Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 13/73/01. The contractual start date was in October 2014. The draft report began editorial review in May 2015 and was accepted for publication in November 2015. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Moira Cruickshank, Lorna Henderson, Graeme MacLennan, Cynthia Fraser, Marion Campbell and Miriam Brazzelli’s institution received funding from the UK Department of Health to undertake this work. Anthony Gordon has received research support and speaker fees from Orion Pharmaceuticals [a manufacturer of dexmedetomidine (Dexdor®, Orion Corporation)] outside the submitted work. He also declares research support and/or personal/speaker fees from Tenax Therapeutics Inc., from HCA International and from Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc., and former membership of the Baxter Healthcare Advisory Board (1-day meeting, 10 September 2012) in relation to previous research projects. Marion Campbell declares former membership of the National Institute for Health Research Health Services and Delivery Research Researcher-led Board (2009–15).
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2016. This work was produced by Cruickshank et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Background and research question
Description of health problem
Introduction
Sedation is ‘a drug-induced depression of consciousness, a continuum culminating in general anaesthesia’. 1 Sedation is a key component of care of critically ill patients, who often need to undergo potentially invasive or uncomfortable procedures such as mechanical ventilation (MV). 2–6 Indications for the use of sedation in the intensive care unit (ICU) include: to alleviate pain; to facilitate use of distressing procedures and minimise patient discomfort; to provide protection from stressful and harmful stimuli; to reduce agitation and control agitation; and to enable nocturnal sleep and, when necessary, amnesia. 6–11 Sedation requirements vary widely between patients and sedative regimens should be tailored to individual patient’s needs [Sheila Harvey, Intensive Care National Audit and Research Centre (ICNARC), 2014].
Evidence from randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and current guidelines supports the use of the minimum possible level of sedation to achieve the desired effects without compromising patient comfort and safety. 12,13 A review of international surveys of critical care clinicians published between 1999 and 2009 confirmed that the trend was towards lighter levels of sedation,4 with only a minority of patients in need of continuous deep sedation. 13–15
The optimal level of sedation varies according to patients’ clinical conditions and treatment requirements. The prevalence of anxiety and agitation in critically ill patients undergoing MV in the ICU has been reported to be > 70%. Hence, assessment of sedation level should be routinely performed in ICUs. 14,16 Sedation level is usually measured by ICU staff by means of scoring sedation scales. Several scales have been developed to monitor sedation levels in critically ill patients. The first standardised measurement for sedation was the Ramsay Sedation Scale (RSS),17 which has been more recently superseded by the Richmond Agitation–Sedation Scale (RASS)18,19 and the Riker Sedation–Agitation Scale (SAS). 20 Scores on the RASS range from 4 (combative) to –5 (cannot be aroused). Riker SAS scores range from 7 (dangerous agitation) to 1 (cannot be aroused). For mechanically ventilated critically ill patients, target scores of between –2 and 0 for the RASS and between 3 and 4 for the Riker SAS are considered appropriate. 13 These scales have been shown to have good reliability and validity in the ICU setting, with neither being definitively superior. 12,14,21 Physiological methods to measure the level of sedation include heart rate variability, auditory-evoked potentials and electroencephalogram. 12,22 Among these, one of the most developed is the bispectral index, which measures the level of consciousness by an algorithmic analysis of the patient’s electroencephalographic and haemodynamic parameters, such as heart rate and arterial pressure. 11,23,24 Current UK and US guidelines do not recommend the use of physiological measures of brain function (e.g. bispectral index) as the primary method to monitor level of sedation in non-comatose, non-paralysed critically ill ICU patients, as these measures cannot adequately replace the existing subjective sedation scoring systems. 12,22
Sedation requirements are often not optimally managed, and poor sedation practice, which encompasses oversedation and undersedation, may have important deleterious effects. 3,6,25 Oversedation can result in cardiorespiratory depression, decreased gastrointestinal motility, immunosuppression and prolonged MV. Undersedation can cause hypertension, tachycardia and discomfort. 6 A variety of strategies have been proposed to address suboptimal management of levels of sedation of critically ill patients in ICUs, including use of sedation guidelines, protocols and goal-directed sedation algorithms,26–29 light target level of sedation and daily sedation interruptions (DSIs),30–34 and regular monitoring of sedation requirements. 35–37
The current Clinical Practice Guidelines from the Society of Critical Care Medicine for the Management of Pain, Agitation, and Delirium in Adult Patients in the Intensive Care Unit12 [pain, agitation and delirium (PAD) guidelines] strongly recommend the use of management guidelines and protocols. Protocolised target-based sedation and analgesia may be regarded as the cornerstone of effective sedation practice. 38
The PAD guidelines also recommend DSI or a light level of sedation in mechanically ventilated adults in ICUs. 12 Current evidence on the use of DSIs is far from conclusive. A RCT conducted by Girard and colleagues39 in four tertiary care hospitals found that a strategy comprising both daily spontaneous breathing attempts and daily spontaneous awakening attempts (i.e. DSIs) resulted in better outcomes (such as days breathing without assistance and length of stay in ICUs and hospital) than standard care. A meta-analysis of five trials published in 201140 highlighted the need for further RCTs with long-term survival follow-up before DSI could become standard sedation practice for critically ill patients. A multicentre RCT by Mehta and colleagues36 found that, in mechanically ventilated patients receiving continuous sedation, the combined use of protocol-guided sedation and DSI did not improve the clinical outcomes observed with the use of protocol-guided sedation alone. Similarly, a recent Cochrane systematic review35 did not find strong evidence that DSIs influence the duration of MV, mortality, length of stay, drug consumption, quality of life or adverse events compared with sedation strategies that do not involve the use of DSIs. The authors, however, considered the results to be unstable because of the small number of identified trials, the clinical and statistical heterogeneity observed among them and the marginally significant overall estimate of effect. Moreover, a reduction in duration of MV was detected when the analyses were restricted to trials conducted in North America. 35
Prior to initiating sedation, it is important to provide appropriate analgesia to all critically ill patients. 3,11,15 Adequate pain control can reduce the need for sedative drugs. 41 Pain can be experienced at rest by patients in the ICU42 or because of a number of other factors, including routine care, underlying disease processes, invasive procedures and immobility. 13,43 Pain is reported as the principal stressor by patients and is the most common memory they have of their ICU stay. 13,44,45 The PAD guidelines stress the importance of routine assessment of pain and provision of pre-emptive analgesia. 12 Analgesics and sedatives work in synergy but actually have discrete targets,6 and some analgesics also have a secondary sedative effect. 3 For example, remifentanil (Ultiva®, GlaxoSmithKline UK Ltd), an opioid, can be administered as a sole agent because of its sedative effects, although it is not commonly used in most ICUs. 13
Clonidine (Catapres®, Boehringer Ingelheim) also has both sedative and analgesic effects. 46 Patient’s requirements for analgesia and sedation should be thoughtfully balanced11 and sedation should never be given as a substitute for analgesia (Sheila Harvey, ICNARC, 2014).
Alongside assessment of pain, the PAD guidelines recommend the routine monitoring of delirium,12 which occurs in around 60–80% of mechanically ventilated patients in ICUs. 47–50 Delirium is associated with higher mortality, prolonged duration of MV, longer hospital stay and an increased risk of cognitive impairment among adult ICU patients 47,51,52 The Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM-ICU)53 and the Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist54 are the two most reliable instruments to assess delirium and their use is recommended by current guidelines. 12
Current service provision
Management of critically ill patients in intensive care units in the UK
A variety of medication is available to treat critically ill patients in ICUs. The choice of sedative or analgesic agents to achieve appropriate levels of sedation and pain relief can be quite challenging and must take account of the pharmacological properties of the different drugs as well as the individual patient’s characteristics and needs. 4,11,55 Sedative agents commonly used in ICUs include propofol (Diprivan®, AstraZeneca), benzodiazepines [midazolam and lorazepam (Ativan®, Pfizer)] and alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists [clonidine and dexmedetomidine (Dexdor®, Orion Corporation)]. 34 Commonly used analgesic agents include alfentanil, fentanyl, morphine and remifentanil. 4,15 The current general trend in the UK, and internationally, is a shift from benzodiazepines to propofol and from morphine to alfentanil and fentanyl. 4,56,57 The 2013 PAD guidelines suggest that sedation strategies using non-benzodiazepines (either propofol or dexmedetomidine) may improve clinical outcomes in mechanically ventilated ICU patients over sedation strategies based on benzodiazepines (either midazolam or lorazepam). 12
Ideally, the optimal sedative regimen for critically ill patients in ICUs should adequately address pain, sedation and anxiety; have favourable kinetics and clinical effects; be easily titrated and monitored; have a tolerable adverse effects profile; and be affordable. 4 At present, none of the commonly used sedative agents fulfil all of these criteria and none of them has demonstrated to be clearly superior to the others. 4,13,56
Variation in services and/or uncertainty about best practice
A recent UK national survey conducted by the ICNARC among 235 adult general critical care units together with a point-prevalence study conducted among 52 adult general critical care units (Sheila Harvey, ICNARC, 2014) showed that just over half of the surveyed units (57%) reported the use of a written sedation or sedation/analgesia protocol and, of those that did, fewer than one-quarter assessed compliance with the protocol. Level of compliance with sedation protocols varied considerably across units, ranging from 26% to 100%. There was considerable variation with regard to the elements of pain, sedation and delirium management that were included in each protocol and the level of details provided. The majority of the units (94%) used a sedation scale/score for assessing the depth of sedation in patients. The RASS was the most frequently reported scale in use (65% of units), followed by the RSS (25%). Small proportions of units reported the use of the Riker SAS (3.5%), the modified RSS (3%), the Bloomsbury Sedation Scale (1%) and other local or modified scales. Most patients (88%) in the point-prevalence study were assessed using the same sedation scale/score reported in the survey, although variations were observed across units (from 63% to 100%). Seventy per cent of units reported screening for delirium daily and, of these, most (92%) reported using the CAM-ICU tool. Most units (94%) reported that a sedation hold was considered daily for sedated patients. The findings of the point-prevalence study indicate, however, that compliance with sedation holding may be quite low. Overall, only 53% of sedated patients who had been in the unit for at least 24 hours had been considered for a sedation hold during the previous 24 hours.
Despite the existence of numerous published studies and clinical guidelines for sedation and analgesia, there is still a great variation between units in terms of actual intensive care, suggesting that there are still some barriers to the implementation of all relevant recommendations into routine clinical practice.
Relevant national guidelines
The current clinical pathway for analgosedation in the ICU was published by the UK Intensive Care Society in 2014 and recommends sequential assessment and treatment of pain, sedation and delirium, with regular monitoring built into the pathway. 22 These guidelines are in line with the current US12 and German58 guidelines. The UK framework is presented in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
General framework for analgosedation in ICUs (the list of drugs is not exhaustive). 22 Reproduced from Grounds M, Snelson C, Whitehouse T, Wilson J, Tulloch L, Linhartova L, et al. Intensive Care Society Review of Best Practice for Analgesia and Sedation in the Critical Care with permission from UK Intensive Care Society (www.ics.ac.uk).

The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Clinical Guidance Number 103,59 published in July 2010, provides general recommendations for the diagnosis, prevention and management of delirium. The only specific recommendations for people in critical care are that the CAM-ICU should be used if indicators of delirium are identified and that consideration should be given to provision of 24-hour clocks to patients to address cognitive impairment and/or disorientation. The UK Intensive Care Society guidelines also provide recommendations for managing delirium. 22 The suggested framework consists of three stages: assess (pain, discomfort, constipation, hunger, delirium, attempts to communicate); treat (analgesia, aperients, feed, drug withdrawal, change or stop sedative regimen); and prevent (alternative analgesia, sleep, quiet and calm environment, diligent and targeted sedation, communication).
Description of technologies under assessment
Alpha-2 agonists
Dexmedetomidine is a newer, selective alpha-2 receptor agonist which has sedative, analgesic, anxiolytic and sympatholytic effects. 11,12,60 The sedative effects are mediated through decreased firing of the locus coeruleus, the predominant noradrenergic nucleus, situated in the brainstem. 61 The pattern of sedation of the alpha-2 agonists is quite different from that of other sedative agents in that patients can be aroused readily and their performance on psychometric tests is usually well preserved. 22,62,63 Moreover, dexmedetomidine does not depress the respiratory system, unlike other sedative agents. 64,65
The dexmedetomidine terminal elimination half-life is around 2 hours. 12,13 Main adverse effects related to dexmedetomidine are hypotension and bradycardia. 11,13,66 Transient hypertension may occur during loading infusion. 13
Dexmedetomidine was granted UK marketing authorisation in September 2011 for ‘sedation of adult ICU patients requiring a sedation level not deeper than arousal in response to verbal stimulation (corresponding to RASS 0 to –3)’. 67 According to the summary of product characteristics,61 dexmedetomidine is for hospital use only and should be administrated by a health-care professional skilled in managing patients requiring intensive care. It should be administered by intravenous infusion only, using a controlled infusion device. Doses are adjusted until the required level of sedation is attained. A loading dose is not recommended, as it is associated with increased adverse reactions. The maximum dose of dexmedetomidine is 1.4 µg/kg/hour. During infusion, all patients should undergo continuous cardiac monitoring, and respiration should be monitored in non-intubated patients. Use of dexmedetomidine for > 14 days requires monitoring and regular assessments. The combined use of dexmedetomidine with anaesthetics, other sedatives, hypnotics or opioids is likely to enhance pharmacological effects and, consequently, a reduced dosage of dexmedetomidine or the concomitant drug may be necessary. 61 In the USA, dexmedetomidine is authorised for infusion of up to 24 hours only in intubated and mechanically ventilated patients. 68
In clinical trials, dexmedetomidine has been shown to be similar to midazolam and propofol on the time in target sedation range in a predominantly medical population requiring prolonged light to moderate sedation (RASS score of 0 to –3) in the ICU for up to 14 days. 61,69 In addition, dexmedetomidine reduced the duration of MV compared with midazolam61,70,71 and reduced the time to extubation compared with midazolam and propofol. Compared with both propofol and midazolam, patients receiving dexmedetomidine were more easily aroused, were more co-operative and better able to communicate whether or not they had pain,61,70 and showed a lower rate of post-operative delirium. 20,64,72 The sedative benefits of dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam are, however, not conclusive. A systematic review of six RCTs (1031 intensive care patients) published in 2013 has highlighted the need for further, more robust, research as, so far, the evidence of the advantages of dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam in the ICU setting is limited. 2 A meta-analysis of 14 trials (3029 critically ill patients) published in 2014 showed that the use of dexmedetomidine in ICUs is associated with a significant reduction in the incidence of delirium, agitation and confusion compared with other sedative agents. 73 Another meta-analysis of 27 RCTs, assessing dexmedetomidine compared with any other comparator in 3648 mechanically ventilated ICU patients, indicated that dexmedetomidine could be useful in reducing ICU stay and time to extubation, although heterogeneity was detected among included studies. 73 Similarly, a Cochrane systematic review published in January 2015 and based on seven RCTs with a total of 1624 patients, concluded that, compared with traditional sedative agents, long-term sedation with dexmedetomidine in critically ill patients may reduce the duration of MV and the length of ICU stay. However, the general methodological quality of evidence was low and there was clinical and statistical heterogeneity among studies. 74
Clonidine is an alpha-2 agonist agent that produces a reduction in sympathetic tone and resultant fall in diastolic and systolic blood pressure and heart rate. 75 Originally marketed as an antihypertensive agent, clonidine has demonstrated sedative and analgesic-sparing properties. The current therapeutic indications include the treatment of hypertensive crises,76 the prophylactic management of migraine or recurrent vascular headache and the management of vasomotor conditions commonly associated with the menopause and characterised by flushing. 75 There is no current marketing authorisation for clonidine as a sedative agent and no dosage recommendation for sedation in the summary of product characteristics. 76
In the ICU setting, clonidine has been used as a treatment for delirium and as a second-line sedative agent. 77–79 The pharmacodynamics pattern of clonidine is broadly similar to that of dexmedetomidine, but clonidine is less specific for alpha-2 receptors and has a lower affinity for alpha-2 receptors than dexmedetomidine. 60,78 Clonidine has been shown to be effective in controlling delirium and withdrawal symptoms from opioids, benzodiazepines, nicotine and alcohol. 78,80–83 Clonidine is a very lipid-soluble agent. Its peak action occurs after 10 minutes and lasts for 3–7 hours after a single intravenous dose. 84 Clonidine is metabolised in the liver and is eliminated primarily through the kidney. The elimination of the half-life of clonidine is 6–23 hours (average 7.7 hours) (Sheila Harvey, ICNARC, 2014), a key difference from dexmedetomidine which has an elimination half-life of around one-quarter the length of clonidine. 85 Sudden cessation of clonidine after prolonged use may cause a withdrawal syndrome leading to rebound hypertension and tachycardia in susceptible patients. 15,77,86 The main adverse effects of clonidine include bradycardia, hypotension and xerostomia (dry mouth). 15
Evidence on the use of clonidine in ICU settings is limited. A recent placebo-controlled RCT found a significant reduction in the need for benzodiazepines and opioids, but not propofol, in mechanically ventilated ICU patients treated with clonidine compared with those receiving placebo. No significant differences in the incidence of adverse events were observed between the groups. 87
A retrospective review of mechanically ventilated ICU patients’ clinical records showed a significantly lower mortality index and no important adverse effects for patients receiving clonidine rather than other sedatives. 88 A prospective study assessing the effects of clonidine among mechanically ventilated ICU patients with withdrawal symptoms after sedation interruption for ventilator weaning showed that the majority responded positively to clonidine and were weaned in a median of 2 days. In addition, clonidine decreased the haemodynamic, metabolic and respiratory parameters to near those observed with sedation. 82
The role of alpha-2 agonists (clonidine and dexmedetomidine) in the sedation of ICU patients has yet to be fully established.
Intravenous anaesthetic agents
Propofol is a short-acting intravenous general anaesthetic agent commonly used in ICUs since the 1980s. It activates gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors and has shown a considerable array of effects including anxiolysis, anticonvulsant activity, antiemesis and the ability to reduce intracranial pressure. 13,89–93 Propofol is a lipid-soluble compound with a rapid onset of action (from seconds to minutes) and a short duration of effect following short-term administration. 12,90,94 Owing to its short duration of sedative effect, propofol may be indicated for patients who require frequent awakening and DSIs. 12,95 The half-life of propofol ranges from 30 to 60 minutes after short-term infusion, but is longer after prolonged infusion (up to 50 ± 18.6 hours). 12,13 The rapid onset and offset are specific features of propofol compared with other common sedative drugs. 96 The most significant side effects of propofol include hypotension as a result of systemic vasodilation and dose-dependent respiratory depression.
Other side effects include hypertriglyceridaemia, acute pancreatitis, arrhythmia, bradycardia and cardiac arrest. 11–13 Propofol administration may rarely cause propofol infusion syndrome, an adverse reaction characterised by lactic acidosis, hypertriglyceridaemia, hypotension and arrhythmia. 12
A systematic review of 16 RCTs with a total of 1386 critically ill adult patients, which compared propofol with alternative sedative agents for medium- or long-term sedation, concluded that propofol is safe and can reduce the duration of MV. In addition, propofol also reduced the length of ICU stay when compared with long-acting benzodiazepines but not when compared with midazolam. 97
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines bind to the GABA receptor complex modulating GABA release in the central nervous system, causing downregulation of neuronal excitation (neurons become less excitable). 11 Depending on the dose used, they can cause sedation, anxiolysis or hypnosis (Sheila Harvey, ICNARC, 2014). Benzodiazepines vary in their potency, onset and duration of effect, uptake, distribution, metabolism and presence or absence of active metabolites. 15,94 Lorazepam is more potent than midazolam, which, in turn, is more potent than diazepam (Diazemuls®, Actavis UK Ltd). As midazolam and diazepam are more lipid soluble than lorazepam, they cross the blood–brain barrier quicker and result in a more rapid onset of action (from 2 to 10 minutes) than lorazepam (from 5 to 20 minutes). 11,13,98–100 The half-life of midazolam is 3–11 hours, compared with 8–15 hours for lorazepam and 20–120 hours for diazepam. 12,13 Midazolam and diazepam metabolites are active and tend to accumulate with prolonged administration, especially in patients with renal dysfunction. 11,101 Lorazepam metabolites are not active and, for this reason, it is the preferred benzodiazepine in patients with renal failure. 11 As all benzodiazepines are metabolised predominantly in the liver, clearance is reduced in patients with hepatic dysfunction. 12 Adverse effects of benzodiazepines include hypotension, respiratory depression, paradoxical agitation, tolerance with acute discontinuation and delirium. 13,15,102
A recent systematic review of six trials (1235 patients) concluded that the use of a dexmedetomidine- or propofol-based sedation regimen rather than a benzodiazepine-based regimen in critically ill patients may reduce ICU length of stay and duration of MV. 103 Indeed, current PAD guidelines suggest that sedation strategies using non-benzodiazepines (either propofol or dexmedetomidine) may be preferred over sedation with benzodiazepines (either midazolam or lorazepam) to improve outcomes in mechanically ventilated adult ICU patients. 12
Identification of important subgroups
Specific subgroups of interests are usually based on severity of disease, primary reasons for admission to the ICU (e.g. admission after elective surgery) and duration of MV. Severity of disease is usually assessed by means of severity scores and risk prediction models. One of the most commonly used methods is the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II severity score system, which uses a point score based on initial values of 12 routine physiological measurements, age and previous health status to provide a general measure of severity of disease. Scores can range from 0 to 71, with higher scores indicating more severe disease and a higher risk of mortality. This severity index has been used to evaluate the use of hospital resources and compare the efficacy of intensive care over time and across different hospitals. The APACHE II scores combined with an accurate description of disease can also be used to stratify, prognostically, acutely ill patients and compare the success of new or differing forms of therapy. 104
Current usage in the NHS
The 2014 ICNARC national survey, conducted among 235 adult general ICUs, together with a point prevalence study conducted among 52 ICUs in the UK, showed that propofol was the most widely used sedative agent, with 88% of the units reporting it as their first choice of agent. Although approximately one-third of the surveyed units (32%) reported frequent use of midazolam, only a small proportion (6%) reported that midazolam was their first choice of sedative agent. Less than 1% of the units reported use of lorazepam. Approximately one-third of the ICUs reported frequent use of clonidine and 10% reported frequent use of dexmedetomidine. The most frequently used agents for analgesia were alfentanil (51% of the units), morphine (42%) and fentanyl (36%). The largest proportion of units (40%) reported that alfentanil was their first choice of analgesic agent. In general, the trend was away from morphine, the first choice of analgesic agent in 20% of the ICUs, towards alfentanil and fentanyl (Sheila Harvey, ICNARC, 2014).
With regard to the strategies on how sedatives and analgesics were used, 66% of surveyed units reported that they occasionally or rarely opted for a single sedative agent and 76% of units for multiple sedative agents together. Most units (82.7%) reported that their first and preferred approach was to use one or more sedatives in combination with one or more analgesics. The expected duration for sedation and/or analgesia was reported to be an important determinant in the choice of sedative and/or analgesic agent. In the point prevalence study, 69% of sedated patients had received both a sedative agent and an analgesic agent in the previous 24 hours and the most frequent choice was propofol combined with either alfentanil or fentanyl (Sheila Harvey, ICNARC, 2014).
Chapter 2 Definition of the decision problem
This chapter defines the main components of this assessment. The current clinical pathway for analgosedation in the ICU is that of the UK Intensive Care Society, shown in Figure 1. 22 The clinical characteristics of the interventions under investigation were reported in Chapter 1. Detailed information on the population, interventions, comparators and relevant outcomes considered for this assessment will be presented in Chapter 3.
Population
The population considered for this assessment was critically ill adults admitted to ICUs who require MV. People with primary brain injuries such as trauma or intracerebral bleed/infarct are not deemed suitable for inclusion, as their clinical conditions require very specific ICU management and, often, a deeper level of sedation.
Interventions assessed
Dexmedetomidine and clonidine for sedation in ICUs.
Relevant comparators
Propofol and benzodiazepines (e.g. midazolam and lorazepam) for sedation in ICUs.
In this assessment, the term ‘standard care’ refers to the use of propofol and/or midazolam, at the discretion of the treating clinician, for sedation of critically ill patients admitted to ICUs, who require MV. The specific use of sedation interruptions and sedation protocols is not included in this definition.
Relevant outcomes
The main outcomes of interest were mortality, duration of MV, ventilator-free days, length of ICU stay, adverse events and unpleasant side effects. Secondary outcomes of interest include duration of weaning, time spent in target sedation range, proportion of patients in target sedation range, discharge readiness, extubation readiness, length of hospital stay, quality of life and cost.
Overall aims and objectives of the assessment
The purpose of this assessment was to systematically review the evidence of the clinical effectiveness of the alpha-2 agonists, propofol and benzodiazepines in ICUs, with the purpose of informing future RCTs.
The specific objectives of this assessment were to (1) compare the effects of dexmedetomidine with those of clonidine in mechanically ventilated adults admitted to ICUs and (2) compare the sedative effects of dexmedetomidine or clonidine with those of other most commonly used sedatives (i.e. propofol and benzodiazepines) in mechanically ventilated adults admitted to ICUs. The structure of this assessment will be that of a Health Technology Assessment short report.
Chapter 3 Assessment of clinical effectiveness
This chapter reports the evidence of the clinical effectiveness of dexmedetomidine compared with clonidine and of dexmedetomidine or clonidine compared with propofol or benzodiazepines (midazolam or lorazepam) in mechanically ventilated adults admitted to ICUs.
Methods for assessing the outcomes arising from the use of the intervention
The methods for this assessment were prespecified in a research protocol (www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.asp?ID=CRD42014014101). 105
Identification of studies (search strategy and information sources/dates)
Highly sensitive literature searches, using an appropriate combination of controlled vocabulary and text word terms, were developed to identify reports of published, ongoing and unpublished studies reporting the clinical effectiveness of dexmedetomidine or clonidine in comparison with propofol and benzodiazepines (e.g. midazolam, lorazepam and diazepam) in mechanically ventilated adults admitted to ICUs. Literature searches were carried out from 12 to 15 November 2014 for publications from 1999 onwards. Details of the search strategies are reported in Appendix 1. Major electronic databases were searched including MEDLINE without revisions, MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, EMBASE, Science Citation Index, Bioscience Information Service and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. Reports of relevant evidence synthesis were sought from the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects. The World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, metaRegister of Controlled Trials and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched for evidence of ongoing studies.
Websites of regulatory bodies and Health Technology Assessment agencies were checked for relevant unpublished reports, while websites of relevant pharmaceutical companies and professional organisations were searched for further pertinent information and reports.
In addition, reference lists of all included studies were perused for further citations.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Types of studies
Evidence was considered from RCTs comparing dexmedetomidine with clonidine or dexmedetomidine or clonidine with propofol or benzodiazepines such as midazolam, lorazepam and diazepam.
The following types of reports were excluded:
-
narrative reviews, editorials and opinions
-
case reports
-
conference abstracts for which a full publication or further methodological information could not be found
-
non-English-language reports for which a translation could not be organised
-
studies that focused predominantly on people with primary brain injuries.
Types of participants
The types of participants considered were critically ill adults in ICUs who required MV. We did not prespecify definitions for ‘critically ill’ or ‘adults’, so any study population described as such was deemed suitable for inclusion.
Interventions
The sedative interventions considered were dexmedetomidine and clonidine.
Comparator interventions
The comparator interventions assessed were propofol and benzodiazepines such as midazolam, lorazepam and diazepam.
Outcomes
The following primary outcomes were considered:
-
mortality
-
duration of MV
-
ventilator-free days
-
length of ICU stay
-
adverse events as reported by trial investigators and including the rate of:
-
hypotension
-
hypertension
-
bradycardia
-
respiratory depression
-
delirium
-
coma
-
non-planned or accidental removal of lines (e.g. extubation) or catheters
-
-
unpleasant side effects as reported by trial investigators (e.g. unpleasant memories, constipation or diarrhoea).
Secondary outcomes considered were:
-
duration of weaning
-
time spent in target sedation range
-
proportion of patients in target sedation range
-
discharge readiness
-
extubation readiness
-
length of hospital stay
-
quality of life
-
cost.
Data extraction strategy (study selection and data collection)
One reviewer (MC) screened all titles and abstracts identified by the search strategies. A second reviewer (MB) independently double-screened the first 100 abstracts and titles of the 2011–14 list. Agreement between the two reviewers was 100%.
All potentially relevant reports were retrieved in full and assessed independently by one reviewer (MC). A total of 40 reports were double-assessed by a second reviewer (Pawana Sharma or MB). Any disagreements were resolved by consensus. The full-text screening form is presented in Appendix 2. A data extraction spreadsheet (Microsoft Excel®, 2013; Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) was developed specifically for the purpose of this assessment, piloted and amended as necessary. From each study, one reviewer (MC) extracted information on geographical location, sponsor, study design, participants’ characteristics, setting and characteristics of ICU practice, characteristics of sedative intervention and outcome measures. Data extraction was double-checked by a second reviewer (MB). Any disagreements were resolved by discussion.
Critical appraisal strategy
The risk of bias of included RCTs was initially assessed by one reviewer (MC) using Cochrane’s risk-of-bias tool106 and, subsequently, cross-checked by a second reviewer (MB). The following domains were assessed: sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and medical personnel, blinding of outcome assessors, incomplete outcome data and selective outcome reporting. Assessment of ‘other bias’ was based on the funding source, and a study was judged to be at high risk of bias if it was funded by the manufacturer(s) of the sedative agent(s) under investigation. Individual outcomes were judged as being at ‘high’, ‘low’ or ‘unclear’ risk of bias. Overall, risk of bias for each study was based on the findings of three key domains: sequence generation, allocation concealment and blinding of outcome assessor.
Studies were classified as follows: (1) high risk of bias if one or more key domains were at high risk; (2) unclear risk of bias if one or more key domains were judged to be at unclear risk; and (3) low risk of bias if all key domains were judged to be at low risk. Any disagreements between reviewers were resolved by discussion.
Method of analysis/synthesis
The general approach recommended by Cochrane was used for data analysis and synthesis. 106 For binary outcomes, the Mantel–Haenszel approach was used to pool risk ratios (RRs) derived from each study. A random-effects model was used to calculate the pooled estimates of effect. For continuous outcomes (duration of MV, ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, time to extubation, time in target sedation range and ventilator-free days), mean differences between groups were pooled when possible using the inverse variance weighted mean difference method and a random-effects model. Random-effects methods, rather than fixed-effects methods, as outlined in the original protocol, were chosen because of the clinical and statistical heterogeneity observed among included studies.
For each continuous outcome, an initial analysis was conducted using only studies where the mean and standard deviation (SD) were provided. In studies that did not report a mean and SD [and we could not derive these summary measures from reported p-values, standard errors or confidence intervals (CIs)], we tried to impute these from the data reported. The imputation strategy was as follows:
-
Where the median, range and n for each group were available, we used the formulae reported by Hozo and colleagues107 to estimate the mean and SD.
-
Where this method proved unfeasible, we imputed a SD from the available data using the methods outlined by Furukawa and colleagues. 108
-
In studies where a median and interquartile range were reported, we used two methods to calculate the mean. If the sample size was < 25, then first the median was used and second the value midway between the lower quartile and upper quartile was used. If the two methods yielded results that reversed the direction of treatment effect for a certain outcome within a study, then the study was excluded from the pooled analysis of that outcome.
For each outcome where the above provided extra data, a second analysis was done using the imputed data.
Heterogeneity across studies was explored by visual inspection of forest plots and using the chi-squared test and I2-statistics.
When data were available, subgroup analyses were performed according to type of comparator intervention.
Results of the evidence synthesis
Quantity of the evidence (studies included and excluded)
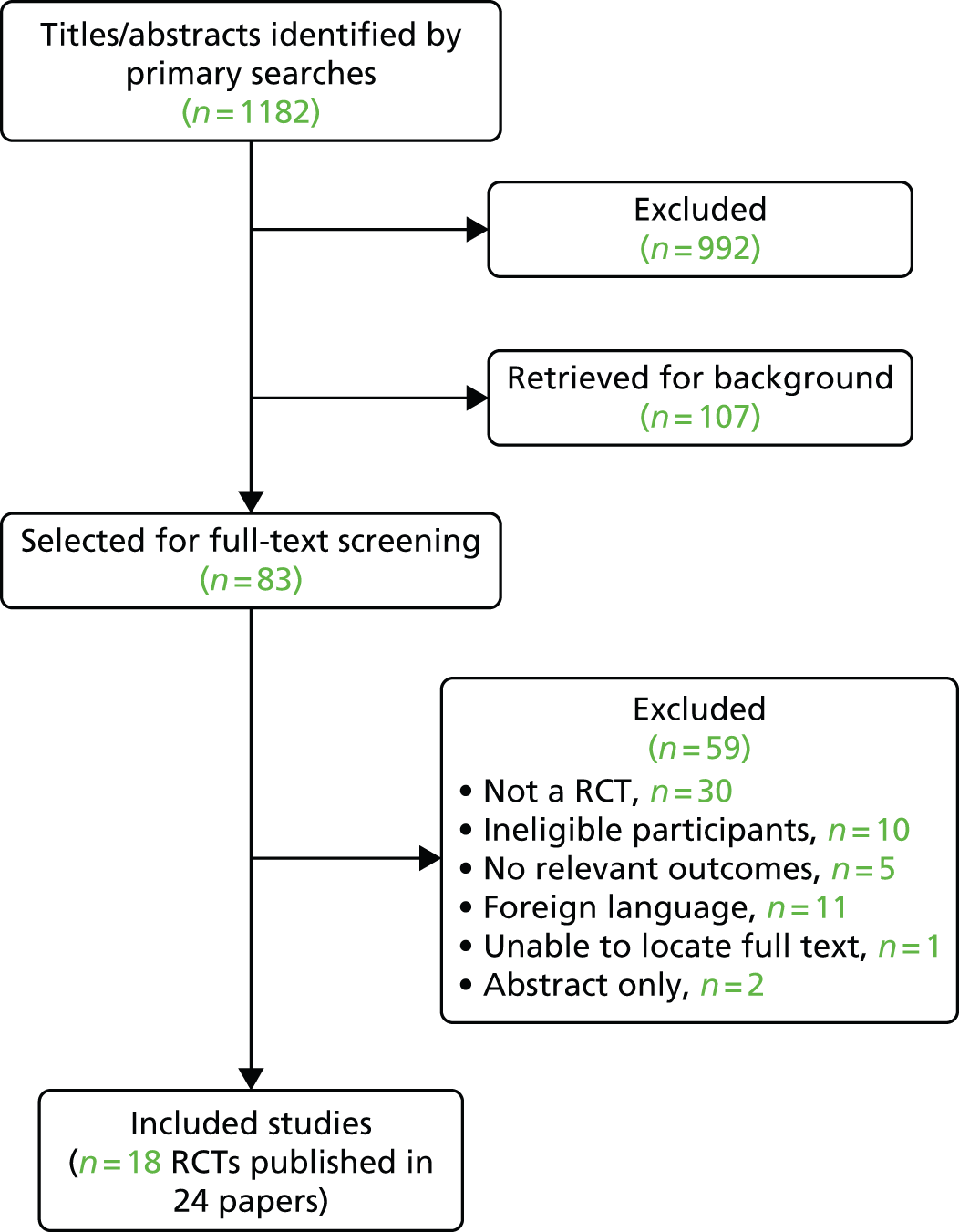
The literature searches identified 1182 potentially relevant citations, of which 83 were selected for full-text assessment and 107 for background information. Of these, 59 were subsequently excluded because the patient population, study design, outcomes reported or publication type were not eligible. A total of 18 RCTs published in 24 papers with a total of 2489 people were included in this assessment. 5,52,69–72,102,109–125 It is worth noting that the results of the two large multicentre trials of PROpofol compared with DEXmedetomidine (the PRODEX trial) and of MIdazolam compared with DEXmedetomidine (the MIDEX trial) were published in a single report by Jakob and colleagues70 for the Dexmedetomidine for Long-Term Sedation investigators. Figure 2 presents the flow chart of the selection process. Appendix 3 provides the details of the 18 included trials and related secondary publications. Appendix 4 categorises the excluded studies according to the main reasons for their exclusion.
FIGURE 2.
Flow chart of the study selection process.
Study characteristics
Appendix 5 details the study characteristics of the 18 included trials. All 18 trials were published in full. Four different comparators were assessed. One trial, with a total of 70 randomised patients, compared the effects and safety of dexmedetomidine with clonidine;55 nine trials, with a total of 1134 randomised patients, compared dexmedetomidine with propofol;70,109–111,114,117,120,122,123 four trials, with a total of 939 randomised patients, compared dexmedetomidine with midazolam;70,71,112,116 one trial, with a total of 118 randomised patients, compared dexmedetomidine with propofol or midazolam (three arms);72 two trials, with a total of 122 randomised patients, compared dexmedetomidine with ‘standard care’ (i.e. propofol and/or midazolam);69,121 and one trial with a total of 106 randomised patients, compared dexmedetomidine with lorazepam. 102 A total of 2446 patients were analysed in the 18 included trials.
Six trials assessed dexmedetomidine in patients admitted to ICUs following elective surgery,72,110,111,114,120,123 whereas the remaining trials included general ICU patients.
Four trials were conducted in the USA,72,102,110,116 two in India,55,120 three in Turkey,112,117,122 two in Egypt,109,111 one in the UK,123 one in North America (USA and Canada),114 one in Finland and Switzerland,69 and one in Australia and New Zealand. 121 The MIDEX multicentre trial70 was conducted in nine European countries; the PRODEX multicentre trial70 was conducted in six European countries and in Russia; and the SEDCOM71 (Safety and Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine COmpared with Midazolam) multicentre trial was conducted in the USA, Argentina, Brazil, Australia and New Zealand. All included trials involved prospective collection of data.
Three trials assessed patients up to 45 days69,70 and one up to 90 days. 121 In one trial,102 participants were observed in the hospital from enrolment until discharge from hospital or death, and survivors were observed for vital status until 1 year after enrolment using hospitals’ electronic record systems and a commercial version of the Social Security Death Master File (http://ssdi.rootsweb.com). One trial114 followed up patients for 24 hours after discharge from ICUs and another trial71 for 48 hours after study drug cessation. One trial72 reported that patients were followed up for 3 days post operatively. In one trial,109 length of follow-up was reported to be 6 hours, in two trials55,120 it was 24 hours and in another trial123 it was 48–72 hours. Two trials reported follow-up in terms of time post extubation: one trial110 assessed patients at least 24 hours post extubation and another trial116 at least 72 hours post extubation. Length of follow-up was not reported in four trials. 111,112,117,122
Appendix 6 presents details of dosage and route of administration of the respective sedative agents.
In general, dexmedetomidine was initiated with a loading dose of 1 µg/kg, administered intravenously over a period of 10–20 minutes. 109,110,112,114,117,120,122 Some trials involved lower55,72,102,116 or higher111,123 loading doses, four trials did not use a loading dose69,70,121 and, in one trial, the loading dose was optional. 71 Dexmedetomidine maintenance doses were fixed in two trials: 0.4 µg/kg/hour110 or 0.7 µg/kg/hour. 112 The remaining trials specified lower and upper limits for maintenance doses, with lower limits ranging from 0 µg/kg/hour121 to 0.015 µg/kg/hour,102,116 0.2 µg/kg/hour,55,70,72,111,114,117,120,122,123 0.4 µg/kg/hour,110 0.5 µg/kg/hour109 and 0.7 µg/kg/hour. 112 The maximum allowable dose was 2.5 µg/kg/hour. 117,122,123
Clonidine was used in one trial. Patients received an infusion of clonidine at 1 µg/kg/hour. Titration was achieved with dosage increments up to 2 µg/kg/hour. 55
Of the 12 trials that included a propofol arm, four trials reported a loading dose: an initial bolus dose of 1 mg/kg in one trial111 and 1 mg/kg over 10–15 minutes in three trials. 117,122,123 Six trials did not use a loading dose69,70,72,109,110,120 and two trials did not provide information on dosage. 114,121 Maintenance infusions of propofol ranged from 0.5–1 mg/kg/hour111 to 4 mg/kg/hour across trials. 69,70
Out of the seven trials that included a midazolam arm, one trial reported a loading dose of 0.05 mg/kg112 and another trial reported an optional loading dose of the same level. 71 The remaining trials did not use a loading dose. One trial did not specify dosage of midazolam. 121 Maintenance doses of midazolam were between 0.03 mg/kg/hour70 and 10 mg/hour across trials. 116
In one trial, lorazepam infusion started at 1 mg/hour and was titrated to a maximum of 10 mg/hour. 102
All trials titrated sedatives to a target sedation level. 55,69–72,102,109–112,114,116,117,120–123 Target sedation level was measured by means of the RSS score in 11 trials,55,72,109–112,114,117,120,122,123 the RASS in six trials69–71,102,121 and the Riker SAS score in one trial. 116
The main characteristics of the 18 included studies are shown in Table 1.
| Study | Double blind | Population | Number of patients randomised | Comparator | Sponsored by industry | Overall risk-of-bias assessment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dexmedetomidine | Comparator | ||||||
| Abdulatif et al., 2004109 | No | Patients with established respiratory failure requiring MV using pressure support ventilation with or without continuous positive airway pressure | 20 | 20 | Propofol | Unclear | Unclear |
| Corbett et al., 2005110 | Unclear | After non-emergent CABG surgery (elective surgery) | 43 | 46 | Propofol | Unclear | Unclear |
| Elbaradie et al., 2004111 | No | After major thoracic, abdominal or pelvic cancer surgeries (elective surgery) | 30 | 30 | Propofol | Unclear | High |
| Esmaoglu et al., 2009112 | Unclear | Patients whose pregnancies were terminated via caesarean delivery because of eclampsia | 20 | 20 | Midazolam | Unclear | Unclear |
| Herr et al., 2003114 | No | After CABG surgery (elective surgery) | 148 | 147 | Propofol | Yes | High |
| Jakob et al., 201270 (MIDEX trial) | Yes | ICU patients requiring MV and light to moderate sedation | 249 | 252 | Midazolam | Yes | Low |
| Jakob et al., 201270 (PRODEX trial) | Yes | ICU patients requiring MV and light to moderate sedation | 251 | 249 | Propofol | Yes | Low |
| MacLaren et al., 2013116 | Yes | Medical or surgical ICU patients requiring MV and receiving benzodiazepines | 11 | 12 | Midazolam | Yes | Unclear |
| Maldonado et al., 200972 | No | After cardiac valve surgery (elective surgery) | 40 | 78 (38 propofol, 40 midazolam) | Midazolam, propofol | Unclear | High |
| Memis et al., 2009117 | No | Patients fulfilling laboratory criteria of septic shock | 20 | 20 | Propofol | Unclear | High |
| Pandharipande et al., 2007102 | Yes | Medical and surgical ICU patients | 54 | 52 | Lorazepam | Yes | Low |
| Riker et al., 200971 | Yes | General ICU patients on MV | 250 | 125 | Midazolam | Yes | Low |
| Ruokonen et al., 200969 | Yes | General ICU patients on MV | 41 | 44 (28 propofol, 16 midazolam) | Midazolam, propofol | Yes | Unclear |
| Shah et al., 2014120 | No | Surgical patients requiring post-operative MV and sedation (elective surgery) | 15 | 15 | Propofol | Yes | High |
| Shehabi et al., 2013121 | No | Medical, operative elective and operative emergency patients | 16 | 21 | Standard care (propofol and/or midazolam) | Yes | High |
| Srivastava et al., 201455 | Unclear | General ICU patients on MV | 35 | 35 | Clonidine | No | Unclear |
| Tasdogan et al., 2009122 | No | Patients with sepsis after ileus surgery | 20 | 20 | Propofol | Unclear | High |
| Venn and Grounds, 2001123 | Unclear | After complex major abdominal or pelvic surgery (elective surgery) | 20 | 20 | Propofol | Yes | Unclear |
Participant characteristics
The 18 included trials randomised a total of 1283 participants to dexmedetomidine and 1206 participants to a control intervention. The sample sizes of included studies ranged from 23 to 501 participants.
There was some doubt whether or not the trial by Memis and colleagues (40 patients in total)117 and that by Tasdogan and colleagues (40 patients in total)122 were mutually exclusive with regard to participants. Even though a number of similarities between the two trials were observed, the characteristics of the two patient populations were clearly not identical and, therefore, we treated them as two separate trials. Correspondence with the trials investigators (Dr Dilek Memis named as corresponding author for both trials) proved unsuccessful and did not elicit any response.
The mean age was reported in 12 trials. 71,72,109–112,114,116,117,120–122 With the exception of one trial112 that focused exclusively on young pregnant women (mean age 25.1 years in the dexmedetomidine group and 26.8 years in the control intervention group), the 11 remaining trials mean age ranged from 43 to 65 years for dexmedetomidine and from 40 to 67 years for the comparator interventions. The median age was reported in six trials55,69,70,102,123 and ranged from 49 to 65 years for dexmedetomidine and from 46 to 67 years for the comparator interventions.
Sixteen studies reported information regarding the sex of participants. 55,69–72,102,109,110,112,114,116,117,120–122 Study populations tended to involve more men than women, with the exception of one trial that involved only pregnant women112 (see Appendix 5 for further details).
The severity of illness at baseline was reported in eight trials55,71,102,112,117,121–123 by means of the APACHE II scores or APACHE III scores (one trial). 116 The APACHE II scores have a possible range of 0–71, whereas the APACHE III scores can range from 0 to 299. In both cases, higher scores indicate more severe disease and a higher risk of death. 104 Across the eight trials that used APACHE II, scores ranged from a mean of 5.1112 to a mean of 22 for dexmedetomidine117 and a mean of 6112 to a mean of 20117 for the control sedative intervention. One trial102 reported a median APACHE II score of 29 for dexmedetomidine and of 27 for the control sedative intervention. The trial116 that assessed severity of disease using the APACHE III scores reported mean scores of 74.1 for dexmedetomidine and of 70.4 for midazolam.
Table 2 presents an overview of the participants’ characteristics of the 18 included trials. It is worth noting that not all trials provided the same participant details or used the same measures to assess them.
| Characteristic | Dexmedetomidine compared with propofol RCTs | Dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam RCTs | Dexmedetomidine compared with other comparators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of participants randomised | 1134 (n = 9 trials) | 939 (n = 4 trials) | Dexmedetomidine compared with clonidine: 70 (n = 1 trial) |
| Dexmedetomidine compared with propofol and midazolam: 118 (n = 1 trial) | |||
| Dexmedetomidine compared with standard care: 122 (n = 2 trials) | |||
| Dexmedetomidine compared with lorazepam: 106 (n = 1 trial) | |||
| Age (years), median of means (range) | Dexmedetomidine: 60 (43–65); propofol: 58 (40–67) (n = 9 trials) | Dexmedetomidine: 41.7 (25.1–58.3); midazolam: 42.3 (26.8–57.8) (n = 2 trials) | Dexmedetomidine: 65; standard care: 61.6 (n = 1 trial) |
| Sex (% men), median of means (range) | 65.5 (51.5–89.9) (n = 7 trials) | 52.7 (0–65.6) (n = 4 trials) | Dexmedetomidine compared with clonidine: 54.3 (n = 1 trial) |
| Dexmedetomidine compared with lorazepam: 51.4 (n = 1 trial) | |||
| Dexmedetomidine compared with propofol and midazolam: 61.5 (n = 1 trial) | |||
| Dexmedetomidine compared with standard care: 68.3 (54.4–82.2) (n = 2 trials) | |||
| APACHE II scores, median of means (range) | Dexmedetomidine: 19 (18–22); propofol: 18 (16.5–20) (n = 3 trials) | Dexmedetomidine: 12.1 (5.1–19.1); midazolam: 12.2 (6–18.3) (n = 2 trials) | Dexmedetomidine (median 15) compared with clonidine (median 16.5) (n = 1 trial) |
| Dexmedetomidine (median 29) compared with lorazepam (median 27) (n = 1 trial) | |||
| Dexmedetomidine (median 20.2) compared with standard care (median 18.6) (n = 1 trial) |
Risk-of-bias assessment of included studies
Figure 3 presents the summary of the risk-of-bias assessments for all included trials. The risk of bias of individual studies is presented in Figure 4.
FIGURE 3.
Summary of risk-of-bias assessments of all included trials.

FIGURE 4.
Risk-of-bias assessments of individual studies. CLON, clonidine compared with dexmedetomidine, LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
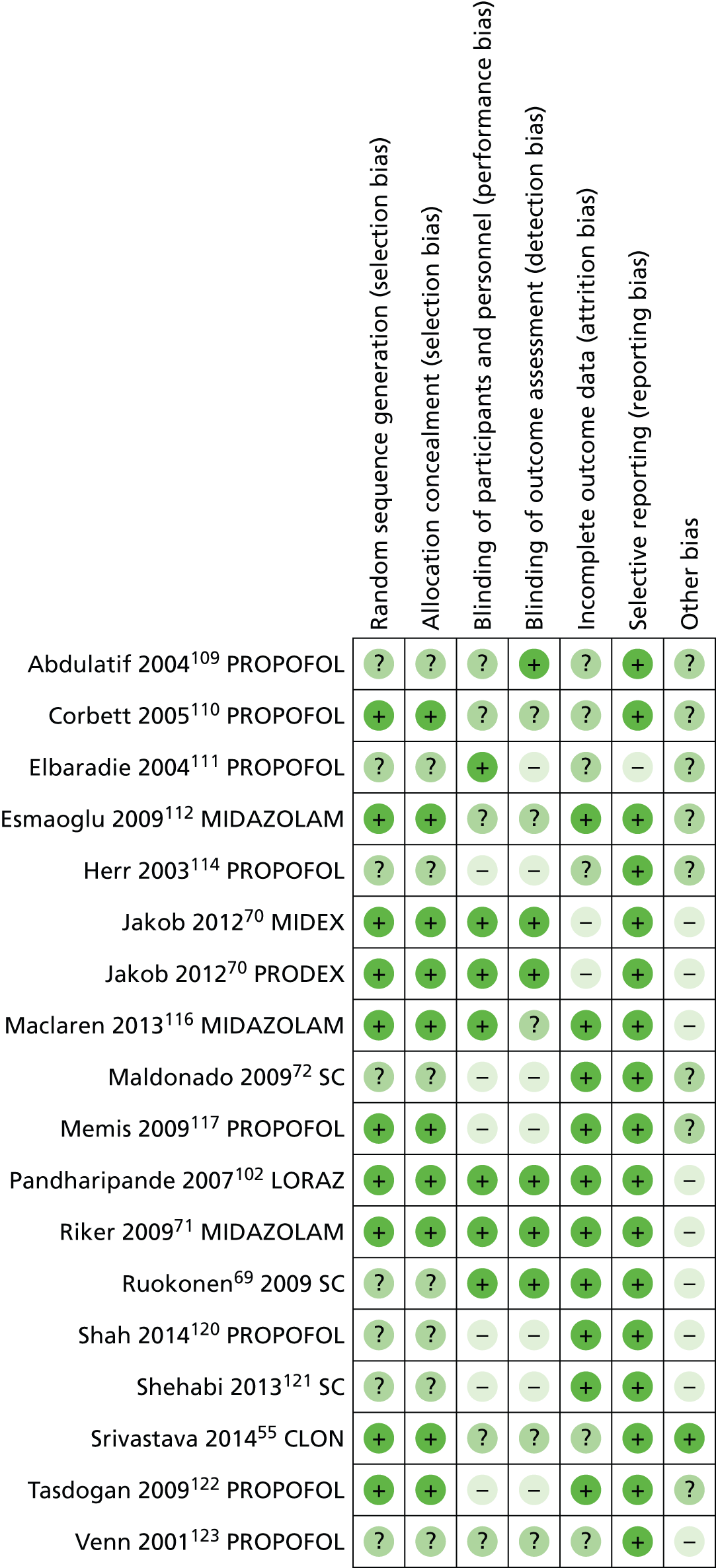
Overall, out of the 18 included trials, four were judged to be at low risk of bias70,71,102 and seven at high risk of bias. 72,111,114,117,120–122 For the remaining seven trials, there was not sufficient information to make an overall judgement. 55,69,109,110,112,116,123
With regard to the assessment of selection bias, around half of the trials were judged to be at low risk (i.e. adequate sequence generation and allocation concealment),55,70,71,102,110,112,116,117,122 whereas the remaining eight trials did not provide sufficient information to formulate a proper judgement. 69,72,109,111,114,120,121,123
In eight of the included trials, participants were reported to be blinded to the intervention received,69–71,102,109,111,116 whereas in six trials they were not. 72,114,117,120–122 The remaining four trials did not report information on blinding of participants. 55,110,112,123 Blinding of outcome assessor was addressed adequately in five trials,69–71,102 not adequately in seven trials72,111,114,117,120–122 and not reported in six trials. 55,109,110,112,116,123
With regard to ‘incomplete outcome data’,10 trials had low withdrawal/discontinuation rates, which were balanced between intervention groups and, therefore, judged to be at low risk of bias. 69,71,72,102,112,116,117,120–122 Two trials reported significantly higher discontinuation rates, owing to lack of efficacy, among people treated with dexmedetomidine, and were judged to be at high risk of bias. 70 The remaining six trials did not provide sufficient information on which to make a definitive judgement. 55,109–111,114,123
There was no evidence of selective reporting in any of the included trials, with the exception of one trial111 in which data on hypotension and bradycardia were mentioned only in the discussion section of the published paper and not properly reported in the results section. For this reason, the study was judged to be at high risk of selective reporting.
With regard to ‘other sources of bias’, nine trials declared financial support by manufacturers of sedative agents and were, therefore, judged to be at high risk of bias. 69–71,102,116,120,121,123 One trial was judged at low risk of bias, as the authors clearly stated that no funding was received from manufacturers. 55 The remaining eight studies were judged to be at unclear risk of bias, as the authors did not explicitly report their source of funding. 72,109–112,114,117,122
Summary of clinical effectiveness
Random-effects meta-analyses of relevant clinical outcomes were performed when appropriate.
We had initially planned to perform subgroup analyses according to the type of clinical setting (patients admitted to ICUs following elective surgery compared with general ICU patients) if enough data had been available. However, only 6 of the 18 studies included patients who were admitted to the ICU after elective surgery, and not all of them provided data for all efficacy outcomes. Therefore, because of the dearth of suitable data, subgroup analyses according to the type of clinical setting were deemed unfeasible. As patients admitted to the ICU after elective surgery represent a distinct type of patient population (short duration of sedation and MV, and lower mortality rate), we deemed it inappropriate to combine trials that included patients after elective surgery with those that enrolled more general, critically ill ICU patients. The results of trials that enrolled patients after elective surgery were instead summarised narratively.
It is worth pointing out that there was considerable variation among included trials in the choice, definitions and measurements of outcomes, especially with regard to measures of ventilator dependence such as duration of MV, ventilator-free days, time to extubation or duration of weaning. Often, trials that assessed duration of MV did not report ventilator-free days as an outcome. The number of ventilator-free days was available from three trials, but details on measurement were lacking. 69,118,121 Information on time to extubation was reported in six trials,70,71,111,114,123 but definition and criteria for extubation were not consistent across trials. Two large trials (MIDEX and PRODEX)70 reported both duration of MV and time to extubation, but did not provide a clear definition or measurement criteria for time to extubation and failed to discuss the clinical difference between the two measures. Similarly, duration of weaning was reported by two trials,69,114 but only one provided a proper outcome definition and a description of the measurement criteria. 114
Clonidine compared with dexmedetomidine
One trial, at unclear risk of bias, randomised a total of 70 general ICU patients requiring MV to dexmedetomidine (35 patients) or to clonidine (35 patients). 55 Both clonidine and dexmedetomidine produced effective sedation. Target sedation was achieved in 86% of observations among patients who received dexmedetomidine and in 62% of observations among patients who received clonidine (p = 0.04). Additional sedation was needed by more patients treated with clonidine than those treated with dexmedetomidine (14 patients and 8 patients, respectively; p = 0.034). Hypotension was observed significantly more frequently among patients who received clonidine (11 out of 35 patients) than among patients who received dexmedetomidine (3 out of 35) (p = 0.02). Rebound hypertension was seen only in four patients receiving clonidine. The authors concluded that both clonidine and dexmedetomidine produced effective sedation. However, the haemodynamic stability provided by dexmedetomidine makes it a preferable option over clonidine for short-term sedation of ICU patients.
Propofol and benzodiazepines (i.e. midazolam and lorazepam) compared with dexmedetomidine
Primary outcomes
Mortality
Nine trials reported mortality data (Figure 5). 69–71,102,116,117,120,121 A total of 196 out of 909 (22%) patients who received dexmedetomidine and 162 out of 783 (21%) of patients who received a control intervention died. Compared with alternative sedative agents, dexmedetomidine had no significant effects on mortality (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.85 to 1.24, I2 = 0%; p = 0.78).
FIGURE 5.
Meta-analysis for mortality. df, degrees of freedom; IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.

Two trials assessing patients after elective surgery reported mortality data. 72,123 In one trial,72 two deaths not attributable to sedation occurred among patients who received the control intervention (propofol), whereas in the other trial123 two patients receiving dexmedetomidine died, compared with one patient receiving the control intervention (propofol).
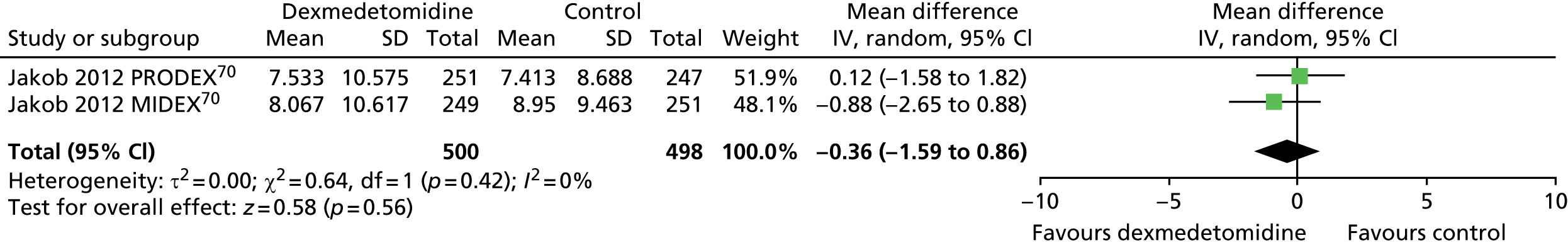
Duration of mechanical ventilation
Two trials reported mean duration of MV (Figure 6). 70 There were no significant differences in the duration of MV between dexmedetomidine and control interventions (mean difference –0.36, 95% CI –1.59 to 0.86, I2 = 0%; p = 0.56).
FIGURE 6.
Meta-analysis for duration of MV. df, degrees of freedom; IV, inverse variance.
Similarly, there was no difference (mean difference –0.30, 95% CI –1.70 to 1.11; p = 0.68) in the duration of MV between dexmedetomidine and control interventions (Figure 7) when all available data suitable for the analysis were considered (including transformed and imputed data). Statistical heterogeneity was observed among trials (I2 = 70%).
FIGURE 7.
Meta-analysis for duration of MV: all available data (including transformed and imputed data). df, degrees of freedom; IV, inverse variance; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.

One trial that assessed patients after elective surgery110 reported no difference between dexmedetomidine and propofol (p > 0.05) with regard to length of intubation.
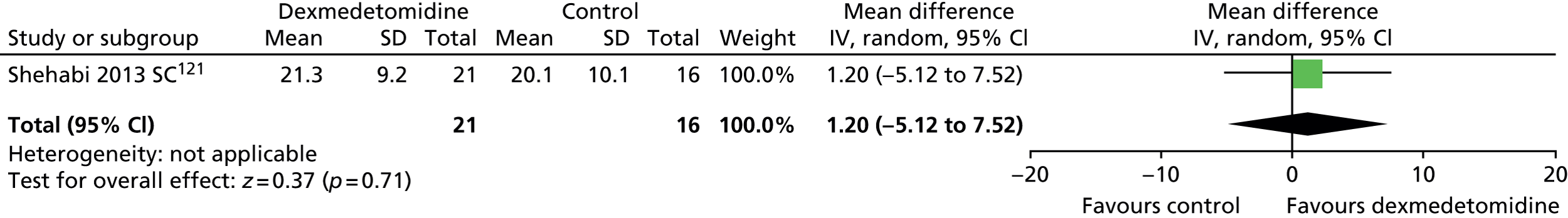
Ventilator-free days
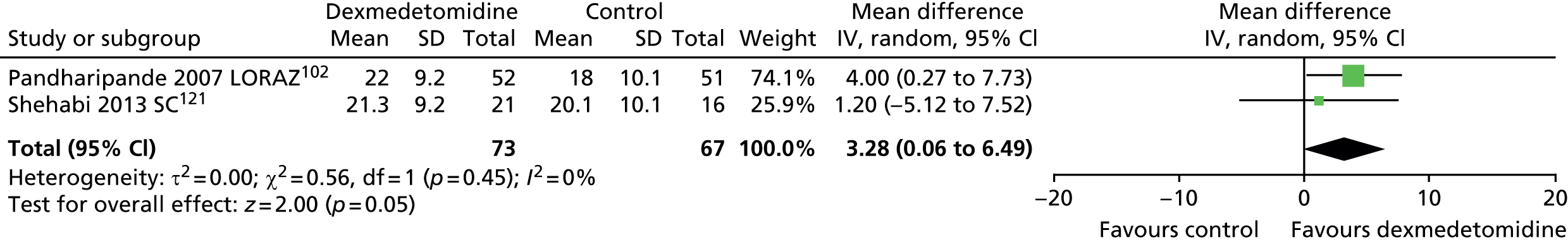
One trial provided suitable data for ventilator-free days (Figure 8). 121 There was no evidence of a statistically significant difference (mean difference 1.20, 95% CI –5.12 to 7.52; p = 0.71) between patients who received dexmedetomidine and those who received standard care (propofol or midazolam).
FIGURE 8.
Meta-analysis for ventilator-free days. IV, inverse variance; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
When all available data suitable for the analysis were considered (including transformed and imputed data) (Figure 9), the mean difference was 3.28 ventilator-free days (95% CI 0.06 to 6.49 ventilator-free days, I2 = 0%; p = 0.046) favouring dexmedetomidine.
FIGURE 9.
Meta-analysis for ventilator-free days: all available data (including transformed and imputed data). df, degrees of freedom; IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
Intensive care unit length of stay
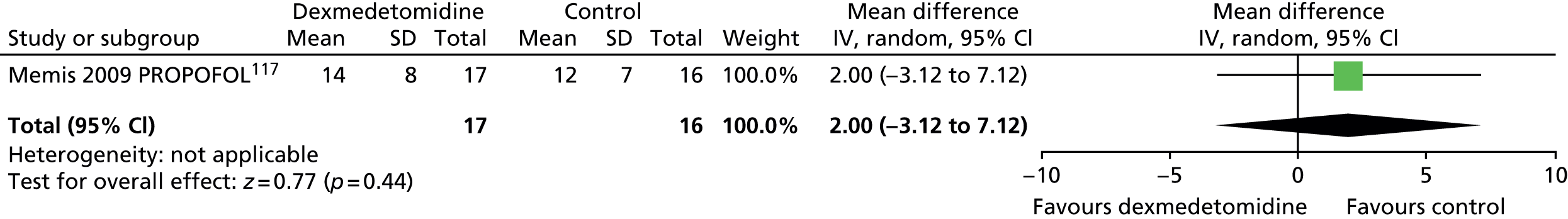
One trial provided mean length of ICU stay data (Figure 10). 117 There was no evidence of a significant difference between sedative agents (mean difference 2.00 days, 95% CI –3.12 to 7.12 days; p = 0.44).
FIGURE 10.
Meta-analysis for ICU length of stay. IV, inverse variance; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine.
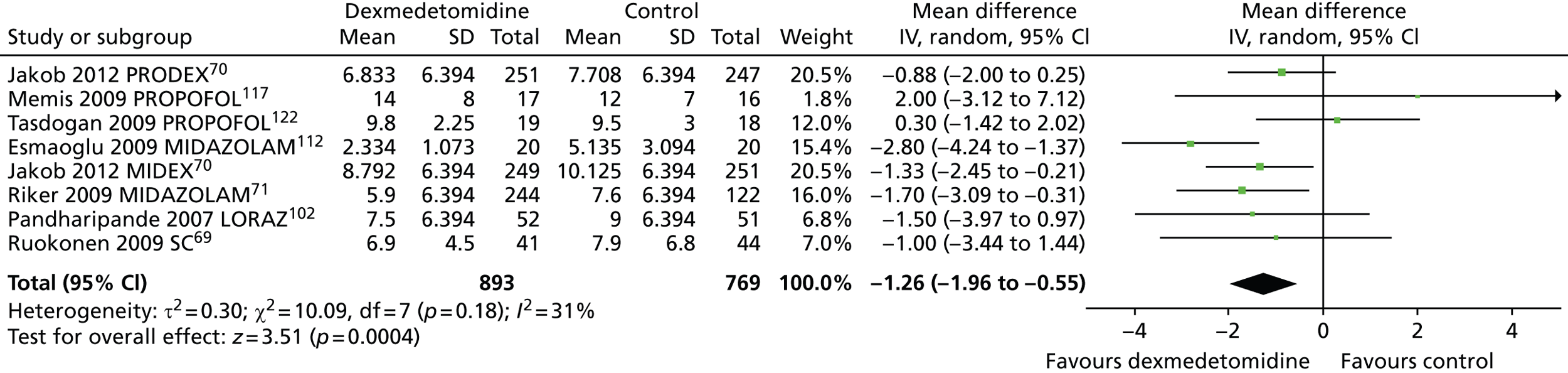
However, Figure 11 shows that when all available data suitable for the analysis were considered (including transformed and imputed data), ICU length of stay was significantly shorter among patients who received dexmedetomidine than among those who received an alternative sedative agent (mean difference –1.26 days, 95% CI –1.96 to –0.55 days, I2 = 31%; p = 0.0004).
FIGURE 11.
Meta-analysis for ICU length of stay: all available data (including transformed and imputed data). IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
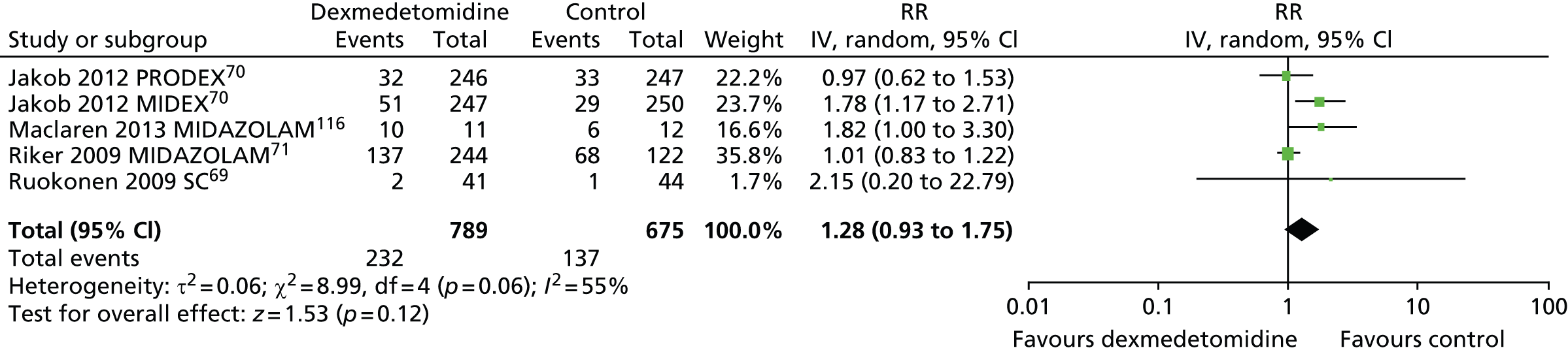
Hypotension
Five trials provided suitable data to assess the incidence of hypotension (Figure 12). 69–71,116 There were no statistically significant differences between participants who received dexmedetomidine (232 out of 789, 29%) and those who received an alternative sedative agent (137 out of 675, 20%) (RR 1.28, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.75, I2 = 55%; p = 0.12).
FIGURE 12.
Meta-analysis for incidence of hypotension. IV, inverse variance; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
The proportion of patients who developed hypotension was reported in two trials that assessed patients after elective surgery. 110,114 No statistically significant differences were found. In one trial,110 35 out of 43 patients who received dexmedetomidine experienced severe hypotension, compared with 31 out of 46 of those who received propofol (p = 0.132). In the other trial,114 hypotension occurred in 36 out of 148 (24%) participants who received dexmedetomidine and in 24 out of 147 (16%) participants who received propofol (p = 0.111).
Hypertension
Three trials reported the incidence of hypertension during sedation (Figure 13). 70,71 There was no evidence of statistically significant differences (RR 1.09, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.33, I2 = 21%; p = 0.43) between dexmedetomidine (211 out of 737, 29%) and alternative sedative agents (143 out of 619, 23%).
FIGURE 13.
Meta-analysis for incidence of hypertension. IV, inverse variance; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine.
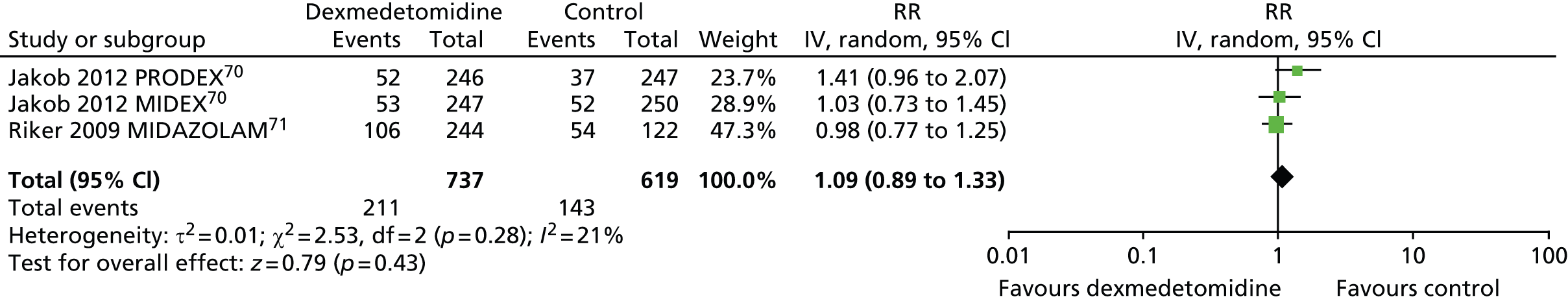
In one trial, in which patients were sedated after elective coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery,114 hypertension occurred more frequently among patients who received dexmedetomidine than among those who received propofol (p = 0.018).
Bradycardia
Six trials assessed the incidence of bradycardia during sedation (Figure 14). 69–71,102,116 Significantly more participants who received dexmedetomidine (189 out of 841, 22%) experienced bradycardia than those who received alternative sedative agents (70 out of 726, 10%) (RR 1.88, 95% CI 1.28 to 2.77, I2 = 46%; p = 0.001).
FIGURE 14.
Meta-analysis for incidence of bradycardia. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
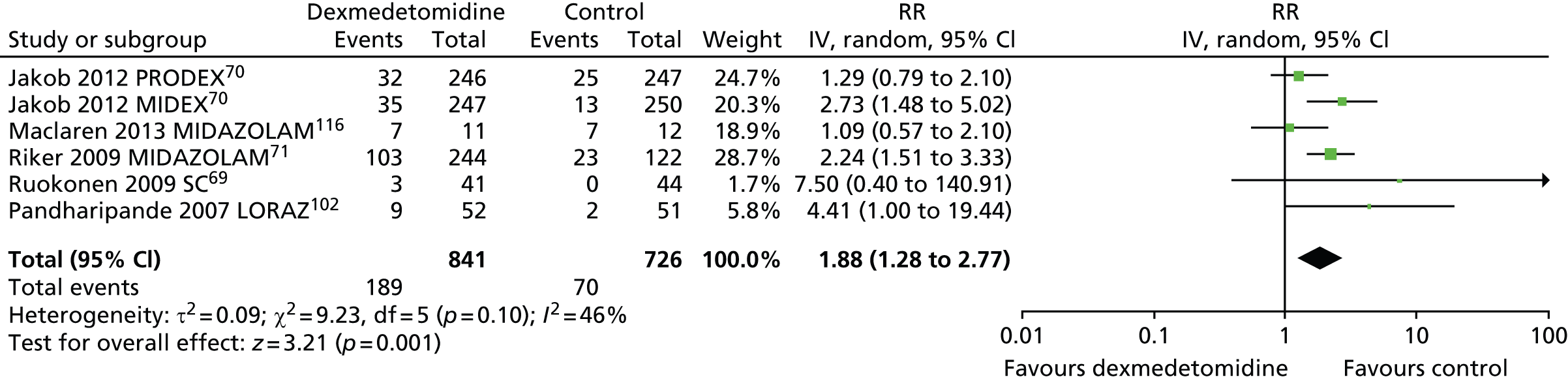
In one trial, which enrolled patients after elective coronary artery bypass graft surgery,114 the frequency of bradycardia was similar between intervention groups [5 out of 148 (3%) in the dexmedetomidine group, compared with 2 out of 147 (1%) in the propofol group; p = 0.448].
Delirium
Seven trials reported the proportion of patients who experienced episodes of delirium during sedation. 69–71,102,116,121 A total of 234 out of 862 (27%) participants who received dexmedetomidine and 209 out of 742 (28%) participants who received an alternative sedative agent experienced delirium (Figure 15). The difference between sedatives was not statistically significant (RR 0.83, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.06, I2 = 60%; p = 0.14). Statistical heterogeneity was observed among trials (I2 = 60%).
FIGURE 15.
Meta-analysis for incidence of delirium. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.

Two trials, which enrolled patients after elective surgery, reported the proportion of patients with episodes of delirium. 72,110 In one trial,110 the number of patients with episodes of delirium was similar in both intervention groups (1 out of 43 in the dexmedetomidine group compared with 1 out of 46 in the propofol group). In the other trial,72 the incidence of delirium was 10% (4 out of 40) among patients who received dexmedetomidine, 44% (16 out of 36) among those who received propofol and 44% (17 out of 40) for those who received midazolam.
Self-extubation
Four trials reported episodes of self-extubation during sedation (Figure 16). 70,102,121 Self-extubation occurred in 12 out of 566 (2%) of patients who received dexmedetomidine and 3 out of 564 (< 1%) of those who received an alternative sedative agent. There was no clear evidence of a statistically significant difference between sedative interventions (RR 2.95, 95% CI 0.96 to 9.06, I2 = 0%; p = 0.06).
FIGURE 16.
Meta-analysis for episodes of self-extubation. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
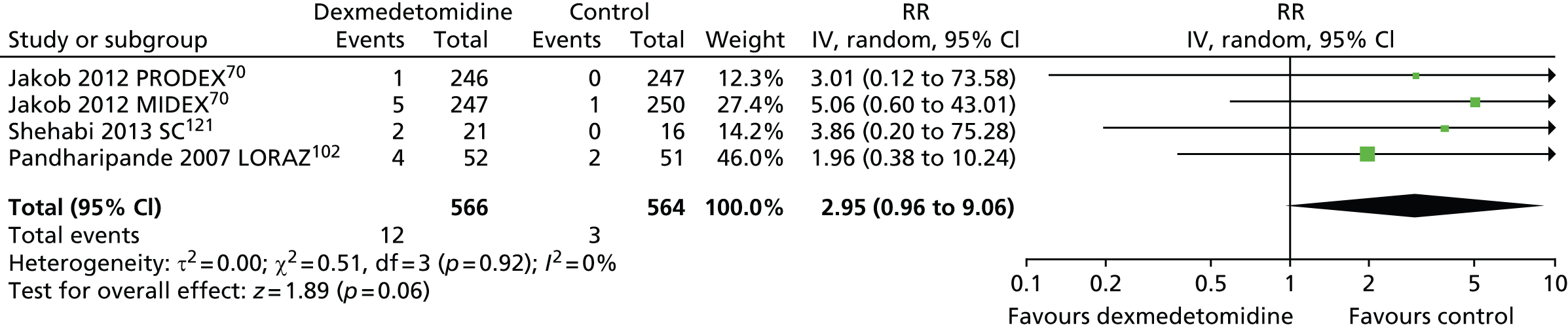
One trial, which assessed patients after elective surgery,110 reported one episode of self-extubation among participants who received propofol (1 out of 46) and none among those who received dexmedetomidine (0 out of 43).
Tachycardia
Five trials assessed the incidence of tachycardia among patients receiving sedation (Figure 17). 70,71,102,116 There was no evidence of a significant difference (RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.63 to 1.39; p = 0.73) between sedative interventions [187 out of 800 (23%) of those who received dexmedetomidine compared with 178 out of 682 (26%) of those who received alternative sedative agents]. Substantial statistical heterogeneity was observed among trials (I2 = 82%).
FIGURE 17.
Meta-analysis for incidence of tachycardia. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine.

Rate of respiratory depression
Rate of respiratory depression was not reported by any of the included trials. However, respiratory rate was reported by two trials. 109,120 In both trials, no significant differences were observed between sedatives. One trial109 recorded mean breaths per minute of 28 (SD 4 breaths per minute), 28 (SD 3 breaths per minute) and 29 (SD 4 breaths per minute) among patients who received dexmedetomidine and 29 (SD 3 breaths per minute), 30 (SD 3 breaths per minute) and 30 (SD 4 breaths per minute) among those who received propofol at 2 hours, 4 hours and 6 hours after infusion of study drug, respectively. The other trial120 reported mean respiratory rate per minute pre and post operatively. For patients who received dexmedetomidine, the pre- and post-operative values were 16.53 (SD 3.83) and 17.07 (SD 3.47) breaths per minute, whereas for those who received propofol the values were 17.25 (SD 3.58) and 20 (SD 4.0) breaths per minute, respectively.
Incidence of coma
One trial assessed the incidence of coma during a 12-day evaluation period. 102 Significantly fewer patients who received dexmedetomidine (63%) than those who received lorazepam (92%) experienced coma (p < 0.001).
Secondary outcomes and other reported outcomes
It is worth noting that no data were available from the included trials for extubation readiness, discharge readiness and quality of life.
Duration of weaning
Two trials reported duration of weaning. 69,114 Ruokonen and colleagues69 did not observe any difference (p = 0.27) between patients who received dexmedetomidine (median 59.4 hours) and those who received propofol and/or midazolam (median 78 hours). Similarly, Herr and colleagues,114 who enrolled patients after elective surgery, found that there was no difference between sedative interventions in median times to weaning. Median time to the start of weaning was 259 minutes (25th–75th percentiles 215–410 minutes) for dexmedetomidine and 300 minutes (25th–75th percentiles 210–482 minutes) for propofol.
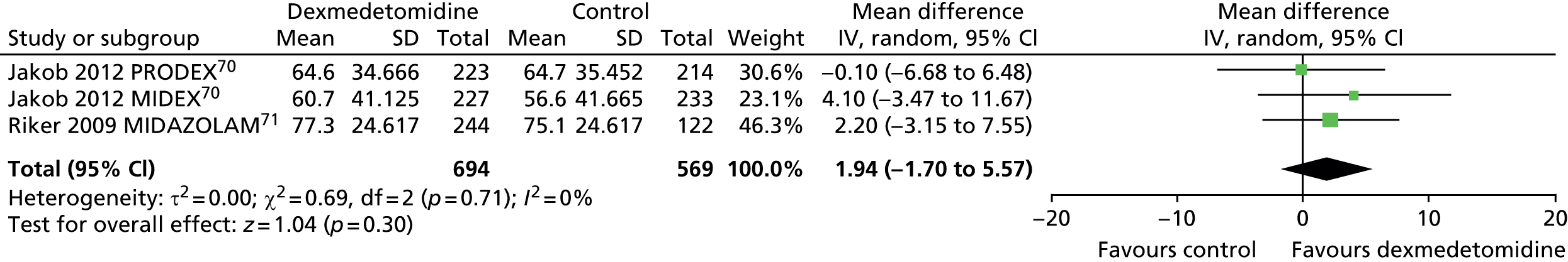
Time in target sedation range
Three trials provided data on percentage of total time in target sedation range (Figure 18). 70,71 There was no evidence of a significant difference between sedative interventions (mean difference 1.94% of total time in target sedation range, 95% CI –1.70 to 5.57% of total time in target sedation range, I2 = 0%).
FIGURE 18.
Meta-analysis for time in target sedation range. IV, inverse variance; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine.
Similarly, Figure 19 shows that no significant differences were evident between dexmedetomidine and alternative sedative agents (mean difference 2.53% of total time in target sedation range, 95% CI –0.82 to 5.87% of total time in target sedation range, I2 = 0%; p = 0.14) when all available data suitable for the analysis (including transformed and imputed data) were considered.
FIGURE 19.
Meta-analysis for time in target sedation range: all available data (including transformed and imputed data). IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
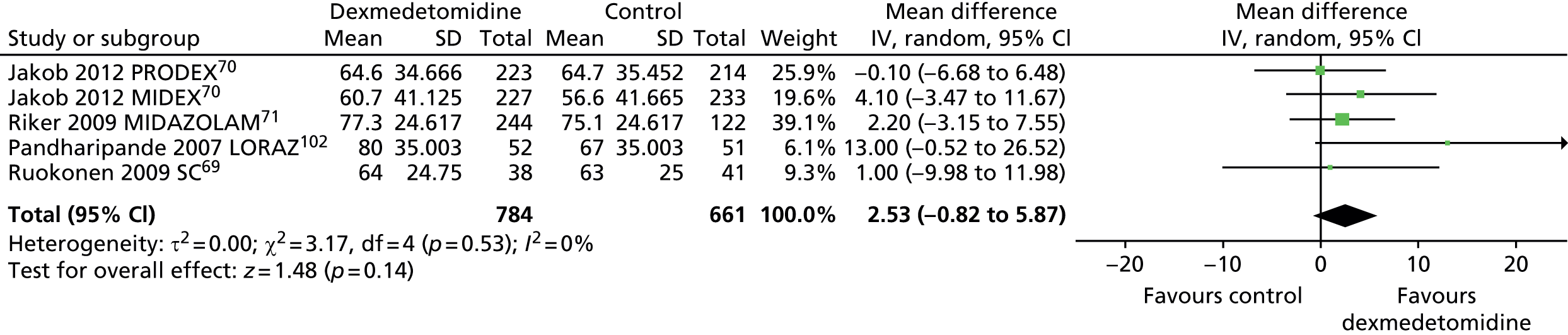
Two trials, which enrolled patients after elective surgery, assessed time in target sedation range. 111,123 Both trials showed that the proportion of time spent at adequate depth of sedation was similar for sedative interventions (46.3% for dexmedetomidine and 49.1% for propofol in one trial,123 and 93% for dexmedetomidine and 92% for propofol in the other trial). 111
Hospital length of stay
Three trials reported overall length of hospital stay and did not find any significant difference between dexmedetomidine and alternative sedative interventions. 70,121 In the MIDEX trial, the median duration of study hospital stay was 35 days (range 14–45 days) for dexmedetomidine and 27 days (range 17–45 days) for midazolam (p = 0.370). In the PRODEX trial, the median duration of study hospital stay was 25 days (range 13–45 days) for dexmedetomidine and 28 days (range 14–45 days) for propofol (p = 0.760). 70 Shehabi and collegues121 reported a median of 16.1 days (interquartile range 9.3–33.3 days) for dexmedetomidine and 17 days (interquartile range 4.0–29.0 days) for standard sedative treatments (p = 0.49).
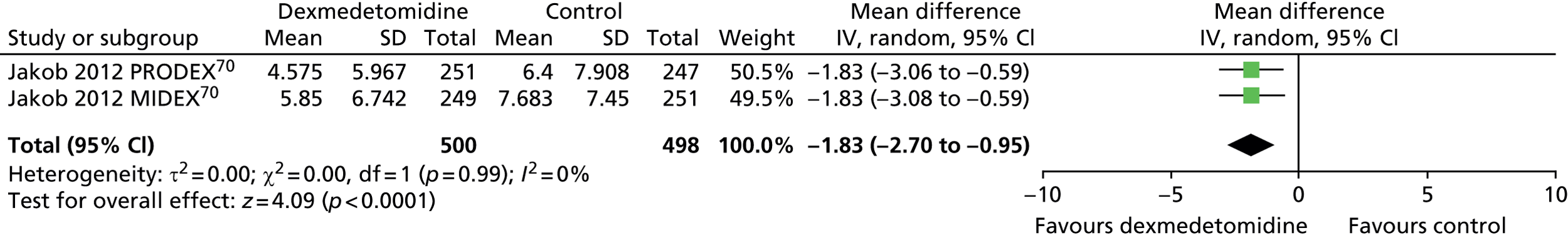
Time to extubation
Two trials reported time to extubation (Figure 20). 70 Time to extubation was significantly shorter among patients who received dexmedetomidine than among those who received an alternative sedative agent (mean difference –1.83 days, 95% CI –2.70 to –0.95 days, I2 = 0%; p < 0.0001).
FIGURE 20.
Meta-analysis for time to extubation. IV, inverse variance.
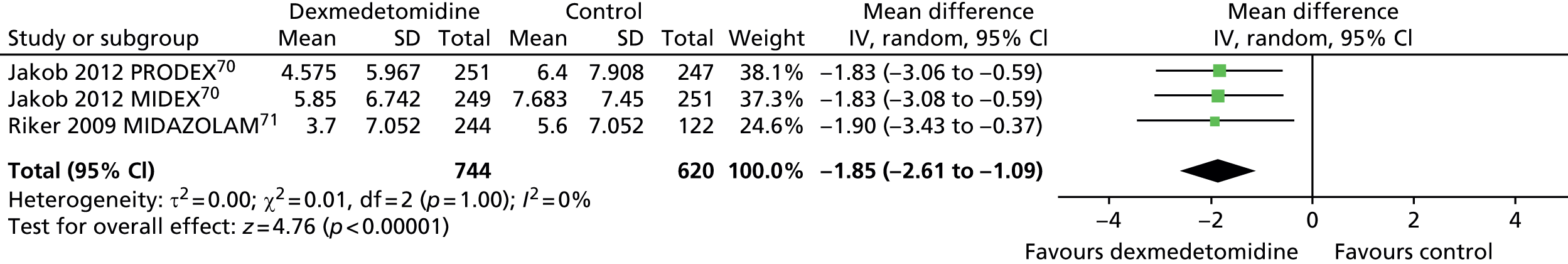
Similarly, time to extubation was significantly shorter for patients who received dexmedetomidine than for those who received an alternative sedative agent (Figure 21) when all available data suitable for the analysis (including transformed and imputed data) were considered (mean difference –1.85 days, 95% CI –2.61 to –1.09 days, I2 = 0%; p < 0.00001).
FIGURE 21.
Meta-analysis for time to extubation: all available data (including transformed and imputed data). IV, inverse variance; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine.
Three trials, which enrolled patients after elective surgery, assessed time to extubation. 111,114,123 All three trials showed that times to extubation were similar between sedative interventions. Elbaradie and colleagues111 reported mean times to extubation of 30 minutes (SD 15 minutes) for dexmedetomidine compared with 35 minutes (SD 12 minutes) for propofol. Herr and colleagues114 reported median times to extubation of 410 minutes (25th–75th percentiles 310 to 584 minutes) for dexmedetomidine and 462 minutes (25th–75th percentiles 323–808 minutes) for propofol. In the trial by Venn and Grounds,123 mean extubation times were 29 minutes (range 15–50 minutes) for dexmedetomidine and 28 minutes (range 20–50 minutes) for propofol (p = 0.63).
Cost of care
Three trials71,72,102 reported costs related to sedation. The trial by Pandharipande and colleagues, published in 2007,102 reported median costs of US$4675 for dexmedetomidine and US$2335 for lorazepam. The median total hospital cost was approximately US$22,500 higher, but not significantly higher, for dexmedetomidine. This difference was attributed to costs that occurred prior to enrolment and randomisation.
The trial by Maldonado and colleagues, published in 2009,72 reported an average total cost for post-operative care of US$7025 for dexmedetomidine, compared with US$9875 and US$9570 for propofol and midazolam, respectively. There were no significant differences between sedative interventions. For patients who developed delirium, the average cost was US$12,965, compared with an average cost of US$6763 for those who did not (p = 0.004).
The SEDCOM trial by Riker and colleagues, published in 2009,71 reported overall economic costs (expressed in Canadian dollars) of CA$7022 for dexmedetomidine and of CA$7680 for midazolam; medication costs of CA$1929.57 for dexmedetomidine and CA$180.10 for midazolam; costs associated with delirium of CA$2127.49 for dexmedetomidine and CA$3012.30 for midazolam; and MV costs were CA$2938.62 for dexmedetomidine and CA$4447.64 for midazolam.
Co-operation and communication
In four multicentre trials with a total of 1461 patients69–71 that compared dexmedetomidine with midazolam or propofol, secondary efficacy outcomes included nurses’ assessment of arousal, co-operation and ability to communicate pain using visual analogue scales. In all four trials,69–71 patients who received dexmedetomidine were significantly more arousable, more co-operative and better able to communicate their pain than those who received an alternative sedative agent (propofol or midazolam) (p ≤ 0.001 in all cases).
Neuropsychological testing
In the trial by Pandharipande and colleagues102 (103 patients in total), neuropsychological tests were administered within 72 hours of discharge from the ICU. A higher proportion of patients who received dexmedetomidine (42%), but not significantly higher, were able to complete the post-ICU neuropsychological testing than those who received lorazepam (31%) (p = 0.61). The median Mini-Mental State Examination score, which evaluates global cognitive ability, was 28 for dexmedetomidine and 27 for lorazepam (p = 0.23), whereas the median Trails-B scores, which assesses motor speed and attention functions corrected for age and level of education, were 18 for dexmedetomidine and 19 for lorazepam (p = 0.75).
Anxiety and depression
The trial by MacLaren and colleagues116 assessed the rates of post-ICU anxiety, depression and acute stress disorder manifestations among 23 mechanically ventilated patients admitted to ICUs. Validated assessment scales were administered 72 hours after extubation but before hospital discharge. Eight patients in each intervention group (midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine) completed the questionnaires. Manifestations of anxiety and depression were similar between sedative interventions. Five patients (62.5%) who received dexmedetomidine and one patient (12.5%) who received midazolam manifested acute stress disorder (p = 0.063).
Memory of intensive care unit experience
Three trials provided information on patients’ ICU recall. 110,116,123 MacLaren and colleagues,116 who assessed a total of 23 patients, reported that the median number of ICU experiences remembered by patients who received dexmedetomidine was significantly higher than that of patients who received midazolam (18.5 compared with 8.5; p = 0.015).
Venn and Grounds123 enrolled a total of 20 patients after elective surgery and assessed recall 48–72 hours after discharge from ICUs. The majority of patients who received dexmedetomidine remembered their length of stay in ICU accurately, compared with those who received propofol (8 out of 10 compared with 2 out of 10 remembered their length of stay in the ICU; p = 0.023), but few remembered the duration of MV (3 out of 10 compared with 2 out of 10). Sleeping difficulty and noise were more often reported by patients who received propofol and discomfort on the ventilator by those who received dexmedetomidine. No patient recorded pain.
Corbett and colleagues,110 who enrolled a total of 89 patients after elective surgery, evaluated patients’ perception regarding their ICU experience. A validated questionnaire was administered after ICU discharge [mean time between discharge and administration of 46.5 hours (SD 24.5 hours) for dexmedetomidine and 45.5 hours (SD 20.7 hours) for propofol; p = 0.847]. Level of overall awareness as a marker to amnesia was similar between sedative interventions as well as the overall level of discomfort and pain. Participants who received dexmedetomidine perceived a significantly shorter length of intubation than those who received propofol (p = 0.044). Perceptions in length of stay were similar between patient groups (p = 0.767). Patients who received dexmedetomidine reported greater difficulty in resting or sleeping than those who received propofol (p = 0.051).
Subgroup analyses
We were able to perform subgroup analyses of primary and secondary outcomes according to type of comparator (see Appendix 7). Generally, results of subgroup analyses were consistent with those of the overall population. However, subgroups were usually too small to provide reliable conclusions and caution should be applied in their interpretation.
No subgroup analyses were possible for age, severity of disease, different duration of MV, type of clinical setting and nurse/patient ratio because of the paucity of suitable data.
Duration of MV was significantly longer for participants treated with dexmedetomidine than for those treated with propofol, but it was significantly shorter than for those who received standard care. There were no differences between participants who received dexmedetomidine and those who received midazolam. Overall, duration of MV was significantly different across the various subgroups. A high level of heterogeneity was evident in the analyses (I2 = 78.1%).
Incidence of delirium was significantly lower in participants treated with dexmedetomidine than among those treated with propofol or midazolam. There were no differences between participants treated with dexmedetomidine than for those treated with standard care or lorazepam. Overall, there were significant differences in the incidence of delirium across the comparator subgroups and there was evidence of high heterogeneity (I2 = 76.9%). The incidence of tachycardia was significantly lower for participants treated with propofol than for those treated with dexmedetomidine. There were no differences between participants who received dexmedetomidine and those who received midazolam or lorazepam. Overall, there were significant differences in the incidence of tachycardia between the comparator subgroups and, again, there was evidence of substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 77.6%).
Table 3 presents an overview of all meta-analyses results including both main analyses and subgroup analyses.
| Outcome or subgroup | Number of studies | Number of participants | RR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | 9 | 1692 | 1.02 (0.85 to 1.24) |
| Propofol | 3 | 578 | 0.86 (0.60 to 1.23) |
| Midazolam | 3 | 889 | 1.11 (0.82 to 1.50) |
| Standard care | 2 | 122 | 1.62 (0.76 to 3.43) |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 103 | 0.63 (0.30 to 1.33) |
| Duration of MV | 4 | 1120 | –0.30 (–1.70 to 1.11) |
| Propofol | 2 | 535 | a0.84 (0.11 to 1.57)** |
| Midazolam | 1 | 500 | –0.88 (–2.65 to 0.88)** |
| Standard care | 1 | 85 | a–2.36 (–4.62 to –0.10)** |
| Ventilator-free days | 2 | 140 | 3.28 (0.06 to 6.49)b |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 103 | 4.00 (0.27 to 7.73)a |
| Standard care | 1 | 37 | 1.20 (–5.12 to 7.52) |
| ICU length of stay | 8 | 1662 | –1.26 (–1.96 to –0.55)* |
| Propofol | 3 | 568 | –0.40 (–1.41 to 0.61) |
| Midazolam | 3 | 906 | –1.86 (–2.71 to –1.01) |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 103 | –1.50 (–3.97 to 0.97) |
| Standard care | 1 | 85 | –1.00 (–3.44 to 1.44) |
| Hypotension | 5 | 1464 | 1.28 (0.93 to 1.75) |
| Propofol | 1 | 493 | 0.97 (0.62 to 1.53) |
| Midazolam | 3 | 886 | 1.41 (0.90 to 2.22) |
| Standard care | 1 | 85 | 2.15 (0.20 to 22.79) |
| Hypertension | 3 | 1356 | 1.09 (0.89 to 1.33) |
| Propofol | 1 | 493 | 1.41 (0.96 to 2.07) |
| Midazolam | 2 | 863 | 1.00 (0.82 to 1.22) |
| Bradycardia | 6 | 1567 | 1.88 (1.28 to 2.77)* |
| Propofol | 1 | 493 | 1.29 (0.79 to 2.10)a |
| Midazolam | 3 | 886 | 1.94 (1.20 to 3.13) |
| Standard care | 1 | 85 | 7.50 (0.40 to 140.91) |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 103 | 4.41 (1.00 to 19.44)c |
| Delirium | 7 | 1604 | 0.83 (0.65 to 1.06) |
| Propofol | 1 | 493 | a0.50 (0.26 to 0.98)** |
| Midazolam | 3 | 886 | a0.71 (0.61 to 0.82)** |
| Standard care | 2 | 122 | 1.44 (0.86 to 2.41)** |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 103 | 0.96 (0.79 to 1.16)** |
| Self-extubation | 4 | 1130 | 2.95 (0.96 to 9.06) |
| Propofol | 1 | 493 | 3.01 (0.12 to 73.58) |
| Midazolam | 1 | 497 | 5.06 (0.60 to 43.01) |
| Standard care | 1 | 37 | 3.86 (0.20 to 75.28) |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 103 | 1.96 (0.38 to 10.24) |
| Tachycardia | 5 | 1482 | 0.93 (0.63 to 1.39) |
| Propofol | 1 | 493 | a1.72 (1.12 to 2.65)** |
| Midazolam | 3 | 886 | 0.71 (0.47 to 1.07)** |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 103 | 0.95 (0.74 to 1.22)** |
| Time in target sedation range | 5 | 1445 | 2.53 (–0.82 to 5.87) |
| Propofol | 1 | 437 | –0.10 (–6.68 to 6.48) |
| Midazolam | 2 | 826 | 2.83 (–1.53 to 7.20) |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 103 | 13.00 (–0.52 to 26.52) |
| Standard care | 1 | 79 | 1.00 (–9.98 to 11.98) |
| Time to extubation | 3 | 1364 | –1.85 (–2.61 to –1.09)* |
| Propofol | 1 | 498 | –1.83 (–3.06 to –0.59)a |
| Midazolam | 2 | 866 | –1.86 (–2.83 to –0.89)a |
Chapter 4 Discussion
Statement of principal findings
The purpose of this assessment was to systematically review the available evidence of the effects of alpha-2 agonists (dexmedetomidine and clonidine) compared with alternative sedative agents in UK ICU clinical practice. We included evidence from published RCTs comparing (1) dexmedetomidine with clonidine, or (2) dexmedetomidine or clonidine with propofol or benzodiazepines in critically ill adults admitted to ICUs who required MV. Relevant RCTs were identified through comprehensive literature searches. We considered the following primary outcomes: mortality, duration of MV, ventilator-free days, length of ICU stay and adverse events (e.g. hypotension, hypertension, bradycardia, delirium or coma). We also considered the following secondary outcomes: time spent in target sedation range, length of hospital stay, extubation readiness, discharge readiness, duration of weaning, quality of life and economic costs. When possible, outcome data across included trials were statistically combined in a formal meta-analysis.
Clinical effectiveness
This assessment is based on evidence from 18 RCTs with a total of 2489 critically ill mechanically ventilated ICU patients. Only 1 of the 18 identified trials compared dexmedetomidine directly with clonidine, while the remaining trials assessed the effects and safety of dexmedetomidine compared with propofol or compared with benzodiazepines (i.e. midazolam or lorazepam). Not all trials provided data for the assessment of all primary and secondary outcomes under consideration. Clinical heterogeneity among trials was mostly because of type of patient population (e.g. general ICU patients and patients admitted to ICU following elective surgical); type of comparator treatment (i.e. propofol, midazolam or lorazepam); type of outcome measures; and length of follow-up. Overall, trials were at high or unclear risk of bias.
Clonidine compared with dexmedetomidine
Srivastava and colleagues5 assessed 70 patients on short-term MV in ICUs and showed that target sedation was achieved in a higher number of patients treated with dexmedetomidine with a lesser need for additional sedation. Haemodynamic/cardiovascular parameters appeared to be more stable among patients who received dexmedetomidine than among those who received clonidine.
Clonidine does not currently have a UK marketing authorisation for use as a sedative agent in ICUs and there is no recommendation or consensus on best dose regimen for sedation. Nevertheless, the recent findings of the UK national survey conducted by the ICNARC (Sheila Harvey, ICNARC, 2014) among 235 adult general ICUs have shown that around one-third of the units (32.7%) reported very frequent use of clonidine while 10.3% reported very frequent use of dexmedetomidine. Occasional use of clonidine was reported by 60.3% of the units, with only 3.7% indicating that it was never used.
Clonidine compared with propofol or benzodiazepines (i.e. midazolam or lorazepam)
No trials of clonidine compared with alternative sedative agents were identified in the included studies.
Propofol or benzodiazepines (i.e. midazolam or lorazepam) compared with dexmedetomidine
Seventeen trials compared the effects of dexmedetomidine with an alternative sedative agent other than clonidine. Nine trials (1134 patients) assessed propofol compared with dexmedetomidine, four trials (939 patients) compared midazolam with dexmedetomidine, one trial (118 patients) compared both propofol and midazolam with dexmedetomidine (three treatment arms), two trials (122 patients) compared ‘standard care’ (i.e. propofol and/or midazolam) with dexmedetomidine (i.e. propofol and/or midazolam) and one trial (106 patients) compared lorazepam with dexmedetomidine.
When all available data were combined in meta-analyses, length of ICU stay and time to extubation were significantly shorter among patients who received dexmedetomidine than among those who received an alternative sedative agent (see Figures 11 and 21). In contrast, we did not observe a significant reduction in duration of MV or ventilator-free days with the use of dexmedetomidine. A reduction in ICU length of stay has been reported consistently in recently published systematic reviews,10,66,73,74,126 while results for other efficacy outcomes have not. Pasin and colleagues,73 in line with our findings, observed a reduction in time to extubation. Chen and colleagues74 demonstrated a significant reduction in the duration of MV after dexmedetomidine while Tan and Ho,66 Xia and colleagues10 and Zhuo and colleagues126 did not. It is worth noting that the inclusion/exclusion criteria and number of assessed studies varied considerably among these previous systematic reviews.
In line with the findings of a recent systematic review that has assessed how outcomes are defined in clinical trials of mechanically ventilated adults and children,127 we found that outcome sets and especially measures of ventilator dependence (e.g. duration of MV, ventilation-free days and time to extubation) differed among included trials. In particular, we observed a considerable variation among trials with regard to outcome definitions, measurement criteria and time of assessment.
The proportion of time spent in adequate sedation range was not different between sedative interventions (see Figure 19), indicating that dexmedetomidine was as effective as common sedative agents.
With regard to the incidence of adverse events, the results of our meta-analyses show an increased risk of bradycardia after dexmedetomidine compared with alternative sedative agents (see Figure 14), but no evidence of an increased risk of hypotension, hypertension or tachycardia. However, bradycardia did not impact negatively on mortality, which showed no evidence of differences between sedative interventions (see Figure 5). In most of the trials that contributed to the meta-analyses, bradycardia required relatively standard intervention and rarely interruption of treatment. Riker and colleagues,71 for example, stated that bradycardia required titration or interruption in 4.9% of the treated patients. Similarly, Ruokonen and colleagues69 indicated that 4.8% of the patients discontinued dexmedetomidine because of bradycardia. Moreover, akin to the findings of the meta-analysis by Tan and Ho,66 bradycardia in our assessment was not observed to be accompanied by an increased risk of hypotension.
We did not observe a reduced risk of delirium among patients treated with dexmedetomidine. However, delirium was not consistently defined in the included studies, different tools were used for its assessment and most trials excluded patients with pre-existing neurological conditions and substance abuse. These inconsistencies across trials may have contributed to the observed level of statistical heterogeneity. In the literature, the systematic reviews by Pasin and colleagues73 and by Zhuo and colleagues126 have suggested a lower incidence of delirium for dexmedetomidine. It is worth noting, however, that the meta-analysis conducted by Pasin and colleagues73 demonstrated a reduced risk for dexmedetomidine compared with other sedative agents when all clinical settings were considered, but not when only trials based on general ICU settings were analysed (p = 0.05). Moreover, their analyses were not limited to mechanically ventilated patients but included all patients admitted to ICUs and statistical heterogeneity was evident in all the analyses. In addition, the systematic reviews by Chen and colleagues74 and by Tan and Ho66 did not show any clear beneficial effect of dexmedetomidine in reducing the risk of delirium.
We observed more episodes of self-extubation among patients treated with dexmedetomidine; however, we could not find clear evidence of a difference between sedative interventions (see Figure 16).
There were not enough data to assess the incidence of coma reliably.
Subgroup analyses according to type of comparator were generally consistent with those of the overall population. However, subgroups were usually too small to provide reliable conclusions.
Only limited data were available for duration of weaning and length of hospital stay, and no data were available for extubation readiness, discharge readiness and quality of life.
Overall, across trials, patients treated with dexmedetomidine were reported to be more arousable, more co-operative and better able to communicate than those who received alternative sedative agents (four trials).
A cost-minimisation analysis conducted by Dasta and colleagues,128 on the results of the Riker and colleagues’ trial,71 showed that compared with midazolam, sedation with dexmedetomidine resulted in significantly lower total ICU costs, mainly resulting from reduced length of ICU stay and lower MV costs.
Uncertainties from the assessment
This assessment was conducted according to current methodological standards and the methods were specified a priori in a research protocol, which was informed by an advisory group established for the purpose of this assessment. In particular, we performed comprehensive literature searches of the major electronic databases and we contacted experts in the field to identify all existing relevant evidence. We reviewed all potential eligible studies for inclusion and assessed their methodological quality using the best recommended risk-of-bias tool. We developed specific data extraction forms on prespecified outcome parameters and data extraction was performed by one reviewer and chekced by a second reviewer. Despite all these efforts, there is still the possibility that some relevant evidence may have been missed. Furthermore, we need to acknowledge the following limitations:
-
This assessment provides mainly evidence on the use of dexmedetomidine as sedative agent in ICUs. The evidence on the effects of clonidine in ICUs was scant (only one trial comparing clonidine with dexmedetomidine was identified in our included studies). Nevertheless, one-third of UK ICUs have reported frequent or very frequent use of clonidine and nearly two-thirds have reported occasional or rare use of clonidine to sedate critically ill adults (Sheila Harvey, ICNARC, 2014). Clonidine appears to be used off-label and evidence regarding its effectiveness and safety profile is clearly needed.
-
The included trials were clinically heterogeneous. In particular, patient populations, comparator interventions, dose of sedative agents, length of follow-up assessments, and choice and definitions of outcome measures varied considerably across trials.
-
The overall risk of bias was high or unclear in the majority of included trials. Only four trials were judged to be at low risk of bias. In particular, blinding of outcome assessors was reported in only 5 of the 18 included trials.
-
Length of follow-up after discharge from ICUs varied among included trials. Apart from one trial in which survivors were followed up for 1 year after discharge from ICUs, none of the remaining trials reported the long-term outcomes of patients receiving dexmedetomidine (generally, length of follow-up ranged from 24 to 72 hours in most trials).
-
Units of measurement, especially for continuous data, varied considerably among trials. This required data transformation and imputation, and it hampered our ability to combine data across trials reliably.
-
Subgroup analyses according to type of comparator were not very informative as subgroups were too small. There were not enough data to perform subgroup analyses according to type of patient population, which is likely to impact on the effects of sedation (e.g. elective ICU setting compared with general ICU setting).
-
There was substantial variation in the choice and definitions of outcome measures among included trials. No trials reported information on extubation readiness, discharge readiness or quality of life.
-
A number of trials and, in particular, all the largest included trials excluded patients with bradycardia and hypotension. This may impact on the generalisability of our findings.
-
In two large multicentre trials (MIDEX and PRODEX, with a total of 1001 patients), discontinuation because of a lack of efficacy was observed significantly more frequently among patients treated with dexmedetomidine. However, patients in these trials received standard sedation prior to randomisation and this may have potentially masked the benefits of dexmedetomidine because a change of sedative drug (from that received prior to randomisation) might have negatively affected the subsequent efficacy of dexmedetomidine.
Chapter 5 Conclusions
This assessment summarised evidence from 18 RCTs, including data from 2489 patients. Data were available to make summary conclusions about several aspects of the use of dexmedetomidine; however, the methodological quality of identified evidence was variable, with many studies at high or unclear risk of bias. Evidence on the use of clonidine as a sedative agent in ICUs was limited. Dexmedetomidine was observed to be as effective as propofol and commonly used benzodiazepines (i.e. midazolam and lorazepam) in ensuring an adequate light sedation level of critically ill, mechanically ventilated adults admitted to ICUs. Compared with propofol and benzodiazepines, dexmedetomidine was also observed to be effective in reducing the ICU length of stay and time to extubation.
Use of dexmedetomidine, however, was associated with an increased risk of bradycardia but not of overall mortality. There was not enough evidence to assess the risk of coma and not clear evidence of a reduced risk of delirium.
Implications for health care
-
Dexmedetomidine was observed to be effective in reducing the ICU length of stay and time to extubation. Use of dexmedetomidine, however, was associated with an increased risk of bradycardia, but not of overall mortality.
-
Owing to the observed heterogeneity among included trials with regard to patients’ characteristics, clinical setting, doses of sedative agents, outcome measures and length of follow-up, our results need to be interpreted with caution and may not be easily generalisable. Moreover, all included trials enrolled adult patients. Therefore, our findings cannot be generalised to paediatric ICU populations.
-
Many trials excluded patients with bradycardia, hypotension, liver disease and neurological conditions and, therefore, we do not know the full effects of dexmedetomidine in these categories of patients.
-
Most of the included trials have reported only short-term outcomes and, therefore, the long-term effects of the use of dexmedetomidine for ICU patients are still to be fully established.
-
Only a few trials included DSI within their study protocol. It is possible that the effects of dexmedetomidine are different when DSIs are implemented in ICU practice.
Recommendations for research
The main gap in the current evidence is the dearth of RCTs comparing clonidine with dexmedetomidine, as well as clonidine with traditional alternative sedative agents (propofol and midazolam).
Larger well-designed RCTs are needed:
-
To assess the use of clonidine as main sedative agent.
-
To define which subgroups of ICU patients are more likely to benefit from dexmedetomidine as main sedative agent. The two main subgroups of interest are patients who require short-term sedation after elective surgery and general critically ill patients who require long-term sedation.
-
To assess the effects of alpha-2 agonists in children admitted to ICUs. This would need to include dose-ranging trials, as different weight-based doses may be required in this patient population.
Future trials should be multicentre, use proper blinding procedures (in particular blinding of outcome assessors), include a common set of relevant outcome measures, define how outcomes will be measured, use validated instruments to assess the level of sedation and the incidence of events such as delirium and coma, assess long-term effects of alpha-2 agonists and include a full economic evaluation.
With regard to the choice of relevant outcome measures, time to extubation, duration of MV, length of ICU stay and incidence of delirium, bradycardia and hypotension are most relevant from an ICU perspective. On the basis of our observed data, mortality remains important but less so as the primary outcome of interest in future trials. Moreover, future trials should assess patients’ ability to communicate with health-care personnel as well as patients’ perspective of quality of sedation (e.g. perception of pain and discomfort, anxiety and memories of ICU experience).
Ideally, future trials should consider the core outcome set for ventilation studies that is currently under development as part of the COMET (Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials) initiative. 129
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Lara Kemp for her secretarial support, to Pawana Sharma for her assistance in the study selection process and to Craig Ramsay for his comments on the research protocol and for providing support and advice for this assessment.
Contributions of authors
Moira Cruickshank (Research Fellow) led the day-to-day running of the assessment, reviewed the evidence on the clinical effectiveness of the sedative interventions under investigation and drafted the first version of this report.
Lorna Henderson (Medical Statistician) contributed to data extraction, interpretation of results and conducted all statistical analyses with supervision from Graeme MacLennan (senior statistician).
Cynthia Fraser (Senior Information Officer) was responsible for running the literature searches, obtaining full-text papers and compiling the reference list of the report.
Marion Campbell (Director of the Health Services Research Unit) provided content expertise and guidance, contributed to the interpretation of results and commented on the draft version of this report.
Bronagh Blackwood (Senior Lecturer) and Anthony Gordon (Clinical Senior Lecturer and Consultant, Critical Care Medicine) provided expert advice, contributed to the interpretation of results and commented on the draft version of this report.
Miriam Brazzelli (Senior Research Fellow) oversaw and co-ordinated all aspects of the assessment, led and co-ordinated the expert advisory group participation, interpreted data and contributed to draft the first version of this report.
All authors approved the final version of the report.
Data sharing statement
All available data and information have been included within this report or added as appendices.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Safe Sedation Practice for Healthcare Procedures: Standards and Guidance. London: Academy of Medical Royal Colleges; 2013.
- Adams R, Brown GT, Davidson M, Fisher E, Mathisen J, Thomson G, et al. Efficacy of dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam for sedation in adult intensive care patients: a systematic review. Br J Anaesth 2013;111:703-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bja/aet194.
- Aitken LM, Bucknall T, Kent B, Mitchell M, Burmeister E, Keogh SJ. Protocol-directed sedation versus non-protocol-directed sedation to reduce duration of mechanical ventilation in mechanically ventilated intensive care patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd009771.
- Mehta S, McCullagh I, Burry L. Current sedation practices: lessons learned from international surveys. Crit Care Clin 2009;25:471-88. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2009.04.001.
- Srivastava VK, Agrawal S, Kumar S, Mishra A, Sharma S, Kumar R. Comparison of dexmedetomidine, propofol and midazolam for short-term sedation in postoperatively mechanically ventilated neurosurgical patients. J Clin Diag Res 2014;8:GC04-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.7860/jcdr/2014/8797.4817.
- Sydow M, Neumann P. Sedation for the critically ill. Intens Care Med 1999;25:634-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s001340050917.
- Ostermann ME, Keenan SP, Seiferling RA, Sibbald WJ. Sedation in the intensive care unit: a systematic review. JAMA 2000;283:1451-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.283.11.1451.
- Rhoney DH, Murry KR. National survey of the use of sedating drugs, neuromuscular blocking agents, and reversal agents in the intensive care unit. J Intens Care Med 2003;18:139-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0885066603251200.
- Tate JA, Devito DA, Hoffman LA, Milbrandt E, Happ MB. Anxiety and agitation in mechanically ventilated patients. Qual Health Res 2012;22:157-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1049732311421616.
- Xia ZQ, Chen SQ, Yao X, Xie CB, Wen SH, Liu KX. Clinical benefits of dexmedetomidine versus propofol in adult intensive care unit patients: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Surg Res 2013;185:833-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2013.06.062.
- Patel SB, Kress JP. Sedation and analgesia in the mechanically ventilated patient. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2012;185:486-97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201102-0273CI.
- Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, Ely EW, Gelinas C, Dasta JF, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 2013;41:263-306. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182783b72.
- Reade MC, Finfer S. Sedation and delirium in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med 2014;370:444-54. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1208705.
- Pun BT, Dunn J. The sedation of critically ill adults: part 1: assessment. The first in a two-part series focuses on assessing sedated patients in the ICU. Am J Nurs 2007;107:40-8.
- Roberts DJ, Haroon B, Hall RI. Sedation for critically ill or injured adults in the intensive care unit: a shifting paradigm. Drugs 2012;72:1881-916. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/11636220-000000000-00000.
- Carrasco G. Instruments for monitoring intensive care unit sedation. Crit Care 2000;4:217-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc697.
- Ramsay MA, Savege TM, Simpson BR, Goodwin R. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone. Br Med J 1974;2:656-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.2.5920.656.
- Ely EW, Truman B, Shintani A, Thomason JW, Wheeler AP, Gordon S, et al. Monitoring sedation status over time in ICU patients: reliability and validity of the Richmond Agitation–Sedation Scale (RASS). JAMA 2003;289:2983-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.22.2983.
- Sessler CN, Gosnell MS, Grap MJ, Brophy GM, O’Neal PV, Keane KA, et al. The Richmond Agitation–Sedation Scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;166:1338-44. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.2107138.
- Riker RR, Picard JT, Fraser GL. Prospective evaluation of the Sedation–Agitation Scale for adult critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 1999;27:1325-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199907000-00022.
- Khan BA, Guzman O, Campbell NL, Walroth T, Tricker J, Hui SL, et al. Comparison and agreement between the Richmond Agitation–Sedation Scale and the Riker Sedation–Agitation Scale in evaluating patients’ eligibility for delirium assessment in the ICU. Chest 2012;142:48-54. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-2100.
- Whitehouse T, Snelson C, Grounds M. Intensive Care Society Review of Best Practice for Analgesia and Sedation in Critical Care. London: Intensive Care Society; 2014.
- Karamchandani K, Rewari V, Trikha A, Batra RK. Bispectral index correlates well with Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients. J Anesth 2010;24:394-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00540-010-0915-4.
- Struys MM, Jensen EW, Smith W, Smith NT, Rampil I, Dumortier FJ, et al. Performance of the ARX-derived auditory evoked potential index as an indicator of anesthetic depth: a comparison with bispectral index and hemodynamic measures during propofol administration. Anesthesiology 2002;96:803-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200204000-00006.
- Jackson DL, Proudfoot CW, Cann KF, Walsh TS. The incidence of sub-optimal sedation in the ICU: a systematic review. Crit Care 2009;13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc8212.
- Brook AD, Ahrens TS, Schaiff R, Prentice D, Sherman G, Shannon W, et al. Effect of a nursing-implemented sedation protocol on the duration of mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med 1999;27:2609-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199912000-00001.
- De Jonghe B, Bastuji-Garin S, Fangio P, Lacherade JC, Jabot J, Appere-De-Vecchi C, et al. Sedation algorithm in critically ill patients without acute brain injury. Crit Care Med 2005;33:120-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000150268.04228.68.
- de Wit M, Gennings C, Jenvey WI, Epstein SK. Randomized trial comparing daily interruption of sedation and nursing-implemented sedation algorithm in medical intensive care unit patients. Crit Care 2008;12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc6908.
- Kollef MH, Levy NT, Ahrens TS, Schaiff R, Prentice D, Sherman G. The use of continuous i.v. sedation is associated with prolongation of mechanical ventilation. Chest 1998;114:541-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.114.2.541.
- Jackson JC, Girard TD, Gordon SM, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, Thomason JW, et al. Long-term cognitive and psychological outcomes in the awakening and breathing controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;182:183-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200903-0442OC.
- Kress JP, Pohlman AS, O’Connor MF, Hall JB. Daily interruption of sedative infusions in critically ill patients undergoing mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1471-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200005183422002.
- Kress JP, Gehlbach B, Lacy M, Pliskin N, Pohlman AS, Hall JB. The long-term psychological effects of daily sedative interruption on critically ill patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003;168:1457-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200303-455OC.
- Samuelson KA, Lundberg D, Fridlund B. Light vs. heavy sedation during mechanical ventilation after oesophagectomy – a pilot experimental study focusing on memory. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2008;52:1116-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01702.x.
- Shehabi Y, Bellomo R, Reade MC, Bailey M, Bass F, Howe B, et al. Early intensive care sedation predicts long-term mortality in ventilated critically ill patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2012;186:724-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201203-0522OC.
- Burry L, Rose L, McCullagh IJ, Fergusson DA, Ferguson ND, Mehta S. Daily sedation interruption versus no daily sedation interruption for critically ill adult patients requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd009176.pub2.
- Mehta S, Burry L, Cook D, Fergusson D, Steinberg M, Granton J, et al. Daily sedation interruption in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients cared for with a sedation protocol: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012;308:1985-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.13872.
- Schweickert WD, Gehlbach BK, Pohlman AS, Hall JB, Kress JP. Daily interruption of sedative infusions and complications of critical illness in mechanically ventilated patients. Crit Care Med 2004;32:1272-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000127263.54807.79.
- Sessler CN, Pedram S. Protocolized and target-based sedation and analgesia in the ICU. Crit Care Clin 2009;25:489-513. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2009.03.001.
- Girard TD, Kress JP, Fuchs BD, Thomason JW, Schweickert WD, Pun BT, et al. Efficacy and safety of a paired sedation and ventilator weaning protocol for mechanically ventilated patients in intensive care (Awakening and Breathing Controlled trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008;371:126-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60105-1.
- Augustes R, Ho KM. Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials on daily sedation interruption for critically ill adult patients. Anaesth Intens Care 2011;39:401-9.
- Strom T, Martinussen T, Toft P. A protocol of no sedation for critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation: a randomised trial. Lancet 2010;375:475-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)62072-9.
- Chanques G, Sebbane M, Barbotte E, Viel E, Eledjam JJ, Jaber S. A prospective study of pain at rest: incidence and characteristics of an unrecognized symptom in surgical and trauma versus medical intensive care unit patients. Anesthesiology 2007;107:858-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.anes.0000287211.98642.51.
- Hynes-Gay P, Leo M, Molino-Carmona S, Tessler J, Wong C, Burry L, et al. Optimizing sedation and analgesia in mechanically ventilated patients – an evidence-based approach. Dynamics 2003;14:10-3.
- Novaes MA, Aronovich A, Ferraz MB, Knobel E. Stressors in ICU: patients’ evaluation. Intens Care Med 1997;23:1282-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s001340050500.
- Pang PS, Suen LK. Stressors in the ICU: a comparison of patients’ and nurses’ perceptions. J Clin Nurs 2008;17:2681-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2008.02280.x.
- Bernard JM, Kick O, Bonnet F. Comparison of intravenous and epidural clonidine for postoperative patient-controlled analgesia. Anesth Analg 1995;81:706-12.
- Ely EW, Shintani A, Truman B, Speroff T, Gordon SM, Harrell FE, et al. Delirium as a predictor of mortality in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit. JAMA 2004;291:1753-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.291.14.1753.
- Fosnight S. Delirium in the Elderly. Pharmacology Self-Assessment Program (PSAP) VII Geriatrics 2015. www.accp.com/docs/bookstore/psap/p7b07.sample02.pdf (accessed March 2015).
- Pandharipande P, Girard TD, Sanders RD, Thompson JL. Comparison of sedation with dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam in septic ICU patients. Crit Care 2008;12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc6496.
- Pisani MA, Murphy TE, Van Ness PH, Araujo KL, Inouye SK. Characteristics associated with delirium in older patients in a medical intensive care unit. Arch Intern Med 2007;167:1629-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archinte.167.15.1629.
- Girard TD, Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Delirium as a predictor of long-term cognitive impairment in survivors of critical illness. Crit Care Med 2010;38:1513-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181e47be1.
- Shehabi Y, Riker RR, Bokesch PM, Wisemandle W, Shintani A, Ely EW, et al. Delirium duration and mortality in lightly sedated, mechanically ventilated intensive care patients. Crit Care Med 2010;38:2311-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181f85759.
- Ely EW, Margolin R, Francis J, May L, Truman B, Dittus R, et al. Evaluation of delirium in critically ill patients: validation of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU). Crit Care Med 2001;29:1370-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200107000-00012.
- Bergeron N, Dubois MJ, Dumont M, Dial S, Skrobik Y. Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist: evaluation of a new screening tool. Intens Care Med 2001;27:859-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s001340100909.
- Srivastava U, Sarkar ME, Kumar A, Gupta A, Agarwal A, Singh TK, et al. Comparison of clonidine and dexmedetomidine for short-term sedation of intensive care unit patients. Indian J Crit Care Med 2014;18:431-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/0972-5229.136071.
- Murdoch S, Cohen A. Intensive care sedation: a review of current British practice. Intens Care Med 2000;26:922-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s001340051282.
- Reschreiter H, Maiden M, Kapila A. Sedation practice in the intensive care unit: a UK national survey. Crit Care 2008;12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc7141.
- Martin J, Heymann A, Basell K, Baron R, Biniek R, Burkle H, et al. Evidence and consensus-based German guidelines for the management of analgesia, sedation and delirium in intensive care – short version. Ger Med Sci 2010;8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3205/000091.
- Delirium: Diagnosis, Prevention and Management. NICE Clinical Guidelines CG103. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; 2010.
- Bhana N, Goa KL, McClellan KJ. Dexmedetomidine. Drugs 2000;59:262-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200059020-00012.
- Dexdor 100 Micrograms/ml Concentrate for Solution for Infusion: Summary of Product Characteristics. Leatherhead: Electronic Medicines Compendium; 2015.
- Belleville JP, Ward DS, Bloor BC, Maze M. Effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine in humans. I. Sedation, ventilation, and metabolic rate. Anesthesiology 1992;77:1125-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000542-199212000-00013.
- Triltsch AE, Welte M, von HP, Grosse J, Genahr A, Moshirzadeh M, et al. Bispectral index-guided sedation with dexmedetomidine in intensive care: a prospective, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled phase II study. Crit Care Med 2002;30:1007-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200205000-00009.
- Hoy SM, Keating GM. Dexmedetomidine: a review of its use for sedation in mechanically ventilated patients in an intensive care setting and for procedural sedation. Drugs 2011;71:1481-501. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/11207190-000000000-00000.
- Venn RM, Hell J, Grounds RM. Respiratory effects of dexmedetomidine in the surgical patient requiring intensive care. Crit Care 2000;4:302-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc712.
- Tan JA, Ho KM. Use of dexmedetomidine as a sedative and analgesic agent in critically ill adult patients: a meta-analysis. Intens Care Med 2010;36:926-39. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00134-010-1877-6.
- Dexdor (Dexmedetomidine) European Public Assessment Report (EPAR). London: European Medicines Agency; 2011.
- Precedex (Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride) Injection Labeling. Silver Spring, MD: FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; 2013.
- Ruokonen E, Parviainen I, Jakob SM, Nunes S, Kaukonen M, Shepherd ST, et al. Dexmedetomidine versus propofol/midazolam for long-term sedation during mechanical ventilation. Intens Care Med 2009;35:282-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1296-0.
- Jakob SM, Ruokonen E, Grounds RM, Sarapohja T, Garratt C, Pocock SJ, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam or propofol for sedation during prolonged mechanical ventilation: two randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2012;307:1151-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.304.
- Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D, Wisemandle W, Koura F, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: a randomized trial. JAMA 2009;301:489-99. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.56.
- Maldonado JR, Wysong A, van der Starre PJ, Block T, Miller C, Reitz BA. Dexmedetomidine and the reduction of postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery. Psychosomatics 2009;50:206-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1176/appi.psy.50.3.206.
- Pasin L, Landoni G, Nardelli P, Belletti A, Di Prima AL, Taddeo D, et al. Dexmedetomidine reduces the risk of delirium, agitation and confusion in critically ill patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2014;28:1459-66. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2014.03.010.
- Chen K, Lu Z, Xin YC, Cai Y, Chen Y, Pan SM. Alpha-2 agonists for long-term sedation during mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015;1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd010269.pub2.
- Clonidine Hydrochloride 25 Microgram Tablets. Public Assessment Report UK/H/1448/DC UK Licence Number PL 17507/0094. London: Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency; 2009.
- Catapres Ampoules: Summary of Product Characteristics. Leatherhead: Electronic Medicines Compendium; 2014.
- Bohrer H, Bach A, Layer M, Werning P. Clonidine as a sedative adjunct in intensive care. Intens Care Med 1990;16:265-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01705163.
- Pichot C, Ghignone M, Quintin L. Dexmedetomidine and clonidine: from second- to first-line sedative agents in the critical care setting?. J Intensive Care Med 2012;27:219-37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0885066610396815.
- Spies CD, Dubisz N, Neumann T, Blum S, Muller C, Rommelspacher H, et al. Therapy of alcohol withdrawal syndrome in intensive care unit patients following trauma: results of a prospective, randomized trial. Crit Care Med 1996;24:414-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199603000-00009.
- Gold MS, Redmond DE, Kleber HD. Clonidine blocks acute opiate-withdrawal symptoms. Lancet 1978;2:599-602. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(78)92823-4.
- Hall JE, Uhrich TD, Ebert TJ. Sedative, analgesic and cognitive effects of clonidine infusions in humans. Br J Anaesth 2001;86:5-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bja/86.1.5.
- Liatsi D, Tsapas B, Pampori S, Tsagourias M, Pneumatikos I, Matamis D. Respiratory, metabolic and hemodynamic effects of clonidine in ventilated patients presenting with withdrawal syndrome. Intens Care Med 2009;35:275-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1251-0.
- Metz G, Nebel B. Clonidine in severe alcohol withdrawal delirium. Fortschr Med 1983;101:1260-4.
- Jamadarkhana S, Gopal S. Clonidine in adults as a sedative agent in the intensive care unit. J Anaesth Clin Pharmacol 2010;26:439-45.
- Davies DS, Wing AM, Reid JL, Neill DM, Tippett P, Dollery CT. Pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationships of intervenous and oral clonidine. Clin Pharmacol Therap 1977;21:593-601. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cpt1977215593.
- Hart GR, Anderson RJ. Withdrawal syndromes and the cessation of antihypertensive therapy. Arch Intern Med 1981;141:1125-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archinte.1981.00340090021007.
- Farasatinasab M, Kouchek M, Sistanizad M, Goharani R, Miri M, Solouki M, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of clonidine impact on sedation of mechanically ventilated ICU patients. Iran J Pharmaceut Res 2015;14:167-75.
- Moritz RD, Machado FO, Pinto EP, Cardoso GS, Nassar SM. Evaluate the clonidine use for sedoanalgesia in intensive care unit patients under prolonged mechanical ventilation. Rev Bras Terap Intens 2008;20:24-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0103-507X2008000100004.
- Brown LA, Levin GM. Role of propofol in refractory status epilepticus. Ann Pharmacother 1998;32:1053-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1345/aph.17367.
- Kotani Y, Shimazawa M, Yoshimura S, Iwama T, Hara H. The experimental and clinical pharmacology of propofol, an anesthetic agent with neuroprotective properties. CNS Neurosci Therap 2008;14:95-106. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1527-3458.2008.00043.x.
- Marik PE. Propofol: therapeutic indications and side-effects. Curr Pharm Des 2004;10:3639-49. http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1381612043382846.
- McCallum RW. The management of esophageal motility disorders. Hosp Pract 1988;23:239-50.
- McKeage K, Perry CM. Propofol: a review of its use in intensive care sedation of adults. CNS Drugs 2003;17:235-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00023210-200317040-00003.
- Jacobi J, Fraser GL, Coursin DB, Riker RR, Fontaine D, Wittbrodt ET, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the sustained use of sedatives and analgesics in the critically ill adult. Crit Care Med 2002;30:119-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200201000-00020.
- Barr J, Egan TD, Sandoval NF, Zomorodi K, Cohane C, Gambus PL, et al. Propofol dosing regimens for ICU sedation based upon an integrated pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic model. Anesthesiology 2001;95:324-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200108000-00011.
- Bailie GR, Cockshott ID, Douglas EJ, Bowles BJ. Pharmacokinetics of propofol during and after long-term continuous infusion for maintenance of sedation in ICU patients. Br J Anaesth 1992;68:486-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bja/68.5.486.
- Ho KM, Ng JY. The use of propofol for medium and long-term sedation in critically ill adult patients: a meta-analysis. Intens Care Med 2008;34:1969-79. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1186-5.
- Diazepam 5mg/ml Solution for Injection: Summary of Product Characteristics. Leatherhead: Electronic Medicines Compendium; 2014.
- Ativan Injection: Summary of Product Characteristics. Leatherhead: Electronic Medicines Compendium; 2014.
- Midazolam 5 mg/ml Solution for Injection or Infusion: Summary of Product Characteristics. Leatherhead: Electronic Medicines Compendium; 2014.
- Bauer TM, Ritz R, Haberthur C, Ha HR, Hunkeler W, Sleight AJ, et al. Prolonged sedation due to accumulation of conjugated metabolites of midazolam. Lancet 1995;346:145-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(95)91209-6.
- Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Herr DL, Maze M, Girard TD, Miller RR, et al. Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: the MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007;298:2644-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.22.2644.
- Fraser GL, Devlin JW, Worby CP, Alhazzani W, Barr J, Dasta JF, et al. Benzodiazepine versus nonbenzodiazepine-based sedation for mechanically ventilated, critically ill adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Crit Care Med 2013;41:S30-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182a16898.
- Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 1985;13:818-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009.
- Brazzelli M, Ramsay C, Campbell M, Cruickshank M, Fraser C, MacLennan G. Sedation in Intensive Care n.d. www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.asp?ID=CRD42014014101 (accessed 14 May 2015).
- Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org/ (accessed April 2015).
- Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 2005;5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-5-13.
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta-analyses can provide accurate results. J Clin Epidemiol 2006;59:7-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.06.006.
- Abdulatif M, Hamed HM, el-Borolossy K, Teima DO. A comparative study of the use of dexmedetomidine and propofol as sedatives for mechanically ventilated patients in ICU. Egypt J Anaesth 2004;20:437-42.
- Corbett SM, Rebuck JA, Greene CM, Callas PW, Neale BW, Healey MA, et al. Dexmedetomidine does not improve patient satisfaction when compared with propofol during mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med 2005;33:940-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000162565.18193.E5.
- Elbaradie S, El Mahalawy FH, Solyman AH. Dexmedetomidine vs. propofol for short-term sedation of postoperative mechanically ventilated patients. J Egypt Natl Cancer Inst 2004;16:153-8.
- Esmaoglu A, Ulgey A, Akin A, Boyaci A. Comparison between dexmedetomidine and midazolam for sedation of eclampsia patients in the intensive care unit. J Crit Care 2009;24:551-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2009.02.001.
- Fine PG. Sedation in mechanically ventilated patients. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacotherap 2008;22.
- Herr DL, Sum-Ping ST, England M. ICU sedation after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: dexmedetomidine-based versus propofol-based sedation regimens. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2003;17:576-84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1053-0770(03)00200-3.
- Lachaine J, Beauchemin C. Economic evaluation of dexmedetomidine relative to midazolam for sedation in the intensive care unit. Can J Hosp Pharm 2012;65:103-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.4212/cjhp.v65i2.1116.
- MacLaren R, Preslaski CR, Mueller SW, Kiser TH, Fish DN, Lavelle JC, et al. A randomized, double-blind pilot study of dexmedetomidine versus midazolam for intensive care unit sedation: patient recall of their experiences and short-term psychological outcomes. J Intens Care Med 2013;30:167-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0885066613510874.
- Memis D, Kargi M, Sut N. Effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine on indocyanine green elimination assessed with LIMON to patients with early septic shock: a pilot study. J Crit Care 2009;24:603-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2008.10.005.
- Pandharipande PP, Sanders RD, Girard TD, McGrane S, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Effect of dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam on outcome in patients with sepsis: an a priori-designed analysis of the MENDS randomized controlled trial. Crit Care 2010;14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc8916.
- Riker R, Shehabi Y, Wisemandle W, Bokesch PM, Rocha MG, Bradt J. Dexmedetomidine improves outcomes for long term ICU sedation when compared to midazolam: the Sedcom study. Chest 2008;134. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.134.4_MeetingAbstracts.p34003.
- Shah PN, Dongre V, Patil V, Pandya S, Mungantiwar A, Choulwar A. Comparison of post-operative ICU sedation between dexmedetomidine and propofol in Indian population. Ind J Crit Care Med 2014;18:291-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/0972-5229.132485.
- Shehabi Y, Bellomo R, Reade MC, Bailey M, Bass F, Howe B, et al. Early goal-directed sedation versus standard sedation in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: a pilot study. Crit Care Med 2013;41:1983-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31828a437d.
- Tasdogan M, Memis D, Sut N, Yuksel M. Results of a pilot study on the effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses and intraabdominal pressure in severe sepsis. J Clin Anesth 2009;21:394-400. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2008.10.010.
- Venn RM, Grounds RM. Comparison between dexmedetomidine and propofol for sedation in the intensive care unit: patient and clinician perceptions. Br J Anaesth 2001;87:684-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bja/87.5.684.
- Venn RM, Bryant A, Hall GM, Grounds RM. Effects of dexmedetomidine on adrenocortical function, and the cardiovascular, endocrine and inflammatory responses in post-operative patients needing sedation in the intensive care unit. Br J Anaesth 2001;86:650-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bja/86.5.650.
- Takala J, Nunes S, Parviainen I, Jakob S, Kaukonen M, Shepherd S. Comparison of dexmedetomidine with propofol/midazolam in sedation of long-stay intensive care patients: a prospective randomized, controlled, multicenter trial. Crit Care 2007;11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc5583.
- Zhuo S, Zheng J, Llu B. Sedative effect of dexmedetomidine versus propofol on postoperative patients in ICU: a systematic review. Chin J Evid Based Med 2012;12:686-93.
- Blackwood B, Clarke M, McAuley DF, McGuigan PJ, Marshall JC, Rose L. How outcomes are defined in clinical trials of mechanically ventilated adults and children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014;189:886-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201309-1645PP.
- Dasta JF, Kane-Gill SL, Pencina M, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Wisemandle W, et al. A cost-minimization analysis of dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam for long-term sedation in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 2010;38:497-503. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181bc81c9.
- Blackwood B, Ringrow S, McAuley DF, Clarke M. Standardizing Reporting of Core Outcome Measures in Ventilation Studies 2012. www.comet-initiative.org/studies/details/292 (accessed April 2015).
Appendix 1 Literature search strategies
Database: EMBASE (1996 to 2014 week 45), MEDLINE without Revisions (1996 to November week 1 2014), MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations (12 November 2014)
Ovid Multifile Search URL: https://shibboleth.ovid.com/.
Date of search: 12 November 2014.
Search strategy
-
Conscious Sedation/
-
exp Respiration, Artificial/ use medf
-
exp artificial ventilation/ use emef
-
exp Critical Care/ use medf
-
Intensive Care/ use emef
-
Critical Illness/
-
(sedation or sedate?).tw.
-
((mechanical$ or artificial$) adj5 ventilat$).tw.
-
or/1-8
-
Dexmedetomidine/
-
(dexmedetomidine or dexdor or precedex or primadex or dexdomitor or mpv1440 or mpv 1440).tw,rn.
-
Clonidine/
-
(clonidine or clofenil or klofenil or m5041t or m 5041t or catapres$ or st155 or st 155).tw,rn.
-
or/10-13
-
exp clinical trial/ use emef
-
randomized controlled trial.pt.
-
controlled clinical trial.pt
-
randomization/ use emef
-
randomi?ed.ab.
-
placebo.ab.
-
drug therapy.fs.
-
randomly.ab.
-
trial.ab.
-
groups.ab.
-
or/15-24
-
exp animals/ not humans/
-
nonhuman/ not human/
-
exp child/ not exp adult/
-
(conference abstract or letter).pt.
-
25 not (26 or 27 or 28 or 29)
-
9 and 14 and 30
-
limit 30 to yr=“1999 -Current”
-
remove duplicates from 31
Science Citation Index (1999 to 13 November 2014)
Bioscience Information Service (1999 to 13 November 2014).
ISI Web of Knowledge URL: http://wok.mimas.ac.uk/.
Date of search: 13 November 2014.
Search strategy
-
(TS=critical illness) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
(TS=critical care) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
(TS=intensive care) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
(TS=(sedation or sedate*)) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
(TS=((mechanical* or artificial*) NEAR/3 ventilat*)) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
#5 OR #4 OR #3 OR #2 OR #1
-
(TS=(dexmedetomidine or dexdor or precedex or primadex or dexdomitor or mpv1440 or “mpv1440”)) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
(TS=(clonidine or clofenil or klofenil or m5041t or “m 5041t” or catapres$ or st155 or “st 155”)) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
#8 OR #7
-
#9 AND #6
-
(TS=trial*) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
(TS=randomized) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
(TS=randomised) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
(TS=randomly) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
-
#14 OR #13 OR #12 OR #11
-
#15 AND #10 Refined by: [excluding] WEB OF SCIENCE CATEGORIES: (PEDIATRICS)
Scopus (14 November 2014)
URL: www.scopus.com/home.url.
Date of search: 14 November 2014.
Search strategy
#1 (Dexmedetomidine or Clonidine).ti [In press articles].
The Cochrane Library [Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (Issue 10 October 2014), Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (Issue 11 November 2014)]
URL: www3.interscience.wiley.com/.
Date of search: 13 November 2014.
Search strategy
-
MeSH descriptor: [Conscious Sedation] explode all tree
-
MeSH descriptor: [Respiration, Artificial] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Critical Care] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Critical Illness] explode all trees
-
(sedation or sedate*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
-
((mechanical* or artificial*) near/5 ventilat*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
-
#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6
-
MeSH descriptor: [Dexmedetomidine] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Clonidine] explode all trees
-
dexmedetomidine or dexdor or precedex or primadex or dexdomitor or mpv1440 or “mpv1440”:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
-
clonidine or clofenil or klofenil or m5041t or “m 5041t” or catapres$ or st155 or “st 155”:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
-
#8 or #9 or #10 or #11
-
#7 and #12
-
MeSH descriptor: [Child] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Adult] explode all trees
-
#14 not #15
-
#13 not #16
Health Technology Assessment Database/Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination URL: http://nhscrd.york.ac.uk/welcome.htm.
Date of search: 12 November 2014.
Search strategy
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Conscious Sedation
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Respiration, Artificial EXPLODE ALL TREES
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Critical Illness
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Critical Care EXPLODE ALL TREES
-
#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR Clonidine EXPLODE ALL TREES
-
MeSH DESCRIPTOR D exmedetomidineEXPLODE ALL TREES
-
#6 OR #7
-
#5 AND #8
Clinical Trials.gov
URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct/gui/c/r.
Date of search: 15 November 2014.
Search strategy
Interventions=Dexmedetomidine or Clonidine
International Clinical Trials Registry Platform
World Health Organization URL: www.who.int/ictrp/en/.
Date of search: 15 November 2014.
Search strategy
Intervention= Dexmedetomidine or Clonidine
Appendix 2 Full-text screening form
Appendix 3 List of included studies (including secondary publications)
Abdulatif 2004
Abdulatif M, Hamed HM, el-Borolossy K, Teima DO. A comparative study of the use of dexmedetomidine and propofol as sedatives for mechanically ventilated patients in ICU. Egypt J Anaesthes 2004;20:437–42.
Corbett 2005
Corbett SM, Rebuck JA, Greene CM, Callas PW, Neale BW, Healey MA, et al. Dexmedetomidine does not improve patient satisfaction when compared with propofol during mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med 2005;33:940–5.
Elbaradie 2004
Elbaradie S, El Mahalawy FH, Solyman AH. Dexmedetomidine vs. propofol for short-term sedation of postoperative mechanically ventilated patients. J Egypt Nat Cancer Inst 2004;16:153–8.
Esmaoglu 2009
Esmaoglu A, Ulgey A, Akin A, Boyaci A. Comparison between dexmedetomidine and midazolam for sedation of eclampsia patients in the intensive care unit. J Crit Care 2009;24:551–5.
Herr 2003
Herr DL, Sum-Ping ST, England M. ICU sedation after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: dexmedetomidine-based versus propofol-based sedation regimens. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesthes 2003;17:576–84.
Jakob 2012
Jakob SM, Ruokonen E, Grounds RM, Sarapohja T, Garratt C, Pocock SJ, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam or propofol for sedation during prolonged mechanical ventilation: two randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2012;307:1151–60.
MacLaren 2013
MacLaren R, Preslaski CR, Mueller SW, Kiser TH, Fish DN, Lavelle JC, et al. A randomized, double-blind pilot study of dexmedetomidine versus midazolam for intensive care unit sedation: patient recall of their experiences and short-term psychological outcomes. J Intensive Care Med 2013;30:167–75.
Maldonado 2009
Maldonado JR, Wysong A, van der Starre PJ, Block T, Miller C, Reitz BA. Dexmedetomidine and the reduction of postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery. Psychosomatics 2009;50:206–17.
Memis 2009
Memis D, Kargi M, Sut N. Effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine on indocyanine green elimination assessed with LIMON to patients with early septic shock: a pilot study. J Crit Care 2009;24:603–8.
Pandharipande 2007
Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Herr DL, Maze M, Girard TD, Miller RR, et al. Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: the MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007;298:2644–53.
Secondary reports
Pandharipande PP, Sanders RD, Girard TD, McGrane S, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Effect of dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam on outcome in patients with sepsis: an a priori-designed analysis of the MENDS randomized controlled trial. Crit Care 2010;14:R38.
Fine PG. Sedation in mechanically ventilated patients. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother 2008;22:15.
Riker 2009
Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D, Wisemandle W, Koura F, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: a randomized trial. JAMA 2009;301:489–99.
Secondary reports
Lachaine J, Beauchemin C. Economic evaluation of dexmedetomidine relative to midazolam for sedation in the intensive care unit. Can J Hosp Pharm 2012;65:103–10.
Shehabi Y, Riker RR, Bokesch PM, Wisemandle W, Shintani A, Ely EW, et al. Delirium duration and mortality in lightly sedated, mechanically ventilated intensive care patients. Crit Care Med 2010;38:2311–18.
Riker R, Shehabi Y, Wisemandle W, Bokesch PM, Rocha MG, Bradt J. Dexmedetomidine improves outcomes for long term ICU sedation when compared to midazolam: the Sedcom study. Chest 2008;134:34003s.
Ruokonen 2009
Ruokonen E, Parviainen I, Jakob SM, Nunes S, Kaukonen M, Shepherd ST, et al. Dexmedetomidine versus propofol/midazolam for long-term sedation during mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Med 2009;35:282–90.
Secondary report
Takala J, Nunes S, Parviainen I, Jakob S, Kaukonen M, Shepherd S. Comparison of dexmedetomidine with propofol/midazolam in sedation of long-stay intensive care patients: a prospective randomized, controlled, multicenter trial. Crit Care 2007;11:P423.
Shah 2014
Shah PN, Dongre V, Patil V, Pandya S, Mungantiwar A, Choulwar A. Comparison of post-operative ICU sedation between dexmedetomidine and propofol in Indian population. Ind J Crit Care Med 2014;18:291–6.
Shehabi 2013
Shehabi Y, Bellomo R, Reade MC, Bailey M, Bass F, Howe B, et al. Early goal-directed sedation versus standard sedation in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: a pilot study. Crit Care Med 2013;41:1983–91.
Srivastava 2014
Srivastava U, Sarkar ME, Kumar A, Gupta A, Agarwal A, Singh TK, et al. Comparison of clonidine and dexmedetomidine for short-term sedation of intensive care unit patients. Ind J Crit Care Med 2014;18:431–6.
Tasdogan 2009
Tasdogan M, Memis D, Sut N, Yuksel M. Results of a pilot study on the effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses and intraabdominal pressure in severe sepsis. J Clin Anesth 2009;21:394–400.
Venn 2001
Venn RM, Grounds RM. Comparison between dexmedetomidine and propofol for sedation in the intensive care unit: patient and clinician perceptions. Br J Anaesth 2001;87:684–90.
Secondary report
Venn RM, Bryant A, Hall GM, Grounds RM. Effects of dexmedetomidine on adrenocortical function, and the cardiovascular, endocrine and inflammatory responses in post-operative patients needing sedation in the intensive care unit. Br J Anaesth 2001;86:650–6.
Appendix 4 Excluded studies grouped according to the rationale for exclusion
Study not a randomised controlled trial (n = 30)
Abd Aziz N, Chue MC, Yong CY, Hassan Y, Awaisu A, Hassan J, et al. Efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine versus morphine in post-operative cardiac surgery patients. Int J Clin Pharm 2011;33:150–4.
Ahmed S, Murugan R. Dexmedetomidine use in the ICU: are we there yet? Crit Care 2013;17:320.
Akin S, Aribogan A, Arslan G. Dexmedetomidine as an adjunct to epidural analgesia after abdominal surgery in elderly intensive care patients: a prospective, double-blind, clinical trial. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 2008;69:16–28.
Anger KE, Szumita PM, Baroletti SA, Labreche MJ, Fanikos J. Evaluation of dexmedetomidine versus propofol-based sedation therapy in mechanically ventilated cardiac surgery patients at a tertiary academic medical center. Crit Pathway Cardiol 2010;9:221–6.
Barletta JF, Miedema SL, Wiseman D, Heiser JC, McAllen KJ. Impact of dexmedetomidine on analgesic requirements in patients after cardiac surgery in a fast-track recovery room setting. Pharmacotherapy 2009;29:1427–32.
Bliesener B, Kleinschmidt S. [Incidence and duration of postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery: comparison between dexmedetomidine and morphine for postoperative sedation and analgesia.] Anaesthesist 2010;59:256–7.
Brar NK. Dexmedetomidine takes on propofol and midazolam. Clin Pulm Med 2012;19:237.
Cox CE, Govert JA. Assessing the comparative value of sedatives in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 2010;38:709–11.
Curtis JA, Hollinger MK, Jain HB. Propofol-based versus dexmedetomidine-based sedation in cardiac surgery patients. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesthes 2013;27:1289–94.
Devabhakthuni S, Pajoumand M, Williams C, Kufera JA, Watson K, Stein DM. Evaluation of dexmedetomidine: safety and clinical outcomes in critically ill trauma patients. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Care 2011;71:1164–71.
Devlin JW, Al-Qadheeb NS, Chi A, Roberts RJ, Qawi I, Garpestad E, et al. Efficacy and safety of early dexmedetomidine during noninvasive ventilation for patients with acute respiratory failure: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Chest 2014;145:1204–12.
Kopel L, Carvalho RT, Araujo H-BN, Fagundes AA, Ribeiro M, Bastos J. Dexmedetomidine for sedation following cardiovascular surgery: a two different loading doses. Crit Care 2005;9:P120.
Liatsi D, Tsapas B, Pampori S, Tsagourias M, Pneumatikos I, Matamis D. Respiratory, metabolic and hemodynamic effects of clonidine in ventilated patients presenting with withdrawal syndrome. Intens Care Med 2009;35:275–81.
Martin E, Ramsay G, Mantz J, Sum-Ping ST. The role of the alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist dexmedetomidine in postsurgical sedation in the intensive care unit. J Intens Care Med 2003;18:29–41.
Mehta S, Burry L, Cook D, Fergusson D, Steinberg M, Granton J, et al. Daily sedation interruption in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients cared for with a sedation protocol: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012;308:1985–92.
Moritz RD, Machado FO, Pinto EP, Cardoso GS, Nassar SM. [Evaluate the clonidine use for sedoanalgesia in intensive care unit patients under prolonged mechanical ventilation.] Rev Brasil Terap Inten 2008;20:24–30.
Nader ND, Li CM, Dosluoglu HH, Ignatowski TA, Spengler RN. Adjuvant therapy with intrathecal clonidine improves postoperative pain in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft. Clin J Pain 2009;25:101–6.
Nour El-Din BM. Clinical evaluation of dexmedetomidine following ultra-fast track off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. Egypt J Anaesthes 2004;20:253–9.
Ozaki M, Takeda J, Tanaka K, Shiokawa Y, Nishi S, Matsuda K, et al. Safety and efficacy of dexmedetomidine for long-term sedation in critically ill patients. J Anesthes 2014;28:38–50.
Pasin L, Landoni G, Nardelli P, Belletti A, Di Prima AL, Taddeo D, et al. Dexmedetomidine reduces the risk of delirium, agitation and confusion in critically ill patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2014;28:1459–66.
Perez-Rada FJ, Franco-Calderon JL, Torres CM. Comparison of cerebral hemodynamic variables in hemorrhagic stroke using dexmedetomidine-propofol versus dexmedetomidine-midazolam. Crit Care 2009;13(Suppl. 1):P402.
Prause A, Wappler F, Scholz J, Bause H, Schulte am EJ. Respiratory depression under long-term sedation with sufentanil, midazolam and clonidine has no clinical significance. Intens Care Med 2000;26:1454–61.
Shehabi Y, Grant P, Wolfenden H, Hammond N, Bass F, Campbell M, et al. Prevalence of delirium with dexmedetomidine compared with morphine based therapy after cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial (DEXmedetomidine COmpared to Morphine – DEXCOM Study). Anesthesiology 2009;111:1075–84.
Shehabi Y, Chan L, Kadiman S, Alias A, Ismail WN, Tan MATI, et al. Sedation depth and long-term mortality in mechanically ventilated critically ill adults: a prospective longitudinal multicentre cohort study. Intens Care Med 2013;39:910–18.
Short J. Use of dexmedetomidine for primary sedation in a general intensive care unit. Crit Care Nurse 2010;30:29–38.
Spiegler P. It is time to wake up in the intensive care unit. Clin Pulmon Med 2008;15:232–3.
Tanaka LMS, Azevedo LCP, Park M, Schettino G, Nassar AP, Rea-Neto A, et al. Early sedation and clinical outcomes of mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective multicenter cohort study. Crit Care 2014;18:R156.
Triltsch AE, Welte M, von HP, Grosse J, Genahr A, Moshirzadeh M, et al. Bispectral index-guided sedation with dexmedetomidine in intensive care: a prospective, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled phase II study. Crit Care Med 2002;30:1007–14.
Venn RM, Bradshaw CJ, Spencer R, Brealey D, Caudwell E, Naughton C, et al. Preliminary UK experience of dexmedetomidine, a novel agent for postoperative sedation in the intensive care unit. Anaesthesia 1999;54:1136–42.
Wajida G, Kelly JS. Sedation in the Intensive Care Setting. In Urman RD, Kaye AD, editors. Moderate and Deep Sedation in Clinical Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012. pp. 218–29.
Participants outwith scope of review (n = 10)
Chen J, Zhou JQ, Chen ZF, Huang Y, Jiang H. Efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine versus propofol for the sedation of tube-retention after oral maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofacial Surg 2014;72:285–7.
Coull JT, Jones ME, Egan TD, Frith CD, Maze M. Attentional effects of noradrenaline vary with arousal level: selective activation of thalamic pulvinar in humans. Neuroimage 2004;22:315–22.
Goodwin HE, Gill RS, Murakami PN, Thompson CB, Lewin JJ, III, Mirski MA. Dexmedetomidine preserves attention/calculation when used for cooperative and short-term intensive care unit sedation. J Crit Care 2013;28:1113.
Huang Z, Chen YS, Yang ZL, Liu JY. Dexmedetomidine versus midazolam for the sedation of patients with non-invasive ventilation failure. Intern Med 2012;51:2299–305.
Memis-D, Lu S, Vatan I, Yandim T, Yüksel M, Süt N. Effects of midazolam and dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses and gastric intramucosal pH to sepsis, in critically ill patients. Br J Anaesth 2007;98:550–2.
Mirski MA, Lewin JJ, III, Ledroux S, Thompson C, Murakami P, Zink EK, et al. Cognitive improvement during continuous sedation in critically ill, awake and responsive patients: the Acute Neurological ICU Sedation Trial (ANIST). Intens Care Med 2010;36:1505–13.
Senoglu N, Oksuz H, Dogan Z, Yildiz H, Demirkiran H, Ekerbicer H. Sedation during noninvasive mechanical ventilation with dexmedetomidine or midazolam: a randomized, double-blind, prospective study. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 2010;71:141–53.
Srivastava VK, Agrawal S, Kumar S, Mishra A, Sharma S, Kumar R. Comparison of dexmedetomidine, propofol and midazolam for short-term sedation in postoperatively mechanically ventilated neurosurgical patients. J Clin Diag Res 2014;8:GC04–7.
Terao Y, Ichinomiya T, Higashijima U, Tanise T, Miura K, Fukusaki M, et al. Comparison between propofol and dexmedetomidine in postoperative sedation after extensive cervical spine surgery. J Anesth 2012;26:179–86.
Yu T, Huang Y, Guo F, Yang Y, Teboul JL, Qiu H. The effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine infusion on fluid responsiveness in critically ill patients. J Surg Res 2013;185:763–73.
No relevant outcomes (n = 5)
Kadoi Y, Saito S, Kawauchi C, Hinohara H, Kunimoto F. Comparative effects of propofol vs dexmedetomidine on cerebrovascular carbon dioxide reactivity in patients with septic shock. Br J Anaesth 2008;100:224–9.
Memis D, Dokmeci D, Karamanlioglu B, Turan A, Ture M. A comparison of the effect on gastric emptying of propofol or dexmedetomidine in critically ill patients: preliminary study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2006;23:700–4.
Pandharipande P, Girard TD, Sanders RD, Thompson JL. Comparison of sedation with dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam in septic ICU patients. Crit Care 2008;12(Suppl. 2):P275.
Sahin N, Kabukou H, Ozkan N, Tirtiz TA. The effects of postoperative dexmedetomidine and midazolam infusion on haemodynamics and sedation in patients after coronary artery bypass grafting. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2005;22(Suppl. 35):40.
Singh A, Ambike D, Thatte WS, Das B. Dexmedetomidine versus midazolam infusion for sedation in mechanically ventilated patients in critical care setting: A randomized controlled trial. Indian J Crit Care Med 2013;17(Suppl. 1):4.
Published as abstract only (n = 2)
Gupta R, Mehta Y, Ali T, Joby GV. A randomized controlled study to compare the efficacy and safety of prolonged sedation with dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care. Intens Care Med 2013;39.
Riker RR, Ramsay MA, Prielipp RC, Jorden V. Long-term dexmedetomidine for ICU sedation: a pilot study. Anesthesiology 2001;95.
Foreign-language article requiring translation (n = 11)
Aoki M, Nishimura Y, Baba H, Okawa Y. [Effects of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride on postoperative sedation in cardiovascular surgery.] Kyobu Geka 2006;59:1181–5.
Cerny V, Samek J, Cichy D. [Postoperative sedation with dexmedetomidine in patients after off pump coronary artery bypass.] Anesteziol Inten Med 2004;15:21–7.
Eremenko AA, Chernova EV. [Dexmedetomidine use for intravenous sedation and delirium treatment during early postoperative period in cardio-surgical patients.] Anesteziol Reanimatol 2013;5:4–8.
Eremenko AA, Chemova EV. [Comparison of dexmedetomidine and propofol for short-term sedation in early postoperative period after cardiac surgery.] Anesteziol Reanimatol 2014;2:37–41.
Fang S, Zhu Y, Xu H, Jiang H. [Dexmedetomidine for sedation during intubation period in postoperative patients receiving orthognathic surgery in intensive care unit.] Zhongguo Xinyao Yu Linchuang Zazhi 2012;31:454–7.
Iwasaki Y, Nakamura T, Hamakawa T. [Retrospective evaluation of dexmedetomidine for postoperative sedation in patients for cerebral aneurysm surgery.] Masui 2010;59:1396–9.
Kaneko T. [Postoperative management of carotid endarterectomy with dexmedetomidine – a comparison with propofol.] Masui 2008;57:696–703.
Karabulut S, Tuncel Z, Kudsioglu T, Coskun FI, Yapici N, Altuntas Y, et al. [Sedation and analgesia after cardiac surgery: comparison of dexmedetomidine, midazolam/fentanyl and midazolam/dexketoprofen trometamol.] Gogus-Kalp-Damar Anestezi ve Yogun Bakim Dernegi Dergisi 2014;20.
Moritz RD, Machado FO, Pinto EP, Cardoso GS, Nassar SM. [Evaluate the clonidine use for sedoanalgesia in intensive care unit patients under prolonged mechanical ventilation.] Revista Brasi Terap Inten 2008;20:24–30.
Wan LJ, Huang QQ, Yue JX, Lin L, Li SH. [Comparison of sedative effect of dexmedetomidine and midazolam for post-operative patients undergoing mechanical ventilation in surgical intensive care unit.] Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2011;23:543–6.
Yao L, Zhou XM, Zhao JJ. [The role of dexmedetomidine in treatment of serious patients in intensive care unit.] Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2010;22:632–4.
Unable to locate full text (n = 1)
Assad Farhat OM, Abdel-Raouf S, Hussien GZ, Labib D. Comparative study between the effects of dexmedetomidine versus propofol infusion on human neutrophil functions in cardiac surgical patients in ICU. Egypt J Anaesth 2010;26:113–22.
Appendix 5 Characteristics of included studies
| Study details | Participant characteristics | Intervention characteristics | Summary of outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| First author, year: Abdulatif, 2004109 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: NR Country: Egypt Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: randomised comparative study Randomisation method: NR Length of follow-up: 6 hours Source of funding: NR |
Type of participants: patients had established respiratory failure requiring MV using pressure support ventilation with or without continuous positive airway pressure Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Exclusion criteria: exclusion criteria included significant renal or hepatic dysfunction, cardiovascular instability, concurrent use of inotropes or vasoactive drugs, CNS or psychological disorders, use of muscle relaxants to facilitate ventilation, pregnancy or morbid obesity |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: RSS score of 2 or 3 Rescue medication: 1-mg bolus of midazolam Pain control: NR Daily interruption: NR |
Physiological parameters, clinical adverse respiratory effects |
| First author, year: Corbett, 2005110 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: USA Start/end dates: October 2002–April 2004 Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: RCT Randomisation method: via a random-number table, occurred in the operating room before sternal closure, and the drug was initiated after bypass Length of follow-up: at least 24 hours after extubation Source of funding: NR |
Type of participants: after non-emergent CABG surgery Enrolled: NR Randomised: NR Analysed:
Exclusion criteria:
|
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Rescue medication: midazolam was allowed for breakthrough anxiety, administered at 1–2 mg every hour in the propofol arm and every 2 hours in the dexmedetomidine arm Pain control: morphine was available as needed for pain every hour in a 1- to 4-mg dose for propofol patients and in a 1- to 2-mg dose for dexmedetomidine patients Daily interruption: NR |
Patient satisfaction, length of MV and ICU stay, vital signs, adverse events |
| First author, year: Elbaradie, 2004111 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: Egypt Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: randomised controlled, patient-blinded study Randomisation method: at the end of surgery, patients were selected randomly using a toss into two equal group Length of follow-up: NR Source of funding: NR |
Type of participants: after major thoracic, abdominal or pelvic cancer surgeries Enrolled: NR Randomised: 30 Analysed: NR Age (years), mean (SD):
Inclusion criteria: adult patients who were expected to require a minimum of 6-hour post-operative sedation and ventilation after major thoracic, abdominal or pelvic cancer surgeries Exclusion criteria: neurosurgical procedures, known allergy to propofol or dexmedetomidine, known or suspected pregnancy, gross obesity (over 50% above ideal bodyweight), severe hepatic or renal disease where the neurological condition was difficult to evaluate, spinal or epidural anaesthesia, history of corticosteroid therapy within the last 3 months, or uncontrolled diabetes |
ICU setting: surgical ICU Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: recorded hourly using the RSS score and continuously using the bispectral index. Three levels of sedation were considered: adequate (sedation level was grade 2, 3, 4 or 5), insufficient (sedation level was 1) and excessive (sedation level was grade 6) Rescue medication: the dose of both drugs was adjusted by varying the dose by 10% increase or decrease in infusion rate in order to maintain the level of sedation within the range previously considered adequate Pain control: all patients received short-acting fentanyl infusion 0.25–0.5 µg/kg/hour Daily interruption: NR |
Sedation, time in adequate sedation under ventilator, extubation times, blood pressure, heart rates, serum levels of cortisol and IL-6, respiratory adverse events |
| First author, year: Esmaoglu, 2009112 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: Turkey Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: RCT Randomisation method: patients were randomly divided into two groups using coin toss Length of follow-up: NR Source of funding: NR |
Type of participants: patients whose pregnancies were terminated via caesarean delivery because of eclampsia Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Exclusion criteria: chronic hypertension; cardiac, neurological, hepatic, renal, or endocrinal disease; or allergic reactions to the medicine used during the treatment or developed haemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and platelets |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
A: loading dose administered at 1 µg/kg per 20 minutes, followed by a continuous infusion at 0.7 µg/kg/hour B: loading dose of 100 mg in 100 ml 0.9% NaCl at 0.05 mg/kg and continued at 0.1 mg/kg/hour Length of infusion of study drug: NR Target sedation level: RSS score 2 or 3 criteria Rescue medication: propofol was given as a bolus (0.5 mg/kg) in both groups Pain control: fentanyl was administered in the dose of 1 µg/kg Daily interruption: NR |
Patients requiring antihypertensive, arterial pressure, ICU length of stay |
| First author, year: Herr, 2003114 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 25 Country: USA, Canada Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: multicentre, open-label, randomised study Randomisation method: randomised before surgery by sealed envelopes provided by the statistician. Investigators did not know the randomisation block size Length of follow-up: 24 hours after discharge from ICU Source of funding: NR |
Type of participants: after CABG surgery Enrolled: NR Randomised: NR Analysed:
Exclusion criteria: women who were pregnant or lactating; patients whose neurological condition or responses could be difficult to evaluate; patients who had unstable or uncontrolled diabetes, were grossly obese, had an ejection fraction of 30% or were hospitalised for a drug overdose |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Target sedation level:
Daily interruption: NR |
Efficacy of sedation of dexmedetomidine compared with propofol-based ICU sedation, total dose of morphine administered for pain by time period; time to weaning; time to extubation, adverse events |
| First author, year: Jakob, 2012; MIDEX70 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 44 Country: nine European countries Start/end dates: 2007–10 Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: Phase 3 multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial Randomisation method: by central interactive voice response system funded by the sponsor and stratified for study centre in blocks of four Length of follow-up: 45 days Source of funding: Orion Pharma, Espoo, Finland |
Type of participants: general ICU Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Exclusion criteria: acute severe neurological disorder, mean arterial pressure < 55 mmHg despite appropriate i.v. volume replacement and vasopressors, heart rate < 50 beats per minute, atrioventricular conduction grade II or III (unless pacemaker installed) and use of alpha-2 agonists or antagonists within 24 hours prior to randomisation |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Length of infusion of study drug: maximum 14 days from randomisation Target sedation level: target RASS score was determined before starting study treatment and at daily sedation stops. Assessment of RASS score was performed every 2 hours and prior to any dose of rescue therapy Rescue medication: propofol Pain control: fentanyl boluses Daily interruption: need for re-sedation and continued ventilation was assessed after a daily sedation stop and spontaneous breathing trial |
Proportion of time in the target sedation range (RASS score 0 to –3) without use of rescue therapy of the total duration of study drug infusion; duration of MV from randomisation until free from MV (including non-invasive) without reinstitution for the following 48 hours; length of ICU stay from randomisation until medically fit for discharge; nurses’ assessment of arousal, ability to co-operate with care and ability to communicate pain using VAS; adverse events and serious adverse events with incidence of > 2% in any treatment group |
| First author, year: Jakob, 2012; PRODEX70 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 33 Country: six European countries and Russia Start/end dates: 2007–10 Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: Phase 3 multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial Randomisation method: by central interactive voice response system funded by the sponsor and stratified for study centre in blocks of four Length of follow-up: 45 days Source of funding: Orion Pharma, Espoo, Finland |
Type of participants: general ICU Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Exclusion criteria: acute severe neurological disorder, mean arterial pressure < 55 mmHg despite appropriate i.v. volume replacement and vasopressors, heart rate < 50 beats per minute, atrioventricular-conduction grade II or III (unless pacemaker installed), and use of alpha-2 agonists or antagonists within 24 hours prior to randomisation |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Length of infusion of study drug: maximum 14 days from randomisation Target sedation level: target RASS score was determined before starting study treatment and at daily sedation stops. Assessment of RASS score was performed every 2 hours and prior to any dose of rescue therapy Rescue medication: midazolam Pain control: fentanyl boluses Daily interruption: need for resedation and continued ventilation was assessed after a daily sedation stop and spontaneous breathing trial |
Proportion of time in the target sedation range (RASS score 0 to –3) without use of rescue therapy of the total duration of study drug infusion; duration of MV from randomisation until free from MV (including non-invasive) without reinstitution for the following 48 hours; length of ICU stay from randomisation until medically fit for discharge; nurses’ assessment of arousal, ability to co-operate with care and ability to communicate pain using VAS; adverse events and serious adverse events with incidence > 2% in any treatment group |
| First author, year: MacLaren, 2013116 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: USA Start/end dates: September 2009–May 2012 Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: prospective, randomised, double-blind pilot study Randomisation method: within 24 hours of qualifying for daily awakenings, patients were randomised by a computer-generated random numbers table Length of follow-up: at least 72 hours after extubation or tracheostomy but before hospital discharge Source of funding: Hospira |
Type of participants: medical or surgical ICU patients Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Analysed:
Age (years), mean (SD):
Sex, n (%):
Exclusion criteria: aged < 18 years or > 85 years; administration of benzodiazepines for purposes other than sedation (e.g. seizure control); administration of neuromuscular blockers for > 12 hours; administration of epidural medications; active myocardial ischaemia; second- or third-degree heart block; haemodynamic instability; active neuromuscular disease; Child–Pugh class C liver disease; alcohol abuse within 6 months of study eligibility; baseline dementia; solid organ transplant; pregnancy; moribund state with planned withdrawal of life support; enrolment in another therapeutic study; or known or suspected severe adverse reactions to any benzodiazepines, dexmedetomidine, or clonidine |
ICU setting: medical and surgical ICUs Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: Riker SAS score 3 or 4 Rescue medication: open-label midazolam Pain control: open-label fentanyl Daily interruption: daily awakenings performed when the following conditions met: patient haemodynamically stable, patient not receiving neuromuscular blockade, and patient on 70% for fraction of inspired oxygen and 14 cmH2O for positive end-expiratory pressure |
Post-ICU anxiety, depression and acute stress disorder manifestations; recall, anxiety, depression and acute stress disorder; successful ventilator liberation (i.e. at least 72 hours of tracheal extubation); hourly and cumulative doses of conventional sedatives and analgesics; percentage of Riker scores at various sedation levels; percentage of PABS scores indicating minimal pain (≤ 3); delirium during each 12-hour nursing shift; ICU and hospital lengths of stay; hypotension, bradycardia, or tachycardia |
| First author, year: Maldonado, 200972 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: USA Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: open-label RCT Randomisation method: randomisation was performed the evening before surgery by random drawing Length of follow-up: 3 days post-operatively Source of funding: NR |
Type of participants: following cardiac valve surgery Enrolled: 179 eligible Randomised:
Analysed:
Age (years), mean (SD):
Inclusion criteria: all patients meeting inclusion and exclusion criteria admitted to a large, tertiary-care university medical centre scheduled for elective cardiac valve operations were eligible for this prospective, randomised clinical trial Exclusion criteria: pre-existing diagnosis of dementia or schizophrenia, the preoperative use of psychotropic medications, active or recent substance abuse or dependence, aged less than 18 years or older than 90 years, documented stroke within the last 6 months, evidence of advanced heart block, pregnancy or anticipated intraoperative deep hypothermic circulatory arrest |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Route/dose/frequency:
Target sedation level: RSS score of 3 before extubation and of 2 after extubation Rescue medication: for additional sedation while intubated, patients received increased doses of the drug they had been randomly assigned to Pain control: fentanyl 25–50 µg every hour as needed for pain was the only opiate used in the first 24 hours; ketorolac, hydrocodone and oxycodone were allowed for pain management after the first 24 hours Daily interruption: NR |
Proportion of patients in each treatment group who received a diagnosis of post-operative delirium, length of stay in ICU, length of stay in hospital, use of post-operative rescue medications, delirium |
| First author, year: Memis, 2009117 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: Turkey Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: RCT (pilot) Randomisation method: an independent nurse prepared sealed envelopes from a computer-generated table before the study started Length of follow-up: NR Source of funding: NR |
Type of participants: all patients fulfilled clinical and laboratory criteria of septic shock Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Exclusion criteria: known allergy to propofol or dexmedetomidine, patients with known or suspected brain death, unstable haemoglobin levels (change in haemoglobin level of > 0.5 g/dl), significant arrhythmias, acute myocardial ischaemia (continuous ST segment analysis), patients requiring continuous renal replacement therapy, pregnancy and aged < 18 years |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: RSS score of below 2 Rescue medication: NR Pain control: alfentanil was infused at 0.25–1.0 µg/kg/minute Daily interruption: NR |
Indocyanine green plasma disappearance rate, mortality, haemodynamic parameters, adverse events |
| First author, year: Pandharipande, 2007102 Secondary reports: Fine, 2008;113 and Pandharipande, 2010118 Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 2 Country: USA Start/end dates: August 2004–April 2006 Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: double-blind RCT Randomisation method: participants were randomised using computer-generated, permuted block randomisation (known only to investigational pharmacists) and stratified by site Length of follow-up: until discharge from hospital or death, and survivors were observed for vital status until 1 year after enrolment Source of funding: Hospira |
Type of participants: medical and surgical ICU patients Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Exclusion criteria: neurological disease that would confound the diagnosis of delirium, active seizures, Child–Pugh class B or C liver disease, moribund state with planned withdrawal of life support, family or physician refusal, alcohol abuse, active myocardial ischaemia, second- or third-degree heart block, severe dementia, benzodiazepine dependency, pregnancy or lactation, and severe hearing disabilities or inability to understand English to allow delirium evaluations |
ICU setting: medical and surgical ICUs Sedative agents:
Length of infusion of study drug: maximum 120 hours Target sedation level: sedation level was assessed using the RASS. Both the physician goal RASS scores and the nurse goal RASS scores were recorded twice daily at the time of the study assessments. No specific RASS score were reported Rescue medication: if 10 ml/hour of the study drug did not result in adequate sedation or if patients required frequent intermittent doses of fentanyl for pain, a continuous infusion of fentanyl was permitted. If a patient experienced sudden and urgent levels of agitation that had the potential to cause harm to the patient or staff, a propofol bolus of 25–50 mg was allowed, while the study drug or fentanyl infusions were titrated upwards Pain control: intermittent doses of fentanyl Daily interruption: the decision to perform daily cessation of sedatives and spontaneous breathing trials was considered part of the managing teams’ protocol and not mandated as part of the study protocol |
Delirium-free and coma-free days, efficacy of the two sedation regimens in achieving clinically individualised target sedation goals, lengths of stay with ventilation, in the ICU, and in the hospital, along with neuropsychological testing after ICU discharge, 28-day mortality and 12-month survival from enrolment |
| First author, year: Riker, 200971 Secondary reports: Riker, 2008;119 Shehabi, 2010;52 and Lachaine, 2012115 Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 68 Country: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, the USA and New Zealand Start/end dates: March 2005–August 2007 Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: double-blind RCT Randomisation method: central randomisation using an interactive voice-response system and computer-generated schedule Length of follow-up: 48 hours after cessation of study drug Source of funding: Hospira |
Type of participants: general ICU Enrolled:
Exclusion criteria: trauma or burns as admitting diagnoses, dialysis of all types, pregnancy or lactation, neuromuscular blockade other than for intubation, epidural or spinal analgesia, general anaesthesia 24 hours prior to or planned after the start of study drug infusion, serious central nervous system pathology (acute stroke, uncontrolled seizures, severe dementia), acute hepatitis or severe liver disease (Child–Pugh class C), unstable angina or acute myocardial infarction, left ventricular ejection fraction < 30%, heart rate < 50 beats per minute, second- or third-degree heart block, or systolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg despite continuous infusions of two vasopressors before the start of study drug infusion |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Length of infusion of study drug: until extubation or to a maximum of 30 days Target sedation level: RASS score target range of −2 to 1 Rescue medication: patients in either group not adequately sedated by study drug titration could receive open-label midazolam bolus doses of 0.01–0.05 mg/kg at 10- to 15-minute intervals until adequate sedation (RASS score of range −2 to 1) was achieved with a maximum dose of 4 mg in 8 hours Pain control: fentanyl bolus doses (0.5–1.0 µg/kg) could be administered as needed every 15 minutes Daily interruption: a daily arousal assessment was performed throughout the treatment period, during which patients within the RASS score range of −2 to 1 were asked to perform four tasks. Patients were considered awake with successful completion of the assessment when they could perform three of four tasks. If the patient’s RASS score was > 1 at the time of a scheduled assessment, study medication was titrated until a RASS score of −2 to 1 was achieved and then the arousal assessment was performed. If patients were oversedated to a RASS value of −3 to −5, study drug was interrupted until a RASS score of −2 to 0 was achieved and then the arousal assessment was performed |
Percentage of time within the target sedation range (RASS score −2 to 1) during the double-blind treatment period, prevalence and duration of delirium, use of fentanyl and open-label midazolam, nursing shift assessments, adverse events |
| First author, year: Ruokonen, 200969 Secondary reports: Takala, 2007125 Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 2 Country: Finland and Switzerland Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: multicentre, prospective, randomised, double-blind, double dummy, active comparator study Randomisation method: NR Length of follow-up: 45 days Source of funding: Orion Pharma, Helsinki, Finland |
Type of participants: general ICU Enrolled:
Exclusion criteria: acute severe neurological disorder, mean arterial pressure < 55 mmHg despite volume and vasopressors, heart rate < 50 beats per minute; atrioventricular conduction block II or III (unless pacemaker installed), hepatic Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score > 2, bilirubin > 101 µmol/l, lactation or positive pregnancy test, muscle relaxation, loss of hearing or vision, any other condition interfering with RASS assessment, use of alpha-2 agonists or antagonists at the time of randomisation |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: RASS score of 0 to –3 or RASS score of –4 Rescue medication: first-line rescue propofol for patients receiving midazolam, midazolam for those receiving propofol before randomisation; further rescue medication decided by clinician in charge Pain control: fentanyl boluses Daily interruption: need for sedation was assessed at a daily sedation stop (used routinely in all centres before the study) conducted at the same time each day. The first sedation stop was 12–36 hours after randomisation, depending on the time of randomisation |
Time at target sedation, length of ICU stay, probability of remaining on MV, adverse events |
| First author, year: Shah, 2014120 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: India Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: phase III, prospective, open, randomised, comparative Randomisation method: NR Length of follow-up: 24 hours Source of funding: Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
Type of participants: surgical patients Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Exclusion criteria: patients currently being treated or were treated within the last 30 days with alpha-2 agonist and blockers, with central nervous system, cardiovascular system, liver, renal problems, history of obstructive sleep apnoea, pregnant or lactating females, in whom propofol would be given for anaesthesia |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: RSS score of 2 or 3 Rescue medication: NR Pain control: if VAS score of > 4, analgesia (fentanyl) was given Daily interruption: NR |
Cardio respiratory parameters, laboratory parameters, adverse events |
| First author, year: Shehabi, 2013121 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 6 Country: Australia and New Zealand Start/end dates: July 2011–December 2011 Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: pilot prospective, multicentre, RCT Randomisation method: block randomisation was undertaken with concealed envelopes Length of follow-up: 90 days after randomisation Source of funding: Hospira |
Type of participants: medical, operative elective and operative emergency Enrolled: 154 Randomised:
male, 9 (56); female, 7 (44) B: male, 11 (52); female, 10 (48) Inclusion criteria: patients were included if they had been intubated within the previous 12 hours, were expected to need MV for longer than 24 hours, and required immediate and ongoing sedation Exclusion criteria: aged < 18 years; pregnancy proven or suspected primary neurological injury; a diagnosis likely to result in prolonged weakness, drug overdose, burn injury, acute liver failure, dementia, or psychiatric illness; need for ongoing neuromuscular blockade, palliative care or treatment limitations; inability to communicate in English; a mean blood pressure of < 55 mmHg; a heart rate of < 55 beats per minute; or a high-grade atrioventricular block in the absence of a functioning pacemaker |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: RASS score range of –2 to 1 unless otherwise clinically indicated Rescue medication:
Daily interruption: no |
Time to randomisation, time in light sedation range (RASS score of –2 to 1) in 48 hours after randomisation, proportion of patients treated with dexmedetomidine, propofol and midazolam, incidence of delirium and delirium-free days, ventilator-free days at 28 days, mortality at discharge from hospital and 90 days after randomisation |
| First author, year: Srivastava, 201455 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: NR Country: India Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: prospective, randomised controlled open-label study Length of randomisation method: NR Length of follow-up: 24 hours Source of funding: none |
Type of participants: general ICU Enrolled:
Exclusion criteria: pregnant females, patients with a neurological condition, central nervous system trauma, asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, haemodynamically unstable patients, known cases of conduction defects, cardiac failure, those patients with a creatinine clearance rate of < 30 ml/minute, and those requiring neuromuscular blockade and prior use of alpha-2 agonists |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: RSS score of 3 or 4 Rescue medication: i.v. diazepam bolus of 0.1 mg/kg Pain control: i.v. bolus of 20 µg of fentanyl or infusion Daily interruption: NR |
Additional sedation with diazepam, proportion of patients in target sedation range, mean maintenance infusion dose, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, adverse events |
| First author, year: Tasdogan, 2009122 Secondary reports: none Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: Turkey Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: RCT (pilot) Randomisation method: an independent nurse prepared sealed envelopes from a computer-generated table before the study started Length of follow-up: NR Source of funding: NR |
Type of participants: patients with sepsis after ileus surgery Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Exclusion criteria: known allergy to propofol or dexmedetomidine, possible or confirmed pregnancy, presence of one of the following conditions at randomisation: haemodynamic instability (defined as a systolic blood pressure of < 100 mmHg), heart failure (class III or IV of the New York Heart Association), renal failure (RIFLE classification), liver failure (manifested by a serum total protein concentration of < 3 g/dl, and total bilirubin level of > 5 mg/dl), and known or suspected brain death |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Length of infusion of study drug: 24 hours Target sedation level: RSS score of < 2 Rescue medication: NR Pain control: alfentanil was infused at 0.25–1.0 µg/kg/minutes Daily interruption: NR |
Physiological parameters, mortality, duration of MV, length of stay in ICU, adverse events |
| First author, year: Venn, 2001123 Secondary reports: Venn, 2001124 Language: English Publication type: full text Number of centres: 1 Country: UK Start/end dates: NR Prospective/retrospective data collection: prospective Study design: RCT Randomisation method: on arrival in the ICU, patients were allocated randomly, using sealed envelopes Length of follow-up: 48–72 hours after discharge from ICU Source of funding: Abbott Laboratories |
Type of participants: after surgery Enrolled: NR Randomised:
Age (years), median (IQR):
Inclusion criteria: adult patients (aged 18 years or older) admitted to the ICU after complex major abdominal or pelvic surgery and expected to require 8-hour post-operative sedation and ventilation Exclusion criteria: allergy to any of the trial drugs, pregnancy, severe hepatic disease, requirement for haemodialysis or haemofiltration, spinal or epidural anaesthesia, use of etomidate in the preceding 24 hours or a history of corticosteroid treatment in the last 3 months |
ICU setting: NR Sedative agents:
Target sedation level: RSS score of > 2 Rescue medication: no other sedative or analgesic agents were given Pain control: alfentanil was infused at 0.25–1.0 µg/kg/minutes Daily interruption: NR |
Sedation, patient experiences, haemodynamic and physiological parameters |
Appendix 6 Dosage and administration of sedative agents
| Study | Dose and frequency of study drugs | |
|---|---|---|
| Dexmedetomidine | Comparator | |
| Abdulatif et al., 2004109 | Loading dose (1 µg/kg) i.v. over 10 minutes, followed by continuous i.v. infusion (5 µg/ml) at a rate of 0.5 µg/kg/hour (0.1 ml/kg/hour) to be increased to a maximum of 1 µg/kg/hour | Propofol: i.v. infusion (10 mg/ml) starting with a dose of 1 mg/kg/hour (0.1 ml/hour) and increasing up to 2 mg/kg/hour |
| Corbett et al., 2005110 | Loading dose 1 µg/kg (actual body weight) intravenously administered over 15 minutes, followed by a 0.4 µg/kg/hour i.v. infusion | Propofol: 5 µg/kg/minute i.v. infusion titrated within the range of 0.2–0.7 µg/kg/hour or 5–75 µg/kg/minute |
| Elbaradie et al., 2004111 | Loading infusion dose of dexmedetomidine 2.5 µg/kg/hour over 10 minutes followed by maintenance infusion at a rate of 0.2–0.5 µg/kg/hour into a peripheral vein, with the dosage adjusted to achieve the desired level of sedation | Propofol: undiluted as a bolus dose of 1 mg/kg initially, followed by an infusion of 0.5–1 mg/kg/hour, with the dosage adjusted to achieve the desired level of sedation varying the dose by 10% increase or decrease in infusion rate in order to maintain the level of sedation within the range previously considered adequate |
| Esmaoglu et al., 2009112 | Loading dose 1 µg/kg per 20 minutes, followed by a continuous infusion at 0.7 µg/kg/hour | Midazolam: loading dose of 100 mg in 100 ml of 0.9% NaCl at 0.05 mg/kg and continued at 0.1 mg/kg/hour |
| Herr et al., 2003114 | Loading dose of 1.0 µg/kg over 20 minutes, followed by a maintenance infusion of 0.4 µg/kg/hour. After transfer to the ICU, the infusion rate was titrated in the range of 0.2 µg/kg/hour to 0.7 µg/kg/hour as necessary to maintain a RSS score of ≥ 3 before extubation, ≥ 2 after extubation | Propofol: no dose or rate of propofol was specified by the protocol. Investigators were told to follow their usual practice with regard to propofol-based sedation |
| Jakob et al., 201270; MIDEX | Six dose levels of each study drug covered the full dose range (dexmedetomidine, 0.2–1.4 µg/kg/hour; midazolam, 0.03–0.2 mg/kg/hour). Study treatments were infused without loading dose at a dose matching the pre-randomisation dose of midazolam for 1 hour. Thereafter, study drugs were titrated by the patient’s nurse stepwise to maintain the target RASS score | Midazolam: six dose levels of each study drug covered the full dose range (dexmedetomidine, 0.2–1.4 µg/kg per hour; midazolam, 0.03–0.2 mg/kg/hour). Study treatments were infused without loading dose at a dose matching the pre-randomisation dose of midazolam for 1 hour. Thereafter, study drugs were titrated by the patient’s nurse stepwise to maintain the target RASS score |
| Jakob et al., 201270; PRODEX | Six dose levels of each study drug covered the full dose range (dexmedetomidine, 0.2–1.4 µg/kg per hour; propofol, 0.3–4.0 mg/kg per hour). Study treatments were infused without loading dose at a dose matching the pre-randomisation dose of propofol for 1 hour. Thereafter, study drugs were titrated by the patient’s nurse stepwise to maintain the target RASS score | Propofol: six dose levels of each study drug covered the full dose range (dexmedetomidine 0.2–1.4 µg/kg per hour; propofol 0.3–4.0 mg/kg per hour). Study treatments were infused without loading dose at a dose matching the pre-randomisation dose of propofol for 1 hour. Thereafter, study drugs were titrated by the patient’s nurse stepwise to maintain the target RASS score |
| MacLaren et al., 2013116 | Dexmedetomidine was started at 0.15 µg/kg/hour and adjusted by 0.15 µg/kg/hour to a maximum of 1.5 µg/kg/hour | Midazolam: midazolam was started at 1 mg/hour and adjusted by 1 mg/hour to a maximum of 10 mg/hour. All infusions were adjusted by increments of 2 ml/hour to maintain blinding |
| Maldonado et al., 200972 | Loading dose of 0.4 µg/kg, followed by a maintenance drip of 0.2–0.7 µg/kg/hour | Propofol: propofol drip (25 µg/kg/minute–50 µg/kg/minute) Midazolam: midazolam drip (0.5 mg/hour–2 mg/hour) |
| Memis et al., 2009117 | Loading dose at 1 µg/kg over 10 minutes, followed by a maintenance dose of 0.2–2.5 µg/kg per hour into a peripheral or central vein over a 24-hour infusion | Propofol: loading dose of 1 mg/kg over 15 minutes, followed by a maintenance dose of 1–3 mg/kg per hour over a 24-hour infusion |
| Pandharipande et al., 2007102 | Started at 1 ml/hour (0.15 µg/kg per hour dexmedetomidine) and titrated by the bedside nurse to a maximum of 10 ml/hour (1.5 µg/kg/hour dexmedetomidine) | Lorazepam: started at 1 ml/hour (1 mg/hour lorazepam) and titrated by the bedside nurse to a maximum of 10 ml/hour (10 mg/hour lorazepam) |
| Riker et al., 200971 | Optional blinded loading doses (up to 1 µg/kg dexmedetomidine) could be administered at the investigator’s discretion. The starting maintenance infusion dose of the blinded study drug was 0.8 µg/kg/hour per hour for dexmedetomidine or responding to the mid-point of the allowable infusion dose range of 4 mg in 8 hours | Midazolam: optional blinded loading doses (0.05 mg/kg midazolam) could be administered at the investigator’s discretion. The starting maintenance infusion dose of blinded study drug was 0.06 mg/kg/hour for midazolam, corresponding to the mid-point of the allowable infusion dose range of 4 mg in 8 hours |
| Ruokonen et al., 200969 | Infused without a loading dose at 0.8 µg/kg/hour for 1 hour and then adjusted stepwise at 0.25, 0.5, 0.8, 1.1 and 1.4 µg/kg/hour | Propofol: infused at 2.4 mg/kg/hour for 1 hour and then adjusted stepwise at 0.8, 1.6, 2.4, 3.2 and 4.0 mg/kg/hour Midazolam: depending on standard care at time of randomisation, midazolam was given either as i.v. boluses (1–2 mg), starting at three boluses per hour for 1 hour, and thereafter one to four boluses per hour and, if not sufficient, as continuous infusion of 0.2 mg/kg/hour, or as a continuous infusion at 0.12 mg/kg/hour for 1 hour, followed by adjustments at 0.04, 0.08, 0.12, 0.16 and 0.20 mg/kg/hour. The initial dose could be reduced, if considered necessary by the treating clinician |
| Shah et al., 2014120 | Loading dose of injection with 1 µg/kg over 10 minutes, followed by a maintenance infusion of 0.2–0.7 µg/kg/hour. The rate of the maintenance infusion was adjusted to achieve the desired level of sedation | Propofol: started at 5 µg/kg/minute (0.3 mg/kg/hour). The infusion rate was increased by increments of 5–10 µg/kg/minute (0.3–0.6 mg/kg/hour) until the desired level of sedation was achieved. A minimum period of 5 minutes between adjustments was allowed for the onset of peak drug effect |
| Shehabi et al., 2013121 | Infusion at a starting dose of 1 µg/kg/hour without a loading dose. Bolus administration of dexmedetomidine was strictly prohibited owing to the risk of severe bradycardia and sinus arrest. If required, sedation could be supplemented with propofol. Dexmedetomidine infusion was administered between a minimum of 0 µg/kg/hour and maximum of 1.5 µg/kg/hour specified by the treating clinician and titrated to achieve the desired level of sedation | Midazolam and/or propofol: the primary sedative agent was at the discretion of the treating clinician and could be midazolam and/or propofol or other agents deemed necessary but not dexmedetomidine. Clonidine and remifentanil could not be administered. Selected agents could be given by infusion or boluses and titrated by bedside nurses, including cessation when necessary, to achieve the default light sedation or level of sedation deemed clinically appropriate and specified by treating clinician |
| Srivastava et al., 201455 | Loading dose of 0.7 µg/kg over a period of 10 minutes followed by maintenance of 0.2 µg/kg/hour, with dosage increments titrated up to 0.7 µg/kg/hour | Clonidine: i.v. infusion of clonidine 1 µg/kg/hour and titration was achieved with dosage increments up to 2 µg/kg/hour |
| Tasdogan et al., 2009122 | Loading dose at 1 µg/kg over 10 minutes, followed by a maintenance 0.2 to 2.5 µg/kg per hour into a peripheral or central vein over a 24-hour infusion | Propofol: loading dose of 1 mg/kg over 15 minutes, followed by a maintenance of 1 mg/kg to 3 mg/kg per hour over a 24-hour infusion |
| Venn and Grounds, 2001123 | Loading dose of dexmedetomidine was 2.5 µg/kg/hour over 10 minutes, followed by a maintenance infusion of 0.2–2.5 µg/kg/hour into a peripheral or central vein | Propofol: propofol was given undiluted as an infusion of 1–3 mg/kg/hour after a loading dose infusion of up to 1 mg/kg over 10 minutes, if required |
Appendix 7 Subgroup analyses: primary and secondary outcomes
FIGURE 22.
Meta-analysis for mortality according to type of comparator. Please note that the totals in the forest plot may be subject to minor rounding errors. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
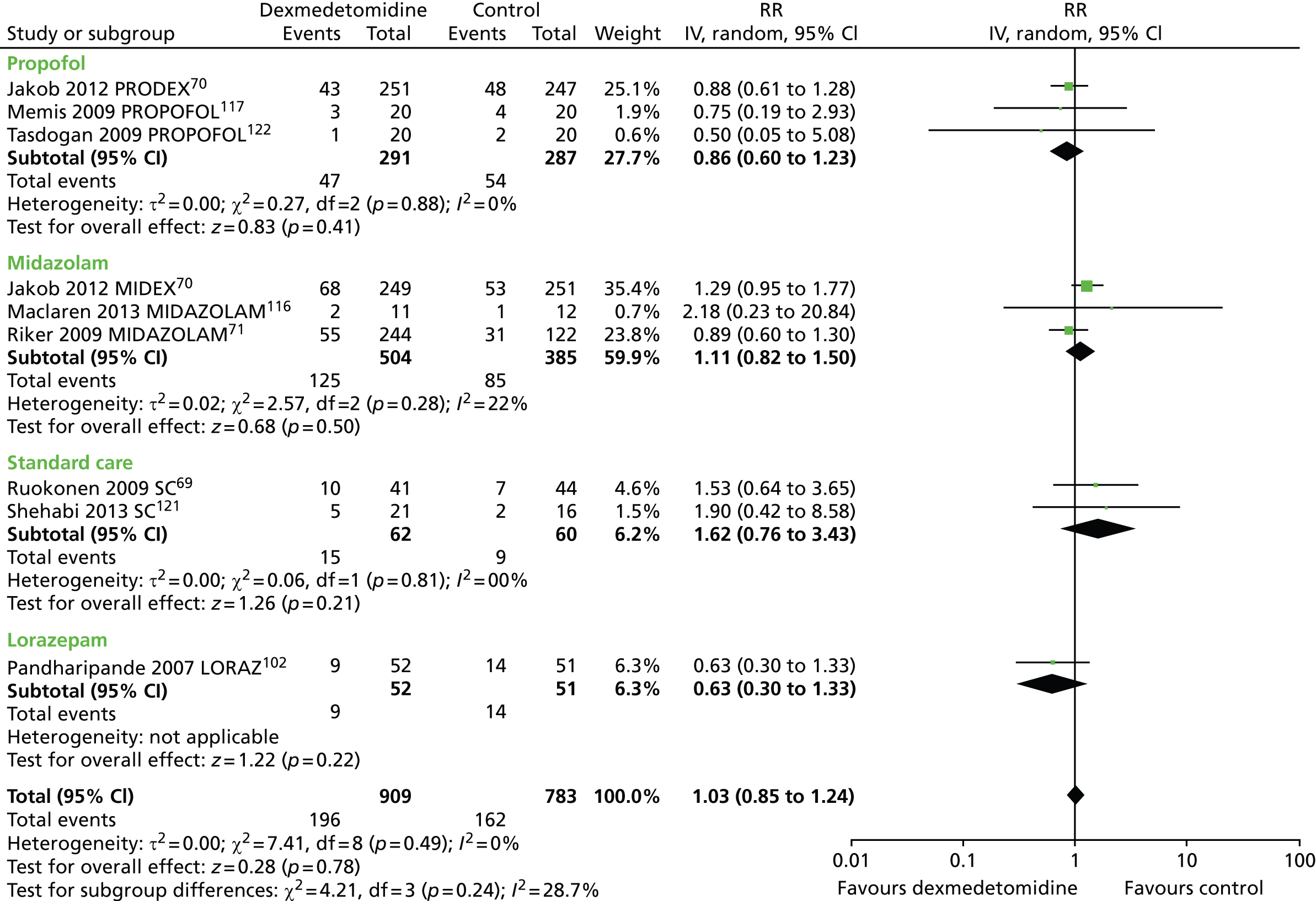
FIGURE 23.
Meta-analysis for duration of MV according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.

FIGURE 24.
Meta-analysis for ventilator-free days according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
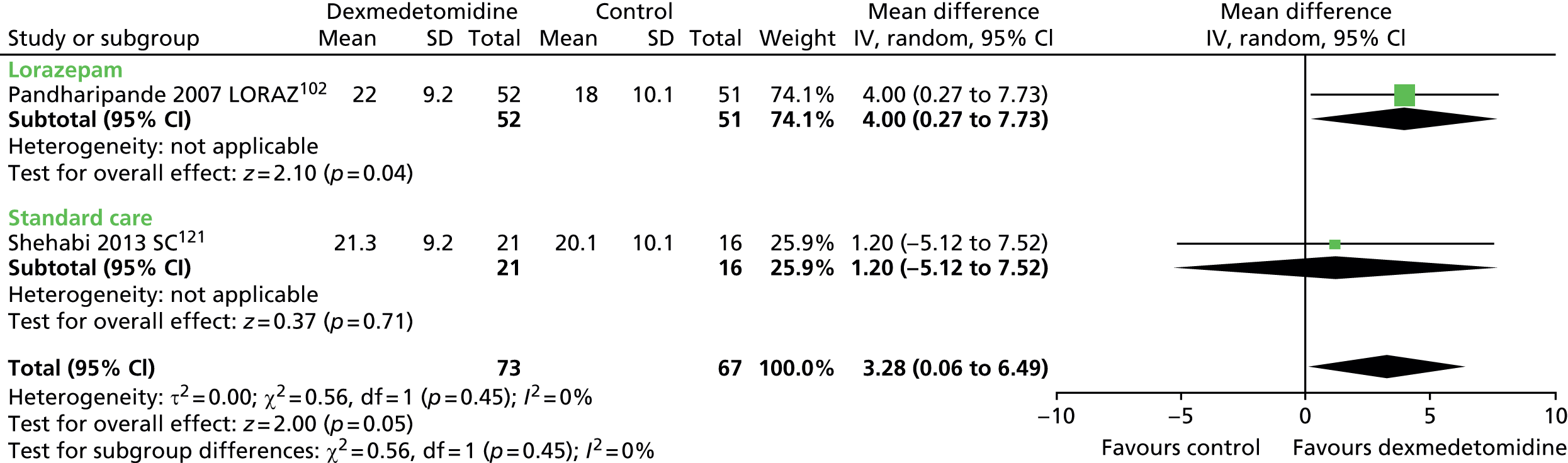
FIGURE 25.
Meta-analysis for length of ICU stay according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.

FIGURE 26.
Meta-analysis for incidence of hypotension according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
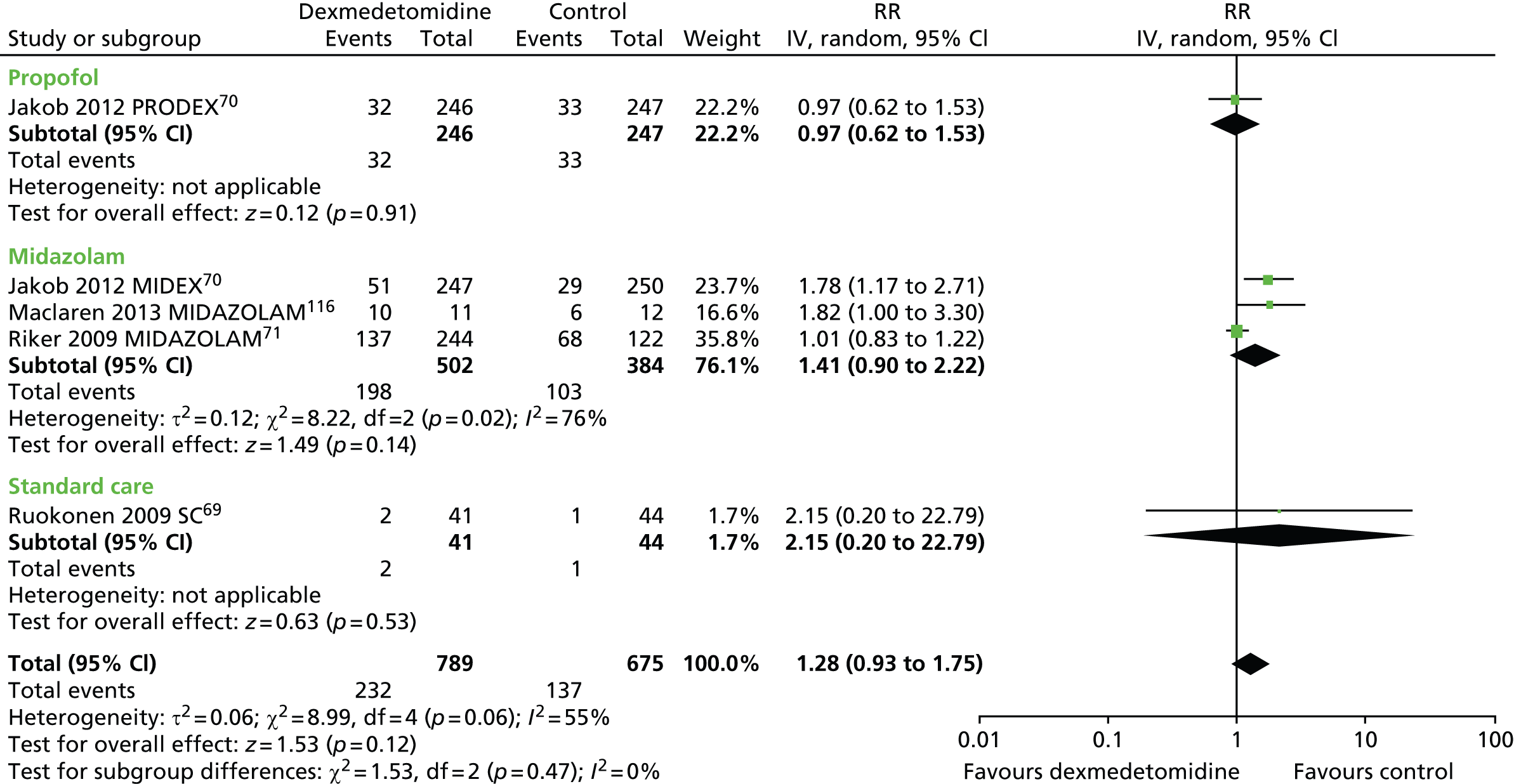
FIGURE 27.
Meta-analysis for incidence of hypertension according to type of comparator. Please note that the totals in the forest plot may be subject to minor rounding errors. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
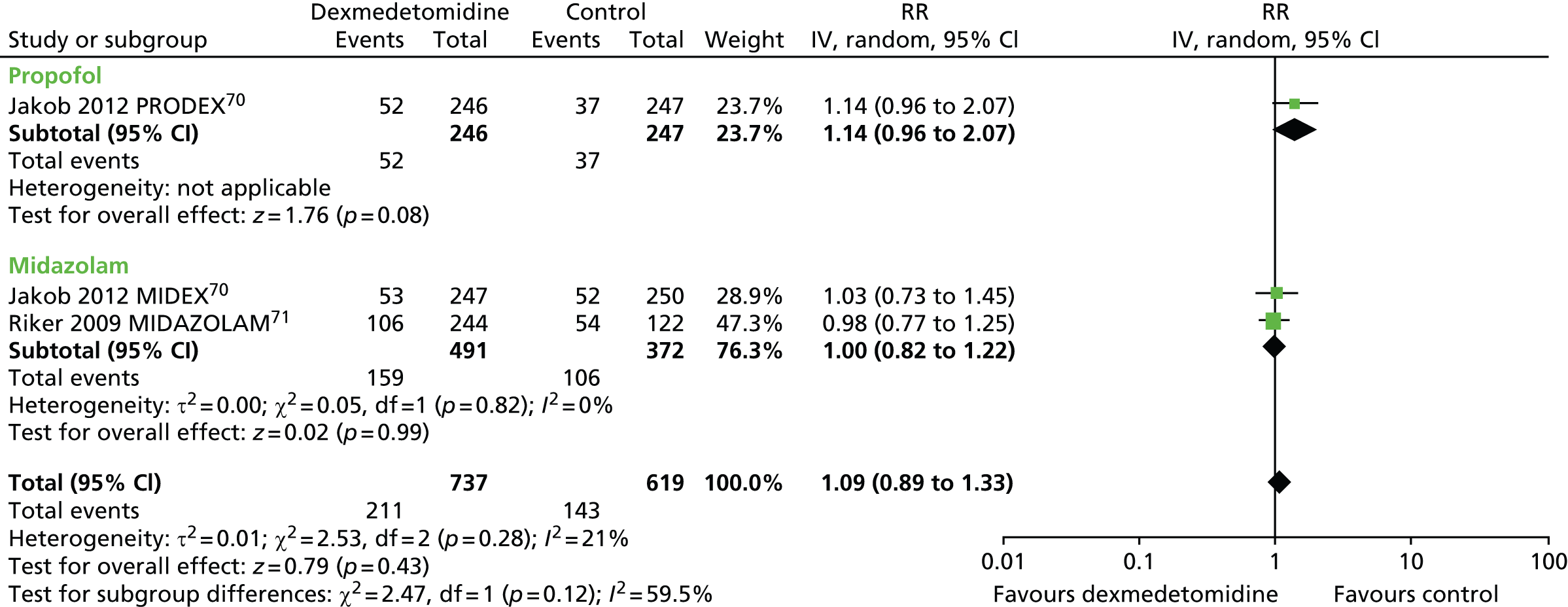
FIGURE 28.
Meta-analysis for incidence of bradycardia according to type of comparator. Please note that the totals in the forest plot may be subject to minor rounding errors. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
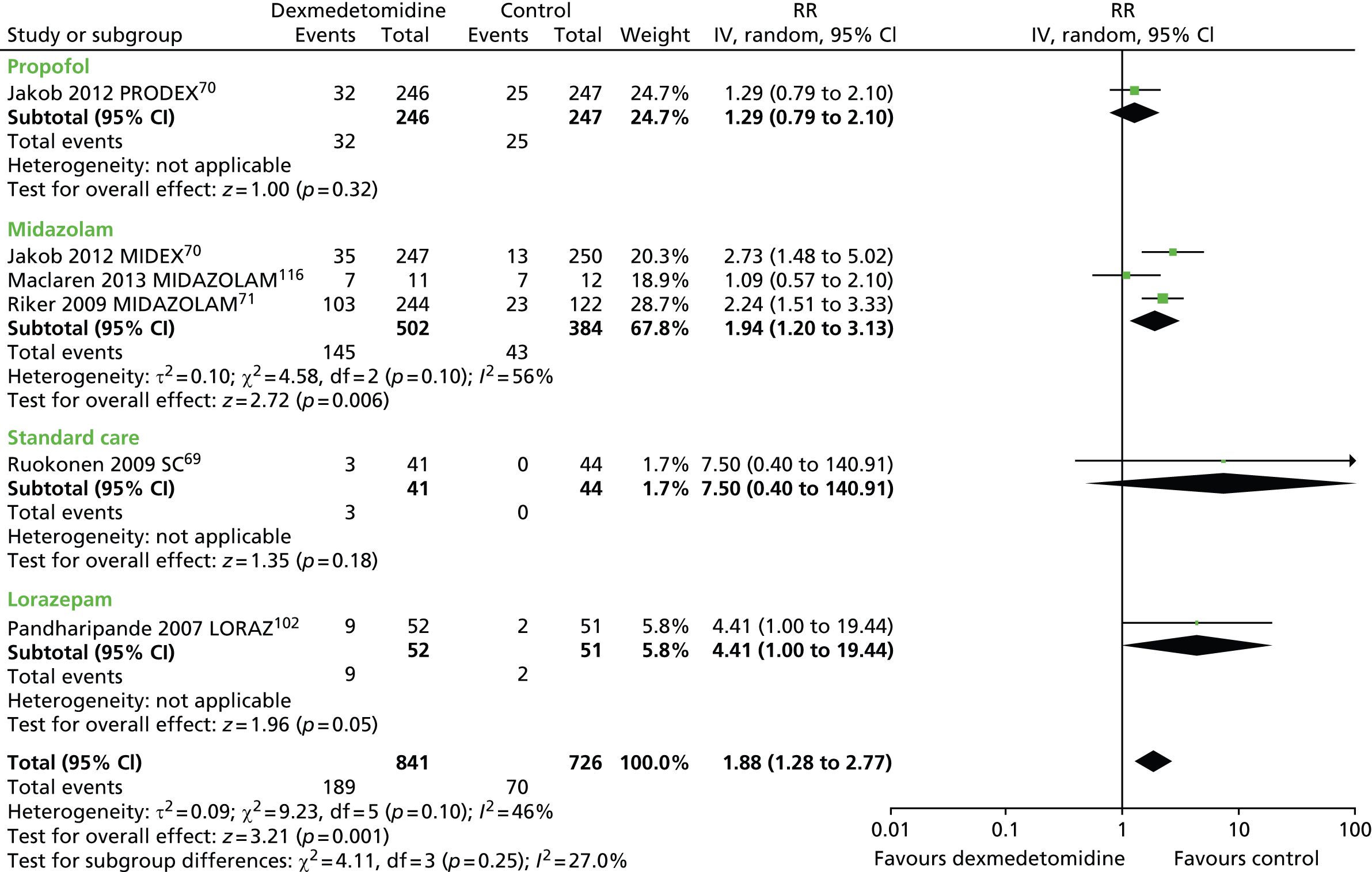
FIGURE 29.
Meta-analysis for incidence of delirium according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
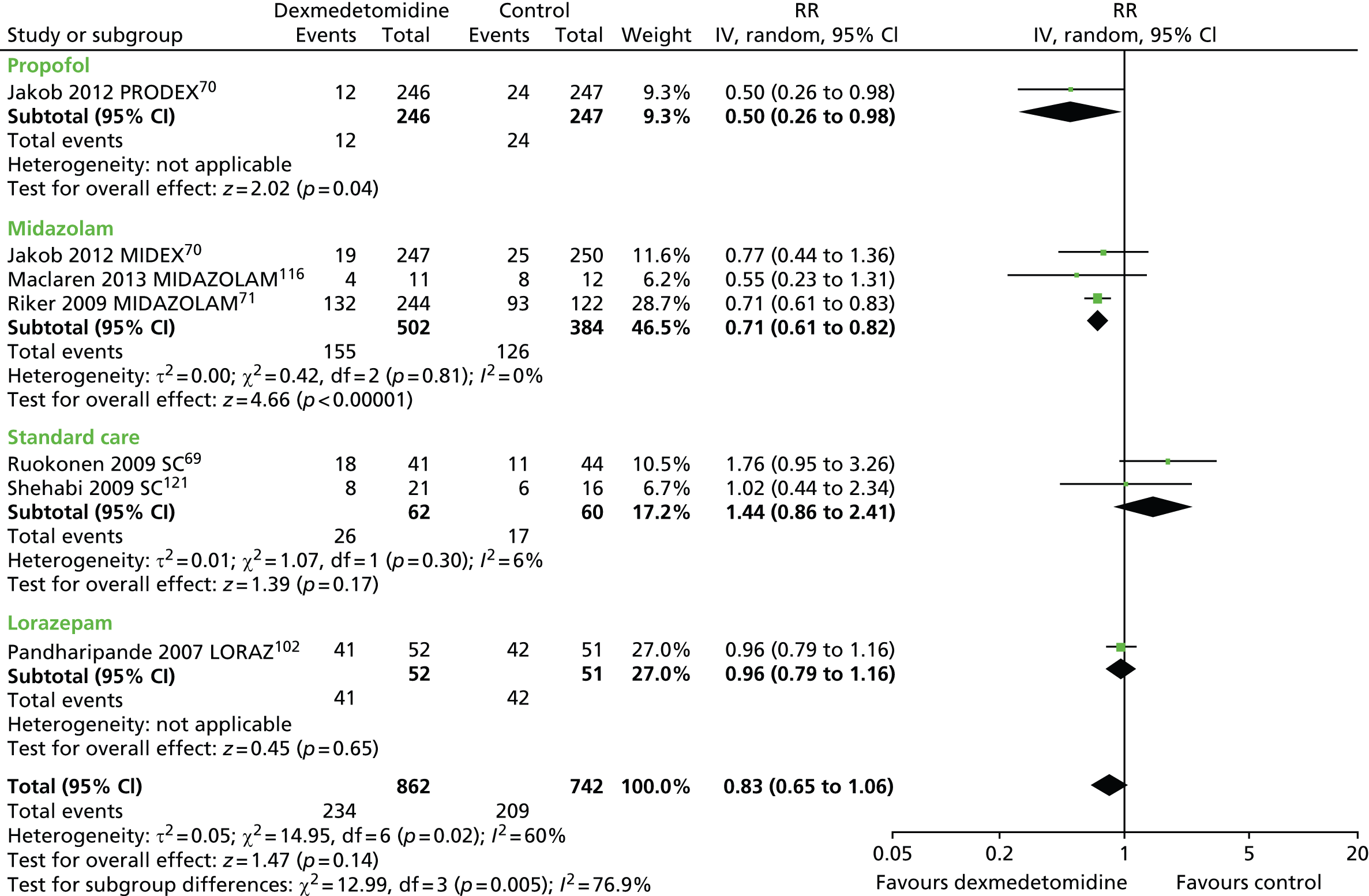
FIGURE 30.
Meta-analysis for self-extubation according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
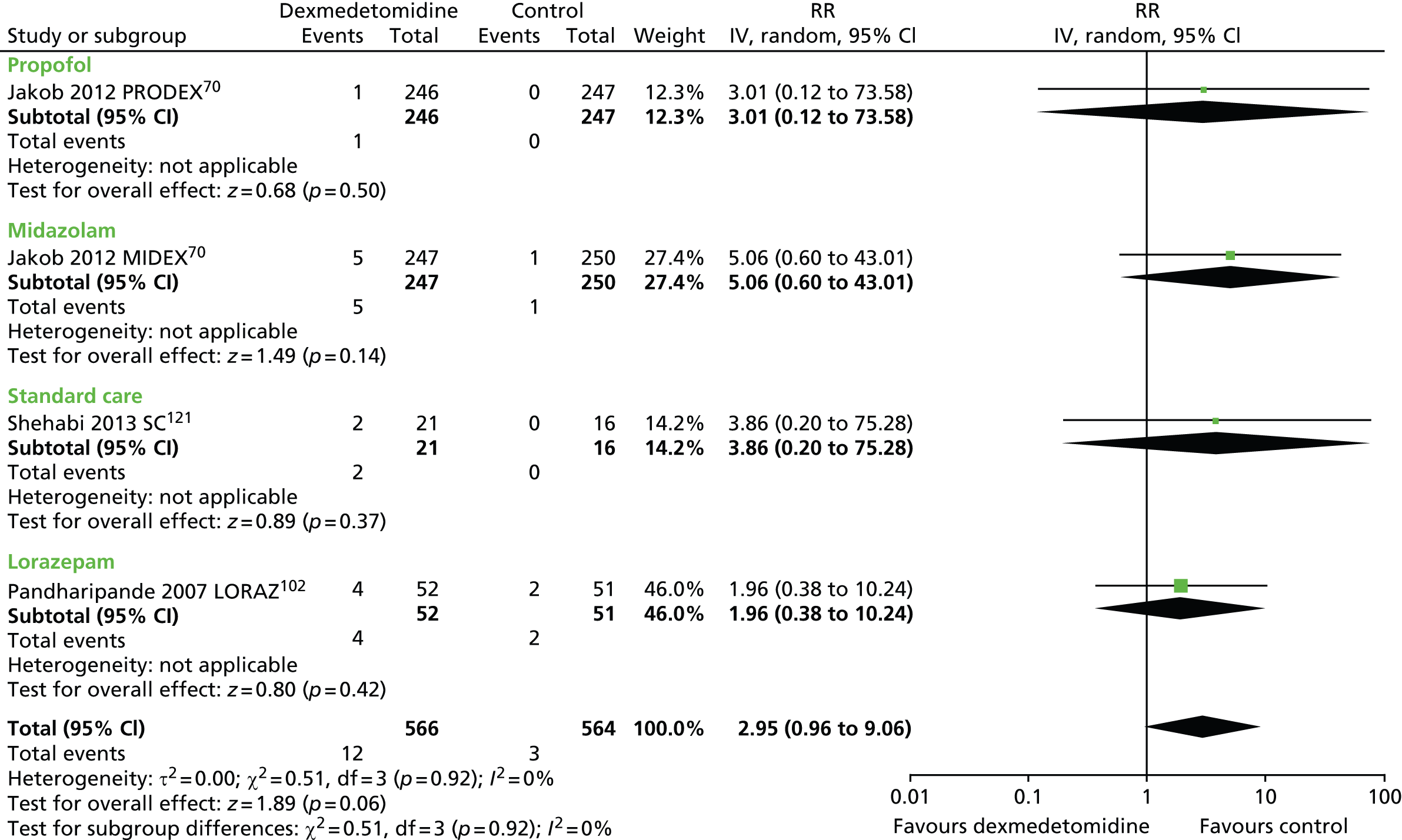
FIGURE 31.
Meta-analysis for incidence of tachycardia according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.
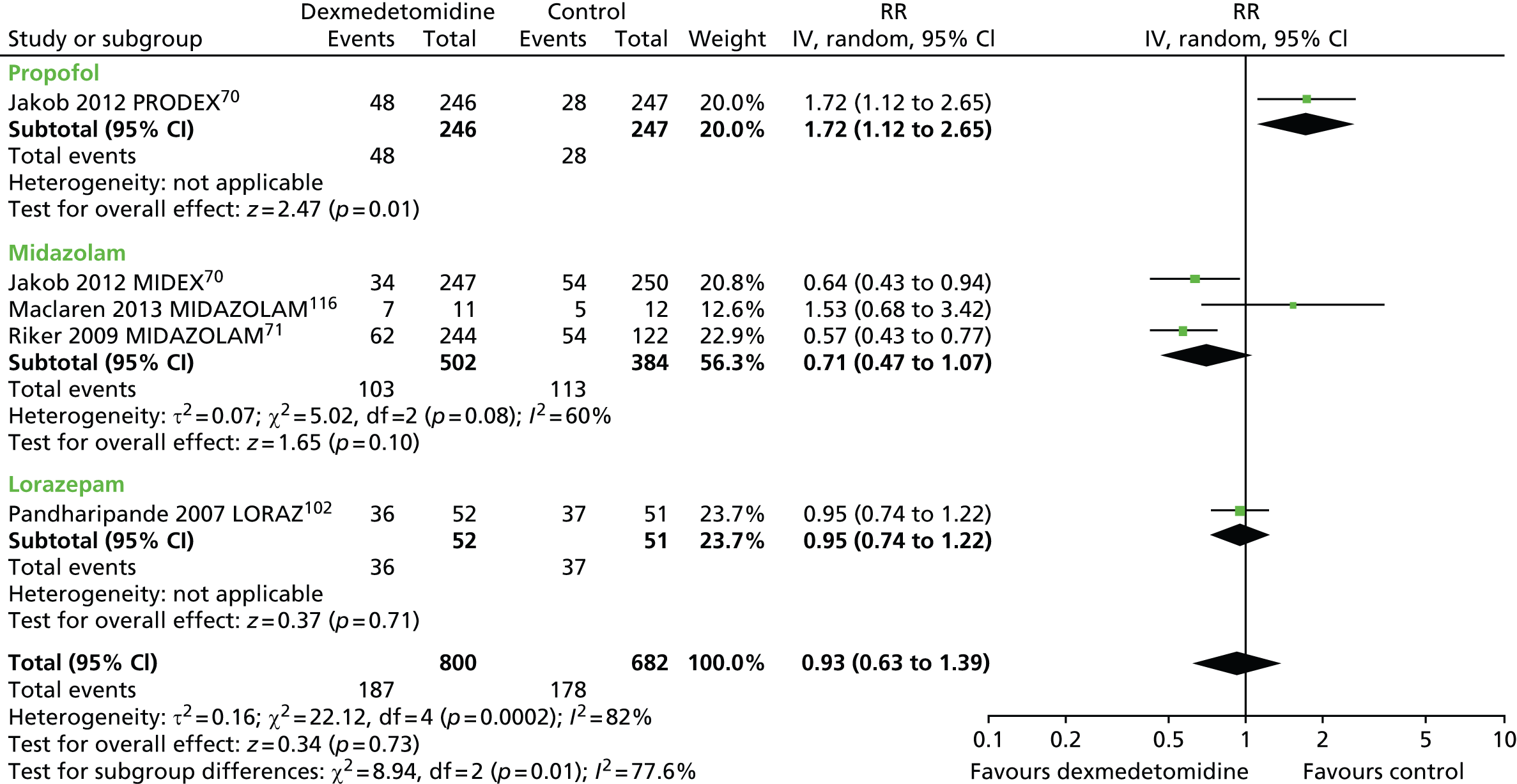
FIGURE 32.
Meta-analysis for time in target sedation range according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; LORAZ, lorazepam compared with dexmedetomidine; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.

FIGURE 33.
Meta-analysis for time to extubation according to type of comparator. IV, inverse variance; MIDAZOLAM, midazolam compared with dexmedetomidine; PROPOFOL, propofol compared with dexmedetomidine; SC, standard care compared with dexmedetomidine.

List of abbreviations
- APACHE
- Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation
- CAM-ICU
- Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit
- CI
- confidence interval
- DSI
- daily sedation interruption
- GABA
- gamma-aminobutyric acid
- ICNARC
- Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre
- ICU
- intensive care unit
- MIDEX
- MIdazolam compared with DEXmedetomidine trial
- MV
- mechanical ventilation
- PAD
- pain, agitation and delirium
- PRODEX
- PROpofol compared with DEXmedetomidine trial
- RASS
- Richmond Agitation–Sedation Scale
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RR
- risk ratio
- RSS
- Ramsay Sedation Scale
- SAS
- Sedation–Agitation Scale
- SD
- standard deviation
- SEDCOM
- Safety and Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine COmpared with Midazolam trial