters and inclusion of people with apparent septic shock |
| Parameter | Estimate | SE/(95% CI) | Distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline duration of antibiotic therapy | ||||
| Children in ED Lower clinical extreme (conditional on initiation of antibiotic therapy) | 9.600 | 35.588 | Gamma | Baer (2013)39 |
| Children in ED Higher clinical extreme (conditional on initiation of antibiotic therapy) | 11.512 | 59.962 | Gamma | Baer (2013)39 |
| Adults in ED Lower clinical extreme (conditional on initiation of antibiotic therapy) | 15.386 | 55.634 | Gamma | Christ-Crain (2004)44 |
| Adults in ED Higher clinical extreme (conditional on initiation of antibiotic therapy) | 13.073 | 54.478 | Gamma | Christ-Crain (2006)42 |
| Adults in ICU Lower clinical extreme | 9.900 | 7.100 | Gamma | Bouadma (2010)41 |
| Adults in ICU Higher clinical extreme | 16.060 | 0.413 | Gamma | Qu (2012)54 |
| Mean difference in duration of antibiotic therapy | ||||
| Children in ED (conditional on initiation of antibiotic therapy) | –3.908 | 123.397 | Normal | aBaer (2013)39 |
| Adults in ED (conditional on initiation of antibiotic therapy) | 1.476 | 7.710 | Normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ICU | 3.190 | 1.145 | Normal | Meta-analysis |
| Baseline probability for antibiotic initiation | ||||
| Children in ED Lower clinical extreme | 0.167 | 0.048 | Beta | Baer (2013)39 |
| Children in ED Higher clinical | 0.790 | 0.040 | Beta | Baer (2013)39 |
| Adults in ED Lower clinical extreme | 0.832 | 0.034 | Beta | Christ-Crain (2004)44 |
| Adults in ED Higher clinical extreme | 0.987 | 0.009 | Beta | Christ-Crain (2006)42 |
| RRs for antibiotic initiation | ||||
| Children in ED | 0.970 | (0.670–1.400) | Log-normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ED | 0.770 | (0.680–0.870) | Log-normal | Meta-analysis |
| Length of hospital stay | ||||
| Children in ED Lower clinical extreme: total | 2.300 | 3.704 | Gamma | Baer (2013)39 |
| Children in ED Lower clinical extreme: % in ICU | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed | E Caroll, personal communication |
| Children in ED Higher clinical extreme: total | 5.010 | 0.330 | Gamma | Esposito (2011)49 |
| Children in ED Higher clinical extreme: % in ICU | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed | AiC information has been removed | E Caroll, personal communication |
| Adults in ED Lower clinical extreme: total | 11.200 | 10.600 | Gamma | Christ-Crain (2004)44 |
| Adults in ED Lower clinical extreme: ICU | 3.700 | 2.100 | Gamma | Stolz (2007)60 |
| Adults in ED Higher clinical extreme: total | 13.000 | 9.000 | Gamma | Christ-Crain (2006)42 |
| Adults in ED Higher clinical extreme: ICU | 3.700 | 2.100 | Gamma | Stolz (2007)60 |
| Adults in ICU Lower clinical extreme: total | 26.400 | 18.300 | Normal | Bouadma (2010)41 |
| Adults in ICU Lower clinical extreme: ICU | 14.400 | 14.100 | Normal | Bouadma (2010)41 |
| Adults in ICU Higher clinical extreme: total | 33.000 | 42.963 | Gamma | SIGN (2008)95 |
| Adults in ICU Higher clinical extreme: ICU | 23.000 | 37.037 | Gamma | SIGN (2008)95 |
| Mean difference in length of hospital stay | ||||
| Children in ED: total | –0.620 | 0.283 | Normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ED: total | –0.800 | 0.804 | Normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ED: ICU | –0.400 | 0.337 | Normal | Stolz (2007)60 |
| Adults in ICU: total | –4.200 | 1.865 | Normal | Meta-analysis |
| Adults in ICU: ICU | –1.620 | 1.222 | Normal | Meta-analysis |
Data for the cost analyses were drawn from routine NHS sources (e.g. NHS reference costs and British National Formulary (BNF)96 and discussions with manufacturers of the PCT tests. Table 16 gives an overview of the unit prices and their sources as used in the health economic analysis.
| Unit prices | Estimates/unit price (£) | Distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic treatment ICU setting/day | 12.90 | Fixed | BNF96 |
| Antibiotic treatment ED setting/day (children) | 3.99 | ||
| Antibiotic treatment ED setting/day (adults) | 2.20 | ||
| Hospital stay/day (children) | 819.56 | Department of Health (2012)97 | |
| Hospital stay/day (adults) | 819.56 | ||
| ICU stay/day (children) | 1493.98 | ||
| ICU stay/day (adults) | 1168.45 | ||
| ED stay/day (children) | 124.41 | ||
| ED stay/day (adults) | 124.41 |
Antibiotic treatment costs were calculated using average unit prices per day. These average prices were calculated separately for the ED setting (children and adults) and for the ICU setting (adults). Antibiotic prices were retrieved from the BNF. 96 The price per day for antibiotic treatment were calculated based on the dosage recommended in the treatment guidelines. LRTI treatment guidelines were used for the hospitalised non-ICU setting,98 and treatment guidelines for suspected or confirmed sepsis were used for the ICU settings. 99 The prices of different antibiotic treatment strategies (recommended by the guideline for a specific setting) were averaged. It was assumed that there was no wastage with regards to the antibiotic use (i.e. antibiotics were provided in perfectly dividable packages that correspond to the duration of the treatment, as in the treatment strategy). This assumption would be plausible especially for the ICU setting given the ‘return for re-issue’ approach used for handling partially used packs in UK hospitals. On the other hand, given the low unit costs of antibiotics the effects of the drug wastage on total costs are expected to be very small for both settings. It should be noted that the costs of antibiotic-related adverse events are conservatively not incorporated.
Costs of hospital stay, ED stay and ICU stay were retrieved from the UK’s National Schedule of Reference Costs. 97 The costs were calculated as weighted averages of the specific services taking into account the national average unit cost and the total number of attendances for each of the cost categories. The reference codes were: XB01Z–XB09Z for paediatric ICU stay, XC01Z–XC07Z for adults ICU stay, VB01Z–VB09Z for children/adults ED stay, and DZ22D–DZ22J for children/adults hospital stay for unspecified acute lower respiratory infection.
The unit price for the PCT test was calculated based on the information provided by assay manufacturers in response to the request for information made by NICE at the beginning of the assessment and forwarded by NICE (F Nixon, Health Technology Analyst, Diagnostics Assessment Programme, NICE, July 2014, personal communication). The average price was based on the listed prices of the test (excluding the VAT) and with no discounts assumed (see the upper part of Table 17). Moreover, overhead costs including capital, service/maintenance and calibration costs (see Table 17) were included. Overhead costs were calculated incorporating the initial capital costs (wherever these were provided by the manufacturer(s), the lifetime of the assay (assumed to be 5 years) and the average number of tests/day (an average of 272 tests/day). A similar estimation was performed taking into account the frequency of the maintenance and calibration costs whenever they were provided by the manufacturers. The inclusion of capital costs and other costs was considered as a conservative approach and therefore used in the base-case analysis. A separate scenario analysis considered the exclusion of overhead costs.
| Name of test | Manufacturer | Listed price/test | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elecsys BRAHMS PCT | Roche | CiC information has been removed | Manufacturers’ response to request for information made by NICE (F Nixon, personal communication) |
| ADVIA Centaur BRAHMS PCT | Siemens | CiC information has been removed | |
| VIDAS BRAHMS PCT | bioMérieux | CiC information has been removed | |
| BRAHMS PCT Kryptor | Thermo Fisher Scientific | CiC information has been removeda | |
| Average price/test | CiC information has been removed | ||
| Overhead costs | Average costs (max or listed) | ||
| Capital costs/test | CiC information has been removed | Manufacturers’ response to request for information made by NICE (F Nixon, personal communication) | |
| Service or maintenance costs/test | CiC information has been removed | ||
| Calibration costs | CiC information has been removed | ||
| Total other costs/test | CiC information has been removed | ||
| Total average costs/test | CiC information has been removedb |
The number of PCT tests used was considered different for the ED and the ICU setting as in Table 18.
Overview of main assumptions
The first phase in the decision tree period is assumed to be 28 days in line with the 28-day mortality reported for most studies. The decision tree period extends to 6 months in the second phase. The main assumptions in the health economic analyses were:
-
The number of hospitalisation days retrieved from the systematic review (see Chapter 3) also includes the hospitalisation days after (potential) infection relapse/recurrence.
-
RRs for all-cause mortality for ED children are assumed to be equal to those for ED adults, as no data were found in the literature.
-
There is no disutility for the hospital stay.
-
The baseline utility for children in the ED was constant over time.
-
The disutility for being on antibiotic treatment was equal for all settings and populations.
-
To estimate the number of PCT tests, it was assumed that PCT testing was used for initiation of antibiotics in the ED and discontinuation of antibiotics in the ICU.
-
There are no costs associated with antibiotic-related adverse events.
-
No differences were considered between comparators in disease-specific complications.
-
No differences were considered between comparators in long-term costs and effects (including any effects on antibiotic resistance).
Model analyses
Expected costs, duration of antibiotic treatment, LYs and QALYs were estimated for both treatment strategies. No discounting was applied because the time horizon was < 1 year. Incremental cost and QALYs were calculated, as well as the ICER. PSAs (10,000 simulations) were performed, and cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEACs) were constructed.
Sensitivity and scenario analyses
One-way sensitivity analyses were performed for all stochastic input parameters between the 95% CIs. Moreover, the following scenario analyses were performed to assess the impact of assumptions on the estimated outcomes.
Assume:
-
no difference in mortality (i.e. a RR of 1)
-
an increased cost of £50 per test
-
no overhead costs for the tests
-
alternative utility value for adults in the ICU (based on Cuthbertson et al. 88)
-
no disutility for being on antibiotic treatment
-
no difference in duration of antibiotic treatment
-
no difference in hospital stay (including ICU stay)
-
lower price for hospital and ICU stay: £886 per paediatric ICU day (Paediatric Critical Care, High Dependency), £619 per ICU day for adults (Adult Critical Care, 0 Organs Supported) and £212 per non-ICU hospital day (Unspecified Acute Lower Respiratory Infection with CC Score 11–14)97
-
that PCT testing in the ED was solely used to initiate antibiotic treatment (not to discontinue antibiotic treatment); given that there were no studies that solely used PCT for the initiation of antibiotic treatment for children in the ED, this was only possible for adults in the ED – for this purpose, the probability of initiating antibiotic treatment from Stolz et al. 60 was used while assuming no difference in the duration of antibiotic treatment; all other parameters were equal to the base-case analysis.
All sensitivity and scenario analyses, where, whether PCT is cost-effective or not, changes compared with the base-case analysis (based on a willingness-to-pay threshold of £30,000 per QALY) or with an ICER of < £100,000, are presented in the results section, below.
Results of cost-effectiveness analyses
Base-case analysis
The base-case analysis compared two strategies: PCT-guided treatment and current clinical practice for each combination of setting and population for which clinical effectiveness data were available, i.e. children in ED, adults in ED, and adults in ICU. Moreover, the results were calculated for both the lower and higher clinical extremes.
Procalcitonin testing resulted in a positive gain in terms of LYs in comparison with current clinical practice, for all settings and scenarios considered (Table 19). However, it should be noted that these gains were relatively small (< 0.01 LYs).
| Population and setting | Scenario | Strategy | LYs (95% CI) | Incremental |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children ED | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 0.496 (0.496 to 0.496) | |
| PCT testing | 0.496 (0.496 to 0.496) | < 0.001 | ||
| Children ED | High risk | Current clinical practice | 0.496 (0.496 to 0.496) | |
| PCT testing | 0.496 (0.496 to 0.496) | < 0.001 | ||
| Adults ED | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 0.439 (0.409 to 0.464) | |
| PCT testing | 0.445 (0.396 to 0.474) | 0.006 | ||
| Adults ED | High risk | Current clinical practice | 0.439 (0.409 to 0.461) | |
| PCT testing | 0.444 (0.397 to 0.472) | 0.006 | ||
| Adults ICU | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 0.390 (0.354 to 0.427) | |
| PCT testing | 0.391 (0.342 to 0.433) | 0.002 | ||
| Adults ICU | High risk | Current clinical practice | 0.388 (0.324 to 0.444) | |
| PCT testing | 0.389 (0.316 to 0.447) | 0.002 |
Table 20 shows the results for antibiotic duration (in days) for all settings and scenarios. The days on antibiotic treatment were reduced with the PCT strategy, for all combinations of setting and population except the lower clinical extreme scenario for children in the ED setting. For children in ED, setting the differences between the PCT and the current clinical practice varied from 0.01 days (lower clinical extreme) to –0.12 days (higher clinical extreme). The differences between PCT and current clinical practice for the adults in ED setting varied from –1.94 days (lower clinical extreme) to –1.69 days (higher clinical extreme), whereas for the ICU setting these differences were –2.96 and –3.18 days, respectively.
| Population and setting | Scenario | Strategy | Antibiotic duration (95% CI) | Incremental |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children ED | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 1.60 (1.56 to 1.64) | |
| PCT testing | 1.61 (0.00 to 6.35) | 0.01 | ||
| Children ED | High risk | Current clinical practice | 9.08 (1.47 to 23.33) | |
| PCT testing | 8.96 (0.00 to 34.27) | –0.12 | ||
| Adults ED | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 12.83 (4.44 to 25.73) | |
| PCT testing | 10.88 (0.00 to 24.58) | –1.94 | ||
| Adults ED | High risk | Current clinical practice | 12.94 (3.47 to 28.24) | |
| PCT testing | 11.25 (0.00 to 27.15) | –1.69 | ||
| Adults ICU | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 9.84 (1.07 to 27.50) | |
| PCT testing | 6.88 (0.00 to 24.50) | –2.96 | ||
| Adults ICU | High risk | Current clinical practice | 16.05 (15.26 to 16.89) | |
| PCT testing | 12.87 (10.55 to 15.24) | –3.18 |
The base-case analyses indicated that PCT dominates current clinical practice for all populations, in that it was both cost-saving and more effective (Table 21). The cost-savings ranged from £368 for children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED (lower clinical extreme) to £3268 for adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in an ICU setting (lower clinical extreme). PCT testing resulted in only a small QALY gain. For adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED this was 0.005 for the lower and higher clinical extremes, and for adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in the ICU setting it was 0.001 for both clinical extremes. For children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED, the QALY gains were < 0.001 for both clinical extremes.
| Population and setting | Scenario | Strategy | Costs (95% CI) | QALYs (95% CI) | ΔCosts (£) | ΔQALYs | ΔCosts/ΔQALYs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children ED | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 2312 (7 to 12,943) | 0.492 (0.489 to 0.495) | |||
| PCT testing | 1943 (25 to 12,269) | 0.492 (0.489 to 0.495) | –368 | < 0.001 | Dominant | ||
| Children ED | High risk | Current clinical practice | 4987 (4167 to 5964) | 0.491 (0.488 to 0.494) | |||
| PCT testing | 4406 (3461 to 5491) | 0.491 (0.487 to 0.494) | –581 | < 0.001 | Dominant | ||
| Adults ED | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 11,004 (2160 to 33,827) | 0.364 (0.337 to 0.388) | |||
| PCT testing | 10,342 (1534 to 32,849) | 0.369 (0.327 to 0.397) | –662 | 0.005 | Dominant | ||
| Adults ED | High risk | Current clinical practice | 12,270 (3073 to 30,341) | 0.364 (0.337 to 0.386) | |||
| PCT testing | 11,556 (2463 to 29,775) | 0.369 (0.327 to 0.396) | –715 | 0.005 | Dominant | ||
| Adults ICU | Low risk | Current clinical practice | 29,890 (6441 to 71,591) | 0.254 (0.230 to 0.280) | |||
| PCT testing | 26,622 (2948 to 68,581) | 0.256 (0.223 to 0.284) | –3268 | 0.001 | Dominant | ||
| Adults ICU | High risk | Current clinical practice | 45,464 (1233 to 174,178) | 0.252 (0.210 to 0.290) | |||
| PCT testing | 42,602 (210 to 170,189) | 0.254 (0.206 to 0.292) | –2862 | 0.001 | Dominant |
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (shown in Appendix 7) illustrate that, for any willingness-to-pay threshold ranging from £0 to £60,000 per QALY, PCT testing always has a higher probability of being cost-effective than current clinical practice. For a willingness-to-pay threshold of £20,000 the probability of PCT testing being cost-effective over current clinical practice is (1) 85% and 98%, respectively, for both the lower and higher clinical extremes for children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED; (2) 88% for adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED (both clinical extremes); (3) 97% and 95%, respectively, for the lower and higher clinical extremes for adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in the ICU setting. It should be noted that these probabilities vary within small limits (1–3 percentage points) for the other willingness-to-pay thresholds (see Appendix 7).
Sensitivity and scenario analyses
The one-way sensitivity analysis for the relative mortality risk for adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED, showed that when using the upper bound of the 95% CI (1.590; base-case value 0.850) PCT-guided treatment was less costly (£772) and less effective (QALY loss 0.025) compared with current clinical practice, leading to savings per QALY lost of £30,469 (lower clinical extreme) and £30,446 (higher clinical extreme). In this case, PCT-guided treatment can be considered cost-effective for all willingness-to-pay thresholds below this ICER, indicating that a QALY loss of 0.025 is accepted, given the obtained savings of £772.
The scenario analyses that assumed no difference in hospital stay had a substantial impact on all analyses. For all analyses, PCT-guided treatment became more costly (incremental costs varied between £7 for adults at the ICU and £25 for children at the ED) and remained more effective (QALY gain varied between < 0.001 for children at the ED and 0.007 for adults at the ICU) than current clinical practice without PCT. For children presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infection, this resulted in an ICER of £287,076 for the lower clinical extreme and £35,219 for the higher clinical extreme. For adults in both settings (and both clinical extremes), the ICER varied between £3390 and £3948.
Neither the remaining sensitivity analyses nor any of the remaining scenario analyses changed whether or not PCT is cost-effective compared with the base-case analysis or provided an ICER of < £100,000 per QALY. Hence, PCT-guided treatment was cost-effective in all remaining one-way sensitivity analyses and scenarios analyses for all settings and populations.
Chapter 5 Discussion
Statement of principal findings
Clinical effectiveness
All studies included in the review were parallel group RCTs. Eight studies33,37,41,45,50,52,54,61 provided data on the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy for the treatment of confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in ICU settings, and all of these studies included only adult participants. Ten studies39,42,44,49,55–57,60,62,69 provided data on the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy in people presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infections, of which eight studies42,44,55–57,60,62,69 included only adults, and two studies39,49 included only children. Additional searches for non-RCT paediatric studies, described in Chapter 3 (see Search strategy), did not identify any studies that met the inclusion criteria for this assessment.
There was a lack of high-quality evidence. Only one62 of the 18 studies33,37,39,41,42,44,45,49,50,52,54–57,60–62,69 included in our systematic review was classified as having as low risk of bias. Three studies45,52,60 were judged at high risk of bias, and all other studies33,37,39,41,42,44,49,50,54–57,61,62,69 were judged at unclear risk of bias, as insufficient information was reported to make a judgement on one or more of the domains of the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool.
The majority (1237,39,41,42,44,49,52,57,60–62,69) of the included studies measured plasma/serum PCT levels using the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay. Two studies45,50 measured plasma/serum PCT levels using the VIDAS BRAHMS PCT (bioMérieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France). The remaining four studies33,54–56 used quantitative PCT assays, but did not specify the assay manufacturer.
Only four33,37,45,52 of the eight studies conducted in ICU settings fully matched the participant inclusion criteria for this review (adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis, in whom antibiotic therapy is indicated, who are being treated in ICUs). One study41 included a mixed population, comprising adults who were being treated in an ICU for suspected bacterial infection and those who developed sepsis during their ICU stay. The inclusion criteria specified in our protocol, for the ICU population, were extended to include studies of people suspected bacterial infections that did not specify sepsis as the target condition. Two additional studies54,61 included as a result of this change were conducted in populations considered to be at increased risk of developing sepsis:101–103 one study54 included adults with acute pancreatitis and the other study61 included adults with VAP. The final ICU study50 included adults who were being treated for suspected bacterial infections; this was the only study, conducted in an ICU setting, to assess the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the initiation of antibiotic treatment, reflecting the lower level of symptom severity in the included population. All of the other studies33,37,41,45,52,54,61 conducted in ICU settings assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment. The details of the PCT algorithm varied between studies; however, all discontinuation algorithms included a component that strongly encouraged/encouraged discontinuation of antibiotics when the PCT level was < 0.25 ng/ml,33,37,41,52,61 and/or encouraged discontinuation of antibiotics when the PCT level was < 0.5 ng/ml. 37,41,45,50,54,61 The results of meta-analysis, including all available data, indicated that addition of a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy (WMD –3.19 days, 95% CI –5.44 to –0.95 days, I2 = 95.2%, four studies33,41,52,54) and uncertainty around this effect was reduced when the analysis was restricted to studies conducted in populations with suspected or confirmed sepsis (WMD –1.20 days, 95% CI –1.33 to –1.07 days, two studies33,52). Three further studies37,45,61 assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, but reported the outcome as median (IQR) duration of antibiotic therapy, with p-values for the between-group comparison. Two of these studies37,45 were conducted in people with suspected or confirmed sepsis, and reported results indicating that adding a PCT algorithm to the clinical decision-making process had no statistically significant effect on the duration of antibiotic treatment. However, these were small studies;37,45 power calculations were based on the use of statistical methods for normally distributed data and it is unlikely that these studies would have been appropriately powered to detect differences between median values. Data on resource use were broadly consistent with the observed reduction in duration of antibiotic treatment, i.e. the results of meta-analysis, including all available data, indicated that addition of a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in the duration of hospital stay (WMD –3.85 days, 95% CI –6.78 to –0.92 days, I2 = 75.2%, four studies33,41,52,54) and a trend towards reduction in the duration of ICU stay (WMD –2.03 days, 95% CI –4.19 to 0.13 days), I2 = 81.0%, four studies33,41,52,54). Again, uncertainty around these effect estimates was reduced when the analysis was restricted to studies conducted in populations with suspected or confirmed sepsis (duration of hospital stay WMD –4.32 days, 95% CI –6.50 to –2.14 days, two studies33,52) and duration of ICU stay (WMD –2.31 days, 95% CI –3.97 to –0.65 days, two studies33,52). For antibiotic treatment and resource-use outcome measures, studies37,45 that reported duration only as median and IQR failed to find any difference between the group in which a PCT algorithm was included in decision-making and the group in which the decision to discontinue antibiotic treatment was made without information on PCT levels. Studies conducted in ICU settings reported a variety of general and disease-specific adverse clinical outcomes, including mortality at various time points, infection relapse/recurrence, mechanical ventilation, MODS and SOFA score. No study reported a statistically significant difference between the intervention and comparator groups for any adverse clinical outcome assessed. No study reported data on antibiotic-related adverse events.
In summary, the limited available data indicate that addition of a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotic treatment in people being treated for suspected or confirmed sepsis, in ICU settings, may result in reduced antibiotic exposure and resource use (hospital and ICU stay) without any adverse consequences for clinical outcome. There was no evidence of variation in these effects between the two PCT assays used (BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay and VIDAS BRAHMS PCT assay).
The clinical presentation of participants varied between ED studies; however, with the exception of one study69 conducted in adults with UTI, all were conducted in people with respiratory presentations and possible bacterial infection. Where specified, all studies39,42,44,49,55–57,60,62,69 conducted in ED settings used the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay. All39,42,44,49,55–57,60,62 but one69 of the studies conducted in ED settings assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the initiation of antibiotic treatment, and six of these studies39,42,49,55–57 also assessed the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used to guide the discontinuation of antibiotic treatment. The details of the PCT intervention varied between studies; however, all studies (both initiation and discontinuation) discouraged antibiotic use when the PCT level was < 0.25 ng/ml. All studies conducted in adults42,44,55–57,60,62 indicated that the addition of PCT to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in the proportion of people receiving antibiotics; the summary RR was 0.77 (95% CI 0.68 to 0.87, seven studies42,44,55–57,60,62). Data for children were sparse; however, meta-analysis restricted to children presenting with CAP also indicated that the addition of PCT to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in antibiotic use (summary RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.80 to 0.93, two studies39,49). The summary effect estimate, derived from the two studies,42,44 conducted in adults, which reported duration of antibiotic therapy as mean and SD, indicated that inclusion of PCT in the clinical decision-making process was associated with reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy, which did not reach statistical significance (WMD –4.49 days, 95% CI –9.59 to 0.61 days); four further studies55–57,69 reporting data in a form that could not be included in the meta-analysis, consistently found that that inclusion of PCT in the clinical decision-making process was associated with reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy. Only one study,39 conducted in children, reported data on duration of antibiotic therapy; as with initiation of antibiotic therapy, subgroup data from this study indicated that the use of PCT was associated with a reduction in antibiotic exposure only for children with CAP (mean difference –3.4 days, 95% CI –4.9 to –1.7 days). It should be noted that data on duration of antibiotic use included participants with a zero value (i.e. participants who did not receive antibiotic treatment) and hence are not strictly applicable to assessing the effectiveness of using PCT algorithms to inform the decision on when to discontinue antibiotics. A meta-analysis, which included data for only those patients in the two adult ED studies42,44 who received antibiotic treatment, resulted in a WMD of 1.48 days (95% CI –13.64 to 16.59 days), indicating no clear effect of PCT testing on duration of treatment; indeed data from one of these studies42 indicated that, in adults presenting to the ED who receive antibiotic treatment PCT testing may be associated with an increased duration of treatment. Data on resource-use outcomes were inconsistent for studies conducted in ED settings. Although meta-analysis of the two studies42,44 conducted in adults, which reported data as mean and SD, indicated that inclusion of PCT in the clinical decision-making process was associated with a trend towards reduction in the duration of hospital stay (WMD –0.80 days, 95% CI –2.37 to 0.78 days), the effect of PCT on duration of hospital stay was inconsistent across the six adult studies42,44,55–57,60 reporting this outcome. As with antibiotic exposure outcomes, data for children were sparse; however, meta-analysis of data from two studies39,49 indicated that including a PCT algorithm in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment was associated with a small reduction in the duration of hospital stay (WMD –0.74 days, 95% CI –1.17 to –0.31 days). For both children and adults, estimates of the effect of PCT testing on duration of hospital stay were small, uncertain and of questionable clinical significance. No study reported a statistically significant difference between the intervention and comparator groups for duration of ICU stay, hospital re-admission, or secondary ED visits. Smaller effect sizes and greater uncertainty around the possible effects of PCT testing on resource-use outcomes in the ED, compared to the ICU setting, may reflect the fact that not all participants in the ED studies were admitted to hospital at all and very few were admitted to the ICU. Studies conducted in ED settings reported a variety of general and disease-specific adverse clinical outcomes including mortality at various time points, infection relapse/recurrence, composite measures of adverse outcomes, mechanical ventilation, need for steroids, and complications of pneumonia. One study57 reported data indicating that inclusion of a PCT algorithm in both the information used to guide initiation and discontinuation of antibiotics was associated with a statistically significant reduction in infection relapse/recurrence rates (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.92), No other study reported a statistically significant difference between the intervention and comparator groups for any adverse clinical outcome assessed. Antibiotic-related adverse events were rarely reported; however, available data from one study57 in adults and two studies in children39,49 indicated that including a PCT algorithm in both the decision on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and the decision on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in antibiotic-related adverse events.
In summary, the limited available data indicate that addition of PCT information to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy in adults presenting to the ED with respiratory symptoms and suspected bacterial infection may result in reduced antibiotic exposure, primarily with respect to a reduction in the numbers of people receiving antibiotic treatment, without any adverse consequences for clinical outcome. However, there appears to be no consistent effect on resource-use outcomes. Very limited data suggest that similar effects may apply for children with CAP. The draft NICE guideline9 on the diagnosis and management of community- and hospital-acquired pneumonia in adults reports that systematic review evidence showed that using PCT testing to inform antibiotic prescribing decisions in people presenting with ARTIs, in any setting, may reduce initiation of antibiotic treatment with no evidence of any difference in mortality or other clinical adverse outcomes. However, the guideline does not currently include any recommendations on the use of PCT testing.
Cost-effectiveness
The review of economic analyses of PCT testing identified two relevant studies in three publications. 72–74 These studies used a short-term decision tree to examine the cost-effectiveness of PCT-guided antibiotic treatment compared with usual care for adult patients with ARTI (outpatient setting)72,73 and CAP (in-hospital setting),74 respectively. The results of both studies74–76 indicated that PCT-guided treatment was more expensive and more effective (in terms of QALYs). Michaelidis et al. 72,73 performed two analyses for two slightly different populations: (1) adults presenting to an outpatient clinic with an ARTI and judged by their physicians to require an antibiotic prescription and (2) all adults presenting to an outpatient clinic with an ARTI prior to any decision to initiate antibiotic therapy. Their analyses resulted in ICERs of US$118,828 and US$575,249 per QALY gained for the first and second analyses, respectively. Smith et al. 74 assumed no differences in length of hospital stay between the treatment strategies and analysed the cost-effectiveness of PT-guided antibiotic therapy for (1) low-risk patients with CAP, using PCT for initiating antibiotic only; (2) low-risk patients with CAP, using PCT also for monitoring antibiotic use for low-risk patients and; (3) using PCT for both initiating antibiotic and monitoring antibiotic use for high-risk patients. These analyses resulted in ICERs of US$90,000, US$40,000 and US$170,000 per QALY gained, respectively. Additionally, an overview of potentially relevant excluded studies (mainly cost-minimisation studies focused on the short term) indicated that PCT-guided treatment could result in cost-savings for adult patients with sepsis, ARTI and pneumonia,45,79–82 while additional costs for PCT-guided treatment were found for adults with LRTI83 and suspected CAP. 42
In a de novo health-economic analysis, the cost-effectiveness of PCT testing in addition to current clinical practice was compared with current clinical practice for (1) adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in an ICU setting; (2) adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED; and (3) children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED. As specified in the protocol for this assessment, lack of evidence meant that the cost-effectiveness of PCT testing in addition to current clinical practice was not considered for children with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis being treated in an ICU setting. Also, as indicated by the design of trials in the clinical effectiveness review, antibiotic duration in the ICU was modelled assuming that PCT was used to decide when to stop treatment, whereas in the ED it was modelled assuming that PCT was used to decide whether to initiate treatment. To examine the impact of variability in the study populations on the economic outcomes, a lower and higher clinical extreme was defined for each setting and population, using baseline risks and baseline resource-use parameters, while assuming an equal RR for mortality and mean difference for resource-use parameters. The base-case analyses indicated that PCT testing was cost-saving for all settings and populations considered, ranging from £368 for children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED (lower clinical extreme) to £3268 for adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in an ICU setting (lower clinical extreme). This could mainly be explained by the reduction in antibiotic treatment and a reduction in hospital stay (both ICU and non-ICU days) for PCT-guided treatment. For children presenting to the ED and adults in both the ED and ICU settings, PCT-guided treatment resulted in a small QALY gain (< 0.001, 0.005 and 0.001, respectively) and thus dominated treatment without PCT guidance. This QALY gain could be attributed to a reduction in mortality and fewer days on antibiotic treatment (leading to a smaller QALY loss due to antibiotic-related adverse events) for PCT-guided treatment. The differences between the lower and higher clinical extremes were small for all settings and populations. CEACs showed that PCT-guided treatment has a probability of 84% or higher of being cost-effective for all settings and populations considered (at willingness-to-pay thresholds of £20,000 and £30,000 per QALY).
It was difficult to compare the total costs estimated in our analyses with those from cost (-effectiveness) studies found in the literature, as most studies did not incorporate hospital stay costs42,45,72,73,79,81–83 or assumed this to be equal for both comparators. 74 However, the cost-minimisation by Wilke et al. 80 did incorporate ICU costs and, consistent with our analyses, estimated cost-savings for PCT-guided treatment for septic patients. The QALY gain of 0.005 estimated in our analysis for adults presenting to the ED was larger than the only other incremental QALY estimate of 0.00019 found in the literature reported by Michaelidis et al. 72,73 for adult patients with ARTI. Differences between these incremental QALY estimates can possibly be explained by the longer time horizon used in our analyses (6 months vs., duration of ARTI treatment episode) and the inclusion of mortality in our analyses.
The one-way sensitivity and scenario analyses indicated that the base-case outcomes were robust. In particular, even if there was no effect on mortality (RR of 1), PCT would remain cost-effective. Only one sensitivity analysis showed a relevant change in the incremental outcomes. This was the one-way sensitivity analysis for the relative mortality risk for adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED. This analysis showed that when using the upper bound of the 95% CI PCT-guided treatment was less costly and less effective compared with current clinical practice, leading to savings of £30,469 (lower clinical extreme) and £30,446 (higher clinical extreme) per QALY lost. This indicates that PCT-guided treatment is cost-effective based on a threshold of £30,000, i.e. that a QALY lost is accepted given the obtained savings for PCT-guided treatment. The scenario analyses that assumed no difference in hospital stay had a substantial impact on all analyses. For all analyses, PCT-guided treatment became more costly and remained more effective (instead of dominating current clinical practice). For the children presenting to the ED, this resulted in an ICER of £287,076 for the lower clinical extreme and £35,219 for the higher clinical extreme. For adults in both settings and both clinical extremes the ICER varied between £3390 and £3948.
In summary, the available evidence suggests that the addition of PCT testing to current clinical practice leads to cost-savings and a very small QALY gain, and thus dominates current practice. Hence PCT testing potentially represents a cost-effective use of NHS resources for adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in an ICU setting, adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED, and children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED.
Strengths and limitations of assessment
Clinical effectiveness
Our assessment included only those study designs with the potential to provide information on the ‘added value’ of including PCT in clinical decision-making processes on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment and when to discontinue treatment. We believe this approach to be most appropriate, as, in practice, PCT would not be used in isolation to determine the presence or absence of bacterial infection and hence appropriate management. A recent systematic review showed that the diagnostic performance of PCT alone is insufficient to distinguish people with sepsis form those with SIRS (sensitivity 77%, 95% CI 72% to 81%; specificity 79%, 95% CI 74% to 84%). 21
Extensive literature searches were conducted in an attempt to maximise retrieval of relevant studies. These included electronic searches of a variety of bibliographic databases, as well as screening of clinical trials registers and conference abstracts to identify unpublished studies. We used a two-stage approach for searching bibliographic databases, which included the use of sensitive search filter to identify RCTs, followed by unrestricted searches for non-RCT studies in children when no RCTs conducted in PICU settings were identified. Despite this, we were unable to identify any studies, conducted in PICU settings, which met the inclusion criteria for this assessment, and available data for children were generally very sparse.
The possibility of publication bias cannot be ruled out. Owing to the small number of included studies (maximum of seven included in any one meta-analysis), we were unable to undertake a formal assessment of publication bias. However, our search strategy included a variety of routes to identify unpublished studies and resulted in the inclusion of a number of conference abstracts.
Clear inclusion criteria were specified in the registered protocol for this review (PROSPERO registration number CRD42014010822). The eligibility of studies for inclusion is therefore transparent. In addition, we have provided specific reasons for exclusion for all of the studies which were considered potentially relevant at initial citation screening and were subsequently excluded on assessment of the full publication (see Appendix 5). The review process followed recommended methods to minimise the potential for error and/or bias;28 studies were independently screened for inclusion by two reviewers and data extraction and quality assessment were done by one reviewer and checked by a second (MW and PW). Any disagreements were resolved by consensus.
Studies included in this review were assessed for risk of bias using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. 34 The results of the risk of bias assessment are reported, in full, for all included studies in Appendix 4 and are summarised in Chapter 3 (see Study quality). Studies were generally of unclear quality owing to limitation in reporting. Three45,52,60 of the 18 studies33,37,39,41,42,44,45,49,50,52,54–57,60–62,70 were judged to be at high risk of bias. Loss to follow-up was the reason for the high risk of bias rating in two studies. 45,52 Both studies45,52 reported per-protocol analyses in addition to the main ITT analyses used in Chapter 3 (see Effectiveness of adding procalcitonin testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy for the treatment of confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in intensive care unit settings); in one case 14% of study participants were not included in the per-protocol analysis,52 and in the other 33% of study participants were not included in the per-protocol analysis. 45 In both studies the per-protocol analyses showed a statistically significant reduction in the duration of antibiotic therapy, associated with the PCT intervention (mean difference –3.2 days (95% CI –5.1 to –1.1 days),52 and median (IQR) 9 (5–24) in the PCT group and 13 (3–45) in the control group,45 which was not apparent from the ITT analyses. In addition, there are some methodological issues that are inherent to the nature of the research question. Because studies are assessing the effects of providing additional information (PCT) to treating clinicians, it is not possible to blind study personnel to intervention group. Similarly, outcomes that relate to the extent of antibiotic exposure (i.e. treatment decisions) cannot be assessed blind to intervention group.
Our findings are in line with those of previously published systematic reviews, conducted in ICU84,104–108 and mixed109–112 settings, which have consistently found that the inclusion of PCT levels/algorithms in the information used to guide antibiotic treatment reduced antibiotic exposure without any adverse effects on clinical outcome.
We believe that our assessment provides information of relevance to UK clinical practice as we focus on two distinct secondary care settings – ED and ICU – in which PCT testing might routinely be applied as part of the decision-making process on antibiotic treatment. These settings are considered separately, as people presenting to the ED are likely to have a different range and severity of conditions to those being treated in ICU settings. When information was available, we have also considered adults and children separately. We have further structured our report to provide information on the potential benefits of including PCT in clinical decision-making processes, balanced against any possible adverse clinical effects.
The majority (1237,39,41,42,44,49,52,57,60–62,69) of the 18 included studies33,37,39,41,42,44,45,49,50,52,54–57,60–62,69 measured plasma/serum PCT levels using the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay. Two studies45,50 measured plasma/serum PCT levels using the VIDAS BRAHMS PCT. We found no data on the clinical effectiveness of PCT algorithms/levels measured using the Elecsys BRAHMS PCT assay, the ADVIA Centaur BRAHMS PCT assay or the LIAISON BRAHMS PCT assay.
It should also be noted that none of the studies included in the systematic review component of this assessment were conducted in the UK. Our review considers the effectiveness of adding PCT testing to the information used by clinicians to inform decisions on antibiotic treatment and, as such, differences in the behaviour/routine practice of clinicians in different countries and health-care settings may influence the apparent effectiveness of the PCT intervention. It is therefore unclear whether the data included in this assessment are generalisible to UK settings. For example, where there is good prescribing guidance and a strong emphasis on controlling antibiotic use, or where ICU provision is at, or close to, capacity, and hence there is a strong focus on prompt discharge of patients from the ICU when clinically appropriate, it may not be possible to achieve the gains reported by some studies included in this review.
Cost-effectiveness
Our analysis is the most comprehensive full economic evaluation to date to examine cost per QALY of the addition of PCT testing to current clinical practice for adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in an ICU setting, adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED, and children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED. In an effort to incorporate all relevant evidence, systematic searches were performed for all stochastic input parameters included in the economic analysis.
As in any economic model, a number of major and minor assumptions had to be made. It is important to understand the impact of these assumptions in order to correctly interpret the results of the economic analysis. The main uncertainty regarding the assessment of cost-effectiveness lies in the inability to explore long-term costs and effects (beyond 6 months), i.e. assuming that long-term costs and effects do not impact on the incremental outcomes. This includes (1) the potential costs and effects arising from reduced antibiotic resistance as a result of a decreased antibiotic treatment duration and (2) the long-term impact of short-term survival differences. Although the long-term costs and effects of antibiotic resistance (due to decreased antibiotic treatment duration) are difficult to quantify, it is likely that inclusion of these costs and effects would make the cost-effectiveness ratio more favourable for PCT-guided treatment. Inclusion of the long-term consequences that originate from short-term survival differences are also likely to favour PCT-guided treatment. However, for children presenting to the ED, these differences were so small that the long-term consequences are likely to be negligible. It was assumed that staying in the hospital would not have any additional impact on the utility (e.g. through adding a disutility). This can be regarded as a conservative assumption, given that the hospital stay (both ICU and non-ICU) was shorter for PCT-guided treatment. Hence adding a disutility for hospital stay would make the results more favourable for PCT-guided treatment. Furthermore, the disutility for being on antibiotic treatment (reflecting antibiotic-related adverse events) was conservatively assumed to be constant for all populations and settings. Although this disutility might be higher for the ICU owing to the intravenous administration, incorporating a higher disutility would also favour PCT-guided treatment. Finally, uncertainty may arise, as not all consequences are incorporated in the economic analysis; this includes adverse events other than antibiotic-related adverse events. However, these adverse events probably do not differ between the comparators (see assessment of clinical effectiveness) and hence are unlikely to impact on the incremental outcomes.
It should be emphasised that the uncertainty resulting from the above mentioned assumptions was not parameterised and is therefore not reflected in the PSAs or in the CEACs.
Uncertainties
Clinical effectiveness
There was a lack of data on the clinical effectiveness of including PCT levels/algorithms in the information used to guide antibiotic treatment decisions in children. We were able to identify only two RCTs,39,49 both conducted in children presenting to the ED with respiratory symptoms, and widening searches to include other study designs failed to yield any further relevant studies. In addition, all but one of the adult studies conducted in ED settings were in people presenting with respiratory symptoms. It is therefore unclear, whether our findings for the ED setting would be generalisable to adults or children with suspected bacterial infections in other sites. We are aware of one RCT,20 conducted in young children (aged 1–36 months) presenting to the ED with fever of unknown origin. This study20 did not meet our inclusion criteria because it used a qualitative PCT assay, but found that whether or not PCT test results were available to treating clinicians had no effect on antibiotic exposure or hospitalisation rates.
There is less uncertainty around which patient groups, in the ICU setting, may benefit from treatment management guided by PCT. Studies in our systematic review,33,41,52,54,61 with a variety of infection-related inclusion criteria (suspected or confirmed sepsis,33,52 suspected bacterial infection or development of sepsis whilst in the ICU,41 severe acute pancreatitis,54 and VAP61), found that the addition of a PCT algorithm to the information used to determine when to discontinue antibiotic treatment was associated with a reduction in the duration of antibiotic treatment. The use of PCT levels to monitor patients who are being treated in ICU settings, regardless of whether or not sepsis or bacterial infection are suspected, was outside the scope of this assessment. One excluded study,113 identified by our searches, randomised people with an expected ICU stay of ≥ 24 hours (no infection criteria specified) to receive antibiotic treatment according to current clinical guidelines or according to current clinical guidelines supplemented by a drug escalation algorithm and intensified diagnostics based on daily PCT measurement. 113 This study113 found that the escalation strategy had no effect on 28-day all-cause mortality (absolute risk reduction 0.6% (95% CI –4.7% to 5.9%) but was associated with small increases in the proportion of ICU days on mechanical ventilation (4.9%, 95% CI 3.0% to 6.7%) and the risk of impaired renal function defined by a glomerular filtration rate of < 60 ml/minute/1.73 m2 (RR 1.21, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.27). The results of this study support the idea that PCT measurements should be used only in selected populations (where bacterial infection/sepsis is suspected) and in conjunction with clinical judgement.
One further possible consideration is the extent to which the apparent effects on antibiotic exposure – seen in our assessment and other systematic reviews – of providing PCT information to treating clinicians may be mediated by increased information/levels of awareness of antibiotic prescribing issues. Trials of PCT algorithms generally provide clinicians with information/education on the interpretation of PCT levels and frequently classify antibiotic prescribing decisions that are not in line with the algorithm as ‘over-rules’; this is unlikely to reflect the way PCT levels are used in practice and it is possible that additional ‘message re-inforcement’ may exaggerate the effects of PCT. It is also possible that information provision or a more structured approach to management (‘protocolisation’), regardless of the nature of the information or procedures used, may result in increased awareness of the issues around overprescribing of antibiotics and hence reduced prescription rates. Conversely, it could be argued that any effects of increased awareness may be expected to be present in both trial arms, simply as a result of participating in a research study. Only one of the studies41 included in our systematic review clearly reported that the information provided to clinicians in the control arm and clinical component of information provided to clinicians in the intervention arm were the same (approved reminder, including condition-specific recommendation for the duration of antibiotic treatment); this study41 found a reduction in antibiotic exposure associated with the PCT intervention, arguing against increased awareness as a mediator of effect. In addition to ensuring that the control arm is similar to the intervention arm in all respects other than the use of PCT testing, the applicability of the comparator to the setting of interest is an important consideration. In this case, if the control is not representative of standard practice in the UK, for example if a more protocolised approach is used in the UK than in the countries in which studies were conducted, then any apparent effects of PCT testing may not be reproducible in the NHS.
Despite the apparent reduction in antibiotic exposure associated with adding PCT levels/algorithms to the information used to guide antibiotic treatment decisions observed in this assessment and in other published systematic reviews, it remains uncertain whether similar effects could be achieved by other means (e.g. other biomarkers such as C-reactive protein (CRP). It may be argued that CRP levels are part of current standard practice and, as such, any studies that included CRP in both arms, i.e. that compared PCT plus standard clinical practice (including CRP) to standard clinical practice (including CRP), would meet the inclusion criteria for this assessment. Studies of this type could provide information on whether the addition of another biomarker (PCT) is beneficial. The studies included in our systematic review do not provide a detailed breakdown of which investigations were included in standard clinical practice. Eight of the RCTs37,39,41,42,44,45,57,62 included in our review reported baseline CRP levels in both study arms, indicating that CRP was part of standard practice. Six of these studies39,41,42,44,57,62 reported results indicating that the PCT intervention arm was associated with a reduction in antibiotic exposure outcomes, i.e. adding PCT to the information available to treating clinicians reduced participant antibiotic exposure in situations in which CRP levels were also available. However, as discussed above, the availability of a biomarker assay result is unlikely to be equivalent to implementation of an algorithm that includes specific treatment advice linked to a range of decision thresholds. Comparison of PCT algorithms plus standard practice to algorithms based on other biomarkers (e.g. CRP) plus standard practice was outside the scope of this assessment; however, our searches identified one RCT114 of this type. This study114 was conducted in ICU settings and included adults with severe sepsis or septic shock. It compared the use of a PCT-based algorithm to a CRP-based algorithm to inform when to discontinue antibiotic treatment. For both study arms the discontinuation algorithm was applied once there were no active signs of infection and the SOFA score was decreasing, and in both arms the final discontinuation decision was at the discretion of the treating clinician. The PCT algorithm specified that where initial levels were < 1 ng/ml PCT should be re-assessed on day 4 and where initial levels were ≥ 1 ng/ml PCT should be re-assessed on day 5; if PCT was then < 0.1 ng/ml or had decreased by ≥ 90% then discontinuation was advised – if these criteria were not met then PCT levels were repeated daily until discontinuation criteria were met or until 7 days of antibiotic treatment. The CRP algorithm followed a similar structure and specified that when initial levels were < 100 mg/l then CRP should be re-assessed on day 4, and when initial levels were ≥ 100 mg/l then PCT should be re-assessed on day 5; if CRP was then < 25 mg/l, or had decreased by ≥ 50%, discontinuation was advised – if these criteria were not met then CRP levels were repeated daily until discontinuation criteria were met or until 7 days of antibiotic treatment. This study114 found no difference in the duration of antibiotic therapy according to which algorithm was used [median (IQR) 7.0 (6.0 to 8.5) days in the PCT group; 6.0 (5.0 to 7.0) days in the CRP group; hazard ratio (HR) 1.21, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.30] and no differences in resource-use outcomes or adverse clinical outcomes. This study114 may indicate that implementation of a CRP-based algorithm may have similar effects to a PCT-based algorithm; however, it should be noted that only a single study of this type was identified and this study did not include a control (standard care only) arm.
There is a lack of direct data to support the clinical effectiveness of PCT testing using some of the PCT assays currently available to NHS laboratories (Elecsys BRAHMS PCT assay, ADVIA Centaur BRAHMS PCT assay, LIAISON BRAHMS PCT assay). Where assay type was specified, most of the studies included in our systematic review used the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay) (see Strengths and limitations of assessment/Clinical effectiveness, above). However, where another assay was used (VIDAS BRAHMS PCT), there was no evidence to suggest a difference in effect between assays (see Chapter 3, Effectiveness of adding procalcitonin testing to the information used to guide antibiotic therapy for the treatment of confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in intensive care unit settings). In addition, all of the commercially available PCT assays use the same monoclonal anti-PCT antibody, under licence from Thermo Fisher Scientific; the main difference between assays being the method of detection (see Chapter 2, Intervention technologies and comparator). All commercial assays have been standardised using the BRAHMS PCT LIA. This was the original manual PCT assay and is not included in this assessment, as it is no longer being marketed. However, two studies115,116 using the LIA were identified by our searches; one study115 assessed the addition of PCT levels to the information used to decide whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment in patients post cardiac surgery and found that use of PCT was associated with a reduction in antibiotic exposure (RR 0.40, 95% CI 0.25 to 0.63), and the other study116 assessed the addition of a PCT algorithm to the information used to decide when to discontinue antibiotics in people with severe sepsis who were being treated in an ICU and found that the PCT algorithm was associated with a reduction in the duration of antibiotic treatment (mean difference –1.70 days, 95% CI –2.39 to –1.01 days). Neither study115,116 found a statistically significant difference in any adverse clinical outcome between the intervention and control groups. The results of these two studies115,116 further support the view that there is no evidence to suggest that the effects of including PCT information in decisions about antibiotic treatment differ according to which PCT assay is used. With regards to the technical performance characteristics of different PCT assays, a study submitted in the information provided by Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics shows good agreement in the PCT levels measured in clinical samples between the Roche Elecsys PCT assay and the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay (r = 0.987), and between the Siemens ADVIA Centaur PCT assay and the BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor assay (r = 0.977). 16 Given the lack of evidence to suggest any differences in clinical effects between different PCT assays, and the availability of data indicating good measurement consistency, it may be reasonable to assume that the clinical effects of including PCT information in decisions about antibiotic treatment are likely to be consistent across different PCT assays.
It has been suggested that, if the use of PCT testing is associated with a reduction in antibiotic prescribing and, in particular, broad spectrum antibiotic use in ICU settings, this may have health-care system benefits in terms of a reduction in antibiotic resistance/health-care associated infections. Evaluation of any possible long-term, health-care system benefits was outside the scope of this assessment; further research in this area may be warranted if PCT testing is recommended.
Cost-effectiveness
The uncertainty regarding the generalisability of the results from the ED setting to other populations than patients with respiratory symptoms, as discussed in the previous section (see Clinical effectiveness), is also applicable to the cost-effectiveness estimates. Additionally, although most clinical studies were based in Europe (whenever reported), none of the studies was based in the UK. Hence the generalisability of the results to the UK settings is uncertain. This is particularly true for the resource-use parameters (hospital stay) and the exact application of PCT (potentially affects antibiotic treatment duration and the number of tests), which might be setting dependent. As hospital stay was one of the main influential parameters, the economic outcomes may well differ for the UK. However, the scenario analyses, assuming no differences in hospital stay between the comparators, are reassuring that PCT might potentially be cost-effective in the UK for adults at the ICU and ED
In short, PCT testing may be cost-effective in the UK. However, although the economic analysis indicates that there is little decision uncertainty, not all uncertainties can be captured in the parameters and thus be reflected in the outcomes of the economic assessment. This ‘scenario uncertainty’ includes the generalisability of the results to the UK setting. Consequently, the presented outcomes might provide a certain degree of pseudo-certainty. Therefore, it is important to note that the results of the economic assessment should be interpreted with caution. This applies, in particular, to the ED setting as another generalisability issue arises: the applicability of the presented outcomes to other patients than patients with respiratory symptoms. The paucity of evidence on long-term outcomes might further add to uncertainty.
Chapter 6 Conclusions
Implications for service provision
The addition of a PCT algorithm to the information used to guide antibiotic treatment may reduce antibiotic exposure in adults being treated for suspected or confirmed sepsis in ICU settings and in adults presenting to the ED with respiratory symptoms and suspected bacterial infection, without any adverse consequences for clinical outcome. In ICU settings, the PCT algorithm was primarily used to inform decisions on when to discontinue antibiotic treatment, whereas in ED settings the primary application was decisions on whether or not to initiate antibiotic treatment. The use of a PCT algorithm may also be associated with reductions hospital and ICU stay. Very limited data suggest that similar effects may apply for children presenting to the ED with respiratory symptoms and suspected bacterial infection, in particular the subgroup with CAP. No evidence was identified on the effectiveness using a PCT algorithm to guide antibiotic treatment for children with suspected or confirmed sepsis in the ICU. However, it is important to note that evidence was limited and none of the identified studies was conducted in the UK. It is not clear whether the control arms of these studies were representative of standard practice in the UK, for example if a more protocolised approach is used in the UK than in the countries in which studies were conducted; if the control arms were not comparable with standard practice in the UK then any apparent effects of PCT testing may not be reproducible in the NHS.
Available evidence suggests that the addition of PCT testing to current clinical practice leads to cost-savings and a very small QALY gain, and thus dominates current practice. Hence PCT testing potentially represents a cost-effective use of NHS resources for adults with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis in an ICU setting, adults with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED, and children with suspected bacterial infection presenting to the ED. However, although the economic analysis indicates that there is little decision uncertainty, not all uncertainties can be captured in the parameters and thus be reflected in the outcomes of the economic assessment. This ‘scenario uncertainty’ includes the generalisability of the results to the UK setting. Therefore, it is important to note that the results of the economic assessment should be interpreted with caution. This applies in particular to the ED setting as another generalisability issue arises: the applicability of the presented outcomes to other patients than patients with respiratory symptoms. The paucity of evidence on long-term outcomes might further add to uncertainty.
Suggested research priorities
Further studies are needed to adequately assess the effectiveness of adding PCT algorithms to the information used to guide antibiotic treatment in adults and children with suspected or confirmed sepsis in ICU settings and in adults and children with suspected bacterial infection in ED settings. Additional research is needed to examine whether the outcomes presented in this report are generalisable to the UK setting. High-quality studies, in which the control arm is similar to the intervention arm in all respects other than the use of PCT testing, are needed to inform the question of whether any observed effects are attributable to PCT testing or may be due the effects of introducing protocolised care. In addition, the control arm of future studies should be carefully matched to standard UK practice, to ensure that any observed effects would be likely to be reproducible in the NHS. Studies are needed for all clinically relevant populations, particularly children and patients presenting to the ED for reasons other than respiratory symptoms, for which data are currently lacking. Moreover, additional research is warranted examining (short-term) health-state utility values in the UK for adults and children with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis at the ICU, and adults and children presenting with suspected bacterial infection at the ED. Finally, it would be of relevance to examine long-term costs and effects of PCT-guided treatment, including its potential impact on antibiotic resistance.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the clinical advice and expert opinion provided by Professor Enitan Carrol, Chair in Paediatric Infection/Consultant in Paediatric Infectious Diseases, University of Liverpool/Alder Hey Children’s Hospital, Liverpool; Dr Marcus Peck, Consultant in Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine, Frimley Park Hospital NHS Foundation trust, Surrey; Dr Jim Gray, Consultant Microbiologist, Birmingham Children’s Hospital NHS Foundation Trust; Dr Paul Dark, Consultant in Intensive Care Medicine, Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust/University of Manchester; Dr John Butler, Consultant in Critical Care and Emergency Medicine, Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust; Dr Chris Chaloner, Consultant in Laboratory Medicine (Paediatric Biochemistry), Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust; Mr Suman Shrestha, Advanced Critical Care Nurse Practitioner, Frimley Park Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Surrey; and Dr Bob Phillips, Senior Clinical Academic and Honorary Consultant in Paediatric and Adolescent Oncology, University of York/Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust. We would also like to thank Gill Worthy, KSR Ltd, for her assistance in checking data extraction for the systematic review. Finally, the authors would like to thank the lay members of the NICE Diagnostics Advisory Committee and Assessment sub-group for providing input on the patients’ perspective at key stages of the assessment process.
Contribution of authors
Marie Westwood and Penny Whiting planned and performed the systematic review and interpretation of evidence.
Bram Ramaekers, Florian Tomini and Manuela Joore planned and performed the cost-effectiveness analyses and interpreted results.
Nigel Armstrong contributed to planning and interpretation of cost-effectiveness analyses, acquisition of input data, and conducted the model peer review.
Steve Ryder contributed to acquisition of model input data.
Lisa Stirk devised and performed the literature searches, and provided information support to the project.
Johan Severens and Jos Kleijnen provided senior advice and support to the systematic review and cost-effectiveness analyses, respectively.
All parties were involved in drafting and/or commenting on the report.
Data sharing statement
This is a systematic review; therefore, there are no data to share. Further information can be obtained from the corresponding author.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Padkin A, Goldfrad C, Brady AR, Young D, Black N, Rowan K. Epidemiology of severe sepsis occurring in the first 24 hrs in intensive care units in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Crit Care Med 2003;31:2332-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000085141.75513.2B.
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med 2013;41:580-637. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af.
- Levy MM, Fink M, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med 2003;31:1250-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000050454.01978.3B.
- National Statistics Hospital Episode Statistics, Admitted Patient Care – England, 2011–12 [NS]. Hospital Episode Statistics, Admitted Patient Care – England, 2011–12: Primary diagnosis, 3 characters table [.xls]. Leeds: HSCIC; 2012.
- McPherson D, Griffiths C, Williams M, Baker A, Klodawski E, Jacobson B, et al. Sepsis-associated mortality in England: an analysis of multiple cause death data from 2001 to 2010. BMJ Open 2013;3:1-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2013-002586.
- Accident and Emergency Attendances in England – 2012–13: Tables. Table 14: Number of A&E Attendances, A&E Primary Diagnosis ‘2 character description field’ 2011–12 and 2012–13. Leeds: HSCIC; 2014.
- Gill PJ, Goldacre MJ, Mant D, Heneghan C, Thomson A, Seagroatt V, et al. Increase in emergency admissions to hospital for children aged under 15 in England, 1999–2010: national database analysis. Arch Dis Child 2013;98:328-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2012-302383.
- Armon K, Stephenson T, Gabriel V, MacFaul R, Eccleston P, Werneke U, et al. Determining the common medical presenting problems to an accident and emergency department. Arch Dis Child 2001;84:390-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/adc.84.5.390.
- Pneumonia: Diagnosis and Management of Community- and Hospital-acquired Pneumonia in Adults. London: NICE; 2014.
- Principi N, Esposito S. Paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: current concept in pharmacological control. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2003;4:761-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1517/14656566.4.5.761.
- Macfarlane JT, Colville A, Guion A, Macfarlane RM, Rose DH. Prospective study of aetiology and outcome of adult lower respiratory tract infections in the community. Lancet 1993;341:511-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(93)90275-L.
- UK 5 Year Antimicrobial Resistance Strategy 2013 to 2018. London: DH; 2013.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence n.d. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/gid-phg89 (accessed 1 September 2015).
- Clayton J. Procalcitonin (Serum, Plasma). London: The Association for Clinical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine; 2013.
- B.R.A.H.M.S PCT Sensitive KRYPTOR. Hennigsdorf: Thermo Scientific; 2012.
- Lloyd MM, Kuyl JM. Comparison of three methods for procalcitonin analysis. Medical Technology SA 2012;26:48-52.
- Product Information – Elecsys BRAHMS PCT: Procalcitonin. Mannheim: Roche Diagnostics GmbH; 2010.
- Morin N, Renard N, Gaude H, Hainque B, Bernard M. Evaluation of the Analytical Performance of Vidas (R) B.R.A.H.M.S PCT n.d.
- LIAISON (R) BRAHMS PCT (R) (Ref 318101). Saluggia: DiaSorin S.p.A.; 2011.
- Manzano S, Bailey B, Girodias JB, Galetto-Lacour A, Cousineau J, Delvin E. Impact of procalcitonin on the management of children aged 1 to 36 months presenting with fever without source: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Emerg Med 2010;28:647-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2009.02.022.
- Wacker C, Prkno A, Brunkhorst FM, Schlattmann P. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker for sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2013;13:426-35. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70323-7.
- Neutropenic Sepsis: Prevention and Management of Neutropenic Sepsis in Cancer Patients. London: NICE; 2012.
- Sepsis: the Recognition, Diagnosis and Management of Severe Sepsis (In-process Guideline). London: NICE; n.d.
- Sepsis Study (ongoing). London: NCEPOD; n.d.
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Schunemann HJ, Tugwell P, Knottnerus A. GRADE guidelines: a new series of articles in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:380-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.09.011.
- Lim WS, Baudouin SV, George RC, Hill AT, Jamieson C, Le Jeune I, et al. BTS guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in adults: update 2009. Thorax 2009;64:iii1-55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thx.2009.121434.
- Feverish Illness in Children: Assessment and Initial Management in Children Younger Than 5 Years. London: NICE; 2013.
- Systematic Reviews: CRD’s Guidance for Undertaking Reviews in Health Care. York: University of York; 2009.
- Diagnostics Assessment Programme Manual. London: NICE; 2012.
- Handbook for DTA Reviews. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2013.
- Wong SS, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically sound treatment studies in EMBASE. J Med Libr Assoc 2006;94:41-7.
- Yu Z, Liu J, Sun Q, Qiu Y, Han S, Guo X. The accuracy of the procalcitonin test for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: a meta-analysis. Scand J Infect Dis 2010;42:723-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2010.489906.
- Liu B-H, Li H-F, Lei Y, Zhao S-X, Sun M-l. Clinical significance of dynamic monitoring of procalcitonin in guiding the use of antibiotics in patients with sepsis in ICU. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2013;25:690-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2013.11.013.
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928.
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 1986;7:177-88. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2.
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002;21:1539-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186.
- Annane D, Maxime V, Faller JP, Mezher C, Clec’h C, Martel P, et al. Procalcitonin levels to guide antibiotic therapy in adults with non-microbiologically proven apparent severe sepsis: a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2013;3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2012-002186.
- Brahms France . Study of Procalcitonin (PCT)-Guided Antibiotic Use in Severe Sepsis Patients Without Obvious Infection 2010. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01025180 (accessed 14 July 2014).
- Baer G, Baumann P, Buettcher M, Heininger U, Berthet G, Schafer J, et al. Procalcitonin guidance to reduce antibiotic treatment of lower respiratory tract infection in children and adolescents (ProPAED): a randomized controlled trial. PLOS One 2013;8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068419.
- Usefulness of a Novel Biomarker Procalcitonin to Guide Antibiotic Therapy in Children with Chest Infections. London: Current Controlled Trials Ltd.; 2009.
- Bouadma L, Luyt C-E, Tubach F, Cracco C, Alvarez A, Schwebel C, et al. Use of procalcitonin to reduce patients’ exposure to antibiotics in intensive care units (PRORATA trial): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010;375:463-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61879-1.
- Christ-Crain M, Stolz D, Bingisser R, Muller C, Miedinger D, Huber PR, et al. Procalcitonin guidance of antibiotic therapy in community-acquired pneumonia: a randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006;174:84-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200512-1922OC.
- Procalcitonin Guided Reduction of the Duration of Antibiotic Therapy in Community Acquired Pneumonia. London: Current Controlled Trials Ltd.; 2005.
- Christ-Crain M, Jaccard-Stolz D, Bingisser R, Gencay MM, Huber PR, Tamm M, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-guided treatment on antibiotic use and outcome in lower respiratory tract infections: cluster-randomised, single-blinded intervention trial. Lancet 2004;363:600-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15591-8.
- Deliberato RO, Marra AR, Sanches PR, Dalla Valle Martino M, Dos Santos Ferreira CE, Pasternak J, et al. Clinical and economic impact of procalcitonin to shorten antimicrobial therapy in septic patients with proven bacterial infection in an intensive care setting. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2013;76:266-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2013.03.027.
- Procalcitonin as a Tool to Shorten Antibiotic Therapy in the ICU. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2011.
- Drozdov D, Thomer A, Meili M, Schwarz S, Kouegbe RB, Regez K, et al. Procalcitonin, pyuria and proadrenomedullin in the management of urinary tract infections – ‘triple p in uti’: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2013;14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-14-84.
- Current Controlled Trials (Kantonsspital Aarau, Switzerland) . Procalcitonin, Pyuria and Proadrenomedullin in the Management of Urinary Tract Infections – the Triple P in UTI Study: Optimal Patient Transfer in the Canton of Argoviah (Optimaler Patiententransfer Im Kanton Aaragau) (OPTIMA III) 2012. http://isrctn.org/ISRCTN13663741 (accessed 14 July 2014).
- Esposito S, Tagliabue C, Picciolli I, Semino M, Sabatini C, Consolo S, et al. Procalcitonin measurements for guiding antibiotic treatment in pediatric pneumonia. Respir Med 2011;105:1939-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2011.09.003.
- Layios N, Lambermont B, Canivet JL, Morimont P, Preiser JC, Garweg C, et al. Procalcitonin usefulness for the initiation of antibiotic treatment in intensive care unit patients. Crit Care Med 2012;40:2304-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e318251517a.
- Layios N, Lambermont B, Ledoux D, Morimont P, Massion P, Garweg C, et al. Usefulness of procalcitonin for the decision of antibiotic treatment in ICU patients. Intensive Care Med 2009;35.
- Nobre V, Harbarth S, Graf JD, Rohner P, Pugin J. Use of procalcitonin to shorten antibiotic treatment duration in septic patients: a randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008;177:498-505. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200708-1238OC.
- Procalcitonin-Guided Antimicrobial Discontinuation. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2008.
- Qu R, Ji Y, Ling Y, Ye C-Y, Yang S-M, Liu Y-Y, et al. Procalcitonin is a good tool to guide duration of antibiotic therapy in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. A randomized prospective single-center controlled trial. Saudi Med J 2012;33:382-7.
- Roh YH. Antibiotic therapy with the guidance of procalcitonin in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Chest 2010;138. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.10630.
- Roh YH, Lee BJ. Treatment of elderly patients with community-acquired pneumonia with the guidance of procalcitonin. Chest 2013;144. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.1703693.
- Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Thomann R, Falconnier C, Wolbers M, Widmer I, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-based guidelines vs standard guidelines on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: the ProHOSP randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc 2009;302:1059-66. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1297.
- Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Thomann R, Falconnier C, Wolbers M, Widmer I, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-based guidelines compared with standard guidelines on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: The randomized-controlled multicenter ProHOSP trial. Crit Care 2009;13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc7550.
- Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Wolbers M, Schild U, Thomann R, Falconnier C, et al. Procalcitonin guided antibiotic therapy and hospitalization in patients with lower respiratory tract infections: a prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial. BMC Health Serv Res 2007;7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-7-102.
- Stolz D, Christ-Crain M, Bingisser R, Leuppi J, Miedinger D, Muller C, et al. Antibiotic treatment of exacerbations of COPD: a randomized, controlled trial comparing procalcitonin-guidance with standard therapy. Chest 2007;131:9-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.06-1500.
- Stolz D, Smyrnios N, Eggimann P, Pargger H, Thakkar N, Siegemund M, et al. Procalcitonin for reduced antibiotic exposure in ventilator-associated pneumonia: a randomised study. Eur Respir J 2009;34:1364-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00053209.
- Tang J, Long W, Yan L, Zhang Y, Xie J, Lu G, et al. Procalcitonin guided antibiotic therapy of acute exacerbations of asthma: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Infect Dis 2013;13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-13-596.
- Bonhoeffer J, Baumann P, Baer G, Heininger U. Procalcitonin guidance to reduce antibiotic treatment of children with lower respiratory tract infection. The ProPAED study. Eur J Pediatr 2011;170.
- PROcalcitonin Reduce Antibiotic Treatments in Acute-Ill Patients (PRORATA). Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2008.
- Brahms AG. Basel Institute of Clinical Epidemiology . Procalcitonin Guided Antibiotic Use in Acute Respiratory Tract Infections (PARTI)-Study 2007. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT00099840 (accessed 14 July 2014).
- Procalcitonin Guided Antibiotic Therapy and Hospitalisation in Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections: The ‘ProHOSP’ Study. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2008.
- Schuetz P, Grolimund E, Kutz A, Haubitz S, Mueller B. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy in patients with congestive heart failure and suspicion of lower respiratory tract infection: Results from a randomized trial. Crit Care 2013;17.
- Schuetz P, Kutz A, Grolimund E, Haubitz S, Demann D, Vogeli A, et al. Excluding infection through procalcitonin testing improves outcomes of congestive heart failure patients presenting with acute respiratory symptoms: results from the randomized ProHOSP trial. Int J Cardiol 2014;175:464-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.06.022.
- Drozdov D, Kutz A, Grolimund E, Rast A, Regez K, Guglielmetti M, et al. A Procalcitonin and Pyuria Based Algorithm Reduces Antibiotic Use in Urinary Tract Infections: A Randomized Controlled Trial n.d.
- Felix K, Gerstmeier S, Kyriakopoulos A, Howard OMZ, Dong HF, Eckhaus M, et al. Selenium deficiency abrogates inflammation-dependent plasma cell tumors in mice. Cancer Res 2004;64:2910-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2672.
- Drummond MF, Sculpher MJ, Torrance GW, O’Brien BJ, Stoddart GL. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2005.
- Michaelidis CI, Zimmerman RK, Nowalk MP, Fine MJ, Smith KJ. Cost-Effectiveness of Procalcitonin-Guided Antibiotic Therapy for Outpatient Management of Acute Respiratory Tract Infections in Adults n.d.
- Michaelidis CI, Zimmerman RK, Nowalk MP, Fine MJ, Smith KJ. Cost-effectiveness of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy for outpatient management of acute respiratory tract infections in adults. J Gen Intern Med 2014;29:579-86. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11606-013-2679-7.
- Smith KJ, Wateska A, Nowalk MP, Raymund M, Lee BY, Zimmerman RK, et al. Cost-effectiveness of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic use in community acquired pneumonia. J Gen Intern Med 2013;28:1157-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11606-013-2400-x.
- Briel M, Schuetz P, Mueller B, Young J, Schild U, Nusbaumer C, et al. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic use vs a standard approach for acute respiratory tract infections in primary care. Arch Intern Med 2008;168:2000-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archinte.168.18.2000.
- Burkhardt O, Ewig S, Haagen U, Giersdorf S, Hartmann O, Wegscheider K, et al. Procalcitonin guidance and reduction of antibiotic use in acute respiratory tract infection. Eur Respir J 2010;36:601-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00163309.
- Oppong R, Kaambwa B, Nuttall J, Hood K, Smith RD, Coast J. The impact of using different tariffs to value EQ-5D health state descriptions: an example from a study of acute cough/lower respiratory tract infections in seven countries. Eur J Health Econ 2013;14:197-209. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10198-011-0360-9.
- Gold MR, Franks P, McCoy KI, Fryback DG. Toward consistency in cost-utility analyses: using national measures to create condition-specific values. Med Care 1998;36:778-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00005650-199806000-00002.
- Diez-Padrisa N, Bassat Q, Morais L, O’Callaghan-Gordo C, Machevo S, Nhampossa T, et al. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as predictors of blood culture positivity among hospitalised children with severe pneumonia in Mozambique. Trop Med Int Health 2012;17:1100-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3156.2012.03035.x.
- Wilke MH, Grube RF, Bodmann KF. The use of a standardized PCT-algorithm reduces costs in intensive care in septic patients – a DRG-based simulation model. Eur J Med Res 2011;16:543-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/2047-783X-16-12-543.
- Heyland DK, Johnson AP, Reynolds SC, Muscedere J. Procalcitonin for reduced antibiotic exposure in the critical care setting: a systematic review and an economic evaluation. Crit Care Med 2011;39:1792-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31821201a5.
- Schuetz P, Balk R, Briel M, Kutz A, Christ-Crain M, Stolz D, et al. Economic evaluation of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy in acute respiratory infections: a U.S. health system perspective. Clin Chem Lab Med 2015;53:583-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2014-1015.
- Cleves A, Williams J, Carolan-Rees G. Economic report: Procalcitonin to Differentiate Bacterial Lower Respiratory Tract Infections from Non-bacterial Causes. London: Centre for Evidence-Based Purchasing; 2010.
- Bennett JE, Sumner W, Downs SM, Jaffe DM. Parents’ utilities for outcomes of occult bacteremia. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000;154:43-8.
- Buysse CMP, Raat H, Hazelzet JA, Hulst JM, Cransberg K, Hop WCJ, et al. Long-term health status in childhood survivors of meningococcal septic shock. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2008;162:1036-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.162.11.1036.
- Contrin LM, Paschoal VDA, Beccaria LM, Cesarino CB, Lobo SMA. Quality of life of severe sepsis survivors after hospital discharge. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem 2013;21:795-802. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0104-11692013000300020.
- Lobo SM, Contrin LM, Cesarino CB, Paschoal VD, Beccaria LM. Quality of life in survivors of severe sepsis: a Brazilian study. Intensive Care Med 2011;37.
- Cuthbertson BH, Elders A, Hall S, Taylor J, MacLennan G, Mackirdy F, et al. Mortality and quality of life in the five years after severe sepsis. Crit Care 2013;17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc12616.
- Granja C, Dias C, Costa-Pereira A, Sarmento A. Quality of life of survivors from severe sepsis and septic shock may be similar to that of others who survive critical illness. Crit Care 2004;8:R91-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc2818.
- Karlsson S, Ruokonen E, Varpula T, Ala-Kokko TI, Pettila V. Finnsepsis Study Group . Long-term outcome and quality-adjusted life years after severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 2009;37:1268-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819c13ac.
- Korosec Jagodic H, Jagodic K, Podbregar M. Long-term outcome and quality of life of patients treated in surgical intensive care: a comparison between sepsis and trauma. Crit Care 2006;10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc5047.
- Orwelius L, Lobo C, Teixeira Pinto A, Carneiro A, Costa-Pereira A, Granja C. Sepsis patients do not differ in health-related quality of life compared with other ICU patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2013;57:1201-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/aas.12164.
- Drabinski A, Williams G, Formica C. Observational evaluation of health state utilities among a cohort of sepsis patients. Value Health 2001;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4733.2001.40202-165.x.
- National Life Tables, 2011–2013. Newport: ONS; 2014.
- Management of Invasive Meningococcal Disease in Children and Young People: A National Clinical Guideline. Edinburgh: SIGN; 2008.
- British National Formulary. London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press; n.d.
- NHS Reference Costs. 2012–13 Tariff information spreadsheet – index. London: DH; 2012.
- Woodhead M, Blasi F, Ewig S, Garau J, Huchon G, Ieven M, et al. Guidelines for the management of adult lower respiratory tract infections – full version. Clin Microbiol Infect 2011;17:SE1-59. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03602.x.
- Guidelines for the Management of Sepsis (Including Neutropenic Sepsis). Manchester: The Christie NHS Foundation Trust; 2013.
- Daily Spot Exchange Rates Against Sterling. London: Bank of England; 2014.
- Mentula P, Leppaniemi A. Position paper: timely interventions in severe acute pancreatitis are crucial for survival. World J Emerg Surg 2014;9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1749-7922-9-15.
- Sharma VK, Howden CW. Prophylactic antibiotic administration reduces sepsis and mortality in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: a meta-analysis. Pancreas 2001;22:28-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006676-200101000-00005.
- Tejerina E, Frutos-Vivar F, Restrepo MI, Anzueto A, Abrouq F, Palizas F, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of ventilator-associated pneumonia. J Crit Care 2006;21:56-65. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2005.08.005.
- Kopterides P, Siempos II, Tsangaris I, Tsantes A, Armaganidis A. Procalcitonin-guided algorithms of antibiotic therapy in the intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care Med 2010;38:2229-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181f17bf9.
- Prkno A, Wacker C, Brunkhorst FM, Schlattmann P. Procalcitonin-guided therapy in intensive care unit patients with severe sepsis and septic shock – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care 2013;17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc13157.
- Soni NJ, Samson DJ, Galaydick JL, Vats V, Huang ES, Aronson N, et al. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hosp Med 2013;8:530-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2067.
- Agarwal R, Schwartz DN. Procalcitonin to guide duration of antimicrobial therapy in intensive care units: a systematic review. Clin Infect Dis 2011;53:379-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/cir408.
- Matthaiou DK, Ntani G, Kontogiorgi M, Poulakou G, Armaganidis A, Dimopoulos G. An ESICM systematic review and meta-analysis of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy algorithms in adult critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 2012;38:940-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00134-012-2563-7.
- Schuetz P, Müller B, Christ-Crain M, Stolz D, Tamm M, Bouadma L, et al. Procalcitonin to initiate or discontinue antibiotics in acute respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd007498.pub2.
- Tang H, Huang T, Jing J, Shen H, Cui W. Effect of procalcitonin-guided treatment in patients with infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infection 2009;37:497-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s15010-009-9034-2.
- Li H, Luo YF, Blackwell TS, Xie CM. Meta-analysis and systematic review of procalcitonin-guided therapy in respiratory tract infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2011;55:5900-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00335-11.
- Schuetz P, Briel M, Christ-Crain M, Stolz D, Bouadma L, Wolff M, et al. Procalcitonin to guide initiation and duration of antibiotic treatment in acute respiratory infections: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis 2012;55:651-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/cis464.
- Jensen JU, Hein L, Lundgren B, Bestle MH, Mohr TT, Andersen MH, et al. Procalcitonin-guided interventions against infections to increase early appropriate antibiotics and improve survival in the intensive care unit: a randomized trial. Crit Care Med 2011;39:2048-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31821e8791.
- Oliveira CF, Botoni FA, Oliveira CRA, Silva CB, Pereira HA, Serufo JC, et al. Procalcitonin versus C-reactive protein for guiding antibiotic therapy in sepsis: a randomized trial. Crit Care Med 2013;41:2336-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31828e969f.
- Maravic-Stojkovic V, Lausevic-Vuk L, Jovic M, Rankovic A, Borzanovic M, Marinkovic J. Procalcitonin-based therapeutic strategy to reduce antibiotic use in patients after cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Srp Arh Celok Lek 2011;139:736-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.2298/SARH1112736M.
- Schroeder S, Hochreiter M, Koehler T, Schweiger AM, Bein B, Keck FS, et al. Procalcitonin (PCT)-guided algorithm reduces length of antibiotic treatment in surgical intensive care patients with severe sepsis: results of a prospective randomized study. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2009;394:221-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00423-008-0432-1.
- Assink-de Jong E, de Lange DW, van Oers JA, Nijsten MW, Twisk JW, Beishuizen A. Stop Antibiotics on guidance of Procalcitonin Study (SAPS): a randomised prospective multicenter investigator-initiated trial to analyse whether daily measurements of procalcitonin versus a standard-of-care approach can safely shorten antibiotic duration in intensive care unit patients: calculated sample size: 1816 patients. BMC Infect Dis 2013;13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-13-178.
- Safety and efficacy of procalcitonin guided antibiotic therapy in adult Intensive Care Units (ICU’s). Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2014.
- PROcalcitonin to SHORTen Antibiotics Duration in PEDiatric ICU Patients (ProShort-Ped) Trial. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2012.
- Procalcitonin to Shorten Antibiotics Duration in ICU Patients. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2012.
- Procalcitonin Guided versus Conventional Antibiotic Therapy in Patients with Sepsis in the ICU. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2012.
- PCT and Clinical Algorithm for Determination of Duration of Antibiotics. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2012.
- Impact of the Lab-score on Antibiotic Prescription Rate in Children with Fever without Source. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2014.
- Procalcitonin as a Marker of Antibiotic Therapy in Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2014.
- Procalcitonin Versus C-reactive Protein to Guide Therapy in Community Acquired Pneumonia. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2012.
- Clinical Reassessment Versus Procalcitonin in Order to Shorten Antibiotic Duration in Community-acquired Pneumonia. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2014.
- Reduction of Antibiotic Therapy by Biomakers in Patients With CAP Episodes (REDUCE Study). Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2013.
- University of Pittsburgh, National Institute of General Medical Sciences, Biomérieux . Procalcitonin Antibiotic Consensus Trial (ProACT) 2014. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02130986 (accessed 14 July 2014).
- Jagminas L. Meta-analysis: Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy reduces treatment failure in acute respiratory infection. ACP J Club 2013;158. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-158-4-201302190-02005.
- A pilot study of procalcitonin-based algorithms to guide antibiotics treatment in secondary peritonitis after surgery. Camperdown, NSW: The Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry; 2012.
- Agarwal V, Baldua V, Garekar S, Mali S, Mhatre A, Patil S, et al. The role of procalcitonin in the pediatric cardiac ICU. Ann Pediatr Cardiol 2014;7.
- Andreola B, Bressan S, Callegaro S, Liverani A, Plebani M, Da Dalt L. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as diagnostic markers of severe bacterial infections in febrile infants and children in the emergency department. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2007;26:672-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/INF.0b013e31806215e3.
- Beni I, Fauzi M, Norzailin A, Shamsul A, Aini UN, Roslina A. Procalcitonin-aided antibiotic therapy management in hospital-acquired pneumonia and healthcare-associated pneumonia: a randomised controlled trial (the Prohap study). Respirology 2011;16.
- Bogner J, Nitschmann S. Management of antibiotics in regard of procalcitonin levels: PRORATA trial (PROcalcitonin to Reduce Antibiotic Treatments in Acutely ill patients). Internist (Berl) 2010;51:1582-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00108-010-2748-5.
- Bollu M, Marte-Grau AC, Bobba RK. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic use in acute respiratory tract infections. Arch Intern Med 2009;169. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2009.27.
- Brahms AG. Procalcitonin Level to Discontinue Antibiotics on ICU Patients with no Obvious Site of Infection. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2012.
- Cals JWL, Metlay JP. Procalcitonin-based guidelines and lower respiratory tract infections. J Am Med Assoc 2010;303. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.52.
- Procalcitonin in Fever of Unknown Etiology. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2007.
- Brahms AG. Stroke Adverse Outcome is Associated with Nosocomial Infections: PCTus- Guided Antibacterial Therapy in Severe Ischemic Stroke Patients (STRAWINSKI). Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2013.
- Charles PE, Ladoire S, Snauwaert A, Prin S, Aho S, Pechinot A, et al. Impact of previous sepsis on the accuracy of procalcitonin for the early diagnosis of blood stream infection in critically ill patients. BMC Infect Dis 2008;8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-8-163.
- Chen S-M, Chang H-M, Hung T-W, Chao Y-H, Tsai J-D, Lue K-H, et al. Diagnostic performance of procalcitonin for hospitalised children with acute pyelonephritis presenting to the paediatric emergency department. Emerg Med J 2013;30:406-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2011-200808.
- Normal procalcitonin guides antibiotic therapy for acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-single center, prospective randomized control study. Sichuan: Chinese Evidence-Based Medicine Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University; 2014.
- Chromik AM, Endter F, Uhl W, Thiede A, Reith HB, Mittelkotter U. Pre-emptive antibiotic treatment vs ‘standard’ treatment in patients with elevated serum procalcitonin levels after elective colorectal surgery: a prospective randomised pilot study. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2006;391:187-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00423-005-0009-1.
- Copenhagen HP. The Procalcitonin and Survival Study. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2010.
- Jensen JU, Lundgren B, Hein L, Mohr T, Petersen PL, Andersen LH, et al. The Procalcitonin And Survival Study (PASS) – A randomised multi-center investigator-initiated trial to investigate whether daily measurements biomarker Procalcitonin and pro-active diagnostic and therapeutic responses to abnormal Procalcitonin levels, can improve survival in intensive care unit patients. Calculated sample size (target population): 1000 patients. BMC Infect Dis 2008;8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-8-91.
- Procalcitonin To Reduce Antibiotics in Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (ProToCOLD). Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2012.
- De Angelis G, Restuccia G, Di Muzio F, Cipriani M, Milozzi E, Cauda R, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for antibiotic usage in the intensive care unit: a systematic review. Clin Microbiol Infect 2011;17.
- De S, Williams GJ, Hayen A, Macaskill P, McCaskill M, Isaacs D, et al. Accuracy of the ‘traffic light’ clinical decision rule for serious bacterial infections in young children with fever: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ 2013;346. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f866.
- Diaz-Flores RF. A letter in response to: Procalcitonin-guided interventions against infections to increase early appropriate antibiotics and improve survival in the intensive care unit: a randomized trial. Crit Care Med 2012;40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31824138c4.
- Ding JJ, Chen ZC, Feng KQ. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic use in acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Med Sci 2013;10:903-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.7150/ijms.4972.
- Dubos F, Moulin F, Gajdos V, De Suremain N, Biscardi S, Lebon P, et al. Serum procalcitonin and other biologic markers to distinguish between bacterial and aseptic meningitis. J Pediatr 2006;149:72-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2006.02.034.
- Brahms AG. Placebo Controlled Trial of Sodium Selenite and Procalcitonin Guided Antimicrobial Therapy in Severe Sepsis. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine; 2013.
- Use of Inflammatory Biomarkers to Guide Antibiotic Therapy in Patients with Severe Infections. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2012.
- Oliveira CF, Oliveira CA, Botoni FA, Silva CB, Pereira HA, Nobre V. C-reactive protein (CRP) is as useful as procalcitonin (PCT) to reduce antibiotic exposure in critically ill patients with sepsis: a randomized clinical trial. Intensive Care Med 2012;38.
- Gibot S. Procalcitonin in intensive care units: the PRORATA trial. Lancet 2010;375:1605-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60696-4.
- Gomez B, Bressan S, Mintegi S, Da Dalt L, Blazquez D, Olaciregui I, et al. Diagnostic value of procalcitonin in well-appearing young febrile infants. Pediatrics 2012;130:815-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-3575.
- Graber MA, Dachs R, Darby-Stewart A. Usefulness of procalcitonin measurement in reducing antibiotic use and identifying serious bacterial illness. Am Fam Physician 2011;84:177-9.
- Herd D. In children under age three does procalcitonin help exclude serious bacterial infection in fever without focus?. Arch Dis Child 2007;92:362-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/adc.2006.112441.
- Hochreiter M, Kohler T, Schweiger AM, Keck FS, Bein B, von Spiegel T, et al. Procalcitonin to guide duration of antibiotic therapy in intensive care patients: a randomized prospective controlled trial. Crit Care 2009;13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc7903.
- Hochreiter M, Koehler T, Schweiger AM, Keck FS, Bein B, von Spiegel T, et al. Procalcitonin to guide duration of antibiotic therapy in intensive care patients: a randomized prospective controlled trial. Infection 2009;37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc7903.
- Hochreiter M, Schroeder S. Procalcitonin to guide duration of antibiotic therapy in intensive care patients: a randomised prospective controlled trial. J Intensive Care Soc 2010;11:48-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/175114371001100115.
- Procalcitonin to guide duration of antibiotic therapy in intensive care patients. London: Current Controlled Trials Ltd.; 2009.
- Procalcitonin for Discontinuation of Antibiotic Therapy in Clinically Diagnosed Ventilator Associated Pneumonia. London: Current Controlled Trials Ltd.; 2006.
- Boeck L, Eggimann P, Smyrnios N, Pargger H, Thakkar N, Siegemund M, et al. Midregional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide and procalcitonin improve survival prediction in VAP. Eur Respir J 2011;37:595-603. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00023810.
- Procalcitonin-guided Antibiotic Therapy in Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) (AECOPD): a Randomised Trial – The ProCOLD Study. London: Current Controlled Trials Ltd.; 2005.
- Iwashyna TJ, Ely EW, Smith DM, Langa KM. Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. J Am Med Assoc 2010;304:1787-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.1553.
- Jaimes FA, De La Rosa GD, Valencia ML, Arango CM, Gomez CI, Garcia A, et al. A latent class approach for sepsis diagnosis supports use of procalcitonin in the emergency room for diagnosis of severe sepsis. BMC Anesthesiol 2013;13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2253-13-23.
- Jaimes F, De La Rosa G, Valencia M, Arango C, Gomez C, Garcia A, et al. Toward an operative diagnosis in sepsis: a latent class approach. Intensive Care Med 2010;36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-8-18.
- Jensen JU, Lundgren B, Lundgren JD. Meta-analysis of procalcitonin for sepsis detection. Lancet Infect Dis 2007;7:499-500. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70164-0.
- Jensen JU, Lungren JD. A letter in response to: Procalcitonin-guided interventions against infections to increase early appropriate antibiotics and improve survival in the intensive care unit: a randomized trial. Reply. Crit Care Med 2012;40:1038-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182451dda.
- Kollef MH. Will procalcitonin reduce antibiotic use in intensive care?. Lancet 2010;375:435-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60140-7.
- Kristoffersen KB, Sogaard OS, Wejse C, Black FT, Greve T, Tarp B, et al. Antibiotic treatment interruption of suspected lower respiratory tract infections based on a single procalcitonin measurement at hospital admission – a randomized trial. Clin Microbiol Infect 2009;15:481-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02709.x.
- Kulik DM, Uleryk EM, Maguire JL. Does this child have bacterial meningitis? A systematic review of clinical prediction rules for children with suspected bacterial meningitis. J Emerg Med 2013;45:508-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2013.03.042.
- Landman GW, Kleefstra N. Procalcitonin in intensive care units: the PRORATA trial. Lancet 2010;375. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60697-6.
- Lee SH, Chan RC, Wu JY, Chen HW, Chang SS, Lee CC. Diagnostic value of procalcitonin for bacterial infection in elderly patients: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract 2013;67:1350-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12278.
- Leroy S, Fernandez-Lopez A, Nikfar R, Romanello C, Bouissou F, Gervaix A, et al. Association of procalcitonin with acute pyelonephritis and renal scars in pediatric UTI. Pediatrics 2013;131:870-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-2408.
- Leroy S, Galetto-Lacour A, Bressan S, Andreola B, Zamora S, Girodias JB, et al. Refinement of a risk score, the Lab-Score, for identification of severe bacterial infection in children with fever without source. Eur J Emerg Med 2013;20.
- Levin PD, Idrees S, Sprung CL, Weissman C, Weiss Y, Moses AE, et al. Antimicrobial use in the ICU: Indications and accuracy – an observational trial. J Hosp Med 2012;7:672-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jhm.1964.
- Mahajan P, Grzybowski M, Chen X, Kannikeswaran N, Stanley R, Singal B, et al. Procalcitonin as a marker of serious bacterial infections in febrile children younger than 3 years old. Acad Emerg Med 2014;21:171-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/acem.12316.
- Mintegi S, Bressan S, Gomez B, Da Dalt L, Blazquez D, Olaciregui I, et al. Markers for invasive bacterial infection in well-appearing young febrile infants. The value of procalcitonin. Arch Dis Child 2012;97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2012-302724.0368.
- Mokart D, Leone M. Procalcitonin in intensive care units: the PRORATA trial. Lancet 2010;375. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60694-0.
- Reduction the Duration of Antibiotic Therapy in the Elderly (PROPAGE). Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2013.
- Niewoehner DE. Procalcitonin level-guided treatment reduced antibiotic use in exacerbations of COPD. ACP J Club 2007;146.
- Nijman RG, Moll HA, Smit FJ, Gervaix A, Weerkamp F, Vergouwe Y, et al. C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and the lab-score for detecting serious bacterial infections in febrile children at the emergency department: a prospective observational study. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2014;33:e273-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000000466.
- Nijman RG, Moll HA, Vergouwe Y, Smit FJ, Weerkamp F, Van Der Lei J, et al. Procalcitonin does not outperform C-reactive protein in diagnosing serious bacterial infections in febrile children: a prospective observational study. Eur J Emerg Med 2013;20:225-6.
- Ning HX, Li DD, Tao CM, Wang TT, Bi XH. Diagnostic value of procalcitonin for infection or noninfection in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Clin Microbiol Infect 2011;17.
- Oliveira CF, Botoni FA, Oliveira CA, Pereira HAC, Padua M, Nobre V. The usefulness of C-reactive protein (CRP) compared to procalcitonin (PCT) to reduce antibiotic exposure in critically ill patients with sepsis: a pilot study. Intensive Care Med 2011;37.
- Oostenbrink R, Kerkhof E, Nijman RG, Smit FJ, Thompson M, Lakhanpaul M, et al. Diagnostic value of alarm signs and their combinations to detect serious infections in febrile children; an international pediatric emergency care study. Eur J Emerg Med 2013;20.
- Prkno A, Wacker C, Brunkhorst FM, Schlattmann P. Procalcitonin-guided therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infection 2013;41.
- Ray P, Badarou-Acossi G, Viallon A, Boutoille D, Arthaud M, Trystram D, et al. Accuracy of the cerebrospinal fluid results to differentiate bacterial from non bacterial meningitis, in case of negative gram-stained smear. Am J Emerg Med 2007;25:179-84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2006.07.012.
- Reinhart K, Brunkhorst FM. Meta-analysis of procalcitonin for sepsis detection. Lancet Infect Dis 2007;7:500-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70165-2.
- Saeed K, Dryden M, Bourne S, Paget C, Proud A. Reduction in antibiotic use through procalcitonin testing in patients in the medical admission unit or intensive care unit with suspicion of infection. J Hosp Infect 2011;78:289-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2011.03.018.
- Sanders S, Barnett A, Correa-Velez I, Coulthard M, Doust J. Systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of C-reactive protein to detect bacterial infection in nonhospitalized infants and children with fever. J Pediatr 2008;153:570-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.04.023.
- Schuetz P, Batschwaroff M, Dusemund F, Albrich W, Burgi U, Maurer M, et al. Effectiveness of a procalcitonin algorithm to guide antibiotic therapy in respiratory tract infections outside of study conditions: a post-study survey. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2010;29:269-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10096-009-0851-0.
- Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Albrich W, Zimmerli W, Mueller B. Guidance of antibiotic therapy with procalcitonin in lower respiratory tract infections: insights into the ProHOSP study. Virulence 2010;1:88-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/viru.1.2.10488.
- Schuetz P, Muller B, Christ-Crain M. Meta-analysis: procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy reduces treatment failure in acute respiratory infection. Ann Intern Med 2013;158.
- Sheu J-N, Chang H-M, Chen S-M, Hung T-W, Lue K-H. The role of procalcitonin for acute pyelonephritis and subsequent renal scarring in infants and young children. J Urol 2011;186:2002-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.07.025.
- Soni NJ, Samson DJ, Galaydick JL, Vats V, Pitrak DL, Aronson N. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2012.
- Sridharan P, Chamberlain RS. The utility of procalcitonin as a biomarker to predict the duration of antibiotic therapy in adult sepsis patients. J Surg Res 2013;179. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2012.10.313.
- Impact of Procalcitonin on the Management of Children Aged 1 to 36 Month Presenting With a Fever Without a Source. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2008.
- Stannard D. Procalcitonin to initiate or discontinue antibiotics in acute respiratory tract infections. Crit Care Nurse 2014;34:75-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.4037/ccn2014559.
- Tang BM, Eslick GD. Procalcitonin for sepsis: methodological issues in meta-analysis lead to further uncertainty. Crit Care Med 2007;35.
- Tarnow-Mordi W, Gebski V. Procalcitonin in intensive care units: the PRORATA trial. Lancet 2010;375. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60695-2.
- Thompson M, Van den Bruel A, Verbakel J, Lakhanpaul M, Haj-Hassan T, Stevens R, et al. Systematic review and validation of prediction rules for identifying children with serious infections in emergency departments and urgent-access primary care. Health Technol Assess 2012;16:1-100. http://dx.doi.org/10.3310/hta16150.
- Ulm L, Ohlraun S, Harms H, Hoffmann S, Klehmet J, Ebmeyer S, et al. STRoke Adverse outcome is associated WIth NoSocomial Infections (STRAWINSKI): procalcitonin ultrasensitive-guided antibacterial therapy in severe ischaemic stroke patients – rationale and protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Int J Stroke 2013;8:598-603. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-4949.2012.00858.x.
- Viral Testing and Biomarkers to Reduce Antibiotic Use for Respiratory Infections. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2014.
- Uusitalo-Seppala R, Koskinen P, Leino A, Peuravuori H, Vahlberg T, Rintala EM. Early detection of severe sepsis in the emergency room: diagnostic value of plasma C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and interleukin-6. Scand J Infect Dis 2011;43:883-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2011.600325.
- Van den Bruel A, Thompson MJ, Haj-Hassan T, Stevens R, Moll H, Lakhanpaul M, et al. Diagnostic value of laboratory tests in identifying serious infections in febrile children: systematic review. BMJ 2011;342. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d3082.
- Yu CW, Juan LI, Wu MH, Shen CJ, Wu JY, Lee CC. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and white blood cell count for suspected acute appendicitis. Br J Surg 2013;100:322-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bjs.9008.
- Zhang L, Huang J, Xu T, Lin Y. Procalcitonin-guided algorithms of antibiotic therapy in community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 2012;35:275-82.
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org/ (accessed 13 October 2014).
Appendix 1 Literature search strategies
Clinical effectiveness search strategies
Rapid appraisal searches
The Cochrane Library
Searched: 7 April 2014.
Records found:
-
CDSR Issue 4 of 12, April 2014 = 14.
-
DARE Issue 1 of 4, January 2014 = 13.
-
HTA Issue 1 of 4, January 2014 = 0.
-
NHS EED Issue 1 of 4, January 2014 = 5.
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome] explode all trees (3265)
#2 “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS (1130)
#3 sepsis* or septic* or sepses (6770)
#4 bacill*emia* or bacter*emia* or endotox*emia* or pyoh*emia* or py*emia* (2020)
#5 fusobacterium near/2 necrophorum (6)
#6 Lemierre* near/2 (disease* or syndrome*) (1)
#7 necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc*emia or urosepsis or fung*emia or candid*emia (265)
#8 Neisseria near/2 meningitidis near/2 bacter*emia (0)
#9 staphylococc* near/2 bacter*emia (74)
#10 (bacter*emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) near/3 shock* (47)
#11 toxic near/2 forward near/2 failure (0)
#12 blood near/2 poison* (136)
#13 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 (9831)
#14 MeSH descriptor: [Protein Precursors] explode all trees (2483)
#15 MeSH descriptor: [Calcitonin] this term only (553)
#16 #14 and #15 (141)
#17 PCT (369)
#18 procalcitonin or “pro-calcitonin” or “56645-65-9” or (calcitonin near/2 precursor*) (270)
#19 brahms or KRYPTOR or “b r a h m s” (21)
#20 #16 or #17 or #18 or #19 (543)
#21 #13 and #20 (131)
(CDSR = 14; DARE = 13; HTA = 0; NHS EED = 5)
PROSPERO
www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/ up to 9 April 2014.
Searched: 7 April 2014.
| Search term (all fields) | Records |
|---|---|
| sepsis or septic or blood poisoning | 49 |
| procalcitonin or pro-calcitonin or calcitonin or brahms or kryptor | 5 |
| Total before deduplication | 54 |
| Total after deduplication | 52 |
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance
URL: www.nice.org.uk/ up to 8 April 2014.
Searched: 8 April 2014.
Limited to information type “Guidance”
| SEARCH TERM (all fields) | Records |
|---|---|
| brahms | 2 |
| kryptor | 1 |
| procalcitonin | 3 |
| pro-calcitonin | 0 |
| calcitonin | 1 |
| Sepsis | 73 |
| Septic | 16 |
| blood poisoning | 10 |
| Total | 106 |
National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment programme
URL: www.hta.ac.uk/ up to 8 April 2014.
Searched: 8 April 2014.
| Search term (all fields) | Search website | Search project portfolio (hand-sifted for relevance) |
|---|---|---|
| brahms | 0 | 0 |
| kryptor | 0 | 0 |
| procalcitonin | 0 | 3 |
| pro-calcitonin | 0 | 0 |
| calcitonin | 0 | 0 |
| Sepsis | 0 | 12 |
| Septic | 0 | 1 |
| blood poisoning | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 0 | 16 |
| Total after deduplication | 0 | 16 |
US Food and Drug Administration
URL: www.fda.gov/ up to 8 April 2014.
Searched: 8 April 2014.
Searched whole site
| Search term (all fields) | Records |
|---|---|
| brahms | 48 |
| procalcitonin | 48 |
| kryptor | 6 |
| Total | 103 |
Guidelines International Network (G-I-N)
URL: www.g-i-n.net/ up to 9 April 2014.
Searched: 9 April 2014.
| Search term | Search website | Search guidelines | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| brahms | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| kryptor | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| procalcitonin | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pro-calcitonin | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| calcitonin | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sepsis | 4 | 11 | 15 |
| Septic | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| blood poisoning | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 6 | 13 | 19 |
| Total after deduplication | 5 | 10 | 15 |
National Guidelines Clearinghouse (NGCH)
URL: www.guideline.gov/index.aspx up to 9 April 2014.
Searched: 9 April 2014.
| Search term (all fields) | Records |
|---|---|
| brahms | 0 |
| kryptor | 0 |
| procalcitonin OR pro-calcitonin | 11 |
| calcitonin | 34 |
| Sepsis or septic | 173 |
| “blood poisoning” | 0 |
| Total | 218 |
Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA)
URL: www.mhra.gov.uk/index.htm up to 9 April 2014.
Searched: 9 April 2014.
| Search term (all fields) | Records |
|---|---|
| brahms or kryptor | 10 |
| procalcitonin or pro-calcitonin | 2 |
| “blood poisoning” | 10 |
| Total | 22 |
The Medion database
URL: www.mediondatabase.nl/ up to 9 April 2014.
Searched: 23 September 2014.
| Search term (topic field) | Records |
|---|---|
| brahms | 0 |
| kryptor | 0 |
| procalcitonin | 0 |
| pro-calcitonin | 0 |
| calcitonin | 0 |
| Sepsis | 0 |
| Septic | 0 |
| blood poisoning | 0 |
| Total | 0 |
Randomised controlled trial searches
EMBASE (OvidSP)
1974 to 27 June 2014.
Searched: 30 June 2014.
Records found: 1210.
-
exp systemic inflammatory response syndrome/ (172,787)
-
exp bacterial infection/ (745,043)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (10,736)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (191,638)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (48,133)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1164)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (798)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (3762)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (19)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (34,768)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (11,163)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (257)
-
infect$.ti,ab,ot. (1,461,612)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (60,674)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (475,125)
-
or/1-16 (2,327,414)
-
Procalcitonin/ (4820)
-
PCT.ti,ab,ot. (6593)
-
(procalcitonin or pro-calcitonin or 56645-65-9 or (calcitonin adj2 precursor$)).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn,tn. (5087)
-
brahms.af. (915)
-
KRYPTOR.af. (221)
-
b r a h m s.af. (11)
-
or/18-23 (10,280)
-
17 and 24 (4786)
-
Random$.tw. or clinical trial$.mp. or exp health care quality/ (3,261,790)
-
25 and 26 (1231)
-
animal/ (1,569,119)
-
animal experiment/ (1,782,343)
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or murine or rodent or rodents or hamster or hamsters or pig or pigs or porcine or rabbit or rabbits or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or cow or bovine or sheep or ovine or monkey or monkeys).ti,ab,ot,hw. (5,658,580)
-
or/28-30 (5,658,580)
-
exp human/ (14,900,947)
-
human experiment/ (326,401)
-
or/32-33 (14,902,376)
-
31 not (31 and 34) (4,528,206)
-
27 not 35 (1218)
-
limit 36 to yr=“1995 -Current” (1210)
Based on trials filter
Wong SS, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically sound treatment studies in EMBASE. J Med Libr Assoc 2006;94:41–7.
MEDLINE (OvidSP)
1946 to June Week 3 2014.
Searched: 30 June 2014.
Records found: 739.
-
exp Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome/ (94,981)
-
exp bacterial infections/ (719,780)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (6774)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (123,216)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (36,734)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (896)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (483)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1520)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (17)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (24,082)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (8473)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (139)
-
infect$.ti,ab,ot. (1,157,024)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (46,704)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (367,834)
-
or/1-16 (1,896,545)
-
exp Protein Precursors/ and Calcitonin/ (2200)
-
PCT.ti,ab,ot. (3921)
-
(procalcitonin or pro-calcitonin or 56645-65-9 or (calcitonin adj2 precursor$)).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2468)
-
brahms.af. (318)
-
KRYPTOR.af. (68)
-
b r a h m s.af. (18)
-
or/18-23 (5718)
-
17 and 24 (2279)
-
randomized controlled trial.pt. (376,175)
-
controlled clinical trial.pt. (88,531)
-
randomized.ab. (274,544)
-
placebo.ab. (146,796)
-
drug therapy.fs. (1,708,719)
-
randomly.ab. (194,627)
-
trial.ab. (284,610)
-
groups.ab. (1,250,317)
-
or/26-33 (3,208,598)
-
exp animals/ not (exp animals/ and humans/) (3,954,108)
-
34 not 35 (2,730,725)
-
25 and 36 (752)
-
limit 37 to yr=“1995 -Current” (739)
Trials filter
Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for Studies. Box 6.4.c: Cochrane Highly sensitive search strategy for identifying randomized controlled trials in Medline: Sensitivity-maximizing version (2008 version); OVID format. In Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. URL: www.cochrane-handbook.org.
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, MEDLINE Daily Update (OvidSP)
27 June 2014.
Searched: 30 June 2014.
Records found: 67.
-
exp Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome/ (100)
-
exp bacterial infections/ (628)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (361)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (6694)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1503)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (52)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (49)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (121)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (2)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (793)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (229)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (15)
-
infect$.ti,ab,ot. (77,602)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1024)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (15,810)
-
or/1-16 (93,626)
-
exp Protein Precursors/ and Calcitonin/ (4)
-
PCT.ti,ab,ot. (358)
-
(procalcitonin or pro-calcitonin or 56645-65-9 or (calcitonin adj2 precursor$)).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (291)
-
brahms.af. (26)
-
KRYPTOR.af. (7)
-
b r a h m s.af. (0)
-
or/18-23 (525)
-
17 and 24 (255)
-
randomized controlled trial.pt. (957)
-
controlled clinical trial.pt. (84)
-
randomized.ab. (23,138)
-
placebo.ab. (8510)
-
drug therapy.fs. (1798)
-
randomly.ab. (20,509)
-
trial.ab. (24,490)
-
groups.ab. (117,569)
-
or/26-33 (157,619)
-
exp animals/ not (exp animals/ and humans/) (2712)
-
34 not 35 (157,125)
-
25 and 36 (67)
-
limit 37 to yr=“1995 -Current” (67)
Trials filter
Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for Studies. Box 6.4.c: Cochrane Highly sensitive search strategy for identifying randomized controlled trials in Medline: Sensitivity-maximizing version (2008 version); OVID format. In Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. URL: www.cochrane-handbook.org.
PubMed
1995 to 14 July 2014.
Searched: 14 July 2014.
Records found: 86.
-
This strategy aims to identify records that are on PubMed, but not included in MEDLINE or MEDLINE In-Process (OvidSP). Line #7 limits the search results in this way.
-
The sepsis/bacterial infection facet was excluded to keep search as broad as possible.
#10 “Search ((((((((((protein precursors[MeSH Terms]) AND calcitonin[MeSH Terms])) OR PCT[Title/Abstract]) OR (((procalcitonin[Title/Abstract]) OR ““pro-calcitonin””[Title/Abstract]) OR ““calcitonin precursor*””[Title/Abstract])) OR (((brahms) OR kryptor) OR ““b r a h m s””))) AND (((((““randomized controlled trial””[Publication Type]) OR ““controlled clinical trial””[Publication Type])) OR (((((randomized[Title/Abstract]) OR placebo[Title/Abstract]) OR randomly[Title/Abstract]) OR trial[Title/Abstract]) OR groups[Title/Abstract])) OR ““drug therapy””[MeSH Subheading])) AND ((pubstatusaheadofprint OR publisher[sb] OR pubmednotmedline[sb])))) NOT (animals [mh] NOT humans [mh])” (86)
#9 “Search animals [mh] NOT humans [mh]” (3,904,987)
#8 “Search ((((((((protein precursors[MeSH Terms]) AND calcitonin[MeSH Terms])) OR PCT[Title/Abstract]) OR (((procalcitonin[Title/Abstract]) OR ““pro-calcitonin””[Title/Abstract]) OR ““calcitonin precursor*””[Title/Abstract])) OR (((brahms) OR kryptor) OR ““b r a h m s””))) AND (((((““randomized controlled trial””[Publication Type]) OR ““controlled clinical trial””[Publication Type])) OR (((((randomized[Title/Abstract]) OR placebo[Title/Abstract]) OR randomly[Title/Abstract]) OR trial[Title/Abstract]) OR groups[Title/Abstract])) OR ““drug therapy””[MeSH Subheading])) AND ((pubstatusaheadofprint OR publisher[sb] OR pubmednotmedline[sb]))” (86)
#7 “Search (pubstatusaheadofprint OR publisher[sb] OR pubmednotmedline[sb])” (1,792,621)
#6 “Search ((((““randomized controlled trial””[Publication Type]) OR ““controlled clinical trial””[Publication Type])) OR (((((randomized[Title/Abstract]) OR placebo[Title/Abstract]) OR randomly[Title/Abstract]) OR trial[Title/Abstract]) OR groups[Title/Abstract])) OR ““drug therapy””[MeSH Subheading]” (3,394,868)
#5 “Search (((((protein precursors[MeSH Terms]) AND calcitonin[MeSH Terms])) OR PCT[Title/Abstract]) OR (((procalcitonin[Title/Abstract]) OR ““pro-calcitonin””[Title/Abstract]) OR ““calcitonin precursor*””[Title/Abstract])) OR (((brahms) OR kryptor) OR ““b r a h m s””)” (6314)
#4 “Search ((brahms) OR kryptor) OR ““b r a h m s””” (394)
#3 “Search ((procalcitonin[Title/Abstract]) OR ““pro-calcitonin””[Title/Abstract]) OR ““calcitonin precursor*””[Title/Abstract]” (2617)
#2 “Search PCT[Title/Abstract]” (4327)
#1 “Search (protein precursors[MeSH Terms]) AND calcitonin[MeSH Terms]” (2189)
Trials filter
Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for Studies. Box 6.4.c: Cochrane Highly sensitive search strategy for identifying randomized controlled trials in Medline: Sensitivity-maximizing version (2008 version); OVID format. In Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. URL: www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) (EBSCOhost)
1995 to 25 June 2014.
Searched: 30 June 2014.
Records found: 205.
S1 (MH “Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome+”) (6393)
S2 (MH “Bacterial Infections+”) (50,338)
S3 “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS (965)
S4 sepsis* or septic* or sepses (11,696)
S5 bacill#emia* or bacter#emia* or endotox#emia* or pyoh#emia* or py#emia* (14,336)
S6 fusobacterium N2 necrophorum (26)
S7 Lemierre* N2 (disease* or syndrome*) (93)
S8 necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc#emia or urosepsis (116)
S9 Neisseria N2 meningitidis N2 bacter#emia (1)
S10 tetanus (1899)
S11 (bacter#emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) N3 shock* (368)
S12 toxic N2 forward N2 failure (0)
S13 blood N2 poison* (133)
S14 infect* (159,239)
S15 bacterial N2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*) (4245)
S16 bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli” (18,464)
S17 S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4 OR S5 OR S6 OR S7 OR S8 OR S9 OR S10 OR S11 OR S12 OR S13 OR S14 OR S15 OR S16 (193,148)
S18 (MH “Protein Precursors+”) (2085)
S19 (MH “Calcitonin”) (816)
S20 S18 AND S19 (199)
S21 PCT (725)
S22 procalcitonin or “pro-calcitonin” or “56645-65-9” or (calcitonin N2 precursor*) (376)
S23 brahms or KRYPTOR or “b r a h m s” (12)
S24 S20 OR S21 OR S22 OR S23 (1011)
S25 S17 AND S24 (393)
S26 (MH “Prognosis+”) (146,028)
S27 (MH “Study Design+”) (521,326)
S28 random* (144,824)
S29 S26 OR S27 OR S28 (629,916)
S30 S25 AND S29 (205)
S31 (ZR “1995”) or (ZR “1996”) or (ZR “1997”) or (ZR “1998”) or (ZR “1999”) or (ZR “2000”) or (ZR “2001”) or (ZR “2002”) or (ZR “2003”) or (ZR “2004”) or (ZR “2005”) or (ZR “2006”) or (ZR “2007”) or (ZR “2008”) or (ZR “2009”) or (ZR “2010”) or (ZR “2011”) or (ZR “2012”) or (ZR “2013”) or (ZR “2014”) (2,807,096)
S32 S30 AND S31 (205)
Trials filter
Wong SS, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Optimal CINAHL search strategies for identifying therapy studies and review articles. J Nurs Scholarsh 2006;38:194–9.
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library – Wiley)
Issue 5 of 12, May 2014.
Searched: 30 June 2014.
Records found: 203.
#1MeSH descriptor: [Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome] explode all trees (3289)
#2 [mh “bacterial infections”] (14,301)
#3 “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS (1164)
#4 sepsis* or septic* or sepses (6903)
#5 bacill*emia* or bacter*emia* or endotox*emia* or pyoh*emia* or py*emia* (2052)
#6 fusobacterium near/2 necrophorum (6)
#7 Lemierre* near/2 (disease* or syndrome*) (1)
#8 necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc*emia or urosepsis (82)
#9 Neisseria near/2 meningitidis near/2 bacter*emia (0)
#10 tetanus (1529)
#11 (bacter*emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) near/3 shock* (47)
#12 toxic near/2 forward near/2 failure (0)
#13 blood near/2 poison* (136)
#14 infect* (69,614)
#15 bacterial near/2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*) (1954)
#16 bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli” (8400)
#17 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 (79,707)
#18 MeSH descriptor: [Protein Precursors] explode all trees (2487)
#19 MeSH descriptor: [Calcitonin] this term only (557)
#20 #18 and #19 (142)
#21 PCT (374)
#22 procalcitonin or “pro-calcitonin” or “56645-65-9” or (calcitonin near/2 precursor*) (288)
#23 brahms or KRYPTOR or “b r a h m s” (22)
#24 #20 or #21 or #22 or #23 (561)
#25 #17 and #24 Publication Year from 1995 to 2014, in Trials (203)
Science Citation Index (Web of Science)
1995 to 27 June 2014.
Searched: 30 June 2014.
Records found: 1292.
#27 (1292) #25 not #26
#26 (1,748,209) TOPIC: (cat or cats or dog or dogs or animal or animals or rat or rats or hamster or hamster or feline or ovine or canine or bovine or sheep)
#25 (1341) #24 AND #20
#24 (4,218,379) #23 OR #22 OR #21
#23 (779,600) TOPIC: ((study OR studies) SAME design)
#22 (3,726,032) TOPIC: ((clinic* SAME trial*) OR (placebo* OR random* OR control* OR prospectiv*))
#21 (173,285) TOPIC: ((singl* or doubl* or trebl* or tripl*) SAME (blind* or mask*))
#20 (3010) #19 AND #15
#19 (9574) #18 OR #17 OR #16
#18 (363) TOPIC: (brahms or KRYPTOR or “b r a h m s”)
#17 (3384) TOPIC: (procalcitonin or “pro-calcitonin” or “56645-65-9” or (calcitonin near/2 precursor*))
#16 (7037) TOPIC: (PCT)
#15 (1,203,220) #14 OR #13 OR #12 OR #11 OR #10 OR #9 OR #8 OR #7 OR #6 OR #5 OR #4 OR #3 OR #2 OR #1
#14 (239,288) TOPIC: (bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli”)
#13 (17,350) TOPIC: (bacterial near/2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*))
#12 (973,337) TOPIC: (infect*)
#11 (108) TOPIC: (blood near/2 poison*)
#10 (0) TOPIC: (toxic near/2 forward near/2 failure)
#9 (6314) TOPIC: ((bacter$emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) near/3 shock*)
#8 (9233) TOPIC: (tetanus)
#7 (7) TOPIC: (Neisseria near/2 meningitidis near/2 bacter$emia)
#6 (1124) TOPIC: (necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc$emia or urosepsis)
#5 (488) TOPIC: (Lemierre* near/2 (disease* or syndrome*))
#4 (525) TOPIC: (fusobacterium near/2 necrophorum)
#3 (4297) TOPIC: (bacill$emia* or bacter$emia* or endotox$emia* or pyoh$emia* or py$emia*)
#2 (87,338) TOPIC: (sepsis* or septic* or sepses)
#1 (14,020) TOPIC: (“systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS)
Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (LILACS)
URL: http://regional.bvsalud.org/php/index.php?lang=en
1995 to date.
Searched: 1 July 2014.
Records found: 5.
procalcitonin OR pct OR brahms OR kryptor AND (instance:”regional”) AND ( db:(“LILACS”) AND type_of_study:(“clinical_trials”)
National Institute of Health Research Health Technology Assessment programme
URL: www.nets.nihr.ac.uk/programmes/hta.
1995 to date.
Searched: 1 July 2014.
Records found: 0.
procalcitonin OR pct OR brahms OR kryptor
ClinicalTrials.gov
URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/.
Searched: 14 July 2014.
Records found: 136.
procalcitonin OR “pro-calcitonin” OR “calcitonin precursor”
Current Controlled Trials
URL: www.controlled-trials.com.
Searched: 14 July 2014.
Records found: 59.
Procalcitonin* OR pro-calcitonin OR calcitonin precursor*
WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP)
URL: www.who.int/ictrp/en/.
Searched: 14 July 2014.
Records found: 118.
Procalcitonin* OR “pro-calcitonin” OR “calcitonin precursor*”
Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health (RCPCH) meetings
URL: http://adc.bmj.com/content/supplemental.
Searched: 16 September 2014.
Records found: 0.
Limits: 2009–14.
Title field only
| PCT | procalcitonin | pro-calcitonin | calcitonin precursor | brahms | KRYPTOR | TOTAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2012 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2013 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2014 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 0 |
European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID)
URL: www.escmid.org/research_projects/eccmid/past_eccmids/.
Searched: 16 September 2014.
Records found: 31.
Limits: 2009–14.
Title field only
| PCT | procalcitonin | pro-calcitonin | calcitonin precursor | brahms | KRYPTOR | TOTAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral |
| 0 – posters | 5 – posters | 0 – posters | 0 – posters | 0 – posters | 0 – posters | 5 – posters | |
| 2010 | 1 – oral | 2 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 3 – oral |
| 2 – posters | 2 – posters | 0 – posters | 0 – posters | 0 – oral | 0 – posters | 4 – posters | |
| 2011 | 0 – oral | 1 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 0 – oral | 1 oral |
| Posters – NA | Posters – NA | Posters – NA | Posters – NA | Posters – NA | Posters – NA | Posters – NA | |
| 2012 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 2013 | 1 | 3 (plus 1 dupe) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 2014 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| TOTAL | 31 |
International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine
URL: http://ccforum.com/supplements/.
Searched: 16 September 2014.
Records found: 25.
Limits: 2009–14.
Title field only
| PCT | procalcitonin | pro-calcitonin | calcitonin precursor | brahms | KRYPTOR | TOTAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 2010 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 2011 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 2012 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 2013 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 2014 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| TOTAL | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 |
Paediatric searches
EMBASE (OvidSP)
1974 to 2014 August 29.
Searched: 2 September 2014.
Records found: 297.
-
exp systemic inflammatory response syndrome/ (175,423)
-
exp bacterial infection/ (750,468)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (10,939)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (194,269)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (48,625)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1168)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (804)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (3815)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (19)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (34,954)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (11,223)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (259)
-
infect$.ti,ab,ot. (1,477,857)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (61,241)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (478,890)
-
or/1-16 (2,349,530)
-
Procalcitonin/ (5000)
-
PCT.ti,ab,ot. (6741)
-
(procalcitonin or pro-calcitonin or 56645-65-9 or (calcitonin adj2 precursor$)).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn,tn. (5268)
-
brahms.af. (929)
-
KRYPTOR.af. (225)
-
b r a h m s.af. (11)
-
or/18-23 (10,524)
-
Emergency Treatment/ (14,191)
-
Evidence Based Emergency Medicine/ (197)
-
Pediatric Advanced Life Support/ (421)
-
exp Emergency Care/ (22,685)
-
Emergency/ (37,050)
-
Emergency Medicine/ (27,958)
-
Emergency Health Service/ (67,376)
-
Emergency Patient/ (1522)
-
Emergency Ward/ (64,201)
-
Intensive Care/ (88,402)
-
Intensive Care Unit/ (86,833)
-
(intensive care or high dependency unit$ or intensive therapy unit$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (213,198)
-
(ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or HDU or HDUs or CCU or CCUs or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs).ti,ab,ot. (224,054)
-
((accident adj2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (31,162)
-
((emergency or emergencies) adj3 (treat$ or admit$ or admission$ or episode$ or case$ or patient$ or department$ or room or rooms or ward$ or care or medic$ or interven$ or therap$ or hospital$ or service$ or patient$ or unit$ or centre$ or center$ or facility or facilities)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (235,516)
-
((acute or critical) adj3 (admit$ or admission$ or care or medic$ or service$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (227,520)
-
acute assessment unit$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (33)
-
(casualty adj2 (department$ or admit$ or admission$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (906)
-
or/25-42 (795,109)
-
child/ or boy/ or girl/ or hospitalized child/ or preschool child/ or school child/ or toddler/ (1,576,924)
-
exp adolescent/ (1,228,544)
-
exp puberty/ (31,712)
-
pediatrics/ or child urology/ (60,377)
-
(paediatr$ or pediatr$).ti,ab,ot. (327,061)
-
(Child$ or preschool$ or pre-school$ or toddler$ or juvenile$ or kid or kids).ti,ab,ot. (1,300,129)
-
(teen or teens or teenage$ or teen-age$ or adolescen$ or postpubescen$ or pubescen$ or minors or youth$ or puberty).ti,ab,ot. (358,040)
-
or/44-50 (2,777,254)
-
17 and 24 and 43 and 51 (299)
-
animal/ (1,574,790)
-
animal experiment/ (1,795,561)
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or murine or rodent or rodents or hamster or hamsters or pig or pigs or porcine or rabbit or rabbits or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or cow or bovine or sheep or ovine or monkey or monkeys).ti,ab,ot,hw. (5,695,924)
-
or/53-55 (5,695,924)
-
exp human/ (15058258)
-
human experiment/ (328,401)
-
or/57-58 (15059687)
-
56 not (56 and 59) (4,553,031)
-
52 not 60 (299)
-
limit 61 to yr=“1995 -Current” (297)
MEDLINE (OvidSP)
1946 to August Week 3 2014.
Searched: 2 September 2014.
Records found: 202.
-
exp Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome/ (96,440)
-
exp bacterial infections/ (728,567)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (6898)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (125,025)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (37,237)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (902)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (488)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1539)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (17)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (24,411)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (8538)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (140)
-
infect$.ti,ab,ot. (1,174,805)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (47,254)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (371,949)
-
or/1-16 (1,922,388)
-
exp Protein Precursors/ and Calcitonin/ (2245)
-
PCT.ti,ab,ot. (4007)
-
(procalcitonin or pro-calcitonin or 56645-65-9 or (calcitonin adj2 precursor$)).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (2522)
-
brahms.af. (323)
-
KRYPTOR.af. (73)
-
b r a h m s.af. (18)
-
or/18-23 (5836)
-
Emergency Treatment/ (8299)
-
Evidence-Based Emergency Medicine/ (216)
-
Life Support Care/ (7323)
-
emergency medical services/ or emergency service, hospital/ (74,803)
-
Emergencies/ (34,784)
-
Emergency Medicine/ (9931)
-
intensive care units/ or intensive care units, pediatric/ or respiratory care units/ (41,628)
-
critical care/ or intensive care/ (40,217)
-
(intensive care or high dependency unit$ or intensive therapy unit$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (111,650)
-
(ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or HDU or HDUs or CCU or CCUs or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs).ti,ab,ot. (138,941)
-
((accident adj2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (18,920)
-
((emergency or emergencies) adj3 (treat$ or admit$ or admission$ or episode$ or case$ or patient$ or department$ or room or rooms or ward$ or care or medic$ or interven$ or therap$ or hospital$ or service$ or patient$ or unit$ or centre$ or center$ or facility or facilities)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (148,389)
-
((acute or critical) adj3 (admit$ or admission$ or care or medic$ or service$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (171,915)
-
acute assessment unit$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (14)
-
(casualty adj2 (department$ or admit$ or admission$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (688)
-
or/25-39 (534,145)
-
adolescent/ or exp child/ (2,449,325)
-
Minors/ (2323)
-
Puberty/ (11,355)
-
Pediatrics/ (40,916)
-
(paediatr$ or pediatr$).ti,ab,ot. (213,041)
-
(Child$ or preschool$ or pre-school$ or toddler$ or juvenile$ or kid or kids).ti,ab,ot. (1,007,516)
-
(teen or teens or teenage$ or teen-age$ or adolescen$ or postpubescen$ or pubescen$ or minors or youth$ or puberty).ti,ab,ot. (271,680)
-
or/41-47 (2,772,896)
-
17 and 24 and 40 and 48 (204)
-
exp animals/ not (exp animals/ and humans/) (3,998,545)
-
49 not 50 (204)
-
limit 51 to yr=“1995 -Current” (202)
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations (OvidSP)
29 August 2014.
Searched: 2 September 2014.
Records found: 12.
-
exp Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome/ (60)
-
exp bacterial infections/ (328)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (399)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (7204)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1555)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (53)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (49)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (123)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (2)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (794)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (251)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (17)
-
infect$.ti,ab,ot. (80,478)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1052)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (16,515)
-
or/1-16 (97,168)
-
exp Protein Precursors/ and Calcitonin/ (5)
-
PCT.ti,ab,ot. (412)
-
(procalcitonin or pro-calcitonin or 56645-65-9 or (calcitonin adj2 precursor$)).ti,ab,ot,hw,rn. (355)
-
brahms.af. (27)
-
KRYPTOR.af. (5)
-
b r a h m s.af. (0)
-
or/18-23 (602)
-
Emergency Treatment/ (7)
-
Evidence-Based Emergency Medicine/ (7)
-
Life Support Care/ (2)
-
emergency medical services/ or emergency service, hospital/ (84)
-
Emergencies/ (7)
-
Emergency Medicine/ (12)
-
intensive care units/ or intensive care units, pediatric/ or respiratory care units/ (34)
-
critical care/ or intensive care/ (28)
-
(intensive care or high dependency unit$ or intensive therapy unit$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (7281)
-
(ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or HDU or HDUs or CCU or CCUs or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs).ti,ab,ot. (14,791)
-
((accident adj2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1794)
-
((emergency or emergencies) adj3 (treat$ or admit$ or admission$ or episode$ or case$ or patient$ or department$ or room or rooms or ward$ or care or medic$ or interven$ or therap$ or hospital$ or service$ or patient$ or unit$ or centre$ or center$ or facility or facilities)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (10,372)
-
((acute or critical) adj3 (admit$ or admission$ or care or medic$ or service$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (11,272)
-
acute assessment unit$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (3)
-
(casualty adj2 (department$ or admit$ or admission$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (34)
-
or/25-39 (38,271)
-
adolescent/ or exp child/ (1534)
-
Minors/ (1)
-
Puberty/ (3)
-
Pediatrics/ (38)
-
(paediatr$ or pediatr$).ti,ab,ot. (18,203)
-
(Child$ or preschool$ or pre-school$ or toddler$ or juvenile$ or kid or kids).ti,ab,ot. (65,057)
-
(teen or teens or teenage$ or teen-age$ or adolescen$ or postpubescen$ or pubescen$ or minors or youth$ or puberty).ti,ab,ot. (23,132)
-
or/41-47 (84,088)
-
17 and 24 and 40 and 48 (12)
-
exp animals/ not (exp animals/ and humans/) (2110)
-
49 not 50 (12)
-
limit 51 to yr=“1995 -Current” (12)
PubMed
URL: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/.
1995 to 2 September 2014.
Searched: 2 September 2014.
Records found: 26.
-
This strategy aims to identify records that are on PubMed, but not included in MEDLINE or MEDLINE In-Process (OvidSP). Line #9 limits the search results in this way.
#10 Search ((((((((((protein precursors[MeSH Terms]) AND calcitonin[MeSH Terms])) OR PCT[Title/Abstract]) OR (procalcitonin[Title/Abstract] OR “pro-calcitonin”[Title/Abstract] OR “calcitonin precursor*”[Title/Abstract])) OR (brahms OR kryptor OR “b r a h m s”))) AND (emergency OR emergencies OR intensive OR acute OR critical OR casualty)) AND (child OR children OR adolescence OR adolescents OR paediatric OR pediatric))) AND (pubstatusaheadofprint OR publisher[sb] OR pubmednotmedline[sb]) (26)
#9 Search pubstatusaheadofprint OR publisher[sb] OR pubmednotmedline[sb] (1,816,157)
#8 Search ((((((((protein precursors[MeSH Terms]) AND calcitonin[MeSH Terms])) OR PCT[Title/Abstract]) OR (procalcitonin[Title/Abstract] OR “pro-calcitonin”[Title/Abstract] OR “calcitonin precursor*”[Title/Abstract])) OR (brahms OR kryptor OR “b r a h m s”))) AND (emergency OR emergencies OR intensive OR acute OR critical OR casualty)) AND (child OR children OR adolescence OR adolescents OR paediatric OR pediatric) (480)
#7 Search child OR children OR adolescence OR adolescents OR paediatric OR pediatric (2,952,782)
#6 Search emergency OR emergencies OR intensive OR acute OR critical OR casualty (1,788,387)
#5 Search (((((protein precursors[MeSH Terms]) AND calcitonin[MeSH Terms])) OR PCT[Title/Abstract]) OR (procalcitonin[Title/Abstract] OR “pro-calcitonin”[Title/Abstract] OR “calcitonin precursor*”[Title/Abstract])) OR (brahms OR kryptor OR “b r a h m s”) (6404)
#4 Search brahms OR kryptor OR “b r a h m s” (398)
#3 Search procalcitonin[Title/Abstract] OR “pro-calcitonin”[Title/Abstract] OR “calcitonin precursor*”[Title/Abstract] (2673)
#2 Search PCT[Title/Abstract] (4389)
#1 Search (protein precursors[MeSH Terms]) AND calcitonin[MeSH Terms] (2205)
Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) (EBSCOhost)
1995 to 27 August 2014.
Searched: 2 September 2014.
Records found: 54.
S1 (MH “Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome+”) ((6506)
S2 (MH “Bacterial Infections+”) (50,875)
S3 “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS (986)
S4 sepsis* or septic* or sepses (11,903)
S5 bacill#emia* or bacter#emia* or endotox#emia* or pyoh#emia* or py#emia* (14,497)
S6 fusobacterium N2 necrophorum (26)
S7 Lemierre* N2 (disease* or syndrome*) (94)
S8 necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc#emia or urosepsis (117)
S9 Neisseria N2 meningitidis N2 bacter#emia (1)
S10 tetanus (1913)
S11 (bacter#emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) N3 shock* (368)
S12 toxic N2 forward N2 failure (0)
S13 blood N2 poison* (134)
S14 infect* (161,096)
S15 bacterial N2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*) (4286)
S16 bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli” (18,644)
S17 S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4 OR S5 OR S6 OR S7 OR S8 OR S9 OR S10 OR S11 OR S12 OR S13 OR S14 OR S15 OR S16 (195,446)
S18 (MH “Protein Precursors+”) (2113)
S19 (MH “Calcitonin”) (826)
S20 S18 AND S19 (202)
S21 PCT (731)
S22 procalcitonin or “pro-calcitonin” or “56645-65-9” or (calcitonin N2 precursor*) (385)
S23 brahms or KRYPTOR or “b r a h m s” (12)
S24 S20 OR S21 OR S22 OR S23 (1022)
S25 (MH “Life Support Care”) (1562)
S26 (MH “Emergency Medical Services”) (15,255)
S27 (MH “Emergency Service”) (25,160)
S28 (MH “Emergencies”) (4480)
S29 (MH “Emergency Medicine”) (5115)
S30 (MH “Intensive Care Units”) OR (MH “Intensive Care Units, Pediatric”) (18,279)
S31 (MH “Respiratory Care Units”) (72)
S32 (MH “Critical Care”) OR (MH “Pediatric Critical Care Nursing”) (11,195)
S33 “intensive care” or “high dependency unit*” or “intensive therapy unit*” (38,473)
S34 “ICU” or “ICUs” or “PICU” or “PICUs” or “HDU” or “HDUs” or “CCU” or “CCUs” or “ITU” or “ITUs” or “ER” or “ERs” or “ED” or “EDs” or “AAU” or “AAUs” (28,451)
S35 (accident N2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E” (3163)
S36 (emergency or emergencies) N3 (treat* or admit* or admission* or episode* or case* or patient* or department* or room or rooms or ward* or care or medic* or interven* or therap* or hospital* or service* or patient* or unit* or centre* or center* or facility or facilities) (76,990)
S37 (acute or critical) N3 (admit* or admission* or care or medic* or service* or patient*) (62,718)
S38 “acute assessment unit*” (6)
S39 casualty N2 (department* or admit* or admission* or patient*) (79)
S40 S25 OR S26 OR S27 OR S28 OR S29 OR S30 OR S31 OR S32 OR S33 OR S34 OR S35 OR S36 OR S37 OR S38 OR S39 (172,300)
S41 (MH “Child+”) (298,779)
S42 (MH “Adolescence+”) (205,802)
S43 (MH “Minors (Legal)”) (381)
S44 (MH “Puberty”) (1088)
S45 (MH “Adolescent Health Services”) OR (MH “Adolescent Medicine”) OR (MH “Adolescent Health”) (5725)
S46 (MH “Pediatrics”) (6891)
S47 paediatr* or pediatr* (71,880)
S48 child* or preschool* or “pre-school*” or toddler* or juvenile* or kid or kids (344,011)
S49 teen or teens or teenage* or “teen-age*” or adolescen* or postpubescen* or pubescen* or minors or youth* or puberty (218,322)
S50 S41 OR S42 OR S43 OR S44 OR S45 OR S46 OR S47 OR S48 OR S49 (498,421)
S51 S17 AND S24 AND S40 AND S50 (54)
S52 (ZR “1995”) or (ZR “1996”) or (ZR “1997”) or (ZR “1998”) or (ZR “1999”) or (ZR “2000”) or (ZR “2001”) or (ZR “2002”) or (ZR “2003”) or (ZR “2004”) or (ZR “2005”) or (ZR “2006”) or (ZR “2007”) or (ZR “2008”) or (ZR “2009”) or (ZR “2010”) or (ZR “2011”) or (ZR “2012”) or (ZR “2013”) or (ZR “2014”) or (ZR “2015”) (2,839,540)
S53 S51 AND S52 (54)
Science Citation Index (Web of Science)
1995 to 29 August 2014.
Searched: 2 September 2014.
Records found: 230.
#34 (230) #32 not #33 Timespan=1995-2014
#33 (1,768,529) TOPIC: (cat or cats or dog or dogs or animal or animals or rat or rats or hamster or hamster or feline or ovine or canine or bovine or sheep)
#32 (235) #31 AND #27 AND #19 AND #15
#31 (1,105,829) #30 OR #29 OR #28
#30 (363,206) TOPIC: (teen or teens or teenage* or “teen-age*” or adolescen* or postpubescen* or pubescen* or minors or youth* or puberty)
#29 (780,508) TOPIC: (child* or preschool* or “pre-school*” or toddler* or juvenile* or kid or kids)
#28 (198,580) TOPIC: (paediatr* or pediatr*)
#27 (415,622) #26 OR #25 OR #24 OR #23 OR #22 OR #21 OR #20
#26 (287) TOPIC: (casualty near/2 (department* or admit* or admission* or patient*))
#25 (13) TOPIC: (“acute assessment unit*”)
#24 (134,942) TOPIC: ((acute or critical) near/3 (admit* or admission* or care or medic* or service* or patient*))
#23 (83,387) TOPIC: ((emergency or emergencies) near/3 (treat* or admit* or admission* or episode* or case* or patient* or department* or room or rooms or ward* or care or medic* or interven* or therap* or hospital* or service* or patient* or unit* or centre* or center* or facility or facilities))
#22 (2441) TOPIC: ((accident near/2 emergency))
#21 (176,728) TOPIC: (“ICU” or “ICUs” or “PICU” or “PICUs” or “HDU” or “HDUs” or “CCU” or “CCUs” or “ITU” or “ITUs” or “ER” or “ERs” or “ED” or “EDs” or “AAU” or “AAUs”)
#20 (80,431) TOPIC: (“intensive care” or “high dependency unit*” or “intensive therapy unit*”)
#19 (9790) #18 OR #17 OR #16
#18 (364) TOPIC: (brahms or KRYPTOR or “b r a h m s”)
#17 (3479) TOPIC: (procalcitonin or “pro-calcitonin” or “56645-65-9” or (calcitonin near/2 precursor*))
#16 (7200) TOPIC: (PCT)
#15 (1,222,200) #14 OR #13 OR #12 OR #11 OR #10 OR #9 OR #8 OR #7 OR #6 OR #5 OR #4 OR #3 OR #2 OR #1
#14 (242,871) TOPIC: (bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli”)
#13 (17,607) TOPIC: (bacterial near/2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*))
#12 (989,171) TOPIC: (infect*)
#11 (112) TOPIC: (blood near/2 poison*)
#10 (0) TOPIC: (toxic near/2 forward near/2 failure)
#9 (6377) TOPIC: ((bacter$emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) near/3 shock*)
#8 (9325) TOPIC: (tetanus)
#7 (7) TOPIC: (Neisseria near/2 meningitidis near/2 bacter$emia)
#6 (1140) TOPIC: (necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc$emia or urosepsis)
#5 (495) TOPIC: (Lemierre* near/2 (disease* or syndrome*))
#4 (532) TOPIC: (fusobacterium near/2 necrophorum)
#3 (4355) TOPIC: (bacill$emia* or bacter$emia* or endotox$emia* or pyoh$emia* or py$emia*)
#2 (88,778) TOPIC: (sepsis* or septic* or sepses)
#1 (14,231) TOPIC: (“systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS)
Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (LILACS) (internet)
URL: http://regional.bvsalud.org/php/index.php?lang=en.
1995 to date.
Date run: 2 September 2014.
Records found: 7.
procalcitonin OR pct OR brahms OR kryptor [Words] and emergency OR emergencies OR intensive OR acute OR critical OR casualty [Words] and child OR children OR adolescence OR adolescents OR paediatric OR pediatric [Words]
Cost-effectiveness search strategies
Economic evaluations
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED) (Wiley)
Issue 3 of 4, July 2014.
Searched: 20 August 2014.
Records found: 122.
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome] explode all trees (3302)
#2 [mh “bacterial infections”] (14,341)
#3 “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS (1169)
#4 sepsis* or septic* or sepses (6946)
#5 bacill*emia* or bacter*emia* or endotox*emia* or pyoh*emia* or py*emia* (2063)
#6 fusobacterium near/2 necrophorum (6)
#7 Lemierre* near/2 (disease* or syndrome*) (1)
#8 necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc*emia or urosepsis (83)
#9 Neisseria near/2 meningitidis near/2 bacter*emia (0)
#10 tetanus (1532)
#11 (bacter*emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) near/3 shock* (47)
#12 toxic near/2 forward near/2 failure (0)
#13 blood near/2 poison* (136)
#14 bacterial near/2 infect* (5074)
#15 bacterial near/2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*) (1967)
#16 bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli” (8436)
#17 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 (29,349)
#18 [mh ^”Emergency Treatment”] (248)
#19 [mh ^”Evidence-Based Emergency Medicine”] (4)
#20 [mh ^”Life Support Care”] (82)
#21 [mh ^”Emergency Medical Services”] (878)
#22 [mh ^”Emergency Service, Hospital”] (1633)
#23 [mh ^Emergencies] (645)
#24 [mh ^”Emergency Medicine”] (214)
#25 [mh “Critical Care”] (1849)
#26 [mh “Intensive Care Units”] (2619)
#27 “intensive care” or ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or NICU or NICUs or “high dependency unit*” or HDU or HDUs or “special care baby unit*” or SCBU or SCBUs or CCU or CCUs or “intensive therapy unit*” or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs or “acute assessment unit*” (34,978)
#28 (accident near/2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E” (1069)
#29 (emergency or emergencies) near/3 (treat* or admit* or admission* or episode* or case* or patient* or department* or room or rooms or ward* or care or medic* or interven* or therap* or hospital* or service* or patient* or unit* or center* or centre* or facility or facilities) (11,157)
#30 (acute or critical) near/3 (admit* or admission* or care or medic* or service* or patient*) (27,057)
#31 casualty near/2 (department* or admit* or admission* or patient*) (54)
#32 #18 or #19 or #20 or #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 or #27 or #28 or #29 or #30 or #31 (64,823)
#33 #17 and #32 Publication Year from 2005 to 2014, in Economic Evaluations 122)
Health Economic Evaluation Database (HEED) (Wiley)
2005 to 20 August 2014.
Searched: 20 August 2014.
Records found: 98.
ALL DATA: sepsis or sepses or septic or ‘systemic inflammatory response syndrome’ or SIRS or bacter* or tetanus
and
ALL DATA: ‘intensive care’ or ICU* or PICU* or NICU* or ‘high dependency unit’ or ‘special care baby unit’ or ‘high dependency units’ or ‘special care baby units’ or SCBU* or ‘acute care’ or ‘critical care’ or emergency or emergencies or casualty
IDEAS via Research Papers in Economics (REPEC)
URL: http://repec.org/.
2005 to 20 August 2014.
Searched: 20 August 2014.
Records found: 4.
(sepsis | sepses | septic | “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” | SIRS | bacteria | bacterial | tetanus) + (“intensive care” | ICU | ICUs | PICU | PICUs | NICU |NICUs | “high dependency unit” | “special care baby unit” | “high dependency units” | “special care baby units” | SCBU | SCBUs | “acute care” | “critical care” | emergency | emergencies | casualty)
EconLit (EBSCOhost)
2005 to 1 July 2014.
Searched: 20 August 2014.
Records found: 4 (5 before hand-sifting to exclude irrelevant hits).
S1 “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS (1144)
S2 sepsis* or septic* or sepses (21)
S3 bacill#emia* or bacter#emia* or endotox#emia* or pyoh#emia* or py#emia* (1776)
S4 fusobacterium N2 necrophorum (0)
S5 Lemierre* N2 (disease* or syndrome*) (0)
S6 necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc#emia or urosepsis (0)
S7 Neisseria N2 meningitidis N2 bacter#emia (0)
S8 tetanus (25)
S9 (bacter#emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) N3 shock* (1)
S10 toxic N2 forward N2 failure (0)
S11 blood N2 poison* (0)
S12 bacterial N2 infect* (6)
S13 bacterial N2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*) (7)
S14 bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli” (68)
S15 S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4 OR S5 OR S6 OR S7 OR S8 OR S9 OR S10 OR S11 OR S12 OR S13 OR S14 (3035)
S16 “intensive care” or “high dependency unit*” or “special care baby unit*” or “intensive therapy unit*” or “acute assessment unit*” (91)
S17 (accident N2 emergency) (9)
S18 (emergency or emergencies) N3 (treat* or admit* or admission* or episode* or case* or patient* or department* or room or rooms or ward* or care or medic* or interven* or therap* or hospital* or service* or patient* or unit* or center* or centre* or facility or facilities) (465)
S19 (acute or critical) N3 (admit* or admission* or care or medic* or service* or patient*) (442)
S20 casualty N2 (department* or admit* or admission* or patient*) (1)
S21 S16 OR S17 OR S18 OR S19 OR S20 (971)
S22 S15 AND S21 (7)
S23 (ZR “2005”) or (ZR “2006”) or (ZR “2007”) or (ZR “2008”) or (ZR “2009”) or (ZR “2010”) or (ZR “2011”) or (ZR “2012”) or (ZR “2013”) or (ZR “2014”) or (ZR “2015”) (538,841)
S24 S22 AND S23 (5)
Utility values
HRQoL free-text terms based on: Figure 4. Common free-text terms for electronic database searching for HSUVs in Papaioannou D, Brazier JE, Paisley S. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 9: The Identification, Review and Synthesis of Health State Utility Values from the Literature. 2011. URL: www.nicedsu.org.uk (accessed 18 August 2011).
MEDLINE (Ovid)
1946 to August Week 3 2014.
Searched: 1 September 2014.
Records found: 178.
-
exp Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome/ (96,440)
-
exp bacterial infections/ (728,567)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (6898)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (125,025)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (37,237)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (902)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (488)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1539)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (17)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (24,411)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (8538)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (140)
-
(bacterial adj2 infect$).ti,ab,ot. (27,855)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (47,254)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (371,949)
-
or/1-16 (1,080,823)
-
Emergency Treatment/ (8299)
-
Evidence-Based Emergency Medicine/ (216)
-
Life Support Care/ (7323)
-
emergency medical services/ or emergency service, hospital/ (74,803)
-
Emergencies/ (34,784)
-
Emergency Medicine/ (9931)
-
exp Critical Care/ (44,541)
-
exp Intensive Care Units/ (57,480)
-
(intensive care or high dependency unit$ or special care baby unit$ or intensive therapy unit$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (111,839)
-
(ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or NICU or NICUs or HDU or HDUs or SCBU or SCBUs or CCU or CCUs or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs).ti,ab,ot. (144,084)
-
((accident adj2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (18,920)
-
((emergency or emergencies) adj3 (treat$ or admit$ or admission$ or episode$ or case$ or patient$ or department$ or room or rooms or ward$ or care or medic$ or interven$ or therap$ or hospital$ or service$ or patient$ or unit$ or centre$ or center$ or facility or facilities)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (148,389)
-
((acute or critical) adj3 (admit$ or admission$ or care or medic$ or service$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (171,915)
-
acute assessment unit$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (14)
-
(casualty adj2 (department$ or admit$ or admission$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (688)
-
or/18-32 (539,004)
-
quality-adjusted life years/ or quality of life/ (127,222)
-
(sf36 or sf 36 or sf-36 or short form 36 or shortform 36 or sf thirtysix or sf thirty six or shortform thirtysix or shortform thirty six or short form thirty six or short form thirtysix or short form thirty six).ti,ab,ot. (15,523)
-
(sf6 or sf 6 or sf-6 or short form 6 or shortform 6 or sf six or sfsix or shortform six or short form six).ti,ab,ot. (998)
-
(sf12 or sf 12 or sf-12 or short form 12 or shortform 12 or sf twelve or sftwelve or shortform twelve or short form twelve).ti,ab,ot. (2664)
-
(sf6D or sf 6D or sf-6D or short form 6D or shortform 6D of sf six D or sfsixD or shortform six D or short form six D).ti,ab,ot. (421)
-
(sf20 or sf 20 or sf-20 or short form 20 or shortform 20 or sf twenty or sftwenty or shortform twenty or short form twenty).ti,ab,ot. (333)
-
(sf8 or sf 8 or sf-8 or short form 8 or shortform 8 or sf eight or sfeight or shortform eight or short form eight).ti,ab,ot. (251)
-
“health related quality of life”.ti,ab,ot. (21,008)
-
(Quality adjusted life or Quality-adjusted-life).ti,ab,ot. (6111)
-
“assessment of quality of life”.ti,ab,ot. (1137)
-
(euroqol or euro qol or eq5d or eq 5d).ti,ab,ot. (3881)
-
(hql or hrql or hqol or h qol or hrqol or hr qol).ti,ab,ot. (9828)
-
(hye or hyes).ti,ab,ot. (54)
-
health$ year$ equivalent$.ti,ab,ot. (39)
-
(hui or hui1 or huI2 or hui3 or hui4 or hui-4 or hui-1 or hui-2 or hui-3).ti,ab,ot. (875)
-
(quality time or qwb or quality of well being or “quality of wellbeing” or “index of wellbeing” or “index of well being”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (608)
-
(Disability adjusted life or Disability-adjusted life or health adjusted life or health-adjusted life or “years of healthy life” or healthy years equivalent or “years of potential life lost” or “years of health life lost”).ti,ab,ot. (1666)
-
(QALY$ or DALY$ or HALY$ or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL or qald$ or qale$ or qtime$ or AQoL$).ti,ab,ot. (6810)
-
(timetradeoff or time tradeoff or time trade-off or time trade off or TTO or Standard gamble$ or “willingness to pay”).ti,ab,ot. (3629)
-
15d.ti,ab,ot. (1121)
-
(HSUV$ or health state$ value$ or health state$ preference$ or HSPV$).ti,ab,ot. (240)
-
(utilit$ adj3 (“quality of life” or valu$ or scor$ or measur$ or health or life or estimat$ or elicit$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot. (6655)
-
(utilities or disutili$).ti,ab,ot. (3927)
-
or/34-56 (150,668)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (3,906,728)
-
57 not 58 (149,111)
-
letter.pt. (824,027)
-
editorial.pt. (345,769)
-
historical article.pt. (305,884)
-
or/60-62 (1,460,723)
-
59 not 63 (142,260)
-
17 and 33 and 64 (178)
MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, MEDLINE Daily Update (Ovid)
2 September 2014.
Searched: 3 September 2014.
Records found: 10.
-
exp Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome/ (78)
-
exp bacterial infections/ (448)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (400)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (7244)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1567)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (53)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (49)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (123)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (2)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (799)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (252)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (17)
-
(bacterial adj2 infect$).ti,ab,ot. (2191)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1060)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (16,657)
-
or/1-16 (27,612)
-
Emergency Treatment/ (8)
-
Evidence-Based Emergency Medicine/ (7)
-
Life Support Care/ (2)
-
emergency medical services/ or emergency service, hospital/ (100)
-
Emergencies/ (14)
-
Emergency Medicine/ (14)
-
exp Critical Care/ (31)
-
exp Intensive Care Units/ (52)
-
(intensive care or high dependency unit$ or special care baby unit$ or intensive therapy unit$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (7364)
-
(ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or NICU or NICUs or HDU or HDUs or SCBU or SCBUs or CCU or CCUs or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs).ti,ab,ot. (15,549)
-
((accident adj2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1814)
-
((emergency or emergencies) adj3 (treat$ or admit$ or admission$ or episode$ or case$ or patient$ or department$ or room or rooms or ward$ or care or medic$ or interven$ or therap$ or hospital$ or service$ or patient$ or unit$ or centre$ or center$ or facility or facilities)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (10,483)
-
((acute or critical) adj3 (admit$ or admission$ or care or medic$ or service$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (11,372)
-
acute assessment unit$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (3)
-
(casualty adj2 (department$ or admit$ or admission$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (34)
-
or/18-32 (38,891)
-
quality-adjusted life years/ or quality of life/ (230)
-
(sf36 or sf 36 or sf-36 or short form 36 or shortform 36 or sf thirtysix or sf thirty six or shortform thirtysix or shortform thirty six or short form thirty six or short form thirtysix or short form thirty six).ti,ab,ot. (1496)
-
(sf6 or sf 6 or sf-6 or short form 6 or shortform 6 or sf six or sfsix or shortform six or short form six).ti,ab,ot. (397)
-
(sf12 or sf 12 or sf-12 or short form 12 or shortform 12 or sf twelve or sftwelve or shortform twelve or short form twelve).ti,ab,ot. (346)
-
(sf6D or sf 6D or sf-6D or short form 6D or shortform 6D or sf six D or sfsixD or shortform six D or short form six D).ti,ab,ot. (51)
-
(sf20 or sf 20 or sf-20 or short form 20 or shortform 20 or sf twenty or sftwenty or shortform twenty or short form twenty).ti,ab,ot. (15)
-
(sf8 or sf 8 or sf-8 or short form 8 or shortform 8 or sf eight or sfeight or shortform eight or short form eight).ti,ab,ot. (27)
-
“health related quality of life”.ti,ab,ot. (2605)
-
(Quality adjusted life or Quality-adjusted-life).ti,ab,ot. (672)
-
“assessment of quality of life”.ti,ab,ot. (102)
-
(euroqol or euro qol or eq5d or eq 5d).ti,ab,ot. (610)
-
(hql or hrql or hqol or h qol or hrqol or hr qol).ti,ab,ot. (1208)
-
(hye or hyes).ti,ab,ot. (1)
-
health$ year$ equivalent$.ti,ab,ot. (1)
-
(hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3 or hui4 or hui-4 or hui-1 or hui-2 or hui-3).ti,ab,ot. (102)
-
(quality time or qwb or quality of well being or “quality of wellbeing” or “index of wellbeing” or “index of well being”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (38)
-
(Disability adjusted life or Disability-adjusted life or health adjusted life or health-adjusted life or “years of healthy life” or healthy years equivalent or “years of potential life lost” or “years of health life lost”).ti,ab,ot. (223)
-
(QALY$ or DALY$ or HALY$ or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL or qald$ or qale$ or qtime$ or AQoL$).ti,ab,ot. (794)
-
(timetradeoff or time tradeoff or time trade-off or time trade off or TTO or Standard gamble$ or “willingness to pay”).ti,ab,ot. (406)
-
15d.ti,ab,ot. (107)
-
(HSUV$ or health state$ value$ or health state$ preference$ or HSPV$).ti,ab,ot. (22)
-
(utilit$ adj3 (“quality of life” or valu$ or scor$ or measur$ or health or life or estimat$ or elicit$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot. (677)
-
(utilities or disutili$ or Rosser).ti,ab,ot. (456)
-
or/34-56 (6892)
-
animals/ not (animals/ and humans/) (2580)
-
57 not 58 (6890)
-
letter.pt. (30,900)
-
editorial.pt. (19,188)
-
historical article.pt. (135)
-
or/60-62 (50,199)
-
59 not 63 (6846)
-
17 and 33 and 64 (10)
EMBASE (Ovid)
1974 to 2 September 2014.
Searched: 3 September 2014.
Records found: 219.
-
exp systemic inflammatory response syndrome/ (175,736)
-
exp bacterial infection/ (751,201)
-
(systemic inflammatory response syndrome$ or SIRS).ti,ab,ot,hw. (10,962)
-
(sepsis$ or septic$ or sepses).ti,ab,ot,hw. (194,582)
-
(bacill?emia$ or bacter?emia$ or endotox?emia$ or pyoh?emia$ or py?emia$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (48,690)
-
(fusobacterium adj2 necrophorum).ti,ab,ot,hw. (1168)
-
(Lemierre$ adj2 (disease$ or syndrome$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (804)
-
(necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc?emia or urosepsis).ti,ab,ot,hw. (3820)
-
(Neisseria adj2 meningitidis adj2 bacter?emia).ti,ab,ot,hw. (19)
-
tetanus.ti,ab,ot,hw. (34,982)
-
((bacter?emic or bacterial or endotoxi$ or toxi$) adj3 shock$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (11,234)
-
(toxic adj2 forward adj2 failure).ti,ab,ot,hw. (0)
-
(blood adj2 poison$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (259)
-
(bacterial adj2 infect$).ti,ab,ot. (37,846)
-
(bacterial adj2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (61,310)
-
(bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter$ or legionnaire$ disease or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc$ or Streptococc$ or “e coli”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (479,436)
-
or/1-16 (1266381)
-
Emergency Treatment/ (14,199)
-
Evidence Based Emergency Medicine/ (199)
-
Pediatric Advanced Life Support/ (421)
-
exp Emergency Care/ (22,751)
-
Emergency/ (37,166)
-
Emergency Medicine/ (28,599)
-
Emergency Health Service/ (67,637)
-
Emergency Patient/ (1529)
-
Emergency Ward/ (64,723)
-
Intensive Care/ (88,509)
-
Intensive Care Unit/ (87,041)
-
(intensive care or high dependency unit$ or special care baby unit$ or intensive therapy unit$).ti,ab,ot,hw. (213,813)
-
(ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or NICU or NICUs or HDU or HDUs or SCBU or SCBUs or CCU or CCUs or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs).ti,ab,ot. (233,355)
-
((accident adj2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E”).ti,ab,ot,hw. (31,213)
-
((emergency or emergencies) adj3 (treat$ or admit$ or admission$ or episode$ or case$ or patient$ or department$ or room or rooms or ward$ or care or medic$ or interven$ or therap$ or hospital$ or service$ or patient$ or unit$ or centre$ or center$ or facility or facilities)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (236,552)
-
((acute or critical) adj3 (admit$ or admission$ or care or medic$ or service$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (227,971)
-
acute assessment unit$.ti,ab,ot,hw. (33)
-
(casualty adj2 (department$ or admit$ or admission$ or patient$)).ti,ab,ot,hw. (906)
-
or/18-35 (799,301)
-
quality adjusted life year/ or quality of life index/ (14,180)
-
Short Form 12/ or Short Form 20/ or Short Form 36/ or Short Form 8/ (14,361)
-
“International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health”/ or “ferrans and powers quality of life index”/ (1336)
-
(sf36 or sf 36 or sf-36 or short form 36 or shortform 36 or sf thirtysix or sf thirty six or shortform thirtysix or shortform thirty six or short form thirty six or short form thirtysix or short form thirty six).ti,ab,ot. (23,787)
-
(sf6 or sf 6 or sf-6 or short form 6 or shortform 6 or sf six or sfsix or shortform six or short form six).ti,ab,ot. (1530)
-
(sf12 or sf 12 or sf-12 or short form 12 or shortform 12 or sf twelve or sftwelve or shortform twelve or short form twelve).ti,ab,ot. (4418)
-
(sf6D or sf 6D or sf-6D or short form 6D or shortform 6D or sf six D or sfsixD or shortform six D or short form six D).ti,ab,ot. (731)
-
(sf20 or sf 20 or sf-20 or short form 20 or shortform 20 or sf twenty or sftwenty or shortform twenty or short form twenty).ti,ab,ot. (341)
-
(sf8 or sf 8 or sf-8 or short form 8 or shortform 8 or sf eight or sfeight or shortform eight or short form eight).ti,ab,ot. (445)
-
“health related quality of life”.ti,ab,ot. (30,295)
-
(Quality adjusted life or Quality-adjusted-life).ti,ab,ot. (8975)
-
“assessment of quality of life”.ti,ab,ot. (1742)
-
(euroqol or euro qol or eq5d or eq 5d).ti,ab,ot. (7306)
-
(hql or hrql or hqol or h qol or hrqol or hr qol).ti,ab,ot. (15,522)
-
(hye or hyes).ti,ab,ot. (95)
-
health$ year$ equivalent$.ti,ab,ot. (38)
-
(hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3 or hui4 or hui-4 or hui-1 or hui-2 or hui-3).ti,ab,ot. (2151)
-
(quality time or qwb or “quality of well being” or “quality of wellbeing” or “index of wellbeing” or index of well being).ti,ab,ot,hw. (797)
-
(Disability adjusted life or Disability-adjusted life or health adjusted life or health-adjusted life or “years of healthy life” or healthy years equivalent or “years of potential life lost” or “years of health life lost”).ti,ab,ot. (2131)
-
(QALY$ or DALY$ or HALY$ or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL or qald$ or qale$ or qtime$ or AQoL$).ti,ab,ot. (11,417)
-
(timetradeoff or time tradeoff or time trade-off or time trade off or TTO or Standard gamble$ or “willingness to pay”).ti,ab,ot. (5436)
-
15d.ti,ab,ot. (1635)
-
(HSUV$ or health state$ value$ or health state$ preference$ or HSPV$).ti,ab,ot. (305)
-
(utilit$ adj3 (“quality of life” or valu$ or scor$ or measur$ or health or life or estimat$ or elicit$ or disease$)).ti,ab,ot. (10,123)
-
(utilities or disutili$ or Rosser).ti,ab,ot. (6550)
-
or/37-61 (96,124)
-
animal/ or animal experiment/ (3,358,705)
-
(rat or rats or mouse or mice or murine or rodent or rodents or hamster or hamsters or pig or pigs or porcine or rabbit or rabbits or animal or animals or dogs or dog or cats or cow or bovine or sheep or ovine or monkey or monkeys).ti,ab,ot,hw. (5,700,949)
-
or/63-64 (5,700,949)
-
exp human/ or human experiment/ (15080879)
-
65 not (65 and 66) (4,556,337)
-
62 not 67 (94,364)
-
letter.pt. (855,048)
-
editorial.pt. (455,483)
-
note.pt. (567,527)
-
or/69-71 (1,878,058)
-
68 not 72 (91,336)
-
17 and 36 and 73 (261)
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (Wiley)
Issue 8 of 12, August 2014.
Searched: 3 September 2014.
Records found: 83.
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome] explode all trees (3307)
#2 [mh “bacterial infections”] (14,352)
#3 “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS (1178)
#4 sepsis* or septic* or sepses (6978)
#5 bacill*emia* or bacter*emia* or endotox*emia* or pyoh*emia* or py*emia* (2069)
#6 fusobacterium near/2 necrophorum (6)
#7 Lemierre* near/2 (disease* or syndrome*) (1)
#8 necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc*emia or urosepsis (85)
#9 Neisseria near/2 meningitidis near/2 bacter*emia (0)
#10 tetanus (1539)
#11 (bacter*emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) near/3 shock* (47)
#12 toxic near/2 forward near/2 failure (0)
#13 blood near/2 poison* (136)
#14 bacterial near/2 infect* (5079)
#15 bacterial near/2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*) (1973)
#16 bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli” (8460)
#17 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 (29,430)
#18 [mh ^”Emergency Treatment”] (249)
#19 [mh ^”Evidence-Based Emergency Medicine”] (4)
#20 [mh ^”Life Support Care”] (83)
#21 [mh ^”Emergency Medical Services”] (880)
#22 [mh ^”Emergency Service, Hospital”] (1633)
#23 [mh ^Emergencies] (645)
#24 [mh ^”Emergency Medicine”] (214)
#25 [mh “Critical Care”] (1851)
#26 [mh “Intensive Care Units”] (2622)
#27 “intensive care” or ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or NICU or NICUs or “high dependency unit*” or HDU or HDUs or “special care baby unit*” or SCBU or SCBUs or CCU or CCUs or “intensive therapy unit*” or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs or “acute assessment unit*” (35,114)
#28 (accident near/2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E” (1072)
#29 (emergency or emergencies) near/3 (treat* or admit* or admission* or episode* or case* or patient* or department* or room or rooms or ward* or care or medic* or interven* or therap* or hospital* or service* or patient* or unit* or center* or centre* or facility or facilities) (11,217)
#30 (acute or critical) near/3 (admit* or admission* or care or medic* or service* or patient*) (27,155)
#31 casualty near/2 (department* or admit* or admission* or patient*) (55)
#32 #18 or #19 or #20 or #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 or #27 or #28 or #29 or #30 or #31 (65,072)
#33 MeSH descriptor: [Quality-Adjusted Life Years] this term only (3652)
#34 MeSH descriptor: [Quality of Life] this term only (14,884)
#35 sf36 or “sf 36” or “sf-36” or “short form 36” or “shortform 36” or “sf thirtysix” or “sf thirty six” or “shortform thirtysix” or “shortform thirty six” or “short form thirty six” or “short form thirtysix” or “short form thirty six” (5057)
#36 sf6 or “sf 6” or “sf-6” or “short form 6” or “shortform 6” or “sf six” or sfsix or “shortform six” or “short form six” (120)
#37 sf12 or “sf 12” or “sf-12” or “short form 12” or “shortform 12” or “sf twelve” or sftwelve or “shortform twelve” or “short form twelve” (766)
#38 sf6D or “sf 6D” or “sf-6D” or “short form 6D” or “shortform 6D” or “sf six D” or sfsixD or “shortform six D” or “short form six D” (152)
#39 sf20 or “sf 20” or “sf-20” or “short form 20” or “shortform 20” or “sf twenty” or sftwenty or “shortform twenty” or “short form twenty” (69)
#40 sf8 or “sf 8” or “sf-8” or “short form 8” or “shortform 8” or “sf eight” or sfeight or “shortform eight” or “short form eight” (42)
#41 “health related quality of life” (5804)
#42 “Quality adjusted life” or “Quality-adjusted-life” (5972)
#43 “assessment of quality of life” (281)
#44 euroqol or “euro qol” or eq5d or “eq 5d” (2180)
#45 hql or hrql or hqol or “h qol” or hrqol or “hr qol” (2026)
#46 hye or hyes (46)
#47 “health* year* equivalent*” (5)
#48 hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3 or hui4 or “hui-4” or “hui-1” or “hui-2” or “hui-3” (1135)
#49 quality time or qwb or “quality of well being” or “quality of wellbeing” or “index of wellbeing” or “index of well being” (33,313)
#50 “Disability adjusted life” or “Disability-adjusted life” or “health adjusted life” or “health-adjusted life” or “years of healthy life” or “healthy years equivalent” or “years of potential life lost” or “years of health life lost” (325)
#51 QALY* or DALY* or HALY* or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL or qald* or qale* or qtime* or AQoL* (4801)
#52 timetradeoff or “time tradeoff” or “time trade-off” or “time trade off” or TTO or “Standard gamble*” or “willingness to pay” (1783)
#53 15d (99)
#54 HSUV* or “health state* value*” or “health state* preference*” or HSPV* (77)
#55 utilit* near/3 (“quality of life” or valu* or scor* or measur* or health or life or estimat* or elicit* or disease*) (4400)
#56 utilities or disutili* or rosser (10,729)
#57 #33 or #34 or #35 or #36 or #37 or #38 or #39 or #40 or #41 or #42 or #43 or #44 or #45 or #46 or #47 or #48 or #49 or #50 or #51 or #52 or #53 or #54 or #55 or #56 (55,551)
#58 #17 and #32 and #57 (1434)
#59 #17 and #32 and #57 in Trials (83)
Health Technology Assessment database (Wiley)
Issue 3 of 4, July 2014.
Searched: 3 September 2014.
Records found: 5.
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome] explode all trees (3307)
#2 [mh “bacterial infections”] (14,352)
#3 “systemic inflammatory response syndrome” or SIRS (1178)
#4 sepsis* or septic* or sepses (6978)
#5 bacill*emia* or bacter*emia* or endotox*emia* or pyoh*emia* or py*emia* (2069)
#6 fusobacterium near/2 necrophorum (6)
#7 Lemierre* near/2 (disease* or syndrome*) (1)
#8 necrobacillosis or necrobacilloses or meningococc*emia or urosepsis (85)
#9 Neisseria near/2 meningitidis near/2 bacter*emia (0)
#10 tetanus (1539)
#11 (bacter*emic or bacterial or endotoxin* or toxi*) near/3 shock* (47)
#12 toxic near/2 forward near/2 failure (0)
#13 blood near/2 poison* (136)
#14 bacterial near/2 infect* (5079)
#15 bacterial near/2 (meningitis or pneumonia or peritonitis or endocarditis or superinfection* or disease*) (1973)
#16 bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc* or “e coli” (8460)
#17 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 (29,430)
#18 [mh ^”Emergency Treatment”] (249)
#19 [mh ^”Evidence-Based Emergency Medicine”] (4)
#20 [mh ^”Life Support Care”] (83)
#21 [mh ^”Emergency Medical Services”] (880)
#22 [mh ^”Emergency Service, Hospital”] (1633)
#23 [mh ^Emergencies] (645)
#24 [mh ^”Emergency Medicine”] (214)
#25 [mh “Critical Care”] (1851)
#26 [mh “Intensive Care Units”] (2622)
#27 “intensive care” or ICU or ICUs or PICU or PICUs or NICU or NICUs or “high dependency unit*” or HDU or HDUs or “special care baby unit*” or SCBU or SCBUs or CCU or CCUs or “intensive therapy unit*” or ITU or ITUs or ER or ERs or ED or EDs or AAU or AAUs or “acute assessment unit*” (35,114)
#28 (accident near/2 emergency) or “A&E” or “A & E” (1072)
#29 (emergency or emergencies) near/3 (treat* or admit* or admission* or episode* or case* or patient* or department* or room or rooms or ward* or care or medic* or interven* or therap* or hospital* or service* or patient* or unit* or center* or centre* or facility or facilities) (11,217)
#30 (acute or critical) near/3 (admit* or admission* or care or medic* or service* or patient*) (27,155)
#31 casualty near/2 (department* or admit* or admission* or patient*) (55)
#32 #18 or #19 or #20 or #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 or #27 or #28 or #29 or #30 or #31 (65,072)
#33 MeSH descriptor: [Quality-Adjusted Life Years] this term only (3652)
#34 MeSH descriptor: [Quality of Life] this term only (14,884)
#35 sf36 or “sf 36” or “sf-36” or “short form 36” or “shortform 36” or “sf thirtysix” or “sf thirty six” or “shortform thirtysix” or “shortform thirty six” or “short form thirty six” or “short form thirtysix” or “short form thirty six” (5057)
#36 sf6 or “sf 6” or “sf-6” or “short form 6” or “shortform 6” or “sf six” or sfsix or “shortform six” or “short form six” (120)
#37 sf12 or “sf 12” or “sf-12” or “short form 12” or “shortform 12” or “sf twelve” or sftwelve or “shortform twelve” or “short form twelve” (766)
#38 sf6D or “sf 6D” or “sf-6D” or “short form 6D” or “shortform 6D” or “sf six D” or sfsixD or “shortform six D” or “short form six D” (152)
#39 sf20 or “sf 20” or “sf-20” or “short form 20” or “shortform 20” or “sf twenty” or sftwenty or “shortform twenty” or “short form twenty” (69)
#40 sf8 or “sf 8” or “sf-8” or “short form 8” or “shortform 8” or “sf eight” or sfeight or “shortform eight” or “short form eight” (42)
#41 “health related quality of life” (5804)
#42 “Quality adjusted life” or “Quality-adjusted-life” (5972)
#43 “assessment of quality of life” (281)
#44 euroqol or “euro qol” or eq5d or “eq 5d” (2180)
#45 hql or hrql or hqol or “h qol” or hrqol or “hr qol” (2026)
#46 hye or hyes (46)
#47 “health* year* equivalent*” (5)
#48 hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3 or hui4 or “hui-4” or “hui-1” or “hui-2” or “hui-3” (1135)
#49 quality time or qwb or “quality of well being” or “quality of wellbeing” or “index of wellbeing” or “index of well being” (33,313)
#50 “Disability adjusted life” or “Disability-adjusted life” or “health adjusted life” or “health-adjusted life” or “years of healthy life” or “healthy years equivalent” or “years of potential life lost” or “years of health life lost” (325)
#51 QALY* or DALY* or HALY* or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL or qald* or qale* or qtime* or AQoL* (4801)
#52 timetradeoff or “time tradeoff” or “time trade-off” or “time trade off” or TTO or “Standard gamble*” or “willingness to pay” (1783)
#53 15d (99)
#54 HSUV* or “health state* value*” or “health state* preference*” or HSPV* (77)
#55 utilit* near/3 (“quality of life” or valu* or scor* or measur* or health or life or estimat* or elicit* or disease*) (4400)
#56 utilities or disutili* or rosser (10,729)
#57 #33 or #34 or #35 or #36 or #37 or #38 or #39 or #40 or #41 or #42 or #43 or #44 or #45 or #46 or #47 or #48 or #49 or #50 or #51 or #52 or #53 or #54 or #55 or #56 (55,551)
#58 #17 and #32 and #57 (1434)
#59 #17 and #32 and #57 in Technology Assessment (5)
PubMed
URL: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/.
Searched: 3 September 2014.
Records found: 76.
This strategy aims to identify records that are on PubMed, but not included in MEDLINE or MEDLINE In-Process (OvidSP). Line #25 limits the search results in this way.
#26 “Search ((((((((((Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome[MeSH Terms]) OR bacterial infections[MeSH Terms]) OR (sepsis* or septic* or sepses)) OR “bacterial infect*”) OR (tetanus or “blood poison*”)) OR (“bacterial meningitis” or “bacterial pneumonia” or “bacterial peritonitis” or “bacterial endocarditis” or “bacterial superinfection*” or “bacterial disease”)) OR (bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or “legionnaire* disease” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc*))) AND (emergency OR emergencies OR intensive OR acute OR critical OR casualty)) AND ((((((((((((((“quality of life”) OR “quality adjusted life years”) OR (“sf36” or “sf-36” or “sf6” or “sf-6” or “sf12” or “sf-12” or “sf6d” or “sf-6d” or “sf20” or “sf-20” or “sf8” or “sf-8”)) OR (euroqol or “euro qol” or “eq5d” or “eq 5d”)) OR (hql or hrql or hqol or “h qol” or hrqol or “hr qol”)) OR (“health* year* equivalent*” or hye or hyes)) OR (“quality of well being” or “quality of wellbeing” or “index of wellbeing” or “index of well being”)) OR (“Disability adjusted life” or “Disability-adjusted life”)) OR (“health adjusted life” or “health-adjusted life” or “years of healthy life” or “healthy years equivalent” or “years of potential life lost” or “years of health life lost”)) OR (QALY* or DALY* or HALY* or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL or qald* or qale* or qtime* or AQoL*)) OR (“time tradeoff” or “time trade-off”)) OR (“Standard gamble*” or “willingness to pay”)) OR (“health state* value*” or “health state* preference*”)) OR (utilities or disutilities))) AND (pubstatusaheadofprint OR publisher[sb] OR pubmednotmedline[sb]) (76)
#25 “Search pubstatusaheadofprint OR publisher[sb] OR pubmednotmedline[sb]” (1,815,126)
#24 “Search ((((((Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome[MeSH Terms]) OR bacterial infections[MeSH Terms]) OR (sepsis* or septic* or sepses)) OR ““bacterial infect*””) OR (tetanus or ““blood poison*””)) OR (““bacterial meningitis”” or ““bacterial pneumonia”” or ““bacterial peritonitis”” or ““bacterial endocarditis”” or ““bacterial superinfection*”” or ““bacterial disease””)) OR (bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or ““legionnaire* disease”” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc*)” (1,122,718)
#23 “Search bartonellosis or bordetellosis or Bordetella or pertussis or botryomycosis or brucellosis or campylobacter* or ““legionnaire* disease”” or listeriosis or mycoplasmosis or pyomyositis or pyonephrosis or Staphylococc* or Streptococc*” (309,305)
#22 “Search ““bacterial meningitis”” or ““bacterial pneumonia”” or ““bacterial peritonitis”” or ““bacterial endocarditis”” or ““bacterial superinfection*”” or ““bacterial disease””” (40,777)
#21 “Search tetanus or ““blood poison*””” (40,459)
#20 “Search ““bacterial infect*””” (367,249)
#19 “Search sepsis* or septic* or sepses” (132,167)
#18 “Search bacterial infections[MeSH Terms]” (726,384)
#17 “Search Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome[MeSH Terms]” (94,444)
#16 “Search (((((((((((((““quality of life””) OR ““quality adjusted life years””) OR (““sf36”” or ““sf-36”” or ““sf6”” or ““sf-6”” or ““sf12”” or ““sf-12”” or ““sf6d”” or ““sf-6d”” or ““sf20”” or ““sf-20”” or ““sf8”” or ““sf-8””)) OR (euroqol or ““euro qol”” or ““eq5d”” or ““eq 5d””)) OR (hql or hrql or hqol or ““h qol”” or hrqol or ““hr qol””)) OR (““health* year* equivalent*”” or hye or hyes)) OR (““quality of well being”” or ““quality of wellbeing”” or ““index of wellbeing”” or ““index of well being””)) OR (““Disability adjusted life”” or ““Disability-adjusted life””)) OR (““health adjusted life”” or ““health-adjusted life”” or ““years of healthy life”” or ““healthy years equivalent”” or ““years of potential life lost”” or ““years of health life lost””)) OR (QALY* or DALY* or HALY* or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL or qald* or qale* or qtime* or AQoL*)) OR (““time tradeoff”” or ““time trade-off””)) OR (““Standard gamble*”” or ““willingness to pay””)) OR (““health state* value*”” or ““health state* preference*””)) OR (utilities or disutilities)” (443,537)
#15 “Search utilities or disutilities” (4299,10:01:10)
#14 “Search ““health state* value*”” or ““health state* preference*””” (48)
#13 “Search ““Standard gamble*”” or ““willingness to pay””” (3097)
#12 “Search ““time tradeoff”” or ““time trade-off””” (991)
#11 “Search QALY* or DALY* or HALY* or YHL or HYES or YPLL or YHLL or qald* or qale* or qtime* or AQoL*” (16,418)
#10 “Search ““health adjusted life”” or ““health-adjusted life”” or ““years of healthy life”” or ““healthy years equivalent”” or ““years of potential life lost”” or ““years of health life lost””” (19,286)
#9 “Search ““Disability adjusted life”” or ““Disability-adjusted life””” (1379)
#8 “Search ““quality of well being”” or ““quality of wellbeing”” or ““index of wellbeing”” or ““index of well being””” (232,441)
#7 “Search ““health* year* equivalent*”” or hye or hyes” (6527)
#6 “Search hql or hrql or hqol or ““h qol”” or hrqol or ““hr qol””” (11,057)
#5 “Search euroqol or ““euro qol”” or ““eq5d”” or ““eq 5d””” (4447)
#4 “Search ““sf36”” or ““sf-36”” or ““sf6”” or ““sf-6”” or ““sf12”” or ““sf-12”” or ““sf6d”” or ““sf-6d”” or ““sf20”” or ““sf-20”” or ““sf8”” or ““sf-8””” (18,526)
#3 “Search ““quality adjusted life years””” (8630)
#2 “Search ““quality of life””” (195,317)
#1 “Search emergency OR emergencies OR intensive OR acute OR critical OR casualty” (1,788,774)
Patient-Reported Outcome and Quality Of Life Instruments Database (PROQOLID)
URL: www.proqolid.org/.
Searched: 3 September 2014.
Records found: 0.
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome – 0 records found
Sepsis or septic or sepses – 0 records found
Bacterial – 0 relevant records
Tetanus – 0 records found
Appendix 2 Ongoing trials and competed trials with no published data
| Contact investigator(s) | Trial title | Population | Setting | Register ID | End date | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completed trials with published protocols, but no published results | ||||||
| Evelien Assink-de Jong Albertus Beishuizen |
Stop Antibiotics on guidance of Procalcitonin Study (SAPS): a randomised prospective multicentre investigator-initiated trial to analyse whether daily measurements of procalcitonin versus a standard-of-care approach can safely shorten antibiotic duration in intensive care unit patients Calculated sample size: 1816 patients |
Adults | ICU | NCT01139489117,118 | August 2014 | Contacted 30 September 2014 No reply received |
| Completed trials with no publication | ||||||
| Chien-Chang Lee, MD, MSc Yi-Min Zhu, BSc |
PROcalcitonin to SHORTen Antibiotics Duration in PEDiatric ICU Patients (ProShort-Ped) Trial | Children | ICU | NCT01652404119 | December 2012 | Contacted 30 September 2014 No reply received |
| Chien-Chang Lee, MD, MSc | Procalcitonin to Shorten Antibiotics Duration in ICU Patients (ProShort) | Adults | ICU | NCT01379547120 | ||
| Hendrikus J van Leeuwen | Procalcitonin Guided Versus Conventional Antibiotic Therapy in Patients With Sepsis in the ICU | Adults | ICU | NCT00987818121 | NR | Contacted 30 September 2014 Replied 30 September 2014 – no data yet available |
| Steven Reynolds, MD | PCT and Clinical Algorithm for Determination of Duration of Antibiotics | Adults | ICU | NCT01572831122 | May 2013 | Contacted 30 September 2014 |
| Laurence E Lacroix Children’s Hospital, Geneva University Hospital | Impact of the Lab-score on Antibiotic Prescription Rate in Children With Fever Without Source | Children | ED | NCT02179398123 | July 2013 | Contacted 24 September 2014 No reply received |
| Ongoing trials | ||||||
| Hans Ibsen, MD, DMSc | Procalcitonin as a Marker of Antibiotic Therapy in Patients With Lower Respiratory Tract Infections | Adults | Unclear ‘hospitalised’ | NCT02171338124 | September 2014 | None |
| Karla F Finotti, MD Vandack A Nobre A Nobre, PhD |
Procalcitonin Versus C-reactive Protein to Guide Therapy in Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAPMarker) | Adults | ICU? | NCT01018199125 | January 2015 | None |
| Emmanuel Montassier, PH | Clinical Reassessment Versus Procalcitonin in Order to Shorten Antibiotic Duration in Community acquired Pneumonia (CLINPCT) | Adults | Unclear ‘hospitalised’ | NCT01723644126 | April 2015 | None |
| Ruud Duijkers, MSc, MD | Reduction of Antibiotic Therapy by Biomakers in Patients With CAP Episodes (REDUCE Study) | Adults | Unclear ‘hospitalised’ | NCT01964495127 | October 2017 | None |
| Tammy L Eaton | Procalcitonin Antibiotic Consensus Trial (ProACT) | Adults | ED | NCT02130986128 | June 2018 | None |
Appendix 3 Data extraction tables
3.1 baseline study details
| Study details | Selection criteria | Participant characteristics | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement | Withdrawals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annane (2013)37,38 NCT01025180 Country: France Funding: Industry – assay manufacturer Recruitment: December 2006 to December 2009 Multicentre study Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 62 |
Setting: ICU Population: Adults Presentation: Apparent septic shock and no clear source of infection Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Adults admitted to participating ICUs; following symptoms in preceding 48 hours: SIRS, acute dysfunction of at least one organ, absence of indisputable clinical infection; negative microbial cultures Exclusion criteria: Pregnancy; burns over ≥ 15% of body surface area; trauma; outpatient or inpatient cardiac arrest; postorthopaedic surgery status; drug-related neutropenia; withdrawal of or decision to withhold life-support therapies; indisputable clinical infection or antibiotic exposure for ≥ 48 hours before ICU admission |
No. randomised | 31 | 31 | PCT: 1 withdrew informed consent Control: 3 withdrew informed consent |
| Age (years) (median, IQR): | 59 (40–67) | 54 (46–73) | |||
| Male (%): | 80 | 67.9 | |||
| SAPS (median, IQR): | 32.5 (27–47) | 43 (32–52) | |||
| SOFA (median, IQR): | 9.5 (8.5–11) | 10 (8–11) | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (median, IQR): | 1 (0.3–5) | 0.7 (0.4–2.4) | |||
| CRP (mg/l) (median, IQR): | 87 (52–142) | 141 (77–220) | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Baer (2013)39,40,63 ProPAED (ISRCTN17057980) Country: Switzerland Funding: Mixed – assay manufacturer provided kits and platform Recruitment: January 2009 to February 2010 Multicentre study Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 339 |
Setting: ED Population: Children Presentation: LRTI Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Children (aged 1 month to 18 years); presenting with LRTI to the EDs of two paediatric hospitals, regardless of antibiotic treatment history. Acute LRTI was defined as < 14 days’ duration, presence of fever (≥ 38° C), at least one symptom (cough, sputum production, pleuritic pain, poor feeding), at least one sign (tachypnoea, dyspnoea, wheezing, late inspiratory crackles, bronchial breathing, pleural rub) Exclusion criteria: Participant or caregiver unwilling; severe immunosuppression or immunosuppressive treatment; neutropenia; cystic fibrosis; acute croup; hospital stay within 14 days; other severe infection |
No. randomised | 168 | 169 | PCT: 1 delayed or incomplete 14-day interview Control: 2 withdrew consent; 1 lost to follow-up; 4 delayed or incomplete 14-day interview |
| Age (years) (median, IQR): | 20.7 (10.1–50.2) | 20.9 (10.2–50.7) | |||
| Male (%): | 58 | 58 | |||
| SAPS (median, IQR): | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA (median, IQR): | NR | NR | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (median, IQR): | 0.26 (0.14–16) | 0.21 (0.12–0.24) | |||
| CRP (mg/l) (median, IQR): | 23 (8–88) | 20 (7–55) | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | Non-CAP LRTI 36; CAP 64 | Non-CAP LRTI 37; CAP 63 | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Bouadma (2010)41,64 PRORATA NCT00472667 Country: France Funding: Industry – assay manufacturer (assay materials and Kryptor machines (if not already available on site) Recruitment: June 2007 to May 2008 Multicentre study Design: Non-inferiority parallel group RCT No. randomised: 630 |
Setting: ICU Population: Adults Presentation: Suspected bacterial infection Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Adults (≥ 18 years) with suspected bacterial infection at admission or during their stay in ICU, or who developed sepsis during their stay in ICU; not receiving antibiotics before inclusion, or received antibiotics for < 24 hours and the interval between admission and inclusion was < 12 hours Exclusion criteria: Known pregnancy; expected ICU stay < 3 days; bone marrow transplant or chemotherapy-induced neutropenia; infections for which long-term antibiotic treatment is strongly recommended (e.g. infective endocarditis, osteoarticular infections, anterior mediastinitis after cardiac surgery, hepatic or cerebral abscess; chronic prostatitis; infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Pneumocystis jirovecii or Toxoplasma gondii; poor chance of survival (SAPS II > 65); do-not-resuscitate order |
No. randomised | 311 | 319 | PCT: 4 withdrew consent; 1 lost to follow-up at day 15 Control: 4 withdrew consent; 1 randomised twice; 1 lost to follow-up at day 22 |
| Age (years) (mean, SD): | 61 (15.2) | 62.1 (15) | |||
| Male (%): | 67 | 65 | |||
| SAPS (mean, SD): | 47.1 (17.9) | 46.9 (17.2) | |||
| SOFA (mean, SD): | 8 (4.7) | 7.7 (4.6) | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (median, IQR): | 1.6 (0.5–6.6) | 1.5 (0.4–6.8) | |||
| CRP (mg/l) (median, IQR): | 144.2 (63–229) | 137.2 (61–244) | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | Reason for admission to ICU: Septic shock 17; non-septic shock 15; acute respiratory failure 37; renal failure 3; neurological failure 11; multiorgan failure 7; other 10 Infection site: Pulmonary 71; urinary tract 9; intra-abdominal 5; skin and soft tissue 2; CNS 3; catheter related 2; primary blood stream 3; other 4 |
Reason for admission to ICU: Septic shock 18; non-septic shock 15; acute respiratory failure 40; renal failure 2; neurological failure 11; multiorgan failure 6; other 8 Infection site: Pulmonary 74; urinary tract 6; intra-abdominal 7; skin and soft tissue 2; CNS 2; catheter related 1; primary blood stream 4; other 3 |
|||
| Comorbidities (%): | Heart failure 5; insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus 9; cirrhosis 7; oxygen therapy at home 7; chronic renal failure requiring dialysis 6; metastatic cancer 3; immunocompromised 15 | Heart failure 4; insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus 7; cirrhosis 4; oxygen therapy at home 6; chronic renal failure requiring dialysis 4; metastatic cancer 2; immunocompromised 16 | |||
| Christ-Crain (2006)42,43 ProCAP-Study; ISRCTN04176397) Country: Switzerland Funding: Industry – drug manufacturer Recruitment: November 2003 to February 2005 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 302 |
Setting: ED Population: Adults Presentation: CAP Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Adults (> 18 years) with principal diagnosis of CAP admitted to the ED; defined by a new infiltrate on chest radiograph and presence of ≥ 1 of the following: cough, sputum production, dyspnoea, core body temperature of > 38 ˚C, auscultatory findings of abnormal breath sounds and rales, and leucocyte count of > 10 × 109 or fewer than 4 × 109 cells/l Exclusion criteria: Cystic fibrosis; active pulmonary tuberculosis; hospital-acquired pneumonia; severely immunocompromised patients |
No. randomised | 151 | 151 | PCT: 18 died; 2 lost to follow-up Control: 20 died |
| Age (years) (mean, SD): | 70 (17) | 70 (17) | |||
| Male (%): | 62 | 62 | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (mean, CI): | 0.5 (0.2 to 2.5) | 0.4 (0.2 to 1.9) | |||
| CRP (mg/l) (mean, CI): | 111 (57 to 204) | 152 (72 to 212) | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | PSI class II (36); IV (45); V (19) | PSI class II (44); IV (41); V (15) | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | CAD (33); hypertensive heart disease (28); congestive heart failure (5); peripheral vascular disease (7); cerebrovascular disease (5); renal dysfunction (24); liver disease (8), diabetes (21); COPD (29); neoplastic disease (17) | CAD (32); hypertensive heart disease (24); congestive heart failure (6); peripheral vascular disease (6); cerebrovascular disease (5); renal dysfunction (30); liver disease (13); diabetes (19); COPD (21); neoplastic disease (15) | |||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44,65 NCT00099840 Country: Switzerland Funding: Mixed Recruitment: December 2002 to April 2003 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 243 |
Setting: ED Population: Adults Presentation: Suspected LRTI Testing application: Initiation Inclusion criteria: Suspected LRTI as the main diagnosis Exclusion criteria: Immunocompromised patients (with HIV and a CD4 count of < 200 cells/ml), neutropenic patients, stem cell transplant recipients, people with cystic fibrosis, active tuberculosis or nosocomial pneumonia |
No. randomised | 124 | 119 | PCT: 4 died; 8 lost to follow-up Control: 4 died; 5 lost to follow-up |
| Age (years) (mean, SD): | 62.8 (19.8) | 65.3 (17.3) | |||
| Male (%): | 54 | 51 | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (mean, SD): | 1.6 (7.7) | 1.6 (4.2) | |||
| CRP (mg/l) (mean, SD): | 82.8 (93.9) | 97.8 (106.1) | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | CAP (34); acute exacerbation of COPD (23); acute bronchitis (23); acute exacerbation of asthma (8); others (12) | CAP (38); acute exacerbation of COPD (26); acute bronchitis (26); acute exacerbation of asthma (3); others (8) | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | CAD (22); congestive heart failure (9); peripheral vascular disease (8); cerebrovascular disease (3); renal dysfunction (18); liver dysfunction (5); diabetes mellitus (12) | CAD (27); congestive heart failure (6); peripheral vascular disease (8); cerebrovascular disease (4); renal dysfunction (15); liver dysfunction (5); diabetes mellitus (14) | |||
| Deliberato (2013)45,46 NCT01494675 Country: Brazil Funding: Not stated Recruitment: March 2008 to February 2010 Only available as conference abstract: False Multicentre study: False Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 81 |
Setting: ICU Population: Adults Presentation: Suspected or confirmed sepsis Testing application: Discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Adults (at least 18 years) with microbiologically confirmed infections (blood, urine, tracheal aspirate, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cultures), and suspected sepsis, severe sepsis or septic shock Exclusion criteria: Onset of antibiotic therapy > 48 hours before cultures were performed; known pregnancy; infections requiring prolonged antibiotic therapy (e.g. bacterial endocarditis, hepatic or brain abscess, mediastinitis, osteomyelitis); severe infection caused by viruses, parasites, fungi, or mycobacteria; chronic localised infections (e.g. chronic osteomyelitis or prostatitis) |
No. randomised: | 42 | 39 | PCT: Refused consent after randomisation 12; complicated infection 5; tunnelled catheter not removed 2; discharged from hospital with antibiotics 2; died 1 Control: Discharged from hospital with antibiotics 3; complicated infection 1; died 4 |
| Age (years) (mean, SD): | 68 (21) | 62 (19) | |||
| Male (%): | 57.2 | 53.8 | |||
| SAPS (mean, SD): | 56.9 (11.7) | 53.8 (12.3) | |||
| SOFA (mean, SD): | 6.3 (2.9) | 5.4 (3.3) | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (median, range): | 5.6 (0–187.5) | 9.9 (0–370.6) | |||
| CRP (mg/l) (mean, SD): | 162 (106.3) | 207 (123.5) | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | Pulmonary sepsis 19; urinary sepsis 66.7; abdominal sepsis 9.5; other sepsis 4.8 | Pulmonary sepsis 17.9; urinary sepsis 48.7; abdominal sepsis 10.3; other sepsis 23.1 | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | COPD 4.8; cardiopathy 16.7; immunosuppression 7.1; diabetes mellitus 19; chronic renal failure 4.8; chronic liver disease 7.1; non-haematological neoplasia 11.9; haematological malignancy 4.8 | COPD 2.6; cardiopathy 18; immunosuppression 12.8; diabetes mellitus 23.1; chronic renal failure 18; chronic liver disease 10.3; non-haematological neoplasia 5.1; haematological malignancy 2.6 | |||
| Drozdov (2014)47,48,69 ‘Triple P in UTI’ (ISRCTN13663741) Country: Switzerland Funding: Public Recruitment: April 2012 to March 2014 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 129 |
Setting: ED Population: Adults Presentation: Community-acquired UTI Testing application: Discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Consecutive immunocompetent adults (≥ 18 years), presenting to the ED of a tertiary care hospital, with community-acquired, non-catheter-related, acute (< 28 days) UTI as the main diagnosis (at least one clinical symptom: core body temperature ≥ 38 °C, urinary urgency, polyuria, dysuria, suprapubic pain, flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, nausea and vomiting, and one urinary criterion: pyuria > 20 leucocytes/µl and/or nitrites) Exclusion criteria: Other infections that required antibiotic therapy; pre-treatment with antibiotics < 48 hours; pregnancy; prostatitis; implanted foreign bodies in the urinary tract; urinary catheter; endovascular prostheses or foreign bodies; non-endovascular prostheses or foreign bodies within 6 months after implantation; foreseeable non-compliance or follow-up issues (e.g. current drug abuse); severe immunodeficiency; severe medical comorbidity with imminent death |
No. randomised | 63 | 66 | Total: 4 withdrew consent immediately after randomisation; 5 died; 3 lost to follow-up |
| Age (years) (median, IQR): | 73 (19–96) | ||||
| Male (%): | NR | NR | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT: | NR | NR | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Esposito (2011)49 NR Country: Italy Funding: Public Recruitment: October 2008 to September 2010 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 319 |
Setting: ED Population: Children Presentation: CAP Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Children (age 1 month to 14 years); diagnosis of CAP made based on clinical signs and symptoms (history of fever or cough, tachypnoea, dyspnoea or respiratory distress, and breathing with grunting or wheezing sounds with rales) and confirmed by chest radiography (i.e. the presence of pulmonary infiltration or segmental or lobar consolidation); no demonstrable complications, i.e. pleural effusion, empyema, lung necrosis, pneumatocoele) Exclusion criteria: Antibiotics < 10 days preceding admission; underlying chronic disease; severe malnutrition or other concurrent infections |
No. randomised | 160 | 159 | PCT: 5 withdrew consent Control: 4 withdrew consent |
| Age (years) (mean, SD): | 4.3 (3.8) | 4.7 (4) | |||
| Male (%): | 55 | 57 | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT: | NR | NR | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Layios (2012)50,51 NR Country: Belgium Funding: Not stated Recruitment: April 2008 to December 2008 Multicentre study Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 509 |
Setting: ICU Population: Adults Presentation: Suspected infection Testing application: Initiation Inclusion criteria: Adults (> 18 years), hospitalised for > 2 days in one of five ICUs Exclusion criteria: NR |
No. randomised | 258 | 251 | None reported |
| Age (years) (median, IQR): | 66 (55–76) | 65 (53–75) | |||
| Male (%): | 59.7 | 61 | |||
| SAPS (median, SD): | 39.3 (16.3) | 39 (16.7) | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT: | NR | NR | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | Underlying disease: non-fatal 62; ultimately fatal 28.7; rapidly fatal 9.3 | Underlying disease: non-fatal 61.4; ultimately fatal 27.1; rapidly fatal 11.6 | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | Coronary disease 11.2; chronic heart failure 14; cerebrovascular disease 4.7; renal dysfunction 11.6; liver disease 7.8; diabetes 17.4; COPD or asthma 27.9; solid cancer 16.3; haematological cancer 6.6; transplant 3.1 | Coronary disease 8.4; chronic heart failure 13.6; cerebrovascular disease 6.4; renal dysfunction 14.3; liver disease 6.4; diabetes 15.1; COPD or asthma 26.3; solid cancer 17.5; haematological cancer 6; transplant 3.2 | |||
| Liu (2013)33 NR Country: China Funding: Public Recruitment: January 2012 to June 2013 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 82 |
Setting: ICU Population: Adults Presentation: Sepsis Testing application: Discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Age > 18 years; suspected bacterial sepsis Exclusion criteria: Patients with positive culture result for Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, M. tuberculosis, fungi; suspected virus or parasite infection; chronic local infection; > 48 hours of antimicrobial treatment before randomisation; immunodeficiency (e.g. HIV or leukaemia); malignant tumour |
No. randomised | 42 | 40 | None reported |
| Age (years) (mean, SD): | 54.9 (13.8) | 53.4 (12.2) | |||
| Male (%): | 47.6 | 45 | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT: | NR | NR | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | Cardiodysfunction (6); kidney dysfunction (10); respiratory failure (18); haemodialysis (11) | Cardiodysfunction (5); kidney dysfunction (8); respiratory failure (15); haemodialysis (9) | |||
| Nobre (2008)52,53 NCT00250666 Country: Switzerland Funding: Industry – assay manufacturer Recruitment: February 2006 to April 2007 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 79 |
Setting: ICU Population: Adults Presentation: Severe sepsis and septic shock Testing application: Discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Patients admitted to a mixed medical/surgical ICU with suspected severe sepsis or septic shock, or who developed severe sepsis or septic shock during their stay Exclusion criteria: Microbiologically documented infections caused by P. aeruginosa, A. baumanni, Listeria spp., Legionella pneumophila, P. jirovecii, or M. tuberculosis, for which a prolonged duration of antibiotic therapy is standard care; severe viral or parasitic infections; chronic infectious conditions requiring prolonged antibiotic therapy; antibiotic therapy started ≥ 48 hours before enrolment; chronic, localised infections (e.g. chronic osteomyelitis); severely immunocompromised or on immunosuppressive therapy after solid organ transplant; neutropenia; withholding of life support; absence of antimicrobial treatment despite clinical suspicion of sepsis |
No. randomised | 39 | 40 | PCT: 4 died or transferred before day 5; 4 complicated infections (pleural empyema, acute mastoiditis, pelvic abscess) Control: 2 died or transferred before day 5; 1 pleural empyema |
| Age (years) (mean, SD, CI): | 64.3 (13.6) | 65.8 (15) | |||
| Male (%): | 67.5 | 69.2 | |||
| SAPS 3 (mean, SD, CI): | 67.5 (11.2) | 69.9 (12.6) | |||
| SOFA (mean, CI): | 5.9 (3.3) | 6.7 (2.9) | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (median, range): | 8.4 (0.1–93) | 5.9 (0.1–497) | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | Sepsis type: Pulmonary 64; abdominal 5; urinary 18; other 13, septic shock 43.6 Organ failure: Acidosis 45.2; ARDS 22.6; coma 16.1; dialysis 16.1; heart failure 6.5; respiratory failure 74.2; shock 45.2; renal failure 3.2 |
Sepsis type: Pulmonary 67; abdominal 15; urinary 10; other 8; septic shock 42.5 Organ failure: Acidosis 54.1; ARDS 16.2; coma 10.8; dialysis 10.8; heart failure 5.4; respiratory failure 75.7; shock 54.1; renal failure 13.5 |
|||
| Comorbidities (%): | Neoplasia 12.8; immunosuppression 2.6; cardiopathy 33.3; COPD 30.8; IDDM 0; NIDDM 10.3; chronic renal failure 5.1; peripheral vascular disease 5.1; chronic hepatopathy 12.8 | Neoplasia 12.5; immunosuppression 2.5; cardiopathy 42.5; COPD 17.5; IDDM 5; NIDDM 15; chronic renal failure 15; peripheral vascular disease 2.5; chronic hepatopathy 12.5 | |||
| Qu (2012)54 NR Country: China Funding: Public Recruitment: March 2009 to September 2011 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 71 |
Setting: ICU Population: Adults Presentation: Severe acute pancreatitis Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Onset of severe acute pancreatitis < 24 hours; age > 18 years Exclusion criteria: Time interval between diagnosis and study inclusion > 24 hours; thyroid disease; shock; need for surgical interventions |
No. randomised | 35 | 36 | No withdrawals |
| Age (years) (mean, CI, SD): | 43.2 (39.4 to 47) (11.1) | 43.7 (40 to 47.4) (11) | |||
| Male (%): | 71 | 72 | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA (mean, CI, SD): | 2.5 (2.3 to 2.7) (0.5) | 2.4 (2.2 to 2.6) (0.5) | |||
| PCT: | NR | NR | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Roh (2010)55 NR Country: NR Funding: Not stated Recruitment: NR Available only as conference abstract Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 122 |
Setting: ED Population: Adults Presentation: CAP Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Adults with CAP Exclusion criteria: NR |
No. randomised | 60 | 62 | No information |
| Age (range): | 24–82 | ||||
| Male (%): | NR | NR | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT: | NR | NR | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Roh (2013)56 NR Country: NR Funding: Not stated Recruitment: NR Available only as conference abstract Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 164 |
Setting: ED Population: Adults Presentation: Elderly patients with CAP Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Elderly patients (age > 70 years) requiring hospitalisation with CAP Exclusion criteria: NR |
No. randomised | 80 | 84 | No information |
| Age (years) (median, range): | NR | NR | |||
| Male (%): | NR | NR | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT: | NR | NR | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | NR | NR | |||
| Schuetz (2009)57–59,66–68 ProHOSP NCT00350987 (ISRCTN95122877) Country: Switzerland Funding: Mixed Recruitment: October 2006 to March 2008 Multicentre study Design: Non-inferiority parallel group RCT No. randomised: 1381 |
Setting: ED Population: Adults Presentation: Primary diagnosis of LRTI Testing application: Initiation and discontinuation Inclusion criteria: Adults (≥ 18 years); admitted from the community or a nursing home, via the ED; diagnosis of acute (< 28 days’ duration) LRTI (presence of at least one respiratory symptom (cough, sputum production, dyspnoea, tachypnoea, pleuritic pain), plus at least one finding during auscultation (rales, crepitation), or one sign of infection (core body temperature of > 38 °C, shivering, leucocyte count of > 10,000/µl or < 4000/µl independent of antibiotic pre-treatment Exclusion criteria: Active intravenous drug use; severe immunosuppression other than corticosteroid use; life-threatening medical comorbidities, leading to possible imminent death; hospital acquired pneumonia at least 48 hours after admission or hospitalised 14 days before presentation; chronic infection requiring antibiotic treatment |
No. randomised | 687 | 694 | PCT: Withdrew consent 16; lost to follow-up 1; died 34 Control: Withdrew consent 6; died 33 |
| Age (years) (median, IQR): | 73 (59–82) | 72 (59–82) | |||
| Male (%): | 59.9 | 55.2 | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (median, IQR): | 0.2 (0.1–1.2) | 0.2 (0.1–1.6) | |||
| CRP (mg/l) (median, IQR): | 115 (38–212) | 114 (4–220) | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | Final diagnosis: CAP 68.6; exacerbation of COPD 17.1; acute bronchitis 10.3; other 4 | Final diagnosis: CAP 67.6; exacerbation of COPD 16.4; acute bronchitis 11.9; other 4 | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | CHD 21.8; cerebrovascular disease 8.1; renal dysfunction 23.3; COPD 39.5; neoplastic disease 10.3; diabetes 17 | CHD 19.8; cerebrovascular disease 8.1; renal dysfunction 21.2; COPD 39; neoplastic disease 14.2; diabetes 16.4 | |||
| Stolz (2007)60 Country: Switzerland Funding: Mixed Recruitment: November 2003 to March 2005 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 226 |
Setting: ED Population: Adults Presentation: Exacerbations of COPD Testing application: Initiation Inclusion criteria: Age ≥ 40 years; ECOPD; met post-bronchodilator therapy spirometric criteria, according to the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease guidelines, < 48 hours of ED admission. An ECOPD was defined as ‘a sustained worsening of the patient’s condition, from the stable state and beyond normal day-to-day variations, that is acute in onset and necessitates a change in regular medication in a patient with underlying COPD’ Exclusion criteria: Alternative explanation for the presenting signs and symptoms other than a worsening of the underlying COPD; psychiatric comorbidities; immunosuppression; asthma; cystic fibrosis; presence of infiltrates on chest radiographs on hospital admission |
No. randomised | 113 | 113 | PCT: 11 excluded after randomisation (did not meet COPD criteria); 3 died within 14 days; 2 died within 6 months Control: 7 excluded after randomisation (did not meet COPD criteria); 2 died within 14 days; 7 died within 6 months |
| Age (years) (median, IQR): | 70 (65–77) | 70 (65–79) | |||
| Male (%): | 49 | 42 | |||
| COPD severity (%): | GOLD I (5.9); GOLD II (14.7): GOLD III (46.1); GOLD IV (33.3) | GOLD I (4.7); GOLD II (23.6); GOLD III (48.1); GOLD IV (23.6) | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | Cardiopathy (41%); arterial hypertension (23%); osteoporosis (17%); malignancy (12%); diabetes (12%); renal insufficiency (5%) | Cardiopathy (46%); arterial hypertension (26%); osteoporosis (9%); malignancy (13%); diabetes (10%); renal insufficiency (11%) | |||
| Stolz (2009)61 ProVAP study (ISRCTN61015974) Country: Switzerland Funding: Mixed Recruitment: NR Multicentre study Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 101 |
Setting: ICU Population: Adults Presentation: VAP Testing application: Discontinuation Inclusion criteria: ICU patients intubated for mechanical ventilation for ≥ 48 hours; > 18 years; clinically diagnosed VAP as defined by the ATS guidelines (new or persistent infiltrate on chest radiography, ≥ 2 of the following: purulent tracheal secretions, temperature of > 38 °C, leucocyte count of > 11,000 µl or < 3000 µl) Exclusion criteria: Pregnant; received immunosuppressants or long-term corticosteroid therapy; severely immunosuppressed, including AIDS; coexisting extrapulmonary infection diagnosed between day 1 and 3 requiring antibiotic therapy for > 3 days |
No. randomised | 51 | 50 | None |
| Age (years) (median, IQR): | 53 (21–88) | 59 (18–83) | |||
| Male (%): | 75 | 74 | |||
| SAPS (mean, SD): | 42 (13) | 45 (14) | |||
| SOFA (mean, SD): | 7.3 (3.4) | 8.2 (3.4) | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (median, IQR): | 0.6 (0.2–2.6) | 0.7 (0.2–2.3) | |||
| CRP: | NR | NR | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | Medical (53); emergency surgery (45); elective surgery (2) | Medical (52); emergency surgery (40); elective surgery (6) | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | Coronary artery disease (18); hypertensive heart disease (16); congestive heart failure (41); renal dysfunction (18); liver disease (8); diabetes (20); COPD (16); neoplastic disease (6); substance abuse (10) | Coronary artery disease (8); hypertensive heart disease (16); congestive heart failure (54); renal dysfunction (14); liver disease (6); diabetes (26); COPD (22); neoplastic disease (10); substance abuse (16) | |||
| Tang (2013)62 ICTRP ChiCTR-TRC-12002534 Country: China Funding: Public Recruitment: February 2005 to July 2010 Design: Parallel group RCT No. randomised: 265 |
Setting: ED Population: Adults Presentation: Suspected acute exacerbation of asthma Testing application: Initiation Inclusion criteria: Adults (≥ 18 years), with at least one of the following clinical features: dyspnoea; wheeze; acute cough; increased effort of breathing; increased requirement for beta-2-agonist; oxygen saturation < 95%; peak expiratory flow of ≤ 80% of their best known value over the preceding 12 months or their predicted value Exclusion criteria: Treatment with antibiotics in the 2 weeks before recruitment; bacterial infection other than in the respiratory system; pneumonia confirmed by chest radiograph; other chronic respiratory disease; severe organ dysfunction |
No. randomised | 132 | 133 | PCT: 1 died; 1 withdrew from study; 2 lost to follow-up Control: 2 died; 1 withdrew from study; 3 lost to follow-up |
| Age (years) (mean, SD): | 54 (14) | 55 (15) | |||
| Male (%): | 50 | 46.5 | |||
| SAPS: | NR | NR | |||
| SOFA: | NR | NR | |||
| PCT (ng/ml) (median, IQR): | 0.137 (0.068–0.252) | 0.119 (0.057–0.267) | |||
| CRP (mg/l) (median, IQR): | 8.2 (4.5–15.7) | 6.9 (5.1–17.6) | |||
| Diagnosis (%): | Severity of asthma: mild 36.7; moderate 42.2; severe 13.3; critical 7.8 | Severity of asthma: mild 39.4; moderate 40.9; severe 13.4; critical 6.3 | |||
| Comorbidities (%): | NR | NR | |||
3.2 intervention and comparator details
| Study details | PCT-based algorithm | Comparator | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCT assay | Timing of PCT measurement | Initiation algorithm | Discontinuation algorithm | Clinical component | ||
| Annane (2013)37 | BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | 6 hours; days 3 and 5 | PCT < 0.25 ng/ml: Do not initiate antibiotics, discontinue antibiotics if already started PCT 0.25–0.49 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly discouraged PCT 0.5–4.99 ng/ml: Antibiotics recommended PCT ≥ 5 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly recommended For participants enrolled ≤ 48 hours after surgery, the respective PCT cut-offs were < 4 ng/ml, 4–9 ng/ml and ≥ 9 ng/ml |
Investigators were strongly asked not to over-rule the algorithm every day up to study day 5 | Doctor’s discretion | |
| Baer (2013)39 | BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline; days 3 and 5 | PCT < 0.1 ng/ml: Definitely not antibiotics PCT 0.1–0.25 ng/ml: Probably not antibiotics PCT 0.26–0.49 ng/ml: Probably require antibiotics PCT ≥ 0.5 ng/ml: Definitely require antibiotics |
PCT < 0.25 ng/ml: Discontinuation encouraged upon clinical stabilisation Initial PCT > 10 ng/ml: Discontinuation encouraged when levels decreased below 90% of initial value Continuation of treatment on day 5 was determined as follows:
|
The PCT algorithm could be over-ruled for patients with life threatening infections, defined as severe comorbidity, emerging ICU need during initial follow-up, or haemodynamic or respiratory instability | Doctor assessment and clinical guidelines for a duration of 7–10 days for uncomplicated CAP, and 14 or more days for complicated CAP |
| Bouadma (2010)41 | BRAHMS PCT Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline, at each infectious episode until day 28, and every morning in participants receiving antibiotics 6–12 hours after admission in patients where antibiotics were initially withheld |
PCT < 0.25 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly discouraged PCT 0.25–0.49 ng/ml: Antibiotics discouraged PCT 0.5–0.99 ng/ml: Antibiotics encouraged PCT ≥ 1 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly encouraged |
PCT < 0.25 ng/ml: Discontinuation strongly encouraged PCT 0.25–0.49 ng/ml or ≤ 80% of peak concentration: Discontinuation encouraged PCT ≥ 0.5 ng/ml or > 80% of peak concentration: Discontinuation strongly discouraged PCT ≥ 0.5 ng/ml rising: Change of antibiotics strongly encouraged |
Before the start of the study, all investigators received an approved reminder including recommendations for duration of antibiotic treatment for most frequent infections. Final treatment decisions were at the discretion of doctors | |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | BRAHMS PCT Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline; days 4, 6 and 8, 6–24 hours after admission in patients for whom antibiotics were initially withheld | PCT < 0.1 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly discouraged PCT 0.1–0.25 ng/ml: Antibiotics discouraged PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml: Antibiotics encouraged PCT > 0.5 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly encouraged |
PCT < 0.1 ng/ml: Discontinuation strongly encouraged PCT 0.1–0.25 ng/ml: Discontinuation encouraged PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml: Discontinuation discouraged PCT > 0.5 ng/ml: Discontinuation strongly discouraged In patients with very high PCT values on admission (e.g. > 10 g/l), discontinuation of antibiotics was encouraged if levels decreased to < 10% of the initial value |
NR | Usual practice guidelines |
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline; 6–24 hours after admission in patients for whom antibiotics were initially withheld | PCT < 0.1 ng/ml: antibiotics strongly discouraged PCT 0.1–0.25 ng/ml: antibiotics discouraged PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml: antibiotics advised PCT > 0.5 ng/ml: antibiotics strongly recommended |
PCT < 0.1 ng/ml: Discontinuation strongly encouraged PCT 0.1–0.25 ng/ml: Discontinuation encouraged PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml: Discontinuation discouraged PCT > 0.5 ng/ml: Discontinuation strongly discouraged For patients on antibiotics on admission, PCT < 0.25 ng/ml: Discontinuation recommended |
Diagnostic procedures, therapeutic and antibiotic regimens were at the doctor’s discretion | |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | VIDAS BRAHMS PCT – bioMérieux | Baseline; day 5 or 7 (blood culture positive) and every 48 hours until hospital discharge, death, or discontinuation of antibiotic therapy | Discontinuation encouraged when PCT fell by > 90% from the peak level or the absolute value of PCT was < 0.5 ng/ml | Continuation of antibiotic therapy against this guidance was classified as ‘antibiotic discontinuation over-ruling’ | No details reported | |
| Drozdov (2014)69 | BRAHMS PCT Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline; days 3, 5 and 7, and every 2 days while on therapy | Discontinuation advised when PCT < 0.25 ng/ml or PCT decrease ≥ 80% of peak value and pyuria normalised or decrease ≥ 90% of peak value | No details reported | Usual proactive guidelines | |
| Esposito (2011)49 | BRAHMS PCT- Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline; every 2 days until discharge, and during the two follow-up visits | < 0.25 ng/ml: Antibiotics not administered ≥ 0.25 ng/ml: Antibiotics given immediately |
Antibiotics given until levels returned to < 0.25 ng/ml, and resumed antibiotics only if their PCT levels subsequently increased to more than this value | Untreated children showing no reduction in the clinical signs and symptoms of disease after 3 days or any severe deterioration could be treated with antibiotics regardless of their PCT levels or treatment could be modified | SIP guidelines: antibiotic monotherapy chosen on the basis of age if mild; combined beta-lactam and macrolide therapy if severe. The duration of administration in the control group was that recommended by the SIP (i.e. 7–14 days depending on disease severity) |
| Layios (2012)50 | VIDAS BRAHMS PCT – bioMérieux | As soon as patients were suspected of developing an infection | PCT < 0.25 ng/ml: Antibiotics more strongly discouraged PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml: Antibiotics less strongly discouraged PCT 0.5–1 ng/ml: Antibiotics less strongly recommended PCT > 1 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly recommended The strategy was applied individually to each infectious episode during the ICU stay |
NR | NR | |
| Liu (2013)33 | Quantitative; not specified | PCT value observed every day | PCT value decreased > 90% or PCT < 0.25 µg/l | Antibiotics could also be stopped when no active symptoms of infection were shown and APACHE II scores declined | Treated according to principles of antibiotic usage | |
| Nobre (2008)52 | BRAHMS PCT Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline (days 1 and 2) and daily until the seventh day of follow-up, and then at 5-day intervals or until antibiotics were stopped, death or hospital discharge | Baseline PCT ≥ 1 ng/ml, re-evaluate at day 5: PCT levels dropped by > 90% from baseline or peak value, discontinuation encouraged; PCT < 0.25 ng/ml, discontinuation encouraged Baseline PCT < 1 ng/ml, re-evaluate at day 3: PCT < 0.1 ng/ml, discontinuation encouraged |
The final decision on antibiotic therapy duration was at the discretion of the treating physician. Patients with positive blood cultures received at least 5 full days parenteral antibiotic therapy | Clinicians decided on the duration of antibiotic therapy, based on empirical rules. Patients with positive blood cultures received at least 5 full days’ parenteral antibiotic therapy | |
| Qu (2012)54 | Quantitative; not specified | Measured daily for a maximum of 28 days | Antibiotic therapy was not applied until clinical signs and symptoms of infection appeared and the PCT value was > 0.5 ng/ml | Antibiotic therapy discontinued if clinical signs and symptoms of infection improved and PCT < 0.5 ng/ml over 3 days | NR | Antibiotic therapy administrated for 14 days, or antibiotic therapy was continued because of confirmed infection until clinical signs and symptoms of infection disappeared over 3 days |
| Roh (2010)55 | Quantitative; not specified | NR | Appears that decision to start antibiotics also influenced by PCT level but this was not explicitly stated | PCT < 0.25 µg/l: Discontinue antibiotics | NR | Usual practice guideline |
| Roh (2013)56 | Quantitative; not specified | NR | PCT > 0.25 µg/l: Start antibiotics | PCT < 0.25 µg/l: Discontinue antibiotics | NR | Usual practice guideline |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | BRAHMS PCT Sensitive Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline, 3, 5 and 7 days after starting antibiotics, and at discharge After 6–24 hours when antibiotics were initially withheld |
PCT < 0.1 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly discouraged PCT 0.1–0.25: Antibiotics discouraged PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml: Antibiotics encouraged PCT > 0.5 ng/ml: Antibiotics strongly encouraged |
PCT < 0.1 ng/ml: Continuation strongly discouraged PCT 0.1–0.25: Continuation discouraged PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml: Continuation encouraged PCT > 0.5 ng/ml: Continuation strongly encouraged |
The PCT algorithm could be over-ruled in patients with: immediate need for ICU admission; respiratory or haemodynamic instability; positive antigen test for L. pneumophila; severe CAP. The PCT algorithm could also be over-ruled after consulting the study centre Other routine laboratory tests were available. The choice of antibiotic regimen was at the discretion of the clinician |
Recommendations from up-to-date guidelines Routine laboratory tests, other than PCT, were available. The choice of antibiotic regimen was at the discretion of the doctor |
| Stolz (2009)61 | BRAHMS PCT Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline, after 72 hours (day 2); daily PCT levels were measured | PCT < 0.25 ng/ml: Discontinuation Strongly encouraged PCT 0.25–0.5 ng/ml or a decrease ≥ 80%: Reduction or discontinuation was encouraged PCT 0.5–1.0 ng/ml or decrease < 80%: Reduction or discontinuation discouraged PCT > 1 ng/ml: Antibiotic discontinuation was strongly discouraged |
NR | NR | |
| Stolz (2007)60 | BRAHMS PCT Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline | PCT < 0.1 µg/l: Antibiotics discouraged 0.1–0.25 µg/l: Antibiotics discouraged or encouraged, based on the stability of the patient’s clinical condition PCT > 0.25: Antibiotic treatment encouraged |
NR | Current guidelines, according to the decision of the attending doctor | |
| Tang (2013)62 | BRAHMS PCT Kryptor – Thermo Fisher | Baseline; after 6–8 hours when antibiotics where initially withheld | PCT < 0.1 ng/ml: Antibiotic treatment strongly discouraged PCT 0.1–0.25 ng/ml: Antibiotic treatment discouraged PCT > 0.25 ng/ml: Antibiotic treatment encouraged |
NR | Antibiotic treatment was decided by the attending doctor | |
3.3 study results (dichotomous outcomes)
| Study details | Subgroup | Outcome | PCT-based algorithm | Clinical judgement alone | Crude RR (95% CI) | Adjusted effect estimate (95% CI) | Analysis details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of events/no. of patients | No. of events/no. of patients | ||||||
| Annane (2013)37 Population ICU; adults (apparent septic shock and no clear source of infection) |
Whole group Analysis ITT |
All-cause mortality Timing: 5 days |
3/31 | 3/31 | 1 (0.25 to 4.04) | NR | |
| ICU mortality | 7/31 | 10/30 | 0.69 (0.31 to 1.53) | ||||
| In-hospital mortality | 7/31 | 10/30 | 0.69 (0.31 to 1.53) | ||||
| Whole group Analysis Modified ITT |
Antibiotic exposure (no. on antibiotics at day 5) Timing: 5 days |
18/30 | 22/28 | 0.77 (0.55 to 1.08) | |||
| Baer (2013)39 Population ED; children (LRTI) Analysis Modified ITT |
Whole group | Adverse outcome [any complication from pneumonia or other LRTI (e.g. parapneumonic infusions in need of puncture, empyema, lung abscess, necrotising pneumonitis, ARDS)] Timing: 14 days |
38/168 | 33/169 | 1.16 (0.77 to 1.74) | NR | |
| CAP | 23/108 | 20/107 | 1.14 (0.67 to 1.93) | ||||
| Non-CAP LRTI | 15/60 | 13/62 | 1.19 (0.63 to 2.25) | ||||
| Whole group | Antibiotic side effects Timing: 14 days |
56/168 | 57/169 | 0.99 (0.73 to 1.33) | |||
| CAP | 42/60 | 51/62 | 0.85 (0.7 to 1.04) | ||||
| Non-CAP LRTI | 14/60 | 6/62 | 2.3 (0.98 to 5.42) | ||||
| Whole group | Hospitalisation Timing: 14 days |
104/168 | 100/169 | 1.05 (0.88 to 1.24) | |||
| CAP | 67/108 | 68/107 | 0.98 (0.8 to 1.2) | ||||
| Non-CAP LRTI | 37/60 | 32/62 | 1.19 (0.87 to 1.62) | ||||
| Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure | 104/168 | 93/169 | 1.12 (0.94 to 1.35) | |||
| CAP | 77/108 | 83/107 | 0.92 (0.79 to 1.08) | ||||
| Non-CAP LRTI | 27/60 | 10/62 | 2.71 (1.46 to 5.01) | ||||
| Bouadma (2010)41 Population ICU; adults (suspected bacterial infection) Analysis Modified ITT |
Whole group | All-cause mortality Timing: 28 days |
65/307 | 64/314 | 1.04 (0.76 to 1.41) | OR: 0.8 (–4.6 to 6.2) |
Adjusted for age, sex, pre-existing comorbidities, location before and reason for admission, baseline SOFA score, infection type, blood culture results, septic shock and mechanical ventilation |
| Whole group | All-cause mortality Timing: 60 days |
92/307 | 82/314 | 1.15 (0.89 to 1.48) | OR: 1.09 (0.79 to 1.51) HR 0.96 (0.84 to 1.09) |
||
| Whole group | Infection (isolation from the same or another site of one or more pathogens different from that identified during the first infectious episode, together with clinical signs or symptoms of infection) Timing: 28 days |
106/307 | 97/314 | 1.12 (0.89 to 1.4) | |||
| Whole group Analysis Modified ITT |
Infection relapse/recurrence (growth of one or more of the initial causative bacterial strains from a second sample taken from the same infection site at ≥ 48 hours after stopping of antibiotics, combined with clinical signs or symptoms of infection) Timing: 28 days |
20/307 | 16/314 | 1.27 (0.68 to 2.38) | |||
| Whole group | Multidrug-resistant bacteria (one of the following: ticarcillin-resistant P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii or Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; extended-spectrum beta-lactam-producing Enterobacteriaceae; high-concentration cephalosporinase-producing AmpC Enterobacteriaceae Timing: 28 days |
55/307 | 52/314 | 1.08 (0.77 to 1.52) | |||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 Population ED; adults (suspected LRTI) Analysis ITT |
Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure (antibiotics prescribed) | 55/124 | 99/119 | 0.54 (0.43 to 0.66) | RR: 0.49 (0.44 to 0.55) | Adjusted for clustering and potential confounding factors (age other NR) |
| COPD acute admissions | 11/29 | 27/31 | 0.45 (0.28 to 0.71) | NR | |||
| Whole group | All-cause mortality Timing: 14 days |
4/124 | 4/119 | 0.96 (0.27 to 3.46) | NR | ||
| COPD acute admissions | 1/29 | 1/31 | 1.07 (0.12 to 9.7) | ||||
| Whole group | Hospitalisation (hospital admission) | 101/124 | 88/119 | 1.1 (0.96 to 1.26) | |||
| COPD acute exacerbations | 27/29 | 25/31 | 1.15 (0.95 to 1.4) | ||||
| Whole group | ICU admission Timing: 14 days |
5/124 | 6/119 | 0.81 (0.27 to 2.46) | |||
| COPD acute exacerbations | 1/29 | 1/31 | 1.07 (0.12 to 9.7) | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 Population ED; adults (CAP) Analysis ITT |
Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure | 128/151 | 149/151 | 0.86 (0.8 to 0.92) | NR | |
| All-cause mortality Timing: 6 weeks |
18/151 | 20/151 | 0.9 (0.5 to 1.62) | ||||
| Adverse outcome (‘failed outcome’ defined as death, recurrence, relapse or persistence of clinical, laboratory and radiological signs of CAP, and patients lost to follow-up) Timing: 6 weeks |
24/151 | 27/151 | 0.89 (0.54 to 1.46) | ||||
| ICU admission Timing: 6 weeks |
20/151 | 21/151 | 0.95 (0.54 to 1.67) | ||||
| Deliberato (2013)45 Population ICU; adults (suspected or confirmed sepsis) Analysis ITT |
Whole group | ICU mortality Timing: NR |
1/42 | 4/39 | 0.31 (0.05 to 1.87) | NR | |
| In-hospital mortality Timing: NR |
2/42 | 4/39 | 0.52 (0.12 to 2.28) | ||||
| Infection relapse/recurrence (primary infection relapse) Timing: NR |
2/42 | 1/39 | 1.55 (0.21 to 11.19) | ||||
| Drozdov (2014)69 Population ED; adults (community-acquired UTI) Analysis Modified ITT |
Whole group | Hospital re-admission Timing: 90 days |
15/59 | 17/63 | 0.95 (0.53 to 1.7) | NR | |
| All hospitalised patients | 13/45 | 15/45 | 0.81 (0.28 to 1.59) | ||||
| Complicated febrile UTI/pyelonephritis | 7/32 | 11/34 | 0.69 (0.32 to 1.52) | ||||
| Uncomplicated simple UTI | 1/2 | 1/6 | 2.6 (0.46 to 14.67) | ||||
| Uncomplicated febrile UTI/pyelonephritis | 1/8 | 2/8 | 0.6 (0.1 to 3.58) | ||||
| Complicated simple UTI | 6/16 | 2/11 | 1.81 (0.52 to 6.32) | ||||
| Whole group | Infection relapse/recurrence Timing: 90 days |
15/59 | 14/63 | 1.14 (0.61 to 2.13) | NR | ||
| All hospitalised patients | 13/45 | 11/45 | 1.1 (0.49 to 2.30) | ||||
| Complicated simple UTI | 6/16 | 3/11 | 1.29 (0.45 to 3.73) | ||||
| Complicated febrile UTI/pyelonephritis | 6/32 | 8/34 | 0.81 (0.33 to 2) | ||||
| Uncomplicated febrile UTI/pyelonephritis | 2/8 | 1/8 | 1.67 (0.28 to 9.95) | ||||
| Uncomplicated simple UTI | 1/2 | 1/6 | 2.6 (0.46 to 14.67) | ||||
| Esposito (2011)49 Population ED; children (CAP) Analysis Modified ITT |
Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure | 131/155 | 155/155 | 0.85 (0.79 to 0.9) | NR | |
| Severe CAP | 76/79 | 76/76 | 0.96 (0.92 to 1.01) | ||||
| Mild CAP | 52/76 | 79/79 | 0.69 (0.59 to 0.8) | ||||
| Whole group | Antibiotic side effects Timing: 28 days |
6/155 | 39/155 | 0.16 (0.07 to 0.37) | |||
| Whole group | Infection relapse/recurrence (CAP recurrence) Timing: 3 weeks |
1/155 | 6/155 | 0.23 (0.04 to 1.34) | |||
| Whole group | Need for antibiotics at follow-up (new antibiotic prescriptions) Timing: 28 days |
1/155 | 4/155 | 0.33 (0.05 to 2.09) | |||
| Layios (2012)50 Population ICU; adults (suspected infection) Analysis ITT |
Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure (no. withheld or withdrawn per episode) | 71/353 | 51/314 | 1.24 (0.89 to 1.71) | NR | |
| Clinician confidence – possible infection | 52/103 | 26/76 | 1.46 (1.02 to 2.1) | ||||
| Clinician confidence – uncertain infection | 13/26 | 16/21 | 0.66 (0.43 to 1.03) | ||||
| Whole group | ICU mortality | 56/258 | 53/251 | 1.03 (0.74 to 1.43) | |||
| Liu (2013)33 Population ICU; adults (sepsis) Analysis ITT |
Whole group | All-cause mortality Timing: 28 days |
6/42 | 5/40 | 1.13 (0.39 to 3.22) | NR | |
| Clinical cure (not defined) Timing: 28 days |
33/42 | 34/40 | 0.93 (0.76 to 1.13) | ||||
| Adverse outcome (relapse) Timing: 28 days |
3/42 | 1/40 | 2.22 (0.34 to 14.34) | ||||
| Nobre (2008)52 Population ICU; adults (severe sepsis and septic shock) |
Whole group | All-cause mortality Timing: 28 days |
8/39 | 8/40 | 1.03 (0.44 to 2.38) | NR | |
| Clinical cure (clinical signs and symptoms present at baseline, which had resolved by the final assessment) Timing: NR |
31/39 | 32/40 | 0.99 (0.8 to 1.24) | ||||
| In-hospital mortality | 9/39 | 9/40 | 1.03 (0.47 to 2.25) | ||||
| Infection relapse/recurrence Timing: NR |
1/39 | 1/40 | 1.03 (0.11 to 9.44) | ||||
| Sepsis-related mortality Timing: NR |
3/39 | 2/40 | 1.44 (0.3 to 6.85) | ||||
| Qu (2012)54 Population ICU; adults (severe acute pancreatitis) Analysis ITT |
Whole group | All-cause mortality Timing: 28 days |
7/35 | 8/36 | 0.91 (0.38 to 2.16) | NR | |
| Whole group | Adverse outcome (multiorgan dysfunction syndrome) Timing: NR |
24/35 | 25/36 | 0.99 (0.73 to 1.34) | |||
| Roh (2013)56 Population ED; adults (elderly patients with CAP) Analysis Not specified |
Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure | 73/80 | 83/84 | 0.92 (0.86 to 0.99) | NR | |
| All-cause mortality Timing: 6 months |
11/80 | 11/84 | 1.05 (0.49 to 2.24) | ||||
| Clinical cure (not defined) Timing: 6 weeks |
65/80 | 70/84 | 0.98 (0.85 to 1.12) | ||||
| Roh (2010)55 Population ED; adults (CAP) Analysis Not specified |
Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure | 55/60 | 61/62 | 0.93 (0.86 to 1.01) | NR | |
| All-cause mortality Timing: 6 weeks |
8/60 | 9/62 | 0.92 (0.39 to 2.17) | ||||
| Clinical cure (not defined) Timing: 6 weeks |
50/60 | 53/62 | 0.98 (0.84 to 1.13) | ||||
| Schuetz (2009)57 Population ED; adults (primary diagnosis of LRTI) Analysis Modified ITT |
Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure | 506/671 | 603/688 | 0.86 (0.82 to 0.91) | ||
| Exacerbation of COPD | 56/115 | 79/113 | 0.7 (0.56 to 0.87) | ||||
| CAP | 417/460 | 461/465 | 0.91 (0.89 to 0.94) | ||||
| Acute bronchitis | 16/69 | 41/82 | 0.47 (0.29 to 0.76) | ||||
| Whole group | Adverse outcome (death, ICU admission, recurrence or re-hospitalisation, or disease-specific complication) Timing: 30 days |
103/671 | 130/688 | 0.81 (0.64 to 1.03) | |||
| Acute bronchitis | 6/69 | 8/82 | 0.91 (0.34 to 2.39) | ||||
| CAP | 74/460 | 94/465 | 0.8 (0.61 to 1.05) | ||||
| Exacerbation of COPD | 15/115 | 21/113 | 0.71 (0.39 to 1.29) | ||||
| Whole group | Adverse outcome (disease-specific complication) Timing: 30 days |
17/671 | 14/688 | 1.24 (0.62 to 2.46) | |||
| Whole group | 34/671 | 33/688 | 1.06 (0.66 to 1.68) | ||||
| CAP | 24/460 | 26/465 | 0.93 (0.55 to 1.59) | ||||
| Exacerbation of COPD | 4/115 | 5/113 | 0.8 (0.24 to 2.72) | ||||
| Acute bronchitis | 1/6 | 0/82 | 3.56 (0.15 to 86.04) | ||||
| Whole group | Antibiotic side effects Timing: 30 days |
133/671 | 193/688 | 0.71 (0.58 to 0.86) | |||
| Acute bronchitis | 7/69 | 11/82 | 0.77 (0.33 to 1.83) | ||||
| CAP | 108/460 | 154/465 | 0.71 (0.58 to 0.87) | ||||
| Exacerbation of COPD | 14/115 | 18/113 | 0.77 (0.41 to 1.46) | ||||
| Whole group | ICU admission Timing: 30 days |
43/671 | 60/688 | 0.74 (0.51 to 1.07) | |||
| Whole group | Infection relapse/recurrence or hospital re-admission Timing: 30 days |
25/671 | 45/688 | 0.57 (0.36 to 0.92) | |||
| Stolz (2007)60 Population ED; adults (COPD exacerbation) Analysis Modified ITT |
Whole group | Antibiotic exposure (number of antibiotic courses) Timing: 6 months |
87/102 | 119/106 | NA | NR | |
| Antibiotic exposure (number of antibiotic prescriptions) Timing: 21 days |
41/102 | 76/106 | NA | ||||
| All-cause mortality Timing: 6 months |
5/102 | 9/106 | 0.6 (0.22 to 1.66) | ||||
| Clinical success (improvement of symptoms compared with exacerbation status) Timing: 21 days |
84/102 | 89/106 | 0.98 (0.87 to 1.11) | ||||
| ICU admission Timing: 21 days |
8/102 | 11/106 | 0.77 (0.33 to 1.79) | ||||
| Need for steroids (steroid use) Timing: 21 days |
89/102 | 93/106 | 0.99 (0.9 to 1.1) | ||||
| Secondary ED visits (hospitalisation for ECOPD) Timing: 6 months |
18/102 | 22/106 | 0.85 (0.49 to 1.48) | ||||
| Stolz (2009)61 Population ICU; adults (VAP) |
Whole group | Antibiotic exposure (antibiotic discontinuation) Timing: 10 days |
NR | NR | NR | HR: 1.66 (1.02 to 2.71) | Cox regression Adjustment for age, respiratory tract culture results and centre effect |
| Antibiotic exposure (antibiotic therapy for > 7 days) Timing: 28 days |
33/51 | 41/50 | 0.79 (0.62 to 1) | NR | |||
| All-cause mortality Timing: 28 days |
8/51 | 12/50 | 0.67 (0.31 to 1.45) | ||||
| In-hospital mortality | 10/51 | 14/50 | 0.71 (0.36 to 1.42) | ||||
| Adverse outcome (VAP-related clinical deterioration) Timing: 28 days |
5/51 | 7/50 | 0.72 (0.26 to 2.01) | ||||
| Tang (2013)62 Population ED; adults (suspected acute exacerbation of asthma) Analysis Per protocol |
Whole group | Initiation of antibiotic exposure | 59/128 | 95/127 | 0.62 (0.5 to 0.76) | NR | |
| Critical asthma | 9/10 | 8/8 | 0.9 (0.74 to 1.1) | ||||
| Severe asthma | 13/17 | 14/17 | 0.93 (0.67 to 1.3) | ||||
| Moderate asthma | 21/54 | 36/52 | 0.57 (0.39 to 0.83) | ||||
| Mild asthma | 16/47 | 37/50 | 0.47 (0.31 to 0.71) | ||||
| Whole group | Hospital re-admission Timing: 6 weeks |
5/128 | 8/127 | 0.64 (0.23 to 1.82) | |||
| Mechanical ventilation Timing: 6 weeks |
8/128 | 9/127 | 0.89 (0.36 to 2.17) | ||||
| Need for antibiotics at follow-up Timing: 6 weeks |
5/128 | 9/127 | 0.57 (0.21 to 1.59) | ||||
| Need for steroids (repeated need for steroids or dosage increase) Timing: 6 weeks |
6/128 | 9/127 | 0.68 (0.26 to 1.79) | ||||
| Secondary ED visits (asthma exacerbation) Timing: 6 weeks |
8/128 | 13/127 | (0.27 to 1.42) | ||||
3.4 study results (continuous outcomes)
| Study details | Outcome | Population | Baseline | Follow-up | MD at follow-up (95% CI) and p-value for difference: | Analysis details | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Comparator | Intervention | Comparator | |||||
| Median IQR or mean (SD) (CI) (no. of participants) | ||||||||
| Annane (2013)37 Population: ICU; adults (apparent septic shock and no clear source of infection) Measure reported: Median, IQR Analysis: Modified ITT |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 5 (2–5) (30) | 5 (3–5) (28) | p-value = 0.52 | NR | |
| Antibiotic exposure (antibiotic-free days) | NA | 0 (0–3) (30) | 0 (0– 2) (28) | NR | ||||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | NA | 27 (9–49) (30) | 33 (11–69) (28) | p-value = 0.22 | ||||
| Length of ICU stay (days) | NA | 22 (8–42) (30) | 23 (10–60) (28) | p-value = 0.58 | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation (duration, days) | NA | 11 (5–25) (30) | 14 (8–25) (28) | p-value = 0.56 | ||||
| SOFA score (5 days) | NR | NR | 8 (5 to 9) (30) | 8 (7 to 11) (28) | p-value = 0.61 | |||
| Baer (2013)39 Population: ED; children (LRTI) Measure reported: Mean (95% CI) Analysis: Modified ITT |
Antibiotic exposure (days) | Whole group | NA | 4.5 (168) | 6.3 (169) | –1.8 (–3.1 to –0.5) | Wilcoxon rank-sum test | |
| Non-CAP LRTI | 2.4 (60) | 1.6 (62) | 0.8 (–0.5 to 2) | |||||
| CAP | 5.7 (108) | 9.1 (107) | –3.4 (–4.9 to –1.7) | |||||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | Whole group | NA | 2.6 (168) | 2.7 (169) | –0.1 (–0.8 to 0.5) | |||
| Non-CAP LRTI | 2.5 (60) | 2.3 (62) | 0.3 (–0.8 to 1.2) | |||||
| CAP | 2.6 (108) | 2.9 (107) | –0.3 (–1.1 to 0.5) | |||||
| Bouadma (2010)41 Population: ICU; adults (suspected bacterial infection) Analysis: Modified ITT Measure reported: Mean, SD, CI |
Antibiotic exposure (days) | Whole group | NA | 6.1 (6) (307) | 9.9 (7.1) (314) | –3.8 (–4.8 to –2.7) p-value < 0.0001 |
t-test | |
| UTI | 7.4 (6.3) (24) | 14.5 (9.3) (18) | –7.1 (–12.08 to –2.12) p-value = 0.0053 |
|||||
| CAP | 5.5 (4) (79) | 10.5 (6.4) (101) | –5 (–6.53 to 3.47) p-value < 0.0001 |
|||||
| VAP | 7.3 (5.3) (75) | 9.4 (5.7) (66) | –2.1 (–3.92 to –0.28) p-value = 0.021 |
|||||
| Infection with positive blood culture | 9.8 (7.7) (55) | 12.8 (8.1) (53) | –3 (–5.98 to –0.02) p-value = 0.06 |
|||||
| Intra-abdominal infection | 8.1 (7.7) (14) | 10.8 (6.7) (20) | –2.7 (–7.69 to 2.29) p-value = 0.29 |
|||||
| Antibiotic exposure (antibiotic-free days) | Whole group | NA | 14.3 (9.1) (307) | 11.6 (8.2) (314) | 2.7 (1.4 to 4.1) p-value < 0.0001 |
|||
| Antibiotic exposure [total exposure days/1000 days (incidence rate ratio)] | NA | 653 (307) | 812 (314) | –159 (–185 to –131) p-value < 0.0001 |
||||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | NA | 26.1 (19.3) (307) | 26.4 (18.3) (314) | –0.3 (–3.2 to 2.7) p-value = 0.87 |
||||
| Length of ICU stay (days) | NA | 15.9 (16.1) (307) | 14.4 (14.1) (314) | 1.5 (–0.9 to 3.9) p-value = 0.23 |
||||
| Mechanical ventilation (no. of days without mechanical ventilation) | NA | 16.2 (11.1) (307) | 16.9 (10.9) (314) | –0.7 (–2.4 to 1.1) p-value = 0.47 |
||||
| SOFA score (28 days) | NR | NR | 1.5 (3) (307) | 0.9 (2.4) (314) | 0.6 (0, 1.1) p-value = 0.037 |
|||
| Christ-Crain (2004)42 Population: ED; adults (CAP) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Median (IQR) or mean (SD) |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 5.8 (5.3) (151) | 12.9 (6.5) (151) | –7.10 (–8.44 to –5.76) p-value < 0.001 |
Mann–Whitney U-test | |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | NA | 12 (9.1) (151) | 13 (9) (151) | –1.00 (–3.04 to 1.04) p-value = 0.35 |
||||
| Quality of life at 6 weeks | NR | NR | 10 (10) (151) | 11 (10) (151) | –1.00 (–3.26 to 1.26) p-value = 0.14 |
|||
| Antibiotic costs [costs per patient (US$)] at 6 weeks | NA | 100 (33–186) (151) | 190 (133–337) (151) | NR | ||||
| Costs (antibiotics plus PCT costs per patient) at 6 weeks | NA | 290 (212–378) (151) | 190 (133–337) (151) | p-value < 0.001 | ||||
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 Population: ED; adults (suspected LRTI) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Mean, SD, CI |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 10.9 (3.6) (124) | 12.8 (5.5) (119) | –1.90 (–3.07 to –0.73) p-value = 0.03 |
t-test | |
| COPD acute exacerbations | NA | 8.7 (2.1) (29) | 9.1 (2.8) (31) | –0.40 (–1.65 to –0.85) p-value = 0.47 |
t-test | |||
| Antibiotic exposure [total exposure days/1000 days (incidence rate ratio)] | Whole group | NA | 332 (433) (124) | 661 (398) (119) | –329.0 (–433.5 to –224.5) p-value < 0.0001 |
t-test | ||
| COPD acute exacerbations | NA | 269 (414) (29) | 682 (369) (31) | –413.0 (–611.9 to –214.1) p-value = 0.0001 |
Mann–Whitney U-test | |||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | Whole group | 10.7 (8.9) (124) | 11.2 (10.6) (119) | –0.50 (–2.97 to 1.97) p-value = 0.89 |
t-test | |||
| COPD acute exacerbations | 13.7 (7.3) (29) | 10.8 (7) (31) | –1.00 (–4.75 to 2.75) p-value = 0.25 |
|||||
| Antibiotic costs [costs per patient (US$)] at 14 days | Whole group: | NA | 96.3 (172.8) (124) | 202.5 (250.6) (119) | –106.2 (–160.5 to –51.9) p-value < 0.0001 |
Mann–Whitney U-test | ||
| COPD acute exacerbations | 64.7 (105.4) (29) | 101.4 (75.9) (31) | –36.7 (–83.5 to 10.1) p-value = 0.01 |
|||||
| Quality of life (no details on questionnaire) at 14 days | Whole group | 41.3 (14.3) (124) | 39.3 (13.2) (119) | 21.9 (14.7) (124) | 22.9 (15.1) (119) | –1.00 (–4.75 to 2.75) p-value = 0.60 |
t-test | |
| COPD acute exacerbations | 46.1 (15.2) (29) | 45.3 (11.4) (31) | 27.9 (15.7) (29) | 25.8 (13.7) (31) | 2.10 (–5.38 to 9.58) p-value = 0.85 |
|||
| Deliberato (2013)45 Population: ICU; adults (suspected or confirmed sepsis) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Median, range |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 10 (3 to 39) (20) | 11 (2 to 45) (31) | p-value = 0.44 | Mann–Whitney U-test | |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | Whole group | NA | 11 (3 to 547) (20) | 11 (2 to 228) (31) | p-value = 0.70 | |||
| Length of ICU stay (days) | Whole group | NA | 3.5 (1 to 57) (20) | 3 (1 to 28) (31) | p-value = 0.60 | |||
| Drozdov (2014)69 Population: ED; adults (community-acquired UTI) Analysis: Modified ITT Measure reported: Median, IQR |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 6 (4 to 8) (61) | 10 (7 to 11) (64) | p-value < 0.001 | Mann–Whitney U-test | |
| Uncomplicated simple UTI | 0.5 (0 to 1) (2) | 1 (1 to 1) (6) | p-value = 0.127 | |||||
| Complicated simple UTI | 4 (2.5 to 5.5) (16) | 7 (7 to 9) (12) | p-value = 0.005 | |||||
| Uncomplicated febrile UTI?pyelonephritis | 4 (4 to 6) (9) | 7 (7 to 7.5) (8) | p-value = 0.009 | |||||
| Complicated febrile UIT?pyelonephritis | 7 (6 to 9) (33) | 10.5 (10 to 11) (34) | p-value < 0.001 | |||||
| All hospitalised patients | 7 (5 to 9) (45) | 10 (8 to 11) (45) | p-value < 0.001 | |||||
| Esposito (2011)49 Population: ED; children (CAP) Analysis: Modified ITT Measure reported: Mean, SD, CI |
Length of hospital stay (days) | Mild CAP | NA | 4.7 (2.88) (76) | 5.61 (1.99) (79) | –0.91 (–1.69 to –0.13) | NR | |
| Severe CAP | 5.01 (2.43) (79) | 5.93 (1.7) (76) | –0.92 (–1.58 to –0.26) | |||||
| Oxygen therapy (duration, days) | Severe CAP | NA | 3.4 (1.99) (79) | 3.88 (1.58) (76) | –0.48 (–1.04 to 0.08) | |||
| Layios (2012)50 Population: ICU; adults (suspected infection) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Mean (SD) or median (IQR) |
Antibiotic exposure (daily dose per 100 ICU-days) | Whole group | NA | 147.3 (206) (258) | 141.1 (136.9) (251) | 6.20 (–24.11 to 36.51) p-value = 0.96 |
ANOVA | |
| Antibiotic exposure (percentage of ICU-days) | NA | 62.6 (34.4) (258) | 57.7 (34.4) (251) | 4.90 (–1.08 to 10.88) p-value = 0.11 |
ANOVA | |||
| Mechanical ventilation (duration, days) | NA | 3 (1 to 11) (258) | 3 (0 to 11) (251) | NA p-value = 0.99 |
NR | |||
| SOFA score (maximum score during ICU stay) | NR | NR | 9.3 (4.9) (258) | 9.1 (5.4) (251) | 0.20 (–0.70 to 1.10) p-value = 0.42 |
ANOVA | ||
| Liu (2013)33 Population: ICU; adults (sepsis) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Mean, SD, CI |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 8.1 (0.3) (42) | 9.3 (0.3) (40) | –1.20 (–1.33 to –1.07) p-value = 0.013 |
Log-rank test | |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | NA | 27 (4.9) (42) | 32 (5.4) (40) | –5.00 (–7.24 to –2.76) p-value = 0.431 |
Mann–Whitney U-test | |||
| Length of ICU stay (days) | NA | 12 (2.9) (42) | 2.7 (NR) (14) | 9.30 (NR) p-value = 0.632 |
Mann–Whitney U-test | |||
| Nobre (2008)52 Population: ICU; adults (severe sepsis and septic shock) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Median, range |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 6 (2 to 33) (39) | 9.5 (3 to 34) (40) | –2.6 (–5.5 to 0.3) p-value = 0.15 |
NR | |
| Antibiotic exposure [total exposure days/1000 days (incidence rate ratio)] | NA | 541 (39) | 644 (40) | NR | ||||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 17 (3 to 96) (39) | 23.5 (5 to 44) (40) | –2.5 (–6.5 to 1.5) p-value = 0.85 |
|||||
| Length of ICU stay (days) | NA | 4 (1 to 21) (39) | 7 (1 to 91) (40) | –4.6 (–8.2 to 1) p-value = 0.02 |
||||
| Qu (2012)54 Population: ICU; adults (severe acute pancreatitis) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Mean, SD, CI |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 10.89 (2.85) (9.91 to 11.9) (35) | 16.06 (2.48) (15.2 to 16.9) (36) | –5.17 (–6.41 to –3.93) p-value < 0.001 |
t-test | |
| Costs (total cost of hospitalisation) at 28 days | NA | 24,401 (2631) (35) | 27,813 (2529.37) (36) | –3412 (–4613 to 2210) p-value < 0.001 |
||||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | NA | 16.66 (4.02) (15.3 to 18) (35) | 23.81 (7.56) (21.3 to 26.4) (36) | –7.15 (–9.96 to –4.34) p-value = NR |
||||
| Length of ICU stay (days) | NA | 11.11 (2.94) (10.1 to 12.1) (35) | 14.83 (2.49) (14 to 15.7) (36) | –3.72 (–4.99 to –2.45) p-value < 0.001 |
||||
| Roh (2013)56 Population: ED; adults (elderly patients with CAP) Analysis: Not specified Measure reported: Mean, SD, CI |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 11.2 (80) | 14.6 (84) | p-value < 0.05 | NR | |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | NA | 14.6 (80) | 16 (84) | p-value > 0.05 | ||||
| Roh (2010)55 Population: ED; adults (CAP) Analysis: Not specified Measure reported: Mean, SD, CI |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 9.2 (60) | 14.6 (62) | p-value < 0.001 | NR | |
| Schuetz (2009)57 Population: ED; adults (primary diagnosis of LRTI) Analysis: Modified ITT Measure reported: Median, IQR |
Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | Whole group | NA | 5 (1–8) (671) | 9 (6–11) (688) | Relative mean change: –34.8 (–40.3 to –28.7) |
Bootstrap percentile method | |
| ECOPD | 0 (0–4) (115) | 6 (0–8) (113) | Relative mean change: –50.4 (–64 to –34) |
|||||
| Acute bronchitis | 0 (0–0) (69) | 1 (0–5) (82) | Relative mean change: –65 (–84.7 to –37.5) |
|||||
| CAP | 7 (4–10) (460) | 10 (8–12) (465) | Relative mean change: –32.4 (–37.6 to –26.9) |
|||||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | Whole group | NA | 8 (4–12) (671) | 8 (4–12) (688) | Relative mean change: 1.8 (–6.9 to 11) | |||
| CAP | 8 (5–13) (460) | 8 (4–12) (465) | Relative mean change: 5.3 (–5.1 to 16.8) | |||||
| ECOPD | 8 (5 to 11) (115) | 8 (5 to 13) (113) | Relative mean change: –4.4 (–19.1 to 12.9) |
|||||
| Acute bronchitis: | 4 (1 to 7) (69) | 4 (0 to 9) (82) | Relative mean change: –10.3 (–37.1 to 27) |
|||||
| Stolz (2007)60 Population: ED; adults (COPD exacerbation) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Median (IQR) or mean (SD) |
Length of hospital stay (days) | Whole group: | NA | 9 (1–15) (102) | 10 (1–15) (106) | p-value = 0.960 | Mann–Whitney U-test | |
| Length of ICU stay (days) | NA | 3.3 (2.7) (102) | 3.7 (2.1) (106) | –0.40 (–1.06 to 0.26) p-value = 0.351 |
t-test | |||
| Stolz (2009)61 Population: ICU; adults (VAP) Analysis: ITT Measure reported: Median, IQR |
Antibiotic exposure (antibiotic-free days alive) | Whole group: | NA | 13 (2–21) (51) | 9.5 (1.5–17) (50) | p-value = 0.049 | Mann–Whitney U-test | |
| Antibiotic exposure (duration, days) | NA | 10 (6–16) (50) | 15 (10–23) (51) | p-value = 0.038 | ||||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | NA | 26 (7–21) (51) | 26 (16.8–22.3) (50) | p-value = 0.153 | ||||
| Length of ICU stay (ICU-free days alive) | NA | 10 (0–18) (51) | 8.5 (0–18) (50) | p-value = 0.526 | ||||
Appendix 4 Risk of bias assessments
| Study | Domain | Support for judgement | Risk of bias |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annane (2013)37 | Random sequence generation | Computer-generated, centralised randomisation, by an independent statistician was used. Randomisation was stratified by the centre and according to whether or not patients underwent surgery in the past 48 hours, using permutation blocks, the size of which was unknown to the investigators | Low |
| Allocation concealment | No information | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | The nature of the intervention precluded full blinding. In the control arm, patients, physicians, nurses, investigators, study coordinators, the statistician and the sponsor remained blinded to PCT levels throughout the study | Low | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | See above | Low | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Modified ITT analyses (four patients who withdrew consent – one from the PCT group and three from the standard care group – were excluded). There were no other exclusions | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results were reported for all listed outcomes | Low | |
| Baer (2013)39 | Random sequence generation | Computer-generated randomisation was used (variable block randomisation with stratification for the participating clinic and the type of LRTI) | Low |
| Allocation concealment | Web-based online patient registration was used | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | Unclear whether participants were blinded and the nature of the intervention prevented blinding of study personnel | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | Outcomes were self-report (parent or caregiver diary) | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Modified ITT (two patients, both in the standard care group, who withdrew consent after randomisation were excluded) | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results were reported for all outcomes listed in the trial registry entry ISRCTN17057980 | Low | |
| Bouadma (2010)41 | Random sequence generation | Independent, centralised, computer-generated randomisation sequence | Low |
| Allocation concealment | Investigators were masked to assignment before, but not after randomisation. This system was password protected and accessed by the principal investigator or study coordinator after the patient or surrogate gave consent and had met inclusion criteria. The patient’s initials and date of birth were entered and then the patient’s allocation was assigned | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | Unclear whether participants were blinded and the nature of the intervention prevented blinding of study personnel | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | All investigators were unaware of aggregate outcomes during the study, and primary end points were strictly defined and not patient reported | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Modified ITT (nine patients – 4/311 from the PCT group and 5/319 from the standard care group – who withdrew consent after randomisation were excluded) analyses were reported | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results were reported for all listed outcomes | Low | |
| Christ-Crain (2004)44 | Random sequence generation | Patients were randomly assigned using a computer-generated week wise randomisation scheme | Low |
| Allocation concealment | No information | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | Says single-blind but it was unclear who was blinded | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | Says single-blind but it was unclear who was blinded | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Analysis was ITT, loss to follow-up was low (8/124 PCT and 5/119 standard group) | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | All outcomes appear to have been reported | Low | |
| Christ-Crain (2006)42 | Random sequence generation | No details on generation of randomisation sequence | Unclear |
| Allocation concealment | Sealed, opaque envelopes were used | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No details on participant blinding | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | Laboratory findings and chest radiographs were reviewed blind to group allocation. No further details on outcome assessor blinding | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | All patients included in ITT analysis; 18 died in PCT group and 2 lost to follow-up (total 151); 20/151 died in control group | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Data reported for all outcomes prespecified in methods; no protocol or trial registry entry available. | Low | |
| Deliberato (2013)45 | Random sequence generation | No information | Unclear |
| Allocation concealment | No information | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | Unclear whether participants were blinded and the nature of the intervention prevented blinding of study personnel | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | The intervention was being used to guide the primary outcome (duration of antibiotic therapy) and blinding was therefore not possible. Mortality and re-infection outcomes are objective | Low | |
| Incomplete outcome data | ITT and per-protocol analyses were reported (ITT data extracted). However, 22/42 patients from the PCT group and 8/39 patients from the standard care group were excluded from the per-protocol analysis and some results varied widely according to analysis method | High | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results were reported for all listed outcomes | Low | |
| Drozdov (2014)47,69 | Random sequence generation | Prespecified computer generated | Low |
| Allocation concealment | Concealed using a centralised, password-secured website | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Modified ITT analyses (2/63 patients from the PCT/pyuria group and 2/66 patients form the standard care group were excluded because they withdrew consent). Per-protocol analyses excluded 19/63 patients from the PCT/pyuria group and 14/66 patients from the standard care group, but results were similar to the ITT analysis | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results reported for all listed outcomes | Low | |
| Esposito (2011)49 | Random sequence generation | Computer-generated randomisation was used | Low |
| Allocation concealment | Sealed envelopes were used | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | Outcomes were assessed by a blinded researcher | Low | |
| Incomplete outcome data | 5/160 patients in PCT and 4/159 in control group withdrew consent following randomisation; these were not included in the ITT analysis | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Outcomes were not clearly prespecified in the methods section but data appear to have been report for all outcomes with no overemphasis on outcomes based on statistical significance | Low | |
| Layios (2012)50 | Random sequence generation | No information | Unclear |
| Allocation concealment | No information | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | Unclear whether participants were blinded and the nature of the intervention prevented blinding of study personnel | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Analyses were ITT. PCT level was not obtained for 16/258 patients allocated to the PCT group. No other missing data were reported | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results were reported for all listed outcomes | Low | |
| Liu (2013)33 | Random sequence generation | Randomisation was based on a random number table | Low |
| Allocation concealment | No information | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | No withdrawals | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results reported for all outcomes specified in the methods | Low | |
| Nobre (2008)52 | Random sequence generation | Computer-generated randomisation was used | Low |
| Allocation concealment | Opaque, sealed, numbered envelopes were used | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | Unclear whether participants were blinded and the nature of the intervention prevented blinding of study personnel | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | ITT and per protocol analyses were reported (ITT data extracted). However, 8/39 patients from the PCT group and 3/40 patients from the standard care group were excluded from the per-protocol analysis and some results varied widely according to analysis method | High | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results were reported for all outcomes listed in the trial registry entry NCT00250666 | Low | |
| Qu (2012)54 | Random sequence generation | No details of the randomisation procedure were reported | Unclear |
| Allocation concealment | See above | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No details on participant blinding | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | No details on outcome assessor blinding | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | All randomised patients included in the analysis | Unclear | |
| Selective outcome reporting | All outcomes prespecified in methods reported in results; no protocol or trial registry entry available | Low | |
| Roh (2013)56 | Random sequence generation | No information | Unclear |
| Allocation concealment | No information | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | No information | Unclear | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Data were reported for outcomes specified as primary and secondary outcomes | Low | |
| Roh (2010)55 | Random sequence generation | No information | Unclear |
| Allocation concealment | No information | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | No information | Unclear | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Data were reported for outcomes specified as primary and secondary outcomes | Low | |
| Schuetz (2009)57 | Random sequence generation | Computer-generated, centralised randomisation was used | Low |
| Allocation concealment | See above | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | Outcomes were independently assessed by medical students, blind to treatment allocation | Low | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Modified ITT analysis reported. Patients who withdrew consent after randomisation were excluded (16/687 from the intervention group and 6/694 from the control group) | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results were reported for all specified outcomes | Low | |
| Stolz (2007)60 | Random sequence generation | No details on how randomisation sequence was generated were reported | Unclear |
| Allocation concealment | No information | Unclear | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | Outcomes were assessed by a blinded nurse or physician | Low | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Modified ITT analysis performed for all those who received allocated intervention; 18/226 (11 from PCT and 7 from standard care) randomised participants who did not meet COPD criteria were excluded | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Data were reported for all outcomes measures prespecified in the results. However, single outcomes were reported in multiple different formats, which could have resulted in confusion and a suggestion of a greater beneficial effect than was actually found | High | |
| Stolz (2009)61 | Random sequence generation | Randomisation used blocks of 20 sealed, opaque envelopes. Treating physicians were not aware of envelope contents before randomisation | Unclear |
| Allocation concealment | Opaque, sealed envelopes were used. Treating physicians were not aware of envelope contents before randomisation | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | No information | Unclear | |
| Incomplete outcome data | No patients lost to follow-up; all randomised patients included in analysis | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | All outcomes prespecified in methods reported in results; no protocol or trial registry entry available | Low | |
| Tang (2013)62 | Random sequence generation | Computer-generated randomisation was performed by an independent statistician | Low |
| Allocation concealment | Opaque, sealed envelopes were used | Low | |
| Participant/personnel blinding | Participants, laboratory technicians, investigators and research designers were blinded to group allocation until the data analysis was completed | Low | |
| Outcome assessor blinding | Outcomes were assessed by an independent, blinded investigator | Low | |
| Incomplete outcome data | Analyses included only those participants who completed 6-week follow-up. However, only 4/132 were missing from the intervention group and 6/133 from the control group | Low | |
| Selective outcome reporting | Results were reported for all listed outcomes | Low |
Appendix 5 Table of excluded studies with rationale
To be included in the review, studies had to fulfil the following criteria:
Population:
-
Adults and children with confirmed or highly suspected sepsis, in whom antibiotic therapy is indicated, who are being treated in ICUs.
-
Adults and children presenting to the ED with suspected bacterial infection.
Setting: ICU or ED
Intervention: Treatment decisions based on laboratory-based PCT testing, using any of the tests currently available to the UK NHS, as described in Chapter 2 (see Intervention technologies and comparator), in addition to standard practice.
Comparator: Treatment decisions based on standard practice (as reported in individual studies), without PCT testing.
Outcome: Antibiotic exposure (initiation/duration of antibiotic therapy), resource use (number of hospital admissions, length of hospital/ICU stay, costs), adverse clinical outcomes (e.g. SOFA scores, in-hospital mortality, condition-specific outcomes), antibiotic-related adverse events.
Study design: RCTs, or CCTs when no RCTs were available. Where no controlled trials were available for a specified population, studies assessing the change in diagnostic accuracy associated with the addition of PCT testing to standard diagnostic work-up were sought; such studies were required to use adjudication of infection by independent panel as the reference standard; microbiological testing alone was not considered adequate.
The table below summarises studies that were screened for inclusion based on full text publication, but did not fulfil one or more of the above criteria. The table shows which of the criteria each study fulfilled (‘Yes’) and on which item it failed (‘No’ or ‘Other’). The comments column provides further details of the reasons for exclusion.
| Study details | Design | Setting | Population | Intervention | Comparator | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jagminas (2013)129 | Other | Duplicate report | ||||
| ACTRN12612000601831 (2012)130 | Duplicate report | |||||
| Agarwal (2014)131 | Unclear | ED | Children | Yes | No | Not an RCT |
| Andreola (2007)132 | Other | ED | Children | Yes | No | Fever without source; multivariable prediction model |
| Beni (2011)133 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Abstract only, non-ICU (hospital-acquired pneumonia) |
| Bogner (2010)134 | Other | Not a primary study – summary of existing report | ||||
| Bollu (2009)135 | Other | Letter | ||||
| Brahms (NR)136 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Trial registry, terminated because of futility (very slow patient enrolment) |
| Brahms (2012)136 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Trial registry only; trial terminated |
| Cals (2010)137 | Other | Letter | ||||
| Changi General Hospital (2007)138 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Trial registry entry for terminated study, no results or publications. Fever of unknown origin |
| Charite University Berlin Germany (NR)139 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Trial registry entry, no results posted and no related publications. Stroke |
| Charles (2008)140 | Other | ICU | Other | No | No | Accuracy of PCT for secondary sepsis |
| Chen (2013)141 | Prediction study | ED | Children | No | Predicting acute pyelonephritis in children with febrile UTI. Only clinical features in model are age, gender, and fever | |
| ChiCTR-TRC-14004726 (2014)142 | Other | Respiratory medicine and critical care medicine, Chinese trial registry | ||||
| Chromik (2006)143 | RCT | Other | Other | No | No | Comparison of pre-emptive antibiotics with standard treatment in patients with elevated PCT |
| Danish Procalcitonin Study (2010)144 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Trial registry entry for other excluded studies113,145 |
| Danish Procalcitonin Study, (2013)146 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Pulmonary medicine department, trial registry only, no results posted or related publications |
| De Angelis (2011)147 | Other | ICU | Other | No | No | Systematic review only, review of antibiotic management measures |
| De (2013)148 | Other | ED | Children | No | No | Accuracy of the traffic light system |
| Diaz-Flores (2012)149 | Other | Letter | ||||
| Ding (2013)150 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Respiratory department admissions for acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| Dubos (2006)151 | Other | Unclear | Children | No | No | PCT alone or with other laboratory tests not combined with clinical judgement. Reference standard acute onset of meningitis (‘meningitis’ in hospital notes) and documented bacterial infection in the CSF. Not ‘adjudication of infection by independent panel’ |
| EUCTR2007-004333-42-DE (2008)152 | RCT | ICU | Adults | No | No | Trial registry |
| Federal University of Minas (2012)153 | RCT | ICU | Other | Yes | Yes | Trial registry entry for excluded study154 Index test: CRP and PCT |
| Gibot (2010)155 | Other | Letter on the PRORATA trial | ||||
| Gomez (2012)156 | Other | ED | Children | Yes | No | ‘IBI was defined as the isolation of a bacterial pathogen in blood or cerebrospinal fluid culture’ |
| Graber (2011)157 | Other | Not a primary study | ||||
| Herd (2007)158 | Other | Not a primary study | ||||
| Hochreiter (2009)159 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Related publication160 Index test: LIA test |
| Hochreiter (2009)160 | RCT | ICU | Other | Yes | Yes | Abstract relating to excluded study159 Index test: LIA test |
| Hochreiter (2010)161 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Commentary on an abstract159 |
| Hospital Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Keelung (NR)130 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Trial registry entry, full paper identified and filed (Huang 2014); secondary peritonitis after surgery |
| ISRCTN10288268 (2009)162 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Trial registry, results page references does not exist Index test: LIA test |
| ISRCTN61015974 (2006)163 | Trial registry entry for excluded study164 | |||||
| ISRCTN77261143 (2005)165 | Trial registry entry for excluded study60 | |||||
| Iwashyna (2010)166 | Long term outcomes following sepsis | |||||
| Jaimes (2013)167 | Other | ED | Other | No | No | Example of latent class ROC analysis |
| Jaimes (2010)168 | Other | Other | Other | No | No | Example of latent class analysis |
| Jensen (2011)113 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Protocol145 Trial registry144 No sepsis or infection inclusion criteria, seems to be about early initiation of antibiotics |
| Jensen (2008)145 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Protocol only Trial registry144 Additional publication113 |
| Jensen (2007)169 | Other | Comment on a meta-analysis | ||||
| Jensen (2012)170 | Other | Letter | ||||
| Kollef (2010)171 | Other | Letter on the PRORATA trial | ||||
| Kompetenznetz Sepsis (NR)152 | RCT | ICU | Adults | No | No | PCT used to guide therapy other than antibiotic |
| Kristoffersen (2009)172 | RCT | Other | Adults | No | Yes | Medical admissions, intervention = single PCT measurement on admission |
| Kulik (2013)173 | Other | Children | No | No | Systematic review of prediction rules for bacterial meningitis (none included PCT) | |
| Landman (2010)174 | Other | Letter | ||||
| Lee (2013)175 | Other | Other | Adults | No | No | Systematic review, accuracy of PCT for bacterial infection in the elderly |
| Leroy (2013)176 | Other | ED | Children | No | No | Predicting acute pyelonephritis; not the same as detecting bacterial infection so exclude? Model included only laboratory values, not clinical diagnosis, so not additive value |
| Leroy (2013)177 | Other | ED | Children | Yes | No | Abstract only; algorithm only include PCT, CRP and dipstick. No details on reference standard. Insufficient data in abstract to be of use |
| Levin (2012)178 | Other | ICU | Other | No | No | Observational study on the ‘accuracy’ of clinical decisions to initiate antibiotics (no PCT) |
| Mahajan (2014)179 | Other | ED | Children | Yes | No | ‘SBI by blood, urine, and/or cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) cultures were included’ |
| Manzano (2010)20 | RCT | ED | Children | Yes | Yes | Wrong PCT test (not quantitative) |
| Maravic-Stojkovic (2011)115 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Quantitative PCT assay (unlisted version of BRAHMS) Index test: LIA test |
| Mintegi (2012)180 | Other | ED | Children | Yes | No | Abstract only; reference standard not reported. |
| Mokart (2010)181 | Other | Letter on the PRORATA trial | ||||
| NCT00099840 (2004)65 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | No | Primary care, trial registry |
| NCT00250666 (2005)53 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT00271752 (2006)144 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT00350987 (2006)66 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT00398775 (2006)138 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT00472667 (2007)66 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT00934011 (2009)153 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT00987818 (2009)121 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01018199 (2009)125 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01025180 (2009)38 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01139489 (2010)118 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01264549 (2010)139 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01379547 (2011)120 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01494675 (2011)46 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01572831 (2012)122 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01652404 (2011)119 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT01950936 (2012)146 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT02130986 (2014)128 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT02171338 (2014)124 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| NCT02173613 (2013)182 | Duplicate trial registry entry | |||||
| Niewoehner (2007)183 | Other | Not a primary study | ||||
| Nijman (2014)184 | Other | Not an RCT | ||||
| Nijman (2013)185 | Other | Not an RCT | ||||
| Ning (2011)186 | Other | Other | Other | Yes | Yes | Systematic review, abstract only |
| Oliveira (2011)187 | RCT | ICU | Other | Yes | Yes | Index test: CRP and PCT |
| Oliveira (2013)114 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | No | Index test: CRP and PCT |
| Oliveira (2012)154 | RCT | ICU | Other | Yes | Yes | Index test: CRP and PCT |
| Oostenbrink (2013)188 | Other | Not an RCT | ||||
| Prkno (2013)189 | Other | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Systematic review, abstract only |
| Ray (2007)190 | Other | ED | Adults | No | No | Accuracy of CSF PCT to differentiate bacterial from viral meningitis |
| Reinhart (2007)191 | Other | Comment on a meta-analysis | ||||
| Saeed (2011)192 | Other | Other | Adults | Yes | No | ICU plus medical admissions, no comparator |
| Sanders (2008)193 | Other | Other | Children | No | No | Systematic review of accuracy of CRP in non-hospitalised children |
| Schroeder (2009)116 | RCT | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Index test: LIA test |
| Schuetz (2010)194 | Other | Survey on guideline adherence | ||||
| Schuetz (2012)109 | Other | ED or ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Systematic review, IPD analysis; studies do not match studies included in our review |
| Schuetz (2010)195 | Other | Guideline, not original research | ||||
| Schuetz (2013)196 | Other | Abstract of systematic review | ||||
| Sheu (2011)197 | Other | ED | Children | Yes | UTI, and prediction of acute pyelonephritis and renal scarring; not detection of bacterial infection | |
| Soni (2012)198 | Other | AHRQ evidence summary for clinicians | ||||
| Sridharan (2013)199 | Other | ICU | Adults | Yes | Yes | Systematic review, abstract only |
| St Justine’s Hospital (NR)200 | RCT | ED | Children | Yes | Yes | Qualitative PCT test |
| Stannard (2014)201 | Other | Summary of Cochrane review | ||||
| Tang (2007)202 | Other | Letter | ||||
| Tarnow-Mordi (2010)203 | Other | Letter on the PRORATA trial | ||||
| Thompson (2012)204 | Other | Systematic review of prediction rules for infection in children (development and accuracy studies) | ||||
| Ulm (2013)205 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Stroke patients, unspecified setting, protocol only |
| University Hospital Basel Switzerland (NR)65 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Primary care |
| University Hospital, Grenoble (2014)182 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Hospitalised elderly, trial registry |
| University of Rochester (2014)206 | RCT | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Hospitalised for RTI, trial registry with no results or publications |
| Uusitalo-Seppala (2011)207 | Other | ED | Adults | Yes | No | Not RCT |
| Van den Bruel (2011)208 | Other | Systematic review of prediction rules for infection in children (development and accuracy studies) | ||||
| Yu (2013)209 | Other | Other | Other | No | No | Systematic review, accuracy of PCT for acute appendicitis |
| Zhang (2012)210 | Other | Other | Adults | Yes | Yes | Systematic review, abstract only |
Appendix 6 Characteristics and results of included health-related quality-of-life studies
| Reference/year | Buysse 2008 85 |
| Location | The Netherlands |
| Setting | PICU |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Patients with septic shock and purpura who required intensive care. Median age at admission: 3.1 years (range: 3.7–17.4 years); median age at measurement 14.5 years (range: 5.3–31.1 years) |
| Sample size sepsis group | 120 (reference group: n = 1435) |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | HUI2 and HUI3; valuation function based on Canadian respondents |
| Time point when measurements were made | Median follow-up interval: 9.8 years (range 3.7–17.4 years) |
| Results | Utility for patients who had meningococcal septic shock: HUI3 0.82 (SD 0.25) HUI2: 0.88 (SD 0.16) |
| Conclusion | Patients who survived meningococcal septic shock in childhood reported poorer general health compared with a representative sample of 1435 Dutch schoolchildren aged 5–13 years |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Appropriate. Although it does not adhere to the NICE reference case (e.g. no EQ-5D), it is the only source available in this population and setting |
| Reference/year | Bennett 2000 84 |
| Location | USA |
| Setting | Paediatric ED |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Parents who presented at the paediatric ED with children aged between 3 and 36 months were asked to evaluate a description of the following health states for their children: death, meningitis with severe brain damage, meningitis with minor brain damage, meningitis with deafness, meningitis with recovery; hospitalisation; local infection and blood drawn |
| Sample size sepsis group | 94 |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | Standard gamble |
| Time point when measurements were made | Presentation at ED |
| Results | Death: 0.0177 (SD 0.07) Meningitis with severe brain damage: 0.3903 (SD 0.37) Meningitis with minor brain damage: 0.7393 (SD 0.29) Meningitis with deafness: 0.8611 (SD 0.22) Meningitis with recovery: 0.9768 (SD 0.08) Hospitalisation: 0.9921 (SD 0.03) Local infection: 0.9941 (SD 0.03) Blood drawn: 0.9971 (SD 0.02) |
| Conclusion | Extremely high mean and median utility values were obtained for outcomes without permanent sequelae |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Appropriate. Although it does not adhere to the NICE reference case (e.g. no EQ-5D), it is the only source available in this population and setting |
| Reference/year | Contrin 201386 and Lobo 2011 (abstract)87 |
| Location | Brazil |
| Setting | ICU |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Patients discharged after being admitted to the ICU with severe sepsis |
| Sample size sepsis group | 50 (control group consisting of critically ill patients admitted to the ICU without sepsis: n = 50) |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | EQ-5D; valuation function based on UK respondents |
| Time point when measurements were made | More than 1 year after discharge |
| Results | Sepsis group: 0.678 (SD 0.427) Control group: 0.747 (SD 0.327) |
| Conclusion | EQ-5D quality of life did not statistically significantly differ between sepsis patients and critically ill patients admitted to the ICU without sepsis. Moreover, older patients with sepsis had more moderate/severe problems in all quality-of-life dimensions (EQ-5D index score not presented; VAS scores are presented in table 3) |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Not appropriate. The exact time since discharge is unclear and the estimated utility values seem high compared with those estimated by Cuthbertson et al.,88 which seems most representative for the UK |
| Reference/year | Cuthbertson 2013 88 |
| Location | Scotland (26 hospitals) |
| Setting | ICU |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Patients were identified as having: evidence of three of four SIRS criteria within the previous 24 hours confirmed or clinically strongly suspected infection two or more sepsis induced organ failures of < 24 hours’ duration an APACHE II score ≥ 25 based within 24 hours |
| Sample size sepsis group | 439; 83 patients filled out the questionnaire at 3.5 years after discharge, whereas this was 66 for 5 years |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | EQ-5D; valuation function not specifically stated but expectedly based on UK respondents |
| Time point when measurements were made | At 3.5 years (n = 83) At 5 years (n = 66) after discharge |
| Results | At 3.5 years: 0.64 (SD 0.36) At 5 years: 0.68 (SD 0.32) |
| Conclusion | Based on a comparison with population (age and sex matched) norms using the SF-36, patients with severe sepsis have a significantly lower physical quality of life but mental quality of life scores were only slightly below population norms up to 5 years after severe sepsis |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Appropriate. This Scottish study probably provides the most representative long-term utility estimates for the UK |
| Reference/year | Granja 2004 89 |
| Location | Portugal |
| Setting | ICU |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Patients in the sepsis group were those in whom severe sepsis and septic shock was the reason for admission to the ICU |
| Sample size sepsis group | 104 (control group consisting of patients admitted to the ICU without sepsis: n = 133) |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | EQ-5D; valuation function based on UK respondents |
| Time point when measurements were made | At 6 months after discharge |
| Results | Sepsis group median: 0.84 (IQR 0.58–1.00) Control group median: 0.76 (IQR 0.56–0.91) |
| Conclusion | Health-related quality of life in sepsis survivors 6 months after ICU discharge is fair, and is no worse than the health-related quality of life of other critically ill patients admitted without sepsis |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Not appropriate. The estimated utility values seem high compared with those estimated by Cuthbertson et al.,88 which seems most representative for the UK |
| Reference/year | Karlsson 2009 90 |
| Location | Finland (24 hospitals) |
| Setting | ICU |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Patients with severe sepsis |
| Sample size sepsis group | 470; 252 and 156 patients filled out the first (Q1) and second (Q2) questionnaire, whereas 98 patients filled out both questionnaires |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | EQ-5D (a majority of first questionnaires (156/252) were completed by next of kin); valuation function unclear |
| Time point when measurements were made | At ICU concerning health-related quality of life before acute critical illness (Q1) and 17 months (range 12–20 months; IQR 16–18) after hospital discharge (Q2) |
| Results | Median Q1: 0.70 (IQR 0.54–0.89) Median Q2: 0.75 (0.56–0.92) For patients (n = 98) who filled out both questionnaires:
|
| Conclusion | Quality of life was lower after severe sepsis than before critical illness as assessed by EQ-5D. For both assessments quality of life for sepsis patients was lower than reference values (age- and sex-adjusted) from the Finnish population. The mean calculated QALYs after severe sepsis was 10.9 (95% CI 9.7–12.1) |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Not appropriate. The estimated utility values seem high compared with those estimated by Cuthbertson et al.,88 which seems most representative for the UK |
| Reference/year | Korosec Jagodic 2006 91 |
| Location | Slovenia |
| Setting | ICU |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Patients with severe sepsis and septic shock |
| Sample size sepsis group | 66 |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | EQ-5D; valuation function based on US respondents |
| Time point when measurements were made | Two years following ICU admission |
| Results | 0.72 (SD 0.24) |
| Conclusion | Quality of life was similar for patients with the two most frequent admission diagnoses admitted to the surgical ICU: sepsis and trauma |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Not appropriate. The estimated utility values seem high compared with those estimated by Cuthbertson et al.,88 which seems most representative for the UK |
| Reference/year | Orwelius 2013 92 |
| Location | Portugal |
| Setting | ICU |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Patients admitted to the hospital with community-acquired sepsis, severe sepsis or septic shock |
| Sample size sepsis group | 91 (control group consisting of patients admitted to the ICU without sepsis: n = 222) |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | EQ-5D; valuation function unclear |
| Time point when measurements were made | Six months after ICU discharge |
| Results | Sepsis group median: 0.67 (IQR 0.49–0.91) Control group median: 0.67 (IQR 0.45–0.86) |
| Conclusion | Patients admitted to ICU for CAS did not perceive different health-related quality of life compared with ICU patients admitted for other diagnoses |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Not appropriate. The estimated utility values seem high compared with those estimated by Cuthbertson et al.,88 which seems most representative for the UK |
| Reference/year | Drabinksi 2001 (abstract) 93 |
| Location | USA |
| Setting | In hospital (not mentioned whether it is ICU) |
| Population for which health effects were measured | Patients with severe sepsis of presumed infectious origin |
| Sample size sepsis group | 93 |
| Method of elicitation and valuation | EQ-5D; valuation function unclear |
| Time point when measurements were made | 30, 60, 90 and 180 days after admission (56% of the patients were in the hospital at day 30, and 7% thereafter) |
| Results | 0.53 (day 30), 0.62 (day 60), 0.68 (day 90), 0.69 (day 180) |
| Conclusion | Sepsis survivors experienced a continual improvement towards population-based normal levels in their health utility scores over a 6-month period |
| Appropriateness for current cost-effectiveness analysis | Appropriate. Although it is unclear whether patients were admitted to the ICU, this is likely the case for patients with severe sepsis. Moreover, this is the only study reporting utility values for sepsis patients before being discharged (56% of the patients were in the hospital at the 30-day measurement) |
Appendix 7 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curves and incremental cost-effectiveness planes for the base-case analyses
FIGURE 25.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve and incremental cost-effectiveness plane (incremental costs and QALYs compared with current clinical practice) for base-case analysis (ED children: low risk).
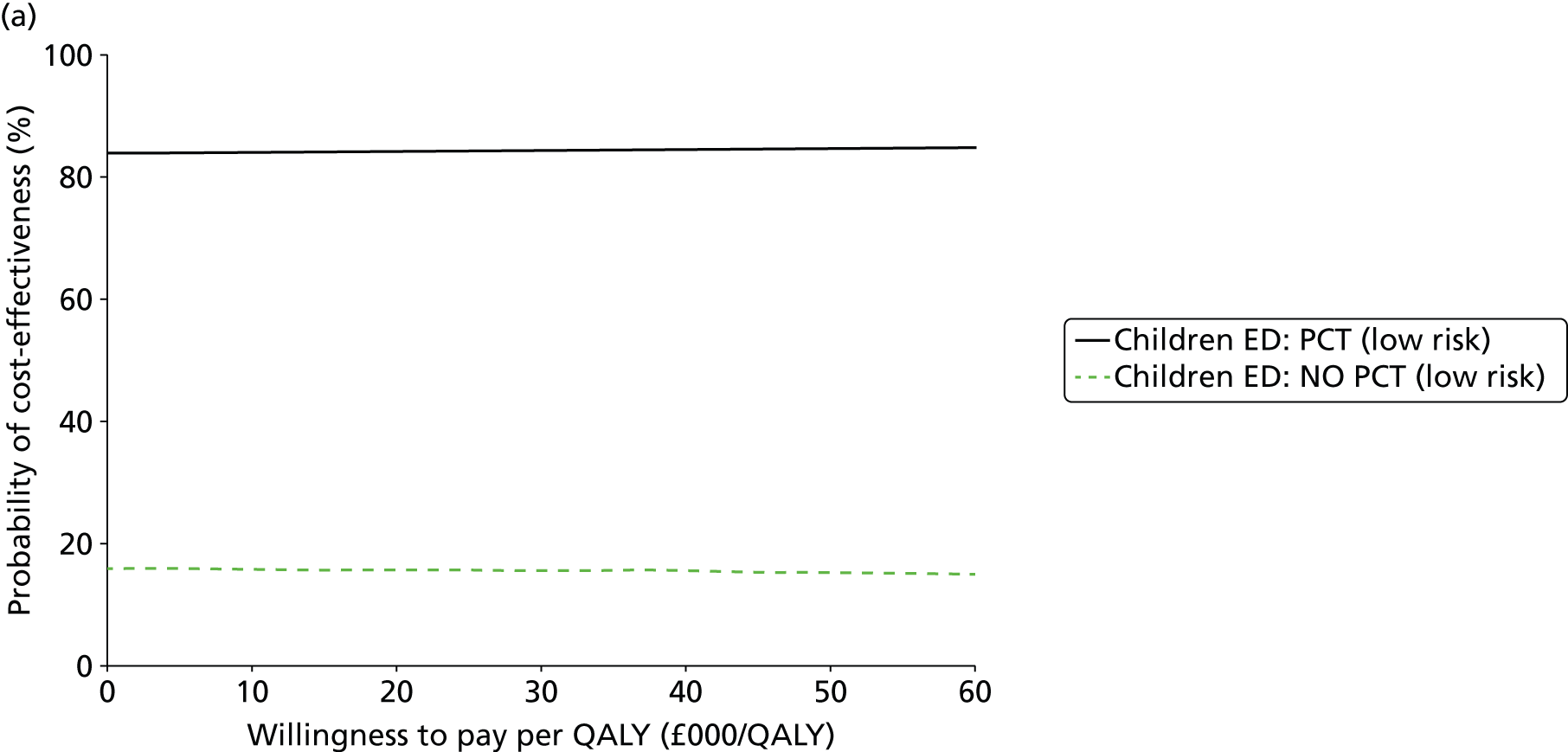

FIGURE 26.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve and incremental cost-effectiveness plane (incremental costs and QALYs compared with current clinical practice) for base-case analysis (ED children: high risk).

FIGURE 27.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve and incremental cost-effectiveness plane (incremental costs and QALYs compared with current clinical practice) for base-case analysis (ED adults: low risk).


FIGURE 28.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve and incremental cost-effectiveness plane (incremental costs and QALYs compared with current clinical practice) for base-case analysis (ED adults: high risk).

FIGURE 29.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve and incremental cost-effectiveness plane (incremental costs and QALYs compared with current clinical practice) for base-case analysis (ICU adults: low risk).

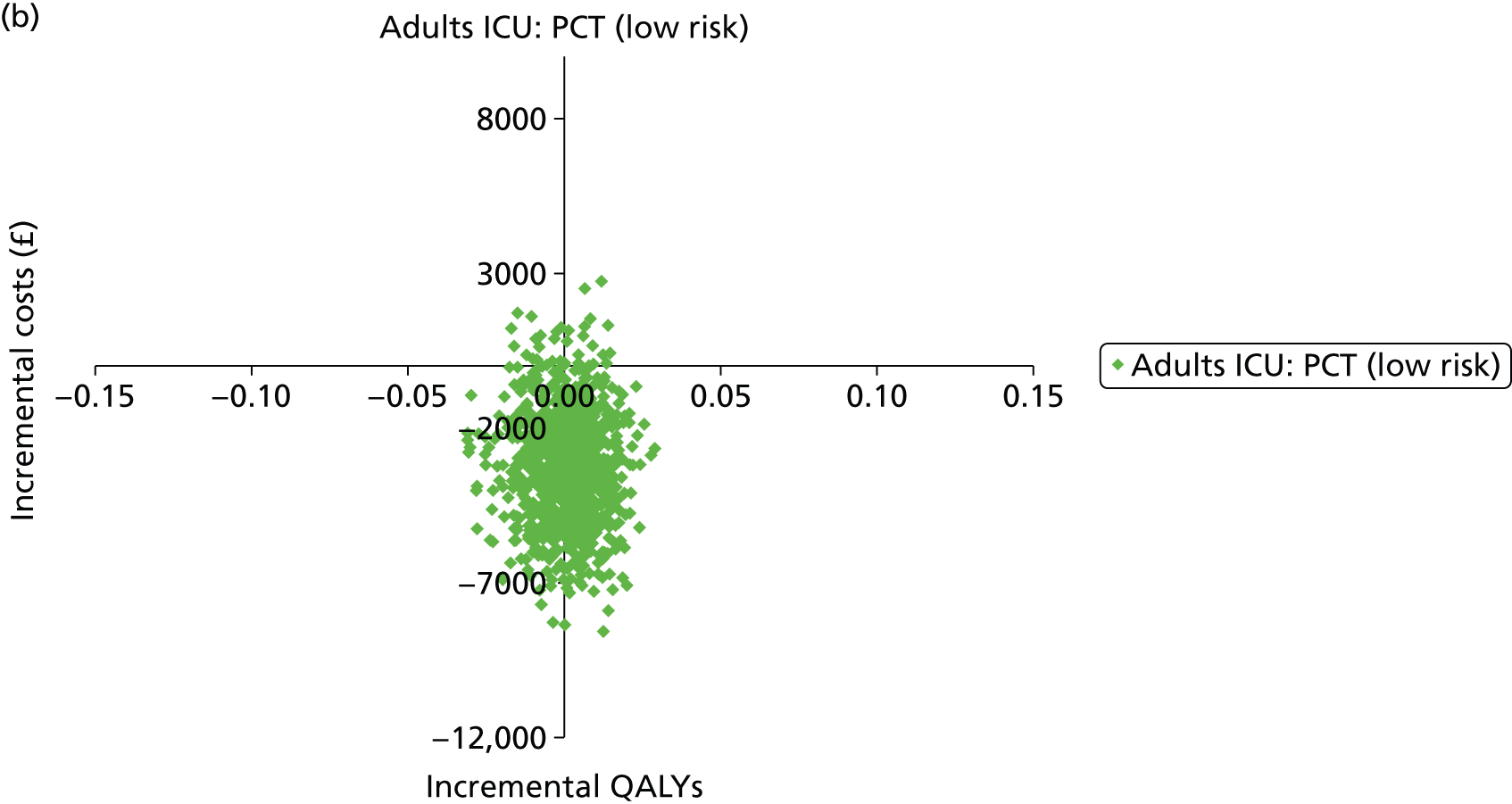
FIGURE 30.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve and incremental cost-effectiveness plane (incremental costs and QALYs compared with current clinical practice) for base-case analysis (ICU adults: high risk).
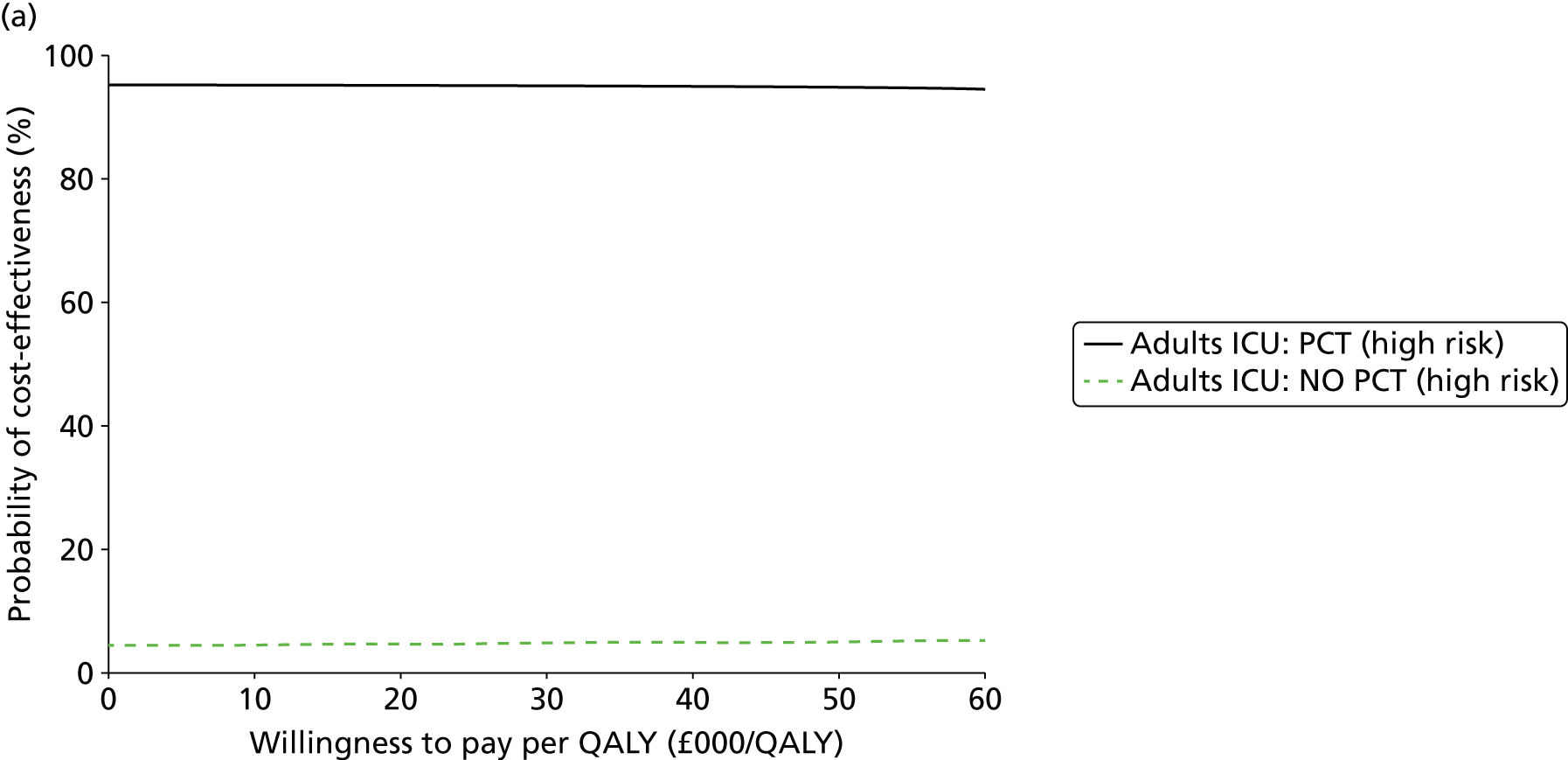
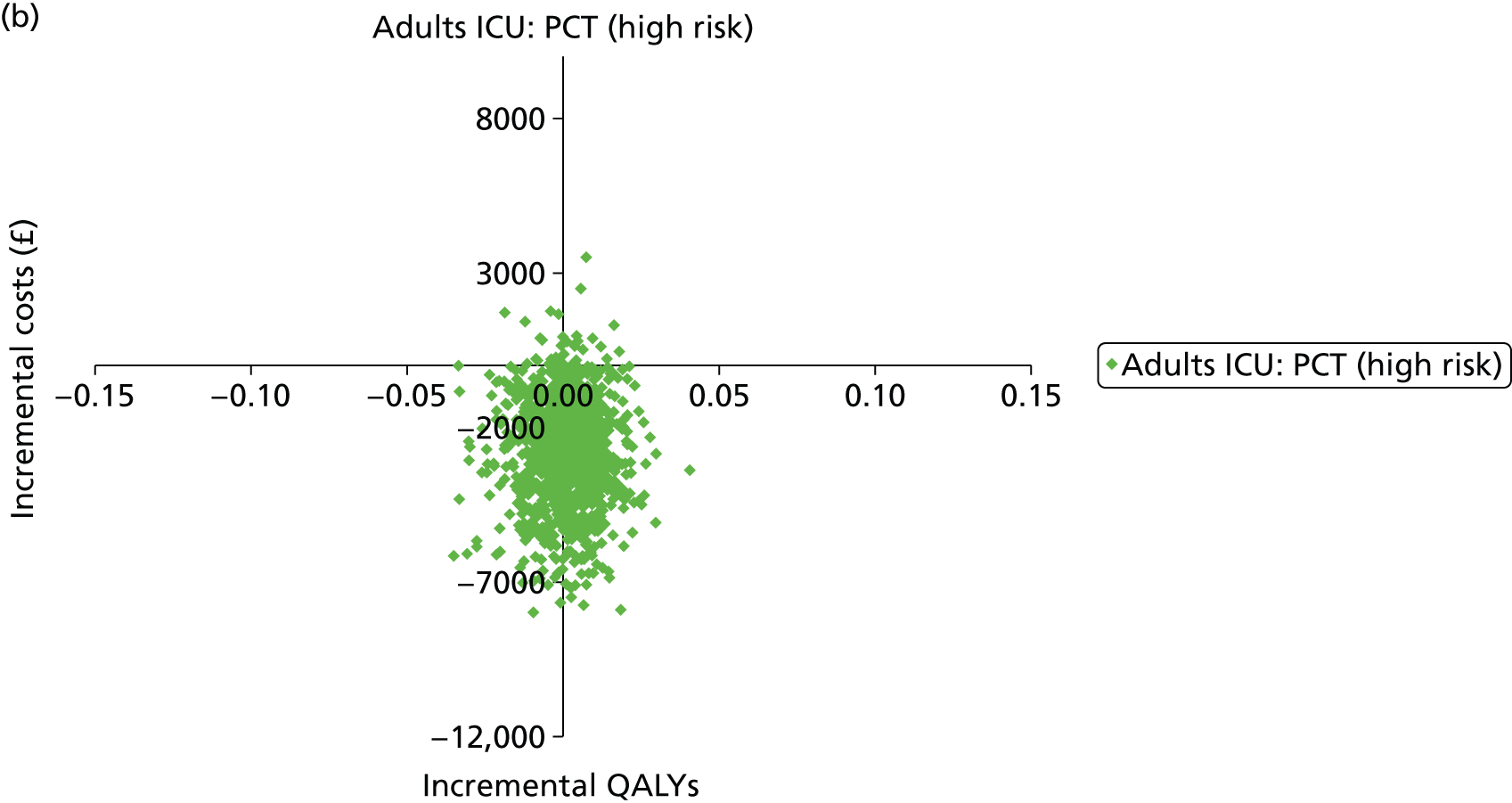
Appendix 8 Additional analysis methods
In order to perform the meta-analysis of the conditional mean duration of antibiotic use (i.e. excluding patients with no antibiotic use), the following data were required from the published papers:
-
number of patients with non-zero antibiotic use (N_nonzero)
-
mean days antibiotic use of patients with non-zero antibiotic use (Mean_nonzero)
-
standard deviation of days antibiotic use (SD_nonzero).
Below are the methods used to obtain these value:
-
N_nonzero was reported in the papers.
-
Use:mean_nonzero=mean_all/p(initiate)where ‘p(intitiate)’ is the proportion who initiated antibiotics, which was reported in the papers.
-
Use:var_all = sum (p(d_all) × (d-mean_all)2)= sum (p(initiate) × (d_nonzero-mean_all)2) + sum (p(0) × (0-mean_all)2)=var_nonzero + (p(0) × mean_all2)
So var_nonzero = var_all – (p(0) × mean_all2)
So SD_nonzero = sqrt (var_all – ((1-p(initiate)) × mean_all2)
where:
p(d_all) is the proportion of the sample for which each day of antibiotic use was observed, such that p(initiate) is the proportion for which the days’ use was greater than zero, and p(0) is the proportion for which the number of days’ use was zero, i.e. no initiation.
p(0) = 1 - p(initiate)
var_all = SD_all2 and SD_all is the SD of days for the whole sample (including the non-zero patients), which is reported in the papers.
There was a problem with this method, which was that the SD (SD_all) reported for the PCT arm of the Christ-Crane study44 was too low, given the low proportion of those who initiated antibiotics. This suggested that there was an error in the paper. Therefore, an alternative value for the PCT arm SD was calculated based on the t-test p-value, which gives a corresponding t-value, where, according to the Cochrane Handbook:211
where ‘meandiff’ is the mean difference between the intervention (PCT) and control arms, ‘SE_meandiff’ is the standard error of the mean difference and ‘i’ and ‘c’ refer to intervention and control, respectively.
Appendix 9 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance relevant to the management of sepsis or suspected bacterial infection in the populations specified in this assessment
Published guidance
Pneumonia: Diagnosis and Management of Community- and Hospital-acquired Pneumonia in Adults. NICE Clinical Guideline CG191 (December 2014). Date for review: December 2016. URL: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg191 (accessed 9 December 2014).
Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Adults in Hospital. NICE Clinical Guideline CG174 (December 2013). Date for review: TBC. URL: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG174 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Feverish Illness in Children: Assessment and Initial Management in Children Younger than 5 Years. NICE Clinical Guideline CG160 (May 2013). Date for review: March 2015. URL: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG160 (accessed 26 November 2014).
The Management of Bacterial Meningitis and Meningococcal Septicaemia in Children and Young People Younger than 16 years in Primary and Secondary Care. NICE Clinical Guideline CG102 (June 2010). Date for review: March 2015. URL: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG102 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Management of Acute Diarrhoea and Vomiting due to Gastroenteritis in Children Under 5. NICE Clinical Guideline CG84 (April 2009). Date for review: June 2012 – following consultation with stakeholders this guideline has now been placed on the static list. URL: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG84 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Prevention and Treatment of Surgical Site Infection. NICE Clinical Guideline CG74 (October 2008). Date for review: December 2016. URL: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG74 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Urinary Tract Infection: Diagnosis, Treatment and Long-term Management of Urinary Tract Infection in Children. NICE Clinical Guideline CG54 (August 2007). Date for review: October 2015. URL: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG54 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Related National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance: under development
Intravenous Fluids Therapy in Children. NICE Clinical Guideline. Expected publication: October 2015. URL: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/GID-CGWAVE0655 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Major Trauma Services: Service Delivery for Major Trauma. NICE Clinical Guideline. Expected publication: February 2016. URL: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/GID-CGWAVE0641 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Major Trauma: Assessment and Management of Airway, Breathing and Ventilation, Circulation, Haemorrhage and Temperature Control. NICE Clinical Guideline. Expected publication: February 2016. URL: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/GID-CGWAVE0642 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Sepsis: the Recognition, Diagnosis and Management of Severe Sepsis. NICE Clinical Guideline. Expected publication date: July 2016. URL: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/GID-CGWAVE0686 (accessed 26 November 2014).
Glossary
- Cost-effectiveness analysis
- An economic analysis that converts effects into health terms and describes the costs for additional health gain.
- Decision modelling
- A mathematical construct that allows the comparison of the relationship between costs and outcomes of alternative health-care interventions.
- False negative
- Incorrect negative test result – number of diseased persons with a negative test result.
- False positive
- Incorrect positive test result – number of non-diseased persons with a positive test result.
- Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- The difference in the mean costs of two interventions in the population of interest divided by the difference in the mean outcomes in the population of interest.
- Index test
- The test for which performance is being evaluated.
- Likelihood ratio
- Likelihood ratios describe how many times more likely it is that a person with the target condition will receive a particular test result than a person without the target condition.
- Markov model
- An analytic method particularly suited to modelling repeated events, or the progression of a chronic disease over time.
- Meta-analysis
- Statistical techniques used to combine the results of two or more studies and obtain a combined estimate of effect.
- Meta-regression
- Statistical technique used to explore the relationship between study characteristics and study results.
- Opportunity costs
- The cost of forgone outcomes that could have been achieved through alternative investments.
- Publication bias
- Bias arising from the preferential publication of studies with statistically significant results.
- Quality-adjusted life-year
- A measure of health gain, used in economic evaluations, in which survival duration is weighted or adjusted by the patient’s quality of life during the survival period.
- Quality of life
- An individual’s emotional, social and physical well-being and their ability to perform the ordinary tasks of living.
- Receiver operating characteristic curve
- A graph that illustrates the trade-offs between sensitivity and specificity which result from varying the diagnostic threshold.
- Reference standard
- The best currently available method for diagnosing the target condition. The index test is compared against this to allow calculation of estimates of accuracy.
- Sensitivity
- Proportion of people with the target disorder who have a positive test result.
- Specificity
- Proportion of people without the target disorder who have a negative test result.
- True negative
- Correct negative test result – number of non-diseased persons with a negative test result.
- True positive
- Correct positive test result – number of diseased persons with a positive test result.
List of abbreviations
- ACB
- Association of Clinical Biochemistry
- AiC
- academic-in-confidence
- ARTI
- acute respiratory tract infection
- BNF
- British National Formulary
- CADTH
- Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health
- CAP
- community-acquired pneumonia
- CCT
- controlled clinical trial
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CI
- confidence interval
- CiC
- commercial-in-confidence
- COPD
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CRD
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination
- CRP
- C-reactive protein
- ED
- emergency department
- EQ-5D
- European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions
- ESICM
- European Society of Intensive Care Medicine
- GRADE
- Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation
- HALex
- Health and Activities Limitation Index
- HES
- Hospital Episode Statistics
- HQIP
- Health Quality Improvement Partnership
- HR
- hazard ratio
- HRQoL
- health-related quality of life
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- HUI
- Health Utilities Index
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- ICU
- intensive care unit
- IQR
- interquartile range
- ITT
- intention to treat
- LIA
- luminescence immunoassay
- LRTI
- lower respiratory tract infection
- LY
- life-year
- MODS
- multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
- NCEPOD
- National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NIHR
- National Institute for Health Research
- ONS
- Office for National Statistics
- PCT
- procalcitonin
- PICU
- paediatric intensive care unit
- PSA
- probabilistic sensitivity analysis
- PSI
- Pneumonia Severity Index
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RR
- relative risk
- SCCM
- Society of Critical Care Medicine
- SCI
- Science Citation Index
- SIRS
- systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- SOFA
- Sequential Organ Failure Assessment
- SSC
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign
- UTI
- urinary tract infection
- VAP
- ventilator-associated pneumonia
- WMD
- weighted mean difference
Note
This monograph is based on the Technology Assessment Report produced for NICE. The full report contained a considerable number of data that were deemed commercial-in-confidence (CiC) and academic-in-confidence (AiC). The full report was used by the Appraisal Committee at NICE in their deliberations. The full report with each piece of CiC and AiC data removed and replaced by the statement ‘commercial-in-confidence and academic-in-confidence information (or data) removed’ is available on the NICE website: www.nice.org.uk.
The present monograph presents as full a version of the report as is possible while retaining readability, but some sections, sentences, tables and figures have been removed. Readers should bear in mind that the discussion, conclusions and implications for practice and research are based on all the data considered in the original full NICE report.