Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 12/126/17. The contractual start date was in September 2013. The draft report began editorial review in March 2015 and was accepted for publication in October 2015. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Sofia Dias reports grants from Novartis and Pfizer, outside the submitted work. Nicky J Welton reports grants from Pfizer, outside the submitted work. Zarko Alfirevic reports being an author on some of the trials included in the review (but was not involved in assessing these trials for eligibility or risk or bias). He is a member of the Health Technology Assessment commissioning board.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2016. This work was produced by Alfirevic et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Introduction
Description of the health problem
There were 698,512 live births in England and Wales in 2013. 1 More than one in five births followed labour induction; this represents > 150,000 pregnant women in England2 and Wales3 per year. There is evidence that the number of labour inductions has been steadily increasing over the past two decades. NHS England maternity statistics for 2010 noted that 21.3% of births followed induction of labour, and by 2012–13 this figure had increased to 23.3%. 4
Induction of labour is carried out for a number of clinical indications. 5,6 The most common reasons include post-term pregnancy (defined as 41+0 weeks’ gestation), prelabour rupture of the amniotic membranes (PROM) or when the well-being of the woman or baby may be compromised by prolonging the pregnancy (e.g. in cases of fetal growth restriction or pre-eclampsia).
There is a broad range of methods available for induction of labour. The choice of method may depend on national guidelines and local protocol, as well as individual clinical factors. The advantages and disadvantages of different methods vary, and the choice of method has implications for women and the UK NHS.
From a clinical perspective, the decision about which method to use for induction of labour can be influenced by the woman’s readiness for labour, for example whether or not membranes have ruptured spontaneously or whether or not the cervix remains undilated at the start of the induction process. Different methods used for inducing labour have different mechanisms of action, and vary in terms of how quickly birth is achieved and the likelihood of causing complications in women with different clinical characteristics. Thus, the choice of method will take into account the reason for induction and its urgency. The woman’s obstetric and medical history is also considered. For example, there is evidence that women may be more sensitive to drugs that stimulate the uterus if they have had a previous birth, and women who have a scar from a previous caesarean birth are at increased risk of uterine rupture, which can result in hysterectomy and fetal death. 7
Different methods also have different direct costs, and some methods require continuous monitoring of the woman throughout labour. Consequently, the choice of induction method may have significant implications for NHS resources, especially if the method is known to increase the risk of complications requiring a caesarean section (CS).
Women may wish to experience a natural onset of labour, and there is evidence that an induced labour can have a negative impact on their overall experience of childbirth. 8 Some methods of induction are painful or unpleasant, and some are associated with distressing side effects, such as headache or nausea. Women may also have preferences about which method is used and may prefer non-pharmacological approaches. On the other hand, women will want their baby to be born safely, and timely induction may improve outcomes for women and babies. 5 Women facing decisions about induction of labour require up-to-date information about the range of options available, including alternative and complementary methods.
Description of available interventions and current service provision/policy
In the NHS context, choice of induction method is typically between prostaglandins and oxytocin combined with artificial rupture of membranes. UK clinical guidelines published in 20089 identified vaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) as ‘the preferred method of induction’. We note that this recommendation was not based on a quantitative overview of the evidence of the effects and safety of all available methods, or from the synthesis and analysis of data from a range of comparisons. Furthermore, this guideline9 did not recommend any particular type (gel, tablet or pessary) or dose of PGE2 because trial evidence has rarely compared different PGE2 preparations. Potential updating of the current guidance is awaiting the publication of this report. 10
Despite its importance, the question of resource use for the NHS has been relatively under-studied, and uncertainty remains about the costs that are associated with induction of labour. There is evidence that inducing labour in women with complications is associated with lower health-service costs than costs associated with expectant management. 11–13 However, there is little evidence on the costs associated with specific methods of induction compared with others. Randomised trials in which one method of induction has been compared with another have only rarely included economic analyses. 14
A broad range of pharmacological, mechanical, complementary and alternative methods have been used to induce labour. In the remaining sections of this chapter, we describe all of the pharmacological and mechanical methods for third-trimester induction of labour or cervical ripening which have been used in clinical practice and that have been examined in randomised trials. Complementary or alternative methods have been less commonly used in NHS settings but have been used in comparable settings in other countries. Complementary and alternative methods are included here, as information on the effects and safety of such methods may be important for women who prefer a less medicalised birth.
Pharmacological methods for the induction of labour
Prostaglandins: prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin F2 alpha
Prostaglandins are hormones produced naturally by the body that are important in the onset of labour. Synthetically manufactured prostaglandins have been used in clinical practice since the 1960s to ripen the cervix and induce uterine contractions. They are more frequently used in women when the cervix is unripe (i.e. with a Bishop score < 6). Prostaglandins promote cervical ripening and encourage the onset of labour by acting on cervical collagen so as to encourage the cervix to soften and stretch in preparation for childbirth. Prostaglandins may also stimulate uterine contractions.
Despite the widespread use of prostaglandins as part of labour induction, they can cause a number of side effects, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and fever. In addition, because of their effect on the uterus, prostaglandins can cause contractions that last too long, or are too frequent or are too strong. Excessive uterine activity, or hyperstimulation, may be associated with fetal distress, and in a small number of cases can lead to uterine rupture, especially in those women who have uterine scarring from surgery or a previous caesarean birth.
A large number of prostaglandin preparations have been available for labour induction, including prostaglandin F2 alpha (PGF2α, dinoprost), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), prostaglandin E (PGE1) and misoprostol (a synthetic analogue of PGE1, which is described separately: see Misoprostol). In the past, PGF2α was frequently used in clinical practice but, more recently, PGE2 (dinoprostone) has become the most commonly used formulation. Commercially produced PGE2 analogues are expensive and require refrigeration. These factors have limited use in low-resource settings.
Prostaglandins are available in a variety of formulations and doses, and may be given via various routes of administration, including vaginally, intracervically, orally and, less frequently, intravenously.
Vaginal and intracervical administration
Prostaglandin preparations for vaginal and intracervical administration include gels, lactose-based vaginal tablets, suppositories, pessaries or inserts. 15,16 Dosages of prostaglandins (mainly PGE2) vary, depending on route and local protocol (frequently 0.5 mg for intracervical use, 2–3 mg for intravaginal use and 10 mg for sustained-release pessaries). There is also variation in terms of the number of applications and time intervals between repeated doses. Sustained-release vaginal pessaries have been developed to reduce the number of applications and vaginal examinations that are needed during induction of labour. Vaginal and intracervical administration are the most common forms of administration in current practice.
In the meta-analysis we have treated different types of vaginal and intracervical PGE2 as different interventions as different preparations may vary in terms of rate of absorption, safety and cost. We have therefore included as separate interventions:
-
PGE2 vaginal tablets (lactose based).
-
PGE2 vaginal pessaries normal release (also sometimes referred to as suppositories), manufactured using various base materials, including wax and glycerine. [Note that this intervention includes a heterogeneous group of vaginal PGE2 preparations of varying composition. The base material used was not always clear, and pessaries were frequently produced in local pharmacies (i.e. not commercially available). We included this group of interventions in the network meta-analysis (NMA) and the cost analysis for completeness, even though they are not generally reproducible or available in the UK NHS.]
-
PGE2 vaginal pessaries sustained release (10- to 12-mg pessaries, single application).
-
PGE2 gel introduced via vaginal applicator.
-
PGE2 for intracervical administration.
Extra-amniotic administration
The administration of extra-amniotic prostaglandin gel was first carried out in the early 1970s. The gel is administered via a Foley catheter inserted through the cervix into the extra-amniotic space. The catheter is frequently left in place with the balloon inflated, and light traction may also be applied by taping the catheter to the woman’s leg. Extra-amniotic administration is no longer common in current practice. 17
Intravenous administration
Intravenous (i.v.) prostaglandins are associated with increased rates of maternal vomiting and diarrhoea and are rarely used in current practice. 18
Oral administration
Oral PGE2 and PGF2α have been available since the early 1970s. Oral administration is associated with gastrointestinal side effects and is seldom used nowadays. 19
Misoprostol
Misoprostol is a PGE1 analogue that is known to be effective in stimulating uterine contractions. Misoprostol is inexpensive and requires no special storage facilities. Several routes of administration and regimens of misoprostol have been studied, including oral (swallowed as a tablet or dissolved in a titrated solution), vaginal (inserted into the vagina as a tablet or gel), rectal (inserted into the rectum as a tablet) and buccal or sublingual (the tablet is dissolved in the cheek or under the tongue, respectively). 20–22 Different routes of administration have advantages and disadvantages. Oral misoprostol achieves rapid onset of action, whereas vaginal administration is associated with slower absorption but more prolonged action. Over the past decade, slow-release misoprostol vaginal pessaries have also been tested in trials.
Although misoprostol is widely used in obstetric practice for other indications (e.g. abortion), there have been concerns about its use due to the increased risk of serious adverse effects, such as uterine rupture. Several small studies have reported excessive uterine activity that is associated with the use of misoprostol, such as uterine tachysystole (more than five contractions per 10 minutes for at least 20 minutes), uterine hypersystole/hypertonus (a contraction lasting ≥ 2 minutes) and/or uterine hyperstimulation syndrome [uterine tachysystole or hypersystole with fetal heart rate (FHR) changes such as persistent decelerations]. A meta-analysis examining the use of vaginal misoprostol suggested that despite excess uterine activity, misoprostol was not associated with adverse fetal outcomes especially at a lower dose (< 25 µg). 23
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a hormone that is produced naturally by the body, and which has a range of functions, including the stimulation of uterine contractions in the second and third stages of labour. Oxytocin analogues, administered intravenously, are the commonest induction agents used worldwide. Oxytocin is frequently administered when the cervix is dilated (or favourable) and may be combined with artificial rupture of the amniotic membranes (amniotomy). Oxytocin may cause excess uterine activity, especially in settings where equipment is not available to titrate doses accurately and monitor contractions.
Current i.v. oxytocin regimens usually involve incremental increases in dosage. Lower-dose regimens typically involve 0.5–2.0 milliunits (mU)/minute starting doses, with incremental increases of 1.0–2.0 mU/minute every 15–60 minutes. Higher-dose regimens have starting doses up to 6.0 mU/minute, with incremental increases of 2.0–6.0 mU/minute every 15–40 minutes. There are advantages and disadvantages of high- or low-dose regimens; higher doses may lead to a shorter period to delivery, but may increase the risk of hyperstimulation, whereas lower doses may increase risk of infection if labour is prolonged. 24–27
Nitric oxide donors
Nitric oxide (NO) is thought to be involved in cervical ripening, and in recent years NO donors [isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN), isosorbide dinitrate, nitroglycerin and sodium nitroprusside] have been used to promote cervical ripening. NO is administered as a vaginal tablet. 28
Mifepristone
Mifepristone is a progesterone antagonist that has been used in the past in combination with prostaglandins in first trimester and early second trimester pregnancy terminations. Mifepristone has been proposed as a method to induce labour because it acts to increase uterine contractions. Mifepristone is administered as an oral tablet. 29
Oestrogens, corticosteroids, relaxin and hyaluronidase
Oestrogens have a role in promoting cervical ripening and, historically, have been administered intravenously or into the extra-amniotic space. There are no commercially available preparations for use in cervical ripening or induction of labour, and the two included trials of this agent date back to 196730 and 1981. 31
The role of corticosteroids in the process of labour is not well understood, and they are currently not used in clinical practice for the induction of labour. 32
Relaxin is a hormone that is thought to encourage cervical ripening, which has been tested in a very small number of trials. 33 Similarly, hyaluronidase is also thought to be implicated in cervical ripening. 34 Both agents have been administered in vaginal or intracervical gel, but neither is common in current practice.
Mechanical and physical methods for induction of labour
Mechanical methods to induce labour have been available for many years. Mechanical devices include various types of catheters and laminaria tents, introduced into or through the cervix and into the extra-amniotic space. The introduction of devices into the cervix may cause the cervix to dilate. Their presence may also increase prostaglandin or oxytocin secretion, which, in turn, may increase cervical dilatation and stimulate uterine contractions. 35 Here we also include descriptions of membrane sweep and amniotomy since they may be considered a physical method of inducing labour.
Catheters
Foley urinary catheters have been used for the induction of labour, as have double-balloon and other catheters that are specifically designed for use in induction of labour (e.g. Cook catheter). The catheter is introduced into the extra-amniotic space, and then the balloon(s) is (are) inflated to keep the catheter in place. Traction may be applied by taping the catheter to the woman’s leg. Catheters are usually left in situ until they are expelled. In some cases a saline infusion is introduced into the extra-amniotic space via the catheter.
Laminaria tents
Laminaria tents are made from sterile seaweed or synthetic materials. These devices are introduced into the cervical canal and expand to gradually stretch the cervix.
Membrane sweep
Stripping or sweeping of the membranes has been used for many years to induce labour, and continues to be carried out in many clinical settings. Membrane sweeping involves the clinician detaching the membranes from the lower uterine segment by a circular movement of the examining finger. Membrane sweeping is thought to lead to an increased production of prostaglandins. When the cervix is closed, a cervical massage may be carried out instead of a membrane sweep to stimulate the production of prostaglandins. 36
Amniotomy
During labour the amniotic membranes usually rupture spontaneously as the cervix dilates and stretches in preparation for the descent of the fetus. Amniotomy refers to rupture of the membranes using a plastic hooked instrument or, occasionally, surgical forceps.
Amniotomy may be carried out alone or in combination with oxytocin or prostaglandins to induce labour. It can be carried out only if the amniotic membranes are accessible to the midwife or doctor, and this may not happen until the cervix has started to dilate.
Amniotomy may cause some potentially serious adverse effects, including cord prolapse. The procedure may introduce infection. For women known to be human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive the procedure is avoided because it may increase the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV. 25
Breast stimulation
Manual breast stimulation has been used in the past to stimulate uterine contractions. 37 It is thought that it may trigger the release of oxytocin.
Sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse at term has been thought to lead to the onset of labour. 38 The hypothesised mechanism of action here is the prostaglandin contained within semen.
Complementary and alternative methods for induction of labour
Castor oil
Castor oil is derived from the bean of the castor plant, and has been used in oral form as a method of stimulating labour. 39 Castor oil has laxative properties, stimulating the intestines and bowel. It is this stimulation that is hypothesised to initiate uterine contractions and labour as a secondary effect.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves the insertion of fine needles by trained staff into the skin at specified points on the body. Stimulation of particular acupuncture points is intended to initiate uterine contractions and labour. 40
Homeopathy
Homoeopathy involves the use of highly diluted solutions that contain tiny amounts of the original substance. Homeopathic preparations are popular and are available over the counter in pharmacies and health food shops. Some homeopathic preparations have been recommended to promote the onset of labour. 41
Overall aims and objectives of assessment
Given the broad range of methods used to induce labour, the main research question addressed by this review is ‘what is the best method for induction of labour?‘. The specific objectives were to:
-
assess the effectiveness and safety of a range of induction methods to determine which method or methods achieves the best outcomes
-
provide a quantitative summary of the evidence on the relative effects of a broad range of induction methods to identify which method works best
-
develop a decision model to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the different methods for induction
-
explore, if sufficient evidence is available, the effect of different clinical subgroups [with intact or ruptured membranes, at different gestational ages, in women following a previous CS and with low (< 6) or higher Bishop scores] on effectiveness and cost-effectiveness.
Specification of the PICO research question
Population Pregnant women carrying a viable fetus and who are eligible for any method of third-trimester cervical ripening or labour induction.
Intervention and relevant comparators No treatment, placebo, all pharmacological (all routes and doses), mechanical and complementary methods used for the induction of labour.
Outcomes Our primary effectiveness outcome was (1) vaginal delivery (VD) not achieved within 24 hours, and our primary measures of safety were (2) uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes and (3) CS. Our secondary outcomes for serious adverse events were (4) serious neonatal morbidity or perinatal death and (5) serious maternal morbidity or death. Other outcomes included were (6) maternal satisfaction with the induction method used, and, for use in the economic model, (7) cost, resource use and utilities.
Definition of the decision problem for the economic evaluation
Our aim was to answer the following question: what is the most cost-effective method (from the interventions described above), for third-trimester cervical ripening or labour induction? Outputs from the economic evaluation include expected costs, expected benefits, incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs), expected net benefit and cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEACs).
Stakeholder involvement in project
The steering group (listed in Appendix 1) and project team included a consumer representative, a health economist, a midwife and an obstetrician engaged in clinical practice.
A consumer representative was included as a collaborator on the project, and she contributed to the early discussions on this project and drafting the application. Induction of labour is known to be of great interest to pregnant women. In particular, women are interested in self-administered ways of initiating labour and for this reason these methods were examined in the proposed work. The consumer representative co-ordinated the involvement of members of the CPCG (Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group) consumer panel, National Childbirth Trust and the Association for Improvements in Maternity Services (AIMS) who expressed an interest in participating. Members of these groups were asked for comments to inform steering group meetings, to determine the final outcomes, to aid in the interpretation of the findings and to shape the papers to be published. The authors of this report include a consumer representative (GG).
The steering group commented on the study design, selection of outcomes, methods for the cost-effectiveness analysis and dissemination strategies.
Overview of report
In Chapter 2 we describe the methods used for the assessment of clinical effectiveness, including the methods for the systematic review to identify relevant evidence on clinical effectiveness, and the methods for the NMA. In Chapter 3 we present the results from the systematic review and NMA, including the relative effectiveness of interventions that have been used to induce labour in women at or near term. In Chapter 4 we describe methods and present results of the cost-effectiveness analysis, taking a UK NHS perspective. In Chapter 5 we summarise findings, set out the strengths and limitations of our approach, consider the implications of our results on recommended practice, and indicate areas for which future research would be beneficial.
Chapter 2 Methods for assessment of clinical effectiveness
Methods for reviewing clinical effectiveness
Identification of studies
We worked with an Information Specialist to identify trials for inclusion in the NMA. We searched the CPCG’s Specialist Register [which incorporates pregnancy and postpartum searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE, the NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED), relevant journals and conference proceedings]. The search strategy was finalised as part of the early consultative stages of the project, and the final search on which this report is based was carried out at the end of March 2014. The search strategy is set out in Appendix 2. A full-text copy of every relevant trial report was obtained and assigned to a topic, depending on the intervention before adding to the database. We then screened all reports that were assigned to the induction of labour topic. Many of the trials identified by the search have already been included in published Cochrane reviews, but further searches identified more recent trials which, when eligible, have been included in the analysis.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Interventions
All randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of induction interventions as identified in Chapter 1 of this report were evaluated. Eligible trials compared any method of third-trimester cervical ripening or labour induction with an alternative intervention, placebo or no treatment. For prespecified treatments we also included trials that compared different means of administration (e.g. vaginal misoprostol vs. oral misoprostol) or different doses [e.g. low-dose misoprostol (< 50 µg) vs. high-dose (≥ 50 µg) misoprostol]. We included studies recruiting women with a viable fetus, but had no other restrictions relating to the indication for labour induction, language or date of publication.
Trials in which women were randomised to receive a combination of interventions were not eligible, except for a small number of prespecified combinations in common use (e.g. amniotomy with oxytocin). We made the decision to exclude lesser-used combinations as the network was already large, and such combinations are rarely used clinically and mainly reported in single trials.
We included all interventions for the induction of labour examined in trials even if such treatments are not used in the NHS. Treatments no longer used may not have been abandoned for evidence-based reasons, and their inclusion adds statistical power to the entire network.
We planned to include multiarm trials and cluster randomised trials with any necessary adjustments to account for cluster design effect (if triallists had not already carried out appropriate adjustment).
Participants
We included trials that recruited pregnant women for third-trimester induction of labour, carrying a viable fetus, with a range of obstetric characteristics, undergoing labour induction for varied reasons.
Outcomes
In consultation with the patient representative from the CPCG we defined seven key outcomes for the clinical evaluation of induction interventions. The first five outcomes are common to all CPCG reviews on induction of labour and have been set out in a generic protocol. 42 Outcomes 6 and 7 were proposed by the consumer representative as of importance to women. Outcomes 8 and 9 were not prespecified; however, in consultation with the steering group we extracted data on neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admission and Apgar score, as proxies for serious neonatal morbidity (as serious neonatal morbidity was poorly reported and inconsistently defined in trials) (Box 1).
-
VD not achieved within 24 hours (or period specified by trial authors).
-
Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
-
CS.
-
Serious neonatal morbidity or death.
-
Serious maternal morbidity or death.
-
Instrumental delivery.
-
Maternal satisfaction with the method used.
-
NICU admission (proxy outcome for serious neonatal morbidity).
-
Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes (proxy outcome for serious neonatal morbidity).
Exclusions
We excluded trials that did not report any of our key outcomes or evaluated combined interventions. The full list of references for excluded studies and the reasons for exclusion are documented in Appendices 3 and 4, Table 37.
Data extraction and risk-of-bias assessment
We obtained full-text copies of all reports identified by the search. A minimum of two investigators independently assessed all reports to determine whether or not trials used random allocation to groups, included one or more of the selected interventions and comparisons, recruited women undergoing third-trimester induction of labour, and included data on at least one of our primary outcomes. Trials meeting all of the eligibility criteria were included in the systematic review.
Data extraction was carried out by one investigator and checked by a second. Preliminary statistical analyses also highlighted some discrepancies in the extracted data, which were then doubled checked by the reviewers, and corrected if appropriate. For all included trials, we extracted data on trial and patient characteristics, and this is summarised in tables of included studies (see Appendix 5, Reference list for included studies, and Appendix 6, Table of included studies characteristics, Table 38). 11,14,30,31,43–936
Study quality was assessed using the methods described in the Cochrane Handbook. 937 For use in a prespecified sensitivity analysis, we assigned a judgement relating to risk of bias (low, high, unclear), based on the allocation concealment domain. We based this decision on meta-epidemiological evidence indicating the importance of this domain as a source of bias938 and on the design of obstetric trials, which often precludes blinding of participants and personnel (although not, of course, of outcome assessors).
Information on study setting (country and whether or not the study was carried out in an inpatient or outpatient setting), method and the type of intervention(s) (dose, mode of administration, type of preparation, e.g. slow-release pessary vs. gel, regimen and any cointerventions) was extracted. We extracted details on comparison arms (e.g. another active treatment, placebo or ‘usual care/no treatment’). Treatment arms were categorised according to the initial randomised allocation, although subsequent clinical management may have included further doses or an alternative treatment. For participants, we recorded important obstetric characteristics, including parity, previous CS, state of cervix and whether or not amniotic membranes were intact. These factors were a priori expected to be possible intervention effect modifiers. There was an additional concern that patient characteristics may be linked to the interventions that have been included in the studies. For example, if it were the case that all of the studies comparing NO with placebo predominantly included women with a previous CS, whereas the studies comparing misoprostol with placebo predominantly excluded women with a previous CS, then the indirect comparison of NO with misoprostol may not be a fair reflection of the true underlying effect in either subgroup of women. For NMA to be valid the different study populations are required to be ‘similar’ in any effect modifying covariate (see Network meta-analysis for a description of the key assumption of transitivity/consistency in NMA). It is therefore important to inspect tables of patient characteristics according to intervention comparison to assess whether or not there is an a priori reason to suspect that the transitivity/consistency assumption may not hold.
In summary, for each trial, information was extracted on:
-
The interventions compared in trials (with details of dosage and regimen for pharmacological interventions).
-
Number of participants in trials.
-
Parity of women recruited to trials (all nulliparous, all multiparous or mixed parity).
-
Whether women had ruptured or intact membranes at recruitment (all ruptured, all intact or the sample included women with both intact or ruptured membranes).
-
Whether or not women had favourable or unfavourable cervical scores at recruitment (Bishop score all < 6, ≥ 6 or included women with either favourable or unfavourable scores).
-
Whether or not trials included women with multiple pregnancies.
-
Gestational age at recruitment (all post dates, all > 37 weeks, or the sample included women at < 37 weeks’ gestation).
-
Treatment setting (women treated as inpatients or outpatients).
-
Risk of bias (high, low or unclear risk of bias, based on allocation concealment).
-
We also recorded whether or not the study had been funded or partly funded by pharmaceutical sponsors.
We compared the distribution of these characteristics in tabular form before we conducted the NMA (see Appendix 7, Table 39). Sensitivity analyses were planned to exclude studies that were assessed as being of unclear or high risk of bias.
Methods of evidence synthesis
Network meta-analysis
A NMA was conducted to simultaneously compare the induction interventions, placebo or no treatment for each outcome. In its simplest form, a NMA is the combination of direct and indirect estimates of relative intervention effect in a single analysis. An indirect estimate of the relative intervention effect B compared with C (dBCI) can be formed by comparing direct trials of A compared with C with trials of A compared with B, such that dBCI=dACD−dABD. A simple approach to combining the indirect and direct estimates of B compared with C would be to take a weighted average, for example using an inverse variance weighting. 939 NMA extends the idea of an indirect comparison to simultaneously combine all evidence in a connected network of intervention comparisons. 940 For random-effects (REs) models, we assume that the between studies variance is the same across all of the pairs of intervention comparisons (known as the homogeneous variance assumption). In a NMA we assume that intervention A is similar (in dose, administration, etc.) when it appears in the A versus B and A versus C studies, and also that every patient included in the network has an equal probability of being assigned to any of the interventions:940 a concept called ‘joint randomisability’. 941 A first step to assess this assumption is by comparing the distribution of potential effect modifiers across the different942 comparisons,942,943 as if there is an imbalance in the presence of effect modifiers across the A versus B and A versus C comparisons, the conclusions about B compared with C may be in doubt. A second step is to use statistical measures of model fit to see if the direct estimate for a particular intervention comparison is discrepant with the NMA estimate944 (see below). When direct data were available, pairwise meta-analyses were also performed for all comparisons, and compared with the NMA treatment effect estimates to informally assess agreement.
All of the analyses were conducted within a Bayesian framework utilising OpenBUGS version 3.2.3 (www.openbugs.net; Medical Research Council Biostatistics Unit, Cambridge), using the NMA code given by Dias et al. 945–948 for binomial data. We provide example code in Appendix 8. A key feature of a Bayesian analysis is that a joint distribution (called the ‘posterior’ distribution) of all model parameters (intervention effect estimates and heterogeneity) is estimated, and results are reported as summaries from this posterior distribution. For example, it is common to report the posterior median and 95% credible intervals (CrIs, which are interpreted upon there being a 95% probability that the parameter lies within this range of values, where 95% of the marginal distribution lies).
Studies with 0% or 100% events in all arms were excluded from the analysis because these studies provide no evidence on relative effects. 946 For studies with 0% or 100% events in one arm only, we planned to analyse the data without continuity corrections when computationally possible. Where this was not possible, we used a continuity correction where we added 0.5 to both the number of events and the number of non-events, which has shown to perform well when there is an approximate 1 : 1 randomisation ratio across intervention arms. 949 In Chapter 3, we report any adjustments made.
Both fixed-effects and REs (when sufficient data were available) models were considered on the basis of model fit. Goodness of fit was measured using the posterior mean of the residual deviance, which is a measure of the magnitude of the difference between the observed data and the model predictions for those data. 950 Smaller values are preferred, and in a well-fitting model the posterior mean residual deviance should be close to the number of data points. 950 Of course, improvements in model fit can always be achieved by making the model more and more complex, but at the risk of losing generalisability and interpretability. To account for this we report the deviance information criterion (DIC), which penalises model fit with model complexity. 950 Finally, we report the between-studies standard deviation (SD) (heterogeneity parameter) to assess the degree of statistical heterogeneity. Model selection was based on all of these statistics: posterior mean residual deviance, posterior median between-study heterogeneity, and DIC. In comparing models, differences of ≥ 5 points for posterior mean residual deviance and DIC were considered meaningful,950 with lower values being favoured. Heterogeneity was reported as the posterior median between trial SD (τ) with its 95% CrI.
We planned to conduct sensitivity analyses excluding studies at high risk of bias for allocation concealment, for all analyses. Consistency between the different sources of indirect and direct evidence was explored statistically by comparing the fit of a model assuming consistency with a model that allowed for inconsistency (also known as an unrelated treatment-effect model). If the inconsistency model had the smallest posterior mean residual deviance, heterogeneity, or DIC value then this indicates potential inconsistency in the data. When model fit was suggestive of inconsistency our first step was to restrict trials to those at low risk of bias. If model fit was not improved, we planned further subgroup analyses using the potential treatment effect modifiers identified above (see Data extraction and risk-of-bias assessment).
A Bayesian analysis requires prior distributions to be specified on all model parameters that are being estimated. A prior distribution reflects our belief about the values that a parameter can take in advance of observing the data. Vague (flat) prior distributions were specified for treatment effect and heterogeneity parameters, so that our results are driven by the observed data (see Appendix 9 for full details of the prior distributions assumed). Convergence was assessed using the Brooks–Gelman–Rubin diagnostic951 and was satisfactory by 68,000 simulations for all outcomes. 952 A further simulation sample of at least 58,000 iterations post convergence was obtained, on which all reported results were based.
Relative intervention effects are reported as posterior median odds ratios (ORs) and 95% CrI. All reported outcomes are negative events and so an OR < 1 is interpreted as the active intervention reducing the odds of the event. We calculated the probability of each treatment being first, second, third, etc. most effective for each outcome and report the results using ‘rankograms’. Peaks in the rankogram graph indicate the most likely rank for each intervention type. Flat lines indicate a high degree of uncertainty for the ranking of that intervention type. As this metric can be unstable and difficult to interpret (e.g. when there is a high probability of being both ‘best’ and ‘worst’ on an outcome), we also report posterior mean rank of each treatment (and 95% CrI), with the convention that the lower the rank the better the treatment. We also report the absolute probability of an event for each intervention. To estimate the absolute probability, we selected vaginal PGE2 (tablet) as the baseline intervention and conducted a fixed-effects meta-analysis on vaginal PGE2 arms to produce only an ‘average’ intervention effect to which the relative treatment effects (as estimated from the NMA) were added. Note that this is modelled externally to the NMA. We note that this may not generalise to any one setting, as it is based on all of the trials in the NMA, and refer the reader to Chapter 4, Assessment of cost-effectiveness for UK-specific absolute estimates.
Pairwise meta-analyses
For completeness, and to informally assess the consistency assumption of NMA, we conducted pairwise meta-analyses for all intervention comparisons for which direct head-to-head evidence was available. The method of estimation was identical to that described above for the NMA, except that we did not apply the consistency assumption, so that we obtained separate intervention effect estimates for each pairwise comparison. For the REs models, we assumed that the heterogeneity parameter was common across intervention comparisons, to reflect the assumption made in the NMA and allow a fair comparison of the intervention effect estimates.
Chapter 3 Results for assessment of clinical effectiveness
Results of the systematic review
The results of the search and the eligibility assessment are summarised in the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram, which indicates the number of included and excluded trials (Figure 1). We identified 1508 reports corresponding to 1190 separate studies. A total of 611 trials that fulfilled our prespecified inclusion criteria were included in the review. Details of the 579 excluded studies (references and reasons for exclusion) are set out in Appendices 3 and 4, Table 37.
FIGURE 1.
A PRISMA study flow diagram for the systematic review.

There were a total of 103,041 women studied in the 611 trials included in this review. Several multiarm trials were identified: one five-arm trial, four four-arm trials and 42 three-arm trials (see Appendix 6, Table 38). The total number of arms in trials relating to different interventions for the induction of labour is set out in Appendix 10.
It is important to bear in mind that trials may not have reported findings for all of the seven prespecified outcomes. We have indicated, in Table 1, the number of studies reporting each of our prespecified outcomes. Trials that did not report any prespecified outcomes were not included in the review, as they did not contribute data to the pairwise analysis or the NMA (see Appendix 4, Table 37, for reasons for exclusion from the review).
| Outcome | Number of trials reporting this outcome | % included trials (613)a | Number of women/infants | Number of events | Events as % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serious maternal morbidity or deathb | 77 | 12 | 19,112 | 5 deaths 14 uterine rupture 1 ICU admission |
0.1 |
| Neonatal death | 131 | 21 | 32,248 | 94 | 0.3 |
| VD not achieved within 24 hours | 142 | 23 | 28,845 | 11,885 | 41.2 |
| Uterine hyperstimulation with (FHR) changes | 251 | 41 | 43,612 | 1594 | 3.6 |
| CS | 587 | 96 | 99,821 | 19,297 | 19.3 |
| Instrumental delivery | 302 | 49 | 54,511 | 8020 | 14.7 |
| NICU admission | 226 | 37 | 52,931 | 4224 | 8.0 |
| Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 289 | 47 | 58,367 | 1244 | 2.1 |
| Maternal satisfactionc | 29 | 5 | 11,901 | NA | NA |
More than 95% of trials reported CS, and data were available for almost 100,000 women for this outcome. However, the proportions of trials reporting our other key outcomes were considerably lower: instrumental delivery was reported in approximately half of trials (49%) and infant Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes was reported in a similar number of studies (47%). Mean Apgar score at 5 minutes was occasionally reported, but there were insufficient studies reporting this outcome for us to be able to use these data.
Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes was reported in 41% of trials. A larger number of trials reported outcomes relating to abnormal uterine activity (tachysystole or hypertonus), but we have included data only for those that were clearly associated with changes in FHR and, therefore, matched our outcome definition for inclusion.
Less than one-quarter of trials reported the number of women achieving VD within 24 hours. Neonatal death was reported in 21% of trials (with data for 32,248 babies) and a composite outcome of maternal death or serious morbidity in 12.6%. As expected, event rates were very low for both of these outcomes and most trials reported no events for either outcome.
Infant admission to NICU was reported for trials that, together, included > 50,000 babies, but findings related to this outcome need to be interpreted with some caution. Results demonstrate that there was considerable variation between trials in terms of rates of admission, and it is possible that this variation may relate to definitions of neonatal intensive care and other types of special care units, rather than being a true reflection of variation in serious infant morbidity in different trial settings. There was very rarely clear information on the level of care provided in facilities described as NICU or special care baby unit or on criteria for admission.
Only 29 trials reported any outcomes relating to satisfaction, and the way satisfaction outcomes were defined and operationalised in questionnaires meant that we were unable to carry out any quantitative analysis. We have, therefore, set out findings in tabular and narrative form.
Although Box 2 sets out the number of trials reporting specific outcomes, we were not able to use all of the reported outcome data in the NMA. Studies that reported no events in either arm were excluded from the NMA. In a small number of cases outcome data were excluded from the analysis for other reasons (see Box 2).
Removed because no data reported (471).
Removed because of 100% cells in both arms (1).
Hyperstimulation (180 studies included)Removed because no data were reported (362).
Removed because of zeros in both arms (71).
Caesarean section (307 studies included)Removed because no data were reported (26).
Removed because of zero cells in both arms (2).
Removed because of high risk of bias (276).
Removed because of automatic CS after 24 hours (2).
Neonatal death (42 studies included)Removed because no data were reported (482).
Removed because of zero events in both arms (89).
Maternal serious morbidity or death (16 studies included)Removed because no data were reported (536).
Removed because of zero cells in both arms (61).
Instrumental delivery (299 studies included)Removed because no data were reported (311).
Removed because of zero cells in both arms (2).
Removed because of serious protocol deviation (1).
Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes (200 studies included)Removed because no data were reported (324).
Removed because of zero cells in both arms (81).
Removed because of inconsistency in reporting (8).
Neonatal intensive care unit admission (204 studies included)Removed because no data were reported (387).
Removed because of zero cells in both arms (21).
Characteristics of women participating in included trials
Summary characteristics of participants and intervention setting across the 611 included studies are reported in Table 2.
| Effect modifier | Number of trials | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parity | Mixed | Multiparous only | Nulliparous only | NR |
| 456 | 15 | 79 | 63 | |
| Previous CS | None with CS | All with CS | Some with CS | NR |
| 396 | 5 | 37 | 175 | |
| Cervix | Unfavourable | Favourable | Mixed | NR |
| 399 | 28 | 111 | 75 | |
| Membranes | All intact | All ruptured | Mixed | NR |
| 296 | 98 | 68 | 151 | |
| Gestational age | All post term | All > 37 weeks | Mixed (some pre term) | NR |
| 72 | 333 | 149 | 59 | |
| Multiple pregnancy | All singleton | All multiple | Mixed | NR |
| 453 | 1 | 13 | 146 | |
| Setting | Inpatient | Some/all arms outpatient | NR | |
| 524 | 79 | 10 | ||
| Pharmaceutical company funding | No funding | Some funding | NR | |
| 109 | 55 | 449 | ||
Trials varied considerably in terms of inclusion/exclusion criteria. For those trials that reported parity as an inclusion criterion, most (83%) recruited both women expecting their first baby and those who had given birth before. More than two-thirds of trials explicitly excluded women who had experienced a previous CS (64.6%). However, 175 trials did not specifically mention excluding these women but may have reported excluding women at ‘high risk’, which may have included women with complications during a previous birth. Women with multiple pregnancies were generally excluded. The majority of trials (73%) that specified inclusion criteria relating to gestational age specifically excluded women at < 37 completed weeks’ gestation. Of these 405 trials, 72 recruited women with post-term pregnancies only, usually defined as gestational age of > 41 weeks. Other trials included a small number of women with preterm pregnancies, although we specifically excluded trials including women with extremely preterm pregnancies as our focus was on third-trimester induction of labour.
Most studies recruited women with intact membranes (64% of those trials specifying inclusion criteria relating to membrane status), although some trials specifically focused on induction of labour for women with premature rupture of the amniotic membranes (21% of trials specifying membrane status).
Finally, the induction process was mainly commenced in those women with a Bishop score < 6 (unfavourable cervix); 28 trials (4.6%) recruited only women with a favourable cervix, although approximately 20% of trials that described membrane status at recruitment included women with a range of Bishop scores.
Other trial characteristics
The vast majority of trials were carried out in hospital settings and women remained inpatients throughout the induction process. For many pharmacological agents constant maternal and fetal monitoring was considered mandatory, and facilities for CS and newborn specialist care were close by in case of complications. Trials looking at non-pharmacological methods of inducing labour (e.g. membrane sweeping) were more likely to take place in outpatient settings.
Trials were assessed for risk of bias relating to the method used to conceal allocation. There was a fairly even balance between those trials assessed as being at low risk of bias and those assessed as being at high or unclear risk of bias (both of these categories were treated as high risk of bias in the sensitivity analysis). There were 300 trials that were judged to be at high risk of bias for allocation concealment compared with 313 trials that were judged to be at low risk of bias.
Finally, we also extracted information from trial reports regarding whether or not the trial was funded by a pharmaceutical company. Unfortunately, the source of funding for most trials was not reported. Of the 164 trials that did report source of funding, one-third were funded by a drug company, although this funding may have been partial (provision of study medication and placebo preparations only).
Results: network and pairwise meta-analysis
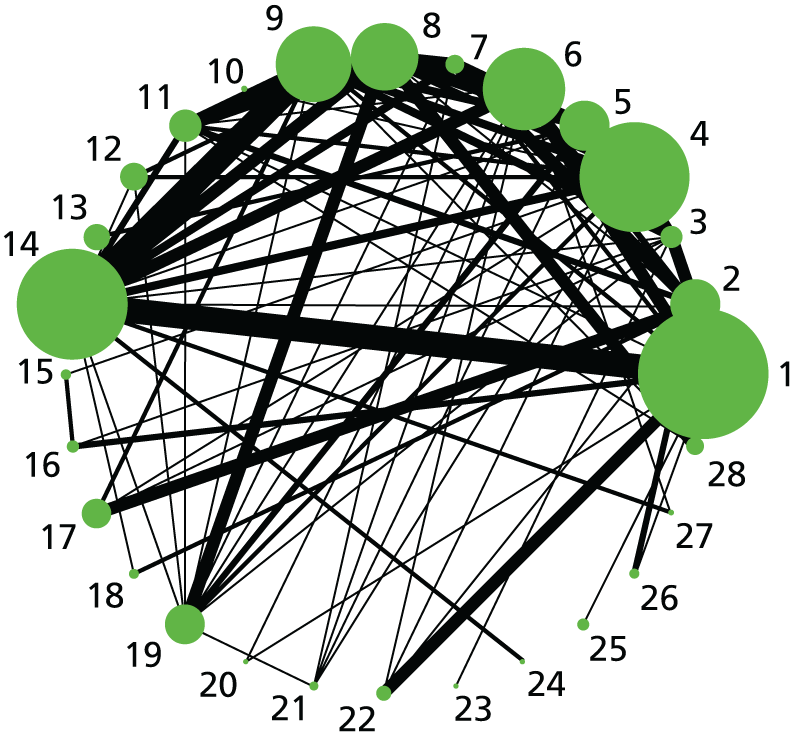
The outcome-specific network diagrams are presented in Figure 2 for failure to achieve VD in 24 hours, Figure 3 for CS, Figure 4 for instrumental delivery, Figure 5 for uterine hyperstimulation, Figure 6 for NICU admission and Figure 7 for Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes. Studies were excluded when there were 0% or 100% events in every arm, for that outcome only. Network diagrams are presented within each relevant section and by outcome. The edges (lines) connecting each pair of interventions represent a direct comparison and are drawn proportional to the number of trials making each direct comparison. 953 However, this weighting is relative within each graph, and edge thickness should not be compared across graphs. For information on the number of trials in each analysis please see Appendix 14. As noted above (see Results of the systematic review), there were insufficient data on serious maternal morbidity or death (20 events) to be used in a NMA. Therefore, these data are summarised narratively below (see Neonatal and maternal mortality and severe morbidity). In addition, only a small proportion of trials reported outcomes relating to women’s perceptions of their care during childbirth and their satisfaction with the induction of labour process. Furthermore, when these outcomes were reported they were defined and measured in different ways across trials. For these reasons we were not able to analyse maternal satisfaction outcomes in a NMA, but we have included a narrative description in the text (see Maternal satisfaction with care and induction of labour method).
FIGURE 2.
Failure to achieve VD in 24 hours. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials comparing directly each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). Interventions are numbered as follows: 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; 16, NO; 17, mifepristone; 18, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 19, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 20, extra-amniotic PGE2; 21, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
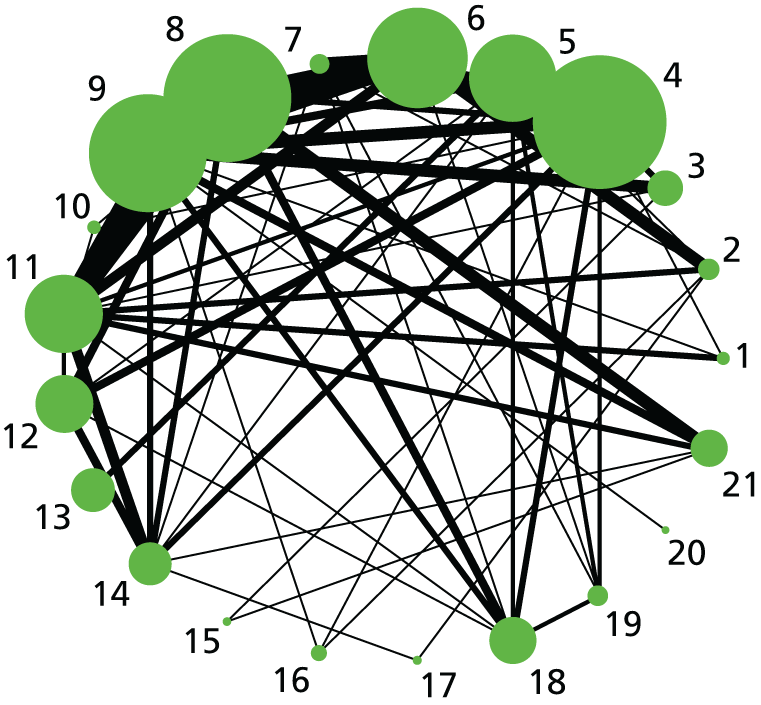
FIGURE 3.
Caesarean section. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials directly comparing each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). Interventions are numbered as follows: 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, PGF2 gel; 7, intracervical PGE2; 8, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 9, vaginal misoprostol (< 50 µg); 10, vaginal misoprostol (≥ 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (< 50 µg); 12, oral misoprostol tablet (≥ 50 µg); 13, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 14, sustained-release misoprostol insert, 15, i.v. oxytocin, 16, amniotomy; 17, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; 18, NO; 19, mifepristone; 20, oestrogens; 21, corticosteroids; 22, relaxin; 23, hyaluronidase; 24, Foley catheter; 25, laminaria; 26, double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 27, membrane sweeping; 28, extra-amniotic PGE2; 29, i.v. prostaglandin; 30, sexual intercourse; 31, acupuncture; 32, oral prostaglandins; 33, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
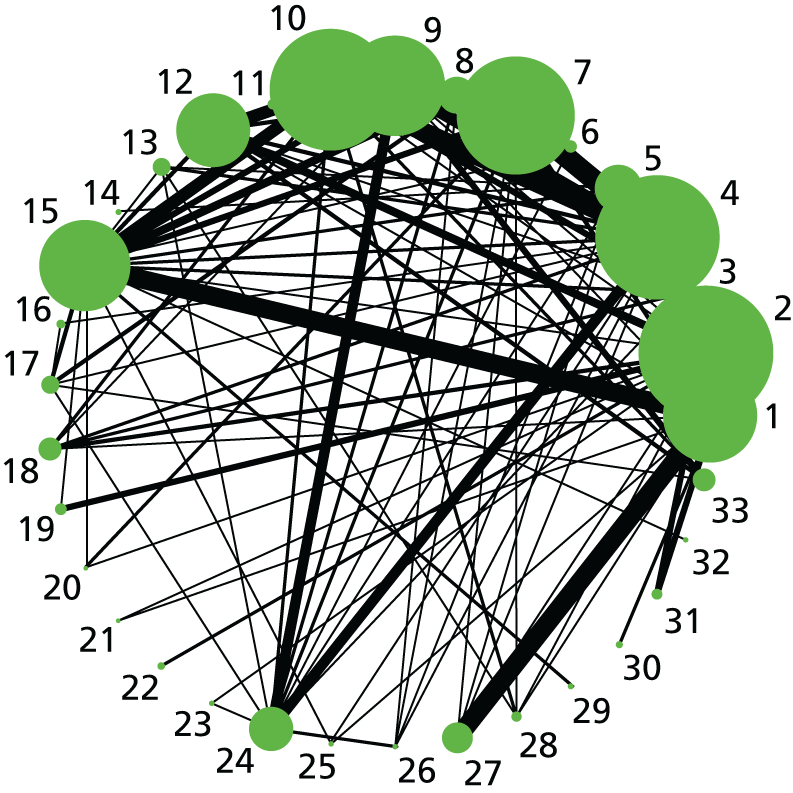
FIGURE 4.
Instrumental delivery. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials directly comparing each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). Interventions are numbered as follows: 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, PGF2 gel; 7, intracervical PGE2; 8, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 9, vaginal misoprostol (< 50 µg); 10, vaginal misoprostol (≥ 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (< 50 µg); 12, oral misoprostol tablet (≥ 50 µg); 13, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 14, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 15, i.v. oxytocin; 16, amniotomy; 17, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; 18, NO; 19, mifepristone; 20, oestrogens; 21, relaxin; 22, Foley catheter; 23, laminaria; 24, double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 25, membrane sweeping; 26, extra-amniotic PGE2; 27, i.v. prostaglandin; 28, sexual intercourse; 29, acupuncture; 30, homeopathy; 31, oral prostaglandins; 32, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
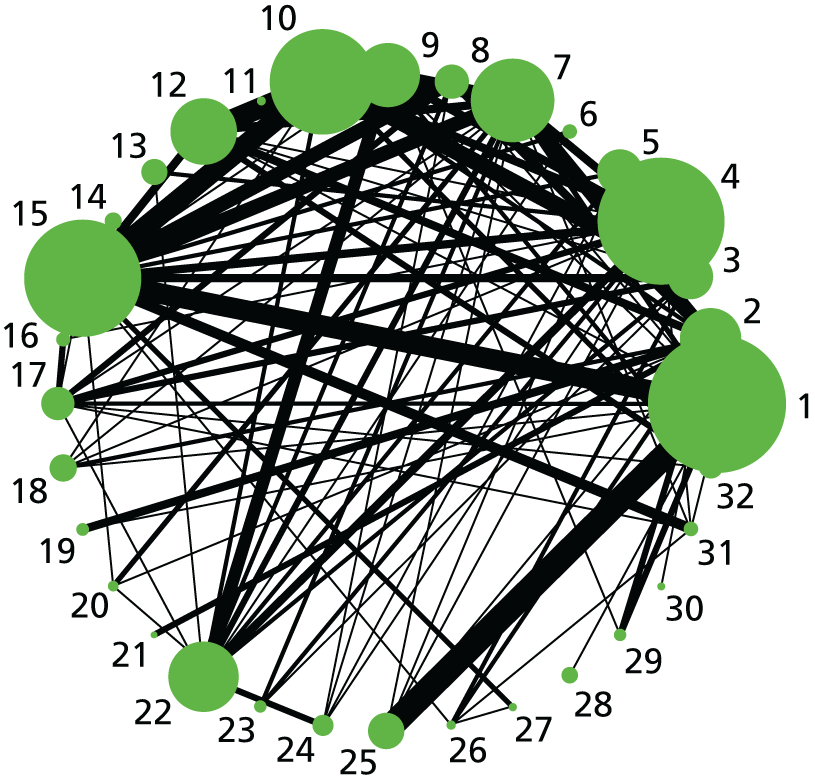
FIGURE 5.
Hyperstimulation with FHR changes. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials directly comparing each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (< 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (< 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; 16, NO; 17, mifepristone; 18, Foley catheter; 19, laminaria; 20, double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 21, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
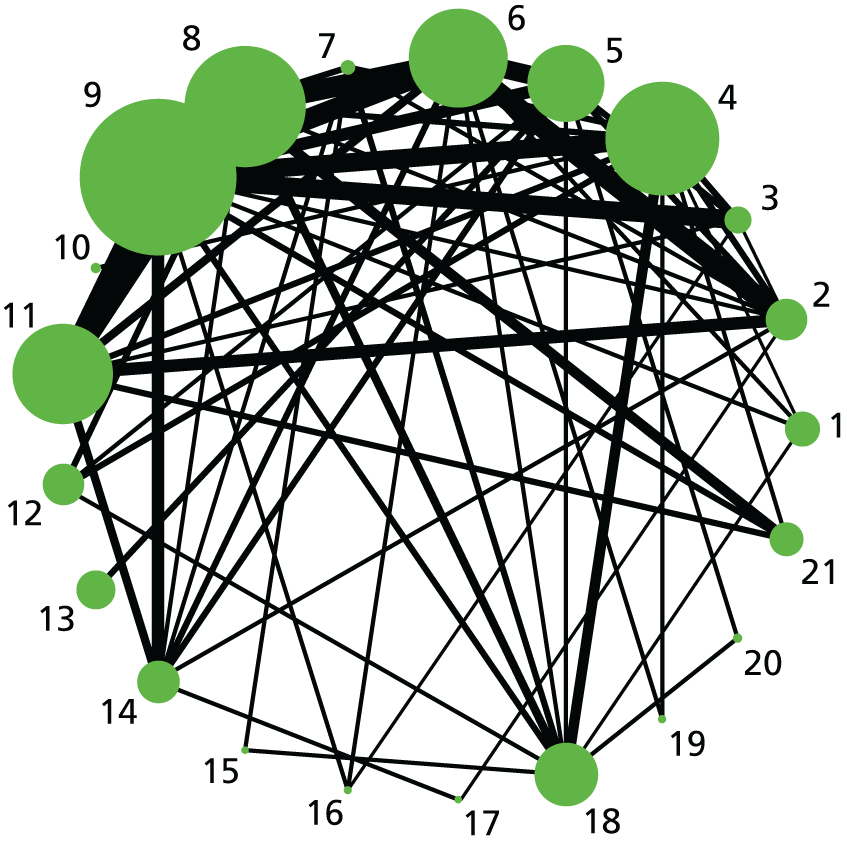
FIGURE 6.
Neonatal intensive care unit admission. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials directly comparing each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, PGF2 gel; 7, intracervical PGE2; 8, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 10, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 12, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 13, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 14, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 15, i.v. oxytocin; 16, amniotomy; 17, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; 18, NO; 19, mifepristone; 20, oestrogens; 21, Foley catheter; 22, laminaria; 23, double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 24, membrane sweeping; 25, extra-amniotic PGE2; 26, sexual intercourse; 27, acupuncture; 28, oral prostaglandins; 29, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
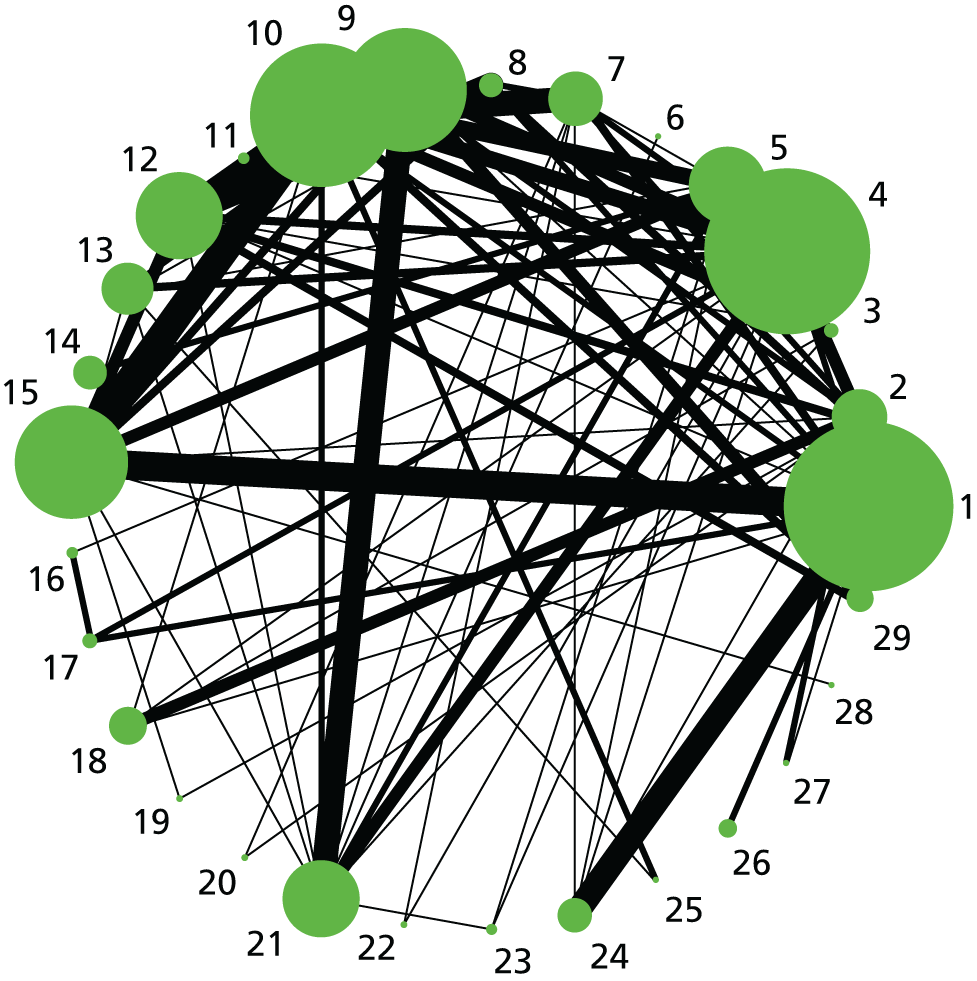
FIGURE 7.
Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials directly comparing each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, amniotomy; 16, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; 17, NO; 18, mifepristone; 19, Foley catheter; 20, laminaria; 21, double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 22, membrane sweeping; 23, extra-amniotic PGE2; 24, i.v. prostaglandin; 25, sexual intercourse; 26, acupuncture; 27, oral prostaglandins; 28, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
Vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours
After excluding trials with zero events in all arms, 141 trials of 19 active interventions were included for the outcome VD not achieved within 24 hours. Placebo and no intervention comparisons were also included. No trials comparing PGF2, amniotomy, oestrogens, corticosteroids, relaxin, hyaluronidase, laminaria, membrane sweeping, i.v. prostaglandin, sexual intercourse, acupuncture, breast stimulation, homeopathy, castor oil or oral prostaglandins reported this outcome. No meaningful differences were observed in posterior mean residual deviance or DIC values, suggesting that there was no evidence of inconsistency (see Appendix 11, Table 44). Reported results are therefore based on the REs NMA model assuming consistency (Table 3 and Figure 8).
| Active intervention vs. placebo | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | Direct trials | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | ||
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.05 | 0.07 to 0.32 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.09 | 0.06 to 0.24 | – | – | 0 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.10 | 0.07 to 0.29 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.11 | 0.09 to 0.32 | – | – | 0 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.11 | 0.05 to 0.22 | – | – | 0 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.11 | 0.05 to 0.19 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.11 | 0.04 to 0.16 | 0.67 | 0.06 to 2.76 | 1 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.13 | 0.08 to 0.50 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.15 | 0.08 to 0.29 | – | – | 0 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.16 | 0.05 to 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.03 to 0.31 | 2 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.16 | 0.03 to 0.26 | – | – | 0 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.18 | 0.09 to 0.38 | 0.09 | 0.03 to 0.19 | 5 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.18 | 0.01 to 0.16 | – | – | 0 |
| Foley catheter | 0.19 | 0.09 to 0.46 | – | – | 0 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.20 | 0.21 to 1.97 | – | – | 0 |
| NO | 0.22 | 0.08 to 0.36 | 1.07 | 0.30 to 2.78 | 1 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.22 | 0.07 to 0.39 | – | – | 0 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.41 | 0.07 to 1.33 | – | – | 0 |
| Mifepristone | 0.76 | 0.05 to 0.20 | 0.81 | 0.16 to 2.52 | 1 |
FIGURE 8.
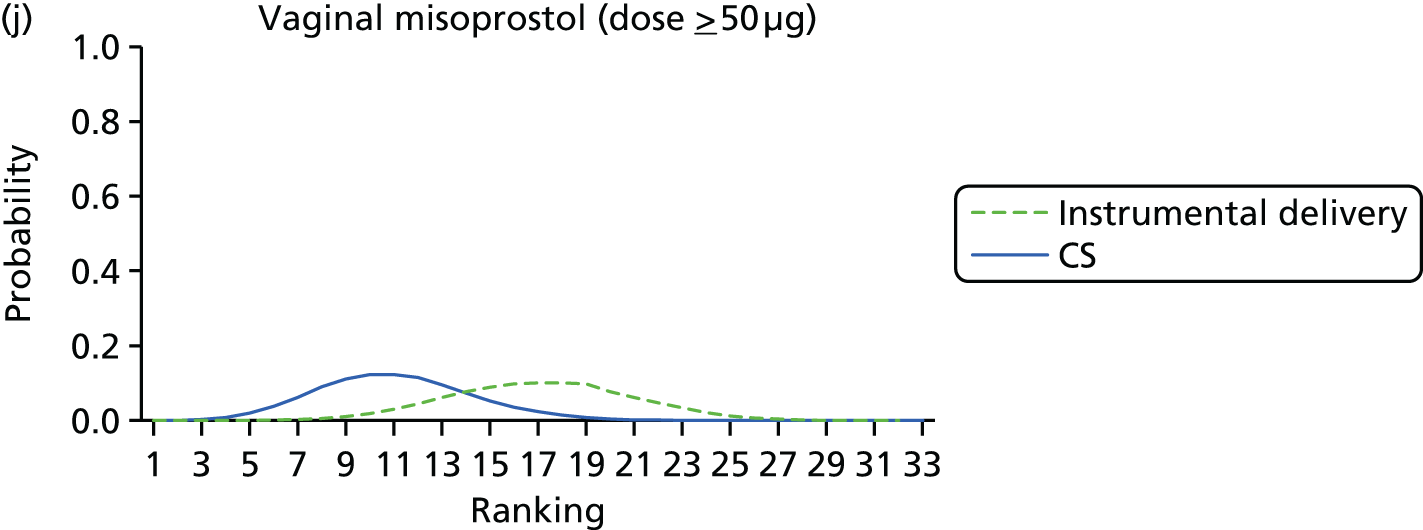
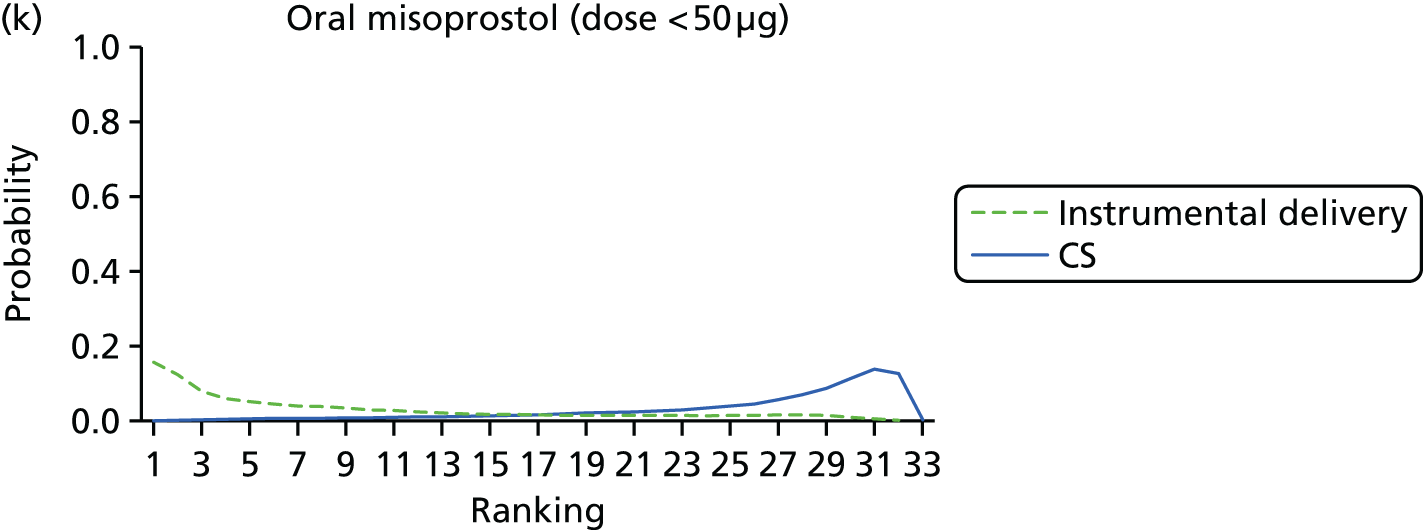
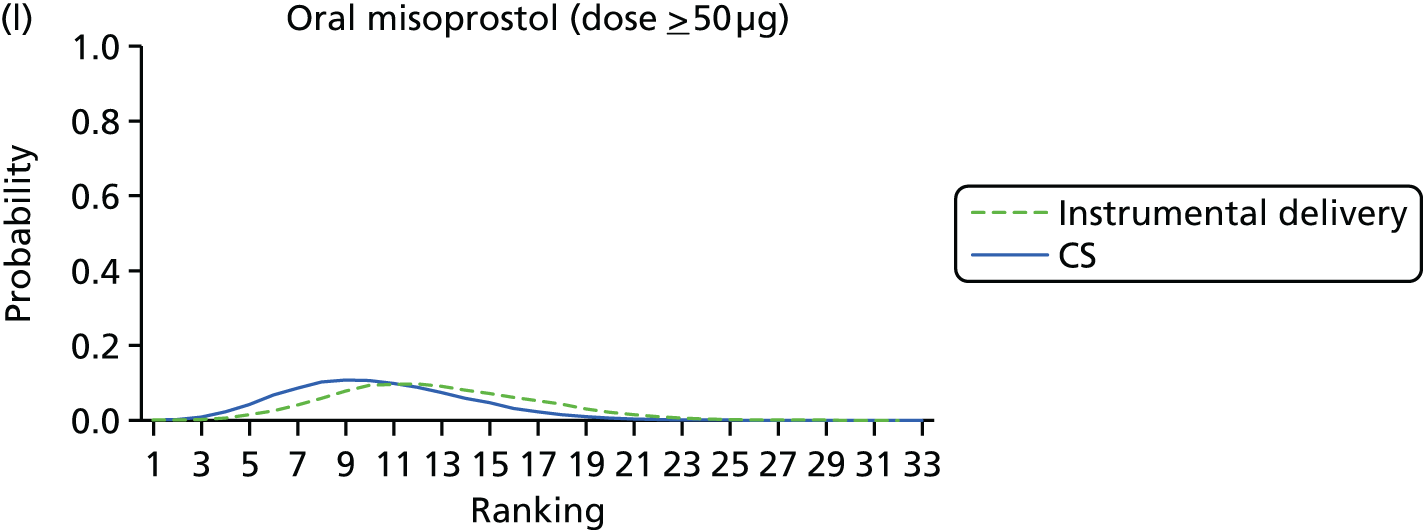
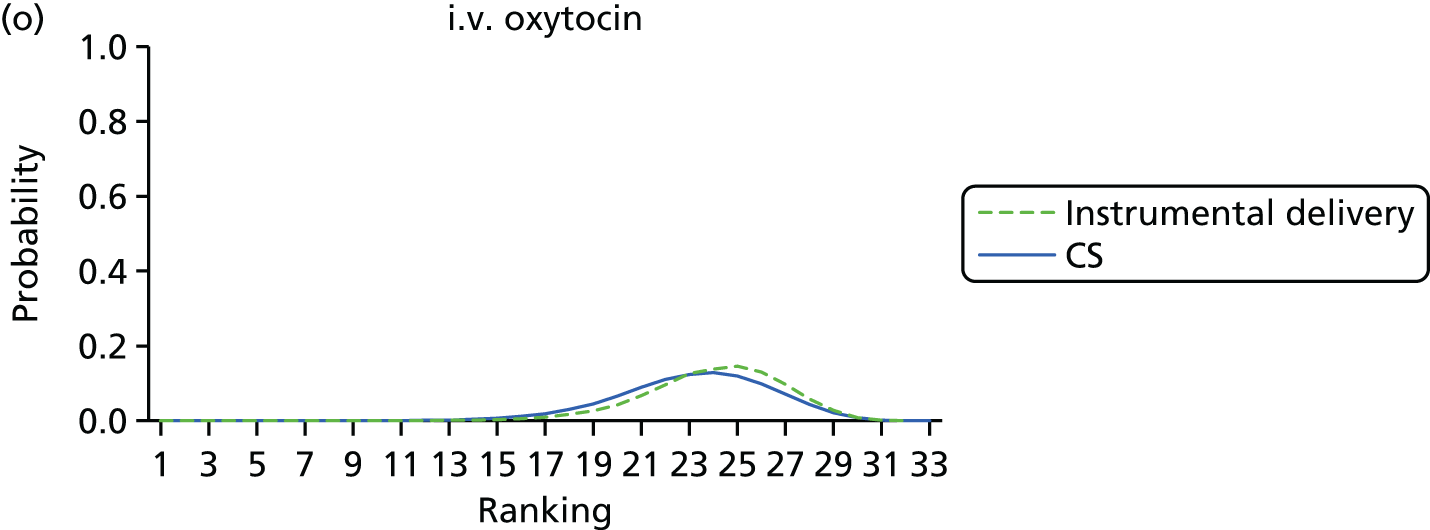
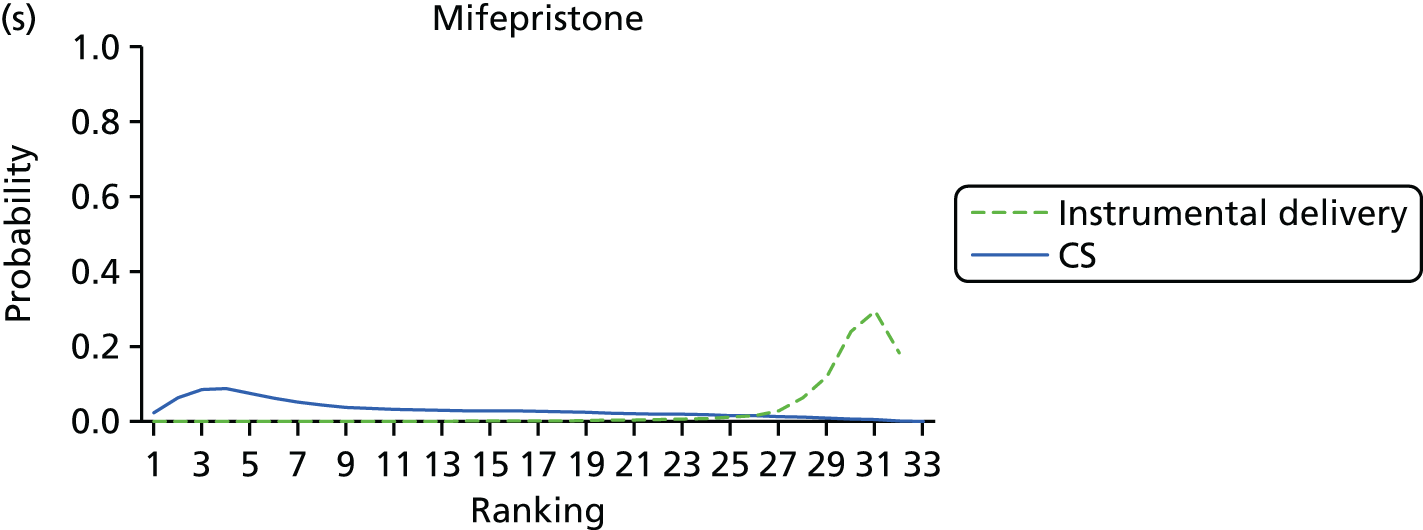
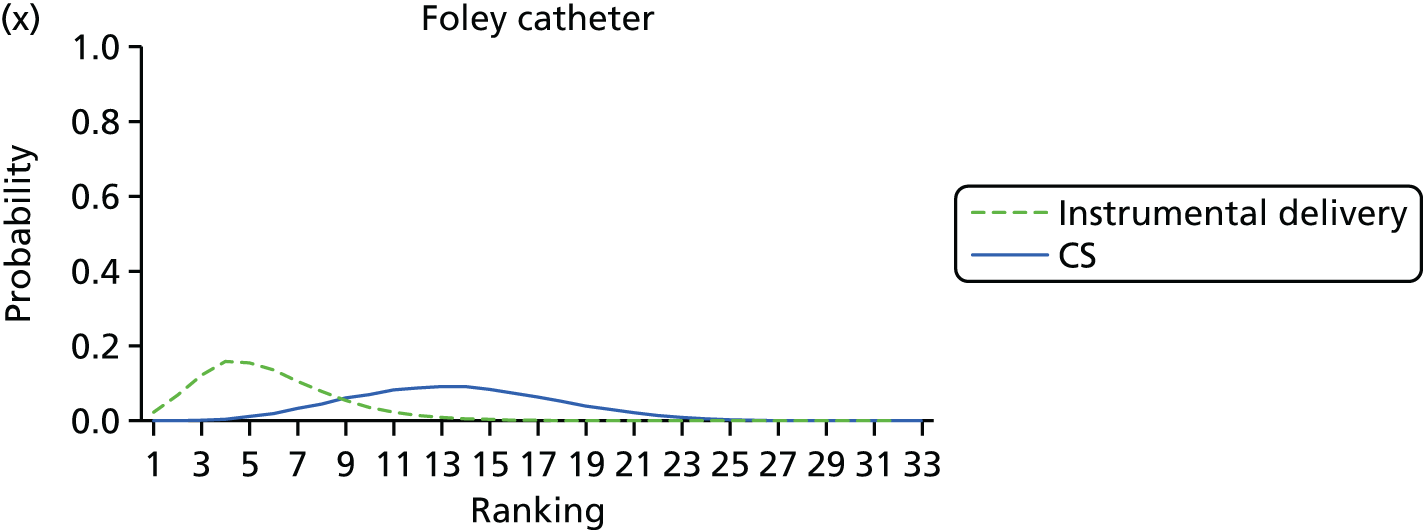
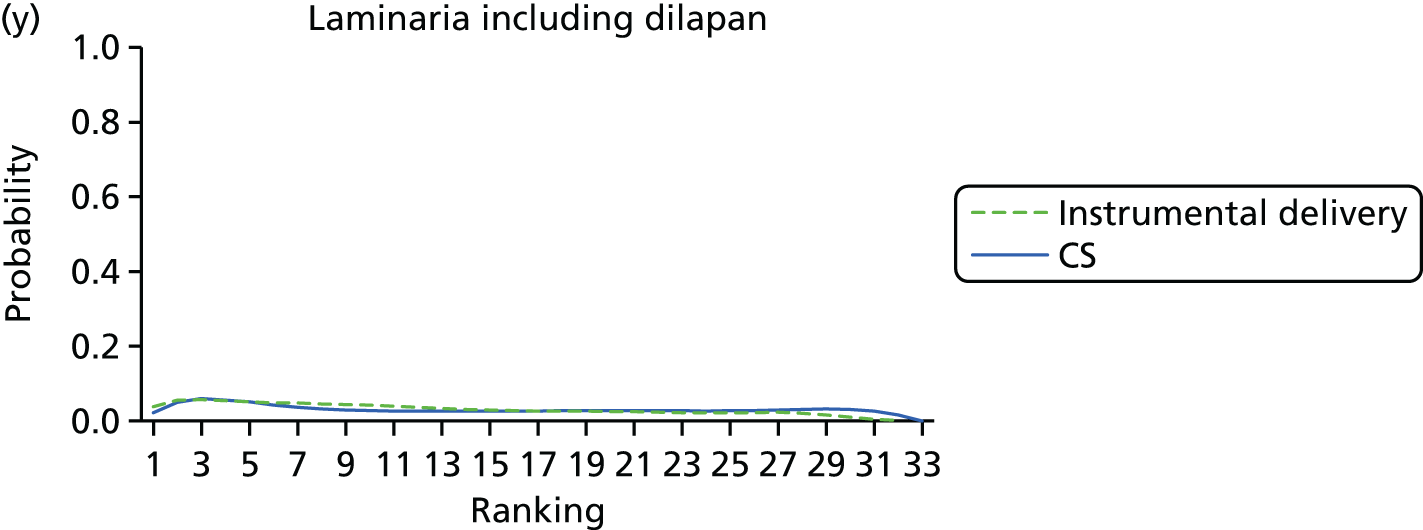
Rankograms for each of the 20 induction interventions for hyperstimulation and VD not achieved within 24 hours. Ranking indicates the probability of being the best intervention, the second best, the third best, etc. The x-axis shows the relative ranking and the y-axis the probability of each ranking. (a) No treatment; (b) placebo; (c) vaginal PGE2 (tablet); (d) vaginal PGE2 (gel); (e) vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); (f) intracervical PGE2; (g) vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); (h) vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); (i) vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥50 µg); (j) oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); (k) oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); (l) titrated (low-dose) misoprostol; (m) sustained-release misoprostol insert; (n) i.v. oxytocin; (o) NO; (p) i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; (q) mifepristone; (r) Foley catheter; (s) laminaria including dilapan; (t) double balloon or Cook’s catheter; and (u) extra-amniotic PGE2.
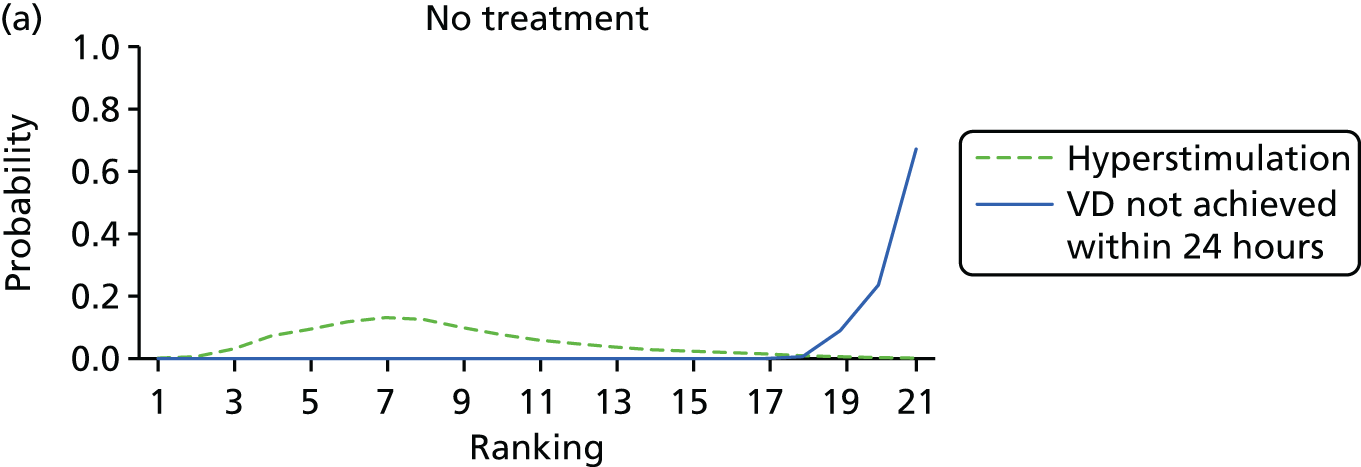
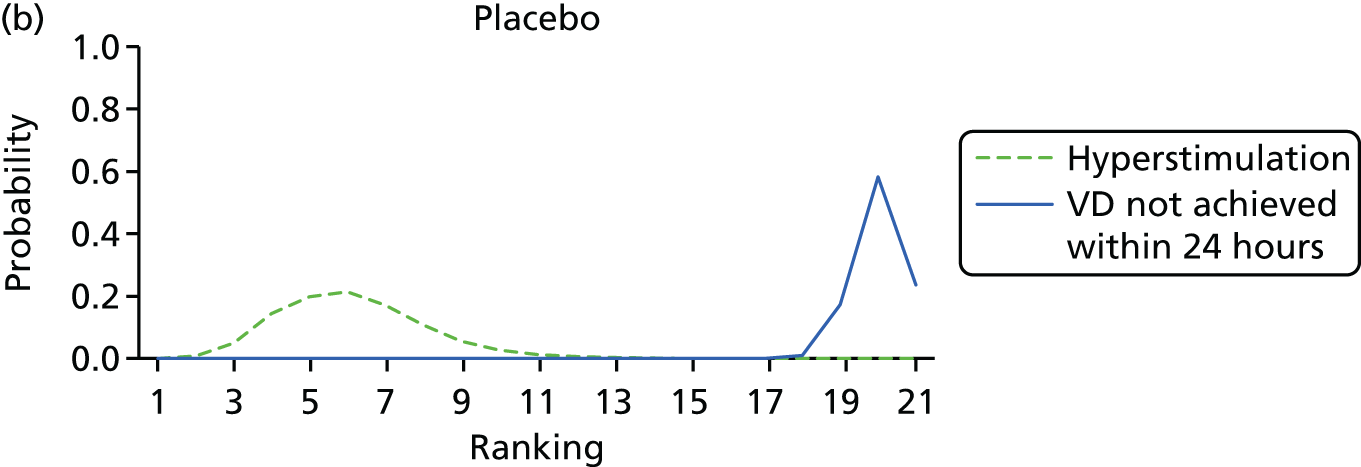

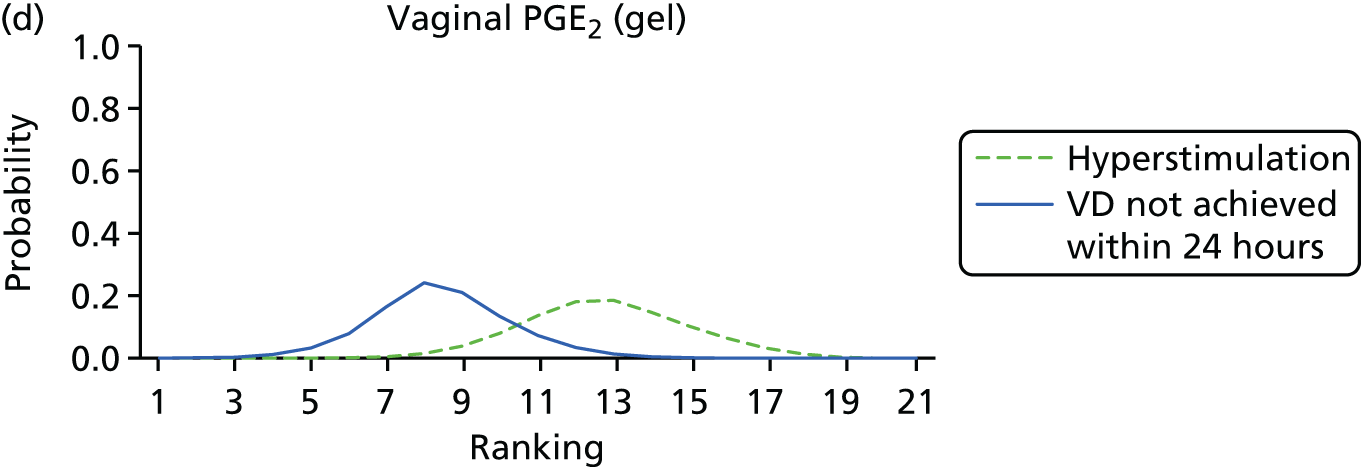
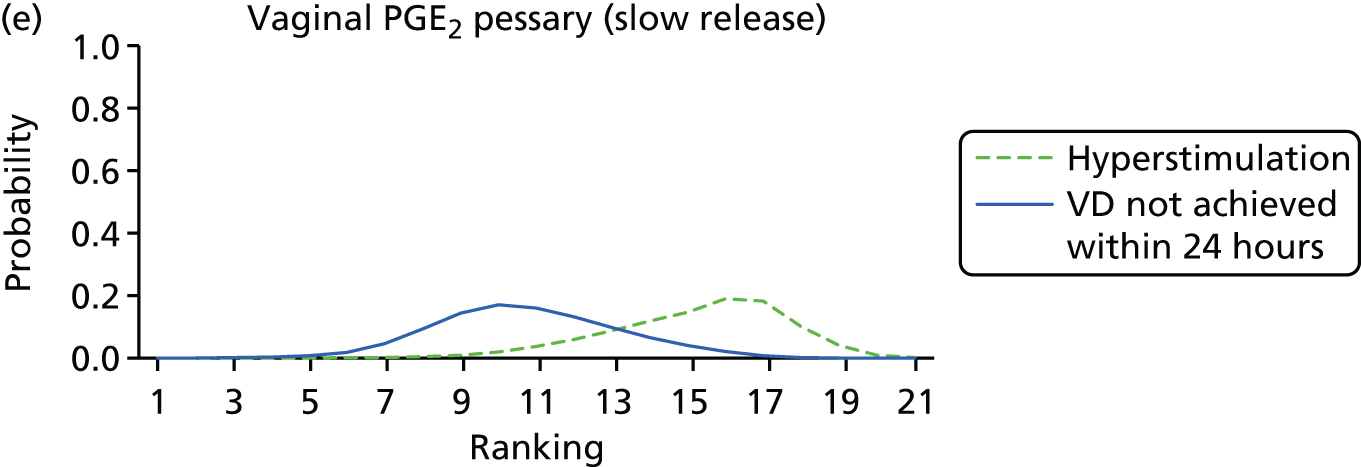
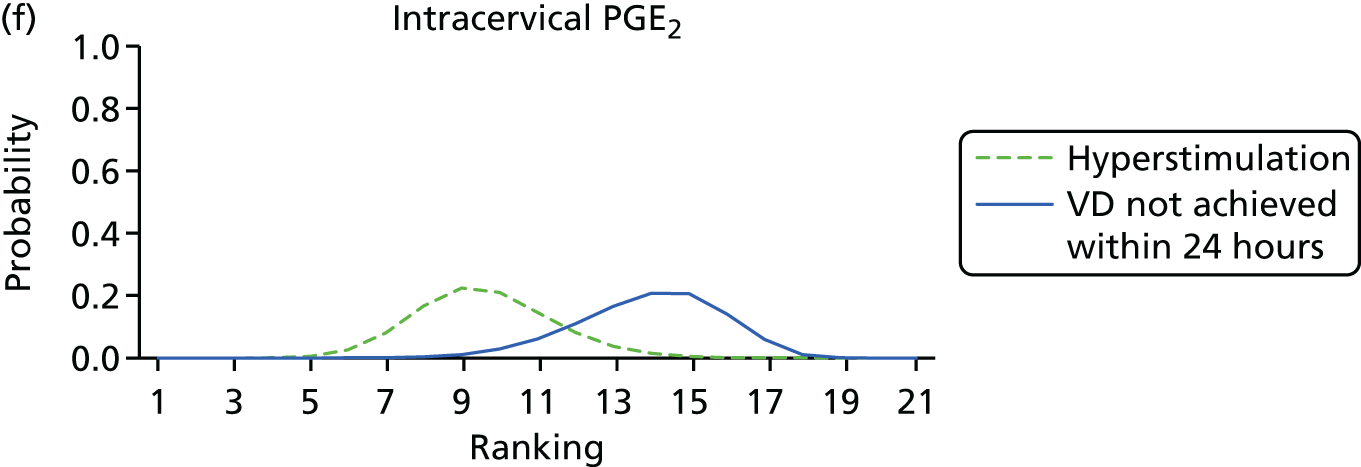






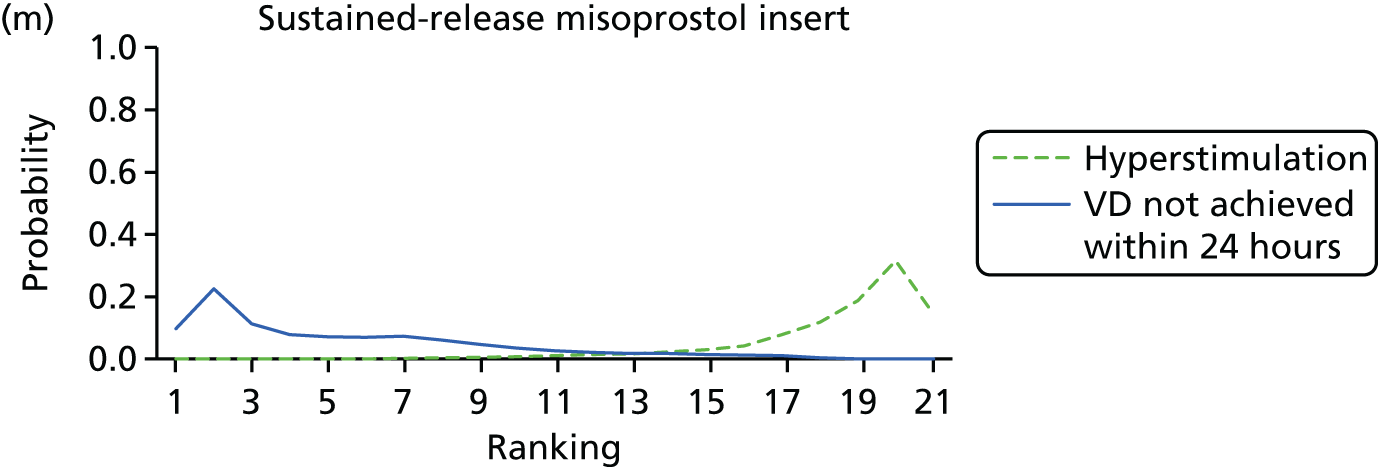
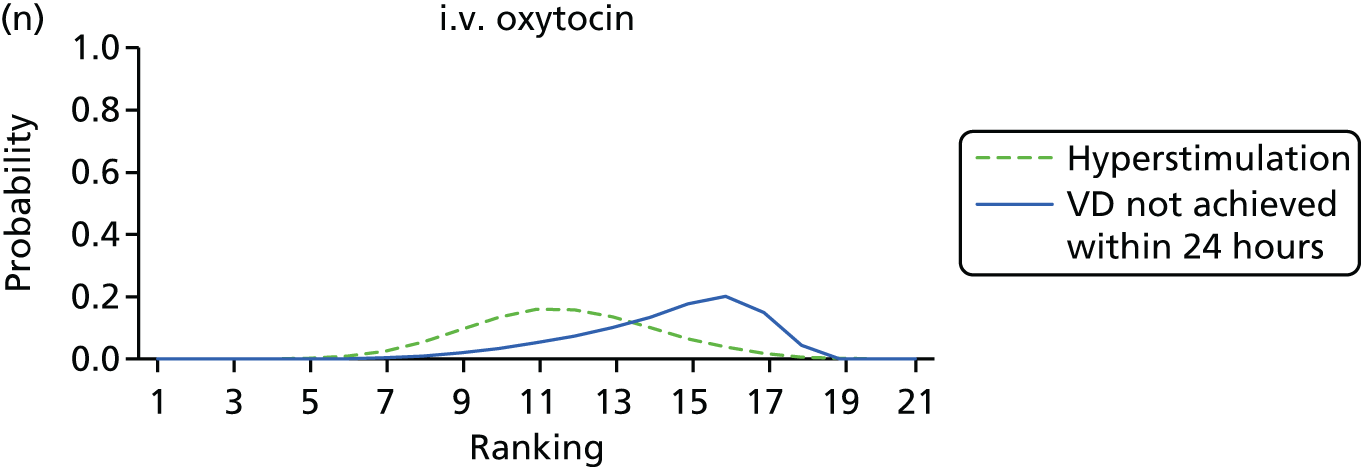


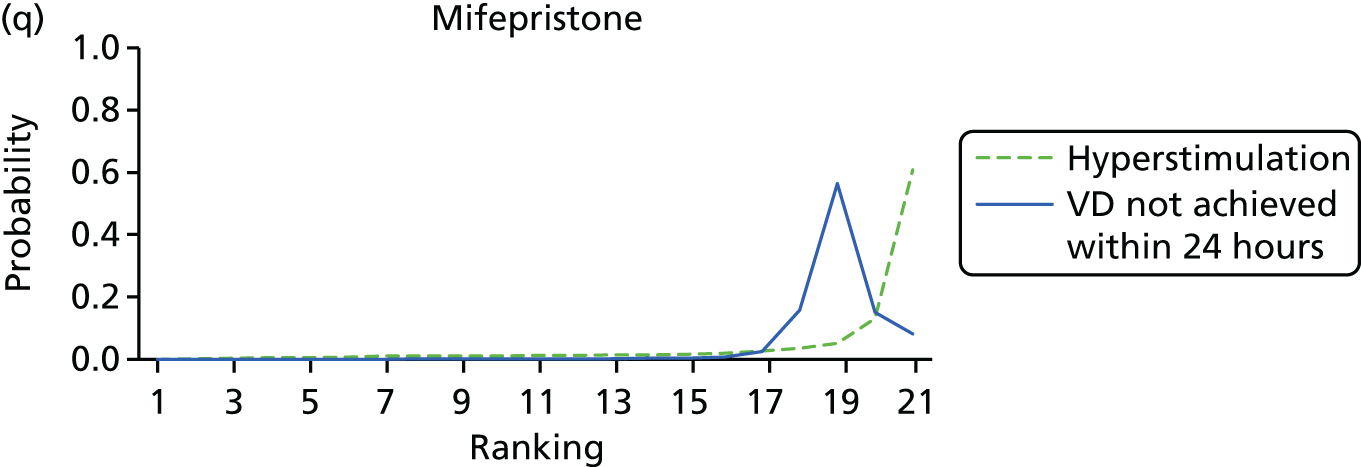
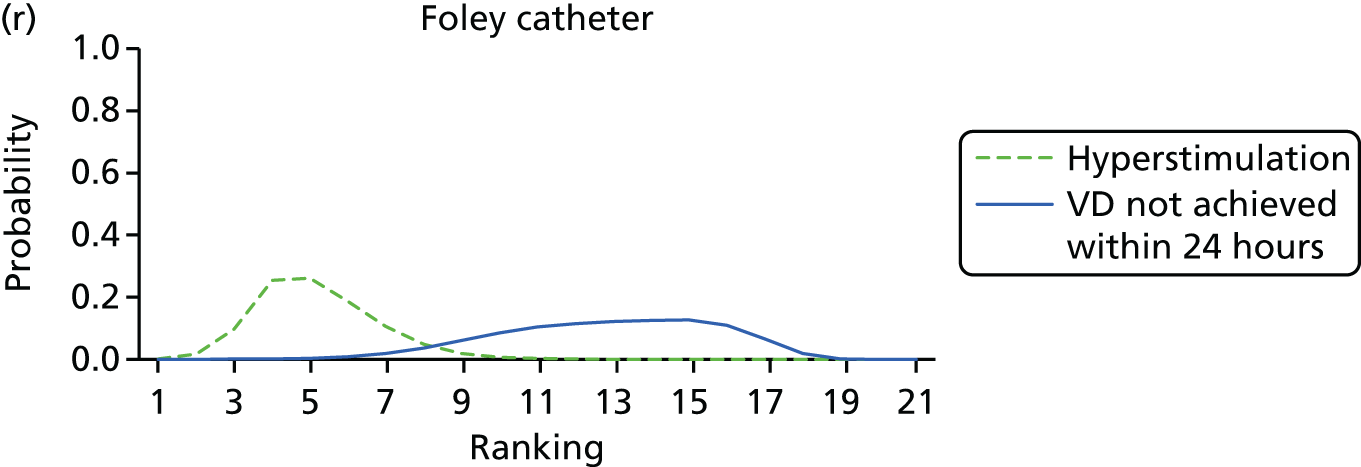
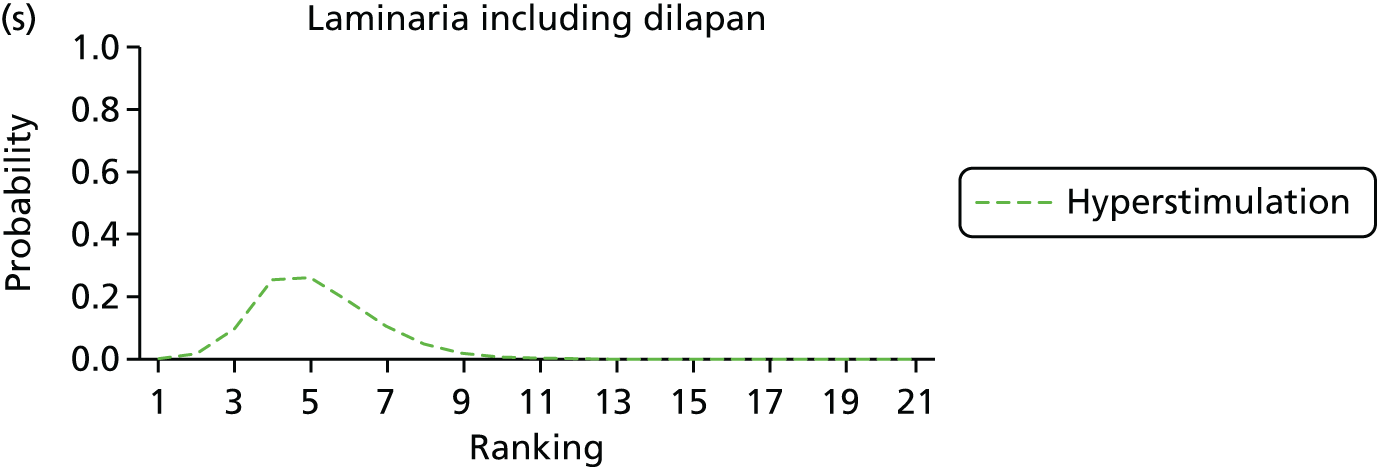
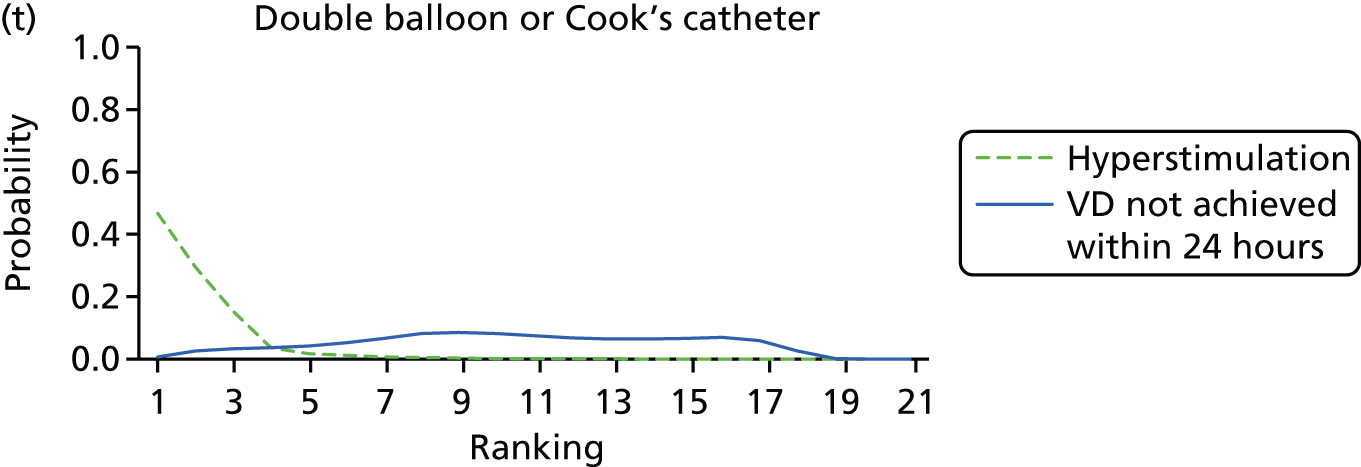

Despite the observation of high between-trials heterogeneity, relative to the size of the intervention effect estimates, [τ = 0.54 (95% CrI 0.44 to 0.65)] there was strong evidence that all interventions, except for mifepristone and extra-amniotic PGE2, increased the probability of vaginal birth within 24 hours (see Table 3). We note that there was some indication that the direct and NMA results were inconsistent for NO, as the point estimate from the NMA (OR 0.21) lies outside the CrI from the direct evidence (95% CrI 0.30 to 2.78). However, the CrIs for both the NMA and direct evidence were overlapping. The full results of each intervention compared with every other have been reported in Appendix 12 (see Table 50) and compared with the direct evidence when it is available.
Figure 8 shows the distribution of the ranks for each of the 20 interventions. The x-axis reports each of the possible ranks, for which position 1 means that the intervention is ranked the highest and position 21 the lowest. Note the number of interventions varies across outcomes because of trial design and reporting. The y-axis shows the probability with which each intervention has been ranked at each of the 21 possible positions and therefore fully encapsulates the uncertainty in the intervention rankings. The peaks in the rankogram plots show the most likely rank for a given intervention. Flat lines indicate a high degree of uncertainty for the ranking of that intervention type.
The highest ranked intervention was i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy, with a probability of being best of 75%, a posterior mean rank of ‘2’ (95% CrI 1 to 10) and an OR of 0.05 (95% CrI 0.01 to 0.14). Intravenous oxytocin with amniotomy had the lowest absolute probability of not achieving VD within 24 hours at 17% (95% CrI 3% to 44%) (Table 4). The probability of being ranked in the top three interventions was 88% for i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy, 51% for vaginal misoprostol (≥ 50 µg) (posterior mean rank 4 (95% CrI 2 to 7), and 50% for vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) (posterior mean rank 4 (95% CrI 1 to 11). The probability of being ranked in the bottom three interventions (i.e. poorest in terms of achieving a vaginal birth within 24 hours) was 80% for mifepristone with a posterior mean rank of 19 (95% CrI 17 to 21). We note from Table 3 that for mifepristone the OR is 0.72 and the 95% CrIs are consistent with both harm and benefit (0.20 to 1.85).
| Intervention | Absolute probability of VD not in 24 hours | Posterior mean rank | 95% CrI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Posterior mean | 95% CrI | |||
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.33 | 0.11 to 0.61 | 2 | 1 to 9 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.48 | 0.34 to 0.61 | 3 | 1 to 6 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.50 | 0.27 to 0.73 | 5 | 1 to 16 |
| Titrated (low) oral misoprostol solution | 0.50 | 0.34 to 0.67 | 5 | 1 to 10 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.51 | 0.37 to 0.65 | 5 | 2 to 8 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.51 | 0.35 to 0.67 | 5 | 2 to 11 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.52 | 0.34 to 0.70 | 6 | 1 to 13 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.57 | 0.42 to 0.70 | 8 | 5 to 12 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.60 | 0.45 to 0.74 | 11 | 6 to 16 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.62 | 0.53 to 0.70 | 11 | 5 to 17 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.62 | 0.48 to 0.75 | 12 | 7 to 16 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.63 | 0.44 to 0.80 | 12 | 4 to 18 |
| Foley catheter | 0.65 | 0.48 to 0.79 | 13 | 7 to 18 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.65 | 0.51 to 0.77 | 14 | 10 to 17 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.66 | 0.51 to 0.80 | 14 | 9 to 18 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.67 | 0.46 to 0.84 | 14 | 5 to 18 |
| NO | 0.68 | 0.46 to 0.84 | 14 | 5 to 18 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.75 | 0.44 to 0.93 | 16 | 3 to 20 |
| Mifepristone | 0.86 | 0.66 to 0.96 | 19 | 16 to 21 |
| No intervention | 0.91 | 0.83 to 0.96 | 20 | 19 to 21 |
| Placebo | 0.94 | 0.86 to 0.98 | 21 | 19 to 21 |
Results were largely robust to a preplanned sensitivity analysis excluding studies at high risk of bias for allocation concealment. The posterior mean ranks were altered for two interventions. A posterior mean rank for vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) changed from 4 to 10, although the 95% CrIs were still overlapping. Sustained-release misoprostol insert changed from 5 to 10. Again 95% CrIs were consistent between the two analyses. Results for the sensitivity analysis are reported in Appendix 13 (see Table 56).
Caesarean section
After the exclusion of trials with 0% or 100% events in all arms, 586 trials with 96,771 women were eligible for inclusion in the NMA. This included 33 active interventions in addition to placebo and no intervention.
Important differences were observed in posterior mean residual deviance and DIC values suggesting that, for the full network, there was evidence of inconsistency (see Appendix 11, Table 45). The addition of a continuity correction of 0.5 for studies with zero events (on either arm) did not improve model fit. We conducted a prespecified sensitivity analysis examining the effect of removing trials at high risk of bias. The REs model, continuity corrected and excluding trials at high risk of bias, provided an adequate fit to the data (see Appendix 11, Table 45). Therefore, reported results are based on this model, with 307 trials and 57,370 women (see Tables 5 and 6, and Figure 3). Thirty-one interventions, in addition to placebo and no intervention are included in the analysis. No trials comparing breast stimulation, homeopathy or castor oil were included in this analysis because of a high risk of bias.
| Active intervention vs. placebo | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Trials | |
| Corticosteroids | 0.53 | 0.20 to 1.12 | 0.72 | 0.25 to 1.65 | 1 |
| Hyaluronidase | 0.61 | 0.34 to 1.00 | 0.24 | 0.10 to 0.46 | 1 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.62 | 0.47 to 0.80 | – | – | 0 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.68 | 0.51 to 0.89 | – | – | 0 |
| PGF2 gel | 0.70 | 0.40 to 1.16 | 0.65 | 0.27 to 1.30 | 3 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.70 | 0.57 to 0.85 | 1.14 | 0.58 to 2.05 | 3 |
| Mifepristone | 0.71 | 0.45 to 1.08 | 0.63 | 0.39 to 0.95 | 5 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.72 | 0.58 to 0.88 | 0.60 | 0.35 to 0.96 | 6 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.72 | 0.08 to 2.59 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.73 | 0.59 to 0.88 | 1.32 | 0.17 to 4.64 | 2 |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.74 | 0.53 to 0.99 | 1.78 | 0.22 to 6.41 | 1 |
| Foley catheter | 0.76 | 0.61 to 0.95 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.79 | 0.65 to 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.63 to 1.37 | 10 |
| Laminaria | 0.80 | 0.43 to 1.38 | – | – | 0 |
| Acupuncture | 0.81 | 0.52 to 1.20 | 0.76 | 0.46 to 1.16 | 4 |
| NO | 0.82 | 0.62 to 1.06 | 1.05 | 0.70 to 1.49 | 4 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.82 | 0.62 to 1.09 | 0.76 | 0.41 to 1.29 | 3 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.83 | 0.69 to 0.98 | 0.85 | 0.66 to 1.09 | 17 |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.85 | 0.54 to 1.29 | – | – | 0 |
| Relaxin | 0.88 | 0.33 to 1.98 | 0.90 | 0.32 to 2.03 | 3 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.89 | 0.57 to 1.34 | – | – | 0 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.93 | 0.75 to 1.14 | 1.74 | 0.53 to 4.29 | 1 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.89 | 0.69 to 1.12 | 0.62 | 0.26 to 1.21 | 2 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.98 | 0.59 to 1.55 | – | – | 0 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.98 | 0.57 to 1.57 | 0.47 | 0.16 to 1.03 | 3 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 1.04 | 0.78 to 1.35 | 0.91 | 0.00 to 5.74 | 1 |
| Amniotomy | 1.06 | 0.51 to 2.02 | – | – | 0 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.11 | 0.73 to 1.63 | – | – | 0 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 1.11 | 0.64 to 1.81 | – | – | 0 |
| Oestrogens | 1.27 | 0.62 to 2.32 | 1.97 | 0.66 to 4.49 | 1 |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 19.94 | 1.61 to 120.5 | – | – | 0 |
| Intervention | Absolute probability of CS | Posterior mean rank and 95% CrI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Posterior mean | 95% CrI | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.15 | 0.02 to 0.48 | 6 | 1 to 29 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.17 | 0.03 to 0.49 | 6 | 2 to 13 |
| Hyaluronidase | 0.17 | 0.02 to 0.50 | 7 | 1 to 26 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.17 | 0.01 to 0.61 | 10 | 1 to 32 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.19 | 0.03 to 0.52 | 9 | 2 to 19 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.19 | 0.03 to 0.52 | 9 | 4 to 16 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.19 | 0.03 to 0.53 | 10 | 4 to 18 |
| Mifepristone | 0.19 | 0.03 to 0.54 | 11 | 2 to 28 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.19 | 0.03 to 0.53 | 11 | 5 to 18 |
| PGF2 gel | 0.19 | 0.03 to 0.54 | 11 | 1 to 29 |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.20 | 0.03 to 0.54 | 12 | 3 to 24 |
| Foley catheter | 0.20 | 0.03 to 0.55 | 14 | 6 to 22 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.21 | 0.03 to 0.55 | 15 | 9 to 21 |
| Laminaria | 0.21 | 0.03 to 0.57 | 15 | 2 to 31 |
| Acupuncture | 0.21 | 0.03 to 0.57 | 16 | 2 to 30 |
| NO | 0.21 | 0.03 to 0.57 | 17 | 5 to 28 |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.21 | 0.03 to 0.58 | 17 | 3 to 31 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.21 | 0.04 to 0.57 | 18 | 11 to 24 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.21 | 0.03 to 0.57 | 17 | 6 to 28 |
| Relaxin | 0.22 | 0.03 to 0.61 | 16 | 1 to 32 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.22 | 0.04 to 0.59 | 20 | 4 to 31 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.22 | 0.04 to 0.58 | 21 | 12 to 28 |
| No intervention | 0.22 | 0.04 to 0.58 | 21 | 13 to 27 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.23 | 0.04 to 0.59 | 23 | 16 to 29 |
| Placebo | 0.24 | 0.04 to 0.61 | 26 | 19 to 31 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.24 | 0.04 to 0.61 | 22 | 5 to 32 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.24 | 0.04 to 0.62 | 22 | 4 to 32 |
| Amniotomy | 0.25 | 0.04 to 0.64 | 22 | 3 to 32 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.25 | 0.05 to 0.62 | 26 | 17 to 31 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.26 | 0.04 to 0.64 | 25 | 7 to 32 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.26 | 0.05 to 0.64 | 27 | 14 to 32 |
| Oestrogens | 0.28 | 0.05 to 0.68 | 27 | 5 to 32 |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 0.66 | 0.16 to 0.98 | 33 | 32 to 33 |
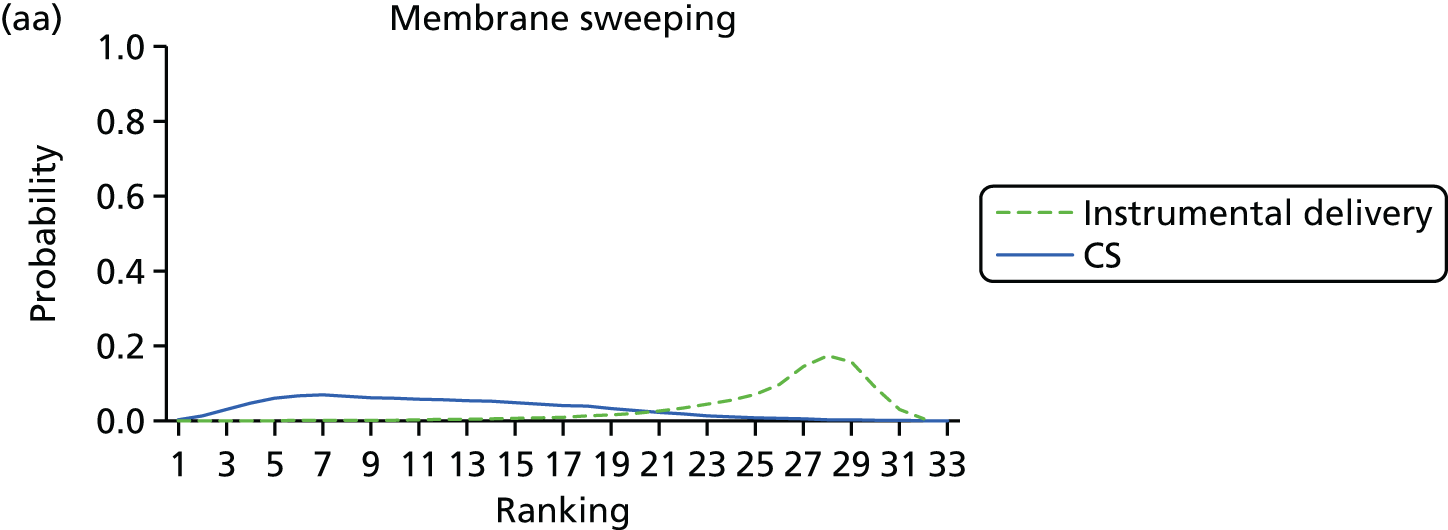
Table 5 reports the posterior median ORs (95% CrI) for each intervention relative to placebo (the full results for all comparisons are reported in Appendix 12, Table 51). As an informal check of consistency, we note that for all interventions, the direct and NMA results are similar. Moderate to low between-trial heterogeneity was observed for this outcome [τ = 0.16 (95% CrI 0.03 to 0.25)]. Using placebo as the reference, nine interventions resulted in significant reduction in CS, namely vaginal PGE2 (gel), intracervical PGE2, vaginal misoprostol tablet < 50 µg, vaginal misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg, oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution, Foley catheter, membrane sweeping and buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
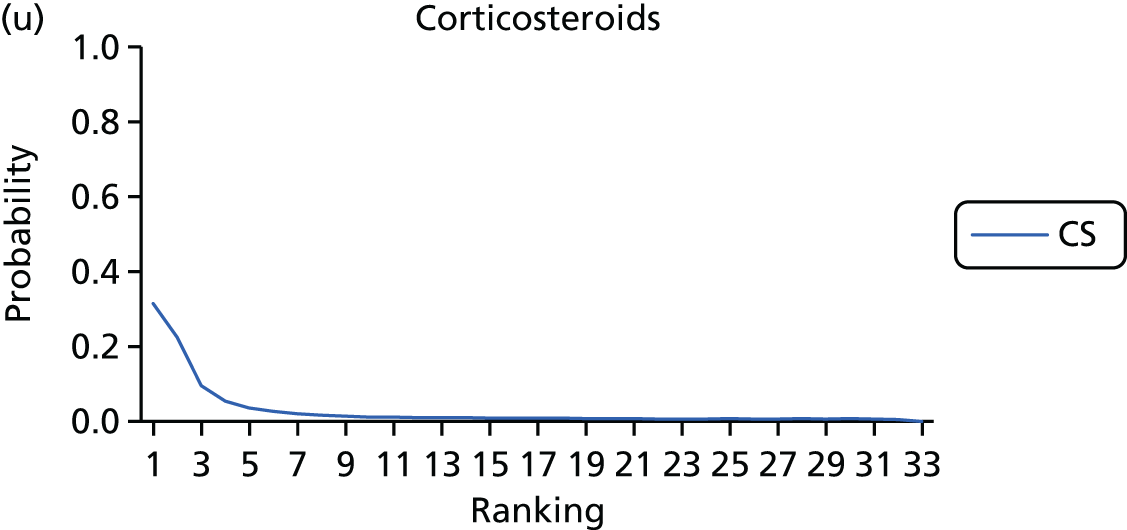
Corticosteroids, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution and hyaluronidase have the largest reduction in odds of CS, but only misoprostol oral solution reached a conventional level of statistical significance. Conversely, i.v. prostaglandin appears to increase odds of CS, although this does not reach statistical significance.
Table 6 reports the posterior mean ranks and absolute probabilities for CS. The interventions with the lowest posterior mean rank (6) were titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution and corticosteroids, with the lowest absolute probability of all interventions at 17% and 15%, respectively. However, the wide CrIs around summary estimates suggest considerable uncertainty. The intervention with the worst posterior mean rank is i.v. prostaglandin ranked 33 (95% CrI 32 to 33) and an absolute probability of CS of 66%, albeit with wide CrIs (95% CrI 16% to 98%).
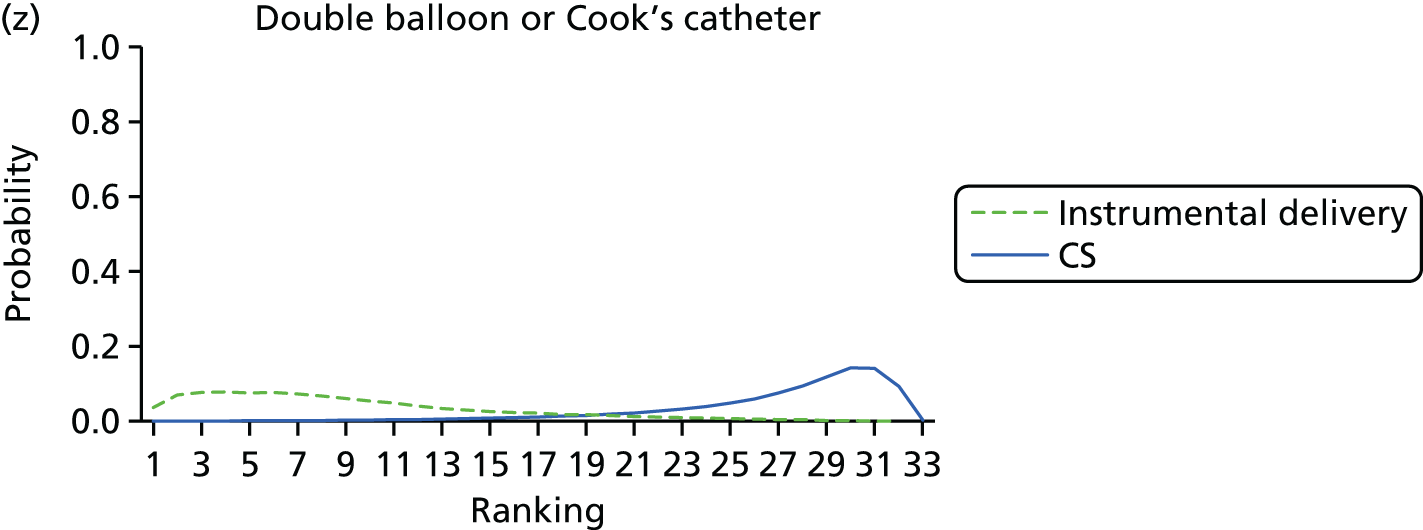
Figure 9 reports the rankograms for this outcome. We note that for all of the interventions the rankograms are flat, with relatively low peaks – indicative of considerable uncertainty around the probability any intervention is the ‘best’. We do not therefore include an assessment of which probability is best in our summary for CS.
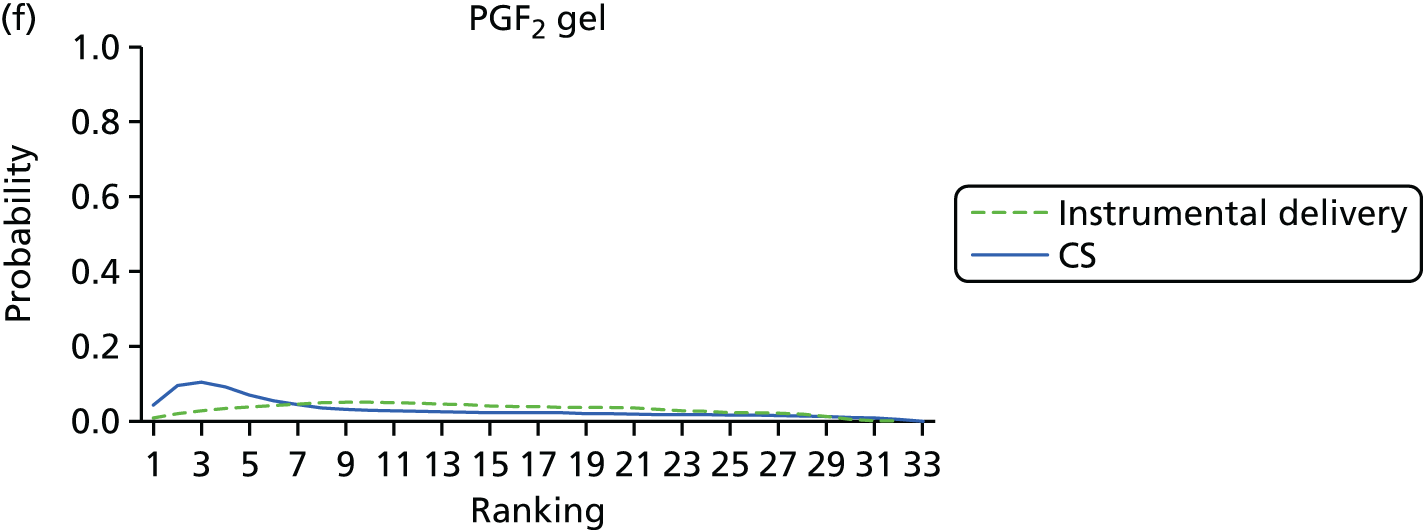
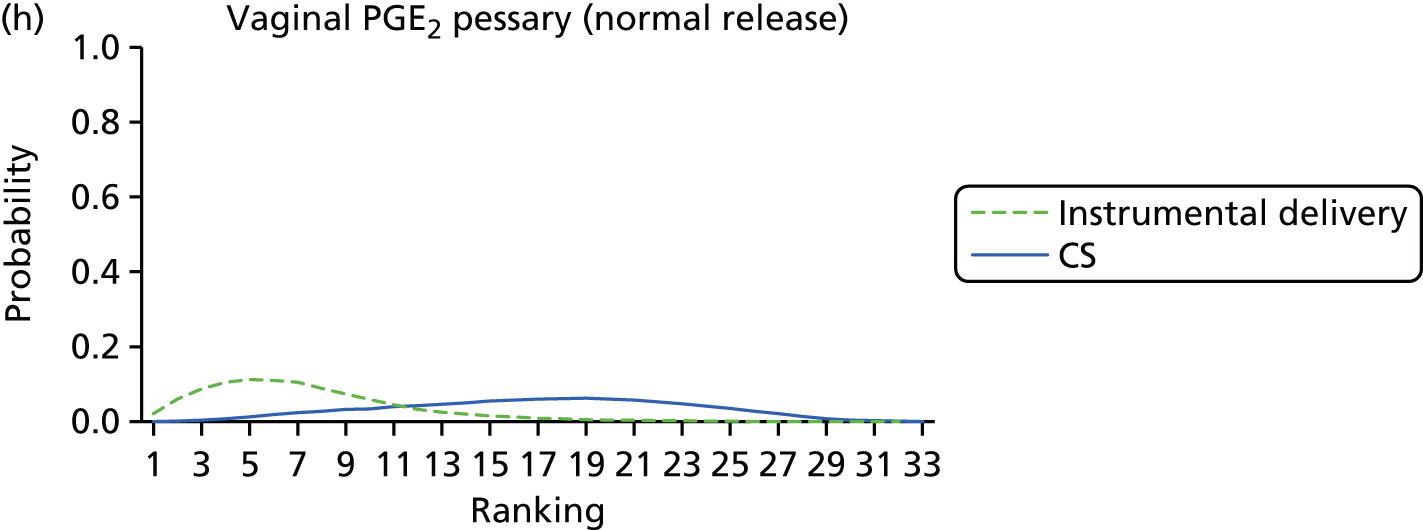
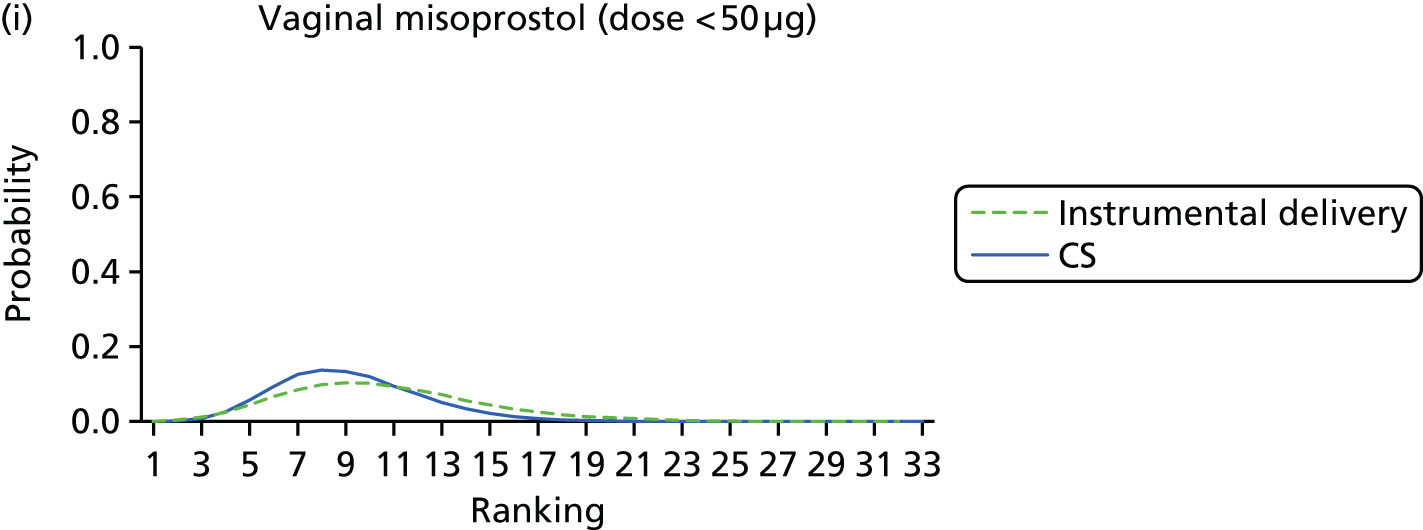
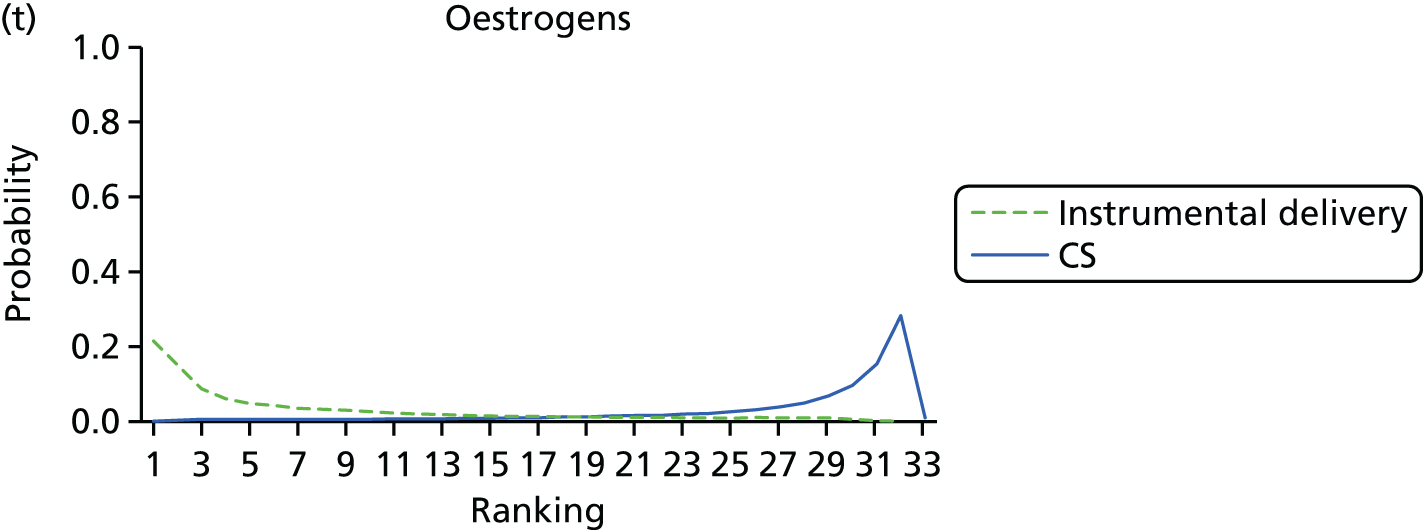
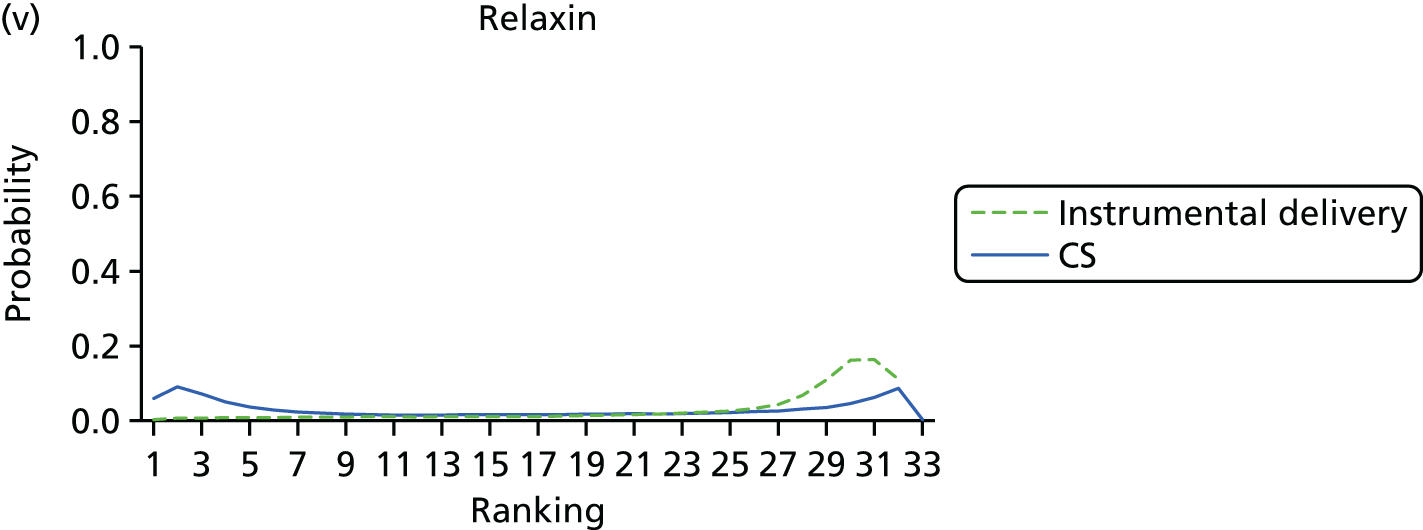
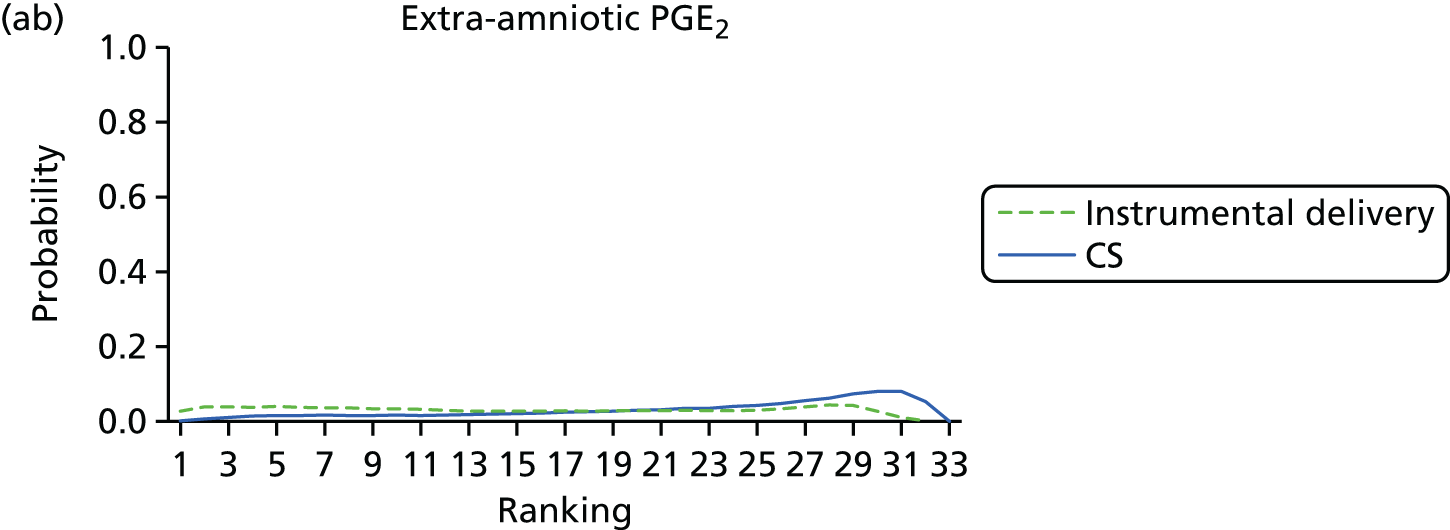
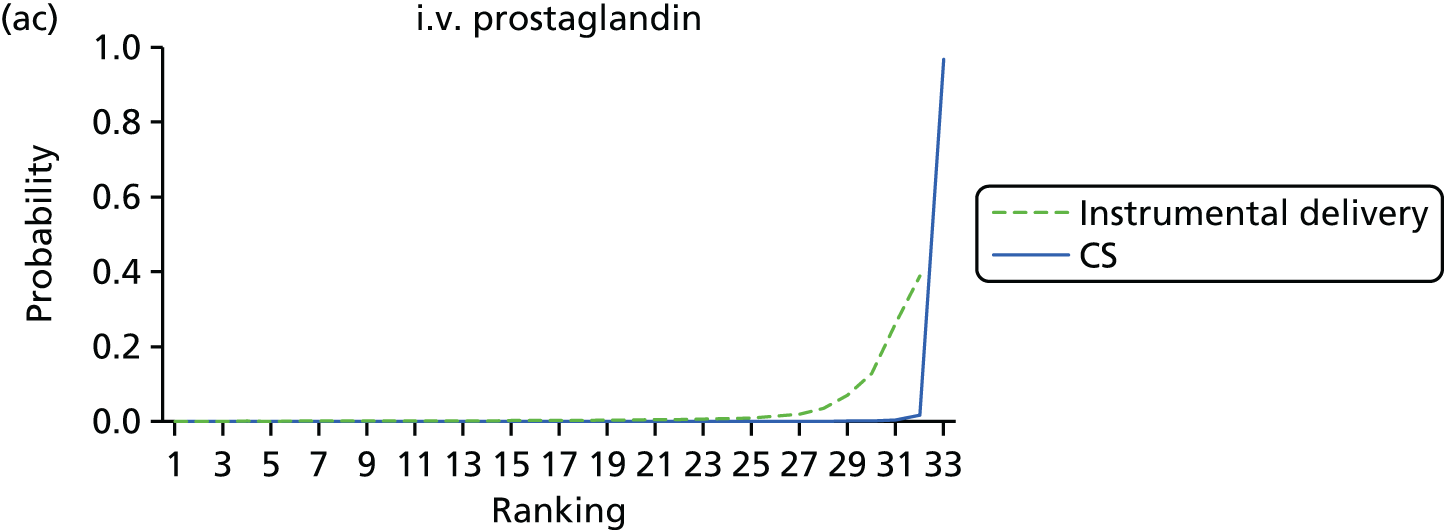
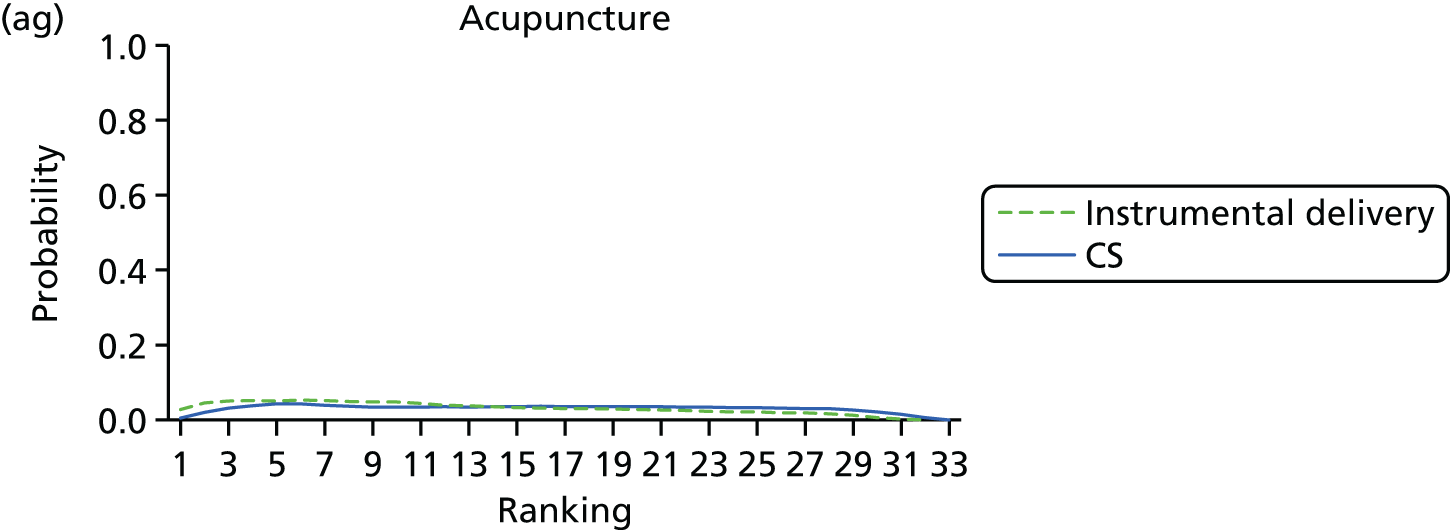
FIGURE 9.
Rankograms for each of the 33 induction interventions for CS and instrumental delivery. Ranking indicates the probability of being the best intervention, the second best, the third best, etc. (a) No treatment; (b) placebo; (c) vaginal PGE2 (tablet); (d) vaginal PGE2 (gel); (e) vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); (f) PGF2 gel; (g) intracervical PGE2; (h) vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); (i) vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); (j) vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); (k) oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); (l) oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); (m) titrated (low-dose) misoprostol; (n) sustained-release misoprostol insert; (o) i.v. oxytocin; (p) amniotomy; (q) i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; (r) NO; (s) mifepristone; (t) oestrogens; (u) corticosteroids; (v) relaxin; (w) hyaluronidase; (x) Foley catheter; (y) laminaria including dilapan; (z) double balloon or Cook’s catheter; (aa) membrane sweeping; (ab) extra-amniotic PGE2; (ac) i.v. prostaglandin; (ad) sexual intercourse; (ae) oral prostaglandins; (af) buccal/sublingual misoprostol; and (ag) acupuncture.















Instrumental delivery
After the exclusion of trials with 0% or 100% events in all arms, 299 trials were included in the NMA for the instrumental delivery outcome (see Figure 4). There were no trials remaining that compared corticosteroids, hyaluronidase, breast stimulation or castor oil. Model fit statistics for the model assuming consistency were indicative of a lack of fit, but this was judged to be borderline. The residual deviance indicated a slight improvement in fit for the model assuming inconsistency. This was accompanied by an increase in heterogeneity and a higher DIC. On balance, therefore, a REs NMA model assuming consistency was still preferred (see Appendix 11, Table 46). Reported results are based on this model, with 299 trials and 32 interventions (see Table 7 and Figure 4).
Table 7 reports the posterior median ORs (95% CrI) for each intervention relative to placebo (the full results are reported in Appendix 12, Table 52). As a further check of consistency, we note that for all of the interventions the direct and NMA results are similar. Using placebo as the reference intervention two interventions resulted in significant reduction in instrumental delivery, namely vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) and Foley catheter.
| Active intervention vs. placebo | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Direct trials | |
| Oestrogens | 0.68 | 0.32 to 1.28 | 0.75 | 0.25 to 1.71 | 1 |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.68 | 0.50 to 0.91 | – | – | 0 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.69 | 0.44 to 1.03 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.72 | 0.50 to 0.99 | 1.05 | 0.40 to 2.26 | 2 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.74 | 0.34 to 1.38 | – | – | 0 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.74 | 0.45 to 1.16 | – | – | 0 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.75 | 0.47 to 1.14 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.80 | 0.59 to 1.05 | 0.64 | 0.09 to 2.23 | 1 |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.83 | 0.47 to 1.38 | – | – | 0 |
| Acupuncture | 0.83 | 0.51 to 1.26 | 1.08 | 0.57 to 1.85 | 3 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.84 | 0.63 to 1.09 | 0.54 | 0.25 to 1.00 | 5 |
| PGF2 gel | 0.86 | 0.58 to 1.25 | 0.74 | 0.43 to 1.20 | 3 |
| Amniotomy | 0.86 | 0.50 to 1.38 | – | – | 0 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.89 | 0.68 to 1.14 | 1.09 | 0.61 to 1.79 | 6 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.91 | 0.67 to 1.22 | – | – | 0 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.91 | 0.49 to 1.52 | 0.88 | 0.32 to 1.91 | 3 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.92 | 0.70 to 1.18 | 1.21 | 0.35 to 3.12 | 2 |
| NO | 0.92 | 0.69 to 1.21 | 0.91 | 0.61 to 1.28 | 2 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.93 | 0.72 to 1.18 | 1.18 | 0.38 to 2.85 | 3 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.93 | 0.46 to 1.71 | – | – | 0 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.93 | 0.64 to 1.31 | – | – | 0 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.00 | 0.62 to 1.52 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.08 | 0.79 to 1.45 | 0.98 | 0.50 to 1.75 | 3 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.08 | 0.83 to 1.39 | – | – | 0 |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.20 | 0.84 to 1.66 | 15.45 | 1.56 to 71.26 | 1 |
| Sexual intercourse | 1.29 | 0.68 to 2.24 | – | – | 0 |
| Relaxin | 1.44 | 0.66 to 2.78 | 1.45 | 0.65 to 2.87 | 3 |
| Mifepristone | 1.68 | 1.05 to 2.59 | 1.84 | 1.08 to 2.98 | 5 |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.04 | 0.85 to 4.12 | – | – | 0 |
| Homeopathy | 2.13 | 0.11 to 10.24 | 2.18 | 0.09 to 11.64 | 1 |
Table 8 reports the posterior mean ranks and absolute probabilities for instrumental delivery. The intervention with the lowest mean rank (6) was Foley catheter, with a 95% CrI ranging from 2 to 12 (of 30 interventions). This intervention had lowest absolute probability of 13% (95% CrI 5% to 28%) jointly with oestrogen (95% CrI 4% to 31%) and buccal/sublingual misoprostol (95% CrI 5% to 29%). However, we note that although the posterior mean rank was ‘8’ for oestrogen and ‘7’ for buccal/sublingual misoprostol, respective 95% CrI were wide (oestrogen: 1 to 28 and buccal misoprostol: 1 to 20). This uncertainty is also reflected in the CrIs around the ORs for these interventions in Table 7. The intervention with the highest absolute probability of instrumental delivery (i.e. worst) was i.v. prostaglandin at 30% (95% CrI 10% to 58%).
| Intervention | Absolute probability of instrumental delivery | Posterior mean rank and 95% CrI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Posterior mean | 95% CrI | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.13 | 0.04 to 0.31 | 8 | 1 to 28 |
| Foley catheter | 0.13 | 0.05 to 0.28 | 6 | 2 to 12 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.13 | 0.05 to 0.29 | 7 | 1 to 20 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.14 | 0.05 to 0.29 | 7 | 2 to 17 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.14 | 0.04 to 0.32 | 9 | 1 to 29 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.14 | 0.05 to 0.31 | 9 | 1 to 25 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.15 | 0.06 to 0.31 | 11 | 4 to 20 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.15 | 0.05 to 0.31 | 9 | 1 to 24 |
| PGF2 gel | 0.16 | 0.06 to 0.34 | 14 | 2 to 28 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.16 | 0.06 to 0.32 | 13 | 6 to 21 |
| Amniotomy | 0.16 | 0.06 to 0.34 | 13 | 2 to 29 |
| Laminaria | 0.16 | 0.05 to 0.34 | 12 | 1 to 29 |
| Acupuncture | 0.16 | 0.05 to 0.34 | 13 | 1 to 28 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.17 | 0.07 to 0.33 | 17 | 8 to 26 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.17 | 0.07 to 0.35 | 18 | 11 to 24 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.17 | 0.06 to 0.34 | 15 | 8 to 23 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.17 | 0.07 to 0.34 | 17 | 10 to 24 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.17 | 0.05 to 0.37 | 16 | 1 to 31 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.17 | 0.06 to 0.35 | 17 | 6 to 28 |
| NO | 0.17 | 0.06 to 0.36 | 17 | 5 to 28 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.17 | 0.06 to 0.36 | 15 | 1 to 30 |
| Titrated (low) oral misoprostol solution | 0.18 | 0.07 to 0.37 | 19 | 5 to 30 |
| No intervention | 0.19 | 0.07 to 0.37 | 21 | 12 to 28 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.19 | 0.07 to 0.38 | 23 | 13 to 30 |
| Placebo | 0.2 | 0.08 to 0.38 | 24 | 17 to 29 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.2 | 0.08 to 0.38 | 24 | 18 to 29 |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.21 | 0.08 to 0.41 | 26 | 16 to 31 |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.22 | 0.08 to 0.45 | 25 | 7 to 32 |
| Relaxin | 0.24 | 0.07 to 0.5 | 25 | 4 to 32 |
| Homeopathy | 0.24 | 0.01 to 0.77 | 18 | 1 to 32 |
| Mifepristone | 0.27 | 0.1 to 0.52 | 30 | 22 to 32 |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 0.3 | 0.1 to 0.58 | 30 | 15 to 32 |
Figure 9 reports the rankograms for instrumental delivery. We note that for all of the interventions the rankograms are flat, with relatively low peaks – indicative of considerable uncertainty around the probability any intervention is the ‘best’. We do not therefore include an assessment of which probability is best in our summary for instrumental delivery.
See Appendix 13 (Table 59) for the results for the sensitivity analysis, excluding trials at high risk of bias. Removing these trials also removed five interventions from the analysis. Consequently, posterior mean ranks appear to have changed (although 95% CrI are overlapping between the two analyses).
Uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate changes
After excluding trials with 0% or 100% events in all arms, 180 trials assessed the outcome of uterine hyperstimulation. The analysis includes 19 interventions, in addition to placebo and no intervention. There were no trials remaining that compared PGF2, amniotomy, oestrogens, corticosteroids, relaxin, hyaluronidase, membrane sweeping, extra-amniotic PGE2, i.v. prostaglandin, sexual intercourse, acupuncture, breast stimulation, homeopathy, castor oil or oral prostaglandins (see Figure 5). Model fit statistics were suggestive of inconsistency for this network (see Appendix 11, Table 47). In the first instance, a continuity correction of 0.5 was added to each cell for those studies with zero events in either arm, allowing the log OR to be estimated. This improved the model fit, and the results presented below are based on the continuity corrected REs NMA model assuming consistency.
Table 9 reports the posterior median ORs (95% CrI) for each intervention relative to placebo (the full results for each intervention compared with every other are reported in Appendix 12, Table 53). We note that for all of the interventions the direct and NMA results are similar. Relative to the size of the intervention effect estimates, high to moderate between-trial heterogeneity was observed for this outcome [τ = 0.54 (95% CrI 0.38 to 0.72)]. Figure 8 reports the rankograms for uterine hyperstimulation. The safest intervention in terms of risk of uterine hyperstimulation was double-balloon or Cook’s catheter, with a 47% probability of being the best and a 91% probability of being in the top three interventions.
| Active intervention | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Direct trials | |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.26 | 0.00 to 1.18 | – | – | 0 |
| NO | 0.38 | 0.02 to 1.54 | – | – | 0 |
| Laminaria | 0.52 | 0.01 to 2.62 | – | – | 0 |
| Foley catheter | 0.92 | 0.37 to 1.93 | – | – | 0 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 1.13 | 0.28 to 3.15 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.40 | 0.37 to 3.68 | 0.46 | 0.00 to 3.00 | 1 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.70 | 0.87 to 3.05 | 1.65 | 0.57 to 3.88 | 8 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.93 | 0.73 to 4.19 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 1.99 | 0.78 to 4.25 | 0.78 | 0.00 to 5.12 | 1 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 2.12 | 0.97 to 4.10 | 0.34 | 0.00 to 2.19 | 1 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 2.33 | 1.10 to 4.40 | 5.81 | 0.32 to 29.93 | 3 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 2.75 | 1.36 to 5.04 | 2.46 | 0.25 to 10.23 | 2 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 2.85 | 1.41 to 5.20 | 7.75 | 1.22 to 30.55 | 5 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 2.97 | 1.36 to 5.73 | 27.00 | 2.01 to 131.2 | 3 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 4.25 | 1.71 to 9.02 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 4.40 | 2.22 to 7.94 | 28.54 | 0.53 to 159.4 | 2 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 5.58 | 1.58 to 14.57 | – | – | 0 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 7.44 | 0.27 to 40.66 | – | – | 0 |
| Mifepristonea | Not estimable | Not estimable | 1 | ||
Table 10 reports the posterior mean ranks and absolute probabilities for this outcome. The mean rank for double-balloon or Cook’s catheter was ‘2’, with a 95% CrI ranging from 1 to 7 (of 19 interventions). Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter also had the lowest absolute probability of hyperstimulation at 1% (95% CrI 0% to 3%). The probability of being ranked in the bottom three (i.e. intervention with highest risk of uterine hyperstimulation) was 64% for sustained-release misoprostol insert and 59% for vaginal misoprostol (≥ 50 µg). The intervention with the worst mean rank was vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg: mean rank 19 (95% CrI 17 to 21). The absolute probability of uterine hyperstimulation for vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg was 9% (95% CrI 2% to 25%).
| Intervention | Absolute probability of hyperstimulation | Posterior mean rank and 95% CrI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Posterior mean | 95% CrI | |||
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.03 | 2 | 1 to 6 |
| NO | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.04 | 3 | 1 to 8 |
| Laminaria | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.06 | 3 | 1 to 13 |
| Foley catheter | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.07 | 5 | 3 to 9 |
| Placebo | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.08 | 6 | 3 to 10 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.09 | 6 | 2 to 15 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.11 | 8 | 3 to 16 |
| No treatment | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.12 | 8 | 3 to 17 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.04 | 0.01 to 0.12 | 10 | 6 to 13 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.04 | 0.01 to 0.11 | 11 | 6 to 17 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.04 | 0.01 to 0.14 | 11 | 5 to 17 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.05 | 0.01 to 0.14 | 12 | 7 to 17 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.05 | 0.01 to 0.15 | 13 | 9 to 17 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.18 | 15 | 11 to 18 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.18 | 15 | 11 to 18 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.19 | 15 | 10 to 19 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.09 | 0.02 to 0.26 | 19 | 13 to 21 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.09 | 0.02 to 0.25 | 19 | 17 to 21 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.11 | 0.02 to 0.34 | 18 | 10 to 21 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.11 | 0.00 to 0.52 | 14 | 3 to 21 |
| Mifepristone | 0.26 | 0.01 to 0.89 | 19 | 7 to 21 |
Results were largely robust to the pre-planned sensitivity analysis based on allocation concealment bias. The posterior mean rank for sustained-release misoprostol insert changed from 18 (95% CrI 11 to 21) to 11 (95% CrI 3 to 19). Full sensitivity analysis results are reported in Appendix 13, Table 57.
Neonatal and maternal mortality and severe morbidity
It was not possible to conduct a NMA for composite outcomes of neonatal mortality and serious morbidity or maternal mortality and serious morbidity, as these were too rare or poorly reported to carry out meaningful analysis. The full data sets for these outcomes are reported in Appendix 14 (Tables 64 and 65). In addition, there is a lack of a universally accepted definition for serious infant or maternal morbidity. Although we planned to include any such reported outcome by individual trials, the outcomes were still rarely reported. Only 21.3% of included trials (131/611) reported perinatal deaths with an incidence of 0.3% (94/32,248). A total of 77 out of 611 trials (12.6%) reported a total of 20 maternal deaths or serious morbidity [five deaths, 14 uterine ruptures and one intensive care unit (ICU) admission for infection], that is, an incidence of 0.1%. For completeness, we included the network diagrams for both outcomes (Figures 10 and 11). The network diagram includes those trials reporting at least one event (42 of the included trials reported at least one perinatal death and 16 trials reported at least one case of maternal death or severe morbidity).
FIGURE 10.
Neonatal mortality. Network diagram of studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials directly comparing each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, PGF2 gel; 7, intracervical PGE2; 8, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 10, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, i.v. oxytocin; 14, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; 15, NO; 16, Foley catheter; 17, laminaria; 18, membrane sweeping; 19, extra-amniotic PGE2; 20, i.v. prostaglandin; 21, sexual intercourse; 22, breast stimulation; 23, oral prostaglandins; 24, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
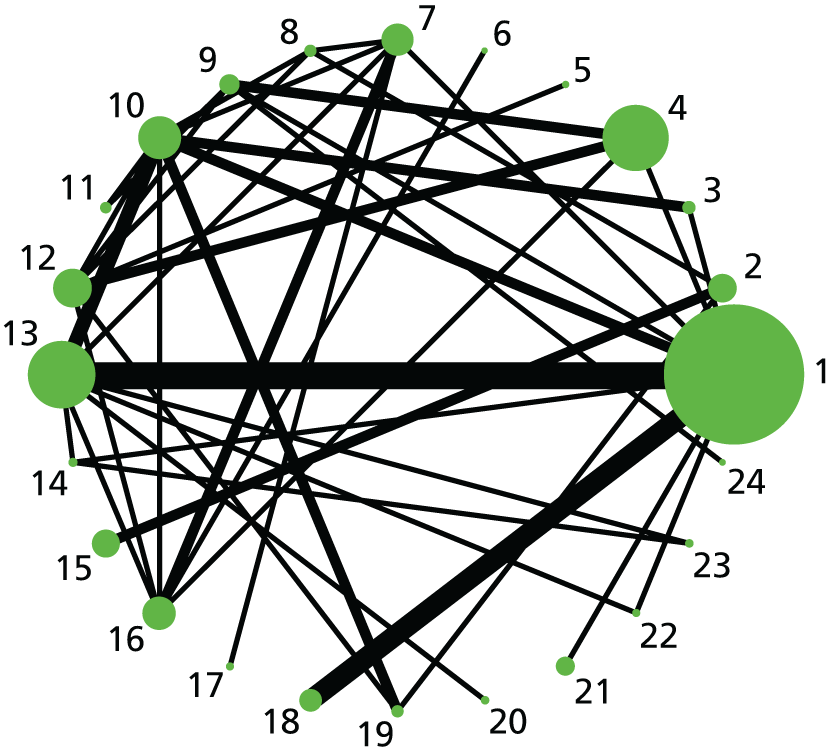
FIGURE 11.
Maternal mortality and serious morbidity. Network diagram of studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials directly comparing each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 11, i.v. oxytocin; 12, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy; 13, mifepristone; 14, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 15, mechanical methods – laminaria; 16, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
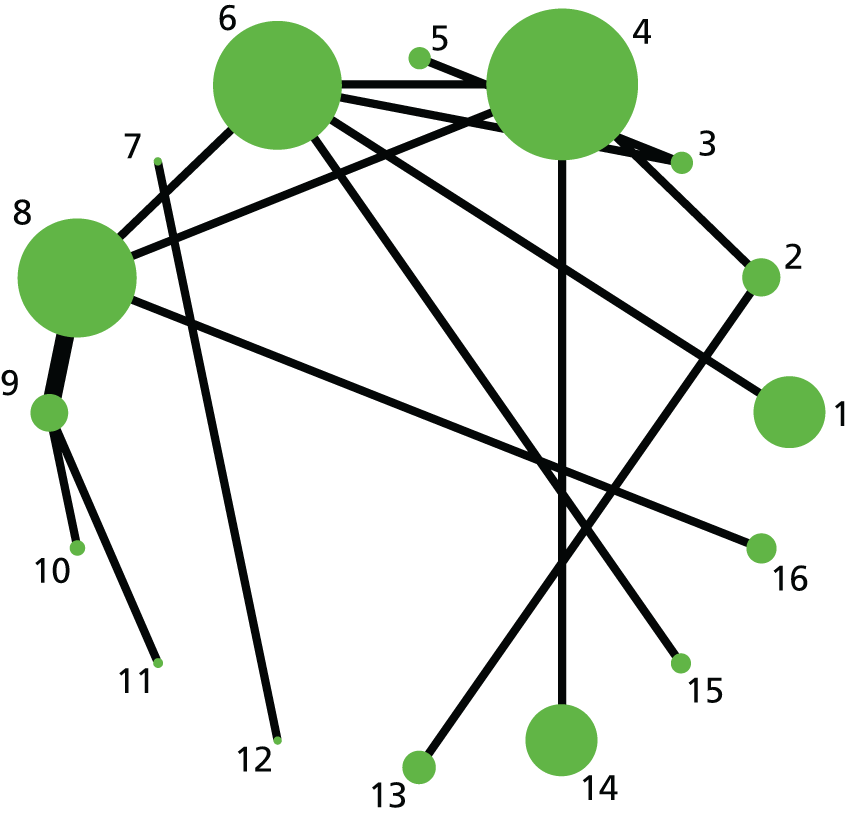
Neonatal intensive care unit admission
After the exclusion of trials with 0% or 100% events in all arms, 205 trials assessed the outcome of admission to the NICU and the network is shown in Figure 6. There were no trials remaining that compared corticosteroids, relaxin, hyaluronidase, i.v. prostaglandin, breast stimulation, homeopathy or castor oil. Model fit statistics indicated evidence of inconsistency for this network, with the inconsistency model resulting in a considerable decrease in between-trial heterogeneity (see Appendix 11, Table 49). Comparing the NMA estimates with those from the pairwise analysis identified 23 intervention comparisons for which the NMA and direct evidence were in disagreement. A further investigation of this apparent inconsistency was conducted using a ‘node-splitting’ approach. 942 Node splitting separates evidence on a particular comparison (node) into direct and indirect to identify how the indirect evidence was combining with, or adding to, the direct evidence to form the NMA estimates. Using this approach, 3 out of 23 comparisons were highlighted as having significant differences in the contribution of the direct and indirect evidence to the NMA estimate. The three comparisons were vaginal misoprostol (≥ 50 µg) against NO, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) against titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution, and no treatment against oral misoprostol tablet (≥ 50 µg). The first two of these were identified as being a consequence of zero cells in the direct evidence estimating a very extreme treatment effect. However, the remaining comparison between no treatment and oral misoprostol tablet (≥ 50 µg) had statistically significant differences in the direct and indirect evidence (Bayesian p-value = 2.98401E-05), even when trials with zero cells were removed.
Within the no treatment against oral misoprostol tablet (≥ 50 µg) comparison, one trial in particular, Rath and Manus,701 was identified as deviant from the rest of the evidence and was therefore re-examined. The criteria for admission to the NICU in this study were unclear, and the description of the facility was given simply as ‘nursery’. A post hoc decision to remove this trial for this outcome was taken and a further analysis was subsequently carried out. The REs model, excluding the Rath and Manus trial701 and assuming consistency, was a good fit to the data, and the results presented here are therefore from this analysis.
Table 11 reports the posterior median ORs (95% CrI) for each intervention relative to placebo (full results are reported in Appendix 12, Table 55). Relative to the size of the intervention effect estimates, moderate between-trial heterogeneity was observed for this outcome [τ = 0.17 (95% CrI 0.04 to 0.30)]. Using placebo as the reference only, extra-amniotic PGE2 resulted in significant reduction in NICU admission. Table 12 reports the posterior mean ranks for NICU admission. Extra-amniotic PGE2 had the best mean rank of all interventions (4), with a 95% CrI ranging from 1 to 15. This intervention also had the lowest absolute probability of NICU admission at 4% (95% CrI 0.6% to 12%) and a 59% chance of being in the top three interventions.
| Active intervention vs. placebo | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Trials | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.40 | 0.16 to 0.82 | – | – | 0 |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.48 | 0.14 to 1.17 | – | – | 0 |
| PGF2 gel | 0.56 | 0.18 to 1.36 | – | – | 0 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.59 | 0.31 to 1.03 | – | – | 0 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.60 | 0.26 to 1.15 | – | – | 0 |
| Foley catheter | 0.66 | 0.41 to 1.00 | – | – | 0 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.67 | 0.39 to 1.07 | – | – | 0 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.68 | 0.09 to 2.40 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.73 | 0.44 to 1.11 | 29.03 | 0.45 to 156.3 | 1 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.73 | 0.42 to 1.19 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.74 | 0.49 to 1.06 | 0.95 | 0.38 to 1.94 | 2 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.76 | 0.48 to 1.12 | 1.06 | 0.08 to 4.41 | 2 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.76 | 0.50 to 1.12 | 0.78 | 0.06 to 3.02 | 1 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.79 | 0.31 to 1.63 | – | – | 0 |
| NO | 0.82 | 0.54 to 1.20 | 0.92 | 0.56 to 1.43 | 5 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.83 | 0.42 to 1.44 | – | – | 0 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.83 | 0.55 to 1.20 | 0.75 | 0.28 to 1.61 | 3 |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.83 | 0.43 to 1.46 | 1.14 | 0.01 to 6.19 | 1 |
| Amniotomy | 0.84 | 0.22 to 2.26 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.85 | 0.57 to 1.23 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.88 | 0.59 to 1.26 | 0.71 | 0.26 to 1.58 | 4 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.88 | 0.51 to 1.40 | 0.86 | 0.30 to 1.94 | 3 |
| Acupuncture | 0.94 | 0.11 to 3.36 | 1.43 | 0.13 to 5.95 | 2 |
| Oestrogens | 1.43 | 0.01 to 7.80 | 2.29 | 0.02 to 12.21 | 1 |
| Laminaria | 1.54 | 0.40 to 4.31 | – | – | 0 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 1.60 | 0.71 to 3.06 | – | – | 0 |
| Mifepristonea | 1.71 | 0.73 to 3.55 | 1.15 | 0.38 to 2.75 | 1 |
| Intervention | Absolute probability of NICU admission | Posterior mean rank and 95% CrI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Posterior mean | 95% CrI | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.04 | 0.01 to 0.12 | 4 | 1 to 15 |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.04 | 0.01 to 0.14 | 6 | 1 to 25 |
| PGF2 gel | 0.05 | 0.01 to 0.16 | 8 | 1 to 26 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.05 | 0.01 to 0.15 | 8 | 2 to 22 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.05 | 0.01 to 0.16 | 9 | 2 to 25 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.18 | 13 | 6 to 23 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.18 | 14 | 7 to 23 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.18 | 13 | 7 to 20 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.17 | 11 | 4 to 22 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.18 | 15 | 8 to 22 |
| Foley catheter | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.16 | 10 | 5 to 19 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.06 | 0.00 to 0.23 | 10 | 1 to 29 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.18 | 13 | 4 to 25 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.07 | 0.02 to 0.17 | 16 | 4 to 27 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.07 | 0.02 to 0.20 | 20 | 13 to 25 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.07 | 0.02 to 0.21 | 18 | 6 to 27 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.07 | 0.02 to 0.20 | 19 | 12 to 25 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.07 | 0.01 to 0.20 | 14 | 2 to 28 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.07 | 0.02 to 0.19 | 18 | 10 to 24 |
| Amniotomy | 0.07 | 0.01 to 0.23 | 14 | 1 to 29 |
| NO | 0.07 | 0.01 to 0.20 | 17 | 5 to 26 |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.07 | 0.01 to 0.20 | 16 | 5 to 27 |
| Placebo | 0.08 | 0.02 to 0.23 | 23 | 16 to 27 |
| No intervention | 0.08 | 0.02 to 0.22 | 23 | 13 to 28 |
| Acupuncture | 0.08 | 0.00 to 0.32 | 14 | 1 to 29 |
| Oestrogens | 0.10 | 0.00 to 0.53 | 14 | 1 to 29 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.12 | 0.02 to 0.33 | 27 | 17 to 29 |
| Laminaria | 0.12 | 0.02 to 0.37 | 23 | 4 to 29 |
| Mifepristone | 0.13 | 0.02 to 0.37 | 26 | 13 to 29 |
Figure 12 reports the rankograms for NICU admission. For all interventions the rankograms are flat and indicative of considerable uncertainty around the probability any intervention is the ‘best’. We do not therefore include an assessment of which probability is ‘best’ in our summary for this outcome as it would be misleading.
FIGURE 12.
Rankograms for each of the 29 induction interventions for Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes and NICU admission. Ranking indicates the probability of being the best intervention, the second best, the third best, etc. The x-axis shows the relative ranking and the y-axis the probability of each ranking. (a) No treatment; (b) placebo; (c) vaginal PGE2 (tablet); (d) vaginal PGE2 (gel); (e) vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); (f) PGF2 gel; (g) intracervical PGE2; (h) vaginal pessary (normal release); (i) vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); (j) vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); (k) oral misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); (l) oral misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); (m) titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; (n) sustained-release misoprostol insert; (o) i.v. oxytocin; (p) amniotomy; (q) i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; (r) NO; (s) mifepristone; (t) oestrogens; (u) Foley catheter; (v) laminaria including dilapan; (w) double balloon or Cook’s catheter; (x) membrane sweeping; (y) extra-amniotic PGE2; (z) sexual intercourse; (aa) acupuncture; (ab) oral prostaglandins; and (ac) buccal/sublingual misoprostol.


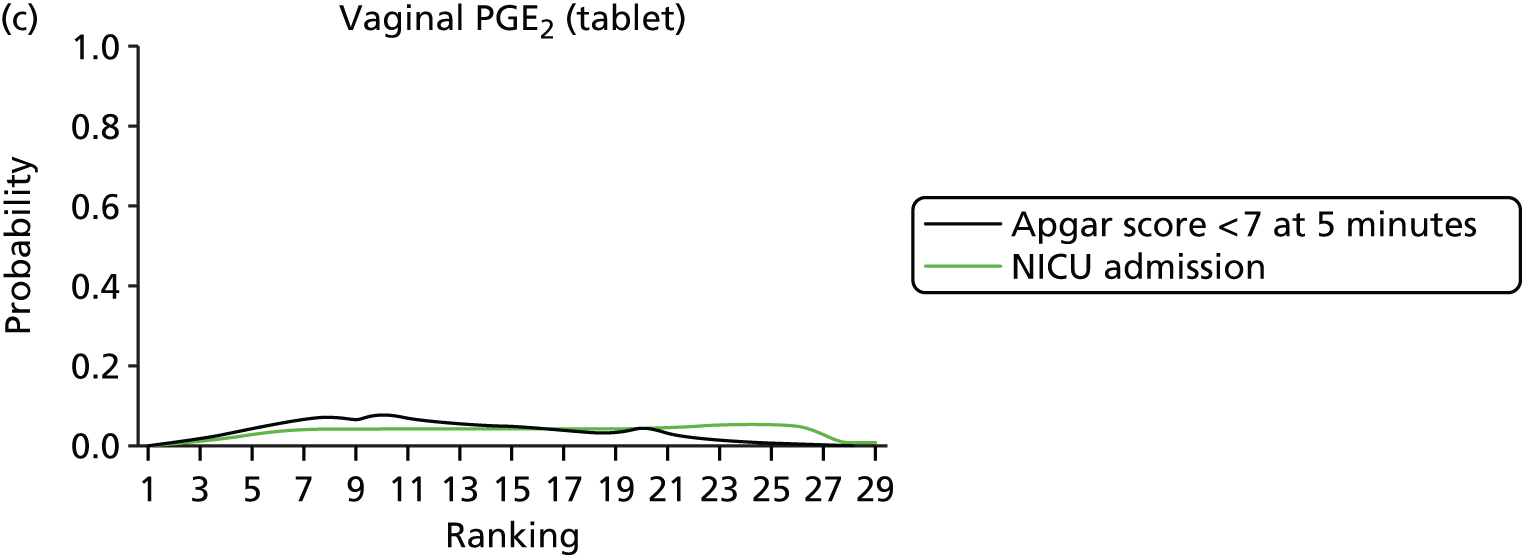
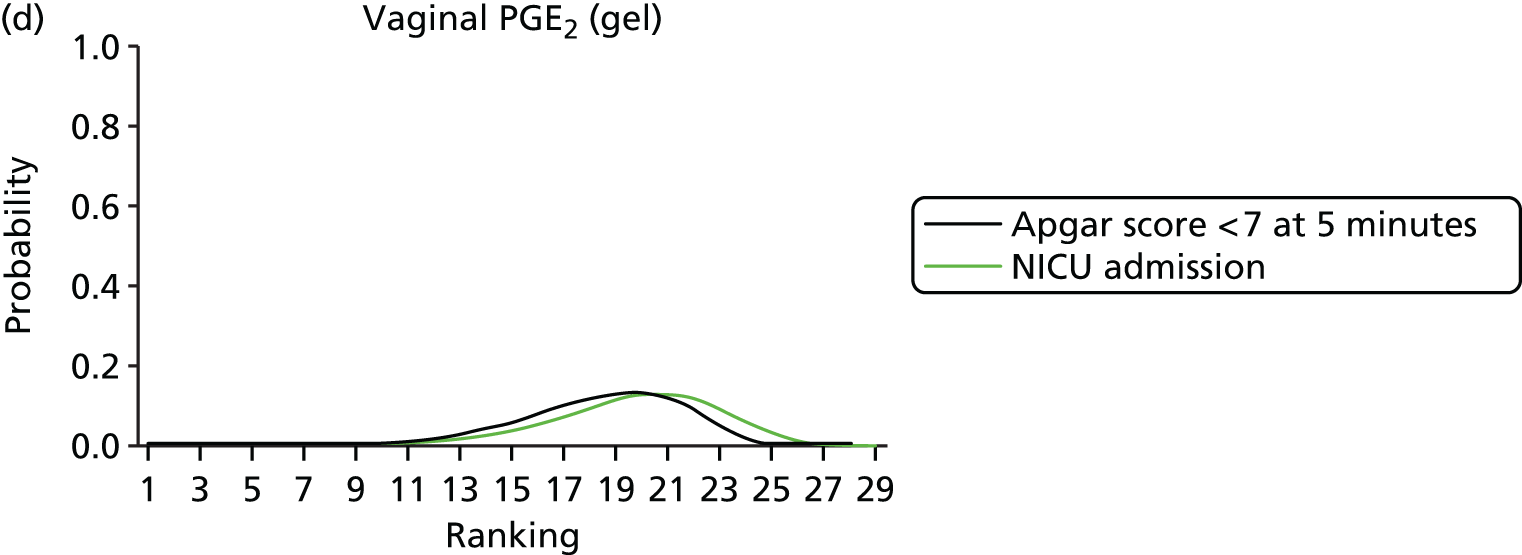
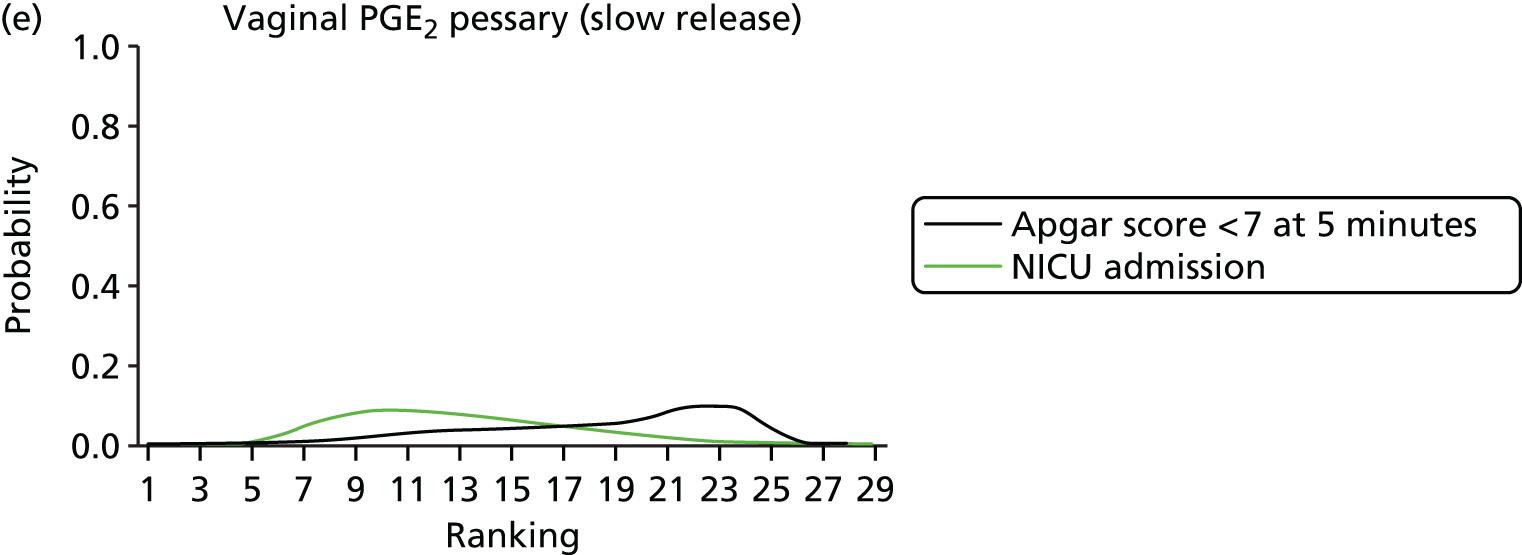
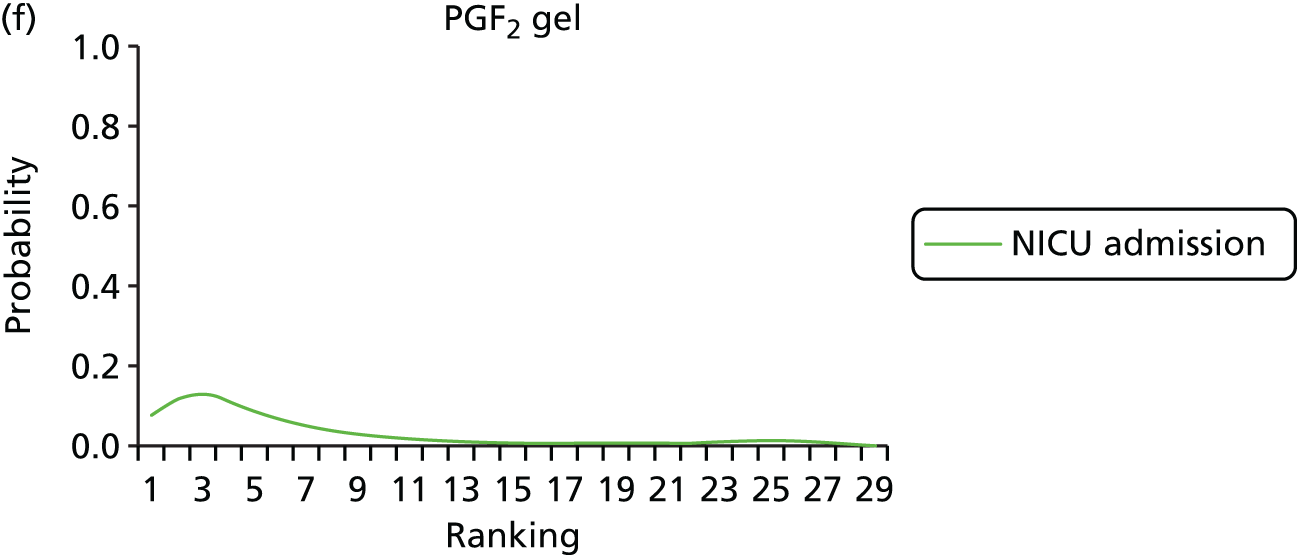
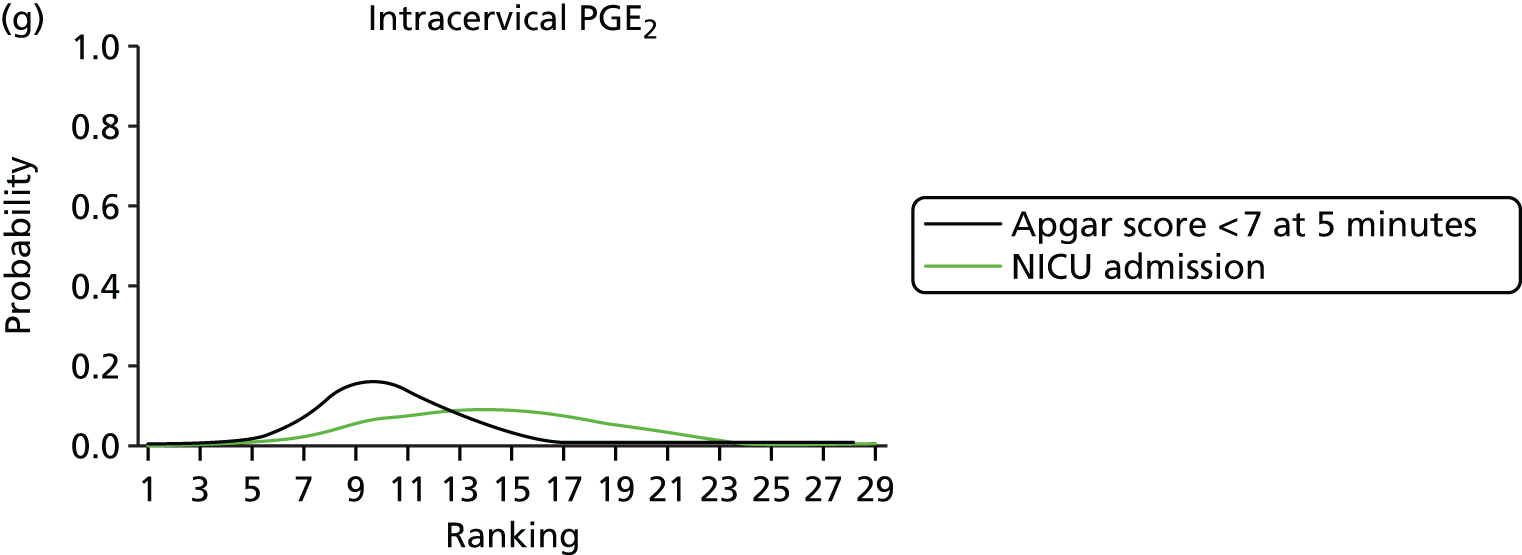
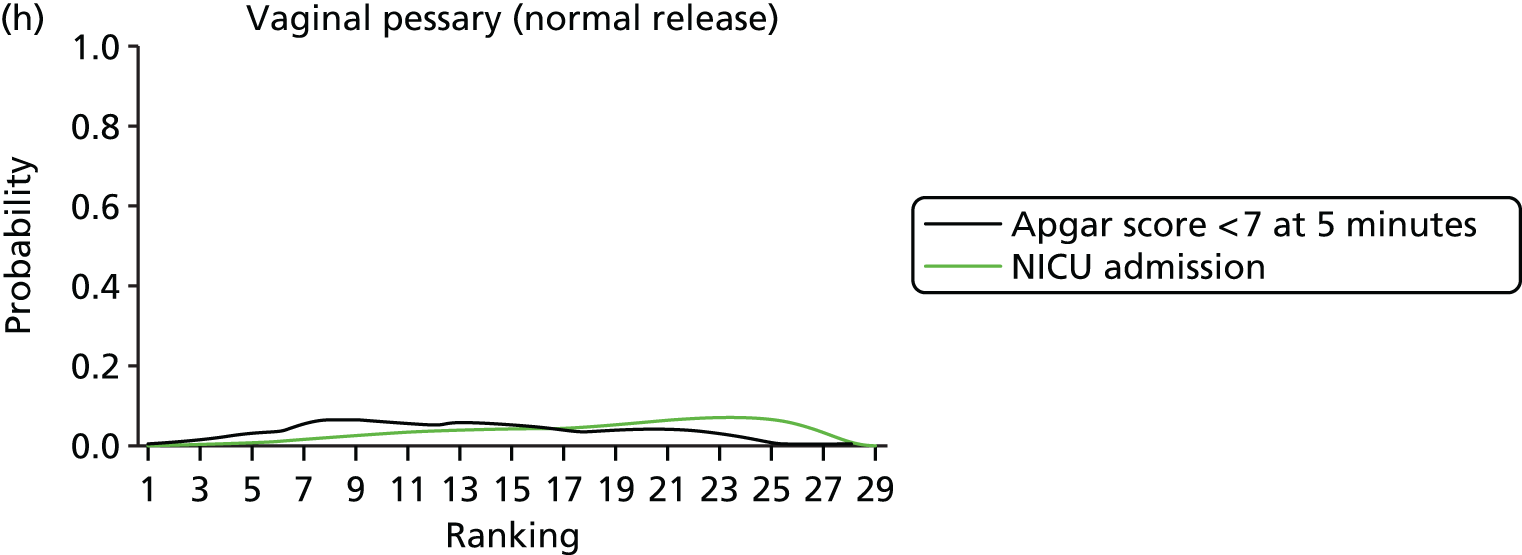
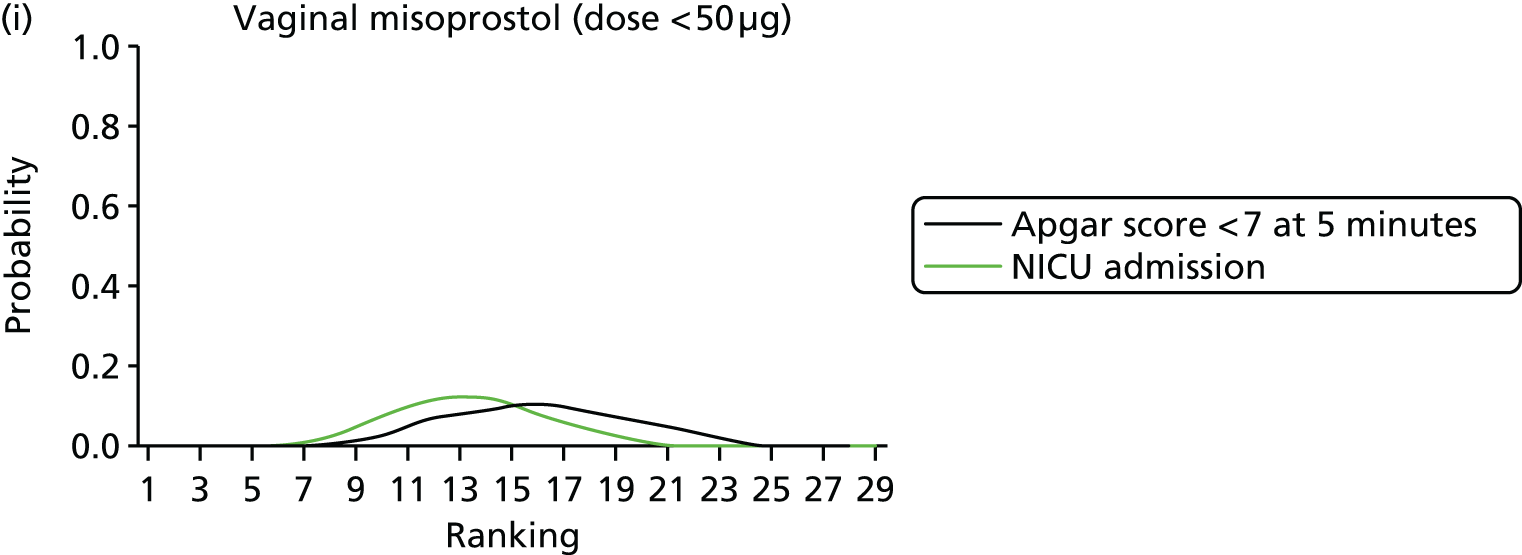


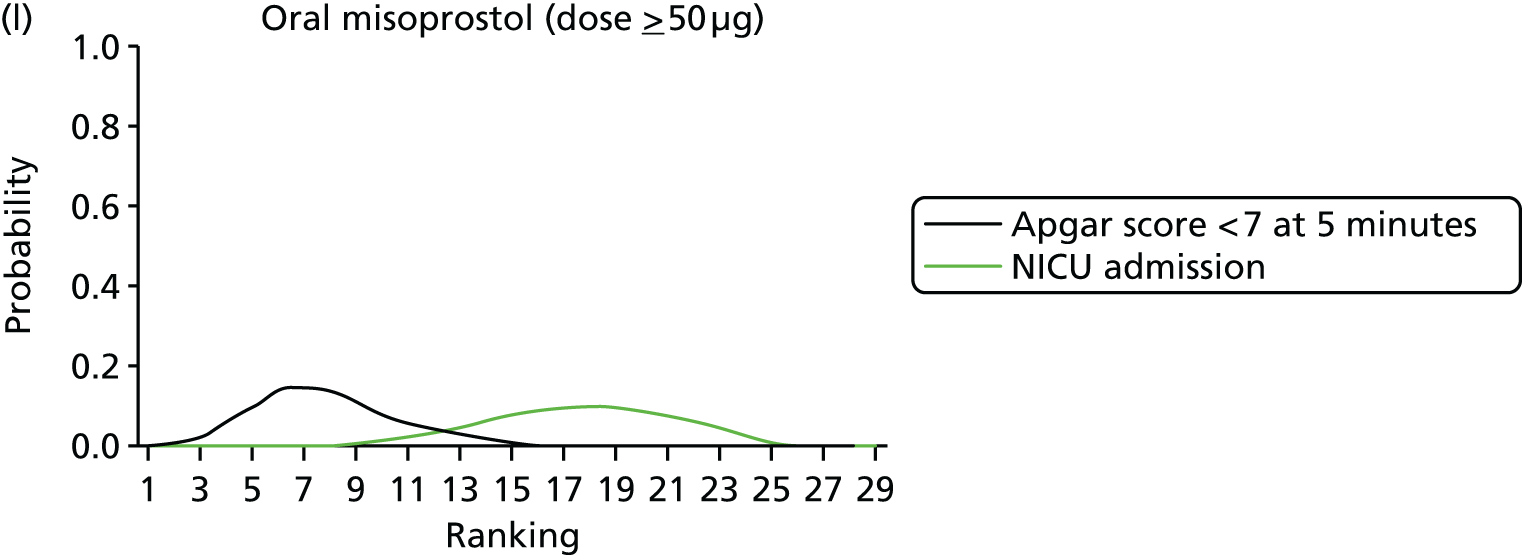
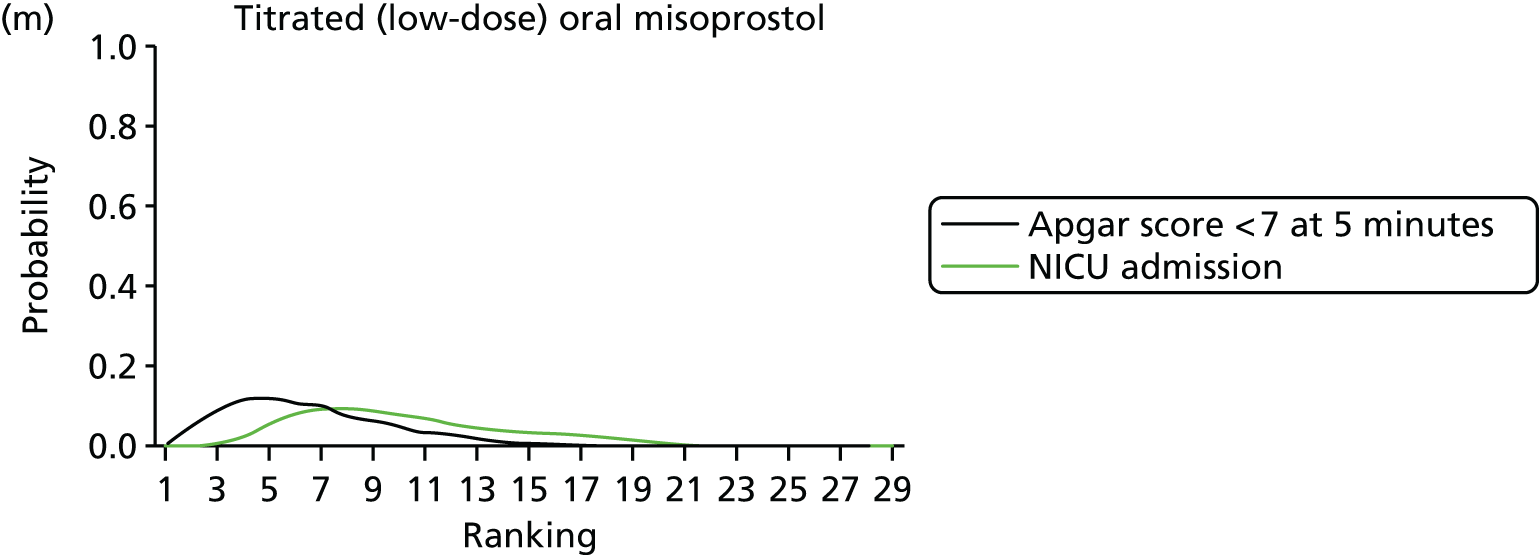
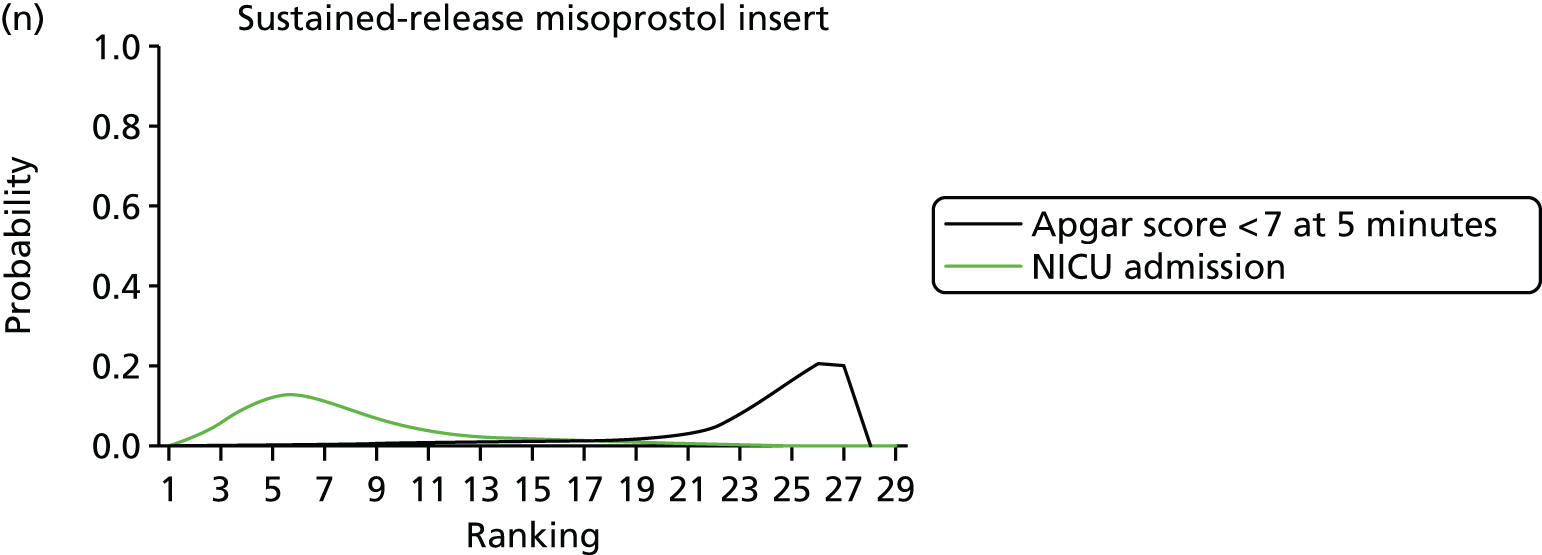


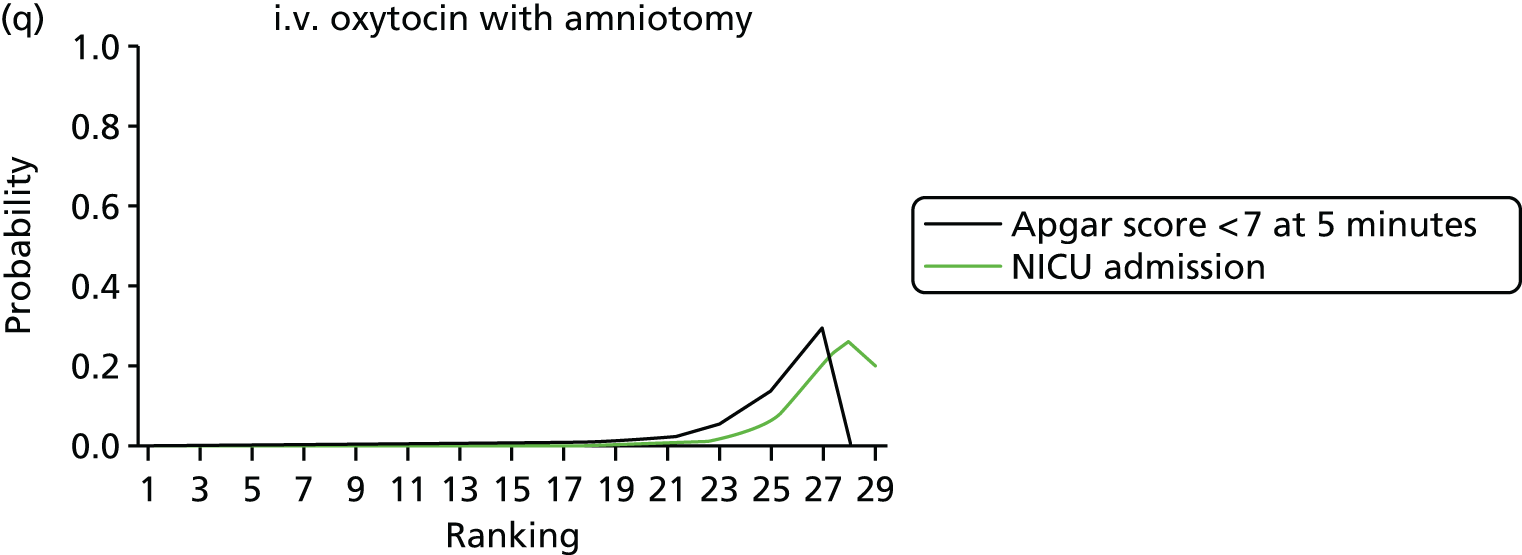
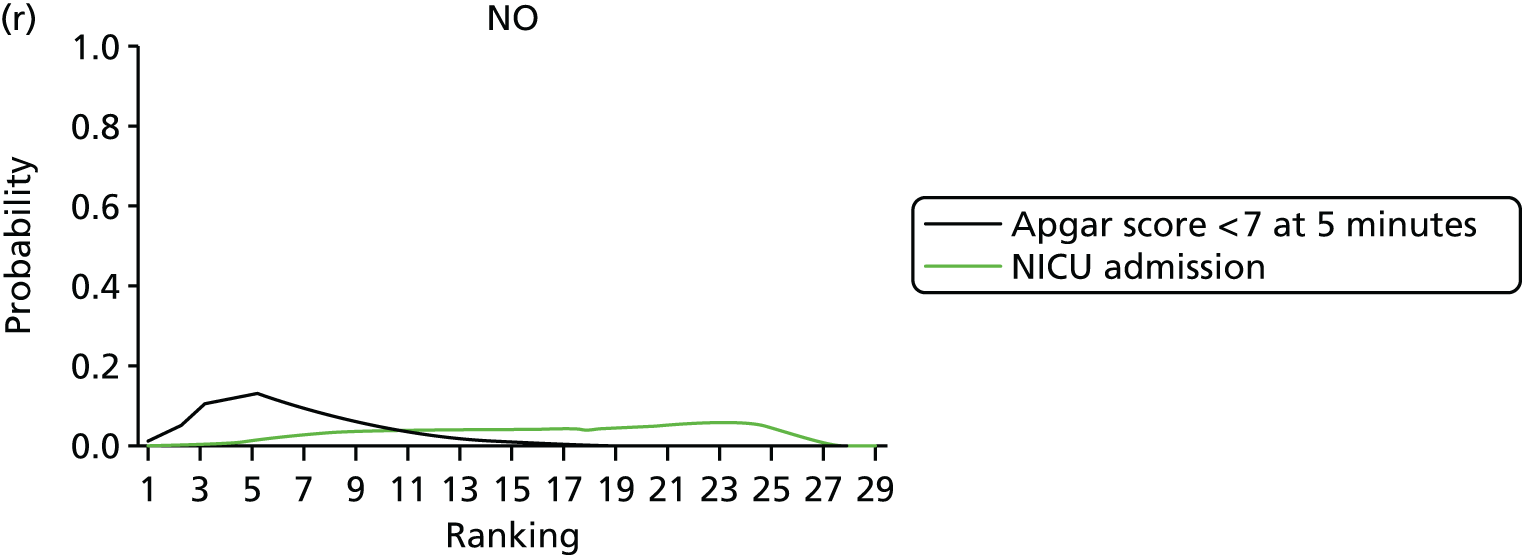

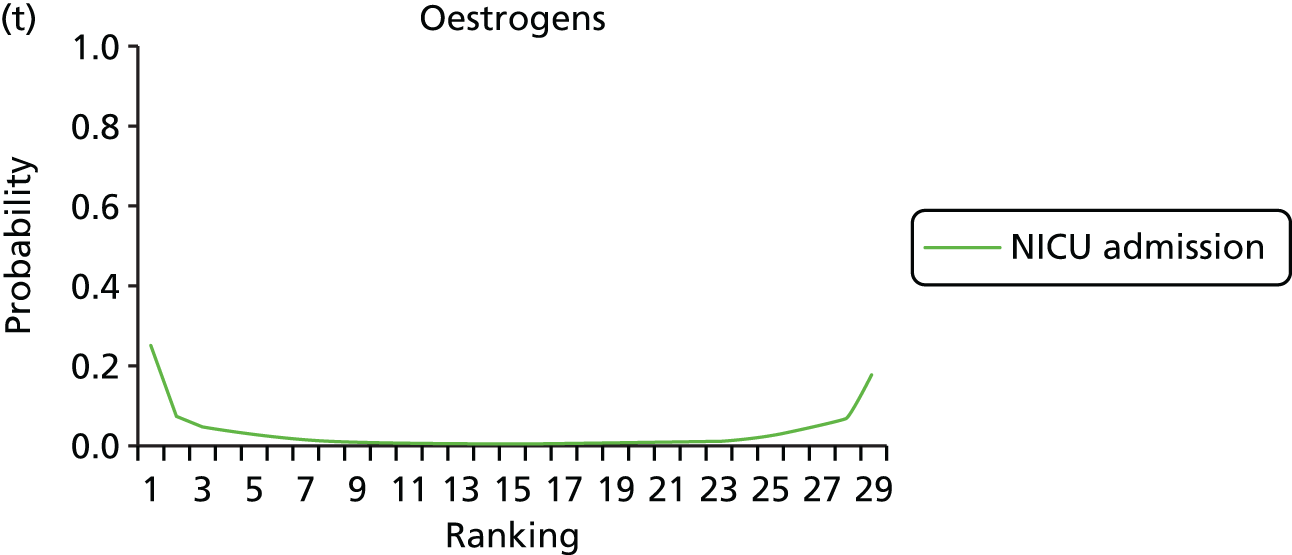


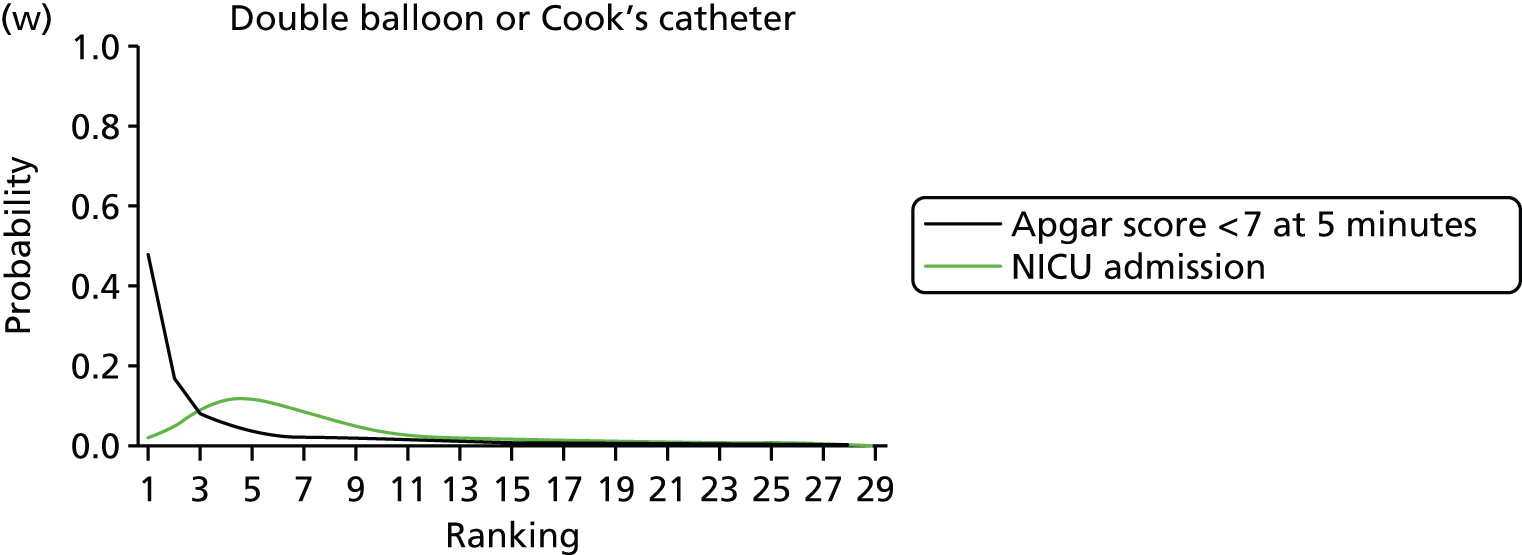
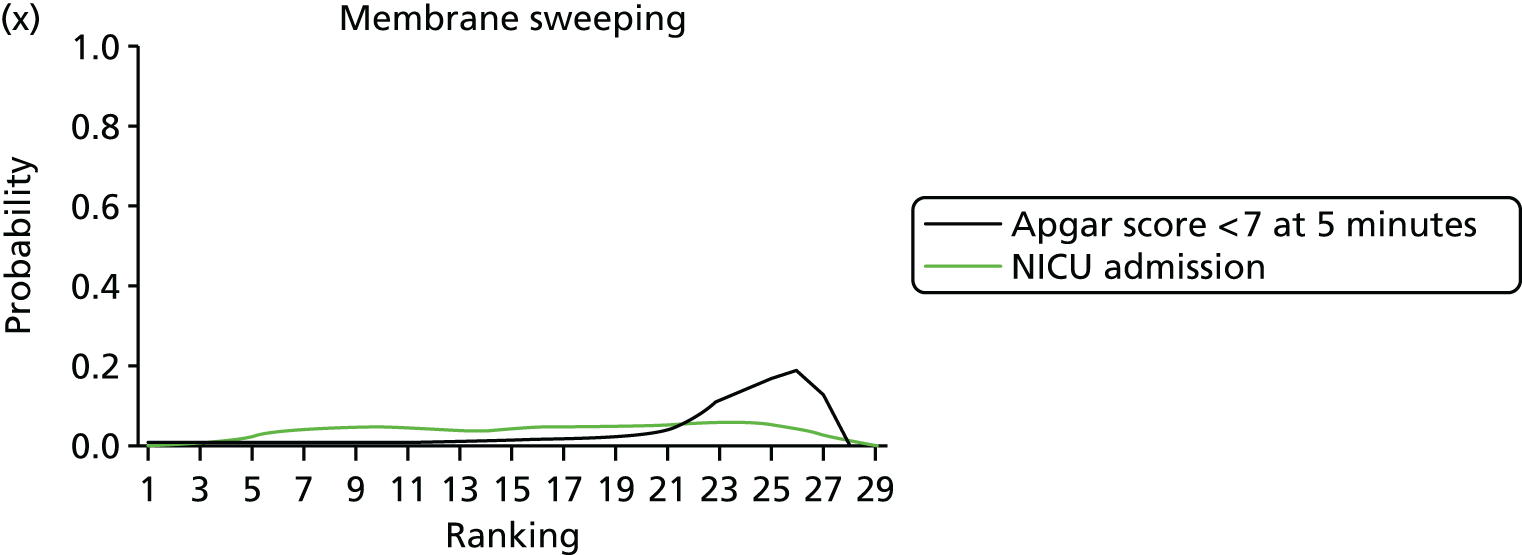


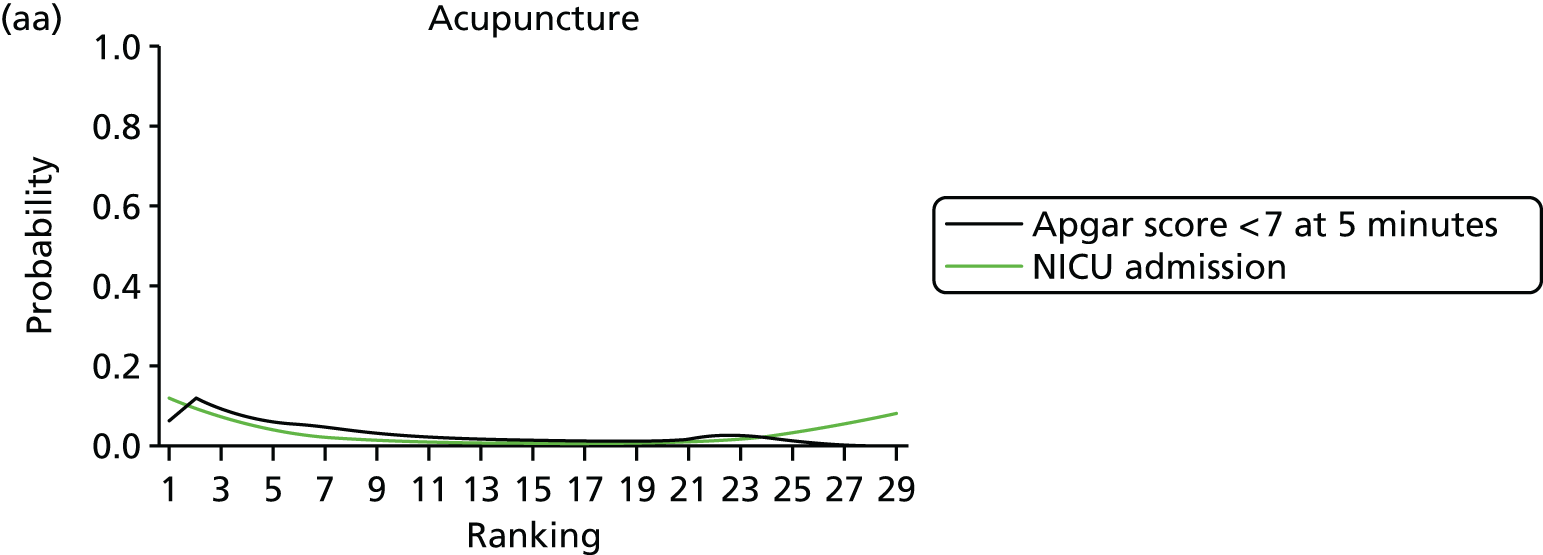


All results were robust to the preplanned sensitivity analysis excluding studies at high risk of bias for allocation concealment and are reported in Appendix 13, Table 58.
Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
After the exclusion of trials with 0% or 100% events in all arms, 200 trials of 28 interventions assessed the outcome of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes (see Figure 7). There were no trials remaining that compared PGF2 gel, oestrogens, corticosteroids, relaxin, hyaluronidase, breast stimulation, homeopathy or castor oil. Residual deviance statistics, for the model assuming consistency, suggested a lack of fit, with the model assuming inconsistency also having slightly lower heterogeneity. Further investigation indicated that this was due to the number of zero events in trial arms rather than heterogeneity in study design. The REs NMA model assuming consistency was therefore the preferred model and reported results are based on this.
Table 13 reports posterior mean ORs (95% CrI) for each intervention relative to placebo (full results are reported in Appendix 12, Table 54). Relative to the size of the intervention effect estimates, moderate to small between-trial heterogeneity was observed for this outcome [τ = 0.19 (95% CrI 0.01 to 0.46)]. Using placebo as the reference intervention, only two interventions resulted in significant reduction in Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes: NO and buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| Active intervention vs. placebo | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Trials | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | Not estimablea | – | – | 0 | |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.17 | 0.01 to 1.67 | – | – | 0 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.35 | 0.06 to 1.68 | – | – | 0 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.41 | 0.15 to 0.99 | – | – | 0 |
| Titrated (low) oral misoprostol solution | 0.46 | 0.19 to 1.09 | – | – | 0 |
| NO | 0.49 | 0.20 to 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.39 to 1.88 | 5 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.53 | 0.13 to 2.08 | – | – | 0 |
| Acupuncture | 0.54 | 0.14 to 1.87 | 0.82 | 0.15 to 2.49 | 3 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.57 | 0.30 to 1.13 | 0.85 | 0.18 to 2.41 | 3 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.67 | 0.38 to 1.20 | 0.46 | 0.14 to 1.11 | 4 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.75 | 0.34 to 1.62 | 0.57 | 0.04 to 2.04 | 1 |
| Mifepristone | 0.77 | 0.23 to 3.37 | 0.78 | 0.16 to 2.59 | 2 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.80 | 0.35 to 1.84 | 1.79 | 0.11 to 8.27 | 4 |
| Foley catheter | 0.82 | 0.41 to 1.65 | – | – | 0 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.85 | 0.45 to 1.62 | Not estimable | ||
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.92 | 0.49 to 1.69 | 0.04 | 0 to 0.32 | 1 |
| Laminaria | 0.92 | 0.25 to 3.41 | – | – | 0 |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.97 | 0.02 to 37.3 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 1.01 | 0.56 to 1.81 | – | – | 0 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 1.03 | 0.58 to 1.85 | 0.70 | 0.12 to 2.21 | 5 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.06 | 0.43 to 2.60 | – | – | 0 |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.12 | 0.29 to 4.25 | – | – | 0 |
| Amniotomy | 1.30 | 0.37 to 4.61 | – | – | 0 |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.85 | 0.63 to 5.40 | – | – | 0 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.91 | 0.57 to 6.35 | – | – | 0 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 2.39 | 0.62 to 9.58 | – | – | 0 |
Table 14 reports the absolute probabilities and posterior mean ranks for each intervention. The safest intervention in terms of risk of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes was double-balloon or Cook’s catheter, with a mean rank of ‘4’; however, the 95% CrI ranged from ‘1’ to ‘22’ out of 28 interventions, reflecting the considerable uncertainty in this estimate. Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter also had the lowest absolute probability of an event at 1.1% (CrI 0.02% to 6.5%). Buccal/sublingual misoprostol had a posterior mean rank of ‘5’ (95% CrI 1 to 15) and an absolute probability of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes of 1.4% (95% CrI 0.2% to 5%).
| Intervention | Absolute probability of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes admission | Posterior mean rank and 95% CrI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Posterior mean | 95% CrI | |||
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.06 | 4 | 1 to 22 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.07 | 7 | 1 to 24 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.05 | 5 | 1 to 15 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.07 | 12 | 3 to 23 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.07 | 10 | 5 to 16 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.08 | 9 | 1 to 24 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.06 | 8 | 3 to 15 |
| Titrated (low) oral misoprostol solution | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.06 | 7 | 2 to 17 |
| NO | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.06 | 7 | 2 to 17 |
| Acupuncture | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.09 | 9 | 1 to 25 |
| Placebo | 0.03 | 0.01 to 0.1 | 17 | 10 to 23 |
| No intervention | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.11 | 17 | 7 to 25 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.03 | 0.01 to 0.1 | 19 | 12 to 23 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.10 | 13 | 4 to 24 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.10 | 16 | 9 to 23 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.03 | 0.01 to 0.10 | 18 | 11 to 23 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.09 | 15 | 8 to 21 |
| Mifepristone | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.13 | 14 | 2 to 27 |
| Foley catheter | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.09 | 14 | 7 to 22 |
| Laminaria | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.13 | 16 | 2 to 27 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.04 | 0.01 to 0.12 | 18 | 7 to 25 |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 0.04 | 0.00 to 0.16 | 18 | 3 to 27 |
| Amniotomy | 0.05 | 0.00 to 0.18 | 20 | 4 to 27 |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.06 | 0.01 to 0.21 | 23 | 12 to 27 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.07 | 0.01 to 0.24 | 24 | 10 to 27 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.08 | 0.01 to 0.29 | 24 | 12 to 27 |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.08 | 0.00 to 0.59 | 15 | 1 to 27 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2a | Not estimable | |||
Table 14 also reports that three further interventions had a posterior mean rank of ‘7’: titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution, NO and oral prostaglandins. However, the uncertainty around these rankings is considerable. Low ranking interventions include i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy, misoprostol vaginal pessary (sustained release) and membrane sweeping. Note that the ORs relative to placebo did not achieve statistical significance for any of these interventions (see Table 13).
Figure 12 reports the rankograms for Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes. For all of the interventions the rankograms are flat and indicative of considerable uncertainty around the probability that any intervention is the ‘best’. Therefore, we did not include an assessment of probability for being the ‘best’ in our summary for this outcome.
Maternal satisfaction with care and induction of labour method
Less than 5% of the studies included in the review reported data relating to maternal satisfaction with the induction process. In Table 15 we set out findings from these trials. We were unable to pool any results from trials in either pairwise or NMA. The trials focused on a broad range of interventions (10/29 examined oxytocin) and comparators. Furthermore, outcome definitions varied considerably. For mechanical methods, the questions related to discomfort during the initial procedure (e.g. insertion of catheter or membrane sweeping). For other methods there were more global assessments of the process. There were no preferred methods and, in general, women were satisfied with (or at least accepted) the induction process.
| Study ID | Intervention | Comparison | Satisfaction outcomes | Results | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adeniji 200551 | Vaginal misoprostol 50 µg (n = 50) | Foley catheter (n = 46) | Maternal discomfort (NC). Maternal questionnaires | Intravaginal Misoprostol was well received by the patients . . . showing 85% acceptance of Misoprostol with average expression of minimal discomfort at insertion, in contrast to 35% acceptance, moderate discomfort and resentment of ‘something between thighs’ in the Foley catheters group (p < 0.05) | Study in Nigeria, 2003. It was not clear when women completed questionnaires or how outcomes were measured. The number of women responding to questionnaires was not stated |
| Ashrafunnessa 199773 | Intracervical PGE2 gel 500 µg (n = 49) | i.v. oxytocin (n = 49) | Women’s opinions regarding acceptability of methods (rated recommendable, acceptable, unsatisfactory or no answer) |
|
Study in India; not clear when the study was carried out. It was not clear when women were asked about their opinions. It was stated that there was no significant difference between groups for rating of labour induction method |
| Bollapragada 2009107 | Self-administered at home NO donor (ISMN) (n = 177) | Placebo (n = 173) | Women’s experience of induction of labour; pain and anxiety Outcomes measured on admission to hospital Discomfort and anxiety measured on a 10-point scale General satisfaction measured post delivery; six questions Likert scale 1–10 (1 best) |
Maternal satisfaction outcomes mean scores and SD:
|
Study in UK. Response rates for satisfaction outcomes approximately 63%. Overall, most women expressed positive views about home treatment. Women in the placebo group had slightly more positive views, and women in the ISMN group who suffered headache had significantly fewer positive views (data not shown) |
| Boulvain 1998110 | Membrane sweep (n = 99) | No treatment (vaginal examination only) (n = 99) | Pain following first visit and 24 hours later VAS Women who had membrane sweep were asked for views postpartum |
Mean pain score during initial vaginal examination/membrane sweep: sweep group 2.4 (1.3–4.3), control 1.5 (0.4–3.4) (p = 0.001) Postpartum women who had had membrane sweep: 86.7% said they would recommend the intervention; some women described the procedure as unpleasant 31% |
Study in Canada 1995–6; response rates to pain questionnaire 87% |
| Bullarbo 2007122 | NO donor (ISMN) (n = 100) | Placebo (n = 100) | Opinion of outpatient procedure and whether or not women would recommend this treatment | Most women in both groups were either positive or very positive to the treatment. Eighty-nine of the women (94.7%) in the isosorbide mononitrate group and 93 of the women (93.9%) in the placebo group reported that they would recommend the procedure | Study in Sweden; 94% of women in intervention group and 99% controls responded |
| De Miranda 2006201 | Membrane sweep (n = 375) | No intervention (n = 367) | Pain and whether or not women would choose the same procedure again | Women who had undergone membrane sweep – report: 51% thought membrane sweep was somewhat painful and 17% painful or very painful; after delivery 88% said that they would choose a membrane sweep in a subsequent pregnancy | The Netherlands, 2000–3; 94% in the intervention group responded to the postpartum survey of views |
| Gribel 2011314 | Acupuncture (n = 35) | Vaginal misoprostol 25 µg (n = 32) | Satisfaction with the labour induction technique. It was not clear how satisfaction outcomes were measured | Satisfaction with the technique was informed by patients in group (acupuncture) 89% and M (misoprostol) 69% with significant difference between groups | Study in Brazil 2007–9 |
| Güngördük 2012319 | i.v. oxytocin (n = 221) | Sustained-release PGE2 (0.3 mg/hour) (n = 223) | Maternal satisfaction with childbirth experience and pain VAS scale 0–10, higher scores greater satisfaction, and worse pain. Reported within 24 hours of the birth |
VAS for satisfaction with birth process (higher scores = better) i.v. oxytocin 8.1 (1.14) vs. PGE2 8.08 (0.6) (p = 0.88) Pain (higher scores = worse) oxytocin 5.16 (2.4) vs. PGE2 4.07 (1.68) (p < 0.001) (oxytocin more painful) |
Study in Turkey 2009–10 |
| Hannah 1996335 | Immediate induction of labour with i.v. oxytocin (n = 1258) or PGE2 vaginal gel (n = 1259) | Expectant management (n = 2524) | Women’s evaluations of care | Compared with expectant management, fewer women in the oxytocin reported that there was nothing that they liked about their treatment (13.7% vs. 5.9%) and more women in the oxytocin group said they would participate in the study again (59.9% vs. 67.3%) Compared with expectant management, fewer women in the PGE2 group reported that there was nothing that they liked about their treatment (11.7% vs. 5.1%) and more women in the PGE2 group said that they would participate in the study again (59.2% vs. 66.5%) It was reported that there were no significant differences between groups for other measures of maternal satisfaction |
Multicentre study in Canada, UK, Australia, Israel, Sweden and Denmark Women recruited between 1992 and 1995 |
| Kennedy 1978419 | i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy (n = 27) | Intracervical PGE2 (n = 28) | Maternal reactions to method (favourable vs. unfavourable) and whether labour was better or worse than previous labours (for multiparous women only) | Reaction unfavourable: 1/27 oxytocin, 1/27 cervical PGE2 gel Labour worse than previous ones: 2/11 oxytocin, 2/14 cervical PGE2 |
UK study. Brief report. Most women 55/60 responded to survey but data on experience of labour for multiparous women only |
| Kennedy 1982420 | Vaginal PGE2 tablet (n = 50) | i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy (n = 50) | Maternal reactions to method (favourable vs. unfavourable) | Reaction unfavourable: PGE2 0/50, oxytocin with amniotomy 26/50 | Study carried out in the UK |
| Legarth 1987460 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary 2.5 mg (n = 49) | i.v. oxytocin (n = 49) | Women’s perceptions of pain and view of method of induction used | In the PGE2 group, 19/47 reported intense pain vs. 11/45 in the oxytocin group The method was reported as unsatisfactory by 1/47 in the PGE2 group and 7/45 in the oxytocin group |
Study in Denmark |
| Lo 1994480 | Vaginal PGE2 tablet (n = 101) | i.v. oxytocin (n = 99) | Maternal acceptance of method It was not clear what women were asked |
Method rated positively by 77/99 in the oxytocin group and 63/101 in the PGE2 group | Study in Hong Kong 1991–2; results stratified by parity |
| Lyndrup 1990494 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary 2.5 mg (n = 43) | i.v. oxytocin (n = 48) | Women’s comments (method recommendable, acceptable or unsatisfactory) | In the PGE2 group, 3/29 described the method as unsatisfactory compared with 8/32 in the oxytocin group (p = 0.001) | Study in Denmark over 3 years |
| Mei-Dan 2012553 | Foley catheter (n = 88) | Double-balloon catheter (Cook) (n = 100) | Pain perception during insertion rated on a 1–10 scale (higher score worse) | Mean pain score Foley catheter group 3.3 (2.3) vs. double-balloon catheter 3.4 (2.3) p = 0.77 | Study in Israel |
| Nassar 2006595 | Vaginal misoprostol 50 µg (n = 85) | Sublingual misoprostol 50 µg (n = 85) | Questionnaire completed following the birth including questions on induction method | In the vaginal misoprostol group, 18/72 said that they would opt for the same route in any subsequent induction vs. 59/76 in the sublingual route In the vaginal misoprostol group, 27/72 reported that they would have a favourable view of induction in a future pregnancy compared with 46/76 in the sublingual group |
Study in Beirut 2004–6 |
| Paul 1992652 | i.v. oxytocin (n = 20) | Oral PGE2 (n = 15) | Women’s view of method (favourable, non-committal, unfavourable) | In the oxytocin group, 13/20 had an unfavourable opinion compared with none in the PGE2 group | |
| Shetty 2002780 | Oral misoprostol 50 µg (n = 50) | Sublingual misoprostol 5 µg (n = 50) | Not clear how satisfaction was measured | It was reported that satisfaction rates were 82.5% and 85.7% in the oral and sublingual groups, respectively | UK study 2000; 82% returned postnatal questionnaires |
| Shetty 2002784 | Oral misoprostol 50 µg (n = 124) | Sublingual misoprostol 5 µg (n = 125) | Brief satisfaction questionnaire about satisfaction and preferences for the future | High levels of satisfaction with induction method in both groups (87–88%) | UK study 2000–1; 78% of women responded to satisfaction questionnaire |
| Surita 2005826 | Foley catheter (n = 70) | Hyaluronidase (n = 70) | Women reported satisfaction with and discomfort associated with each method | In the Foley catheter group, 56/70 were satisfied, and 12/70 reported that the method was very or relatively uncomfortable In the hyaluronidase group, 49/70 were satisfied and 10/70 were very or relatively uncomfortable |
Study in Brazil 2000–2 |
| Tan 2013837 | i.v. oxytocin (105) | Placebo (101) | Satisfaction with the birth process on a 1–10 scale (lower score better) 24 hours after the birth | i.v. oxytocin mean score 3 (3–4), placebo 3 (3–5) p = 0.36 | Study in Malaysia 2010–12 |
| Cardozo 1986137 | PGE2 vaginal pessary 3 mg (n = 195) | Expectant management (n = 207) | Satisfaction with management (pleased, no comment, disappointed) | In the PGE2 group, 97/195 reported that they were pleased with their management compared with 110/207 in the expectant management group | Study in UK |
| Colon 2005173 | Vaginal misoprostol 25 µg (n = 111) | Oral misoprostol 50 µg (n = 93) | Not clear how satisfaction was measured post delivery | Ninety-eight per cent of women in both groups expressed satisfaction with their overall experience in hospital; 14% of vaginal group vs. 7.5% in oral group were dissatisfied with the use of misoprostol | Study in USA; 153/204 responded to survey |
| Dodd 2006214 | Oral misoprostol solution 20 µg (n = 365) | Vaginal PGE2 gel (n = 376) | Women’s preferences | Overall 58.5% said that that they would prefer an oral induction agentWomen in the misoprostol group were more likely to say they ‘liked everything’ with their labour and birth | Study in Australia |
| Ferraiolo 2010258 | PGE2 vaginal gel 1 mg (n = 72) | PGE2 vaginal pessary (sustained release) 10 mg (n = 79) | Pre and post delivery maternal questionnaires | It was reported that in the post-induction questionnaires there was no significant difference in anxiety (p = 0.073) or discomfort (0.073). A burning sensation on application was experienced by 31.9% of women in the vaginal gel group and 26.6% in the sustained-release pessary group | Study in Italy 2007–8; 173 recruited but 22 excluded as they did not complete questionnaires or did not complete them correctly |
| Girija 2009293 | Vaginal misoprostol 25 µg (n = 50) | Vaginal misoprostol 50 µg (n = 50) | Not clear when or how satisfaction was measured | Eighty percent (22/25) women in the 25 µg group and 100% 23/23 of women in the 50 µg group had a satisfaction level of more than 50% (p = 0.23) | Study in India 2004–5; data on satisfaction available for only 48/100 randomised |
| Girija 2011294 | Vaginal misoprostol 25 µg (n = 159) | PGE2 gel 0.5 mg, intracervical (n = 161) | Not clear how or when satisfaction was measured | More than 50% satisfaction of (sic) was observed in 107 (89.2%) mothers in misoprostol group and 109 (91.6%) which was not statistically significant p = 0.6762 | Study in India 2006–8; 239/320 responded to satisfaction questionnaire |
| Tomlinson 2001856 | PGE2 vaginal gel 1–2 mg (n = 34) | PGE2 vaginal pessary (sustained release) (n = 35) | Outcomes measured on a Likert scale | Pain on insertion: 2.7 (0–8) in the PGE2 gel group compared with 3.0 (0–10) in the sustained-release pessary group (difference not significant) Satisfaction with induction score: 3.9 (1–6) in the PGE2 gel group and 4.3 (1–6) in the sustained-release pessary group (not significant) |
Study in UK |
| Van Gemund 2004879 | 1 mg of vaginal PGE2 gel (n = 340) | 25 µg of misoprostol vaginal (n = 341) | Preference for subsequent labour | In the PGE2 gel group, 164/286 would choose the same method again compared with 179/291 in the misoprostol group | Study in the Netherlands |
Complementary methods
Unfortunately, it was not possible to assess the efficacy (VD within 24 hours) of trials of complementary interventions or membrane sweeping. Relative to placebo, membrane sweeping performed marginally better than acupuncture or sexual intercourse, with an OR of 0.74 (95% CrI 0.53 to 0.99) for CS and an absolute probability of CS of 20% (95% CrI 3% to 54%) compared with 21% for both sexual intercourse (95% CrI 3% to 58%) and acupuncture (95% CrI 3% to 57%). For instrumental delivery, membrane sweeping was consistent, with both an increased and decreased odds of assisted birth, and was ranked ‘26’ (95% CrI 16 to 31) out of 32 interventions. For both ‘NICU admission’ and ‘Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes’ outcomes, membrane sweeping was associated with a low absolute probability of either event.
Subgroup analyses
We planned to conduct subgroup analyses to explore the effect of different clinical subgroups on effectiveness data. Here we present subgroup analyses for three outcomes: (1) failure to achieve VD within 24 hours of induction; (2) CS; and (3) Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes. The prespecified confounders were (1) women with intact or ruptured membranes; (2) different gestational ages; (3) women with or without a previous CS; and (4) women with low (< 6) or higher (≥ 6) Bishop scores. Table 16 reports the breakdown of trials for each of these possible subgroups.
| Trials included | VD not achieved | CS | Apgar |
|---|---|---|---|
| 141 studies, 21 treatments | 307 studies, 33 treatments | 200 studies, 28 treatments | |
| All women with a previous CS | 0 studies | Not connected | 0 studies |
| No women with a previous CS | 115 studies | 215 studies | 153 studies |
| All women with intact membranes | 58 studies | 161 studies | 98 studies |
| 19 treatments | 29 treatments | 28 treatments | |
| All women with ruptured membranes | 17 studies | 49 studies | 37 studies |
| 12 treatments | 17 treatments | 18 treatments | |
| All women with Bishop scores of ≥ 6 | 5 studies | 13 studies | 6 studies |
| 5 treatments | 8 treatments | 7 treatments | |
| All women with Bishop scores of < 6 | 106 studies | 202 studies | 128 studies |
| 19 treatments | 18 treatments | 25 treatments |
Subgroup analysis for intact membranes compared with ruptured membranes
When the analysis was limited to only those trials in which all women had intact membranes, 56 trials of 15 treatments formed a connected network for the outcome of no VD within 24 hours (see Appendix 15). When restricted to those trials that included only women with ruptured membranes, a connected network of 17 trials of 12 treatments was possible. Note that studies including women with both intact or ruptured membranes, which did not report results for each subgroup separately, are not included here. Reported results are based on the REs NMA model, assuming consistency (see Appendix 15). All active interventions are compared with vaginal PGE2 gel, as placebo is no longer available in the restricted networks.
Outcome: vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours
Results are reasonably robust across the analyses: Table 17 compares all treatments with vaginal PGE2 (gel) for all studies and the two subgroups: (1) intact and (2) ruptured membranes. For the subgroup including only women with intact membranes, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy and vaginal misoprostol (≥ 50 µg) are still ranked ‘best’ for achieving VD within 24 hours.
| Active intervention vs. vaginal PGE2 gel | All studies | Intact membranes only | Ruptured membranes only | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | Reference treatment | 8 | 5 to 12 | Reference treatment | 9 | 5 to 13 | Reference treatment | 3 | 1 to 9 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.42 | 0.1 to 1.15 | 2 | 1 to 9 | 0.16 | 0.02 to 0.96 | 2 | 1 to 8 | Not in network | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.69 | 0.51 to 0.93 | 3 | 1 to 6 | 0.57 | 0.38 to 0.84 | 4 | 2 to 6 | 2.61 | 0.11 to 137.2 | 6 | 1 to 12 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.79 | 0.5 to 1.2 | 5 | 1 to 10 | 1.49 | 0.71 to 3.26 | 12 | 5 to 14 | 1.42 | 0.11 to 34.13 | 5 | 1 to 10 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.82 | 0.59 to 1.1 | 5 | 2 to 8 | 0.56 | 0.35 to 0.89 | 4 | 2 to 6 | 1.67 | 0.16 to 37.5 | 5 | 1 to 10 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0.82 | 0.31 to 1.78 | 5 | 1 to 16 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.82 | 0.5 to 1.27 | 5 | 2 to 11 | 0.60 | 0.25 to 1.42 | 5 | 2 to 12 | Not in network | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.87 | 0.46 to 1.5 | 6 | 1 to 13 | 0.49 | 0.2 to 1.2 | 4 | 1 to 10 | Not in network | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.20 | 0.79 to 1.75 | 11 | 6 to 16 | 0.82 | 0.48 to 1.37 | 7 | 4 to 12 | 0.92 | 0.06 to 35.39 | 3 | 1 to 10 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.27 | 0.89 to 1.75 | 12 | 7 to 16 | 1.05 | 0.66 to 1.66 | 10 | 6 to 13 | 1.33 | 0.19 to 17.99 | 4 | 1 to 8 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.43 | 1.03 to 1.92 | 14 | 10 to 17 | 1.11 | 0.74 to 1.65 | 11 | 7 to 13 | 3.50 | 0.16 to 150.2 | 7 | 1 to 12 |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.43 | 0.71 to 2.58 | 12 | 4 to 18 | 0.92 | 0.5 to 1.73 | 8 | 3 to 13 | Not in network | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.45 | 0.89 to 2.24 | 13 | 7 to 18 | 0.85 | 0.49 to 1.45 | 7 | 4 to 12 | Not in network | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.57 | 1 to 2.35 | 14 | 9 to 18 | 1.63 | 0.67 to 3.93 | 13 | 6 to 14 | 6.98 | 0.3 to 29.88 | 6 | 3 to 9 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.71 | 0.77 to 3.33 | 14 | 5 to 18 | Not in network | 5.89 | 0.26 to 312.7 | 9 | 2 to 12 | |||
| NO | 1.76 | 0.77 to 3.49 | 14 | 5 to 18 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 3.18 | 0.66 to 9.62 | 16 | 3 to 20 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Mifepristone | 6.25 | 1.67 to 16.71 | 19 | 16 to 21 | Not in network | 6.98 | 0.38 to 305.5 | 9 | 2 to 12 | |||
Amniotomy is clearly not a feasible option for women with ruptured membranes, and this is reflected in the subgroup analysis for ruptured membranes, in which it does not feature in any of the trials. For this subgroup the CrIs are extremely wide, reflecting extreme uncertainty in which treatment is best for women with ruptured membranes.
Outcome: caesarean section
A total of 160 trials of 31 treatments were available for analysis when restricted to trials in which all women had intact membranes. The subgroup for trials that included only women with ruptured membranes formed a connected network of 47 trials of 17 treatments (see Appendix 15). As before, studies reporting pooled data for women with both intact or ruptured membranes, or those who did not report details for this characteristic, are not included here. Reported results are therefore based on the REs NMA model, assuming consistency (see Appendix 15).
For the subgroup of women with intact membranes we note that the posterior mean rank for titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution has changed from ‘6’ to ‘14’, albeit with considerable uncertainty in the relative ranking (95% CrI 3 to 28) (Table 18). Similarly, the mean rank for PGF2 gel has decreased from 11 to 21, with very wide CrIs (95% CrI 3 to 30), showing that there is considerable uncertainty in the relative rankings. The mean rank for extra-amniotic PGE2 has improved from ‘22’ to ‘4’, although, again, the CrIs indicate considerable uncertainty, which should be taken into consideration in any conclusions (95% CrI 1 to 26).
| Active intervention vs. placebo | All studies | Intact membranes only | Ruptured membranes only | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | |
| Corticosteroids | 0.5 | 0.2 to 1.12 | 6 | 1 to 29 | 0.56 | 0.21 to 1.23 | 5 | 1 to 26 | Not in network | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.6 | 0.47 to 0.8 | 6 | 2 to 13 | 0.91 | 0.53 to 1.53 | 14 | 3 to 28 | 0.62 | 0.22 to 1.35 | 6 | 1 to 14 |
| Hyaluronidase | 0.6 | 0.34 to 1 | 7 | 1 to 26 | 0.69 | 0.37 to 1.15 | 7 | 1 to 24 | Not in network | |||
| PGF2 gel | 0.7 | 0.4 to 1.16 | 11 | 1 to 29 | 1.28 | 0.52 to 2.7 | 21 | 3 to 30 | Not estimable | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.57 to 0.85 | 9 | 4 to 16 | 0.82 | 0.62 to 1.08 | 10 | 5 to 18 | 0.47 | 0.21 to 0.89 | 3 | 1 to 7 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.59 to 0.88 | 11 | 5 to 18 | 0.92 | 0.69 to 1.21 | 15 | 8 to 24 | 0.52 | 0.23 to 1.01 | 4 | 1 to 11 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.58 to 0.88 | 10 | 4 to 18 | 0.80 | 0.58 to 1.08 | 10 | 4 to 19 | 0.84 | 0.49 to 1.32 | 10 | 4 to 14 |
| Mifepristone | 0.7 | 0.45 to 1.08 | 11 | 2 to 28 | 0.58 | 0.29 to 1.02 | 5 | 1 to 20 | 3.40 | 0.48 to 16.01 | 14 | 5 to 17 |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.7 | 0.53 to 0.99 | 12 | 3 to 24 | 0.93 | 0.59 to 1.43 | 14 | 4 to 26 | Not in network | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.7 | 0.08 to 2.59 | 10 | 1 to 32 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.7 | 0.51 to 0.89 | 9 | 2 to 19 | 0.86 | 0.54 to 1.3 | 12 | 3 to 26 | Not in network | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.8 | 0.65 to 0.94 | 15 | 9 to 21 | 1.00 | 0.77 to 1.3 | 19 | 11 to 26 | 0.72 | 0.38 to 1.29 | 8 | 4 to 12 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.8 | 0.69 to 0.98 | 18 | 11 to 24 | 1.02 | 0.8 to 1.3 | 19 | 11 to 26 | 0.58 | 0.25 to 1.18 | 5 | 1 to 13 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.8 | 0.62 to 1.09 | 17 | 6 to 28 | 0.88 | 0.52 to 1.4 | 13 | 3 to 27 | 0.89 | 0.46 to 1.61 | 10 | 3 to 15 |
| NO | 0.8 | 0.62 to 1.06 | 17 | 5 to 28 | 0.91 | 0.64 to 1.25 | 14 | 5 to 26 | Not in network | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.61 to 0.95 | 14 | 6 to 22 | 0.94 | 0.69 to 1.25 | 16 | 7 to 25 | 0.86 | 0.38 to 1.7 | 10 | 4 to 15 |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.8 | 0.43 to 1.38 | 15 | 2 to 31 | 1.02 | 0.49 to 1.89 | 17 | 3 to 30 | Not in network | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.8 | 0.54 to 1.29 | 17 | 3 to 31 | 1.11 | 0.61 to 1.95 | 19 | 4 to 30 | Not in network | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.2 | 16 | 2 to 30 | 0.89 | 0.54 to 1.38 | 13 | 3 to 28 | 4.22 | 0.27 to 23.7 | 13 | 2 to 17 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.9 | 0.69 to 1.12 | 21 | 12 to 28 | 1.14 | 0.82 to 1.55 | 23 | 13 to 29 | 0.49 | 0.21 to 0.96 | 4 | 1 to 9 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.9 | 0.75 to 1.14 | 23 | 16 to 29 | 0.94 | 0.65 to 1.34 | 16 | 6 to 26 | 0.83 | 0.46 to 1.43 | 10 | 6 to 13 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.57 to 1.34 | 20 | 4 to 31 | 0.99 | 0.6 to 1.59 | 17 | 4 to 28 | Not in network | |||
| Relaxin | 0.9 | 0.33 to 1.98 | 16 | 1 to 32 | 0.86 | 0.3 to 1.99 | 12 | 1 to 30 | Not in network | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 1.0 | 0.78 to 1.35 | 26 | 17 to 31 | 1.15 | 0.76 to 1.68 | 22 | 9 to 30 | 2.36 | 0.65 to 6.12 | 15 | 10 to 17 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.0 | 0.59 to 1.55 | 22 | 5 to 32 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.57 to 1.57 | 22 | 4 to 32 | 0.51 | 0.16 to 1.2 | 4 | 1 to 26 | Not in network | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.1 | 0.64 to 1.81 | 25 | 7 to 32 | 1.08 | 0.18 to 3.5 | 14 | 1 to 30 | 1.15 | 0.38 to 2.73 | 12 | 4 to 16 |
| Amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.51 to 2.02 | 22 | 3 to 32 | 1.22 | 0.56 to 2.48 | 21 | 4 to 30 | Not in network | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.1 | 0.73 to 1.63 | 27 | 14 to 32 | 1.38 | 0.88 to 2.11 | 26 | 15 to 30 | Not in network | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.3 | 0.62 to 2.32 | 27 | 5 to 32 | 1.42 | 0.68 to 2.63 | 25 | 6 to 30 | Not in network | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 19.9 | 1.61 to 120.5 | 33 | 32 to 33 | 47.75 | 1.88 to 253.7 | 31 | 30 to 31 | Not in network | |||
When limiting the network to trials that included only women with ruptured membranes, we observe that vaginal misoprostol (both doses), intracervical PGE2, vaginal slow-release PGE2 pessary and titrated low-dose oral misoprostol solution have the highest rankings, with 95% CrI including the best ranking. As with other subgroup analyses the CrIs are very wide, making clinical interpretation quite difficult.
Outcome: Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
For the outcome of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes, the subgroup in which all women had intact membranes was a connected network of 98 trials of 26 treatments. When the analysis was limited to only those trials in which all women had ruptured membranes, 37 trials of 16 treatments assessed the outcome of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes (see Appendix 15). However, we observed meaningful differences in the posterior mean residual deviance, suggesting that there was evidence of unresolved inconsistency (see Appendix 15). As such we do not report the findings for these subgroups.
Subgroup analysis for women with low Bishop score (< 6) or higher Bishop score (≥ 6)
Outcome: vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours
For the outcome of no VD within 24 hours when the analysis was limited to only those trials in which all women had a Bishop score < 6, 106 trials of 17 treatments assessed the outcome of no VD within 24 hours. However, we observed meaningful differences in the posterior mean residual deviance, the DIC values and the SDs, suggesting that there is evidence of inconsistency. Consequently, we do not report results for this subgroup here. No meaningful analysis could be carried out on women with a Bishop score ≥ 6, as the network only included five studies comparing seven treatments and was not connected (see Appendix 15).
Outcome: caesarean section
For the CS outcome, restricting to trials in which all women had a Bishop score < 6 allowed a connected network of 203 trials comparing 28 treatments. When the analysis was limited to only those trials that included women with a Bishop score ≥ 6, a connected network of 10 trials of 10 treatments assessed the outcome of CS (see Appendix 15). Full results are shown in Table 19. Results are largely robust to the analysis, only including studies with women with a Bishop score < 6. A posterior mean rank for extra-amniotic PGE2 changed from ‘22’ to ‘4’ and this treatment became significantly better than placebo for preventing a CS. Similarly, acupuncture changed from having a mean rank of ‘16’ to ‘3’ and became significantly better than placebo.
| Interventions | Number of trials reporting cervical status | Number of trials recruiting women with different cervical status | Percentage of trials including only women unfavourable cervix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxytocin with amniotomy | 22 | 1 unfavourable 11 mixed 10 favourable 3 not reported |
4.5 |
| Vaginal and intracervical PGE2 | 284 | 233 unfavourable 43 mixed 8 favourable 11 not reported |
82 |
| Misoprostol | 209 | 168 unfavourable 33 mixed 8 favourable 37 not reported |
80 |
| Mechanical methods | 69 | 66 unfavourable 2 mixed 1 favourable 3 not reported |
96 |
Outcome: Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
For the outcome of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes, restricting the analysis to only those trials in which all women had Bishop scores of < 6 produced a connected network of 128 trials comparing 24 treatments. However, because of the number of zero events, the NMA model would not converge and therefore we cannot report results. Similarly, we do not report results for women with a Bishop score ≥ 6 due to zero events, as the network included only six studies and seven treatments.
Formal subgroup analysis either was not possible or did not show clear subgroup differences in terms of cervical status. It is noteworthy that far fewer trials tested i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy in women with unfavourable cervix than other interventions, such as PGE2, misoprostol and mechanical methods (see Table 19). This is hardly surprising, given that amniotomy is very difficult or even impossible in women with very unfavourable cervix. Overall, women with favourable cervix are more likely to achieve VD within 24 hours, but this should not produce biased results in our NMA as this would apply to both the experimental group (e.g. oxytocin with amniotomy) and the control group (e.g. any prostaglandin) as well (i.e. the relative effect between two treatments is not affected). Nevertheless, as oxytocin with amniotomy has been predominantly tested in women with favourable cervix, our recommendations relating to this intervention are restricted to this subgroup.
Gestational age and previous caesarean section subgroups
The reporting of gestational age by trial authors made it difficult to define mutually exclusive subgroups and so we do not report analyses for this characteristic.
For women with a previous CS there were no trials remaining which would allow an analysis based on failure to achieve VD within 24 hours, or Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes (Table 20). There were only four trials remaining for the outcome of CS; however, the network was not connected and so an analysis was not possible.
| Active intervention vs. placebo | All studies | Bishop score < 6 | Bishop score ≥ 6 [vs. vaginal PGE2 (tablet)] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 1.0 | 0.78 to 1.35 | 26 | 17 to 31 | 1.03 | 0.74 to 1.41 | 22 | 13 to 27 | Reference treatment | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.8 | 0.65 to 0.94 | 15 | 9 to 21 | 0.78 | 0.63 to 0.97 | 13 | 7 to 19 | 0.72 | 0.02 to 24.86 | 5 | 1 to 9 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.9 | 0.69 to 1.12 | 21 | 12 to 28 | 0.92 | 0.68 to 1.2 | 19 | 11 to 25 | Not in network | |||
| PGF2 gel | 0.7 | 0.4 to 1.16 | 11 | 1 to 29 | 1.04 | 0.42 to 2.2 | 18 | 2 to 28 | Not in network | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.8 | 0.69 to 0.98 | 18 | 11 to 24 | 0.83 | 0.68 to 1.01 | 15 | 9 to 21 | Not in network | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.8 | 0.62 to 1.09 | 17 | 6 to 28 | 0.88 | 0.62 to 1.23 | 17 | 6 to 25 | 0.10 | 0 to 219.8 | 1 | 1 to 9 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 0.7 | 0.57 to 0.85 | 9 | 4 to 16 | 0.71 | 0.56 to 0.88 | 9 | 4 to 15 | Not in network | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 0.7 | 0.59 to 0.88 | 11 | 5 to 18 | 0.72 | 0.57 to 0.9 | 10 | 5 to 16 | Not in network | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet< 50 µg | 1.1 | 0.64 to 1.81 | 25 | 7 to 32 | 1.11 | 0.61 to 1.87 | 21 | 6 to 28 | Not in network | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0.7 | 0.58 to 0.88 | 10 | 4 to 18 | 0.70 | 0.54 to 0.91 | 9 | 4 to 17 | 0.56 | 0 to 1041 | 5 | 1 to 9 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.6 | 0.47 to 0.8 | 6 | 2 to 13 | 0.62 | 0.43 to 0.87 | 6 | 2 to 15 | 0.49 | 0 to 824.8 | 4 | 1 to 9 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.0 | 0.59 to 1.55 | 22 | 5 to 32 | 1.02 | 0.56 to 1.73 | 19 | 4 to 28 | Not in network | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.9 | 0.75 to 1.14 | 23 | 16 to 29 | 0.94 | 0.72 to 1.21 | 20 | 13 to 25 | 0.62 | 0 to 447.7 | 5 | 2 to 9 |
| Amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.51 to 2.02 | 22 | 3 to 32 | Not in network | 0.86 | 0 to 127.9 | 6 | 2 to 9 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.57 to 1.34 | 20 | 4 to 31 | 1.83 | 0.44 to 5.11 | 23 | 2 to 28 | 0.78 | 0 to 190.8 | 6 | 2 to 9 |
| NO | 0.8 | 0.62 to 1.06 | 17 | 5 to 28 | 0.81 | 0.6 to 1.06 | 14 | 5 to 23 | Not in network | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.7 | 0.45 to 1.08 | 11 | 2 to 28 | 0.72 | 0.45 to 1.1 | 10 | 2 to 24 | Not in network | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.3 | 0.62 to 2.32 | 27 | 5 to 32 | 1.28 | 0.61 to 2.38 | 23 | 5 to 28 | Not in network | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.5 | 0.2 to 1.12 | 6 | 1 to 29 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Relaxin | 0.9 | 0.33 to 1.98 | 16 | 1 to 32 | 1.67 | 0.36 to 5.23 | 21 | 2 to 28 | Not in network | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.6 | 0.34 to 1 | 7 | 1 to 26 | 0.61 | 0.33 to 1.04 | 7 | 1 to 23 | Not in network | |||
| Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.61 to 0.95 | 14 | 6 to 22 | 0.77 | 0.59 to 0.98 | 12 | 6 to 19 | Not in network | |||
| Laminaria | 0.8 | 0.43 to 1.38 | 15 | 2 to 31 | 0.81 | 0.4 to 1.45 | 13 | 2 to 27 | Not in network | |||
| Double balloon/Cook’s catheter | 1.1 | 0.73 to 1.63 | 27 | 14 to 32 | 1.14 | 0.72 to 1.72 | 23 | 12 to 28 | Not in network | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.7 | 0.53 to 0.99 | 12 | 3 to 24 | 0.77 | 0.47 to 1.19 | 12 | 3 to 25 | Not in network | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.57 to 1.57 | 22 | 4 to 32 | 0.46 | 0.17 to 0.99 | 4 | 1 to 22 | Not in network | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 19.9 | 1.61 to 120.5 | 33 | 32 to 33 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.8 | 0.54 to 1.29 | 17 | 3 to 31 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Acupuncture | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.2 | 16 | 2 to 30 | 0.38 | 0.13 to 0.86 | 3 | 1 to 16 | Not in network | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.7 | 0.08 to 2.59 | 10 | 1 to 32 | Not in network | Not in network | ||||||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.7 | 0.51 to 0.89 | 9 | 2 to 19 | 0.62 | 0.42 to 0.89 | 6 | 2 to 16 | 0.53 | 0 to 413.6 | 5 | 1 to 9 |
Summary
We presented the impact of 31 interventions (excluding no treatment and placebo) on failure to achieve VD within 24 hours, CS, instrumental delivery, uterine hyperstimulation, Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes and NICU admission. For a total of 17 methods (11 prostaglandins, two mechanical methods, oxytocin with or without amniotomy, NO and mifepristone) we were able to produce rankings for all six outcomes (Table 21). The data were incomplete for other methods and other key safety outcomes, namely neonatal mortality/morbidity, maternal mortality/morbidity and maternal satisfaction, which we have described narratively. Table 21 is intended to provide a broad summary of findings across outcomes; however, it does not report CrIs. Therefore, it is important that this table is interpreted in the context of relevant tables for each outcome, which set out the uncertainty around rankings.
| Induction method | Posterior mean rank | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VD within 24 hours | CS | Ins del | HS | NICU | Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | |
| Complete rankings | ||||||
| Prostaglandins | ||||||
| Titrated (low) oral misoprostol solution | 5 | 6 | 19 | 10 | 11 | 7 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 6 | 9 | 7 | 18 | 13 | 5 |
| Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 6 | 9 | 11 | 14 | 14 | 16 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 12 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 8 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 14 | 25 | 9 | 7 | 14 | 9 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 4 | 17 | 23 | 8 | 18 | 13 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 11 | 21 | 7 | 15 | 13 | 18 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 12 | 26 | 17 | 11 | 16 | 12 |
| Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 4 | 11 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 18 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol pessary | 5 | 22 | 16 | 18 | 8 | 24 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 8 | 15 | 18 | 13 | 20 | 19 |
| Other methods | ||||||
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 10 | 27 | 9 | 2 | 9 | 4 |
| Foley catheter | 13 | 14 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 14 |
| NO | 15 | 17 | 17 | 3 | 17 | 7 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 14 | 23 | 24 | 12 | 15 | 15 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 2 | 20 | 17 | 16 | 27 | 24 |
| Mifepristone | 19 | 11 | 30 | 18 | 26 | 14 |
| Incomplete rankings | ||||||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 14 | 18 | 15 | 9 | – | 10 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 16 | 22 | 15 | – | 4 | 27 |
| Laminaria | – | 15 | 12 | 3 | 23 | 16 |
| Membrane sweeping | – | 12 | 26 | – | 16 | 23 |
| Acupuncture | – | 16 | 13 | – | 14 | 9 |
| Sexual intercourse | – | 17 | 25 | – | 6 | 15 |
| Oral prostaglandins | – | 10 | 9 | – | 10 | 7 |
| Amniotomy | – | 22 | 13 | – | 14 | 20 |
| PGF2 gel | – | 11 | 14 | – | 8 | – |
| Oestrogens | – | 27 | 8 | – | 14 | – |
| i.v. prostaglandin | – | 33 | 30 | – | – | 18 |
| Relaxin | – | 16 | 25 | – | – | – |
| Corticosteroids | – | 6 | – | – | – | – |
| Hyaluronidase | – | 7 | – | – | – | – |
We observed moderate heterogeneity across all of the analyses, with a considerable uncertainty in the rankings of interventions across all outcomes.
Our analysis shows that i.v. oxytocin combined with amniotomy has the best chance of achieving VD within 24 hours of induction, but this intervention is restricted to women with intact membranes. Misoprostol (vaginal route, titrated oral solution, buccal/sublingual) and vaginal PGE2 normal-release pessaries also performed well.
Compared with placebo, corticosteroids and titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol achieved the lowest odds of an eventual CS; however, there was considerable uncertainty in these findings.
For instrumental delivery, Foley catheter performed well taking into account the OR, posterior mean ranks and absolute probabilities. However, we again note the uncertainty which surrounds these estimates and the moderate degree of observed heterogeneity.
The safest intervention in terms of risk for uterine hyperstimulation was double-balloon or Cook’s catheter. The intervention with the worst mean rank was vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg, with a 9% absolute probability of uterine hyperstimulation.
Neonatal intensive care unit admission and an Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes were used as proxies for neonatal safety outcomes in the absence of consistent definitions of neonatal mortality and morbidity across the trials. The safest intervention in terms of risk of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes was double-balloon or Cook’s catheter, with a mean rank of ‘4’; however, the 95% CrI ranged from 1 to 22 out of 26 interventions, reflecting the considerable uncertainty in this estimate.
Unfortunately, it was not possible to assess the efficacy (VD within 24 hours) of trials of complementary interventions or membrane sweeping. Relative to placebo, membrane sweeping performed marginally better than acupuncture or sexual intercourse for CS. For both NICU admission and Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes outcomes, membrane sweeping was associated with a low absolute probability of either event.
In broad terms, our subgroup analyses, when available, were consistent with overall results.
Chapter 4 Assessment of cost-effectiveness
Introduction
In this chapter we compare the cost-effectiveness of different methods of induction of labour. We begin by setting out our decision question. We then describe previous studies that have addressed this question; however, we found that none of these provided a model that we could apply to compare the cost-effectiveness of the different methods of induction identified in our review. We then describe our de novo decision model, which we developed to answer our decision question, followed by a description of the evidence sources that were used to provide inputs to the model effectiveness, treatment costs, other resource-use (hospital) costs and utilities. We used the results of the NMA presented in Chapter 3 when possible. Because modes of delivery are not independent (a woman must deliver one of three ways: CS, VD within 24 hours or VD after 24 hours of induction), we need to estimate these outcomes jointly. In order to include as many studies as possible in our analysis, we condition on CS. This means we use the NMA for the CS outcome as presented in Chapter 3, but conduct a new NMA for the ‘failure to achieve vaginal delivery within 24 hours’ outcome, conditional on not having had a CS, using the subset of studies which reported both outcomes. We then present results and end with a discussion.
Decision question
Population
The population of interest was defined in accordance with the inclusion criteria for the systematic review and NMA (i.e. pregnant women carrying a viable fetus and who are eligible for any method of third trimester labour induction).
Interventions
We included all of the interventions that were identified in the systematic review (see Chapter 3) for which we had sufficient information to evaluate the model. This meant that 19 interventions out of a total of 34 (Box 3) were included in the cost-effectiveness analysis, and the remaining 15 were excluded (PGF2α gel, amniotomy, oestrogens, corticosteroids, relaxin, hyaluronidase, laminaria, membrane sweeping, i.v. prostaglandin, sexual intercourse, acupuncture, breast stimulation, homeopathy, castor oil and oral prostaglandins). Note that this does not mean that the excluded interventions were not cost-effective – simply that we did not have enough information to assess their cost-effectiveness. The included interventions were a variety of pharmacological and mechanical interventions. A further issue arose with the vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) intervention which, as described in Chapter 3, was a heterogeneous mix of interventions in which PGE2 was administered vaginally using a range of ‘pessaries’ (frequently produced in trial hospital pharmacies) that are either not readily reproducible or not currently available to the NHS. It is important that this group is distinguished from PGE2 slow-release pessaries that are used in current NHS practice. We included placebo in the results but interpret this as ‘no intervention’, as it would be delivered on the NHS.
-
Vaginal PGE2 tablet.
-
Vaginal PGE2 gel.
-
Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release).
-
Intracervical PGE2.
-
Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release).
-
Vaginal misoprostol – dose < 50 µg.
-
Vaginal misoprostol – dose ≥ 50 µg.
-
Oral misoprostol – dose < 50 µg.
-
Oral misoprostol – dose ≥ 50 µg.
-
Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution.
-
Sustained-release misoprostol insert.
-
i.v. oxytocin.
-
i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy.
-
NO.
-
Mifepristone.
-
Mechanical methods – Foley catheter.
-
Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter.
-
Extra-amniotic PGE2.
-
Buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
-
Placebo.
Outcomes
Obstetrics is different from most other medical specialties in that decision problems involve the health of two patients (mother and child) and an intervention or treatment can affect the health of both. Often, an intervention that is beneficial to the mother can carry a higher risk for the child and vice versa. The birth of a child also has a major impact on the new mother, and the health of the child in the time immediately following birth can have a significant impact on the mother’s own health. Our model includes both maternal and neonatal outcomes, and we attempted to capture the costs and utilities of both mother and baby, giving equal weight to both individuals. We report expected total costs (treatment costs plus other resource costs), expected utility (for mother and baby combined) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs), which measure the additional expected cost per 1 unit of additional utility for one intervention compared with another. We conducted a fully incremental analysis. We report a probabilistic sensitivity analysis, which reflects uncertainty in model inputs. The probabilistic sensitivity analysis is summarised with expected total costs, expected total benefits, ICER, an incremental cost-effectiveness plane and a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC), which plots the probability of each intervention being the most cost-effective, based on expected net benefit for a given willingness-to-pay per unit increase in utility.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) methods of technology appraisal guide954 suggests that the time horizon of the model applied should be long enough to capture all relevant costs and benefit differences between the interventions. We acknowledge that there are some potential long-term adverse events that are associated with the process of labour and that some outcomes, such as CS and serious birth canal injuries, can have a life-long impact on health-related quality of life (e.g. urinary incontinence) and costs. However, we assumed that most cost differences that are related to methods of induction are likely to be realised during and immediately after the birth. The evidence sources that were used to inform utilities did not explicitly state a time frame; however, they are unlikely to reflect many consequences that occur post discharge. The time frame of the analysis was, therefore, taken to be from induction to hospital discharge. We acknowledge that this is a limitation that ignores cost and utility consequences in the longer term. Discounting was deemed unnecessary because of this short time frame. We take a UK NHS perspective.
Previous economic evaluations
We performed a review of the literature (details in Appendix 17) to identify previous studies that have attempted to address our decision question. We identified two RCTs14,955 in which an economic evaluation was also conducted. In both of these trials,14,955 only two methods of induction were compared using costs and efficacy data that were collected alongside the trials; however, neither of them attempted to quantify quality of life. Petrou et al. 14 compared PGE2 gel to PGE2 tablets in a cost-effectiveness analysis with the main outcome measure being incremental cost per hour prevented between induction and delivery. Van Baaren et al. 955 assessed the economic consequences of labour induction with Foley catheter compared with PGE2 gel, in an economic evaluation conducted alongside the PROBAAT (prostaglandin or balloon catheter for induction of labour at term) RCT. This study calculated the cost to prevent one CS, or maternal/neonatal morbidity.
The latest clinical guideline on induction of labour produced by NICE in 2008 included a cost-effectiveness analysis of the timing of the first offer of induction of labour. 9 This analysis used a state-transition (Markov) model to simulate the cost-effectiveness of the different timing strategies, with benefits measured in quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). The primary source of clinical data was the systematic review undertaken as part of the guideline. The QALY estimation took into account only the health of the infant and not the health of the mother, as no studies could be identified in the literature that estimated the utility gain or loss to women as a result of induction. The assumption made was that a baby who survived with a serious morbidity gained only 0.75 QALYs for each 1 QALY gained by a healthy baby.
Despite the large number of RCTs that were identified in our systematic review (see Chapter 3), there has been no attempt to examine all induction methods together within an economic model. We have, therefore, developed a de novo model (described below) to estimate the cost-effectiveness of various methods for the induction of labour using the data obtained from the systematic review and NMA of RCTs, along with hospital costs and utilities.
Health-economic model
A decision-analytic model956 was constructed to compare the costs and effects of the different methods of induction of labour. Because we consider only short-term consequences, we chose to use a decision tree to represent the costs and consequences of different methods of induction. A decision tree is a graphical representation of different possible outcomes following a decision, in which probabilities are given to different paths along the branches of the tree, and costs and utilities attached to each branch. This enables us to compute probability-weighted costs and outcomes to arrive at an expected cost and utility value for each alternative treatment option.
The outcomes included were rate of VD within 24 hours, CS rate and frequency of admission to the NICU, as well as resource use and utilities. This structure was informed by the literature and expert opinion, and was finalised through discussions with the steering group. An illustration of the model structure is provided in Figure 13. Squares represent decision nodes for the method of delivery chosen, whereas circles represent chance nodes at which different possible outcomes are assigned a probability, and triangles represent outcomes.
FIGURE 13.
Decision tree for comparison of different methods of induction.
The model starts by dividing the population into those who deliver vaginally within the first 24 hours; have an emergency CS; and deliver vaginally after 24 hours.
Under each model of delivery, babies can either be born with no complications or be admitted to the NICU, which, in the context of randomised trials, we assumed relates to intervention and/or mode of delivery (CS or VD), but is less likely to relate to length of labour (i.e. whether a VD was within 24 hours of induction or not). NICU admission is divided into transitional care for those babies who need some medical treatment but are well enough to be cared for at the mother’s bedside, high-dependency care for babies who are recovering from critical illness and need a great deal of observation and support, and intensive care for babies who have serious potential health problems and need constant care to be kept alive. Utility scores and resource use were thought to vary depending on these levels of care.
Inputs to economic model
Effectiveness inputs
We required absolute probabilities for each of the paths in the branches of the tree shown in Figure 13, for each intervention. The NMA presented in Chapter 3 provided information on relative effects on these probabilities (in the form of ORs). In order to obtain absolute probabilities on all interventions we needed to apply these relative effects to absolute probabilities on a reference intervention. The choice of reference intervention is not important; however, it needs to be an intervention for which there is evidence available on absolute probabilities for all paths in our decision tree, and that evidence is relevant to the decision population under consideration. We chose vaginal PGE2 (tablet) as the reference intervention, as there were several UK-based RCTs including this intervention for each of the probabilities that were required in the model.
The NMA presented in Chapter 3 analyses each of the outcomes independently. However, as can be seen from Figure 13, these outcomes are not independent. For example, a failure to achieve a VD in 24 hours includes both women who deliver by CS and those who deliver vaginally but not within 24 hours. A woman has to deliver in one of three ways: a VD within 24 hours (VD24), a CS or a VD after 24 hours (VD > 24). We therefore re-analysed the data, as described in Appendix 16, to estimate these three probabilities allowing for the dependence in the data. We assumed that the relative effects for NICU admission are independent of timing of delivery but dependent on mode of delivery. We also assumed that the probability of NICU admission is 1.5 times higher for a CS delivery (according to data on 2837 inductions of labour for live births in Liverpool Women’s NHS Foundation Trust in 2014). Under this assumption it can be verified that the probability of NICU admission for VD, p(NICUvd), and the probability of NICU admission for CS, p(NICUcs), can be obtained from the overall probability of NICU admission, p(NICU) using the following formulae: p(NICUvd) = p(NICU) × 2/(2 + p(CS)) and p(NICUcs) = p(NICU) × 3/(2 + p(CS)).
The proportion of CS births, p(CS), is based on the NMA presented in Chapter 3 being applied to the proportion estimated on the reference intervention, as described below and in Appendix 16. The relative effects for NICU admission from the NMA in Chapter 3 are applied to the probability of NICU admission on the reference intervention (Table 22) to obtain the absolute probability of NICU admission, p(NICU) for each intervention. The formulae above are then used to obtain p(NICUvd) and p(NICUcs).
| Probability of | Posterior mean estimate (%) | 95% CrI |
|---|---|---|
| VD within 24 hours | 46 | 30 to 69 |
| VD after 24 hours | 30 | 15 to 49 |
| CS | 24 | 8 to 36 |
| NICU admission | 14 | 0 to 71 |
Note that all of these quantities are estimated using Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation, which samples directly from the joint posterior distribution. The decision tree is evaluated for each of these simulated samples so that we have a simulation of utility and cost estimates for each intervention. These simulations ensure that the uncertainty in the model inputs are fully reflected in the estimation of costs and utilities.
There were five UK studies315,549,834,957 in our review that provided information on the probability of a CS on the reference intervention. There was one UK study in our review that provided information on the probability of VD within 24 hours, given no CS, on the reference intervention. There were two UK studies834 providing information on the probability of NICU admission on the reference intervention. These studies were chosen as they were the only UK-based studies that evaluated the reference treatment and were therefore thought to be most representative of the target population. Where there was more than one study, the reference intervention arms were pooled using single-arm meta-analysis (results shown in Table 22). A REs model was used for both the probability of CS and the probability of NICU admission as a result of the heterogeneity between the included studies. This is reflected in the wide CrIs for these probabilities (see Table 22).
We applied the ORs from the NMAs (see Chapter 3 and Appendix 16) to the absolute probabilities for the reference intervention (see Table 22), to obtain absolute probabilities for all interventions. Note that this was done within the Bayesian MCMC simulation, which samples from the joint posterior distribution so that all correlations and uncertainties are fully reflected in the estimates. The resulting estimates are given in Tables 23–26. Note that these results differ from those presented in Chapter 3. First, we are using a different reference intervention on which to apply relative effects. Second, because we are modelling the mode of delivery jointly (so probabilities sum to 1), the number of studies from which the VD within 24 hours is estimated is reduced (as we require studies to report all delivery outcomes fully). One point to note is that the estimate of the probability of a VD after 24 hours with i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy is ‘0’, based on a single small study (25 women in this arm) with no women delivering vaginally after 24 hours.
| Treatment | Probability of achieving VD within 24 hours | 95% CrI |
|---|---|---|
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.78 | 0.6 to 0.91 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.64 | 0.43 to 0.81 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.62 | 0.43 to 0.77 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.55 | 0.31 to 0.74 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose < 50 µg | 0.52 | 0.33 to 0.71 |
| Vaginal PGE2 gel | 0.51 | 0.3 to 0.69 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.48 | 0.28 to 0.66 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.47 | 0.24 to 0.69 |
| Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 0.46 | 0.3 to 0.69 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0.44 | 0.14 to 0.74 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.42 | 0.2 to 0.65 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.42 | 0.19 to 0.66 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.41 | 0.21 to 0.62 |
| Foley catheter | 0.41 | 0.19 to 0.63 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.40 | 0.2 to 0.59 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.36 | 0.09 to 0.7 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose < 50 µg | 0.33 | 0.1 to 0.61 |
| NO | 0.27 | 0.06 to 0.57 |
| Mifepristone | 0.16 | 0.16 to 0.16 |
| Placebo | 0.14 | 0.03 to 0.32 |
| Treatment | Probability of achieving VD after 24 hours | 95% CrI |
|---|---|---|
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0 | 0 to 0 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.19 | 0.06 to 0.39 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.20 | 0.09 to 0.36 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.29 | 0.12 to 0.51 |
| Vaginal PGE2 gel | 0.30 | 0.15 to 0.49 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose < 50 µg | 0.30 | 0.14 to 0.49 |
| Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 0.30 | 0.15 to 0.49 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.31 | 0.12 to 0.54 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.33 | 0.13 to 0.56 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0.33 | 0.07 to 0.65 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.34 | 0.16 to 0.53 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.37 | 0.18 to 0.59 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.38 | 0.15 to 0.63 |
| Foley catheter | 0.40 | 0.19 to 0.62 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.40 | 0.21 to 0.6 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.41 | 0.1 to 0.73 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose < 50 µg | 0.43 | 0.16 to 0.7 |
| NO | 0.53 | 0.21 to 0.77 |
| Mifepristone | 0.60 | 0.28 to 0.83 |
| Placebo | 0.63 | 0.41 to 0.8 |
| Treatment | Probability of CS | 95% CrI |
|---|---|---|
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.16 | 0.06 to 0.31 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.17 | 0.07 to 0.33 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose < 50 µg | 0.18 | 0.07 to 0.34 |
| Mifepristone | 0.18 | 0.06 to 0.36 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.18 | 0.07 to 0.34 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.18 | 0.07 to 0.35 |
| Foley catheter | 0.19 | 0.07 to 0.36 |
| Vaginal PGE2 gel | 0.19 | 0.08 to 0.36 |
| NO | 0.20 | 0.08 to 0.37 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.20 | 0.08 to 0.38 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.20 | 0.08 to 0.38 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.21 | 0.08 to 0.39 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.21 | 0.08 to 0.41 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.22 | 0.09 to 0.41 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.23 | 0.08 to 0.44 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0.23 | 0.09 to 0.43 |
| Placebo | 0.23 | 0.09 to 0.42 |
| Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 0.24 | 0.08 to 0.3 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose < 50 µg | 0.25 | 0.09 to 0.46 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.25 | 0.1 to 0.46 |
| Treatment | Probability of NICU admission | 95% CrI |
|---|---|---|
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.09 | 0 to 0.57 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.11 | 0 to 0.66 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0.11 | 0 to 0.66 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.12 | 0 to 0.69 |
| Foley catheter | 0.12 | 0 to 0.68 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.13 | 0 to 0.71 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.13 | 0 to 0.7 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.13 | 0 to 0.71 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose < 50 µg | 0.13 | 0 to 0.7 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose < 50 µg | 0.13 | 0 to 0.72 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.13 | 0 to 0.71 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.13 | 0 to 0.7 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.14 | 0 to 0.74 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.14 | 0 to 0.74 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.14 | 0 to 0.73 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.14 | 0 to 0.73 |
| NO | 0.14 | 0 to 0.73 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 0.19 | 0 to 0.84 |
| Mifepristone | 0.2 | 0 to 0.85 |
| Placebo (no intervention) | 0.16 | 0 to 0.77 |
Cost inputs
The perspective adopted for the economic evaluation was that of the service provider (UK NHS). In accordance with this perspective, the costs included in the economic analysis were the direct costs incurred as a result of the interventions. These included the intervention costs, costs of method of delivery and length of neonatal stay in level I, II or III units. The price year was 2012–13.
The costs of each method of delivery are given in Table 27, along with the minimum and maximum estimates. These were taken from the NHS reference costs 2012/13,958 which are the average unit cost to the NHS of providing secondary health care to NHS patients. These are calculated on a full absorption basis to identify the full cost of delivering the service. It was assumed that a VD within 24 hours would constitute a short stay under the costing code, whereas a VD after 24 hours would be coded as long stay and therefore incur higher costs. The cost of a long-stay emergency CS was also used as most emergency CSs result in a stay of > 24 hours. A uniform distribution for these costs was assumed in the model.
| Outcome | Cost (£) | Lower (£) | Upper (£) | Currency code | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VD within 24 hours | 1110 | 815 | 1345 | NZ30C NEI-S | Uniform |
| VD after 24 hours | 1919 | 1547 | 2344 | NZ30C NEI-L | Uniform |
| Emergency CS | 3727 | 2926 | 4289 | NEI-L | Uniform |
| Neonatal critical care, transitional care (per day) | 382 | 306 | 473 | XA04Z | Uniform |
| Neonatal critical care, intensive care (per day) | 1118 | 819 | 1301 | XA01Z | Uniform |
| Neonatal critical care, high-dependency care (per day) | 791 | 685 | 902 | XA02Z | Uniform |
Supporting documents for the NHS Reference Costs958 indicate that all activity relating to healthy babies is reported as part of the total costs of the maternity delivery episode, whereas babies who are unwell generate their own admission record. All hospitalised infants incur per-patient/day costs. The unit cost for an inpatient day is also given in Table 27.
Probability of admission to each level of neonatal care, and average length of stay in each level, was taken from data on term admissions at Liverpool Women’s NHS Foundation Trust. The data from 100 at-term NICU admissions between July and October 2014 showed that 19% of admissions were to intensive care, 7% were to high-dependency care and 74% were to transitional care. Median length of stay was 2 days for intensive care, 1.5 days for high-dependency care and 2 days for transitional care.
The other costs included in the analysis were the costs that were associated with the different methods of induction. These were taken from the British National Formulary (BNF)959 for the pharmacological interventions and from the published literature or manufacturer costs for the mechanical interventions.
Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) preparation varied considerably across trials and is not currently available on the NHS (see Chapter 3). In order to include this method, we assumed that the cost is equal to that for vaginal PGE2 tablet and gel. Given these uncertainties, we have presented results excluding this intervention. The intervention costs are shown in Table 28.
| Induction method | Cost (£) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| NO | 0.16 | BNF959 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose ≥ 50 µg | 0.67 | BNF959 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose < 50 µg | 1.02 | BNF959 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose ≥ 50 µg | 1.02 | BNF959 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.71 | BNF959 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose < 50 µg | 2.04 | BNF959 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 2.04 | BNF959 |
| Buccal sublingual misoprostol | 2.04 | BNF959 |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 2.67 | BNF959 |
| Mechanical methods: Foley catheter | 4.00 | Van Baaren 2013955 |
| Mifepristone | 17.50 | BNF959 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 26.56 | BNF959 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 26.56 | BNF959 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 26.56 | BNF959 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 26.56 | Estimated |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 30.00 | BNF959 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 30.00 | BNF959 |
| Mechanical methods: double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 47.90 | Manufacturer cost |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 47.90 | BNF959 |
Utility inputs
Ideally, we would capture health-related outcomes using QALYs measured using the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D™) instrument. However, our literature review did not identify any evidence on the EQ-5D for the outcomes in our model. Furthermore, because of the short time-horizon of our model, the EQ-5D is unlikely to be very sensitive to changes in outcomes in our model. Instead, we attributed a utility score to each of the outcomes in our model, which represents the strength of preferences for a set of health-related outcomes, where utility scores take values of between ‘0’ and ‘1’, with ‘1’ representing perfect health.
It was necessary to identify the best available utility estimates for health states that were associated with the consequences of induction of labour for use in the model. The health states used in the model included emergency CS and VD for the mother, and transitional care, high-dependency care and intensive care for the child.
A literature search was undertaken to identify evidence on these utility values within published literature. A search was carried out in PubMed, The Cochrane Library [including Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), CENTRAL, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) and Economic Evaluations Databases], NHS EED and the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) database. Details of the search strategy are presented in Appendix 17. The number of studies retrieved in each search is shown in Table 29.
| Database | Number retrieved |
|---|---|
| HTA database | 199 |
| NHS EED | 2247 |
| The Cochrane Library | 8908 |
| PubMed | 30,029 |
Studies were also identified through searching specialist health economics resources, such as the Cost-effectiveness Analysis Registry and reference list checking. After examining titles and abstracts to identify those that were likely to be relevant, 12 studies were found and full papers were obtained. The full-text papers were then screened by two reviewers (EK and NJW) to identify four relevant studies (Figure 14). The list of excluded full articles and reasons for their exclusion can be found in Appendix 17.
FIGURE 14.
Flow chart summarising the review process.

Many of the studies that were deemed inappropriate to inform the model relied on the use of assumptions or judgements obtained from expert panels to assign a utility value to the health states of emergency CS, VD and NICU admission, rather than using empirical evidence. Three of the studies960–962 identified that were deemed relevant elicited health-state valuations for these states using the standard gamble technique, which is a recognised preference-based measures of health-related quality of life. The other study963 elicited utilities using the prospective measure of preference method, which is a prospective modification of the time trade-off method and standard gamble tools that have been previously described and validated in other settings. 964
Table 30 lists the four studies,960–963 the utility values that the studies use and how they were derived. Three of the studies used appropriate respondents (patients) of a sufficient sample size to give robust estimates. The exception was the study by Plunkett and Grobman,962 which used a panel of five experts to assign utilities.
| Study | Utility value given for: | How derived | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NICU | VD | Emergency CS | ||
| Turner et al.963 Vaginal delivery compared with elective CS: the views of pregnant women and clinicians. BJOG 2008;115:1494–502 |
Pain during labour: 0.92 | 0.59 | Prospective Measure of Preference method Participant’s responses indicating the maximum level of risk (0–100%) that they would accept before opting for an elective CS were converted into utility scores, which ranged from 0 to 1 (n = 102 pregnant women) |
|
| Vandenbussche et al.960 Differences in the valuation of birth outcomes among pregnant women, mothers, and obstetricians. Birth 1999;26:178–83 |
Transient neurological symptoms: median 0.99; range 0.72–0.99 | VAS and standard reference gamble given to 12 obstetricians, 15 pregnant women and 15 mothers (Used utilities elicited from mothers.) |
||
| Pham and Crowther961 Birth outcomes: utility values that postnatal women, midwives and medical staff express. BJOG 2003;110:121–7 |
Admission to neonatal nursery: median: 0.99, range: 0.70–0.99 | VAS and standard gamble administered to 90 women in postnatal ward: 59 midwives and 31 medical staff (Used utilities elicited from postnatal women.) |
||
| Plunkett and Grobman962 Routine hepatitis C virus screening in pregnancy: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:1153–61 |
Disutility of 0.0027, range 0.0037–0.0017 | Disutility of 0.0046, range 0.0056–0.0036 | Panel of five experts assigned utility values using time trade-off technique | |
None of the studies gives utility values for intensive, high dependency and transitional neonatal care, as required in our model. Vandenbussche et al. 960 gives utilities for ‘transient neurological symptoms’, and Pham and Crowther961 give utilities for admission to ‘neonatal nursery’. It was not clear in either of these studies if the utilities relate to the mother, baby, or both. In the absence of utilities specifically for the health states in our model, we used the lower interval reported in these two studies (0.7 from Table 30) to represent intensive care, the higher interval (0.99 from Table 30) to represent transitional care and the midpoint (0.845) to represent high-dependency care. There is clearly a high degree of uncertainty in these values, and so we conducted a sensitivity analysis as detailed in Table 31.
| Model run | Intensive care | High-dependency care | Transitional care |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base case | 0.7 | 0.845 | 0.99 |
| Sensitivity analysis 1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.99 |
| Sensitivity analysis 2 | 0.7 | 0.7725 | 0.99 |
| Sensitivity analysis 3 | 0.57 | 0.78 | 0.99 |
| Sensitivity analysis 4 | 0.57 | 0.675 | 0.99 |
In sensitivity analyses 1 and 2 we vary the utility for high-dependency care to 0.7 (equal to intensive care), and 0.7725 [midpoint between 0.7 and 0.845 (base case)]. In sensitivity analyses 3 and 4 we assume a lower utility score for intensive care (0.57 based on our own small survey described below). In sensitivity analysis 3 we use the midpoint between 0.57 and 0.99 (0.78) for high-dependency care, and in sensitivity analysis 4 we use a quarter of the way between the 0.57 and 0.99 (0.675) for high-dependency care.
Both the Turner et al. study963 and the Plunkett and Grobman study962 provide estimates of utilities relating to mode of delivery; however, we use only the values from Turner et al. ,963 as it is based on 102 pregnant women, rather than five experts. We therefore used the utility values of 0.92 and 0.59 for VD and emergency CS, respectively, as reported in Turner et al. 963 (see Table 30). However, no confidence intervals are reported for these figures, so we cannot reflect the uncertainty in the estimates.
Because of the limited evidence in the literature on utilities, we conducted our own small survey to help us reflect uncertainty in the utilities and obtain limits for sensitivity analysis. We administered a questionnaire asking respondents to rate different health states. The full questionnaire and results are given in Appendix 18. An example question is given in Figure 15.
FIGURE 15.
Example question from questionnaire on different health states.

This type of rating scale is called a visual analogue scale (VAS) and is commonly used as a method of measuring preferences for health outcomes. 965
Ten respondents completed this questionnaire. This group included all members of the project steering group including clinicians, health economists, systematic reviewers and a patient representative. The health states evaluated were the health of the mother following normal VD and CS, and the health of the mother and child following the child’s admission to the ICU, high dependency unit or transitional care unit. The data were analysed using a model that accounted for the between-respondent variability in overall level of the utility scores, and assumed common mean differences in utility scores for the different outcomes. Details of the statistical model are given in Appendix 18.
The estimated scores from this questionnaire were 0.65 (CrI 0.51 to 0.79) for a VD and 0.42 (CrI 0.17 to 0.67) for CS. Interestingly, although the absolute values of the scores differ, the ratio of the utilities for VD and CS taken from Turner et al. 963 agrees almost exactly with those arising from our own questionnaire. We therefore felt it appropriate to calibrate the scores from our questionnaire to those obtained in Turner et al. 963 to obtain uncertainty limits to put around the estimates from Turner et al. 963 for use in the economic model.
Our questionnaire obtained scores for intensive care, high-dependency care and transitional care from both the mother’s and baby’s perspective. Summing these scores for mother and baby for transitional care gave a value of ‘1’, very similar to the 0.99 obtained from the literature review. On this basis, summing the values for mother and baby from our questionnaire for intensive care gives a value of 0.57, which we use as a lower limit in our sensitivity analysis (detailed in Table 31).
The final utility values that went into the model are shown in Table 32.
| Delivery mode: utility (95% CrI) | NICU admission (base-case utility, see Table 27) | Delivery mode and NICU admission: product of utilities (95% CrI) |
|---|---|---|
| VD 0.92 (0.72 to 1) | None (1) | 0.92 (0.72 to 1) |
| Transitional care (0.99) | 0.91 (0.71 to 0.99) | |
| High-dependency care (0.845) | 0.78 (0.61 to 0.85) | |
| Intensive care (0.7) | 0.64 (0.50 to 0.7) | |
| Emergency CS 0.59 (0.25 to 0.95) | None (1) | 0.59 (0.25 to 0.95) |
| Transitional care (0.99) | 0.58 (0.25 to 0.94) | |
| High-dependency care (0.845) | 0.50 (0.21 to 0.80) | |
| Intensive care (0.7) | 0.41 (0.18 to 0.67) |
Methods of economic evaluation
We present a probabilistic cost-effectiveness analysis, which reflects the joint uncertainties in model inputs. This can be conceptualised as a hypothetical cohort of patients who vary in their probabilities, utilities and costs, as described by our joint uncertainty in the parameter estimates, and who experience the consequences of each induction strategy. Total utilities and costs are then averaged over this cohort to obtain the expected total utility and expected total cost for each induction strategy. This allows the assessment of multiple clinical outcomes as well as costs and cost-effectiveness and ensures that full joint uncertainty and correlations between parameters are taken into account.
The cost-effectiveness model was evaluated using Microsoft Excel® version 2013 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). The analysis requires simulated samples from the joint distributions of all model inputs. For the cost parameters, Monte Carlo simulation was performed within Excel to obtain the simulated samples. The absolute probabilities and utility inputs were estimated using Bayesian inference, computed using MCMC simulation in OpenBUGS. A total of 60,000 MCMC samples from the posterior distributions were taken from OpenBUGS and read into Excel, from which the simulated samples were drawn for the model, taking care to preserve correlations from the MCMC.
For each intervention we present the expected total utility and expected total cost, averaged over the simulation sample, together with 95% CrIs. We present an incremental analysis in which (1) interventions are ordered by increasing expected cost; (2) interventions that are dominated (have a higher expected cost and lower expected utility than another intervention) are identified; and (3) ICERs are computed for each non-dominated intervention relative to the previous (lower expected cost) non-dominated intervention, for which the ICER is:
The reported ICERs can be interpreted as the additional expected cost per additional unit gain in utility for an intervention compared with the previous non-dominated intervention in the table.
We also report cost-efficiency frontiers, which plots expected cost against expected utility for each intervention. The frontier line indicates the intervention with the lowest expected cost for a given expected utility, so that interventions above the line are not cost-effective compared with interventions lower down for a given expected utility. The choice between interventions on the frontier line will depend on willingness-to-pay per additional unit of utility.
For each intervention we computed net benefit for given willingness-to-pay per additional unit of utility, λ, (ceiling ratio) where net benefit is defined as:
‘Net benefit’ converts utilities to a monetary scale, so that the costs and utilities can be compared directly. Expected net benefit is the average net benefit over the simulation samples. For a given willingness-to-pay threshold λ, the optimal intervention is that with the highest expected net benefit. We present expected net benefit for λ = £20,000.
We present the uncertainty in the optimal intervention by plotting the probability that each intervention is the most cost-effective (has highest net benefit) against willingness-to-pay per unit of utility (CEACs). Probabilities that are close to 1 indicate that the optimal intervention is very certain, whereas probabilities that are much lower indicate that there is uncertainty as to which intervention is best. Because CEACs can be misleading when there are interventions with a very high degree of uncertainty,966 we exclude interventions from the plot that have both a high probability of being most cost-effective and a high probability of being least cost-effective.
We also present uncertainty using the incremental cost-effectiveness plane, which displays the incremental cost of each treatment compared with vaginal PGE2 tablet from each simulated sample against the incremental utility of each treatment compared with vaginal PGE2 tablet. Owing to the large numbers of interventions being compared, and the high degree of overlap of some of these, we include only the top three or four interventions (according to probability of being the most cost-effective) in the incremental cost-effectiveness planes.
We use value of information methods967 to explore how sensitive the optimal intervention is to uncertainty in the model inputs, and to guide research recommendations. If there was no uncertainty in the model inputs then we would know the optimal intervention perfectly. The expected value of perfect information (EVPI) measures the value (in terms of net benefit) resulting from elimination of uncertainty in all model inputs. The expected value of partial perfect information (EVPPI) measures the value (in terms of net benefit) from elimination of uncertainty in a some of the model inputs, and can be used to explore which model inputs are the key drivers of decision uncertainty, and may be most beneficial for further research efforts. We compute EVPI and EVPPI per person for a willingness-to-pay per unit of utility threshold of £20,000. We also present population-level EVPI and EVPPI, given an annual incidence of labour inductions in England and Wales of 150,000,2,3 and assuming a lifetime of the intervention of T = 1 year and 5 years, respectively, discounted at 3.5%. The lifetime of the intervention represents the time until the intervention becomes obsolete, for example by being superseded by a new intervention. EVPPI for subsets of parameters were computed using a Gaussian process emulator968 using the Sheffield Accelerated Value of Information web application. 969
Results
Base-case results
Table 33 shows the expected total cost and expected total utility for each treatment, averaged over the simulation sample along with their CrIs. Interventions are ordered by increasing expected total cost (treatment costs plus resource costs), with buccal/sublingual misoprostol and i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy having the lowest expected total cost, and placebo (no intervention) having the highest expected total cost. Note that all methods of induction have lower expected total costs than placebo (no intervention) because they reduce costly outcomes (VD in > 24 hours, CS and NICU admission). Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution has the highest expected utility, very closely followed by buccal/sublingual misoprostol, mifepristone, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy and vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg). Intracervical PGE2 has the lowest expected utility. As the majority of interventions (all except intracervical PGE2) have no more than a 0.02 difference in expected utility between them, they could be assumed to be clinically equivalent, so that a decision between them is effectively based on minimising total costs. Note that the confidence intervals show that there is a high degree of uncertainty in these estimates.
| Treatment | Expected total cost, £ (95% CI) | Expected total utility (95% CI) | Expected net benefit (£) | ICER (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1747.18 (1341.57 to 1472.34) | 0.821 (0.68 to 0.95) | 14,668.72 | |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 1747.80 (1275.41 to 2370.82) | 0.82 (0.67 to 0.95) | 14,652.13 | Dominated |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose ≥ 50 µg | 1789.56 (1386.41 to 2270.74) | 0.82 (0.68 to 0.95) | 14,603.51 | Dominated |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1799.55 (1403.44 to 2262.1) | 0.823 (0.68 to 0.96) | 14,658.28 | 21,190 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose < 50 µg | 1852.56 (1456.01 to 2325.54) | 0.819 (0.68 to 0.95) | 14,533.98 | Dominated |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose ≥ 50 µg | 1906.19 (1499.21 to 2384.89) | 0.819 (0.68 to 0.95) | 14,467.15 | Dominated |
| Vaginal PGE2 gel | 1935.79 (1517.97 to 2429.53) | 0.817 (0.67 to 0.95) | 14,402.37 | Dominated |
| Foley catheter | 1968.64 (1550.28 to 2463.38) | 0.815 (0.67 to 0.95) | 14,328.52 | Dominated |
| i.v. oxytocin | 1977.39 (1536.48 to 2518.6) | 0.809 (0.66 to 0.95) | 14,195.63 | Dominated |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 1997.08 (1480.46 to 2597.86) | 0.805 (0.65 to 0.95) | 14,108.39 | Dominated |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 2015.76 (1569.43 to 2533.94) | 0.811 (0.66 to 0.95) | 14,210.27 | Dominated |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 2033.03 (1614.6 to 2532.76) | 0.633 (0.53 to 0.74) | 10,617.17 | Dominated |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 2036.15 (1602.91 to 2551.89) | 0.81 (0.66 to 0.95) | 14,162.42 | Dominated |
| Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 2042.64 (1638.01 to 2565.19) | 0.805 (0.65 to 0.95) | 14,054.25 | Dominated |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2093.96 (1567.05 to 2684.18) | 0.804 (0.65 to 0.95) | 13,982.18 | Dominated |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 2097.74 (1618.43 to 2682.1) | 0.8 (0.64 to 0.95) | 13,906.29 | Dominated |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose < 50 µg | 2140.28 (1644.79 to 2738.28) | 0.802 (0.64 to 0.94) | 13,898.03 | Dominated |
| NO | 2141.74 (1662.1 to 2676.64) | 0.816 (0.67 to 0.94) | 14,179.69 | Dominated |
| Mifepristone | 2202.28 (1709.58 to 2742.8) | 0.821 (0.69 to 0.95) | 14,210.41 | Dominated |
| Placebo (‘no intervention’) | 2304.82 (1847.79 to 2822.48) | 0.805 (0.65 to 0.94) | 13,788.52 | Dominated |
Any intervention that has a higher expected cost and lower expected utility than another intervention is said to be dominated by that intervention. As can be seen from Table 33, all treatments apart from titrated low-dose oral misoprostol solution are dominated by buccal/sublingual misoprostol, which is more effective, in terms of increased utility, and less expensive than the other interventions.
As titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution is non-dominated relative to buccal/sublingual misoprostol, an ICER is computed:
Therefore, £21,190 is the additional expected cost per additional unit gain in utility required for titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution compared with buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
The expected total costs and expected utilities are displayed graphically in a cost-efficiency frontier (Figure 16). Any intervention above the line is not cost-effective compared with interventions lower down for a given expected utility. The graph shows that all of the other interventions apart from buccal/sublingual misoprostol and titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol are above the line and are therefore dominated, as they are more expensive and less effective. i.v. oxytocin lies very close to the line. Intracervical PGE2 is removed from the graph for visualisation purposes, as it is considerably less effective than the rest of the treatments and also relatively expensive, placing it far from the line. Placebo is the treatment that has the highest expected total cost and is therefore far from the line.
FIGURE 16.
Base case: cost-effectiveness efficiency frontier.
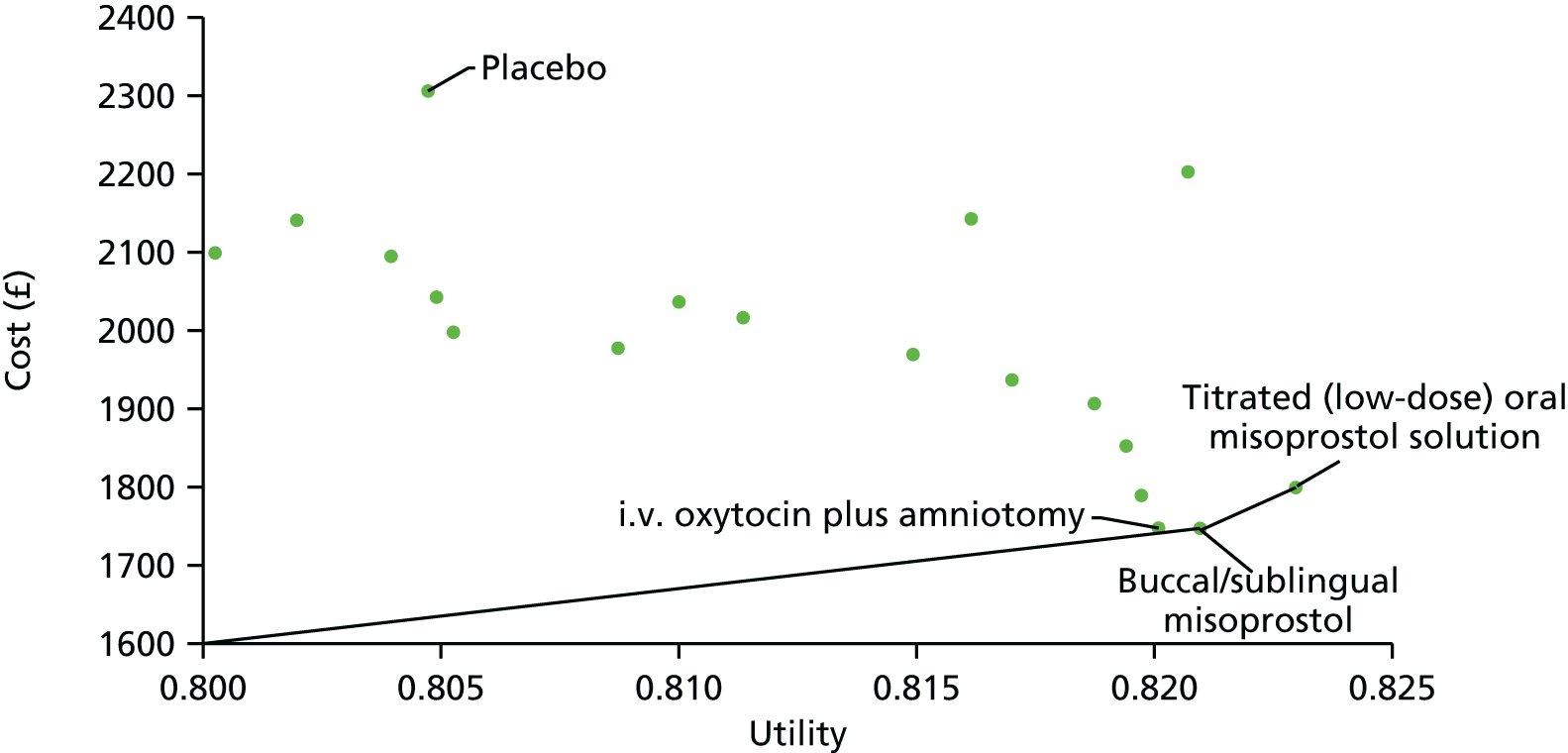
The expected net benefit at a £20,000 willingness-to-pay threshold (see Table 33) is highest for buccal/sublingual misoprostol (£14,669), closely followed by titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution (£14,658) and i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy (£14,652) and lowest for intracervical PGE2 (£10,617).
We present the uncertainty surrounding the cost-effectiveness of the various interventions, using a CEAC (Figure 17) and the cost-effectiveness plane (Figure 18).
FIGURE 17.
Base-case CEAC. Plotted against different willingness-to-pay per unit increase in utility (ceiling ratio). Note the curves are unchanged for ceiling ratios of > £50,000. Note: The non-labelled interventions have not been specified because of their close proximity to each other.
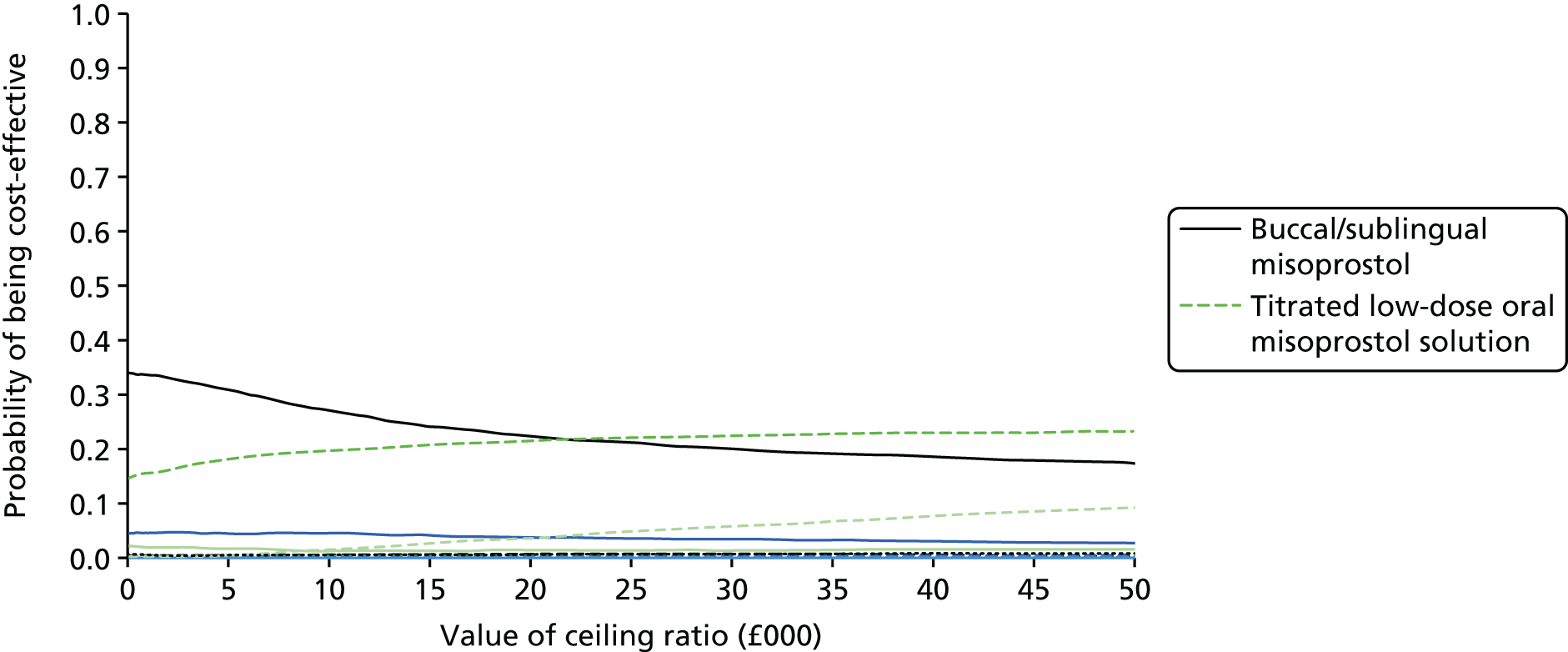
FIGURE 18.
Base case: incremental cost-effectiveness plane.
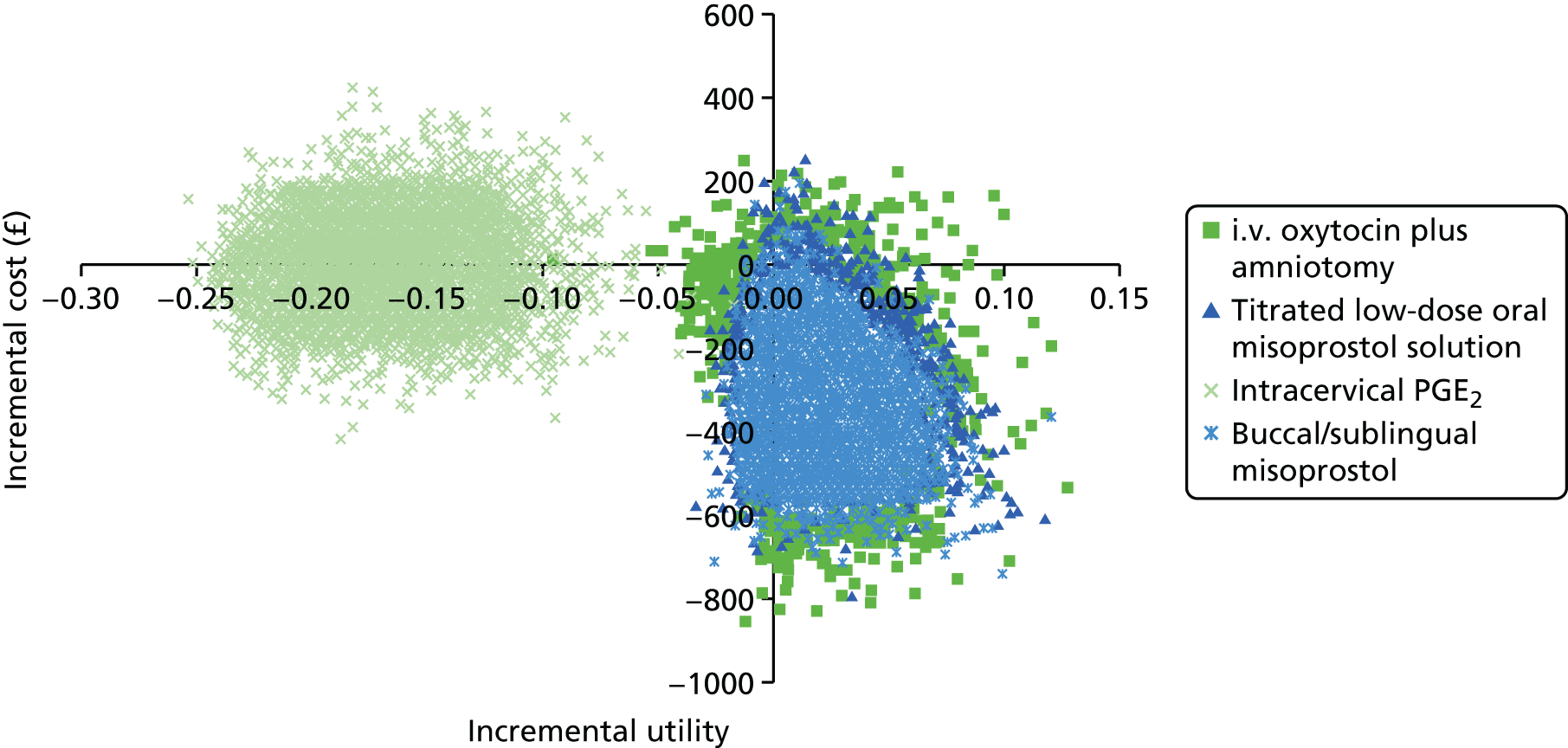
The CEACs (see Figure 17) plot the probability that each of the interventions is the most cost-effective by computing the proportion of simulations for which that intervention had the highest net benefit for a given willingness-to-pay per unit increase in utility. Out of the 19 interventions evaluated, only three had a probability of > 10% of being cost-effective at any willingness-to-pay value: titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution, buccal/sublingual misoprostol and i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy. However, the results for i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy were very uncertain, and i.v. oxytocin also had a high probability of being the least cost-effective. To avoid misleading conclusions, we have removed i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy from Figure 17, and, for clarity, give labels only for interventions for which it was clear that the probability of being cost-effective is > 10%. Figure 17 shows that at any willingness-to-pay value up until around £23,000, buccal/sublingual misoprostol has the highest probability of being cost-effective. Above this threshold, titrated low-dose oral misoprostol solution has the highest probability of being cost-effective. This probability is never > 35%, indicating a large degree of uncertainty in the optimal intervention.
The high degree of uncertainty between these interventions is seen clearly in the cost-effectiveness plane (see Figure 18), which plots the simulated pairs of incremental utility and incremental cost values for each intervention (compared with vaginal PGE2 tablet). As there are a large number of interventions to display, and the majority of interventions were very similar in terms of costs and utilities, the plot is unreadable if all interventions are included. For visual clarity, we plot only the interventions that were found to have had a > 10% probability of being cost-effective of at any willingness-to-pay value, along with intracervical PGE2, the intervention with the lowest average utility.
As can be seen from the graph, the majority of the points for buccal/sublingual misoprostol, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution and i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy are plotted in the bottom right-hand corner, indicating that these interventions are more effective and less expensive than vaginal PGE2 tablet. However, the location of some of the points in the other quadrants indicates that this is not certain. All of the points for intracervical PGE2, for example, are plotted in the top- and bottom-left quadrants, showing that although there is uncertainty in the cost, intracervical PGE2 never has a utility score higher than vaginal PGE2 tablet.
Sensitivity analysis to assumed utilities
Varying the utility estimates, as detailed in Table 31, had a very minor effect on the results. The interventions were ranked from lowest to highest expected cost in the same order and the expected utilities varied only on the second or third decimal point.
Subgroup analysis (i): women with intact membranes only
To examine the effect that membrane status had on the results, a scenario analysis was carried out restricting to mothers with intact membranes only. When we included all interventions for which we had sufficient information to evaluate the model, only 13 out of a total of 34 interventions (see Table 34 and see Appendix 16) were included in analysis, and the remaining interventions were excluded. Note that placebo (no intervention) was not included in this analysis, so comparisons with no intervention cannot be made.
Table 34 shows the expected total utility and expected total cost for each treatment when the analysis is limited to women with intact membranes. Interventions are again ordered in order of increasing expected cost (treatment costs plus resource costs) with titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution now having the highest expected total cost and vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) and i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy having the lowest expected cost. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution still has the highest expected utility, and intracervical PGE2 still has the lowest expected utility. The confidence intervals again show that there is a high degree of uncertainty in these estimates.
| Treatment | Expected total cost, £ (95% CI) | Expected total utility (95% CI) | Expected net benefit (£) | ICER (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose < 50 µg | 1928.96 (1571.86 to 2338.89) | 0.82 (0.69 to 0.94) | 14,464.22 | |
| i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy | 1929.9 (1487.64 to 2439.18) | 0.826 (0.7 to 0.94) | 14,586.48 | 156.66 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1936.01 (1516.6 to 1816.31) | 0.817 (0.68 to 0.94) | 14,400.68 | Dominated |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose ≥ 50 µg | 2000.32 (1634.83 to 2416.3) | 0.815 (0.69 to 0.94) | 14,287.56 | Dominated |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 2018.92 (1612.79 to 2494.27) | 0.814 (0.68 to 0.94) | 14,252.13 | Dominated |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose ≥ 50 µg | 2028.67 (1662.47 to 2439.99) | 0.82 (0.7 to 0.94) | 14,362.26 | Dominated |
| Foley catheter | 2065.24 (1691.42 to 2497.22) | 0.813 (0.68 to 0.94) | 14,185.49 | Dominated |
| Vaginal PGE2 gel | 2165.47 (1777.15 to 2608.8) | 0.813 (0.68 to 0.94) | 14,096.27 | Dominated |
| Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 2193.74 (1809.57 to 2617.3) | 0.803 (0.67 to 0.93) | 13,861.77 | Dominated |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 2195.47 (1809.48 to 2640.88) | 0.638 (0.54 to 0.74) | 10,563.31 | Dominated |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 2219.12 (1851.24 to 2668.99) | 0.807 (0.68 to 0.93) | 13,924.89 | Dominated |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 2249.43 (1824.03 to 2759.69) | 0.793 (0.65 to 0.93) | 13,607.27 | Dominated |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 2403.92 (1841.58 to 3084.74) | 0.832 (0.71 to 0.93) | 14,224.30 | 39,501.66 |
As can be seen from Table 34, all interventions apart from titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution and i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy are dominated by vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg), which is more effective in terms of increased utility, and less expensive.
As i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy is non-dominated relative to vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg), an ICER is computed:
Therefore, £156.66 is the additional expected cost per additional unit gain in utility required for i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy compared with vaginal misoprostol in women with intact membranes only.
As titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution is non-dominated relative to i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy, an ICER is also computed:
Therefore, £39,501.66 is the additional expected cost per additional unit gain in utility required for titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution compared with i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy in women with intact membranes only.
The intervention with the highest expected net benefit at £20,000 threshold is i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy (£14,586), followed by vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) (£14,464), and the intervention with the lowest expected net benefit is intracervical PGE2 at £10,563.
The CEAC for women with intact membranes only is presented in Figure 19. i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution, buccal/sublingual misoprostol and vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) were the only four treatments with a probability of being cost-effective of > 10% of any willingness-to-pay value (ceiling ratio). i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy has the highest probability of being cost-effective at any value of the ceiling ratio with a probability of around 45%.
FIGURE 19.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for subgroup analysis (i): women with intact membranes only. Note: The non-labelled interventions have not been specified because of their close proximity to each other.

The incremental cost-effectiveness plane for the four interventions with probability of being cost-effective of > 10% is presented in Figure 20, showing the high degree of uncertainty in the costs and effects of these interventions.
FIGURE 20.
Incremental cost-effectiveness plane for subgroup analysis (i): women with intact membranes only.
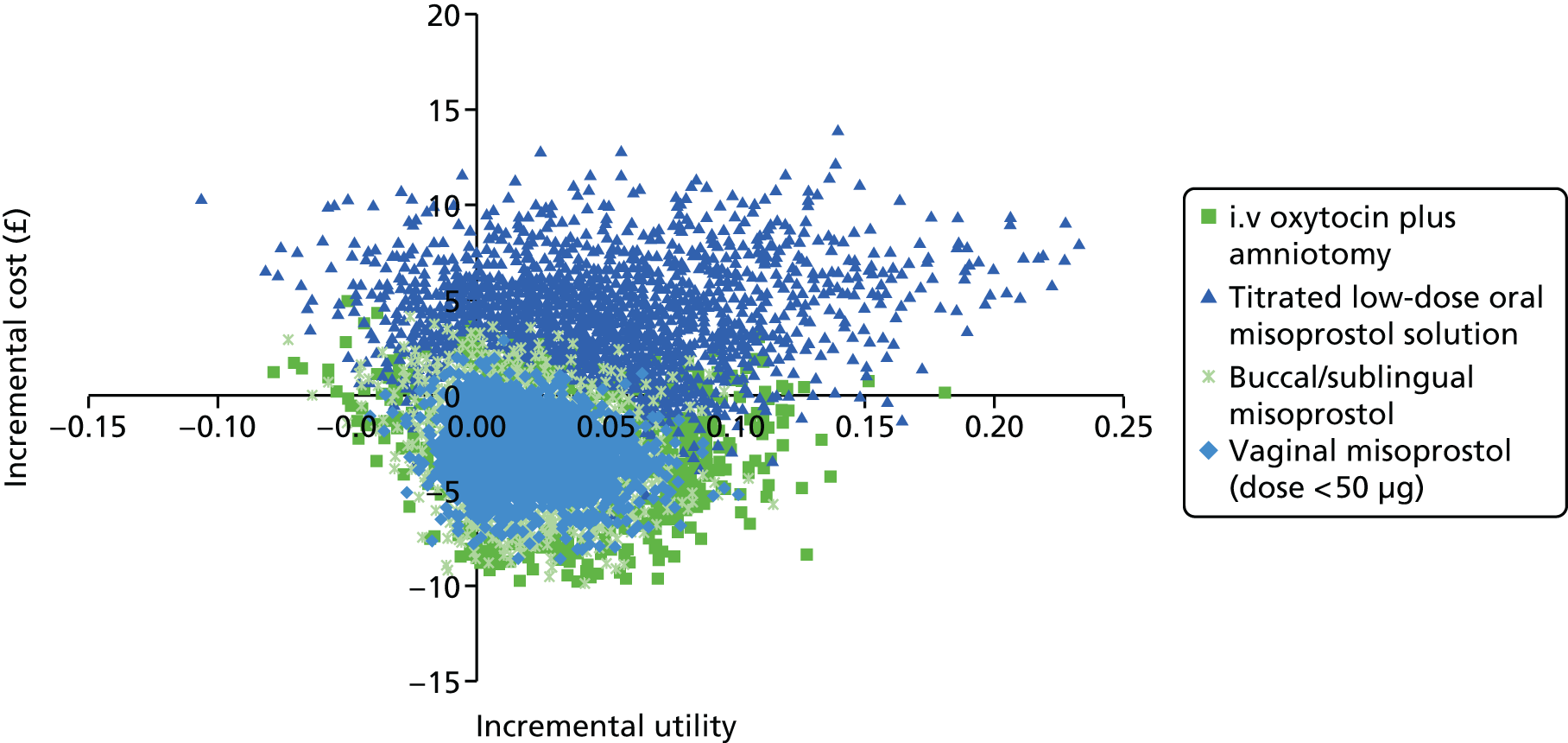
Subgroup analysis (ii): women with an unfavourable cervix only
To examine the effect that Bishop score had on the results, a scenario analysis was carried out restricting to mothers with an unfavourable cervix (Bishop score < 6). When we included all of the interventions for which we had sufficient information to evaluate the model, 19 interventions out of a total of 34 interventions (see Table 35 and Appendix 16) were included in the analysis, and the remaining were excluded.
Table 35 shows the expected total utility and expected total cost for each intervention when the analysis is limited to women with an unfavourable cervix. Interventions are again ordered by increasing expected total cost with buccal/sublingual misoprostol having the lowest expected total cost and placebo having the highest expected total cost, as in the base case. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution and buccal/sublingual misoprostol have the highest expected utility, and intracervical PGE2 still has the lowest expected utility. The confidence intervals again show that there is a high degree of uncertainty in these estimates.
| Treatment | Expected total cost, £ (95% CI) | Expected total utility (95% CI) | ICER | Expected net benefit (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1803.03 (1209.38 to 2293.03) | 0.805 (0.62 to 0.96) | 14,296.29 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1833.93 (1228.19 to 2681.17) | 0.805 (0.62 to 0.95) | Dominated | 14,268.94 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose ≥ 50 µg | 1860.48 (1237.3 to 2736.31) | 0.799 (0.61 to 0.95) | Dominated | 14,125.24 |
| Vaginal misoprostol: dose < 50 µg | 1900.34 (1269.91 to 2767.69) | 0.8 (0.61 to 0.95) | Dominated | 14,096.55 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose ≥ 50 µg | 1922.13 (1281.71 to 2778.67) | 0.8 (0.61 to 0.95) | Dominated | 14,083.50 |
| Vaginal PGE2 gel | 1966.08 (1316.53 to 2849.77) | 0.796 (0.6 to 0.95) | Dominated | 13,958.18 |
| Foley catheter | 1984.89 (1332.08 to 2845.84) | 0.796 (0.6 to 0.95) | Dominated | 13,937.91 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 2033.89 (1370.72 to 2917.34) | 0.642 (0.5 to 0.8) | Dominated | 10,797.93 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 2047.53 (1367.65 to 2942.25) | 0.79 (0.58 to 0.95) | Dominated | 13,750.04 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 2082.66 (1352.56 to 3024.87) | 0.784 (0.57 to 0.95) | Dominated | 13,594.43 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 2102.42 (1412.2 to 2993.83) | 0.788 (0.58 to 0.95) | Dominated | 13,666.30 |
| Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 2106.02 (1418.6 to 3012.11) | 0.783 (0.57 to 0.94) | Dominated | 13,562.65 |
| NO | 2115.85 (1424.43 to 2958.84) | 0.795 (0.59 to 0.94) | Dominated | 13,792.94 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 2137.78 (1433.27 to 3017.3) | 0.787 (0.58 to 0.95) | Dominated | 13,604.63 |
| Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 2159.86 (1422.1 to 3114.44) | 0.778 (0.55 to 0.94) | Dominated | 13,397.99 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet: dose < 50 µg | 2166.04 (1420.9 to 3096.83) | 0.78 (0.56 to 0.95) | Dominated | 13,434.70 |
| Mifepristone | 2182.01 (1516.15 to 2987.41) | 0.801 (0.61 to 0.95) | Dominated | 13,831.39 |
| Placebo | 2276.45 (1599 to 3112.04) | 0.784 (0.57 to 0.94) | Dominated | 13,407.56 |
As can be seen from Table 35, all other interventions are dominated by buccal/sublingual misoprostol, which is more effective in terms of increased utility (or equivalent in the case of titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol) and less expensive than all other treatments. However, as in the other analyses, there is little difference between the utility scores.
The intervention with the highest expected net benefit is buccal/sublingual misoprostol (£14,296) followed by titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution (£14,269) then vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) (£14,125), and the intervention with the lowest expected net benefit is intracervical PGE2 at £10,798.
The CEAC for women with an unfavourable cervix subgroup is presented in Figure 21. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol has the highest probability of being most cost-effective, followed by titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution, but there is a high degree of uncertainty in these results, with the probability being around 50%.
FIGURE 21.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for subgroup analysis (ii): women with an unfavourable cervix only. Note: The non-labelled interventions have not been specified because of their close proximity to each other.
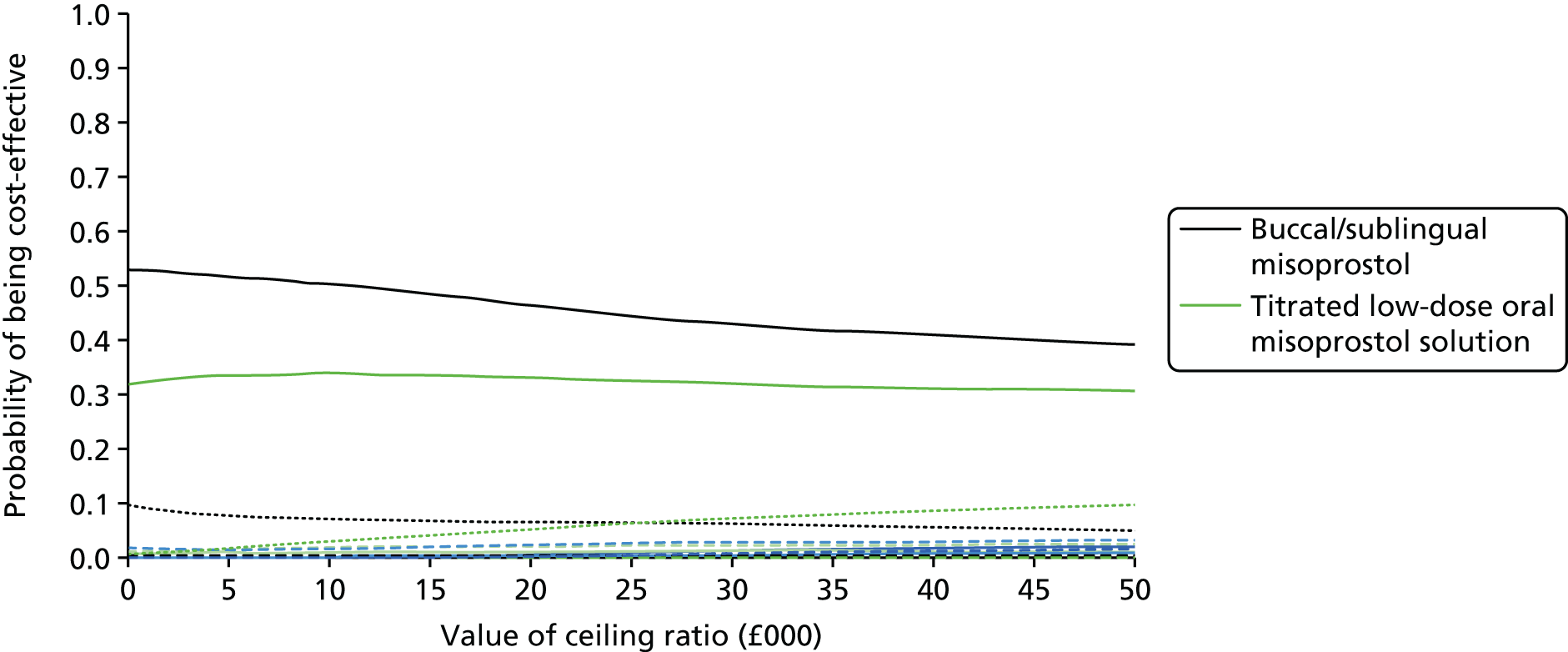
The incremental cost-effectiveness plane for the subgroup analysis (Figure 22) shows incremental costs and utilities (compared with vaginal PGE2 tablet) for the two interventions that had a probability of being cost-effective of > 10%. The majority of the points are located in the bottom right-hand quadrant, indicating that they are likely to be less expensive and more effective than vaginal PGE2 tablet.
FIGURE 22.
Incremental cost-effectiveness plane for subgroup analysis (ii): women with an unfavourable cervix only.
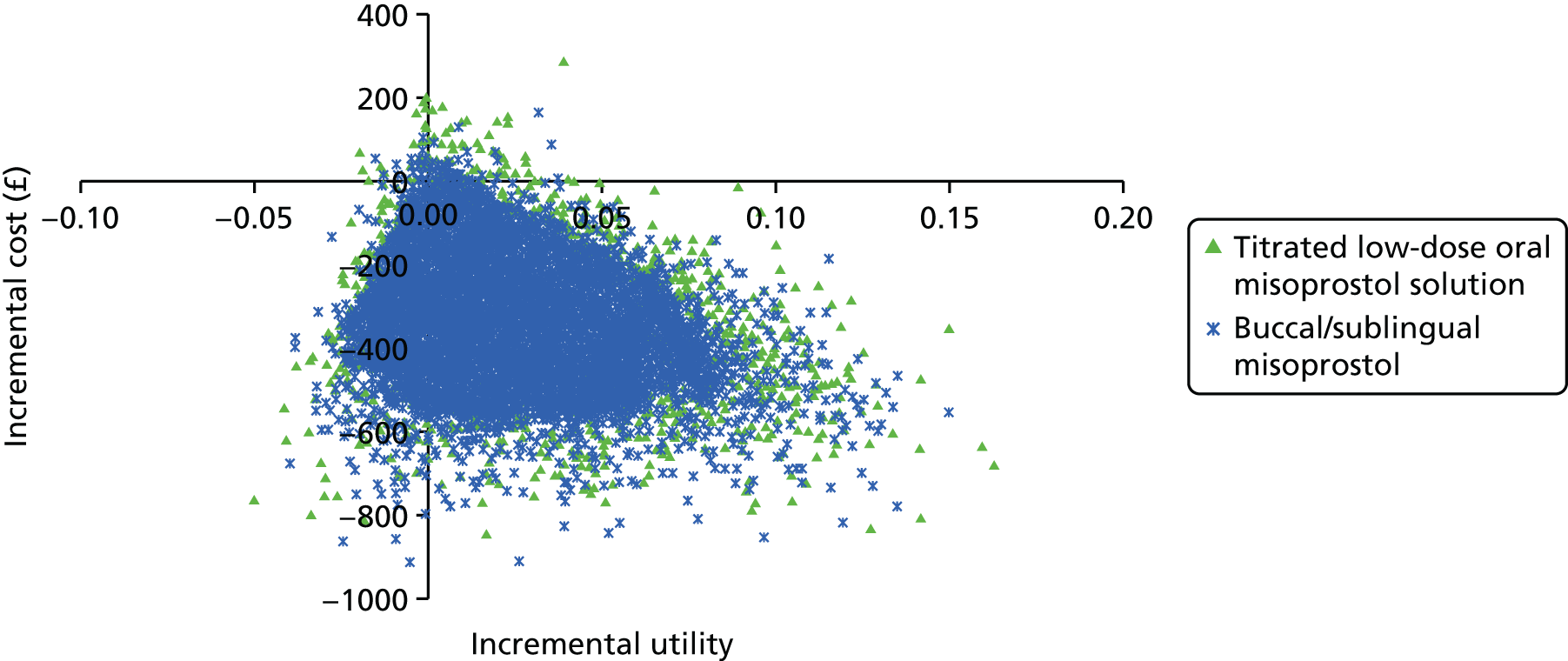
Value-of-information analysis
Table 36 shows the results of the value-of-information analyses for the base-case model at a willingness-to-pay per unit utility threshold of £20,000. The per-woman EVPI is £187, which corresponds to a population EVPI of £28M for all of the inductions in England and Wales over a 1-year time horizon, increasing to £131M over a 5-year time horizon. This large value suggests that the decision is sensitive to uncertainty in the model inputs, and so it is potentially of value to reduce this uncertainty through future research studies. Comparing EVPPI for different subsets of model inputs indicates to which model inputs the decision is most sensitive and where future research efforts may be best invested. EVPPI is higher for cost parameters (£19) than for utility parameters (£0); however, EVPPI for both cost and utility parameters together (£102) is higher than for cost parameters alone. This suggests that there is no value in reducing uncertainty in either costs or utilities without also reducing uncertainty in the other. There is a high value in reducing uncertainty in all of the transition parameters for mode of delivery (£114). We explored the potential value of a new trial comparing the two interventions with the highest expected net benefit in the base case [buccal/sublingual misoprostol vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol] providing information on all transitions for those interventions, costs and utilities. This gives an EVPPI of £110, which corresponds to a population EVPPI of £16.5M over a 1-year time horizon, increasing to £77M over a 5-year time horizon. However, if costs and utilities are not collected then this value disappears (EVPPI of £2). This suggests that a large well-conducted trial may be a worthwhile use of resources, but it is essential to collect information on costs and utilities as well as transition probabilities for mode of delivery and NICU admission.
| Model parameter subsets | EVPPI per woman induced (£) | 1-year population EVPPI (£) | 5-year population EVPPI (£) |
|---|---|---|---|
| All (EVPI) | 186.71 | 28,006,500 | 130,876,593 |
| All costs | 19.31 | 2,896,500 | 13,535,574 |
| All utilities | 0.09 | 13,500 | 63,087 |
| All costs and utilities | 101.71 | 15,256,500 | 71,294,833 |
| All NICU transition probabilities | 12.47 | 1,870,500 | 8,740,995 |
| All mode of delivery transition probabilities | 113.81 | 17,071,500 | 79,776,472 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol (transition probabilities, costs, utilities) | 110.08 | 16,512,000 | 77,161,884 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol (transition probabilities only) | 2.11 | 316,500 | 1,479,030 |
Limitations
The model made a number of assumptions that need to be kept in mind when interpreting the results.
-
We were able to perform the analysis only for the interventions for which we had sufficient information on all outcomes required in the model. This does not mean the excluded interventions are not cost-effective, just that we have no evidence. Therefore, our conclusions on the cost-effectiveness of the included interventions needs to be interpreted within the set of interventions that we were able to include. However there were no interventions that were identified by the NMA as being effective that were not included in the cost-effectiveness analysis. Furthermore, only a subset (86) of the studies provided information on both VD within 24 hours and CS for the joint modelling required in the economic model. Therefore, the economic evaluation is based on fewer studies than the NMA presented in Chapter 3 for VD within 24 hours.
-
It is assumed that the proportion of babies who are admitted to NICU depends on mode of delivery (CS or VD), but not on whether a VD was within 24 hours of induction or not. Of those admitted to NICU, we assumed that the proportion of babies cared for in intensive (19%), high dependency (7%) or transitional care (74%) would not vary depending on method (vaginal vs. CS) or timing of delivery (< 24 hours; > 24 hours), or intervention.
-
It was also assumed that the length of stay in intensive, high dependency and transitional care was fixed at 2, 1.5 and 2 days, respectively, based on the data from the Liverpool Women’s Hospital.
-
It was assumed that long-term costs and benefits would be equal across induction methods, and that any variation would be captured in the time between induction and discharge.
-
The NMA gave estimates on the rate of instrumental delivery, Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes and uterine hyperstimulation, but these were assumed to be unnecessary in the model, as the differences in costs and benefits would be captured in the other outcomes included.
-
Some important outcomes, such as post-partum haemorrhage, were not reported as an outcome in trials and therefore could not be included in the economic model.
-
Although we would have liked to, we did not have enough evidence on parity to explore cost-effectiveness in primiparous and multiparous women separately.
Conclusions
In summary, the base-case analysis found that all of the methods of induction were cost-saving compared with no treatment. It is noteworthy that there is considerable uncertainty in our cost-effectiveness estimates, with the majority of the interventions having very similar utility values, and mainly differing in total costs.
With this caveat, buccal/sublingual misoprostol and titrated oral misoprostol were identified as being the interventions with the highest expected net benefit and the highest probability of being cost-effective. At any willingness-to-pay value of > £23,000 per unit increase in utility, titrated low-dose oral misoprostol solution seems to be the intervention that is most likely to be the most cost-effective for use on the UK NHS. Given that we were able to analyse only two subgroups (intact membranes and unfavourable cervix), and the number of interventions compared – and studies included – were lower than in the base case, the results of subgroup analyses should be interpreted cautiously (i.e. as hypothesis generating).
In the subgroup of women with intact membranes, and limiting to interventions feasible on the NHS, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy was identified as being the intervention with the highest expected net benefit and the optimal intervention at any willingness-to-pay value. However, there was again a lot of uncertainty in this estimate, with buccal/sublingual misoprostol and titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol also with a moderate probability of being most cost-effective.
Buccal/sublingual misoprostol and titrated low-dose oral misoprostol solution were found to be the interventions that were most likely to be cost-effective in women with an unfavourable cervix.
The majority of the interventions, with a few notable exceptions, such as intracervical PGE2, result in similar expected utility and vary mainly in terms of cost. There is a considerable degree of uncertainty in these estimates, demonstrated by the wide confidence intervals around the values.
There is a need to study further utilities on both mother and baby outcomes from both mother and baby perspectives. This research should be conducted using preference-based measures on large samples and with uncertainties fully reported. We would urge future trials in this area to present results according to mutually exclusive clinically relevant subgroups (e.g. parity, membrane and cervical status, previous CS) to allow more evidence to inform subgroup analyses. We would also urge trialists to report results in a format that allows the construction of the number of vaginal deliveries within 24 hours, the number CSs and the number of vaginal deliveries after 24 hours. It would also be useful to report the NICU admissions according to mode of delivery. Haemorrhage and sepsis (antibiotic usage) are also important adverse outcomes that have consequences for the economic evaluation but which are inconsistently reported. The value-of-information analysis suggests that the decision is very sensitive to uncertainty in the model inputs, and there is potential value in reducing this uncertainty through future research studies. Further large well-conducted trials may be a worthwhile use of resources, but it is essential to collect information on costs and utilities, as well as transition probabilities for mode of delivery and NICU admission.
Chapter 5 Discussion
Statement of overall/principal findings
In this final chapter, we begin with a summary of the systematic review, NMA and the cost-effectiveness analysis. We then set out the strengths and limitations of analyses before considering the clinical implication of findings. Finally, we offer recommendations for future research.
Key findings of the systematic review and network meta-analysis
Thirty-four active treatment types/regimens were included in our review, including different dose regimes and routes of administration. Overall, the search identified > 1000 studies and, after eligibility assessment using our PICO (population, intervention and relevant comparators, outcomes) criteria, 611 trials were included in the review. Together, these trials reported findings for > 100,000 women who were randomised to different methods for third-trimester induction of labour.
The active interventions most likely to achieve VD within 24 hours were i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy, misoprosotol (vaginal tablets – high and low dose; pessary – sustained release; low-dose oral solution; and buccal/sublingual misoprotol) closely followed by vaginal administration of PGE2 (pessary – normal release). It should be stressed that the rankings have wide CrIs for all of the above methods, indicating considerable uncertainty. The rankings range from 1st to 6th and 1st to 9th for vaginal misoprostol (≥ 50 µg) and i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy, respectively, to 1st to 13th for PGE2 pessary.
Compared with placebo, several treatments showed a statistically significant reduction in the odds of CS: titrated low-dose misoprostol, vaginal misoprostol at both ≥ 50 µg and < 50 µg, vaginal PGE2 gel, intracervical PGE2, oral misoprostol tablet (≥ 50 µg), Foley catheter, membrane sweeping and buccal/sublingual misoprostol. In this group, titrated oral misoprostol achieved the lowest odds of an eventual CS but there was still considerable uncertainty in this finding, as observed by the posterior mean rank of 6th (out of 33) and 95% CrI from 2nd to 13th (out of 33) for oral misoprostol solution. There was little to distinguish between the other interventions with considerable uncertainty in treatment rankings. i.v. prostaglandins performed worse than placebo and significantly increased the odds of CS. Other poorly performing interventions included vaginal PGE2 tablet, oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg, double-balloon catheters and oestrogens.
Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes was one of the key safety outcomes. Here double-balloon catheter, NO and laminaria had the highest probability of being among the best three treatments, whereas i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy, slow-release misoprostol pessary and high-dose vaginal misoprostol tablets (which was among the best treatments for efficacy) were most likely to increase the odds of excessive uterine activity. For other safety outcomes there were insufficient data or too much uncertainty around estimates to identify which treatments performed ‘best’.
Few studies collected information on women’s views. On the whole, women tended to have positive views, or at least accepted the induction process, but there was insufficient information to determine whether or not some methods were preferred over others.
Our findings also suggest that of the seemingly less ‘medicalised’ induction methods, there is little to choose among them in terms of safety. Of interest is that none of the included studies examining these methods (membrane sweeping, acupuncture and sexual intercourse) reported our effectiveness outcome – failure to achieve VD within 24 hours – suggesting that when it comes to the urgency of delivery, the expectations from these methods is very different.
We planned to carry out subgroup analyses to check that our findings were robust in different groups of women: women with intact amniotic membranes compared with ruptured amniotic membranes; women with unfavourable Bishop scores compared with favourable Bishop scores; women who had had a previous CS and women undergoing induction of labour at different gestational ages. Unfortunately, it was possible to carry out only two of these analyses (membrane status and Bishop scores) owing to lack of data or inconsistency in the results for other subgroups.
Our two subgroup analyses were restricted to only a fraction of 611 included trials and three outcomes (VD within 24 hours, CS and low Apgar score). The results were broadly in agreement with overall results. i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy and high-dose vaginal misoprostol tablets remained the most effective interventions for achieving VD within 24 hours in women with intact membranes.
Key findings of the cost-effectiveness analysis
All methods of induction were cost-saving compared with no treatment, although there is considerable uncertainty in our cost-effectiveness estimates. It is important to stress that the interventions have very similar expected utility values, and differ mainly in expected total costs. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol and buccal/sublingual misoprostol had the highest probability of being the most cost-effective intervention at any willingness-to-pay value. Given that we were able to analyse only two subgroups (intact membranes and unfavourable cervix), and the number of interventions compared and studies included were lower than in the base case, the results of subgroup analyses should be interpreted cautiously (i.e. as hypothesis generating). In the subgroup of women with intact membranes, and limiting to interventions that were feasible through the NHS, i.v. oxytocin with amniotomy was identified as the intervention that was most likely to be most cost-effective. In the subgroup of women with an unfavourable cervix, buccal/sublingual misoprostol and titrated low-dose oral misoprostol solution were found to be the interventions that were most likely to be most cost-effective.
Strengths
In our systematic review we made considerable effort to include all RCTs with no language restrictions, which led to the inclusion of > 600 trials, with data for > 100,000 women and babies. The NMA provided an opportunity to examine the relative effectiveness of all treatments used for the induction of labour in a coherent and methodologically robust way across important clinical outcomes. Although there are now increasing numbers of NMAs reported in the literature, and some relate to competing treatments in obstetrics,970 as far as we are aware this NMA includes more trials and participants than any other in this topic area.
Network meta-analysis is only valid on the assumption that all of the treatments in the network would be suitable for all included women. We were thorough in our evaluation of six important potential treatment effect modifiers (previous CS, parity, membrane status, Bishop score, gestational age and single/multiple pregnancy) and found no clinically important differences in the distribution of these potential effect modifiers across the interventions. We also conducted informal and formal statistical checks of model fit and inconsistency. When lack of fit and/or inconsistency between evidence sources was observed, it was resolved by excluding studies that were assessed as being at high risk of bias.
To our knowledge this is the first attempt to simultaneously compare more than two treatments for the induction of labour in a cost-effectiveness analysis. A study by Petrou et al. 14 suggested that PGE2 gel was more cost-effective than PGE2 tablets, and Van Baaren et al. ’s study955 concluded that Foley catheter induction was more cost-effective than PGE2 gel. These results are not directly comparable with the results from this study, as they use different measures of benefit, but it is still worth mentioning that in our cost-effectiveness analysis these interventions were found to be less effective and more expensive than titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) and vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg).
Limitations
Systematic review and network meta-analysis
Broadly, the aim of induction of labour is to achieve early delivery of the baby with the minimum harm to women and babies, and we selected outcomes to reflect these aims. However, not all of the included trials provided data on all of our key outcomes. The number of women undergoing CS was generally well reported. However, in view of high heterogeneity and apparent inconsistency it was necessary to restrict our analysis to RCTs at low risk of bias for the allocation concealment domain.
The number of women who did not give birth vaginally within 24 hours (our main efficacy outcome) was reported in less than one-quarter of trials.
Key safety outcomes were also reported relatively infrequently. Approximately one-third of trials were included in the NMA for infant admission to NICU (205) and there was considerable heterogeneity between trials (possibly as a result of inconsistent definitions of this outcome). Similarly, uterine hyperstimulation and low infant Apgar score were reported in fewer than one-third of trials.
Overall, maternal mortality and severe morbidity and infant mortality event rates, when reported, were very low. Unfortunately, these outcomes were too infrequently reported to make the pooled analysis possible. We had also intended to report serious infant morbidity but this outcome was poorly reported and inconsistently defined in trials. Consequently, we used admission to NICU as a proxy outcome for infant morbidity. Neonatal mortality was reported in only 21.3% of these trials and the incidence was low at 0.3%. Of course, it should not be assumed that if infant mortality was not reported then it did not occur, but it is probable that death rates were also low in those trials failing to report this important outcome.
Very few trials collected data and reported findings relating to women’s views about the induction process. This was surprising, as some methods of induction are likely to be both painful and unpleasant. Again, because of the dearth of data and inconsistency in the way outcomes were measured and reported across trials, we were unable to include findings on maternal preferences and satisfaction in our formal quantitative analysis. There was also insufficient information from trials evaluating alternative and complementary methods to include them in the analysis of our main efficacy outcome. None of the trials included for the analysis of number of women failing to deliver within 24 hours included an alternative method of induction. For safety outcomes, alternative and complementary methods of induction did not appear to be safer than pharmacological and mechanical methods.
The trials included in the review recruited women with varied clinical characteristics, and it is important to bear this in mind when interpreting results. The indications for induction were not always reported and, when they were, these varied across trials. Many trials excluded women with a history of CS or multiple pregnancies. Predominantly, women recruited to trials were at > 37 weeks’ gestation, including post-term pregnancies and term PROM. Most of the trials were carried out in hospital settings because most methods of labour induction require constant attendance and monitoring by skilled clinical staff. However, we did include 79 trials examining interventions that were carried out in outpatient, community or home settings.
For all outcomes we observed moderate heterogeneity between study effects. This is not surprising, given the clinical heterogeneity described above in settings and women who present for induction of labour. Heterogeneity may also be attributable to the varied quality of included studies. Overall, approximately half of the studies were assessed as being at high or unclear risk of bias. Consequently, we conducted REs NMA for all outcomes to allow for this heterogeneity. We report the mean from the REs distribution of study effects, although this assumes that our focus is on the effects observed in an ‘average study’, whereas other summaries might be more appropriate, such as the shrunken estimate for the UK trials971 or a prediction for a new study population.
Although NMA offers the opportunity to rank treatments in terms of relative effects for each outcome, for many results there was considerable uncertainty around effect estimates. Particularly for the analysis of safety outcomes, the findings were not clear-cut (i.e. there were no clear ‘best’ or ‘worst’ treatments for most of these outcomes). This uncertainty did not apply just to results for CS. This uncertainty is not necessarily surprising, as a large number of interventions were examined in the network. Although some interventions were examined in a large number of trials, data for other interventions were sparse, event rates for some outcomes were very low, and some outcomes were also inconsistently defined (e.g. hyperstimulation syndrome). This means that we were not able to use all of the available data in our analysis. In particular, the low event rates for NICU admission meant that in some arms of trials no events were reported, which led to problems in estimation of relative effects and also increased uncertainty in the economic analyses.
Heterogeneity in the analyses may also have been caused by the fact that trials were carried out over a long time period during which induction and CS rates in particular have increased steadily. These temporal changes could have contributed to heterogeneity and increased uncertainty of findings. More intensive surveillance may also have led to apparent increases in some outcomes (e.g. hyperstimulation).
Cost-effectiveness analysis
Our cost-effectiveness analysis was confined to short-term outcomes up until discharge from hospital, although we are aware that some outcomes may have a longer-term impact on women and their families, and also on NHS resources. The analysis was complicated by the fact that outcomes related to both women and their babies, and the two are interlinked. Women may be profoundly affected by any adverse outcomes in their newborn and, conversely, the baby may be affected by adverse outcomes for the mother. In our analysis the well-being of women and babies were combined in a single utility value for each outcome. The evidence sources informing utilities for method of delivery were assumed to represent the mothers’ well-being. However it was not clear whether the utilities for NICU admission and intensity of care required represented utility for the mother, baby or both (and, if so, the relative weight given to mother and baby: women (and even society) may value the health of the baby above their own).
We needed to distinguish those women who had a CS, those who had a VD within 24 hours, and those who had a VD after 24 hours. We found that results from trials were not always reported in a way that allowed us to estimate the outcomes together in this way. There was sufficient information to estimate effects for only 18 interventions and our conclusions on cost-effectiveness are therefore limited to this data subset.
The RCTs identified in the systematic review did not provide any evidence on the proportion of NICU admissions following births by CSs, nor on the proportion of babies admitted to different intensities of NICU care (intensive care, high-dependency care and transitional care). We have, therefore, used routinely collected hospital activity data from Liverpool Women’s Hospital to inform these inputs to our model.
We identified only four studies960–963 reporting preference-based measures of utility relevant to the outcomes in our model, none of which reported EQ-5D, our preferred measure. The health states did not correspond directly with those in our model, and so assumptions were necessary. It was also not clear in these studies960–963 whether or not the utility was for the mother, baby or both (and if so the relative weight given to mother and baby). Furthermore, measures of uncertainty were not reported alongside the utility estimates. In an attempt to address these limitations, we used our own small-scale survey to put uncertainty limits on the literature-based utilities and to define sensitivity analyses. However, note that our survey is severely limited due to being restricted to the project steering group and also limitations with the VAS instrument that it used. 972 Although the scores are bias prone and may not be comparable to utilities elicited through other measures, the resulting ordinal preferences we obtained were found to have some face validity (the patterns seen across respondents were broadly comparable and in line with intuition) and can be considered as a first step towards defining utilities for mother/baby pairs. A large-scale study measuring utilities (preferably using EQ-5D) on antenatal and postnatal women, reporting results (together with uncertainty estimates) from both the mother and baby perspective, including time post discharge, would be of great value in addressing the limitations described above.
Discussion of the clinical implications of findings
Our NMA suggests that oxytocin with amniotomy and misoprostol are the most effective in achieving vaginal births relatively quickly. Interestingly, there was little difference between different misoprostol regimens, with the exception of oral tablets. Both high- and low-dose oral tablets, appear to be inferior to low-dose oral solution, buccal/sublingual and all vaginal regimens. Vaginal PGE2 also performed well, although our results favoured pessary (normal release) over methods currently available in the NHS (gel, tablet and slow-release pessary). We have already mentioned that in our NMA the term ‘PGE2 pessary’ captures vaginal administration that could not be classified as tablets, gel or slow-release pessaries which are currently commercially available. Consequently, this is a rather heterogeneous mix of study-specific dinoprostone preparations, often produced by local pharmacies.
Intravenous oxytocin with amniotomy performed well, but this method was used only with intact membranes and therefore can be recommended only in this subgroup. Furthermore, the majority of the trials evaluating this method included women with more favourable cervix for whom delivery within 24 hours is more likely. However, just because the absolute rate of VD in 24 hours is higher when the cervix is favourable does not necessarily mean that the relative effects between tested interventions would differ. It is important to stress again that oxytocin with amniotomy has been mainly tested, and has been shown to perform well, in women with a favourable cervix, and the intervention is therefore recommended only for this group.
The safety profile of different methods was less clear. For example, misoprostol (low-dose vaginal tablets and buccal/sublingual) was associated with relatively high hyperstimulation; however, this finding was not borne out in increased rates of CS. One would expect that the two are related with persistent and clinically important uterine hyperstimulation eventually resulting in CS.
The cost-effectiveness analysis suggested that titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution had the highest utility for mothers and babies, and buccal/sublingual misoprostol had the lowest cost to the NHS. Notwithstanding the considerable uncertainty of cost-effectiveness results, it is still surprising that treatments in common use in the NHS (e.g. PGE2 vaginal gel) did not appear to be the most effective, most cost-effective or safest. Therefore, our findings may have important implications for clinical practice in the UK.
The current recommendation of the World Health Organization973 is for low-dose oral misoprostol tablets rather than titrated oral solution and, therefore, not in line with the findings from this analysis.
Our main measure of efficacy was whether or not treatments resulted in VD within 24 hours. This definition of efficacy may be controversial given that cervical ripening has often been regarded as a distinctly different process from induction of labour. This view is reflected in the fact that changes in Bishop scores were often the main measure of efficacy in many of the included randomised trials. We argue that women and clinicians view cervical ripening and labour induction as part of the same seamless process, with the main aim to achieve a safe vaginal birth of a healthy baby in the shortest time possible.
The outcomes we used in the cost-effectiveness analysis were VD within 24 hours, CS and NICU admission; these outcomes were reported reasonably frequently and we thought that these outcomes provided a reasonable balance of efficacy (benefit) and harm. At the same time, as we have seen from the results of the NMA, there may be a trade-off in terms of harms and benefits of different treatments: those agents that stimulate contractions and thereby achieve faster delivery may cause excessive uterine activity that may lead to problems for women and babies.
We had expected that serious maternal and neonatal adverse events would be rare in the cohorts of women recruited to RCTs of induction of labour. Nevertheless, it was disappointing how infrequently mortality and serious morbidity were reported. Our assessment of safety was therefore limited to CS, hyperstimulation with fetal heart changes, NICU admission and infant Apgar score, at best proxies for serious adverse events.
Observational data suggest that all prostaglandins (especially misoprostol) and oxytocin can cause uterine rupture, with possible catastrophic consequences, particularly in women with previous CS. It was not surprising to us that many trials included in the review excluded women with previous CS or uterine scar for other reasons. The efficacy of induction agents that may cause excessive uterine activity must be seen in this context.
We took the view that country of setting was not likely to be a critical treatment effect modifier, because in all included RCTs intrapartum fetal monitoring and early access to CS were available to most women. Even in those trials for which the induction agent was administered outside a hospital setting, arrangements were in place for monitoring and emergency admission in case of complications. Given these circumstances, the findings from our analysis are more likely to be applicable in high-resource settings, such as the NHS.
Very few trials considered women’s views. Our own small-scale utility elicitation exercise showed that respondents set great store by the health of babies and women may therefore would be likely to accept induction if a clinician considered that this would potentially improve neonatal outcomes. At the same time, given the similar utility values for a broad range of induction agents, there is surely scope for taking women’s views into account. Women need to be informed of the advantages and drawbacks of different methods of induction and to be aware that there is a choice of interventions available.
Recommendations for future research
The considerable uncertainty in our findings points the way for further research. In terms of populations, it is striking how little randomised evidence relates to important subgroups, such as women with previous CSs. Future studies should, at the very least, make available the results by subgroups when they are included.
When induction of labour is clinically indicated, a placebo or no-intervention arm in a trial may not be feasible or even ethical (our study shows that placebo is neither effective nor cost-effective). We suggest that titrated oral misoprostol solution should be used as a comparator, particularly in the NHS setting, and future RCTs should be powered to detect a method that is more cost-effective than misoprostol solution. Clearly, the fact that this method is currently unlicensed with virtually no pharmacokinetic data poses a considerable challenge.
We are conscious that, at present there are no internationally agreed core outcome sets for labour induction studies. Until such time, we urge all triallists to report 11 outcomes included in this NMA in all future RCTs:
-
failure to achieve VD within 24 hours
-
CS
-
instrumental delivery
-
uterine hyperstimulation resulting in FHR changes
-
NICU admissions (by level of care and mode of delivery)
-
Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
-
neonatal deaths
-
serious neonatal morbidity
-
maternal deaths
-
maternal serious morbidity
-
maternal satisfaction.
It is also important to report results separately for all clinically important subgroups (e.g. parity, membrane and cervical status and previous CS) to allow individual patient data meta-analysis and network analysis.
There is also an urgent need to explore women’s views of the process as part of any future trial.
Finally, there is a need for well-conducted studies to measure utilities from the perspective of the mother and baby, preferably using the EQ-5D instrument.
Acknowledgements
Steering group members: Declan Devane, Polly Griffiths, Paul Jacklin, Tony Kelly.
Thanks to members of the steering group for providing valuable advice at various stages of the project and for completing the utilities questionnaires. We would also like to thanks staff in the CPCG: Frances Kellie managed project finances, Lynn Hampson and Sarah Perry carried out the search and retrieved copies of reports, and Jill Fitzpatrick, Helen West and Kate Navratavan contributed to data extraction. Finally, we would like to thank Professor Stavros Petrou, University of Warwick, for advice regarding the utilities, and Liverpool Women’s NHS Trust for providing data to inform the economic model cost-effectiveness analysis.
Contributions of authors
Zarko Alfirevic (Professor, Head of Department of Women’s and Children’s Health) conceived the project and contributed to protocol development, management of the project, planning of the systematic review and NMA, clinical interpretation of findings and writing of the report.
Edna Keeney (Research Associate) conducted statistical analyses, economic analysis and modelling, and drafted and edited report.
Therese Dowswell (Research Associate) contributed to planning the systematic review, data collection and quality assessment, and drafted and edited report.
Nicky J Welton (Reader in Statistical and Health Economic Modelling) contributed to the protocol development, managed the project in Bristol, provided advice on the statistical analyses, supervised the economic modelling, wrote code to provide inputs to the economic model, and drafted and edited the report.
Nancy Medley (Research Associate) contributed to data collection, data set management and quality assessment, and commented on drafts of the report.
Sofia Dias (Research Fellow) contributed to protocol development, provided advice on statistical analyses and economic modelling, and commented and edited report.
Leanne V Jones (Research Associate) contributed to data collection, quality assessment, and commented and edited the report.
Gillian Gyte (Consumer Representative) contributed to protocol development, commented on drafts of all project documentation, and commented on drafts of the report.
Deborah M Caldwell (Lecturer in Public Health Research) conceived the project, contributed to protocol development, supervised statistical analyses for the NMA, and drafted and edited the report.
Publications
Alfirevic Z, Keeney E, Dowswell T, Welton NJ, Dias S, Jones LV. Labour induction with prostaglandins: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2015;350:h217.
Alfirevic Z, Keeney E, Dowswell T, Welton NJ, Medley N, Dias S, et al. Methods to induce labour: a systematic review, network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis. BJOG 2016;123:1462–70.
Data sharing statement
Data files for all outcomes considered in the NMA are provided in Appendix 14 of the report.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Office for National Statistics . Births in England and Wales: 2012 2013. www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/vsob1/birth-summary-tables:england-and-wales/2013/stb-births-in-england-and-wales-2013.html (accessed 17 March 2015).
- NHS . NHS Maternity Statistics, England 2010–11 2011. www.ic.nhs.uk/pubs/maternity1011 (accessed 10 March 2015).
- NHS . Welsh Government. Maternity Statistics: Method of Delivery 2001–11 2012. http://wales.gov.uk/docs/statistics/2012/120131sdr132012en.pdf (accessed 10 March 2015).
- Session 2013–14. London: HMSO; 2013.
- Gülmezoglu AM, Crowther CA, Middleton P, Heatley E. Induction of labour for improving birth outcomes for women at or beyond term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd004945.pub3.
- Irion O, Boulvain M. Induction of labour for suspected fetal macrosomia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000;2.
- Guise JM, McDonagh MS, Osterweil P, Nygren P, Chan BK, Helfand M. Systematic review of the incidence and consequences of uterine rupture in women with previous caesarean section. BMJ 2004;329:19-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.329.7456.19.
- Shetty A, Burt R, Rice P, Templeton A. Women’s perceptions, expectations and satisfaction with induced labour – a questionnaire-based study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;123:56-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.03.004.
- Induction of Labour. London, UK: NICE; 2008.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Induction of Labour (Clinical Guideline 70) 2014. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg70/documents/cg70-induction-of-labour-surveillance-review-decision-may-20142 (accessed 14 March 2015).
- Eddama O, Petrou S, Schroeder L, Bollapragada SS, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, et al. The cost-effectiveness of outpatient (at home) cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate prior to induction of labour. BJOG 2009;116:1196-203. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02236.x.
- Kaimal AJ, Little SE, Odibo AO, Stamilio DM, Grobman WA, Long EF, et al. Cost-effectiveness of elective induction of labor at 41 weeks in nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:137.e1-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.08.012.
- Vijgen SM, Koopmans CM, Opmeer BC, Groen H, Bijlenga D, Aarnoudse JG, et al. An economic analysis of induction of labour and expectant monitoring in women with gestational hypertension or pre-eclampsia at term (HYPITAT trial). BJOG 2010;117:1577-85. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2010.02710.x.
- Petrou S, Taher S, Abangma G, Eddama O, Bennett P. Cost-effectiveness analysis of prostaglandin E2 gel for the induction of labour at term. BJOG 2011;118:726-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2011.02902.x.
- Boulvain M, Kelly A, Irion O. Intracervical prostaglandins for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008;1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd006971.
- Kelly A, Malik S, Smith L, Kavanagh J, Thomas J. Vaginal prostaglandin (PGE2 and PGF2a) for induction of labour at term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003101.pub2.
- Hutton E, Mozurkewich E. Extra-amniotic prostaglandin for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001;2.
- Luckas M, Bricker L. Intravenous prostaglandin for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd002864.
- French L. Oral prostaglandin E2 for induction of labour. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2001.
- Alfirevic Z, Weeks A. Oral misoprostol for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd001338.pub2.
- Hofmeyr GJ, Gulmezoglu AM, Pileggi C. Vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010;10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd000941.pub2.
- Muzonzini G, Hofmeyr GJ. Buccal or sublingual misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd004221.pub2.
- Wing DA, Lovett K, Paul RH. Disruption of prior uterine incision following misoprostol for labor induction in women with previous cesarean delivery. Obstet Gynecol 1998;91:828-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-199805001-00015.
- Alfirevic Z, Kelly AJ, Dowswell T. Intravenous oxytocin alone for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003246.pub2.
- Bricker L, Luckas M. Amniotomy alone for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000;4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd002862.
- Budden A, Chen LJ, Henry A. High-dose versus low-dose oxytocin infusion regimens for induction of labour at term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd009701.pub2.
- Howarth GR, Botha DJ. Amniotomy plus intravenous oxytocin for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001;3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003250.
- Kelly AJ, Munson C, Minden L. Nitric oxide donors for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd006901.pub2.
- Hapangama D, Neilson JP. Mifepristone for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd002865.pub2.
- Pinto RM, Leon C, Mazzocco N, Scasserra V. Action of estradiol-17-beta at term and at onset of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1967;98:540-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(67)90108-1.
- Tromans PM, Beazley J, Shenouda PI. Comparative study of oestradiol and prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel for ripening the unfavourable cervix before induction of labour. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981;282:679-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.282.6265.679.
- Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ, Thomas J. Corticosteroids for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003100.pub2.
- Kelly Anthony J, Kavanagh J, Thomas J. Relaxin for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001;2.
- Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ, Thomas J. Hyaluronidase for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003097.pub2.
- Jozwiak M, Bloemenkamp KW, Kelly AJ, Mol BW, Irion O, Boulvain M. Mechanical methods for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd001233.pub2.
- Boulvain M, Stan CM, Irion O. Membrane sweeping for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005;1.
- Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ, Thomas J. Breast stimulation for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005;3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.0730-7659.2005.00391.x.
- Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ, Thomas J. Sexual intercourse for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001;2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003093.
- Kelly AJ, Kavanagh J, Thomas J. Castor oil, bath and/or enema for cervical priming and induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003099.pub2.
- Smith CA, Crowther CA, Grant SJ. Acupuncture for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;8.
- Smith CA. Homoeopathy for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;4.
- Hofmeyr G, Alfirevic Z, Kelly T, Kavanagh J, Thomas J, Brocklehurst P, et al. Methods for cervical ripening and labour induction in later pregnancy: generic protocol. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000;2.
- Aalami-Harandi R, Karamali M, Moeini A. Induction of labor with titrated oral misoprostol solution versus oxytocin in term pregnancy: randomized controlled trial. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2013;35:60-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-72032013000200004.
- Abdul MA, Ibrahim UN, Yusuf MD, Musa H. Efficacy and safety of misoprostol in induction of labour in a Nigerian tertiary hospital. West Afr J Med 2007;26:213-16.
- Abedi-Asl Z, Farrokhi M, Rajaee M. Comparative efficacy of misoprostol and oxytocin as labor preinduction agents: a prospective randomized trial. Acta Medica Iranica 2007;45:443-8.
- Abramovici H, Hallak M, Zarfati D, Packer T, Calderon I, Auslender R, et al. Induction of labor in patients with unfavorable cervices: a randomized comparison among intravaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), intravenous oxytocin, and the double balloon ripener device. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1994;46.
- Adair CD, Weeks JW, Barrilleaux PS, Philibert L, Edwards MS, Lewis DF. Labor induction with oral versus vaginal misoprostol: a randomized, double-blind trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178.
- Adair CD, Weeks JW, Barrilleaux S, Edwards M, Burlison K, Lewis DF. Oral or vaginal misoprostol administration for induction of labor: a randomized, double-blind trial. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92:810-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-199811000-00014.
- Adam I, Hassan OA, Elhassan EM. Oral misoprostol vs. vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and labour induction. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2005;89:142-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.11.033.
- Adeniji AO, Olayemi O, Odukogbe AA. Intravaginal misoprostol versus transcervical foley catheter in pre-induction cervical ripening. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2006;92:130-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2005.10.010.
- Adeniji AO, Olayemi O, Odukogbe AA, Aimakhu CO, Oladokun A, Akindele FO, et al. Comparison of changes in pre-induction cervical factors’ scores following ripening with transcervical foley catheter and intravaginal misoprostol. Afr J Med Med Sci 2005;34:377-82.
- Adeniji AO, Olayemi O, Odukogbe AA, Oladokun A, Adeniji OI, Egbewale BE, et al. Cervico-vaginal foetal fibronectin: a predictor of cervical response at pre-induction cervical ripening. West Afr J Med 2005;24:334-7.
- Adeniji OA, Oladokun A, Olayemi O, Adeniji OI, Odukogbe AA, Ogunbode O, et al. Pre-induction cervical ripening: transcervical foley catheter versus intravaginal misoprostol. J Obstet Gynaecol 2005;25:134-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443610500040737.
- Agarwal K, Batra A, Dabral A, Aggarwal A. Evaluation of isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening prior to induction of labor for postdated pregnancy in an outpatient setting. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2012;118:205-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2012.04.017.
- Agarwal N, Gupta A, Kriplani A, Bhatla N, Parul N. Six hourly vaginal misoprostol versus intracervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2003;29:147-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1341-8076.2003.00091.x.
- Ajori L, Nazari L, Eliaspour D. Effects of acupuncture for initiation of labor: a double-blind randomized sham-controlled trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2013;287:887-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-012-2674-y.
- Akay NO, Hizil D, Ylmaz SS, Yalvac S, Kandemir O. Comparison of low-dose oxytocin and dinoprostone for labor induction in postterm pregnancies: a randomized controlled prospective study. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2012;73:242-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000334404.
- Akyol D, Mungan T, Unsal A, Yuksel K. Prelabour rupture of the membranes at term: no advantage of delaying induction for 24 hours. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;39:291-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1999.tb03399.x.
- Alcalay M, Hourvitz A, Reichman B, Luski A, Quint J, Barkai G, et al. Prelabour rupture of membranes at term: early induction of labour versus expectant management. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1996;70:129-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0301-2115(95)02586-3.
- Alcoseba-Lim W, Famador-Juario H. Stripping of membranes to induce labor at term. Philippine J Surg Surg Special 1992;47:139-42.
- Al-Hussaini TK, Abdel-Aal SA, Youssef MA. Oral misoprostol vs intravenous oxytocin for labor induction in women with prelabor rupture of membranes at term. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2003;82:73-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(03)00136-X.
- Allott HA, Palmer CR. Sweeping the membranes: a valid procedure in stimulating the onset of labour?. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;100:898-903. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1993.tb15103.x.
- Allouche C, Dommesent D, Barjot P, Levy G. Cervical ripening: comparison of three methods. Preliminary results of a randomized prospective study. Rev Fr Gynecol Obstet 1993;88:492-7.
- Al-Malt A, Ashmead G, Amini S. Cervical ripening: effect of vaginal PGE2 on bishop score. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)90819-6.
- Al-Sebai MAH, Manasse PR. Induction of labour in primigravid women with an unfavourable cervix: a prospective comparative study of prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets and gel. J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;13:112-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443619309151795.
- Al-Taani MI. Comparison of prostaglandin E2 tablets or foley catheter for labour induction in grand multiparas. East Med Health J 2004;10:547-53.
- Amador LAV, Carmona JCF, Gallego FG, Texido CS, Esteve JLC. Randomized clinical trial of the safety and efficacy of 50 microg sublingual misoprostol versus 25 microg vaginal misoprostol for labor induction at term in pregnant women with diabetes. Progresos De Obstetricia Y Ginecologia 2007;50:473-83.
- Anand AK, Mir S. A randomized comparison between intravaginal misoprostol and intracervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction in participants with unfavourable cervices. JK Sci 2012;14:115-19.
- Andersen K, Moller M, Rix P, Larsen KW, Ladehoff P, Zdravkovic M. Induction of labor. Prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets compared with intravenous oxytocin for induction of labor in premature rupture of the membranes and immature cervix. Ugeskr Laeger 1990;152:3705-7.
- Arias F, Buser D, Mora G. Randomized comparison of misoprostol vs dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80554-6.
- Arias F, Rouben D. Extraamniotic saline infusion with foley catheter is better than 2.9 mg prostaglandin E2 gel in ripening the cervix but does not result in vaginal delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(12)91121-7.
- Asher GN, Coeytaux RR, Chen W, Reilly AC, Loh YL, Harper TC. Acupuncture to initiate labor (Acumoms 2): a randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2009;22:843-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14767050902906386.
- Ashrafunnessa, Khatun SS, Chowdhury SA, Begum SR, Rashid M, Khatun MS. Induction of labor by intracervical prostaglandin gel and oxytocin infusion in primigravid women with unfavorable cervix. Bangladesh Med Res Council Bull 1997;23:66-71.
- Atad J, Hallak M, Auslender R, Porat-Packer T, Zarfati D, Abramovici H. A randomized comparison of prostaglandin E2, oxytocin, and the double-balloon device in inducing labor. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:223-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(95)00389-4.
- Atad J, Peer G. Combination of the Double Balloon Device (ARD) and Half Doses of PGE2 Vaginal Gel for Labor Induction n.d.
- Ayad IA. Vaginal misoprostol in managing premature rupture of membranes. East Mediterr Health J 2002;8:515-20.
- Ayaz A, Saeed S, Farooq MU, Ahmad F, Bahoo LA, Ahmad I. Pre-labor rupture of membranes at term in patients with an unfavorable cervix: active versus conservative management. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2008;47:192-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1028-4559(08)60079-0.
- Ayaz A, Shaukat S, Farooq MU, Mehmood K, Ahmad I, Ali Bahoo ML. Induction of labor: a comparative study of intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2010;49:151-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1028-4559(10)60032-0.
- Bagratee JS, Moodley J. Synthetic laminaria tent for cervical ripening. S Afr Med J 1990;78:738-41.
- Bakos O, Bäckström T. Induction of labor: a prospective, randomized study into amniotomy and oxytocin as induction methods in a total unselected population. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1987;66:537-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348709015731.
- Balci O, Mahmoud AS, Acar A, Colakoglu MC. Comparison of induction of labor with vaginal misoprostol plus oxytocin versus oxytocin alone in term primigravidae. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2011;24:1084-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2010.531798.
- Balci O, Mahmoud AS, Ozdemir S, Acar A. Induction of labor with vaginal misoprostol plus oxytocin versus oxytocin alone. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2010;110:64-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2010.02.004.
- Barcaite E, Bartusevicius A, Krikstolaitis R, Gintautas V, Nadisauskiene R. A Comparison of Sublingual and Vaginal Misoprostol for Induction of Labour: A Randomized Controlled Trial n.d.
- Barrilleaux P, Bofill J, Rodts-Palenik S, Moore L, May W, Martin J. A randomized clinical trial comparing three methods of cervical ripening to efficiently effect delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Bartha JL, Comino-Delgado R, Garcia-Benasach F, Martinez-Del-Fresno P, Moreno-Corral LJ. Oral misoprostol and intracervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction: a randomized comparison. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:465-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200009000-00025.
- Bartusevicius A, Barcaite E, Krikstolaitis R, Gintautas V, Nadisauskiene R. Sublingual compared with vaginal misoprostol for labour induction at term: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2006;113:1431-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.01108.x.
- Beer AM, Heiliger F. Randomized, double-blind trial of caulophyllum d4 for induction of labor after premature rupture of the membranes at term. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 1999;59:431-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-1999-5969.
- Beigi A, Kabiri M, Zarrinkoub F. Cervical ripening with oral misoprostol at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;83:251-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(03)00275-3.
- Bell RJ, Permezel M, MacLennan A, Hughes C, Healy D, Brennecke S. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the safety of vaginal recombinant human relaxin for cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:328-33.
- Benedetto C, Pastore G, Zonca M, Ardizzoja M, Mascherpa F, Bocci A. Induction of labour with PGE2 intravaginal gel or oxytocin: a technical comparison. Giornale Italiano Di Obstetricia E Ginecologia 1987;5:447-52.
- Bennett K, Butt K, Crane J, Hutchens D, Young D. Misoprostol for Labour Induction at Term n.d.
- Bennett KA, Butt K, Crane JM, Hutchens D, Young DC. A masked randomized comparison of oral and vaginal administration of misoprostol for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92:481-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-199810000-00001.
- Benzineb N, Bouhaouala S, Sfar R. Prostaglandin E2 versus Foley catheter for cervical maturation at term. Rev Fr Gynecol Obstet 1996;91:173-6.
- Berghella V, Mickens R. Stripping of Membranes As a Safe Method to Reduce Prolonged Pregnancies n.d.
- Berghella V, Rogers RA, Lescale K. Stripping of membranes as a safe method to reduce prolonged pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:927-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(96)00046-4.
- Bergsjo P, Jenssen H. Comparison between intranasal and transbuccal oxytocin for the induction of labour. Preliminary report. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1969;48. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016346909157732.
- Berkane N, Verstraete L, Uzan S, Boog G, Maria B. Use of mifepristone to ripen the cervix and induce labor in term pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:114-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.05.084.
- Bernstein P. Prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and labour induction: a multicentre placebo-controlled trial. CMAJ 1991;145:1249-54.
- Bernstein EP. Prostaglandin E2 Gel for Cervical Ripening and Labour Induction. A Canadian Multi-Centre PlAcebo-Controlled Trial n.d.
- Bernstein P, Leyland N, Gurland P, Gare D. Cervical ripening and labor induction with prostaglandin E2 gel: a placebo-controlled study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1987;156:336-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(87)90279-1.
- Bezircioglu I, Akin MK, Baloglu A, Bicer M. The efficacy of dinoprostone vaginal insert for active management of premature rupture of membranes at term: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2012;39:356-8.
- Bilgin T, Kadioglu M, Yildirim V, Cengiz C. A randomised trial of intracervical prostaglandin gel and intravenous oxytocin in prelabor rupture of membranes with unripe cervix at term. Prenatal Neonatal Med 1996;1.
- Bilgin T, Kadioğlu M, Yildirim V, Cengiz C. A randomized trial of intracervical prostaglandin gel and intravenous oxytocin in prelabor rupture of membranes with unripe cervix at term. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1998;25:46-8.
- Biron-Shental T, Fishman A, Fejgin MD. Medical and mechanical methods for cervical ripening. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;85:159-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2003.08.006.
- Bollapragada S, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, Petrou S, Reid M, Greer I, et al. IMOP: randomised placebo controlled trial of outpatient cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour: clinical trial with analyses of efficacy, cost effectiveness and acceptability. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2006;6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-6-25.
- Bollapragada SS, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Petrou S, Reid M, Greer IA, et al. Randomized placebo controlled trial of outpatient cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour – clinical trial with analyses of efficacy, cost effectiveness and acceptability. The IMOP study. J Obstet Gynaecol 2007;27.
- Bollapragada SS, MacKenzie F, Norrie JD, Eddama O, Petrou S, Reid M, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of outpatient (at home) cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour-clinical trial with analyses of efficacy and acceptability. The IMOP study. BJOG 2009;116:1185-95. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02216.x.
- Bolnick J, Velazquez M, Gonzalez J, Leslie K, Rappaport V, McIlwane G, et al. Randomized trial of sustained-release vaginal dinoprostone (PGE2) with concurrent oxytocin versus vaginal misoprostol (PGE2) for induction of labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Boulvain M, Fraser WD, Marcoux S, Fontaine JY, Bazin S, Blouin D. Randomised trial of sweeping the membranes. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1997;76.
- Boulvain M, Fraser WD, Marcoux S, Fontaine JY, Bazin S, Pinault JJ, et al. Does sweeping of the membranes reduce the need for formal induction of labour? A randomised controlled trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:34-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb09347.x.
- Bounyasong S. A randomized comparison between 25 microgram misoprostol gel and 50 microgram misoprostol vaginal tablet for induction of labour. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;12:21-5.
- Brandel E, Bascou V, Meeus JB, Magnin G. Results of a randomized trial of cervical maturation in premature rupture of membranes at term: prostine E, intravenous versus prostine E2 vaginal gel. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1998;27.
- Bremme K, Bygdeman M. A comparative study of uterine activity and fetal heart rate pattern in labor induced with oral prostaglandin E2 or oxytocin. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1980;92:23-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348009156934.
- Bremme K, Eneroth P. Changes in serum hormone levels during labor induced by oral PGE2 or oxytocin infusion. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1980;92:31-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348009156935.
- Bremme K, Eneroth P, Samuelson K. Estriol and cholic acid in maternal serum in induced labor. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1984;17:120-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000299134.
- Bremme K, Nilsson B. Prediction of Time to Delivery in Labour Induced With Oral Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) or Intravenous Oxytocin (OXY), Both in Combination With Early Amniotomy n.d.
- Brennan MC, Pevzner L, Wing DA, Powers BL, Rayburn WF. Retention of dinoprostone vaginal insert beyond 12 hours for induction of labor. Am J Perinatol 2011;28:479-84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1271208.
- Brennand JE, Calder AA, Leitch CR, Greer IA, Chou MM, MacKenzie IZ. Recombinant human relaxin as a cervical ripening agent. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;104:775-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1997.tb12019.x.
- Bricker L, Peden H, Tomlinson AJ, Al-Hussaini TK, Idama T, Candelier C, et al. Titrated low-dose vaginal and/or oral misoprostol to induce labour for prelabour membrane rupture: a randomised trial. BJOG 2008;115:1503-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01890.x.
- Browning J, Gherman RB. Oral misoprostol versus intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(00)00758-4.
- Buchanan D, Macer J, Yonekura ML. Cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppositories. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:659-63.
- Bullarbo M, Norström A, Andersch B, Ekerhovd E. Isosorbide mononitrate induces increased cervical expression of cyclooxygenase-2, but not of cyclooxygenase-1, at term. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2007;130:160-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2006.01.021.
- Bullarbo M, Orrskog ME, Andersch B, Granström L, Norström A, Ekerhovd E. Outpatient vaginal administration of the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening and labor induction postterm: a randomized controlled study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;196:50.e1-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2006.08.034.
- Bung P, Baer S, Djahanschahi D, Huch R, Huch A, Huber JF, et al. Multicenter experiences with the intracervical administration of a new PGE2 gel in labor induction. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1986;46:93-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1036170.
- Buser D, Mora G, Arias F. A randomized comparison between misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction in patients with unfavorable cervices. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:581-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00015-X.
- Butt KD, Bennett KA, Crane JM, Hutchens D, Young DC. Randomized comparison of oral misoprostol and oxytocin for labor induction in term prelabor membrane rupture. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:994-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-199912000-00017.
- Buttino LT, Garite TJ. Intracervical prostaglandin in postdate pregnancy. A randomized trial. J Reprod Med 1990;35:155-8.
- Byrne JD, Wing DA, Fraser M, Fassett MJ, Goodwin TM, Challis JRG. Mifepristone: effect on plasma corticotropin-releasing hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and cortisol in term pregnancy. J Perinatol 2004;24:416-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211127.
- Cabrol D, Bernard N, Chouraqui A, Domenichini Y, Lemaire P, Lopes P, et al. Ripening of the cervix uteri at term by a single intracervical application of prostaglandin E2 gel. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1988;17:527-34.
- Cahill DJ, Clark HS, Martin DH. Cervical ripening: the comparative effectiveness of Lamicel and prostaglandin E2 tablets. Ir J Med Sci 1988;157:113-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02950366.
- Cammu H, Haitsma V. Sweeping of the membranes at 39 weeks in nulliparous women: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:41-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb09348.x.
- Campbell JM. Induction of labour using prostaglandin E2 pessaries. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1984;11:1-5.
- Campos G, Guzman S, Rodriguez J, Voto L, Margulies M. Misoprostol un analogo de la PGE1-para la induccion de parto a termino: studio comparative y randomizado con oxitocina. Revista Chilena De Obstetricia Y Ginerologia 1994;59:190-6.
- Campos GA, Guzman S, Rodriguez JG, Voto LS, Margulies M. Misoprostol: a PGE1 analog for induction of labor at term: comparative and randomized study with oxytocin. Rev Chil Obstet Ginecol 1994;59:190-5.
- Cararach V, Sentis J, Botet F, Costa J, Manau D, Arimany MC. Cervical Prostaglandin E2 Compared With Expectant Management or Systematic Induction in PROM With Bad Cervical CondItions: I-Maternal Results n.d.
- Cararach V, Sentis J, Botet F, Foradada C, Manau D, Figueras F, et al. Cervical Prostaglandin E1 Compared With Expectant Management and With Systematic Induction in PROM Near Term, With Bad Cervical Conditions. I-Maternal Results n.d.
- Cardozo L, Fysh J, Pearce JM. Prolonged pregnancy: the management debate. Br Med J 1986;293:1059-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.293.6554.1059.
- Carlan SJ, Blust D, O’Brien WF. Buccal versus intravaginal misoprostol administration for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:229-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2002.119630.
- Carlan SJ, Bouldin S, Blust D, O’Brien WF. Safety and efficacy of misoprostol orally and vaginally: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 2001;98:107-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200111000-00034.
- Cecatti JG, Aquino MMA, Garcia GM, Rodrigues TMC. Misoprostol Versus Oxytocin for Labor Induction: Randomized Controlled Trial n.d.
- Chang CH, Chang FM. Randomized comparison of misoprostol and dinoprostone for preinduction cervical ripening and labor induction. J Formos Med Assoc 1997;96:366-9.
- Chang P, Langer O. Premature rupture of membranes at term; a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80580-7.
- Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y. Postterm with favorable cervix: is induction necessary?. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;106:154-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0301-2115(02)00243-9.
- Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Randomized comparison of glyceryl trinitrate and prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening at term. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:549-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200010000-00013.
- Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Potential efficacy of nitric oxide for cervical ripening in pregnancy at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2000;71:217-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(00)00284-8.
- Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Randomized trial of isosorbide mononitrate versus misoprostol for cervical ripening at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002;78:139-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(02)00128-5.
- Chanrachakul B, Herbutya Y. Phase II to Determine the Potential Efficacy and Safety of Nitric OXide for Cervical Ripening in PregNancy at Term n.d. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7292(00)81900-1.
- Chanrachakul B, Punyavachira P, Preechapornprasert D, Srilar A, Promsonthi P. Randomized comparison of sublingual and vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening at term. Reprod Sci 2010;17:A352-3.
- Charoenkul S, Sripramote M. A randomized comparison of one single dose of vaginal 50 microg misoprostol with 3 mg dinoprostone in pre-induction cervical ripening. J Med Assoc Thai 2000;83:1026-34.
- Chatterjee MS, Ramchandran K, Ferlita J, Mitrik L. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) vaginal gel for cervical ripening. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1990;38:197-202. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(91)90291-R.
- Chaudhuri S, Mitra SN, Banerjee PK, Biswas PK, Bhattacharyya S. Comparison of vaginal misoprostol tablets and prostaglandin E2 gel for the induction of labor in premature rupture of membranes at term: a randomized comparative trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2011;37:1564-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.2011.01575.x.
- Chayen B, Tejani N, Verma U. Induction of labor with an electric breast pump. J Reprod Med 1986;31:116-18.
- Chen TM. Clinical analysis of misoprostol on induction of labor in term pregnancy. J Zhenjiang Med Coll 2000;4:652-3.
- Cheng SY, Ming H, Lee JC. Titrated oral compared with vaginal misoprostol for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:119-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000297313.68644.71.
- Cheung PC, Yeo EL, Wong KS, Tang LC. Oral misoprostol for induction of labor in prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM) at term: a randomized control trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2006;85:1128-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00016340600589636.
- Chitrakar NS. Comparison of Misoprostol versus Dinoprostone for pre-induction cervical ripening at-term. J Nepal Health Res Counc 2012;10:10-5.
- Christensen F, Tehranifar M, Gonzalez J, Rappaport V, Gilson G, Rayburn W. Randomized trial of concurrent oxytocin and sustained-release dinoprostone for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- Christilaw J, King JF. A Randomised, Placebo Controlled Trial to Determine the Effect of Intracervical Prostaglandin Gel on the Unripe Cervix, Prior to Induction of Labour n.d.
- Chua S, Arulkumaran S, Kurup A, Anandakumar C, Tay D, Ratnam SS. Does prostaglandin confer significant advantage over oxytocin infusion for nulliparas with pre-labor rupture of membranes at term?. Obstet Gynecol 1991;77:664-7.
- Chua S, Arulkumaran S, Vanaja K, Ratnam SS. Preinduction cervical ripening: prostaglandin E2 gel vs hygroscopic mechanical dilator. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 1997;23:171-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.1997.tb00828.x.
- Chua S, Arulkumaran S, Yap C, Selamat N, Ratnam SS. Premature rupture of membranes in nulliparas at term with unfavorable cervices: a double-blind randomized trial of prostaglandin and placebo. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:550-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(95)80014-X.
- Chua SM, Lee KW, Phua SM. Comparative study between prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet and intravenous oxytocin in induction of labour. Singapore Med J 1988;29:379-82.
- Chuck F, Huffaker J. Labor induction with intravaginal prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) (misoprostol, cytotec) vs intracervical prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (dinoprostone, prepidil gel): a randomized comparison. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)91290-8.
- Chuck FJ, Huffaker BJ. Labor induction with intravaginal misoprostol versus intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel (Prepidil gel): randomized comparison. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1137-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)91340-8.
- Chung JH, Huang WH, Rumney PJ, Garite TJ, Nageotte MP. A prospective randomized controlled trial that compared misoprostol, Foley catheter, and combination misoprostol-Foley catheter for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:1031-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/S0002-9378(03)00842-1.
- Chung T, Rogers MS, Gordon H, Chang A. Prelabour rupture of the membranes at term and unfavourable cervix; a randomized placebo-controlled trial on early intervention with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;32:25-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1992.tb01892.x.
- Chyu JK, Strassner HT. Prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening: a randomized comparison of Cervidil versus Prepidil. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:606-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70153-4.
- Clark A, Cook V, Hill P, Spinnato J. Cervical ripening and labor induction: misoprostol vs dinoprostone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178.
- Coeytaux RR, Harper T, Chen W, Reilly A, Loh YL. Acupuncture to initiate labor (ACUMOMS 2): a randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial. J Alt Complement Med 2007;13.
- Cohen SB, Schiff E, Kees S, Lusky A, Mashiach S. Induction of labor using a foley catheter and extra-amniotic corticosteroids. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80746-6.
- The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Network (NICHHD) of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units . A clinical trial of induction of labor versus expectant management in postterm pregnancy. The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Network of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:716-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(94)70269-1.
- Collingham J, Fuh K, Caughey A, Pullen K, Lyell D, Druzin M, et al. Randomized clinical trial of cervical ripening and labor induction using oral misoprostol with or without intravaginal isosorbide mononitrate. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008;199. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2008.09.172.
- Colon I, Clawson K, Hunter K, Druzin ML, Taslimi MM. Prospective randomized clinical trial of inpatient cervical ripening with stepwise oral misoprostol vs vaginal misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:747-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.12.051.
- Colon I, Clawson K, Taslimi M, Druzin M. Prospective randomized clinical trial of inpatient cervical ripening with stepwise oral misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.09.068.
- Corrado F, Cannata ML, Facciola G, Stella NC. Intravaginal vs. intracervical PGE2 gel first application for labor induction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;75:195-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(01)00503-3.
- Crane J, Bennett K, Windrim R, Kravitz H, Young D. Prospective Randomized Study of Sweeping Membranes at Term n.d.
- Crane J, Bennett K, Young D, Windrim R, Kravitz H. The effectiveness of sweeping membranes at term: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:586-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00004-5.
- Crane J, Delaney T, Hutchens D. Oral misoprostol labor induction in term prelabor membrane rupture. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Crane JM, Delaney T, Hutchens D. Oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:720-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/S0002-9378(03)00768-3.
- Cromi A, Ghezzi F, Agosti M, Serati M, Uccella S, Arlant V, et al. Is transcervical Foley catheter actually slower than prostaglandins in ripening the cervix? A randomized study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:338.e1-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.11.029.
- Cromi A, Ghezzi F, Uccella S, Agosti M, Serati M, Marchitelli G, et al. A randomized trial of preinduction cervical ripening: dinoprostone vaginal insert versus double-balloon catheter. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;207:125.e1-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2012.05.020.
- Culver J, Strauss R, Brody S, Dorman K, Timlin S, McMahon M. A randomized trial of intracervical foley catheter with concurrent oxytocin compared to vaginal misoprostol for labor induction in nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(01)80474-9.
- Curet LB, Gauger LJ. Cervical ripening with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1989;28:221-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7292(89)90722-4.
- Da Graça Krupa F, Cecatti JG, de Castro Surita FG, Milanez HM, Parpinelli MA. Misoprostol versus expectant management in premature rupture of membranes at term. BJOG 2005;112:1284-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00700.x.
- Dällenbach P, Boulvain M, Viardot C, Irion O. Oral misoprostol or vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction? A randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(01)80130-7.
- Dällenbach P, Boulvain M, Viardot C, Irion O. Oral misoprostol or vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:162-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2003.108.
- Dalui R, Suri V, Ray P, Gupta I. Comparison of extraamniotic Foley catheter and intracervical prostaglandin E gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005;84:362-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/j.0001-6349.2005.00662.x.
- Damania KK, Natu U, Mhatre PN, Mataliya M, Mehta AC, Daftary SN. Evaluation of two methods employed for cervical ripening. J Postgrad Med 1992;38:58-9.
- Danielian P, Porter B, Ferri N, Summers J, Templeton A. Misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a more effective agent than dinoprostone vaginal gel. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;106:793-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1999.tb08399.x.
- Danielian PJ, Porter B. Induction of labour with misoprostol. J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;18:18-9.
- Dare FO, Oboro VO. The role of membrane stripping in prevention of post-term pregnancy: a randomised clinical trial in Ile-lfe, Nigeria. J Obstet Gynaecol 2002;22:283-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443610220130571.
- Darroca RJ, Buttino L, Miller J, Khamis HJ. Prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening in patients with an indication for delivery. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:228-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(95)00409-2.
- Davey DA, Macnab M. Oral and intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and induction of labour. S Afr Med J 1979;55:837-42.
- Davies NJ, Martindale E, Haddad NG. Cervical Ripening With Oral PGE2 Tablets and the Effect of the Latent Period in Patients With Premature Rupture of the Membranes at Term 1991.
- Day A, MacLennan A, Green R. A comparison of intravaginal PGF2 alpha and intravenous oxytocin to stimulate labour after membrane rupture. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1985;25:252-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1985.tb00738.x.
- Day AR, MacLennan A, Green R. A Comparison of Intravaginal PGF2 Alpha and Intravenous Oxytocin to Stimulate Labour After Membrane Rupture n.d.
- De A, Bagga R, Gopalan S. The routine use of oxytocin after oral misoprostol for labour induction in women with an unfavourable cervix is not of benefit. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2006;46:323-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.2006.00600.x.
- De Aquino MM, Cecatti JG. Misoprostol versus oxytocin for labor induction in term and post-term pregnancy: randomized controlled trial. Sao Paulo Med J 2003;121:102-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-31802003000300003.
- De Koning Gans GHJ, Keirse M. A Comparison Between Intra-Cervical and Intra-Vaginal Application of Prepidil Gel for the Induction of Labour 1988.
- De la Torre S, Gilson GJ, Flores S, Curet LB, Qualls CE, Rayburn WF. Is high-dose misoprostol able to lower the incidence of cesarean section? A randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Med 2001;10:85-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/jmf.10.2.85.90.
- De Miranda E, van der Bom JG, Bonsel GJ, Bleker OP, Rosendaal FR. Membrane sweeping and prevention of post-term pregnancy in low-risk pregnancies: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2006;113:402-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.00870.x.
- De Moraes Filho OB, de Albuquerque RM, Pacheco AJC, Ribeiro RH, Cecatti JG, Welkovic S. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for labor induction of term pregnancies. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2005;27:24-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-72032005000100006.
- Delaney S, Shaffer B, Cheng Y, Vargas J, Sparks T, Paul K, et al. Labor induction with a foley balloon trial (LIFT) – a randomized controlled trial of 30 ml versus 60 ml foley balloon inflation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009;201:23-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2009.10.038.
- Deng LL, Huang ZJ. Observation on the efficacy of intravaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening in the third trimester of pregnancy. J Nurs Sci 1999;14:67-8.
- Denguezli W, Trimech A, Haddad A, Hajjaji A, Saidani Z, Faleh R, et al. Efficacy and safety of six hourly vaginal misoprostol versus intracervical dinoprostone: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2007;276:119-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-006-0313-1.
- Deo S, Iqbal B, Das V, Agarwal A, Singh R. Evaluation of non-pharmacological method-transcervical foley catheter to intravaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Biomed Res 2012;23:247-52.
- Deshmukh VL, Yelikar KA, Deshmukh AB. Comparative study of intra-cervical Foley’s catheter and PGE(2) gel for pre-induction ripening (cervical). J Obstet Gynaecol India 2011;61:418-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13224-011-0063-2.
- Deshmukh VL, Yelikar KA, Waso V. Comparative study of efficacy and safety of oral versus vaginal misoprostol for induction or labour. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2013;63:321-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13224-012-0337-3.
- Di Cecco R, Hannah M, Hodnett E, Foster G, Farine D, Helewa M. Prelabor rupture of the membranes (PROM) at term: expectant management at home vs in hospital. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178.
- Diro M, Adra A, Gilles JM, Nassar A, Rodriguez A, Salamat SM, et al. A double-blind randomized trial of two dose regimens of misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Matern Fetal Med 1999;8:114-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(199905/06)8:3<114::AID-MFM8>3.0.CO;2-5.
- Doany W. Outpatient management of postdate pregnancy with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 and membrane stripping. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174.
- Doany W, McCarty J. Outpatient management of the uncomplicated postdate pregnancy with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel and membrane stripping. J Matern Fetal Med 1997;6:71-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(199703/04)6:2<71::AID-MFM2>3.0.CO;2-M.
- Dodd J, Crowther C, Ronbinson J. Misoprostol for the induction of labour at term: a randomised controlled trial. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2005;45:347-8.
- Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS. Oral misoprostol for induction of labour at term: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2006;332:509-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38729.513819.63.
- Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS. Oral Misoprostol Versus Intravenous Oxytocin for Induction of Labour Following Artificial or Spontaneous Rupture of Membranes: A Randomised Controlled Trial n.d.
- Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS. Factors Associated With Adverse Maternal Health Outcomes Following Induction of Labour at Term: Analyses from a Randomised Trial n.d.
- Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS. Time of Commencing Induction of Labour: A Nested RANDOMISED Controlled Trial n.d.
- Domínguez Salgado CR, Gorostieta García A, Vázquez Bretón S. Induction of labor in patients with premature rupture of membranes in term pregnancy using dinoprostone vs oxytocin. An aleatory study. Ginecol Obstet Mex 1999;67:461-6.
- Dommisse J, Davey DA, Allerton G. The induction of labour with prostaglandin E2 tablets administered intravaginally. S Afr Med J 1980;58:518-19.
- Dommisse J, Wild JM. Assessment of a new prostaglandin E2 gel in labour induction. S Afr Med J 1987;71:506-7.
- Duff P, Huff RW, Gibbs RS. Management of premature rupture of membranes and unfavorable cervix in term pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:697-702.
- Dyar TR, Greig P, Cummings R, Nichols K. The efficacy and safety of oral versus vaginal misoprostol for the induction of term labour. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182.
- Edwards R, Szychowski J, Berger J, Petersen M, Ingersoll M, Bodea Braescu A, et al. Randomized trial comparing Foley catheter to the prostaglandin E2 vaginal insert for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210:39-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2013.10.093.
- Edwards R, Szychowski J, Berger J, Petersen M, Ingersoll M, Bodea Braescu A, et al. Effect of parity on duration of labor inductions with either Foley catheter or the prostaglandin E2 vaginal insert. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2013.10.626.
- Edwards R, Szychowski J, Berger J, Petersen M, Ingersoll M, Bodea Braescu A, et al. Effect of obesity on duration and outcome of labor inductions with either the Foley catheter or the prostaglandin E2 vaginal insert. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2013.10.599.
- Egarter C, Husslein P. Sensitivity test in labor induction with prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets. Zentralbl Gynakol 1988;110:345-53.
- Egarter C, Kofler E, Fitz R, Husslein P. Is induction of labor indicated in prolonged pregnancy? Results of a prospective randomised trial. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1989;27:6-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000293605.
- Egarter C, Schurz B, Wagner G, Grunnberger W, Husslein P. Comparison between prostaglandin E2 gel and oxytocin in medically indicated labor induction. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1987;47:337-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1035832.
- Ekman G, Forman A, Marsal K, Ulmsten U. Intravaginal versus intracervical application of prostaglandin E2 in viscous gel for cervical priming and induction of labor at term in patients with an unfavorable cervical state. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;147:657-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(83)90445-3.
- Ekman G, Granstrom L, Ulmsten U. Induction of labor with intravenous oxytocin or vaginal PGE2 suppositories. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1986;65:857-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348609157038.
- Ekman-Ordeberg G, Uldbjerg N, Ulmsten U. Comparison of intravenous oxytocin and vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel in women with unripe cervixes and premature rupture of the membranes. Obstet Gynecol 1985;66:307-10.
- El-Torkey M, Grant JM. Sweeping of the membranes is an effective method of induction of labour in prolonged pregnancy: a report of a randomized trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;99:455-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1992.tb13780.x.
- El-Azeem S, Samuels P, Welch G, Staisch K. Term labor induction with PGE1 Misoprostol versus PGE2 Dinoprostone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80446-2.
- El-Din NMN, El-Moghazt DAM. Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour With Misoprostol, Prostaglandin E2 or Prostaglandin E2 Gel: A Randomized Comparative Clinical Trial n.d.
- Elhassan EM, Mirghani OA, Adam I. Cervical ripening and labor induction with 25 microg vs. 50 microg of intravaginal misoprostol. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;90:234-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2005.03.026.
- Elhassan EM, Mirghani OA, Adam I. Misoprostol vs. oxytocin for induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;91:254-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2005.08.003.
- Elhassan EM, Nasr AM, Adam I. Sublingual compared with oral and vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2007;97:153-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2007.02.014.
- Elhassan M, Mirghani OA, Adam I. Intravaginal misoprostol vs. dinoprostone as cervical ripening and labor-inducing agents. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;85:285-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2003.11.016.
- Elliot CL, Brennand Je, Calder A. The Effect of Mifepristone (RU486) on Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour in Human Pregnancy n.d.
- El-Mardi AA, el-Qarmalawi MA, Siddik M, el-Haroni A, Ammar A, Madkoor SA. A comparison of single prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet with prostaglandin E2 vaginal pessaries for induction of labor at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1991;35:221-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7292(91)90289-H.
- El-Shawarby SA, Connell RJ. Induction of labour at term with vaginal prostaglandins preparations: a randomised controlled trial of Prostin vs Propess. J Obstet Gynaecol 2006;26:627-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443610600903362.
- El-Sherbiny M. Vaginal Misoprostol for Labor Induction 25 ug Versus 50 ug Dose Regimens n.d.
- El-Sherbiny MT, El-Gharieb IH, Gewely HA. Vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor: 25 vs. 50 microg dose regimen. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;72:25-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(00)00308-8.
- Eroglu D, Oktem M, Yanik F, Kuscu E. Labor induction at term: a comparison of the effects of 50 microg and 25 microg vaginal misoprostol. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2007;34:102-5.
- Escudero F, Contreras H. A comparative trial of labor induction with misoprostol versus oxytocin. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;57:139-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(97)02873-7.
- Esteve JLC, Garcia TJP, Iturralde AS, Ferrer YA, Teixido CS. Randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of 25 microg of vaginal misoprostol versus 50 microg of sublingual misoprostol for labor induction. Prog Obstet Ginecol 2006;49:369-79.
- Ezechi OC, Loto OM, Ezeobi PM, Okogbo FO, Gbajabiamila T, Nwokoro CA. Safety and efficacy of misoprostol in induction of labour in prelabour rupture of fetal membrane in Nigerian women: a multicenter study. Iran J Reprod Med 2008;6:83-7.
- Facchinetti F, Venturini P, Fazzio M, Volpe A. Elective cervical ripening in women beyond the 290th day of pregnancy: a randomized trial comparing 2 dinoprostone preparations. J Reprod Med 2007;52:945-9.
- Facchinetti F, Venturini P, Verocchi G, Volpe A. Comparison of two preparations of dinoprostone for pre-induction of labour in nulliparous women with very unfavourable cervical condition: a randomised clinical trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;119:189-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2004.06.039.
- Farah LA, Sanchez-Ramos L, Rosa C, Del Valle GO, Gaudier FL, Delke I, et al. Randomized trial of two doses of the prostaglandin E1 analog misoprostol for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:364-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70199-6.
- Fassett MJ, Lachelin GC, McGarrigle HH, Wing DA. Alterations in saliva steroid hormone levels after oral mifepristone administration in women with pregnancies of greater than 41 weeks’ gestation. Reprod Sci 2008;15:394-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1933719107310305.
- Fassett MJ, Wing DA. Salivary estriol/progesterone ratio and the success of labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(01)80503-2.
- Fassett MJ, Wing DA. Uterine activity after oral mifepristone administration in human pregnancies beyond 41 weeks’ gestation. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2008;65:112-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000109167.
- Feitosa F. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2006;28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-72032006000900012.
- Feitosa FE, Sampaio ZS, Alencar CA, Amorim MM, Passini R. Sublingual vs. vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2006;94:91-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2006.04.031.
- Fenton DW, Speedie J, Duncan SL. Does cervical ripening with PGE2 affect subsequent uterine activity in labour?. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1985;64:27-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348509154683.
- Ferguson JE, Head BH, Frank FH, Frank ML, Singer JS, Stefos T, et al. Misoprostol versus low-dose oxytocin for cervical ripening: a prospective, randomized, double-masked trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:273-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2002.126202.
- Ferraiolo A, Dellacasa I, Bentivoglio G, Ferrero S, Ragni N. Evaluation of patients’ satisfaction of cervical ripening using dinoprostone by either intravaginal gel or pessary: an open-label, randomized, prospective study. J Reprod Med 2010;55:423-9.
- Filho OBM. Misoprostol versus foley catheter and oxytocin for induction of labour. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2002;24.
- Fisher S, Davies G, Mackenzie P. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- Fisher SA, Mackenzie VP, Davies GA. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:906-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2001.117303.
- Fletcher H, Mitchell S, Frederick J, Simeon D, Brown D. Intravaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone as cervical ripening and labor-inducing agents. Obstet Gynecol 1994;83:244-7.
- Fletcher HM, Mitchell S, Simeon D, Frederick J, Brown D. Intravaginal misoprostol as a cervical ripening agent. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;100:641-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1993.tb14230.x.
- Fonseca L, Lucas M, Wood H, Phat’ak D, Susan R, Gilstrap L, et al. RCT of misoprostol pre-induction ripening vs oxytocin induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;197. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2007.10.364.
- Fonseca L, Wood HC, Lucas MJ, Ramin SM, Phatak D, Gilstrap LC III, et al. Randomized trial of preinduction cervical ripening: misoprostol vs oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008;199:305.e1-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2008.07.014.
- Foong LC, Vanaja K, Tan G, Chua S. Effect of Cervical Membrane Sweeping on Induction of Labour. Women’s Health – Into the New Millennium n.d.
- Foradada C, Cararach V, Sentis J, Botet F, Manau D, Figueras F, et al. Cervical Prostaglandin E1 Compared With Expectant Management and With Systematic Induction in PROM Near Term, With Bad Cervical Conditions. II-Fetal and Neonatal Results n.d.:51-2.
- Frass KA, Shuaib AA, Al-Harazi AH. Misoprostol for induction of labor in women with severe preeclampsia at or near term. Saudi Med J 2011;32:679-84.
- Frohn WE, Simmons S, Carlan SJ. Prostaglandin E2 gel versus misoprostol for cervical ripening in patients with premature rupture of membranes after 34 weeks. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:206-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200202000-00008.
- Frydman R, Baton C, Lelaidier C, Vial M, Bourget P, Fernandez H. Mifepristone for induction of labour. Lancet 1991;337:488-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(91)93421-5.
- Frydman R, Lelaidier C, Baton-Saint-Mleux C, Fernandez H, Vial M, Bourget P. Labor induction in women at term with mifepristone (RU 486): a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 1992;80:972-5.
- Frydman R, Lelaidier C, Baton-Saint-Mleux C, Fernandez H, Vial M, Bourget P. Labor induction in women at term with mifepristone (RU 486): a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1993;42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7292(93)90660-O.
- Frydman R, Taylor S, Paoli C, Pourade A. RU 486 (mifepristone): a new tool for labor induction women at term with live fetus. Contracept Fertil Sex 1992;20:1133-6.
- Gafni A, Goeree R, Myhr TL, Hannah ME, Blackhouse G, Willan AR, et al. Induction of labour versus expectant management for prelabour rupture of the membranes at term: an economic evaluation. TERMPROM Study Group. Term Prelabour Rupture of the Membranes. CMAJ 1997;157:1519-25.
- Gagnon-Gervais K, Bujold E, Iglesias MH, Duperron L, Masse A, Mayrand MH, et al. Early versus late amniotomy for labour induction: a randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:2326-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2012.695819.
- Gagnon-Gervais K, Iglesias MH, Duperron L, Masse A, Mayrand MH, Sansregret A, et al. Early vs late amniotomy for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.10.327.
- Garry D, Figueroa R, Guillaume J, Cucco V. Use of castor oil in pregnancies at term. Altern Ther Health Med 2000;6:77-9.
- Garry D, Figueroa R, Kalish RB, Catalano CJ, Maulik D. Randomized controlled trial of vaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone vaginal insert for labor induction. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2003;13:254-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/jmf.13.4.254.259.
- Gaudernack LC, Forbord S, Hole E. Acupuncture administered after spontaneous rupture of membranes at term significantly reduces the length of birth and use of oxytocin. A randomized controlled trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2006;85:1348-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00016340600935839.
- Gaudet LM, Dyzak R, Aung SK, Smith GN. Effectiveness of acupuncture for the initiation of labour at term: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2008;30:1118-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1701-2163(16)34021-X.
- Gelisen O, Caliskan E, Dilbaz S, Ozdas E, Dilbaz B, Ozdas E, et al. Induction of labor with three different techniques at 41 weeks of gestation or spontaneous follow-up until 42 weeks in women with definitely unfavorable cervical scores. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;120:164-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2004.08.013.
- Getgan M, Paisarntantiwong R, Sripramote M. A randomized comparison between 50 micrograms orally and misoprostol 25 micrograms vaginally for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;15.
- Gherman RB. A randomized double-blind comparison of oral misoprostol dosing regimens for cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200204001-00103.
- Gherman RB, Browning J, O’Boyle A, Goodwin TM. Oral misoprostol vs. intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for preinduction cervical ripening. A randomized trial. J Reprod Med 2001;46:641-6.
- Giacalone PL, Targosz V, Laffargue F, Boog G, Faure JM. Cervical ripening with mifepristone before labor induction: a randomized study. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92:487-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-199810000-00002.
- Gibson K, Mercer B, Louis J. A randomized control trial of inner thigh taping versus traction for cervical ripening with a Foley catheter. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2013;208:145-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2012.10.490.
- Gihwala N. A Comparison of Prostaglandin E2 and Oxytocin for the Induction of Labour: A Randomised Trial n.d.
- Gihwala N, Moodley J, Hansen J, Naicker SN. Prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel: a new formulation for the induction of labour. S Afr Med J 1987;72:615-17.
- Gilson GJ, Curet LB. Intracervical dinoprostone (PGE2): does it actually lower the Cesarean section rate?. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(91)91320-V.
- Gilson GJ, Izquierdo LA, Chatterjee MS, Curet LB, Qualls CR. Prevention of cesarean section. Does intracervical dinoprostone work?. West J Med 1993;159:149-52.
- Gilson GJ, Russell DJ, Izquierdo LA, Qualls CR, Curet LB. A prospective randomized evaluation of a hygroscopic cervical dilator, Dilapan, in the preinduction ripening of patients undergoing induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:145-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(96)70264-8.
- Gilson GJ, Smith JF, Curet LB, Izquierdo LA, Chatterjee MS, Joffe GM, et al. Efficacy of preinduction Dilapan on lowering the Cesarean section rate. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(12)91708-1.
- Girija S, Manjunath AP. Comparison of two dosing regimens of vaginal misoprostol for labour induction: a randomised controlled trial. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc 2009;10:220-5.
- Girija S, Manjunath AP. A randomized controlled trial comparing low dose vaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone gel for labor induction. J Obstet Gynecol India 2011;61:153-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13224-011-0031-x.
- Gittens L, Schenkel C, Strassberg S, Apuzzio J. Vaginal birth after cesarean section: comparison of outpatient use of prostaglandin gel to expectant management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174.
- Glagoleva EA, Nikonov AP. Preinduction cervical ripening: a comparison of intracervical prostaglandin e2 gel versus the hygroscopic cervical dilator dilapan. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1999;86.
- Goel G, Shirazee HH, Phadikar A, Saha SK. Sublingual Versus Vaginal Misoprostol Induction of Labour and Its Fetomaternal Outcome n.d.
- Goeschen K. Premature rupture of membranes near term: induction of labor with endocervical prostaglandin E2 gel or intravenous oxytocin. Am J Perinatol 1989;6:181-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-999572.
- Golbus MS, Creasy RK. Uterine priming with oral prostaglandin E2 prior to elective induction with oxytocin. Prostaglandins 1977;14:577-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0090-6980(77)90272-6.
- Goldenberg M, Dulitzky M, Feldman B, Zolti M, Bider D. Stretching of the cervix and stripping of the membranes at term: a randomised controlled study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1996;66:129-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0301-2115(96)02405-0.
- Gonen R, Samberg I, Degani S. Intracervical prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor in patients with premature rupture of membranes and an unripe cervix. Am J Perinatol 1994;11:436-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-994615.
- Gottschall D, Borgida AF, Mihalek JJ, Sauer F, Rodis JF. Misoprostol versus prostin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80553-4.
- Gottschall DS, Borgida AF, Mihalek JJ, Sauer F, Rodis JF. A randomized clinical trial comparing misoprostol with prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1067-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70016-4.
- Gower RH, Toraya J, Miller JM. Laminaria for preinduction cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 1982;60:617-19.
- Grant JM. Comparison of Hydrostatic Sweeping of the Membranes (Extra-Amniotic Foley Catheter Plus Extra-Amniotic Water Injection) and Vaginal Prostaglandin Gel in Women With an Unfavourable Cervix Who Require Induction of Labour 1993.
- Grant JM, Serle E, Mahmood T, Sarmandal P, Conway DI. Management of prelabour rupture of the membranes in term primigravidae: report of a randomized prospective trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;99:557-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1992.tb13820.x.
- Graves GR, Baskett TF, Gray JH, Luther ER. The effect of vaginal administration of various doses of prostaglandin E2 gel on cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;151:178-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(85)90007-9.
- Green C, Pedder G, Mason G. A randomised trial of Propess against prostin gel for induction of labour at term. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105.
- Greer IA, Calder AA. Pre-induction cervical ripening with extra-amniotic and vaginal prostaglandin E2. J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;10:18-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443618909151086.
- Greer IA, McLaren M, Calder AA. Vaginal administration of PGE2 for induction of labor stimulates endogenous PGF2 alpha production. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1990;69:621-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349009028707.
- Gregson S. To Compare the Safety and Efficacy of ‘Low Dose’ Vaginal Misoprostol and Dinoprostone Vaginal Gel for Induction of Labour at Term 2004. www.controlled-trials.com/mrct (accessed 15 September 2004).
- Gregson S, Waterstone M, Norman I, Murrells T. A randomised controlled trial comparing low dose vaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone vaginal gel for inducing labour at term. BJOG 2005;112:438-44. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00496.x.
- Greybush M, Singleton C, Atlas RO, Balducci J, Rust OA. Preinduction cervical ripening techniques compared. J Reprod Med 2001;46:11-7.
- Gribel GP, Coca-Velarde LG, Moreira de SRA. Electroacupuncture for cervical ripening prior to labor induction: a randomized clinical trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2011;283:1233-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-010-1526-x.
- Griffith-Jones MD, Tyrrell SN, Tuffnell DJ. A prospective trial comparing intravenous oxytocin with vaginal prostaglandin E2 tablets for labour induction in cases of spontaneous rupture of the membranes. Obstet Gynaecol Today 1990;1:104-5.
- Grünnberger W, Spona J. The effect of pericervical PGE2 instillation on levels of maternal serum 13,14-dihydro-15-keto-PGF2 alpha and progesterone. Arch Gynecol 1986;239:93-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02133968.
- Guinn D, Davies J, Jones RO, Wolf D. Foley catheter with extraamniotic saline infusion (easi) versus foley catheter alone for induction of labor in gravidas with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Guinn DA, Goepfert AR, Owen J, Christine M, Hauth J. Laminaria, extraamniotic saline induction (EASI) or prepidil for cervical ripening prior to labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80559-5.
- Güngördük K, Asicioglu O, Besimoglu B, Güngördük OC, Yildirm G, Ark C, et al. Labor induction in term premature rupture of membranes: comparison between oxytocin and dinoprostone followed 6 hours later by oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206:60.e1-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2011.07.035.
- Gupta HP, Singh U, Mehrotra S. Comparative evaluation of 25 ug and 50 ug of intravaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. J Obstet Gynecol India 2010;60:51-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13224-010-0009-0.
- Gupta N, Mishra SL, Shradha J. A randomized clinical trial comparing misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Obstet Gynecol India 2006;56:149-51.
- Gupta R, Vasishta K, Sawhney H, Ray P. Safety and efficacy of stripping of membranes at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1998;60:115-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(97)00249-X.
- Haas S, Lucas MJ. Impact of prepidil pre-induction cervical treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(12)90639-0.
- Habib SM, Emam SS, Saber AS. Outpatient cervical ripening with nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate prior to induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2008;101:57-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2007.09.027.
- Haghighi L. Intravaginal misoprostol in preterm premature rupture of membranes with low Bishop scores. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2006;94:121-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2006.02.018.
- Haghighi L, Homam H, Raoofi Z, Najmi Z. Intravaginal isosorbide dinitrate or misoprostol for cervical ripening prior to induction of labour: a randomised controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2013;33:272-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443615.2012.753422.
- Haitsma V, Cammu H. Is Stripping of Membranes Useful in Reducing Duration of Pregnancy? n.d.
- Hales K, Rayburn W, Turnbull G, Christensen D, Patatanian E. Double-blind comparison of intracervical and intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(94)90041-8.
- Hales KA, Rayburn WF, Turnbull GL, Christensen HD, Patatanian E. Double-blind comparison of intracervical and intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1087-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(94)90041-8.
- Hall R, Duarte-Gardea M, Harlass F. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:1044-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200206000-00017.
- Hallak M. Mechanical ripening of the unfavorable cervix for induction of labor. Contemp Rev Obstet Gynaecol 1997;9:99-105.
- Hamdan M, Sidhu K, Sabir N, Omar SZ, Tan PC. Serial membrane sweeping at term in planned vaginal birth after cesarean: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2009;114:745-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181b8fa00.
- Hannah M, Ohlsson A, Farine D, Hewson S, Hodnett E, Myhr T, et al. Vaginal Prostaglandin E2 Gel Vs Intravenous Oxytocin Vs Expectant Management for Prelabour Rupture of Membranes at Term. A Randomised Clinical Trial n.d.
- Hannah M, Ohlsson A, Wang E, Myhr T, Farine D, Hewson S, et al. Inducing labor with iv oxytocin may reduce the risk of neonatal infection in GBS positive women with PROM at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80145-7.
- Hannah ME, Ohlsson A, Farine D, Hewson SA, Hodnett ED, Myhr RL, et al. Induction of labor compared with expectant management for prelabor rupture of the membranes at term. N Engl J Med 1996;334:1005-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199604183341601.
- Hannah ME, Ohlsson A, Wang EE, Matlow A, Foster GA, Willan AR, et al. Maternal colonization with group B Streptococcus and prelabor rupture of membranes at term: the role of induction of labor. TermPROM Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:780-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70268-0.
- Harper TC, Coeytaux RR, Chen W, Campbell K, Kaufman JS, Moise KJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of acupuncture for initiation of labor in nulliparous women. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2006;19:465-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14767050600730740.
- Harper TC, Coeytaux RR, Chen W, Campbell K, Kaufman JS, Thorp J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of acupuncture for initiation of labor in nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;193. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2005.10.123.
- Has R, Batukan C, Ermis H, Cevher E, Araman A, Kiliç G, et al. Comparison of 25 and 50 microg vaginally administered misoprostol for preinduction of cervical ripening and labor induction. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2002;53:16-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000049405.
- Haugland B, Albrechtsen S, Lamark E, Rasmussen S, Kessler J. Induction of labor with single- versus double-balloon catheter: a randomized controlled trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2012;91:84-5.
- Hauth JC, Cunningham FG, Whalley PJ. Early labor initiation with oral PGE2 after premature rupture of the membranes at term. Obstet Gynecol 1977;49:523-6.
- Hay D, Robinson G, Filshie M, James D. Cervical Ripening With Prostaglandin E2 Gel and Hygroscopic Cervical Dilators n.d.
- Hayashi R, Keirse M. PGE2 Gel (Prepidil Gel) for Preinduction Cervical Softening 1983.
- Heden L, Ingemarsson I, Ahlstrom H, Solum T. Induction of labor vs conservative management in prolonged pregnancy: controlled study. Int J Feto-Maternal Med 1991;4:148-52.
- Heinzl S, Ramzin MS, Schneider M, Luescher KP. Priming of cervix with prostaglandin gel during immature birth situation at term. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol 1980;184:395-400.
- Hemlin J, Möller B. Extraamniotic saline infusion is promising in preparing the cervix for induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1998;77:45-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00016349808565810.
- Henrich W, Dudenhausen JW, Hanel C, Chen FC. Oral misoprostol against vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction at term: a randomized comparison. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol 2008;212:183-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1077027.
- Henry A, Reid R, Madan A, Tracy S, Sharpe V, Welsh A, et al. Satisfaction survey: outpatient Foley catheter versus inpatient prostin gel for cervical ripening. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2011;51.
- Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P. A comparison of oral and intracervical prostaglandin E2 for ripening of the unfavourable cervix prior to induction of labour. J Med Assoc Thai 1988;71:269-73.
- Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P. Ripening of the unfavorable cervix with prostaglandin E2: intracervical versus intravaginal route. J Med Assoc Thai 1993;76:63-8.
- Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P, Pokpirom J. A comparison of intravaginal misoprostol and intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for ripening of unfavorable cervix and labor induction. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 1997;23:369-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.1997.tb00860.x.
- Herabutya Y, Prasertsawat PO, Tongyai T, Isarangura Na Ayudthya N. Prolonged pregnancy: the management dilemma. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1992;37:253-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7292(92)90325-D.
- Herabutya Y, Suchatwatnachai C, O-Prasertsawat P. Comparison of intravenous oxytocin with and without vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel in term pregnancy with premature rupture of membranes and unfavorable cervix. J Med Assoc Thai 1991;74:92-6.
- Hidar S, Bibi M, Jerbi M, Bouguizene S, Nouira M, Mellouli R, et al. Contribution of intracervical PGE2 administration in premature rupture of the membranes at term. Prospective randomised clinical trial. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 2000;29:607-13.
- Hill MJ. Safety Study of Membrane Sweeping in Pregnancy 2006. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00294242 (accessed 21 March 2006).
- Hill MJ, McWilliams GD, Garcia D, Chen B, Munroe M, Hoeldtke NJ. The effect of membrane sweeping in uncomplicated pregnancies on prelabor rupture of membranes, a prospective randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e31816fdcf3.
- Hill MJ, McWilliams GD, Garcia-Sur D, Chen B, Munroe M, Hoeldtke NJ. The effect of membrane sweeping on prelabor rupture of membranes: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:1313-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e31816fdcf3.
- Hjertberg R, Berg A, Ekman G, Granstrom L, Hammarstrom M, Moberger B, et al. Twelve or 24-Hours Expectancy in Premature Rupture of the Membranes (PROM) at Term n.d.
- Hjertberg R, Hammarström M, Moberger B, Nordlander E, Granström L. Premature rupture of the membranes (PROM) at term in nulliparous women with a ripe cervix. A randomized trial of 12 or 24 hours of expectant management. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:48-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349609033283.
- Hodnett ED, Hannah ME, Weston JA, Ohlsson A, Myhr TL, Wang EEI, et al. Women’s evaluations of induction of labor versus expectant management for prelabor rupture of the membranes at term. Birth 1997;24:214-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-536X.1997.tb00593.x.
- Hoffmann RA, Anthony J, Fawcus S. Oral misoprostol vs. placebo in the management of prelabor rupture of membranes at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;72:215-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(00)00337-4.
- Hoffmann RAM, Fawcus S, Anthony J. Oral Misoprostol Versus Placebo in the Management of Prelabour Rupture of Membranes at Term. Women’s Health – Into the New Millennium n.d.
- Hofmeyr GJ, Alfirevic Z, Matonhodze B, Brocklehurst P, Campbell E, Nikodem VC. Titrated oral misoprostol solution for induction of labour: a multi-centre, randomised trial. BJOG 2001;108:952-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2001.00231.x.
- Hosli I, Zanetti-Daellenbach R, Gairing A, Holzgreve W, Lapaire O. Selection of appropriate prostaglandin for the induction of labor at term is more predictive for the achievement of delivery within 24 hours than pre-assessed cervical parameters: a prospective, randomized trial. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 2008;68:147-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-989479.
- How H, Leaseburge L, Khoury J, Siddiqi T, Sibai B. Is there an ideal route of misoprostol administration for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- How HY, Leaseburge L, Khoury JC, Siddiqi TA, Spinnato JA, Sibai BM. A comparison of various routes and dosages of misoprostol for cervical ripening and the induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:911-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2001.117358.
- Howarth GR, Funk M, Steytler P, Pistorius L, Makin J, Pattinson RC. A Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Vaginally Administered Misoprostol to Vaginal Dinoprostone Gel in Labour Induction n.d.
- Howarth GR, Funk M, Steytler P, Pistorius L, Makin J, Pattinson RC. A randomised controlled trial comparing vaginally administered misoprostol to vaginal dinoprostone gel in labour induction. J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;16:474-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443619609030076.
- Huang W, Chung J, Rumney P, Pattillo C, Garite T, Nageotte M. A prospective, randomized controlled trial comparing misoprostol, foley catheter, and combination misoprostol-foley for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Hudon L, Belfort MA, Dorman K, Wilkins IA, Moise KJ. Comparison between intracervical PGE2 and supracervical foley catheter for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180.
- Husslein P, Egarter C, Sevelda P, Genger H, Salzer H, Kofler E. Labor induction with 3 mg of prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets. A renaissance of programmed labor? Results of a prospective randomized study. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1986;46:83-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1036167.
- Hutchon DJ, Geirsson R, Patel NB. A double-blind controlled trial of PGE2 gel in cervical ripening. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1980;17:604-7.
- Hutchon DJR, Geirsson RT, Patel NB. A double-blind controlled trial of intracervical prostaglandin E2 in cervical ripening. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1980;59.
- Incerpi M, Fassett M, Kjos S, Tran S, Wing D. Vaginally administered misoprostol for outpatient labor induction in pregnancies with diabetes mellitus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- Incerpi MH, Fassett MJ, Kjos SL, Tran SH, Wing DA. Vaginally administered misoprostol for outpatient cervical ripening in pregnancies complicated by diabetes mellitus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:916-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2001.117306.
- Irion O, Pedrazzoli J, Mermillod B. A randomized trial comparing vaginal and cervical prostaglandin gel for cervical ripening and labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1998;91:65-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00608-X.
- Iskander MN. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of extra-amniotic prostaglandin E2 and intravenous prostaglandin E2 for the induction of labour in patients with unripe cervices. J Int Med Res 1978;6:144-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/030006057800600214.
- Jackson GM, Sharp HT, Varner MW. Pre-induction cervical ripening: low dose oxytocin is as effective as intracervical prostaglandin E2. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170.
- Jackson GM, Sharp HT, Varner MW. Cervical ripening before induction of labor: a randomized trial of prostaglandin E2 gel versus low-dose oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1092-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(94)90042-6.
- Jackson N, Paterson-Brown S. Labour characteristics and uterine activity: misoprostol compared with oxytocin in women at term with prelabour rupture of the membranes. BJOG 2000;107:1181-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2000.tb11130.x.
- Jagani N, Schulman H, Fleischer A, Mitchell J, Blattner P. Role of prostaglandin-induced cervical changes in labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:225-9.
- Jagani N, Schulman H, Fleischer A, Mitchell J, Randolph G. Role of the cervix in the induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1982;59:21-6.
- Janakiraman V, Ojo L, Sheth S, Keller J, Young H. Membrane sweeping in GBS positive patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:41-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.10.086.
- Jeeva MA, Dommisse J. Laminaria tents or vaginal prostaglandins for cervical ripening. A comparative trial. S Afr Med J 1982;61:402-3.
- Jindal P, Avasthi K, Kaur M. A comparison of vaginal vs. oral misoprostol for induction of labor-double blind randomized trial. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2011;61:538-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13224-011-0081-0.
- Johnson IR, Macpherson MB, Welch CC, Filshie GM. A comparison of Lamicel and prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel for cervical ripening before induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;151:604-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(85)90147-4.
- Jozwiak M, Benthem M, Oude RK, Dijksterhuis M, de Graaf I, van Pampus M, et al. Randomized clinical trial for the comparison of Foley catheter and prostaglandin inserts in induction of labor at term (trial registration NTR 1646). Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2011.10.088.
- Jozwiak M, Oude Rengerink K, Benthem M, van Beek E, Dijksterhuis MG, de Graaf IM, et al. Foley catheter versus vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel for induction of labour at term (PROBAAT trial): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2011;378:2095-103. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61484-0.
- Jozwiak M, Oude Rengerink K, Ten Eikelder ML, van Pampus MG, Dijksterhuis MG, de Graaf IM, et al. Foley catheter or prostaglandin E2 inserts for induction of labour at term: an open-label randomized controlled trial (PROBAAT-P trial) and systematic review of literature. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2013;170:137-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.06.017.
- Jozwiak M, Rengerink KO, Doornbos H, Drogtrop A, de Groot C, Huisjes A, et al. Prediction of cesarean section in women with an unfavorable cervix at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2011.10.324.
- Jozwiak M, ten Eikelder M, Oude Rengerink K, de Groot C, Feitsma H, Spaanderman M, et al. Foley catheter versus vaginal misoprostol: randomized controlled trial (PROBAAT-M study) and systematic review and meta-analysis of literature. Am J Perinatol 2014;31:145-56.
- Kadanali S, Küçüközkan T, Zor N, Kumtepe Y. Comparison of labor induction with misoprostol vs. oxytocin/prostaglandin E2 in term pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1996;55:99-104. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(96)02710-5.
- Kadian ND. Comparison of nitric oxide donor isosorbide dinitrate (IDN) and dinoprostone for cervical ripening before induction of labor at term. BJOG 2008;115.
- Kalkat RK, McMillan E, Cooper H, Palmer K. Comparison of Dinoprostone slow release pessary (Propess) with gel (Prostin) for induction of labour at term: a randomised trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2008;28:695-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443610802462522.
- Kalkat RKB, McMillan E, Cooper H, Palmer K. Comparative Study of Dinoprostone Slow Release Pessary (propess) Versus Gel (prostin) for Induction of Labour n.d.
- Kaminski K, Rechberger T, Oleszczuk J, Jakowicki J, Oleszczuk J. Biochemical and clinical evaluation of the efficiency of intracervical extraamniotic prostaglandin F2 alpha and intravenous oxytocin infusion to induce labour at term. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;34:409-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1994.tb01258.x.
- Kandil M, Emarh M, Sayyed T, Masood A. Foley catheter versus intra-vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor in post-term gestations. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;286:303-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-012-2292-8.
- Kanhai HHH, Keirse M. Intravenous Administration of Sulprostone for the Induction of Labour After FEtal Death: A Randomized Comparison of Two Dose Schedules n.d.
- Kanhai HHH, Keirse M. Intravenous Administration of Sulfprostone for the Induction of Labour After Fetal Death: A Randomized Comparison of Two Dose Schedules n.d.:201-2.
- Kashanian M, Afshar A, Zarrin Z. A comparison between the effect of oxytocine only and oxytocine plus propanolol on the labor (a double blind randomized trial. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2008;21.
- Kashanian M, Akbarian A, Baradaran H, Samiee MM. Effect of membrane sweeping at term pregnancy on duration of pregnancy and labor induction: a randomized trial. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2006;62:41-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000091842.
- Kashanian M, Akbarian AR, Fekrat M. Cervical ripening and induction of labor with intravaginal misoprostol and Foley catheter cervical traction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2006;92:79-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2005.09.010.
- Kashanian M, Baradaran H, Meshki M. The effect of membrane sweeping at term pregnancy on the duration of pregnancy and labor induction: a randomized trial. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;23.
- Kashanian M, Dadkhah F, Mokhtari F. Effect of intramuscular administration of dexamethasone on the duration of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2008;102:259-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2008.04.009.
- Kashanian M, Fekrat M. The cervical ripening and induction of labor with intravaginal misoprostol, traction on the cervix with intracervical Foley catheter, and a combination of the two methods: a randomized trial of 3 techniques. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2009;107. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(09)61732-X.
- Kashanian M, Naghghash S. A Comparison Between the Effect of Oxitocin Only and Oxitocin Plus Propranolol on the Labor (a Double Blind Randomized Trial) n.d.
- Kashanian M, Zarrin DR. Evaluation of the Effect of Extra-Amniotic Normal Saline Infusion (EASI) Alone or in Combination With Dexamethazone for the Induction of Labor n.d.
- Kashanian M, Zarrin Z. A comparison between the effect of oxytocin only and oxytocin plus propanolol on the labor: a double blind randomized trial. J Kashan Uni Med Sci 2006;10:7-11.
- Kashanian M, Zarrin Z. A comparison between the effect of oxytocin only and oxytocin plus propranolol on the labor (a double blind randomized trial). J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;23:616-17.
- Katz Z, Yemini M, Lancet M, Mogilner BM, Ben-Hur H, Caspi B. Non-aggressive management of post-date pregnancies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1983;15:71-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(83)90175-2.
- Kaul V, Aggarwal N, Ray P. Membrane stripping versus single dose intracervical prostaglandin gel administration for cervical ripening. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;86:388-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.04.035.
- Kehl S, Welzel G, Ehard A, Berlit S, Spaich S, Siemer J, et al. Women’s acceptance of a double-balloon device as an additional method for inducing labour. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2013;168:30-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.12.018.
- Kehl S, Ziegler J, Schleussner, Tuschy B, Berlit S, Mayer J, et al. Induction of labour with a balloon catheter and misoprostol - a randomised controlled multi centre study. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;286:145-6.
- Keirse MJ, de Koning Gans HJ. Randomized comparison of the effects of endocervical and vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel in women with various degrees of cervical ripeness. Dutch Collaborative Prostaglandin Trialists’ Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1859-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)90441-7.
- Keirse M, Kanhai HHH, Verwey RA, Bennebroek Gravenhorst J, Wood C. The Role of Prostaglandins in Labour. London: RSM Services; 1985.
- Keirse M, Schulpen M, Corbeij R, Oosterbaan HP, Keirse MJNC, De Koning Gans HJ. A State of the Art. Leiden: Postgrad Med Ed Committee; 1987.
- Keirse M, Schulpen M, De Koning Gans HJ. A Randomized Controlled Comparison of Endocervical and Vaginal PGE2 in Triacetin Gel for Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour n.d.
- Kemp B, Winkler M, Rath W. Induction of labor by prostaglandin E(2) in relation to the Bishop score. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2000;71:13-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(00)00253-8.
- Kennedy JH, Quinn MA, Howie PW, Calder AA. Single shot prostaglandin gel for labor induction. Prostaglandins 1978;15:169-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0090-6980(78)80015-X.
- Kennedy JH, Stewart P, Barlow DH, Hillan E, Calder AA. Induction of labour: a comparison of a single prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet with amniotomy and intravenous oxytocin. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1982;89:704-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1982.tb05094.x.
- Khazardoost S, Hakimi P, Noorzadeh M, Shafaat M. Misoprostol for cervical ripening: a clinical trial in 60 pregnant women. Tehran Uni Med J 2011;68:595-9.
- Khoury A, Zhou Q, Gorenberg D, Nies B, Manley G, Mecklenburg F. A randomized clinical trial comparing misoprostol suppositories with continuous dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- Khoury AN, Zhou QP, Gorenberg DM, Nies BM, Manley GE, Mecklenburg FE. A comparison of intermittent vaginal administration of two different doses of misoprostol suppositories with continuous dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Maternal Fetal Med 2001;10:186-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/jmf.10.3.186.192.
- Kidanto HL, Kaguta MM, van Roosmalen J. Induction of labor with misoprostol or oxytocin in Tanzania. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2007;96:30-1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2006.09.015.
- Kieback DG, Zahradnik HP, Quaas L, Kröner-Fehmel EE, Lippert TH. Clinical evaluation of endocervical prostaglandin E2-triacetin-gel for preinduction cervical softening in pregnant women at term. Prostaglandins 1986;32:81-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0090-6980(86)90145-0.
- Kim JH, Yang HS. A comparison of intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor inducton in term pregnancy with unfavorable cervix. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 2000;43:243-7.
- Kimball FA, Ruppel PL, Noah ML, Decoster JM, delaFuente P, Castillo JM, et al. The effect of endocervical PGE2-gel (Prepidil) gel on plasma levels of 13,14-dihydro-15-keto-PGE2 (PGEM) in women at term. Prostaglandins 1986;32:527-37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0090-6980(86)90035-3.
- Kipikasa JH, Adair CD, Williamson J, Breen JM, Medford LK, Sanchez-Ramos L. Use of misoprostol on an outpatient basis for postdate pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;88:108-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.10.006.
- Koc O, Duran B, Ozdemirci S, Albayrak M, Koc U. Oxytocin versus sustained-release dinoprostone vaginal pessary for labor induction of unfavorable cervix with Bishop score ≥ 4 and ≤ 6: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2013;39:790-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.2012.02045.x.
- Kolderup L, McLean L, Grullon K, Safford K, Kilpatrick SJ. Misoprostol is more efficacious for labor induction than prostaglandin E2, but is it associated with more risk?. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:1543-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(99)70050-5.
- Komala K, Reddy M, Quadri IJ, Suneetha B, Ramya V. Comparative study of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour, maternal and foetal outcome. J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:2866-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.7860/jcdr/2013/5825.3779.
- Kovavisarach E, Wattanasiri S. Comparison of intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction at term with unfavourable cervix: a randomized controlled study. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;9:175-81.
- Kovavisarach E, Worachet W. Randomized controlled trial of intravaginal 50 mcg misoprostol and 3 mg dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction at term with unfavorable cervix. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;10:27-32.
- Kramer RL, Gilson G, Morrison DS, Martin D, Gonzalez JL, Curet LB. A randomized trial of misoprostol and oxytocin for induction of labor: safety and efficacy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80440-1.
- Kramer RL, Gilson GJ, Morrison DS, Martin D, Gonzales JL, Qualls CR. A randomized trial of misoprostol and oxytocin for induction of labor: safety and efficacy. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:387-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00363-3.
- Krammer J, O’Brien W, Williams M, Sawai S. A prospective randomized comparison of dilapan vs PGE2 for preinduction cervical ripening and their effect on labor kinetics. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;70.
- Krammer J, O’Brien W, Williams M, Sawai S. Success of labor induction varies by post-ripening cervical dilation and agent used. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;170.
- Krammer J, Williams MC, Sawai SK, O’Brien WF. Pre-induction cervical ripening: a randomized comparison of two methods. Obstet Gynecol 1995;85:614-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(95)00013-H.
- Kristoffersen M, Sande HA, Sande OS. Ripening of the cervix with prostaglandin E2-gel. A randomized study with a new ready-to-use compound of triacetin-prostaglandin-E2-gel. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1986;24:297-300. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7292(86)90087-1.
- Krithika KS, Aggarwal N, Suri V. Prospective randomised controlled trial to compare safety and efficacy of intravaginal misoprostol with intracervical cerviprime for induction of labour with unfavourable cervix. J Obstet Gynaecol 2008;28:294-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443610802054972.
- Kulshreshtha S, Sharma P, Mohan G, Singh S, Singh S. Comparative study of misoprostol vs dinoprostone for induction of labour. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2007;51:55-61.
- Kumar S, Awasthi RT, Kapur A, Srinivas S, Parikh H, Sarkar S. Induction of labour with misoprostol – a prostaglandin E1 analogue. Med J Armed Forces India 2001;57:107-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0377-1237(01)80125-8.
- Kunt C, Kanat-Pektas M, Gungor AN, Kurt RK, Ozat M, Gulerman C, et al. Randomized trial of vaginal prostaglandin E2 versus oxytocin for labor induction in term premature rupture of membranes. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2010;49:57-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1028-4559(10)60010-1.
- Kwon JS, Davies GA, Mackenzie VP. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a randomised trial. BJOG 2001;108:23-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2001.00007.x.
- Kwon JS, Mackenzie VP, Davies GAL. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a randomised trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180.
- Lackritz R, Gibson M, Frigoletto FD. Preinduction use of laminaria for the unripe cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1979;134:349-50.
- Ladfors L, Mattsson LA, Eriksson M, Fall O. A randomised trial of two expectant managements of prelabour rupture of the membranes at 34 to 42 weeks. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;103:755-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1996.tb09869.x.
- Ladfors L, Tessin I, Fall O, Erikson M, Matsson LA. A comparison of neonatal infectious outcome comparing two expectant managements of women with prelabor rupture of the membranes at 34–42 weeks. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178.
- Lamki H, Roberts A, Dunlop JM, Pinkerton JH. Induction of labour by prostaglandin E2 compared with Syntocinon. Ir Med J 1974;67:515-19.
- Lange AP, Secher NJ, Nielsen FH, Pedersen GT. Stimulation of labor in cases of premature rupture of the membranes at or near term. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1981;60:207-10.
- Lange I, St Onge R, Connors G, Ingelson B. A comparison of PGE2 gel vs the foley catheter for pre-induction cervical ripening. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1994;46.
- Lange IR, Collister C, Johnson J, Cote D, Torchia M, Freund G, et al. The effect of vaginal prostaglandin E2 pessaries on induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984;148:621-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(84)90762-2.
- Langenegger EJ, Odendaal HJ, Grové D. Oral misoprostol versus intracervical dinoprostone for induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;88:242-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.12.005.
- Larmon JE, Magann EF, Dickerson GA, Morrison JC. Outpatient cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 and estradiol. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2002;11:113-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/jmf.11.2.113.117.
- Laube DW, Zlatnik FJ, Pitkin RM. Preinduction cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 intracervical gel. Obstet Gynecol 1986;68:54-7.
- Le Roux PA, Olarogun JO, Penny J, Anthony J. Oral and vaginal misoprostol compared with dinoprostone for induction of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:201-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200202000-00007.
- Lee HY. A randomised double-blind study of vaginal misoprostol vs dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction in prolonged pregnancy. Singapore Med J 1997;38:292-4.
- Legarth J, Guldbaek E, Scher NJ. The efficiency of prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppositories versus intracervical prostaglandin gel for induction of labor in patients with unfavorable inducibility prospects. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1988;27:93-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(88)90001-9.
- Legarth J, Guldbaek E, Secher NJ. The efficiency of prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppository vs intracervical prostaglandin gel for induction of labor in patients with unfavorable Bishop score. Arch Gynecol 1985;237.
- Legarth J, Lyndrup J, Dahl C, Philipsen T, Eriksen PS. Prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppository for induction of labour: an efficient, safe and popular method. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1987;26:233-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(87)90073-6.
- Lelaidier C, Baton C, Benifla JL, Fernandez H, Bourget P, Frydman R. Mifepristone for labour induction after previous caesarean section. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;101:501-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1994.tb13150.x.
- Lelaidier C, Benifla JL, Fernandez H, Baton C, Bourget P, Bourrier MC, et al. The value of RU-486 (mifepristone) in medical indications of the induction of labor at term. Results of a double-blind randomized prospective study (RU-486 versus placebo). J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1993;22:91-100.
- Lemancewicz A, Urban R, Skotnicki MZ, Karpiuk A, Urban J. Uterine and fetal Doppler flow changes after misoprostol and oxytocin therapy for induction of labor in post-term pregnancies. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1999;67:139-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(99)00160-5.
- Lemke M, Turnquest M. Laminaria tents plus vaginal prostaglandin versus vaginal prostaglandin alone for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174.
- Lemyre M, Verret N, Turcot-Lemay L, Brassard N, Morin V. Foley catheter or vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2006.10.350.
- Levy R, Vaisbuch E, Furman B, Brown D, Volach V, Hagay ZJ. Induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes at term in women with unfavorable cervix: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Perinat Med 2007;35:126-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/JPM.2007.026.
- Levy R, Vaisbuch E, Furman B, Doitch H, Oron S, Hagay Z. Prospective randomized clinical trial of immediate induction of labor with oral misoprostol for prelabor rupture of the membranes in women with unfavorable cervix at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;193. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2005.10.127.
- Lewis GJ. Cervical ripening before induction of labour with prostaglandin E2 pessaries or a Foley’s catheter. J Obstet Gynaecol 1983;3:173-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443618309081139.
- Li XH, Ma WZ, Xu SY. The clinical observation on the effect of electroacupuncture to Sanyinjiao(SP6) and Hegu(L14) in influencing parturients’ uterine contraction in the first stage. J Beijing Uni Trad Chinese Med 1996;19.
- Lien JM, Morgan MA, Garite TJ, Kennedy KA, Sassoon DA, Freeman RK. Antepartum cervical ripening: applying prostaglandin E2 gel in conjunction with scheduled nonstress tests in postdate pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:453-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(98)70378-3.
- Liggins GC. Controlled trial of induction of labor by vaginal suppositories containing prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins 1979;18:167-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0090-6980(79)80035-0.
- Lin M, Ramsey P, Reid K, Treaster M, Nuthalapaty F, Lu G. The impact of maternal BMI, parity and GA on the comparative efficacy of transcervical foley catheter with or without an extraamniotic saline infusion for cervical ripening and labor induction in women with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2006.10.363.
- Lin M, Treaster M, Reid K, Nuthalapaty F, Ramsey P, Lu G. A randomized controlled trial of transcervical foley catheter with and without extra-amniotic saline infusion (EASI) for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2006.10.079.
- Lin MG, Ramsey PS. Foley Catheter for Labor Induction in Women With Term or Near Term Membrane Rupture 2006. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01973036 (accessed 21 March 2006).
- Livingstone I, Acharya S, Shetty A, Rice P, Danielian P, Templeton A. 100 ug of oral misoprostol versus 25 ug of vaginal misoprostol in term labour induction: a randomised comparison. J Obstet Gynaecol 2004;24.
- Lo JY, Alexander JM, McIntire DD, Leveno KJ. Efficacy of oral misoprostol in nulliparous women with premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9378(01)80478-6.
- Lo JY, Alexander JM, McIntire DD, Leveno KJ. Randomized trial of oral misoprostol in nulliparous women with premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9378(01)80477-4.
- Lo JY, Alexander JM, McIntire DD, Leveno KJ. Ruptured membranes at term: randomized, double-blind trial of oral misoprostol for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:685-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200304000-00013.
- Lo L, Ho MW, Leung P. Comparison of Prostaglandin E2 Vaginal Tablet With Amniotomy and Intravenous Oxytocin for Induction of Labour n.d.
- Lo L, Ho MW, Leung P. Comparison of prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet with amniotomy and intravenous oxytocin for induction of labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;34:149-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1994.tb02678.x.
- Lo TK, Lau WL, Wong KS, Tang LC. Sublingual misoprostol compared to artificial rupture of membranes plus oxytocin infusion for labour induction in nulliparous women with a favourable cervix at term. Hong Kong Med J 2006;12:345-50.
- Lokugamage AU, Forsyth SF, Sullivan KR, El Refaey H, Rodeck CH. Dinoprostone versus misoprostol: a randomized study of nulliparous women undergoing induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003;82:133-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0412.2003.00066.x.
- Lopes P, Besse O, Sagot P, Dantal F, De Morel P, Panel N, et al. Induction of labour with vaginal prostaglandin E2 with a ‘Spongel’. Results of a prospective randomised study taking into account Bishop’s score and the dose of PGE2 used. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1990;19.
- Lopes P, Besse O, Sagot P, Dantal F, De Morel P, Panel N, et al. PGE2 Application on a Biodegradable Support for Cervix Ripening and Induction of Labour n.d.
- Lopes P, Besse O, Sagot P, Dantal F, de Morel P, Panel N, et al. The value of the administration of prostaglandin E2 on the biodegradable support of the maturation of the cervix uteri and the induction of labor. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1991;20:827-32.
- Lopez-Farfan JA, Gamez-Guevara C. Comparison of dinoprostone (ovules and gel) to achieve cervical ripening in patients with term pregnancy that occurs with premature membranes rupture. Ginecol Obstet Mex 2010;78:110-15.
- Lucas MJ, Leveno KJ, Williams ML, Brewster S. Efficacy of Prostaglandin-E2 Gel in Cervical Ripening: Preliminary Results n.d.
- Lughmani S. Vaginal misoprostol versus oxytocin infusion for labour induction in great grand multipara. A randomized controlled trial. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2009;107. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(09)60923-1.
- Luther ER, Roux J, Popat R, Gardner A, Gray J, Soubiran E, et al. The effect of estrogen priming on induction of labor with prostaglandins. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980;137:351-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(80)90920-5.
- Lykkesfeldt G, Osler M. A comparison of three methods for inducing labor: oral prostaglandin E2, buccal desaminooxytocin, intravenous oxytocin. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1979;58:321-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016347909154590.
- Lyndrup J. Induction of labor by PGE2 and other local methods. Physiology, methods and guidelines for patient selection. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:86-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349609033293.
- Lyndrup J, Legarth J, Dahl C, Philipsen T, Eriksen PS. Induction of Labour: the Effect of Prostaglandin Pessary, i.V. Oxytocin and Lamicel n.d.
- Lyndrup J, Legarth J, Dahl C, Philipsen T, Eriksen PS. Lamicel does not promote induction of labour. A randomized controlled study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1989;30:205-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(89)90002-6.
- Lyndrup J, Legarth J, Dahl C, Philipsen T, Eriksen PS, Weber T. Induction of labour: the effect of vaginal prostaglandin or i.v. oxytocin: a matter of time only?. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1990;37:111-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(90)90104-9.
- Lyndrup J, Nickelsen C, Guldbaek E, Weber T. Induction of labour by prostaglandin-E2: intracervical gel or vaginal pessaries?. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1991;36.
- Lyndrup J, Nickelsen C, Guldbaek E, Weber T. Induction of labor by prostaglandin E2: intracervical gel or vaginal pessaries?. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1991;42:101-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(91)90169-L.
- Lyndrup J, Nickelsen C, Weber T, Mølnitz E, Guldbaek E. Induction of labour by balloon catheter with extra-amniotic saline infusion (BCEAS): a randomised comparison with PGE2 vaginal pessaries. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1994;53:189-97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(94)90118-X.
- Macer J, Buchanan D, Yonekura ML. Induction of labor with prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppositories. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:664-8.
- MacKenzie IZ. Acupuncture for Pain Relief During Induced Labour for Nulliparae 2011. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01165099 (accessed 6 January 2011).
- MacKenzie IZ, Bradley S, Embrey MP. A simpler approach to labor induction using lipid-based prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppository. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981;141:158-62.
- MacKenzie IZ, Embrey MP. A comparison of PGE2 and PGF2 alpha vaginal gel for ripening the cervix before induction of labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1979;86:167-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1979.tb10588.x.
- MacLennan AH, Fraser I, Jakubowicz DL, Murray-Arthur F, Quinn MA, Trudinger BJ. Labour Induction With PGE2 Vaginal Gel: Results of an Australian Multicentre Randomised Trial n.d.
- MacLennan A, Fraser I, Jakubowicz D, Murray-Arthur F, Quinn M, Trudinger B. Labour induction with low dose PGE2 vaginal gel: result of an Australian multicentre randomized trial. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;29:124-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1989.tb01700.x.
- MacLennan AH, Green RC. Cervical ripening and induction of labour with intravaginal prostaglandin F2 alpha. Lancet 1979;1:117-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(79)90515-4.
- MacLennan AH, Green RC. The effect of intravaginal prostaglandin F2 alpha on labour after spontaneous and artificial rupture of the membranes. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1980;20:87-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1980.tb00100.x.
- MacLennan AH, Green RC. A double blind dose trial of intravaginal prostaglandin F2 alpha for cervical ripening and the induction of labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1980;20:80-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1980.tb00098.x.
- MacLennan AH, Green RC, Bryant-Greenwood GD, Greenwood FC, Seamark RF. Ripening of the human cervix and induction of labour with purified porcine relaxin. Lancet 1980;1:220-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(80)90714-X.
- MacLennan AH, Green RC, Grant P, Nicolson R. Ripening of the human cervix and induction of labor with intracervical purified porcine relaxin. Obstet Gynecol 1986;68:598-601.
- Macones G, Stamilio D, Rampersad R, Cahill AG, Odibo AO. The efficacy of early amniotomy in nulliparous labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.10.012.
- MacPherson M. Comparison of Lamicel with prostaglandin E2 gel as a cervical ripening agent before the induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol 1984;4:205-6.
- Magann EF, Chauhan SP, McNamara MF, Bass JD, Estes CM, Morrison JC. Membrane stripping vs dinoprostone vaginal insert in the management of pregnancies beyond 41 weeks with unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(98)70334-5.
- Magann EF, Chauhan SP, McNamara MF, Bass JD, Estes CM, Morrison JC. Membrane sweeping versus dinoprostone vaginal insert in the management of pregnancies beyond 41 weeks with an unfavorable cervix. J Perinatol 1999;19:88-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7200133.
- Magann EF, Chauhan SP, Nevils BG, McNamara MF, Kinsella MJ, Morrison JC. Management of pregnancies beyond forty-one weeks’ gestation with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:1279-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(98)70334-5.
- Magann EF, McNamara MF, Whitworth NS, Chauhan SP, Thorpe RA, Morrison JC. Can we decrease postdatism in women with an unfavorable cervix and a negative fetal fibronectin test result at term by serial membrane sweeping?. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:890-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(98)70184-X.
- Magann EF, McNamara MJ, Whitworth NS, Chauhan SP, Thorp RA, Morrison JC. Can we decrease postdatism in women with an unfavorable cervix and a negative fetal fibronectin at term by serial membrane stripping. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178.
- Magann EF, Perry KG, Dockery JR, Bass JD, Chauhan SP, Morrison JC. Cervical ripening before medical induction of labor: a comparison of prostaglandin E2, estradiol, and oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1702-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)91401-3.
- Magnani M, Cabrol D. Induction of labour with PGE2 after cervical ripening with oestradiol. Control and Management of Parturition 23rd Baudelocque Symposium 1986;151:109-18.
- Magos AL, Noble MCB, Yuen AWT, Rodeck CH. Controlled study comparing vaginal prostaglandin E2 pessaries with intravenous oxytocin for the stimulation of labour after spontaneous rupture of the membranes. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1983;90:726-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1983.tb09302.x.
- Magtibay P, Ogburn P, Harris D, Suman V, Ramin K. Misoprostol as a labour induction agent: a pilot study comparing efficacy, safety and cost. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174.
- Magtibay PM, Ramin KD, Harris DY, Ramsey PS, Ogburn L. Misoprostol as a labor induction agent. J Maternal Fetal Med 1998;7:15-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(199801/02)7:1<15::AID-MFM4>3.3.CO;2-S.
- Mahmood TA. Induction of Labour in Primigravid With Unfavourable Cervices: A Comparison of PGE2 Gel (2 mg) With PGE2 Pessary (3 mg) n.d.
- Mahmood TA. A prospective comparative study on the use of prostaglandin E2 gel (2 mg) and prostaglandin E2 tablet (3 mg) for the induction of labour in primigravid women with unfavorable cervices. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1989;33:169-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(89)90210-4.
- Mahmood TA, Dick MJ. A randomized trial of management of pre-labor rupture of membranes at term in multiparous women using vaginal prostaglandin gel. Obstet Gynecol 1995;85:71-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(94)00316-6.
- Mahmood TA, Dick MJW, Smith NC. Management of spontaneous rupture of the membranes and no uterine activity in healthy primigravidae after 34 weeks’ gestation. Lancet 1989;1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(89)92231-9.
- Mahmood TA, Dick MJW, Smith NC, Templeton A. Management of Spontaneous Rupture of Membranes at Term Without Uterine Activity in Healthy Primigravidae: A Prospective Study (PGE2 Gel Vs Conservative Treatment) n.d.
- Mahmood TA, Dick MJ, Smith NC, Templeton AA. Role of prostaglandin in the management of prelabour rupture of the membranes at term. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;99:112-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1992.tb14466.x.
- Mahmood TA, Rayner A, Smith NC, Beat I. A randomized prospective trial comparing single dose prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel with forewater amniotomy for induction of labour. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1995;58:111-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(95)80008-G.
- Mahmood TA, Reyner A, Smith NC. A Prospective Randomized Study of Induction of Labour With Favourable Cervix at Term: A Comparison Between PGE2 Gel Single Dose Vs Forewater Amniotomy and Delayed Oxytocin Infusion n.d.
- Majoko F, Zwizwai M, Lindmark G, Nyström L. Labor induction with vaginal misoprostol and extra-amniotic prostaglandin F2alpha gel. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002;76:127-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(01)00570-7.
- Majoko F, Zwizwai M, Nystrom L, Lindmark G. Vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour: a more effective agent than prostaglandin f2 alpha gel and prostaglandin e2 pessary. Central Afr J Med 2002;48:123-8.
- Malik HZ, Khawaja NP, Zahid B, Rehman R. Sublingual versus oral misoprostol for induction of labour in prelabour rupture of membranes at term. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2010;20:242-5.
- Malik N, Gittens L, Gonzalez D, Bardeguez A, Ganesh V, Apuzzio J. Clinical amnionitis and endometritis in patients with premature rupture of membranes: endocervical prostaglandin E2 gel versus oxytocin for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1996;88:540-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(96)00266-9.
- Manley J, Nguyen L, Shlossman P, Colmorgen G, Sciscione A. A randomized prospective comparison of the intracervical foley bulb to intravaginal misoprostol (cytotec) for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180.
- Margulies M, Campos Perez GA, Voto LS. Misoprostol to induce labour. Lancet 1992;339. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(92)90194-8.
- Massil HY, Baker AC, O’Brien PM. A comparison of oral prostaglandin E2 tablets with intravenous oxytocin for stimulation of labor after premature rupture of membranes at term. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1988;67:703-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349809004293.
- Matonhodze B, Alfirevic Z, Hofmeyr J, Brocklehurst P. Titrated oral misoprostol for labour induction: a randomised trial. Prenatal Neonatal Med 2000;5.
- Matonhodze B, Alfirevic Z, Hofmeyr J, Campbell L, Brocklehurst P. Titrated oral misoprostol for labour induction: a random allocation trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20.
- Matonhodze BB, Hofmeyr GJ, Levin J. Labour induction at term: a randomised trial comparing Foley catheter plus titrated oral misoprostol solution, titrated oral misoprostol solution alone, and dinoprostone. S Afr Med J 2003;93:375-9.
- Mawire CJ, Chipato T, Rusakaniko S. Extra-amniotic saline infusion versus extra-amniotic prostaglandin F2alpha for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1999;64:35-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(98)00174-X.
- McCaul JF, Williams LM, Martin RW, Magann EF, Gallagher L, Morrison JC. Comparison of induction methods for premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(12)91174-6.
- McCaul JF, Rogers LW, Perry KG, Martin RW, Allbert JR, Morrison JC. Premature rupture of membranes at term with an unfavorable cervix: comparison of expectant management, vaginal prostaglandin, and oxytocin induction. Southern Med J 1997;90:1229-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00007611-199712000-00013.
- McColgin SW, Hampton HL, McCaul JF, Howard PR, Andrew ME, Morrison JC. Stripping membranes at term: can it safely reduce the incidence of post-term pregnancies?. Obstet Gynecol 1990;76:678-80.
- McColgin SW, Patrissi GA, Morrison JC. Stripping Membranes at Term: Is It Safe and Efficacious? n.d.
- McColgin SW, Patrissi GA, Morrison JC. Stripping the fetal membranes at term. Is the procedure safe and efficacious?. J Reprod Med 1990;35:811-14.
- McKenna DS, Costa SW, Samuels P. Prostaglandin E2 cervical ripening without subsequent induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:11-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-199907000-00003.
- McKenna DS, Ester JB, Proffitt M, Waddell KR. Misoprostol outpatient cervical ripening without subsequent induction of labor: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 2004;104:579-84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000136479.72777.56.
- McLaren M, Greer IA, Smith JR, Godfree V, Graham N, Calder AA. Maternal plasma bicycling PGE2 levels following vaginal administration of prostaglandin E2 pessaries in full term pregnancies. Prog Clin Biol Res 1987;242:199-203.
- McQueen D. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Expectant With Active Management in Early Rupture of the Membranes at Term 1992.
- McQueen D, Neilson JP, Whittle MJ. Pre-labour rupture of membranes with an unripe cervix: a random trial of management. J Obstet Gynaecol 1990;10:495-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443619009151252.
- Medearis AL. Postterm Pregnancy: Active Labor Induction (PGE2 Gel) Not Associated With Improved Outcomes Compared to Expectant Management. A Preliminary Report n.d.
- Megalo A, Petignat P, Hohlfeld P. Influence of misoprostol or prostaglandin E(2) for induction of labor on the incidence of pathological CTG tracing: a randomized trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2004;116:34-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2004.01.038.
- Mehrotra S, Singh U, Gupta HP. A prospective double blind study using oral versus vaginal misoprostol for labour induction. J Obstet Gynaecol 2010;30:461-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443615.2010.485253.
- Mei-Dan E. Cervical ripening with extra amniotic saline infusion: a randomized comparison of two mechanical devices. Reprod Sci 2012;19.
- Mei-Dan E, Walfisch A, Easton SS, Hallak M. Foley’s catheter with extra-amniotic saline infusion – a faster and cheaper ripener device: prospective randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009;201. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2009.10.329.
- Mei-Dan E, Walfisch A, Suarez-Easton S, Hallak M. Comparison of two mechanical devices for cervical ripening: a prospective quasi-randomized trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:723-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2011.591459.
- Mercer B, Pilgram P, Sibai B. Low Dose Oxytocin Vs a Routine Induction Protocol for the Induction of Labor n.d.
- Mercer BM, Crocker LG, Boe NM, Sibai BM. Induction versus expectant management in premature rupture of the membranes with mature amniotic fluid at 32 to 36 weeks: a randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:775-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(93)90004-3.
- Mercer BM, McNanley T, O’Brien JM, Randal L, Sibai BM. Early versus late amniotomy for labor induction: a randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1321-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)91379-3.
- Meydanli MM, Calişkan E, Burak F, Narin MA, Atmaca R. Labor induction post-term with 25 micrograms vs. 50 micrograms of intravaginal misoprostol. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;81:249-55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(03)00042-0.
- Meyer M, Pflum J. Outpatient administration of misoprostol decreases induction time. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Meyer M, Pflum J, Howard D. Outpatient misoprostol compared with dinoprostone gel for preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105:466-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000152341.31873.d9.
- Milchev N, Kuzmanov B, Terzhumanov R. Cytotec: an effective drug for the induction of labor. Akush Ginekol 2003;42:9-11.
- Miller AM, Rayburn WF, Smith CV. Patterns of uterine activity after intravaginal prostaglandin E2 during preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:1006-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(91)90459-5.
- Miller AM, Rayburn WF, Smith CV, Allen K, Bane T. Uterine activity using ambulatory tocodynamometry after intravaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(91)90997-6.
- Misra M, Vavre S. Labour induction with intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel and intravenous oxytocin in women with a very unfavourable cervix. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;34:511-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1994.tb01097.x.
- Moberger B, Hammarstrom M, Hjertberg R, Berg A. Neonatal Outcome After 12 Vs 24 Hours of Conservative Management in Primigravidae With PROM at Term n.d.
- Modarres M, Rahime KF. The use of breast stimulation to prevent postdate pregnancy. Med J Islamic Republic Iran 2000;14:211-15.
- Modlock J. Can Acupuncture Be Used As Preparation for Induction of Labour 2006. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00279071 (accessed 21 March 2006).
- Modlock J, Nielsen BB, Uldbjerg N. Acupuncture for the induction of labour: a double-blind randomised controlled study. BJOG 2010;117:1255-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2010.02647.x.
- Moini A, Riazi K, Honar H, Hasanzadeh Z. Preinduction cervical ripening with the Foley catheter and saline infusion vs. cervical dinoprostone. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;83:211-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(03)00266-2.
- Mol BW, van der Post J, Rengerink KO, Papatsonis D, Jozwiak M, van Huizen M, et al. Induction of labor at term: a comparison of Foley catheter and prostaglandins (trial registration NTR 1646). Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:3-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.10.011.
- Moldin PG, Sundell G. Induction of labour: a randomised clinical trial of amniotomy versus amniotomy with oxytocin infusion. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;103:306-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1996.tb09733.x.
- Moller M. Trial to Assess the Effects of Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour by Prostaglandin Administration 1991.
- Müller M, Thomsen AC, Sørensen J, Forman A. Oxytocin- or low-dose prostaglandin F2 alpha-infusion for stimulation of labor after primary rupture of membranes. A prospective, randomized trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1987;66:103-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348709083028.
- Montealegre JA, Botero LF, Sabogal G. Labor induction with unfavorable cervix: randomized controlled trial double blind method. Oxitocyn vs. misoprostol. Rev Colomb Obstet Ginecol 1999;50:133-7.
- Moodley J, Venkatachalam S, Songca P. Misoprostol for cervical ripening at and near term: a comparative study. S Afr Med J 2003;93:371-4.
- Moraes Filho OB, Albuquerque RM, Cecatti JG. A randomized controlled trial comparing vaginal misoprostol versus Foley catheter plus oxytocin for labor induction. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2010;89:1045-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349.2010.499447.
- Morales WJ, Lazar AJ. Expectant management of rupture of membranes at term. South Med J 1986;79:955-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00007611-198608000-00010.
- Morgan Ortiz F, Báez Barraza J, Quevedo Castro E, Cuetos Martínez CB, Osuna Ramírez I. Misoprostol and oxytocin for induction of cervical ripening and labor in patients with term pregnancy and premature membrane rupture. Ginecol Obstet Mex 2002;70:469-76.
- Mosquera J, Mesa JC, Navarro H, Cobo E, Neira C, Zuniga J. Study of the efficacy of misoprostol compared with oxytocin for labor induction in women with prolonged amenorrhea. Rev Colomb Obstet Ginecol 1999;50:7-12.
- Mozurkewich E, Horrocks J, Daley S, Von Oeyen P, Sarvis A, Halvorson M, et al. The misoprom study: a randomized controlled trial of misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Mozurkewich E, Horrocks J, Daley S, Von Oeyen P, Halvorson M, Johnson M, et al. The MisoPROM study: a multicenter randomized comparison of oral misoprostol and oxytocin for premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:1026-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/S0002-9378(03)00845-7.
- Mullin P, House M, Paul R, Wing D. A comparison of vaginally administered misoprostol with extraamniotic saline infusion for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(01)80475-0.
- Murphy AJ, Jalland M, Pepperell RJ, Quinn MA. Use of vaginal prostaglandin gel before induction of labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1980;20:84-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1980.tb00099.x.
- Murray HG, Buonocore A, Hawley J. A randomized trial of two preparations of vaginal prostaglandin for pre-induction cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:880-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(95)00302-8.
- Murray HG, Buonocore A, Hawley J. A Randomised Trial of Two Preparations of Vaginal Prostaglandin for Pre-Induction Cervical Ripening n.d.
- Murthy BK, Arkalgud MS. Misoprostol alone versus a combination of dinoprostone and oxytocin for induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2006;56:413-16.
- Naef RW, Allbert JR, Ross EL, Weber M, Martin RW, Morrison JC. Premature rupture of membranes at 34 to 37 weeks’ gestation: aggressive versus conservative management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:126-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(98)70638-6.
- Naef RW, Allbert JR, Weber BM, Roach H, Martin RW, Morrison JC. Premature rupture of membranes at 34-37 weeks’ gestation: aggressive vs conservative management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170.
- Nager CW, Key TC, Moore TR. Cervical ripening and labor outcome with preinduction intracervical prostaglandin E2 (Prepidil) gel. J Perinatol 1987;7:189-93.
- Nagpal MB, Raghunandan C, Saili A. Oral misoprostol versus intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for active management of premature rupture of membranes at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2009;106:23-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2009.03.014.
- Naismith WC, Barr W, MacVicar J. Comparison of intravenous prostaglandins F 2 and E 2 with intravenous oxytocin in the induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1973;80:531-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1973.tb15975.x.
- Nanda S, Singhal SR, Papneja A. Induction of labour with intravaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 gel: a comparative study. Trop Doct 2007;37:21-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/004947507779952032.
- Nasir S, Chaudhry R. Comparison of intracervical foley catheter plus oral misoprostol with oral misoprostol alone for cervical ripening in primigravidas at term. BJOG 2012;119:11-2.
- Nassar A, Awwad J, Khalil A, Abu-Musa A, Mehio G, Usta I. A Randomised Comparison of Patient Satisfaction With Vaginal and Sublingual Misoprostol for Induction of Labour at Term 2007. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00140114 (accessed 21 March 2006).
- Natale R, Milne JK, Campbell MK, Potts PG, Webster K, Halinda E. Management of premature rupture of membranes at term: randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:936-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(94)70062-1.
- Natale R, Milne K, Campbell K, Wester K, Halinda E. Management of premature rupture of membranes at term: randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9378(94)70062-1.
- Neiger R, Greaves PC. Comparison between vaginal misoprostol and cervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Tenn Med 2001;94:25-7.
- Neilson DR, Prins RP, Bolton RN, Mark C, Watson P. A comparison of prostaglandin E2 gel and prostaglandin F2 alpha gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;146:526-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(83)90795-0.
- Netta D, Visintainer P, Bayliss P. Does cervical membrane stripping increase colonization of group b streptococcus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187.
- Newman M, Newman R. Multiple-dose PGE2 cervical ripening on an outpatient basis: safety and efficacy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80444-9.
- Ngai CSW, To WWK, Lao T, Ho PC. Cervical Priming With Oral Misoprostol in Prelabour Rupture of Membranes at Term n.d.
- Ngai SW, Chan YM, Lam SW, Lao T. Prospective randomised study to compare misoprostol and oxytocin for labour induction in prelabour rupture of membranes in term pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105.
- Ngai SW, Chan YM, Lam SW, Lao TT. Labour characteristics and uterine activity: misoprostol compared with oxytocin in women at term with prelabour rupture of the membranes. BJOG 2000;107:222-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2000.tb11693.x.
- Ngai SW, To WK, Lao T, Ho PC. Cervical priming with oral misoprostol in pre-labor rupture of membranes at term. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:923-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(96)00072-5.
- Nguyen VT, Do DV, Tran TS, Nguyen PT. Labor induction using sub-lingual misoprostol for prelabor rupture of membranes at term: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2012;119. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(12)62021-9.
- Nicoll AE, Mackenzie F, Greer IA, Norman JE. Vaginal application of the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized controlled trial to determine effects on maternal and fetal hemodynamics. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:958-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2001.111797.
- Nigam A, Madan M, Puri M, Agarwal S, Trivedi SS. Labour induction with 25 micrograms versus 50 micrograms intravaginal misoprostol in full term pregnancies. Trop Doct 2010;40:53-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/td.2009.090203.
- Nigam A, Singh VK, Dubay P, Pandey K, Bhagoliwal A, Prakash A. Misoprostol vs. oxytocin for induction of labor at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;86:398-400. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.05.010.
- Nimrod C, Currie J, Yee J, Dodd G, Persaud D. Cervical ripening and labor induction with intracervical triacetin base prostaglandin E2 gel: a placebo-controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 1984;64:476-9.
- Niromanesh S, Mosavi-Jarrahi A, Samkhaniani F. Intracervical Foley catheter balloon vs. prostaglandin in preinduction cervical ripening. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;81:23-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(02)00392-2.
- Noah ML, DeCoster JM, Fraser TJ, Orr JD. Preinduction cervical softening with endocervical PGE2 gel. A multi-center trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1987;66:3-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348709092944.
- Noah ML, Kimball FA, Ruppel PL, de la Fuente P, Decoster JM. The effect of intracervical PGEz-gel on plasma levels of 13,14-hihydro-15-keto-PGE2 (PGEM) in women at term. Arch Gynecol 1985;237.
- Nopdonrattakoon L. A comparison between intravaginal and oral misoprostol for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2003;29:87-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1341-8076.2003.00084.x.
- Norman J. Pharmacokinetics of Nitric Oxide Donors Administered Per Vaginam in the Third Trimester of Pregnancy 2001. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN14616088 (accessed 26 July 2001).
- Norzilawati MN, Mashita MK, Shuhaila A, Zaleha AM. Vaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone for induction of labor. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;23.
- Ntsaluba A. The use of an indwelling catheter compared to intracervical prostaglandin gel for cervical ripening prior to induction of labour. O&Amp;G Forum n.d.:17-21.
- Nunes F, Rodrigues R, Meirinho M. Randomized comparison between intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:626-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(99)70503-X.
- Nuutila M, Kajanoja P. Cervical ripening prior to labor induction with intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel in patients with preeclampsia: a placebo-controlled study. Hypertens Pregn 1995;14:313-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/10641959509015677.
- Nuutila M, Kajanoja P. A randomized comparison of intravaginal and intracervical administration of prostaglandin E2 in cervical ripening. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1995;73:110-11.
- Nuutila M, Kajanoja P. Local administration of prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and labor induction: the appropriate route and dose. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:135-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349609033305.
- Oboro VO, Tabowei TO. Outpatient misoprostol cervical ripening without subsequent induction of labor to prevent post-term pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005;84:628-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.0001-6349.2005.00655.x.
- O’Brien JM, Mercer B, Cleary N, Sibai BM. Efficacy of outpatient induction with low dose intravaginal prostaglandin E2: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)91293-2.
- O’Brien JM, Mercer BM, Cleary NT, Sibai BM. Efficacy of outpatient induction with low-dose intravaginal prostaglandin E2: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1855-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)90440-9.
- Oliveira MV, Oberst PV, Leite GK, Aguemi A, Kenj G, Leme VD, et al. Cervical Foley catheter versus vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labor: a randomized clinical trial. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2010;32:346-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-72032010000700007.
- Olmo I, Rodenas JJ, Bou J, Jaca A, Moraga R, Monleon J. Labour induction. Oxytocin ev vs dinoprostone (PGE2) vaginal propess. J Perinatal Med 2001;29.
- Omar NS, Tan PC, Sabir N, Yusop ES, Omar SZ. Coitus to expedite the onset of labour: a randomised trial. BJOG 2013;120:338-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12054.
- Ophir E, Haj N, Korenblum R, Oettinger M. Cervical ripening before induction of labor: comparison of an intracervical Foley catheter and prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets. Int J Feto-Maternal Med 1992;5:101-6.
- Orhue AA. Induction of labour at term in primigravidae with low Bishop’s score: a comparison of three methods. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1995;58:119-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(95)80009-H.
- Osman I, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, Greer A, Norman JE. The ‘PRIM’ study: a randomised comparison of prostaglandin with isosorbide mononitrate for preinduction cervical ripening at term. J Obstet Gynaecol 2004;24.
- Osman I, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Murray HM, Greer IA, Norman JE. The ‘PRIM’ study – a randomised comparison of prostaglandin with isosorbide mononitrate for pre-induction cervical ripening at term. BJOG 2005;112.
- Osman I, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Murray HM, Greer IA, Norman JE. The ‘PRIM’ study: a randomized comparison of prostaglandin E2 gel with the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening before the induction of labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;194:1012-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2005.10.812.
- Osman I, Norman J, Mackenzie F, Murray H, Norrie J, Greer I. The ‘PRIM’ study: a randomised comparison of prostaglandin E2 gel with the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening prior to the induction of labour at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.10.561.
- Ottervanger HP, Holm JP, Keirse M. Premature rupture of the membranes at term: induction of labour or expectant care?. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1991;36.
- Ottervanger HP, Holm JP, Keirse M. A randomized trial of expectant vs active management for prelabour rupture of the membranes at term. J Perinatal Med 1992;20.
- Ottervanger HP, Keirse MJ, Smit W, Holm JP. Controlled comparison of induction versus expectant care for prelabor rupture of the membranes at term. J Perinat Med 1996;24:237-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/jpme.1996.24.3.237.
- Ottinger WS, Menard MK, Brost BC. A randomized clinical trial of prostaglandin e2 intracervical gel and a slow release vaginal pessary for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:349-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(98)70363-1.
- Owen J, Winkler CL, Harris BA, Hauth JC, Smith MC. A randomized, double-blind trial of prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:991-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(91)90456-2.
- Owen J, Winkler CL, Hauth JC, Harris BA, Smith MC. A randomized, double blind trial of prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and a meta analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(91)90982-W.
- Owolabi AT, Kuti O, Ogunlola IO. Randomised trial of intravaginal misoprostol and intracervical Foley catheter for cervical ripening and induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol 2005;25:565-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443610500231450.
- Ozkan S, Calişkan E, Doğer E, Yücesoy I, Ozeren S, Vural B. Comparative efficacy and safety of vaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone vaginal insert in labor induction at term: a randomized trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2009;280:19-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-008-0843-9.
- Paisarntantiwong R, Getgan M. A comparison between single dose of 50 microg oral misoprostol and 25 microg vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. J Med Assoc Thai 2005;88:56-62.
- Pandis GK, Papageorghiou AT, Otigbah CM, Howard RJ, Nicolaides KH. Randomized study of vaginal misoprostol (PGE(1)) and dinoprostone gel (PGE(2)) for induction of labor at term. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;18:629-35. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.0960-7692.2001.00595.x.
- Papageorgiou I, Tsionou C, Minaretzis D, Michalas S, Aravantinos D. Labor characteristics of uncomplicated prolonged pregnancies after induction with intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel versus intravenous oxytocin. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1992;34:92-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000292734.
- Papanikolaou EG, Plachouras N, Drougia A, Andronikou S, Vlachou C, Stefos T, et al. Comparison of misoprostol and dinoprostone for elective induction of labour in nulliparous women at full term: a randomized prospective study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2004;2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-2-70.
- Parazzini F, Benedetto C, Danti L, Zanini A, Facchinetti F, Ettore G, et al. A randomized comparison of vaginal prostaglandin E2 with oxytocin plus amniotomy for induction of labour in women with intermediately ripe cervices. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1998;81:15-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0301-2115(98)00148-1.
- Parewijck W, Thiery M. Cervical Ripening: Randomized Comparative Study of Extra-Amniotic Vs Intracervical PGE2 Gel n.d.
- Parikh SC, Parikh NS. Comparison of local PGE2 gel & iv oxytocin in induction of labour. J Obstet Gynecol India 2001;51:57-9.
- Parisaei M, Erskine KJ. Is expensive always better? Comparison of two induction agents for term rupture of membranes. J Obstet Gynaecol 2008;28:290-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443610802042951.
- Parisaei MP, Erskine KJE. Comparison of sub-lingual misoprostol with standard regime vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel for the induction of labour after term rupture of membranes. J Obstet Gynaecol 2005;25.
- Patil PK, Swamy MK, Rao Radhika K. Oral misoprostol vs intra-cervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2005;55:128-31.
- Paul S, Bhowmick R. A Randomised Controlled Trial of Oral Prostaglandin E2 (Dinoprostone) and Oxytocin Infusion in Induction of Labour 1992:1-4.
- Paungmora N, Herabutaya Y. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a randomised controlled trial. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;15.
- Paungmora N, Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P, Punyavachira P. Comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor at term: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2004;30:358-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.2004.00215.x.
- Pearce JM, Cardozo L. Prolonged pregnancy: results of supplemental analysis. BMJ 1988;297:715-17.
- Peccerillo JA, Egan JFX, Borgida A, Campbell WA. Comparison of intracervical PGE2 to intravaginal PGE2 for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)90821-8.
- Pedrazzoli J, Irion O, Mermillod B, Beguin F. A Randomized Comparison of an Intravaginal and an Intracervical Prostaglandin E2 Gel for Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour n.d.
- Pedrazzoli J, Irion O, Mermillod B, Beguin F. A randomised comparison of an intravaginal and an intracervical Prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80439-5.
- Peedicayil A, Jasper P, Francis S, Jayakrishnan K, Mathai M, Regi A. A randomized trial of extra-amniotic Foley catheter and intra-cervical prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening. J Clin Epidemiol 1998;51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0895-4356(98)90065-8.
- Pennell CE, Henderson JJ, O’Neill MJ, McCleery S, Doherty DA, Dickinson JE. Induction of labour in nulliparous women with an unfavourable cervix: a randomised controlled trial comparing double and single balloon catheters and PGE2 gel. BJOG 2009;116:1443-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02279.x.
- Pennell CE, Jewell M, Doherty D, Dickinson JE. Induction of labor with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2003.10.550.
- Perche S, Guerra M, Reyna E, Hidalgo M, Santos J, Mejia J, et al. Vaginal isosorbide mononitrate or misoprostol for cervical ripening in term pregnancies. Clin Invest Ginecol Obstet 2009;36:203-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gine.2009.03.005.
- Perez Picanol E, Gamissans O, Lecumberri J, Jimenez M, Vernet M. Ripening the Cervix With Intracervical PGE2 Gel in Term Pregnancies With Premature Rupture of Membranes n.d.
- Perez Picanol E, Vernet M, Armengol R, Perez Ares C, Lecumberri J, Gamissans O. Comparison of two different therapeutic attitudes in premature rupture of membranes. J Perinatal Med 1992;20.
- Perry MY, Leaphart WL. A randomized controlled trial using intracervical versus posterior fornix placement of dinoprostone. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200304001-00080.
- Perry MY, Leaphart WL. Randomized trial of intracervical versus posterior fornix dinoprostone for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200304001-00024.
- Perry MY, Leaphart WL. Randomized trial of intracervical versus posterior fornix dinoprostone for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 2004;103:13-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000109217.24211.9D.
- Perryman D, Yeast JD, Holst V. Cervical Ripening: A Prospective, Randomized Study Comparing Prostaglandin E2 Gel With Prostaglandin E2 Suppositories n.d.
- Perryman D, Yeast JD, Holst V. Cervical ripening: a randomized study comparing prostaglandin E2 gel to prostaglandin E2 suppositories. Obstet Gynecol 1992;79:670-2.
- Pevzner L, Alfirevic Z, Powers B, Wing D. Cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with misoprostol and dinoprostone cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009;201. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2009.10.324.
- Pevzner L, Alfirevic Z, Powers BL, Wing DA. Cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with misoprostol and dinoprostone cervical ripening and labor induction. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2011;156:144-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2011.01.015.
- Pevzner L, Rayburn WF, Rumney P, Wing DA. Factors predicting successful labor induction with dinoprostone and misoprostol vaginal inserts. Obstet Gynecol 2009;114:261-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181ad9377.
- Pevzner L, Rumney P, Petersen R, Wing D. Predicting a successful induction of labor: a secondary analysis of misoprostol vaginal insert trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008;199. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2008.09.245.
- Pezvner L, Powers BL, Wing DA. Factors predicting successful induction of labor with misoprostol vaginal insert. Reprod Sci 2011;18:A182-3.
- Pi P, Zhu F. Clinical observation of misoprostol on induction in late pregnancy. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 1999;24:195-7.
- Pollnow DM, Broekhuizen FF. Randomized, double-blind trial of prostaglandin E2 intravaginal gel versus low-dose oxytocin for cervical ripening before induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:1910-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(96)70228-4.
- Pongsatha S, Vijittrawiwat A, Tongsong T. A comparison of labor induction by oral and vaginal misoprostol. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;88:140-1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.10.011.
- Poornima B, Dharma Reddy DB. Premature rupture of membranes at term: immediate induction with PGE(2) gel compared with delayed induction with oxytocin. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2011;61:516-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13224-011-0086-8.
- Poulsen HK, Müller LK, Westergaard JG, Thomsen SG, Giersson RT, ArngrÌmsson R. Open randomized comparison of prostaglandin E2 given by intracervical gel or vagitory for preinduction cervical ripening and induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1991;70:549-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349109007915.
- Shetty A, Martin R, Danielian P, Templeton A. A comparison of two dose regimens of oral misoprostol in the induction of labour at term: a random allocation controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;21.
- Prager M, Eneroth-Grimfors E, Edlund M, Marions L. A randomised controlled trial of intravaginal dinoprostone, intravaginal misoprostol and transcervical balloon catheter for labour induction. BJOG 2008;115:1443-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01843.x.
- Powers B, Parker L, Miller H, Wing DA, Rayburn W. A double-blind, randomized, multicenter, dose-ranging phase II study of the misoprostol vaginal insert. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.10.101.
- Prager M, Eneroth-Grimfors E, Edlund M, Marions L. A randomised controlled trial of intravaginal dinoprostone, intravaginal misoprostol and transcervical balloon catheter for labour induction. BJOG 2008;115:1443-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01843.x.
- Prasad RNV, Adaikan PG, Arulkumaran S, Ratnam SS. Preinduction cervical priming with PGE2 vaginal film in primigravidae: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study. Prostag Leukotr Ess 1989;36:185-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0952-3278(89)90060-4.
- Prins RP, Bolton RN, Mark C, Neilson DR, Watson P. Cervical ripening with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Obstet Gynecol 1983;61:459-62.
- Puertas A, Mino M, Manzanares S, Ceballos C, Alamo F, Miranda JA. Labor induction with intracervical prostaglandin E2 versus oxytocin in premature rupture of membranes. Prenatal Neonatal Med 1996;1.
- Puertas A, Mino M, Moreno I, Carrillo MP, Mozas J, Miranda JA. Induced labour in the premature rupture of membranes at term. Comparison of E2 intracervical prostaglandine with oxytocine. Prog Obstet Ginecol 1997;40:13-8.
- Puga O, Nien JK, Gomez R, Medina L, Carstens M, Gonzalez R, et al. Premature rupture of membranes after 35 weeks: a randomized clinical trial of induction of labor with oral versus vaginal administration of misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- Pulle C, Granese D, Panama S, Celona A. Cervical ripening and induction of labour by single intracervical PGE2-gel application. Acta Ther 1986;12:5-12.
- Putnam K, Magann EF, Doherty DA, Poole AT, Magann MI, Warner WB, et al. Randomized clinical trial evaluating the frequency of membrane sweeping with an unfavorable cervix at 39 weeks. Int J Womens Health 2011;3:287-94.
- Quinn MA, Murphy AJ, Kuhn RJP, Robinson HP, Brown JB. A double blind trial of extra-amniotic oestriol and prostaglandin F2alpha gels in cervical ripening. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1981;88:644-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1981.tb01223.x.
- Rabl M, Ahner R, Bitschnau M, Zeisler H, Husslein P. Acupuncture for cervical ripening and induction of labor at term: a randomized controlled trial. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2001;113:942-6.
- Rabl M, Joura EA, Yücel Y, Egarter C. A randomized trial of vaginal prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor. Insert vs. tablet. J Reprod Med 2002;47:115-19.
- Rahman H. Comparative evaluation of 50 ug oral misoprostol and 25 ug iIntra-vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2013;35:408-16.
- Rahman H, Pradhan A, Kharka L, Renjhen P, Kar S, Dutta S. Comparative evaluation of 50 microgram oral misoprostol and 25 microgram intravaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a randomized trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2013;35:408-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1701-2163(15)30931-2.
- Rameez MF, Goonewardene IM. Nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for pre-induction cervical ripening at 41 weeks’ gestation: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2007;33:452-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.2007.00573.x.
- Ramsey P, Harris D, Ogburn P, Heise R, Magtibay P, Ramin K. Comparative efficacy of prostaglandin analogues dinoprostone and misoprostol as labor preinduction agents. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178.
- Ramsey P, Meyer L, Harris D, Ogburn P, Ramin K. Characterization of cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with dinoprostone and misoprostol cervical ripening/labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184.
- Ramsey PS, Harris DY, Ogburn PL, Heise RH, Magtibay PM, Ramin KD. Comparative efficacy and cost of the prostaglandin analogs dinoprostone and misoprostol as labor preinduction agents. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:560-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2003.150.
- Ramsey PS, Meyer L, Walkes BA, Harris D, Ogburn PL, Heise RH, et al. Cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with dinoprostone and misoprostol cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105:85-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000146638.51536.09.
- Rath DM, Manas K. Induction of labor with oral misoprostol in women with prelabor rupture of membranes at term. J Obstet Gynecol India 2007;57:505-8.
- Rath W, Heyl W, Kemp B. Intracervical versus intravaginal PGE2 gel for induction of labor. Perinatal Medizin 1998;10:81-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s001520050089.
- Rath W, Kemp B, Heyl W. Prostaglandin E2 as a vaginal gel, intracervical gel or vaginal tablet for induction of labor: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 1999;59:323-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-1999-15369.
- Ratnam SS, Khew KS, Chen C, Lim TC. Oral prostaglandin E2 in induction of labour. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1974;14:26-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1974.tb00818.x.
- Ray DA, Garite TJ. Prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor in patients with premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:836-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(92)91344-A.
- Rayburn W, Barss V, Caritis S, Mandsager N, Molina R, Spitzberg E, et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Multicenter Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of an Intravaginal Hydrogel Controlled Release Pessary for the Delivery of Prostaglandin E2 for Cervical Ripening Prior to Induction of Labor n.d.
- Rayburn W, Gosen R, Ramadei C, Woods R, Scott J. Outpatient cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 gel in uncomplicated postdate pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988;158:1417-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(88)90376-6.
- Rayburn W, Lucas M, Gittens L, Goodwin TM, Baxi L, Gall S, et al. Attempted vaginal birth after cesarean section: a multicenter comparison of outpatient prostaglandin E2 gel with expectant management. Prim Care Update Ob Gyns 1998;5:182-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1068-607X(98)00096-1.
- Rayburn WF, Gittens LN, Lucas MJ, Gall SA, Martin ME. Weekly administration of prostaglandin e2 gel compared with expectant management in women with previous cesareans Prepidil gel study group. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:250-4.
- Rayburn WF, Wapner RJ, Barss VA, Spitzberg E, Molina RD, Mandsager N, et al. An intravaginal controlled-release prostaglandin E2 pessary for cervical ripening and initiation of labor at term. Obstet Gynecol 1992;79:374-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-199203000-00009.
- Richardson CJ, Evans JF, Meisel RL. Duration of intracervical prostaglandin and Cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(91)91314-M.
- Rix P, Andersen K, Ladehoff P, Moller AM, Zdravkovic M. PGE2 Vaginal Tablets Compared to Ready Prepared Cervical PGE2 Gel in Ability to Induce Cervical Ripening and Labour by Low Bishop Scores n.d.
- Rix P, Ladehoff P, Moller AM, Tilma KA, Zdravkovic M. Cervical ripening and induction of delivery by local administration of prostaglandin E2 gel or vaginal tablets is equally effective. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:45-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349609033282.
- Rizvi S, Umber F, Yusuf AW. Labour induction at term; oral versus intravaginal misoprostol. Ann King Edward Med Coll 2007;13:119-21.
- Roach VJ, Rogers MS. Pregnancy outcome beyond 41 weeks gestation. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;59:19-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(97)00179-3.
- Roberts WE, North DH, Speed JE, Martin JN, Palmer SM, Morrison JC. Comparative study of prostaglandin, laminaria, and minidose oxytocin for ripening of the unfavorable cervix prior to induction of labor. J Perinatol 1986;6:16-9.
- Rolland de Souza A . Oral Misoprostol Titrated Solution Versus Vaginal Misoprostol for Induction of Labour: Randomized Controlled Trial 2011. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT00992524 (accessed 22 January 2013).
- Rolland Souza A. Titrated oral suspension compared with vaginal misoprostol for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2011;33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-72032011000900010.
- Romer A, Weigel M, Zieger W, Melchert F. Changes in cervix maturity and length of birth after birth-preparation accupuncture therapy: Mannheim Rome Scheme. DZA 1998;41:93-100.
- Romero-Gutiérrez G, Bernal González OE, Ponce-Ponce de León AL. Comparison of isosorbide dinitrate and dinoprostone for induction of labor in term pregnancy. Ginecol Obstet Mex 2011;79:285-91.
- Rouben D, Arias F. A randomized trial of extra-amniotic saline infusion plus intracervical foley catheter balloon vs prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel for ripening the cervix and inducing labour in patients with unfavourable cervices. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:290-4.
- Roudsari FV, Ayati S, Ghasemi M, Hasanzadeh Mofrad M, Shakeri MT, Farshidi F, et al. Comparison of vaginal misoprostol with foley catheter for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Iran J Pharm Res 2011;10:149-54.
- Roudsari FV, Ghasemi M, Ayati S, Shakeri MT, Farshidi F, Shahabian M. Comparison of vaginal misoprostol with foley catheter for cervical ripening and induction of labor. J Isfahan Med School 2010;28:177-85.
- Rouzi AA. Randomized Clinical Trial Between Titrated Oral Dose of Misoprostol and Propess for Induction of Labor 2011. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReviewaspx?ACTRN=12611000420943 (accessed 22 January 2013).
- Rouzi AA, Alsibiani S, Mansouri N, Alsinani N, Darhouse K. Randomized clinical trial between hourly titrated oral misoprostol and vaginal dinoprostone for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210:56.e1-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2013.08.033.
- Rowlands S, Bell R, Donath S, Morrow S, Trudinger BJ. Misoprostol versus dinoprostone for cervical priming prior to induction of labour in term pregnancy: a randomised controlled trial. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;41:145-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.2001.tb01199.x.
- Rozenberg P, Chevret S, Goffinet F, Durand-Zaleski I, Ville Y, Vayssiere C, et al. Induction of labour with a viable infant: a randomised clinical trial comparing intravaginal misoprostol and intravaginal dinoprostone. BJOG 2001;108:1255-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2001.00270.x.
- Rozenberg P, Chevret S, Senat MV, Bretelle F, Bonnal AP, Ville Y. A randomized trial that compared intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone vaginal insert in pregnancies at high risk of fetal disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:247-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2003.12.038.
- Roztocil A. A comparison of three preinduction cervical priming methods: prostaglandin E2 gel, dilapan s rods, and estradiol gel. J Perinatal Med 2013;41.
- Roztocil A, Pilka L, JelÌnek J, Koudelka M, Miklica J. A comparison of three preinduction cervical priming methods: prostaglandin E2 gel, Dilapan S rods and Estradiol gel. Ceska Gynekol 1998;63:3-9.
- Russell Z, O’Leary T, Destefano K, Deutsch A, Carlan S. Buccal versus vaginal misoprostol administration for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;197. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2007.10.095.
- Rust OA, Greybush M, Singleton C, Atlas RO, Balducci J. A comparison of preinduction cervical ripening techniques. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180.
- Rydhström H, Ingemarsson I. No benefit from conservative management in nulliparous women with premature rupture of the membranes (PROM) at term. A randomized study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1991;70:543-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349109007914.
- Rymer J, Parker A. A comparison of syntocinon infusion with prostaglandin vaginal pessaries when spontaneous rupture of the membranes occurs without labour after 34 weeks gestation. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;32:22-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1992.tb01891.x.
- Saeed GA, Fakhar S, Nisar N, Alam AY. Misoprostol for term labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2011;50:15-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tjog.2009.08.001.
- Saggaf A, Rouzi AA, Radhan B, Alshehry S, Yamani T, Abduljabbar H. Misoprostol for preinduction cervical ripening and induction of labour: a randomized controlled trial. Saudi J Obstet Gynecol 2001;1:89-93.
- Sahraoui W, Hajji S, Bibi M, Nouira M, Essaidi H, Khairi H. Management of pregnancies beyond forty-one week’s gestation with an unfavorable cervix. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 2005;34:454-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0368-2315(05)82853-4.
- Sahu L, Chakravertty B. Comparison of prostaglandin E1 (misoprostol) with prostaglandin E2 (dinoprostone) for labor induction. J Obstet Gynecol India 2004;54:139-42.
- Salamalekis E, Vitoratos N, Kassanos D, Loghis C, Batalias L, Panayotopoulos N, et al. Sweeping of the membranes versus uterine stimulation by oxytocin in nulliparous women. A randomized controlled trial. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2000;49:240-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000010267.
- Saleem S. Efficacy of dinoprostone, intracervical foleys and misoprostol in labor induction. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2006;16:276-9.
- Saleh YZ. Surgical induction of labour with and without oxytocin infusion. A prospective study. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1975;15:80-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1975.tb00077.x.
- Salim R, Zafran N, Nachum Z, Garmi G, Kraiem N, Shalev E. Single-balloon compared with double-balloon catheters for induction of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2011;118:79-86. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e318220e4b7.
- Salmon YM, Kee WH, Tan SL, Jen SW. Cervical ripening by breast stimulation. Obstet Gynecol 1986;67:21-4.
- Sanchez-Ramos L, Chen A, Briones D, Del Valle GO, Gaudier FL, Delke I. Premature rupture of membranes at term: induction of labor with intravaginal misoprostol tablets (PGE1) or intravenous oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170.
- Sanchez-Ramos L, Chen AH, Kaunitz AM, Gaudier FL, Delke I. Labor induction with intravaginal misoprostol in term premature rupture of membranes: a randomized study. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:909-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00113-0.
- Sanchez-Ramos L, Conner PM, Kaunitz AM. Prostaglandin E2 Gel Vs Hypan in Cervical Ripening Before Induction of Labor n.d.
- Sanchez-Ramos L, Farah L, Rosa C, Johnson J, Delke I, Del Valle G. Comparative study of a two dose schedule of the PGE1 analogue misoprostol for labor induction in patients with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174.
- Sanchez-Ramos L, Kaunitz AM, Connor PM. Hygroscopic cervical dilators and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. A randomized, prospective comparison. J Reprod Med 1992;37:355-9.
- Sanchez-Ramos L, Peterson DE, Delke I, Gaudier FL, Kaunitz AM. Labor induction with prostaglandin E1 misoprostol compared with dinoprostone vaginal insert: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 1998;91:401-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00673-X.
- Sande HA, Tuveng J, Fønstelien T. A prospective randomized study of induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1983;21:333-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7292(83)90025-5.
- Satin AJ, Hankins GDV, Yeomans ER. A randomized study of two dosing regimens of oxytocin for the induction of patients with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(91)90961-P.
- Sawai SK, O’Brien WF, Mastrogiannis DS, Krammer J, Mastry MG, Porter GW. Patient-administered outpatient intravaginal prostaglandin E2 suppositories in post-date pregnancies: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 1994;84:807-10.
- Sawai SK, O’Brien WF, Mastrogiannis MS, Mastry MG, Porter GW, Johnson L. Outpatient prostaglandin E2 suppositories in postdates pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(12)91618-X.
- Sawai SK, Williams MC, O’Brien WF, Angel JL, Mastrogiannis DS, Johnson L. Sequential outpatient application of intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel in the management of postdates pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol 1991;78:19-23.
- Saxena P, Puri M, Bajaj M, Mishra A, Trivedi SS. A randomized clinical trial to compare the efficacy of different doses of intravaginal misoprostol with intracervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2011;15:759-63.
- Schmitz T, Closset E, Fuchs F, Maillard F, Rozenberg P, Anselem O, et al. Outpatient cervical ripening with nitric oxide (NO) donors for prolonged pregnancy in nullipara: the NOCETER randomized, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2013.10.060.
- Schneider M, Ramsey R, Kao L, Bennett KA. Misoprostol is effective for induction of labor in high risk pregnant women: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.10.135.
- Sciscione A, McCullough H, Shlossman P, Manley J, Pollock M, Colmorgan G. A randomized prospective comparison intracervical PGE2 gel (prepidil) versus foley bulb for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80555-8.
- Sciscione AC, McCullough H, Manley JS, Shlossman PA, Pollock M, Colmorgen GH. A prospective, randomized comparison of Foley catheter insertion versus intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:55-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(99)70149-3.
- Sciscione AC, Nguyen L, Manley J, Pollock M, Maas B, Colmorgen G. A randomized comparison of transcervical Foley catheter to intravaginal misoprostol for preinduction cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 2001;97:603-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200104000-00022.
- Seaward PG, Hannah ME, Myhr TL, Farine D, Ohlsson A, Wang EE, et al. International multicenter term PROM study: evaluation of predictors of neonatal infection in infants born to patients with premature rupture of membranes at term. Premature Rupture of the Membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:635-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(98)70056-0.
- Secher NJ, Lange AP, Nielsen FH, Pedersen GT, Westergaard JG. Induction of labor with and without primary amniotomy. A randomized study of prostaglandin E2 tablets and intravenous oxytocin. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1981;60:237-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348109158124.
- Seeras RC. Induction of labor utilizing vaginal vs. intracervical prostaglandin E2. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1995;48:163-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7292(94)02260-6.
- Sellers SM, Ah-Moye M, MacKenzie IZ. Comparison of Vaginal Prostaglandin E2 and Intravenous Oxytocin for Induction of Labour in Women Previously Delivered by Caesarean Section n.d.
- Selmer-Olsen T, Lydersen S, M¯rkved S. Does acupuncture used in nulliparous women reduce time from prelabour rupture of membranes at term to active phase of labour? A randomised controlled trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2007;86:1447-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00016340701645287.
- Selo-Ojeme D. A Randomised Controlled Trial of Amniotomy and Immediate Oxytocin Infusion Versus Amniotomy and Delayed Oxytocin Infusion for Induction of Labour at Term 2007. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN35919840 (accessed 30 October 2007).
- Selo-Ojeme DO, Pisal P, Lawal O, Rogers C, Shah A, Sinha S. A randomised controlled trial of amniotomy and immediate oxytocin infusion versus amniotomy and delayed oxytocin infusion for induction of labour at term. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2009;279:813-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-008-0818-x.
- Shakya R, Shrestha J, Thapa P. Safety and efficacy of misoprostol and dinoprostone as cervical ripening agents. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc 2010;49:33-7.
- Sharma Y, Kumar S, Mittal S, Misra R, Dadhwal V. Evaluation of glyceryl trinitrate, misoprostol, and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening in term pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2005;31:210-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.2005.00271.x.
- Shechter-Maor G, Biron-Shental T, Haran G, Ganor-Paz Y, Fejgin M. Intravaginal prostaglandin E2 versus double balloon catheter for labor induction in term isolated oligohydramnios. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2013;208:78-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2012.10.324.
- Sheela CN, Mhaskar A, George S. Comparison of vaginal misoprostol and oral misoprostol with intracervical dinoprostone gel for labor induction at term. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2007;57:327-30.
- Sheikher C, Suri N, Kholi U. Comparative evaluation of oral misoprostol, vaginal misoprostol and intracervical Foley’s catheter for induction of labour at term. JK Sci 2009;11:75-7.
- Shepherd J, Sims C, Craft I. Extra-amniotic prostaglandin E2 and the unfavourable cervix. Lancet 1976;2:709-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(76)90006-4.
- Sherman DJ, Frenkel E, Pansky M, Caspi E, Bukovsky I, Langer R. Balloon cervical ripening with extra-amniotic infusion of saline or prostaglandin E2: a double-blind, randomized controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 2001;97:375-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200103000-00010.
- Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol in the induction of labour at term: a random allocation trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20.
- Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol in the induction of labour at term: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2000;107.
- Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. A Comparison of Oral and Vaginal Misoprostol Tablets in the Induction of Labor at Term n.d.:28-9.
- Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol tablets in induction of labour at term. BJOG 2001;108:238-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2001.00073.x.
- Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. Sublingual misoprostol in the induction of labour at term. J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;21.
- Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. Sublingual misoprostol for the induction of labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:72-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2002.118917.
- Shetty A, Livingstone I, Acharya S, Danielian P, Rice P, Templeton A. A randomised comparison of oral misoprostol and vaginal prostaglandin E2 tablets in labour induction at term. BJOG 2003;110.
- Shetty A, Livingstone I, Acharya S, Rice P, Danielian P, Templeton A. A randomised comparison of oral misoprostol and vaginal prostaglandin E2 tablets in labour induction at term. BJOG 2004;111:436-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00107.x.
- Shetty A, Livingstone I, Acharya S, Rice P, Danielian P, Templeton A. Oral misoprostol (100 microg) versus vaginal misoprostol (25 microg) in term labor induction: a randomized comparison. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003;82:1103-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1600-0412.2003.00246.x.
- Shetty A, Mackie L, Danielian P, Rice P, Templeton A. Sublingual compared with oral misoprostol in term labour induction: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2002;109:645-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2002.01459.x.
- Shoaib F. Management of premature rupture of membranes with unfavourable cervix at term, by prostaglandins. Specialist 1994;10:227-32.
- Sifakis S, Angelakis E, Avgoustinakis E, Fragouli Y, Mantas N, Koukoura O, et al. A randomized comparison between intravaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 for labor induction. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2007;275:263-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-006-0258-4.
- Silva-Cruz A, Godinho F, Pinto JM, Andrade L, Simıes D. Prostaglandin E2 gel compared to oxytocin for medically-indicated labour induction at term: a controlled clinical trial. Pharmatherapeutica 1988;5:228-32.
- Sitthiwattanawong W. A comparison between oral and intravaginal administration of 50 microgram misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;12.
- Sitthiwattanawong W, Pongsatha S. Oral misoprostol for cervical ripening and labour induction: a randomized controlled trial. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;11:87-92.
- Skupski D, Normand N, Eglinton G, Witkin SS. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) gene polymorphisms influence the time interval between labor induction and delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;197. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2007.10.338.
- Smith C. The Influence of Acupuncture Stimulation on the Induction of Labour: A Randomised Controlled Trial 2000.
- Smith CA, Crowther CA, Collins CT, Coyle ME. Acupuncture to induce labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;112:1067-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e31818b46bb.
- Smith CV, Rayburn WF, Connor RE, Fredstrom GR, Phillips CB. Double-Blind Comparison of Intravaginal Prostaglandin E2 Gel and ‘Chip’ for Preinduction Cervical Ripening n.d. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(90)91081-m.
- Smith CV, Rayburn WF, Connor RE, Fredstrom GR, Phillips CB. Double-blind comparison of intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel and ‘chip’ for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:845-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(90)91081-M.
- Smith CV, Rayburn WF, Miller AM. Intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and initiation of labor. Comparison of a multidose gel and single, controlled-release pessary. J Reprod Med 1994;39:381-4.
- Souza AS, Feitosa FE, Costa AA, Pereira AP, Carvalho AS, Paixão RM, et al. Titrated oral misoprostol solution versus vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2013;123:207-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2013.06.028.
- Spallicci MD, Chiea MA, Singer JM, Albuquerque PB, Bittar RE, Zugaib M. Use of hyaluronidase for cervical ripening: a randomized trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2007;130:46-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.10.028.
- Spallicci MDB, Bittar RE. Randomized double blind study of ripening the cervix with hyaluronidase in term gestations. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2003;25.
- Sparks T, Caughey AB, Shaffer B, Cheng YW, Vargas J, Delaney S, et al. Predictors of cesarean delivery in women undergoing labor induction with a Foley balloon. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.10.182.
- Spellacy WN, Gall SA, Southern EM. The Prostaglandins Clinical Applications in Human Reproduction. Mount Kisko, NY: Futura Press; 1972.
- Spellacy WN, Gall SA, Shevach AB, Holsinger KK. The induction of labor at term. Comparisons between prostaglandin F 2 and oxytocin infusions. Obstet Gynecol 1973;41:14-21.
- Sperling LS, Schantz AL, Wåhlin A, Duun S, Jaszczak P, Scherling B, et al. Management of prelabor rupture of membranes at term. A randomized study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1993;72:627-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349309021155.
- Srisomboon J, Singchai S. A comparison between 25 micrograms and 50 micrograms of intravaginal misoprostol for labor induction. J Med Assoc Thai 1998;81:779-83.
- Srisomboon J, Tongsong T, Tosiri V. Preinduction cervical ripening with intravaginal prostaglandin E1 methyl analogue misoprostol: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 1996;22:119-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.1996.tb00952.x.
- St Onge RD, Connors GT. Preinduction cervical ripening: a comparison of intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel versus the Foley catheter. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:687-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)90594-4.
- Stampe Sørensen S, Palmgren Colov N, Andreasson B, Bock JE, Berget A, Schmidt T. Induction of labor by vaginal prostaglandin E2. A randomized study comparing pessaries with vaginal tablets. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1992;71:201-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016349209009919.
- Stampe Sorensen S, Palmgren N, Andreasson B, Bock JE, Berget A, Schmidt T. PGE2 pessaries versus PGE2 vaginal tablets for induction of labour. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1991;36.
- Stampe Sorenson S, Bock J, Berget A. Pharmacy Prepared Prostaglandin E2 Pessaries Versus Prostin E2 Vaginal Tablets for Induction of Labour n.d.
- Stempel JE, Prins RP, Dean S. Preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized prospective comparison of the efficacy and safety of intravaginal and intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:1305-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70350-8.
- Stenlund PM, Bygdeman M, Ekman G. Induction of labor with mifepristone (RU 486). A randomized double-blind study in post-term pregnant women with unripe cervices. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1994;73.
- Stenlund PM, Ekman G, Aedo AR, Bygdeman M. Induction of labor with mifepristone: a randomized, double-blind study versus placebo. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1999;78:793-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/j.1600-0412.1999.780910.x.
- Stephenson ML, Pevzner L, Powers BL, Wing DA. Race/ethnicity differences in labor outcomes with misoprostol and dinoprostone vaginal inserts. Reprod Sci 2011;18.
- Stephenson ML, Powers BL, Wing DA. Fetal heart rate and cardiotocographic abnormalities with varying dose misoprostol vaginal inserts. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;26:127-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2012.703715.
- Stewart JD, Rayburn WF, Farmer K, Liles E, Schipul A, Stanley J. Effectiveness of prostaglandin E2 as an intracervical gel with immediate oxytocin, or as a sustained-release vaginal insert for induction of labour. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178.
- Stewart P, Kennedy JH, Hillan E, Calder AA. The unripe cervix: management with vaginal or extra-amniotic prostaglandin E2. J Obstet Gynaecol 1983;4:90-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443618309071252.
- Steytler P, Howarth G, Makin J. Cervical Ripening and Labour Induction. Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Misoprostol and Dinoprostone Vaginal Gel n.d.:167-70.
- Stitely ML, Browning J, Fowler M, Gendron RT, Gherman RB. Outpatient cervical ripening with intravaginal misoprostol. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:684-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200011000-00008.
- Strobelt N, Meregalli V, Ratti M, Mariani S, Zani G, Morana S. Randomized study on removable PGE2 vaginal insert versus PGE2 cervical gel for cervical priming and labor induction in low-Bishop-score pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2006;85:302-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00016340500523685.
- Strobelt N, Ratti M, Zani G, Meregalli V. Randomized study on two dinoprostone administration routes for cervical priming and labor induction in low bishop pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2003.10.544.
- Su H, Li E, Weng L. Mifepristone for induction of labor. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1996;31:676-80.
- Sultana N, Rouf S, Rashid M. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour. J Bangladesh Coll Phys Surg 2006;24:44-9.
- Surbek DV, Boesiger H, Hoesli I, Pavic N, Holzgreve W. A double-blind comparison of the safety and efficacy of intravaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 to induce labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1018-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70006-1.
- Surbek DV, Bosiger H, Hosli I, Pavic N, Holzgreve W. Cervical priming and labor induction with intravaginal misoprostol versus PGE2: a double-blind randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80443-7.
- Surbek DV, Bosiger H, Pavic N, Hosli I, Stoz F, Holzgreve W. The safety of misoprostol for labor induction. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1997;76.
- Surbek DV, Bosiger H, Pavic N, Stoz F, Holzgreve W. Misoprostol (Cytotec) for Labor Induction in TeRm Pregnancies n.d.
- Surita FG, Cecatti JG, Parpinelli MA, Krupa F, Pinto E, Silva JL. Hyaluronidase versus Foley catheter for cervical ripening in high-risk term and post term pregnancies. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;88:258-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.12.006.
- Suvobrata S, Shyamal D. A Comparative Study of Sublingual Misoprostol and Oxytocin Infusion in Induction of Labor in Nulliparous Women at Term n.d.
- Suzuki S, Otsubo Y, Sawa R, Yoneyama Y, Araki T. Clinical trial of induction of labor versus expectant management in twin pregnancy. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2000;49:24-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000010207.
- Tabasi Z, Behrashi M, Mahdian M. Vaginal Misoprostol versus high dose of oxytocin for labor induction: a comparative study. Pak J Biol Sci 2007;10:920-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2007.920.923.
- Tabor B, Anderson J, Stettler B, Wetwiska N, Howard T. Misoprostol vs prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)91294-0.
- Tabowei TO, Oboro VO. Low dose intravaginal misoprostol versus intracervical baloon catheter for pre-induction cervical ripening. East Afr Med J 2003;80:91-4.
- Taechakraichana N, Jaisamrarn U, Tannirandorn Y, Trivijitsilp P, Termrungruanglert W. Induction of labour by prostaglandin E2 intracervical gel or vaginal suppository. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;8:9-14.
- Taher S, Eliahoo J, Edmonds K, Bennett P. Compare the effectiveness of prostaglandin gel versus tablets in labour induction at term: randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness. BJOG 2008;115.
- Taher SE, Inder JW, Soltan SA, Eliahoo J, Edmonds DK, Bennett PR. Prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel or tablets for the induction of labour at term: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2011;118:719-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2011.02901.x.
- Taher S, Riden JI, Soltan S, Elihoo J, Terzidou V, Bennett P. Randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness of prostaglandin gel versus tablets in labour induction at term. Arch Dis Childhood Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008;93.
- Tamsen L, Lyrenas S, Cnattingius S. Premature rupture of the membranes: intervention or not. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1990;29:128-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000293318.
- Tan PC, Soe MZ, Sulaiman S, Omar SZ. Immediate compared with delayed oxytocin after amniotomy labor induction in parous women: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2013;121:253-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e31827e7fd9.
- Tan PC, Yow CM, Omar SZ. Effect of coital activity on onset of labor in women scheduled for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2007;110:820-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000267201.70965.ec.
- Tan PC, Yow CM, Omar SZ. Coitus and orgasm at term: effect on spontaneous labour and pregnancy outcome. Singapore Med J 2009;50:1062-7.
- Tan TC, Yan SY, Chua TM, Biswas A, Chong YS. A randomised controlled trial of low-dose misoprostol and dinoprostone vaginal pessaries for cervical priming. BJOG 2010;117:1270-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2010.02602.x.
- Tannirandorn Y, Jumrustanasan T. A comparative study of membrane stripping and nonstripping for induction of labor in uncomplicated term pregnancy. J Med Assoc Thai 1999;82:229-33.
- Taylor AVG, Sellers S, Ah-Moye M, MacKenzie IZ. A prospective random allocation trial to compare vaginal prostaglandin e2 with intravenous oxytocin for labour induction in women previously delivered by caesarean section. J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;13:333-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443619309151705.
- Ten Eikelder ML, Neervoort F, Oude Rengerink K, van Baaren GJ, Jozwiak M, de Leeuw JW, et al. Induction of labour with a Foley catheter or oral misoprostol at term: the PROBAAT-II study, a multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2013;13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-13-67.
- Tessier F, Danserau J. Oral Misoprostol Versus Vaginal Dinoprostone for Labor Induction: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial 1997.
- Tessier F, Dansereau J. A double-blind randomized controlled trial comparing oral misoprostol to vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel for the induction of labour at or near term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80441-3.
- Tey A, Eriksen NL, Blanco JD. A prospective randomized trial of induction vs expectant management in nondiabetic pregnancies with fetal macrosomia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)90803-X.
- Thaisomboon A, Russameecharoen K, Wanitpongpan P, Phattanachindakun B, Changnoi A. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of titrated oral misoprostol and a conventional oral regimen for cervical ripening and labor induction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2012;116:13-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2011.07.027.
- Thakur V, Dorman E, Sanu L, Harrington K. Mifepristone is an effective ripening agent in postdates primips with cervical length ≥ 2.5cm, but mode of delivery correlates with birthweight: a randomised, placebo controlled double blind study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/uog.2514.
- Thavarasah AS, Arulkumaran S, Almohdzar SA. A prospective randomized study comparing the effect of intracervical to intravaginal administration of prostaglandin E2, in patients with poor cervical scores at term. Int J Feto-Maternal Med 1990;3:177-81.
- Thiery M, De Gezelle H, Van Kets H, Voorhoof L, Verheugen C, Smis B, et al. Extra-amniotic oestrogens for the unfavourable cervix. Lancet 1978;2:835-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(78)92608-9.
- Thiery M, Decoster JM, Parewijck W, Noah ML, Derom R, Van Kets H, et al. Endocervical prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical softening. Prostaglandins 1984;27:429-39. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0090-6980(84)90201-6.
- Thigpen B, Bofill J, Bufkin L, Woodring T, Moore L, Morrison J. A randomized controlled trial comparing vaginal misoprostol to cervical foley plus oral misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.09.076.
- Thomas IL, Chenoweth JN, Tronc GN, Johnson IR. Preparation for induction of labour of the unfavourable cervix with Foley catheter compared with vaginal prostaglandin. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1986;26:30-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1986.tb01524.x.
- Thomas N, Longo SA, Rumney PJ, Nageotte MP, Asrat T. Intravaginal misoprostol in prelabor rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182.
- Tomlinson AJ, Archer P, Hobson S. Prostin or propess: which method of induction of labour do patients prefer?. J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20.
- Tomlinson AJ, Archer PA, Hobson S. Induction of labour: a comparison of two methods with particular concern to patient acceptability. J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;21:239-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443610120046314.
- Toppozada MK, Anwar MY, Hassan HA, el-Gazaerly WS. Oral or vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;56:135-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(96)02805-6.
- Trabelsi H, Mathlouthi N, Zayen S, Dhouib M, Chaabene K, Trabelsi K, et al. Cervical ripening at term. A randomized and prospective study: Misoprotol versus dinoprostone. Tunis Med 2012;90:362-9.
- Tremeau ML, Fontanie-Ravier P, Teurnier F, Demouzon J. Protocol of cervical maturation by acupuncture. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1992;21:375-80.
- Triglia MT, Palamara F, Lojacono A, Prefumo F, Frusca T. A randomized controlled trial of 24-hour vaginal dinoprostone pessary compared to gel for induction of labor in term pregnancies with a Bishop score < or = 4. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2010;89:651-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016340903575998.
- Trofatter KF, Bowers D, Gall SA, Killam AP. Preinduction cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 (Prepidil) gel. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;153:268-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(85)80111-3.
- Trofatter K, Wing D, Miller H, Plante L, Rugarn O, Powers B. Efficacy and safety of misoprostol vaginal insert compared with dinoprostone vaginal insert for labor induction. J Perinatal Med 2013;41.
- Trofatter KF. Effect of preinduction cervical softening with dinoprostone gel on outcome of oxytocin-induced labor. Clin Ther 1993;15:838-44.
- Troostwijk AL, Van Veen JBC, Doesburg WH. Pre-induction intracervical application of a highly viscous prostaglandin E2 gel in pregnant women with an unripe uterine cervix: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1992;43:105-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(92)90066-8.
- Tylleskar J, Finnstrom O, Hedenskog S, Leijon I, Ryden G. Spontaneous Delivery-Elective Induction for Convenience. A Comparative Study n.d.
- Tylleskar J, Finnstrom O, Leijon I, Hedenskog S, Ryden G. Spontaneous labor and elective induction – a prospective randomized study. I Effects on mother and fetus. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1979;58:513-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016347909154610.
- Ugwu EO, Obi SN, Iferikigwe ES, Dim CC, Ezugwu FO. Membrane stripping to prevent post-term pregnancy in Enugu, Nigeria: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2014;289:29-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-2918-5.
- Ugwu EO, Onah HE, Obi SN, Dim CC, Okezie OA, Chigbu CO, et al. Effect of the Foley catheter and synchronous low dose misoprostol administration on cervical ripening: a randomised controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2013;33:572-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01443615.2013.786030.
- Ulmsten U, Ekman G, Belfrage P, Bygdeman M, Nyberg C. Intracervical versus intravaginal PGE2 for induction of labor at term in patients with an unfavorable cervix. Arch Gynecol 1985;236:243-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02133942.
- Ulmsten U, Wingerup L, Andersson KE. Comparison of prostaglandin E2 and intravenous oxytocin for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1979;54:581-4.
- Ulmsten U, Wingerup L, Belfrage P, Ekman G, Wiqvist N. Intracervical application of prostaglandin gel for induction of term labor. Obstet Gynecol 1982;59:336-9.
- Uludag S, Salihoglu Saricali F, Madazli R, Cepni I. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;122:57-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2004.11.028.
- Urban R, Lemancewicz A, Urban J, Skotnicki MZ, Kretowska M. Misoprostol and dinoprostone therapy for labor induction: a Doppler comparison of uterine and fetal hemodynamic effects. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;106:20-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0301-2115(02)00198-7.
- Vakhariya VR, Sherman AI. Prostaglandin F2α for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1972;113:212-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(72)90770-3.
- Valadan M, Niroomanesh S, Noori K, Khalilian S, Tehrani M. Comparison of dinoprostone plus oxytocin and oxytocin alone for induction of labour. Acta Med Iranica 2005;43:259-62.
- Valentine BH. Intravenous oxytocin and oral prostaglandin E2 for ripening of the unfavourable cervix. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1977;84:846-54. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1977.tb12506.x.
- Van Baaren GJ, Jozwiak M, Rengerink KO, Benthem M, Dijksterhuis MGK, van Huizen ME, et al. Cost-effectiveness of induction of labor at term with a Foley catheter compared to prostaglandin E2 gel (based on the PROBAAT trial; registration NTR 1646). Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206:139-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2011.10.307.
- Van der Walt D, Venter PF. Management of term pregnancy with premature rupture of the membranes and unfavourable cervix. S Afr Med J 1989;75:54-6.
- Van Gemund N, Scherjon S, LeCessie S, van Leeuwen JH, van Roosmalen J, Kanhai HH. A randomised trial comparing low dose vaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone for labour induction. BJOG 2004;111:42-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-0528.2003.00010.x.
- Varaklis K, Gumina R, Stubblefield PG. Randomized controlled trial of vaginal misoprostol and intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for induction of labor at term. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:541-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(95)00231-f.
- Vernant M, Perez Picanol E, Armengol R, Carreras N, Gamissans O. Intracervical Prostaglandins Vs Oxytocin in Premature Rupture of Membranes n.d.
- Wagner MV, Chin VP, Peters CJ, Drexler B, Newman LA. A comparison of early and delayed induction of labor with spontaneous rupture of membranes at term. Obstet Gynecol 1989;74:93-7.
- Wang H, Li L, Pu L. The effect of 25 micrograms misoprostol on induction of labor in late pregnancy. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1998;33:469-71.
- Weston J, Hannah M, Ohlsson A. Changing the study design during the recruitment phase of an international perinatal multicentre clinical trial. Controlled Clin Trials 1993;14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0197-2456(93)90072-L.
- Wieland D, Friedman F. Comparing two dinoprostone agents for preinduction cervical ripening at term. A randomized trial. J Reprod Med 1999;44:724-8.
- Wielgos M, Szymusik I, Kosinska-Kaczynska K, Suchonska B, Kaminski P, Banaszek-Wysoczanska A, et al. The influence of dinoprostone on uterine cervix ripening and the course of labor. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2007;28:513-17.
- Williams MC, Krammer J, O’Brien WF. The value of the cervical score in predicting successful outcome of labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1997;90:784-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00415-8.
- Williams MG, O’Brien WF, Sawai SK, Knuppel RA. Outpatient Cervical Ripening in the Postdates Pregnancy n.d.
- Wilson PD. A comparison of four methods of ripening the unfavourable cervix. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1978;85:941-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1978.tb15858.x.
- Wing D, Brown R, Plante L, Miller H, Rugarn O, Powers B. Efficacy and safety of misoprostol vaginal insert compared with dinoprostone vaginal insert for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2013;208. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2012.10.248.
- Wing D, Guberman C, Fassett M. A comparison of oral mifepristone to intravenous oxytocin for pre-induction cervical ripening and labor induction in women with prelabor rupture of membranes beyond 36 weeks gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2003.10.536.
- Wing DA, Brown R, Plante LA, Miller H, Rugarn O, Powers BL. Misoprostol vaginal insert and time to vaginal delivery: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2013;122:201-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e31829a2dd6.
- Wing DA, Fassett MJ, Guberman C, Tran S, Parrish A, Guinn D. A comparison of orally administered misoprostol to intravenous oxytocin for labor induction in women with favorable cervix examinations. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;190:1689-96. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.02.045.
- Wing DA, Fassett MJ, Mishell DR. Effect of mifepristone on cervical ripening and labor induction in pregnancies beyond 41 weeks gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182.
- Wing DA, Fassett MJ, Mishell DR. Mifepristone for preinduction cervical ripening beyond 41 weeks’ gestation: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:543-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0029-7844(00)00947-9.
- Wing DA. Misoprostol vaginal insert compared with dinoprostone vaginal insert: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;112:801-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e318187042e.
- Wing DA, Guberman C, Fassett M. A randomized comparison of oral mifepristone to intravenous oxytocin for labor induction in women with prelabor rupture of membranes beyond 36 weeks’ gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:445-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.07.058.
- Wing DA, Ham D, Paul RH. A comparison of orally administered misoprostol to vaginally administered misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(99)70610-1.
- Wing DA, Ham D, Paul RH. A comparison of orally administered misoprostol with vaginally administered misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:1155-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(99)70610-1.
- Wing DA, Jones MM, Rahall A, Goodwin TM, Paul RH. A comparison of misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1804-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)91415-3.
- Wing DA, Ortiz-Omphroy G, Paul RH. A comparison of intermittent vaginal administration of misoprostol with continuous dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:612-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70154-6.
- Wing DA, Park MR, Paul RH. A randomized comparison of oral and intravaginal misoprostol for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95:905-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200006000-00023.
- Wing DA, Paul RH. Vaginally administered misoprostol (Cytotec) versus the dinoprostone vaginal insert (Cervidil) for pre-induction cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(97)80447-4.
- Wing DA, Paul RH. Induction of labor with misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes beyond 36 weeks gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178.
- Wing DA, Paul RH. Induction of labor with misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes beyond thirty-six weeks’ gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:94-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9378(98)70256-X.
- Wing DA, Rahall A, Jones MM, Goodwin TM, Paul RH. Misoprostol: an effective agent for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1811-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(95)91416-1.
- Wingerup L, Andersson KE, Ulmsten U. Ripening of the uterine cervix and induction of labour at term with prostaglandin E2 in viscous gel. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1978;57:403-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016347809156519.
- Wingerup L, Andersson KE, Ulmsten U. Intracervical PGE2-Gel Contra i.V. Oxytocin for Cervical Ripening and or Induction of Labour at Term n.d.
- Wiqvist I, Norstrôm A, Wiqvist N. Induction of labor by intra-cervical PGE2 in viscous gel. Mechanism of action and clinical treatment routines. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1986;65:485-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00016348609157391.
- Wiriyasirivaj B, Vutyavanich T, Ruangsri RA. A randomized controlled trial of membrane stripping at term to promote labor. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:767-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(96)00015-4.
- Witter FR, Mercer BM. Improved intravaginal controlled-release prostaglandin E2 insert for cervical ripening at term. Prenatal Neonatal Med 1996;1.
- Witter FR, Mercer BM. Improved intravaginal controlled-release prostaglandin E2 insert for cervical ripening at term. The Prostaglandin E2 Insert Study Group. J Maternal Fetal Med 1996;5:64-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(199603/04)5:2<64::AID-MFM3>3.0.CO;2-O.
- Witter FR, Rocco L, Johnson TRB. A randomized trial of prostaglandin E2 in a controlled release vaginal pessary for cervical ripening at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(91)90965-T.
- Witter FR, Rocco LE, Johnson TR. A randomized trial of prostaglandin E2 in a controlled-release vaginal pessary for cervical ripening at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:830-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(92)91342-8.
- Witter FR, Weitz CM. A randomized trial of induction at 42 weeks gestation versus expectant management for postdates pregnancies. Am J Perinatol 1987;4:206-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-999774.
- Wong SF, Hui SK, Choi H, Ho LC. Does sweeping of membranes beyond 40 weeks reduce the need for formal induction of labour?. BJOG 2002;109:632-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2002.01193.x.
- Yang ZY, Li E, Yu SS. 15-Methyl-PGF2 alpha vaginal suppository for induction of term labor. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1994;29:273-5.
- Yazdani SH, Bouzari Z, Farahi S, Tabary AM. Oral misoprostol with oxytocin versus oxytocin alone for labor induction in pre-labor rupture of membranes (PROM) at term pregnancy. J Babol Uni Med Sci 2012;14:7-12.
- Yazdizadeh H, Abedi P, Najar S, Angali KA. The impact of isosorbide mononitrate on cervical ripening and labor induction in primiparous women with term pregnancy: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Iranian J Nurs Midwifery Res 2013;18:246-50.
- Yildirim G, Gungorduk K, Idem O, Aslam H, Ceylan Y. Membrane sweeping. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2008;21.
- Yildirim G, Güngördük K, Karadağ OI, Aslan H, Turhan E, Ceylan Y. Membrane sweeping to induce labor in low-risk patients at term pregnancy: a randomised controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;23:681-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14767050903387078.
- Yin CY, Zhou JZ, Wang BP, Lü XY. Effect and risk analysis of misoprostol in stimulating cervical maturity for post-term pregnancy. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2006;26:182-4.
- Yonekura ML, Songster G, Smith-Wallace T. Preinduction cervical priming with PGE2 intracervical gel. Am J Perinatol 1985;2:305-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-999976.
- Yuen PM, Pang HYY, Chung T, Chang A. Cervical ripening before induction of labour in patients with an unfavourable cervix: a comparative randomized study of the Atad ripener device, prostaglandin E2 vaginal pessary, and prostaglandin E2 intracervical gel. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;36:291-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.1996.tb02713.x.
- Yuen PM, Pang YYH. A Randomized Study of Two Different Methods for Cervical Ripening n.d.
- Zahradnik HP, Quaas L, Kröner-Fehmel EE, Kieback DG, Lippert TH. Cervix ripening using drugs before oxytocin labor induction. Clinical study of a new prostaglandin E2 triacetin gel. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1987;47:190-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1035805.
- Zahran KM, Shahin AY, Abdellah MS, Elsayh KI. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor at term: a randomized prospective placebo-controlled study. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2009;35:1054-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0756.2009.01030.x.
- Zanconato G, Bergamini V, Mantovani E, Carlin R, Bortolami O, Franchi M. Induction of labor and pain: a randomized trial between two vaginal preparations of dinoprostone in nulliparous women with an unfavorable cervix. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2011;24:728-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2011.557108.
- Zanini A, Ghidini A, Norchi S, Beretta E, Cortinovis I, Bottino S. Pre-induction cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 gel: intracervical versus intravaginal route. Obstet Gynecol 1990;76:681-3.
- Zanini A, Norchi S, Beretta E, Cortinovis I, Fenaroli G, Scian A. Cervical ripening and induction of labor in term pregnancy using prostaglandin E2. Controlled clinical study comparing the intracervical and intravaginal routes. Ann Ostet Ginecol Med Perinat 1989;110:209-16.
- Zeteroğlu S, Engin-Ustün Y, Ustün Y, Güvercinçi M, Sahin G, Kamaci M. A prospective randomized study comparing misoprostol and oxytocin for premature rupture of membranes at term. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2006;19:283-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14767050600589807.
- Zeteroğlu S, Sahin GH, Sahin HA. Induction of labor with misoprostol in pregnancies with advanced maternal age. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2006;129:140-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.11.040.
- Zeteroğlu S, Sahin HG, Sahin HA. Induction of labor with misoprostol in grand multiparous patients. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;87:155-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.06.021.
- Zeteroğlu S, Sahin HG, Sahin HA. Induction of labor in great grandmultipara with misoprostol. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2006;126:27-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.07.012.
- Ziaei S, Rosebehani N, Kazeminejad A, Zafarghandi S. The effects of intramuscular administration of corticosteroids on the induction of parturition. J Perinat Med 2003;31:134-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/JPM.2003.018.
- Zvandasara P, Saungweme G, Mlambo J, Chidembo W, Madzivanzira N, Mwanjira C. Induction of labour with titrated oral misoprostol suspension. A comparative study with vaginal misoprostol. Cent Afr J Med 2008;54:43-9.
- Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version, 5.1.0 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org (accessed 10 March 2015).
- Wood S, Cooper S, Ross S. Does induction of labour increase the risk of caesarean section? A systematic review and meta-analysis of trials in women with intact membranes. BJOG 2014;121:674-85. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12328.
- Glenny AM, Altman DG, Song F, Sakarovitch C, Deeks JJ, D’Amico R, et al. Indirect comparisons of competing interventions. Health Technol Assess 2005;9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3310/hta9260.
- Caldwell DM, Ades AE, Higgins JP. Simultaneous comparison of multiple treatments: combining direct and indirect evidence. BMJ 2005;331:897-900. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.331.7521.897.
- Salanti G. Indirect and mixed-treatment comparison, network, or multiple-treatments meta-analysis: many names, many benefits, many concerns for the next generation evidence synthesis tool. Res Synth Methods 2012;3:80-97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1037.
- Dias S, Welton NJ, Caldwell DM, Ades AE. Checking consistency in mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis. Stat Med 2010;29:932-44. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.3767.
- Jansen JP, Naci H. Is network meta-analysis as valid as standard pairwise meta-analysis? It all depends on the distribution of effect modifiers. BMC Med 2013;11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-159.
- Welton N, Sutton A, Cooper N, Abrams K, Ades A. Evidence Synthesis for Decision Making in Healthcare. London: Wiley; 2012.
- Dias S, Sutton AJ, Ades AE, Welton NJ. Evidence synthesis for decision making 2: a generalized linear modeling framework for pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Med Decis Making 2013;33:607-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0272989X12458724.
- Dias S, Welton N, Sutton A, Ades A. A Generalised Linear Modelling Framework for Pairwise and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. NICE Decision Support Unit Evidence Synthesis Technical Support Document 2 2011. www.nicedsu.org.uk/Evidence-Synthesis-TSD-series(2391675).htm (accessed 10 March 2015).
- Dias S, Welton N, Sutton A, Caldwell D, Lu G, Ades AE. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 4: Inconsistency in Networks of Evidence Based on Randomised Controlled Trials. London: NICE; 2011.
- Dias S, Welton NJ, Sutton AJ, Caldwell DM, Lu G, Ades AE. Evidence synthesis for decision making 4: inconsistency in networks of evidence based on randomized controlled trials. Med Decis Making 2013;33:641-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0272989X12455847.
- Sweeting MJ, Sutton AJ, Lambert PC. What to add to nothing? Use and avoidance of continuity corrections in meta-analysis of sparse data. Stat Med 2004;23:1351-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.1761.
- Spiegelhalter DJ, Best NG, Carlin BP, van der Linde A. Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J R Stat Soc 2002;64:583-616. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1467-9868.00353.
- Brooks S, Gelman A. Alternative methods for monitoring convergence of iterative simulations. J Computl Graphical Stat 1998;7:434-55.
- Gelman A, Rubin D. Inferences from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat Sci 1992;7:457-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1214/ss/1177011136.
- Chaimani A, Higgins JP, Mavridis D, Spyridonos P, Salanti G. Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA. PLOS ONE 2013;8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076654.
- Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal. London: NICE; 2004.
- Van Baaren GJ, Jozwiak M, Opmeer BC, Oude Rengerink K, Benthem M, Dijksterhuis MG, et al. Cost-effectiveness of induction of labour at term with a Foley catheter compared to vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel (PROBAAT trial). BJOG 2013;120:987-95. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12221.
- Briggs A, Claxton K, Sculpher M. Decision Modelling for Health Economic Evaluation. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006.
- Mahmood TA. A prospective comparative study on the use of prostaglandin E2 gel (2 mg) and prostaglandin E2 tablet (3 mg) for the induction of labour in primigravid women with unfavorable cervices. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1989;33:169-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(89)90210-4.
- NHS Reference Costs 2012–2013. London: DH; 2013.
- British National Formulary. London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press; n.d.
- Vandenbussche FP, De Jong-Potjer LC, Stiggelbout AM, Le Cessie S, Keirse MJ. Differences in the valuation of birth outcomes among pregnant women, mothers, and obstetricians. Birth 1999;26:178-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-536x.1999.00178.x.
- Pham CT, Crowther CA. Birth outcomes: utility values that postnatal women, midwives and medical staff express. BJOG 2003;110:121-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-0528.2003.02021.x.
- Plunkett BA, Grobman WA. Routine hepatitis C virus screening in pregnancy: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:1153-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.10.600.
- Turner CE, Young JM, Solomon MJ, Ludlow J, Benness C, Phipps H. Vaginal delivery compared with elective caesarean section: the views of pregnant women and clinicians. BJOG 2008;115:1494-502. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01892.x.
- Byrne CM, Solomon MJ, Young JM, Selby W, Harrison JD. Patient preferences between surgical and medical treatment in Crohn’s disease. Dis Colon Rectum 2007;50:586-97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10350-006-0847-0.
- Brazier J, Ratcliffe J, Tsuchiya A, Salomon J. Measuring and Valuing Health for Economic Evaluation. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2007.
- Fenwick E, Claxton K, Sculpher M. Representing uncertainty: the role of cost-effectiveness acceptability curves. Health Econ 2001;10:779-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hec.635.
- Claxton K, Posnett J. An economic approach to clinical trial design and research priority-setting. Health Econ 1996;5:513-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1050(199611)5:6<513::AID-HEC237>3.0.CO;2-9.
- Rasmussen CE, Williams CKI. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2006.
- Accelerated Value of Information Release version 2.0.8. Sheffield, UK: University of Sheffield; 2015.
- Haas DM, Caldwell DM, Kirkpatrick P, McIntosh JJ, Welton NJ. Tocolytic therapy for preterm delivery: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2012;345. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e6226.
- Welton N, Ades AE. Research decisions in the face of heterogeneity: what can a new study tell us?. Health Econ 2012;21:1196-200. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hec.1797.
- Torrance GW, Feeny D, Furlong W. Visual analog scales: do they have a role in the measurement of preferences for health states?. Med Decis Making 2001;21:329-34.
- Tang J, Kapp N, Dragoman M, de Souza JP. WHO recommendations for misoprostol use for obstetric and gynecologic indications. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2013;121:186-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2012.12.009.
- Shetty A, Stewart K, Stewart G, Rice P, Danielian P, Templeton A. Active management of term prelabour rupture of membranes with oral misoprostol. BJOG 2002;109:1354-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-0528.2002.02082.x.
- Caughey AB, Nicholson JM, Cheng YW, Lyell DJ, Washington AE. Induction of labor and cesarean delivery by gestational age. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195:700-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2006.07.003.
- Melchior J, Bernard N, André-David F. Déclenchement artificiel du travail á terme pour raisons médicales. Comparaison de deux techniques d'induction du travail, ocytocine + rupture artificielle des membranes précoce versus prostine E2 gel vaginal. Étude ouverte contrôlee randomisée. Rev Fr Gynecol Obstet 1989;84:747-52.
- Pixiang P, Fufan Z. Clinical observation of misoprostol on induction in late pregnancy. Bulletin of Hunan Medical University 1999;24:195-7.
Appendix 1 Project steering group
D eclan Devane
Professor of Midwifery
School of Nursing and Midwifery, NUI Galway
West, North-West Hospitals Group
Polly Griffiths
Consumer Representative
Paul Jacklin
Senior Health Economist
National Collaborating Centre for Women and Children’s Health
Tony Kelly
Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist, Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer & Associate Medical Director for Quality & Innovation
Brighton & Sussex University Hospitals, The Royal Sussex County Hospital
Appendix 2 Search strategy: Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group
Detailed search methods used to maintain and update the Group’s database of trials
The Group’s information specialist:
-
Runs a very broad generic preconception, pregnancy, childbirth and immediate postpartum/breastfeeding search that aims to encompass our whole scope. See below for searches run and strategies used.
-
Screens the results, gets hard copies of all relevant papers.
-
Assigns each paper reporting a RCT/clinical controlled trial (CCT) (by Cochrane definition) to a review topic or topics, depending on the intervention, and adds it to the database with a topic classification number to aid retrieval. The Group has a very detailed topic list.
For this project, all of the papers assigned to the ‘Induction of labour’ topic were identified using the broad classification number for this topic.
Search strategies for the identification of studies
Electronic searches
MEDLINE
This current search strategy is run weekly via OVID MEDLINE and uses the Highly Sensitive Search Strategy for identifying randomised trials in MEDLINE: sensitivity-maximising version (2008 revision) published in chapter 6, section 6.4.11, of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Version 5.0.2).
-
randomized controlled trial.pt.
-
controlled clinical trial.pt.
-
randomized.ab.
-
placebo.ab.
-
drug therapy.fs.
-
randomly.ab.
-
trial.ab.
-
groups.ab.
-
or/1-8
-
exp Pregnancy/
-
exp Pregnancy Complications/
-
exp Maternal Health Services/
-
exp Fetus/
-
exp Fetal Therapies/
-
exp Fetal Monitoring/
-
exp Prenatal Diagnosis/
-
Perinatal Care/
-
Labor pain/
-
Analgesia, Obstetric/
-
exp Obstetric Surgical Procedures/
-
Infant, Newborn/
-
exp Postpartum Period/
-
Breastfeeding/
-
or/10-23
-
9 and 24
-
exp animals/ not humans.sh.
-
25 not 26
EMBASE
The following search strategy is run weekly via NHS Evidence: Health Information Resources.
-
CROSSOVER PROCEDURE/
-
allocat$.ti,ab
-
(cross ADJ over$).ti,ab
-
trial$.ti
-
placebo$.ti,ab
-
(doubl$ ADJ blind$).ti,ab
-
DOUBLE BLIND PROCEDURE/
-
crossover$.ti,ab
-
SINGLE BLIND PROCEDURE/
-
RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL/
-
random$.ti,ab
-
1 OR 3 OR 2 OR 6 OR 4 OR 5 OR 11 OR 7 OR 8 OR 9 OR 10
-
exp PREGNANCY/
-
exp PREGNANCY DISORDER/
-
exp OBSTETRIC PROCEDURE/
-
exp BREAST FEEDING/ OR exp BREAST FEEDING EDUCATION/
-
exp CHILDBIRTH/
-
CHILDBIRTH EDUCATION/
-
(antenatal* OR prenatal* OR puerper* OR postnatal* OR postpartum OR post ADJ partum OR post ADJ natal* OR peripartum).ti,ab
-
(prepregnancy OR pre-pregnancy OR “pre pregnancy” OR preconception* OR “pre conception” OR pre-conception* OR “pre conceptionally” OR periconceptional*).ti,ab
-
((preterm OR premature) AND (labor OR labour)).ti,ab
-
(eclamp* OR preeclamp* OR pre-eclamp*).ti,ab
-
amniocentes*.ti,ab
-
(chorion* ADJ vill*).ti,ab
-
(breastfe* OR breast-fe* OR breast ADJ fe* OR lactation*).ti,ab
-
(cesarean OR caesarean OR cesarian OR caesarian OR cesarien OR caesarien).ti,ab
-
(newborn OR new ADJ born OR newborn).ti,ab
-
(pregnant OR pregnancy OR pregnancies).ti
-
(tocolysis OR tocolytic*).ti,ab
-
(fetal OR foetal OR fetus OR foetus).ti,ab
-
miscarriage*.ti,ab
-
LABOR PAIN/
-
OR 14 OR 15 OR 16 OR 17 OR 18 OR 19 OR 20 OR 21 OR 22 OR 23 OR 24 OR 25 OR 26 OR 27 OR 28 OR 29 OR 30 OR 31 OR 32
-
12 AND 33
The Cochrane Library [includes Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) and Economic Evaluations Databases]
This search is run monthly with each new issue of The Cochrane Library:
#1 MeSH descriptor Pregnancy explode all trees
#2 MeSH descriptor Pregnancy Complications explode all trees
#3 MeSH descriptor Fetal Therapies explode all trees
#4 MeSH descriptor Labor Pain explode all trees
#5 MeSH descriptor Infant, Newborn explode all trees
#6 MeSH descriptor Fetus explode all trees
#7 MeSH descriptor Fetal Development explode all trees
#8 MeSH descriptor Extraembryonic Membranes explode all trees
#9 MeSH descriptor Heart Rate, Fetal explode all trees
#10 MeSH descriptor Placenta explode all trees
#11 MeSH descriptor Placental Function Tests explode all trees
#12 MeSH descriptor Umbilical Cord explode all trees
#13 MeSH descriptor Prenatal Diagnosis explode all trees
#14 MeSH descriptor Uterine Monitoring explode all trees
#15 MeSH descriptor Pelvimetry explode all trees
#16 MeSH descriptor Fetal Monitoring explode all trees
#17 MeSH descriptor Obstetrical Nursing explode all trees
#18 MeSH descriptor Oxytocics explode all trees
#19 MeSH descriptor Tocolytic Agents explode all trees
#20 MeSH descriptor Tocolysis explode all trees
#21 MeSH descriptor Anesthesia, Obstetrical explode all trees
#22 MeSH descriptor Obstetric Surgical Procedures explode all trees
#23 MeSH descriptor Maternal Health Services explode all trees
#24 MeSH descriptor Maternal-Child Nursing explode all trees
#25 MeSH descriptor Analgesia, Obstetrical explode all trees
#26 MeSH descriptor Midwifery explode all trees
#27 MeSH descriptor Perinatal Care explode all trees
#28 MeSH descriptor Parity explode all trees
#29 MeSH descriptor Apgar Score explode all trees
#30 MeSH descriptor Postpartum Period explode all trees
#31 MeSH descriptor Breast Feeding explode all trees
#32 MeSH descriptor Milk, Human explode all trees
#33 pregnan* in All Fields in all products
#34 fetus in All Fields in all products
#35 foetus in All Fields in all products
#36 fetal in All Fields in all products
#37 foetal in All Fields in all products
#38 newborn in All Fields in all products
#39 “new born”
#40 birth or childbirth in All Fields in all products
#41 labor or laboring in All Fields in all products
#42 labour* in All Fields in all products
#43 antepart* in All Fields in all products
#44 prenatal* in All Fields in all products
#45 antenatal* in All Fields in all products
#46 perinatal* in All Fields in all products
#47 postnatal* in All Fields in all products
#48 postpart* in All Fields in all products
#49 caesar* in All Fields in all products
#50 cesar* in All Fields in all products
#51 obstetric* in All Fields in all products
#52 oxytoci* in All Fields in all products
#53 tocoly* in All Fields in all products
#54 placenta* in All Fields in all products
#55 prostaglandin in All Fields in all products
#56 parturi* in All Fields in all products
#57 preeclamp* in All Fields in all products
#58 pre next eclamp* in All Fields in all products
#59 eclamp* in All Fields in all products
#60 intrapart* in All Fields in all products
#61 puerper* in All Fields in all products
#62 episiotom* in All Fields in all products
#63 amnio* in All Fields in all products
#64 matern* in All Fields in all products
#65 gestation* in All Fields in all products
#66 lactati* in All Fields in all products
#67 breastfe* in All Fields in all products
#68 breast next fe* in All Fields in all products
#69 (#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20 OR #21 OR #22 OR #23 OR #24 OR #25 OR #26 OR #27 OR #28 OR #29 OR #30 OR #31 OR #32 OR #33 OR #34 OR #35 OR #36 OR #37 OR #38 OR #39 OR #40 OR #41 OR #42 OR #43 OR #44 OR #45 OR #46 OR #47 OR #48 OR #49 OR #50 OR #51 OR #52 OR #53 OR #54 OR #55 OR #56 OR #57 OR #58 OR #59 OR #60 OR #61 OR #62 OR #63 OR #64 OR #65 OR #66 OR #67 OR #68)
Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature
The following search strategy is run weekly via NHS Evidence: Health Information Resources.
-
exp CLINICAL TRIALS/
-
(clinic* ADJ trial*).ti,ab
-
(trebl* ADJ mask*).ti,ab
-
(tripl* ADJ blind*).ti,ab
-
(tripl* ADJ mask*).ti,ab
-
(doubl* ADJ blind*).ti,ab
-
(doubl* ADJ mask*).ti,ab
-
(singl* ADJ blind*).ti,ab
-
(singl* ADJ mask*).ti,ab
-
(randomi* ADJ control* ADJ trial*).ti,ab
-
RANDOM ASSIGNMENT/
-
(random* ADJ allocat*).ti,ab
-
placebo*.ti,ab
-
PLACEBOS/
-
QUANTITATIVE STUDIES/
-
(allocat* ADJ random*).ti,ab
-
breastfeeding.ti,ab
-
breastfed.ti,ab
-
exp BREAST FEEDING/
-
breast-fe*.ti,ab
-
exp PREGNANCY/
-
exp PREGNANCY COMPLICATIONS/
-
1 OR 2 OR 3 OR 4 OR 5 OR 6 OR 7 OR 8 OR 9 OR 10 OR 11 OR 12 OR 13 OR 14 OR 15 OR 16
-
(prenatal OR antenatal OR antepartum OR postpartum OR postnatal).ti,ab
-
(pregnant OR pregnancy).ti
-
((preterm OR premature) AND (labor OR labour)).ti,ab
-
(midwife OR midwifery).ti,ab
-
CHILDBIRTH EDUCATION/
-
17 OR 18 OR 19 OR 20 OR 21 OR 22 OR 24 OR 25 OR 26 OR 27 OR 28 123752.
-
23 AND 29
ClinicalTrials.gov and World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Portal
preconception* or antenatal or prenatal or perinatal or puerperal or puerperium or postnatal or postpartum or peripartum or post-natal or post-partum or ante-natal or ante-partum or obstetric*
Journal and conference proceedings screening and trial identification (hand-searching)
Journals
| Acta Anaethesiologica Scandinavica (and supplements) | 1950 and continuing |
| Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica (and supplements) | 1950 and continuing |
| Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica | First issue to 1993 |
| American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | First issue and continuing |
| American Journal of Diseases of the Child | 1950 to 1993 |
| American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology | 1950 and continuing |
| Anaesthesia and Intensive Care | First issue and continuing |
| Anaesthesia | 1950 and continuing |
| Anesthesia and Analgesia | First issue and continuing |
| Anesthesiology | 1950 and continuing |
| Archives of Diseases of the Child | 1950–93 |
| Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology | First issue and continuing |
| Birth | First issue and continuing |
| British Medical Journal | 1950–96 |
| British Journal of Anaesthesia | 1950 and continuing |
| British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology | First issue and continuing |
| Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia | First issue and continuing |
| Canadian Medical Association Journal | 1950–96 |
| Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics | First issue to 1998 |
| Current Medical Research and Opinion | First issue to 1993 |
| Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology | First issue to 1993 |
| Early Human Development | First issue to 1993 |
| European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology and Reproductive Biology | First issue and continuing |
| Geburtshilfe und Frauenheilkunde | 1950 and continuing |
| Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation | First issue to 1996, 2005 and continuing |
| Hypertension in Pregnancy | 2006 and continuing |
| Indian Journal of Anaesthesia | 2002 issue 3 to 2005 issue 5 |
| Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynecology | First issue and continuing |
| International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics | First issue and continuing |
| International Journal of Obstetric Anaesthesia | October 1994 to Oct 1995, January 2003 and continuing |
| Journal of the American Medical Association | First issue to 1996 |
| Journal of the American College of Surgeons | 1950–03 |
| Journal de Gynecologie, Obstetrique et Biologie de la Reproduction | First issue to 1998 |
| Journal of Human Lactation | 2001 and continuing |
| Journal of International Medical Research | First issue to 1993 |
| Journal of Midwifery and Women’s Health | First issue and continuing |
| Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology | First issue and continuing |
| Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research | 2003 and continuing |
| Journal of Obstetric Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing | First issue to 1993, 2001–06 |
| Journal of Pediatrics | 1950–93 |
| Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition | First issue to 1993 |
| Journal of Perinatal Medicine | First issue to 1998 |
| Journal of Reproductive Medicine | First issue to 2003 |
| Lancet | 1950–96 |
| Medical Journal of Australia | 1950–96 |
| Midwifery | First issue and continuing |
| New England Journal of Medicine | 1950–96 |
| Nurse Research | First issue to 1993 |
| New Zealand Medical Journal | 1950–96 |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | First issue and continuing |
| Pediatric Research | First issue to 93 |
| Pediatrics | 1950–93 |
| Practitioner | 1950–96 |
| Prostaglandins | First issue to 1993 |
| Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine | First issue and continuing |
| Revista Brasileira de Anestesiologia | 2003–06 |
| Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetricia | 2001–05 |
| South African Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology | First issue to 1993 |
| South African Medical Journal | 1950–93 |
| Surgery Gynecology and Obstetrics | 1950–93 |
| Ugeskrift for Laeger | 1950–93 |
| Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology | 2002 and continuing |
| Zeitschrift fur Geburtshilfe und Perinatologie | First issue to 1997 |
| Zentrablatt fur Gynakologie | First issue to 1997 |
Conference proceedings
| All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology | 49th, 54th |
| American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Annual Meeting | 36th, 37th, 39th, 40th, 41st, 55th, 58th |
| American Society of Anaesthesiologists Annual Meeting | 2008, 2009 |
| American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine Annual Spring Meeting | 26th to 28th |
| American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine Annual Fall Meeting | 2002, 2003, 2007 |
| Argentinean Congress of Perinatology | 3rd |
| Australian Perinatal Society | 14th |
| Australian Society of Anaesthetists National Scientific Congress | 58th, 61st |
| Birth Conference | 1st to 9th |
| British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology | 23rd, 25th, 26th, 27th, 28th |
| British Maternal and Fetal Medicine Society | 6th, 10th |
| British Paediatric Association Annual Meeting | 14th, 15th, 27th, 60th, 61st, 62nd, 63rd, 65th |
| Congress of Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology | 34th |
| European Congress of Allied Specialists in Maternal and Neonatal Care | 4th |
| European Congress of Obstetrical Anaesthesia and Analgesia | 1st |
| European Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology | 18th |
| European Congress of Perinatal Medicine | 5th, 6th, 8th, 10th, 11th, 12th, 14th, 15th, 16th, 21st |
| European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction | 1st, 2nd |
| European Congress on Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology | 6th |
| European Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine | 26th, 29th, 32nd |
| Federation of the Asia–Oceania Perinatal Societies’ Congress | 6th, 9th |
| International Anesthesia Research Society Clinical and Scientific Congress | 76th, 78th, 80th |
| International Confederation of Midwives Triennial Congress | 24th |
| International Conference of Maternity Care Researchers | 10th |
| International Congress on Psychosomatic Medicine in Obstetrics and Gynaecology | 3rd, 5th |
| International Scientific Meeting of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists | 4th |
| International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy (ISSHP) European Branch | 1st |
| International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy (ISSHP) World Branch | 1st, 2nd, 4th to 16th, 18th |
| Japanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology | 54th, 56th |
| Maternity Care Researchers International Conference | 10th |
| Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology Congress | 34th, 35th, 38th |
| Obstetric Anaesthetists Association | 2005, 2009 |
| Pediatric Academic Society Annual Meeting | 2004–13 |
| Perinatal Society of Australia and New Zealand Annual Congress | 4th, 7th |
| Priorities in Perinatal Care in South Africa | 2nd, 4th, 7th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th, 14th, 15th, 16th, 17th |
| Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists International Meeting | 7th, 10th |
| Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada Annual Meeting | 49th, 54th, 63rd |
| Society of Perinatal Obstetricians’ (USA) Annual Meeting | 3rd, 6th to 10th, 14th, 17th, 18th |
| Society for Gynecologic Investigation (USA) Annual Program | 31st, 34th, 37th, 39th, 40th |
| Society for Maternal–Fetal Medicine | 19th to 22nd, 25th to 32nd, 33rd, 34th |
| Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology Annual Meeting | 30th, 31st, 33rd, 34th, 37th |
| Swiss Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics | 19th to 22nd |
| World Congress of Perinatal Medicine | 1st, 2nd, 5th, 10th, 11th |
| World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics | 11th to 16th,19th, 20th |
| World Congress on Controversies in Obstetrics, Gynecology & Infertility | 4th |
| World Congress on Twin Pregnancy | 1st |
| World Congress on Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology | 13th, 15th 16th, 17th, 18th, 19th, 20th, 21st |
Other strategies
Current awareness
(a) ZETOC,The British Library’s Electronic Table of Contents service sends the contents tables, via e-mail, of the journals listed below. The contents are reviewed by the Trials Search Co-ordinator. Hard copies of all possible reports of RCTs/CCTs that are relevant to the scope of the group are obtained, reviewed and added to the register by the Trials Search Co-ordinator if they meet the inclusion criteria.
-
African Journal of Reproductive Health
-
American Journal of Perinatology
-
Archives of Disease in Childhood
-
Archives of Disease in Childhood Fetal and Neonatal Edition
-
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics
-
Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine
-
British Journal of Midwifery
-
Chinese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology
-
Clinica e Investigacion en Ginecologia y Obstetricia
-
Clinical and Experimental Obstetrics and Gynecology
-
Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology
-
Current Obstetrics and Gynecology
-
Current Opinion in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
-
Fetal and Maternal Medicine Review
-
Fetal Diagnosis and Therapy
-
Ginecologia y Obstetricia de Mexico
-
Giornale Italiano di Ostetricia e Ginecologia
-
Gynakologisch Geburtshilfliche Rundschau
-
Human Reproduction
-
Hypertension in Pregnancy
-
International Journal of Childbirth Education
-
Italian Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics
-
JOGC: Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology Canada
-
Journal de Gynecologie, Obstetrique et Biologie de la Reproduction (Paris)
-
Journal of Maternal Fetal and Neonatal Medicine
-
Journal of Paediatrics Obstetrics and Gynaecology
-
Journal of Perinatology
-
Journal of Prenatal and Perinatal Psychology and Health
-
Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics and Gynaecology
-
Journal of Reproductive Medicine
-
Journal-New Zealand College of Midwives
-
MCN, The American Journal of Maternal Child Nursing
-
MIDIRS Midwifery Digest
-
Obstetrical and Gynecological Survey
-
Obstetrics, Gynaecology and Reproductive Medicine
-
Prenatal Diagnosis
-
Progresos de Obstetricia y Ginecologia
-
Revista Chilena de Obstetricia y Ginecologia
-
Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology
-
Tokogynecologica Praktica
-
Women and Birth
-
Zeitschrift fur Geburtshilfe und Neonatologie.
(b) BioMed Central (www.biomedcentral.com/home/) sends an e-mail alert every 30 days for anything new published in the following:
-
BMC: Pregnancy and Childbirth
-
International Breastfeeding
-
Anything related to the subject areas of pregnancy and childbirth, pediatrics or women’s health.
Specialised register inclusion criteria
Topic scope Controlled trials comparing alternative forms of care used either during pregnancy (but not to terminate early pregnancy) or within 28 days of delivery.
Study design A controlled trial has been defined as a trial involving humans in which allocation to the intervention has either been at random, or by some quasi-random method, such as by alternation, or on the basis of the case record number or date of birth.
These criteria have been applied fairly liberally to avoid excluding potentially useful studies involving concurrent comparisons of alternative policies. In other words, the register includes reports that, if necessary, can subsequently be rejected as methodologically inadequate by a member of the Group preparing a systematic review.
No language restrictions are applied.
Appendix 3 Reference list for excluded studies
Abbassi RM, Sirichand P, Rizvi S. Safety and efficacy of oral versus vaginal misoprostol use for induction of labour at term. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2008;18:625–9.
Abdellah MS, Hussien M, AboAlhassan A. Intravaginal administration of isosorbide mononitrate and misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labour: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2011;284:25–30.
Abramovici D, Goldwasser S, Mabie BC, Mercer BM, Goldwasser R, Sibai BM. A randomized comparison of oral misoprostol versus Foley catheter and oxytocin for induction of labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:1108–12.
Abramovici D, Goldwasser S, Mabie BC, Mercer BM, Sibai BM. Cervical ripening and labor induction, with oral misoprostol vs mechanical methods of cervical ripening and oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:S126.
Adewole IF, Franklin O, Matiluko AA. Cervical ripening and induction of labour by breast stimulation. Afr J Med Med Sci 1993;22:81–5.
Afolabi BB, Oyeneyin OL, Ogedengbe OK. Intravaginal misoprostol versus Foley catheter for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;89:263–7.
Aggarwal N, Kirthika KS, Suri V, Malhotra S. Comparative Evaluation of Vaginal PGE-1 Analogue (Misoprostol) and Intracervical PGE-2 Gel for Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labor. 49TH All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology; 6–9 January 2006, Cochin, Kerala State, India, abstract no. 95.
Aghamohammadi A, Behmanesh F, Zafari M, Tofighi M. Effect of using Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) in acupuncture points [Hegu (Li4) and Sanyinjiao (Sp6)] on duration of the first stage of labor. J Babol Uni Med Sci 2011;13:19–24.
Akhtar A, Talib W, Shami N, Anwar S. Induction of labour – a comparison between misoprostol and dinoprostone. Pakistan J Med Health Sci 2011;5:617–19.
Akram H, Khan Z, Rana T. Vaginal prostaglandin e2 pessary versus gel in induction of labor at term. Ann King Edward Med Coll 2005;11:370–2.
Al-Assadi AF, Al-Waeely FA, Kadhim SS. The use of extraamniotic dexamethasone for ripening the unfavourable cervix. J Bahrain Med Soc 2007;19:148–53.
Amano K, Saito K, Shoda T, Tani A, Yoshihara H, Nishijima M. Elective induction of labor at 39 weeks of gestation: a prospective randomized trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 1999;25:33–7.
Anderson G, Cordero L, Speroff L, Hobbins J. Clinical use of prostaglandins as oxytocin substances. Ann N York Acad Sci 1971;180:499–512.
Anderson GG, Hobbins JC, Speroff L. Intravenous prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha for the induction of term labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1972;112:382–6.
Andreasson B, Bock JE, Larsen J. Induction of labour. A double-blind randomized controlled study of prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppositories compared with intranasal oxytocin and with sequential treatment. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1985;64:157–61.
Anonymous. Efficacy & Safety Study Comparing Misoprostol Vaginal Insert (MVI) versus Dinoprostone Vaginal Insert for Reducing Time to Vaginal Delivery (EXPEDITE). 2010. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 May 2013).
Arrieta OB, Yances BR, Ciodaro CM, Penaranda WA, Aguilera JB. Induction of labor at term with misoprostol versus oxytocin. Rev Colomb Obstet Ginecol 2000;51:8–11.
Arsenijevic S, Vukcevic-Globarevic G, Volarevic V, Macuzic I, Todorovic P, Tanaskovic I, et al. Continuous controllable balloon dilation: a novel approach for cervix dilation. Trials 2012;13:196.
Arulkumaran S, Gibb DM, Ratnam SS, Lun KC, Heng SH. Total uterine activity in induced labour – an index of cervical and pelvic tissue resistance. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1985;92:693–7.
Arulkumaran S, Ingemarsson I, Ratnam SS. Oxytocin titration to achieve preset active contraction area values does not improve the outcome of induced labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1987;94:242–8.
Ascher-Walsh C, Burke B, Baxi L. Outpatient management of prolonged pregnancy with misoprostol (mp): a randomized double-blind placebo controlled study, prelim data. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:S20.
Ashworth MF. Comparison of Pulsatile Infusion of Oxytocin vs Continuous Infusion in the Induction of Labour. Personal communication. 1988.
Atad J, Bornstein J, Calderon I, Petrikovsky BM, Sorokin Y, Abramovici H. Nonpharmaceutical ripening of the unfavorable cervix and induction of labor by a novel double balloon device. Obstet Gynecol 1991;77:146–52.
Atad J, Calderon I, Hallah M, Peer G, Abramovici H. Labour Induction: A New Approach. Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, New Zealand Committee Meeting, 8–11 April 2000, Queenstown, New Zealand, abstract no. 8.
Atkinson MW, Van Kessel K, Benedetti T. The use of low dose oral misoprostol to induce labor in the third trimester. Am J Obstet Gynecology 2000;182:S129.
Augensen K, Bergsjo P, Eikeland T, Askvik K, Carlsen J. Induction of Labour in Prolonged Pregnancy. A Prospective, Randomized Study. Proceedings of 10th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 12–16 August 1986; Leipzig, Germany, abstract no. 242.
Augensen K, Bergsjø P, Eikeland T, Askvik K, Carlsen J. Randomised comparison of early versus late induction of labour in post-term pregnancy. Br Med J 1987;294:1192–5.
Auner H, Adelwohrer NE, Semmelrock HJ, Lorenz-Eberhardt G, Haas J, Grubock K. [Pulsatile oxytocin for inducing labor after premature rupture of fetal membranes.] Gynakol Geburtshilfliche Rundsch 1993;33(Suppl. 1):256–7.
Averill KA, Scardo JA, Chauhan SP. Weekly membrane stripping to decrease the incidence of postterm pregnancy: a randomized clinical trial. Obstet Gynecol 1999;93(Suppl. 4):47.
Azarkish F, Absalan N, Roudbari M, Barahooie F, Mirlashari S, Bameri M. Effect of oral castor oil on labor pain in post term pregnancy. Sci J Kurdistan Uni Med Sci 2008;13:e1–6.
Azeem S. Buccal vs. Intravaginal Misoprostol Administration for Cervical Ripening in Induction of Labor. 49th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 6–9 January 2006, Cochin, Kerala State, India, abstract no. 95.
Azhari S, Pirdadeh S, Lotfalizadeh M, Shakeri MT. Evaluation of the effect of castor oil on initiating labor in term pregnancy. Saudi Med J 2006;27:1011–14.
Babcock RJ, Peterson JH. Relaxin; its effect on electively induced labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1959;78:33–7.
Baev O, Rumyantseva V. Mifepristone versus intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and labor induction. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 2011;71:904–5.
Balintona J, Meyer L, Ramin K, Vasdev G, Ramsey P. Cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with labor induction. Anesthesiology 2001;94: abstract no. 67.
Bamford PN. Trial to Compare Prostaglandin Gel vs Prostaglandin Pessary in Nulliparous Inductions. Personal communication. 1992.
Barkai G, Cohen SB, Kees S, Lusky A, Margalit V, Mashiach S, et al. Induction of labor with use of a Foley catheter and extraamniotic corticosteroids. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1145–8.
Barrilleaux PS, Bofill JA, Terrone DA, Magann EF, May WL, Morrison JC. Cervical ripening and induction of labor with misoprostol, dinoprostone gel, and a foley catheter: a randomized trial of 3 techniques. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:1124–9.
Bates CD, Nicoll AE, Mullen AB, Mackenzie F, Thomson AJ, Norman JE. Serum profile of isosorbide mononitrate after vaginal administration in the third trimester. BJOG 2003;110:64–7.
Baxi LV, Petrie RH, Caritis SN. Induction of labor with low-dose prostaglandin F2 alpha and oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980;136:28–31.
Beard RJ, Harrison R, Kiriakidis J, Underhill R, Craft I. A clinical and biochemical assessment of the use of oral prostaglandin E2 compared with intravenous oxytocin for labor induction in multiparous patients. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1975;5:203–7.
Beazley JM, Gillespie A. Double-blind trial of prostaglandin E2 and oxytocin in induction of labour. Lancet 1971;1:152–5.
Bebbington M, Pevzner L, Schmuel E, Bernstein P, Dayal A, Barnhard J, et al. Uterine tachysystole and hyperstimulation during induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189(Suppl. 1):211.
Bebbington M, Schmuel E, Pevzner L, Bernstein P, Dayal A, Barnhard J, et al. Misoprostol versus dinoprostone for labor induction at term: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189(Suppl. 1):211.
Beigi A, Kazemipour SM, Tabarestani H. Induction of labor in term pregnancy: sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol. Tehran Uni Med J 2010;68:175–81.
Belfrage P, Smedvig E, Gjessing L, Eggebo TM, Okland I. A randomized prospective study of misoprostol and dinoproston for induction of labour. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2000;79:1065–8.
Ben-Aroya Z, Hallak M, Segal D, Friger M, Katz M, Mazor M. Ripening of the uterine cervix in post cesarean parturient: PGE2 vs intracervical foley catheter. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S117.
Bendvold E. Coitus and induction of labour. Tidsskrift for Jordmodre 1990;96:6–8.
Bergsjö P, Huang GD, Yu SQ, Gao ZZ, Bakketeig LS. Comparison of induced versus non-induced labor in post-term pregnancy. A randomized prospective study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1989;68:683–7.
Bergsjö P, Jenssen H. Nasal and buccal oxytocin for the induction of labour: a clinical trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1969;76:131–6.
Bernstein EP, Leyland N, Gurland P, Gare D. Effect of Administration of PGE2 Gel and Placebo Gel into the Cervical Canal on Cervical Softening and Induction of Labour. Proceedings of Annual Meeting of Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada, 1986, Vancouver, BC, Canada, abstract no. 108.
Bex P, Gunasekera PC, Phipps JH. Difficulties with controlled release prostaglandin E2 pessaries (letter). Lancet 1990;336:119.
Bi S, Xu K, Xing A, Liu Y. Labor induced by low dose misoprostol in late gestation: a randomized controlled trial. J West China Uni Med Sci 2000;31:518–19.
Blackburn MG, Mancusi-Ungaro HR, Orzalesi MM, Hobbins JC, Anderson GG. Effects on the neonate of the induction of labor with prostaglandin F2alpha and oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1973;116:847–53.
Blakemore KJ, Qin NG, Petrie RH, Paine LL. A prospective comparison of hourly and quarter-hourly oxytocin dose increase intervals for the induction of labor at term. Obstet Gynecol 1990;75:757–61.
Bloch B. Induction of labour with prostaglandin E2 tablets. South Afr Med J 1975;49:2001–3.
Blumenthal PD, Ramanauskas R. Randomized trial of dilapan and laminaria as cervical ripening agents before induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1990;75:365–8.
Bo QX, Zhang JX. Observation on therapeutic effect of scalp acupuncture analgesia on labor. Zhongguo Zhenjiu 2006;26:659–61.
Bolnick JM, Velazquez MD, Gonzalez JL, Rappaport VJ, McIlwain-Dunivan G, Rayburn WF. Randomized trial between two active labor management protocols in the presence of an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;190:124–8.
Bonebrake R, Haag T, Fleming A, Temp M, Haynatzki G. Vaginal misoprostol is more effective with fewer side effects than oral misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):204.
Borisov I, Starkalev I. Comparison of oral PGE2 and intravenous oxytocin for stimulation of labor in cases of premature rupture of the membranes. Arch Gynecol 1985;237:305.
Botero L. Labor Induction with Unfavourable Cervix. Randomized controlled trial. Double blind method. Oxytocin vs misoprostol. Personal communication. 1998.
Bozhinova S. [Is it already time to legalize the usage of Cytotec (Misoprostol) in the obstetrics’ practice?] Akush Ginekol 2007;46:56–61.
Brandel E, Bascou V, Meeus JB, Magnin G. Results of a randomized trial of cervical maturation in premature rupture of membranes at term: prostine E, intravenous versus prostine E2 vaginal gel. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1998;27:111.
Breart G, Du Mazaubrun C, Maillard F, Garel M. Comparison of two policies of management of labour for primiparous women: effects of early rupture of membranes and use of oxytocin. Results of randomized controlled trial. Proceedings of International Conference on Primary Care, Obstetrics and Perinatal Health, 1991, Utrecht, The Netherlands, abstract no. 49.
Bréart G, Goujard J, Maillard F, Chavigny C, Rumeau-Rouquette C, Sureau C. [Comparison of 2 obstetrical attitudes vis-à-vis inducing labor at term. Randomized study.] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1982;11:107–12.
Bredow V, Straube W, Göretzlehner G. [Experiences with labor induction at term with a PGE2 gel (Prepidil Gel) in unripe cervix.] Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1990;50:865–9.
Bredow V, Straube W. [Fetal outcome after cervical ripeness-adjusted labor induction with prostaglandin E2 in relation to cervix status. Results of a multicenter study.] Zentralbl Gynakol 1993;115:530–6.
Bremme K, Bygdeman M. Induction of labor by oxytocin or prostaglandin E2. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1980;92:11–21.
Bremme K, Eneroth P, Kindahl H. 15-keto-13,14-dihydroprostaglandin F2alpha and prolactin in maternal and cord blood during prostaglandin E2 or oxytocin therapy for labor induction. J Perinatal Med 1987;15:143–51.
Bremme K, Nilsson B. Prediction of time to delivery from start of contractions in induced labor: a life table analysis approach. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1984;22:225–9.
Bricker L, Peden H, Alfirevic Z. The PROMMIS trial: a multicentre randomised trial to evaluate a low dose misoprostol regimen for induction of labour in the presence of prelabour rupture of the amniotic membranes. J Obstet Gynaecol 2007;27(Suppl. 1):22–3.
Browne MJ, Lang GD, Dougall A. Oral prostaglandin E2 in the management of patients with spontaneously ruptured membranes and no uterine activity. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 105.
Browne PC. Comparison of Pre-Induction Cervical Ripening using Prepidil Gel Administered Through a Urinary Balloon Catheter. 2011. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 May 2013).
Buccellato CA, Stika CS, Frederiksen MC. A randomized trial of misoprostol versus extra-amniotic sodium chloride infusion with oxytocin for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:1039–44.
Butler B, Crane J, Delaney T. Induction of labour with misoprostol in women at term with an unfavorable cervix: a randomized comparison of oral and vaginal administration. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191(Suppl. 1):190.
Cabrol D, Dubois C, Cronje H, Gonnet JM, Guillot M, Maria B, et al. Induction of labor with mifepristone (RU 486) in intrauterine fetal death. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:540–2.
Cai LL, Hu LQ, Hua YR. [Effect of cuichan zhunsheng decoction for promoting cervical ripening in late pregnancy.] Chin J Integrat Trad West Med 2010;30:682–5.
Calder AA, Embrey MP. Comparison of intravenous oxytocin and prostaglandin E2 for induction of labour using automatic and non-automatic infusion techniques. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1975;82:728–33.
Calder AA, Loughney AD, Weir CJ, Barber JW. Induction of labour in nulliparous and multiparous women: a UK, multicentre, open-label study of intravaginal misoprostol in comparison with dinoprostone. BJOG 2008;115:1279–88.
Calder AA, Loughney AJ, Denison F, Polson D, Erskine K, Dally JJ, et al. A randomised, open-label comparison of intravaginal (APL202) and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction in nulliparae. BJOG 2008;115:58–9.
Calder AA, Moar VA, Ounsted MK, Turnbull AC. Increased bilirubin levels in neonates after induction of labour by intravenous prostaglandin E2 or oxytocin. Lancet 1974;2:1339–42.
Caliskan E, Bodur H, Ozeren S, Corakci A, Ozkan S, Yucesoy I. Misoprostol 50 µg sublingually versus vaginally for labor induction at term: a randomized study. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2005;59:155–61.
Cameron A. High Bishop Score and Labour Induction. In Wood C, editor. The Role of Prostaglandins in Labour. London: RSM Services; 1985. pp. 61–7.
Cameron AD, Calder AA, Walker JJ. Randomised Comparison of PGE2 Vaginal Gel vs Amniotomy and Intravenous Oxytocin in Favourable Induction. Proceedings of 11th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 1988, Rome, Italy, abstract no. 157.
Carbone JF, Tuuli MG, Fogertey PJ, Roehl KA, Macones GA. Combination of Foley bulb and vaginal misoprostol compared with vaginal misoprostol alone for cervical ripening and labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2013;121:247–52.
Carlan SJ, Bouldin S, O’Brien WF. Extemporaneous preparation of misoprostol gel for cervical ripening: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 1997;90:911–15.
Carlan SJ, Danna P, Durkee D, Quinsey C, Lanaris B. Randomized study of pre-induction cervical ripening with sequential use of intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Obstet Gynecol 1995;85:608–13.
Casey BM, Smith LG, Wolf EJ. Combined therapy for preinduction cervical ripening is more effective than PGE2 alone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:424.
Casey C, Kehoe J, Mylotte MJ. Vaginal prostaglandins for the ripe cervix. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1993;44:21–6.
Castle B, Mountford L, Brennecke S, Embrey MP, MacKenzie IZ. In-vivo Studies using the Bicyclo PGEM Assay to Assess Release of PGE2 from Vaginal Preparations used for Labour Induction. Proceedings of 23rd British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 12–15 July 1983, Birmingham, UK, abstract no. 89.
Cecatti JG, Faundes A, Pires HMB, Calderon IMP. Labor induction in women with unripe cervix using two products containing misoprostol. J Perinatal Med 2001;29(Suppl. 1):283.
Cecatti JG, Tedesco RP, Pires HM, Calderon IM, Faúndes A. Effectiveness and safety of a new vaginal misoprostol product specifically labeled for cervical ripening and labor induction. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2006;85:706–11.
Cetin A, Cetin M, Taskurt A, Izgic E. Misoprostol versus dinoprostone for labor induction in term pregnancies. Jinekoloji Ve Obstetrik Dergisi 1997;11:51–4.
Chang YK, Chen WH, Yu MH, Liu HS. Intracervical misoprostol and prostaglandin e2 for labor induction. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2003;80:23–8.
Chen DC, Ku CH, Huang YC, Chen CH, Wu GJ. Urinary nitric oxide metabolite changes in spontaneous and induced onset active labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2004;83:641–6.
Chen DC, Yuan SS, Su HY, Lo SC, Ren SS, Wu GJ. Urinary cyclic guanosine 3’,5’-monophosphate and cyclic adenosine 3’,5’-monophosphate changes in spontaneous and induced onset active labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005;84:1081–6.
Chestnut DH, Vincent RD, McGrath JM, Choi WW, Bates JN. Does early administration of epidural analgesia affect obstetric outcome in nulliparous women who are receiving intravenous oxytocin? Anesthesiology 1994;80:1193–200.
Chia YT, Arulkumaran S, Soon SB, Norshida S, Ratnam SS. Induction of labour: does internal tocography result in better obstetric outcome than external tocography. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;33:159–61.
Chipato T, Mawire CJ. RCT of extra-amniotic saline infusion versus extra-amniotic PGF2alpha for cervical ripening and induction of labor. J Clin Epidemiol 1997;50(Suppl. 1):21.
Chou MM. Double-Blind Randomized Trial of Human Relaxin Gel for Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour. Personal communication. 1991.
Christensen FC, Tehranifar M, Gonzalez JL, Qualls CR, Rappaport VJ, Rayburn WF. Randomized trial of concurrent oxytocin with a sustained-release dinoprostone vaginal insert for labor induction at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:61–5.
Chua S, Arulkumaran S, Kurup A, Tay D, Ratnam SS. Oxytocin titration for induction of labour: a prospective randomized study of 15 versus 30 minute dose increment schedules. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1991;31:134–7.
Cole RA, Howie PW, Macnaughton MC. Elective induction of labour. A randomised prospective trial. Lancet 1975;1:767–70.
Coleman FH, Rayburn WF, Burks LS, Farmer KC, Larson JD, Turnbull GL. Patterns of uterine activity using oxytocin after intracervical PGE2. J Reprod Med 1997;42:44–8.
Collingham JP, Fuh KC, Caughey AB, Pullen KM, Lyell DJ, El-Sayed YY. Oral misoprostol and vaginal isosorbide mononitrate for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2010;116:121–6.
Coltart TH, Nash TG. Letter: Pitocin buccal in late pregnancy. Br Med J 1974;3:467.
Craft I, Brummer V, Horwell D, Morgan H. Betamethazone induction of labour. Proc R Soc Med 1976;69:827–8.
Craft IL, Cullum AR, May DT, Noble AD, Thomas DJ. Prostaglandin E2 compared with oxytocin for the induction of labour. Br Med J 1971;3:276–9.
Crane J, Reardon E. A Prospective Randomized Study of High Dose vs Low Dose Oxytocin Infusion for Labour Induction. Proceedings of 49th Annual Clinical Meeting of the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada, 22–26 June 1993, Ottawa, ON, Canada, abstract no. 109.
Critchley HO, Healy DL, Chard T. Is ovarian relaxin a stimulus to placental protein 14 secretion in pregnancy? J Endocrinol 1994;142:375–8.
Cross WG, Pitkin RM. Laminaria as an adjunct in induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1978;51:606–8.
Culver J, Strauss RA, Brody S, Dorman K, Timlin S, McMahon MJ. A randomized trial comparing vaginal misoprostol versus foley catheter with concurrent oxytocin for labor induction in nulliparous women. Am J Perinatol 2004;21:139–46.
Cummiskey KC, Dawood MY. Induction of labor with pulsatile oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:1868–74.
D’Aniello G, Bocchi C, Florio P, Ignacchiti E, Guidoni CG, Centini G, et al. Cervical ripening and induction of labor by prostaglandin E2: a comparison between intracervical gel and vaginal pessary. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2003;14:158–62.
D’Souza SW, Lieberman B, Cadman J, Richards B. Oxytocin induction of labour: hyponatraemia and neonatal jaundice. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1986;22:309–17.
Damania KR, Nanavati MS, Dastur NA, Daftary SN. Breast stimulation for cervical ripening. J Obstet Gynaecol India 1988;58:663–5.
Danezis J, Cohen J, Burnhill MS. A comparison of synthetic and natural oxytocin as determined by intra-amniotic fluid pressure recordings. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1962;83:770–3.
Daniel-Spiegel E, Weiner Z, Ben-Shlomo I, Shalev E. For how long should oxytocin be continued during induction of labour? BJOG 2004;111:331–4.
Danna P, Carlan S, Logan S, Durkee D, Gushwa J, Fuentes A, et al. Randomised prospective study of preinduction cervical ripening with sequential use of intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:298.
Dasgupta E, Singh G. Vaginal Misoprostol vs Vaginal Misoprostol With Estradiol for Labor Induction: A Prospective Double Blind Study. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2012;62:47–51.
Davies NJ, Martindale E, Haddad NG. Cervical ripening with oral prostaglandin E2 tablets and the effect of the latent period in patients with premature rupture of the membranes at term. J Obstet Gynaecol 1991;11:405–8.
Day L, Fleener D, Andrews J. Membrane sweeping with labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009;201(Suppl. 1):47.
De Laat W, Egberink J. A Highly Viscous Prostaglandin E2 gel (Cerviprost) for Cervical Ripening. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April–3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 98.
De Leon-Casasola OA, Kirch D, Karas P, Syed N, Blumenson L, Lema MJ. The influence of birthweight and oxytocin in the quality of epidural analgesia during labor. Anesthes Analges 1993;76:S74.
De Oliveira MGM. A prospective randomized study of the foley catheter for ripening of the unfavourable cervix before induction of labour. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2003;25:375.
DebBarma AM. A Comparative Study of Misoprostol Oral versus Vaginal Route for Induction of Labour. 2013. URL: www.ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2php?trialid=4251 (accessed 22 January 2013).
Decker WH, Thwaite W, Bordat S, Kayser R, Harami T, Campbell J. Some effects of relaxin in obstetrics. Obstet Gynecol 1958;12:37–46.
Delaney S, Shaffer BL, Cheng YW, Vargas J, Sparks TN, Paul K, et al. Labor induction with a Foley balloon inflated to 30 ml compared with 60 ml: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2010;115:1239–45.
Delaney T, Crane JM, Hutchens D, Fanning CA, Young DC. Induction of labor with intravaginal misoprostol: a comparison of dosing intervals. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):202.
Delaney T, Crane JM, Hutchens D, Fanning CA, Young DC. Oral misoprostol labor induction in patients with a favorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):202.
Deo S, Iqbal B, Das V, Agarwal A, Singh R. Preinduction cervical ripening: a prospective randomised comparison of intracervical foley catheter versus PGE2 gel. BJOG 2013;120(Suppl. 1):85.
Di Lieto A, Miranda L, Ardito P, Favale P, Albano G. Changes in the bishop score induced by manual nipple stimulation. A cross-over randomized study. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1989;16:26–9.
Dietl J. Induction of Labour by Prostaglandins. Personal communication. 1987.
Ding DC, Hsu S, Su HY. Low dose intravaginal misoprostol for induction of labor at term. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2005;90:72–3.
Dionne MD, Dube J, Chaillet N. Randomized study comparing Foley catheter and intravaginal misoprostol as cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204(Suppl. 1):48.
Dogra Y. Elective Induction vs Spontaneous Labour in Patients with Heart Disease. 2012. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 May 2013).
Dommisse J, Davey DA, Martin B, Cohen M. An evaluation of prostaglandin E2 administered intrarectally to induce labour. S Afr Med J 1981;59:817–18.
Dorfman P, Lasserre MN, Tetau M. Preparation for childbirth by homeopathy. Cahiers de BiothÄrapie 1987;94:77–81.
Dorr A. The possibility of inducing labor using acupuncture. Am J Acupunct 1990;18:213–18.
Du S, Guo Z, Liu H. Clinical study on colloidal bismuth subcitrate used in treating induce labor at late pregnancy. Heilongjiang Med J 2000;9:6–7.
Duhl A, Tolosa J, Leiva M, Nemiroff R. Randomized trial of intravaginal gel, intravaginal time release insert, and intracervical gel with prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S113.
Dundas KC, Howe D, Hughes RG. Misoprostol for induction of labour in primigravidae. J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20(Suppl. 1):50.
Dunn PA, Rogers D, Halford K. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation at acupuncture points in the induction of uterine contractions. Obstet Gynecol 1989;73:286–90.
Dunston-Boone G, Turzo E, Wapner RJ. A randomized prospective trial of the slow release prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) vaginal pessary. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:405.
Duru NK, Atay V, Pabuccu R, Ergun A, Tokac G, Aydin BA. Vaginal misoprostol versus oxytocin-prostaglandin e2 gel in severe preeclampsia remote from term. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1997;76:37.
Echeverría E, Rocha M. [Randomized comparative study of induced labor with oxytocin and misoprostol in prolonged pregnancies.] Rev Chil Obstet Ginecol 1995;60:108–11.
Edelstein H. Value of sparteine sulphate as an oxytocic: a preliminary report. S Afr J Obstet Gynaecol 1964;2:9–14.
Eftekhavi N. A comparison of vaginal misoprostol with intravenous oxytocin for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2002;28:47–8.
Ehrenberg-Buchner S, Wing D, Brown R, Plante L, Rugarn O, Powers B. Comparison of misoprostol vaginal insert and dinoprostone vaginal insert: incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2013;208(Suppl. 1):150.
Ekblad U, Erkkola R, Pirhonen J. Comparison of intravaginal and two intracervical prostaglandin E2 gels in pre-induction of labour. Ann Chir Gynaecol 1994;83:64–7.
Ekerhovd E, Bullarbo M, Andersch B, Norstrom A. Vaginal administration of the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening at term: a randomized controlled study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:1692–7.
El-Torkey M, Grant JM. Hydrostatic sweeping of the membranes is an effective method of preparing the unripe cervix for induction of labour. A random allocation prospective trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 1995;15:100–3.
Elliott CL, Brennand JE, Calder AA. The effects of mifepristone on cervical ripening and labor induction in primigravidae. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92:804–9.
Elliott JP, Flaherty JF. The use of breast stimulation to prevent postdate pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984;149:628–32.
Elliott JP, Flaherty JF. The use of breast stimulation to ripen the cervix in term pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;145:553–6.
ElSedeek MSh, Awad EE, ElSebaey SM. Evaluation of postpartum blood loss after misoprostol-induced labour. BJOG 2009;116:431–5.
Emery S, Neal E, Ward S, Morrison R, Filshie M. Prospective Controlled Trial of Three Methods for Ripening the Unfavourable Cervix Prior to Induction of Term Labour. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 140.
Engleman SR, Hilland MA, Howie PW, Mcllwaine GM, McNay MB. An analysis of the economic implications of elective induction of labour at term. Community Med 1979;1:191–8.
Escalante G, Ribas D, Esquivel A, Moya R, Sanchez LO, Pena YC. Misoprostol intracervical vs. vaginal: clinical characteristics in induction of labor. Rev Costarric Cienc Med 1993;14:43–50.
Evans MI, Dougan MB, Moawad AH, Evans WJ, Bryant-Greenwood GD, Greenwood FC. Ripening of the human cervix with porcine ovarian relaxin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;147:410–14.
Ewert K, Powers B, Robertson S, Alfirevic Z. Controlled-release misoprostol vaginal insert in parous women for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2006;108:1130–7.
Fekih M, Ben Zina N, Jnifen A, Nouri S, Ben Regaya L, Memmi A, et al. [Comparing two Prepidil gel regimens for cervical ripening before induction of labor at term: a randomized trial.] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 2009;38:335–40.
Filho FAR, Alencar Junior CA, Feitosa FE, Arcanjo FCN. Low-dose vaginal misoprostol (12.5 versus 25 mcg) for induction of labor at term. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2007;29:639–46.
Filshie GM. Trial to Determine the Relative Efficacy of Prostaglandins vs Dilapan in Ripening the Unripe Cervix prior to Induction of Labour. Personal communication. 1992.
Fitzpatrick CB, Grotegut CA, Bishop TS, Canzoneri BJ, Heine RP, Swamy GK. Cervical ripening with foley balloon plus fixed versus incremental low-dose oxytocin: a randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:1006–10.
Foong LC, Vanaja K, Tan G, Chua S. Membrane sweeping in conjunction with labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:539–42.
Freeman RK, Mishell DR. Induction of labor with sparteine sulfate for premature rupture of the fetal membranes near term. A double-blind study. Pac Med Surg 1968;76:43–7.
Friedman EA, Sachtleben MR, Green W. Oral prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor at term. II. Comparison of two low-dosage regimens. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1975;123:671–4.
Friedman EA, Sachtleben MR. Oral prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor at term. Obstet Gynecol 1974;43:178–85.
Friedman EA, Sachtleben MR. Preinduction priming with oral prostaglandin E2. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1975;121:521–3.
Fuchs AR, Goeschen K, Rasmussen AB, Rehnstrom JV. Cervical ripening and plasma prostaglandin levels Comparison of endocervical and extra-amniotic PGE2. Prostaglandins 1984;28:217–27.
Fuchs K, Brard L, Hodgman D, Silver H. Prostaglandin E1 gel vs. oxytocin for induction of labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195(Suppl. 1):101.
Fusi L, Macaulay J, Gordon H. A Prospective and Partly Randomised Trial on the Use of Vaginal Prostaglandin Preparations for Induction of Labour. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 107.
Fusi L, Macaulay J. Induction of labour with vaginal prostaglandins. A random trial comparing pessaries and gels with different concentrations. J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;10:76–7.
Garcia AA, Chavez AJ, Jimenez SG, Isquierdo PJC, Angeles WD, Santos GJ, et al. Preinduction Cervical Ripening with PGE2: a Double Blind Study. 12th FIGO World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 23–28 October 1988, Brazil, abstract no. 197.
Gauger LJ, Curet LB. Comparative efficacy of intravaginal prostaglandin E2 in the gel and suppository forms for cervical ripening. DICP Ann Pharmacother 1991;25:456–60.
Gemer O, Kapustian V, Harari D, Sassoon E, Segal S. Sweeping of membranes vs. intracervical prostaglandin e2 gel for cervical ripening. Randomized trial. J Reprod Med 2001;46:706–8.
Ghanaei MM, Sharami H, Asgari A. Labor induction in nulliparous women: a randomized controlled trial of foley catheter with extra-amniotic saline infusion. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc Artemis 2009;10:71–5.
Ghanaie MM, Mirblouk F, Godarzi R, Shakiba M. Effect of outpatient isosorbide mononitrate on success of labor induction. J Babol Uni Med Sci 2013;15:12–17.
Ghidini A, Spong CY, Korker V, Mariani E. Randomized controlled trial of 50 and 100 mcg of misoprostol for induction of labor at term. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2001;265:128–30.
Gibb DM, Arulkumaran S, Ratnam SS. A comparative study of methods of oxytocin administration for induction of labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1985;92:688–92.
Gibson KS, Mercer BM, Louis JM. Inner thigh taping vs traction for cervical ripening with a Foley catheter: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2013;209:272.
Gilad R, Hochner H, Vinograd O, Saam R, Hochner-Celnikier D, Porat S. The CIC Trial - castor oil for induction of contractions in post-term pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206(Suppl. 1):77–8.
Gillot M, Lambotte R. Comparison of efficacy of dinoprostone (PGE2) and demoxytocin (deaminooxytocin) in induction of labor. Rev Fr Gynecol Obstet 1974;69:617–21.
Girija S, Munjunath AP. Randomized Controlled Trial of Vaginal Misoprostol: Single 50 micrograms Dose versus Multiple 25 micrograms Dose for Labor Induction. 49th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 6–9 January 2006, Cochin, Kerala State, India, abstract no. 40.
Glanville T, Griffin C, Mason GC. A randomised controlled trial of prolonged 10 mg dinoprostone pessary (Propess) vs. dinoprostone gel (Prostin) for induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol 2002;22(Suppl. 2):55.
Gloeb DJ, O’Sullivan MJ, Beydoun SN. Relationship of the Interval Between Spontaneous Premature Rupture of the Membranes and Inducibility of Labor. Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of the Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 1–4 February 1989, New Orleans, LA, USA, abstract no. 493.
Goedken J, Poehlmann S. A blinded randomized controlled trial of misoprostol, dinoprostone, and oxytocin for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95(Suppl. 4):73.
Goeree R, Hannah M, Hewson S. Cost-effectiveness of induction of labour versus serial antenatal monitoring in the Canadian Multicentre Postterm Pregnancy Trial. CMAJ 1995;152:1445–50.
Gonen O, Rosen DJ, Dolfin Z, Tepper R, Markov S, Fejgin MD. Induction of labor versus expectant management in macrosomia: a randomized study. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:913–17.
Gonen R, Samberg I, Degani S, Sharf M. Intracervical prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor in patients with premature rupture of membranes and an unfavourable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168:362.
Goni S, Sawhney H, Gopalan S. Oxytocin induction of labor: a comparison of 20- and 60-min dose increment levels. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1995;48:31–6.
Gonsoulin W, Moise KJ, Cano L. Efficacy of Dilapan (TM) Laminaria to Intracervical Prostaglandin E2 Gel in Cervical Ripening. Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of the Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 1–4 February 1989, New Orleans, LA, USA, abstract no. 94.
Gordon AJ, Calder AA. Oestradiol applied locally to ripen the unfavourable cervix. Lancet 19772431;2:1319–21.
Gordon-Wright AP, Elder MG. Prostaglandin E2 tablets used intravaginally for the induction of labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1979;86:32–6.
Gottschall D, Borgida AF, Feldman DM, Alberti W, Rodis JF. Preinduction cervical ripening comparing 50 and 100 mcg of misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S93.
Gowenlock AH, Taylor DS, Sanderson JH. Biochemical and haematological changes during the induction of labour at term with oxytocin, prostaglandin E-2 and prostaglandin F-2alpha. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1975;82:215–20.
Granstrom L, Hammarstrom M, Hjertberg R, Moberger B, Berg A, Norlander E. Expectant management in nulliparous term pregnant women with premature rupture of membranes and an unripe cervix. J Obstet Gynaecol 1995;15:366–72.
Green PS. Intracervical injection of hyaluronidase. Effect on dilatation and length of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1967;99:337–40.
Greenberg RA. Acupuncture for Promation of Timely Delivery. 2006. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 May 2013).
Greer IA, McLaren M, Calder AA. Endogenous PGE2 and PGE2 alpha Production is Stimulated by Vaginal PGE2 Administration for the Induction of Labour. Proceedings of 11th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 10–13 April 1988, Rome, Italy, abstract no. 57.
Greer IA, McLaren M, Godfree V, Michie B, Calder AA. The Effects of Vaginal Prostaglandin E2 Administration on Plasma Concentrations of Prostaglandin E3 and Prostaglandin F2 Metabolites. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 108.
Greer IA, Smith JR, Godfree V, McLaren M, Graham N, Calder AA. PGE2 Absorption After Slow Release PGE2 Pessaries for the Induction of Labour. Proceedings of the 24th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 15–18 April 1986, Cardiff, UK, abstract no. 237.
Griffin C. Outpatient cervical ripening using sequential oestrogen: a randomised controlled pilot study. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;43:183.
Grudev D, Novachkov L, Geshev G, Krushkov I. [Use of aprophen in the preparation for and induction of labor.] Akush Ginekol 1988;27:39–43.
Grunstein S, Jaschevatzky OE, Shalit A, Noy Y, Davidson A, Ellenbogen A. A scoring system for induction of labor using prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1990;31:131–4.
Guinn DA, Davies JK, Jones RO, Sullivan L, Wolf D. Labor induction in women with an unfavorable bishop score: randomized controlled trial of intrauterine foley catheter with concurrent oxytocin infusion versus foley catheter with extra-amniotic saline infusion with concurrent oxytocin infusion. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:225–9.
Guinn DA, Goepfert AR, Christine M, Owen J, Hauth JC. Extra-amniotic saline, laminaria, or prostaglandin e(2) gel for labor induction with unfavorable cervix: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:106–12.
Güngördük K, Yildirim G, Güngördük O, Ark C, Tekirdag I. Sustained-release dinoprostone vaginal pessary with concurrent high-dose oxytocin infusion compared to sustained-release dinoprostone vaginal pessary followed 6 h later by high-dose oxytocin infusion for labor induction in women at term with unfavorable cervix: a randomized controlled trial. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2011;71:32–40.
Haddad N. Oral Prostaglandin E2 vs Oxytocin in the Management of Prelabour Rupture of the Membranes at Term. Personal communication. 1987.
Haeri AD, Scher J, Davey DA, Leader M. Comparison of oral prostaglandin E2 and intravenous oxytocin for induction of labour. S Afr Med J 1976;50:516–18.
Hage P, Shaw J, Zarou D, Fleisher J, Wehbeh H. Double blind randomized trial to evaluate the role of outpatient use of PGE 2 in cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168:430.
Hallak M. Induction of Labor in Patients with Unfavorable Cervical Conditions. 2008. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 9 April 2008).
Hannah ME, Hannah WJ, Hellmann J, Hewson S, Milner R, Willan A. Induction of labor as compared with serial antenatal monitoring in post-term pregnancy. A randomized controlled trial. The Canadian Multicenter Post-term Pregnancy Trial Group. N Engl J Med 1992;326:1587–92.
Harms K, Nguyen C, Toy EC, Baker B. Intravaginal misoprostol versus cervidil for cervical ripening in term pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol 2001;97(Suppl. 4):36.
Harrington K. What shall we do with the Postdates Woman who is not in Labour? 2003. URL: www.controlled-trials.com/ISRCTN74323479 (accessed 12 December 2011).
Hassan AA. A comparison of oral misoprostol tablets and vaginal prostaglandin E2 pessary in induction of labour at term. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2005;15:284–7.
He HY. Discussion on the nursing care of air-vesicle odinopoeia in post-term pregnancy. Nurs J Chin People’s Liberation Army 2000;17:7–8.
Helal AMM, Abd El-Razek MME, Ahmed RE. Randomized double-blind controlled study to determine the effect of vaginally applied nitric oxide donor (isosorbide mononitrate) for preinduction cervical ripening on maternal & fetal hemodynamics and the ripening of the cervix. El-Minia Med Bull 2004;15:32–42.
Hendricks CH, Brenner WE. Patterns of increasing uterine activity in late pregnancy and the development of uterine responsiveness to oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1964;90:485–92.
Hennessey MH, Rayburn WF, Stewart JD, Liles EC. Pre-eclampsia and induction of labor: a randomized comparison of prostaglandin e2 as an intracervical gel, with oxytocin immediately, or as a sustained-release vaginal insert. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:1204–9.
Henry A, Madan A, Reid R, Tracy S, Sharpe V, Austin K, et al. Outpatient Foley catheter versus inpatient Prostin gel for cervical ripening: the FOG (Foley or Gel) trial. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2011;51:473–4.
Henry A, Madan A, Reid R, Tracy SK, Austin K, Welsh A, et al. Outpatient Foley catheter versus inpatient prostaglandin E2 gel for induction of labour: a randomised trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2013;13:25.
Henry GR. A controlled trial of surgical induction of labour and amnioscopy in the management of prolonged pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1969;76:795–8.
Henson BV. Cervical Ripening with Prostaglandin E2. Personal communication. 1987.
Hernandez-Castro F, Alvarez-Chavez LD, Martinez-Gaytan V, Cortes-Flores R. Ambulatory treatment of prolonged pregnancy with prostaglandin E2 gel. Rev Med Instit Mex Seguro 2008;46:191–4.
Hibbard JU, Shashoua A, Adamczyk C, Ismail M. Cervical ripening with prostaglandin gel and hygroscopic dilators. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol 1998;6:18–24.
Hill JB, Thigpen BD, Bofill JA, Magann E, Moore LE, Martin JN, Jr. A randomized clinical trial comparing vaginal misoprostol versus cervical Foley plus oral misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Perinatol 2009;26:33–8.
Hill NCW, Selinger M, Ferguson J, MacKenzie IZ. Management of intra-uterine fetal death with vaginal administration of gemeprost or prostaglandin E2: a random allocation controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 1991;11:422–6.
Ho M, Cheng SY, Li TC. Titrated oral misoprostol solution compared with intravenous oxytocin for labor augmentation: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2010;116:612–18.
Hoesli I, Gairing A, Lapaire O, Tercanli S, Holzgreve W. Induction of labour: cervical length measurement beside misoprostol or dinoproston – is it a reliable factor both for patients and their obstetrical team? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(Suppl. 1):149.
Hoppe K, Schiff M, Peterson S, Gravett M. Randomized controlled trial: comparing 80 ml double versus 30 ml single balloon catheters for pre-induction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210(Suppl. 1):326.
Hourvitz A, Alcalay M, Korach J, Lusky A, Barkai G, Seidman DS. A prospective study of high- versus low-dose oxytocin for induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:636–41.
Hu Y. Foley Catheter Balloon for Cervical Ripening in Term Pregnancy: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. 2013. Chinese Clinical Trial Register. URL: www.who.int/ictrp/network/chictr2/en/ (accessed 31 May 2013).
Hughes L, El-Azeem S. Induction of labor: a randomized comparison between the intracervical balloon catheter and slow release dinoprostone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S166.
Hunter G, Parveen R. A comparison of an intravaginal controlled release prostaglandin E2 (10 mg) for cervical ripening and initiation of labour versus prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet (3 mg). J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;18:460–1.
Hunter IW, Hammad MK. Induction of labour using prostaglandin pessaries of varying strength. Ulster Med J 1982;51:141–5.
Hunter IWE, Cato E, Ritchie JWK. Induction of labor using high-dose or low-dose prostaglandin vaginal pessaries. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:418–20.
Hussein M. A comparison between vaginal misoprostol and a combination of misoprostol and Foley catheter for cervical ripening and labour induction in early third trimester pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206(Suppl. 1):147.
Ifnan F, Jameel MB. Ripening of cervix for induction of labour by hydrostatic sweeping of membrane versus Foley’s catheter ballooning alone. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2006;16:347–50.
Iftikhar M, Price J, Beattie RB, Heasley RN, Armstrong MJ. Pre-induction cervical ripening in primigravida with unfavourable cervix. A randomised controlled trial using PGE2 intracervical gel or vaginal pessary. J Perinatal Med 1992;20(Suppl. 1):96.
Iftikhar M, Price J, Beattie RB, Heasley RN. Evaluation of PGE2 Intracervical Gel for Cervical Ripening in Primigravidae with Unfavourable Cervices. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April 30–3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 139.
Imsuwan Y, Tanapat Y. Reduction of pregnancy with gestational age more than 41 weeks by membrane stripping to induce labor: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;11:267.
Ingemarsson I, Heden L, Montan S, Sjoberg NO. Effect of Intracervical Prostaglandin Gel in Postterm Women. Personal communication. 1991.
Ismail AA, Khowesah MM, Shaala SA, Anwar MY, Darwish EA, Haiba NA. Induction of labor by oral prostaglandin E2 in protracted pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1989;29:325–8.
Jackson NV, Irvine R, Edmonds DK, Paterson-Brown S. Random allocation controlled trial of intravaginal misoprostol versus intravaginal dinoprostone for the induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20(Suppl. 1):52.
Jackson NV, Irvine R, Paterson-Brown S. Randomised Controlled Trial of Intravaginal Misoprostol versus Intravaginal Dinoprostone Gel in the Induction of Labour at Term. Women’s Health: Into the New Millennium. Proceedings of the 4th International Scientific Meeting of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, 3–6 October 1999, Cape Town, South Africa, abstract no. 32.
Jackson NV, Terzidou V, Irvine RE, Edmonds DK, Paterson-Brown S. Randomised controlled trial of intravaginal misoprostol versus intravaginal dinoprostone for the induction of labour. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 3–8 September 2000, Washington DC, USA, Book 4, pp. 29–30.
Jalilian N, Fakheri T, Ghadami MR. Intravaginal dinoprostone versus intra cervical foley catheter for induction of labor. Acta Med Iran 2011;49:831.
Jasper MP, Blossom S, Peedicayil A. A Randomised Controlled Trial of Extra Amniotic Saline Infusion and Intracervical Foley Catheter for Cervical Ripening. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Washington DC, USA, 3–8 September 2000, Book 4, pp. 69–70.
Javaid MK, Hassan S, Tahira T. Management pre labour rupture of the membranes at term; induction of labor compared with expectant. Profes Med J 2008;15:216–19.
Jazayeri A, Jazayeri M, Jamal A, Eslamian L, Maroosi V, Borna S. Prospective randomized clinical trial of cervical ripening with misoprostol for either 8 or 24 hours. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189(Suppl. 1):70.
Jenssen H, Wright PB. The effect of dexamethasone therapy in prolonged pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1977;56:467–73.
Jiang X, Wang H, Zhang Z. Determination of fetal umbilical artery flow velocity during induction of term labor by mifepristone. Chin J Obstet Gynecol 1997;32:732–4.
Jigyasa S, Rajkumar PP. Prelabour Rupture of Membranes At and Beyond 34 Weeks of Gestation: Immediate Induction with PGE2 Gel Compared with Immediate Induction with Oxytocin. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, abstract no. 115.
Jindal P, Gill BK, Tirath B. A comparison of vaginal misoprostol versus Foley’s catheter with oxytocin for induction of labor. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2007;57:42–7.
Jonsson M, Hellgren C, Wiberg-Itzel E, Akerud H. Assessment of pain in women randomly allocated to speculum or digital insertion of the Foley catheter for induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2011;90:997–1004.
Joo SH, Hur EJ, Park JW, Lee WK. A comparison of the safety and efficacy of intravaginal prostaglandin e1 (misoprostol) and prostaglandin e2 (dinoprostone) to induce labor. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 2000;43:444–50.
Kadar N, Tapp A, Wong A. The influence of nipple stimulation at term on the duration of pregnancy. J Perinatol 1990;10:164–6.
Kamat DS, Kamat VD, Mulary AA, Kharat A, Thomas EV. Induction and augmentation of labour by intracervical and/or intravaginal PGE2 tablet (Primiprost). J Obstet Gynecol India 2002;52:33–4.
Kanade T, Mundle S. Misoprostol for Cervical Ripening: Sublingual versus Vaginal Route. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, pp. 316–17.
Kanhai HH, Keirse MJ. Induction of labour after fetal death: a randomized controlled trial of two prostaglandin regimens. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;96:1400–4.
Karjane NW, Brock EL, Walsh SW. Induction of labor using a foley balloon, with and without extra-amniotic saline infusion. Obstet Gynecol 2006;107:234–9.
Karpovich E. Recombinant Human Relaxin (rhRIx) in Pregnant Women Scheduled for Induction of Labor (Ongoing Trial). 2006. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 March 2006).
Kasdaglis T, Adamczak J, Rinehart B, Antebi Y, Mendise T, Terrone D. A randomized controlled trial of cervical ripening in patients with PROM using an intracervical balloon catheter and oxytocin versus dinoprostone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;197(Suppl. 1):104.
Kashanian M, Fekrat M, Naghghash S, Ansari NS. Evaluation of the effect of extra-amniotic normal saline infusion alone or in combination with dexamethasone for the induction of labor. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2008;34:47–50.
Kashanian M, Fekrat M, Zarrin Z, Ansari NS. A comparison between the effect of oxytocin only and oxytocin plus propranolol on the labor (a double blind randomized trial). J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2008;34:354–8.
Kashanian M, Nazemi M, Malakzadegan A. Comparison of 30-ml and 80-ml Foley catheter balloons and oxytocin for preinduction cervical ripening. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2009;105:174–5.
Kehl S, Ehard A, Berlit S, Spaich S, Sutterlin M, Siemer J. Combination of misoprostol and mechanical dilation for induction of labour: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2011;159:315–19.
Keirse M, Thiery M, Parewijck W, Mitchell MD. Chronic stimulation of uterine prostaglandin synthesis during cervical ripening before the onset of labor. Prostaglandins 1983;25:671–82.
Keller JM. Membrane Sweeping in GBS Positive Patients at 37 weeks Gestation: A randomized Controlled Trial. 2010. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 May 2013).
Khan ZA, Abdul B, Majoko F. Induction of labour with vaginal prostaglandin tablet vs gel. J Obstet Gynaecol 2011;31:492–4.
Kjos SL, Henry OA, Montoro M, Buchanan TA, Mestman JH. Insulin-requiring diabetes in pregnancy: a randomized trial of active induction of labor and expectant management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:611–15.
Klopper A, Farr V, Dennis KJ. The effect of intra-amniotic oestriol sulphate on uterine contractility at term. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1973;80:34–40.
Klopper AI, Dennis KJ, Farr V. Effect of intra-amniotic oestriol sulphate on uterine contractions. Br Med J 1969;2:786–9.
Klopper AI, Dennis KJ. Effect of oestrogens on myometrial contractions. Br Med J 1962;2:1157–9.
Knogler W, Egarter C, Fitz R, Husslein P. Comparison of Prostaglandin (PG) E2 Vaginal Gel and Tablet for Elective Induction of Labor. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 111.
Knox GE, Huddleston JF, Flowers CE. Management of prolonged pregnancy: results of a prospective randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1979;134:376–84.
Krammer J, O’Brien W, Williams M. Outpatient cervical ripening does not affect gestational age at delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:425.
Kubista E, Kucera H. Acupuncture as a method of preparation in obstetrics. Am J Chin Med 1974;2:283–7.
Kupietz R, Faber J, Heidegger H. [Comparison of the effectiveness of prostaglandin E2 gel in evening and morning induction of labor.] Zentralbl Gynakol 1994;116:468–73.
Ladfors L, Mattsson LA, Eriksson M, Fall O. A randomized prospective trial of two expectant managements of pre-labor rupture of the membranes (PROM) at 34–42 weeks. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:344.
Lamont RF, Neave S, Baker AC, Steer PJ. Intrauterine pressures in labours induced by amniotomy and oxytocin or vaginal prostaglandin gel compared with spontaneous labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1991;98:441–7.
Lange AP, Secher NJ, Westergaard JG, Skovgard I. Neonatal jaundice after labour induced or stimulated by prostaglandin E2 or oxytocin. Lancet 1982;1:991–4.
Lanka S. A clinical study to compare the combined efficacy of mechanical and pharmacological methods versus pharmacological method alone when used for induction of labor. 2012. Clinical Trials Registry – India. URL: www.ctri.nic.in/ (accessed 31 May 2013).
Larsen J, Andreasson B, Bock JE. Induction of labour. A double-blind randomized investigation of prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppositories compared with intranasal oxytocin. Ugeskr Laeger 1983;145:2588–90.
Lass A, Rosen DJD, Nahum R, Markov S, Kaneti HY, Fejgin MD, et al. Variable Decelerations during Pre-induction Oxytocin Challenge Test Predict Fetal Distress During Labor In Pregnancies With Uncomplicated Oligohydramnios. Proceedings of 14th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 5–8 June 1994, Helsinki, Finland, abstract no. 475.
Lazor LZ, Philipson EH, Ingardia CJ, Kobetitsch ES, Curry SL. A randomized comparison of 15- and 40-minute dosing protocols for labor augmentation and induction. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:1009–12.
Leiberman JR, Piura B, Chaim W, Cohen A. The cervical balloon method for induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1977;56:499–503.
Leijon I, Finnstrom O, Hedenskog S, Ryden G, Tylleskar J. Spontaneous labour and elective induction – a prospective randomised study. Behavioural assessment and neurological examination in the newborn period. Acta Paediatrica Scand 1979;68:553–60.
Leijon I, Finnstrom O, Hedenskog S, Ryden G, Tylleskar J. Spontaneous labor and elective induction – a prospective randomized study. II Bilirubin levels in the neonatal period. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1980;59:103–6.
LeMaire WJ, Spellacy WN, Shevach AB, Gall SA. Changes in plasma estriol and progesterone during labor induced with prostaglandin F2alpha or oxytocin. Prostaglandins 1972;2:93–101.
Leszczyńska-Gorzelak B, Jakimiuk A, Oleszczuk J. Cortisol in amniotic fluid during induced deliveries by prostaglandin E2. Zentralblatt fur Gynakologie 1993;115:550–2.
Leszczyńska-Gorzelak B, Laskowska M, Oleszczuk J. Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of misoprostol and prostaglandin E(2) in the preinduction and induction of labor. Med Sci Monit 2001;7:1023–8.
Leszczyńska-Gorzelak B, Laskowska M, Oleszczuk J. Using of misoprostol for preinduction and induction of labor in term pregnancy. Ginekologia Polska 1999;70:881–9.
Levy R, Ben-Arie A, Paz B, Hazan I, Blickstein I, Hagay Z. Randomized clinical trial of early vs late amniotomy following cervical ripening with a Foley catheter. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:S136.
Levy R, Kanengiser B, Furman B, Ben-Arie A, Brown D, Hagay ZJ. A randomized trial comparing a 30-ml and an 80-ml foley catheter balloon for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:1632–6.
Li FM. A study of misoprostol on induction of labor in term pregnancy. J Pract Obstet Gynecol 2000;16:139–41.
Li GQ. [Effect of electrode-stimulation point for oxytocic.] Shanghai J Acupunct Moxibustion 1996;15:16.
Li WJ, Li ZL, Ha KW. Effect of hyaluronidase on cervical ripening. Chin Med J 1994;107:552–3.
Lin A, Kupferminc M, Dooley SL. A randomized trial of extra-amniotic saline infusion versus laminaria for cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:545–9.
Lin MG, Reid KJ, Treaster MR, Nuthalapaty FS, Ramsey PS, Lu GC. Transcervical foley catheter with and without extraamniotic saline infusion for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2007;110:558–65.
Lindblad A, Ekman G, Marsal K, Ulmsten U. Fetal circulation 60 to 80 minutes after vaginal prostaglandin E2 in pregnant women at term. Arch Gynecol 1985;237:31–6.
Lindholm P. Induced labor. A comparative study of prostaglandin gel placed in the cervix and parenteral oxytocin. Ugeskr Laeger 1981;143:878–81.
Lindmark G, Nilsson BA. A comparative study of uterine activity in labour induced with prostaglandin F2alpha or oxytocin and in spontaneous labour I. Pattern of uterine contractions. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1976;55:453–60.
Lipshitz J, Lipshitz EM. Uterine and cardiovascular effects of fenoterol and hexoprenaline in prostaglandin F2 alpha-induced labor in humans. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:396–400.
Liu YL, Jin ZG. [Clinical observation of the impacts and safety of electroacupuncture at Sanyinjiao (SP 6) on labor.] Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2012;32:409–12.
Lokugamage AU, Forsyth SF, Sullivan KR, El Refaey H, Rodeck CH. Randomized trial in multiparous patients: investigating a single vs two-dose regimen of intravaginal misoprostol for induction of labour. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003;82:138–42.
Long Z. Auricular point-pressing therapy for induced labor in mid- and late pregnancy. Acupunct Res 1994;19:181.
Long ZG. 200 cases of ear acupoint press therapy for induced labor by rivanol at middle and late stage. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion 1994;14:26.
Lorentzen IP. Use of Acupuncture for Stimulation of Labour (Ongoing Trial). 2006. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 March 2006).
Lorenz RP, Botti JJ, Chez RA, Bennett N. Variations of biologic activity of low-dose prostaglandin E2 on cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 1984;64:123–7.
Loria-Casanova ML, Lemus-Maichel M, Kably-Ambe A. Evaluation of prostaglandin E2 in cervical maturation. Ginecol Obstet Mex 1989;57:193–5.
Lorrain J, Beaumont L, Desaulniers G, Chemaly R. Comparative study of synthetic and natural prostaglandins in the induction of labour. Med Union Canada 1982;111:563–8.
Loto OM, Ikuomola AA, Ayuba I, Onwudiegwu U. Comparative study of outcome of induction of labor using 25 µg and 50 µg of vaginal misoprostol. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2012;119(Suppl. 3):805.
Loto OM, Ikuomola AA, Ayuba II, Onwudiegwu U. Comparative study of the outcome of induction of labor using 25 µg and 50 µg of vaginal misoprostol. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:2359–62.
Lotshaw RR, Gordon HR. Optimal interval between prostaglandin E2 ripening of the cervix and oxytocin induction of labor: a prospective clinical trial. J Maternal-Fetal Med 1994;3:153–6.
Lowensohn RI, Jensen JT. Oxytocin Use in Induction and Augmentation of Labor. Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 23–27 January 1990, Houston, TX, USA, abstract no. 76.
Lunkad A, Kriplani A, Agarwal N, Bhatla N, Kulshreshtha V, Mahey R. Intravaginal versus Intracervical PGE2 Gel for Induction of Labor. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, abstract no. 123.
Lutgendorf MA, Johnson A, Terpstra ER, Snider TC, Magann EF. Extra-amniotic balloon for preinduction cervical ripening: A randomized comparison of weighted traction versus unweighted. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:581–6.
Luther ER, Gray JH, Young D, Gouin JA, Lorrain J. Comparison of natural and synthetic prostaglandin E2 tablets in labour induction. Can Med Assoc J 1983;128:1189–91.
Lykkesfeldt G, Osler M. Induction of labor with oral prostaglandin E2 and buccal demoxytocin without amniotomy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1981;60:429–30.
Lyndrup J, Legarth J, Weber T, Nickelsen C, Guldbaek E. Predictive value of pelvic scores for induction of labor by local PGE2. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1992;47:17–23.
Lyons C, Rumney P, Huang W, Morrison E, Thomas S, Nageotte M, et al. Outpatient cervical ripening with oral misoprostol post-term: induction rates decreased. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S116.
Moller T, Rempen A. [Induced labor with prostaglandins: 0.5 mg PGE2 intracervical gel versus 3 mg PGE2 vaginal tablet.] Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol 1995;199:30–4.
Mackenzie I, Xu J, Cusick C, Midwinter-Morten H, Meacher H, Mollison J, et al. Acupuncture for pain relief during induced labour in nulliparae: a randomised controlled study. BJOG 2011;118:440–7.
MacKenzie IZ, Annan B, Jackson C, Hurley P, Hey F, Newman M. A Randomised Trial Comparing a Non-biodegradable Polymer PGE2 Pessary with a Glyceride PGE2 Pessary for Labour Induction. 12th World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 23–28 October 1988, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, pp. 199–200.
Mackenzie IZ, Annan B, Jackson C, Hurley P, Hey F, Newman M. A Randomized Trial Comparing a Non-biodegradable Polymer PGE2 Pessary with a Glyceride PGE2 Pessary for Labour Induction. 12th FIGO World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 23–28 October 1988, Brazil, abstract no. 199.
MacKenzie IZ, Burns E. Randomised trial of one versus two doses of prostaglandin E2 for induction of labour: 1 Clinical outcome. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;104:1062–7.
MacKenzie IZ, Embrey MP. Cervical ripening with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Br Med J 1977;2:1381–4.
MacKenzie IZ, Magill P, Burns E. Randomised trial of one versus two doses of prostaglandin E2 for induction of labour: 2 Analysis of cost. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;104:1068–72.
MacLennan AH, Day A, Green RC. Intravaginal PGF2alpha vs Intravenous Oxytocin to Stimulate Labour After Membrane Rupture: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 118.
MacLennan AH, Green RC, Bryant-Greenwood GD, Greenwood FC, Seamark RF. Cervical ripening with combinations of vaginal prostaglandin F2alpha, estradiol and relaxin. Obstet Gynecol 1981;58:601–4.
Macones GA, Cahill A, Stamilio DM, Odibo AO. The efficacy of early amniotomy in nulliparous labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;207:403.e1–5.
Macpherson M, Welch C, Powell M, Filshie M. A Trial to Compare Lamicel, a New Induction Agent with Prostaglandin E2 Gel to Ripen the Cervix Prior to Induction of Labour. Proceedings of 23rd British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 12–15 July 1983, Birmingham, UK, abstract no. 79.
Madhavi N, Jahan A. Prospective Randomised Comparative Study of Labour with Misoprostol vs Oxytocin in Pre Labour Rupture of Membranes. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, 2011, abstract no. 106.
Mahendru R, Yadav S. Shortening the induction delivery interval with prostaglandins: a randomized controlled trial of solo or in combination. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc 2011;12:80–5.
Mahomed K. Foley catheter under traction versus extra-amniotic prostaglandin gel in pre-treatment of unripe cervix: a randomised controlled trial. Central Afr J Med 1988;34:98–102.
Majoko F, Nystrom L, Lindmark G. No benefit, but increased harm from high dose (100 microg) misoprostol for induction of labour: a randomised trial of high vs. low (50 microg) dose misoprostol. J Obstet Gynaecol 2002;22:614–17.
Majoko F, Zwizwai M, Lindmark G, Nystrom L. A Randomised Controlled Trial of Labour Induction with Misoprostol and Prostaglandin F2alpha Gel. 20th Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care in Southern Africa, 6–9 March 2001, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.
Makarem MH, Zahran KM, Abdellah MS, Karen MA. Early amniotomy after vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor: a randomized clinical trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2013;288:261–5.
Makary NA. Trial to Investigate the Effects of Oral vs Vaginal Prostaglandin E2 on Induction of Labour in Women with Premature Rupture of Membranes at 37–41 Completed Week’s Gestation with Unfavourable Cervix. Personal communication. 1990.
Mamo J. Intravaginal oestriol pessary for preinduction cervical ripening. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1994;46:137.
Manabe Y, Yoshimura S, Mori T, Aso T. Plasma levels of 13,14-dihydro-15-keto prostaglandin F2 alpha, estrogens, and progesterone during stretch-induced labor at term. Prostaglandins 1985;30:141–52.
Mancuso S, Ferrazzani S, De Carolis S, Carducci B, De Santis L, Caruso A. Term and postterm low-risk pregnancies: management schemes for the reduction of high rates of cesarean section. Minerva Ginecol 1996;48:95–8.
Manidakis G, Sifakis S, Orfanoudaki E, Mikelakis G, Prokopakis P, Magou M, et al. Prostaglandin versus stripping of membranes in management of pregnancy beyond 40–1 weeks. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1999;86:S79–80.
Mansouri M, Pour Javad A, Panahi G. Induction of labor with use of a Foley catheter and extra-amniotic corticosteroids. Med J Islamic Republic Iran 2003;17:97–100.
Manyonda IT. A Randomised Controlled Trial of the Use of the Foley Catheter Balloon for Induction of Labour to Reduce the Incidence of Caesarean Section in Diabetic Pregnancies: A Prospective Clinical, Economic and Psychological Evaluation. 2007. URL: www.controlled-trials.com/ (accessed 30 October 2007).
Marconi AM, Bozzetti P, Morabito A, Pardi G. Comparing two dinoprostone agents for cervical ripening and induction of labor: a randomized trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2008;138:135–40.
Mariani Neto C, Delbin AL, do Val Júnior R. [Tocographic pattern induced by misoprostol.] Rev Paul Med 1988;106:205–8.
Martin DH, Thompson W, Pinkerton JH, Watson JD. A randomized controlled trial of selective planned delivery. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1978;85:109–13.
Martin JN, Sessums JK, Howard P, Martin RW, Morrison JC. Alternative approaches to the management of gravidas with prolonged-postterm-postdate pregnancies. J Miss State Med Assoc 1989;30:105–11.
Martin RH, Menzies DN. Oestrogen therapy in missed abortion and labour. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp 1955;62:256–8.
Martinez AC, Rivera LN, Arangel CR. Acupuncture as an Alternative Technique for Uterine Contraction in Term Pregnant Patients. 5th World Congress on Controversies in Obstetrics and Gynecology, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 3–6 June 2004.
Marzouk AF. Oral and intravenous prostaglandin E2 in induction of labour. Br J Clin Prac 1975;29:68–70.
Mateos D, Cararach V, Sentis J, Botet F, Figueras F, Arimany MC, et al. Cervical prostaglandin E2 compared with expectant management or systematic induction in premature rupture of membranes with bad cervical conditions. Prenatal Neonatal Med 1996;1(Suppl. 1):85.
Mathews DD, Hossain H, Bhargava S, D’Souza F. A randomised controlled trial of an oral solution of prostaglandin E2 and oral oxytocin used immediately after low amniotomy for induction of labour in the presence of a favourable cervix. Curr Med Res Opin 1976;4:233–40.
Mathie JG, Dawson BH. Effect of castor oil, soap enema, and hot bath on the pregnant human uterus near term; a tocographic study. Br Med J 1959;1:1162–5.
Mati JK, Horrobin DF, Bramley PS. Induction of labour in sheep and in humans by single doses of corticosteroids. Br Med J 1973;2:149–51.
Mazhar SB, Imran R, Alam K. Trial of extra amniotic saline infusion with oxytocin versus prostaglandin E2 pessary for induction of labor. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2003;13:317–20.
McColgin SW, Bennett WA, Roach H, Cowan BD, Martin JN, Morrison JC. Parturitional factors associated with membrane stripping. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:71–7.
Megalo A, Hohlfeld P. Cervical ripening with vaginal misoprostol or PGE2 gel. Gynakol Geburtshilfliche Rundsch 1999;39:165.
Megalo A, Hohlfeld P. Misoprostol (PGE1) as an Alternative to PGE2 for Pre-induction Cervical Ripening and Labour Induction. 21st Conference of the Swiss Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 1998, abstract no. 19.
Mercer B, Pilgrim P, Sibai B. Labor induction with continuous low-dose oxytocin infusion: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 1991;77:659–63.
Merrill DC, Zlatnik FJ. Randomized, double-masked comparison of oxytocin dosage in induction and augmentation of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:455–63.
Milasinović L, Vuleta P, Radeka G, Petrović D, Orelj M. [Prostaglandins in the induction of labor at term with premature rupture of fetal membranes.] Med Pregl 1997;50:175–80.
Miller JF, Welply GA, Elstein M. Prostaglandin E2 tablets compared with intravenous oxytocin in induction of labour. Br Med J 1975;1:14–16.
Milliez JM, Jannet D, Touboul C, Khelifati Y, El Medjadji M. Two different regimens of preinduction ripening of the uterine cervix with prostaglandin E2: a randomized clinical study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1993;50:163–8.
Minaretzis D, Tsionu C, Papageorgiou I, Michalas S, Aravantinos D. Intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and labor induction: what is the appropriate dose? Gynecol Obstet Invest 1993;35:34–7.
Mink D, Boos R, Heiss C, Schmidt W. PGE2 gel and PGE2 intravaginal tablets to induce delivery at term – a prospective randomised study. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 1994;54:409–13.
Moghadam AD, Jaafarpour M, Khani A. Comparison effect of oral propranolol and oxytocin versus oxytocin only on induction of labour in nulliparous women (a double blind randomized trial). J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:2567–9.
Moghadam AD, Jaafarpour M, Nouri M, Abbasi N. Effects of oral propranolol on duration of labor and type of delivery in nulliparus women with prolonged pregnancy. Iranian J Obstet Gynecol Infertility 2012;15:31–6.
Moghtadaei P. A randomized trial comparing outpatient vaginal isosorbide-mononitrate versus extra-amnion saline infusion with concurrent oxytocin for cervical ripening and labor induction in nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;197(Suppl. 1):103.
Moghtadei P, Sardari F. A randomized trial comparing outpatient vaginal isosorbide mononitrate versus extra-amnion saline infusion with concurrent oxytocin for cervical ripening and labor induction in nulliparous women. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2008;21(Suppl. 1):77.
Moise KJ, Cano LE, Hesketh DE. A Prospective, Randomized Comparison of a New Synthetic Laminaria, Intracervical Prostaglandin E2 gel, and Oxytocin for Preinduction Ripening of the Term Cervix. Proceedings of 39th Annual Clinical Meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 1991, USA, abstract no. 24.
Mokgokong E. Induction of labour with oral prostaglandin E2. S Afr Med J 1976;50:699–701.
Mokgokong ET. Use of prostaglandins in minor cephalopelvic disproportion and abnormal uterine action. S Afr Med J 1974;48(Suppl.):15–19.
Molina M, Perez R, Fraenkel K, Vergara X. Oxitocin and Misoprostol in the Inducement of the Delivery Work of Full-term Pregnant Women. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 3–8 September 2000, Washington DC, USA, Book 1.
Mollo M. Trial to Assess the Effects of PGE2 Vaginal Tablets vs iv Oxytocin for Induction in Pregnancies with Favourable Cervical Scores. Personal communication. 1991.
Moran DJ, McGarrigle HH, Lachelin GC. Maternal plasma progesterone levels fall after rectal administration of estriol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994;78:70–2.
Muhammad Ali A, Mubasher S. A comparison of vaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 for induction of labour at term. BJOG 2013;120(Suppl. 1):57.
Mukhopadhyay M, Lim KJ, Fairlie FM. Is Propess a better method of induction of labour in nulliparous women? J Obstet Gynaecol 2002;22:294–5.
Muller PR, Stubbs TM, Laurent SL. A prospective randomized clinical trial comparing two oxytocin induction protocols. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;167:373–80.
Muller T, Schildhauer K, Gross M, Dietl J. Induction of labour with prostaglandins with unripe cervix: 0.5 mg intracervical PG-E2 versus 3 mg PG-E2 vaginal tablet. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 2000;60(Suppl. 1):71.
Mullin PM, House M, Paul RH, Wing DA. A comparison of vaginally administered misoprostol with extra-amniotic saline infusion for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:847–52.
Mundle WR, Young DC. Vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 1996;88:521–5.
Murray CP, Clinch J. Comparative study of labour induced by oral prostaglandin E2 and intravenous syntocinon. Irish Med J 1975;68:135–9.
Nabors GC. Castor oil as an adjunct to induction of labor: critical re-evaluation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1958;75:36–8.
Naismith WC, Barr W, MacVicar J. Induction of labour by simultaneous intravenous administration of prostaglandin E2 and oxytocin. Br Med J 1972;4:461–2.
Nassief SA, McFaul P, Rane A. Clinical trial comparing artificial rupture of membranes plus oral PGE2 tablets versus artificial rupture of membranes plus intravenous oxytocin for induction of labour in primigravid patients at term. Ulster Med J 1996;65:145–8.
Neri I, Chiesa V, Facchinetti F. Acupuncture in post-date pregnancy: a pilot study. Eur J Integr Med 2012;4(Suppl. 1):53.
Nesbitt RE, Cirigliano G. Use of relaxin during parturition. Clinical observations. N Y State J Med 1961;61:90–7.
Nikolov A, Dimitrov A, Krusteva K, Nashar S. Study of the effect of Propess for ripening of the unfavorable cervix for the induction of labor due to medical indications. Akush Ginekol 2003;42:5–8.
Nilsson B, Bremme K. Prediction of start of contractions in labor induced with oral prostaglandin E2 or oxytocin: a life table analysis approach. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1984;22:145–50.
Niroomanesh S, Dadashaliha M, Akrami M. Titrated oral misoprostol solution compared with oxytocin for induction of labor in women with unfavorable cervix. Tehran Uni Med J 2011;69:413–19.
Noah ML, Thiery M, Parewijck W, Decoster JM. Assessment of a two dose scheme of PGE2 gel for preinduction cervical softening. Prostaglandins 1985;30:305–11.
Norchi S, Zanini A, Ragusa A, Maccario L, Valle A. Induction of labor with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1993;42:103–7.
Nunes FP, Campos AP, Pedroso SR, Leite CF, Avillez TP, Rodrigues RD, et al. Intravaginal glyceryl trinitrate and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;194:1022–6.
Nuthalapaty FS, Ramsey PS, Biggio JR, Owen J. High-dose vaginal misoprostol versus concentrated oxytocin plus low-dose vaginal misoprostol for midtrimester labor induction: a randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;193:1065–70.
Nuutila M, Cacciatore B, Ylikorkala O. Effect of local prostaglandin E2 on uterine and fetal Doppler flow in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Hypertens Pregn 1997;16:357–66.
Obel EB, Larsen JF. A study of comparative efficacy of oral prostaglandin E2 as liquid formulation and tablets for induction of labour. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1975;37:35–8.
Odem RR, Work BA, Dawood MY. Pulsatile oxytocin for induction of labor: a randomized prospective controlled study. J Perinat Med 1988;16:31–7.
Odum CU, Isika AN, Lambo AO. Induction of labour with single insertion of vaginal tablet of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), amniotomy, and oxytocin infusion. West Afr J Med 1993;12:153–7.
Ohel G, Rahav D, Rothbart H, Ruach M. Ambulatory induction of labor at 40–1 weeks of gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:425.
Ohel G, Rahav D, Rothbart H, Ruach M. Randomised trial of outpatient induction of labor with vaginal PGE2 at 40–1 weeks of gestation versus expectant management. Arch Gynecol Obstet 1996;258:109–12.
Omer H, Sirkovitz A. Failure of hypnotic relaxation in the treatment of postterm pregnancies. Psychosom Med 1987;49:606–9.
Orhue A. A randomized trial of 45 minutes and 15 minutes incremental oxytocin infusion regimes for the induction of labour in women of high parity. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;100:126–9.
Orhue AA. A randomized trial of 30-min and 15-min oxytocin infusion regimen for induction of labor at term in women of low parity. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1993;40:219–25.
Orhue AAE. Incremental increases in oxytocin infusion regimens for induction of labor at term in primigravidas: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 1994;83:229–33.
Ozgur K. Induction of labor with intravaginal misoprostol versus intracervical dinoprostone. Arch Gynecol Obstet 1997;261:9–13.
Ozsoy M, Ozsoy D. Induction of labor with 50 and 100 microg of misoprostol: comparison of maternal and fetal outcomes. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2004;113:41–4.
Padayachi T, Norman RJ, Moodley J, Heyns A. Mifepristone and induction of labour in second half of pregnancy. Lancet 1988;1:647.
Palermo MSF, Damiano MS, Lijdens E, Cassale E, Monaco A, Gamarino S, et al. Dinoprostone vs oestradiol for induction to delivery Clinical controlled trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1997;76:97.
Parewijck W. Cervical Ripening with Intracervical Application of Prostaglandin E2 Gel. Personal communication. 1987.
Parker M. Comparison of Prostaglandin E2 Gel vs Vaginal Tablet for Cervical Ripening. Personal communication. 1990.
Parpas G, Gondry J, Verhoest P, Martinez C, Boulanger J. Randomised trial of 2 dosages of oxytocin for labour induction or augmentation. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1995;24:873.
Patel A, Giles JM, Moffett D, Mahram R, Diro M, Burkett G. Can misoprostol be interchanged with oxytocin for augmentation of labor? Obstet Gynecol 2000;95(Suppl. 4):10.
Patnaik P, Rout GC. Prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical priming and induction of labour in unfavourable cervical state. J Indian Med Assoc 1995;93:140–1, 135.
Patterson WM. Amniotomy, with or without simultaneous oxytocin infusion. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonwealth 1971;78:310–16.
Paul R, Romero R. Clinical Trial of Induction vs Expectant Management in Post-Term Pregnancy. Personal communication. 1988.
Pavlou C, Barker GH, Roberts A, Chamberlain GV. Pulsed oxytocin infusion in the induction of labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1978;85:96–100.
Payne E, Reed MF, Cietak KA, Anderson WR, Sant-Cassia LJ. A comparison of prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets with vaginal gel for ripening the unfavourable cervix and induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;13:103–6.
Pearce DJ. Pre-induction priming of the uterine cervix with oral prostaglandin E2 and a placebo. Prostaglandins 1977;14:571–6.
Pearson M, Hollier L, Shah A, Yeomans E. A randomized comparison of oral misoprostol versus intravenous oxytocin for induction of labor with term premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S174.
Pedersen S, Moller-Petersen J, Aegidius J. Comparison of oestradiol and prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel for ripening the unfavourable cervix. Br Med J 1981;282:1395.
Pedersen S, Moller-Petersen J, Aegidius J. The effect on induction of labour of endocervical balloon catheter with and without oestradiol therapy. Ugeskr Laeger 1981;143:3379–81.
Peedicayil A, Jasper P, Balasubramaniam N, Jairaj P. A randomized controlled trial of extra-amniotic ethinyloestradiol in ripening the cervix at term. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;96:973–7.
Peedicayil A, Jasper P, Balasubramaniam N, Jairaj P. A randomized controlled trial of extra-amniotic ethinyloestradiol for cervical ripening in multiparas. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1990;30:127–30.
Penna LK, MacLachlan NA, Dunlop D, Spencer JAD. Intracervical or Intravaginal Prostaglandin E2 gel for Cervical Ripening in the Unfavourable Cervix: A Randomized Trial. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April–3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 141.
Pentecost AF. The effect of buccal ‘pitocin’ on the unripe cervix. Curr Med Res Opin 1973;1:482–4.
Perales AJ, Diago VJ, Monleon-Sancho J, Grifol R, Dominguez R, Minguez JA, et al. Pulsatile Oxytocin Challenge Test. Proceedings of 14th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 5–8 June 1994, Helsinki, Finland, abstract no. 520.
Perry KG, Larmon JE, May WL, Robinette LG, Martin RW. Cervical ripening: a randomized comparison between intravaginal misoprostol and an intracervical balloon catheter combined with intravaginal dinoprostone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:1333–40.
Perry KG, Larmon JE, Rinehart BK, Gebhart LD, May WL, Martin RW. Cervical ripening: a randomized clinical trial of an intracervical balloon catheter combined with either intravaginal dinoprostone or misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:S127.
Pettker CM, Pocock SB, Smok DP, Devine PC. A prospective, randomized trial of transcervical foley catheter with or without oxytocin for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195(Suppl. 1):27.
Pettker CM, Pocock SB, Smok DP, Lee SM, Devine PC. Transcervical foley catheter with and without oxytocin for cervical ripening: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:1320–6.
Picasso DG. Cervical ripening with extra amniotic saline infusion: a randomized comparison of two mechanical devices. Reprod Sci 2012;19(Suppl. 3):180A.
Polvi HJ, Pirhonen JP, Erkkola RU. Vaginal and intracervical prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening: a Doppler study of hemodynamic effects. Am J Perinatol 1994;11:337–9.
Pongsatha S, Sirisukkasem S, Tongsong T. A comparison of 100 microg oral misoprostol every 3 hours and 6 hours for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2002;28:308–12.
Pongsatha S, Tongsong T, Somsak T. A comparison between 50 mcg oral misoprostol every 4 hours and 6 hours for labor induction: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Med Assoc Thailand 2001;84:989–94.
Porat S. The Use of Castor Oil as a Labor Initiator in Post-Date Pregnancies. 2006. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 March 2006).
Porozhanova V, Sampat D, Porozhanova K. [Misoprostol and induction of labour.] Akush Ginekol 2005;44:27–30.
Pranuthi R, Padmaja A, Padmaja P. Comparison of Oral Misoprostol with Vaginal Misoprostol For Induction of Labour. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, abstract no. 118.
Ramsey PS, Harris DY, Ogburn PL, Heise RH, Magtibay PM, Ramin KD. Comparative cost analysis of prostaglandin analogues dinoprostone and misoprostol as labor preinduction agents. Primary Care Update Ob/Gyns 1998;5:182.
Rangarajan NS, LaCroix GE, Moghissi KS. Induction of labor with prostaglandin. Obstet Gynecol 1971;38:546–50.
Rasheed R, Alam AA, Younus S, Raza F. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for labour induction. J Pakistan Med Assoc 2007;57:404–7.
Rath W, Adelmann-Grill BC, Schauer A, Hilgers R, Harder D, Kuhn W. Clinical, morphological and biochemical aspects of cervical ripening by intracervically applied sulprostone-gel. Arch Gynecol 1985;237(Suppl. 1):342.
Raymond S. The Use of Pulsed Oxytocin Infusion for the Induction of Labour. Personal communication. 1989.
Read MD, Martin RH. A comparison between intravenous oxytocin and oral prostaglandin E2 for the induction of labour in parous patients. Curr Med Res Opin 1974;2:236–9.
Rees AEJ. Randomised Trial Comparing Oxytocin with Vaginal Prostaglandin E2 Gel in the Induction of Labour in the Presence of Ruptured Membranes. Personal communication. 1992.
Reichel R, Husslein P, Göschen K, Rasche M, Sinzinger H. [Resorption of prostaglandin E2 following various methods of local administration for ripening of the cervix and end the induction of labor.] Wien Klin Wochenschr 1985;97:500–3.
Reid G, Helewa M. Pulsatile vs Continuous Oxytocin Infusion for Induction of Labour. Proceedings of 49th Annual Clinical Meeting of the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada, 22–26 June 1993, Ottawa, ON, Canada, abstract no. 14.
Reid GJ, Helewa ME. A trial of pulsatile versus continuous oxytocin administration for the induction of labor. J Perinatol 1995;15:364–6.
Reyna-Villasmil E, Guerra-Velasquez M, Torres-Montilla M, Reyna-Villasmil N, Mejia-Montilla J, Labarca-Vincero N. Comparative study of the effect of intravaginal misoprostol at 50 and 100 micrograms in cervical ripening and labor induction. Invest Clin 2005;46:179–86.
Ridgway L, Berkus M, Wright J. A randomized comparison of intracervical PGE2 vs intracervical prostin and Lamicel cervical dilator for ripening of the unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:307.
Rijnders MEB. Costs and Effects of Amniotomy at Home for Induction of Post Term Pregnancy. 2007. URL: www.controlled-trials.com (accessed 15 February 2007).
Roberts G. Induction of labour using prostaglandins. J Reprod Fertility 1970;23:370–1.
Robinson D. Efficacy and Safety of Titrated Oral Misoprostol Solution for Labor Induction at Term. 2011. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01070472 (accessed 22 January 2013).
Romer A, Weigel M, Zieger W, Melchert F. Prenatal acupuncture: effects on cervical maturation and duration of labor. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 2000;60:513–18.
Rosa P. A comparison of the efficiency of oxytocin and prostaglandin F2alpha in the treatment of dystocia in the primiparous woman at term. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1974;6:571–80.
Ross EL, Bofill JA, Keith SJ, Martin RW, Morrison JC. High-dose versus standard-dose oxytocin in parturients with high uterine risk factors: a randomized double blind trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S95.
Rudra T. Is Foley’s catheter a safe and cost effective way of IOL in low resource countries? Int J Gynecol Obstet 2012;119(Suppl. 3):468.
Rust O, Greybush M, Atlas R, Balducci J, Jones K. Does combination pharmacologic and mechanical preinduction cervical ripening improve ripening to delivery interval? Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:S136.
Rust OA, Greybush M, Atlas RO, Jones KJ, Balducci J. Preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized trial of intravaginal misoprostol alone vs a combination of transcervical foley balloon and intravaginal misoprostol. J Reprod Med 2001;46:899–904.
Saberi F, Abedzadeh M, Sadat Z, Eslami A. Effect of castor oil on induction of labour. J Kashan Uni Med Sci 2008;11:19–23.
Sabir N. Randomised Control Trial of the Effect of Advice on Sexual Intercourse after 36 Weeks on Pregnancy Duration and the Rate of Induction of Labour Thereafter. 2007. URL: www.controlled-trials.com/ (accessed 30 October 2007).
Sabra A, Abdel-Aleem H, Abdel-Aleem A, Shaheen A. Misoprostol versus Oxytocin Safety and Efficacy in Induction of Labor. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 3–8 September 2000, Washington DC, USA, Book 1, abstract no. 95–6.
Sadaty A, Pagano M, Greer C, Sison C, Schaffir J. A randomized trial of vaginal prostaglandin E(2) gel and dinoprostone vaginal insert for induction of labor at term. Prim Care Update Ob Gyns 1998;5:183.
Sahin HG, Sahin HA, Kocer M. Induction of labor in toxemia with misoprostol. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2002;81:252–7.
Saito K, Shoda T, Tani A, Yoshihara H, Amano K, Shimada N, et al. Pre-induction priming method for unripe cervix: comparative study with laminaria tents and metreurynter. Acta Obstet Gynaecol Japonica 1999;51:474–8.
Salamalekis E, Vitoratos N, Kassanos D, Loghis C, Panayotopoulos N, Sykiotis C. A randomized trial of pulsatile vs continuous oxytocin infusion for labor induction. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2000;27:21–3.
Saldivar D, Triana H, Soria A, Guzman A, Cabero L, Farran I, et al. Oral misoprostol versus intracervical dinoprostone for induction of labour in women with an unfavourable cervix. J Perinatal Med 2001;29(Suppl. 1):293.
Salmanian R, Khayamzadeh M. Prostaglandin & stripping in ripening of cervix and shortening of labor in post date pregnancies. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2012;119(Suppl. 3):811.
Samal S, Gupta U, Kumar SP, Agarwal P. A comparative study of oral prostaglandin (PGE2) & intravenous oxytocin in induction of labour. J Obstet Gynecol India 2000;50:49–51.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Danner CJ, Delke I. The effect of tablet moistening on labor induction with intravaginal misoprostol: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:1080–4.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Farah L, Kaunitz AM, Adair CD, Walker C, Del Valle GO, et al. Prepidil gel vs an extemporaneous preparation of prostaglandin E2 for pre-induction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:298.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Farah LA, Kaunitz AM, Adair D, Del Valle GO, Fuqua P. Preinduction cervical ripening with commercially available prostaglandin E2 gel: a randomized, double-blind comparison with a hospital-compounded preparation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1079–84.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Kaunitz AM, Del Valle GO, Delke I, Schroeder PA, Briones DK. Labor induction with the prostaglandin E1 methyl analogue misoprostol versus oxytocin: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 1993;81:332–6.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Kaunitz AM, Del Valle GO, Delke I, Schroeder PA, Briones DK. Labor induction with the prostaglandin E1 methyl analog misoprostol vs oxytocin: a randomized trial. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1993;43:229.
Sasaki K, Nakano R, Kadoya Y, Iwao M, Shima K, Sowa M. Cervical ripening with dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1982;89:195–8.
Satin AJ, Hankins GD, Yeomans ER. A prospective study of two dosing regimens of oxytocin for the induction of labor in patients with unfavorable cervices. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:980–4.
Satin AJ, Leveno KJ, Sherman ML, McIntire D. High-dose oxytocin: 20- versus 40-minute dosage interval. Obstet Gynecol 1994;83:234–8.
Scher J, Davey DA, Baillie P, Friend J, Friend DM. A comparison of prostaglandin F2 alpha and oxytocin in the induction of labour. S Afr Med J 1972;46:2009–12.
Schneider KT, Lüftner D, Rath W. Efficacy and safety of a 2-tier prostaglandin labor induction schedule. J Perinat Med 1994;22:399–407.
Schreyer P, Sherman DJ, Ariely S, Herman A, Caspi E. Ripening the highly unfavorable cervix with extra-amniotic saline instillation or vaginal prostaglandin E2 application. Obstet Gynecol 1989;73:938–42.
Sciscione AC, Muench M, Pollock M, Jenkins TM, Tildon-Burton J, Colmorgen GHC. Transcervical foley catheter for preinduction cervical ripening in an outpatient versus inpatient setting. Obstet Gynecol 2001;98:751–6.
Seeras RC, Olatunbosun OA, Pierson RA, Turnell RW. Induction of labor using prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) vaginal gel in triacetin base. An efficacy study comparing two dosage regimens. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1995;22:105–10.
Seidl A, Stopfer H, Gruber W, Fröhlich H, Baumgarten K. [Prostaglandins compared with oxytocin for induction of labour at term.] Wien Klin Wochenschr 1976;88:315–18.
Sellers S, MacKenzie IZ. Prostaglandin Release following Vaginal Prostaglandin Treatment for Labour Induction. In Wood C, editor. The Role of Prostaglandins in Labour. London: RSM Services; 1985. pp. 80–3.
Shaala S, Darwish E, Anwar M, Rocca M, Ismail AA. Cervical prostaglandin injection: a novel method of administration for ripening the cervix and induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1989;30:221–3.
Shanmugham D, Behera AK. Comparison of Prostaglandin E1 (misoprostol) with Prostaglandin E2 (Cerviprime gel) for Induction of Labour in Primigravidae. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, abstract no. 112.
Sharami SH, Milani F, Zahiri Z, Mansour-Ghanaei F. A randomized trial of prostaglandin E2 gel and extra-amniotic saline infusion with high dose oxytocin for cervical ripening. Med Sci Monit 2005;11:CR381–6.
Sharami SH. Comparison of Sublingual and Vaginal Misoprostol in Primiparous Women. 2010. URL: www.irct.ir (accessed 6 December 2010).
Sharma C. Induction Of labor in Women with Previous One Cesarean Section: Prospective Double Blind Randomized Control Trial Comparing the Effect of Mifepristone with Sweeping Stretching and Trans-Cervical Foley’s Catheterization. 2012. URL: www.ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2php?trialid=4745 (accessed 14 November 2012).
Sharma K, Grubbs B, Mullin P, Opper N, Lee R. Labor induction utilizing the Foley balloon: a randomized trial comparing delayed versus immediate removal. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210(Suppl. 1):326.
Sheela SR, Swamy NM, Ambika V. Induction of Labour with 25 mcg versus 100 mcg of Misoprostol. 49th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology; 6–9 January 2006, Cochin, Kerala State, India, abstract no. 54.
Shennan A. A Physiological Approach to Induction of Labour: PULSE – A Randomised, Controlled Trial of Pulsatile versus Continuous Oxytocin Administration. 2006. URL: www.nrr.nhs.uk (accessed 6 July 2006).
Shennan AH, Smith R, Browne D, Edmonds DK, Morgan B. The elective use of oxytocin infusion during labour in nulliparous women using epidural analgesia: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Int J Obstet Anesth 1995;4:78–81.
Shetty A, Martin R, Danielian P, Templeton A. A comparison of two dosage regimens of oral misoprostol for labor induction at term. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2002;81:337–42.
Shipman M. The SNS Trial: Sweeping vs no Sweeping of Membranes in Uncomplicated Post-Date Pregnancies. 2000. URL: www.nrr.nhs.uk (accessed 8 March 2000).
Shravage J. Effect of sweeping of membranes at initiation of formal induction of labour – a randomised controlled trial. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2009;107(Suppl. 2):338.
Singh PM, Young DC. A RCT of High Dose vs Low Dose Oxytocin for Induction of Labour. Proceedings of 49th Annual Clinical Meeting of the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada, 22–26 June 1993, Ottawa, ON, Canada, abstract no. 48.
Sivasuriya M, Tan KL, Salmon YM, Karim SM. Neonatal serum bilirubin levels in spontaneous and induced labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1978;85:619–23.
Sjostedt S. Induction of labour. A comparison of intranasal and transbuccal administration of oxytocin. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1969;48:1–17.
Skajaa K, Mamsen A, Secher NJ. Cervical Ripening with Prostaglandin E2 in Different Vehicle Forms. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 196.
Skajaa K, Mamsen A, Secher NJ. Influence of vehicle form on efficiency of prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1991;42:177–80.
Skupski D, Cabbad M, Luo G, Feingold L, Sharma G, Eglinton G. Simultaneous versus sequential dinoprostone and oxytocin for induction of labor at term with intact membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195(Suppl. 1):91.
Smith CV, Miller A, Livezey GT. Double-blind comparison of 2.5 and 5.0 mg of prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. J Reprod Med 1996;41:745–8.
So LK, Sung ML, Yeung KK. Induction of Labour by Acupuncture. 9th World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 26–31 October 1979, Tokyo, Japan, abstract no. 281.
Solt I, Ben-Harush S, Kaminskey S, Sosnovsky V, Ophir E, Bornstein J. A prospective randomized study comparing induction of labor with the foley catheter and the cervical ripening double balloon catheter in nulliparous and multiparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009;201(Suppl. 1):124.
Somell C, Larsson B. Priming and induction of labor with oral PGE2 in patients with low Bishop score. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1983;62:315–20.
Somell C. Induction of labor and cervical ripening with oral PGE2 in risk pregnancies: a placebo-controlled study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1987;66:633–7.
Somsak T, Pongsatha S. A comparison between oral misoprostol 50 micrograms every 4 hours and every 6 hours for labor induction. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;12:334.
Soni M, Sachdeva L. Induction of labour with oral PGE2 and its comparison with intravenous oxytocin. J Obstet Gynecol India 2000;50:51–3.
Sorensen MB, Evans C, Ekpe A, Cotzias C. Comparison of Three Modes of Administration of Prostaglandin for Induction of Labour. 36th Nordic Congress of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 14–17 June 2008, Reykjavik, Iceland, pp. 123–4.
Sørensen SS, Brocks V, Lenstrup C. Induction of labor and cervical ripening by intracervical prostaglandin E2. Obstet Gynecol 1985;65:110–14.
Sorokin Y, Hallak M, Klein O, Kalderon I, Abramovici H. Effects of induction of labor with prostaglandin E2 on fetal breathing and body movements: controlled, randomized, double-blind study. Obstet Gynecol 1992;80:788–91.
Sorokin Y, Hallak M, Klein O, Kalderon I, Abramovici H. Effects of induction of labor with prostaglandin E2 on fetal breathing and body movements: controlled, randomized, double-blind study. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1993;42:84.
Sorokin Y, Hallak M, Klein O, Kalderon I, Abramovici H. Prostaglandin and Fetal Breathing Movement: Controlled Randomized Double Blind Study. Proceedings of 11th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 1988, Rome, Italy, abstract no. 11.
Spellacy WN, Buhi WC, Holsinger KK. The effect of prostaglandin F 2 and E 2 on blood glucose and plasma insulin levels during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1971;111:239–43.
Spitzberg E, Yonekura ML. Preinduction cervical ripening with controlled-release PGE2 pessary. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:313.
Srisomboon J, Piyamongkol W, Aiewsakul P. Comparison of intracervical and intravaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and labour induction in patients with an unfavourable cervix. J Med Assoc Thailand 1997;80:189–94.
Srividhya S, Raghavan S. Endocervical prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) gel in premature rupture of membranes. J Obstet Gynecol India 2001;51:122–6.
Steer PJ, Carter MC, Choong K, Hanson M, Gordon AJ, Pradhan P. A multicentre prospective randomized controlled trial of induction of labour with an automatic closed-loop feedback controlled oxytocin infusion system. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1985;92:1127–33.
Steer PJ, Little DJ, Lewis NL, Kelly MC, Beard RW. The effect of membrane rupture on fetal heart rate in induced labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1976;83:454–9.
Steer PJ. Trial to Compare Prostaglandins with Oxytocin for Active Management of Prelabour Rupture of Membranes at Term. Personal communication. 1992.
Stewart JD, Rayburn WF, Farmer KC, Liles EM, Schipul A, Stanley JR. Effectiveness of prostaglandin e2 intracervical gel (prepidil), with immediate oxytocin, versus vaginal insert (cervidil) for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:1175–80.
Stewart P, Kennedy JH, Barlow DH, Calder AA. A comparison of oestradiol and prostaglandin E2 for ripening the cervix. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1981;88:236–9.
Stiver KH, Davis MJ, Golichowski AM. Repeated intracervical prostaglandin administration for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:315.
Suikkari AM, Jalkanen M, Heiskala H, Koskela O. Prolonged pregnancy: induction or observation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1983;116:58.
Sullivan CA, Benton LW, Roach H, Smith LG, Martin RW, Morrison JC. Combining medical and mechanical methods of cervical ripening. J Reprod Med 1996;41:823–8.
Suri V, Dalui R, GuptaI, Ray P. Preinduction Cervical Ripening: A Comparison of Extraamniotic Foley Catheter Balloon and Intracervical Prostaglandin E2 gel. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 3–8 September 2000, Washington DC, USA, Book 4, abstract no. 69.
Swann O. Induction of labor by stripping membranes. Obstet Gynecol 1958;11:74–8.
Tadmor OP, Keren A, Rosenak D, Gal M, Shaia M, Hornstein E, et al. The effect of disopyramide on uterine contractions during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;162:482–6.
Tan ASA, Abu J, Cheng HH, Liauw P. Comparing the efficacy of prepidil gel vs prostin E2 vaginal pessaries in cervical priming and induction of labour. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1994;46:7.
Tan LK, Tay SK. Two dosing regimens for preinduction cervical priming with intravaginal dinoprostone pessary: a randomised clinical trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;106:907–12.
Tan PC, Daud SA, Omar SZ. Concurrent dinoprostone and oxytocin for labor induction in term premature rupture of membranes: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2009;113:1059–65.
Tan PC, Jacob R, Omar SZ. Membrane sweeping at initiation of formal labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2006;107:569–77.
Tan PC, Valiapan SD, Tay PY, Omar SZ. Concurrent oxytocin with dinoprostone pessary versus dinoprostone pessary in labour induction of nulliparas with an unfavourable cervix: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. BJOG 2007;114:824–32.
Tang L, Zhu Q, Wang S. [Dose study of methyl carboprost suppository for planned delivery at term.] Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1997;32:19–21.
Tanir HM, Sener T, Yildiz C, Kaya M, Kurt I. A prospective randomized trial of labor induction with vaginal controlled-release dinoprostone inserts with or without oxytocin and misoprostol+oxytocin. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2008;35:65–8.
Tedesco RP, Cecatti JG, Lourenco N, Filho M. Effectiveness of two different doses of vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2002;24:614–16.
Thach TS, Jamulitrat S, Chongsuviwatong V, Geater A, Pham TD. Misoprostol: An Effective Alternative to Oxytocin for Labour Induction in Term Premature Rupture of Membrane and Unfavourable Cervix. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 3–8 September 2000, Washington DC, USA, Book 3, abstract no. 53.
Thiery M, Benijts G, Martens G, Sian AY, Amy JJ, Derom R. A comparison of buccal (oromucosal) and oral prostaglandin E2 for the elective induction of labor. Prostaglandins 1977;14:371–9.
Thiery M, De Gezelle H, Van Kets H, Voorhoof L, Verheugen C, Smis B, et al. The effect of locally administered estrogens on the human cervix. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol 1979;183:448–52.
Thiery M, Parewijck W, Martens G, Derom R, Van Kets H. Extra-amniotic prostaglandin E2 gel vs amniotomy for elective induction of labour. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol 1981;185:323–6.
Thomas G, Blackwell RJ. A controlled trial of the Cardiff automatic infusion system in the management of induced labour. Br J Clin Prac 1974;28:203–6.
Thompson JH. Induction of Labour: A Comparison between Intravaginal Prostaglandin E2 gel and Oxytocin Infusion with Low Amniotomy. Proceedings of 21st International Congress of International Confederation of Midwives, 1987, The Hague, The Netherlands: 1–8.
Thomsen AC. Induction of Labour by Low-Dose PGF2 alpha and Oxytocin. A Randomised Double-Blind Study. Personal communication. 1987.
Thornton S, Davison JM, Baylis PH. Amniotomy-induced labour is not mediated by endogenous oxytocin. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;96:945–8.
Tiwari N, Maru L. Comparative Study of Sublingual versus Pervaginal Misoprostol in Induction of Term Labor. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, abstract no. 122.
Toplis PJ, Sims CD. Prospective study of different methods and routes of administration of prostaglandin E2 to improve the unripe cervix. Prostaglandins 1979;18:127–36.
Toppozada M, El-Ghazzawi E, Meleis M, Abd-Rabbo S. Effect of 9-deoxo-16,16-dimethy-l9-methylene-prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel on the tissues of the pregnant unripe cervix at term. J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;12:228–31.
Torres R, Santiago P, Rivera J, Adamsons K. Reduction of the duration of induced labor after blockade of myometrial adrenergic beta receptors with propanolol. J Perinatal Med 2001;29(Suppl. 1):708.
Tsitsis V, Tsokaki T. The use of misoprostol in cervical ripening in full-term pregnancies and the perinatal result. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:84.
Tsitsis V, Tsokaki TK. The use of misoprostol in cervical ripening in full-term pregnancies and the perinatal result: Tsitsis Vasileios, Tsokaki Theodora Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, General Hospital of Pirgos, Peloponnisos, Greece. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2012;119:S812.
Tuipae S, Khooarmornpattana S. Effectiveness of oral misoprostol for cervical priming in term pre-labor rupture of membranes (PROM). Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;11:276.
Turnquest MA, Lemke MD, Brown HL. Cervical ripening: randomized comparison of intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel with prostaglandin E2 gel plus laminaria tents. J Matern Fetal Med 1997;6:260–3.
Ulstein M, Sagen N, Eikhom SN. A comparative study of labor induced by prostaglandin E2 and buccal tablets of demoxytocin. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1979;17:243–5.
Vaisanen-Tommiska M, Mikkola T, Ylikorkala O. Vaginal Nitro Induces Cervical Nitric Oxide Release in Women Postterm. 36th Nordic Congress of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 14–17 June, Reykjavik, Iceland. abstract no. 123.
Van Dessel T, Frijns JHM, Kok F, Wallenburg HCS. Prostaglandins and Dilatation of the Human Cervix. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April–3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 121.
Van Heerden J, Steyn DW. Management of Premature Rupture of Membranes after 34 Weeks Gestation. Proceedings of 11th Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care in South Africa, March 1992, Caledon, South Africa, pp. 98–9.
Varaklis K, Cuming R, Stubblefield P. Misoprostol: a prostaglandin E1 analogue. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1994;46:105.
Varma R, Norman J, Cowell L. Induction of labour with vaginal prostaglandin E2 pessaries. J Obstet Gynaecol 1981;2:65–70.
Varma TR, Norman J. Comparison of three dosages of prostaglandin E2 pessaries for ripening the unfavourable cervix prior to induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1984;63:17–21.
Veligati P, Broekhuizen FF, Kirby RS, Malnory M. A randomized trial comparing prostaglandin E(2) vaginal insert (Cervidil) to vaginal gel for cervical ripening before induction of labor. Prim Care Update Ob Gyns 1998;5:182.
Vengalil SR, Guinn DA, Olabi NF, Burd LI, Owen J. A randomized trial of misoprostol and extra-amniotic saline infusion for cervical ripening and labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1998;91:774–9.
Vidanagamage RS, Goonewardene IM. The efficacy of two different doses of vaginal isosorbide mononitrate in pre induction cervical ripening: a double blind randomised controlled trial. Ceylon Med J 2011;56:91–100.
Vijitrawiwat A, Pongsatha S. A comparison between oral misoprostol 100 micrograms every 3 hours and vaginal misoprostol 50 micrograms every 4 hours for labor induction. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;15:285.
Voss DH, Cumminsky KC, Cook VD, Nethers MS, Spinnato JA, Gall SA. Effect of three concentrations of intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening. J Matern Fetal Med 1996;5:186–93.
Vroman S, Thiery M, Yo Le Sian A, Depiere M, Vanderheyden C, Derom R, et al. A double blind comparative study of prostaglandin F2alpha and oxytocin for the elective induction of labor. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1972;4S:115–23.
Walker E, Gordon AJ. Length of exposure to prostaglandin E2 and cervical ripening in primigravidae. J Obstet Gynaecol 1983;4:88–9.
Wang L, Shi C, Yang G. Comparison of misoprostol and ricinus oil meal for cervical ripening and labor induction. Chung-Hua Fu Chan Ko Tsa Chih 1997;32:666–8.
Wang Z, Li W, Ouyang W, Ding Y, Wang F, Xu L, et al. Cervical ripening in the third trimester of pregnancy with intravaginal misoprostol: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Tongji Med Uni 1998;18:183–6.
Wang Z, Li W, Ouyang W. Safety and efficacy of intravaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening in the third trimester of pregnancy. Chung-Hua Fu Chan Ko Tsa Chih 1997;32:326–8.
Ward SJ. Induction of Labour Using Prostaglandin Gel in Patients with a Favourable Cervix. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April–3 May, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 143.
Webb GW, Raynor BD, Huddleston JHW. Induction of labor with an unfavorable cervix: a randomized prospective trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S22.
Weeks AD. Induction of Labour in Pre-Eclamptic Women: A Randomised Trial Comparing the Foley Balloon Catheter with Oral Misoprostol. 2013. URL: www.clinicaltrials.gov (accessed 28 May 2013).
Wei ZT, Wang XY. Analysis of 98 cases about labour induction in women at term with mifepristone and oxytocin. J Weifang Med Coll 2000;22:184–5.
Weiss G, Teichman S, Stewart D, Nader D, Wood S, Unemori E. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of relaxin for cervical ripening in post-delivery date pregnancies. Ann N York Acad Sci 2009;1160:385–6.
Weiss RR, Tejani N, Israeli I, Evans MI, Bhakthavathsalan A, Mann LI. Priming of the uterine cervix with oral prostaglandin E2 in the term multigravida. Obstet Gynecol 1975;46:181–4.
Weissberg SM, Spellacy WN. Membrane stripping to induce labor. J Reprod Med 1977;19:125–7.
Welt SI. Comparison of Mechanical and Pharmacologic Means for Induction of Labor. Personal communication. 1987.
Westergaard JG, Lange AP, Pedersen GT, Secher NJ. Oral oxytocics for induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1983;62:103–10.
Westergaard JG, Lange AP, Pedersen GT, Secher NJ. Use of oral oxytocics for stimulation of labor in cases of premature rupture of the membranes at term. A randomized comparative study of prostaglandin E2 tablets and demoxytocin resoriblets. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1983;62:111–16.
Wicker R, Albert J, Laurent S, Bellitt P. Evaluation of misoprostol and dinoprostone in cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:424.
Wildemeersch DA, Schellen AM. Double-blind trial of prostaglandin F2alpha and oxytocin in the induction of labour. Curr Med Res Opin 1976;4:263–6.
Wilk M, Jureczko T, Poreba R, Sipinski A. Misoprostol and oxytocin in induction of labour in women with prolonged pregnancy: safety and effectiveness comparison. Wiadomosci Lekarskie 2001;54:662–7.
Willcourt RJ, Pager D, Wendel J, Hale RW. Induction of labor with pulsatile oxytocin by a computer-controlled pump. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:603–8.
Williams JK, Lewis ML, Cohen GR, O’Brien WF. The sequential use of estradiol and prostaglandin E2 topical gels for cervical ripening in high-risk term pregnancies requiring induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988;158:55–8.
Williams JK, Wilkerson WG, O’Brien WF, Knuppel RA. Use of prostaglandin E2 topical cervical gel in high-risk patients: a critical analysis. Obstet Gynecol 1985;66:769–73.
Windrim R, Bennett K, Mundle W, Young DC. Oral administration of misoprostol for labor induction: a randomised controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:392–7.
Wing DA, Lovett K, Paul RH. Disruption of prior uterine incision following misoprostol for labor induction in women with previous cesarean delivery. Obstet Gynecol 1998;91:828–30.
Wing DA, Miller H, Parker L, Powers BL, Rayburn WF, for the Misoprostol Vaginal Insert Miso-Obs I. Misoprostol vaginal insert for successful labor induction. A randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2011;117:533–41.
Wing DA, Paul RH. A comparison of differing dosing regimens of vaginally administered misoprostol for preinduction cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:158–64.
Witter FR, Weitz CM. Cervical examination prior to induction in postdate pregnancies. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1989;168:214–16.
Wolf SB, Sanchez-Ramos L, Kaunitz AM. Sublingual misoprostol for labor induction: a randomized clinical trial. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105:365–71.
Wolfler MM, Facchinetti F, Venturini P, Huber A, Helmer H, Husslein P, et al. Induction of labor at term using isosorbide mononitrate simultaneously with dinoprostone compared to dinoprostone treatment alone: a randomized, controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195:1617–22.
Wyldes MP. Trial to Compare 0.5 mg PGE2 Intracervical Gel (Prepadil) vs Vaginal PGE2 Gel (1 mg or 2 mg) in Induction of Labour. Personal communication. 1992.
Yacoob T, Lloyd M, Unwin A, Harrison RF. Intracervical prostaglandin E2, 0.5 mg; gel or tablet for cervical ripening and induction of labour with an unfavourable cervix? J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;13:167–70.
Yang Z, Wang YL. A comparison of misoprostol and prostaglandin e2 gel for cervical ripening and induction of labour: a clinical study on efficacy of two different dosages gemfibrozil administered in hyperlipidemic patients. J Jinzhou Med Coll 2000;21:10–12.
Yang ZY, Li E, Yu SS. [15-Methyl-PGF2 alpha vaginal suppository for induction of term labor.] Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1994;29:273–5.
Yeung KK, Pang JC. Oral prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha in the induction of labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1977;17:32–5.
Young D, Delaney T, Armson T, Fanning C. Lower dose vaginal and oral misoprostol in labor induction: RCT. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):203.
Zafarghandi A, Zafarghandi N, Baghaii N. Foley catheter cervical ripening with extra-amniotic infusion of saline or corticosteroids: a double-blind randomized controlled study. Acta Med Iranica 2004;42:338–42.
Zanini A, Norchi S, Ragusa A, Strobelt N, Lissoni A. Induction of Labour with Vaginal PGE2 Gel: a Controlled Clinical Trial. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction; 1991 30 April to 3 May, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 144.
Zimmer EZ, Jakobi P, Weissman A. The effect of ripening the cervix with prostaglandin E2 or transcervical catheter on fetal breathing and body movements. J Maternal-Fetal Invest 1996;6:104–6.
Appendix 4 Characteristics of excluded studies
| Author | Year | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Abbassi RM | 2008 | Not a RCT |
| Abdellah MS | 2011 | Complex intervention |
| Abramovici D | 1999 | Methodological issues – not all women received intervention as protocol stated; unclear. Women received catheter based on Bishop score |
| Abramovici D | 1999 | Complex intervention |
| Adewole IF | 1993 | No data |
| Afolabi BB | 2005 | Outcome data not usable |
| Aggarwal N | 2006 | Methodological inconsistencies |
| Aghamohammadi A | 2011 | Insufficient information for assessment |
| Akhtar A | 2011 | No details of doses or regimens |
| Akram H | 2005 | Not a RCT |
| Al-Assadi AF | 2007 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Amano K | 1999 | No relevant data; induction group received several methods not reported separately Method of randomisation unclear |
| Anderson G | 1971 | No relevant data. Results not reported by randomised group |
| Anderson GG | 1972 | Unclear if RCT |
| Andreasson B | 1985 | Not a relevant comparison. Intranasal oxytocin |
| Anonymous – Ferring Pharmaceuticals | 2010 | Trial registration. No results reported |
| Arrieta OB | 2000 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Arsenijevic S | 2012 | Not clear for induction of labour |
| Arulkumaran S | 1987 | Not a relevant comparison. Regimen comparison |
| Arulkumaran S | 1985 | Not a relevant comparison. Regimen comparison |
| Ascher-Walsh C | 2000 | Dose comparison |
| Ashworth MF | 1988 | Not a relevant comparison. Pulsatile i.v. oxytocin vs. continuous oxytocin |
| Atad J | 2000 | Not a RCT |
| Atad J | 1996 | Methodological reasons. Crossover design |
| Atad J | 1991 | Complex intervention |
| Atkinson MW | 2000 | Dose comparison |
| Augensen K | 1987 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Augensen K | 1986 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Auner H | 1993 | Regimen comparison. Not a relevant comparison |
| Averill KA | 1999 | No relevant data |
| Azarkish F | 2008 | Insufficient information to assess |
| Azeem S | 2006 | Not a RCT |
| Azhari S | 2006 | No relevant outcome data |
| Babcock RJ | 1959 | No relevant data |
| Baev O | 2011 | No relevant data |
| Balintona J | 2001 | No outcome data |
| Bamford PN | 1992 | No outcome data |
| Barkai G | 1997 | Complex intervention |
| Barrilleaux PS | 2002 | Complex intervention |
| Bates CD | 2003 | No relevant outcome data |
| Baxi LV | 1980 | No data |
| Beard RJ | 1975 | Complex intervention |
| Beazley JM | 1971 | No data |
| Bebbington M | 2003 | Unclear definition of relevant outcomes. No usable data |
| Beigi A | 2010 | No data |
| Belfrage P | 2000 | Excluded for methodological reasons |
| Ben-Aroya Z | 2001 | Not a RCT |
| Bendvold E | 1990 | No relevant outcome data |
| Bergsjo P | 1989 | Complex intervention |
| Bergsjo P | 1969 | Not a relevant comparison. Intranasal oxytocin |
| Bernstein EP | 1986 | No relevant outcome data |
| Bex P | 1990 | No outcome data |
| Bi S | 2000 | Excluded for methodological reasons |
| Blackburn MG | 1973 | No relevant outcome data |
| Blakemore KJ | 1990 | Regimen comparison. Not a relevant comparison |
| Bloch B | 1975 | Not a RCT |
| Blumenthal PD | 1990 | Not a relevant comparison. Both interventions same code |
| Bo QX | 2006 | This study explored acupuncture for pain relief |
| Bolnick JM | 2004 | Complex intervention |
| Bonebrake R | 2001 | No data |
| Borisov I | 1985 | Insufficient information for assessment |
| Botero L | 1998 | Trial registration. No relevant outcome data |
| Bozhinova S | 2007 | Not a relevant comparison. Both arms high dose |
| Brandel E | 1998 | Excluded from 0317 – possibly allocation bias, primary outcome statistics not adequately reported |
| Breart G | 1991 | Not clear that this trial is for induction. Not relevant intervention |
| Breart G | 1982 | Not clear that this trial is for induction. Not relevant intervention |
| Bredow V | 1993 | Not a RCT |
| Bredow V | 1990 | Not a RCT. Allocation by Bishop scores |
| Bremme K | 1987 | Complex intervention |
| Bremme K | 1984 | Complex intervention |
| Bremme K | 1980 | Complex intervention |
| Browne MJ | 1988 | Insufficient information for assessment |
| Browne PC | 2011 | Trial registration. No data |
| Buccellato CA | 2000 | Complex intervention |
| Butler B | 2004 | Oral misoprostol review – no group denominators |
| Cabrol D | 1990 | Not a relevant participant group |
| Cai LL | 2010 | No relevant data |
| Calder AA | 2008 | Misoprostol group included both high- and low-dose regimens. Results were not reported by dose |
| Calder AA | 1975 | Complex intervention |
| Calder AA | 1974 | No relevant data |
| Caliskan E | 2005 | No relevant data |
| Cameron A | 1985 | No usable outcome data. Denominators unclear |
| Cameron AD | 1988 | No data |
| Carbone JF | 2013 | Complex intervention |
| Carlan SJ | 1997 | Comparing tablet with gel |
| Carlan SJ | 1995 | Dose comparison, both high dose |
| Casey BM | 1995 | Complex intervention |
| Casey C | 1993 | Not a relevant comparison. Comparison group did not all receive the same protocol |
| Castle B | 1983 | No outcome data, looking at absorption |
| Cecatti JG | 2006 | Both groups received 25 µg of vaginal misoprostol |
| Cetin A | 1997 | No outcome data |
| Chang YK | 2003 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Chen DC | 2005 | Exclude for methodological reasons |
| Chen DC | 2004 | Analysis not by randomisation group |
| Chestnut DH | 1994 | Not a relevant intervention |
| Chia YT | 1993 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Chipato T | 1997 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Chou MM | 1991 | No data |
| Christensen FC | 2002 | Complex intervention |
| Chua S | 1991 | Dose and regimen comparison. Not a relevant comparison |
| Cole RA | 1975 | Regiment comparison |
| Coleman FH | 1997 | Complex intervention |
| Collingham JP | 2010 | Complex intervention |
| Coltart TH | 1974 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Craft I | 1976 | Not a RCT |
| Craft IL | 1971 | No relevant data |
| Crane J | 1993 | Regimen comparison. Not a relevant comparison |
| Critchley HOD | 1994 | Dose comparison |
| Cross WG | 1978 | Attrition |
| Culver J | 2004 | Complex intervention |
| Cummiskey KC | 1990 | Not a relevant comparison |
| D’Aniello G | 2003 | Not a RCT |
| D’Souza SW | 1986 | No relevant data |
| Damania KR | 1988 | Not a RCT |
| Danezis J | 1962 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Daniel-Spiegel E | 2004 | Regimen comparison |
| Danna P | 1995 | No outcome data |
| Dasgupta E | 2012 | Complex intervention |
| Davies NJ | 1991 | Regimen comparison |
| Day L | 2009 | No relevant data |
| De Laat WNGM | 1991 | No outcome data |
| De Leon-Casasola OA | 1993 | Not a relevant comparison |
| De Oliveira MGM | 2003 | No data |
| DebBarma AM | 2013 | Trial registration |
| Decker WH | 1958 | Not a RCT |
| Delaney S | 2010 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Delaney T | 2001 | Comparison of different dosing regimens |
| Delaney T | 2001 | Insufficient information |
| Deo S | 2013 | No data for primary outcomes |
| Di Lieto A | 1989 | No data |
| Dietl J | 1987 | Trial registration |
| Ding DC | 2005 | Not a RCT |
| Dionne MD | 2011 | Complex intervention |
| Dogra Y | 2012 | No data |
| Dommisse J | 1981 | No outcome data |
| Dorfman P | 1987 | Inadequate details of treatment/intervention |
| Dorr A | 1990 | Complex intervention |
| Du S | 2000 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Duhl A | 1997 | No data |
| Dundas KC | 2000 | Insufficient information |
| Dunn PA | 1989 | No relevant data |
| Dunston-Boone G | 1991 | Includes non-randomised participants |
| Duru NK | 1997 | Not relevant participant group |
| Echeverria EL | 1995 | Not a RCT |
| Edelstein H | 1964 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Eftekhavi N | 2002 | Brief abstract, insufficient information |
| Ehrenberg-Buchner S | 2013 | No outcome data |
| Ekblad U | 1994 | Not a RCT |
| Ekerhovd E | 2003 | Not an induction of labour trial |
| Elliott CL | 1998 | No data |
| Elliott JP | 1984 | No data |
| Elliott JP | 1983 | No relevant data |
| El Sedeek MSh | 2009 | No relevant outcome data |
| El-Torkey M | 1995 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Emery S | 1988 | No relevant data |
| Engleman SR | 1979 | Not a RCT |
| Escalante G | 1993 | Results not reported by randomisation group |
| Evans MI | 1983 | Complex intervention |
| Ewert K | 2006 | Dose ranging study, same code |
| Fekih M | 2009 | Dose comparison study |
| Filho FAR | 2007 | Dose comparison: both low dose |
| Filshie GM | 1992 | Trial registration |
| Fitzpatrick CB | 2012 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Foong LC | 2000 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Freeman RK | 1968 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Friedman EA | 1975 | Dose comparison |
| Friedman EA | 1975 | Dose comparison |
| Friedman EA | 1974 | No relevant data |
| Fuchs AR | 1984 | Not a RCT |
| Fuchs K | 2006 | No outcome data |
| Fusi L | 1989 | No outcome data, no denominators |
| Garcia AA | 1988 | Not a RCT |
| Gauger LJ | 1991 | Data not in form we can use |
| Gemer O | 2001 | No data |
| Ghanaei MM | 2013 | No data |
| Ghanaei MM | 2009 | Complex intervention |
| Ghidini A | 2001 | Dose comparison: both high dose |
| Gibb DMF | 1985 | Dose comparison |
| Gibson KS | 2013 | Not a relevant comparison. Both code 24 |
| Gilad R | 2012 | No data |
| Gillot M | 1974 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Girija S | 2006 | Insufficient information |
| Glanville T | 2002 | No denominators and no relevant outcome data |
| Gloeb DJ | 1989 | No relevant outcome data |
| Goedken J | 2000 | No denominators |
| Goeree R | 1995 | Does not compare methods for the induction of labour |
| Gonen O | 1997 | Methodological issues. Women in the intervention group received multiple interventions based on Bishop score, and data are not presented by this division |
| Goni S | 1995 | Dose comparison |
| Gonsoulin W | 1989 | No relevant outcome data |
| Gordon AJ | 1977 | No data |
| Gordon-Wright AP | 1979 | No outcome data |
| Gottschall D | 1998 | Dose comparison: both high dose |
| Gowenlock AH | 1975 | No relevant data |
| Granstrom L | 1995 | Both arms received the same intervention at different times |
| Green PS | 1967 | No data |
| Greenberg RA | 2006 | No data. Trial not complete |
| Greer IA | 1988 | No relevant data |
| Greer IA | 1988 | No outcome data |
| Griffin C | 2003 | > 20% attrition |
| Grudev D | 1988 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Grunstein S | 1990 | Dose comparison, both groups high dose |
| Guinn DA | 2004 | Complex intervention |
| Guinn DA | 2000 | Complex intervention |
| Güngördük K | 2011 | Complex intervention |
| Haddad N | 1987 | Trial registration |
| Haeri AD | 1976 | Not a RCT |
| Hage P | 1993 | No data |
| Hallak M | 2008 | Trial registration |
| Hannah ME | 1992 | Induction group received multiple methods; data reported represent multiple methods |
| Harms K | 2001 | No relevant outcome data |
| Harrington K | 2003 | No data. Trial registration |
| Hassan AA | 2005 | Not a RCT |
| He HY | 2000 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Helal AMM | 2004 | Not a RCT |
| Hendricks CH | 1964 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Hennessey MH | 1998 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Henry A | 2013 | Not a relevant comparison (inpatient vs. outpatient) |
| Henry A | 2011 | Complex intervention |
| Henry GR | 1969 | Intervention unclear |
| Henson BV | 1987 | No outcome data |
| Hernandez-Castro F | 2008 | Not clear that this is a trial. Insufficient information |
| Hibbard JU | 1998 | Complex intervention |
| Hill JB | 2009 | Complex intervention |
| Hill NCW | 1991 | Not induction of labour |
| Ho M | 2010 | Augmentation of labour |
| Hoesli I | 2003 | Insufficient information |
| Hoppe K | 2014 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Hourvitz A | 1996 | Dose comparison |
| Hu Y | 2013 | No data. Trial registration |
| Hughes L | 2002 | Complex intervention |
| Hunter G | 1998 | Mixed interventions, not possible to separate data |
| Hunter IWE | 1984 | Both arms received the same intervention, at different doses and times |
| Hunter IWE | 1982 | Both arms received the same intervention, at different doses and times |
| Hussein M | 2012 | No relevant data. Data not reported by randomisation group |
| Ifnan F | 2006 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Iftikhar M | 1992 | No outcome data reported |
| Imsuwan Y | 1999 | No relevant outcomes |
| Ingemarsson I | 1991 | No outcome data |
| Ismail AAA | 1989 | Not a RCT |
| Jackson NV | 2000 | Insufficient information |
| Jalilian N | 2011 | No relevant data – not reported by randomisation group |
| Jasper MP | 2000 | No relevant outcome data |
| Javaid MK | 2008 | Dose and frequency not stated. E-mail sent |
| Jazayeri A | 2003 | No group denominators |
| Jenssen H | 1977 | No usable outcome data |
| Jiang X | 1997 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Jigyasa S | 2011 | No denominators |
| Jindal P | 2007 | Complex intervention |
| Jonsson M | 2011 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Joo SH | 2000 | No outcome data or primary outcomes |
| Kadar N | 1990 | No relevant data |
| Kamat DS | 2002 | Not a RCT |
| Kanade T | 2011 | No group denominators |
| Kanhai HHH | 1989 | Not a relevant participant group. This is a trial of induction for fetal death |
| Karjane NW | 2006 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Karpovich E | 2006 | No data. Trial registration |
| Kasdaglis T | 2007 | Complex intervention |
| Kashanian M | 2009 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Kashanian M | 2008 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Kashanian M | 2008 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Kehl S | 2011 | Complex intervention |
| Keirse MJNC | 1983 | No relevant outcome data |
| Keller JM | 2010 | No data. Trial registration |
| Khan ZA | 2011 | Not a RCT |
| Kjos SL | 1993 | Women had variety of induction methods |
| Klopper AI | 1973 | Not relevant intervention |
| Klopper AI | 1969 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Klopper AI | 1962 | No denominators |
| Knogler W | 1988 | No outcome data |
| Knox GE | 1979 | No outcome data |
| Krammer J | 1995 | No outcome data |
| Kubista E | 1974 | Not a RCT |
| Kupietz R | 1994 | Not a relevant comparison (comparing time of day PGE2 administered) |
| Ladfors L | 1994 | Dose comparison |
| Lamont RF | 1991 | No relevant data |
| Lange AP | 1982 | No relevant data |
| Lanka S | 2012 | No data. Trial registration |
| Larsen J | 1983 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Lass A | 1994 | No outcome data |
| Lazor LZ | 1993 | Dose comparison |
| Le Maire WJ | 1972 | No relevant data |
| Leiberman JR | 1977 | Not a RCT |
| Leijon I | 1980 | No relevant data |
| Leijon I | 1979 | No relevant data |
| Leszczynska-Gorzelak B | 2001 | Dosage not clear |
| Leszczynska-Gorzelak B | 1999 | Not a RCT |
| Leszczynska-Gorzelak B | 1993 | No relevant data |
| Levy R | 2004 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Levy R | 2000 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Li FM | 2000 | No group denominators, no outcome data |
| Li GQ | 1996 | No relevant data |
| Li WJ | 1994 | No relevant data |
| Lin A | 1995 | Complex intervention |
| Lin MG | 2007 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Lindblad A | 1985 | No outcome data |
| Lindholm P | 1981 | No relevant data |
| Lindmark G | 1976 | No relevant data |
| Lipshitz J | 1984 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Liu YL | 2012 | No relevant data reported |
| Lokugamage AU | 2003 | Both high dose |
| Long Z | 1994 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Lorentzen IP | 2006 | Trial not complete |
| Lorenz RP | 1984 | Not relevant participants, 25% < 20 weeks |
| Loria-Casanova ML | 1989 | Preterm labour only |
| Lorrain J | 1982 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Loto OM | 2012 | No outcome data or primary outcomes |
| Lotshaw RR | 1994 | Comparison of regimen. Both groups received intracervical PGE2 |
| Lowensohn RI | 1990 | Regimen comparison |
| Lunkad A | 2011 | No denominators, no outcome data |
| Lutgendorf MA | 2012 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Luther ER | 1983 | Comparing synthetic and natural PGE2. Same dose |
| Lykkesfeldt G | 1981 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Lyndrup J | 1992 | This is a secondary analysis of Lyndrup 1991, Legarth 1988 and Legarth 1989. No relevant outcome data |
| Lyons C | 2001 | No relevant data |
| Mackenzie I | 2011 | Trial for pain relief only |
| MacKenzie IZ | 1997 | Dose comparison |
| MacKenzie IZ | 1988 | Dose comparison |
| Mackenzie IZ | 1988 | No outcome data |
| MacKenzie IZ | 1977 | No outcome data |
| MacLennan AH | 1988 | No relevant outcome data |
| MacLennan AH | 1981 | Complex intervention |
| Macones GA | 2012 | Complex intervention |
| Macpherson M | 1983 | No relevant outcome data |
| Madhavi N | 2011 | No group denominators, no results |
| Mahendru R | 2011 | Interventions not clear |
| Mahomed K | 1988 | Complex intervention |
| Majoko F | 2002 | Both high dose |
| Majoko F | 2001 | Comparison not relevant |
| Makarem MH | 2013 | Complex intervention |
| Makary NA | 1990 | Trial registration |
| Mamo J | 1994 | No relevant data |
| Manabe Y | 1985 | No relevant data |
| Mancuso S | 1996 | Not a RCT |
| Manidakis G | 1999 | No relevant data |
| Mansouri M | 2003 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Manyonda IT | 2007 | Trial registration |
| Marconi AM | 2008 | Control group included two different treatments |
| Martin DH | 1978 | > 20% excluded for labour outcomes; unbalanced treatment groups |
| Martin JN | 1989 | No relevant data |
| Martin RH | 1955 | Not only induction of labour |
| Martinez AC | 2004 | No relevant data |
| Marzouk AF | 1975 | Complex intervention |
| Mathews DD | 1976 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Mathie JG | 1959 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Mati JKG | 1973 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Mazhar SB | 2003 | Complex intervention |
| McColgin SW | 1993 | No relevant data |
| Megalo A | 1999 | No relevant outcomes |
| Megalo A | 1998 | No group denominators |
| Mercer B | 1991 | Dose comparison |
| Merrill DC | 1999 | Dose comparison |
| Milasinovic L | 1997 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Miller JF | 1975 | Complex intervention |
| Milliez JM | 1993 | Dose comparison study |
| Minaretzis D | 1993 | All women received intracervical PGE2 |
| Mink D | 1994 | Not a RCT |
| Moghadam AD | 2012 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Moghadem DA | 2013 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Moghadem DA | 2008 | Insufficient information |
| Moise KJ | 1991 | No relevant outcome data |
| Mokgokong E | 1976 | Dose comparison |
| Mokgokong ET | 1974 | No relevant outcome data |
| Molina M | 2000 | Insufficient information |
| Mollo M | 1991 | No relevant outcome data |
| Moran DJ | 1994 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Muhammad Ali A | 2013 | No group denominators |
| Mukhopadhyay M | 2002 | No data |
| Muller PR | 1992 | Not a relevant comparison. Regimen comparison |
| Muller T | 2000 | Very high sample attrition |
| Muller T | 1995 | Not a RCT |
| Mullin PM | 2002 | Complex intervention |
| Mundle WR | 1996 | Comparison not relevant |
| Murray CP | 1975 | No denominators |
| Nabors GC | 1958 | Complex intervention |
| Naismith WCMK | 1972 | Complex intervention |
| Nasir S | 2012 | Not a RCT |
| Nassief SA | 1996 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Neri I | 2012 | No group denominators |
| Nesbitt REL | 1961 | No relevant data |
| Neto CM | 1988 | No relevant outcome data |
| Nikolov A | 2003 | No outcome data |
| Nilsson B | 1984 | No relevant data |
| Niroomanesh S | 2011 | Insufficient information. No denominators |
| Noah ML | 1985 | Dose comparison |
| Norchi S | 1993 | No outcome data |
| Nunes FP | 2006 | Complex intervention |
| Nuthalapaty FS | 2005 | Not relevant participant group |
| Nuutila M | 1997 | No relevant outcomes reported |
| Obel EB | 1975 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Odem RR | 1988 | Not a relevant comparison. Regimen comparison |
| Odum CU | 1993 | Not relevant participant group |
| Ohel G | 1996 | High risk of bias |
| Omer H | 1987 | Not a RCT. A case–control study |
| Orhue A | 1993 | Regimen comparison |
| Orhue AAE | 1994 | Regimen comparison |
| Orhue AAE | 1993 | Dose comparison |
| Ozgur K | 1997 | Not a RCT |
| Ozsoy M | 2004 | Both high dose |
| Padayachi T | 1988 | For intrauterine death |
| Palermo MSF | 1997 | No relevant data |
| Parewijck W | 1987 | Insufficient information to assess |
| Parker M | 1990 | No outcome data |
| Parpas G | 1995 | Not a relevant comparison. Regimen comparison |
| Patel A | 2000 | Augmentation not induction |
| Patnaik P | 1995 | Not a RCT |
| Patterson WM | 1971 | No relevant data |
| Paul R | 1988 | No relevant outcome data |
| Pavlou C | 1978 | Regimen comparison |
| Payne E | 1993 | Not randomised properly |
| Pearce DJ | 1977 | No relevant data |
| Pearson M | 2002 | No doses for miso stated |
| Pedersen S | 1981 | Complex intervention |
| Peedicayil A | 1990 | Not a relevant treatment |
| Peedicayil A | 1989 | Complex intervention |
| Penna LK | 1991 | Varying dosing regimens. Data not reported by dose |
| Pentecost AF | 1973 | Buccal oxytocin. Not a relevant comparison |
| Perales AJ | 1994 | No relevant outcome data |
| Perry KG | 1998 | Complex intervention |
| Pettker CM | 2008 | Complex intervention |
| Picasso DG | 2012 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Polvi HJ | 1994 | No relevant outcomes reported |
| Pongsatha S | 2002 | Dose comparison, same codes |
| Pongsatha S | 2001 | Dose comparison, same codes |
| Porat S | 2006 | No data |
| Porojanova V | 2005 | Not a RCT |
| Pranuthi R | 2011 | No relevant data |
| Rangarajan NS | 1971 | No data |
| Rasheed R | 2007 | Included non-randomised participants |
| Rath W | 1985 | Dose comparison |
| Raymond S | 1989 | Trial registration |
| Read MD | 1974 | Complex intervention |
| Rees AEJ | 1992 | No outcome data |
| Reichel R | 1985 | No relevant outcomes reported |
| Reid GJ | 1995 | Regimen comparison |
| Ridgway L | 1991 | Complex intervention |
| Rijnders MEB | 2007 | Control group received a range of induction methods |
| Roberts G | 1970 | Complex intervention |
| Robinson D | 2011 | Trial registration |
| Romer A | 2000 | No relevant outcome data |
| Rosa P | 1974 | No relevant data |
| Ross EL | 1998 | Dose comparison |
| Rudra T | 2012 | No relevant data. Unclear |
| Rust O | 2000 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Rust OA | 2001 | Complex intervention |
| Saberi F | 2008 | No relevant data. Unclear |
| Sabir N | 2007 | No data |
| Sabra A | 2000 | Insufficient information |
| Sadaty A | 1998 | No outcome data |
| Sahin HG | 2002 | Methodological reasons. Women not in labour after 12 hours were excluded for all outcomes, including 3/50 receiving misoprostol and 10/50 in the oxytocin group |
| Saito K | 1999 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Salamalekis E | 2000 | Regimen comparison |
| Saldivar D | 2001 | No data |
| Salmanian R | 2012 | No relevant outcomes |
| Samal S | 2000 | Not a RCT |
| Sanchez-Ramos L | 2002 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Sanchez-Ramos L | 1995 | Both groups received PGE2 |
| Sanchez-Ramos L | 1993 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Sasaki K | 1982 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Satin AJ | 1994 | Not a relevant comparison. Regimen comparison |
| Satin AJ | 1991 | Dose comparison |
| Scher J | 1972 | Observational study. Not a RCT |
| Schneider KTM | 1994 | Not a RCT |
| Schreyer P | 1989 | Incomplete reporting of data |
| Sciscione AC | 2001 | Not a relevant comparison – setting comparison |
| Seeras RC | 1995 | Dose comparison, both arms high dose |
| Seidl A | 1976 | No relevant data |
| Sellers S | 1985 | No outcome data |
| Shaala S | 1989 | Not a relevant intervention |
| Shanmugham D | 2011 | Not a RCT |
| Sharami SH | 2010 | No data |
| Sharami SH | 2005 | Complex intervention |
| Sharma C | 2012 | No data, not clear if completed |
| Sharma K | 2014 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Sheela SR | 2006 | Not a RCT |
| Shennan A | 2006 | Trial registration |
| Shennan AH | 1995 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Shetty A | 2002 | Dose comparison |
| Shipman M | 2000 | Trial registration |
| Shravage J | 2009 | Complex intervention |
| Singh PM | 1993 | Not a relevant comparison. Dose comparison |
| Sivasuriya M | 1978 | > 20% excluded |
| Sjostedt S | 1969 | Intranasal oxytocin. Not a relevant comparison |
| Skajaa K | 1991 | Both groups received PGE2, same dose |
| Skupski D | 2006 | Complex intervention |
| Smith CV | 1996 | Dose comparison, both arms high dose |
| So LK | 1979 | No data |
| Solt I | 2009 | No denominators |
| Somell C | 1987 | Arms received different management protocols |
| Somell C | 1983 | One group primed and the other not; those failed at 8 hours excluded |
| Soni M | 2000 | Not a RCT |
| Sorensen MB | 2008 | No data |
| Sorensen S | 1985 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Sorokin Y | 1992 | No outcome data |
| Spellacy WN | 1971 | No relevant data |
| Spitzberg E | 1991 | No outcome data |
| Srisomboon J | 1997 | No code for intracervical misoprostol |
| Srividhya S | 2001 | Not a RCT |
| Steer PJ | 1992 | Trial registration |
| Steer PJ | 1985 | Regimen comparison |
| Steer PJ | 1976 | No relevant data |
| Stewart JD | 1998 | Complex intervention |
| Stewart P | 1981 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Stiver KH | 1991 | Dose comparison study |
| Suikkari AM | 1983 | Induction group received two different methods |
| Sullivan CA | 1996 | Complex intervention |
| Suri V | 2000 | No data |
| Swann RO | 1958 | No relevant data |
| Tadmor OP | 1990 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Tan ASA | 1994 | No outcome data |
| Tan LK | 1999 | Dose comparison, all high dose |
| Tan PC | 2009 | Complex intervention |
| Tan PC | 2006 | Complex intervention |
| Tan PC | 2007 | Complex intervention |
| Tang L | 1997 | Dose comparison, all high dose |
| Tanir HM | 2008 | Complex intervention |
| Tedesco RP | 2002 | Both low dose |
| Thach TS | 2000 | Insufficient information |
| Thiery M | 1981 | Examining combination of methods |
| Thiery M | 1979 | Complex intervention. Control group received PGE2 plus oxytocin at the same time |
| Thiery M | 1977 | Not a relevant comparison. Regimen comparison |
| Thomas G | 1974 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Thompson JH | 1987 | Unclear group denominators |
| Thomsen AC | 1987 | Trial registration |
| Thornton S | 1989 | No relevant data |
| Tiwari N | 2011 | No data |
| Toplis PJ | 1979 | Insufficient information |
| Toppozada M | 1992 | No outcome data |
| Torres R | 2001 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Tsitsis V | 2012 | Not a RCT |
| Tsitsis V | 2012 | Not a RCT |
| Tuipae S | 1999 | No data. for primary outcomes |
| Turnquest MA | 1997 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Ulstein M | 1979 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Vaisanen-Tommiska M | 2008 | No data |
| Van Dessel T | 1991 | Women were already in labour |
| Van Heerden J | 1992 | Data unclear |
| Varaklis K | 1994 | No outcome data |
| Varma R | 1981 | Not a RCT |
| Varma TR | 1984 | Not a RCT |
| Veligati P | 1998 | Insufficient information reported |
| Vengalil SR | 1998 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Vidanagamage RS | 2011 | No data |
| Vijitrawiwat A | 2003 | No data. for primary outcomes |
| Voss DH | 1996 | Dose comparison |
| Vroman S | 1972 | No relevant data |
| Walker E | 1983 | Dose comparison |
| Wang L | 1997 | Excluded for methodological reasons |
| Wang Z | 1998 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Ward SJ | 1991 | No relevant data |
| Webb GW | 1997 | No denominator data given |
| Weeks AD | 2013 | No data. Trial registration |
| Wei ZT | 2000 | No relevant data |
| Weiss G | 2009 | No data |
| Weiss RR | 1975 | Dose comparison |
| Weissberg SM | 1977 | No relevant data |
| Welt SI | 1987 | Insufficient information reported to assess the trial |
| Westergaard JG | 1983 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Westergaard JG | 1983 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Wicker R | 1995 | Insufficient information |
| Wildemeersch DA | 1976 | No data |
| Wilk M | 2001 | Excluded for methodological reasons |
| Willcourt RJ | 1994 | Not a relevant comparison. Regimen comparison |
| Williams JK | 1988 | Not a relevant participant group. Induction for fetal death |
| Williams JK | 1985 | Dose comparison |
| Windrim R | 1997 | No clear comparison group (control group interventions differed) |
| Wing DA | 2011 | Sustained-release misoprostol – three doses |
| Wing DA | 1998 | No data. Trial stopped early |
| Wing DA | 1996 | Same dose each group |
| Witter FR | 1989 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Wolf SB | 2005 | Dose comparison |
| Wolfler MM | 2006 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Wyldes MP | 1992 | Trial never commenced |
| Yacoob T | 1993 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Yang Z | 2000 | Insufficient information in abstract |
| Yeung KK | 1977 | No usable outcome data |
| Young D | 2001 | Insufficient information, no group denominators, variable dose of vaginal misoprostol |
| Zafarghandi A | 2004 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Zanini A | 1991 | Dose comparison, all high dose |
| Zhen-yun Y | 1994 | Not a relevant comparison |
| Zimmer EZ | 1996 | No relevant outcome data |
Appendix 5 Reference list for included studies
Aalami-Harandi R, Karamali M, Moeini A. Induction of labor with titrated oral misoprostol solution versus oxytocin in term pregnancy: randomized controlled trial. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2013;35:60–5.
Abdul MA, Ibrahim UN, Yusuf MD, Musa H. Efficacy and safety of misoprostol in induction of labour in a Nigerian tertiary hospital. West Afr J Med 2007;26:213–16.
Abedi-Asl Z, Farrokhi M, Rajaee M. Comparative efficacy of misoprostol and oxytocin as labor preinduction agents: a prospective randomized trial. Acta Medica Iranica 2007;45:443–8.
Abramovici H, Hallak M, Zarfati D, Packer T, Calderon I, Auslender R, et al. Induction of labor in patients with unfavorable cervices: a randomized comparison among intravaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), intravenous oxytocin, and the double balloon ripener device. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1994;46:7.
Adair CD, Weeks JW, Barrilleaux PS, Philibert L, Edwards MS, Lewis DF. Labor induction with oral versus vaginal misoprostol: A randomized, double-blind trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S93.
Adair CD, Weeks JW, Barrilleaux S, Edwards M, Burlison K, Lewis DF. Oral or vaginal misoprostol administration for induction of labor: a randomized, double-blind trial. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92:810–13.
Adam I, Hassan OA, Elhassan EM. Oral misoprostol vs. vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and labour induction. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2005;89:142–3.
Adeniji AO, Olayemi O, Odukogbe AA, Aimakhu CO, Oladokun A, Akindele FO, et al. Comparison of changes in pre-induction cervical factors’ scores following ripening with transcervical foley catheter and intravaginal misoprostol. Afr J Med Med Sci 2005;34:377–82.
Adeniji AO, Olayemi O, Odukogbe AA, Oladokun A, Adeniji OI, Egbewale BE, et al. Cervico-vaginal foetal fibronectin: a predictor of cervical response at pre-induction cervical ripening. West Afr J Med 2005;24:334–7.
Adeniji AO, Olayemi O, Odukogbe AA. Intravaginal misoprostol versus transcervical foley catheter in pre-induction cervical ripening. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2006;92:130–2.
Adeniji OA, Oladokun A, Olayemi O, Adeniji OI, Odukogbe AA, Ogunbode O, et al. Pre-induction cervical ripening: transcervical foley catheter versus intravaginal misoprostol. J Obstet Gynaecol 2005;25:134–9.
Agarwal K, Batra A, Dabral A, Aggarwal A. Evaluation of isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening prior to induction of labor for postdated pregnancy in an outpatient setting. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2012;118:205–9.
Agarwal N, Gupta A, Kriplani A, Bhatla N, Parul N. Six hourly vaginal misoprostol versus intracervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2003;29:147–51.
Ajori L, Nazari L, Eliaspour D. Effects of acupuncture for initiation of labor: a double-blind randomized sham-controlled trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2013;287:887–91.
Akay NO, Hizil D, Ylmaz SS, Yalvac S, Kandemir O. Comparison of low-dose oxytocin and dinoprostone for labor induction in postterm pregnancies: a randomized controlled prospective study. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2012;73:242–7.
Akyol D, Mungan T, Unsal A, Yuksel K. Prelabour rupture of the membranes at term: no advantage of delaying induction for 24 hours. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;39:291–5.
Al-Hussaini TK, Abdel-Aal SA, Youssef MA. Oral misoprostol vs intravenous oxytocin for labor induction in women with prelabor rupture of membranes at term. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2003;82:73–5.
Al-Malt A, Ashmead G, Amini S. Cervical ripening: effect of vaginal PGE2 on bishop score. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:297.
Al-Sebai MAH, Manasse PR. Induction of labour in primigravid women with an unfavourable cervix: a prospective comparative study of prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets and gel. J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;13:112–13.
Al-Taani MI. Comparison of prostaglandin E2 tablets or foley catheter for labour induction in grand multiparas. East Med Health J 2004;10:547–53.
Alcalay M, Hourvitz A, Reichman B, Luski A, Quint J, Barkai G, et al. Prelabour rupture of membranes at term: early induction of labour versus expectant management. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1996;70:129–33.
Alcoseba-Lim W, Famador-Juario H. Stripping of membranes to induce labor at term. Philippine J Surg Surg Special 1992;47:139–42.
Allott HA, Palmer CR. Sweeping the membranes: a valid procedure in stimulating the onset of labour? Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;100:898–903.
Allouche C, Dommesent D, Barjot P, Levy G. Cervical ripening: comparison of three methods. Preliminary results of a randomized prospective study. Rev Fr Gynecol Obstet 1993;88:492–7.
Amador LAV, Carmona JCF, Gallego FG, Texido CS, Esteve JLC. Randomized clinical trial of the safety and efficacy of 50 microg sublingual misoprostol versus 25 microg vaginal misoprostol for labor induction at term in pregnant women with diabetes. Prog Obstet Ginecol 2007;50:473–83.
Anand AK, Mir S. A randomized comparison between intravaginal misoprostol and intracervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction in participants with unfavourable cervices. JK Sci 2012;14:115–19.
Andersen K, Moller M, Rix P, Larsen KW, Ladehoff P, Zdravkovic M. Induction of labor. Prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets compared with intravenous oxytocin for induction of labor in premature rupture of the membranes and immature cervix. Ugeskr Laeger 1990;152:3705–7.
Arias F, Buser D, Mora G. Randomized comparison of misoprostol vs dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S141.
Arias F, Rouben D. Extraamniotic saline infusion with foley catheter is better than 2.9 mg prostaglandin E2 gel in ripening the cervix but does not result in vaginal delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168:429.
Asher GN, Coeytaux RR, Chen W, Reilly AC, Loh YL, Harper TC. Acupuncture to initiate labor (Acumoms 2): a randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2009;22:843–8.
Ashrafunnessa, Khatun SS, Chowdhury SA, Begum SR, Rashid M, Khatun MS. Induction of labor by intracervical prostaglandin gel and oxytocin infusion in primigravid women with unfavorable cervix. Bangladesh Med Res Council Bull 1997;23:66–71.
Atad J, Hallak M, Auslender R, Porat-Packer T, Zarfati D, Abramovici H. A randomized comparison of prostaglandin E2, oxytocin, and the double-balloon device in inducing labor. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:223–7.
Atad J, Peer G. Combination of the Double Balloon Device (ARD) and Half Doses of PGE2 Vaginal Gel for Labor Induction. 1st World Congress on Controversies in Obstetrics Gynecology and Infertility, Prague, Czech Republic, 28–31 October 1999.
Ayad IA. Vaginal misoprostol in managing premature rupture of membranes. East Mediterr Health J 2002;8:515–20.
Ayaz A, Saeed S, Farooq MU, Ahmad F, Bahoo LA, Ahmad I. Pre-labor rupture of membranes at term in patients with an unfavorable cervix: active versus conservative management. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2008;47:192–6.
Ayaz A, Shaukat S, Farooq MU, Mehmood K, Ahmad I, Ali Bahoo ML. Induction of labor: a comparative study of intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2010;49:151–5.
Bagratee JS, Moodley J. Synthetic laminaria tent for cervical ripening. S Afr Med J 1990;78:738–41.
Bakos O, Bäckström T. Induction of labor: a prospective, randomized study into amniotomy and oxytocin as induction methods in a total unselected population. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1987;66:537–41.
Balci O, Mahmoud AS, Acar A, Colakoglu MC. Comparison of induction of labor with vaginal misoprostol plus oxytocin versus oxytocin alone in term primigravidae. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2011;24:1084–7.
Balci O, Mahmoud AS, Ozdemir S, Acar A. Induction of labor with vaginal misoprostol plus oxytocin versus oxytocin alone. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2010;110:64–7.
Barcaite E, Bartusevicius A, Krikstolaitis R, Gintautas V, Nadisauskiene R. A Comparison of Sublingual and Vaginal Misoprostol for Induction of Labour: a Randomized Controlled Trial. 35th Nordic Congress of Obstetrics and Gynecology; 23–25 May 2006; Goteburg, Sweden, abstract no. 54.
Barkai G, Cohen SB, Kees S, Lusky A, Margalit V, Mashiach S, et al. A clinical trial of induction of labor versus expectant management in postterm pregnancy. The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Network of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:716–23.
Barrilleaux P, Bofill J, Rodts-Palenik S, Moore L, May W, Martin J Jr. A randomized clinical trial comparing three methods of cervical ripening to efficiently effect delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S174.
Bartha JL, Comino-Delgado R, Garcia-Benasach F, Martinez-Del-Fresno P, Moreno-Corral LJ. Oral misoprostol and intracervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction: a randomized comparison. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:465–9.
Bartusevicius A, Barcaite E, Krikstolaitis R, Gintautas V, Nadisauskiene R. Sublingual compared with vaginal misoprostol for labour induction at term: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2006;113:1431–7.
Beer AM, Heiliger F. Randomized, double-blind trial of caulophyllum d4 for induction of labor after premature rupture of the membranes at term. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 1999;59:431–5.
Beigi A, Kabiri M, Zarrinkoub F. Cervical ripening with oral misoprostol at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;83:251–5.
Bell RJ, Permezel M, MacLennan A, Hughes C, Healy D, Brennecke S. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the safety of vaginal recombinant human relaxin for cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:328–33.
Benedetto C, Pastore G, Zonca M, Ardizzoja M, Mascherpa F, Bocci A. Induction of labour with PGE2 intravaginal gel or oxytocin: a technical comparison. Giornale Italiano di Obstetricia e Ginecologia 1987;5:447–52.
Bennett K, Butt K, Crane J, Hutchens D, Young D. Misoprostol for Labour Induction at Term. Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada, 54th Annual Meeting, Victoria, BC, Canada, June 1998, abstract no. 11.
Bennett KA, Butt K, Crane JM, Hutchens D, Young DC. A masked randomized comparison of oral and vaginal administration of misoprostol for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92(Suppl. 1):481–6.
Benzineb N, Bouhaouala S, Sfar R. Prostaglandin E2 versus Foley catheter for cervical maturation at term. Rev Fr Gynecol Obstet 1996;91:173–6.
Berghella V, Mickens R. Stripping of Membranes as a Safe Method to Reduce Prolonged Pregnancies. XIV World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO), Montreal, QC, Canada, 26–30 September 1994, PO34. 16.
Berghella V, Rogers RA, Lescale K. Stripping of membranes as a safe method to reduce prolonged pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:927–31.
Bergsjo P, Jenssen H. Comparison between intranasal and transbuccal oxytocin for the induction of labour. Preliminary report. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1969;48(Suppl. 3):134.
Berkane N, Verstraete L, Uzan S, Boog G, Maria B. Use of mifepristone to ripen the cervix and induce labor in term pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:114–20.
Bernstein EP. Prostaglandin E2 Gel for Cervical Ripening and Labour Induction. A Canadian Multi-centre plAcebo-Controlled Trial. Proceedings of Annual Meeting of Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada, Toronto, ON, Canada, 11–15 June 1991.
Bernstein P, Leyland N, Gurland P, Gare D. Cervical ripening and labor induction with prostaglandin E2 gel: a placebo-controlled study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1987;156:336–40.
Bernstein P. Prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and labour induction: a multicentre placebo-controlled trial. CMAJ 1991;145:1249–54.
Bezircioglu I, Akin MK, Baloglu A, Bicer M. The efficacy of dinoprostone vaginal insert for active management of premature rupture of membranes at term: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2012;39:356–8.
Bilgin T, Kadioglu M, Yildirim V, Cengiz C. A randomised trial of intracervical prostaglandin gel and intravenous oxytocin in prelabor rupture of membranes with unripe cervix at term. Prenatal Neonatal Med 1996;1(Suppl. 1):89.
Bilgin T, Kadioğlu M, Yildirim V, Cengiz C. A randomized trial of intracervical prostaglandin gel and intravenous oxytocin in prelabor rupture of membranes with unripe cervix at term. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1998;25:46–8.
Biron-Shental T, Fishman A, Fejgin MD. Medical and mechanical methods for cervical ripening. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;85:159–60.
Bollapragada S, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, Petrou S, Reid M, Greer I, et al. IMOP: randomised placebo controlled trial of outpatient cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour: clinical trial with analyses of efficacy, cost effectiveness and acceptability. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2006;6:25.
Bollapragada SS, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Petrou S, Reid M, Greer IA, et al. Randomized placebo controlled trial of outpatient cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour – clinical trial with analyses of efficacy, cost effectiveness and acceptability. The IMOP study. J Obstet Gynaecol 2007;27(Suppl. 1):22.
Bollapragada SS, MacKenzie F, Norrie JD, Eddama O, Petrou S, Reid M, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of outpatient (at home) cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour-clinical trial with analyses of efficacy and acceptability. The IMOP study. BJOG 2009;116:1185–95.
Bolnick J, Velazquez M, Gonzalez J, Leslie K, Rappaport V, McIlwane G, et al. Randomized trial of sustained-release vaginal dinoprostone (PGE2) with concurrent oxytocin versus vaginal misoprostol (PGE1) for induction of labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S175.
Boulvain M, Fraser WD, Marcoux S, Fontaine JY, Bazin S, Blouin D. Randomised trial of sweeping the membranes. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1997;76:32.
Boulvain M, Fraser WD, Marcoux S, Fontaine JY, Bazin S, Pinault JJ, et al. Does sweeping of the membranes reduce the need for formal induction of labour? A randomised controlled trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:34–40.
Bounyasong S. A randomized comparison between 25 microgram misoprostol gel and 50 microgram misoprostol vaginal tablet for induction of labour. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;12:21–5.
Brandel E, Bascou V, Meeus JB, Magnin G. Results of a randomized trial of cervical maturation in premature rupture of membranes at term: prostine E, intravenous versus prostine E2 vaginal gel. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1998;27:111.
Bremme K, Bygdeman M. A comparative study of uterine activity and fetal heart rate pattern in labor induced with oral prostaglandin E2 or oxytocin. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1980;92:23–9.
Bremme K, Eneroth P, Samuelson K. Estriol and cholic acid in maternal serum in induced labor. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1984;17:120–6.
Bremme K, Eneroth P. Changes in serum hormone levels during labor induced by oral PGE2 or oxytocin infusion. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1980;92:31–43.
Bremme K, Nilsson B. Prediction of Time to Delivery in Labour Induced with Oral Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) or Intravenous Oxytocin (OXY), Both in Combination with Early Amniotomy. Proceedings of 8th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 7–10 September 1982, Brussels, Belgium, abstract no. 86.
Brennan MC, Pevzner L, Wing DA, Powers BL, Rayburn WF. Retention of dinoprostone vaginal insert beyond 12 hours for induction of labor. Am J Perinatol 2011;28:479–84.
Brennand JE, Calder AA, Leitch CR, Greer IA, Chou MM, MacKenzie IZ. Recombinant human relaxin as a cervical ripening agent. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;104:775–80.
Bricker L, Peden H, Tomlinson AJ, Al-Hussaini TK, Idama T, Candelier C, et al. Titrated low-dose vaginal and/or oral misoprostol to induce labour for prelabour membrane rupture: a randomised trial. BJOG 2008;115:1503–11.
Browning J, Gherman RB. Oral misoprostol versus intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95(Suppl. 4):76.
Buchanan D, Macer J, Yonekura ML. Cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppositories. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:659–63.
Bullarbo M, Norström A, Andersch B, Ekerhovd E. Isosorbide mononitrate induces increased cervical expression of cyclooxygenase-2, but not of cyclooxygenase-1, at term. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2007;130:160–4.
Bullarbo M, Orrskog ME, Andersch B, Granström L, Norström A, Ekerhovd E. Outpatient vaginal administration of the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening and labor induction postterm: a randomized controlled study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;196:50.e1–5.
Bung P, Baer S, Djahanschahi D, Huch R, Huch A, Huber JF, et al. [Multicenter experiences with the intracervical administration of a new PGE2 gel in labor induction.] Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1986;46:93–7.
Buser D, Mora G, Arias F. A randomized comparison between misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction in patients with unfavorable cervices. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:581–5.
Butt KD, Bennett KA, Crane JM, Hutchens D, Young DC. Randomized comparison of oral misoprostol and oxytocin for labor induction in term prelabor membrane rupture. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:994–9.
Buttino LT, Garite TJ. Intracervical prostaglandin in postdate pregnancy. A randomized trial. J Reprod Med 1990;35:155–8.
Byrne JD, Wing DA, Fraser M, Fassett MJ, Goodwin TM, Challis JRG. Mifepristone: effect on plasma corticotropin-releasing hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and cortisol in term pregnancy. J Perinatol 2004;24:416–20.
Cabrol D, Bernard N, Chouraqui A, Domenichini Y, Lemaire P, Lopes P, et al. [Ripening of the cervix uteri at term by a single intracervical application of prostaglandin E2 gel.] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1988;17:527–34.
Cahill DJ, Clark HS, Martin DH. Cervical ripening: the comparative effectiveness of Lamicel and prostaglandin E2 tablets. Ir J Med Sci 1988;157:113–14.
Cammu H, Haitsma V. Sweeping of the membranes at 39 weeks in nulliparous women: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:41–4.
Campbell JM. Induction of labour using prostaglandin E2 pessaries. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1984;11:1–5.
Campos GA, Guzmn S, RodrÌguez JG, Voto LS, Margulies M. [Misoprostol: a PGE1 analog for induction of labor at term: comparative and randomized study with oxytocin.] Rev Chil Obstet Ginecol 1994;59:190–5.
Campos Perez GA, Margulies M, Ortega I, Voto LS. Induction of Labor with Misoprostol, a PGE1 Analog. A Comparative Study. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April to 3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 97.
Cararach V, Sentis J, Botet F, Costa J, Manau D, Arimany MC. Cervical Prostaglandin E2 Compared with Expectant Management or Systematic Induction in PROM with Bad Cervical condItions: I-Maternal Results. Proceedings of 14th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 5–8 June 1994, Helsinki, Finland, abstract no. 405.
Cararach V, Sentis J, Botet F, Foradada C, Manau D, Figueras F, et al. Cervical Prostaglandin E1 Compared with Expectant Management and with Systematic Induction in PROM Near Term, with Bad Cervical Conditions. I-Maternal Results. 3rd World Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 20–24 October 1996, San Francisco, CA, USA, abstract no. 44.
Cardozo L, Fysh J, Pearce JM. Prolonged pregnancy: the management debate. Br Med J1986;293:1059–63.
Carlan SJ, Blust D, O’Brien WF. Buccal versus intravaginal misoprostol administration for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:229–33.
Carlan SJ, Bouldin S, Blust D, O’Brien WF. Safety and efficacy of misoprostol orally and vaginally: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 2001;98:107–12.
Cecatti JG, Aquino MMA, Garcia GM, Rodrigues TMC. Misoprostol Versus Oxytocin for Labor Induction: Randomized Controlled Trial. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology; 3–8 September 2000, Washington DC, USA, Book 4, 28.
Chang CH, Chang FM. Randomized comparison of misoprostol and dinoprostone for preinduction cervical ripening and labor induction. J Formos Med Assoc 1997;96:366–9.
Chang P, Langer O. Premature rupture of membranes at term; a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S148.
Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Potential efficacy of nitric oxide for cervical ripening in pregnancy at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2000;71:217–19.
Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Randomized comparison of glyceryl trinitrate and prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening at term. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:549–53.
Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Randomized trial of isosorbide mononitrate versus misoprostol for cervical ripening at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002;78:139–45.
Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y. Postterm with favorable cervix: is induction necessary? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;106:154–7.
Chanrachakul B, Herbutya Y. Phase II to Determine the Potential Efficacy and Safety of Nitric oXide for Cervical Ripening in pregNancy at Term. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 3–8 September 2000; Washington DC, USA, Book 4: 68–9.
Chanrachakul B, Punyavachira P, Preechapornprasert D, Srilar A, Promsonthi P. Randomized comparison of sublingual and vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening at term. Reprod Sci 2010;17(Suppl. 1):A352–3.
Charoenkul S, Sripramote M. A randomized comparison of one single dose of vaginal 50 microg misoprostol with 3 mg dinoprostone in pre-induction cervical ripening. J Med Assoc Thai 2000;83:1026–34.
Chatterjee MS, Ramchandran K, Ferlita J, Mitrik L. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) vaginal gel for cervical ripening. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1991;38:197–202.
Chaudhuri S, Mitra SN, Banerjee PK, Biswas PK, Bhattacharyya S. Comparison of vaginal misoprostol tablets and prostaglandin E2 gel for the induction of labor in premature rupture of membranes at term: a randomized comparative trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2011;37:1564–71.
Chayen B, Tejani N, Verma U. Induction of labor with an electric breast pump. J Reprod Med 1986;31:116–18.
Chen TM. Clinical analysis of misoprostol on induction of labor in term pregnancy. J Zhenjiang Med Coll 2000;4:652–3.
Cheng SY, Ming H, Lee JC. Titrated oral compared with vaginal misoprostol for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:119–25.
Cheung PC, Yeo EL, Wong KS, Tang LC. Oral misoprostol for induction of labor in prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM) at term: a randomized control trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2006;85:1128–33.
Chitrakar NS. Comparison of Misoprostol versus Dinoprostone for pre-induction cervical ripening at-term. J Nepal Health Res Counc 2012;10:10–15.
Christensen F, Tehranifar M, Gonzalez J, Rappaport V, Gilson G, Rayburn W. Randomized trial of concurrent oxytocin and sustained-release dinoprostone for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S118.
Christilaw J, King JF. A Randomised, Placebo Controlled Trial to Determine the Effect of Intracervical Prostaglandin Gel on the Unripe Cervix, Prior to Induction of Labour. Proceedings of Annual Meeting of Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada, 27 July to 1 August 1986, Vancouver, BC, Canada, abstract no. 107.
Chua S, Arulkumaran S, Kurup A, Anandakumar C, Tay D, Ratnam SS. Does prostaglandin confer significant advantage over oxytocin infusion for nulliparas with pre-labor rupture of membranes at term? Obstet Gynecol 1991;77:664–7.
Chua S, Arulkumaran S, Vanaja K, Ratnam SS. Preinduction cervical ripening: prostaglandin E2 gel vs hygroscopic mechanical dilator. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 1997;23:171–7.
Chua S, Arulkumaran S, Yap C, Selamat N, Ratnam SS. Premature rupture of membranes in nulliparas at term with unfavorable cervices: a double-blind randomized trial of prostaglandin and placebo. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:550–4.
Chua SM, Lee KW, Phua SM. Comparative study between prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet and intravenous oxytocin in induction of labour. Singapore Med J 1988;29:379–82.
Chuck F, Huffaker J. Labor induction with intravaginal prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) (misoprostol, cytotec) vs intracervical prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (dinoprostone, prepidil gel): a randomized comparison. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:424.
Chuck FJ, Huffaker BJ. Labor induction with intravaginal misoprostol versus intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel (Prepidil gel): randomized comparison. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1137–42.
Chung JH, Huang WH, Rumney PJ, Garite TJ, Nageotte MP. A prospective randomized controlled trial that compared misoprostol, Foley catheter, and combination misoprostol-Foley catheter for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:1031–5.
Chung T, Rogers MS, Gordon H, Chang A. Prelabour rupture of the membranes at term and unfavourable cervix; a randomized placebo-controlled trial on early intervention with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;32:25–7.
Chyu JK, Strassner HT. Prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening: a randomized comparison of Cervidil versus Prepidil. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:606–11.
Clark A, Cook V, Hill P, Spinnato J. Cervical ripening and labor induction: misoprostol vs dinoprostone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S30.
Coeytaux RR, Harper T, Chen W, Reilly A, Loh YL. Acupuncture to initiate labor (ACUMOMS 2): a randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial. J Alt Complement Med 2007;13:886.
Cohen SB, Schiff E, Kees S, Lusky A, Mashiach S. Induction of labor using a foley catheter and extra-amniotic corticosteroids. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S191.
Collingham J, Fuh K, Caughey A, Pullen K, Lyell D, Druzin M, et al. Randomized clinical trial of cervical ripening and labor induction using oral misoprostol with or without intravaginal isosorbide mononitrate. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008;199(Suppl. 1):57.
Colon I, Clawson K, Hunter K, Druzin ML, Taslimi MM. Prospective randomized clinical trial of inpatient cervical ripening with stepwise oral misoprostol vs vaginal misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:747–52.
Colon I, Clawson K, Taslimi M, Druzin M. Prospective randomized clinical trial of inpatient cervical ripening with stepwise oral misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191(Suppl. 1):15.
Corrado F, Cannata ML, Facciola G, Stella NC. Intravaginal vs. intracervical PGE2 gel first application for labor induction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;75:195–7.
Crane J, Bennett K, Windrim R, Kravitz H, Young D. Prospective Randomized Study of Sweeping Membranes at Term. Society of Obstetrics and Gynaecology of Canada Meeting, Quebec, QC, Canada, June 1996.
Crane J, Bennett K, Young D, Windrim R, Kravitz H. The effectiveness of sweeping membranes at term: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:586–90.
Crane J, Delaney T, Hutchens D. Oral misoprostol labor induction in term prelabor membrane rupture. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S168.
Crane JM, Delaney T, Hutchens D. Oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:720–4.
Cromi A, Ghezzi F, Agosti M, Serati M, Uccella S, Arlant V, et al. Is transcervical Foley catheter actually slower than prostaglandins in ripening the cervix? A randomized study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:338.e1–7.
Cromi A, Ghezzi F, Uccella S, Agosti M, Serati M, Marchitelli G, et al. A randomized trial of preinduction cervical ripening: dinoprostone vaginal insert versus double-balloon catheter. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;207:125.e1–7.
Culver J, Strauss R, Brody S, Dorman K, Timlin S, McMahon M. A randomized trial of intracervical foley catheter with concurrent oxytocin compared to vaginal misoprostol for labor induction in nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):203.
Curet LB, Gauger LJ. Cervical ripening with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1989;28:221–8.
Da Graça Krupa F, Cecatti JG, de Castro Surita FG, Milanez HM, Parpinelli MA. Misoprostol versus expectant management in premature rupture of membranes at term. BJOG 2005;112:1284–90.
Dällenbach P, Boulvain M, Viardot C, Irion O. Oral misoprostol or vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction? A randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):108.
Dällenbach P, Boulvain M, Viardot C, Irion O. Oral misoprostol or vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:162–7.
Dalui R, Suri V, Ray P, Gupta I. Comparison of extraamniotic Foley catheter and intracervical prostaglandin E gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005;84:362–7.
Damania KK, Natu U, Mhatre PN, Mataliya M, Mehta AC, Daftary SN. Evaluation of two methods employed for cervical ripening. J Postgrad Med 1992;38:58–9.
Danielian P, Porter B, Ferri N, Summers J, Templeton A. Misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a more effective agent than dinoprostone vaginal gel. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;106:793–7.
Danielian PJ, Porter B. Induction of labour with misoprostol. J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;18(Suppl. 1):18–19.
Dare FO, Oboro VO. The role of membrane stripping in prevention of post-term pregnancy: a randomised clinical trial in Ile-lfe, Nigeria. J Obstet Gynaecol 2002;22:283–6.
Darroca RJ, Buttino L, Miller J, Khamis HJ. Prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening in patients with an indication for delivery. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:228–30.
Davey DA, Macnab M. Oral and intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and induction of labour. S Afr Med J 1979;55:837–42.
Davies NJ, Martindale E, Haddad NG. Cervical Ripening with Oral PGE2 Tablets and the Effect of the Latent Period in Patients with Premature Rupture of the Membranes at Term. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April to 3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, 1991, abstract no. 156.
Day A, MacLennan A, Green R. A comparison of intravaginal PGF2 alpha and intravenous oxytocin to stimulate labour after membrane rupture. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1985;25:252–5.
Day AR, MacLennan A, Green R. A Comparison of Intravaginal PGF2 alpha and Intravenous Oxytocin to Stimulate Labour after Membrane Rupture. Proceedings of the 24th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 15–18 April 1986, Cardiff, UK, abstract no. 251.
De A, Bagga R, Gopalan S. The routine use of oxytocin after oral misoprostol for labour induction in women with an unfavourable cervix is not of benefit. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2006;46:323–9.
De Aquino MM, Cecatti JG. Misoprostol versus oxytocin for labor induction in term and post-term pregnancy: randomized controlled trial. Sao Paulo Med J 2003;121:102–6.
De Koning Gans GHJ, Keirse M. A Comparison Between Intra-Cervical and Intra-Vaginal Application of Prepidil Gel for the Induction of Labour. Personal communication. 1988.
De la Torre S, Gilson GJ, Flores S, Curet LB, Qualls CE, Rayburn WF. Is high-dose misoprostol able to lower the incidence of cesarean section? A randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Med 2001;10:85–90.
De Miranda E, van der Bom JG, Bonsel GJ, Bleker OP, Rosendaal FR. Membrane sweeping and prevention of post-term pregnancy in low-risk pregnancies: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2006;113:402–8.
De Moraes Filho OB, de Albuquerque RM, Pacheco AJC, Ribeiro RH, Cecatti JG, Welkovic S. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for labor induction of term pregnancies. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2005;27:24–31.
Delaney S, Shaffer B, Cheng Y, Vargas J, Sparks T, Paul K, et al. Labor induction with a foley balloon trial (LIFT) – a randomized controlled trial of 30 ml versus 60 ml foley balloon inflation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009;201(Suppl. 1):23–4.
Deng LL, Huang ZJ. Observation on the efficacy of intravaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening in the third trimester of pregnancy. J Nurs Sci 1999;14:67–8.
Denguezli W, Trimech A, Haddad A, Hajjaji A, Saidani Z, Faleh R, et al. Efficacy and safety of six hourly vaginal misoprostol versus intracervical dinoprostone: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2007;276:119–24.
Deo S, Iqbal B, Das V, Agarwal A, Singh R. Evaluation of non-pharmacological method-transcervical foley catheter to intravaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Biomed Res 2012;23:247–52.
Deshmukh VL, Yelikar KA, Deshmukh AB. Comparative study of intra-cervical Foley’s catheter and PGE(2) gel for pre-induction ripening (cervical). J Obstet Gynaecol India 2011;61:418–21.
Deshmukh VL, Yelikar KA, Waso V. Comparative study of efficacy and safety of oral versus vaginal misoprostol for induction or labour. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2013;63:321–4.
Di Cecco R, Hannah M, Hodnett E, Foster G, Farine D, Helewa M. Prelabor rupture of the membranes (PROM) at term: expectant management at home vs in hospital. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S30.
Diro M, Adra A, Gilles JM, Nassar A, Rodriguez A, Salamat SM, et al. A double-blind randomized trial of two dose regimens of misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Matern Fetal Med 1999;8:114–18.
Doany W, McCarty J. Outpatient management of the uncomplicated postdate pregnancy with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel and membrane stripping. J Matern Fetal Med 1997;6:71–8.
Doany W. Outpatient management of postdate pregnancy with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 and membrane stripping. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:351.
Dodd J, Crowther C, Ronbinson J. Misoprostol for the induction of labour at term: a randomised controlled trial. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2005;45:347–8.
Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS. Factors Associated with Adverse Maternal Health Outcomes Following Induction of Labour at Term: Analyses from a Randomised Trial. Perinatal Society of Australia and New Zealand 10th Annual Congress, 3–6 April 2006, Perth, WA, Australia, abstract no. 86.
Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS. Oral misoprostol for induction of labour at term: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2006;332:509–13.
Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS. Oral Misoprostol versus Intravenous Oxytocin for Induction of Labour Following Artificial or Spontaneous Rupture of Membranes: a Randomised Controlled Trial. Perinatal Society of Australia and New Zealand 10th Annual Congress, 3–6 April 2006, Perth, WA, Australia, abstract no. 258.
Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS. Time of Commencing Induction of Labour: a Nested RANDOMISED Controlled Trial. Perinatal Society of Australia and New Zealand 10th Annual Congress, 3–6 April 2006, Perth, WA, Australia, abstract no. 85.
Domínguez Salgado CR, Gorostieta García A, Vázquez Bretón S. [Induction of labor in patients with premature rupture of membranes in term pregnancy using dinoprostone vs oxytocin. An aleatory study.] Ginecol Obstet Mex 1999;67:461–6.
Dommisse J, Davey DA, Allerton G. The induction of labour with prostaglandin E2 tablets administered intravaginally. S Afr Med J 1980;58:518–19.
Dommisse J, Wild JM. Assessment of a new prostaglandin E2 gel in labour induction. S Afr Med J 1987;71:506–7.
Duff P, Huff RW, Gibbs RS. Management of premature rupture of membranes and unfavorable cervix in term pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:697–702.
Dyar TR, Greig P, Cummings R, Nichols K. The efficacy and safety of oral versus vaginal misoprostol for the induction of term labour. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:S135.
Eddama O, Petrou S, Schroeder L, Bollapragada SS, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, et al. The cost-effectiveness of outpatient (at home) cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate prior to induction of labour. BJOG 2009;116:1196–203.
Edwards R, Szychowski J, Berger J, Petersen M, Ingersoll M, Bodea Braescu A, et al. Randomized trial comparing Foley catheter to the prostaglandin E2 vaginal insert for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210(Suppl. 1):39–40.
Edwards R, Szychowski J, Berger J, Petersen M, Ingersoll M, Bodea Braescu A, et al. Effect of parity on duration of labor inductions with either Foley catheter or the prostaglandin E2 vaginal insert. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210(Suppl. 1):292.
Edwards R, Szychowski J, Berger J, Petersen M, Ingersoll M, Bodea Braescu A, et al. Effect of obesity on duration and outcome of labor inductions with either the Foley catheter or the prostaglandin E2 vaginal insert. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210(Suppl. 1):278.
Egarter C, Husslein P. [Sensitivity test in labor induction with prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets.] Zentralbl Gynakol 1988;110:345–53.
Egarter C, Kofler E, Fitz R, Husslein P. Is induction of labor indicated in prolonged pregnancy? Results of a prospective randomised trial. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1989;27:6–9.
Egarter C, Schurz B, Wagner G, Grünnberger W, Husslein P. [Comparison between prostaglandin E2 gel and oxytocin in medically indicated labor induction.] Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1987;47:337–40.
Ekman G, Forman A, Mars??l K, Ulmsten U. Intravaginal versus intracervical application of prostaglandin E2 in viscous gel for cervical priming and induction of labor at term in patients with an unfavorable cervical state. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;147:657–61.
Ekman G, Granstrom L, Ulmsten U. Induction of labor with intravenous oxytocin or vaginal PGE2 suppositories. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1986;65:857–9.
Ekman-Ordeberg G, Uldbjerg N, Ulmsten U. Comparison of intravenous oxytocin and vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel in women with unripe cervixes and premature rupture of the membranes. Obstet Gynecol 1985;66:307–10.
El-Azeem S, Samuels P, Welch G, Staisch K. Term labor induction with PGE1 Misoprostol versus PGE2 Dinoprostone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S113.
El-Din NMN, El-Moghazt DAM. Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour with Misoprostol, Prostaglandin E2 or Prostaglandin E2 gel: A Randomized Comparative Clinical Trial. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 8 September 2000, Washington DC, USA, Book 4, abstract no. 329.
El-Mardi AA, el-Qarmalawi MA, Siddik M, el-Haroni A, Ammar A, Madkoor SA. A comparison of single prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet with prostaglandin E2 vaginal pessaries for induction of labor at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1991;35:221–4.
El-Shawarby SA, Connell RJ. Induction of labour at term with vaginal prostaglandins preparations: a randomised controlled trial of Prostin vs Propess. J Obstet Gynaecol 2006;26:627–30.
El-Sherbiny M. Vaginal Misoprostol for Labor Induction 25 µg versus 50 µg Dose Regimens. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 3–8 September 2000, Washington DC, USA, Book 4, abstract no. 30.
El-Sherbiny MT, El-Gharieb IH, Gewely HA. Vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor: 25 vs. 50 microg dose regimen. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;72:25–30.
El-Torkey M, Grant JM. Sweeping of the membranes is an effective method of induction of labour in prolonged pregnancy: a report of a randomized trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;99:455–8.
Elhassan EM, Mirghani OA, Adam I. Cervical ripening and labor induction with 25 microg vs. 50 microg of intravaginal misoprostol. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;90:234–5.
Elhassan EM, Mirghani OA, Adam I. Misoprostol vs. oxytocin for induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;91:254–5.
Elhassan EM, Nasr AM, Adam I. Sublingual compared with oral and vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2007;97:153–4.
Elhassan M, Mirghani OA, Adam I. Intravaginal misoprostol vs. dinoprostone as cervical ripening and labor-inducing agents. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;85:285–6.
Elliot CL, BrennandJe, Calder A. The Effect of Mifepristone (RU486) on Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour in Human Pregnancy. 27th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 4–7 July 1995, Dublin, Ireland, abstract no. 207.
Eroglu D, Oktem M, Yanik F, Kuscu E. Labor induction at term: a comparison of the effects of 50 microg and 25 microg vaginal misoprostol. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2007;34:102–5.
Escudero F, Contreras H. A comparative trial of labor induction with misoprostol versus oxytocin. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;57:139–43.
Esteve JLC, Garcia TJP, Iturralde AS, Ferrer YA, Teixido CS. Randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of 25 microg of vaginal misoprostol versus 50 microg of sublingual misoprostol for labor induction. Prog Obstet Ginecol 2006;49:369–79.
Ezechi OC, Loto OM, Ezeobi PM, Okogbo FO, Gbajabiamila T, Nwokoro CA. Safety and efficacy of misoprostol in induction of labour in prelabour rupture of fetal membrane in Nigerian women: a multicenter study. Iran J Reprod Med 2008;6:83–7.
Facchinetti F, Venturini P, Fazzio M, Volpe A. Elective cervical ripening in women beyond the 290th day of pregnancy: a randomized trial comparing 2 dinoprostone preparations. J Reprod Med 2007;52:945–9.
Facchinetti F, Venturini P, Verocchi G, Volpe A. Comparison of two preparations of dinoprostone for pre-induction of labour in nulliparous women with very unfavourable cervical condition: a randomised clinical trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;119:189–93.
Farah LA, Sanchez-Ramos L, Rosa C, Del Valle GO, Gaudier FL, Delke I, et al. Randomized trial of two doses of the prostaglandin E1 analog misoprostol for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:364–9.
Fassett MJ, Lachelin GC, McGarrigle HH, Wing DA. Alterations in saliva steroid hormone levels after oral mifepristone administration in women with pregnancies of greater than 41 weeks’ gestation. Reprod Sci 2008;15:394–9.
Fassett MJ, Wing DA. Salivary estriol/progesterone ratio and the success of labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):210.
Fassett MJ, Wing DA. Uterine activity after oral mifepristone administration in human pregnancies beyond 41 weeks’ gestation. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2008;65:112–15.
Feitosa F. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2006;28:566.
Feitosa FE, Sampaio ZS, Alencar CA, Amorim MM, Passini R. Sublingual vs. vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2006;94:91–5.
Fenton DW, Speedie J, Duncan SL. Does cervical ripening with PGE2 affect subsequent uterine activity in labour? Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1985;64:27–30.
Ferguson JE, Head BH, Frank FH, Frank ML, Singer JS, Stefos T, et al. Misoprostol versus low-dose oxytocin for cervical ripening: a prospective, randomized, double-masked trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:273-9.
Ferraiolo A, Dellacasa I, Bentivoglio G, Ferrero S, Ragni N. Evaluation of patients’ satisfaction of cervical ripening using dinoprostone by either intravaginal gel or pessary: an open-label, randomized, prospective study. J Reprod Med 2010;55:423–9.
Filho OBM. Misoprostol versus foley catheter and oxytocin for induction of labour. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2002;24:685.
Fisher S, Davies G, Mackenzie P. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S117.
Fisher SA, Mackenzie VP, Davies GA. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:906–10.
Fletcher H, Mitchell S, Frederick J, Simeon D, Brown D. Intravaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone as cervical ripening and labor-inducing agents. Obstet Gynecol 1994;83:244–7.
Fletcher HM, Mitchell S, Simeon D, Frederick J, Brown D. Intravaginal misoprostol as a cervical ripening agent. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;100:641–4.
Fonseca L, Lucas M, Wood H, Phat’ak D, Susan R, Gilstrap L, et al. RCT of misoprostol pre-induction ripening vs oxytocin induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;197(Suppl. 1):106.
Fonseca L, Wood HC, Lucas MJ, Ramin SM, Phatak D, Gilstrap LC III, et al. Randomized trial of preinduction cervical ripening: misoprostol vs oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008;199:305.e1–5.
Foong LC, Vanaja K, Tan G, Chua S. Effect of Cervical Membrane Sweeping on Induction of Labour. Women’s Health – Into the New Millennium. Proceedings of the 4th International Scientific Meeting of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, 3–6 October 1999, Cape Town, South Africa, abstract no. 63.
Foradada C, Cararach V, Sentis J, Botet F, Manau D, Figueras F, et al. Cervical Prostaglandin E1 Compared with Expectant Management and with Systematic Induction in PROM Near Term, with Bad Cervical Conditions. II-Fetal and Neonatal Results. 3rd World Congress of Perinatal Medicine, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 October, 1996, pp. 51–2.
Frass KA, Shuaib AA, Al-Harazi AH. Misoprostol for induction of labor in women with severe preeclampsia at or near term. Saudi Med J 2011;32:679–84.
Frohn WE, Simmons S, Carlan SJ. Prostaglandin E2 gel versus misoprostol for cervical ripening in patients with premature rupture of membranes after 34 weeks. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:206–10.
Frydman R, Baton C, Lelaidier C, Vial M, Bourget P, Fernandez H. Mifepristone for induction of labour. Lancet 1991;337:488–9.
Frydman R, Lelaidier C, Baton-Saint-Mleux C, Fernandez H, Vial M, Bourget P. Labor induction in women at term with mifepristone (RU 486): a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 1992;80:972–5.
Frydman R, Lelaidier C, Baton-Saint-Mleux C, Fernandez H, Vial M, Bourget P. Labor induction in women at term with mifepristone (RU 486): a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1993;42:220.
Frydman R, Taylor S, Paoli C, Pourade A. [RU 486 (mifepristone): a new tool for labor induction women at term with live fetus.] Contracept Fertil Sex 1992;20:1133–6.
Gafni A, Goeree R, Myhr TL, Hannah ME, Blackhouse G, Willan AR, et al. Induction of labour versus expectant management for prelabour rupture of the membranes at term: an economic evaluation. TERMPROM Study Group. Term Prelabour Rupture of the Membranes. CMAJ 1997;157:1519–25.
Gagnon-Gervais K, Bujold E, Iglesias MH, Duperron L, Masse A, Mayrand MH, et al. Early versus late amniotomy for labour induction: a randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:2326–9.
Gagnon-Gervais K, Iglesias MH, Duperron L, Masse A, Mayrand MH, Sansregret A, et al. Early vs late amniotomy for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204(Suppl. 1):127.
Garry D, Figueroa R, Guillaume J, Cucco V. Use of castor oil in pregnancies at term. Altern Ther Health Med 2000;6:77–9.
Garry D, Figueroa R, Kalish RB, Catalano CJ, Maulik D. Randomized controlled trial of vaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone vaginal insert for labor induction. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2003;13:254–9.
Gaudernack LC, Forbord S, Hole E. Acupuncture administered after spontaneous rupture of membranes at term significantly reduces the length of birth and use of oxytocin. A randomized controlled trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2006;85:1348–53.
Gaudet LM, Dyzak R, Aung SK, Smith GN. Effectiveness of acupuncture for the initiation of labour at term: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2008;30:1118–23.
Gelisen O, Caliskan E, Dilbaz S, Ozdas E, Dilbaz B, Ozdas E, et al. Induction of labor with three different techniques at 41 weeks of gestation or spontaneous follow-up until 42 weeks in women with definitely unfavorable cervical scores. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;120:164–9.
Getgan M, Paisarntantiwong R, Sripramote M. A randomized comparison between 50 micrograms orally and misoprostol 25 micrograms vaginally for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;15:276.
Gherman RB, Browning J, O’Boyle A, Goodwin TM. Oral misoprostol vs. intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for preinduction cervical ripening. A randomized trial. J Reprod Med 2001;46:641–6.
Gherman RB. A randomized double-blind comparison of oral misoprostol dosing regimens for cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99(Suppl. 4):47.
Giacalone PL, Targosz V, Laffargue F, Boog G, Faure JM. Cervical ripening with mifepristone before labor induction: a randomized study. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92:487–92.
Gibson K, Mercer B, Louis J. A randomized control trial of inner thigh taping versus traction for cervical ripening with a Foley catheter. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2013;208(Suppl. 1):145–6.
Gihwala N, Moodley J, Hansen J, Naicker SN. Prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel: a new formulation for the induction of labour. S Afr Med J 1987;72:615–17.
Gihwala N. A Comparison of Prostaglandin E2 and Oxytocin for the Induction of Labour: a Randomised Trial. Proceedings of 23rd Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 23–26 September 1986, South Africa, abstract no. 52.
Gilson GJ, Curet LB. Intracervical dinoprostone (PGE2): does it actually lower the Cesarean section rate? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:405.
Gilson GJ, Izquierdo LA, Chatterjee MS, Curet LB, Qualls CR. Prevention of cesarean section. Does intracervical dinoprostone work? West J Med 1993;159:149–52.
Gilson GJ, Russell DJ, Izquierdo LA, Qualls CR, Curet LB. A prospective randomized evaluation of a hygroscopic cervical dilator, Dilapan, in the preinduction ripening of patients undergoing induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:145–9.
Gilson GJ, Smith JF, Curet LB, Izquierdo LA, Chatterjee MS, Joffe GM, et al. Efficacy of preinduction Dilapan on lowering the Cesarean section rate. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:423.
Girija S, Manjunath AP. A randomized controlled trial comparing low dose vaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone gel for labor induction. J Obstet Gynecol India 2011;61:153–60.
Girija S, Manjunath AP. Comparison of two dosing regimens of vaginal misoprostol for labour induction: a randomised controlled trial. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc 2009;10:220–5.
Gittens L, Schenkel C, Strassberg S, Apuzzio J. Vaginal birth after cesarean section: comparison of outpatient use of prostaglandin gel to expectant management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:354.
Glagoleva EA, Nikonov AP. Preinduction cervical ripening: a comparison of intracervical prostaglandin e2 gel versus the hygroscopic cervical dilator dilapan. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1999;86:S67.
Goel G, Shirazee HH, Phadikar A, Saha SK. Sublingual versus Vaginal Misoprostol Induction of Labour and its Fetomaternal Outcome. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 23–26 September 1986, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, abstract no. 160.
Goeschen K. Premature rupture of membranes near term: induction of labor with endocervical prostaglandin E2 gel or intravenous oxytocin. Am J Perinatol 1989;6:181–4.
Golbus MS, Creasy RK. Uterine priming with oral prostaglandin E2 prior to elective induction with oxytocin. Prostaglandins 1977;14:577–81.
Goldenberg M, Dulitzky M, Feldman B, Zolti M, Bider D. Stretching of the cervix and stripping of the membranes at term: a randomised controlled study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1996;66:129–32.
Gonen R, Samberg I, Degani S. Intracervical prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor in patients with premature rupture of membranes and an unripe cervix. Am J Perinatol 1994;11:436–8.
Gottschall D, Borgida AF, Mihalek JJ, Sauer F, Rodis JF. Misoprostol versus prostin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S141.
Gottschall DS, Borgida AF, Mihalek JJ, Sauer F, Rodis JF. A randomized clinical trial comparing misoprostol with prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1067–70.
Gower RH, Toraya J, Miller JM. Laminaria for preinduction cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 1982;60:617–19.
Grant JM, Serle E, Mahmood T, Sarmandal P, Conway DI. Management of prelabour rupture of the membranes in term primigravidae: report of a randomized prospective trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;99:557–62.
Grant JM. Comparison of Hydrostatic Sweeping of the Membranes (Extra-Amniotic Foley Catheter plus Extra-Amniotic Water Injection) and Vaginal Prostaglandin Gel in Women with an Unfavourable Cervix who Require Induction of Labour. Personal communication. 1993.
Graves GR, Baskett TF, Gray JH, Luther ER. The effect of vaginal administration of various doses of prostaglandin E2 gel on cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;151:178–81.
Green C, Pedder G, Mason G. A randomised trial of Propess against prostin gel for induction of labour at term. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105(Suppl. 17):82.
Greer IA, Calder AA. Pre-induction cervical ripening with extra-amniotic and vaginal prostaglandin E2. J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;10:18–22.
Greer IA, McLaren M, Calder AA. Vaginal administration of PGE2 for induction of labor stimulates endogenous PGF2 alpha production. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1990;69:621–5.
Gregson S, Waterstone M, Norman I, Murrells T. A randomised controlled trial comparing low dose vaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone vaginal gel for inducing labour at term. BJOG 2005;112:438–44.
Gregson S. To Compare the Safety and Efficacy of ‘Low Dose’ Vaginal Misoprostol and Dinoprostone Vaginal Gel for Induction of Labour at Term. 2004. URL: www.controlled-trials.com/mrct (accessed 15 September 2004).
Greybush M, Singleton C, Atlas RO, Balducci J, Rust OA. Preinduction cervical ripening techniques compared. J Reprod Med 2001;46:11–17.
Gribel GP, Coca-Velarde LG, Moreira de SRA. Electroacupuncture for cervical ripening prior to labor induction: a randomized clinical trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2011;283:1233–8.
Griffith-Jones MD, Tyrrell SN, Tuffnell DJ. A prospective trial comparing intravenous oxytocin with vaginal prostaglandin E2 tablets for labour induction in cases of spontaneous rupture of the membranes. Obstet Gynaecol Today 1990;1:104–5.
Grünnberger W, Spona J. The effect of pericervical PGE2 instillation on levels of maternal serum 13,14-dihydro-15-keto-PGF2 alpha and progesterone. Arch Gynecol 1986;239:93–9.
Guinn D, Davies J, Jones RO, Wolf D. Foley catheter with extraamniotic saline infusion (easi) versus foley catheter alone for induction of labor in gravidas with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S169.
Guinn DA, Goepfert AR, Owen J, Christine M, Hauth J. Laminaria, extraamniotic saline induction (EASI) or prepidil for cervical ripening prior to labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S143.
Güngördük K, Asicioglu O, Besimoglu B, Güngördük OC, Yildirm G, Ark C, et al. Labor induction in term premature rupture of membranes: comparison between oxytocin and dinoprostone followed 6 hours later by oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206:60.e1–8.
Gupta HP, Singh U, Mehrotra S. Comparative evaluation of 25 µg and 50 µg of intravaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. J Obstet Gynecol India 2010;60:51–4.
Gupta N, Mishra SL, Shradha J. A randomized clinical trial comparing misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Obstet Gynecol India 2006;56:149–51.
Gupta R, Vasishta K, Sawhney H, Ray P. Safety and efficacy of stripping of membranes at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1998;60:115–21.
Haas S, Lucas MJ. Impact of prepidil pre-induction cervical treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;168:361.
Habib SM, Emam SS, Saber AS. Outpatient cervical ripening with nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate prior to induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2008;101:57–61.
Haghighi L, Homam H, Raoofi Z, Najmi Z. Intravaginal isosorbide dinitrate or misoprostol for cervical ripening prior to induction of labour: a randomised controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2013;33:272–6.
Haghighi L. Intravaginal misoprostol in preterm premature rupture of membranes with low Bishop scores. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2006;94:121–2.
Haitsma V, Cammu H. Is Stripping of Membranes Useful in Reducing Duration of Pregnancy? 15th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 10–13 September 1996, Glasgow, UK, abstract no. 202.
Hales K, Rayburn W, Turnbull G, Christensen D, Patatanian E. Double-blind comparison of intracervical and intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:365.
Hales KA, Rayburn WF, Turnbull GL, Christensen HD, Patatanian E. Double-blind comparison of intracervical and intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1087–91.
Hall R, Duarte-Gardea M, Harlass F. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:1044–8.
Hallak M. Mechanical ripening of the unfavorable cervix for induction of labor. Contemp Rev Obstet Gynaecol 1997;9:99–105.
Hamdan M, Sidhu K, Sabir N, Omar SZ, Tan PC. Serial membrane sweeping at term in planned vaginal birth after cesarean: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2009;114:745–51.
Hannah M, Ohlsson A, Farine D, Hewson S, Hodnett E, Myhr T, et al. Vaginal Prostaglandin E2 Gel vs Intravenous Oxytocin vs Expectant Management for Prelabour Rupture of Membranes at Term. A Randomised Clinical Trial. Proceedings of the 15th Conference of Priorities in Perinatal Care, 1996, South Africa, abstract no. 14.
Hannah M, Ohlsson A, Wang E, Myhr T, Farine D, Hewson S, et al. Inducing labor with iv oxytocin may reduce the risk of neonatal infection in GBS positive women with PROM at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S32.
Hannah ME, Ohlsson A, Farine D, Hewson SA, Hodnett ED, Myhr RL, et al. Induction of labor compared with expectant management for prelabor rupture of the membranes at term. N Engl J Med 1996;334:1005–10.
Hannah ME, Ohlsson A, Wang EE, Matlow A, Foster GA, Willan AR, et al. Maternal colonization with group B Streptococcus and prelabor rupture of membranes at term: the role of induction of labor. TermPROM Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:780–5.
Harper TC, Coeytaux RR, Chen W, Campbell K, Kaufman JS, Moise KJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of acupuncture for initiation of labor in nulliparous women. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2006;19:465–70.
Harper TC, Coeytaux RR, Chen W, Campbell K, Kaufman JS, Thorp J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of acupuncture for initiation of labor in nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;193(Suppl. 6):43.
Has R, Batukan C, Ermis H, Cevher E, Araman A, Kiliç G, et al. Comparison of 25 and 50 microg vaginally administered misoprostol for preinduction of cervical ripening and labor induction. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2002;53:16–21.
Haugland B, Albrechtsen S, Lamark E, Rasmussen S, Kessler J. Induction of labor with single- versus double-balloon catheter: a randomized controlled trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2012;91(Suppl. 159):84–5.
Hauth JC, Cunningham FG, Whalley PJ. Early labor initiation with oral PGE2 after premature rupture of the membranes at term. Obstet Gynecol 1977;49:523–6.
Hay D, Robinson G, Filshie M, James D. Cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 gel and hygroscopic cervical dilators. 27th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 4–7 July 1995, Dublin, Ireland, abstract no. 480.
Hayashi R, Keirse M. PGE2 Gel (Prepidil Gel) for Preinduction Cervical Softening. Personal communication. 1983.
Heden L, Ingemarsson I, Ahlstrom H, Solum T. Induction of labor vs conservative management in prolonged pregnancy: controlled study. Int J Feto-Maternal Med 1991;4:148–52.
Heinzl S, Ramzin MS, Schneider M, Luescher KP. [Priming of cervix with prostaglandin gel during immature birth situation at term.] Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol 1980;184:395–400.
Hemlin J, Möller B. Extraamniotic saline infusion is promising in preparing the cervix for induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1998;77:45–9.
Henrich W, Dudenhausen JW, Hanel C, Chen FC. [Oral misoprostol against vaginal dinoprostone for labor induction at term: a randomized comparison.] Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol 2008;212:183–8.
Henry A, Reid R, Madan A, Tracy S, Sharpe V, Welsh A, et al. Satisfaction survey: outpatient Foley catheter versus inpatient prostin gel for cervical ripening. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2011;51:474.
Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P, Pokpirom J. A comparison of intravaginal misoprostol and intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for ripening of unfavorable cervix and labor induction. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 1997;23:369–74.
Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P. A comparison of oral and intracervical prostaglandin E2 for ripening of the unfavourable cervix prior to induction of labour. J Med Assoc Thai 1988;71:269–73.
Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P. Ripening of the unfavorable cervix with prostaglandin E2: intracervical versus intravaginal route. J Med Assoc Thai 1993;76(Suppl. 1):63–8.
Herabutya Y, Prasertsawat PO, Tongyai T, Isarangura Na Ayudthya N. Prolonged pregnancy: the management dilemma. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1992;37:253–8.
Herabutya Y, Suchatwatnachai C, O-Prasertsawat P. Comparison of intravenous oxytocin with and without vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel in term pregnancy with premature rupture of membranes and unfavorable cervix. J Med Assoc Thai 1991;74:92–6.
Hidar S, Bibi M, Jerbi M, Bouguizene S, Nouira M, Mellouli R, et al. [Contribution of intracervical PGE2 administration in premature rupture of the membranes at term. Prospective randomised clinical trial.] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 2000;29:607–13.
Hill MJ, McWilliams GD, Garcia D, Chen B, Munroe M, Hoeldtke NJ. The effect of membrane sweeping in uncomplicated pregnancies on prelabor rupture of membranes, a prospective randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111(Suppl. 4):11.
Hill MJ, McWilliams GD, Garcia-Sur D, Chen B, Munroe M, Hoeldtke NJ. The effect of membrane sweeping on prelabor rupture of membranes: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:1313–9.
Hill MJ. Safety Study of Membrane Sweeping in Pregnancy. 2006. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 March 2006).
Hjertberg R, Berg A, Ekman G, Granstrom L, Hammarstrom M, Moberger B, et al. Twelve or 24-hours Expectancy in Premature Rupture of the Membranes (PROM) at Term. Proceedings of 14th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 5–8 June 1994, Helsinki, Finland, abstract no. 408.
Hjertberg R, Hammarström M, Moberger B, Nordlander E, Granström L. Premature rupture of the membranes (PROM) at term in nulliparous women with a ripe cervix. A randomized trial of 12 or 24 hours of expectant management. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:48–53.
Hodnett ED, Hannah ME, Weston JA, Ohlsson A, Myhr TL, Wang EEI, et al. Women’s evaluations of induction of labor versus expectant management for prelabor rupture of the membranes at term. Birth 1997;24:214–20.
Hoffmann RA, Anthony J, Fawcus S. Oral misoprostol vs. placebo in the management of prelabor rupture of membranes at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;72:215–21.
Hoffmann RAM, Fawcus S, Anthony J. Oral Misoprostol versus Placebo in the Management of Prelabour Rupture of Membranes at Term. Women’s Health – Into the New Millennium. Proceedings of the 4th International Scientific Meeting of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, 3–6 October 1999, Cape Town, South Africa, abstract no. 65.
Hofmeyr GJ, Alfirevic Z, Matonhodze B, Brocklehurst P, Campbell E, Nikodem VC. Titrated oral misoprostol solution for induction of labour: a multi-centre, randomised trial. BJOG 2001;108:952–9.
Hosli I, Zanetti-Daellenbach R, Gairing A, Holzgreve W, Lapaire O. Selection of appropriate prostaglandin for the induction of labor at term is more predictive for the achievement of delivery within 24 hours than pre-assessed cervical parameters: a prospective, randomized trial. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 2008;68:147–51.
How H, Leaseburge L, Khoury J, Siddiqi T, Sibai B. Is there an ideal route of misoprostol administration for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S118.
How HY, Leaseburge L, Khoury JC, Siddiqi TA, Spinnato JA, Sibai BM. A comparison of various routes and dosages of misoprostol for cervical ripening and the induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:911–15.
Howarth GR, Funk M, Steytler P, Pistorius L, Makin J, Pattinson RC. A Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Vaginally Administered Misoprostol to Vaginal Dinoprostone Gel in Labour Induction. 15th Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care in Southern Africa, 5–8 March 1996, Goudini Spa, South Africa.
Howarth GR, Funk M, Steytler P, Pistorius L, Makin J, Pattinson RC. A randomised controlled trial comparing vaginally administered misoprostol to vaginal dinoprostone gel in labour induction. J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;16:474–8.
Huang W, Chung J, Rumney P, Pattillo C, Garite T, Nageotte M. A prospective, randomized controlled trial comparing misoprostol, foley catheter, and combination misoprostol-foley for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S57.
Hudon L, Belfort MA, Dorman K, Wilkins IA, Moise KJ. Comparison between intracervical PGE2 and supracervical foley catheter for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:S126.
Husslein P, Egarter C, Sevelda P, Genger H, Salzer H, Kofler E. [Labor induction with 3 mg of prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets. A renaissance of programmed labor? Results of a prospective randomized study.] Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1986;46:83–7.
Hutchon DJ, Geirsson R, Patel NB. A double-blind controlled trial of PGE2 gel in cervical ripening. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1980;17:604–7.
Hutchon DJR, Geirsson RT, Patel NB. A double-blind controlled trial of intracervical prostaglandin E2 in cervical ripening. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1980;59(Suppl. 93):83.
Incerpi M, Fassett M, Kjos S, Tran S, Wing D. Vaginally administered misoprostol for outpatient labor induction in pregnancies with diabetes mellitus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S120.
Incerpi MH, Fassett MJ, Kjos SL, Tran SH, Wing DA. Vaginally administered misoprostol for outpatient cervical ripening in pregnancies complicated by diabetes mellitus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185:916–19.
Irion O, Pedrazzoli J, Mermillod B. A randomized trial comparing vaginal and cervical prostaglandin gel for cervical ripening and labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1998;91:65–71.
Iskander MN. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of extra-amniotic prostaglandin E2 and intravenous prostaglandin E2 for the induction of labour in patients with unripe cervices. J Int Med Res 1978;6:144–6.
Jackson GM, Sharp HT, Varner MW. Cervical ripening before induction of labor: a randomized trial of prostaglandin E2 gel versus low-dose oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1092–6.
Jackson GM, Sharp HT, Varner MW. Pre-induction cervical ripening: low dose oxytocin is as effective as intracervical prostaglandin E2. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:379.
Jackson N, Paterson-Brown S. Labour characteristics and uterine activity: misoprostol compared with oxytocin in women at term with prelabour rupture of the membranes. BJOG 2000;107:1181–2.
Jagani N, Schulman H, Fleischer A, Mitchell J, Blattner P. Role of prostaglandin-induced cervical changes in labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:225–9.
Jagani N, Schulman H, Fleischer A, Mitchell J, Randolph G. Role of the cervix in the induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1982;59:21–6.
Janakiraman V, Ojo L, Sheth S, Keller J, Young H. Membrane sweeping in GBS positive patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204(Suppl. 1):41–2.
Jeeva MA, Dommisse J. Laminaria tents or vaginal prostaglandins for cervical ripening. A comparative trial. S Afr Med J 1982;61:402–3.
Jindal P, Avasthi K, Kaur M. A Comparison of Vaginal vs. Oral Misoprostol for Induction of Labor-Double Blind Randomized Trial. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2011;61:538–42.
Johnson IR, Macpherson MB, Welch CC, Filshie GM. A comparison of Lamicel and prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel for cervical ripening before induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;151:604–7.
Jozwiak M, Benthem M, Oude RK, Dijksterhuis M, de Graaf I, van Pampus M, et al. Randomized clinical trial for the comparison of Foley catheter and prostaglandin inserts in induction of labor at term (trial registration NTR 1646). Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206(Suppl. 1):40.
Jozwiak M, Oude Rengerink K, Benthem M, van Beek E, Dijksterhuis MG, de Graaf IM, et al. Foley catheter versus vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel for induction of labour at term (PROBAAT trial): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2011;378:2095–103.
Jozwiak M, Oude Rengerink K, Ten Eikelder ML, van Pampus MG, Dijksterhuis MG, de Graaf IM, et al. Foley catheter or prostaglandin E2 inserts for induction of labour at term: an open-label randomized controlled trial (PROBAAT-P trial) and systematic review of literature. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2013;170:137–45.
Jozwiak M, Rengerink KO, Doornbos H, Drogtrop A, de Groot C, Huisjes A, et al. Prediction of cesarean section in women with an unfavorable cervix at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206(Suppl. 1):146.
Jozwiak M, ten Eikelder M, Oude Rengerink K, de Groot C, Feitsma H, Spaanderman M, et al. Foley catheter versus vaginal misoprostol: randomized controlled trial (PROBAAT-M study) and systematic review and meta-analysis of literature. Am J Perinatol 2014;31:145–56.
Kadanali S, Küçüközkan T, Zor N, Kumtepe Y. Comparison of labor induction with misoprostol vs. oxytocin/prostaglandin E2 in term pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1996;55:99–104.
Kadian ND. Comparison of nitric oxide donor isosorbide dinitrate (IDN) and dinoprostone for cervical ripening before induction of labor at term. BJOG 2008;115(Suppl. 1):76.
Kalkat RK, McMillan E, Cooper H, Palmer K. Comparison of Dinoprostone slow release pessary (Propess) with gel (Prostin) for induction of labour at term: a randomised trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2008;28:695–9.
Kalkat RKB, McMillan E, Cooper H, Palmer K. Comparative Study of Dinoprostone Slow Release Pessary (propess) versus Gel (prostin) for Induction of Labour. 31st British International Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 4–6 July 2007, London, UK, abstract no. 209.
Kaminski K, Rechberger T, Oleszczuk J, Jakowicki J, Oleszczuk J. Biochemical and clinical evaluation of the efficiency of intracervical extraamniotic prostaglandin F2 alpha and intravenous oxytocin infusion to induce labour at term. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;34:409–13.
Kandil M, Emarh M, Sayyed T, Masood A. Foley catheter versus intra-vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor in post-term gestations. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;286:303–7.
Kanhai HHH, Keirse M. Intravenous administration of sulfprostone for the induction of labour after fetal death: a randomized comparison of two dose schedules. 12th FIGO World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 23–8 October 1988, Brazil, pp. 201–2.
Kanhai HHH, Keirse M. Intravenous Administration of Sulprostone for the Induction of Labour After Fetal Death: a Randomized Comparison of Two Dose Schedules. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 45.
Kashanian M, Afshar A, Zarrin Z. A comparison between the effect of oxytocine only and oxytocine plus propanolol on the labor (a double blind randomized trial). J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2008;21(Suppl. 1):73.
Kashanian M, Akbarian A, Baradaran H, Samiee MM. Effect of membrane sweeping at term pregnancy on duration of pregnancy and labor induction: a randomized trial. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2006;62:41–4.
Kashanian M, Akbarian AR, Fekrat M. Cervical ripening and induction of labor with intravaginal misoprostol and Foley catheter cervical traction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2006;92:79–80.
Kashanian M, Baradaran H, Meshki M. The effect of membrane sweeping at term pregnancy on the duration of pregnancy and labor induction: a randomized trial. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;23(Suppl. 1):226.
Kashanian M, Dadkhah F, Mokhtari F. Effect of intramuscular administration of dexamethasone on the duration of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2008;102:259–62.
Kashanian M, Fekrat M. The cervical ripening and induction of labor with intravaginal misoprostol, traction on the cervix with intracervical Foley catheter, and a combination of the two methods: a randomized trial of 3 techniques. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2009;107(Suppl. 2):481.
Kashanian M, Naghghash S. A Comparison Between the Effect of Oxitocin only and Oxitocin plus Propranolol on the Labor (a Double Blind Randomized Trial). 31st British International Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 2007, London, UK, abstract no. 158.
Kashanian M, Zarrin DR. Evaluation of the effect of extra-amniotic normal saline infusion (EASI) alone or in combination with dexamethazone for the induction of labor. 31st British International Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, July 4–6 2007, London, UK, abstract no. 210.
Kashanian M, Zarrin Z. A comparison between the effect of oxytocin only and oxytocin plus propanolol on the labor: a double blind randomized trial. J Kashan Uni Med Sci 2006;10:7–11.
Kashanian M, Zarrin Z. A comparison between the effect of oxytocin only and oxytocin plus propranolol on the labor (a double blind randomized trial). J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;23(Suppl. 1):616–17.
Katz Z, Yemini M, Lancet M, Mogilner BM, Ben-Hur H, Caspi B. Non-aggressive management of post-date pregnancies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1983;15:71–9.
Kaul V, Aggarwal N, Ray P. Membrane stripping versus single dose intracervical prostaglandin gel administration for cervical ripening. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;86:388–9.
Kehl S, Welzel G, Ehard A, Berlit S, Spaich S, Siemer J, et al. Women’s acceptance of a double-balloon device as an additional method for inducing labour. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2013;168:30–5.
Kehl S, Ziegler J, Schleussner, Tuschy B, Berlit S, Mayer J, et al. Induction of labour with a balloon catheter and misoprostol - a randomised controlled multi centre study. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;286(Suppl. 1):145–6.
Keirse M, Kanhai HHH, Verwey RA, Bennebroek Gravenhorst J. European Multi-centre Trial of Intra-cervical PGE2 in Triacetin Gel: Report on the Leiden Data. In Wood C, editor. The Role of Prostaglandins in Labour. London: RSM Services;1985. pp. 93–100.
Keirse M, Schulpen M, Corbeij R, Oosterbaan HP. Vaginal PGE2 gel vs Intravenous Oxytocin after Cervical Ripening with Endocervical PGE2 gel. Priming and Induction of Labour by Prostaglandins. In Keirse MJNC, De Koning Gans HJ. A State of the Art. Leiden: Postgrad Med Ed Committee; 1987. pp. 53–76.
Keirse M, Schulpen M, De Koning Gans HJ. A Randomized Controlled Comparison of Endocervical and Vaginal PGE2 in Triacetin Gel for Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April–3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 214.
Keirse MJ, de Koning Gans HJ. Randomized comparison of the effects of endocervical and vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel in women with various degrees of cervical ripeness. Dutch Collaborative Prostaglandin Trialists’ Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1859–64.
Kemp B, Winkler M, Rath W. Induction of labor by prostaglandin E(2) in relation to the Bishop score. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2000;71:13–17.
Kennedy JH, Quinn MA, Howie PW, Calder AA. Single shot prostaglandin gel for labor induction. Prostaglandins 1978;15:169–73.
Kennedy JH, Stewart P, Barlow DH, Hillan E, Calder AA. Induction of labour: a comparison of a single prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet with amniotomy and intravenous oxytocin. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1982;89:704–7.
Khazardoost S, Hakimi P, Noorzadeh M, Shafaat M. Misoprostol for cervical ripening: a clinical trial in 60 pregnant women. Tehran Uni Med J 2011;68:595–9.
Khoury A, Zhou Q, Gorenberg D, Nies B, Manley G, Mecklenburg F. A randomized clinical trial comparing misoprostol suppositories with continuous dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S118.
Khoury AN, Zhou QP, Gorenberg DM, Nies BM, Manley GE, Mecklenburg FE. A comparison of intermittent vaginal administration of two different doses of misoprostol suppositories with continuous dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. J Maternal Fetal Med 2001;10:186–92.
Kidanto HL, Kaguta MM, van Roosmalen J. Induction of labor with misoprostol or oxytocin in Tanzania. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2007;96:30–1.
Kieback DG, Zahradnik HP, Quaas L, Kröner-Fehmel EE, Lippert TH. Clinical evaluation of endocervical prostaglandin E2-triacetin-gel for preinduction cervical softening in pregnant women at term. Prostaglandins 1986;32:81–5.
Kim JH, Yang HS. A comparison of intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor inducton in term pregnancy with unfavorable cervix. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 2000;43:243–7.
Kimball FA, Ruppel PL, Noah ML, Decoster JM, delaFuente P, Castillo JM, et al. The effect of endocervical PGE2-gel (Prepidil) gel on plasma levels of 13,14-dihydro-15-keto-PGE2 (PGEM) in women at term. Prostaglandins 1986;32:527–37.
Kipikasa JH, Adair CD, Williamson J, Breen JM, Medford LK, Sanchez-Ramos L. Use of misoprostol on an outpatient basis for postdate pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;88:108–11.
Koc O, Duran B, Ozdemirci S, Albayrak M, Koc U. Oxytocin versus sustained-release dinoprostone vaginal pessary for labor induction of unfavorable cervix with Bishop score ≥ 4 and ≤ 6: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2013;39:790–8.
Kolderup L, McLean L, Grullon K, Safford K, Kilpatrick SJ. Misoprostol is more efficacious for labor induction than prostaglandin E2, but is it associated with more risk? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:1543–50.
Komala K, Reddy M, Quadri IJ, Suneetha B, Ramya V. Comparative study of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour, maternal and foetal outcome. J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:2866–9.
Kovavisarach E, Wattanasiri S. Comparison of intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction at term with unfavourable cervix: a randomized controlled study. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;9:175–81.
Kovavisarach E, Worachet W. Randomized controlled trial of intravaginal 50 mcg misoprostol and 3 mg dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction at term with unfavorable cervix. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;10:27–32.
Kramer RL, Gilson G, Morrison DS, Martin D, Gonzalez JL, Curet LB. A randomized trial of misoprostol and oxytocin for induction of labor: safety and efficacy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S111.
Kramer RL, Gilson GJ, Morrison DS, Martin D, Gonzales JL, Qualls CR. A randomized trial of misoprostol and oxytocin for induction of labor: safety and efficacy. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:387–91.
Krammer J, O’Brien W, Williams M, Sawai S. A prospective randomized comparison of dilapan vs PGE2 for preinduction cervical ripening and their effect on labor kinetics. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;70:408.
Krammer J, O’Brien W, Williams M, Sawai S. Success of labor induction varies by post-ripening cervical dilation and agent used. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;170:403.
Krammer J, Williams MC, Sawai SK, O’Brien WF. Pre-induction cervical ripening: a randomized comparison of two methods. Obstet Gynecol 1995;85:614–18.
Kristoffersen M, Sande HA, Sande OS. Ripening of the cervix with prostaglandin E2-gel. A randomized study with a new ready-to-use compound of triacetin-prostaglandin-E2-gel. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1986;24:297–300.
Krithika KS, Aggarwal N, Suri V. Prospective randomised controlled trial to compare safety and efficacy of intravaginal misoprostol with intracervical cerviprime for induction of labour with unfavourable cervix. J Obstet Gynaecol 2008;28:294–7.
Kulshreshtha S, Sharma P, Mohan G, Singh S, Singh S. Comparative study of misoprostol vs dinoprostone for induction of labour. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2007;51:55–61.
Kumar S, Awasthi RT, Kapur A, Srinivas S, Parikh H, Sarkar S. Induction of labour with misoprostol – a prostaglandin E1 analogue. Med J Armed Forces India 2001;57:107–9.
Kunt C, Kanat-Pektas M, Gungor AN, Kurt RK, Ozat M, Gulerman C, et al. Randomized trial of vaginal prostaglandin E2 versus oxytocin for labor induction in term premature rupture of membranes. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2010;49:57–61.
Kwon JS, Davies GA, Mackenzie VP. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a randomised trial. BJOG 2001;108:23–6.
Kwon JS, Mackenzie VP, Davies GAL. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a randomised trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:S128.
Lackritz R, Gibson M, Frigoletto FD. Preinduction use of laminaria for the unripe cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1979;134:349–50.
Ladfors L, Mattsson LA, Eriksson M, Fall O. A randomised trial of two expectant managements of prelabour rupture of the membranes at 34 to 42 weeks. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;103:755–62.
Ladfors L, Tessin I, Fall O, Erikson M, Matsson LA. A comparison of neonatal infectious outcome comparing two expectant managements of women with prelabor rupture of the membranes at 34–42 weeks. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S197.
Lamki H, Roberts A, Dunlop JM, Pinkerton JH. Induction of labour by prostaglandin E2 compared with Syntocinon. Ir Med J 1974;67:515–19.
Lange AP, Secher NJ, Nielsen FH, Pedersen GT. Stimulation of labor in cases of premature rupture of the membranes at or near term. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1981;60:207–10.
Lange I, St Onge R, Connors G, Ingelson B. A comparison of PGE2 gel vs the foley catheter for pre-induction cervical ripening. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1994;46:7.
Lange IR, Collister C, Johnson J, Cote D, Torchia M, Freund G, et al. The effect of vaginal prostaglandin E2 pessaries on induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984;148:621–5.
Langenegger EJ, Odendaal HJ, Grové D. Oral misoprostol versus intracervical dinoprostone for induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;88:242–8.
Larmon JE, Magann EF, Dickerson GA, Morrison JC. Outpatient cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 and estradiol. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2002;11:113–17.
Laube DW, Zlatnik FJ, Pitkin RM. Preinduction cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 intracervical gel. Obstet Gynecol 1986;68:54–7.
Le Roux PA, Olarogun JO, Penny J, Anthony J. Oral and vaginal misoprostol compared with dinoprostone for induction of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:201–5.
Lee HY. A randomised double-blind study of vaginal misoprostol vs dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction in prolonged pregnancy. Singapore Med J 1997;38:292–4.
Legarth J, Guldbaek E, Scher NJ. The efficiency of prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppositories versus intracervical prostaglandin gel for induction of labor in patients with unfavorable inducibility prospects. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1988;27:93–8.
Legarth J, Guldbaek E, Secher NJ. The efficiency of prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppository vs intracervical prostaglandin gel for induction of labor in patients with unfavorable Bishop score. Arch Gynecol 1985;237(Suppl.1):103.
Legarth J, Lyndrup J, Dahl C, Philipsen T, Eriksen PS. Prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppository for induction of labour: an efficient, safe and popular method. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1987;26:233–8.
Lelaidier C, Baton C, Benifla JL, Fernandez H, Bourget P, Frydman R. Mifepristone for labour induction after previous caesarean section. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;101:501–3.
Lelaidier C, Benifla JL, Fernandez H, Baton C, Bourget P, Bourrier MC, et al. [The value of RU-486 (mifepristone) in medical indications of the induction of labor at term. Results of a double-blind randomized prospective study (RU-486 versus placebo).] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1993;22:91–100.
Lemancewicz A, Urban R, Skotnicki MZ, Karpiuk A, Urban J. Uterine and fetal Doppler flow changes after misoprostol and oxytocin therapy for induction of labor in post-term pregnancies. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1999;67:139–45.
Lemke M, Turnquest M. Laminaria tents plus vaginal prostaglandin versus vaginal prostaglandin alone for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:482.
Lemyre M, Verret N, Turcot-Lemay L, Brassard N, Morin V. Foley catheter or vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195(Suppl. 1):105.
Levy R, Vaisbuch E, Furman B, Brown D, Volach V, Hagay ZJ. Induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes at term in women with unfavorable cervix: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Perinat Med 2007;35:126–9.
Levy R, Vaisbuch E, Furman B, Doitch H, Oron S, Hagay Z. Prospective randomized clinical trial of immediate induction of labor with oral misoprostol for prelabor rupture of the membranes in women with unfavorable cervix at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;193(Suppl. 6):44.
Lewis GJ. Cervical ripening before induction of labour with prostaglandin E2 pessaries or a Foley’s catheter. J Obstet Gynaecol 1983;3:173–6.
Li XH, Ma WZ, Xu SY. The clinical observation on the effect of electroacupuncture to Sanyinjiao(SP6) and Hegu(L14) in influencing parturients’ uterine contraction in the first stage. J Beijing Uni Trad Chinese Med 1996;19:38.
Lien JM, Morgan MA, Garite TJ, Kennedy KA, Sassoon DA, Freeman RK. Antepartum cervical ripening: applying prostaglandin E2 gel in conjunction with scheduled nonstress tests in postdate pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:453–8.
Liggins GC. Controlled trial of induction of labor by vaginal suppositories containing prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins 1979;18:167–72.
Lin M, Ramsey P, Reid K, Treaster M, Nuthalapaty F, Lu G. The impact of maternal BMI, parity and GA on the comparative efficacy of transcervical foley catheter with or without an extraamniotic saline infusion for cervical ripening and labor induction in women with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195(Suppl. 1):109.
Lin M, Treaster M, Reid K, Nuthalapaty F, Ramsey P, Lu G. A randomized controlled trial of transcervical foley catheter with and without extra-amniotic saline infusion (EASI) for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;195(Suppl. 1):30.
Lin MG, Ramsey PS. Foley Catheter for Labor Induction in Women with Term or Near Term Membrane Rupture. 2006. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 March 2006).
Livingstone I, Acharya S, Shetty A, Rice P, Danielian P, Templeton A. 100 µg of oral misoprostol versus 25 µg of vaginal misoprostol in term labour induction: a randomised comparison. J Obstet Gynaecol 2004;24:106.
Lo JY, Alexander JM, McIntire DD, Leveno KJ. Efficacy of oral misoprostol in nulliparous women with premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):204.
Lo JY, Alexander JM, McIntire DD, Leveno KJ. Randomized trial of oral misoprostol in nulliparous women with premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):204.
Lo JY, Alexander JM, McIntire DD, Leveno KJ. Ruptured membranes at term: randomized, double-blind trial of oral misoprostol for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:685–9.
Lo L, Ho MW, Leung P. Comparison of Prostaglandin E2 Vaginal Tablet with Amniotomy and Intravenous Oxytocin for Induction of Labour. The Second International Scientific Meeting of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, 1993, Hong Kong, abstract no.155.
Lo L, Ho MW, Leung P. Comparison of prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablet with amniotomy and intravenous oxytocin for induction of labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;34:149–53.
Lo TK, Lau WL, Wong KS, Tang LC. Sublingual misoprostol compared to artificial rupture of membranes plus oxytocin infusion for labour induction in nulliparous women with a favourable cervix at term. Hong Kong Med J 2006;12:345–50.
Lokugamage AU, Forsyth SF, Sullivan KR, El Refaey H, Rodeck CH. Dinoprostone versus misoprostol: a randomized study of nulliparous women undergoing induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003;82:133–7.
Lopes P, Besse O, Sagot P, Dantal F, De Morel P, Panel N, et al. Induction of labour with vaginal prostaglandin E2 with a ‘Spongel’. Results of a prospective randomised study taking into account Bishop’s score and the dose of PGE2 used. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1990;19:505.
Lopes P, Besse O, Sagot P, Dantal F, De Morel P, Panel N, et al. PGE2 Application on a Biodegradable Support for Cervix Ripening and Induction of Labour. Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April–3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 147.
Lopes P, Besse O, Sagot P, Dantal F, de Morel P, Panel N, et al. [The value of the administration of prostaglandin E2 on the biodegradable support of the maturation of the cervix uteri and the induction of labor.] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1991;20:827–32.
Lopez-Farfan JA, Gamez-Guevara C. Comparison of dinoprostone (ovules and gel) to achieve cervical ripening in patients with term pregnancy that occurs with premature membranes rupture. Ginecol Obstet Mex 2010;78:110–15.
Lucas MJ, Leveno KJ, Williams ML, Brewster S. Efficacy of Prostaglandin-E2 Gel in Cervical Ripening: Preliminary Results. Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of the Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 30 January–1 February 1986, San Antonio, TX, USA, p. 240, p. 256.
Lughmani S. Vaginal misoprostol versus oxytocin infusion for labour induction in great grand multipara. A randomized controlled trial. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2009;107(Suppl. 2):250.
Luther ER, Roux J, Popat R, Gardner A, Gray J, Soubiran E, et al. The effect of estrogen priming on induction of labor with prostaglandins. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980;137:351–7.
Lykkesfeldt G, Osler M. A comparison of three methods for inducing labor: oral prostaglandin E2, buccal desaminooxytocin, intravenous oxytocin. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1979;58:321–5.
Lyndrup J, Legarth J, Dahl C, Philipsen T, Eriksen PS, Weber T. Induction of labour: the effect of vaginal prostaglandin or i.v. oxytocin: a matter of time only? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1990;37:111–19.
Lyndrup J, Legarth J, Dahl C, Philipsen T, Eriksen PS. Induction of Labour: the Effect of Prostaglandin Pessary, i.v. Oxytocin and Lamicel. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 117.
Lyndrup J, Legarth J, Dahl C, Philipsen T, Eriksen PS. Lamicel does not promote induction of labour. A randomized controlled study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1989;30:205–8.
Lyndrup J, Nickelsen C, Guldbaek E, Weber T. Induction of labor by prostaglandin E2: intracervical gel or vaginal pessaries? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1991;42:101–9.
Lyndrup J, Nickelsen C, Guldbaek E, Weber T. Induction of labour by prostaglandin-E2: intracervical gel or vaginal pessaries? Int J Gynecol Obstet 1991;36(Suppl.):70.
Lyndrup J, Nickelsen C, Weber T, Mølnitz E, Guldbaek E. Induction of labour by balloon catheter with extra-amniotic saline infusion (BCEAS): a randomised comparison with PGE2 vaginal pessaries. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1994;53:189–97.
Lyndrup J. Induction of labor by PGE2 and other local methods. Physiology, methods and guidelines for patient selection. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:86–7.
Macer J, Buchanan D, Yonekura ML. Induction of labor with prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppositories. Obstet Gynecol 1984;63:664–8.
MacKenzie IZ, Bradley S, Embrey MP. A simpler approach to labor induction using lipid-based prostaglandin E2 vaginal suppository. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981;141:158–62.
MacKenzie IZ, Embrey MP. A comparison of PGE2 and PGF2 alpha vaginal gel for ripening the cervix before induction of labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1979;86:167–70.
MacKenzie IZ. Acupuncture for Pain Relief during Induced Labour for Nulliparae. 2011. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01165099 (accessed 6 January 2011).
MacLennan A, Fraser I, Jakubowicz D, Murray-Arthur F, Quinn M, Trudinger B. Labour induction with low dose PGE2 vaginal gel: result of an Australian multicentre randomized trial. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1989;29:124–8.
MacLennan AH, Fraser I, Jakubowicz DL, Murray-Arthur F, Quinn MA, Trudinger BJ. Labour Induction with PGE2 Vaginal Gel: Results of an Australian Multicentre Randomised Trial. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 119.
MacLennan AH, Green RC, Bryant-Greenwood GD, Greenwood FC, Seamark RF. Ripening of the human cervix and induction of labour with purified porcine relaxin. Lancet 1980;1:220–3.
MacLennan AH, Green RC, Grant P, Nicolson R. Ripening of the human cervix and induction of labor with intracervical purified porcine relaxin. Obstet Gynecol 1986;68:598–601.
MacLennan AH, Green RC. A double blind dose trial of intravaginal prostaglandin F2 alpha for cervical ripening and the induction of labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1980;20:80–3.
MacLennan AH, Green RC. Cervical ripening and induction of labour with intravaginal prostaglandin F2 alpha. Lancet 1979;1:117–19.
MacLennan AH, Green RC. The effect of intravaginal prostaglandin F2 alpha on labour after spontaneous and artificial rupture of the membranes. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1980;20:87–90.
Macones G, Stamilio D, Rampersad R, Cahill AG, Odibo AO. The efficacy of early amniotomy in nulliparous labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204(Suppl. 1):4.
MacPherson M. Comparison of Lamicel with prostaglandin E2 gel as a cervical ripening agent before the induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol 1984;4:205–6.
Magann EF, Chauhan SP, McNamara MF, Bass JD, Estes CM, Morrison JC. Membrane stripping vs dinoprostone vaginal insert in the management of pregnancies beyond 41 weeks with unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S30.
Magann EF, Chauhan SP, McNamara MF, Bass JD, Estes CM, Morrison JC. Membrane sweeping versus dinoprostone vaginal insert in the management of pregnancies beyond 41 weeks with an unfavorable cervix. J Perinatol 1999;19:88–91.
Magann EF, Chauhan SP, Nevils BG, McNamara MF, Kinsella MJ, Morrison JC. Management of pregnancies beyond forty-one weeks’ gestation with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:1279–87.
Magann EF, McNamara MF, Whitworth NS, Chauhan SP, Thorpe RA, Morrison JC. Can we decrease postdatism in women with an unfavorable cervix and a negative fetal fibronectin test result at term by serial membrane sweeping? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:890–4.
Magann EF, McNamara MJ, Whitworth NS, Chauhan SP, Thorp RA, Morrison JC. Can we decrease postdatism in women with an unfavorable cervix and a negative fetal fibronectin at term by serial membrane stripping. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S96.
Magann EF, Perry KG, Dockery JR, Bass JD, Chauhan SP, Morrison JC. Cervical ripening before medical induction of labor: a comparison of prostaglandin E2, estradiol, and oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1702–6.
Magnani M, Cabrol D. Induction of labour with PGE2 after cervical ripening with oestradiol. Control and management of parturition 23rd Baudelocque symposium. 1986;151:109–18.
Magos AL, Noble MCB, Yuen AWT, Rodeck CH. Controlled study comparing vaginal prostaglandin E2 pessaries with intravenous oxytocin for the stimulation of labour after spontaneous rupture of the membranes. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1983;90:726–31.
Magtibay P, Ogburn P, Harris D, Suman V, Ramin K. Misoprostol as a labour induction agent: a pilot study comparing efficacy, safety and cost. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:327.
Magtibay PM, Ramin KD, Harris DY, Ramsey PS, Ogburn L. Misoprostol as a labor induction agent. J Maternal Fetal Med 1998;7:15–18.
Mahmood TA, Dick MJ, Smith NC, Templeton AA. Role of prostaglandin in the management of prelabour rupture of the membranes at term. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;99:112–17.
Mahmood TA, Dick MJ. A randomized trial of management of pre-labor rupture of membranes at term in multiparous women using vaginal prostaglandin gel. Obstet Gynecol 1995;85:71–4.
Mahmood TA, Dick MJW, Smith NC, Templeton A. Management of Spontaneous Rupture of Membranes at Term without Uterine Activity in Healthy Primigravidae: A Prospective Study (PGE2 Gel vs Conservative Treatment). Proceedings of 2nd European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 30 April–3 May 1991, The Hague, The Netherlands, abstract no. 95.
Mahmood TA, Dick MJW, Smith NC. Management of spontaneous rupture of the membranes and no uterine activity in healthy primigravidae after 34 weeks’ gestation. Lancet 1989;1:721.
Mahmood TA, Rayner A, Smith NC, Beat I. A randomized prospective trial comparing single dose prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel with forewater amniotomy for induction of labour. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1995;58:111–17.
Mahmood TA, Reyner A, Smith NC. A Prospective Randomized Study of Induction of Labour with Favourable Cervix at Term: A Comparison between PGE2 Gel Single Dose vs Forewater Amniotomy and Delayed Oxytocin Infusion. Proceedings of 26th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 7–10 July 1992, Manchester, UK, abstract no. 403.
Mahmood TA. A prospective comparative study on the use of prostaglandin E2 gel (2 mg) and prostaglandin E2 tablet (3 mg) for the induction of labour in primigravid women with unfavorable cervices. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1989;33:169–75.
Mahmood TA. Induction of Labour in Primigravid with Unfavourable Cervices: A Comparison of PGE2 Gel (2 mg) with PGE2 Pessary (3 mg). Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 149.
Majoko F, Zwizwai M, Lindmark G, Nyström L. Labor induction with vaginal misoprostol and extra-amniotic prostaglandin F2alpha gel. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002;76:127–33.
Majoko F, Zwizwai M, Nystrom L, Lindmark G. Vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour: a more effective agent than prostaglandin f2 alpha gel and prostaglandin e2 pessary. Central Afr J Med 2002;48:123–8.
Malik HZ, Khawaja NP, Zahid B, Rehman R. Sublingual versus oral misoprostol for induction of labour in prelabour rupture of membranes at term. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2010;20:242–5.
Malik N, Gittens L, Gonzalez D, Bardeguez A, Ganesh V, Apuzzio J. Clinical amnionitis and endometritis in patients with premature rupture of membranes: endocervical prostaglandin E2 gel versus oxytocin for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1996;88:540–3.
Manley J, Nguyen L, Shlossman P, Colmorgen G, Sciscione A. A randomized prospective comparison of the intracervical foley bulb to intravaginal misoprostol (cytotec) for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:S76.
Margulies M, Campos Perez GA, Voto LS. Misoprostol to induce labour. Lancet 1992;339:64.
Massil HY, Baker AC, O’Brien PM. A comparison of oral prostaglandin E2 tablets with intravenous oxytocin for stimulation of labor after premature rupture of membranes at term. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1988;67:703–9.
Matonhodze B, Alfirevic Z, Hofmeyr J, Brocklehurst P. Titrated oral misoprostol for labour induction: a randomised trial. Prenatal Neonatal Med 2000;5(Suppl. 2):148.
Matonhodze B, Alfirevic Z, Hofmeyr J, Campbell L, Brocklehurst P. Titrated oral misoprostol for labour induction: a random allocation trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20(Suppl. 1):19.
Matonhodze BB, Hofmeyr GJ, Levin J. Labour induction at term: a randomised trial comparing Foley catheter plus titrated oral misoprostol solution, titrated oral misoprostol solution alone, and dinoprostone. S Afr Med J 2003;93:375–9.
Mawire CJ, Chipato T, Rusakaniko S. Extra-amniotic saline infusion versus extra-amniotic prostaglandin F2alpha for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1999;64:35–41.
McCaul JF, Williams LM, Martin RW, Magann EF, Gallagher L, Morrison JC. Comparison of induction methods for premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:275.
McCaul JFt, Rogers LW, Perry KG, Jr, Martin RW, Allbert JR, Morrison JC. Premature rupture of membranes at term with an unfavorable cervix: comparison of expectant management, vaginal prostaglandin, and oxytocin induction. Southern Med J 1997;90:1229–33.
McColgin SW, Hampton HL, McCaul JF, Howard PR, Andrew ME, Morrison JC. Stripping membranes at term: can it safely reduce the incidence of post-term pregnancies? Obstet Gynecol 1990;76:678–80.
McColgin SW, Patrissi GA, Morrison JC. Stripping Membranes at Term: Is It Safe and Efficacious? Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of the Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 1–4 February 1989, New Orleans, LA, USA, abstract no. 100.
McColgin SW, Patrissi GA, Morrison JC. Stripping the fetal membranes at term. Is the procedure safe and efficacious? J Reprod Med 1990;35:811–14.
McKenna DS, Costa SW, Samuels P. Prostaglandin E2 cervical ripening without subsequent induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:11–14.
McKenna DS, Ester JB, Proffitt M, Waddell KR. Misoprostol outpatient cervical ripening without subsequent induction of labor: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 2004;104:579–84.
McLaren M, Greer IA, Smith JR, Godfree V, Graham N, Calder AA. Maternal plasma bicycling PGE2 levels following vaginal administration of prostaglandin E2 pessaries in full term pregnancies. Prog Clin Biol Res 1987;242:199–203.
McQueen D, Neilson JP, Whittle MJ. Pre-labour rupture of membranes with an unripe cervix: a random trial of management. J Obstet Gynaecol 1990;10:495–8.
McQueen D. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Expectant with Active Management in Early Rupture of the Membranes at Term. Personal communication. 1992.
Medearis AL. Postterm Pregnancy: Active Labor Induction (PGE2 gel) Not Associated with Improved Outcomes Compared to Expectant Management. A Preliminary Report. Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 23–27 January 1990, Houston, TX, USA, abstract no. 17.
Megalo A, Petignat P, Hohlfeld P. Influence of misoprostol or prostaglandin E(2) for induction of labor on the incidence of pathological CTG tracing: a randomized trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2004;116:34–8.
Mehrotra S, Singh U, Gupta HP. A prospective double blind study using oral versus vaginal misoprostol for labour induction. J Obstet Gynaecol 2010;30:461–4.
Mei-Dan E, Walfisch A, Easton SS, Hallak M. Foley’s catheter with extra-amniotic saline infusion – a faster and cheaper ripener device: prospective randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009;201(Suppl. 1):125.
Mei-Dan E, Walfisch A, Suarez-Easton S, Hallak M. Comparison of two mechanical devices for cervical ripening: a prospective quasi-randomized trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:723–7.
Mei-Dan E. Cervical ripening with extra amniotic saline infusion: a randomized comparison of two mechanical devices. Reprod Sci 2012;19(Suppl. 3):229A.
Mercer B, Pilgram P, Sibai B. Low Dose Oxytocin vs a Routine Induction Protocol for the Induction of Labor. Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 23–27 January 1990, Houston, TX, USA, abstract no. 21.
Mercer BM, Crocker LG, Boe NM, Sibai BM. Induction versus expectant management in premature rupture of the membranes with mature amniotic fluid at 32 to 36 weeks: a randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:775–82.
Mercer BM, McNanley T, O’Brien JM, Randal L, Sibai BM. Early versus late amniotomy for labor induction: a randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1321–5.
Meydanli MM, Calişkan E, Burak F, Narin MA, Atmaca R. Labor induction post-term with 25 micrograms vs. 50 micrograms of intravaginal misoprostol. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;81:249–55.
Meyer M, Pflum J, Howard D. Outpatient misoprostol compared with dinoprostone gel for preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105:466–72.
Meyer M, Pflum J. Outpatient administration of misoprostol decreases induction time. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S167.
Milchev N, Kuzmanov B, Terzhumanov R. [Cytotec: an effective drug for the induction of labor.] Akush Ginekol 2003;42:9–11.
Miller AM, Rayburn WF, Smith CV, Allen K, Bane T. Uterine activity using ambulatory tocodynamometry after intravaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:317.
Miller AM, Rayburn WF, Smith CV. Patterns of uterine activity after intravaginal prostaglandin E2 during preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:1006–9.
Misra M, Vavre S. Labour induction with intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel and intravenous oxytocin in women with a very unfavourable cervix. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1994;34:511–15.
Moberger B, Hammarstrom M, Hjertberg R, Berg A. Neonatal Outcome After 12 vs 24 Hours of Conservative Management in Primigravidae with PROM at Term. Proceedings of 14th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 5–8 June 1994, Helsinki, Finland, abstract no. 415.
Modarres M, Rahime KF. The use of breast stimulation to prevent postdate pregnancy. Med J Islamic Republic Iran 2000;14:211–15.
Modlock J, Nielsen BB, Uldbjerg N. Acupuncture for the induction of labour: a double-blind randomised controlled study. BJOG 2010;117:1255–61.
Modlock J. Can Acupuncture be used as Preparation for Induction of Labour. 2006. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 March 2006).
Moini A, Riazi K, Honar H, Hasanzadeh Z. Preinduction cervical ripening with the Foley catheter and saline infusion vs. cervical dinoprostone. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;83:211–13.
Mol BW, van der Post J, Rengerink KO, Papatsonis D, Jozwiak M, van Huizen M, et al. Induction of labor at term: a comparison of Foley catheter and prostaglandins (trial registration NTR 1646). Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204(Suppl. 1):3–4.
Moldin PG, Sundell G. Induction of labour: a randomised clinical trial of amniotomy versus amniotomy with oxytocin infusion. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;103:306–12.
Møller M, Thomsen AC, Sørensen J, Forman A. Oxytocin- or low-dose prostaglandin F2 alpha-infusion for stimulation of labor after primary rupture of membranes. A prospective, randomized trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1987;66:103–6.
Moller M. Trial to Assess the Effects of Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour by Prostaglandin Administration. Personal communication. 1991.
Montealegre JA, Botero LF, Sabogal G. Labor induction with unfavorable cervix: randomized controlled trial double blind method. Oxitocyn vs. misoprostol. Rev Colomb Obstet Ginecol 1999;50:133–7.
Moodley J, Venkatachalam S, Songca P. Misoprostol for cervical ripening at and near term: a comparative study. S Afr Med J 2003;93:371–4.
Moodley J, Venkatachalam S, Songca P. Misoprostol for cervical ripening at and near term: a comparative study. South Afr J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;9:34–7.
Moraes Filho OB, Albuquerque RM, Cecatti JG. A randomized controlled trial comparing vaginal misoprostol versus Foley catheter plus oxytocin for labor induction. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2010;89:1045–52.
Morales WJ, Lazar AJ. Expectant management of rupture of membranes at term. South Med J 1986;79:955–8.
Morgan Ortiz F, Báez Barraza J, Quevedo Castro E, Cuetos Martínez CB, Osuna Ramírez I. [Misoprostol and oxytocin for induction of cervical ripening and labor in patients with term pregnancy and premature membrane rupture.] Ginecol Obstet Mex 2002;70:469–76.
Mosquera J, Mesa JC, Navarro H, Cobo E, Neira C, Zuniga J. Study of the efficacy of misoprostol compared with oxytocin for labor induction in women with prolonged amenorrhea. Rev Colomb Obstet Ginecol 1999;50:7–12.
Mozurkewich E, Horrocks J, Daley S, Von Oeyen P, Halvorson M, Johnson M, et al. The MisoPROM study: a multicenter randomized comparison of oral misoprostol and oxytocin for premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:1026–30.
Mozurkewich E, Horrocks J, Daley S, Von Oeyen P, Sarvis A, Halvorson M, et al. The misoprom study: a randomized controlled trial of misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S168.
Mullin P, House M, Paul R, Wing D. A comparison of vaginally administered misoprostol with extraamniotic saline infusion for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(Suppl. 6):203.
Murphy AJ, Jalland M, Pepperell RJ, Quinn MA. Use of vaginal prostaglandin gel before induction of labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1980;20:84–6.
Murray HG, Buonocore A, Hawley J. A Randomised Trial of Two Preparations of Vaginal Prostaglandin for Pre-induction Cervical Ripening. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Congress of the Australian Perinatal Society in conjunction with the New Zealand Perinatal Society, 24–27 March 1996, Adelaide, SA, Australia, abstract no. 24.
Murray HG, Buonocore A, Hawley J. A randomized trial of two preparations of vaginal prostaglandin for pre-induction cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:880–5.
Murthy BK, Arkalgud MS. Misoprostol alone versus a combination of dinoprostone and oxytocin for induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2006;56:413–16.
Naef RW, Allbert JR, Ross EL, Weber M, Martin RW, Morrison JC. Premature rupture of membranes at 34 to 37 weeks’ gestation: aggressive versus conservative management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:126–30.
Naef RW, Allbert JR, Weber BM, Roach H, Martin RW, Morrison JC. Premature rupture of membranes at 34-37 weeks’ gestation: aggressive vs conservative management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:340.
Nager CW, Key TC, Moore TR. Cervical ripening and labor outcome with preinduction intracervical prostaglandin E2 (Prepidil) gel. J Perinatol 1987;7:189–93.
Nagpal MB, Raghunandan C, Saili A. Oral misoprostol versus intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for active management of premature rupture of membranes at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2009;106:23–6.
Naismith WC, Barr W, MacVicar J. Comparison of intravenous prostaglandins F 2 and E 2 with intravenous oxytocin in the induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1973;80:531–5.
Nanda S, Singhal SR, Papneja A. Induction of labour with intravaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 gel: a comparative study. Trop Doct 2007;37:21–4.
Nasir S, Chaudhry R. Comparison of intracervical foley catheter plus oral misoprostol with oral misoprostol alone for cervical ripening in primigravidas at term. BJOG 2012;119(Suppl. 1):11–12.
Nassar AH. Sublingual versus Vaginal Misoprostol for Labor Induction at Term. 2006. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed 21 March 2006).
Natale R, Milne JK, Campbell MK, Potts PG, Webster K, Halinda E. Management of premature rupture of membranes at term: randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:936–9.
Natale R, Milne K, Campbell K, Wester K, Halinda E. Management of premature rupture of membranes at term: randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:285.
Neiger R, Greaves PC. Comparison between vaginal misoprostol and cervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Tenn Med 2001;94:25–7.
Neilson DR, Prins RP, Bolton RN, Mark C, Watson P. A comparison of prostaglandin E2 gel and prostaglandin F2 alpha gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;146:526–32.
Netta D, Visintainer P, Bayliss P. Does cervical membrane stripping increase colonization of group b streptococcus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:S221.
Newman M, Newman R. Multiple-dose PGE2 cervical ripening on an outpatient basis: safety and efficacy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S112.
Ngai CSW, To WWK, Lao T, Ho PC. Cervical Priming with Oral Misoprostol in Prelabour Rupture of Membranes at Term. 27th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 4–7 July 1995, Dublin, Ireland, abstract no. 479.
Ngai SW, Chan YM, Lam SW, Lao T. Prospective randomised study to compare misoprostol and oxytocin for labour induction in prelabour rupture of membranes in term pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105(Suppl. 17):82.
Ngai SW, Chan YM, Lam SW, Lao TT. Labour characteristics and uterine activity: misoprostol compared with oxytocin in women at term with prelabour rupture of the membranes. BJOG 2000;107:222–7.
Ngai SW, To WK, Lao T, Ho PC. Cervical priming with oral misoprostol in pre-labor rupture of membranes at term. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:923–6.
Nguyen VT, Do DV, Tran TS, Nguyen PT. Labor induction using sub-lingual misoprostol for prelabor rupture of membranes at term: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2012;119(Suppl. 3):802.
Nicoll AE, Mackenzie F, Greer IA, Norman JE. Vaginal application of the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized controlled trial to determine effects on maternal and fetal hemodynamics. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:958–64.
Nigam A, Madan M, Puri M, Agarwal S, Trivedi SS. Labour induction with 25 micrograms versus 50 micrograms intravaginal misoprostol in full term pregnancies. Trop Doct 2010;40:53–5.
Nigam A, Singh VK, Dubay P, Pandey K, Bhagoliwal A, Prakash A. Misoprostol vs. oxytocin for induction of labor at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;86:398–400.
Nimrod C, Currie J, Yee J, Dodd G, Persaud D. Cervical ripening and labor induction with intracervical triacetin base prostaglandin E2 gel: a placebo-controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 1984;64:476–9.
Niromanesh S, Mosavi-Jarrahi A, Samkhaniani F. Intracervical Foley catheter balloon vs. prostaglandin in preinduction cervical ripening. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;81:23–7.
Noah ML, DeCoster JM, Fraser TJ, Orr JD. Preinduction cervical softening with endocervical PGE2 gel. A multi-center trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1987;66:3–7.
Noah ML, Kimball FA, Ruppel PL, de la Fuente P, Decoster JM. The effect of intracervical PGEz-gel on plasma levels of 13,14-hihydro-15-keto-PGE2 (PGEM) in women at term. Arch Gynecol 1985;237(Suppl. 1):8.
Nopdonrattakoon L. A comparison between intravaginal and oral misoprostol for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2003;29:87–91.
Norman J. Pharmacokinetics of Nitric Oxide Donors Administered per Vaginam in the Third Trimester of Pregnancy. 2001. URL: www.controlled-trials.com (accessed 26 July 2001).
Norzilawati MN, Mashita MK, Shuhaila A, Zaleha AM. Vaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone for induction of labor. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;23(Suppl. 1):244.
Ntsaluba A. The use of an indwelling catheter compared to intracervical prostaglandin gel for cervical ripening prior to induction of labour. O&G Forum 1997:17–21.
Nunes F, Rodrigues R, Meirinho M. Randomized comparison between intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;181:626–9.
Nuutila M, Kajanoja P. A randomized comparison of intravaginal and intracervical administration of prostaglandin E2 in cervical ripening. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1995;73:110–11.
Nuutila M, Kajanoja P. Cervical ripening prior to labor induction with intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel in patients with preeclampsia: a placebo-controlled study. Hypertens Pregn 1995;14:313–17.
Nuutila M, Kajanoja P. Local administration of prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and labor induction: the appropriate route and dose. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:135–8.
O’Brien JM, Mercer B, Cleary N, Sibai BM. Efficacy of outpatient induction with low dose intravaginal prostaglandin E2: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:424.
O’Brien JM, Mercer BM, Cleary NT, Sibai BM. Efficacy of outpatient induction with low-dose intravaginal prostaglandin E2: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:1855–9.
Oboro VO, Tabowei TO. Outpatient misoprostol cervical ripening without subsequent induction of labor to prevent post-term pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005;84:628–31.
Oliveira MV, Oberst PV, Leite GK, Aguemi A, Kenj G, Leme VD, et al. [Cervical Foley catheter versus vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labor: a randomized clinical trial.] Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2010;32:346–51.
Olmo I, Rodenas JJ, Bou J, Jaca A, Moraga R, Monleon J. Labour induction. Oxytocin ev vs dinoprostone (PGE2) vaginal propess. J Perinatal Med 2001;29(Suppl. 1):14.
Omar NS, Tan PC, Sabir N, Yusop ES, Omar SZ. Coitus to expedite the onset of labour: a randomised trial. BJOG 2013;120:338–45.
Ophir E, Haj N, Korenblum R, Oettinger M. Cervical ripening before induction of labor: comparison of an intracervical Foley catheter and prostaglandin E2 vaginal tablets. Int J Feto-Maternal Med 1992;5:101–6.
Orhue AA. Induction of labour at term in primigravidae with low Bishop’s score: a comparison of three methods. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1995;58:119–25.
Osman I, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, Greer A, Norman JE. The ‘PRIM’ study: a randomised comparison of prostaglandin with isosorbide mononitrate for preinduction cervical ripening at term. J Obstet Gynaecol 2004;24(Suppl. 1):67.
Osman I, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Murray HM, Greer IA, Norman JE. The ‘PRIM’ study: a randomised comparison of prostaglandin with isosorbide mononitrate for pre-induction cervical ripening at term. BJOG 2005;112:512.
Osman I, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Murray HM, Greer IA, Norman JE. The ‘PRIM’ study: a randomized comparison of prostaglandin E2 gel with the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening before the induction of labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006;194:1012–21.
Osman I, Norman J, Mackenzie F, Murray H, Norrie J, Greer I. The ‘PRIM’ study: a randomised comparison of prostaglandin E2 gel with the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening prior to the induction of labour at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191(Suppl. 1):184.
Ottervanger HP, Holm JP, Keirse M. A randomized trial of expectant vs active management for prelabour rupture of the membranes at term. J Perinatal Med 1992;20(Suppl. 1):223.
Ottervanger HP, Holm JP, Keirse M. Premature rupture of the membranes at term: induction of labour or expectant care? Int J Gynecol Obstet 1991;36(Suppl.):432.
Ottervanger HP, Keirse MJ, Smit W, Holm JP. Controlled comparison of induction versus expectant care for prelabor rupture of the membranes at term. J Perinat Med 1996;24:237–42.
Ottinger WS, Menard MK, Brost BC. A randomized clinical trial of prostaglandin e2 intracervical gel and a slow release vaginal pessary for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:349–53.
Owen J, Winkler CL, Harris BA, Hauth JC, Smith MC. A randomized, double-blind trial of prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:991–6.
Owen J, Winkler CL, Hauth JC, Harris BA, Smith MC. A randomized, double blind trial of prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and a meta analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:313.
Owolabi AT, Kuti O, Ogunlola IO. Randomised trial of intravaginal misoprostol and intracervical Foley catheter for cervical ripening and induction of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol 2005;25:565–8.
Ozkan S, Calişkan E, Doğer E, Yücesoy I, Ozeren S, Vural B. Comparative efficacy and safety of vaginal misoprostol versus dinoprostone vaginal insert in labor induction at term: a randomized trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2009;280:19–24.
Paisarntantiwong R, Getgan M. A comparison between single dose of 50 microg oral misoprostol and 25 microg vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. J Med Assoc Thai 2005;88(Suppl. 2):56–62.
Pandis GK, Papageorghiou AT, Otigbah CM, Howard RJ, Nicolaides KH. Randomized study of vaginal misoprostol (PGE(1)) and dinoprostone gel (PGE(2)) for induction of labor at term. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;18:629–35.
Papageorgiou I, Tsionou C, Minaretzis D, Michalas S, Aravantinos D. Labor characteristics of uncomplicated prolonged pregnancies after induction with intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel versus intravenous oxytocin. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1992;34:92–6.
Papanikolaou EG, Plachouras N, Drougia A, Andronikou S, Vlachou C, Stefos T, et al. Comparison of misoprostol and dinoprostone for elective induction of labour in nulliparous women at full term: a randomized prospective study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2004;2:70.
Parazzini F, Benedetto C, Danti L, Zanini A, Facchinetti F, Ettore G, et al. A randomized comparison of vaginal prostaglandin E2 with oxytocin plus amniotomy for induction of labour in women with intermediately ripe cervices. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1998;81:15–20.
Parewijck W, Thiery M. Cervical Ripening: Randomized Comparative Study of Extra-amniotic vs Intracervical PGE2 Gel. Proceedings of 10th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, Leipzig, Germany, 12–16 August 1986, abstract no. 165.
Parikh SC, Parikh NS. Comparison of local PGE2 gel & iv oxytocin in induction of labour. J Obstet Gynecol India 2001;51:57–9.
Parisaei M, Erskine KJ. Is expensive always better? Comparison of two induction agents for term rupture of membranes. J Obstet Gynaecol 2008;28:290–3.
Parisaei MP, Erskine KJE. Comparison of sub-lingual misoprostol with standard regime vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel for the induction of labour after term rupture of membranes. J Obstet Gynaecol 2005;25(Suppl. 1):69.
Patil PK, Swamy MK, Rao Radhika K. Oral misoprostol vs intra-cervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labour induction. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2005;55:128–31.
Paul S, Bhowmick R. A Randomised Controlled Trial of Oral Prostaglandin E2 (Dinoprostone) and Oxytocin Infusion in Induction of Labour. Personal communication. 1992. pp. 1–4.
Paungmora N, Herabutaya Y, P OP. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a randomised controlled trial. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;15:272.
Paungmora N, Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P, Punyavachira P. Comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor at term: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2004;30:358–62.
Pearce JM, Cardozo L. Prolonged pregnancy: results of supplemental analysis. BMJ 1988;297:715–17.
Peccerillo JA, Egan JFX, Borgida A, Campbell WA. Comparison of intracervical PGE2 to intravaginal PGE2 for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:298.
Pedrazzoli J, Irion O, Mermillod B, Beguin F. A randomised comparison of an intravaginal and an intracervical Prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S111.
Pedrazzoli J, Irion O, Mermillod B, Beguin F. A Randomized Comparison of an Intravaginal and an Intracervical Prostaglandin E2 Gel for Cervical Ripening and Induction of Labour. 20th Congress of the Swiss Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics, June 1997, Lugano, Switzerland, abstract no. 10.
Peedicayil A, Jasper P, Francis S, Jayakrishnan K, Mathai M, Regi A. A randomized trial of extra-amniotic Foley catheter and intra-cervical prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening. J Clin Epidemiol 1998;51(Suppl. 1):21.
Pennell CE, Henderson JJ, O’Neill MJ, McCleery S, Doherty DA, Dickinson JE. Induction of labour in nulliparous women with an unfavourable cervix: a randomised controlled trial comparing double and single balloon catheters and PGE2 gel. BJOG 2009;116:1443–52.
Pennell CE, Jewell M, Doherty D, Dickinson JE. Induction of labor with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189(Suppl. 1):207.
Perche S, Guerra M, Reyna E, Hidalgo M, Santos J, Mejia J, et al. Vaginal isosorbide mononitrate or misoprostol for cervical ripening in term pregnancies. Clin Invest Ginecol Obstet 2009;36:203–8.
Perez Picanol E, Gamissans O, Lecumberri J, Jimenez M, Vernet M. Ripening the Cervix with Intracervical PGE2 Gel in Term Pregnancies with Premature Rupture of Membranes. Proceedings of 12th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 11–14 September 1990, Lyon, France, abstract no. 197.
Perez Picanol E, Vernet M, Armengol R, Perez Ares C, Lecumberri J, Gamissans O. Comparison of two different therapeutic attitudes in premature rupture of membranes. J Perinatal Med 1992;20(Suppl. 1):353.
Perry MY, Leaphart WL. A randomized controlled trial using intracervical versus posterior fornix placement of dinoprostone. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:35S.
Perry MY, Leaphart WL. Randomized trial of intracervical versus posterior fornix dinoprostone for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:11S.
Perry MY, Leaphart WL. Randomized trial of intracervical versus posterior fornix dinoprostone for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 2004;103:13–17.
Perryman D, Yeast JD, Holst V. Cervical Ripening: a Prospective, Randomized Study Comparing Prostaglandin E2 Gel with Prostaglandin E2 Suppositories. Proceedings of 39th Annual Clinical Meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 4–9 May 1991, New Orleans, LA, USA, abstract no. 26.
Perryman D, Yeast JD, Holst V. Cervical ripening: a randomized study comparing prostaglandin E2 gel to prostaglandin E2 suppositories. Obstet Gynecol 1992;79:670–2.
Petrou S, Taher S, Abangma G, Eddama O, Bennett P. Cost-effectiveness analysis of prostaglandin E2 gel for the induction of labour at term. BJOG 2011;118:726–34.
Pevzner L, Alfirevic Z, Powers B, Wing D. Cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with misoprostol and dinoprostone cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009;201(Suppl. 1):124.
Pevzner L, Alfirevic Z, Powers BL, Wing DA. Cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with misoprostol and dinoprostone cervical ripening and labor induction. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2011;156:144–8.
Pevzner L, Rayburn WF, Rumney P, Wing DA. Factors predicting successful labor induction with dinoprostone and misoprostol vaginal inserts. Obstet Gynecol 2009;114:261–7.
Pevzner L, Rumney P, Petersen R, Wing D. Predicting a successful induction of labor: a secondary analysis of misoprostol vaginal insert trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008;199(Suppl. 1):72.
Pezvner L, Powers BL, Wing DA. Factors predicting successful induction of labor with misoprostol vaginal insert. Reprod Sci 2011;18(Suppl. 1):A182–3.
Pi P, Zhu F. [Clinical observation of misoprostol on induction in late pregnancy.] Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 1999;24:195–7.
Pinto RM, Leon C, Mazzocco N, Scasserra V. Action of estradiol-17-beta at term and at onset of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1967;98:540–6.
Pollnow DM, Broekhuizen FF. Randomized, double-blind trial of prostaglandin E2 intravaginal gel versus low-dose oxytocin for cervical ripening before induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:1910–13.
Pongsatha S, Vijittrawiwat A, Tongsong T. A comparison of labor induction by oral and vaginal misoprostol. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;88:140–1.
Poornima B, Dharma Reddy DB. Premature rupture of membranes at term: immediate induction with PGE(2) gel compared with delayed induction with oxytocin. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2011;61:516–18.
Poulsen HK, Müller LK, Westergaard JG, Thomsen SG, Giersson RT, Arngrìmsson R. Open randomized comparison of prostaglandin E2 given by intracervical gel or vagitory for preinduction cervical ripening and induction of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1991;70:549–53.
Powers B, Parker L, Miller H, Wing DA, Rayburn W. A double-blind, randomized, multicenter, dose-ranging phase II study of the misoprostol vaginal insert. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204(Suppl. 1):48.
Prager M, Eneroth-Grimfors E, Edlund M, Marions L. A randomised controlled trial of intravaginal dinoprostone, intravaginal misoprostol and transcervical balloon catheter for labour induction. BJOG 2008;115:1443–50.
Prager M, Eneroth-Grimfors E, Edlund M, Marions L. A randomised controlled trial of intravaginal dinoprostone, intravaginal misoprostol and transcervical balloon catheter for labour induction. BJOG 2008;115:1443–50.
Prasad RNV, Adaikan PG, Arulkumaran S, Ratnam SS. Preinduction cervical priming with PGE2 vaginal film in primigravidae: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study. Prostag Leukotr Ess 1989;36:185–8.
Prins RP, Bolton RN, Mark C, Neilson DR, Watson P. Cervical ripening with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Obstet Gynecol 1983;61:459–62.
Puertas A, Mino M, Manzanares S, Ceballos C, Alamo F, Miranda JA. Labor induction with intracervical prostaglandin E2 versus oxytocin in premature rupture of membranes. Prenatal Neonatal Med 1996;1(Suppl. 1):89.
Puertas A, Mino M, Moreno I, Carrillo MP, Mozas J, Miranda JA. Induced labour in the premature rupture of membranes at term. Comparison of E2 intracervical prostaglandine with oxytocine. Prog Obstet Ginecol 1997;40:13–18.
Puga O, Nien JK, Gomez R, Medina L, Carstens M, Gonzalez R, et al. Premature rupture of membranes after 35 weeks: a randomized clinical trial of induction of labor with oral versus vaginal administration of misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S85.
Pulle C, Granese D, Panama S, Celona A. Cervical ripening and induction of labour by single intracervical PGE2-gel application. Acta Ther 1986;12:5–12.
Putnam K, Magann EF, Doherty DA, Poole AT, Magann MI, Warner WB, et al. Randomized clinical trial evaluating the frequency of membrane sweeping with an unfavorable cervix at 39 weeks. Int J Womens Health 2011;3:287–94.
Quinn MA, Murphy AJ, Kuhn RJP, Robinson HP, Brown JB. A double blind trial of extra-amniotic oestriol and prostaglandin F2alpha gels in cervical ripening. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1981;88:644–9.
Rabl M, Ahner R, Bitschnau M, Zeisler H, Husslein P. Acupuncture for cervical ripening and induction of labor at term: a randomized controlled trial. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2001;113:942–6.
Rabl M, Joura EA, Yücel Y, Egarter C. A randomized trial of vaginal prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor. Insert vs. tablet. J Reprod Med 2002;47:115–19.
Rahman H, Pradhan A, Kharka L, Renjhen P, Kar S, Dutta S. Comparative evaluation of 50 microgram oral misoprostol and 25 microgram intravaginal misoprostol for induction of labour at term: a randomized trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2013;35:408–16.
Rahman H. Comparative Evaluation of 50 µg Oral Misoprostol and 25 µg Intra-vaginal Misoprostol For Induction of Labour at term. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, abstract no. 316.
Rameez MF, Goonewardene IM. Nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for pre-induction cervical ripening at 41 weeks’ gestation: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2007;33:452–6.
Ramsey P, Harris D, Ogburn P, Heise R, Magtibay P, Ramin K. Comparative efficacy of prostaglandin analogues dinoprostone and misoprostol as labor preinduction agents. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S94.
Ramsey P, Meyer L, Harris D, Ogburn P, Jr, Ramin K. Characterization of cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with dinoprostone and misoprostol cervical ripening/labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:S115.
Ramsey PS, Harris DY, Ogburn PL, Jr, Heise RH, Magtibay PM, Ramin KD. Comparative efficacy and cost of the prostaglandin analogs dinoprostone and misoprostol as labor preinduction agents. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:560–5.
Ramsey PS, Meyer L, Walkes BA, Harris D, Ogburn PL, Heise RH, et al. Cardiotocographic abnormalities associated with dinoprostone and misoprostol cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105:85–90.
Rath DM, Manas K. Induction of labor with oral misoprostol in women with prelabor rupture of membranes at term. J Obstet Gynecol India 2007;57:505–8.
Rath W, Heyl W, Kemp B. Intracervical versus intravaginal PGE2 gel for induction of labor. Perinatal Medizin 1998;10:81–3.
Rath W, Kemp B, Heyl W. Prostaglandin E2 as a vaginal gel, intracervical gel or vaginal tablet for induction of labor: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 1999;59:323–9.
Ratnam SS, Khew KS, Chen C, Lim TC. Oral prostaglandin E2 in induction of labour. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1974;14:26–30.
Ray DA, Garite TJ. Prostaglandin E2 for induction of labor in patients with premature rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:836–43.
Rayburn W, Barss V, Caritis S, Mandsager N, Molina R, Spitzberg E, et al. A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Multicenter Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of an Intravaginal Hydrogel Controlled Release Pessary for the Delivery of Prostaglandin E2 for Cervical Ripening Prior to Induction of Labor. Proceedings of 39th Annual Clinical Meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 4–9 May 1991, New Orleans, LA, USA, abstract no. 29.
Rayburn W, Gosen R, Ramadei C, Woods R, Scott J. Outpatient cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 gel in uncomplicated postdate pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988;158:1417–23.
Rayburn W, Lucas M, Gittens L, Goodwin TM, Baxi L, Gall S, et al. Attempted vaginal birth after cesarean section: a multicenter comparison of outpatient prostaglandin E2 gel with expectant management. Prim Care Update Ob/Gyns 1998;5:182–3.
Rayburn WF, Gittens LN, Lucas MJ, Gall SA, Martin ME. Weekly administration of prostaglandin e2 gel compared with expectant management in women with previous cesareans Prepidil gel study group. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:250–4.
Rayburn WF, Wapner RJ, Barss VA, Spitzberg E, Molina RD, Mandsager N, et al. An intravaginal controlled-release prostaglandin E2 pessary for cervical ripening and initiation of labor at term. Obstet Gynecol 1992;79:374–9.
Richardson CJ, Evans JF, Meisel RL. Duration of intracervical prostaglandin and Cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:403.
Rix P, Andersen K, Ladehoff P, Moller AM, Zdravkovic M. PGE2 Vaginal Tablets Compared to Ready Prepared Cervical PGE2 Gel in Ability to Induce Cervical Ripening and Labour by Low Bishop Scores. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 151.
Rix P, Ladehoff P, Moller AM, Tilma KA, Zdravkovic M. Cervical ripening and induction of delivery by local administration of prostaglandin E2 gel or vaginal tablets is equally effective. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1996;75:45–7.
Rizvi S, Umber F, Yusuf AW. Labour induction at term; oral versus intravaginal misoprostol. Ann King Edward Med Coll 2007;13:119–21.
Roach VJ, Rogers MS. Pregnancy outcome beyond 41 weeks gestation. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;59:19–24.
Roberts WE, North DH, Speed JE, Martin JN, Palmer SM, Morrison JC. Comparative study of prostaglandin, laminaria, and minidose oxytocin for ripening of the unfavorable cervix prior to induction of labor. J Perinatol 1986;6:16–19.
Rolland de Souza A. Oral Misoprostol Titrated Solution versus Vaginal Misoprostol for Induction of Labour: Randomized Controlled Trial. 2011. URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT00992524 (accessed 22 January 2013).
Rolland Souza A. [Titrated oral suspension compared with vaginal misoprostol for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial.] Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2011;33:270.
Romer A, Weigel M, Zieger W, Melchert F. Changes in cervix maturity and length of birth after birth-preparation accupuncture therapy: Mannheim Rome Scheme. DZA 1998;41:93–100.
Romero-Gutiérrez G, Bernal González OE, Ponce-Ponce de León AL. [Comparison of isosorbide dinitrate and dinoprostone for induction of labor in term pregnancy.] Ginecol Obstet Mex 2011;79:285–91.
Rouben D, Arias F. A randomized trial of extra-amniotic saline infusion plus intracervical foley catheter balloon vs prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel for ripening the cervix and inducing labour in patients with unfavourable cervices. Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:290–4.
Roudsari FV, Ghasemi M, Ayati S, Shakeri MT, Farshidi F, Shahabian M. [Comparison of vaginal misoprostol with foley catheter for cervical ripening and induction of labor.] J Isfahan Med School 2010;28:177–85.
Rouzi AA, Alsibiani S, Mansouri N, Alsinani N, Darhouse K. Randomized clinical trial between hourly titrated oral misoprostol and vaginal dinoprostone for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210:56.e1–6.
Rouzi AA. Randomized Clinical Trial between Titrated Oral Dose of Misoprostol and Propess for Induction of Labor. 2011. URL: www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReviewaspx?ACTRN=12611000420943 (accessed 22 January 2013).
Rowlands S, Bell R, Donath S, Morrow S, Trudinger BJ. Misoprostol versus dinoprostone for cervical priming prior to induction of labour in term pregnancy: a randomised controlled trial. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;41:145–52.
Rozenberg P, Chevret S, Goffinet F, Durand-Zaleski I, Ville Y, Vayssiere C, et al. Induction of labour with a viable infant: a randomised clinical trial comparing intravaginal misoprostol and intravaginal dinoprostone. BJOG 2001;108:1255–62.
Rozenberg P, Chevret S, Senat MV, Bretelle F, Bonnal AP, Ville Y. A randomized trial that compared intravaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone vaginal insert in pregnancies at high risk of fetal disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:247–53.
Roztocil A, Pilka L, JelÌnek J, Koudelka M, Miklica J. A comparison of three preinduction cervical priming methods: prostaglandin E2 gel, Dilapan S rods and Estradiol gel. Ceska Gynekol 1998;63:3–9.
Roztocil A. A comparison of three preinduction cervical priming methods: prostaglandin E2 gel, dilapan s rods, and estradiol gel. J Perinatal Med 2013;41(Suppl. 1):557.
Russell Z, O’Leary T, Destefano K, Deutsch A, Carlan S. Buccal versus vaginal misoprostol administration for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;197(Suppl. 1):37.
Rust OA, Greybush M, Singleton C, Atlas RO, Balducci J. A comparison of preinduction cervical ripening techniques. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:S126.
Rydhström H, Ingemarsson I. No benefit from conservative management in nulliparous women with premature rupture of the membranes (PROM) at term. A randomized study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1991;70:543–7.
Rymer J, Parker A. A comparison of syntocinon infusion with prostaglandin vaginal pessaries when spontaneous rupture of the membranes occurs without labour after 34 weeks gestation. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;32:22–4.
Saeed GA, Fakhar S, Nisar N, Alam AY. Misoprostol for term labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2011;50:15–19.
Saggaf A, Rouzi AA, Radhan B, Alshehry S, Yamani T, Abduljabbar H. Misoprostol for preinduction cervical ripening and induction of labour: a randomized controlled trial. Saudi J Obstet Gynecol 2001;1:89–93.
Sahraoui W, Hajji S, Bibi M, Nouira M, Essaidi H, Khairi H. [Management of pregnancies beyond forty-one week’s gestation with an unfavorable cervix.] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 2005;34:454–62.
Sahu L, Chakravertty B. Comparison of prostaglandin E1 (misoprostol) with prostaglandin E2 (dinoprostone) for labor induction. J Obstet Gynecol India 2004;54:139–42.
Salamalekis E, Vitoratos N, Kassanos D, Loghis C, Batalias L, Panayotopoulos N, et al. Sweeping of the membranes versus uterine stimulation by oxytocin in nulliparous women. A randomized controlled trial. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2000;49:240–3.
Saleem S. Efficacy of dinoprostone, intracervical foleys and misoprostol in labor induction. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2006;16:276–9.
Saleh YZ. Surgical induction of labour with and without oxytocin infusion. A prospective study. Aus N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1975;15:80–3.
Salim R, Zafran N, Nachum Z, Garmi G, Kraiem N, Shalev E. Single-balloon compared with double-balloon catheters for induction of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2011;118:79–86.
Salmon YM, Kee WH, Tan SL, Jen SW. Cervical ripening by breast stimulation. Obstet Gynecol 1986;67:21–4.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Chen A, Briones D, Del Valle GO, Gaudier FL, Delke I. Premature rupture of membranes at term: induction of labor with intravaginal misoprostol tablets (PGE1) or intravenous oxytocin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:377.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Chen AH, Kaunitz AM, Gaudier FL, Delke I. Labor induction with intravaginal misoprostol in term premature rupture of membranes: a randomized study. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:909–12.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Conner PM, Kaunitz AM. Prostaglandin E2 Gel vs Hypan in Cervical Ripening Before Induction of Labor. Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 23–27 January 1990, Houston, TX, USA, abstract no. 481.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Farah L, Rosa C, Johnson J, Delke I, Del Valle G. Comparative study of a two dose schedule of the PGE1 analogue misoprostol for labor induction in patients with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:319.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Kaunitz AM, Connor PM. Hygroscopic cervical dilators and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. A randomized, prospective comparison. J Reprod Med 1992;37:355–9.
Sanchez-Ramos L, Peterson DE, Delke I, Gaudier FL, Kaunitz AM. Labor induction with prostaglandin E1 misoprostol compared with dinoprostone vaginal insert: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 1998;91:401–5.
Sande HA, Tuveng J, Fønstelien T. A prospective randomized study of induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1983;21:333–6.
Satin AJ, Hankins GDV, Yeomans ER. A randomized study of two dosing regimens of oxytocin for the induction of patients with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:307.
Sawai SK, O’Brien WF, Mastrogiannis DS, Krammer J, Mastry MG, Porter GW. Patient-administered outpatient intravaginal prostaglandin E2 suppositories in post-date pregnancies: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 1994;84:807–10.
Sawai SK, O’Brien WF, Mastrogiannis MS, Mastry MG, Porter GW, Johnson L. Outpatient prostaglandin E2 suppositories in postdates pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:400.
Sawai SK, Williams MC, O’Brien WF, Angel JL, Mastrogiannis DS, Johnson L. Sequential outpatient application of intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel in the management of postdates pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol 1991;78:19–23.
Saxena P, Puri M, Bajaj M, Mishra A, Trivedi SS. A randomized clinical trial to compare the efficacy of different doses of intravaginal misoprostol with intracervical dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2011;15:759–63.
Schmitz T, Closset E, Fuchs F, Maillard F, Rozenberg P, Anselem O, et al. Outpatient cervical ripening with nitric oxide (NO) donors for prolonged pregnancy in nullipara: the NOCETER randomized, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210(Suppl. 1):19.
Schneider M, Ramsey R, Kao L, Bennett KA. Misoprostol is effective for induction of labor in high risk pregnant women: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191(Suppl. 1):73.
Sciscione A, McCullough H, Shlossman P, Manley J, Pollock M, Colmorgan G. A randomized prospective comparison intracervical PGE2 gel (prepidil) versus foley bulb for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S142.
Sciscione AC, McCullough H, Manley JS, Shlossman PA, Pollock M, Colmorgen GH. A prospective, randomized comparison of Foley catheter insertion versus intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:55–60.
Sciscione AC, Nguyen L, Manley J, Pollock M, Maas B, Colmorgen G. A randomized comparison of transcervical Foley catheter to intravaginal misoprostol for preinduction cervical ripening. Obstet Gynecol 2001;97:603–7.
Seaward PG, Hannah ME, Myhr TL, Farine D, Ohlsson A, Wang EE, et al. International multicenter term PROM study: evaluation of predictors of neonatal infection in infants born to patients with premature rupture of membranes at term. Premature Rupture of the Membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:635–9.
Secher NJ, Lange AP, Nielsen FH, Pedersen GT, Westergaard JG. Induction of labor with and without primary amniotomy. A randomized study of prostaglandin E2 tablets and intravenous oxytocin. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1981;60:237–41.
Seeras RC. Induction of labor utilizing vaginal vs. intracervical prostaglandin E2. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1995;48:163–7.
Sellers SM, Ah-Moye M, MacKenzie IZ. Comparison of Vaginal Prostaglandin E2 and Intravenous Oxytocin for Induction of Labour in Women Previously Delivered by Caesarean Section. Proceedings of 1st European Congress on Prostaglandins in Reproduction, 6–9 July 1988, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 128.
Selmer-Olsen T, Lydersen S, M¯rkved S. Does acupuncture used in nulliparous women reduce time from prelabour rupture of membranes at term to active phase of labour? A randomised controlled trial. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2007;86:1447–52.
Selo-Ojeme D. A Randomised Controlled Trial of Amniotomy and Immediate Oxytocin Infusion versus Amniotomy and Delayed Oxytocin Infusion for Induction of Labour at Term. 2007. URL: www.controlled-trials.com/ (accessed 30 October 2007).
Selo-Ojeme DO, Pisal P, Lawal O, Rogers C, Shah A, Sinha S. A randomised controlled trial of amniotomy and immediate oxytocin infusion versus amniotomy and delayed oxytocin infusion for induction of labour at term. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2009;279:813–20.
Shakya R, Shrestha J, Thapa P. Safety and efficacy of misoprostol and dinoprostone as cervical ripening agents. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc 2010;49:33–7.
Sharma Y, Kumar S, Mittal S, Misra R, Dadhwal V. Evaluation of glyceryl trinitrate, misoprostol, and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening in term pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2005;31:210–15.
Shechter-Maor G, Biron-Shental T, Haran G, Ganor-Paz Y, Fejgin M. Intravaginal prostaglandin E2 versus double balloon catheter for labor induction in term isolated oligohydramnios. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2013;208(Suppl. 1):78–9.
Sheela CN, Mhaskar A, George S. Comparison of vaginal misoprostol and oral misoprostol with intracervical dinoprostone gel for labor induction at term. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2007;57:327–30.
Sheikher C, Suri N, Kholi U. Comparative evaluation of oral misoprostol, vaginal misoprostol and intracervical Foley’s catheter for induction of labour at term. JK Sci 2009;11:75–7.
Shepherd J, Sims C, Craft I. Extra-amniotic prostaglandin E2 and the unfavourable cervix. Lancet 1976;2:709–10.
Sherman DJ, Frenkel E, Pansky M, Caspi E, Bukovsky I, Langer R. Balloon cervical ripening with extra-amniotic infusion of saline or prostaglandin E2: a double-blind, randomized controlled study. Obstet Gynecol 2001;97:375–80.
Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol in the induction of labour at term: a random allocation trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20(Suppl. 1):19.
Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol tablets in the induction of labor at term. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Washington DC, USA, 3–8 September 2000, Book 4, pp. 28–9.
Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol tablets in induction of labour at term. BJOG 2001;108:238–43.
Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol in the induction of labour at term: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2000;107:813.
Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. Sublingual misoprostol for the induction of labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:72–6.
Shetty A, Danielian P, Templeton A. Sublingual misoprostol in the induction of labour at term. J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;21(Suppl. 1):51.
Shetty A, Livingstone I, Acharya S, Danielian P, Rice P, Templeton A. A randomised comparison of oral misoprostol and vaginal prostaglandin E2 tablets in labour induction at term. BJOG 2003;110:963.
Shetty A, Livingstone I, Acharya S, Rice P, Danielian P, Templeton A. A randomised comparison of oral misoprostol and vaginal prostaglandin E2 tablets in labour induction at term. BJOG 2004;111:436–40.
Shetty A, Livingstone I, Acharya S, Rice P, Danielian P, Templeton A. Oral misoprostol (100 microg) versus vaginal misoprostol (25 microg) in term labor induction: a randomized comparison. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2003;82:1103–6.
Shetty A, Mackie L, Danielian P, Rice P, Templeton A. Sublingual compared with oral misoprostol in term labour induction: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2002;109:645–50.
Shetty A, Martin R, Danielian P, Templeton A. A comparison of two dose regimens of oral misoprostol in the induction of labour at term: a random allocation controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;21:91.
Shoaib F. Management of premature rupture of membranes with unfavourable cervix at term, by prostaglandins. Specialist 1994;10:227–32.
Sifakis S, Angelakis E, Avgoustinakis E, Fragouli Y, Mantas N, Koukoura O, et al. A randomized comparison between intravaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 for labor induction. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2007;275:263–7.
Silva-Cruz A, Godinho F, Pinto JM, Andrade L, Simıes D. Prostaglandin E2 gel compared to oxytocin for medically-indicated labour induction at term: a controlled clinical trial. Pharmatherapeutica 1988;5:228–32.
Sitthiwattanawong W, Pongsatha S. Oral misoprostol for cervical ripening and labour induction: a randomized controlled trial. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;11:87–92.
Sitthiwattanawong W. A comparison between oral and intravaginal administration of 50 microgram misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;12:352.
Skupski D, Normand N, Eglinton G, Witkin SS. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) gene polymorphisms influence the time interval between labor induction and delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;197(Suppl. 1):99.
Smith C. The Influence of Acupuncture Stimulation on the Induction of Labour: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Personal communication. 2000.
Smith CA, Crowther CA, Collins CT, Coyle ME. Acupuncture to induce labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;112:1067–74.
Smith CV, Rayburn WF, Connor RE, Fredstrom GR, Phillips CB. Double-blind Comparison of Intravaginal Prostaglandin E2 Gel and ‘Chip’ for Preinduction Cervical Ripening. Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 23–27 January 1990, Houston, TX, USA, abstract no. 134.
Smith CV, Rayburn WF, Connor RE, Fredstrom GR, Phillips CB. Double-blind comparison of intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel and ‘chip’ for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:845–7.
Smith CV, Rayburn WF, Miller AM. Intravaginal prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening and initiation of labor. Comparison of a multidose gel and single, controlled-release pessary. J Reprod Med 1994;39:381–4.
Souza AS, Feitosa FE, Costa AA, Pereira AP, Carvalho AS, Paixão RM, et al. Titrated oral misoprostol solution versus vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2013;123:207–12.
Spallicci MD, Chiea MA, Singer JM, Albuquerque PB, Bittar RE, Zugaib M. Use of hyaluronidase for cervical ripening: a randomized trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2007;130:46–50.
Spallicci MDB, Bittar RE. Randomized double blind study of ripening the cervix with hyaluronidase in term gestations. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2003;25:67.
Sparks T, Caughey AB, Shaffer B, Cheng YW, Vargas J, Delaney S, et al. Predictors of cesarean delivery in women undergoing labor induction with a Foley balloon. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204(Suppl. 1):78.
Spellacy WN, Gall SA, Shevach AB, Holsinger KK. The induction of labor at term. Comparisons between prostaglandin F 2 and oxytocin infusions. Obstet Gynecol 1973;41:14–21.
Spellacy WN, Gall SA. Prostaglandin F2alpha and Oxytocin for Term Labor Induction. In Southern EM, editor. The Prostaglandins Clinical Applications in Human Reproduction. Mount Kisko, NY: Futura Press; 1972. pp. 107–13.
Sperling LS, Schantz AL, Wåhlin A, Duun S, Jaszczak P, Scherling B, et al. Management of prelabor rupture of membranes at term. A randomized study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1993;72:627–32.
Srisomboon J, Singchai S. A comparison between 25 micrograms and 50 micrograms of intravaginal misoprostol for labor induction. J Med Assoc Thai 1998;81:779–83.
Srisomboon J, Tongsong T, Tosiri V. Preinduction cervical ripening with intravaginal prostaglandin E1 methyl analogue misoprostol: a randomized controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 1996;22:119–24.
St Onge RD, Connors GT. Preinduction cervical ripening: a comparison of intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel versus the Foley catheter. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:687–90.
Stampe Sørensen S, Palmgren Colov N, Andreasson B, Bock JE, Berget A, Schmidt T. Induction of labor by vaginal prostaglandin E2. A randomized study comparing pessaries with vaginal tablets. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1992;71:201–6.
Stampe Sorensen S, Palmgren N, Andreasson B, Bock JE, Berget A, Schmidt T. PGE2 pessaries versus PGE2 vaginal tablets for induction of labour. Int J Gynecol Obstet 1991;36(Suppl.):34.
Stampe Sorenson S, Bock J, Berget A. Pharmacy Prepared Prostaglandin e2 Pessaries Versus Prostin e2 Vaginal Tablets for Induction of Labour. 12th FIGO World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 23–28 October 1988, Brazil, abstract no. 199.
Stempel JE, Prins RP, Dean S. Preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized prospective comparison of the efficacy and safety of intravaginal and intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:1305–9.
Stenlund PM, Bygdeman M, Ekman G. Induction of labor with mifepristone (RU 486). A randomized double-blind study in post-term pregnant women with unripe cervices. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 1994;73:FP50.
Stenlund PM, Ekman G, Aedo AR, Bygdeman M. Induction of labor with mifepristone: a randomized, double-blind study versus placebo. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1999;78:793–8.
Stephenson ML, Pevzner L, Powers BL, Wing DA. Race/ethnicity differences in labor outcomes with misoprostol and dinoprostone vaginal inserts. Reprod Sci 2011;18(Suppl. 1):183A.
Stephenson ML, Powers BL, Wing DA. Fetal heart rate and cardiotocographic abnormalities with varying dose misoprostol vaginal inserts. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;26:127–31.
Stewart JD, Rayburn WF, Farmer K, Liles E, Schipul A, Stanley J. Effectiveness of prostaglandin E2 as an intracervical gel with immediate oxytocin, or as a sustained-release vaginal insert for induction of labour. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S92.
Stewart P, Kennedy JH, Hillan E, Calder AA. The unripe cervix: management with vaginal or extra-amniotic prostaglandin E2. J Obstet Gynaecol 1983;4:90–3.
Steytler P, Howarth G, Makin J. Cervical Ripening and Labour Induction. Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Misoprostol and Dinoprostone Vaginal Gel. Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care in South Africa, South Africa, 7–10 March 1995: 167–70.
Stitely ML, Browning J, Fowler M, Gendron RT, Gherman RB. Outpatient cervical ripening with intravaginal misoprostol. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:684–8.
Strobelt N, Meregalli V, Ratti M, Mariani S, Zani G, Morana S. Randomized study on removable PGE2 vaginal insert versus PGE2 cervical gel for cervical priming and labor induction in low-Bishop-score pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2006;85:302–5.
Strobelt N, Ratti M, Zani G, Meregalli V. Randomized study on two dinoprostone administration routes for cervical priming and labor induction in low bishop pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189(Suppl. 1):206.
Su H, Li E, Weng L. [Mifepristone for induction of labor.] Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1996;31:676–80.
Sultana N, Rouf S, Rashid M. Oral versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour. J Bangladesh Coll Phys Surg 2006;24:44–9.
Surbek DV, Boesiger H, Hoesli I, Pavic N, Holzgreve W. A double-blind comparison of the safety and efficacy of intravaginal misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 to induce labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1018–23.
Surbek DV, Bosiger H, Hosli I, Pavic N, Holzgreve W. Cervical priming and labor induction with intravaginal misoprostol versus PGE2: a double-blind randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S112.
Surbek DV, Bosiger H, Pavic N, Hosli I, Stoz F, Holzgreve W. The safety of misoprostol for labor induction. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1997;76:36.
Surbek DV, Bosiger H, Pavic N, Stoz F, Holzgreve W. Misoprostol (Cytotec) for Labor Induction in teRm Pregnancies. 20th Congress of the Swiss Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics, June 1997, Lugano, Switzerland, abstract no. 11.
Surita FG, Cecatti JG, Parpinelli MA, Krupa F, Pinto E Silva JL. Hyaluronidase versus Foley catheter for cervical ripening in high-risk term and post term pregnancies. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;88:258–64.
Suvobrata S, Shyamal D. A Comparative Study of Sublingual Misoprostol and Oxytocin Infusion in Induction of Labor in Nulliparous Women at Term. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5–9 January 2011, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India, abstract no. 83.
Suzuki S, Otsubo Y, Sawa R, Yoneyama Y, Araki T. Clinical trial of induction of labor versus expectant management in twin pregnancy. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2000;49:24–7.
Tabasi Z, Behrashi M, Mahdian M. Vaginal Misoprostol versus high dose of oxytocin for labor induction: a comparative study. Pak J Biol Sci 2007;10:920–3.
Tabor B, Anderson J, Stettler B, Wetwiska N, Howard T. Misoprostol vs prostaglandin E2 gel for cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:425.
Tabowei TO, Oboro VO. Low dose intravaginal misoprostol versus intracervical baloon catheter for pre-induction cervical ripening. East Afr Med J 2003;80:91–4.
Taechakraichana N, Jaisamrarn U, Tannirandorn Y, Trivijitsilp P, Termrungruanglert W. Induction of labour by prostaglandin E2 intracervical gel or vaginal suppository. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;8:9–14.
Taher S, Eliahoo J, Edmonds K, Bennett P. Compare the effectiveness of prostaglandin gel versus tablets in labour induction at term: randomised controlled trial and cost-effectiveness. BJOG 2008;115(Suppl. 1):59.
Taher S, Riden JI, Soltan S, Elihoo J, Terzidou V, Bennett P. Randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness of prostaglandin gel versus tablets in labour induction at term. Arch Dis Childhood Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008;93(Suppl. 1):F51.
Taher SE, Inder JW, Soltan SA, Eliahoo J, Edmonds DK, Bennett PR. Prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel or tablets for the induction of labour at term: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2011;118:719–25.
Tamsen L, Lyrenas S, Cnattingius S. Premature rupture of the membranes: intervention or not. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1990;29:128–31.
Tan PC, Soe MZ, Sulaiman S, Omar SZ. Immediate compared with delayed oxytocin after amniotomy labor induction in parous women: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2013;121:253–9.
Tan PC, Yow CM, Omar SZ. Coitus and orgasm at term: effect on spontaneous labour and pregnancy outcome. Singapore Med J 2009;50:1062–7.
Tan PC, Yow CM, Omar SZ. Effect of coital activity on onset of labor in women scheduled for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2007;110:820–6.
Tan TC, Yan SY, Chua TM, Biswas A, Chong YS. A randomised controlled trial of low-dose misoprostol and dinoprostone vaginal pessaries for cervical priming. BJOG 2010;117:1270–7.
Tannirandorn Y, Jumrustanasan T. A comparative study of membrane stripping and nonstripping for induction of labor in uncomplicated term pregnancy. J Med Assoc Thai 1999;82:229–33.
Taylor AVG, Sellers S, Ah-Moye M, MacKenzie IZ. A prospective random allocation trial to compare vaginal prostaglandin e2 with intravenous oxytocin for labour induction in women previously delivered by caesarean section. J Obstet Gynaecol 1993;13:333–6.
Ten Eikelder ML, Neervoort F, Oude Rengerink K, van Baaren GJ, Jozwiak M, de Leeuw JW, et al. Induction of labour with a Foley catheter or oral misoprostol at term: the PROBAAT-II study, a multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2013;13:67.
Tessier F, Danserau J. Oral Misoprostol versus Vaginal Dinoprostone for Labor Induction: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Personal communication. 1997.
Tessier F, Dansereau J. A double-blind randomized controlled trial comparing oral misoprostol to vaginal prostaglandin E2 gel for the induction of labour at or near term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S111.
Tey A, Eriksen NL, Blanco JD. A prospective randomized trial of induction vs expectant management in nondiabetic pregnancies with fetal macrosomia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:293.
Thaisomboon A, Russameecharoen K, Wanitpongpan P, Phattanachindakun B, Changnoi A. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of titrated oral misoprostol and a conventional oral regimen for cervical ripening and labor induction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2012;116:13–16.
Thakur V, Dorman E, Sanu L, Harrington K. Mifepristone is an effective ripening agent in postdates primips with cervical length ≥ 2.5cm, but mode of delivery correlates with birthweight: a randomised, placebo controlled double blind study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26:452.
Thavarasah AS, Arulkumaran S, Almohdzar SA. A prospective randomized study comparing the effect of intracervical to intravaginal administration of prostaglandin E2, in patients with poor cervical scores at term. Int J Feto-Maternal Med 1990;3:177–81.
Thiery M, De Gezelle H, Van Kets H, Voorhoof L, Verheugen C, Smis B, et al. Extra-amniotic oestrogens for the unfavourable cervix. Lancet 1978;2:835–6.
Thiery M, Decoster JM, Parewijck W, Noah ML, Derom R, Van Kets H, et al. Endocervical prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical softening. Prostaglandins 1984;27:429–39.
Thigpen B, Bofill J, Bufkin L, Woodring T, Moore L, Morrison J. A randomized controlled trial comparing vaginal misoprostol to cervical foley plus oral misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191(Suppl. 1):18.
Thomas IL, Chenoweth JN, Tronc GN, Johnson IR. Preparation for induction of labour of the unfavourable cervix with Foley catheter compared with vaginal prostaglandin. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1986;26:30–5.
Thomas N, Longo SA, Rumney PJ, Nageotte MP, Asrat T. Intravaginal misoprostol in prelabor rupture of membranes at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:S136.
Tomlinson AJ, Archer P, Hobson S. Prostin or propess: which method of induction of labour do patients prefer? J Obstet Gynaecol 2000;20(Suppl. 1):58.
Tomlinson AJ, Archer PA, Hobson S. Induction of labour: a comparison of two methods with particular concern to patient acceptability. J Obstet Gynaecol 2001;21:239–41.
Toppozada MK, Anwar MY, Hassan HA, el-Gazaerly WS. Oral or vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1997;56:135–9.
Trabelsi H, Mathlouthi N, Zayen S, Dhouib M, Chaabene K, Trabelsi K, et al. [Cervical ripening at term. A randomized and prospective study: Misoprotol versus dinoprostone.] Tunis Med 2012;90:362–9.
Tremeau ML, Fontanie-Ravier P, Teurnier F, Demouzon J. [Protocol of cervical maturation by acupuncture.] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 1992;21:375–80.
Triglia MT, Palamara F, Lojacono A, Prefumo F, Frusca T. A randomized controlled trial of 24-hour vaginal dinoprostone pessary compared to gel for induction of labor in term pregnancies with a Bishop score < or = 4. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2010;89:651–7.
Trofatter K, Wing D, Miller H, Plante L, Rugarn O, Powers B. Efficacy and safety of misoprostol vaginal insert compared with dinoprostone vaginal insert for labor induction. J Perinatal Med 2013;41(Suppl. 1):710.
Trofatter KF, Bowers D, Gall SA, Killam AP. Preinduction cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 (Prepidil) gel. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;153:268–71.
Trofatter KF. Effect of preinduction cervical softening with dinoprostone gel on outcome of oxytocin-induced labor. Clin Ther 1993;15:838–44.
Tromans PM, Beazley J, Shenouda PI. Comparative study of oestradiol and prostaglandin E2 vaginal gel for ripening the unfavourable cervix before induction of labour. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981;282:679–81.
Troostwijk AL, Van Veen JBC, Doesburg WH. Pre-induction intracervical application of a highly viscous prostaglandin E2 gel in pregnant women with an unripe uterine cervix: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1992;43:105–11.
Tylleskar J, Finnstrom O, Hedenskog S, Leijon I, Ryden G. Spontaneous Delivery-elective Induction for Convenience. A Comparative Study. Proceedings of 6th European Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 29 August to 1 September 1978, Vienna, Austria, abstract no. 345.
Tylleskar J, Finnstrom O, Leijon I, Hedenskog S, Ryden G. Spontaneous labor and elective induction – a prospective randomized study. I Effects on mother and fetus. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1979;58:513–18.
Ugwu EO, Obi SN, Iferikigwe ES, Dim CC, Ezugwu FO. Membrane stripping to prevent post-term pregnancy in Enugu, Nigeria: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2014;289:29–34.
Ugwu EO, Onah HE, Obi SN, Dim CC, Okezie OA, Chigbu CO, et al. Effect of the Foley catheter and synchronous low dose misoprostol administration on cervical ripening: a randomised controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol 2013;33:572–7.
Ulmsten U, Ekman G, Belfrage P, Bygdeman M, Nyberg C. Intracervical versus intravaginal PGE2 for induction of labor at term in patients with an unfavorable cervix. Arch Gynecol 1985;236:243–8.
Ulmsten U, Wingerup L, Andersson KE. Comparison of prostaglandin E2 and intravenous oxytocin for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 1979;54:581–4.
Ulmsten U, Wingerup L, Belfrage P, Ekman G, Wiqvist N. Intracervical application of prostaglandin gel for induction of term labor. Obstet Gynecol 1982;59:336–9.
Uludag S, Salihoglu Saricali F, Madazli R, Cepni I. A comparison of oral and vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005;122:57–60.
Urban R, Lemancewicz A, Urban J, Skotnicki MZ, Kretowska M. Misoprostol and dinoprostone therapy for labor induction: a Doppler comparison of uterine and fetal hemodynamic effects. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;106:20–4.
Vahid Roudsari F, Ayati S, Ghasemi M, Hasanzadeh Mofrad M, Shakeri MT, Farshidi F, et al. Comparison of vaginal misoprostol with foley catheter for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Iran J Pharm Res 2011;10:149–54.
Vakhariya VR, Sherman AI. Prostaglandin F2α for induction of labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1972;113:212–22.
Valadan M, Niroomanesh S, Noori K, Khalilian S, Tehrani M. Comparison of dinoprostone plus oxytocin and oxytocin alone for induction of labour. Acta Med Iranica 2005;43:259–62.
Valentine BH. Intravenous oxytocin and oral prostaglandin E2 for ripening of the unfavourable cervix. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1977;84:846–54.
Van Baaren GJ, Jozwiak M, Rengerink KO, Benthem M, Dijksterhuis MGK, van Huizen ME, et al. Cost-effectiveness of induction of labor at term with a Foley catheter compared to prostaglandin E2 gel (based on the PROBAAT trial; registration NTR 1646). Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206(Suppl. 1):139–40.
van der Walt D, Venter PF. Management of term pregnancy with premature rupture of the membranes and unfavourable cervix. S Afr Med J 1989;75:54–6.
van Gemund N, Scherjon S, LeCessie S, van Leeuwen JH, van Roosmalen J, Kanhai HH. A randomised trial comparing low dose vaginal misoprostol and dinoprostone for labour induction. BJOG 2004;111:42–9.
Varaklis K, Gumina R, Stubblefield PG. Randomized controlled trial of vaginal misoprostol and intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for induction of labor at term. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86:541–4.
Vernant M, Perez Picanol E, Armengol R, Carreras N, Gamissans O. Intracervical Prostaglandins vs Oxytocin in Premature Rupture of Membranes. Proceedings of 2nd World Congress of Perinatal Medicine, 1993, Rome, Italy, abstract no. 449.
Wagner MV, Chin VP, Peters CJ, Drexler B, Newman LA. A comparison of early and delayed induction of labor with spontaneous rupture of membranes at term. Obstet Gynecol 1989;74:93–7.
Wang H, Li L, Pu L. [The effect of 25 micrograms misoprostol on induction of labor in late pregnancy.] Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1998;33:469–71.
Weston J, Hannah M, Ohlsson A. Changing the study design during the recruitment phase of an international perinatal multicentre clinical trial. Controlled Clin Trials 1993;14:401.
Wieland D, Friedman F. Comparing two dinoprostone agents for preinduction cervical ripening at term. A randomized trial. J Reprod Med 1999;44:724–8.
Wielgos M, Szymusik I, Kosinska-Kaczynska K, Suchonska B, Kaminski P, Banaszek-Wysoczanska A, et al. The influence of dinoprostone on uterine cervix ripening and the course of labor. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2007;28:513–17.
Williams MC, Krammer J, O’Brien WF. The value of the cervical score in predicting successful outcome of labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 1997;90:784–9.
Williams MG, O’Brien WF, Sawai SK, Knuppel RA. Outpatient Cervical Ripening in the Postdates Pregnancy. Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 23–27 January 1990, Houston, TX, USA, abstract no. 533.
Wilson PD. A comparison of four methods of ripening the unfavourable cervix. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1978;85:941–4.
Wing D, Brown R, Plante L, Miller H, Rugarn O, Powers B. Efficacy and safety of misoprostol vaginal insert compared with dinoprostone vaginal insert for labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2013;208(Suppl. 1):49.
Wing D, Guberman C, Fassett M. A comparison of oral mifepristone to intravenous oxytocin for pre-induction cervical ripening and labor induction in women with prelabor rupture of membranes beyond 36 weeks gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189(Suppl. 1):204.
Wing DA, Brown R, Plante LA, Miller H, Rugarn O, Powers BL. Misoprostol vaginal insert and time to vaginal delivery: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2013;122:201–9.
Wing DA, Fassett MJ, Guberman C, Tran S, Parrish A, Guinn D. A comparison of orally administered misoprostol to intravenous oxytocin for labor induction in women with favorable cervix examinations. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;190:1689–96.
Wing DA, Fassett MJ, Mishell DR. Effect of mifepristone on cervical ripening and labor induction in pregnancies beyond 41 weeks gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;182:S133.
Wing DA, Fassett MJ, Mishell DR. Mifepristone for preinduction cervical ripening beyond 41 weeks’ gestation: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:543–8.
Wing DA, Guberman C, Fassett M. A randomized comparison of oral mifepristone to intravenous oxytocin for labor induction in women with prelabor rupture of membranes beyond 36 weeks’ gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:445–51.
Wing DA, Ham D, Paul RH. A comparison of orally administered misoprostol to vaginally administered misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:S127.
Wing DA, Ham D, Paul RH. A comparison of orally administered misoprostol with vaginally administered misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:1155–60.
Wing DA, Jones MM, Rahall A, Goodwin TM, Paul RH. A comparison of misoprostol and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1804–10.
Wing DA, Ortiz-Omphroy G, Paul RH. A comparison of intermittent vaginal administration of misoprostol with continuous dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:612–18.
Wing DA, Park MR, Paul RH. A randomized comparison of oral and intravaginal misoprostol for labor induction. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95:905–8.
Wing DA, Paul RH. Induction of labor with misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes beyond 36 weeks gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178:S93.
Wing DA, Paul RH. Induction of labor with misoprostol for premature rupture of membranes beyond thirty-six weeks’ gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179:94–9.
Wing DA, Paul RH. Vaginally administered misoprostol (Cytotec) versus the dinoprostone vaginal insert (Cervidil) for pre-induction cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:S113.
Wing DA, Rahall A, Jones MM, Goodwin TM, Paul RH. Misoprostol: an effective agent for cervical ripening and labor induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1811–16.
Wing DA. Misoprostol vaginal insert compared with dinoprostone vaginal insert: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;112:801–12.
Wingerup L, Andersson KE, Ulmsten U. Intracervical PGE2 -Gel contra i.v. Oxytocin for Cervical Ripening and or Induction of Labour at Term. 9th World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 26–31 October 1979, Tokyo, Japan, abstract no. 291.
Wingerup L, Andersson KE, Ulmsten U. Ripening of the uterine cervix and induction of labour at term with prostaglandin E2 in viscous gel. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1978;57:403–6.
Wiqvist I, Norstrôm A, Wiqvist N. Induction of labor by intra-cervical PGE2 in viscous gel. Mechanism of action and clinical treatment routines. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1986;65:485–92.
Wiriyasirivaj B, Vutyavanich T, Ruangsri RA. A randomized controlled trial of membrane stripping at term to promote labor. Obstet Gynecol 1996;87:767–70.
Witter FR, Mercer BM. Improved intravaginal controlled-release prostaglandin E2 insert for cervical ripening at term. Prenatal Neonatal Med 1996;1(Suppl. 1):249.
Witter FR, Mercer BM. Improved intravaginal controlled-release prostaglandin E2 insert for cervical ripening at term. The Prostaglandin E2 Insert Study Group. J Maternal Fetal Med 1996;5:64–9.
Witter FR, Rocco L, Johnson TRB. A randomized trial of prostaglandin E2 in a controlled release vaginal pessary for cervical ripening at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;164:308.
Witter FR, Rocco LE, Johnson TR. A randomized trial of prostaglandin E2 in a controlled-release vaginal pessary for cervical ripening at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:830–4.
Witter FR, Weitz CM. A randomized trial of induction at 42 weeks gestation versus expectant management for postdates pregnancies. Am J Perinatol 1987;4:206–11.
Wong SF, Hui SK, Choi H, Ho LC. Does sweeping of membranes beyond 40 weeks reduce the need for formal induction of labour? BJOG 2002;109:632–6.
Yang ZY, Li E, Yu SS. [15-Methyl-PGF2 alpha vaginal suppository for induction of term labor.] Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1994;29:273–5.
Yazdani SH, Bouzari Z, Farahi S, Tabary AM. Oral misoprostol with oxytocin versus oxytocin alone for labor induction in pre-labor rupture of membranes (PROM) at term pregnancy. J Babol Uni Med Sci 2012;14:7–12.
Yazdizadeh H, Abedi P, Najar S, Angali KA. The impact of isosorbide mononitrate on cervical ripening and labor induction in primiparous women with term pregnancy: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Iranian J Nurs Midwifery Res 2013;18:246–50.
Yildirim G, Güngördük K, Idem O, Aslam H, Ceylan Y. Membrane sweeping. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med 2008;21(Suppl. 1):36.
Yildirim G, Güngördük K, Karadağ OI,Aslan H, Turhan E, Ceylan Y. Membrane sweeping to induce labor in low-risk patients at term pregnancy: a randomised controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2010;23:681–7.
Yin CY, Zhou JZ, Wang BP, Lü XY. [Effect and risk analysis of misoprostol in stimulating cervical maturity for post-term pregnancy.] Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2006;26:182–4.
Yonekura ML, Songster G, Smith-Wallace T. Preinduction cervical priming with PGE2 intracervical gel. Am J Perinatol 1985;2:305–10.
Yuen PM, Pang HYY, Chung T, Chang A. Cervical ripening before induction of labour in patients with an unfavourable cervix: a comparative randomized study of the Atad ripener device, prostaglandin E2 vaginal pessary, and prostaglandin E2 intracervical gel. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;36:291–5.
Yuen PM, Pang YYH. A Randomized Study of Two Different Methods for Cervical Ripening. Proceedings of 2nd International Scientific Meeting of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, 7–10 September 1993, Hong Kong, abstract no. 154.
Zahradnik HP, Quaas L, Kröner-Fehmel EE, Kieback DG, Lippert TH. [Cervix ripening using drugs before oxytocin labor induction. Clinical study of a new prostaglandin E2 triacetin gel.] Geburtshilfe Frauenheilk 1987;47:190–2.
Zahran KM, Shahin AY, Abdellah MS, Elsayh KI. Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for induction of labor at term: a randomized prospective placebo-controlled study. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2009;35:1054–60.
Zanconato G, Bergamini V, Mantovani E, Carlin R, Bortolami O, Franchi M. Induction of labor and pain: a randomized trial between two vaginal preparations of dinoprostone in nulliparous women with an unfavorable cervix. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2011;24:728–31.
Zanini A, Ghidini A, Norchi S, Beretta E, Cortinovis I, Bottino S. Pre-induction cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2 gel: intracervical versus intravaginal route. Obstet Gynecol 1990;76:681–3.
Zanini A, Norchi S, Beretta E, Cortinovis I, Fenaroli G, Scian A. [Cervical ripening and induction of labor in term pregnancy using prostaglandin E2. Controlled clinical study comparing the intracervical and intravaginal routes.] Ann Ostet Ginecol Med Perinat 1989;110:209–16.
Zeteroğlu S, Engin-Ustün Y, Ustün Y, Güvercinçi M, Sahin G, Kamaci M. A prospective randomized study comparing misoprostol and oxytocin for premature rupture of membranes at term. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2006;19:283–7.
Zeteroğlu S, Sahin GH, Sahin HA. Induction of labor with misoprostol in pregnancies with advanced maternal age. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2006;129:140–4.
Zeteroğlu S, Sahin HG, Sahin HA. Induction of labor in great grandmultipara with misoprostol. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2006;126:27–32.
Zeteroğlu S, Sahin HG, Sahin HA. Induction of labor with misoprostol in grand multiparous patients. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2004;87:155–6.
Ziaei S, Rosebehani N, Kazeminejad A, Zafarghandi S. The effects of intramuscular administration of corticosteroids on the induction of parturition. J Perinat Med 2003;31:134–9.
Zvandasara P, Saungweme G, Mlambo J, Chidembo W, Madzivanzira N, Mwanjira C. Induction of labour with titrated oral misoprostol suspension. A comparative study with vaginal misoprostol. Cent Afr J Med 2008;54:43–9.
Appendix 6 Characteristics of included studies
| Study identifier | Comparison | Sample size | Previous CS | Parity | Membranes | Cervix | Gestational age | Number of fetuses | Risk of bias | Setting | Financial disclosure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aalami-Harandi 201343 | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution vs. i.v. oxytocin | 256 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Abdul 200744 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 62 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Abedi-Asl 200745 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Adair 199847 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 178 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Adam 200549 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Adeniji 200553 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 96 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Agarwal 200355 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Agarwal 201254 | Placebo vs. NO | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Ajori 201356 | Placebo vs. acupuncture | 75 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Akay 201257 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 144 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Akyol 199958 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 126 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Alcalay 199659 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 154 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Alcoseba-Lim 199260 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 130 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Al-Hussaini 200361 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 130 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Allott 199362 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 195 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Allouche 199363 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 119 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Al-Malt 199564 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 103 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Al-Sebai 199365 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 73 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Al-Taani 200466 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 147 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Amador 200767 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 300 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Anand 201268 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Andersen 199069 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 88 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Asher 200972 | No treatment vs. placebo vs. acupuncture | 89 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Ashrafunnessa 199773 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 98 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Ayad 200276 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 238 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ayaz 200877 | No treatment vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 84 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ayaz 201078 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 120 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bagatree 199079 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bakos 198780 | i.v. oxytocin vs. amniotomy | 223 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Balci 201082 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 100 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (<6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias. | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Balci 201181 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 101 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Bartha 200085 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 200 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bartusevicius 200686 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 140 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Beer 199987 | Placebo vs. homeopathy | 40 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Beigi 200388 | Placebo vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 156 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bell 199389 | Placebo vs. relaxin | 40 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Benedetto 198790 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 50 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bennett 199892 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 206 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Benzineb 199693 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Berghella 199695 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 142 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Berkane 200597 | Placebo vs. mifepristone | 346 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Bernstein 199198 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 397 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Berzircioglu 2012101 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bilgin 1998103 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 45 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Biron-Shental 2004104 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 53 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bollapragada 2009107 | Placebo vs. NO | 350 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Boulvain 1997109 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 198 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Bounyasong 2000111 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 166 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Brandel 1998112 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. prostaglandin | 79 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bremme 1984115 | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy vs. oral prostaglandins | 83 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Brennand 1997118 | Placebo vs. relaxin | 96 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Bricker 2008119 | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution vs. i.v. oxytocin | 303 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All favourable (> 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Buchanan 1984121 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 77 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Bullarbo 2007123 | Placebo vs. NO | 200 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Bung 1986124 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Buser 1997125 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 155 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Butt 1999126 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 108 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Buttino 1990127 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 43 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All post term | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Cabrol 1988129 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 217 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Cahill 1988130 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 42 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Cammu 1998131 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 278 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Campbell 1984132 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 199 | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Campos 1994133 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 153 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Cararach 1996136 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 341 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Cardozo 1986137 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 402 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | Mixed | All post term | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Carlan 2001139 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1004 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Carlan 2002138 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 152 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Cecatti 2000140 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 106 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chang 1997142 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 193 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chang 1997141 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 60 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Chanrachakul 2000144 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. NO | 30 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chanrachakul 2003143 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 249 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Chanrachakul 2010148 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 218 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chanrachakul 2000145 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. NO | 110 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Chanrachakul 2002146 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. NO | 107 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Charoenkul 2000149 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 143 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chatterjee 1990150 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 33 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chaudhuri 2011151 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 207 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Chayen 1986152 | i.v. oxytocin vs. breast stimulation | 61 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chen 2000153 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 239 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All favourable (> 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Cheng 2008154 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 207 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Cheung 2006155 | Placebo vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 98 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chitraker 2012156 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chua 1988162 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 80 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chua 1991159 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 94 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Chua 1995161 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 155 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chua 1997160 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 185 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chuck 1995163 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 99 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chung 1992166 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 59 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Chung 2003165 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 103 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Chyu 1997167 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 73 | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Clark 1998168 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 138 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Colon 2005173 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 204 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Corrado 2001175 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 233 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Crane 1997177 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 150 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Crane 2003179 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 105 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Cromi 2011180 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 397 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Cromi 2012181 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 208 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Curet 1989183 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 54 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Da Graça 2005184 | No treatment vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 150 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Dällenbach 2003186 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Dalui 2005187 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Damania 1992188 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin vs. breast stimulation | 57 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Danielian 1999189 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 211 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Dare 2002191 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 137 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Darroca 1996192 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 118 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Davey 1979193 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. oral prostaglandins | 33 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Day 1985195 | PGF2 gel vs. i.v. oxytocin | 202 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| De 2006197 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| De Aquino 2003198 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 210 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| De la Torre 2001200 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 360 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| De Miranda 2006201 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 742 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| De Moraes Filho 2005202 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Deng 1999204 | Placebo vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 85 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Denguezli 2007205 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 130 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Deo 2012206 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 158 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Deshmukh 2011207 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 400 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Deshmukh 2013208 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Diro 1999210 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 251 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Doany 1997212 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. membrane sweeping | 115 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Dodd 2005213 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 741 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Dodd 2006215 | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution vs. i.v. oxytocin | 30 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Domínguez Salgado 1999218 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 156 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Domisse 1980219 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 56 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Dommisse 1987220 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 50 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Duff 1984221 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 134 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Dyar 2000222 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 153 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Edwards 2014223 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 386 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Egarter 1987228 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 99 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Egarter 1989227 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 345 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Ekman 1983229 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 60 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ekman 1986230 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 38 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Ekman-Ordeberg 1985231 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 20 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| El-Torkey 1992232 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 65 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| El-Azeem 1997233 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 29 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| El-Din 2000234 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 149 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Elhassan 2004238 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Elhassan 2005235 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 63 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Elhassan 2005236 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 140 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Elhassan 2007237 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 150 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| El-Mardi 1991240 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 200 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| El-Shawarby 2006241 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 72 | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| El-Sherbiny 2001243 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 185 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Eroglu 2007244 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 147 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Escudero 1997245 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Esteve 2006246 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 450 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ezechi 2008247 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 339 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Facchinetti 2005249 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 144 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Facchinetti 2007248 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 116 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Farah 1997250 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 399 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Feitosa 2006255 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 150 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Fenton 1985256 | Placebo vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 30 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ferguson 2002257 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 104 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ferraiolo 2010258 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 144 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Fisher 2001260 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 126 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Fletcher 1993263 | Placebo vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 45 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Fletcher 1994262 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 63 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Fonseca 2008265 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 327 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Frass 2011268 | No treatment vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 113 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Frohn 2002269 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 109 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Frydman 1992271 | Placebo vs. mifepristone | 120 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Gagnon-Gervais 2012275 | i.v. oxytocin vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 143 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Garry 2000277 | No treatment vs. caster oil | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Garry 2003278 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 186 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Gaudernack 2006279 | No treatment vs. acupuncture | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Gaudet 2008280 | Placebo vs. acupuncture | 16 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Gelisen 2005281 | No treatment vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 600 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Getgan 2003282 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 72 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Gherman 2001284 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 58 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Giacalone 1998285 | Placebo vs. mifepristone | 83 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Gihwala 1987288 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 50 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Gilson 1993290 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 79 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Gilson 1996291 | No treatment vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 240 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Girija 2009293 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Girija 2011294 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 320 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Gittens 1996295 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 32 | All with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Glagoleva 1999296 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 53 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Goel 2011297 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 200 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Goeschen 1989298 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 60 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Golbus 1977299 | Placebo vs. oral prostaglandins | 50 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Goldenberg 1996300 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 293 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Gonen 1994301 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 50 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Gottschall 1997303 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 75 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Gower 1982304 | Placebo vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 48 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Grant 1992306 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 444 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Graves 1985307 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Green 1998308 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 107 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Greer 1989309 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 50 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Greer 1990310 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 24 | NR/NC | Multiparous only | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Gregson 2005312 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 268 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Greybush 2001313 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 136 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Gribel 2011314 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. acupuncture | 67 | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Griffith-Jones 1990315 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 200 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Grünnberger 1986316 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 30 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Güngördük 2012319 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 444 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Gupta 1998322 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 100 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Gupta 2006321 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Gupta 2010320 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 148 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Habib 2008324 | Placebo vs. NO | 102 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Haghighi 2006325 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 108 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All preterm | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Haghighi 2013326 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. NO | 132 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Hales 1994329 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 100 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Hall 2002330 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 107 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hamdan 2009332 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 214 | All with previous CS | Multiparous only | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Hannah 1996335 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 2520 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Hannah 1996335 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 2521 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Harper 2005338 | No treatment vs. acupuncture | 56 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Has 2002339 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 114 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Haugland 2012340 | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter vs. mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 178 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hauth 1977341 | No treatment vs. oral prostaglandins | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Hay 1995342 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 28 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hayashi 1983343 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 60 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Heden 1991344 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 238 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Heinzl 1980345 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hemlin 1998346 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 85 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Henrich 2008347 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 224 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Herabutya 1988349 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. oral prostaglandins | 50 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Herabutya 1991353 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 47 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Herabutya 1992352 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 108 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Herabutya 1993350 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 48 | NR/NC | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Herabutya 1997351 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 110 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hidar 2000354 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 88 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hill 2008357 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 300 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Hjertberg 1996359 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 201 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hoffman 2001361 | Placebo vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 96 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hofmeyr 2001363 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 866 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hosli 2008364 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 107 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| How 2001366 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 219 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Howarth 1996368 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 72 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hudon 1999370 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 111 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Husslein 1986371 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 345 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Hutchon 1980372 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 67 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Incerpi 2001375 | Placebo vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Irion 1998376 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 247 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Iskander 1978377 | Extra-amniotic PGE2 vs. i.v. prostaglandin | 40 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Jackson 1994378 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 158 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Jagani 1982382 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin vs. amniotomy vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 50 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Jagani 1984381 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 47 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Janakiraman 2011383 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 123 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Jeeva 1982384 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 20 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Jindal 2011385 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 103 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Johnson 1985386 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 80 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Jozwiak 2012387 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 819 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Jozwiak 2013389 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 226 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Kadanali 1996392 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 224 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kadian 2008393 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. NO | 400 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kalkat 2008394 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kaminski 1994396 | PGF2 gel vs. i.v. oxytocin | 296 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kandil 2012397 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 100 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kashanian 2006402 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 200 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kashanian 2006401 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 101 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Kashanian 2008404 | Placebo vs. corticosteroids | 122 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Katz 1983410 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 156 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | All post term | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kaul 2004411 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. membrane sweeping | 60 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Keirse 1995414 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 282 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Kemp 2000418 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 470 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kennedy 1978419 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 60 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kennedy 1982420 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Khazardoost 2011421 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 60 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Khoury 2001423 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 118 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Kidanto 2007424 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 142 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kim 2000426 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 113 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kipikasa 2005428 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 52 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Koc 2013429 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 168 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Kolderup 1999430 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 159 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Komala 2013431 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Kovavisarach 1997432 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 60 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kovavisarach 1998433 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 80 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Krammer 1995438 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 416 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Krithika 2008440 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Kulshreshtha 2007441 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 40 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kumar 2001442 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kunt 2010443 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 240 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Kwon 2001444 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 160 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lackritz 1979446 | Placebo vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 12 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ladfors 1996447 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 1012 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Lamki 1974449 | i.v. oxytocin vs. i.v. prostaglandin | 48 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lange 1981450 | i.v. oxytocin vs. oral prostaglandins | 201 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Lange 1984452 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 185 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Langenegger 2005453 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 191 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Larmon 2002454 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 vs. oestrogens | 128 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Laube 1986455 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 45 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Le Roux 2002456 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 480 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lee 1997457 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 50 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Legarth 1987460 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 98 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All favourable (> 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Legarth 1988458 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 113 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lelaidier 1994461 | Placebo vs. mifepristone | 32 | All with previous CS | Multiparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Lemancewicz 1999463 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 131 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lemyre 2006465 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 62 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Levy 2005467 | Placebo vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 130 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lewis 1983468 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 66 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lien 1998470 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 93 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Liggins 1979471 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 84 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Lo 1994480 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Lo 2003478 | Placebo vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 102 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lo 2006481 | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 50 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lokugamage 2003482 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 191 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lopes 1991485 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 50 | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lopez-Farfan 2010486 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 50 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lughmani 2009488 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 48 | NR/NC | Multiparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Luther 1980489 | Placebo vs. oestrogens | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lykkesfeldt 1979490 | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy vs. oral prostaglandins | 161 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All favourable (> 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Lyndrup 1989493 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 43 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lyndrup 1990494 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 91 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lyndrup 1991496 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 125 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Lyndrup 1994497 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 109 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Macer 1984498 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 85 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| MacKenzie 1979501 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. PGF2 gel | 48 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| MacKenzie 1981500 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 526 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| MacLennan 1979504 | Placebo vs. PGF2 gel | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| MacLennan 1980507 | Placebo vs. relaxin | 60 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| MacLennan 1980506 | PGF2 gel vs. i.v. oxytocin | 85 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| MacLennan 1980505 | Placebo vs. PGF2 gel | 90 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| MacLennan 1986508 | Placebo vs. relaxin | 71 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| MacLennan 1989503 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 320 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Magann 1995516 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin vs. oestrogens | 99 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Magann 1998515 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 65 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Magann 1998511 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 vs. membrane sweeping | 105 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Magann 1999512 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. membrane sweeping | 182 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Magnani 1986517 | Placebo vs. oestrogens | 29 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Magos 1983518 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 36 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Magtibay 1998520 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 36 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Mahmood 1989522 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 80 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Mahmood 1992526 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 220 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Mahmood 1995523 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 100 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Mahmood 1995527 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. amniotomy | 260 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Majoko 2002530 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 406 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Majoko 2002529 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 152 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Malik 1996532 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 118 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Malik 2010531 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 100 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Massil 1988535 | i.v. oxytocin vs. oral prostaglandins | 69 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Mawire 1999539 | PGF2 gel vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 162 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| McCaul 1997541 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 91 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| McColgin 1990542 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 180 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| McColgin 1990544 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 99 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| McKenna 1999545 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 61 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| McKenna 2004546 | Placebo vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 68 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| McLaren 1987547 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 24 | NR/NC | Multiparous only | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| McQueen 1990549 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 50 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| McQueen 1992548 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 40 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Megalo 2004551 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Mehrotra 2010552 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 128 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Mei-Dan 2012555 | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter vs. mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 188 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Melchior 1989976 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 50 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Mercer 1993557 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 93 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All preterm | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Mercer 1995558 | i.v. oxytocin vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 209 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Meydanli 2003559 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Meyer 2002560 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 84 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Milchev 2003562 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 275 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Miller 1991563 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 40 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Misra 1994565 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 263 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Modarres 2000567 | No treatment vs. breast stimulation | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Modlock 2010569 | Placebo vs. acupuncture | 118 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Moini 2003570 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 70 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Moldin 1996572 | Amniotomy vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 196 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Müller 1987574 | i.v. oxytocin vs. i.v. prostaglandin | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Montealegre 1999575 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 159 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Moodley 2003576 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 396 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Moraes Filho 2010577 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 240 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Morales 1986578 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 317 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Morgan Ortiz 2002579 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 71 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Mosquera 1999580 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 89 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Mozurkewich 2003582 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 305 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Murphy 1980584 | Placebo vs. PGF2 gel | 265 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Murray 1995585 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 200 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Murthy 2006587 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 72 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Naef 1998588 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 120 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All preterm | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nager 1987590 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 34 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nagpal 2009591 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 61 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Naismith 1973592 | i.v. oxytocin vs. i.v. prostaglandin | 40 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Nanda 2007593 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Nassar 2007595 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 170 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Natale 1994596 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 242 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Neiger 2001598 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 61 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient. | NR/NC |
| Neilson 1983599 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. PGF2 gel | 76 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Netta 2002600 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 98 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Newman 1997601 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 58 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Ngai 1996605 | Placebo vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ngai 2000604 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nguyen 2012606 | i.v. oxytocin vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1208 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| NICHHD 1994171 | No treatment vs. placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 440 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Nicoll 2001607 | No treatment vs. NO | 36 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nigam 2004609 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 70 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nigam 2010608 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nimrod 1984610 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 45 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Niromanesh 2003611 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 89 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Noah 1987612 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 816 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Nopdonrattakoon 2003614 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 106 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Norzilawati 2010616 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 130 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ntsaluba 1997617 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 112 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nunes 1999618 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 189 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nuutila 1995620 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 45 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Nuutila 1996621 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 110 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Oboro 2005622 | No treatment vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 77 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| O’Brien 1995624 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 100 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Oliveira 2010625 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 160 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Olmo 2001626 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 50 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Omar 2013627 | No treatment vs. sexual intercourse | 1150 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Ophir 1992628 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 54 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Orhue 1995629 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 94 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Osman 2006632 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. NO | 395 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Ottervanger 1996636 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 123 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ottinger 1998637 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 90 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Owen 1991638 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Owolabi 2005640 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ozkan 2009641 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 112 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Paisarntantiwong 2005642 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 146 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Pandis 2001643 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 435 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Papageorgiou 1992644 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 165 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Papanikolaou 2004645 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 163 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Parazzini 1998646 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 320 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Parewijck 1986647 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 196 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Parikh 2001648 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 30 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Parisaei 2008649 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 57 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Patil 2005651 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 190 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Paul 1992652 | i.v. oxytocin vs. oral prostaglandins | 35 | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Paungmora 2004654 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 151 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Peccerillo 1995656 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 67 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Pedrazzoli 1997658 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 247 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Peedicayil 1998659 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 60 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Pennell 2009660 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter vs. mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 330 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Perche 2009662 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. NO | 60 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Perez Picanol 1990664 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 71 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Perry 2004667 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 63 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Perryman 1992669 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 90 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Pi 1999675 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 60 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Pinto 196730 | Placebo vs. oestrogens | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Pollnow 1996676 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 200 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Pongsatha 2005677 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 166 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Poornima 2011678 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 100 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Poulsen 1991679 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 226 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Prager 2008681 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 588 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Prasad 1989684 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 69 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Prins 1983685 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 30 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Puertas 1997687 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Puga 2001688 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 270 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Pulle 1986689 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 50 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Putnam 2011690 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 350 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Quinn 1981691 | Placebo vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 25 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Rabl 2001692 | No treatment vs. acupuncture | 45 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Rabl 2002693 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 200 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Rahman 2013695 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 220 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (<6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias. | Inpatient. | NR/NC |
| Rameez 2007696 | Placebo vs. NO | 156 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ramsey 2003699 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 111 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rath 1999703 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 468 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rath 1999703 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 328 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All favourable (> 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rath 2007701 | No treatment vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 300 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ratnam 1974704 | i.v. oxytocin vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy vs. oral prostaglandins | 154 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Ray 1992705 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 143 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rayburn 1988707 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 118 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Rayburn 1992710 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 215 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Rayburn 1999709 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 294 | All with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Richardson 1991711 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 48 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rix 1996713 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 208 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rizvi 2007714 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 59 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Roach 1997715 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 201 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Roberts 1986716 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 104 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Romero-Gutiérrez 2011720 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. NO | 66 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC. |
| Rouben 1993721 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 112 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Roudsari 2011722 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 108 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rouzi 2014725 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 160 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Rowlands 2001726 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 125 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Rozenberg 2001727 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 369 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Rozenberg 2004728 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 140 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Roztocil 1998730 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. oestrogens vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 247 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Roztocil 2013729 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. oestrogens vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 247 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Russell 2007731 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 738 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rydhström 1991733 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 277 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Rymer 1992734 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 106 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Saeed 2011735 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Saggaf 2001736 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 57 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sahraoui 2005737 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 150 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Sahu 2004738 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 50 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Salamalekis 2000739 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin vs. membrane sweeping | 104 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Saleem 2006740 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 226 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Saleh 1975741 | Amniotomy vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 100 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Salim 2011742 | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter vs. mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 293 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Salmon 1986743 | No treatment vs. breast stimulation | 100 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Sanchez-Ramos 1992748 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. mechanical methods – laminaria | 74 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sanchez-Ramos 1997745 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 141 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sanchez-Ramos 1998749 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 223 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sande 1983750 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 166 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Sawai 1991754 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 50 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Sawai 1994752 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Saxena 2011755 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 210 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Schmitz 2014756 | Placebo vs. NO | 1363 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Schneider 2004757 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 296 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sciscione 1999759 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 149 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sciscione 2001760 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 111 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Secher 1981762 | i.v. oxytocin vs. oral prostaglandins | 244 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Seeras 1995763 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 68 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Selmer-Olsen 2007765 | No treatment vs. acupuncture | 101 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Selo-Ojeme 2009767 | Amniotomy vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 123 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Shakya 2010768 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 66 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sharma 2005769 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 65 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shechter-Maor 2013770 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 50 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sheela 2007771 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 150 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sheikher 2009772 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 90 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shepherd 1976773 | Placebo vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 30 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Sherman 2001774 | Placebo vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 116 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shetty 2001778 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 245 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shetty 2002780 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shetty 2002784 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 249 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shetty 2002974 | No treatment vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 61 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shetty 2003781 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 101 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shetty 2004782 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Shoaib 1994785 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 200 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sifakis 2007786 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 415 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Silva-Cruz 1988787 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 50 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sitthiwattanawong 1999789 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 131 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Smith 1990794 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 69 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Smith 1994795 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 121 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Smith 2008792 | Placebo vs. acupuncture | 360 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Souza 2013796 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Spallicci 2007797 | Placebo vs. hyaluronidase | 168 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Spellacy 1973801 | i.v. oxytocin vs. i.v. prostaglandin | 222 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Sperling 1993802 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 124 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Srisomboon 1996804 | Placebo vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 62 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Srisomboon 1998803 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 50 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| St Onge 1995805 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 62 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Stampe Sørensen 1992806 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 267 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Stempel 1997809 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 83 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Stenlund 1999811 | Placebo vs. mifepristone | 36 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Stewart 1983815 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 | 62 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Steytler 1995816 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 30 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Stitely 2000817 | Placebo vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 60 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Strobelt 2006818 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 107 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Su 1996820 | No treatment vs. mifepristone | 124 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Sultana 2006821 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Surbek 1997822 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Surita 2005826 | Hyaluronidase vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 140 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Suvobrata 2011827 | i.v. oxytocin vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 95 | NR/NC | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Suzuki 2000828 | No treatment vs. oral prostaglandins | 36 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | All multiple | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Tabasi 2007829 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 110 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Tabor 1995830 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 127 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Tabowei 2003831 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 121 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Taechakraichana 1996832 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 19 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Taher 2011834 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 165 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Tamsen 1990836 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 93 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Tan 2007838 | No treatment vs. sexual intercourse | 210 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Tan 2010840 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 169 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Tan 2013837 | Amniotomy vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 206 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Tannirandorn 1999841 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 80 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Taylor 1993842 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 42 | All with previous CS | Multiparous only | Mixed | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ten Eikelder 2013843 (Jozwiak 2014391) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Tessier 1997844 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 267 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Tey 1995846 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 40 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Thaisomboon 2012847 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 64 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Thakur 2005848 | Placebo vs. mifepristone | 50 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Thavarahsah 1990849 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Thiery 1984851 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 121 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Thomas 1986853 | PGF2 gel vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 57 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Thomas 2000854 | Placebo vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 52 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Tomlinson 2000855 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 69 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Toppozada 1997857 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 40 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Trabelsi 2012858 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 300 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Tremeau 1992859 | No treatment vs. placebo vs. acupuncture | 98 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Triglia 2010860 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 130 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Trofatter 1985861 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 59 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Trofatter 1993863 | No treatment vs. intracervical PGE2 | 488 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Tromans 198131 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. oestrogens | 60 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Troostwijk 1992864 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 139 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Tylleskar 1979866 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 84 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Ugwu 2013868 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 90 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Ugwu 2014867 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 123 | NR/NC | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Ulmsten 1979870 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 100 | NR/NC | Nulliparous only | All intact | Mixed | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ulmsten 1982871 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 | 50 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ulmsten 1985869 | Placebo vs. intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 58 | NR/NC | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Uludag 2005872 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 99 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Vakhariya 1972874 | i.v. oxytocin vs. i.v. prostaglandin | 150 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | All intact | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Valadan 2005875 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 91 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Valentine 1977876 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin vs. oral prostaglandins | 60 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Van der Walt 1989878 | No treatment vs. vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 60 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Van Gemund 2004879 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 681 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Mixed | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Varaklis 1995880 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 69 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Vernant 1993881 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 80 | NR/NC | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wagner 1989882 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 182 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Wang 1998883 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 48 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Wieland 1999885 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 66 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wielgos 2007886 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 128 | NR/NC | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wilson 1978889 | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) vs. i.v. oxytocin vs. extra-amniotic PGE2 vs. oral prostaglandins | 60 | NR/NC | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | NR/NC | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wing 1995900 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 135 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wing 1995906 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 275 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wing 1997903 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 197 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wing 1998905 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 197 | None with previous CS | NR/NC | All ruptured | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wing 1999899 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 220 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wing 2000902 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 234 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wing 2000895 | Placebo vs. mifepristone | 180 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Wing 2004893 | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 198 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All favourable (> 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Wing 2005897 | i.v. oxytocin vs. mifepristone | 65 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Wing 2008896 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. sustained-release misoprostol insert | 1307 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Wing 2013892 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) vs. sustained-release misoprostol insert | 1358 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Wiriyasirivaj 1996910 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Witter 1987915 | No treatment vs. i.v. oxytocin | 200 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | NR/NC | All post term | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | NR/NC | NR/NC |
| Witter 1992914 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 72 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Witter 1996912 | Placebo vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 193 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Wong 2002916 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 120 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | Mixed | All post term | NR/NC | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Yang 1994917 | PGF2 gel vs. i.v. oxytocin | 55 | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Yazdani 2012918 | Placebo vs. oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 99 | NR/NC | NR/NC | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Yazdizadeh 2013919 | Placebo vs. NO | 80 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Yildirim 2010921 | No treatment vs. membrane sweeping | 346 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Yin 2006922 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 71 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All post term | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Yuen 1996924 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) vs. mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 119 | Some with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Zahradnik 1987926 | Intracervical PGE2 vs. i.v. oxytocin | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | NR/NC | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | Some or all funding from pharmaceutical industry |
| Zahran 2009927 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 480 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Zanconato 2011928 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 52 | None with previous CS | Nulliparous only | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | No pharmaceutical industry funding/ no conflicts of interest |
| Zanini 1990929 | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) vs. intracervical PGE2 | 100 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Zeteroğlu 2004933 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 104 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | NR/NC | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Zeteroğlu 2006931 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 97 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All ruptured | NR/NC | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Zeteroğlu 2006932 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 100 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | All > 37 weeks | Singleton | No description of allocation concealment or unclear description. High risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Zeteroğlu 2006934 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. i.v. oxytocin | 64 | None with previous CS | Multiparous only | Mixed | All unfavourable (< 6) | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
| Ziaei 2003935 | No treatment vs. corticosteroids | 65 | None with previous CS | Mixed | All intact | All favourable (> 6) | All post term | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | One or both arms outpatient | NR/NC |
| Zvandasara 2008936 | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) vs. titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 134 | None with previous CS | Mixed | Mixed | NR/NC | Mixed (includes preterm) | Singleton | Report describes allocation concealment. Low risk of bias | Inpatient | NR/NC |
Appendix 7 Characteristics of study participants
| Treatment | Previous CS | Parity | Membranes | Cervix | Gestation | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | None | Some | All | NR | Nulli only | Mixed | Multi only | NR | Intact | Mixed | Ruptured | NR | Fav | Mixed | Unfav | NR | All post term | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | All preterm | |
| 1. No treatment | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 75 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 0 |
| 2. Placebo | 20 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 60 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 70 | 0 | 30 | 70 | 0 | 0 |
| 3. Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 9 | 82 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 73 | 0 | 36 | 36 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 27 | 64 | 0 | 18 | 73 | 9 | 0 |
| 4. Vaginal PGE2 gel | 4 | 83 | 13 | 0 | 4 | 17 | 75 | 4 | 13 | 33 | 46 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 13 | 83 | 8 | 4 | 54 | 33 | 0 |
| 5. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 6 | 78 | 17 | 0 | 11 | 17 | 72 | 0 | 17 | 50 | 28 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 78 | 0 | 6 | 44 | 50 | 0 |
| 6. Intracervical PGE2 | 15 | 74 | 10 | 0 | 8 | 10 | 82 | 0 | 31 | 51 | 15 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 15 | 79 | 3 | 10 | 49 | 38 | 0 |
| 7. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 43 | 43 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 86 | 0 | 71 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 14 | 0 | 43 | 43 | 0 |
| 8. Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 3 | 90 | 8 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 13 | 44 | 36 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 13 | 82 | 0 | 3 | 62 | 36 | 0 |
| 9. Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 9 | 80 | 11 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 93 | 0 | 13 | 56 | 29 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 82 | 0 | 4 | 62 | 33 | 0 |
| 10. Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 |
| 11. Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 0 | 97 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 90 | 3 | 16 | 39 | 19 | 26 | 13 | 3 | 19 | 65 | 0 | 3 | 65 | 32 | 0 |
| 12. Titrated (low) oral misoprostol solution | 10 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 60 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 70 | 0 | 10 | 40 | 50 | 0 |
| 13. Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 14. i.v. oxytocin | 24 | 71 | 6 | 0 | 18 | 18 | 65 | 0 | 24 | 12 | 12 | 53 | 18 | 18 | 6 | 59 | 0 | 0 | 76 | 24 | 0 |
| 15. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 16. NO | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 17. Mifepristone | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| 18. Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 10 | 70 | 20 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 40 | 0 |
| 19. Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 |
| 20. Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 21. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 25 | 67 | 8 | 0 | 25 | 17 | 58 | 0 | 50 | 25 | 25 | 0 | 8 | 17 | 25 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 92 | 8 | 0 |
| Treatment | Singleton/multiple pregnancy | Risk level | Setting | Funding | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | Singleton | Mixed | Multiple | Low (1) | High (2) | NR | Hospital | Outpatient | NR/NC | None | Some | |
| 1. No treatment | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 |
| 2. Placebo | 30 | 70 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 90 | 0 | 80 | 20 | 70 | 10 | 20 |
| 3. Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 55 | 9 | 91 | 0 | 82 | 9 | 9 |
| 4. Vaginal PGE2 gel | 13 | 79 | 8 | 0 | 79 | 21 | 4 | 96 | 0 | 71 | 25 | 4 |
| 5. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0 | 94 | 6 | 0 | 72 | 28 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 33 | 17 |
| 6. Intracervical PGE2 | 13 | 87 | 0 | 0 | 54 | 46 | 62 | 36 | 3 | 90 | 10 | 0 |
| 7. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 29 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 86 | 14 | 0 |
| 8. Vaginal misoprostol < 50 µg | 38 | 59 | 3 | 0 | 69 | 31 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 82 | 13 | 5 |
| 9. Vaginal misoprostol ≥ 50 µg | 2 | 96 | 2 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 78 | 20 | 2 |
| 10. Oral misoprostol tablet < 50 µg | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 11. Oral misoprostol tablet ≥ 50 µg | 3 | 97 | 0 | 0 | 74 | 26 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 87 | 13 | 0 |
| 12. Titrated (low) oral misoprostol solution | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 10 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 0 |
| 13. Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 14. i.v. oxytocin | 18 | 82 | 0 | 0 | 59 | 41 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 65 | 29 | 6 |
| 15. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| 16. NO | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 33 | 67 | 0 |
| 17. Mifepristone | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 18. Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 10 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 70 | 20 | 10 |
| 19. Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 |
| 20. Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 21. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 75 | 17 | 8 |
| Treatment | Previous CS | Parity | Membranes | Cervix | Gestation | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | None | Some | All | NR | Nulli only | Mixed | Multi only | NR | Intact | Mixed | Ruptured | NR | Fav | Mixed | Unfav | NR | All post term | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | All preterm | |
| 1. No treatment | 38 | 53 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 13 | 77 | 3 | 12 | 52 | 0 | 36 | 27 | 4 | 26 | 42 | 2 | 25 | 56 | 16 | 2 |
| 2. Placebo | 36 | 57 | 6 | 1 | 9 | 16 | 74 | 1 | 29 | 55 | 4 | 12 | 11 | 3 | 15 | 72 | 15 | 24 | 41 | 20 | 0 |
| 3. PGE2 tablet | 30 | 68 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 28 | 64 | 4 | 36 | 46 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 6 | 20 | 72 | 10 | 10 | 64 | 16 | 0 |
| 4. PGE2 gel | 31 | 60 | 9 | 0 | 10 | 13 | 76 | 1 | 20 | 47 | 19 | 13 | 4 | 4 | 19 | 73 | 8 | 7 | 58 | 27 | 0 |
| 5. PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 28 | 65 | 7 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 74 | 2 | 16 | 58 | 16 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 81 | 5 | 7 | 58 | 30 | 0 |
| 6. PGF2 gel | 36 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 82 | 0 | 64 | 18 | 0 | 18 | 36 | 0 | 36 | 27 | 18 | 0 | 55 | 27 | 0 |
| 7. PGE2 intracervical | 34 | 57 | 7 | 1 | 12 | 7 | 81 | 0 | 28 | 54 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 87 | 13 | 7 | 50 | 29 | 0 |
| 8. PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 41 | 54 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 14 | 81 | 3 | 43 | 38 | 5 | 14 | 5 | 5 | 22 | 68 | 16 | 8 | 41 | 35 | 0 |
| 9. Misoprostol < 50 µg vaginal | 9 | 86 | 5 | 0 | 13 | 3 | 85 | 0 | 14 | 50 | 29 | 8 | 9 | 1 | 14 | 76 | 5 | 10 | 58 | 26 | 1 |
| 10. Misoprostol > 50 µg vaginal | 13 | 80 | 7 | 0 | 10 | 7 | 80 | 3 | 23 | 48 | 22 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 11 | 75 | 11 | 5 | 54 | 30 | 0 |
| 11. Misoprostol < 50 µg oral | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 0 |
| 12. Misoprostol > 50 µg oral | 5 | 89 | 6 | 0 | 9 | 11 | 78 | 2 | 20 | 32 | 18 | 29 | 20 | 2 | 17 | 62 | 6 | 5 | 58 | 29 | 0 |
| 13. Misoprostol titrated | 8 | 92 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 92 | 0 | 8 | 17 | 58 | 17 | 25 | 0 | 17 | 58 | 0 | 8 | 42 | 50 | 0 |
| 14. Misoprostol pessary (slow release) | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 15. Oxytocin i.v. | 32 | 64 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 13 | 73 | 4 | 18 | 31 | 7 | 44 | 22 | 7 | 21 | 50 | 11 | 8 | 49 | 30 | 2 |
| 16. Amniotomy | 43 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 57 | 14 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 86 | 14 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 71 | 14 | 0 |
| 17. Oxytocin i.v. + amniotomy | 42 | 50 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 17 | 67 | 8 | 29 | 67 | 4 | 0 | 13 | 42 | 42 | 4 | 8 | 17 | 71 | 4 | 0 |
| 18. NO | 18 | 82 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 47 | 47 | 0 | 35 | 65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 6 | 41 | 53 | 0 | 0 |
| 19. Mifepristone | 0 | 67 | 22 | 11 | 0 | 22 | 67 | 11 | 22 | 56 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 0 | 44 | 44 | 11 | 0 |
| 20. Oestrogens | 75 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 88 | 0 | 63 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 13 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 21. Corticosteroids | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| 22. Relaxin | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| 23. Hyaluronidase | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 24. Foley catheter | 23 | 66 | 11 | 0 | 11 | 13 | 74 | 2 | 9 | 81 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 94 | 4 | 6 | 60 | 30 | 0 |
| 25. Laminaria | 44 | 44 | 13 | 0 | 19 | 13 | 69 | 0 | 63 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 81 | 31 | 0 | 38 | 31 | 0 |
| 26. Ballon catheter | 25 | 63 | 13 | 0 | 25 | 13 | 63 | 0 | 13 | 88 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 27. Membrane sweeping | 61 | 32 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 86 | 4 | 4 | 96 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 61 | 21 | 0 | 32 | 64 | 4 | 0 |
| 28. PGE2 extra-amniotic | 27 | 73 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 55 | 0 | 55 | 36 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 82 | 27 | 0 | 64 | 9 | 0 |
| 29. Prostaglandins i.v. | 29 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 14 | 57 | 14 | 0 | 57 | 0 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 71 | 29 | 0 | 14 | 43 | 43 | 0 |
| 30. Sexual intercourse | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 31. Acupuncture | 27 | 73 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 64 | 0 | 9 | 64 | 9 | 18 | 27 | 0 | 18 | 55 | 0 | 64 | 27 | 9 | 0 |
| 32. Breast stimulation | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 33. Homeopathy | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 34. Castor oil | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 35. Prostaglandins oral | 64 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 14 | 71 | 0 | 29 | 43 | 7 | 21 | 29 | 7 | 36 | 29 | 21 | 0 | 64 | 14 | 0 |
| 36. Misoprostol buccal | 22 | 72 | 6 | 0 | 22 | 17 | 61 | 0 | 39 | 22 | 22 | 17 | 11 | 11 | 22 | 56 | 6 | 0 | 78 | 17 | 0 |
| Treatment | Singleton/multiple pregnancy | Risk level | Setting | Funding | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singleton | Mixed | Multiple | Low (1) | High (2) | NR | Hospital | Outpatient | NR/NC | None | Some | |
| 1. No treatment | 64 | 2 | 1 | 46 | 54 | 4 | 52 | 44 | 71 | 23 | 7 |
| 2. Placebo | 66 | 1 | 0 | 73 | 27 | 3 | 68 | 28 | 65 | 15 | 20 |
| 3. PGE2 tablet | 70 | 2 | 0 | 34 | 66 | 0 | 96 | 4 | 84 | 12 | 4 |
| 4. PGE2 gel | 65 | 7 | 0 | 62 | 38 | 1 | 93 | 6 | 69 | 22 | 9 |
| 5. PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 84 | 2 | 0 | 56 | 44 | 0 | 98 | 2 | 58 | 30 | 12 |
| 6. PGF2 gel | 82 | 0 | 0 | 55 | 45 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 82 | 0 | 18 |
| 7. PGE2 intracervical | 66 | 1 | 0 | 44 | 56 | 0 | 90 | 10 | 81 | 12 | 7 |
| 8. PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 65 | 3 | 0 | 49 | 51 | 0 | 92 | 8 | 86 | 8 | 5 |
| 9. Misoprostol < 50 µg vaginal | 89 | 4 | 0 | 63 | 38 | 1 | 93 | 6 | 78 | 19 | 4 |
| 10. Misoprostol > 50 µg vaginal | 89 | 2 | 0 | 53 | 47 | 1 | 98 | 1 | 84 | 14 | 2 |
| 11. Misoprostol < 50 µg oral | 100 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 75 | 25 | 0 |
| 12. Misoprostol > 50 µg oral | 92 | 2 | 0 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 97 | 3 | 85 | 14 | 2 |
| 13. Misoprostol titrated | 100 | 0 | 0 | 92 | 8 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 14. Misoprostol pessary (slow release) | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 15. Oxytocin i.v. | 72 | 3 | 0 | 42 | 58 | 2 | 97 | 2 | 71 | 19 | 10 |
| 16. Amniotomy | 86 | 0 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 |
| 17. Oxytocin i.v. + amniotomy | 63 | 4 | 0 | 38 | 63 | 4 | 96 | 0 | 50 | 21 | 29 |
| 18. NO | 100 | 0 | 0 | 71 | 29 | 0 | 65 | 35 | 65 | 35 | 0 |
| 19. Mifepristone | 89 | 11 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 22 | 44 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 33 |
| 20. Oestrogens | 75 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 88 | 13 | 75 | 25 | 0 |
| 21. Corticosteroids | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 22. Relaxin | 100 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 23. Hyaluronidase | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| 24. Foley catheter | 89 | 0 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 74 | 21 | 4 |
| 25. Laminaria | 44 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 88 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 88 | 13 | 0 |
| 26. Ballon catheter | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 38 | 50 | 13 |
| 27. Membrane sweeping | 64 | 0 | 0 | 61 | 39 | 0 | 7 | 93 | 61 | 32 | 7 |
| 28. PGE2 extra-amniotic | 55 | 0 | 0 | 55 | 45 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 64 | 9 | 27 |
| 29. Prostaglandins i.v. | 71 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 71 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 43 | 0 | 57 |
| 30. Sexual intercourse | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 31. Acupuncture | 82 | 0 | 0 | 64 | 36 | 0 | 18 | 82 | 36 | 64 | 0 |
| 32. Breast stimulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 33. Homeopathy | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 34. Castor oil | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 35. Prostaglandins oral | 29 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 93 | 7 | 93 | 0 | 29 | 7 | 64 |
| 36. Misoprostol buccal | 83 | 0 | 0 | 61 | 39 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 83 | 11 | 6 |
| Treatment | Previous CS | Parity | Membranes | Cervix | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | None | Some | All | NR | Nulli only | Mixed | Multi only | NR | Intact | Mixed | Ruptured | NR | Fav | Mixed | Unfav | |
| 1. No treatment | 38 | 51 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 17 | 74 | 2 | 9 | 51 | 0 | 40 | 32 | 2 | 43 | 23 |
| 2. Placebo | 24 | 69 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 19 | 76 | 2 | 26 | 50 | 7 | 17 | 14 | 2 | 21 | 62 |
| 3. Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 29 | 68 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 35 | 58 | 6 | 32 | 45 | 10 | 13 | 3 | 3 | 29 | 65 |
| 4. Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 18 | 68 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 86 | 0 | 7 | 52 | 27 | 14 | 5 | 2 | 34 | 59 |
| 5. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 26 | 68 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 84 | 5 | 5 | 53 | 26 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 37 | 63 |
| 6. PGF2 gel | 29 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 57 | 14 | 0 | 29 | 43 | 0 | 29 | 29 |
| 7. Intracervical PGE2 | 24 | 65 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 11 | 87 | 0 | 20 | 53 | 18 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 11 | 85 |
| 8. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 32 | 59 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 18 | 73 | 5 | 41 | 36 | 9 | 14 | 0 | 9 | 27 | 64 |
| 9. Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 11 | 86 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 92 | 3 | 8 | 50 | 39 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 19 | 72 |
| 10. Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 7 | 87 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 13 | 76 | 6 | 21 | 41 | 31 | 6 | 13 | 1 | 17 | 69 |
| 11. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 12. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 3 | 87 | 11 | 0 | 3 | 16 | 82 | 0 | 26 | 24 | 16 | 34 | 16 | 3 | 26 | 55 |
| 13. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 80 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 60 |
| 14. Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 15. i.v. oxytocin | 24 | 73 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 17 | 71 | 7 | 16 | 26 | 11 | 47 | 21 | 7 | 24 | 47 |
| 16. Amniotomy | 20 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 20 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| 17. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 39 | 50 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 22 | 61 | 11 | 33 | 61 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 39 | 56 | 6 |
| 18. NO | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 19. Mifepristone | 0 | 50 | 33 | 17 | 0 | 17 | 67 | 17 | 17 | 67 | 17 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 83 |
| 20. Oestrogens | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 21. Relaxin | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 33 | 33 |
| 22. Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 19 | 78 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 78 | 4 | 7 | 81 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 96 |
| 23. Mechanical methods – laminaria | 20 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 0 | 80 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 24. Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 29 | 57 | 14 | 0 | 29 | 14 | 57 | 0 | 14 | 86 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 25. Membrane sweeping | 53 | 35 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 12 | 82 | 6 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 71 | 12 |
| 26. Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 29 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 27. i.v. prostaglandin | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 |
| 28. Sexual intercourse | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 29. Acupuncture | 43 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 57 | 14 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 29 | 43 |
| 30. Homeopathy | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 31. Oral prostaglandins | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 25 | 63 | 0 | 38 | 38 | 0 | 25 | 13 | 13 | 25 | 50 |
| 32. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0 | 89 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 78 | 0 | 44 | 11 | 33 | 11 | 0 | 11 | 22 | 67 |
| Treatment | Gestation | Singleton/multiple pregnancy | Risk level | Setting | Funding | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | All post term | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | All preterm | NR | Singleton | Mixed | Multiple | Low (1) | High (2) | NR | Hospital | Outpatient | NR/NC | None | Some | |
| 1. No treatment | 0 | 26 | 64 | 9 | 2 | 26 | 74 | 0 | 0 | 49 | 51 | 6 | 43 | 51 | 70 | 21 | 9 |
| 2. Placebo | 7 | 26 | 48 | 19 | 0 | 24 | 74 | 2 | 0 | 81 | 19 | 2 | 74 | 24 | 60 | 12 | 29 |
| 3. Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 10 | 6 | 74 | 10 | 0 | 23 | 74 | 3 | 0 | 26 | 74 | 90 | 6 | 3 | 84 | 10 | 6 |
| 4. Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 7 | 7 | 64 | 23 | 0 | 20 | 68 | 11 | 0 | 68 | 32 | 0 | 93 | 7 | 66 | 25 | 9 |
| 5. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 5 | 5 | 58 | 32 | 0 | 21 | 74 | 5 | 0 | 58 | 42 | 0 | 95 | 5 | 42 | 42 | 16 |
| 6. PGF2 gel | 29 | 0 | 43 | 29 | 0 | 14 | 86 | 0 | 0 | 71 | 29 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 71 | 0 | 29 |
| 7. Intracervical PGE2 | 5 | 5 | 56 | 33 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 49 | 51 | 0 | 95 | 5 | 80 | 9 | 11 |
| 8. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 18 | 5 | 41 | 36 | 0 | 18 | 77 | 5 | 0 | 55 | 45 | 0 | 95 | 5 | 86 | 5 | 9 |
| 9. Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 6 | 14 | 64 | 17 | 0 | 8 | 92 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 3 | 92 | 6 | 81 | 17 | 3 |
| 10. Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 11 | 4 | 53 | 31 | 0 | 6 | 93 | 1 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 1 | 97 | 1 | 84 | 14 | 1 |
| 11. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 12. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 5 | 0 | 66 | 29 | 0 | 3 | 95 | 3 | 0 | 74 | 26 | 0 | 97 | 3 | 87 | 11 | 3 |
| 13. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0 | 0 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 20 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 60 | 40 | 0 |
| 14. Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 15. i.v. oxytocin | 14 | 4 | 56 | 24 | 1 | 14 | 84 | 1 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 1 | 97 | 1 | 69 | 20 | 11 |
| 16. Amniotomy | 20 | 0 | 60 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 0 |
| 17. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 6 | 17 | 72 | 6 | 0 | 17 | 78 | 6 | 0 | 39 | 61 | 11 | 89 | 0 | 56 | 17 | 28 |
| 18. NO | 0 | 40 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 60 | 40 | 60 | 40 | 0 |
| 19. Mifepristone | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 83 | 17 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 17 | 33 | 50 | 83 | 0 | 17 |
| 20. Oestrogens | 0 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 67 | 33 | 0 |
| 21. Relaxin | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 67 |
| 22. Foley catheter | 4 | 4 | 56 | 37 | 0 | 4 | 96 | 0 | 0 | 63 | 37 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 63 | 30 | 7 |
| 23. Laminaria | 20 | 0 | 60 | 20 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 24. Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 43 | 43 | 14 |
| 25. Membrane sweeping | 0 | 41 | 59 | 0 | 0 | 47 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 65 | 35 | 0 | 6 | 94 | 59 | 29 | 12 |
| 26. Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 43 | 0 | 43 | 14 | 0 | 43 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 71 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 57 | 0 | 43 |
| 27. i.v. prostaglandin | 0 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| 28. Sexual intercourse | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 29. Acupuncture | 0 | 71 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 86 | 0 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 0 | 29 | 71 | 29 | 71 | 0 |
| 30. Homeopathy | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 31. Oral prostaglandins | 25 | 0 | 63 | 13 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 75 |
| 32. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 11 | 0 | 78 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 78 | 22 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 89 | 11 | 0 |
| Treatment | Previous CS | Parity | Membranes | Cervix | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | None | Some | All | NR | Nulli only | Mixed | Multi only | NR | Intact | Mixed | Ruptured | NR | Fav | Mixed | Unfav | |
| 1. No treatment | 37 | 54 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 85 | 4 | 13 | 44 | 0 | 42 | 35 | 6 | 23 | 37 |
| 2. Placebo | 26 | 64 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 18 | 77 | 0 | 15 | 64 | 8 | 13 | 10 | 0 | 15 | 74 |
| 3. Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 19 | 77 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 31 | 58 | 8 | 27 | 46 | 15 | 12 | 4 | 8 | 19 | 69 |
| 4. Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 21 | 63 | 17 | 0 | 6 | 15 | 77 | 2 | 10 | 46 | 29 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 23 | 67 |
| 5. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 23 | 64 | 14 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 91 | 0 | 9 | 55 | 32 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 82 |
| 6. PGF2 gel | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7. Intracervical PGE2 | 34 | 56 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 85 | 0 | 24 | 55 | 15 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 15 | 79 |
| 8. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 48 | 48 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 76 | 0 | 38 | 43 | 0 | 19 | 5 | 10 | 14 | 71 |
| 9. Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 93 | 7 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 91 | 0 | 7 | 43 | 37 | 13 | 9 | 0 | 17 | 74 |
| 10. Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 7 | 85 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 89 | 0 | 11 | 56 | 25 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 18 | 79 |
| 11. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 12. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0 | 94 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 85 | 3 | 15 | 26 | 29 | 29 | 18 | 3 | 24 | 56 |
| 13. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 86 |
| 14. Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 15. i.v. oxytocin | 28 | 66 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 15 | 78 | 1 | 18 | 24 | 4 | 54 | 21 | 4 | 24 | 51 |
| 16. Amniotomy | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 17. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 36 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 73 | 9 | 36 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 45 | 36 | 0 |
| 18. NO | 20 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 70 | 0 | 10 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 19. Mifepristone | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 25 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 20. Oestrogens | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 21. Corticosteroids | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 22. Relaxin | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 23. Foley catheter | 15 | 80 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 80 | 5 | 0 | 90 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 85 |
| 24. Laminaria | 25 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 25. Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 26. Membrane sweeping | 64 | 27 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 91 | 9 | 9 | 91 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 64 | 27 |
| 27. Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 28. i.v. prostaglandin | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 29. Sexual intercourse | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30. Acupuncture | 40 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 40 | 20 |
| 31. Breast stimulation | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 32. Castor oil | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 33. Oral prostaglandins | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 83 | 0 | 33 | 33 | 17 | 17 | 50 | 0 | 33 | 17 |
| 34. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 82 | 0 | 18 | 36 | 36 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 36 | 45 |
| Treatment | Gestation | Singleton/multiple pregnancy | Risk level | Setting | Funding | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | All post term | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | All preterm | NR | Singleton | Mixed | Multiple | Low | High | NR | Hospital | Outpatient | NR/NC | None | Some | |
| 1. No treatment | 2 | 29 | 48 | 17 | 4 | 29 | 67 | 2 | 2 | 48 | 52 | 8 | 56 | 37 | 65 | 29 | 6 |
| 2. Placebo | 18 | 33 | 41 | 8 | 0 | 18 | 79 | 3 | 0 | 77 | 23 | 3 | 64 | 33 | 67 | 21 | 13 |
| 3. Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 8 | 12 | 77 | 4 | 0 | 15 | 81 | 4 | 0 | 31 | 69 | 0 | 96 | 4 | 77 | 15 | 8 |
| 4. Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 8 | 8 | 58 | 25 | 0 | 25 | 67 | 8 | 0 | 73 | 27 | 0 | 92 | 8 | 67 | 29 | 4 |
| 5. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 5 | 5 | 45 | 45 | 0 | 5 | 95 | 0 | 0 | 68 | 32 | 0 | 95 | 5 | 45 | 45 | 9 |
| 6. PGF2 gel | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 7. Intracervical PGE2 | 10 | 10 | 50 | 31 | 0 | 31 | 68 | 2 | 0 | 48 | 52 | 0 | 92 | 8 | 82 | 8 | 10 |
| 8. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 10 | 14 | 33 | 43 | 0 | 38 | 62 | 0 | 0 | 48 | 52 | 0 | 86 | 14 | 90 | 10 | 0 |
| 9. Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 7 | 65 | 26 | 2 | 7 | 89 | 4 | 0 | 83 | 17 | 0 | 93 | 7 | 74 | 20 | 7 |
| 10. Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 5 | 7 | 62 | 26 | 0 | 2 | 95 | 3 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 98 | 2 | 80 | 18 | 2 |
| 11. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 75 | 25 | 0 |
| 12. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 3 | 6 | 62 | 29 | 0 | 3 | 94 | 3 | 0 | 76 | 24 | 0 | 94 | 6 | 82 | 18 | 0 |
| 13. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0 | 14 | 43 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 86 | 14 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 29 | 71 | 0 |
| 14. Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 15. i.v. oxytocin | 4 | 9 | 53 | 29 | 4 | 22 | 75 | 3 | 0 | 49 | 51 | 3 | 96 | 1 | 68 | 24 | 9 |
| 16. Amniotomy | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 17. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0 | 27 | 73 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 73 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 73 | 9 | 91 | 0 | 45 | 36 | 18 |
| 18. NO | 10 | 30 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 70 | 30 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 60 | 0 |
| 19. Mifepristone | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| 20. Oestrogens | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 21. Corticosteroids | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 22. Relaxin | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 23. Foley catheter | 5 | 5 | 65 | 25 | 0 | 5 | 95 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 65 | 30 | 5 |
| 24. Laminaria | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 |
| 25. Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 |
| 26. Membrane sweeping | 0 | 45 | 55 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 18 | 0 | 9 | 91 | 45 | 45 | 9 |
| 27. Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 33 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 33 |
| 28. i.v. prostaglandin | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 67 |
| 29. Sexual intercourse | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 30. Acupuncture | 0 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 80 | 20 | 80 | 0 |
| 31. Breast stimulation | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 32. Castor oil | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 33. Oral prostaglandins | 17 | 0 | 83 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 17 | 0 | 17 | 17 | 83 | 17 | 83 | 0 | 50 | 17 | 33 |
| 34. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0 | 0 | 91 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 91 | 0 | 0 | 91 | 9 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 73 | 18 | 9 |
| Treatment | Previous CS | Parity | Membranes | Cervix | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | None | Some | All | NR | Nulli only | Mixed | Multi only | NR | Intact | Mixed | Ruptured | NR | Fav | Mixed | Unfav | |
| 1. No treatment | 43 | 49 | 8 | 0 | 5 | 16 | 78 | 0 | 8 | 54 | 0 | 38 | 38 | 3 | 30 | 30 |
| 2. Placebo | 21 | 71 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 4 | 71 | 4 | 21 | 13 | 0 | 21 | 67 |
| 3. Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 67 | 11 | 22 | 44 | 22 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 11 | 78 |
| 4. Vaginal PGE2 gel | 9 | 74 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 88 | 0 | 3 | 41 | 35 | 21 | 6 | 3 | 29 | 62 |
| 5. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 16 | 79 | 5 | 0 | 11 | 5 | 84 | 0 | 11 | 58 | 21 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 95 |
| 6. PGF2 gel | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 7. Intracervical PGE2 | 16 | 76 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 96 | 0 | 12 | 72 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 20 | 76 |
| 8. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 30 | 70 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 30 | 60 | 0 | 30 | 30 | 0 | 40 | 20 | 0 | 30 | 50 |
| 9. Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 92 | 8 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 94 | 0 | 8 | 45 | 39 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 18 | 76 |
| 10. Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 2 | 87 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 87 | 5 | 15 | 47 | 31 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 16 | 76 |
| 11. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 12. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0 | 92 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 90 | 0 | 13 | 31 | 28 | 28 | 15 | 3 | 23 | 59 |
| 13. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 11 | 11 | 78 | 0 | 22 | 0 | 11 | 67 |
| 14. Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 15. i.v. oxytocin | 23 | 69 | 9 | 0 | 6 | 11 | 74 | 9 | 11 | 20 | 9 | 60 | 29 | 3 | 26 | 43 |
| 16. Amniotomy | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 17. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 17 | 83 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 67 | 17 | 17 | 83 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 18. NO | 22 | 78 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 44 | 56 | 0 | 22 | 78 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 19. Mifepristone | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 20. Oestrogens | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 21. Foley catheter | 5 | 84 | 11 | 0 | 5 | 11 | 79 | 5 | 0 | 74 | 21 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 95 |
| 22. Laminaria | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 23. Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 24. Membrane sweeping | 64 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 91 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 45 | 45 |
| 25. Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| 26. Sexual intercourse | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 27. Acupuncture | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 33 | 33 |
| 28. Oral prostaglandins | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 29. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0 | 90 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 80 | 0 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 70 |
| Treatment | Gestation | Singleton/multiple pregnancy | Risk level | Setting | Funding | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | All post term | All > 37 weeks | Mixed | All preterm | NR | Singleton | Mixed | Multiple | Low (1) | High (2) | NR | Hospital | Outpatient | NR/NC | None | Some | |
| 1. No treatment | 0 | 32 | 51 | 14 | 3 | 16 | 84 | 0 | 0 | 57 | 43 | 5 | 46 | 49 | 59 | 38 | 3 |
| 2. Placebo | 4 | 42 | 50 | 4 | 0 | 17 | 83 | 0 | 0 | 83 | 17 | 0 | 38 | 63 | 63 | 29 | 8 |
| 3. Vaginal PGE2 tablet | 11 | 0 | 89 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 78 | 11 | 0 | 56 | 44 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 78 | 22 | 0 |
| 4. Vaginal PGE2 gel | 3 | 9 | 68 | 21 | 0 | 12 | 76 | 12 | 0 | 91 | 9 | 0 | 88 | 12 | 59 | 35 | 6 |
| 5. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 5 | 11 | 42 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 74 | 26 | 0 | 95 | 5 | 42 | 47 | 11 |
| 6. PGF2 gel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 7. Intracervical PGE2 | 4 | 12 | 56 | 28 | 0 | 16 | 84 | 0 | 0 | 52 | 48 | 0 | 76 | 24 | 84 | 16 | 0 |
| 8. Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0 | 30 | 50 | 20 | 0 | 30 | 70 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 70 | 30 | 90 | 10 | 0 |
| 9. Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 2 | 8 | 55 | 35 | 0 | 8 | 88 | 4 | 0 | 76 | 24 | 0 | 92 | 8 | 78 | 20 | 2 |
| 10. Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 7 | 4 | 49 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 96 | 4 | 0 | 73 | 27 | 0 | 98 | 2 | 29 | 24 | 47 |
| 11. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 0 | 75 | 25 | 75 | 25 | 0 |
| 12. Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0 | 5 | 56 | 36 | 0 | 3 | 95 | 3 | 0 | 69 | 31 | 0 | 95 | 5 | 85 | 13 | 3 |
| 13. Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0 | 0 | 44 | 56 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 11 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 56 | 44 | 0 |
| 14. Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 15. i.v. oxytocin | 3 | 9 | 51 | 34 | 3 | 3 | 91 | 6 | 0 | 63 | 37 | 3 | 94 | 3 | 63 | 31 | 6 |
| 16. Amniotomy | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 17. i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 83 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 17 | 83 | 0 | 33 | 50 | 17 |
| 18. NO | 11 | 44 | 44 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 44 | 56 | 44 | 56 | 0 |
| 19. Mifepristone | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 20. Oestrogens | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 21. Foley catheter | 0 | 5 | 68 | 26 | 0 | 5 | 95 | 0 | 0 | 74 | 26 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 58 | 37 | 5 |
| 22. Laminaria | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 23. Double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 24. Membrane sweeping | 0 | 36 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 91 | 0 | 0 | 73 | 27 | 0 | 9 | 91 | 27 | 64 | 9 |
| 25. Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 26. Sexual intercourse | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 27. Acupuncture | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 28. Oral prostaglandins | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 29. Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0 | 0 | 80 | 20 | 0 | 10 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 10 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 70 | 20 | 10 |
Appendix 8 Example OpenBUGS code
Appendix 9 Details of priors and convergence checks
Prior distributions used in the network meta-analyses of outcomes reported in the paper
No vaginal delivery within 24 hours
All prior distributions in the VD REs consistency model were vague.
Trial baseline parameter: mu∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Treatment effect parameter: d∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Heterogeneity parameter: sd∼dunif (0,5)
Caesarean section
All prior distributions in the CS REs consistency model were vague.
Trial baseline parameter: mu∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Treatment effect parameter: d∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Heterogeneity parameter: sd∼dunif (0,5)
Hyperstimulation
All prior distributions in the hyperstimulation REs consistency model were vague.
Trial baseline parameter: mu∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Treatment effect parameter: d∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Heterogeneity parameter: sd∼dunif (0,5)
Instrumental delivery
All prior distributions in the hyperstimulation REs consistency model were vague.
Trial baseline parameter: mu∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Treatment effect parameter: d∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Heterogeneity parameter: sd∼dunif (0,5)
Neonatal intensive care unit admission
All prior distributions in the hyperstimulation REs consistency model were vague.
Trial baseline parameter: mu∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Treatment effect parameter: d∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Heterogeneity parameter: sd∼dunif (0,5)
Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
All prior distributions in the hyperstimulation REs consistency model were vague.
Trial baseline parameter: mu∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Treatment effect parameter: d∼dnorm(0, 0001)
Heterogeneity parameter: sd∼dunif (0, 2)
Details of convergence for all three outcomes reported in the paper for random-effects consistency models
No vaginal delivery within 24 hours
Convergence was assessed using two chains using the Brooks–Gelman–Rubin tool in OpenBUGS, and was achieved by 15,000 simulations for VD (REs consistency model). Estimates are based on a further 100,000 updates.
Caesarean section
Convergence was assessed using two chains using the Brooks–Gelman–Rubin tool in OpenBUGS, and was achieved by 49,000 simulations for CS (REs consistency model – risk of bias – continuity corrected model). Estimates are based on a further 150,000 updates.
Hyperstimulation
Convergence was assessed using two chains using the Brooks–Gelman–Rubin tool in OpenBUGS and was achieved by 26,000 simulations (REs consistency – continuity corrected model). Estimates are based on a further 75,000 updates.
Instrumental delivery
Convergence was assessed using two chains using the Brooks–Gelman–Rubin tool in OpenBUGS, and was achieved by 58,000 simulations (REs consistency model). Estimates are based on a further 58,000 updates.
Neonatal intensive care unit admission
Convergence was assessed using two chains using the Brooks–Gelman–Rubin tool in OpenBUGS, and was achieved by 36,000 simulations (REs consistency model – Rath 2007 removed). Estimates are based on a further 100,000 updates.
Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
Convergence was assessed using two chains using the Brooks–Gelman–Rubin tool in OpenBUGS, and was achieved by 68,000 simulations (REs consistency model). Estimates are based on a further 68,000 updates.
Appendix 10 Total number of arms in trials
| Treatment | Number of arms |
|---|---|
| No treatment | 108 |
| Placebo | 99 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 54 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 103 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 46 |
| PGF2 gel | 11 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 140 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 37 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 86 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 129 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 4 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 67 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 12 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 2 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 135 |
| Amniotomy | 7 |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 25 |
| NO | 17 |
| Mifepristone | 9 |
| Oestrogens | 8 |
| Corticosteroids | 2 |
| Relaxin | 4 |
| Hyaluronidase | 2 |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 51 |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 16 |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 9 |
| Membrane sweeping | 30 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 11 |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 7 |
| Sexual intercourse | 2 |
| Acupuncture | 11 |
| Breast stimulation | 4 |
| Homeopathy | 1 |
| Castor oil | 1 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 14 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 19 |
Appendix 11 Model fit and heterogeneity
Model fit and selection statistics by outcomes: fixed- and random-effects models
For REs models we also compared the fit of consistency and inconsistency models.
| Model | Number of data points | Residual deviance (posterior mean) | SD (posterior median) and 95% CrI | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency | 290 | 301.1 | 0.54 (0.44 to 0.65) | 1854 |
| REs inconsistency | 290 | 293.2 | 0.48 (0.37 to 0.62) | 1855 |
| Model | Number of data points | Residual deviance (posterior mean) | SD (posterior median) and 95% CrI | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency | 1217 | 1275 | 0.25 (0.18 to 0.31) | 6668 |
| REs inconsistency | 1217 | 1266 | 0.22 (0.15 to 0.3) | 6729 |
| REs consistency – continuity corrected | 1217 | 1248 | 0.2463 (0.1824 to 0.3075) | 6678 |
| REs inconsistency – continuity corrected | 1217 | 1242 | 0.2224 (0.1494 to 0.2927) | 6741 |
| FEs consistency – ROB | 640 | 696.0 | 3607 | |
| REs consistency – ROB – continuity corrected | 640 | 650.6 | 0.1558 (0.02545 to 0.2502) | 3600 |
| REs inconsistency – ROB – continuity corrected | 640 | 647.7 | 0.1349 (0.014 to 0.243) | 3658 |
| Model | Number of data points | Residual deviance (posterior mean) | SD (posterior median) and 95% CrI | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency | 616 | 622.8 | 0.1506 (0.028 to 0.269) | 3198 |
| REs inconsistency | 616 | 617.4 | 0.1903 (0.047 to 0.325) | 3266 |
| Model | Number of data points | Residual deviance (posterior mean) | SD (posterior median) and 95% CrI | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency | 374 | 395.7 | 0.7008 (0.4895 to 0.9465) | 1509 |
| REs inconsistency | 374 | 368.7 | 0.7053 (0.4656 to 0.9909) | 1491 |
| REs consistency – zeros in baseline removed | 284 | 283.3 | 0.5684 (0.3898 to 0.7779) | 1226 |
| REs consistency – continuity corrected | 374 | 349 | 0.54 (0.38 to 0.72) | 1590 |
| REs inconsistency – continuity corrected | 374 | 359.7 | 0.55 (0.36 to 0.77) | 1630 |
| Model | Number of data points | Residual deviance (posterior mean) | SD (posterior mean) and 95% CrI | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency | 413 | 450 | 0.1867 (0.011 to 0.458) | 1569 |
| REs inconsistency | 413 | 423.2 | 0.1617 (0.004 to 0.482) | 1573 |
| REs consistency – continuity corrected | 413 | 374.9 | 0.1323 (0.008 to 0.3486) | 1626 |
| REs consistency – zeros in baseline removed | 335 | 341.8 | 0.1547 (0.006 to 0.4242) | 1337 |
| REs consistency – no zeros | 250 | 213.5 | 0.1209 (0.005 to 0.3337) | 1059 |
| Model | Number of data points | Residual deviance (posterior mean) | SD (posterior median) and 95% CrI | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency | 428 | 449.4 | 0.2843 (0.1801 to 0.3949) | 2116 |
| REs inconsistency | 428 | 449.4 | 0.1983 (0.05142 to 0.3426) | 2144 |
| REs consistency – Rath 2007504 removed | 426 | 454.4 | 0.1704 (0.044 to 0.293) | 2091 |
| REs inconsistency – Rath 2007504 removed | 426 | 443.8 | 0.2021 (0.0397 to 0.3479) | 2126 |
Appendix 12 Results of active versus active comparisons from network meta-analysis
Odds ratios and 95% CrIs for failure to achieve VD within 24 hours, CS, instrumental delivery, uterine hyperstimulation, NICU and Apgar score for every intervention compared with every other.
Results from NMA and pairwise meta-analysis (when possible). All are considered undesirable outcomes. An OR of > 1 favours placebo (i.e. fewer events occur on a placebo than active treatment). An OR of < 1 favours the active treatment (i.e. fewer undesirable events occurred on the active treatment). Empty cells indicate that direct evidence was not available for that comparison.
| Control treatment | Active treatment | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | ||
| No treatment | Placebo | 0.84 | 0.28 to 1.97 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.11 | 0.04 to 0.24 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.09 | 0.04 to 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.08 to 1.14 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.10 | 0.04 to 0.22 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.13 | 0.05 to 0.26 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.06 | 0.02 to 0.15 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.07 | 0.03 to 0.14 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.06 | 0.03 to 0.12 | 0.00 | 0 to 0 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.15 | 0.05 to 0.37 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.11 | 0.05 to 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.04 to 0.32 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.07 | 0.03 to 0.15 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.07 | 0.02 to 0.19 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.14 | 0.05 to 0.29 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.04 | 0.01 to 0.11 | |||
| NO | 0.16 | 0.05 to 0.4 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.58 | 0.12 to 1.77 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.12 | 0.05 to 0.26 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.11 | 0.03 to 0.26 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.28 | 0.05 to 0.94 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.07 | 0.03 to 0.15 | |||
| Placebo | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.15 | 0.06 to 0.29 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.12 | 0.06 to 0.21 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.14 | 0.06 to 0.26 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.17 | 0.08 to 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.03 to 0.19 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.08 | 0.03 to 0.18 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.09 | 0.05 to 0.17 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.08 | 0.04 to 0.14 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose > 50 µg) | 0.20 | 0.07 to 0.45 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.15 | 0.07 to 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.03 to 0.31 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.09 | 0.04 to 0.18 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.09 | 0.03 to 0.23 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.18 | 0.08 to 0.34 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.05 | 0.01 to 0.14 | |||
| NO | 0.21 | 0.08 to 0.42 | 1.07 | 0.3 to 2.78 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.72 | 0.2 to 1.85 | 0.8148 | 0.16 to 2.52 | |
| Mechanical method – Foley catheter | 0.16 | 0.07 to 0.31 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.14 | 0.05 to 0.32 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.37 | 0.07 to 1.2 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.10 | 0.04 to 0.18 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.83 | 0.51 to 1.27 | 0.9212 | 0.36 to 1.96 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.97 | 0.57 to 1.55 | 1.384 | 0.39 to 3.58 | |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.19 | 0.74 to 1.82 | 1.512 | 0.42 to 3.93 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.60 | 0.27 to 1.14 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.67 | 0.41 to 1.03 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.57 | 0.37 to 0.85 | 0.495 | 0.27 to 0.84 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.41 | 0.57 to 2.92 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.05 | 0.64 to 1.62 | 1.28 | 0.36 to 3.33 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.65 | 0.35 to 1.1 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.67 | 0.24 to 1.49 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.28 | 0.71 to 2.13 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.34 | 0.08 to 0.9 | 0.5467 | 0.09 to 1.77 | |
| NO | 1.50 | 0.6 to 3.19 | |||
| Mifepristone | 5.39 | 1.36 to 14.92 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.14 | 0.61 to 1.95 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.01 | 0.42 to 2.07 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.62 | 0.53 to 8.07 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.68 | 0.37 to 1.13 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.19 | 0.78 to 1.73 | 1.415 | 0.34 to 3.97 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.45 | 1.05 to 1.96 | 1.455 | 0.85 to 2.33 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.73 | 0.37 to 1.3 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.82 | 0.59 to 1.1 | 1.346 | 0.6 to 2.63 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.70 | 0.51 to 0.93 | 0.6249 | 0.37 to 0.98 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.72 | 0.78 to 3.32 | 1.508 | 0.42 to 3.91 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.28 | 0.9 to1.76 | 1.883 | 0.81 to 3.76 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.79 | 0.5 to 1.19 | 1.15 | 0.61 to 1.99 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.81 | 0.31 to 1.75 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.56 | 1 to 2.32 | 3.315 | 1.04 to 8.21 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.42 | 0.1 to 1.15 | |||
| NO | 1.83 | 0.81 to 3.62 | 0.5922 | 0.18 to 1.47 | |
| Mifepristone | 6.57 | 1.78 to 17.45 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.39 | 0.85 to 2.13 | 1.498 | 0.66 to 2.95 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.23 | 0.56 to 2.35 | 1.603 | 0.45 to 4.12 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 3.20 | 0.67 to 9.66 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.83 | 0.51 to 1.27 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | Intracervical PGE2 | 1.26 | 0.85 to 1.79 | 1.914 | 0.99 to 3.37 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.63 | 0.31 to 1.15 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.71 | 0.48 to 1.01 | 0.8789 | 0.34 to 1.86 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.60 | 0.41 to 0.85 | 0.5678 | 0.3 to 0.98 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.49 | 0.63 to 3.02 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.10 | 0.72 to 1.63 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.68 | 0.41 to 1.08 | 0.617 | 0.16 to 1.65 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.68 | 0.29 to 1.36 | 0.674 | 0.31 to 1.27 | |
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.35 | 0.82 to 2.09 | 2.448 | 0.74 to 6.12 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.36 | 0.09 to 1.01 | |||
| NO | 1.59 | 0.65 to 3.29 | |||
| Mifepristone | 5.68 | 1.49 to 15.4 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.20 | 0.71 to 1.9 | 0.87 | 0.27 to 2.15 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.06 | 0.48 to 2.02 | 0.5246 | 0.15 to 1.37 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.76 | 0.57 to 8.46 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.71 | 0.42 to 1.15 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.50 | 0.27 to 0.85 | 0.7594 | 0.39 to 1.34 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.57 | 0.43 to 0.74 | 0.5204 | 0.34 to 0.75 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.49 | 0.36 to 0.64 | 0.4747 | 0.3 to 0.71 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.20 | 0.53 to 2.34 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.89 | 0.64 to 1.2 | 0.955 | 0.49 to 1.68 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.55 | 0.34 to 0.84 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.57 | 0.22 to 1.21 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.09 | 0.69 to 1.62 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.29 | 0.07 to 0.8 | |||
| NO | 1.27 | 0.56 to 2.55 | |||
| Mifepristone | 4.57 | 1.25 to 12.05 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.97 | 0.59 to 1.5 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.86 | 0.39 to 1.66 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.23 | 0.47 to 6.71 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.57 | 0.36 to 0.87 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.23 | 0.63 to 2.17 | ||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.05 | 0.54 to 1.86 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 2.60 | 0.93 to 5.85 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.92 | 0.97 to 3.46 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.19 | 0.55 to 2.27 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.22 | 0.39 to 2.96 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 2.34 | 1.13 to 4.35 | 37.7 | 2.63 to 187.2 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.63 | 0.13 to 1.88 | |||
| NO | 2.76 | 0.96 to 6.37 | |||
| Mifepristone | 9.86 | 2.3 to 28.31 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 2.07 | 0.99 to 3.85 | 4.696 | 1.09 to 13.54 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.85 | 0.68 to 4.09 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 4.81 | 0.89 to 15.63 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.24 | 0.58 to 2.36 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.86 | 0.65 to 1.1 | 1.122 | 0.68 to 1.76 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 2.12 | 0.97 to 4.07 | 4.206 | 1.18 to 10.86 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.57 | 1.17 to 2.08 | 1.347 | 0.84 to 2.07 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.98 | 0.63 to 1.46 | 0.3878 | 0.15 to 0.8 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.00 | 0.39 to 2.15 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.92 | 1.27 to 2.8 | 1.843 | 0.75 to 3.83 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.52 | 0.13 to 1.41 | |||
| NO | 2.26 | 0.98 to 4.56 | |||
| Mifepristone | 8.11 | 2.21 to 21.51 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.71 | 1.07 to 2.61 | 2.508 | 1.17 to 4.81 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.52 | 0.69 to 2.93 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 3.95 | 0.85 to 11.91 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.01 | 0.67 to 1.47 | 1.045 | 0.61 to 1.68 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 2.49 | 1.12 to 4.84 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.84 | 1.36 to 2.45 | 1.608 | 0.9 to 2.67 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.15 | 0.72 to 1.74 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.17 | 0.46 to 2.5 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 2.25 | 1.47 to 3.32 | 2.558 | 0.78 to 6.32 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.61 | 0.15 to 1.65 | |||
| NO | 2.64 | 1.17 to 5.24 | 2.17 | 0.52 to 6.15 | |
| Mifepristone | 9.50 | 2.59 to 25.22 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 2.01 | 1.24 to 3.08 | 1.646 | 0.43 to 4.45 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.78 | 0.81 to 3.43 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 4.58 | 1.02 to 13.56 | 4.469 | 1.09 to 12.59 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.19 | 0.78 to 1.74 | 1.01 | 0.49 to 1.84 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.84 | 0.38 to 1.62 | 1.395 | 0.37 to 3.72 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.52 | 0.21 to 1.07 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.54 | 0.15 to 1.38 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.03 | 0.43 to 2.1 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.28 | 0.05 to 0.85 | |||
| NO | 1.21 | 0.38 to 2.96 | |||
| Mifepristone | 4.35 | 0.93 to 13.12 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.92 | 0.37 to 1.91 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.82 | 0.27 to 1.94 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.11 | 0.36 to 7.05 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.54 | 0.23 to 1.11 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.63 | 0.39 to 0.96 | 3.052 | 0.57 to 9.83 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.65 | 0.25 to 1.4 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.24 | 0.8 to 1.82 | 0.8035 | 0.35 to 1.59 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.33 | 0.08 to 0.91 | |||
| NO | 1.46 | 0.63 to 2.93 | |||
| Mifepristone | 5.21 | 1.42 to 13.82 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.10 | 0.66 to 1.73 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.98 | 0.44 to 1.91 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.54 | 0.54 to 7.7 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.65 | 0.42 to 0.97 | 0.6002 | 0.24 to 1.25 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.07 | 0.38 to 2.37 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin | 2.03 | 1.23 to 3.18 | 1.868 | 0.84 to 3.64 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.55 | 0.13 to 1.56 | |||
| NO | 2.41 | 0.96 to 5.12 | |||
| Mifepristone | 8.61 | 2.23 to 23.54 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.82 | 1.01 to 3.03 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.62 | 0.68 to 3.27 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 4.21 | 0.85 to 13.02 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.08 | 0.6 to 1.8 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | i.v. oxytocin | 2.29 | 0.84 to 5.1 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.62 | 0.11 to 1.99 | |||
| NO | 2.70 | 0.76 to 7.03 | |||
| Mifepristone | 9.69 | 1.87 to 30.74 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 2.04 | 0.73 to 4.57 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.80 | 0.55 to 4.46 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 4.71 | 0.73 to 16.36 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.22 | 0.43 to 2.74 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.28 | 0.06 to 0.78 | ||
| NO | 1.22 | 0.49 to 2.54 | |||
| Mifepristone | 4.29 | 1.19 to 11.25 | 4.687 | 0.83 to 15.59 | |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.92 | 0.51 to 1.53 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.82 | 0.35 to 1.65 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.12 | 0.43 to 6.54 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.55 | 0.32 to 0.88 | 1.464 | 0.3 to 4.46 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | NO | 6.34 | 1.23 to 20.21 | ||
| Mifepristone | 22.76 | 3.17 to 83.58 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 4.80 | 1.12 to 14.05 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 4.27 | 0.85 to 13.41 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 11.04 | 1.25 to 43.52 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.80 | 0.71 to 7.82 | 5.601 | 0.73 to 21.59 | |
| NO | Mifepristone | 4.06 | 0.9 to 11.86 | ||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.87 | 0.34 to 1.84 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.77 | 0.25 to 1.86 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.00 | 0.34 to 6.72 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.52 | 0.2 to 1.08 | |||
| Mifepristone | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.29 | 0.07 to 0.8 | ||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.26 | 0.05 to 0.77 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.68 | 0.08 to 2.56 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.17 | 0.04 to 0.47 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.91 | 0.43 to 1.7 | 1.335 | 0.39 to 3.41 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.41 | 0.48 to 7.48 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.62 | 0.34 to 1.05 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.94 | 0.51 to 9.76 | ||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.76 | 0.31 to 1.55 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.40 | 0.08 to 1.22 | ||
| Control treatment | Active treatment | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | ||
| No treatment | Placebo | 1.2 | 0.91 to 1.44 | 0.53 | 0.05 to 1.91 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 1.2 | 0.9 to 1.57 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.9 | 0.74 to 1.08 | 0.86 | 0.6 to 1.17 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.0 | 0.8 to 1.28 | 16.68 | 0.43 to 105.7 | |
| PGF2 gel | 0.8 | 0.44 to 1.35 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.9 | 0.78 to 1.14 | 0.92 | 0.65 to 1.27 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.9 | 0.7 to 1.24 | 1.05 | 0.44 to 2.15 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.65 to 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.25 to 1.04 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.68 to 1.01 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.3 | 0.73 to 2.08 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.66 to 1.01 | 1.39 | 0.25 to 4.61 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.7 | 0.53 to 0.92 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.1 | 0.68 to 1.77 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.1 | 0.89 to 1.27 | 1.16 | 0.93 to 1.44 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.2 | 0.58 to 2.31 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.66 to 1.53 | |||
| NO | 0.9 | 0.69 to 1.26 | 1.41 | 0.22 to 5.09 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.8 | 0.48 to 1.29 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.5 | 0.71 to 2.68 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.6 | 0.22 to 1.3 | 0.22 | 0 to 1.05 | |
| Relaxin | 1.0 | 0.36 to 2.34 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.7 | 0.38 to 1.17 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.9 | 0.69 to 1.09 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.9 | 0.51 to 1.51 | 0.92 | 0.51 to 1.49 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.3 | 0.84 to 1.87 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.8 | 0.66 to 1.05 | 0.86 | 0.67 to 1.08 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.1 | 0.65 to 1.82 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 23.2 | 1.84 to 135.6 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.0 | 0.65 to 1.39 | 0.95 | 0.66 to 1.36 | |
| Acupuncture | 0.9 | 0.58 to 1.43 | 1.04 | 0.42 to 2.22 | |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.8 | 0.09 to 2.94 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.58 to 1.02 | |||
| Placebo | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 1.0 | 0.78 to 1.35 | 0.91 | 0 to 5.74 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.8 | 0.65 to 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.63 to 1.37 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.9 | 0.69 to 1.12 | 0.62 | 0.26 to 1.21 | |
| PGF2 gel | 0.7 | 0.4 to 1.16 | 0.65 | 0.27 to 1.3 | |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.8 | 0.69 to 0.98 | 0.85 | 0.66 to 1.09 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.8 | 0.62 to 1.09 | 0.76 | 0.41 to 1.29 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.57 to 0.85 | 1.14 | 0.58 to 2.05 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.59 to 0.88 | 1.32 | 0.17 to 4.64 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.1 | 0.64 to 1.81 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.58 to 0.88 | 0.60 | 0.35 to 0.96 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.6 | 0.47 to 0.8 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.0 | 0.59 to 1.55 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.9 | 0.75 to 1.14 | 1.74 | 0.53 to 4.29 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.51 to 2.02 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.57 to 1.34 | |||
| NO | 0.8 | 0.62 to 1.06 | 1.05 | 0.7 to 1.49 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.7 | 0.45 to 1.08 | 0.63 | 0.39 to 0.95 | |
| Oestrogens | 1.3 | 0.62 to 2.32 | 1.97 | 0.66 to 4.49 | |
| Corticosteroids | 0.5 | 0.2 to 1.12 | 0.72 | 0.25 to 1.65 | |
| Relaxin | 0.9 | 0.33 to 1.98 | 0.90 | 0.32 to 2.03 | |
| Hyaluronidase | 0.6 | 0.34 to 1 | 0.24 | 0.1 to 0.46 | |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.61 to 0.95 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.8 | 0.43 to 1.38 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.1 | 0.73 to 1.63 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.7 | 0.53 to 0.99 | 1.78 | 0.22 to 6.41 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.57 to 1.57 | 0.47 | 0.16 to 1.03 | |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 19.9 | 1.61 to 120.5 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.8 | 0.54 to 1.29 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.2 | 0.76 | 0.46 to 1.16 | |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.7 | 0.08 to 2.59 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.7 | 0.51 to 0.89 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.77 | 0.6 to 0.96 | 0.84 | 0 to 0.83 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.86 | 0.64 to 1.14 | |||
| PGF2 gel | 0.68 | 0.37 to 1.17 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.81 | 0.62 to 1.03 | 0.78 | 0 to 0.74 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.80 | 0.57 to 1.11 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.68 | 0.52 to 0.87 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.71 | 0.55 to 0.89 | 0.69 | 0 to 0.68 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.08 | 0.6 to 1.8 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.70 | 0.53 to 0.9 | 0.95 | 0 to 0.89 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.60 | 0.43 to 0.81 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.96 | 0.55 to 1.54 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.91 | 0.69 to 1.17 | 0.44 | 0 to 0.4 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.03 | 0.48 to 1.98 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.87 | 0.54 to 1.33 | |||
| NO | 0.80 | 0.57 to 1.09 | 0.88 | 0.01 to 0.81 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.70 | 0.4 to 1.12 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.24 | 0.58 to 2.32 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.52 | 0.19 to 1.14 | |||
| Relaxin | 0.86 | 0.3 to 1.98 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.59 | 0.32 to 1.01 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.74 | 0.56 to 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.01 to 0.88 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.78 | 0.4 to 1.35 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.08 | 0.69 to 1.62 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.72 | 0.49 to 1.01 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.96 | 0.53 to 1.59 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 19.56 | 1.54 to 118 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.82 | 0.5 to 1.28 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.79 | 0.47 to 1.25 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.70 | 0.08 to 2.55 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.66 | 0.48 to 0.9 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.13 | 0.91 to 1.38 | 1.579 | 0.72 to 3.03 |
| PGF2 gel | 0.89 | 0.5 to 1.48 | 1.196 | 0.33 to 3.22 | |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.06 | 0.91 to 1.23 | 1.3 | 0.94 to 1.76 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.05 | 0.8 to 1.35 | 1.753 | 0.59 to 4.1 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.89 | 0.77 to 1.03 | 0.9487 | 0.73 to 1.2 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.93 | 0.8 to 1.06 | 0.8462 | 0.66 to 1.06 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.41 | 0.83 to 2.25 | 1.005 | 0.43 to 2.02 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.91 | 0.77 to 1.07 | 1.107 | 0.77 to 1.55 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.79 | 0.63 to 0.97 | 0.8214 | 0.61 to 1.08 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.25 | 0.76 to 1.95 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.19 | 1 to 1.4 | 1.156 | 0.47 to 2.4 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.35 | 0.66 to 2.53 | 1.55 | 0.35 to 4.78 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.14 | 0.76 to 1.66 | 0.7504 | 0.35 to 1.39 | |
| NO | 1.05 | 0.79 to 1.35 | 0.9331 | 0.57 to 1.43 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.91 | 0.55 to 1.41 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.62 | 0.79 to 2.99 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.68 | 0.25 to 1.45 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.13 | 0.41 to 2.58 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.78 | 0.44 to 1.29 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.97 | 0.82 to 1.15 | 0.9701 | 0.76 to 1.22 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.02 | 0.55 to 1.72 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.42 | 0.97 to 2.02 | 1.338 | 0.72 to 2.27 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.94 | 0.69 to 1.25 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.26 | 0.73 to 2 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 25.56 | 2.05 to 155.1 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.08 | 0.7 to 1.61 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.04 | 0.65 to 1.59 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.92 | 0.1 to 3.29 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.87 | 0.68 to 1.1 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | PGF2 gel | 0.80 | 0.44 to 1.35 | ||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.94 | 0.76 to 1.17 | 0.9169 | 0.5 to 1.55 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.94 | 0.68 to 1.26 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.80 | 0.64 to 0.98 | 1.155 | 0.62 to 2 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.83 | 0.67 to 1.01 | 0.9019 | 0.61 to 1.26 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.26 | 0.72 to 2.06 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.82 | 0.64 to 1.02 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.70 | 0.53 to 0.91 | 0.4783 | 0.17 to 1.07 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.11 | 0.71 to 1.65 | 1.103 | 0.73 to 1.61 | |
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.06 | 0.85 to 1.3 | 1.502 | 0.93 to 2.29 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.21 | 0.58 to 2.3 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.02 | 0.65 to 1.53 | |||
| NO | 0.93 | 0.67 to 1.26 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.81 | 0.48 to 1.29 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.44 | 0.69 to 2.69 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.61 | 0.22 to 1.3 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.01 | 0.36 to 2.33 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.69 | 0.38 to 1.17 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.87 | 0.69 to 1.08 | 0.7321 | 0.47 to 1.09 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.91 | 0.48 to 1.57 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.26 | 0.85 to 1.83 | 0.9315 | 0.44 to 1.76 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.84 | 0.6 to 1.13 | 0.6474 | 0.28 to 1.28 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.12 | 0.63 to 1.82 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 22.76 | 1.82 to 135.4 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.96 | 0.6 to 1.47 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.93 | 0.56 to 1.45 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.82 | 0.09 to 2.94 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.78 | 0.58 to 1.02 | |||
| PGF2 gel | Intracervical PGE2 | 1.28 | 0.71 to 2.1 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.27 | 0.67 to 2.18 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.08 | 0.59 to 1.78 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.12 | 0.62 to 1.85 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.71 | 0.76 to 3.31 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.10 | 0.6 to 1.83 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.95 | 0.51 to 1.61 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.51 | 0.7 to 2.89 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.43 | 0.79 to 2.38 | 358,300 | 1.09 to 22,380 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.63 | 0.63 to 3.56 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.37 | 0.67 to 2.54 | |||
| NO | 1.26 | 0.67 to 2.16 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.09 | 0.51 to 2.03 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.95 | 0.76 to 4.11 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.82 | 0.25 to 1.96 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.36 | 0.42 to 3.47 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.94 | 0.41 to 1.82 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.17 | 0.65 to 1.94 | 0.7658 | 0.22 to 1.9 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.23 | 0.52 to 2.47 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.71 | 0.85 to 3.09 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.13 | 0.59 to 1.95 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.51 | 0.68 to 2.91 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 31.34 | 2.13 to 191 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.30 | 0.63 to 2.41 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.25 | 0.6 to 2.29 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.11 | 0.11 to 4.17 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.05 | 0.55 to 1.79 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.00 | 0.76 to 1.3 | 1.12 | 0.57 to 2 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.85 | 0.72 to 0.99 | 0.8757 | 0.61 to 1.23 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.88 | 0.75 to 1.03 | 1.035 | 0.74 to 1.4 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.34 | 0.78 to 2.17 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.87 | 0.72 to 1.03 | 0.8622 | 0.54 to 1.3 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.75 | 0.58 to 0.95 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.19 | 0.72 to 1.86 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.13 | 0.94 to 1.34 | 0.8863 | 0.46 to 1.56 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.29 | 0.62 to 2.42 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.08 | 0.7 to 1.6 | |||
| NO | 0.99 | 0.74 to 1.3 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.86 | 0.52 to 1.34 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.54 | 0.75 to 2.81 | 0.9795 | 0.33 to 2.32 | |
| Corticosteroids | 0.65 | 0.24 to 1.38 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.07 | 0.39 to 2.46 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.74 | 0.41 to 1.22 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.92 | 0.76 to 1.12 | 1.085 | 0.59 to 1.83 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.97 | 0.52 to 1.65 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.35 | 0.9 to 1.94 | 2.867 | 0.83 to 7.15 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.89 | 0.66 to 1.18 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.19 | 0.69 to 1.91 | 0.9298 | 0.01 to 4.69 | |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 24.08 | 1.94 to 145.6 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.02 | 0.66 to 1.54 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.98 | 0.62 to 1.5 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.87 | 0.1 to 3.12 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.82 | 0.64 to 1.06 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.86 | 0.65 to 1.12 | ||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.90 | 0.68 to 1.16 | 0.6225 | 0.31 to 1.11 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.37 | 0.75 to 2.31 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.88 | 0.66 to 1.16 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.76 | 0.54 to 1.04 | 0.6755 | 0.26 to 1.42 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.21 | 0.7 to 1.97 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.15 | 0.87 to 1.49 | 0.8613 | 0.46 to 1.49 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.31 | 0.61 to 2.51 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.10 | 0.68 to 1.68 | 2.528 | 0.86 to 5.92 | |
| NO | 1.01 | 0.7 to 1.42 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.88 | 0.5 to 1.43 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.56 | 0.73 to 2.96 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.66 | 0.24 to 1.43 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.09 | 0.38 to 2.55 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.75 | 0.4 to 1.29 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.94 | 0.7 to 1.25 | 2.107 | 0.86 to 4.39 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.99 | 0.51 to 1.72 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.37 | 0.87 to 2.08 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.91 | 0.62 to 1.28 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.21 | 0.67 to 2.02 | 1.343 | 0.51 to 2.86 | |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 24.70 | 1.95 to 147.7 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.04 | 0.63 to 1.63 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.00 | 0.59 to 1.6 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.89 | 0.1 to 3.19 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.84 | 0.59 to 1.16 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.04 | 0.9 to 1.21 | 1.22 | 0.86 to 1.69 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.59 | 0.94 to 2.52 | 2.442 | 1.11 to 4.72 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.03 | 0.87 to 1.21 | 0.767 | 0.57 to 1.02 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.89 | 0.7 to 1.11 | 0.7473 | 0.42 to 1.23 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.41 | 0.86 to 2.2 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.34 | 1.12 to 1.58 | 1.599 | 1.11 to 2.24 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.52 | 0.74 to 2.87 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.28 | 0.84 to 1.89 | |||
| NO | 1.18 | 0.88 to 1.54 | 0.6798 | 0.24 to 1.51 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.02 | 0.62 to 1.6 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.82 | 0.89 to 3.37 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.77 | 0.28 to 1.63 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.27 | 0.46 to 2.91 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.87 | 0.49 to 1.45 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.10 | 0.92 to 1.31 | 1.53 | 1.08 to 2.12 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.15 | 0.62 to 1.95 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.60 | 1.08 to 2.3 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.06 | 0.77 to 1.41 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.41 | 0.81 to 2.26 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 28.69 | 2.31 to 172.9 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.21 | 0.78 to 1.82 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.17 | 0.73 to 1.79 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.04 | 0.11 to 3.73 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.98 | 0.78 to 1.21 | 1.09 | 0.81 to 1.45 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.53 | 0.89 to 2.45 | ||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.99 | 0.84 to 1.15 | 1.092 | 0.83 to 1.39 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.85 | 0.67 to 1.07 | 2.558 | 0.4 to 9.6 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.35 | 0.83 to 2.11 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.28 | 1.09 to 1.51 | 1.13 | 0.82 to 1.52 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.46 | 0.71 to 2.75 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.23 | 0.81 to 1.82 | |||
| NO | 1.13 | 0.85 to 1.47 | 1.055 | 0.49 to 1.96 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.98 | 0.59 to 1.53 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.75 | 0.85 to 3.23 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.74 | 0.27 to 1.57 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.22 | 0.44 to 2.8 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.84 | 0.47 to 1.39 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.05 | 0.87 to 1.26 | 1.05 | 0.57 to 1.81 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.11 | 0.59 to 1.87 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.53 | 1.03 to 2.21 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.01 | 0.75 to 1.35 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.36 | 0.79 to 2.14 | 3.248 | 0.95 to 8.74 | |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 27.56 | 2.24 to 164.1 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.17 | 0.75 to 1.75 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.12 | 0.7 to 1.72 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.00 | 0.11 to 3.55 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.94 | 0.74 to 1.17 | 0.8972 | 0.62 to 1.25 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.69 | 0.4 to 1.1 | 1.241 | 0.22 to 3.93 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.59 | 0.34 to 0.97 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.94 | 0.45 to 1.75 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.90 | 0.51 to 1.44 | |||
| Amniotomy | 1.02 | 0.41 to 2.17 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.86 | 0.43 to 1.55 | |||
| NO | 0.79 | 0.43 to 1.32 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.69 | 0.32 to 1.28 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.22 | 0.49 to 2.55 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.51 | 0.16 to 1.21 | |||
| Relaxin | 0.85 | 0.26 to 2.09 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.59 | 0.26 to 1.13 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.73 | 0.42 to 1.18 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.77 | 0.34 to 1.51 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.07 | 0.55 to 1.88 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.71 | 0.39 to 1.19 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.95 | 0.44 to 1.77 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 19.15 | 1.38 to 114 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.81 | 0.41 to 1.47 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.78 | 0.38 to 1.44 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.69 | 0.07 to 2.6 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.65 | 0.37 to 1.07 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.87 | 0.66 to 1.11 | 1.942 | 0.6 to 4.84 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.38 | 0.83 to 2.17 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.31 | 1.07 to 1.58 | 1.05 | 0.54 to 1.83 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.49 | 0.72 to 2.83 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.25 | 0.81 to 1.88 | |||
| NO | 1.15 | 0.85 to 1.51 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.00 | 0.59 to 1.57 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.78 | 0.86 to 3.3 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.75 | 0.27 to 1.6 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.24 | 0.45 to 2.85 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.86 | 0.47 to 1.42 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.07 | 0.87 to 1.32 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.13 | 0.6 to 1.92 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.56 | 1.04 to 2.28 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.03 | 0.75 to 1.38 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.38 | 0.79 to 2.22 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 28.01 | 2.27 to 168.8 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.19 | 0.76 to 1.8 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.14 | 0.71 to 1.77 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.01 | 0.11 to 3.63 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.95 | 0.74 to 1.21 | 0.7876 | 0.44 to 1.3 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.61 | 0.94 to 2.58 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.53 | 1.18 to 1.94 | 1.57 | 0.76 to 2.93 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.74 | 0.82 to 3.32 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.46 | 0.92 to 2.23 | |||
| NO | 1.35 | 0.95 to 1.85 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.17 | 0.68 to 1.88 | |||
| Oestrogens | 2.08 | 0.98 to 3.93 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.88 | 0.32 to 1.91 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.45 | 0.52 to 3.39 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 1.00 | 0.54 to 1.7 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.25 | 0.97 to 1.6 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.31 | 0.69 to 2.28 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.82 | 1.18 to 2.71 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.21 | 0.84 to 1.68 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.61 | 0.91 to 2.62 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 32.79 | 2.59 to 201 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.39 | 0.85 to 2.15 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.34 | 0.79 to 2.12 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.18 | 0.13 to 4.26 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.12 | 0.81 to 1.5 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | i.v. oxytocin | 1.00 | 0.6 to 1.56 | ||
| Amniotomy | 1.14 | 0.47 to 2.39 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.96 | 0.5 to 1.68 | |||
| NO | 0.88 | 0.5 to 1.43 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.77 | 0.38 to 1.38 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.37 | 0.57 to 2.78 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.57 | 0.19 to 1.33 | |||
| Relaxin | 0.95 | 0.3 to 2.32 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.66 | 0.31 to 1.24 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.82 | 0.5 to 1.28 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.86 | 0.39 to 1.65 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.19 | 0.65 to 2.04 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.79 | 0.45 to 1.28 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.06 | 0.51 to 1.96 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 21.53 | 1.59 to 126.3 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.91 | 0.47 to 1.6 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.88 | 0.44 to 1.58 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.77 | 0.08 to 2.85 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.73 | 0.42 to 1.18 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | Amniotomy | 1.14 | 0.56 to 2.15 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.96 | 0.63 to 1.41 | 1.115 | 0.58 to 1.95 | |
| NO | 0.89 | 0.65 to 1.17 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.77 | 0.46 to 1.2 | 3.904 | 0.58 to 14.91 | |
| Oestrogens | 1.37 | 0.67 to 2.5 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.58 | 0.21 to 1.22 | |||
| Relaxin | 0.95 | 0.34 to 2.19 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.66 | 0.36 to 1.1 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.82 | 0.67 to 1.01 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.86 | 0.47 to 1.45 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.20 | 0.8 to 1.74 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.79 | 0.59 to 1.04 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.06 | 0.61 to 1.71 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 21.48 | 1.76 to 127.4 | 19.76 | 1.7 to 87.58 | |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.91 | 0.59 to 1.36 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.88 | 0.55 to 1.35 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.77 | 0.09 to 2.74 | 0.7501 | 0.07 to 2.74 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.74 | 0.56 to 0.95 | |||
| Amniotomy | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.92 | 0.48 to 1.59 | 0.3188 | 0.45 to 1.67 |
| NO | 0.87 | 0.39 to 1.64 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.75 | 0.3 to 1.53 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.34 | 0.47 to 3.05 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.56 | 0.16 to 1.41 | |||
| Relaxin | 0.94 | 0.25 to 2.46 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.65 | 0.25 to 1.38 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.81 | 0.38 to 1.48 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.85 | 0.31 to 1.82 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.18 | 0.51 to 2.29 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.78 | 0.35 to 1.48 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.04 | 0.41 to 2.18 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 20.98 | 1.35 to 123.2 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.89 | 0.37 to 1.8 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.86 | 0.35 to 1.75 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.76 | 0.07 to 2.87 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.72 | 0.33 to 1.36 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | NO | 0.96 | 0.58 to 1.48 | ||
| Mifepristone | 0.83 | 0.43 to 1.44 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.48 | 0.64 to 2.95 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.62 | 0.21 to 1.39 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.03 | 0.34 to 2.46 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.71 | 0.35 to 1.3 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.89 | 0.57 to 1.31 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.93 | 0.44 to 1.74 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.30 | 0.74 to 2.11 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.86 | 0.52 to 1.33 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.15 | 0.57 to 2.05 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 23.58 | 1.74 to 143 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.98 | 0.54 to 1.66 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.95 | 0.51 to 1.63 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.84 | 0.09 to 3.09 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.79 | 0.49 to 1.21 | 1.191 | 0.11 to 4.07 | |
| NO | Mifepristone | 0.88 | 0.51 to 1.43 | ||
| Oestrogens | 1.57 | 0.74 to 2.99 | |||
| Corticosteroids | 0.66 | 0.24 to 1.43 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.09 | 0.39 to 2.56 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.75 | 0.4 to 1.3 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.95 | 0.7 to 1.27 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.99 | 0.5 to 1.75 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.38 | 0.86 to 2.11 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.91 | 0.62 to 1.3 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.22 | 0.67 to 2.04 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 24.59 | 1.96 to 148.3 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.05 | 0.63 to 1.66 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.01 | 0.6 to 1.6 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.89 | 0.1 to 3.22 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.84 | 0.59 to 1.17 | |||
| Mifepristone | Oestrogens | 1.87 | 0.8 to 3.77 | ||
| Corticosteroids | 0.79 | 0.26 to 1.8 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.31 | 0.41 to 3.21 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.90 | 0.43 to 1.67 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.13 | 0.68 to 1.79 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.19 | 0.54 to 2.33 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.65 | 0.88 to 2.86 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.09 | 0.61 to 1.79 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.46 | 0.7 to 2.66 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 29.53 | 2.14 to 184.7 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.25 | 0.65 to 2.22 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.20 | 0.63 to 2.09 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.07 | 0.11 to 3.96 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.01 | 0.58 to 1.64 | |||
| Oestrogens | Corticosteroids | 0.47 | 0.14 to 1.19 | ||
| Relaxin | 0.78 | 0.22 to 2.03 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | 0.54 | 0.21 to 1.13 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.67 | 0.32 to 1.25 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.71 | 0.27 to 1.5 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.98 | 0.43 to 1.92 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.65 | 0.3 to 1.22 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.87 | 0.35 to 1.8 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 17.12 | 1.16 to 103.7 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.74 | 0.32 to 1.47 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.71 | 0.3 to 1.42 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.64 | 0.06 to 2.46 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.60 | 0.28 to 1.12 | |||
| Corticosteroids | Relaxin | 2.01 | 0.48 to 5.89 | ||
| Hyaluronidase | 1.39 | 0.45 to 3.38 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.74 | 0.66 to 3.89 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.83 | 0.57 to 4.58 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 2.54 | 0.89 to 5.91 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.67 | 0.62 to 3.79 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 2.24 | 0.74 to 5.43 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 44.81 | 2.65 to 274.6 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.92 | 0.67 to 4.5 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.85 | 0.64 to 4.31 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.66 | 0.14 to 6.9 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.55 | 0.58 to 3.5 | |||
| Relaxin | Hyaluronidase | 0.85 | 0.26 to 2.1 | ||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.07 | 0.37 to 2.38 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.13 | 0.33 to 2.79 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.56 | 0.51 to 3.66 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.03 | 0.34 to 2.36 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.38 | 0.42 to 3.36 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 28.53 | 1.53 to 182.5 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.19 | 0.38 to 2.81 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.14 | 0.37 to 2.66 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.00 | 0.08 to 4.01 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.95 | 0.33 to 2.13 | |||
| Hyaluronidase | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.35 | 0.76 to 2.21 | 0.5359 | 0.24 to 1.04 |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.42 | 0.6 to 2.85 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.96 | 0.98 to 3.52 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.30 | 0.68 to 2.28 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.74 | 0.78 to 3.36 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 35.16 | 2.49 to 212.7 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.49 | 0.72 to 2.77 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.43 | 0.7 to 2.63 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.27 | 0.13 to 4.74 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.20 | 0.65 to 2.05 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.06 | 0.56 to 1.81 | ||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.46 | 1 to 2.08 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.97 | 0.7 to 1.31 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.30 | 0.74 to 2.09 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 26.39 | 2.11 to 158.7 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.11 | 0.7 to 1.69 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.07 | 0.66 to 1.66 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.95 | 0.11 to 3.4 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.90 | 0.68 to 1.16 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.51 | 0.73 to 2.8 | ||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.99 | 0.53 to 1.71 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.33 | 0.58 to 2.59 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 27.45 | 1.9 to 158.3 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.14 | 0.56 to 2.09 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.10 | 0.51 to 2.08 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.97 | 0.1 to 3.64 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.92 | 0.48 to 1.63 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | Membrane sweeping | 0.68 | 0.42 to 1.06 | ||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.92 | 0.46 to 1.61 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 18.82 | 1.39 to 113.3 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.79 | 0.44 to 1.3 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.76 | 0.41 to 1.28 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.67 | 0.07 to 2.46 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.63 | 0.4 to 0.94 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.36 | 0.74 to 2.29 | ||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 27.89 | 2.19 to 163.7 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.17 | 0.74 to 1.79 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.13 | 0.67 to 1.81 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.00 | 0.11 to 3.6 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.94 | 0.65 to 1.33 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | i.v. prostaglandin | 21.62 | 1.56 to 125.8 | ||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.92 | 0.46 to 1.66 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.88 | 0.43 to 1.61 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.78 | 0.08 to 2.87 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.74 | 0.42 to 1.23 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | Sexual intercourse | 0.15 | 0.01 to 0.54 | ||
| Acupuncture | 0.14 | 0.01 to 0.52 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.12 | 0 to 0.61 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.12 | 0.01 to 0.42 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | Acupuncture | 1.00 | 0.53 to 1.73 | ||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.89 | 0.09 to 3.25 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.84 | 0.51 to 1.3 | |||
| Acupuncture | Oral prostaglandins | 0.93 | 0.1 to 3.47 | ||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.88 | 0.52 to 1.4 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.04 | 0.26 to 8.56 | ||
| Control treatment | Active treatment | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | ||
| No treatment | Placebo | 0.9 | 0.71 to 1.21 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.8 | 0.66 to 1.08 | 0.96 | 0.46 to 1.77 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.9 | 0.7 to 1.04 | 0.99 | 0.61 to 1.49 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.7 | 0.48 to 0.9 | |||
| PGF2 gel | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.19 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.8 | 0.66 to 1.02 | 1.05 | 0.56 to 1.77 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.0 | 0.76 to 1.29 | 0.74 | 0.37 to 1.32 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.57 to 0.94 | 1.37 | 0.41 to 3.43 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.68 to 1.05 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.32 to 1.28 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.61 to 0.97 | 1.73 | 0.46 to 4.66 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.9 | 0.59 to 1.36 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.9 | 0.43 to 1.56 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.0 | 0.84 to 1.19 | 1.09 | 0.86 to 1.4 | |
| Amniotomy | 0.8 | 0.47 to 1.24 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.63 to 1.16 | 0.20 | 0.05 to 0.52 | |
| NO | 0.9 | 0.6 to 1.21 | 2.03 | 0.27 to 7.93 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.6 | 0.92 to 2.56 | 1.06 | 0.12 to 3.85 | |
| Oestrogens | 0.6 | 0.3 to 1.19 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.4 | 0.58 to 2.73 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.6 | 0.48 to 0.82 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.8 | 0.44 to 1.24 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.7 | 0.45 to 1.03 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.1 | 0.87 to 1.38 | 1.07 | 0.82 to 1.37 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.9 | 0.45 to 1.44 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.9 | 0.81 to 3.8 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.2 | 0.68 to 1.95 | 1.20 | 0.64 to 2.06 | |
| Acupuncture | 0.8 | 0.46 to 1.19 | 0.49 | 0.2 to 0.98 | |
| Homeopathy | 2.0 | 0.1 to 9.79 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.7 | 0.44 to 1.04 | 1.28 | 0.34 to 3.48 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.6 | 0.42 to 0.92 | |||
| Placebo | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.9 | 0.67 to 1.22 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.9 | 0.72 to 1.18 | 1.18 | 0.38 to 2.85 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.7 | 0.5 to 0.99 | 1.05 | 0.4 to 2.26 | |
| PGF2 gel | 0.9 | 0.58 to 1.25 | 0.74 | 0.43 to 1.2 | |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.9 | 0.68 to 1.14 | 1.09 | 0.61 to 1.79 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.1 | 0.79 to 1.45 | 0.98 | 0.5 to 1.75 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.59 to 1.05 | 0.64 | 0.09 to 2.23 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.7 to 1.18 | 1.21 | 0.35 to 3.12 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.34 to 1.38 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.63 to 1.09 | 0.54 | 0.25 to 1 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.0 | 0.62 to 1.52 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.9 | 0.46 to 1.71 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.1 | 0.83 to 1.39 | |||
| Amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.5 to 1.38 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.64 to 1.31 | |||
| NO | 0.9 | 0.69 to 1.21 | 0.91 | 0.61 to 1.28 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.7 | 1.05 to 2.59 | 1.84 | 1.08 to 2.98 | |
| Oestrogens | 0.7 | 0.32 to 1.28 | 0.75 | 0.25 to 1.71 | |
| Relaxin | 1.4 | 0.66 to 2.78 | 1.45 | 0.65 to 2.87 | |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.7 | 0.5 to 0.91 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.8 | 0.47 to 1.38 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.8 | 0.47 to 1.14 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.2 | 0.84 to 1.66 | 15.45 | 1.56 to 71.26 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.9 | 0.49 to 1.52 | 0.88 | 0.32 to 1.91 | |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.0 | 0.85 to 4.12 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.3 | 0.68 to 2.24 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.8 | 0.51 to 1.26 | 1.08 | 0.57 to 1.85 | |
| Homeopathy | 2.1 | 0.11 to 10.24 | 2.18 | 0.09 to 11.64 | |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.7 | 0.45 to 1.16 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.7 | 0.44 to 1.03 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 1.0 | 0.8 to 1.28 | 0.74 | 0.41 to 1.23 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.8 | 0.56 to 1.08 | 0.61 | 0.21 to 1.38 | |
| PGF2 gel | 1.0 | 0.61 to 1.45 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.76 to 1.26 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.2 | 0.87 to 1.59 | 1.02 | 0.31 to 2.56 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.66 to 1.15 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.0 | 0.81 to 1.26 | 1.13 | 0.76 to 1.61 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.38 to 1.55 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.71 to 1.19 | 1.25 | 0.55 to 2.44 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.1 | 0.7 to 1.67 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.0 | 0.51 to 1.88 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.2 | 0.94 to 1.51 | 1.77 | 0.92 to 3.12 | |
| Amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.56 to 1.51 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.74 to 1.4 | 0.91 | 0.46 to 1.6 | |
| NO | 1.0 | 0.7 to 1.48 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.9 | 1.05 to 3.11 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.35 to 1.44 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.6 | 0.69 to 3.25 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.56 to 0.99 | 1.03 | 0.32 to 2.5 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.9 | 0.53 to 1.49 | 1.58 | 0.24 to 5.53 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.25 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.3 | 0.93 to 1.82 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.55 to 1.7 | 1.21 | 0.52 to 2.41 | |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.3 | 0.95 to 4.58 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.4 | 0.76 to 2.45 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.9 | 0.54 to 1.47 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.4 | 0.11 to 11.74 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.8 | 0.5 to 1.26 | 1.61 | 0.21 to 5.53 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.5 to 1.12 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.8 | 0.57 to 1.03 | 0.55 | 0.28 to 0.97 |
| PGF2 gel | 0.9 | 0.61 to 1.39 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.79 to 1.16 | 0.91 | 0.56 to 1.4 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.2 | 0.89 to 1.51 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.69 to 1.06 | 1.35 | 0.87 to 2.05 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.0 | 0.83 to 1.19 | 0.94 | 0.63 to 1.33 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.39 to 1.46 | 0.72 | 0.31 to 1.46 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.73 to 1.12 | 0.99 | 0.43 to 1.95 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.1 | 0.73 to 1.53 | 1.07 | 0.67 to 1.61 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.0 | 0.51 to 1.82 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.2 | 0.97 to 1.42 | 0.85 | 0.45 to 1.47 | |
| Amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.56 to 1.43 | 0.96 | 0.39 to 1.99 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.75 to 1.34 | 1.27 | 0.68 to 2.12 | |
| NO | 1.0 | 0.72 to 1.38 | 1.08 | 0.57 to 1.86 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.8 | 1.07 to 2.99 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.7 | 0.35 to 1.38 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.6 | 0.69 to 3.17 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.7 | 0.59 to 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.51 to 1.03 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.9 | 0.53 to 1.42 | 0.73 | 0.32 to 1.41 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.8 | 0.54 to 1.18 | 0.82 | 0.38 to 1.56 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.3 | 0.95 to 1.72 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.53 to 1.68 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.2 | 0.94 to 4.43 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.4 | 0.77 to 2.37 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.9 | 0.54 to 1.41 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.3 | 0.11 to 11.5 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.8 | 0.51 to 1.21 | 2.18 | 0.1 to 10.86 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.7 | 0.5 to 1.07 | 0.00 | 0 to 0 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | PGF2 gel | 1.2 | 0.75 to 1.93 | 0.00 | 0 to 0 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.3 | 0.92 to 1.7 | 1.45 | 0.57 to 3.08 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.5 | 1.06 to 2.17 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.1 | 0.8 to 1.56 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.3 | 0.96 to 1.74 | 1.41 | 0.58 to 2.91 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.1 | 0.48 to 2.01 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.2 | 0.86 to 1.62 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.4 | 0.87 to 2.19 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.3 | 0.71 to 2.21 | 1.31 | 0.68 to 2.3 | |
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.5 | 1.12 to 2.07 | 1.18 | 0.4 to 2.75 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.2 | 0.69 to 2.02 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.3 | 0.88 to 1.92 | |||
| NO | 1.3 | 0.86 to 1.96 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.4 | 1.3 to 4.12 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.0 | 0.44 to 1.88 | |||
| Relaxin | 2.1 | 0.86 to 4.27 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.0 | 0.7 to 1.32 | 0.71 | 0.34 to 1.31 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.2 | 0.65 to 1.97 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.1 | 0.66 to 1.62 | 7.10 | 0.87 to 30.16 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.7 | 1.16 to 2.44 | 1.20 | 0.3 to 3.24 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.3 | 0.67 to 2.3 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.9 | 1.19 to 6.07 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.8 | 0.95 to 3.24 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.2 | 0.67 to 1.94 | |||
| Homeopathy | 3.1 | 0.15 to 15.33 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.1 | 0.62 to 1.67 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.0 | 0.61 to 1.49 | |||
| PGF2 gel | Intracervical PGE2 | 1.1 | 0.69 to 1.57 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.3 | 0.81 to 1.95 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.0 | 0.6 to 1.44 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.1 | 0.72 to 1.62 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.37 to 1.78 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.0 | 0.65 to 1.49 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.2 | 0.66 to 1.99 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.1 | 0.49 to 2.17 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.3 | 0.86 to 1.88 | 1.01 | 0.52 to 1.78 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.54 to 1.77 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.68 to 1.74 | |||
| NO | 1.1 | 0.68 to 1.71 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.0 | 1.06 to 3.51 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.35 to 1.64 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.7 | 0.7 to 3.63 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.23 | 1.41 | 0.25 to 4.6 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.0 | 0.51 to 1.76 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.9 | 0.5 to 1.49 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.4 | 0.87 to 2.23 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.1 | 0.53 to 1.97 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.4 | 0.94 to 5.19 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.5 | 0.75 to 2.88 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.0 | 0.54 to 1.68 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.5 | 0.13 to 12.5 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.9 | 0.49 to 1.5 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.47 to 1.34 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.2 | 0.93 to 1.58 | 1.39 | 0.69 to 2.53 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.71 to 1.13 | 0.67 | 0.41 to 1.05 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.0 | 0.86 to 1.26 | 1.09 | 0.74 to 1.55 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.4 to 1.57 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.0 | 0.76 to 1.18 | 0.98 | 0.51 to 1.72 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.1 | 0.73 to 1.67 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.1 | 0.53 to 1.9 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.2 | 1 to 1.5 | 1.60 | 0.94 to 2.59 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.58 to 1.54 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.76 to 1.43 | 2.60 | 0.6 to 7.76 | |
| NO | 1.1 | 0.74 to 1.47 | 2.27 | 0.03 to 13.17 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.9 | 1.11 to 3.14 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.37 to 1.43 | 1.09 | 0.29 to 2.78 | |
| Relaxin | 1.7 | 0.71 to 3.35 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.6 to 0.99 | 0.90 | 0.45 to 1.62 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.9 | 0.56 to 1.5 | 1.23 | 0.53 to 2.42 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.9 | 0.56 to 1.25 | 0.51 | 0.08 to 1.58 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.4 | 0.98 to 1.82 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.56 to 1.77 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.3 | 0.97 to 4.64 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.5 | 0.79 to 2.49 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.9 | 0.56 to 1.49 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.4 | 0.12 to 11.99 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.8 | 0.53 to 1.28 | 1.95 | 0.29 to 7.01 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.13 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.55 to 1 | ||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.66 to 1.12 | 0.84 | 0.33 to 1.79 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.7 | 0.32 to 1.32 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.58 to 1.04 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.9 | 0.58 to 1.43 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.9 | 0.42 to 1.61 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.0 | 0.79 to 1.29 | 0.78 | 0.51 to 1.14 | |
| Amniotomy | 0.8 | 0.47 to 1.29 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.61 to 1.22 | 1.41 | 0.55 to 3.04 | |
| NO | 0.9 | 0.59 to 1.26 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.6 | 0.91 to 2.65 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.6 | 0.3 to 1.23 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.4 | 0.58 to 2.8 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.6 | 0.47 to 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.34 to 1.7 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.8 | 0.44 to 1.31 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.7 | 0.45 to 1.07 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.1 | 0.78 to 1.55 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.9 | 0.45 to 1.49 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.9 | 0.8 to 3.96 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.2 | 0.64 to 2.09 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.8 | 0.45 to 1.26 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.0 | 0.1 to 9.89 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.7 | 0.42 to 1.09 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.6 | 0.41 to 0.97 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.2 | 0.94 to 1.43 | 1.07 | 0.71 to 1.54 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.44 to 1.78 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.1 | 0.83 to 1.34 | 1.61 | 0.92 to 2.66 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.3 | 0.81 to 1.88 | 2.32 | 0.09 to 11.01 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.2 | 0.58 to 2.17 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.4 | 1.07 to 1.74 | 2.61 | 0.44 to 9 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.64 to 1.73 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.2 | 0.83 to 1.64 | |||
| NO | 1.2 | 0.81 to 1.68 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.2 | 1.21 to 3.56 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.9 | 0.4 to 1.64 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.8 | 0.79 to 3.74 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.9 | 0.66 to 1.11 | 1.03 | 0.56 to 1.74 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.1 | 0.6 to 1.71 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.0 | 0.62 to 1.41 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.5 | 1.07 to 2.09 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.2 | 0.61 to 2.02 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.6 | 1.08 to 5.27 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.6 | 0.88 to 2.83 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.1 | 0.62 to 1.69 | 9.47 | 0.15 to 63.5 | |
| Homeopathy | 2.7 | 0.13 to 13.49 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.9 | 0.58 to 1.46 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.9 | 0.58 to 1.24 | 0.89 | 0.4 to 1.73 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.8 | 0.38 to 1.51 | ||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.9 | 0.76 to 1.1 | 0.86 | 0.65 to 1.11 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.1 | 0.71 to 1.6 | 1.49 | 0.14 to 5.9 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.0 | 0.51 to 1.84 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.2 | 0.97 to 1.43 | 1.68 | 1.1 to 2.51 | |
| Amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.56 to 1.47 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.74 to 1.37 | |||
| NO | 1.0 | 0.72 to 1.42 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.9 | 1.07 to 3.04 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.35 to 1.4 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.6 | 0.69 to 3.2 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.7 | 0.58 to 0.94 | 1.02 | 0.22 to 2.96 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.9 | 0.53 to 1.46 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.8 | 0.54 to 1.21 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.3 | 0.95 to 1.76 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.54 to 1.69 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.2 | 0.95 to 4.48 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.4 | 0.77 to 2.41 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.9 | 0.54 to 1.42 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.4 | 0.12 to 11.54 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.8 | 0.51 to 1.23 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.51 to 1.06 | 0.37 | 0.18 to 0.65 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.3 | 0.6 to 2.39 | 1.01 | 0.12 to 3.64 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.5 | 0.66 to 3.02 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.4 | 0.51 to 3.23 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.6 | 0.78 to 3.11 | |||
| Amniotomy | 1.3 | 0.54 to 2.67 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.4 | 0.65 to 2.75 | |||
| NO | 1.4 | 0.64 to 2.77 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.6 | 1.04 to 5.43 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.0 | 0.36 to 2.39 | |||
| Relaxin | 2.2 | 0.71 to 5.28 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.0 | 0.48 to 1.97 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.3 | 0.52 to 2.67 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.1 | 0.49 to 2.3 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.8 | 0.82 to 3.53 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.4 | 0.54 to 3.06 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 3.1 | 0.99 to 7.47 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 2.0 | 0.75 to 4.28 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.3 | 0.51 to 2.61 | |||
| Homeopathy | 3.3 | 0.14 to 16.77 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.1 | 0.47 to 2.3 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.0 | 0.46 to 2.08 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.2 | 0.76 to 1.79 | ||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.1 | 0.55 to 2.04 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.3 | 1.05 to 1.61 | 1.06 | 0.65 to 1.63 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.6 to 1.64 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.8 to 1.52 | |||
| NO | 1.1 | 0.77 to 1.58 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.0 | 1.16 to 3.36 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.39 to 1.54 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.8 | 0.75 to 3.54 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.62 to 1.06 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.0 | 0.57 to 1.63 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.9 | 0.58 to 1.35 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.4 | 1.03 to 1.96 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.1 | 0.58 to 1.9 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.5 | 1.04 to 4.95 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.6 | 0.83 to 2.66 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.0 | 0.59 to 1.58 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.6 | 0.13 to 12.62 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.9 | 0.55 to 1.37 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.57 to 1.15 | 1.38 | 0.74 to 2.34 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.0 | 0.44 to 1.91 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.1 | 0.74 to 1.69 | |||
| Amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.47 to 1.55 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.59 to 1.51 | |||
| NO | 1.0 | 0.58 to 1.55 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.8 | 0.9 to 3.17 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.7 | 0.3 to 1.44 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.5 | 0.59 to 3.25 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.7 | 0.46 to 1.06 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.9 | 0.45 to 1.52 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.8 | 0.45 to 1.29 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.3 | 0.76 to 1.95 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.46 to 1.77 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.1 | 0.82 to 4.56 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.4 | 0.65 to 2.51 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.9 | 0.45 to 1.51 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.3 | 0.1 to 11.24 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.8 | 0.42 to 1.31 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.7 | 0.41 to 1.17 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | i.v. oxytocin | 1.3 | 0.64 to 2.32 | ||
| Amniotomy | 1.0 | 0.43 to 2.05 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.52 to 2.06 | |||
| NO | 1.1 | 0.52 to 2.09 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.0 | 0.83 to 4.14 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.29 to 1.83 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.7 | 0.58 to 4.12 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.4 to 1.47 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.0 | 0.41 to 2 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.9 | 0.41 to 1.7 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.4 | 0.68 to 2.63 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.1 | 0.43 to 2.33 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.4 | 0.8 to 5.81 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.5 | 0.61 to 3.25 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.0 | 0.42 to 1.97 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.6 | 0.11 to 13.06 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.9 | 0.38 to 1.74 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.37 to 1.56 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | Amniotomy | 0.8 | 0.48 to 1.24 | 0.91 | 0.24 to 2.37 |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 0.9 | 0.63 to 1.15 | 1.19 | 0.34 to 3.08 | |
| NO | 0.9 | 0.61 to 1.2 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.6 | 0.91 to 2.56 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.6 | 0.3 to 1.19 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.4 | 0.59 to 2.71 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.6 | 0.49 to 0.81 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.8 | 0.45 to 1.24 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.7 | 0.45 to 1.02 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.1 | 0.82 to 1.45 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.9 | 0.46 to 1.43 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.9 | 0.82 to 3.72 | 1.86 | 0.73 to 3.95 | |
| Sexual intercourse | 1.2 | 0.66 to 2.01 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.8 | 0.46 to 1.2 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.0 | 0.1 to 9.73 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.7 | 0.45 to 1.01 | 0.64 | 0.33 to 1.13 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.6 | 0.42 to 0.93 | |||
| Amniotomy | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.1 | 0.7 to 1.75 | ||
| NO | 1.2 | 0.64 to 1.93 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.1 | 1.01 to 3.86 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.34 to 1.76 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.8 | 0.67 to 3.94 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.49 to 1.35 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.0 | 0.49 to 1.92 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.9 | 0.49 to 1.61 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.5 | 0.84 to 2.42 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.1 | 0.51 to 2.13 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.5 | 0.94 to 5.49 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.6 | 0.73 to 3.06 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.0 | 0.5 to 1.84 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.7 | 0.12 to 13.54 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.9 | 0.48 to 1.59 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.9 | 0.45 to 1.44 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | NO | 1.0 | 0.66 to 1.52 | ||
| Mifepristone | 1.9 | 1 to 3.15 | |||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.34 to 1.45 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.6 | 0.66 to 3.28 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.7 | 0.52 to 1.04 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.9 | 0.5 to 1.51 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.8 | 0.5 to 1.28 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.3 | 0.88 to 1.88 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.51 to 1.75 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.2 | 0.92 to 4.65 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.4 | 0.73 to 2.48 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.9 | 0.51 to 1.5 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.4 | 0.11 to 11.72 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.8 | 0.5 to 1.25 | 0.62 | 0.22 to 1.37 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.47 to 1.15 | 1.87 | 0.29 to 6.64 | |
| NO | Mifepristone | 1.9 | 1.05 to 3.06 | ||
| Oestrogens | 0.8 | 0.34 to 1.45 | |||
| Relaxin | 1.6 | 0.68 to 3.2 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.8 | 0.51 to 1.07 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.9 | 0.49 to 1.57 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.8 | 0.49 to 1.3 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.3 | 0.85 to 1.93 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.0 | 0.51 to 1.76 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.2 | 0.9 to 4.63 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.4 | 0.72 to 2.55 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.9 | 0.52 to 1.46 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.3 | 0.12 to 11.58 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.8 | 0.47 to 1.32 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.45 to 1.2 | |||
| Mifepristone | Oestrogens | 0.4 | 0.17 to 0.89 | ||
| Relaxin | 0.9 | 0.35 to 1.95 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.4 | 0.24 to 0.71 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.5 | 0.24 to 0.99 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.5 | 0.24 to 0.83 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.8 | 0.41 to 1.27 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.6 | 0.26 to 1.09 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.3 | 0.46 to 2.8 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.8 | 0.36 to 1.57 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.5 | 0.26 to 0.93 | |||
| Homeopathy | 1.3 | 0.06 to 6.52 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.5 | 0.23 to 0.84 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.4 | 0.22 to 0.77 | |||
| Oestrogens | Relaxin | 2.4 | 0.77 to 5.89 | ||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.1 | 0.52 to 2.16 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.3 | 0.57 to 2.74 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.2 | 0.53 to 2.48 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 2.0 | 0.89 to 3.81 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.5 | 0.57 to 3.2 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 3.3 | 1.05 to 8.1 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 2.1 | 0.81 to 4.64 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.4 | 0.56 to 2.81 | |||
| Homeopathy | 3.6 | 0.15 to 18.23 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.2 | 0.51 to 2.51 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.1 | 0.49 to 2.22 | |||
| Relaxin | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.5 | 0.23 to 1.09 | ||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.7 | 0.24 to 1.44 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.6 | 0.23 to 1.27 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.0 | 0.39 to 1.94 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.7 | 0.26 to 1.6 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.6 | 0.48 to 4.03 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.0 | 0.36 to 2.34 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.7 | 0.26 to 1.42 | |||
| Homeopathy | 1.7 | 0.07 to 8.78 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.6 | 0.22 to 1.27 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.6 | 0.22 to 1.15 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.2 | 0.7 to 2.02 | ||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.1 | 0.75 to 1.56 | 1.14 | 0.66 to 1.85 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.8 | 1.24 to 2.46 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.4 | 0.72 to 2.33 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 3.0 | 1.26 to 6.11 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.9 | 1.01 to 3.31 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.2 | 0.72 to 1.98 | |||
| Homeopathy | 3.2 | 0.15 to 15.55 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.1 | 0.67 to 1.71 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.0 | 0.66 to 1.49 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.0 | 0.49 to 1.71 | ||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.5 | 0.84 to 2.58 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.2 | 0.52 to 2.29 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.6 | 0.93 to 5.84 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.7 | 0.73 to 3.24 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.1 | 0.51 to 1.95 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.8 | 0.12 to 13.79 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.9 | 0.47 to 1.72 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.9 | 0.45 to 1.61 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | Membrane sweeping | 1.7 | 1.01 to 2.57 | ||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1.3 | 0.61 to 2.35 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.8 | 1.1 to 6.01 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.8 | 0.86 to 3.3 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.2 | 0.6 to 2 | |||
| Homeopathy | 3.0 | 0.14 to 14.77 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.0 | 0.56 to 1.73 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.0 | 0.54 to 1.55 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.8 | 0.4 to 1.39 | ||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.7 | 0.72 to 3.59 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.1 | 0.59 to 1.88 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.7 | 0.4 to 1.15 | |||
| Homeopathy | 1.8 | 0.09 to 9.03 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.6 | 0.38 to 0.99 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.6 | 0.36 to 0.89 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | i.v. prostaglandin | 2.4 | 0.87 to 5.32 | 17.37 | 0.18 to 73.85 |
| Sexual intercourse | 1.5 | 0.65 to 3.1 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.0 | 0.46 to 1.89 | |||
| Homeopathy | 2.6 | 0.12 to 13.14 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.9 | 0.42 to 1.64 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.8 | 0.4 to 1.53 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | Sexual intercourse | 0.7 | 0.26 to 1.67 | ||
| Acupuncture | 0.5 | 0.17 to 1.04 | |||
| Homeopathy | 1.2 | 0.05 to 5.98 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.4 | 0.16 to 0.91 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.4 | 0.15 to 0.82 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | Acupuncture | 0.7 | 0.32 to 1.32 | ||
| Homeopathy | 1.8 | 0.08 to 9.06 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.6 | 0.3 to 1.16 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.6 | 0.28 to 1.05 | |||
| Acupuncture | Homeopathy | 2.7 | 0.13 to 13.58 | ||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.9 | 0.48 to 1.68 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.9 | 0.47 to 1.49 | |||
| Homeopathy | Oral prostaglandins | 1.4 | 0.07 to 7.09 | ||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.3 | 0.06 to 6.64 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.0 | 0.53 to 1.64 | ||
| Control treatment | Active treatment | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | ||
| No treatment | Placebo | 0.88 | 0.26 to 2.19 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 1.60 | 0.46 to 4.13 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 1.86 | 0.64 to 4.34 | 28,310.00 | 0.42 to 3659 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 2.40 | 0.76 to 5.92 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.35 | 0.5 to 3.01 | 1.64 | 0.38 to 4.68 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.12 | 0.23 to 3.35 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 2.21 | 0.77 to 5.06 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 3.52 | 1.26 to 8 | 2.79 | 0.28 to 11.03 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.90 | 0.18 to 2.82 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 2.29 | 0.78 to 5.37 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.55 | 0.43 to 3.99 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 4.51 | 0.96 to 13.54 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.70 | 0.56 to 4.06 | 1.95 | 0.15 to 8.08 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 5.98 | 0.18 to 33.89 | |||
| NO | 0.31 | 0.01 to 1.34 | |||
| Mifepristone | 315.50 | 0.69 to 309.5 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.73 | 0.22 to 1.84 | 0.38 | 0 to 2.36 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.41 | 0 to 2.13 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.21 | 0 to 1.02 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 3.41 | 1.01 to 8.65 | |||
| Placebo | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 1.99 | 0.78 to 4.25 | 0.78 | 0 to 5.12 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 2.33 | 1.1 to 4.4 | 5.81 | 0.32 to 29.93 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 2.97 | 1.36 to 5.73 | 27.00 | 2.01 to 131.2 | |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.70 | 0.87 to 3.05 | 1.65 | 0.57 to 3.88 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.40 | 0.37 to 3.68 | 0.46 | 0 to 3 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 2.75 | 1.36 to 5.04 | 2.46 | 0.25 to 10.23 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 4.40 | 2.22 to 7.94 | 28.54 | 0.53 to 159.4 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.13 | 0.28 to 3.15 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 2.85 | 1.41 to 5.2 | 7.75 | 1.22 to 30.55 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.93 | 0.73 to 4.19 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 5.58 | 1.58 to 14.57 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 2.12 | 0.97 to 4.1 | 0.34 | 0 to 2.19 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 7.44 | 0.27 to 40.66 | |||
| NO | 0.38 | 0.02 to 1.54 | |||
| Mifepristone | 329.20 | 1.12 to 357.1 | 144,400.00 | 0.84 to 9849 | |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.92 | 0.37 to 1.93 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.52 | 0.01 to 2.62 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.26 | 0 to 1.18 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 4.25 | 1.71 to 9.02 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 1.28 | 0.61 to 2.41 | 1.99 | 0.4 to 6.21 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.65 | 0.73 to 3.24 | 2.37 | 0.2 to 10.35 | |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.95 | 0.44 to 1.79 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.78 | 0.2 to 2.08 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.53 | 0.72 to 2.89 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 2.41 | 1.25 to 4.29 | 1.84 | 0.78 to 3.73 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.62 | 0.15 to 1.75 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.58 | 0.74 to 2.99 | 10,220.00 | 0.39 to 3491 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.07 | 0.39 to 2.33 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 3.09 | 0.85 to 8.13 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.18 | 0.52 to 2.33 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 4.14 | 0.15 to 22.8 | |||
| NO | 0.21 | 0.01 to 0.8 | 0.39 | 0 to 2.49 | |
| Mifepristone | 194.30 | 0.55 to 208.3 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.51 | 0.2 to 1.08 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.28 | 0 to 1.44 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.14 | 0 to 0.65 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.34 | 0.93 to 4.98 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.33 | 0.7 to 2.32 | ||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.76 | 0.45 to 1.2 | 0.87 | 0.16 to 2.67 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.62 | 0.19 to 1.51 | 17,770.00 | 0.4 to 6593 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.22 | 0.76 to 1.85 | 1.38 | 0.54 to 2.86 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.95 | 1.25 to 2.92 | 1.18 | 0.55 to 2.26 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.49 | 0.15 to 1.22 | 0.77 | 0.14 to 2.47 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.27 | 0.74 to 2.02 | 2.13 | 0.24 to 8.62 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.85 | 0.41 to 1.52 | 1.28 | 0.5 to 2.68 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 2.50 | 0.77 to 6.12 | |||
| Intravenous oxytocin | 0.95 | 0.51 to 1.62 | |||
| Intravenous oxytocin plus amniotomy | 3.29 | 0.13 to 17.77 | |||
| NO | 0.17 | 0.01 to 0.66 | |||
| Mifepristone | 140.90 | 0.48 to 168.7 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.41 | 0.2 to 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.21 to 1.43 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.23 | 0 to 1.1 | 1.31 | 0 to 6.91 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.11 | 0 to 0.5 | 0.14 | 0 to 0.84 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.89 | 0.9 to 3.52 | 2189.00 | 0.4 to 4820 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | Intracervical PGE2 | 0.60 | 0.33 to 1.01 | 0.99 | 0.26 to 2.57 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.50 | 0.14 to 1.26 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.98 | 0.54 to 1.64 | 0.33 | 0.02 to 1.4 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.55 | 0.9 to 2.51 | 2.71 | 1.11 to 5.69 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.40 | 0.1 to 1.07 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.01 | 0.54 to 1.73 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.68 | 0.29 to 1.34 | 2.12 | 0.28 to 7.9 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.88 | 0.73 to 4 | 1.89 | 0.72 to 4.09 | |
| Intravenous oxytocin | 0.75 | 0.39 to 1.31 | 0.87 | 0.21 to 2.37 | |
| Intravenous oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.63 | 0.1 to 14.43 | |||
| NO | 0.14 | 0.01 to 0.53 | |||
| Mifepristone | 106.00 | 0.38 to 136.4 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.32 | 0.14 to 0.62 | 0.04 | 0 to 0.21 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.18 | 0 to 0.91 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.09 | 0 to 0.39 | 0.10 | 0 to 0.62 | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.50 | 0.67 to 2.97 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.85 | 0.25 to 2.07 | ||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.65 | 1.06 to 2.47 | 1.47 | 0.7 to 2.78 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 2.64 | 1.76 to 3.83 | 3.04 | 1.53 to 5.53 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.68 | 0.19 to 1.75 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.71 | 1.07 to 2.61 | 2.12 | 0.75 to 4.91 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.16 | 0.52 to 2.23 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 3.37 | 1.07 to 8.18 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.28 | 0.72 to 2.1 | 3.33 | 0.52 to 11.85 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 4.50 | 0.18 to 24.61 | |||
| NO | 0.23 | 0.01 to 0.88 | 0.79 | 0 to 5.18 | |
| Mifepristone | 200.70 | 0.67 to 223.4 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.55 | 0.27 to 1.01 | 1.17 | 0 to 7.37 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.31 | 0 to 1.48 | 0.24 | 0 to 1.53 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.15 | 0 to 0.69 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.55 | 1.24 to 4.73 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 2.53 | 0.79 to 6.34 | 0.59 | 0.01 to 3.34 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 4.05 | 1.31 to 10.04 | 22,750.00 | 3.18 to 28,850 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.04 | 0.19 to 3.38 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 2.64 | 0.81 to 6.76 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.77 | 0.46 to 4.85 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 5.17 | 1 to 16.23 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.95 | 0.59 to 4.98 | 18.29 | 0.22 to 103.5 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 5.90 | 0.26 to 31.66 | 12.32 | 0.28 to 71.07 | |
| NO | 0.35 | 0.01 to 1.57 | |||
| Mifepristone | 271.00 | 0.74 to 350.2 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.83 | 0.24 to 2.14 | 2.26 | 0.09 to 11.72 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.47 | 0.01 to 2.53 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.24 | 0 to 1.18 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 3.92 | 1.06 to 10.62 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.63 | 1.1 to 2.35 | 1.95 | 0.78 to 4.19 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.41 | 0.13 to 1.02 | 0.33 | 0.05 to 1.1 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.06 | 0.68 to 1.59 | 0.61 | 0.25 to 1.23 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.71 | 0.34 to 1.29 | 0.22 | 0.02 to 0.77 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 2.09 | 0.66 to 5.05 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.79 | 0.45 to 1.29 | 2.27 | 0.42 to 7.45 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.77 | 0.11 to 15.05 | |||
| NO | 0.14 | 0.01 to 0.55 | |||
| Mifepristone | 121.10 | 0.41 to 139.8 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.34 | 0.17 to 0.59 | 0.37 | 0.1 to 0.91 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.19 | 0 to 0.94 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.10 | 0 to 0.43 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.57 | 0.82 to 2.76 | 1.47 | 0.5 to 3.42 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.26 | 0.08 to 0.66 | ||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.66 | 0.44 to 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.43 to 1.25 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.45 | 0.21 to 0.83 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.29 | 0.42 to 3.06 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.49 | 0.3 to 0.76 | 0.29 | 0.1 to 0.65 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.72 | 0.07 to 9.37 | |||
| NO | 0.09 | 0 to 0.33 | 0.06 | 0 to 0.39 | |
| Mifepristone | 77.21 | 0.26 to 86.53 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.21 | 0.11 to 0.37 | 0.43 | 0.04 to 1.58 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.12 | 0 to 0.58 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.06 | 0 to 0.26 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.97 | 0.52 to 1.68 | 1.02 | 0.42 to 2.09 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 3.39 | 0.95 to 8.72 | ||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 2.26 | 0.56 to 6.25 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 6.66 | 1.21 to 21.51 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 2.52 | 0.68 to 6.71 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 8.79 | 0.25 to 49.68 | |||
| NO | 0.46 | 0.02 to 2.04 | |||
| Mifepristone | 349.30 | 0.9 to 442.9 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.08 | 0.28 to 2.95 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.61 | 0.01 to 3.26 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.30 | 0 to 1.54 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 5.01 | 1.27 to 13.91 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.70 | 0.31 to 1.34 | ||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 2.02 | 0.63 to 4.95 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.76 | 0.45 to 1.2 | 0.85 | 0.37 to 1.68 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.70 | 0.1 to 14.79 | |||
| NO | 0.14 | 0.01 to 0.53 | |||
| Mifepristone | 118.70 | 0.4 to 135.8 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.33 | 0.16 to 0.61 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.19 | 0 to 0.91 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.09 | 0 to 0.42 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.52 | 0.76 to 2.77 | 2.76 | 0.23 to 12.25 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 3.22 | 0.87 to 8.6 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.23 | 0.52 to 2.48 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 4.26 | 0.15 to 23.41 | |||
| NO | 0.22 | 0.01 to 0.9 | |||
| Mifepristone | 191.90 | 0.56 to 221.2 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.52 | 0.22 to 1.07 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.30 | 0 to 1.52 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.15 | 0 to 0.67 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.45 | 0.95 to 5.28 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | i.v. oxytocin | 0.48 | 0.15 to 1.18 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.70 | 0.05 to 9.65 | |||
| NO | 0.09 | 0 to 0.38 | |||
| Mifepristone | 70.70 | 0.19 to 87.16 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.21 | 0.06 to 0.54 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.12 | 0 to 0.62 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.06 | 0 to 0.27 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.97 | 0.27 to 2.54 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 3.68 | 0.14 to 20.13 | ||
| NO | 0.19 | 0.01 to 0.75 | |||
| Mifepristone | 152.30 | 0.55 to 182.9 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.45 | 0.2 to 0.87 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 152.30 | 0.55 to 182.9 | 87,840.00 | 0.13 to 1813 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.25 | 0 to 1.27 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.10 | 0.96 to 4.05 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | NO | 0.25 | 0 to 1.56 | ||
| Mifepristone | 155.00 | 0.11 to 229.8 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.57 | 0.02 to 2.85 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.33 | 0 to 2.15 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.16 | 0 to 1.05 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.74 | 0.09 to 14.33 | |||
| NO | Mifepristone | 2238.00 | 2.26 to 2959 | ||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 8.59 | 0.54 to 46.06 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 5.14 | 0.02 to 29.25 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 2.50 | 0.01 to 14.17 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 39.35 | 2.53 to 210.4 | |||
| Mifepristone | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.16 | 0 to 0.83 | ||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.09 | 0 to 0.63 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.05 | 0 to 0.29 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.76 | 0.01 to 3.86 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.61 | 0.01 to 3.06 | ||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.30 | 0 to 1.38 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 5.04 | 2.05 to 10.57 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 5.50 | 0.01 to 31.59 | ||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 107.70 | 1.51 to 539.2 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 629.00 | 3.28 to 947.3 | ||
| Control treatment | Active treatment | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | ||
| No treatment | Placebo | 1.04 | 0.54 to 1.94 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.78 | 0.38 to 1.52 | 0.5181 | 0.01 to 2.4 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 1.07 | 0.68 to 1.67 | 1.704 | 0.77 to 3.3 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.10 | 0.5 to 2.44 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.70 | 0.44 to 1.07 | 1.014 | 0.42 to 2.04 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.82 | 0.39 to 1.71 | 0.5491 | 0.05 to 2 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.96 | 0.57 to 1.6 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.04 | 0.65 to 1.6 | 2.279 | 0.65 to 5.72 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.55 | 0.14 to 1.99 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.59 | 0.34 to 1.05 | 1.969 | 0.1 to 8.97 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.48 | 0.21 to 1.03 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.97 | 0.61 to 6.18 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.88 | 0.58 to 1.32 | 0.7168 | 0.39 to 1.18 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.35 | 0.41 to 4.39 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.48 | 0.75 to 8.72 | 7.825 | 0.92 to 34 | |
| NO | 0.51 | 0.18 to 1.13 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.80 | 0.21 to 3.8 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.85 | 0.48 to 1.46 | 0.03123 | 0 to 0.24 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.95 | 0.29 to 3.14 | 0.456 | 0.04 to 1.61 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.18 | 0.01 to 1.67 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.92 | 0.75 to 5.22 | 2.081 | 0.68 to 5.33 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 659,329,628,928,704,000.00 | 70.53 to 3.60054679804453E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.16 | 0.34 to 4.03 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.00 | 0.02 to 36.27 | 7.846 | 0.03 to 51.88 | |
| Acupuncture | 0.56 | 0.13 to 2.17 | 0.02285 | 0 to 0.15 | |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.36 | 0.07 to 1.6 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.43 | 0.17 to 0.97 | |||
| Placebo | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.75 | 0.34 to 1.62 | 0.5717 | 0.04 to 2.04 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 1.03 | 0.58 to 1.85 | 0.7006 | 0.12 to 2.21 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.06 | 0.43 to 2.6 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.67 | 0.38 to 1.2 | 0.4624 | 0.14 to 1.11 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.80 | 0.35 to 1.84 | 1.791 | 0.11 to 8.27 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.92 | 0.49 to 1.69 | 0.0389 | 0 to 0.32 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.01 | 0.56 to 1.81 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.53 | 0.13 to 2.08 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.57 | 0.3 to 1.13 | 0.8518 | 0.18 to 2.41 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.46 | 0.19 to 1.09 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.91 | 0.57 to 6.35 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.85 | 0.45 to 1.62 | 3.65E+22 | 1.77 to 3,182,000,000,000,000,000 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.30 | 0.37 to 4.61 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.39 | 0.62 to 9.58 | |||
| NO | 0.49 | 0.2 to 0.95 | 0.9444 | 0.39 to 1.88 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.77 | 0.23 to 3.37 | 0.7804 | 0.16 to 2.59 | |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.82 | 0.41 to 1.65 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.92 | 0.25 to 3.41 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.17 | 0.01 to 1.67 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.85 | 0.63 to 5.4 | 88.42 | 0.12 to 203 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 633,476,944,394,919,000.00 | 69.9 to 2.94787839145551E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.12 | 0.29 to 4.25 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.97 | 0.02 to 37.3 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.54 | 0.14 to 1.87 | 0.8182 | 0.15 to 2.49 | |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.35 | 0.06 to 1.68 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.41 | 0.15 to 0.99 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 1.37 | 0.71 to 2.71 | 1.857 | 0.36 to 5.94 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.41 | 0.56 to 3.65 | 4.7E+24 | 2.08 to 478,900,000,000,000,000 | |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.89 | 0.46 to 1.77 | 6.88E+20 | 0.74 to 6,076,000,000,000,000,000 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.05 | 0.42 to 2.7 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.23 | 0.6 to 2.52 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.33 | 0.7 to 2.66 | 1.348 | 0.23 to 4.45 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.70 | 0.17 to 2.82 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.76 | 0.36 to 1.66 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.61 | 0.25 to 1.54 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 2.53 | 0.73 to 8.77 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.13 | 0.57 to 2.29 | 0.03475 | 0 to 0.37 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.73 | 0.47 to 6.55 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 3.17 | 0.81 to 13.3 | 0.236 | 0 to 0.75 | |
| NO | 0.65 | 0.24 to 1.63 | 0.1239 | 0 to 0.21 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.02 | 0.25 to 5.15 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.09 | 0.54 to 2.3 | 2.726 | 0.41 to 10.52 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.22 | 0.32 to 4.82 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.23 | 0.01 to 2.34 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 2.45 | 0.81 to 7.97 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 838,172,230,557,343,000.00 | 80.8 to 4.39771779001637E+46 | 1.63E+25 | 0.83 to 1.911E+24 | |
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.48 | 0.37 to 6.09 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.28 | 0.02 to 51.11 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.71 | 0.16 to 3.1 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.46 | 0.08 to 2.26 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.55 | 0.2 to 1.45 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 1.03 | 0.47 to 2.24 | ||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.65 | 0.44 to 0.97 | 0.5104 | 0.2 to 1.07 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.77 | 0.36 to 1.62 | 3.342 | 0.56 to 12.17 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.90 | 0.57 to 1.54 | 1.146 | 0.35 to 2.74 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.97 | 0.64 to 1.48 | 1.135 | 0.38 to 2.69 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.51 | 0.14 to 1.77 | 0.9368 | 0.01 to 4.78 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.56 | 0.33 to 0.94 | 0.474 | 0.04 to 1.72 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.45 | 0.22 to 0.88 | 0.6843 | 0.28 to 1.37 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.85 | 0.6 to 5.69 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.82 | 0.52 to 1.26 | 1.429 | 0.41 to 3.77 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.26 | 0.41 to 3.99 | 1.539 | 0.34 to 4.66 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.31 | 0.65 to 8.44 | |||
| NO | 0.48 | 0.21 to 1.01 | 0.7503 | 0.11 to 2.55 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.74 | 0.2 to 3.53 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.80 | 0.48 to 1.31 | 0.8217 | 0.28 to 1.94 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.89 | 0.24 to 3.1 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.17 | 0.01 to 1.52 | 0.008447 | 0 to 0.07 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.79 | 0.68 to 5.06 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 614,754,871,294,005,000.00 | 59.98 to 2.94787839145551E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.08 | 0.31 to 3.91 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.94 | 0.02 to 35.52 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.52 | 0.12 to 2.03 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.34 | 0.06 to 1.51 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.40 | 0.17 to 0.97 | 0.6413 | 0 to 1.88 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | Intracervical PGE2 | 0.63 | 0.29 to 1.38 | 2.066 | 0.12 to 8.9 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.75 | 0.28 to 1.99 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.87 | 0.38 to 1.93 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.95 | 0.45 to 2.03 | 1.282 | 0.26 to 3.93 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.50 | 0.12 to 2.08 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.54 | 0.23 to 1.24 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.43 | 0.16 to 1.18 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.79 | 0.8 to 4.06 | 1.955 | 0.84 to 4.11 | |
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.80 | 0.36 to 1.71 | 1.043 | 0.01 to 6.38 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.22 | 0.32 to 4.68 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.25 | 0.56 to 9.37 | |||
| NO | 0.46 | 0.13 to 1.28 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.72 | 0.16 to 3.83 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.77 | 0.37 to 1.67 | 0.7099 | 0.2 to 1.71 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.87 | 0.22 to 3.46 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.16 | 0.01 to 1.46 | 3.77E+24 | 1.54 to 9.266E+20 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.74 | 0.52 to 5.94 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 596,586,119,074,455,000.00 | 51.16 to 2.94787839145551E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.05 | 0.26 to 4.34 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.91 | 0.02 to 37.86 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.51 | 0.1 to 2.27 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.33 | 0.05 to 1.65 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.39 | 0.13 to 1.1 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.18 | 0.57 to 2.52 | 2.118 | 0.1 to 8.33 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.37 | 0.89 to 2.14 | 1.842 | 0.77 to 3.8 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.50 | 1.03 to 2.24 | 0.8695 | 0.41 to 1.52 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.79 | 0.21 to 2.8 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.85 | 0.5 to 1.45 | 0.4558 | 0 to 2.62 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.69 | 0.31 to 1.44 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 2.83 | 0.91 to 8.71 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.26 | 0.81 to 1.92 | 2.349 | 1 to 4.91 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.94 | 0.59 to 6.4 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 3.55 | 0.99 to 12.96 | |||
| NO | 0.73 | 0.25 to 1.56 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.14 | 0.31 to 5.26 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.22 | 0.76 to 2.01 | 1.014 | 0.4 to 2.15 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.37 | 0.42 to 4.61 | 29.62 | 0.95 to 210 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.26 | 0.01 to 2.35 | 0.2309 | 0 to 1.31 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 2.75 | 1.04 to 7.82 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 945,036,551,034,665,000.00 | 94.92 to 4.86022980742998E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.66 | 0.48 to 5.97 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.44 | 0.02 to 54.87 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.80 | 0.19 to 3.15 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.52 | 0.1 to 2.28 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.61 | 0.26 to 1.36 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.16 | 0.51 to 2.56 | ||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.27 | 0.58 to 2.68 | 1.61E+28 | 0.88 to 1.142E+23 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.67 | 0.15 to 2.9 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.72 | 0.31 to 1.71 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.58 | 0.22 to 1.54 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 2.40 | 0.67 to 8.58 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.07 | 0.5 to 2.28 | 0.849 | 0.06 to 3.66 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.64 | 0.43 to 6.17 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 3.01 | 0.76 to 12.82 | |||
| NO | 0.62 | 0.18 to 1.63 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.97 | 0.22 to 4.98 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.03 | 0.47 to 2.3 | 2.36E+15 | 3.25 to 324,300,000,000,000 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.16 | 0.28 to 4.67 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.22 | 0.01 to 2.27 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 2.33 | 0.71 to 7.92 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 797,294,088,505,538,000.00 | 84.86 to 5.37138463833599E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.41 | 0.35 to 5.76 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.21 | 0.02 to 47.04 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.68 | 0.14 to 2.85 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.44 | 0.08 to 2.12 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.52 | 0.17 to 1.46 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.09 | 0.7 to 1.66 | 1.849 | 0.73 to 4.3 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.57 | 0.16 to 1.97 | 1.034 | 0.18 to 3.23 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.62 | 0.37 to 1.01 | 0.4391 | 0.17 to 0.91 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.50 | 0.21 to 1.06 | 0.1201 | 0 to 0.5 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 2.06 | 0.65 to 6.61 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.92 | 0.56 to 1.48 | 1.861 | 0.63 to 4.36 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.41 | 0.42 to 4.8 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.58 | 0.74 to 9.96 | |||
| NO | 0.53 | 0.19 to 1.19 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.83 | 0.21 to 3.96 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.89 | 0.51 to 1.53 | 0.9552 | 0.3 to 2.3 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.00 | 0.27 to 3.51 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.19 | 0.01 to 1.77 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 2.00 | 0.75 to 5.77 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 686,237,381,533,263,000.00 | 72.46 to 3.25790946826023E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.21 | 0.34 to 4.44 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.04 | 0.02 to 39.92 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.58 | 0.14 to 2.31 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.38 | 0.07 to 1.72 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.45 | 0.2 to 0.92 | 0.7231 | 0.26 to 1.52 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.53 | 0.15 to 1.88 | ||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.57 | 0.35 to 0.9 | 0.4848 | 0.21 to 0.9 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.46 | 0.21 to 0.96 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.89 | 0.6 to 5.62 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.84 | 0.56 to 1.26 | 0.9704 | 0.38 to 1.92 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.29 | 0.39 to 4.31 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.38 | 0.68 to 8.66 | |||
| NO | 0.49 | 0.19 to 1.02 | 0.07819 | 0 to 0.34 | |
| Mifepristone | 0.76 | 0.2 to 3.53 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.82 | 0.49 to 1.36 | 3.702 | 0.65 to 13.54 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.92 | 0.27 to 3.17 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.17 | 0.01 to 1.55 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.84 | 0.69 to 5.2 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 627,173,743,482,117,000.00 | 62.68 to 3.25790946826023E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.11 | 0.31 to 3.98 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.96 | 0.02 to 37.49 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.54 | 0.13 to 2.06 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.35 | 0.07 to 1.52 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.41 | 0.18 to 0.87 | 0.6738 | 0.05 to 2.8 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.08 | 0.3 to 3.98 | 6.78E+25 | 0.56 to 1.802E+25 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.87 | 0.22 to 3.68 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 3.60 | 0.68 to 19.2 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.60 | 0.45 to 6.03 | |||
| Amniotomy | 2.46 | 0.47 to 13.89 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 4.51 | 0.78 to 27.36 | |||
| NO | 0.93 | 0.22 to 3.94 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.45 | 0.24 to 10.22 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.55 | 0.42 to 5.86 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.74 | 0.3 to 9.87 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.33 | 0.01 to 4.18 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 3.49 | 0.74 to 17.57 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1,201,376,912,525,490,000.00 | 130.19 to 5.37138463833599E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.11 | 0.38 to 12.65 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.82 | 0.03 to 80.32 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.02 | 0.15 to 6.25 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.66 | 0.08 to 4.48 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.78 | 0.18 to 3.26 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.80 | 0.34 to 1.84 | ||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 3.32 | 1.01 to 10.77 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.48 | 0.88 to 2.51 | 0.8381 | 0.17 to 2.39 | |
| Amniotomy | 2.27 | 0.67 to 7.88 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 4.16 | 1.17 to 16.48 | |||
| NO | 0.86 | 0.3 to 1.98 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.34 | 0.34 to 6.52 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.43 | 0.78 to 2.74 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.60 | 0.42 to 5.91 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.30 | 0.01 to 2.93 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 3.22 | 1.15 to 9.52 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1,109,010,666,123,780,000.00 | 104.69 to 5.37138463833599E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.95 | 0.54 to 7.21 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.68 | 0.03 to 64.59 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.94 | 0.21 to 3.7 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.61 | 0.11 to 2.89 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.72 | 0.31 to 1.62 | 0.2451 | 0.01 to 1.09 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 4.13 | 1.18 to 15.1 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.84 | 0.86 to 4.09 | 8.687 | 0.04 to 48.74 | |
| Amniotomy | 2.82 | 0.75 to 10.77 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 5.18 | 1.24 to 22.07 | |||
| NO | 1.06 | 0.41 to 2.92 | |||
| Mifepristone | 1.67 | 0.38 to 9 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.78 | 0.83 to 4.01 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.99 | 0.47 to 8.09 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.38 | 0.02 to 3.76 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 4.01 | 1.25 to 13.76 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1,368,162,127,054,920,000.00 | 132.42 to 7.25061086293636E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.42 | 0.6 to 9.93 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 2.09 | 0.04 to 85.54 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.17 | 0.24 to 5.32 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.75 | 0.12 to 3.64 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.89 | 0.32 to 2.84 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | i.v. oxytocin | 0.45 | 0.14 to 1.38 | ||
| Amniotomy | 0.68 | 0.14 to 3.26 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.25 | 0.25 to 6.55 | |||
| NO | 0.26 | 0.06 to 0.96 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.40 | 0.07 to 2.59 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.43 | 0.14 to 1.32 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.48 | 0.1 to 2.4 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.09 | 0 to 0.99 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.97 | 0.23 to 4.24 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 334,027,593,585,380,000.00 | 27.19 to 1.78797862552213E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 0.59 | 0.11 to 2.96 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.51 | 0.01 to 23.81 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.28 | 0.05 to 1.65 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.18 | 0.03 to 1.15 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.22 | 0.06 to 0.8 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | Amniotomy | 1.53 | 0.46 to 5.2 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.82 | 0.81 to 10.34 | |||
| NO | 0.58 | 0.2 to 1.31 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.91 | 0.24 to 4.34 | 5.44E+27 | 2.41 to 4.997E+25 | |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.97 | 0.57 to 1.66 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.08 | 0.31 to 3.74 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.20 | 0.01 to 1.82 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 2.18 | 0.82 to 5.94 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 743,392,080,770,109,000.00 | 74.96 to 3.60054679804453E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.32 | 0.41 to 4.37 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.14 | 0.02 to 43.42 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.64 | 0.15 to 2.51 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.41 | 0.08 to 1.73 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.48 | 0.2 to 1.09 | |||
| Amniotomy | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.83 | 0.47 to 7.62 | 3.534 | 0.2 to 14.52 |
| NO | 0.38 | 0.09 to 1.48 | |||
| Mifepristone | 0.59 | 0.11 to 4.15 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.63 | 0.18 to 2.16 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.71 | 0.14 to 3.82 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.13 | 0.01 to 1.65 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.42 | 0.32 to 6.3 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 488443402545697000.00 | 51.62 to 2.66735067240862E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 0.86 | 0.16 to 4.83 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.74 | 0.01 to 31.25 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.41 | 0.07 to 2.44 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.27 | 0.03 to 1.73 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.32 | 0.08 to 1.24 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | NO | 0.21 | 0.04 to 0.89 | ||
| Mifepristone | 0.32 | 0.05 to 2.44 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.34 | 0.09 to 1.27 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 0.39 | 0.07 to 2.17 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.07 | 0 to 0.96 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.77 | 0.16 to 3.66 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 265,396,147,266,911,000.00 | 22.13 to 1.61782996302093E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 0.47 | 0.08 to 2.61 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.40 | 0.01 to 18.21 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.23 | 0.04 to 1.47 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.15 | 0.02 to 0.99 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.17 | 0.04 to 0.69 | |||
| NO | Mifepristone | 1.57 | 0.39 to 7.55 | ||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.67 | 0.72 to 5.03 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.87 | 0.44 to 7.5 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.35 | 0.01 to 3.63 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 3.77 | 1.13 to 13.03 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 1,288,486,567,453,520,000.00 | 136.73 to 5.93629809208726E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 2.28 | 0.55 to 10.51 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.97 | 0.03 to 74.14 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.10 | 0.24 to 4.42 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.71 | 0.11 to 3.57 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.84 | 0.28 to 3.14 | |||
| Mifepristone | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.07 | 0.22 to 4.25 | ||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.20 | 0.18 to 6.94 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.23 | 0.01 to 2.92 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 2.41 | 0.41 to 12.57 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 821,575,308,394,869,000.00 | 78.26 to 4.86022980742998E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.45 | 0.21 to 8.38 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.26 | 0.02 to 56.6 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.70 | 0.1 to 4.04 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.45 | 0.05 to 3.16 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.54 | 0.09 to 2.39 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.12 | 0.33 to 4.1 | ||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.21 | 0.01 to 1.86 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 2.25 | 0.81 to 6.78 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 773,730,487,114,827,000.00 | 75.49 to 3.60054679804453E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.36 | 0.38 to 5.06 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.18 | 0.02 to 45.92 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.66 | 0.14 to 2.66 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.42 | 0.08 to 1.89 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.50 | 0.2 to 1.2 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.19 | 0.01 to 2.44 | ||
| Membrane sweeping | 2.01 | 0.45 to 8.76 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 686,237,381,533,263,000.00 | 66.29 to 3.97921961036919E+46 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 1.21 | 0.22 to 6.61 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.05 | 0.02 to 41.43 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.59 | 0.09 to 3.34 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.38 | 0.05 to 2.57 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.45 | 0.11 to 1.93 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | Membrane sweeping | 10.63 | 0.93 to 246.66 | ||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 3,645,408,119,402,930,000.00 | 676.55 to 1.19542363552926E+47 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 6.42 | 0.51 to 166 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 5.55 | 0.06 to 476.28 | |||
| Acupuncture | 3.10 | 0.21 to 90.02 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 2.00 | 0.12 to 62.3 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.37 | 0.21 to 60.95 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 344,200,248,275,638,000.00 | 39.33 to 1.19851791457072E+46 | ||
| i.v. prostaglandin | 0.60 | 0.13 to 2.81 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.52 | 0.01 to 23.9 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.29 | 0.05 to 1.51 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.19 | 0.03 to 1.06 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.22 | 0.06 to 0.74 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | i.v. prostaglandin | 0.00 | 0 to 0.02 | ||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.00 | 0 to 0.01 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.00 | 0 to 0.01 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.00 | 0 to 0.01 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.00 | 0 to 0.01 | |||
| i.v. prostaglandin | Sexual intercourse | 0.86 | 0.01 to 42.18 | ||
| Acupuncture | 0.48 | 0.07 to 2.84 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.31 | 0.04 to 2.06 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.37 | 0.09 to 1.5 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | Acupuncture | 0.56 | 0.01 to 36.49 | ||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.36 | 0.01 to 27.49 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.43 | 0.01 to 26.39 | |||
| Acupuncture | Oral prostaglandins | 0.65 | 0.08 to 5.26 | ||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.76 | 0.16 to 3.94 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.18 | 0.22 to 7.31 | ||
| Control treatment | Active treatment | NMA | Pairwise meta-analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CrI | OR | 95% CrI | ||
| No treatment | Placebo | 1.07 | 0.7 to 1.56 | 0.7355 | 0 to 0.77 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.85 | 0.48 to 1.41 | 0.5082 | 0.08 to 1.63 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.91 | 0.7 to 1.15 | 0.899 | 0.56 to 1.36 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.75 | 0.52 to 1.05 | |||
| PGF2 gel | 0.58 | 0.19 to 1.34 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.78 | 0.56 to 1.05 | 0.8517 | 0.16 to 2.54 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.91 | 0.57 to 1.36 | 1.535 | 0.71 to 2.91 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.76 | 0.58 to 0.97 | 12.27 | 0.03 to 42.75 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.88 | 0.67 to 1.13 | 1.238 | 0.46 to 2.64 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.81 | 0.35 to 1.61 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.85 | 0.64 to 1.12 | 1.335E+28 | 0.52 to 9.656E+21 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.69 | 0.45 to 1.01 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.61 | 0.35 to 0.99 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.79 | 0.63 to 0.97 | 0.7211 | 0.54 to 0.93 | |
| Amniotomy | 0.86 | 0.24 to 2.19 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.64 | 0.82 to 2.96 | 2.001 | 0.61 to 4.99 | |
| NO | 0.87 | 0.5 to 1.37 | 1.247 | 0.13 to 5.08 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.80 | 0.73 to 3.83 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.50 | 0.01 to 8.27 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.68 | 0.48 to 0.94 | 0.6182 | 0.11 to 1.75 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.59 | 0.43 to 4.34 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.62 | 0.3 to 1.13 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.85 | 0.52 to 1.33 | 0.9813 | 0.57 to 1.57 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.41 | 0.17 to 0.81 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.49 | 0.16 to 1.12 | 0.4972 | 0.16 to 1.16 | |
| Acupuncture | 1.00 | 0.11 to 3.69 | 0.09124 | 0 to 0.17 | |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.70 | 0.1 to 2.4 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.75 | 0.47 to 1.15 | |||
| Placebo | Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 0.83 | 0.42 to 1.44 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 0.88 | 0.59 to 1.26 | 0.7141 | 0.26 to 1.58 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.73 | 0.44 to 1.11 | 29.03 | 0.45 to 156.3 | |
| PGF2 gel | 0.56 | 0.18 to 1.36 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.76 | 0.48 to 1.12 | 1.059 | 0.08 to 4.41 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 0.88 | 0.51 to 1.4 | 0.8597 | 0.3 to 1.94 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.74 | 0.49 to 1.06 | 0.9459 | 0.38 to 1.94 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.85 | 0.57 to 1.23 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.79 | 0.31 to 1.63 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.83 | 0.55 to 1.2 | 0.7459 | 0.28 to 1.61 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.67 | 0.39 to 1.07 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.59 | 0.31 to 1.03 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.76 | 0.5 to 1.12 | 0.7765 | 0.06 to 3.02 | |
| Amniotomy | 0.84 | 0.22 to 2.26 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.60 | 0.71 to 3.06 | |||
| NO | 0.82 | 0.54 to 1.2 | 0.9191 | 0.56 to 1.43 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.71 | 0.73 to 3.55 | 1.149 | 0.38 to 2.75 | |
| Oestrogens | 1.43 | 0.01 to 7.8 | 2.287 | 0.02 to 12.21 | |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.66 | 0.41 to 1 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.54 | 0.4 to 4.31 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.60 | 0.26 to 1.15 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.83 | 0.43 to 1.46 | 1.141 | 0.01 to 6.19 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.40 | 0.16 to 0.82 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.48 | 0.14 to 1.17 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.94 | 0.11 to 3.36 | 1.429 | 0.13 to 5.95 | |
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.68 | 0.09 to 2.4 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.73 | 0.42 to 1.19 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 1.14 | 0.65 to 1.88 | 0.9833 | 0.01 to 5.19 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.94 | 0.5 to 1.6 | |||
| PGF2 gel | 0.72 | 0.22 to 1.82 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.98 | 0.55 to 1.64 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.14 | 0.56 to 2.09 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.95 | 0.54 to 1.56 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.10 | 0.64 to 1.77 | 0.8967 | 0.33 to 1.93 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.02 | 0.37 to 2.21 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.07 | 0.62 to 1.74 | 1.136 | 0.38 to 2.65 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.86 | 0.44 to 1.52 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.76 | 0.36 to 1.44 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.99 | 0.56 to 1.64 | |||
| Amniotomy | 1.09 | 0.27 to 3.01 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.06 | 0.85 to 4.28 | |||
| NO | 1.08 | 0.52 to 2.03 | 0.09229 | 0 to 0.47 | |
| Mifepristone | 2.26 | 0.78 to 5.32 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.88 | 0.02 to 10.41 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.85 | 0.47 to 1.43 | 1.641 | 0.33 to 5.09 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.99 | 0.48 to 5.81 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.77 | 0.31 to 1.59 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.08 | 0.51 to 2.08 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.51 | 0.19 to 1.11 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.62 | 0.17 to 1.57 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.26 | 0.12 to 4.97 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.88 | 0.11 to 3.2 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.94 | 0.48 to 1.69 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 0.83 | 0.58 to 1.14 | ||
| PGF2 gel | 0.64 | 0.22 to 1.48 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 0.86 | 0.65 to 1.13 | 0.8812 | 0.43 to 1.61 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.01 | 0.62 to 1.53 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.84 | 0.67 to 1.04 | 0.9043 | 0.62 to 1.3 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.97 | 0.77 to 1.21 | 1.194 | 0.76 to 1.8 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.89 | 0.4 to 1.74 | 0.7755 | 0.21 to 1.99 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.95 | 0.73 to 1.2 | 0.5218 | 0.23 to 1 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.76 | 0.51 to 1.09 | 0.835 | 0.45 to 1.42 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.68 | 0.39 to 1.09 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.87 | 0.67 to 1.12 | |||
| Amniotomy | 0.95 | 0.27 to 2.4 | 1.437 | 0.35 to 4.07 | |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.81 | 0.92 to 3.23 | 1.459 | 0.57 to 3.01 | |
| NO | 0.96 | 0.57 to 1.49 | 1.03 | 0.37 to 2.29 | |
| Mifepristone | 1.99 | 0.81 to 4.26 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.66 | 0.02 to 9.07 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.75 | 0.56 to 1.01 | 0.7575 | 0.43 to 1.21 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.75 | 0.49 to 4.72 | 1.061 | 0.07 to 4.61 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.68 | 0.34 to 1.22 | 0.5625 | 0.22 to 1.18 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 0.95 | 0.54 to 1.56 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.46 | 0.19 to 0.89 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.55 | 0.17 to 1.29 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.11 | 0.12 to 4.03 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.78 | 0.11 to 2.67 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.83 | 0.53 to 1.24 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | PGF2 gel | 0.78 | 0.26 to 1.83 | ||
| Intracervical PGE2 | 1.07 | 0.72 to 1.51 | 7.959 | 0.51 to 41.36 | |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.24 | 0.72 to 1.99 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.04 | 0.74 to 1.41 | 1.177 | 0.52 to 2.28 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.20 | 0.86 to 1.63 | 1.089 | 0.57 to 1.92 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.11 | 0.46 to 2.24 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.17 | 0.81 to 1.63 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.94 | 0.58 to 1.42 | 5.206E+12 | 8.7 to 553,300,000,000 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.82 | 0.55 to 1.18 | 0.8202 | 0.53 to 1.22 | |
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.08 | 0.76 to 1.48 | 1.217 | 0.62 to 2.13 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.18 | 0.32 to 3.06 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.25 | 1.03 to 4.25 | |||
| NO | 1.18 | 0.65 to 1.97 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.45 | 0.96 to 5.35 | |||
| Oestrogens | 2.03 | 0.02 to 11.13 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.93 | 0.65 to 1.27 | 0.7907 | 0.45 to 1.28 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.17 | 0.57 to 5.94 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.84 | 0.41 to 1.52 | 2.092 | 0.49 to 6.2 | |
| Membrane sweeping | 1.18 | 0.64 to 2.01 | 0.2399 | 0 to 1.11 | |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.56 | 0.23 to 1.13 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.67 | 0.2 to 1.62 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.37 | 0.15 to 5.05 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.96 | 0.13 to 3.29 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.03 | 0.62 to 1.62 | |||
| PGF2 gel | Intracervical PGE2 | 1.71 | 0.57 to 3.98 | ||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 2.00 | 0.61 to 4.91 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 1.66 | 0.57 to 3.86 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.93 | 0.65 to 4.49 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.78 | 0.44 to 4.91 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.87 | 0.63 to 4.36 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 1.52 | 0.49 to 3.65 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 1.33 | 0.41 to 3.31 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.73 | 0.58 to 4.05 | |||
| Amniotomy | 1.90 | 0.34 to 6.14 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 3.60 | 0.97 to 9.39 | |||
| NO | 1.90 | 0.57 to 4.67 | |||
| Mifepristone | 3.96 | 0.93 to 11.34 | |||
| Oestrogens | 3.26 | 0.02 to 18.77 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.47 | 0.53 to 3.3 | 1.479 | 0.52 to 3.4 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 3.48 | 0.61 to 11.7 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.35 | 0.37 to 3.5 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.89 | 0.55 to 4.73 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.91 | 0.22 to 2.49 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 1.09 | 0.21 to 3.35 | |||
| Acupuncture | 2.18 | 0.18 to 9.13 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.55 | 0.16 to 6.24 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.65 | 0.51 to 4.01 | |||
| Intracervical PGE2 | Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 1.18 | 0.7 to 1.88 | ||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.98 | 0.76 to 1.26 | 0.9989 | 0.66 to 1.47 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.14 | 0.87 to 1.47 | 1.187 | 0.73 to 1.83 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.05 | 0.45 to 2.07 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.11 | 0.82 to 1.46 | 1.15 | 0.39 to 2.71 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.90 | 0.57 to 1.33 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.79 | 0.45 to 1.3 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.03 | 0.75 to 1.38 | |||
| Amniotomy | 1.13 | 0.31 to 2.91 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.14 | 1.01 to 4 | |||
| NO | 1.13 | 0.65 to 1.82 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.34 | 0.94 to 5.1 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.94 | 0.02 to 10.61 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.88 | 0.63 to 1.2 | 0.9001 | 0.44 to 1.64 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.05 | 0.57 to 5.51 | 4.442 | 0.68 to 17.69 | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.80 | 0.38 to 1.47 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.12 | 0.62 to 1.89 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.54 | 0.22 to 1.06 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.64 | 0.19 to 1.54 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.30 | 0.14 to 4.82 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.91 | 0.13 to 3.17 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.98 | 0.61 to 1.49 | |||
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 0.87 | 0.54 to 1.34 | 4.653 | 0.01 to 21.17 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.01 | 0.64 to 1.54 | 1.879 | 0.76 to 4.08 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.93 | 0.36 to 1.98 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.98 | 0.61 to 1.51 | |||
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.79 | 0.45 to 1.31 | 1.523 | 0.51 to 3.63 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.70 | 0.35 to 1.26 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.91 | 0.57 to 1.38 | 1.478 | 0.15 to 5.7 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.00 | 0.26 to 2.7 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.89 | 0.81 to 3.7 | |||
| NO | 0.99 | 0.52 to 1.72 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.06 | 0.78 to 4.64 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.73 | 0.02 to 9.35 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.79 | 0.46 to 1.26 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.83 | 0.46 to 5.18 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.71 | 0.31 to 1.41 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.99 | 0.5 to 1.77 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.47 | 0.18 to 0.97 | 0.9191 | 0.23 to 2.48 | |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.57 | 0.16 to 1.41 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.14 | 0.12 to 4.29 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.81 | 0.11 to 2.9 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.87 | 0.47 to 1.49 | |||
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.16 | 0.94 to 1.42 | 1.441 | 0.85 to 2.31 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 1.07 | 0.47 to 2.08 | 1.825 | 0.42 to 5.4 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.13 | 0.9 to 1.4 | 0.9496 | 0.64 to 1.35 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.91 | 0.61 to 1.31 | 0.5433 | 0.13 to 1.43 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.81 | 0.48 to 1.29 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.05 | 0.82 to 1.33 | 1.681 | 0.96 to 2.72 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.15 | 0.32 to 2.93 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.18 | 1.07 to 3.97 | |||
| NO | 1.15 | 0.68 to 1.8 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.39 | 0.98 to 5.13 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.99 | 0.02 to 10.82 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.90 | 0.67 to 1.19 | 0.9504 | 0.5 to 1.66 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.10 | 0.58 to 5.67 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.82 | 0.4 to 1.48 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.14 | 0.65 to 1.88 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.55 | 0.23 to 1.06 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.66 | 0.2 to 1.54 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.33 | 0.15 to 4.81 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.93 | 0.13 to 3.18 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.99 | 0.66 to 1.45 | 1.043 | 0.53 to 1.83 | |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 0.93 | 0.4 to 1.82 | ||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 0.98 | 0.79 to 1.2 | 1.234 | 0.87 to 1.7 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.79 | 0.53 to 1.12 | 0.7044 | 0.23 to 1.65 | |
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.70 | 0.41 to 1.11 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.90 | 0.71 to 1.14 | 0.9313 | 0.55 to 1.48 | |
| Amniotomy | 0.99 | 0.28 to 2.54 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.89 | 0.92 to 3.46 | |||
| NO | 0.99 | 0.59 to 1.56 | 0.01104 | 0 to 0.1 | |
| Mifepristone | 2.07 | 0.84 to 4.41 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.72 | 0.02 to 9.36 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.78 | 0.57 to 1.04 | 1.725 | 0.42 to 4.97 | |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.82 | 0.5 to 4.9 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.71 | 0.34 to 1.28 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.99 | 0.56 to 1.63 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.47 | 0.2 to 0.89 | 0.4223 | 0.11 to 1.07 | |
| Sexual intercourse | 0.57 | 0.17 to 1.33 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.15 | 0.13 to 4.26 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.81 | 0.11 to 2.77 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.86 | 0.57 to 1.25 | 1.078 | 0.47 to 2.11 | |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 1.21 | 0.54 to 2.4 | 2.856 | 0.18 to 12.83 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.98 | 0.4 to 2.02 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.87 | 0.33 to 1.91 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.12 | 0.49 to 2.25 | |||
| Amniotomy | 1.23 | 0.26 to 3.68 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.33 | 0.78 to 5.43 | |||
| NO | 1.23 | 0.47 to 2.67 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.56 | 0.73 to 6.67 | |||
| Oestrogens | 2.14 | 0.02 to 12.26 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.97 | 0.41 to 1.97 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.25 | 0.48 to 6.95 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.88 | 0.29 to 2.06 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.22 | 0.45 to 2.68 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.58 | 0.18 to 1.43 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.70 | 0.17 to 1.94 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.42 | 0.13 to 5.56 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.00 | 0.11 to 3.76 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.07 | 0.43 to 2.25 | |||
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 0.81 | 0.54 to 1.19 | ||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.72 | 0.42 to 1.17 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | 0.93 | 0.72 to 1.19 | 0.8406 | 0.5 to 1.33 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.03 | 0.28 to 2.63 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 1.94 | 0.94 to 3.57 | |||
| NO | 1.02 | 0.6 to 1.61 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.13 | 0.86 to 4.58 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.77 | 0.02 to 9.78 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.81 | 0.57 to 1.1 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.88 | 0.51 to 5.07 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.73 | 0.35 to 1.34 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.02 | 0.57 to 1.68 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.49 | 0.21 to 0.95 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.58 | 0.18 to 1.37 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.18 | 0.13 to 4.3 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.83 | 0.12 to 2.84 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.89 | 0.58 to 1.3 | 0.7847 | 0.38 to 1.43 | |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | 0.91 | 0.49 to 1.58 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin | 1.18 | 0.78 to 1.73 | 31.66 | 0.89 to 177.1 | |
| Amniotomy | 1.30 | 0.34 to 3.4 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.46 | 1.11 to 4.75 | |||
| NO | 1.30 | 0.69 to 2.21 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.70 | 1.02 to 6.11 | |||
| Oestrogens | 2.25 | 0.02 to 12.26 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.02 | 0.65 to 1.54 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.38 | 0.61 to 6.66 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.92 | 0.42 to 1.79 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.29 | 0.66 to 2.28 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.61 | 0.25 to 1.23 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.74 | 0.22 to 1.82 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.50 | 0.16 to 5.6 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.06 | 0.14 to 3.72 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.13 | 0.64 to 1.83 | |||
| Sustained-release misoprostol vaginal pessary | i.v. oxytocin | 1.37 | 0.8 to 2.2 | ||
| Amniotomy | 1.51 | 0.37 to 4.05 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.86 | 1.17 to 5.83 | |||
| NO | 1.51 | 0.72 to 2.76 | |||
| Mifepristone | 3.13 | 1.1 to 7.26 | |||
| Oestrogens | 2.59 | 0.02 to 14.3 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.18 | 0.69 to 1.9 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.76 | 0.68 to 7.86 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 1.07 | 0.46 to 2.1 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.50 | 0.71 to 2.8 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.72 | 0.26 to 1.56 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.86 | 0.24 to 2.17 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.75 | 0.18 to 6.59 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.22 | 0.16 to 4.34 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.31 | 0.68 to 2.3 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin | Amniotomy | 1.11 | 0.31 to 2.82 | ||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.10 | 1.03 to 3.85 | |||
| NO | 1.11 | 0.65 to 1.76 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.29 | 0.94 to 4.83 | 7.815 | 1.31 to 28.37 | |
| Oestrogens | 1.91 | 0.02 to 10.47 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.87 | 0.62 to 1.19 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.03 | 0.55 to 5.49 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.79 | 0.38 to 1.44 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.10 | 0.63 to 1.77 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.53 | 0.22 to 1.03 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.63 | 0.2 to 1.46 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.28 | 0.14 to 4.67 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.89 | 0.13 to 3.01 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.96 | 0.61 to 1.45 | |||
| Amniotomy | i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2.56 | 0.64 to 7.17 | 2.553E+23 | 21.92 to 1.433E+22 |
| NO | 1.37 | 0.34 to 3.81 | |||
| Mifepristone | 2.86 | 0.57 to 9.12 | |||
| Oestrogens | 2.36 | 0.02 to 14.08 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 1.08 | 0.3 to 2.87 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.51 | 0.39 to 8.88 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.97 | 0.23 to 2.83 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.36 | 0.34 to 3.74 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.65 | 0.14 to 1.99 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.79 | 0.13 to 2.65 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.61 | 0.1 to 7.07 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.11 | 0.1 to 4.65 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.19 | 0.32 to 3.22 | |||
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | NO | 0.58 | 0.25 to 1.18 | ||
| Mifepristone | 1.22 | 0.38 to 3.03 | |||
| Oestrogens | 1.03 | 0.01 to 5.84 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.46 | 0.22 to 0.86 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.07 | 0.24 to 3.24 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.42 | 0.15 to 0.92 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.58 | 0.24 to 1.18 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.28 | 0.09 to 0.66 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.33 | 0.08 to 0.88 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.68 | 0.06 to 2.62 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.48 | 0.06 to 1.77 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.51 | 0.22 to 1.01 | |||
| NO | Mifepristone | 2.16 | 0.83 to 4.75 | ||
| Oestrogens | 1.81 | 0.02 to 9.98 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.83 | 0.47 to 1.38 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.94 | 0.49 to 5.52 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.75 | 0.32 to 1.51 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.05 | 0.5 to 1.94 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.50 | 0.19 to 1.07 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.60 | 0.17 to 1.52 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.20 | 0.13 to 4.31 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.86 | 0.11 to 3.09 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.92 | 0.49 to 1.6 | |||
| Mifepristone | Oestrogens | 0.97 | 0.01 to 5.52 | ||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 0.45 | 0.17 to 0.94 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 1.04 | 0.21 to 3.26 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.41 | 0.12 to 0.98 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.57 | 0.19 to 1.26 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.27 | 0.07 to 0.69 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.33 | 0.07 to 0.93 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.65 | 0.06 to 2.58 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.47 | 0.05 to 1.8 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.50 | 0.18 to 1.08 | |||
| Oestrogens | Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 9.68 | 0.08 to 49.08 | ||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 20.18 | 0.12 to 102.9 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 8.64 | 0.07 to 43.03 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 12.43 | 0.09 to 62.02 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 5.32 | 0.04 to 28.61 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 6.83 | 0.04 to 33.44 | |||
| Acupuncture | 10.98 | 0.05 to 64.12 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 9.58 | 0.04 to 50.55 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 10.48 | 0.09 to 52.25 | |||
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | Mechanical methods – laminaria | 2.37 | 0.64 to 6.44 | ||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.91 | 0.45 to 1.64 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | 1.29 | 0.71 to 2.19 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.62 | 0.25 to 1.23 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.74 | 0.22 to 1.79 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.50 | 0.16 to 5.53 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.05 | 0.14 to 3.65 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.12 | 0.69 to 1.75 | |||
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 0.54 | 0.12 to 1.56 | ||
| Membrane sweeping | 0.76 | 0.18 to 2.12 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.36 | 0.07 to 1.11 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.43 | 0.07 to 1.42 | |||
| Acupuncture | 0.89 | 0.06 to 3.85 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.62 | 0.05 to 2.58 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.66 | 0.16 to 1.81 | |||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | Membrane sweeping | 1.55 | 0.64 to 3.23 | ||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.74 | 0.24 to 1.72 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.89 | 0.22 to 2.39 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.80 | 0.17 to 7.02 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.27 | 0.15 to 4.7 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.36 | 0.6 to 2.7 | |||
| Membrane sweeping | Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 0.51 | 0.18 to 1.11 | ||
| Sexual intercourse | 0.61 | 0.17 to 1.54 | |||
| Acupuncture | 1.24 | 0.13 to 4.69 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 0.87 | 0.11 to 3.13 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 0.93 | 0.46 to 1.68 | |||
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | Sexual intercourse | 1.38 | 0.33 to 3.8 | ||
| Acupuncture | 2.79 | 0.25 to 11.14 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.98 | 0.22 to 7.6 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.11 | 0.85 to 4.5 | |||
| Sexual intercourse | Acupuncture | 2.59 | 0.2 to 11.03 | ||
| Oral prostaglandins | 1.83 | 0.19 to 7.23 | |||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.98 | 0.59 to 5.17 | |||
| Acupuncture | Oral prostaglandins | 1.59 | 0.07 to 8.28 | ||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 1.70 | 0.19 to 7.02 | |||
| Oral prostaglandins | Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 2.06 | 0.3 to 7.72 | ||
Appendix 13 Sensitivity analysis excluding trials at high risk of bias
Comparison of mean ranks (95% CrI) from complete analysis and ranks, having removed studies at high risk of bias on the allocation concealment domain.
| Intervention | All studies (141 trials) | Only studies at low ROB (97 trials) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean rank | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | |
| No treatment | 21 | 19 to 21 | 19 | 14 to 21 |
| Placebo | 20 | 19 to 21 | 21 | 19 to 21 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 12 | 6 to 17 | 9 | 3 to 16 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 8 | 5 to 12 | 7 | 3 to 11 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 11 | 6 to 16 | 12 | 7 to 16 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 14 | 10 to 17 | 12 | 8 to 16 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 4 | 1 to 11 | 10 | 2 to 17 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 6 | 3 to 9 | 6 | 3 to 9 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 4 | 2 to 7 | 3 | 1 to 6 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 14 | 5 to 18 | 15 | 6 to 19 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 12 | 8 to 16 | 9 | 5 to 14 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 5 | 2 to 10 | 4 | 2 to 9 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 5 | 1 to 16 | 10 | 2 to 18 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 14 | 9 to 18 | 11 | 5 to 16 |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 2 | 1 to 10 | 1 | 1 to 8 |
| NO | 15 | 6 to 18 | 18 | 13 to 20 |
| Mifepristone | 19 | 17 to 21 | 19 | 15 to 21 |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 13 | 7 to 17 | 12 | 6 to 17 |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 10 | 2 to 18 | 12 | 4 to 17 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 16 | 4 to 20 | 16 | 4 to 21 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 6 | 2 to 11 | 4 | 2 to 9 |
| Intervention | All studies (180 trials) | Only studies at low ROB (127 trials) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean rank | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | |
| No treatment | 8 | 3 to 17 | 8 | 3 to 17 |
| Placebo | 6 | 3 to 10 | 4 | 3 to 7 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 11 | 6 to 17 | 9 | 4 to 16 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 13 | 9 to 17 | 13 | 9 to 17 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 15 | 10 to 19 | 13 | 8 to 18 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 10 | 6 to 13 | 9 | 5 to 14 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 8 | 3 to 16 | 5 | 3 to 14 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 15 | 11 to 18 | 15 | 11 to 18 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 19 | 17 to 21 | 17 | 15 to 19 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 6 | 2 to 15 | 7 | 3 to 16 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 15 | 11 to 18 | 14 | 10 to 18 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 11 | 5 to 17 | 11 | 5 to 17 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 18 | 11 to 21 | 11 | 3 to 19 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 12 | 7 to 17 | 12 | 6 to 17 |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 14 | 3 to 21 | 15 | 3 to 19 |
| NO | 3 | 1 to 8 | 2 | 1 to 2 |
| Mifepristone | 19 | 7 to 21 | 20 | 20 to 20 |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 5 | 3 to 9 | 6 | 3 to 11 |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 3 | 1 to 13 | Not in network | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 2 | 1 to 6 | 1 | 1 to 2 |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 18 | 13 to 21 | 17 | 11 to 19 |
| Intervention | All studies (204 trials) | Only studies at low ROB (145 trials) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean rank | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | |
| No treatment | 23 | 16 to 27 | 19 | 10 to 25 |
| Placebo | 23 | 13 to 28 | 19 | 8 to 25 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 16 | 4 to 27 | 20 | 5 to 27 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 20 | 13 to 25 | 18 | 11 to 24 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 13 | 6 to 23 | 14 | 6 to 24 |
| PGF2 gel | 8 | 1 to 26 | 8 | 1 to 25 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 14 | 7 to 23 | 13 | 5 to 24 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 18 | 6 to 27 | 15 | 4 to 25 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 13 | 7 to 20 | 12 | 6 to 19 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 19 | 12 to 25 | 19 | 12 to 24 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 14 | 2 to 28 | 13 | 2 to 26 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 18 | 10 to 24 | 16 | 8 to 23 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 11 | 4 to 22 | 12 | 4 to 23 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 8 | 2 to 22 | 9 | 1 to 24 |
| i.v. oxytocin | 15 | 8 to 22 | 15 | 7 to 23 |
| Amniotomy | 14 | 1 to 29 | 13 | 1 to 27 |
| i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy | 27 | 17 to 29 | 24 | 7 to 27 |
| NO | 17 | 5 to 26 | 17 | 5 to 26 |
| Mifepristone | 26 | 13 to 29 | 24 | 11 to 27 |
| Oestrogens | 14 | 1 to 29 | 13 | 1 to 27 |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 10 | 5 to 19 | 10 | 4 to 20 |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 23 | 4 to 29 | Not in network | |
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 9 | 2 to 25 | 9 | 2 to 24 |
| Membrane sweeping | 16 | 5 to 27 | 12 | 3 to 25 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 4 | 1 to 15 | 4 | 1 to 16 |
| Sexual intercourse | 6 | 1 to 25 | 5 | 1 to 23 |
| Acupuncture | 14 | 1 to 29 | 12 | 1 to 27 |
| Oral prostaglandins | 10 | 1 to 29 | Not in network | |
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 13 | 4 to 25 | 13 | 4 to 24 |
| Intervention | All studies (299 trials) | Only studies at low ROB (163) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean rank | 95% CrI | Mean rank | 95% CrI | |
| No treatment | 24 | 17 to 29 | 17 | 9 to 23 |
| Placebo | 21 | 12 to 28 | 18 | 8 to 24 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (tablet) | 17 | 8 to 26 | 12 | 3 to 23 |
| Vaginal PGE2 (gel) | 18 | 11 to 24 | 12 | 7 to 19 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) | 7 | 2 to 17 | 7 | 1 to 17 |
| PGF2 gel | 14 | 2 to 28 | 8 | 1 to 22 |
| Intracervical PGE2 | 15 | 8 to 23 | 19 | 11 to 25 |
| Vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release) | 23 | 13 to 30 | 24 | 18 to 27 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg) | 11 | 4 to 20 | 12 | 5 to 21 |
| Vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 17 | 10 to 24 | 16 | 8 to 23 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg) | 9 | 1 to 29 | 6 | 1 to 23 |
| Oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg) | 13 | 6 to 21 | 14 | 7 to 22 |
| Titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution | 19 | 5 to 30 | 15 | 4 to 25 |
| Sustained-release misoprostol insert | 16 | 1 to 31 | ||
| Intravenous oxytocin | 24 | 18 to 29 | 19 | 11 to 24 |
| Amniotomy | 13 | 2 to 29 | 10 | 1 to 25 |
| Intravenous oxytocin plus amniotomy | 17 | 6 to 28 | 13 | 2 to 25 |
| NO | 17 | 5 to 28 | 13 | 3 to 24 |
| Mifepristone | 30 | 22 to 32 | 26 | 21 to 27 |
| Oestrogens | 8 | 1 to 28 | 9 | 1 to 25 |
| Relaxin | 25 | 4 to 32 | 22 | 4 to 27 |
| Mechanical methods – Foley catheter | 6 | 2 to 12 | 4 | 1 to 9 |
| Mechanical methods – laminaria | 12 | 1 to 29 | ||
| Mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter | 9 | 1 to 24 | 11 | 2 to 24 |
| Membrane sweeping | 26 | 16 to 31 | 21 | 9 to 26 |
| Extra-amniotic PGE2 | 15 | 1 to 30 | 8 | 1 to 26 |
| Intravenous prostaglandin | 30 | 15 to 32 | ||
| Sexual intercourse | 25 | 7 to 32 | 19 | 4 to 27 |
| Acupuncture | 13 | 1 to 28 | 12 | 2 to 25 |
| Homeopathy | 18 | 1 to 32 | ||
| Oral prostaglandins | 9 | 1 to 25 | ||
| Buccal/sublingual misoprostol | 7 | 1 to 20 | 11 | 2 to 23 |
Appendix 14 Data files for all outcomes considered in network meta-analysis
Data file for OpenBUGS analysis of failure to achieve vaginal delivery within 24 hours
Treatments included in analysis:
-
no treatment
-
placebo
-
vaginal PGE2 (tablet)
-
vaginal PGE2 (gel)
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release)
-
intracervical PGE2
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution
-
sustained-release misoprostol insert
-
i.v. oxytocin
-
i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy
-
NO
-
mifepristone
-
mechanical methods – Foley catheter
-
mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter
-
extra-amniotic PGE2
-
buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| [r,1] | [n,1] | [r,2] | [n,2] | [r,3] | [n,3] | [r,4] | [n,4] | [t,1] | [t,2] | [t,3] | [t,4] | [t,5] | na[] | Author/year, trial no. (where applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 86 | 121 | 81 | 117 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 16 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Bollapragada 2009,107 18183 |
| 22 | 52 | 31 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 16 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul, 2002146 12397 |
| 76 | 200 | 48 | 200 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 16 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Kadian 2008,393 17403 |
| 2 | 19 | 12 | 19 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Ekman 1986,230 3199 |
| 4 | 10 | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Ekman-Ordeberg 1985,231 759 |
| 48 | 223 | 81 | 221 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Güngördük 2012,319 20462 |
| 32 | 83 | 41 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Jackson 1994,379 8574 |
| 46 | 150 | 41 | 150 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Amador 2007,67 16714 |
| 17 | 70 | 12 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Bartusevicius 2006,86 15686 |
| 45 | 79 | 38 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2002,138 12232 |
| 68 | 107 | 68 | 111 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2010,148 20064 |
| 71 | 225 | 70 | 225 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Esteve 2006,246 15559 |
| 34 | 75 | 40 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Feitosa 2006,255 15685 |
| 24 | 100 | 30 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Goel 2011,297 19230 |
| 4 | 25 | 10 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 2006,481 15814 |
| 27 | 85 | 30 | 85 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Nassar 2007,595 16675 |
| 34 | 50 | 19 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,780 12234 |
| 61 | 124 | 58 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,784 12287 |
| 12 | 50 | 12 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Suvobrata 2011,827 19237 |
| 76 | 83 | 85 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 17 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000,902 11237 |
| 7 | 32 | 16 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 | 17 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2005,897 14330 |
| 3 | 50 | 1 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Adeniji 2005,53 14393 |
| 52 | 103 | 33 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 19 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2012,181 21024 |
| 21 | 50 | 43 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1994,497 8315 |
| 51 | 119 | 57 | 121 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Moraes Filho 2010,577 18961 |
| 64 | 113 | 57 | 110 | 67 | 107 | NA | NA | 4 | 18 | 19 | NA | NA | 3 | Pennell 2009,660 18562 |
| 40 | 145 | 45 | 148 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 18 | 19 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Salim 2011,742 19948 |
| 8 | 53 | 16 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Sciscione 2001,760 11601 |
| 16 | 60 | 29 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Tabowei 2003,831 2003 |
| 25 | 100 | 28 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | De 2006,197 1563 |
| 14 | 76 | 34 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Majoko 2002,529 111995 |
| 11 | 101 | 5 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 1994,480 9055 |
| 115 | 191 | 104 | 195 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Edwards 2014,224 22692 |
| 20 | 20 | 19 | 23 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Buttino 1990127 |
| 13 | 15 | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Grünnberger 1986316 |
| 36 | 48 | 42 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Hales 1994329 |
| 56 | 60 | 40 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Heinzl 1980345 |
| 36 | 140 | 39 | 142 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Keirse 1995414 |
| 42 | 229 | 78 | 241 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Kemp 2000418 |
| 32 | 50 | 13 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 7 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Legarth 1988458 |
| 53 | 64 | 50 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 7 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1991496 |
| 24 | 45 | 27 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Ottinger 1998637 |
| 49 | 116 | 45 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 7 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Poulsen 1991679 |
| 35 | 226 | 59 | 242 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Rath 1999703 |
| 36 | 155 | 42 | 173 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Rath 1999702 |
| 42 | 98 | 54 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Rix 1996713 |
| 18 | 56 | 25 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Strobelt 2006818 |
| 23 | 25 | 14 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Ulmsten 1982871 |
| 18 | 20 | 8 | 19 | 15 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Ulmsten 1985869 |
| 22 | 41 | 25 | 40 | 28 | 38 | NA | NA | 6 | 7 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Yuen 1996924 |
| 25 | 58 | 39 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Facchinetti 2007248 |
| 31 | 72 | 38 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Facchinetti 2005249 |
| 23 | 85 | 26 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Adair 1998,47,48 |
| 5 | 65 | 8 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Al-Hussaini 200361 |
| 50 | 100 | 36 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Bartha 200085 |
| 49 | 106 | 6 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 12 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Cheng 2008154 |
| 48 | 111 | 37 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Colon 2005173 |
| 10 | 52 | 6 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Crane 2003179 |
| 38 | 100 | 44 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Dällenbach 2003186 |
| 155 | 376 | 168 | 365 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Dodd 2006214 |
| 5 | 14 | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Dodd 2006215 |
| 47 | 64 | 32 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Fisher 2001261 |
| 52 | 112 | 66 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Henrich 2008347 |
| 20 | 49 | 3 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Hoffman 2001361 |
| 123 | 349 | 133 | 346 | 95 | 174 | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | 18 | NA | NA | 3 | Hofmeyr 2001363 |
| 36 | 110 | 69 | 109 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 10 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | How 2001366 |
| 50 | 95 | 45 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Langenegger 2005453 |
| 109 | 240 | 51 | 120 | 73 | 120 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 3 | Le Roux 2002456 |
| 19 | 66 | 3 | 64 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Levy 2005467 |
| 18 | 68 | 25 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Mehrotra 2010552 |
| 89 | 193 | 46 | 100 | 46 | 103 | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | 12 | NA | NA | 3 | Moodley 2003576 |
| 8 | 30 | 4 | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Nagpal 2009591 |
| 3 | 36 | 2 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Nigam 2004609 |
| 4 | 53 | 15 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Nopdonrattakoon 2003614 |
| 14 | 30 | 12 | 29 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Rizvi 2007714 |
| 28 | 50 | 17 | 50 | 40 | 50 | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 3 | Sheela 2007771 |
| 4 | 30 | 17 | 30 | 20 | 30 | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | 18 | NA | NA | 3 | Sheikher 2009772 |
| 47 | 123 | 78 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2001779 |
| 24 | 31 | 12 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002974 |
| 24 | 50 | 35 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2003783 |
| 60 | 100 | 62 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2004782 |
| 17 | 32 | 23 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 12 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Thaisomboon 2012847 |
| 58 | 110 | 76 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1999899 |
| 59 | 113 | 47 | 121 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000902 |
| 20 | 110 | 10 | 88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2004893 |
| 25 | 42 | 4 | 42 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Ayaz 200877 |
| 24 | 155 | 24 | 148 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Bricker 2008119 |
| 52 | 110 | 56 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Rahman 2013694 |
| 36 | 80 | 24 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 12 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Rouzi 2014725 |
| 58 | 100 | 63 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 12 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Souza 2013796 |
| 24 | 36 | 20 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Al-Sebai 199365 |
| 20 | 60 | 22 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 5 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Kalkat 2008395 |
| 22 | 50 | 10 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1995524 |
| 45 | 100 | 49 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 5 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Rabl 2002693 |
| 51 | 71 | 47 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Charoenkul 2000149 |
| 23 | 50 | 10 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Chuck 1995164 |
| 52 | 106 | 21 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Danielian 1999189 |
| 20 | 105 | 38 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | De Aquino 2003198 |
| 30 | 65 | 16 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Denguezli 2007205 |
| 47 | 192 | 56 | 207 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Farah 1997250 |
| 55 | 89 | 31 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Garry 2003278 |
| 33 | 58 | 35 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Has 2002339 |
| 33 | 58 | 35 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1997351 |
| 22 | 39 | 21 | 39 | 21 | 40 | NA | NA | 5 | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 3 | Khoury 2001423 |
| 50 | 78 | 38 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Kolderup 1999430 |
| 26 | 50 | 6 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Krithika 2008440 |
| 3 | 20 | 1 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Kulshreshtha 2007441 |
| 30 | 100 | 26 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Kumar 2001442 |
| 39 | 100 | 20 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Megalo 2004551 |
| 11 | 60 | 13 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Meydanli 2003559 |
| 4 | 37 | 3 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Morgan Ortiz 2002579 |
| 25 | 94 | 23 | 95 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Nunes 1999618 |
| 6 | 83 | 1 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Papanikolaou 2004645 |
| 103 | 225 | 72 | 210 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Pandis 2001643 |
| 80 | 185 | 60 | 184 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2001727 |
| 45 | 115 | 31 | 108 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1998749 |
| 82 | 211 | 61 | 204 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Sifakis 2007786 |
| 5 | 24 | 3 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Srisomboon 1998803 |
| 31 | 50 | 19 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Surbek 1997822 |
| 96 | 137 | 66 | 138 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995906 |
| 23 | 98 | 26 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1998905 |
| 31 | 100 | 16 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Anand 201268 |
| 50 | 100 | 40 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Chitraker 2012156 |
| 57 | 57 | 17 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Frass 2011268 |
| 16 | 50 | 20 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2009293 |
| 55 | 161 | 61 | 159 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2011294 |
| 38 | 80 | 24 | 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 2010320 |
| 32 | 74 | 8 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Kim 2000426 |
| 14 | 60 | 20 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Nigam 2010608 |
| 20 | 56 | 15 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Ozkan 2009641 |
| 29 | 70 | 26 | 70 | 24 | 70 | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 3 | Saxena 2011755 |
| 141 | 340 | 177 | 341 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Van Gemund 2004879 |
| 35 | 67 | 20 | 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995900 |
| 53 | 98 | 48 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1997903 |
| 214 | 426 | 424 | 871 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 13 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2008896 |
| 7 | 25 | 2 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Sahu 2004738 |
| 42 | 111 | 43 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Corrado 2001175 |
| 15 | 35 | 8 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Murthy 2006587 |
| 449 | 680 | 308 | 678 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 13 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2013,890,892 |
| 15 | 55 | 31 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Tabasi 2007829 |
| 26 | 128 | 49 | 128 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | Aalami-Harandi 201343 |
Data file for OpenBUGS analysis of caesarean section
Treatments included in analysis:
-
no treatment
-
placebo
-
vaginal PGE2 (tablet)
-
vaginal PGE2 (gel)
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release)
-
PGF2 gel
-
intracervical PGE2
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution
-
sustained-release misoprostol insert
-
i.v. oxytocin
-
amniotomy
-
i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy
-
NO
-
mifepristone
-
oestrogens
-
corticosteroids
-
relaxin
-
hyaluronidase
-
mechanical methods – Foley catheter
-
mechanical methods – laminaria
-
mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter
-
membrane sweeping
-
extra-amniotic PGE2
-
i.v. prostaglandin
-
sexual intercourse
-
acupuncture
-
oral prostaglandins
-
buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| [r,1] | [n,1] | [r,2] | [n,2] | [r,3] | [n,3] | [r,4] | [n,4] | [t,1] | [t,2] | [t,3] | [t,4] | na[] | Author/year, trial number (where applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56 | 173 | 65 | 177 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Bollapragada 2009,107 18183 |
| 17 | 100 | 14 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Bullarbo 2007,123 15979 |
| 16 | 52 | 20 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2002,146 12397 |
| 20 | 56 | 19 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2000,144 11236 |
| 6 | 10 | 8 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2000,145 11245 |
| 16 | 66 | 11 | 66 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Haghighi 2013,326 21669 |
| 4 | 12 | 8 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Nicoll 2001,607 11517 |
| 61 | 198 | 65 | 197 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Osman 2006,632 15372 |
| 11 | 30 | 8 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Perche 2009,662 18430 |
| 12 | 78 | 11 | 78 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Rameez 2007,696 16662 |
| 18 | 72 | 14 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Akay 2012,57 20824 |
| 13 | 92 | 14 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Chang 1997,141,142 10210 |
| 9 | 47 | 7 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1991,159 6450 |
| 25 | 225 | 38 | 219 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Grant 1992,306 6422 |
| 11 | 98 | 4 | 102 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Griffith-Jones 1990,315 3129 |
| 41 | 223 | 67 | 221 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Güngördük 2012,319 20462 |
| 123 | 1263 | 127 | 1258 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996,335 9118a |
| 17 | 83 | 16 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Jackson 1994,379 8574 |
| 16 | 510 | 19 | 502 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ladfors 1996,447 9252 |
| 1 | 49 | 4 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Legarth 1987,460 3900 |
| 3 | 19 | 4 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1989,493 4666 |
| 9 | 43 | 8 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1990,494 5660 |
| 0.5 | 41 | 4.5 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1980,506 1766 |
| 19 | 33 | 20 | 33 | 19 | 33 | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | 20 | NA | 3 | Magann 1995,516 9168 |
| 5 | 27 | 3 | 23 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | McQueen 1990,549 5921 |
| 2 | 62 | 4 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ottervanger 1996,636 8661 |
| 7 | 100 | 4 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Pollnow 1996,676 9220 |
| 4 | 40 | 2 | 40 | 5 | 40 | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | 15 | NA | 3 | Puertas 1997,687 12325 |
| 7 | 47 | 3 | 41 | 10 | 55 | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | 15 | NA | 3 | Ray 1992,705 7125 |
| 8 | 24 | 3 | 27 | 6 | 25 | 5 | 28 | 1 | 4 | 15 | 25 | 4 | Roberts 1986,716 1396 |
| 5 | 138 | 4 | 139 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Rydhström 1991,733 3226 |
| 9 | 57 | 4 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Rymer 1992,734 7399 |
| 8 | 62 | 6 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Sperling 1993,802 8195 |
| 5 | 96 | 4 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Allott 1993,62 8211 |
| 3.5 | 70 | 0.5 | 74 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Berghella 1996,95 9250 |
| 8 | 138 | 5 | 140 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Cammu 1998,131 9535 |
| 10 | 74 | 10 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Crane 1997,177 9416 |
| 13 | 68 | 6 | 69 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Dare 2002,191 12270 |
| 9 | 141 | 10 | 152 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Goldenberg 1996,300 9089 |
| 8 | 50 | 6 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 1998,322 9935 |
| 46 | 107 | 43 | 107 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Hamdan 2009,332 18438 |
| 5 | 32 | 4 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Magann 1998,515 10430 |
| 5 | 35 | 8 | 35 | 5 | 35 | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | 27 | NA | 3 | Magann 1998,513 11075 |
| 25 | 91 | 17 | 91 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Magann 1999,512 11100 |
| 33 | 116 | 58 | 234 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Putnam 2011,690 20595 |
| 3 | 59 | 6 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Wiriyasirivaj 1996,910 9050 |
| 10 | 60 | 8 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Wong 2002,916 12285 |
| 32 | 167 | 38 | 179 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Yildirim 2010,921 19038 |
| 7 | 37 | 3 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Ajori 2013,56 21872 |
| 3 | 30 | 2 | 29 | 6 | 30 | NA | NA | 1 | 2 | 31 | NA | 3 | Asher 2009,72 18576 |
| 2 | 52 | 4 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Gaudernack 2006,279 15847 |
| 2 | 7 | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Gaudet 2008,280 17891 |
| 10 | 26 | 5 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Harper 2005,338 16027 |
| 11 | 58 | 11 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Modlock 2010,569 19120 |
| 42 | 180 | 34 | 180 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Smith 2008,792 17746 |
| 46 | 150 | 41 | 150 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Amador 2007,67 16714 |
| 14 | 70 | 12 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartusevicius 2006,86 15686 |
| 28 | 79 | 18 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2002,138 12232 |
| 15 | 62 | 20 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Moraes Filho 2010,577 14544 |
| 71 | 225 | 70 | 225 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Esteve 2006,246 15559 |
| 23 | 75 | 32 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Feitosa 2006,255 15685 |
| 4 | 25 | 3 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 17 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 2006,481 15814 |
| 24 | 85 | 30 | 85 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Nassar 2006,595 16675 |
| 15 | 50 | 8 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,780 12234 |
| 32 | 124 | 31 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,784 12287 |
| 80 | 240 | 71 | 240 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 33 | NA | NA | 2 | Zahran 2009,927 18699 |
| 14 | 61 | 10 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Kashanian 2008,404 17709 |
| 5 | 33 | 1 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Ziaei 2003,935 13355 |
| 42 | 85 | 15 | 83 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 23 | NA | NA | 2 | Spallicci 2007,797 12096 |
| 40 | 70 | 28 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 23 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Surita 2005,826 14379 |
| 4 | 22 | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Bell 1993,89 7978 |
| 4 | 23 | 15 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Brennand 1997,118 9990 |
| 3 | 30 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1980,507 1765 |
| 116 | 576 | 101 | 574 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | 2 | Omar 2013,627 21571 |
| 21 | 102 | 27 | 108 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | 2 | Tan 2007,838 16801 |
| 5 | 130 | 6 | 130 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1995,527 8658 |
| 6 | 72 | 7 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Gagnon-Gervais 2012,275 21163 |
| 23 | 103 | 24 | 106 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Mercer 1995,558 9004 |
| 1 | 98 | 1 | 98 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Moldin 1996,572 9225 |
| 6 | 34 | 7 | 30 | 3 | 30 | NA | NA | 8 | 17 | 24 | NA | 3 | Orhue 1995,629 8657 |
| 28 | 157 | 22 | 163 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Parazzini 1998,646 10784 |
| 17 | 62 | 12 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Selo-Ojeme 2009,767 18022 |
| 7 | 101 | 9 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Tan 2013,837 21568 |
| 4 | 21 | 6 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Taylor 1993,842 11078 |
| 22 | 57 | 89 | 289 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Berkane 2005,97 14327 |
| 6 | 42 | 7 | 41 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Giacalone 1998,285 10355 |
| 8 | 16 | 5 | 16 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Lelaidier 1994,461 8619 |
| 3 | 12 | 4 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Stenlund 1991,811 10786 |
| 18 | 83 | 9 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000,902 11237 |
| 3 | 32 | 7 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2005,897 14330 |
| 22 | 33 | 15 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Romero-Gutiérrez 2011,720 19787 |
| 3 | 63 | 4 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Naef 1998,588 9772 |
| 3 | 50 | 1 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Adeniji 2005,53 14393 |
| 27 | 103 | 25 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2012,181 21024 |
| 49 | 128 | 41 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Gilson 1996,291 9212 |
| 13 | 65 | 15 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Greybush 2001,313 11975 |
| 6 | 42 | 11 | 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Hemlin 1998,346 9674 |
| 5 | 50 | 18 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1994,497 8315 |
| 10 | 81 | 7 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Mawire 1999,539 10676 |
| 32 | 119 | 44 | 121 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Moraes Filho 2010,577 18961 |
| 12 | 44 | 11 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Niromanesh 2003,611 13049 |
| 34 | 80 | 41 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Oliveira 2010,625 19204 |
| 11 | 60 | 17 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Owolabi 2005,640 14892 |
| 42 | 113 | 40 | 110 | 46 | 107 | NA | NA | 4 | 24 | 26 | NA | 3 | Pennell 2009,660 18562 |
| 26 | 56 | 26 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Rouben 1993,721 7918 |
| 15 | 145 | 26 | 148 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 24 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Salim 2011,742 19948 |
| 21 | 72 | 21 | 77 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Sciscione 1999,759 10512 |
| 20 | 53 | 18 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Sciscione 2001,760 11601 |
| 7 | 28 | 6 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | St Onge 1995,805 8689 |
| 8 | 60 | 10 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Tabowei 2003831 |
| 5 | 45 | 12 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Ugwu 2013,868 22498 |
| 5 | 15 | 2 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Fenton 1985,256 107 |
| 6 | 76 | 14 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Majoko 2002,529 111995 |
| 2 | 95 | 1 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Parewijck 1986,647 2809 |
| 2 | 10 | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Quinn 1981,691 1917 |
| 10 | 58 | 6 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Sherman 2001,774 11529 |
| 0.5 | 108 | 9.5 | 116 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Spellacy 1972800 |
| 1 | 75 | 1 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Vakhariya 1972,874 787 |
| 11 | 61 | 11 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Ugwu 2014,867 22655 |
| 27 | 97 | 30 | 103 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Witter 1987,915 3636 |
| 10 | 39 | 10 | 41 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Yazdizadeh 2013,919 22483 |
| 6 | 20 | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Paul 1992,652 10915 |
| 73 | 191 | 56 | 195 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Edwards 2014,223 22692 |
| 3 | 30 | 3 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1980,506 1767 |
| 82 | 408 | 93 | 411 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2012,390 20221 |
| 26 | 119 | 21 | 107 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2013,389 22497 |
| 11 | 64 | 14 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Ten Eikelder 2013,843 21691 (Jozwiak 2014391) |
| 65 | 194 | 56 | 203 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Bernstein 199198 |
| 7 | 20 | 5 | 23 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Buttino 1990127 |
| 23 | 107 | 30 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Cabrol 1988129 |
| 18 | 57 | 8 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Darroca 1996192 |
| 6 | 38 | 16 | 41 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Gilson 1993290 |
| 11 | 48 | 14 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Hales 1994328,329 |
| 6 | 60 | 3 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Heinzl 1980345 |
| 13 | 35 | 11 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Hutchon 1980372 |
| 9 | 140 | 12 | 142 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Keirse 1995414 |
| 10 | 43 | 5 | 41 | 13 | 44 | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | 20 | NA | 3 | Larmon 2002454 |
| 1 | 15 | 8 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Laube 1986455 |
| 8 | 47 | 6 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Lien 1998470 |
| 3 | 31 | 4 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | McKenna 1999545 |
| 0.5 | 16 | 4.5 | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Nimrod 1984610 |
| 10 | 21 | 4 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Nuutila 1995619 |
| 17 | 71 | 6 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Nuutila 1996621 |
| 13 | 45 | 11 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Ottinger 1998637 |
| 16 | 53 | 13 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Owen 1991638 |
| 7 | 30 | 9 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Perry 2004667 |
| 21 | 116 | 22 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Poulsen 1991679 |
| 49 | 226 | 68 | 242 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Rath 1999703 |
| 19 | 155 | 16 | 173 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Rath 1999703 |
| 5 | 27 | 6 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Richardson 199711 |
| 4 | 38 | 5 | 35 | 5 | 38 | NA | NA | 5 | 7 | 10 | NA | 3 | Ramsey 2003699 |
| 18 | 98 | 16 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Rix 1996713 |
| 3 | 31 | 5 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Seeras 1995763 |
| 0.5 | 41 | 0.5 | 42 | 1.5 | 41 | NA | NA | 2 | 3 | 7 | NA | 3 | Thiery 1984851 |
| 26 | 236 | 26 | 252 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Trofatter 1993863 |
| 7 | 68 | 6 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Troostwijk 1992864 |
| 6 | 20 | 3 | 19 | 7 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | 8 | NA | 3 | Ulmsten 1985869 |
| 11 | 31 | 9 | 35 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Wieland 1999885 |
| 6 | 41 | 5 | 40 | 10 | 38 | NA | NA | 7 | 8 | 26 | NA | 3 | Yuen 1996924 |
| 20 | 115 | 17 | 120 | 20 | 106 | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | 15 | NA | 3 | Cararach 1996136 |
| 15 | 112 | 9 | 88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Thavarahsah 1990849 |
| 31 | 125 | 39 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Pedrazzoli 1997658 |
| 68 | 151 | 61 | 143 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Rayburn 1999709 |
| 13 | 85 | 17 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Adair 199848 |
| 20 | 100 | 14 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartha 200085 |
| 22 | 78 | 10 | 78 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Beigi 200388 |
| 23 | 102 | 16 | 104 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Bennett 199892 |
| 8 | 55 | 7 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Butt 1999126 |
| 120 | 501 | 147 | 503 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2001139 |
| 18 | 106 | 4 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Cheng 2008154 |
| 3 | 32 | 7 | 66 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Cheung 2006155 |
| 36 | 111 | 18 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Colon 2005173 |
| 6 | 52 | 5 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Crane 2003179 |
| 19 | 100 | 18 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Dällenbach 2003186 |
| 100 | 376 | 83 | 365 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Dodd 2006214 |
| 4 | 14 | 8 | 16 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 13 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Dodd 2006215 |
| 14 | 64 | 12 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Fisher 2001261 |
| 6 | 30 | 9 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Gherman 2001284 |
| 8 | 48 | 9 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Hall 2002330 |
| 17 | 112 | 20 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Henrich 2008347 |
| 8 | 49 | 4 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Hoffman 2001361 |
| 68 | 347 | 54 | 345 | 36 | 174 | NA | NA | 4 | 13 | 24 | NA | 3 | Hofmeyr 2001363 |
| 19 | 110 | 35 | 109 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | How 2001366 |
| 5 | 52 | 13 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Jindal 2011385 |
| 5 | 23 | 6 | 29 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Kipikasa 2005428 |
| 19 | 82 | 13 | 78 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Kwon 2001444 |
| 22 | 95 | 22 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Langenegger 2005453 |
| 82 | 240 | 42 | 120 | 39 | 120 | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | 12 | NA | 3 | Le Roux 2002456 |
| 4 | 66 | 1 | 64 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Levy 2005467 |
| 11 | 51 | 10 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 2003478 |
| 13 | 75 | 11 | 128 | 13 | 127 | 14 | 76 | 8 | 10 | 13 | 28 | 4 | Majoko 2002529 |
| 80 | 193 | 40 | 100 | 41 | 103 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 13 | NA | 3 | Moodley 2003576 |
| 3 | 30 | 3 | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Nagpal 2009591 |
| 3 | 41 | 3 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Ngai 1996605 |
| 2 | 40 | 3 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ngai 2000604 |
| 7 | 53 | 3 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Nopdonrattakoon 2003614 |
| 18 | 73 | 23 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Paisarntantiwong 2005642 |
| 19 | 95 | 17 | 95 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Patil 2005651 |
| 28 | 123 | 30 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2001778 |
| 5 | 31 | 5 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002974 |
| 14 | 50 | 13 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2003783 |
| 27 | 100 | 25 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2004782 |
| 13 | 32 | 17 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Thaisomboon 2012847 |
| 25 | 110 | 15 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1999899 |
| 25 | 113 | 15 | 121 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000902 |
| 9 | 110 | 8 | 88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2004893 |
| 17 | 155 | 20 | 148 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 13 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Bricker 2008119 |
| 32 | 110 | 34 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Rahman 2013694 |
| 3 | 65 | 5 | 69 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Zvandasara 2008936 |
| 18 | 80 | 9 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Rouzi 2014725 |
| 37 | 100 | 41 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Souza 2013796 |
| 1 | 50 | 3 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Berzircioglu 2012101 |
| 5 | 18 | 7 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Chatterjee 1991150 |
| 12 | 76 | 11 | 79 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1995161 |
| 7 | 29 | 7 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Chung 1992166 |
| 13 | 26 | 14 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Curet 1989183 |
| 1 | 28 | 3 | 37 | 4 | 50 | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | 27 | NA | 3 | Doany 1997212 |
| 3 | 38 | 5 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | El-Shawarby 2006241 |
| 3 | 20 | 16 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Graves 1985307 |
| 4 | 15 | 12 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Hayashi 1983343 |
| 8 | 60 | 14 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Kalkat 2008394 |
| 9 | 32 | 7 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Liggins 1979471 |
| 12 | 40 | 6 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1989522 |
| 12 | 110 | 13 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1992526 |
| 2.5 | 51 | 0.5 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1995523 |
| 1 | 31 | 3 | 35 | 2 | 25 | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | 15 | NA | 3 | McCaul 1997541 |
| 9 | 100 | 10 | 165 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Murphy 1980584 |
| 25 | 100 | 24 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Murray 1995585 |
| 9 | 38 | 9 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Neilson 1983599 |
| 10 | 50 | 7 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | O’Brien 1995624 |
| 11 | 45 | 15 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Perryman 1992669 |
| 11 | 36 | 8 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Prasad 1989684 |
| 7 | 15 | 4 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Prins 1983685 |
| 21 | 63 | 10 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Rayburn 1988707 |
| 18 | 105 | 16 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Roach 1997715 |
| 4 | 26 | 6 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Sawai 1991754 |
| 28 | 83 | 29 | 82 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Taher 2011834 |
| 6 | 34 | 4 | 35 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Tomlinson 2001856 |
| 13 | 33 | 9 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Witter 1992914 |
| 5 | 34 | 4 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Abdul 200744 |
| 17 | 79 | 27 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Buser 1997125 |
| 10 | 50 | 10 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Chuck 1995164 |
| 23 | 75 | 15 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Da Graça 2005184 |
| 14 | 106 | 12 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Danielian 1999189 |
| 20 | 105 | 38 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | De Aquino 2003198 |
| 36 | 168 | 38 | 192 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | De la Torre 2001200 |
| 44 | 125 | 40 | 126 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Diro 1999210 |
| 23 | 192 | 33 | 207 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Farah 1997250 |
| 20 | 51 | 18 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ferguson 2002257 |
| 3 | 21 | 2 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Fletcher 1993263 |
| 31 | 164 | 22 | 163 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Fonseca 2008265 |
| 14 | 55 | 10 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Frohn 2002269 |
| 35 | 89 | 28 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Garry 2003278 |
| 10 | 37 | 7 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Gottschall 1997303 |
| 31 | 129 | 36 | 139 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Gregson 2005312 |
| 9 | 54 | 13 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Haghighi 2006325 |
| 12 | 58 | 22 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Has 2002339 |
| 15 | 36 | 6 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Howarth 1996368 |
| 11 | 63 | 14 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Incerpi 2001374,375 |
| 22 | 112 | 12 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kadanali 1996392 |
| 11 | 39 | 15 | 39 | 11 | 40 | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | 10 | NA | 3 | Khoury 2001423 |
| 7 | 71 | 23 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Kidanto 2007424 |
| 21 | 78 | 23 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kolderup 1999430 |
| 4 | 25 | 2 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Lee 1997457 |
| 10 | 40 | 10 | 44 | 10 | 47 | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | 15 | NA | 3 | Lemancewicz 1999463 |
| 9 | 35 | 9 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | McKenna 2004546 |
| 14 | 100 | 18 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Megalo 2004551 |
| 11 | 60 | 13 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Meydanli 2003559 |
| 18 | 68 | 46 | 91 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Montealegre 1999575 |
| 4 | 37 | 3 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Morgan Ortiz 2002579 |
| 12 | 94 | 13 | 95 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Nunes 1999618 |
| 7 | 39 | 3 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Oboro 2005622 |
| 43 | 225 | 38 | 210 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Pandis 2001643 |
| 16 | 63 | 13 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Rowlands 2001726 |
| 30 | 185 | 33 | 184 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2001727 |
| 16 | 70 | 13 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2004728 |
| 5 | 27 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Saggaf 2001736 |
| 8 | 70 | 9 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1997745 |
| 15 | 115 | 24 | 108 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1998749 |
| 55 | 211 | 51 | 204 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Sifakis 2007786 |
| 8 | 33 | 4 | 27 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Stitely 2000817 |
| 7 | 50 | 6 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Surbek 1997822 |
| 38 | 137 | 28 | 138 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995900 |
| 13 | 98 | 17 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1998904 |
| 5 | 32 | 4 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2006934 |
| 18 | 60 | 4 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayaz 201078 |
| 15 | 102 | 8 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Chaudhuri 2011151 |
| 12 | 52 | 16 | 54 | 9 | 52 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 24 | NA | 3 | Deo 2012206 |
| 12 | 50 | 10 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2009293 |
| 42 | 161 | 40 | 159 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2011294 |
| 15 | 55 | 13 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Hosli 2008364 |
| 37 | 95 | 29 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Lokugamage 2003482 |
| 18 | 56 | 14 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Ozkan 2009641 |
| 50 | 191 | 56 | 199 | 45 | 198 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 24 | NA | 3 | Prager 2008681 |
| 70 | 340 | 53 | 341 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Van Gemund 2004879 |
| 3 | 33 | 8 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Varaklis 1995880 |
| 13 | 67 | 10 | 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995901 |
| 20 | 98 | 18 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1997903 |
| 115 | 436 | 243 | 871 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2008896 |
| 0.5 | 43 | 1.5 | 44 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Deng 1999204 |
| 8 | 42 | 9 | 42 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Meyer 2002560 |
| 11 | 47 | 8 | 42 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Mosquera 1999580 |
| 138 | 1261 | 121 | 1259 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996335 |
| 3 | 40 | 2 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1979504 |
| 13 | 35 | 8 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Murthy 2006587 |
| 29 | 132 | 34 | 135 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Tessier 1997845 |
| 13 | 60 | 14 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Abedi-Asl 200745 |
Data file for OpenBUGS analysis of instrumental delivery
Treatments included in analysis:
-
no treatment
-
placebo
-
vaginal PGE2 (tablet)
-
vaginal PGE2 (gel)
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release)
-
PGF2 gel
-
intracervical PGE2
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution
-
sustained-release misoprostol insert
-
i.v. oxytocin
-
amniotomy
-
i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy
-
NO
-
mifepristone
-
oestrogens
-
relaxin
-
mechanical methods – Foley catheter
-
mechanical methods – laminaria
-
mechanical methods – double-balloon or cook’s catheter
-
membrane sweeping
-
extra-amniotic PGE2
-
i.v. prostaglandin
-
sexual intercourse
-
acupuncture
-
homeopathy
-
oral prostaglandins
-
buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| [r,1] | [n,1] | [r,2] | [n,2] | [r,3] | [n,3] | [r,4] | [n,4] | [t,1] | [t,2] | [t,3] | [t,4] | na[] | Author/year, trial number (where applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 54 | 173 | 47 | 177 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Bollapragada 2009,107 18183 |
| 3 | 12 | 7 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Nicoll 2001,607 11517 |
| 60 | 198 | 61 | 197 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Osman 2006,632 15372 |
| 1 | 21 | 1 | 23 | 1 | 21 | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | 18 | NA | 3 | Sharma 2005,769 14435 |
| 0 | 74 | 1 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Akyol 1999,58 11035 |
| 3 | 80 | 12 | 74 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Alcalay 1996,59 9273 |
| 9 | 49 | 5 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ashrafunnessa 1997,73 10447 |
| 8 | 41 | 7 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Bung 1986,124 2000 |
| 9 | 47 | 10 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1991,159 6450 |
| 27 | 105 | 21 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Day 1985,195 1701 |
| 3 | 165 | 4 | 180 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 3 | NA | NA | 2 | Egarter 1989,227 4739 |
| 9 | 35 | 12 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Goeschen 1989,298 7124 |
| 59 | 225 | 68 | 219 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Grant 1992,306 6422 |
| 10 | 98 | 23 | 102 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Griffith-Jones 1990,315 3129 |
| 5 | 223 | 7 | 221 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Güngördük 2012,319 20462 |
| 256 | 1263 | 233 | 1258 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996,335 9118a |
| 13 | 24 | 7 | 23 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1997351 |
| 15 | 83 | 16 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Jackson 1994,379 8574 |
| 5 | 89 | 3 | 79 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Koc 2013,429 21668 |
| 5 | 23 | 9 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Lamki 1974,449 18219 |
| 26 | 95 | 29 | 90 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Lange 1984,452 2447 |
| 13 | 49 | 7 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Legarth 1987,460 3900 |
| 5 | 19 | 4 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1989,493 4666 |
| 9 | 43 | 9 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1990,494 5660 |
| 3 | 45 | 3 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Macer 1984,498 2594 |
| 10 | 40 | 14 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1980,505 1766 |
| 2 | 33 | 2 | 33 | 2 | 33 | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | 20 | NA | 3 | Magann 1995,516 9168 |
| 3 | 15 | 1 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Magos 1983,518 2157 |
| 9 | 27 | 8 | 23 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | McQueen 1990,549 5921 |
| 4 | 62 | 10 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ottervanger 1992,635 8661 |
| 11 | 40 | 13 | 40 | 15 | 40 | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | 15 | NA | 3 | Puertas 1997,687 12325 |
| 21 | 138 | 13 | 139 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Rydhström 1991,733 3226 |
| 21 | 57 | 10 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Rymer 1992,734 7399 |
| 11 | 62 | 12 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Sperling 1993,802 8195 |
| 6 | 50 | 3 | 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Tamsen 1990,836 5545 |
| 1 | 50 | 3 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ulmsten 1979,870 1693 |
| 4 | 15 | 7 | 15 | 11 | 30 | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | 31 | NA | 3 | Valentine 1977,876 1317 |
| 15 | 96 | 7 | 86 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Wagner 1989,882 4992 |
| 3 | 15 | 2 | 15 | 4 | 15 | 3 | 15 | 3 | 15 | 26 | 31 | 4 | Wilson 1978,889 1487 |
| 5 | 50 | 10 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zahradnik 1987,926 3681 |
| 7 | 83 | 9 | 82 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Papageorgiou 1992,644 7364 |
| 4 | 65 | 7 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Alcoseba-Lim 1992,60 9534 |
| 12 | 96 | 11 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Allott 1993,62 8211 |
| 7 | 69 | 7 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Berghella 1994,94 1996,95 9250 |
| 27 | 99 | 36 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Boulvain 1998,110 9919 |
| 18 | 138 | 23 | 140 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Cammu 1998,131 9535 |
| 12 | 74 | 15 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Crane 1997,177 9416 |
| 53 | 367 | 55 | 375 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | De Miranda 2006,201 15427 |
| 3 | 32 | 2 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | El-Torkey 1992,232 7221 |
| 9 | 50 | 13 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 1998,322 9935 |
| 4 | 107 | 4 | 107 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Hamdan 2009,332 18438 |
| 5 | 35 | 3 | 35 | 4 | 35 | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | 25 | NA | 3 | Magann 1998,511 11075 |
| 7 | 91 | 7 | 91 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Magann 1999,512 11100 |
| 4 | 48 | 2 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | McColgin 1990,544 6231 |
| 9 | 39 | 4 | 41 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Tannirandorn 1999,841 11231 |
| 11 | 59 | 10 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Wiriyasirivaj 1996,910 9050 |
| 13 | 60 | 12 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Wong 2002,916 12285 |
| 13 | 52 | 6 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Gaudernack 2006,279 15847 |
| 2 | 7 | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Gaudet 2008,280 17891 |
| 1 | 32 | 2 | 35 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Gribel 2011,314 19759 |
| 8 | 58 | 8 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Modlock 2010,569 19120 |
| 3 | 20 | 3 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Rabl 2002693 |
| 10 | 53 | 4 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Selmer-Olsen 2007,765 16795 |
| 25 | 180 | 27 | 180 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Smith 2008,792 17746 |
| 2 | 70 | 5 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartusevicius 2006,86 15686 |
| 9 | 79 | 3 | 79 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2002,138 12232 |
| 19 | 225 | 12 | 225 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Esteve 2006,246 15559 |
| 4 | 25 | 5 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 17 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 2006,481 15814 |
| 2 | 50 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Malik 2010,531 18700 |
| 12 | 85 | 5 | 85 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Nassar 2007,595 16675 |
| 7 | 50 | 11 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,780 12234 |
| 28 | 124 | 34 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 32 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,782 12287 |
| 2 | 20 | 2 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 30 | NA | NA | 2 | Beer 1999,87 11214 |
| 6 | 22 | 6 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Bell 1993,89 7978 |
| 2 | 23 | 15 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Brennand 1997,118 9990 |
| 15 | 30 | 14 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1980,507 1765 |
| 46 | 576 | 52 | 574 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Omar 2013,627 21571 |
| 19 | 130 | 17 | 130 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1995,527 8658 |
| 6 | 30 | 10 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Kennedy 1978,419 1413 |
| 4 | 50 | 7 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Kennedy 1982,420 2046 |
| 31 | 165 | 45 | 155 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1989,503 5027 |
| 4 | 40 | 4 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1988,162 18082 |
| 9 | 72 | 9 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Gagnon-Gervais 2012,275 21163 |
| 7 | 25 | 3 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Melchior 1989,976 5333 |
| 4 | 34 | 5 | 30 | 6 | 30 | NA | NA | 8 | 17 | 22 | NA | 3 | Orhue 1995,629 8657 |
| 4 | 157 | 2 | 163 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Parazzini 1998,646 10784 |
| 25 | 50 | 25 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Saleh 1975,741 1064 |
| 10 | 62 | 12 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Selo-Ojeme 2009,767 18022 |
| 2 | 101 | 2 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Tan 2013,837 21568 |
| 5 | 21 | 4 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Taylor 1993,842 11078 |
| 9 | 57 | 80 | 289 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Berkane 2005,97 14327 |
| 6 | 42 | 9 | 41 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Giacalone 1998,285 10355 |
| 17 | 60 | 20 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Frydman 1992,271 7447 |
| 4 | 16 | 5 | 16 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Lelaidier 1994,461 8619 |
| 1 | 12 | 8 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Stenlund 1999,811 10786 |
| 4 | 62 | 3 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Su 1996,820 10911 |
| 2 | 17 | 2 | 16 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Davey 1979,193 1535 |
| 12 | 63 | 12 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Naef 1998,588 9772 |
| 3 | 50 | 2 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Adeniji 2005,53 14393 |
| 8 | 75 | 8 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Al-Taani 2004,66 15001 |
| 13 | 95 | 14 | 90 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 23 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1997,160 9722 |
| 3 | 49 | 7 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Chung 2003,165 13321 |
| 7 | 132 | 9 | 265 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2011,180 19650 |
| 1 | 103 | 6 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2012,181 21024 |
| 6 | 200 | 8 | 200 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2011,207 20161 |
| 10 | 50 | 4 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Dalui 2005,187 14334 |
| 20 | 90 | 24 | 88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 22 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Haugland 2012,340 20890 |
| 3 | 42 | 1 | 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Hemlin 1998,346 9674 |
| 21 | 40 | 15 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 23 | NA | NA | 2 | Johnson 1985,386 192 |
| 2 | 50 | 3 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Kandil 2012,397 21031 |
| 16 | 50 | 11 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1994,497 8315 |
| 1 | 81 | 1 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Mawire 1999,539 10676 |
| 18 | 88 | 13 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 22 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Mei-Dan 2012,555 20791 |
| 2 | 27 | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Ophir 1992,628 10910 |
| 3 | 60 | 3 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Owolabi 2005,640 14892 |
| 28 | 113 | 25 | 110 | 23 | 107 | NA | NA | 4 | 22 | 24 | NA | 3 | Pennell 2009,660 18562 |
| 5 | 83 | 4 | 82 | 5 | 82 | NA | NA | 7 | 20 | 23 | NA | 3 | Roztocil 1998,730 10466 |
| 6 | 145 | 12 | 148 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 22 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Salim 2011,742 19948 |
| 10 | 38 | 9 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 23 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1992,748 7847 |
| 1 | 24 | 1 | 26 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Shechter-Maor 2013,770 21802 |
| 8 | 28 | 13 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | St Onge 1995,805 8689 |
| 13 | 60 | 15 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Tabowei 2003831 |
| 1 | 45 | 2 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Ugwu 2013,868 22498 |
| 1 | 50 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Balci 2010,82 19116 |
| 0 | 50 | 1 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Balci 2011,81 20050 |
| 4 | 100 | 3 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | De 2006,197 1563 |
| 8 | 25 | 8 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Greer 1989,309 5049 |
| 7 | 10 | 6 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Quinn 1981,691 1917 |
| 7 | 15 | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Shepherd 1976,773 1194 |
| 5 | 58 | 5 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Sherman 2001,774 11529 |
| 12 | 30 | 11 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Stewart 1983,815 2580 |
| 1 | 20 | 2 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 26 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Iskander 1978,377 1403 |
| 4 | 43 | 3 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Moller 1991,573 3597 |
| 10 | 20 | 14 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Naismith 1973,592 857 |
| 9 | 113 | 7 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Bakos 1987,80 3890 |
| 5 | 22 | 5 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 23 | NA | NA | 2 | Cahill 1988,130 16551 |
| 10 | 100 | 6 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2013,208 22653 |
| 6 | 100 | 2 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 2006,321 17823 |
| 20 | 129 | 3 | 109 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Heden 1991,344 6018 |
| 26 | 101 | 18 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 1994,480 9055 |
| 3 | 136 | 6 | 127 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Misra 1994,565 8632 |
| 221 | 684 | 211 | 679 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Schmitz 2014,756 22698 |
| 3 | 25 | 4 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Thomas 1986,853 2883 |
| 4 | 25 | 5 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1988,349 4482 |
| 9 | 102 | 8 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Lange 1981,450 1271 |
| 23 | 92 | 11 | 69 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 17 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Lykkesfeldt 1979,490 1578 |
| 8 | 33 | 7 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Massil 1988,535 5006 |
| 20 | 119 | 10 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 31 | NA | NA | 2 | Secher 1981,762 1981 |
| 2 | 42 | 5 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Andersen 1990,69 6220 |
| 2 | 41 | 1 | 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Tylleskar 1979,866 1827 |
| 12 | 76 | 17 | 90 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Sande 1983,750 2434 |
| 15 | 30 | 19 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1980,506 1767 |
| 54 | 408 | 45 | 411 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2012,390 20221 |
| 20 | 119 | 13 | 107 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2013,389 22497 |
| 18 | 64 | 8 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Ten Eikelder 2013,843 21691 (Jozwiak 2014391) |
| 5 | 60 | 5 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Heinzl 1980345 |
| 4 | 44 | 2 | 44 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Hidar 2000354 |
| 32 | 125 | 24 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Irion 1998376 |
| 17 | 140 | 16 | 140 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Keirse 1995414 |
| 14 | 43 | 17 | 41 | 12 | 44 | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | 20 | NA | 3 | Larmon 2002454 |
| 8 | 56 | 9 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Legarth 1988458 |
| 3 | 47 | 6 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Lien 1998470 |
| 5 | 22 | 4 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Lopes 1991485 |
| 10 | 64 | 9 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1991495 |
| 9 | 31 | 14 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Seeras 1995763 |
| 8 | 29 | 6 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Trofatter 1985861 |
| 3 | 68 | 3 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Troostwijk 1992864 |
| 6 | 20 | 3 | 19 | 4 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | 8 | NA | 3 | Ulmsten 1985869 |
| 4 | 31 | 12 | 35 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Wieland 1999885 |
| 5 | 41 | 10 | 40 | 3 | 38 | NA | NA | 7 | 8 | 24 | NA | 3 | Yuen 1996924 |
| 1 | 48 | 2 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Zanini 1990929 |
| 9 | 151 | 12 | 143 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Rayburn 1999709 |
| 7 | 40 | 8 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Adam 200549 |
| 27 | 100 | 23 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartha 200085 |
| 23 | 102 | 30 | 104 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Bennett 199892 |
| 12 | 55 | 12 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Butt 1999126 |
| 66 | 501 | 56 | 503 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2001139 |
| 3 | 32 | 2 | 66 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Cheung 2006155 |
| 7 | 111 | 4 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Colon 2005173 |
| 10 | 52 | 10 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Crane 2003179 |
| 27 | 100 | 20 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Dällenbach 2003186 |
| 63 | 376 | 65 | 365 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Dodd 2006214 |
| 25 | 50 | 8 | 50 | 9 | 50 | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | 32 | NA | 3 | Elhassan 2007237 |
| 6 | 64 | 8 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Fisher 2001261 |
| 3 | 48 | 7 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Hall 2002330 |
| 3 | 49 | 1 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Hoffman 2001361 |
| 28 | 347 | 24 | 345 | 4 | 174 | NA | NA | 4 | 13 | 22 | NA | 3 | Hofmeyr 2001363 |
| 3 | 52 | 2 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Jindal 2011385 |
| 2 | 66 | 3 | 64 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Levy 2005467 |
| 10 | 51 | 4 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 2003478 |
| 17 | 159 | 18 | 146 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Mozurkewich 2003582 |
| 2 | 30 | 1 | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Nagpal 2009591 |
| 10 | 41 | 7 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Ngai 1996605 |
| 10 | 40 | 10 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ngai 2000604 |
| 1 | 53 | 3 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Nopdonrattakoon 2003614 |
| 1 | 73 | 5 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Paisarntantiwong 2005642 |
| 6 | 95 | 9 | 95 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Patil 2005651 |
| 12 | 84 | 11 | 82 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Pongsatha 2005677 |
| 30 | 123 | 28 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2001778 |
| 9 | 31 | 11 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002974 |
| 7 | 50 | 18 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2003783 |
| 26 | 100 | 29 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2004782 |
| 15 | 66 | 14 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Sitthiwattanawong 1999789 |
| 4 | 20 | 2 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Toppozada 1997857 |
| 5 | 110 | 3 | 88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2004893 |
| 14 | 110 | 12 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Rahman 2013694 |
| 3 | 65 | 3 | 69 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Zvandasara 2008936 |
| 2 | 100 | 2 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Souza 2013796 |
| 2 | 35 | 1 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Buchanan 1984121 |
| 14 | 95 | 13 | 104 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Campbell 1984132 |
| 49 | 207 | 35 | 195 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Cardozo 1986137 |
| 2 | 29 | 6 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Chung 1992166 |
| 1 | 28 | 1 | 37 | 9 | 50 | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | 25 | NA | 3 | Doany 1997212 |
| 3 | 165 | 4 | 180 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 3 | NA | NA | 2 | Husslein 1986371 |
| 10 | 100 | 9 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | El-Mardi 1991240 |
| 10 | 38 | 4 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | El-Shawarby 2006241 |
| 9 | 60 | 10 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Kalkat 2008394 |
| 5 | 32 | 11 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Liggins 1979471 |
| 0 | 12 | 1 | 12 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | McLaren 1987547 |
| 33 | 100 | 32 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Murphy 1980584 |
| 40 | 100 | 35 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Murray 1995585 |
| 3 | 50 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Poornima 2011678 |
| 7 | 36 | 10 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Prasad 1989684 |
| 17 | 100 | 9 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Rabl 2002693 |
| 7 | 63 | 3 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Rayburn 1988707 |
| 19 | 100 | 15 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 3 | NA | NA | 2 | Shoaib 1994785 |
| 20 | 83 | 13 | 82 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Taher 2011834 |
| 7 | 34 | 5 | 35 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Tomlinson 2001856 |
| 10 | 65 | 2 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Triglia 2010860 |
| 9 | 33 | 6 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Witter 1992914 |
| 3 | 34 | 5 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Abdul 200744 |
| 12 | 120 | 19 | 118 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayad 200276 |
| 9 | 83 | 10 | 83 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Bounyasong 2000111 |
| 3 | 30 | 2 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Chang 1997141 |
| 3 | 50 | 1 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Chuck 1995163,164 |
| 18 | 106 | 20 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Danielian 1999189 |
| 25 | 168 | 23 | 192 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | De la Torre 2001200 |
| 3 | 65 | 4 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Denguezli 2007205 |
| 9 | 93 | 10 | 92 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | El Sherbiny 2001243 |
| 8 | 60 | 6 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Elhassan 2004238 |
| 6 | 70 | 12 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Elhassan 2005236 |
| 2 | 31 | 1 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Elhassan 2005235 |
| 5 | 73 | 4 | 74 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Eroglu 2007244 |
| 2 | 53 | 2 | 63 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Escudero 1997245 |
| 50 | 192 | 59 | 207 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Farah 1997250 |
| 1 | 21 | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Fletcher 1993263 |
| 0 | 31 | 4 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Fletcher 1994262 |
| 26 | 129 | 29 | 139 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Gregson 2005312 |
| 5 | 112 | 4 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kadanali 1996392 |
| 9 | 78 | 16 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kolderup 1999430 |
| 3 | 30 | 2 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kovavisarach 1997432 |
| 8 | 40 | 3 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kovavisarach 1998433 |
| 1 | 20 | 0 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kulshreshtha 2007441 |
| 2 | 25 | 3 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Lee 1997457 |
| 6 | 35 | 3 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | McKenna 2004546 |
| 13 | 100 | 18 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Megalo 2004551 |
| 2 | 60 | 3 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Meydanli 2003559 |
| 3 | 68 | 16 | 91 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Montealegre 1999575 |
| 11 | 39 | 12 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Oboro 2005622 |
| 2 | 25 | 3 | 35 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Pixiang 1999977 |
| 20 | 83 | 28 | 83 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Papanikolaou 2004645 |
| 23 | 63 | 19 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Rowlands 2001726 |
| 56 | 185 | 47 | 184 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2001727 |
| 3 | 27 | 0 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Saggaf 2001736 |
| 10 | 70 | 15 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1997745 |
| 18 | 115 | 21 | 108 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1998749 |
| 9 | 30 | 10 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Srisomboon 1996804 |
| 5 | 24 | 3 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Srisomboon 1998803 |
| 6 | 50 | 10 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Surbek 1997822 |
| 19 | 137 | 9 | 138 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995906 |
| 1 | 52 | 2 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2004933 |
| 0 | 50 | 2 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2006932 |
| 0 | 32 | 1 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2006934 |
| 0 | 48 | 2 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2006931 |
| 6 | 100 | 10 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Anand 201268 |
| 16 | 60 | 14 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayaz 201078 |
| 3 | 102 | 13 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Chaudhuri 2011151 |
| 3 | 52 | 6 | 54 | 1 | 52 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 22 | NA | 3 | Deo 2012206 |
| 2 | 50 | 2 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2009293 |
| 12 | 161 | 11 | 159 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2011294 |
| 13 | 55 | 5 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Hosli 2008364 |
| 21 | 74 | 12 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kim 2000426 |
| 24 | 95 | 36 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Lokugamage 2003482 |
| 31 | 191 | 33 | 199 | 29 | 198 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 22 | NA | 3 | Prager 2008681 |
| 17 | 150 | 9 | 150 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Trabelsi 2012858 |
| 11 | 33 | 6 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Varaklis 1995880 |
| 2 | 27 | 2 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Wang 1998883 |
| 8 | 67 | 7 | 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995880,900,906 |
| 2 | 25 | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Sahu 2004738 |
| 10 | 37 | 6 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Chyu 1997167 |
| 226 | 1261 | 228 | 1259 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996335 |
| 16 | 40 | 12 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | MacLennan 1979504 |
| 2 | 35 | 1 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Murthy 2006587 |
| 1 | 50 | 2 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Sultana 2006821 |
| 24 | 132 | 23 | 135 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Tessier 1997845 |
| 35 | 680 | 43 | 678 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2013892 |
| 1 | 263 | 5 | 263 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | MacKenzie 1981500 |
| 4 | 25 | 6 | 23 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Lughmani 2009488 |
| 3 | 49 | 2 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Egarter 1987228 |
Data file for OpenBUGS analysis of hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate changes
Treatments included in analysis:
-
no treatment
-
placebo
-
vaginal PGE2 (tablet)
-
vaginal PGE2 (gel)
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release)
-
intracervical PGE2
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution
-
sustained-release misoprostol insert
-
i.v. oxytocin
-
i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy
-
NO
-
mifepristone
-
mechanical methods – Foley catheter
-
mechanical methods – laminaria
-
mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter
-
buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| [r,1] | [n,1] | [r,2] | [n,2] | [r,3] | [n,3] | [r,4] | [n,4] | [t,1] | [t,2] | [t,3] | [t,4] | na[] | Author/year, trial number (where applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 194 | 2 | 203 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Bernstein 199198 |
| 0.5 | 21 | 1.5 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Buttino 1990127 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 1.5 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Hales 1994329 |
| 1.5 | 126 | 0.5 | 123 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Irion 1998376 |
| 0.5 | 16 | 1.5 | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Laube 1986455 |
| 1 | 47 | 2 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Lien 1998470 |
| 1 | 22 | 1 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Lopes 1991485 |
| 0.5 | 32 | 1.5 | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | McKenna 2004546 |
| 1 | 403 | 1 | 413 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Noah 1987612 |
| 1 | 71 | 1 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Nuutila 1996621 |
| 0.5 | 54 | 1.5 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Owen 1991638 |
| 3 | 30 | 3 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Perry 2004667 |
| 2 | 38 | 2 | 35 | 5 | 38 | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | 9 | NA | 3 | Ramsey 2003699 |
| 1.5 | 41 | 0.5 | 42 | 1.5 | 41 | NA | NA | 2 | 3 | 6 | NA | 3 | Thiery 1984851 |
| 1 | 29 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Trofatter 1985861 |
| 11 | 249 | 16 | 265 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Trofatter 1993863 |
| 0.5 | 26 | 1.5 | 26 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Ulmsten 1982871 |
| 2.5 | 35 | 0.5 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Wieland 1999885 |
| 2.5 | 49 | 0.5 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Zanini 1990929 |
| 1 | 25 | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Lopez-Farfan 2010486 |
| 5 | 65 | 1 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Al-Hussaini 200361 |
| 2 | 100 | 6 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartha 200085 |
| 6 | 102 | 5 | 104 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Bennett 199892 |
| 3 | 55 | 4 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Butt 1999126 |
| 66 | 501 | 90 | 503 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2001139 |
| 12.5 | 107 | 0.5 | 102 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Cheng 2008154 |
| 0.5 | 33 | 2.5 | 67 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Cheung 2006155 |
| 6 | 111 | 2 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Colon 2005173 |
| 3 | 50 | 13 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Crane 2003179 |
| 14 | 100 | 9 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Dällenbach 2003186 |
| 6 | 376 | 3 | 365 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Dodd 2006214 |
| 15 | 77 | 5 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Dyar 2000222 |
| 5 | 64 | 1 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Fisher 2001261 |
| 1 | 30 | 1 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Gherman 2001284 |
| 4 | 48 | 4 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Hall 2002330 |
| 1 | 112 | 1 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Henrich 2008347 |
| 0.5 | 50 | 1.5 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Hoffman 2001361 |
| 10 | 334 | 13 | 328 | 6 | 163 | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | 18 | NA | 3 | Hofmeyr 2001363 |
| 17 | 110 | 5 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | How 2001366 |
| 12 | 95 | 12 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Langenegger 2005453 |
| 0.5 | 67 | 2.5 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Levy 2005467 |
| 0.5 | 52 | 3.5 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 2003478 |
| 17 | 193 | 21 | 100 | 17 | 103 | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | 12 | NA | 3 | Moodley 2003576 |
| 22 | 159 | 13 | 146 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Mozurkewich 2003582 |
| 0.5 | 42 | 1.5 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Ngai 1996605 |
| 0.5 | 54 | 1.5 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Nopdonrattakoon 2003614 |
| 2.5 | 74 | 0.5 | 74 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Paisarntantiwong 2005642 |
| 0.5 | 96 | 5.5 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Patil 2005651 |
| 6 | 84 | 1 | 82 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Pongsatha 2005677 |
| 16 | 124 | 24 | 146 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Puga 2001688 |
| 1 | 50 | 2 | 50 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | 11 | NA | 3 | Sheela 2007771 |
| 6 | 123 | 1 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2001778,779 |
| 2 | 50 | 1 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2003781,783 |
| 0.5 | 101 | 2.5 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2004782 |
| 0.5 | 67 | 2.5 | 66 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Sitthiwattanawong 1999789 |
| 3 | 48 | 4 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Uludag 2005872 |
| 3 | 110 | 2 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1999899 |
| 0.5 | 113 | 3.5 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000902 |
| 7.5 | 111 | 0.5 | 89 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2004893 |
| 1.5 | 37 | 0.5 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Getgan 2003282 |
| 2.5 | 111 | 0.5 | 111 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Rahman 2013694 |
| 5 | 80 | 7 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Rouzi 2014725 |
| 2 | 100 | 2 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Souza 2013796 |
| 0.5 | 27 | 1.5 | 29 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Curet 1989183 |
| 0.5 | 21 | 2.5 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Graves 1985307 |
| 0.5 | 16 | 1.5 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Hayashi 1983343 |
| 0.5 | 111 | 2.5 | 111 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1992526 |
| 1 | 100 | 2 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Murray 1995585 |
| 0.5 | 46 | 2.5 | 46 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Perryman 1992669 |
| 3 | 100 | 4 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Rabl 2002693 |
| 0.5 | 115 | 4.5 | 102 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Rayburn 1992710 |
| 7 | 83 | 7 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Taher 2011834 |
| 0.5 | 40 | 3.5 | 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Witter 1992914 |
| 0.5 | 105 | 3.5 | 103 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Witter 1996912 |
| 1 | 120 | 5 | 118 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayad 200276 |
| 0.5 | 80 | 14.5 | 77 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Buser 1997125 |
| 2 | 53 | 4 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Cecatti 2000140 |
| 0.5 | 72 | 5.5 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Charoenkul 2000149 |
| 2 | 50 | 1 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Chuck 1995164 |
| 14 | 66 | 13 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Clark 1998168 |
| 1.5 | 107 | 0.5 | 106 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Danielian 1999189 |
| 3 | 105 | 4 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | De Aquino 2003198 |
| 27 | 168 | 9 | 192 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | De la Torre 2001200 |
| 3 | 65 | 5 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Denguezli 2007205 |
| 0.5 | 94 | 6.5 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | El Sherbiny 2001243 |
| 0.5 | 74 | 1.5 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Eroglu 2007244 |
| 5.5 | 58 | 0.5 | 64 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Escudero 1997245 |
| 10 | 192 | 12 | 207 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Farah 1997250 |
| 4 | 51 | 1 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Ferguson 2002257 |
| 4 | 31 | 3 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Fletcher 1994262 |
| 1 | 89 | 4 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Garry 2003278 |
| 5.5 | 301 | 3.5 | 101 | 2.5 | 101 | 0.5 | 101 | 1 | 9 | 14 | 18 | 4 | Gelisen 2005281 |
| 0.5 | 38 | 1.5 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Gottschall 1997303 |
| 4 | 129 | 1 | 139 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Gregson 2005312 |
| 4 | 36 | 5 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Howarth 1996368 |
| 2 | 63 | 3 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Incerpi 2001375 |
| 6 | 112 | 4 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Kadanali 1996392 |
| 1.5 | 40 | 0.5 | 40 | 3.5 | 41 | NA | NA | 5 | 8 | 9 | NA | 3 | Khoury 2001423 |
| 1 | 78 | 5 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Kolderup 1999430 |
| 2 | 30 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Kovavisarach 1997432 |
| 6 | 100 | 7 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Kumar 2001442 |
| 1.5 | 26 | 0.5 | 26 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Lee 1997457 |
| 0.5 | 41 | 0.5 | 45 | 1.5 | 48 | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | 14 | NA | 3 | Lemancewicz 1999463 |
| 0.5 | 20 | 3.5 | 18 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Magtibay 1998520 |
| 1 | 35 | 1 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | McKenna 2004546 |
| 3 | 60 | 2 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Meydanli 2003559 |
| 0.5 | 30 | 4.5 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Neiger 2001598 |
| 4 | 94 | 3 | 95 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Nunes 1999618 |
| 1 | 83 | 2 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Papanikolaou 2004645 |
| 2 | 225 | 5 | 210 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Pandis 2001643 |
| 0.5 | 64 | 10.5 | 63 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Rowlands 2001726 |
| 2 | 185 | 5 | 184 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2001727 |
| 1 | 70 | 5 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2004728 |
| 6 | 70 | 4 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1997745 |
| 9 | 115 | 12 | 108 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1998749 |
| 0.5 | 31 | 2.5 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Srisomboon 1996804 |
| 1.5 | 51 | 0.5 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Surbek 1997822 |
| 3 | 137 | 8 | 138 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995906 |
| 2 | 60 | 6 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayaz 201078 |
| 1.5 | 51 | 0.5 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2009293 |
| 2.5 | 162 | 0.5 | 160 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2011294 |
| 1 | 80 | 3 | 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 2010320 |
| 2.5 | 56 | 0.5 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Hosli 2008364 |
| 12 | 95 | 10 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Lokugamage 2003482 |
| 0.5 | 61 | 1.5 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Nigam 2010608 |
| 1 | 56 | 2 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Ozkan 2009641 |
| 4 | 100 | 10 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Saeed 2011735 |
| 1 | 70 | 1 | 70 | 2 | 70 | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | 9 | NA | 3 | Saxena 2011755 |
| 2 | 57 | 1 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Tan 2010840 |
| 26 | 340 | 29 | 341 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Van Gemund 2004879 |
| 0.5 | 34 | 2.5 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Varaklis 1995880 |
| 2 | 67 | 5 | 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995880,900,906 |
| 4 | 98 | 1 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1997903 |
| 28 | 436 | 39 | 871 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2008896 |
| 0.5 | 43 | 1.5 | 44 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Deng 1999204 |
| 1.5 | 101 | 0.5 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Komala 2013431 |
| 0.5 | 38 | 1.5 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Chyu 1997167 |
| 0.5 | 36 | 1.5 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Murthy 2006587 |
| 2 | 50 | 3 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Nanda 2007593 |
| 1 | 132 | 2 | 135 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Tessier 1997845 |
| 18 | 680 | 70 | 678 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2013892 |
| 8.5 | 53 | 0.5 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2002,146 12397 |
| 2.5 | 57 | 0.5 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2000,144 11236 |
| 1.5 | 22 | 2.5 | 24 | 0.5 | 22 | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | 16 | NA | 3 | Sharma 2005,769 14435 |
| 5 | 72 | 6 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Akay 2012,57 20824 |
| 4 | 120 | 2 | 120 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Kunt 2010,443 18965 |
| 1 | 15 | 3 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Magos 1983,518 2157 |
| 1.5 | 26 | 0.5 | 26 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Olmo 2001,626 11763 |
| 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Parikh 2001,648 13941 |
| 2.5 | 48 | 0.5 | 42 | 0.5 | 56 | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | 14 | NA | 3 | Ray 1992,705 7125 |
| 2 | 83 | 4 | 82 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Papageorgiou 1992,644 7364 |
| 2 | 150 | 2 | 150 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Amador 2007,67 16714 |
| 5 | 70 | 5 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartusevicius 2006,86 15686 |
| 14 | 79 | 19 | 73 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2002,138 12232 |
| 2 | 62 | 1 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Moraes Filho 2010,577 14544 |
| 2 | 225 | 4 | 225 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Esteve 2006,246 15559 |
| 1 | 75 | 3 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Feitosa 2006,255 15685 |
| 8 | 85 | 7 | 85 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Nassar 2007,595 16675 |
| 0.5 | 29 | 2.5 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Parisaei 2008,649 17372 |
| 0.5 | 51 | 1.5 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,780 12234 |
| 2 | 124 | 2 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,784 12287 |
| 25 | 240 | 16 | 240 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Zahran 2009,927 18699 |
| 0.5 | 35 | 2.5 | 31 | 1.5 | 31 | NA | NA | 7 | 15 | 18 | NA | 3 | Orhue 1995,629 8657 |
| 0.5 | 84 | 4.5 | 98 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000,902 11237 |
| 0.5 | 33 | 1.5 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2005,897 14330 |
| 3.5 | 96 | 0.5 | 91 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1995,160 9722 |
| 16 | 49 | 6 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Chung 2003,165 13321 |
| 8.5 | 133 | 0.5 | 266 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2011,180 19650 |
| 6.5 | 104 | 0.5 | 106 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 20 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2012,181 21024 |
| 1.5 | 41 | 0.5 | 41 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Johnson 1985,386 192 |
| 1.5 | 51 | 0.5 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Kandil 2012,397 21031 |
| 1.5 | 51 | 0.5 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1994,497 8315 |
| 3 | 119 | 2 | 121 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Moraes Filho 2010,577 18961 |
| 1.5 | 60 | 0.5 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Ntsaluba 1997,617 9924 |
| 4 | 60 | 2 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Owolabi 2005,640 14892 |
| 6.5 | 114 | 0.5 | 111 | 0.5 | 108 | NA | NA | 4 | 18 | 20 | NA | 3 | Pennell 2009,660 18562 |
| 2.5 | 54 | 0.5 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Sciscione 2001,760 11601 |
| 3 | 60 | 1 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Tabowei 2003831 |
| 2 | 100 | 1 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2013,208 22653 |
| 12 | 408 | 8 | 411 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2012,390 20221 |
Data file for OpenBUGS analysis of Neonatal mortality and serious morbidity
Treatments included in analysis:
-
no treatment
-
placebo
-
vaginal PGE2 (tablet)
-
vaginal PGE2 (gel)
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release)
-
PGF2 gel
-
intracervical PGE2
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution
-
i.v. oxytocin
-
i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy
-
NO
-
mechanical methods – Foley catheter
-
mechanical methods – laminaria
-
membrane sweeping
-
extra-amniotic PGE2
-
i.v. prostaglandin
-
sexual intercourse
-
breast stimulation
-
oral prostaglandins
-
buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| [r,1] | [n,1] | [r,2] | [n,2] | [r,3] | [n,3] | [r,4] | [n,4] | [t,1] | [t,2] | [t,3] | [t,4] | na[] | Author/year, trial number (where applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 173 | 0 | 177 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Bollapragada 2009,107 18183 |
| 0 | 20 | 1 | 20 | 3 | 17 | NA | NA | 1 | 13 | 22 | NA | 3 | Damania 1992,188 7763 |
| 2 | 1263 | 0 | 1258 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996,335 9118a |
| 1 | 20 | 0 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | McQueen 1990,549 5921 |
| 2 | 367 | 2 | 375 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | De Miranda 2006,201 15427 |
| 0 | 50 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 1998,322 9935 |
| 0 | 90 | 1 | 90 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | McColgin 1990542 |
| 1 | 167 | 0 | 179 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Yildirim 2010,921 19038 |
| 0 | 62 | 1 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Moraes Filho 2010,577 14544 |
| 2 | 576 | 1 | 574 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Omar 2013,627 21571 |
| 1 | 50 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Benzineb 1996,93 10103 |
| 0 | 95 | 1 | 90 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1997,160 9722 |
| 9 | 200 | 7 | 200 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2011,207 20161 |
| 2 | 81 | 3 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Mawire 1999,539 10676 |
| 1 | 76 | 1 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Majoko 2002,529 111995 |
| 0 | 10 | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Quinn 1981,691 1917 |
| 0 | 107 | 1 | 115 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 13 | 20 | NA | NA | 2 | Spellacy 1973,801 876 |
| 1 | 100 | 0 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2013,208 22653 |
| 1 | 78 | 1 | 78 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Katz 1983,410 2289 |
| 1 | 136 | 0 | 127 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Misra 1994,565 8632 |
| 0 | 684 | 3 | 679 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Schmitz 2014,756 22698 |
| 1 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 54 | NA | NA | 13 | 14 | 23 | NA | 3 | Ratnam 1974,704 966 |
| 1 | 75 | 0 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Duff 1984,221 2592 |
| 0 | 64 | 1 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1991495 |
| 2 | 403 | 0 | 413 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Noah 1987612 |
| 1 | 349 | 1 | 345 | 1 | 171 | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | 16 | NA | 3 | Hofmeyr 2001363 |
| 1 | 75 | 2 | 128 | 1 | 127 | 1 | 76 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 19 | 4 | Majoko 2002529 |
| 1 | 193 | 2 | 100 | 0 | 103 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 12 | NA | 3 | Moodley 2003576 |
| 1 | 110 | 0 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Rahman 2013694 |
| 1 | 80 | 1 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Rouzi 2014725 |
| 1 | 165 | 0 | 180 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 3 | NA | NA | 2 | Husslein 1986371 |
| 0 | 32 | 1 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Liggins 1979471 |
| 3 | 34 | 2 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Abdul 200744 |
| 0 | 79 | 2 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Buser 1997125 |
| 1 | 300 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 1 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 4 | Gelisen 2005281 |
| 1 | 39 | 0 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Oboro 2005622 |
| 1 | 83 | 0 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Papanikolaou 2004645 |
| 1 | 60 | 0 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayaz 201078 |
| 1 | 102 | 1 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Chaudhuri 2011151 |
| 0 | 57 | 1 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Frass 2011268 |
| 2 | 1261 | 0 | 1259 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996335 |
| 1 | 167 | 2 | 172 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Ezechi 2008247 |
Data file for OpenBUGS analysis of maternal mortality and serious morbidity
Treatments included in analysis:
-
no treatment
-
placebo
-
vaginal PGE2 (tablet)
-
vaginal PGE2 (gel)
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release) Intracervical PGE2
-
intracervical PGE2
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
i.v. oxytocin
-
i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy
-
mifepristone
-
mechanical methods – Foley catheter
-
mechanical methods – laminaria
-
buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| [r,1] | [n,1] | [r,2] | [n,2] | [r,3] | [n,3] | [r,4] | [n,4] | [t,1] | [t,2] | [t,3] | [t,4] | na[] | Author/year, trial number (where applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 150 | 1 | 150 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Amador 2007,67 16714 |
| 1 | 21 | 0 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Taylor 1993,842 11078 |
| 0 | 57 | 3 | 289 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Berkane 2005,97 14327 |
| 1 | 95 | 0 | 95 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1997,160 9722 |
| 2 | 408 | 0 | 411 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2012,390 20221 |
| 0 | 125 | 1 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Irion 1998376 |
| 1 | 403 | 0 | 413 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Noah 1987612 |
| 0 | 26 | 1 | 22 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1993350 |
| 0 | 64 | 1 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Fisher 2001261 |
| 0 | 29 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Chung 1992166 |
| 1 | 100 | 0 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Rabl 2002693 |
| 1 | 34 | 0 | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Abdul 200744 |
| 1 | 58 | 0 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Has 2002339 |
| 0 | 100 | 1 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Chitraker 2012156 |
| 0 | 50 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2009293 |
| 1 | 340 | 1 | 341 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Van Gemund 2004879 |
Data file for OpenBUGS analysis of NICU admission
Treatments included in analysis:
-
no treatment
-
placebo
-
vaginal PGE2 (tablet)
-
vaginal PGE2 (gel)
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release)
-
PGF2 gel
-
intracervical PGE2
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution
-
sustained-release misoprostol insert
-
i.v. oxytocin
-
amniotomy
-
i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy
-
NO
-
mifepristone
-
oestrogens
-
mechanical methods – Foley catheter
-
mechanical methods – laminaria
-
mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter
-
membrane sweeping
-
extra-amniotic PGE2
-
sexual intercourse
-
acupuncture
-
oral prostaglandins
-
buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| [r,1] | [n,1] | [r,2] | [n,2] | [r,3] | [n,3] | [r,4] | [n,4] | [t,1] | [t,2] | [t,3] | [t,4] | na[] | Author/year, trial number (where applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 100 | 5 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Agarwal 2012,54 21275 |
| 16 | 173 | 18 | 177 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Bollapragada 2009,107 18183 |
| 9 | 100 | 13 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Bullarbo 2007,123 15979 |
| 3 | 52 | 0 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2002,146 12397 |
| 1 | 56 | 0 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2000,144 11236 |
| 3 | 12 | 5 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Nicoll 2001,607 11517 |
| 14 | 198 | 13 | 197 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Osman 2006,632 15372 |
| 3 | 72 | 0 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Akay 2012,57 20824 |
| 14 | 74 | 5 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Akyol 1999,58 11035 |
| 16 | 92 | 21 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Chang 1997,142 10210 |
| 3 | 47 | 2 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1991,159 6450 |
| 4 | 223 | 6 | 221 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Güngördük 2012,319 20462 |
| 146 | 1259 | 83 | 1256 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996335 9118a |
| 10 | 100 | 6 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Hjertberg 1996,359 9117 |
| 6 | 89 | 4 | 79 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Koc 2013,429 21668 |
| 13 | 120 | 20 | 120 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Kunt 2010,443 18965 |
| 59 | 510 | 73 | 502 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ladfors 1996,447 9252 |
| 0 | 15 | 1 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Magos 1983,518 2157 |
| 3 | 47 | 2 | 41 | 2 | 55 | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | 15 | NA | 3 | Ray 1992,705 7125 |
| 5 | 62 | 2 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Sperling 1993,802 8195 |
| 4 | 50 | 0 | 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Tamsen 1990,836 5545 |
| 6 | 99 | 6 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Boulvain 1998,110 9919 |
| 11 | 68 | 9 | 69 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Dare 2002,191 12270 |
| 2 | 367 | 2 | 375 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | De Miranda 2006,201 15427 |
| 2 | 50 | 0 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 1998,322 9935 |
| 2 | 138 | 3 | 162 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Hill 2008,357 17311 |
| 2 | 32 | 2 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Magann 1998,514 10430 |
| 0 | 35 | 3 | 35 | 2 | 35 | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | 24 | NA | 3 | Magann 1998,513 11075 |
| 5 | 91 | 1 | 91 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Magann 1999,512 11100 |
| 4 | 116 | 4 | 234 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Putnam 2011,690 20595 |
| 5 | 167 | 10 | 179 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Yildirim 2010,921 19038 |
| 1 | 30 | 0 | 29 | 0 | 30 | NA | NA | 1 | 2 | 27 | NA | 3 | Asher 2009,72 18576 |
| 0 | 7 | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Gaudet 2008,280 17891 |
| 3 | 183 | 0 | 181 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Smith 2008,792 17746 |
| 9 | 150 | 8 | 150 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Amador 2007,67 16714 |
| 2 | 70 | 2 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartusevicius 2006,86 15686 |
| 10 | 79 | 11 | 79 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2002,138 12232 |
| 14 | 225 | 15 | 225 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Esteve 2006,246 15559 |
| 1 | 75 | 1 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Feitosa 2006,255 15685 |
| 6 | 50 | 4 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Malik 1996,531 18700 |
| 3 | 85 | 3 | 85 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Nassar 2007,595 16675 |
| 6 | 50 | 5 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,780 12234 |
| 15 | 124 | 12 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,784 12287 |
| 5 | 240 | 4 | 240 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 29 | NA | NA | 2 | Zahran 2009,927 18699 |
| 12 | 576 | 5 | 574 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Omar 2013,627 21571 |
| 3 | 102 | 2 | 108 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Tan 2007,838 16801 |
| 6 | 130 | 7 | 130 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1995,527 8658 |
| 0 | 125 | 1 | 124 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2003,143 12688 |
| 5 | 25 | 6 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Melchior 1989,976 5333 |
| 15 | 157 | 8 | 63 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Parazzini 1998,646 10784 |
| 0 | 62 | 2 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Selo-Ojeme 2009,767 18022 |
| 0 | 101 | 1 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Tan 2013,837 21568 |
| 11 | 83 | 13 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000,902 11237 |
| 3 | 32 | 11 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2005,897 14330 |
| 15 | 63 | 11 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Naef 1998,588 9772 |
| 5 | 75 | 6 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Al-Taani 2004,66 15001 |
| 3 | 95 | 7 | 90 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1997,160 9722 |
| 5 | 49 | 5 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Chung 1992166 |
| 7 | 132 | 11 | 265 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2011,180 19650 |
| 5 | 103 | 8 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 23 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2012,181 21024 |
| 42 | 200 | 37 | 200 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2011,207 20161 |
| 10 | 65 | 9 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Greybush 2001,313 11975 |
| 12 | 81 | 15 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Mawire 1999,539 10676 |
| 5 | 80 | 3 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Oliveira 2010,625 19204 |
| 6 | 60 | 8 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Owolabi 2005,640 14892 |
| 21 | 113 | 22 | 110 | 13 | 107 | NA | NA | 4 | 21 | 23 | NA | 3 | Pennell 2009,660 18562 |
| 3 | 38 | 2 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1992,748 7847 |
| 4 | 60 | 3 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Tabowei 2003831 |
| 2 | 45 | 3 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Ugwu 2013,868 22498 |
| 2 | 50 | 2 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Balci 2010,82 19116 |
| 1 | 100 | 1 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | De 2006,197 1563 |
| 14 | 76 | 6 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Majoko 2002,529 111995 |
| 28 | 100 | 30 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2013,208 22653 |
| 10 | 100 | 14 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 2006,321 17823 |
| 1 | 51 | 0 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Habib 2008324 |
| 8 | 129 | 10 | 109 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Heden 1991,344 6018 |
| 11 | 684 | 11 | 679 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Schmitz 2014,756 22698 |
| 5 | 33 | 4 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Massil 1988,535 5006 |
| 34 | 191 | 30 | 195 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Edwards 2014,224 22692 |
| 10 | 76 | 2 | 90 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Sande 1983,750 2434 |
| 4 | 408 | 3 | 411 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2012,390 20221 |
| 8 | 119 | 4 | 107 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2013,389 22497 |
| 1 | 64 | 2 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Ten Eikelder 2013,843 21691 (Jozwiak 2014391) |
| 27 | 140 | 25 | 142 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Keirse 1995414 |
| 1 | 43 | 1 | 41 | 1 | 44 | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | 20 | NA | 3 | Larmon 2002454 |
| 2 | 31 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | McKenna 1999545 |
| 1 | 38 | 3 | 35 | 1 | 38 | NA | NA | 5 | 7 | 10 | NA | 3 | Ramsey 2003699 |
| 5 | 31 | 4 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Seeras 1995763 |
| 4 | 51 | 1 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1992352 |
| 1 | 75 | 0 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Sahraoui 2005737 |
| 11 | 85 | 17 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Adair 199848 |
| 11 | 100 | 12 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartha 200085 |
| 2 | 78 | 2 | 78 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Beigi 200388 |
| 10 | 55 | 8 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Butt 1999126 |
| 37 | 501 | 43 | 503 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Carlan 2001139 |
| 6 | 106 | 0 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Cheng 2008154 |
| 11 | 111 | 11 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Colon 2005173 |
| 2 | 52 | 3 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Crane 2003,179 9416 |
| 10 | 100 | 7 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Dällenbach 2003186 |
| 2 | 376 | 5 | 365 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Dodd 2006214 |
| 9 | 64 | 9 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Fisher 2001261 |
| 3 | 48 | 0 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Hall 2002330 |
| 17 | 112 | 9 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Henrich 2008347 |
| 12 | 49 | 9 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Hoffman 2001361 |
| 14 | 346 | 9 | 345 | 2 | 171 | NA | NA | 4 | 13 | 21 | NA | 3 | Hofmeyr 2001363 |
| 5 | 110 | 7 | 109 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | How 2001366 |
| 0 | 52 | 2 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Jindal 2011385 |
| 4 | 30 | 5 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Khazardoost 2011421 |
| 1 | 23 | 2 | 29 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Kipikasa 2005428 |
| 8 | 240 | 6 | 120 | 2 | 120 | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | 12 | NA | 3 | Le Roux 2002456 |
| 8 | 75 | 19 | 128 | 16 | 127 | 6 | 76 | 8 | 10 | 13 | 25 | 4 | Majoko 2002529 |
| 19 | 49 | 12 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Mehrotra 2010552 |
| 29 | 193 | 21 | 100 | 12 | 103 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 13 | NA | 3 | Moodley 2003576 |
| 32 | 159 | 18 | 146 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Mozurkewich 2003582 |
| 3 | 41 | 1 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Ngai 1996605 |
| 3 | 40 | 4 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ngai 2000604 |
| 0 | 76 | 1 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Paungmora 2004654 |
| 96 | 150 | 35 | 150 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Rath 2007701 |
| 4 | 30 | 5 | 29 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Rizvi 2007714 |
| 0 | 50 | 1 | 50 | 0 | 50 | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | 12 | NA | 3 | Sheela 2007771 |
| 0 | 30 | 1 | 30 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | 21 | NA | 3 | Sheikher 2009772 |
| 7 | 123 | 17 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2001779 |
| 0 | 31 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002974 |
| 4 | 50 | 7 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2003783 |
| 12 | 100 | 12 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2004782 |
| 3 | 48 | 0 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Uludag 2005872 |
| 31 | 110 | 29 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1999898 |
| 36 | 113 | 34 | 121 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000902 |
| 11 | 110 | 10 | 88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2004893 |
| 9 | 110 | 5 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Rahman 2013694 |
| 15 | 65 | 11 | 69 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Zvandasara 2008936 |
| 0 | 80 | 6 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Rouzi 2014725 |
| 4 | 100 | 5 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Souza 2013796 |
| 3 | 207 | 6 | 195 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Cardozo 1986137 |
| 6 | 76 | 6 | 79 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1995161 |
| 9 | 29 | 9 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Chung 1992166 |
| 0 | 28 | 2 | 37 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | 24 | NA | 3 | Doany 1997212 |
| 8 | 110 | 7 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1992526 |
| 5 | 50 | 1 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | O’Brien 1995624 |
| 4 | 50 | 3 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Poornima 2011678 |
| 1 | 36 | 3 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Prasad 1989684 |
| 20 | 105 | 22 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Roach 1997715 |
| 2 | 26 | 0 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Sawai 1991754 |
| 4 | 42 | 2 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Sawai 1994752 |
| 7 | 100 | 3 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 3 | NA | NA | 2 | Shoaib 1994785 |
| 2 | 83 | 1 | 83 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Taher 2011834 |
| 30 | 120 | 24 | 118 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayad 200276 |
| 1 | 71 | 0 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Charoenkul 2000149 |
| 6 | 106 | 8 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Danielian 1999189 |
| 15 | 168 | 13 | 192 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | De la Torre 2001200 |
| 6 | 65 | 4 | 65 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Denguezli 2007205 |
| 11 | 93 | 13 | 92 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | El Sherbiny 2001243 |
| 6 | 60 | 6 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Elhassan 2004238 |
| 3 | 31 | 2 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Elhassan 2005235 |
| 11 | 192 | 23 | 207 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Farah 1997250 |
| 10 | 53 | 7 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Ferguson 2002257 |
| 5 | 164 | 3 | 163 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Fonseca 2008265 |
| 11 | 55 | 10 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Frohn 2002269 |
| 6 | 89 | 12 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Garry 2003278 |
| 15 | 300 | 5 | 100 | 5 | 100 | 3 | 100 | 1 | 10 | 15 | 21 | 4 | Gelisen 2005281 |
| 2 | 129 | 1 | 139 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Gregson 2005312 |
| 3 | 58 | 4 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Has 2002339 |
| 20 | 63 | 18 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Incerpi 2001375 |
| 0 | 39 | 0 | 39 | 1 | 40 | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | 10 | NA | 3 | Khoury 2001423 |
| 17 | 71 | 32 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Kidanto 2007424 |
| 2 | 67 | 10 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Kolderup 1999430 |
| 6 | 50 | 6 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Krithika 2008440 |
| 6 | 100 | 7 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Kumar 2001442 |
| 4 | 100 | 10 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Megalo 2004551 |
| 2 | 60 | 2 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Meydanli 2003559 |
| 1 | 39 | 1 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Oboro 2005622 |
| 3 | 225 | 6 | 210 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Pandis 2001643 |
| 3 | 63 | 6 | 62 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Rowlands 2001726 |
| 16 | 185 | 15 | 184 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2001727 |
| 9 | 70 | 4 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2004728 |
| 8 | 115 | 8 | 108 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1998749 |
| 3 | 33 | 1 | 27 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Stitely 2000817 |
| 3 | 50 | 0 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Surbek 1997822 |
| 23 | 137 | 17 | 138 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995900 |
| 25 | 98 | 32 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1998905 |
| 2 | 50 | 2 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2006932 |
| 3 | 32 | 2 | 32 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2006934 |
| 3 | 48 | 4 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2006931 |
| 4 | 60 | 6 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayaz 201078 |
| 9 | 102 | 12 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Chaudhuri 2011151 |
| 22 | 100 | 22 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Chitraker 2012156 |
| 3 | 57 | 5 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Frass 2011268 |
| 7 | 50 | 8 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2009293 |
| 1 | 161 | 0 | 159 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2011294 |
| 6 | 55 | 0 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Hosli 2008364 |
| 4 | 95 | 11 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Lokugamage 2003482 |
| 3 | 56 | 2 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Ozkan 2009641 |
| 12 | 191 | 7 | 199 | 7 | 198 | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | 21 | NA | 3 | Prager 2008681 |
| 1 | 57 | 1 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Tan 2010840 |
| 89 | 340 | 67 | 341 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Van Gemund 2004879 |
| 11 | 67 | 13 | 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995900 |
| 27 | 98 | 30 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1997903 |
| 33 | 436 | 50 | 871 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2008896 |
| 5 | 42 | 4 | 42 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Meyer 2002560 |
| 2 | 25 | 0 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Sahu 2004738 |
| 128 | 1259 | 116 | 1258 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996335 |
| 5 | 132 | 3 | 135 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Tessier 1997844 |
| 71 | 680 | 61 | 678 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2013892 |
| 9 | 60 | 12 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Abedi-Asl 200745 |
| 1 | 128 | 5 | 128 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 13 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Aalami-Harandi 201343 |
Data file for OpenBUGS analysis of Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
Treatments included in analysis:
-
no treatment
-
placebo
-
vaginal PGE2 (tablet)
-
vaginal PGE2 (gel)
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release)
-
PGF2 gel
-
intracervical PGE2
-
vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg)
-
vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg)
-
oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg)
-
titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution
-
sustained-release misoprostol insert
-
i.v. oxytocin
-
amniotomy
-
i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy
-
NO
-
mifepristone
-
mechanical methods – Foley catheter
-
mechanical methods – laminaria
-
mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter
-
membrane sweeping
-
extra-amniotic PGE2
-
i.v. prostaglandin
-
sexual intercourse
-
acupuncture
-
oral prostaglandins
-
buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
| [r,1] | [n,1] | [r,2] | [n,2] | [r,3] | [n,3] | [r,4] | [n,4] | [t,1] | [t,2] | [t,3] | [t,4] | na[] | Author/year, trial number (where applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 | 101 | 0.5 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Agarwal 2012,54 21275 |
| 2 | 173 | 3 | 177 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Bollapragada 2009,107 18183 |
| 1 | 100 | 2 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Bullarbo 2007,123 15979 |
| 3.5 | 53 | 0.5 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2002,146 12397 |
| 1.5 | 57 | 0.5 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2002,144 11236 |
| 5 | 198 | 3 | 198 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Osman 2006,632 15372 |
| 8 | 30 | 1 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Perche 2009,662 18430 |
| 1 | 47 | 1 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1991,159 6450 |
| 0.5 | 79 | 2.5 | 79 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Domínguez Salgado 1999,218 11479 |
| 0.5 | 11 | 2.5 | 11 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Ekman-Ordeberg 1985,231 759 |
| 2 | 223 | 1 | 221 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Güngördük 2012,319 20462 |
| 16 | 1259 | 13 | 1256 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996,335 9118a |
| 1.5 | 101 | 0.5 | 102 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Hjertberg 1996,359 9117 |
| 5 | 83 | 5 | 75 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Jackson 1994,379 8574 |
| 6 | 510 | 6 | 502 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Ladfors 1996,447 9252 |
| 1.5 | 50 | 0.5 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Legarth 1987,460 3900 |
| 1 | 15 | 1 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Magos 1983,518 2157 |
| 3.5 | 28 | 0.5 | 24 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | McQueen 1990,549 5921 |
| 4 | 20 | 1 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | McQueen 1992,548 7430 |
| 0.5 | 48 | 0.5 | 42 | 1.5 | 56 | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | 14 | NA | 3 | Ray 1992,705 7125 |
| 2.5 | 139 | 0.5 | 140 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Rydhström 1991,733 3226 |
| 1 | 25 | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Silva-Cruz 1988,787 4525 |
| 0.5 | 51 | 1.5 | 44 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Tamsen 1990,836 5545 |
| 0.5 | 97 | 1.5 | 87 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Wagner 1989,882 4992 |
| 0.5 | 51 | 1.5 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Zahradnik 1987,926 3681 |
| 2 | 83 | 8 | 82 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Papageorgiou 1992,644 7364 |
| 0.5 | 100 | 3.5 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Boulvain 1998,110 9919 |
| 1 | 68 | 2 | 69 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Dare 2002,191 12270 |
| 1 | 32 | 1 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | El-Torkey 1992,232 7221 |
| 3 | 141 | 4 | 152 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Goldenberg 1996,300 9089 |
| 1.5 | 36 | 1.5 | 36 | 0.5 | 36 | NA | NA | 1 | 6 | 22 | NA | 3 | Magann 1998,513 11075 |
| 0.5 | 117 | 2.5 | 235 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 22 | NA | NA | 2 | Putnam 2011,690 20595 |
| 0.5 | 8 | 1.5 | 10 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Gaudet 2008,280 17891 |
| 1 | 58 | 1 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Modlock 2010,569 19120 |
| 1.5 | 54 | 0.5 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Selmer-Olsen 2007,765 16795 |
| 5 | 183 | 2 | 181 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 26 | NA | NA | 2 | Smith 2008,792 17746 |
| 5 | 150 | 3 | 150 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Amador 2007,67 16714 |
| 2 | 70 | 2 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Bartusevicius 2006,86 15686 |
| 3 | 62 | 2 | 58 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Moraes Filho 2010,577 14544 |
| 2 | 225 | 2 | 225 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Esteve 2006,246 15559 |
| 2.5 | 76 | 0.5 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Feitosa 2006,255 15685 |
| 1.5 | 29 | 0.5 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Parisaei 2008,649 17372 |
| 5 | 124 | 1 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Shetty 2002,782 12287 |
| 4 | 240 | 2 | 240 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 28 | NA | NA | 2 | Zahran 2009,927 18699 |
| 1 | 576 | 1 | 574 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | 2 | Omar 2013,627 21571 |
| 5 | 130 | 6 | 130 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 15 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1995,527 8658 |
| 0.5 | 126 | 1.5 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Chanrachakul 2003,143 12688 |
| 2 | 62 | 2 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Selo-Ojeme 2009,767 18022 |
| 0.5 | 102 | 1.5 | 106 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Tan 2013,837 21568 |
| 4 | 57 | 7 | 289 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Berkane 2005,97 14327 |
| 0.5 | 84 | 2.5 | 98 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000,902 11237 |
| 0.5 | 33 | 1.5 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 | 18 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2005,897 14330 |
| 3 | 75 | 5 | 72 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Al-Taani 2004,66 15001 |
| 1 | 95 | 5 | 95 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 20 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1997,160 9722 |
| 2 | 132 | 1 | 265 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2011,180 19650 |
| 0.5 | 104 | 1.5 | 106 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 21 | NA | NA | 2 | Cromi 2012,181 21024 |
| 16 | 200 | 15 | 200 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2011,207 20161 |
| 6 | 128 | 2 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 20 | NA | NA | 2 | Gilson 1996,291 9212 |
| 0.5 | 51 | 2.5 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Lyndrup 1994,497 8315 |
| 0.5 | 120 | 1.5 | 122 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Moraes Filho 2010,577 18961 |
| 3 | 80 | 3 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Oliveira 2010,625 19204 |
| 3 | 60 | 7 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Owolabi 2005,640 14892 |
| 3.5 | 114 | 2.5 | 111 | 0.5 | 108 | NA | NA | 4 | 19 | 21 | NA | 3 | Pennell 2009,660 18562 |
| 4 | 60 | 3 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Tabowei 2003831 |
| 1 | 50 | 1 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Balci 2011,81 20050 |
| 0.5 | 31 | 1.5 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 23 | NA | NA | 2 | Stewart 1983,815 2580 |
| 6 | 107 | 7 | 115 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Spellacy 1973,801 876 |
| 0.5 | 76 | 1.5 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 | 24 | NA | NA | 2 | Vakhariya 1972,874 787 |
| 19 | 100 | 9 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Deshmukh 2013,208 22653 |
| 6 | 100 | 8 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Gupta 2006,321 17823 |
| 1.5 | 52 | 0.5 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Habib 2008324 |
| 1 | 129 | 3 | 109 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Heden 1991,344 6018 |
| 1 | 78 | 3 | 78 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Katz 1983,410 2289 |
| 1.5 | 102 | 0.5 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 16 | NA | NA | 2 | Lo 1994,480 9055 |
| 4 | 136 | 2 | 127 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Misra 1994,565 8632 |
| 9 | 684 | 9 | 679 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 17 | NA | NA | 2 | Schmitz 2014,756 22698 |
| 2.5 | 98 | 0.5 | 104 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Witter 1987,915 3636 |
| 1 | 25 | 1 | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1988,349 4482 |
| 3 | 102 | 1 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Lange 1981,450 1271 |
| 2 | 119 | 1 | 125 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 14 | 27 | NA | NA | 2 | Secher 1981762 |
| 2 | 191 | 2 | 195 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Edwards 2014,223 22692 |
| 2 | 76 | 1 | 90 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Sande 1983,750 2434 |
| 2 | 75 | 1 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Duff 1984221 |
| 6 | 119 | 4 | 107 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Jozwiak 2013,389 22497 |
| 2.5 | 65 | 0.5 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 19 | NA | NA | 2 | Ten Eikelder 2013,843 21691 (Jozwiak 2014391) |
| 1 | 107 | 3 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Cabrol 1988129 |
| 2 | 48 | 1 | 48 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Hales 1994329 |
| 4.5 | 126 | 0.5 | 123 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Irion 1998376 |
| 0.5 | 141 | 1.5 | 143 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Keirse 1995414 |
| 3 | 229 | 5 | 241 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Kemp 2000418 |
| 1 | 56 | 2 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Legarth 1988458 |
| 1.5 | 48 | 0.5 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Lien 1998470 |
| 2.5 | 32 | 0.5 | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | McKenna 1999545 |
| 2.5 | 404 | 0.5 | 414 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Noah 1987612 |
| 1 | 45 | 2 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Ottinger 1998637 |
| 6 | 226 | 3 | 242 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Rath 1999703 |
| 3 | 155 | 3 | 173 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Rath 1999703 |
| 1.5 | 32 | 0.5 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Seeras 1995763 |
| 4 | 40 | 2 | 41 | 2 | 40 | NA | NA | 2 | 3 | 6 | NA | 3 | Thiery 1984851 |
| 9 | 249 | 14 | 266 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Trofatter 1993863 |
| 5 | 68 | 1 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Troostwijk 1992864 |
| 1.5 | 40 | 0.5 | 40 | 0.5 | 37 | NA | NA | 6 | 7 | 21 | NA | 3 | Yuen 1996924 |
| 4 | 51 | 1 | 57 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1992352 |
| 0.5 | 27 | 1.5 | 23 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1993350 |
| 0.5 | 26 | 3.5 | 26 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Pulle 1986689 |
| 4.5 | 126 | 0.5 | 123 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Pedrazzoli 1997658 |
| 3 | 85 | 2 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Adair 199848 |
| 4 | 40 | 2 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Adam 200549 |
| 3 | 78 | 3 | 78 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Beigi 200388 |
| 0.5 | 103 | 1.5 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Bennett 199892 |
| 2.5 | 56 | 0.5 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Butt 1999126 |
| 6.5 | 107 | 0.5 | 102 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Cheng 2008154 |
| 1 | 52 | 2 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Crane 2003179 |
| 2 | 100 | 1 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | Dällenbach 2003186 |
| 5 | 376 | 2 | 365 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Dodd 2006214 |
| 2.5 | 49 | 0.5 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Hall 2002330 |
| 1 | 112 | 1 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Henrich 2008347 |
| 3 | 49 | 1 | 47 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Hoffman 2001361 |
| 15 | 349 | 11 | 346 | 6 | 171 | NA | NA | 4 | 12 | 19 | NA | 3 | Hofmeyr 2001363 |
| 5 | 110 | 4 | 109 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 10 | NA | NA | 2 | How 2001366 |
| 0.5 | 24 | 1.5 | 30 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Kipikasa 2005428 |
| 2.5 | 83 | 0.5 | 79 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Kwon 2001444 |
| 3 | 159 | 2 | 146 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Mozurkewich 2003582 |
| 1 | 41 | 1 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Ngai 1996605 |
| 0.5 | 51 | 1.5 | 51 | 0.5 | 51 | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | 11 | NA | 3 | Sheela 2007771 |
| 0.5 | 31 | 1.5 | 31 | 1.5 | 31 | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | 19 | NA | 3 | Sheikher 2009772 |
| 4 | 113 | 1 | 121 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2000902 |
| 2 | 42 | 2 | 42 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayaz 200877 |
| 15 | 110 | 8 | 110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Rahman 2013694 |
| 3 | 100 | 1 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 12 | NA | NA | 2 | Souza 2013796 |
| 1.5 | 36 | 0.5 | 39 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Buchanan 1984121 |
| 4 | 207 | 2 | 195 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Cardozo 1986137 |
| 0.5 | 77 | 1.5 | 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Chua 1995161 |
| 0.5 | 29 | 1.5 | 38 | 2.5 | 51 | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | 22 | NA | 3 | Doany 1997212 |
| 1 | 20 | 2 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Graves 1985307 |
| 1 | 40 | 1 | 40 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Mahmood 1989522 |
| 2.5 | 51 | 0.5 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | O’Brien 1995624 |
| 3 | 45 | 4 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Perryman 1992669 |
| 2 | 50 | 2 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Poornima 2011678 |
| 0.5 | 16 | 1.5 | 16 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Prins 1983685 |
| 0.5 | 101 | 1.5 | 101 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 5 | NA | NA | 2 | Rabl 2002693 |
| 2.5 | 64 | 0.5 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Rayburn 1988707 |
| 1.5 | 106 | 0.5 | 97 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Roach 1997715 |
| 1 | 42 | 1 | 38 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Sawai 1994752 |
| 3 | 100 | 1 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 3 | NA | NA | 2 | Shoaib 1994785 |
| 0.5 | 35 | 2.5 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 7 | NA | NA | 2 | Smith 1990794 |
| 0.5 | 84 | 2.5 | 83 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Taher 2011834 |
| 10 | 120 | 10 | 118 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayad 200276 |
| 2.5 | 78 | 0.5 | 76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Campos 1991133 |
| 1 | 105 | 2 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | De Aquino 2003198 |
| 1 | 168 | 4 | 192 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | De la Torre 2001200 |
| 3.5 | 66 | 0.5 | 66 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Denguezli 2007205 |
| 2 | 93 | 2 | 92 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | El Sherbiny 2001243 |
| 4 | 60 | 2 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Elhassan 2004238 |
| 1 | 192 | 7 | 207 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Farah 1997250 |
| 3 | 53 | 1 | 53 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Ferguson 2002257 |
| 1 | 164 | 2 | 163 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Fonseca 2008265 |
| 1 | 55 | 2 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Frohn 2002269 |
| 3.5 | 301 | 2.5 | 101 | 1.5 | 101 | 0.5 | 101 | 1 | 9 | 14 | 19 | 4 | Gelisen 2005281 |
| 1 | 54 | 1 | 54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Haghighi 2006325 |
| 3 | 58 | 4 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Has 2002339 |
| 1.5 | 51 | 0.5 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Herabutya 1997351 |
| 2 | 112 | 2 | 112 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Kadanali 1996392 |
| 2 | 71 | 4 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Kidanto 2007424 |
| 2 | 100 | 3 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Kumar 2001442 |
| 2 | 44 | 3 | 47 | 2 | 40 | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | 14 | NA | 3 | Lemancewicz 1999463 |
| 2.5 | 36 | 0.5 | 34 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | McKenna 2004546 |
| 3 | 100 | 2 | 100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Megalo 2004551 |
| 3 | 60 | 2 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Meydanli 2003559 |
| 0.5 | 84 | 1.5 | 81 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Papanikolaou 2004645 |
| 3 | 225 | 2 | 210 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Pandis 2001643 |
| 0.5 | 64 | 1.5 | 63 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Rowlands 2001726 |
| 3 | 185 | 2 | 184 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2001727 |
| 1 | 70 | 2 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Rozenberg 2004728 |
| 1 | 70 | 2 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1997745 |
| 2 | 115 | 1 | 108 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Sanchez-Ramos 1998749 |
| 2 | 98 | 2 | 99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1998905 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 1.5 | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Zeteroğlu 2006931 |
| 0.5 | 61 | 1.5 | 61 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Ayaz 201078 |
| 1 | 102 | 1 | 105 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Chaudhuri 2011151 |
| 4 | 57 | 7 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Frass 2011268 |
| 1 | 161 | 3 | 159 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Girija 2011294 |
| 2 | 95 | 3 | 96 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Lokugamage 2003482 |
| 2 | 56 | 2 | 56 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Ozkan 2009641 |
| 1 | 70 | 2 | 70 | 2 | 70 | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | 9 | NA | 3 | Saxena 2011755 |
| 1.5 | 32 | 0.5 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Shakya 2010768 |
| 8 | 340 | 8 | 341 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Van Gemund 2004879 |
| 1 | 33 | 1 | 36 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Varaklis 1995880 |
| 0.5 | 68 | 1.5 | 69 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 1995900 |
| 4 | 436 | 11 | 871 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2008896 |
| 0.5 | 43 | 1.5 | 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 8 | NA | NA | 2 | Meyer 2002560 |
| 2.5 | 26 | 0.5 | 26 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 9 | NA | NA | 2 | Sahu 2004738 |
| 1.5 | 38 | 0.5 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 6 | NA | NA | 2 | Chyu 1997167 |
| 15 | 1259 | 25 | 1258 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 4 | NA | NA | 2 | Hannah 1996335 |
| 4 | 132 | 1 | 135 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 11 | NA | NA | 2 | Tessier 1997844 |
| 7 | 680 | 14 | 678 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 13 | NA | NA | 2 | Wing 2013892 |
| 1 | 60 | 1 | 60 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Abedi-Asl 200745 |
| 6 | 55 | 4 | 55 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Tabasi 2007829 |
| 1 | 128 | 1 | 128 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 12 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Aalami-Harandi 201343 |
| 1.5 | 50 | 0.5 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 14 | NA | NA | 2 | Egarter 1987228 |
Appendix 15 Subgroup analysis for intact membranes compared with ruptured membranes
Outcome: vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours
FIGURE 23.
Network for intact membranes only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 3, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 4, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 5, intracervical PGE2; 6, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 7, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 9, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 11, i.v. oxytocin; 12, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 13, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 14, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 15, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
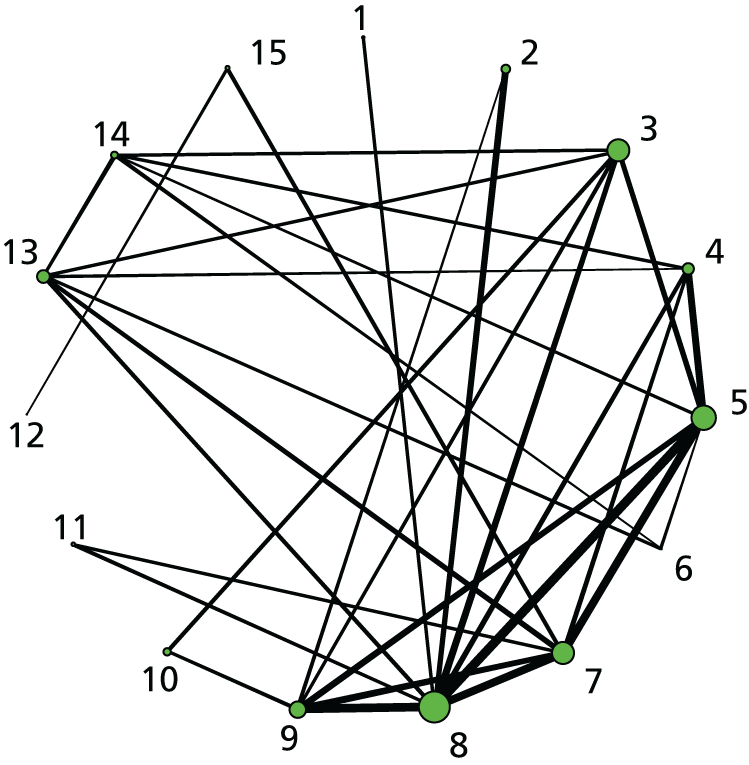
| Number of data points | totresdeva | Between-study SD: posterior mean (95% Crl) | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency: 118 | 119.9 | 0.42 (0.27 to 0.60) | 750 |
| REs inconsistency: 118 | 119.1 | 0.43 (0.24 to 0.66) | 756.6 |
Outcome: vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours
FIGURE 24.
Network for ruptured membranes only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 4, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 5, intracervical PGE2; 6, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 7, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 8, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 9, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 11, i.v. oxytocin; 12, mifepristone.

| Number of data points | totresdeva | Between-study SD: posterior mean (95% Crl) | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency: 34 | 35.42 | 0.90 (0.08 to 2.38) | 199.8 |
Note: The REs inconsistency model would not compile.
Outcome: caesarean section
FIGURE 25.
Network for intact membranes only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, PGF2 gel; 7, intracervical PGE2; 8, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 10, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 12, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 13, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, amniotomy; 16, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 17, NO; 18, mifepristone; 19, oestrogens; 20, corticosteroids; 21, relaxin; 22, hyaluronidase; 23, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 24, mechanical methods – laminaria; 25, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 26, membrane sweeping; 27, extra-amniotic PGE2; 28, i.v. prostaglandin; 29, sexual intercourse; 30, acupuncture; 31, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.

| Number of data points | totresdeva | Between-study SD: posterior mean (95% Crl) | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency: 335 | 346.2 | 0.1823 (0.008 to 0.32) | 1890 |
| REs inconsistency: 335 | 340.1 | 0.2 (0.04 to 0.36) | 1928 |
FIGURE 26.
Network for ruptured membranes only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 tablet; 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, PGF2 gel; 7, intracervical PGE2; 8, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 10, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 12, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 13, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, mifepristone; 16, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 17, acupuncture.

| Number of data points | totresdeva | Between-study SD: posterior mean (95% Crl) | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency: 98 | 87.02 | 0.11 (0.004 to 0.297) | 520.4 |
| REs inconsistency: 98 | 87.19 | 0.11 (0.007 to 0.324) | 529.9 |
Outcome: Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
Subgroup analysis for women with low Bishop score (< 6) or higher Bishop score ( ≥ 6)
FIGURE 27.
Network for intact membranes only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, i.v. oxytocin; 14, amniotomy; 15, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 16, NO; 17, mifepristone; 18, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 19, mechanical methods – laminaria; 20, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 21, membrane sweeping; 22, i.v. prostaglandin; 23, sexual intercourse; 24, acupuncture; 25, oral prostaglandins; 26, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.

| Number of data points | totresdeva | Between-study SD: posterior mean (95% Crl) | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency: 205 | 230.8 | 0.36 (0.01 to 0.898) | 762 |
| REs inconsistency: 205 | 209.9 | 0.47 (0.03 to 1.34) | 760 |
Subgroup analysis for women with low Bishop score (< 6) or higher Bishop score (≥ 6)
Outcome: vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours
FIGURE 28.
Network for unfavourable cervix only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, NO; 16, mifepristone; 17, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 18, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 19, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.

| Number of data points | totresdeva | Between-study SD: posterior mean (95% Crl) | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency: 221 | 233.5 | 0.59 (0.47 to 0.73) | 1429 |
| REs inconsistency: 221 | 225.8 | 0.53 (0.38 to 0.70) | 1429 |
FIGURE 29.
Network for favourable cervix only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 2, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 3, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 4, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 5, i.v. oxytocin; 6, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 7, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
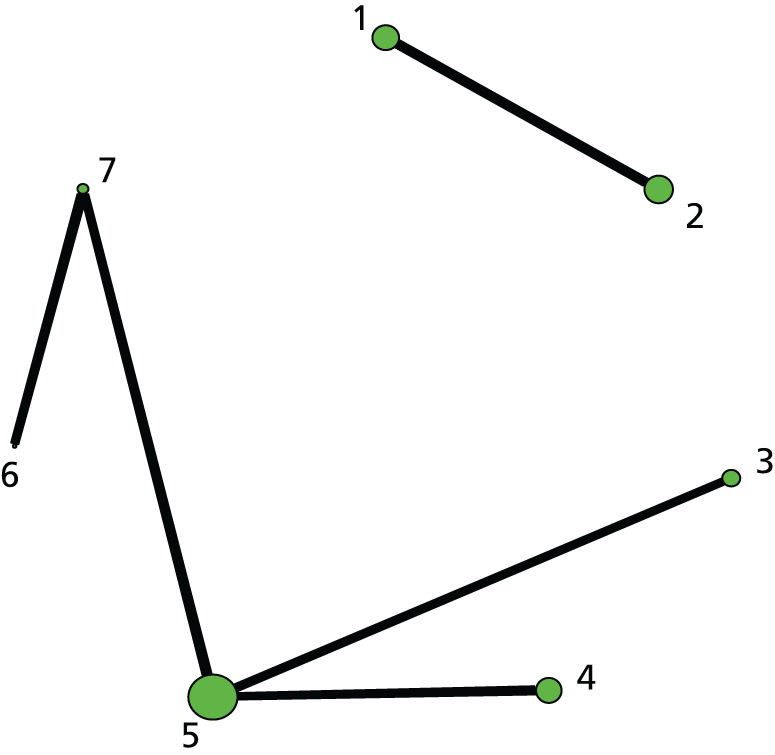
Outcome: caesarean section
FIGURE 30.
Network for unfavourable cervix only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, PGF2 gel; 7, intracervical PGE2; 8, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 10, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 12, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 13, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 14, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 15, i.v. oxytocin; 16, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 17, NO; 18, mifepristone; 19, oestrogens; 20, relaxin; 21, hyaluronidase; 22, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 23, mechanical methods – laminaria; 24, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 25, membrane sweeping; 26, extra-amniotic PGE2; 27, acupuncture; 28, i.v. prostaglandin.

| Number of data points | totresdeva | Between-study SD: posterior mean (95% Crl) | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency: 429 | 440 | 0.2 (0.09 to 0.3) | 2461 |
| REs inconsistency: 429 | 440.7 | 0.19 (0.05 to 0.32) | 2505 |
FIGURE 31.
Network for favourable cervix only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 6, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 7, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 8, i.v. oxytocin; 9, amniotomy; 10, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 11, corticosteroids; 12, relaxin, 13; buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
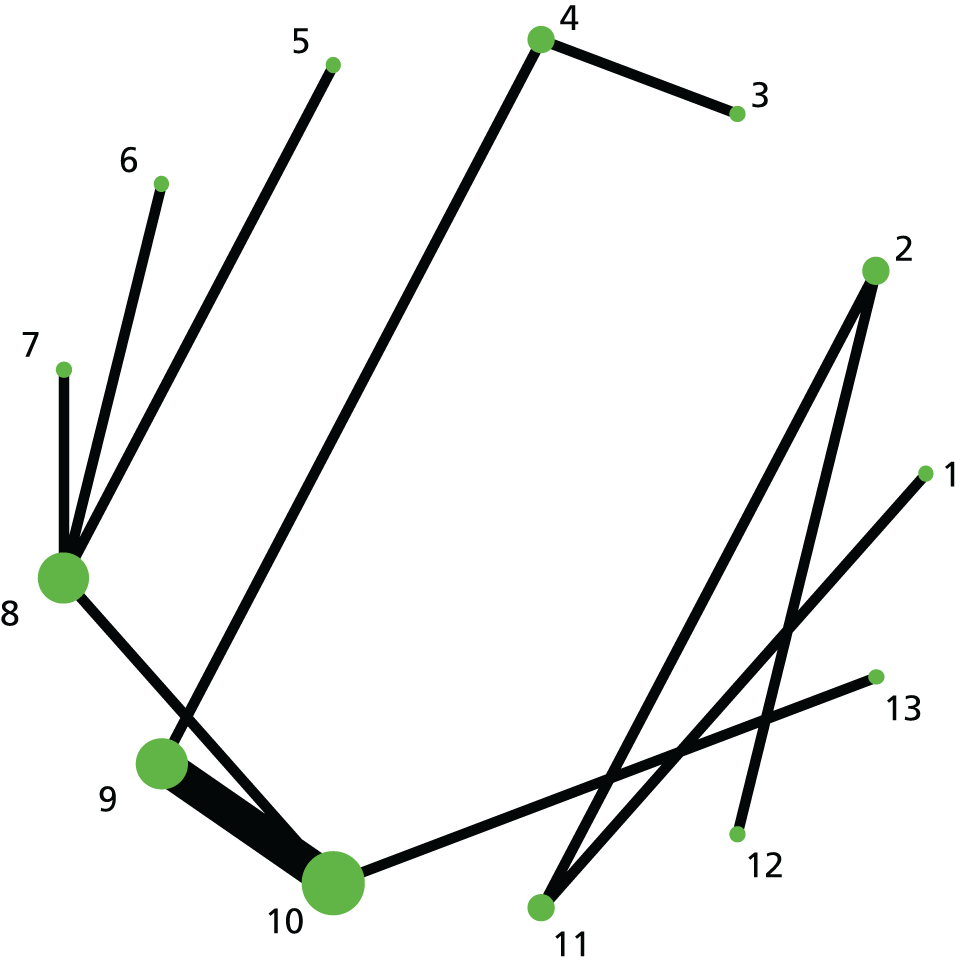
| Number of data points | totresdeva | Between-study SD: posterior mean (95% Crl) | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| REs consistency: 20 | 19.8 | 1.17 (0.04 to 4.23) | 110.4 |
| REs inconsistency: 20 | 19.77 | 1.05 (0.03 to 3.49) | 110.4 |
Outcome: Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes
FIGURE 32.
Network for unfavourable cervix only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, NO; 16, mifepristone; 17, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 18, mechanical methods – laminaria; 19, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 20, membrane sweeping; 21, extra-amniotic PGE2; 22, acupuncture; 23, oral prostaglandins; 24, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
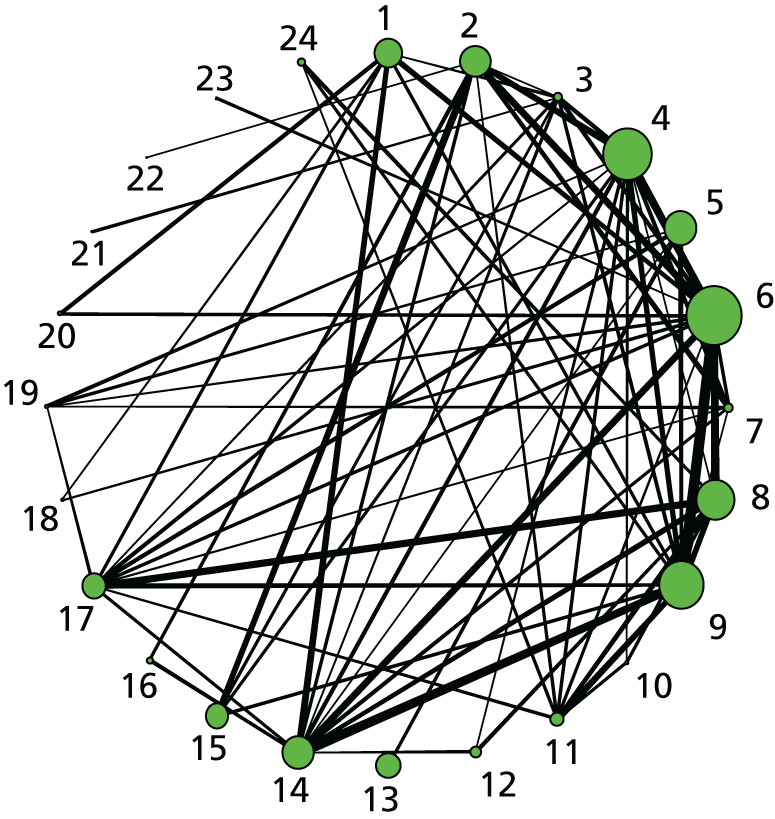
FIGURE 33.
Network for favourable cervix only. Treatments are numbered as follows: 1, no treatment; 2, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 3, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 4, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 5, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 6, amniotomy; 7, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 8, corticosteroids; 9, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
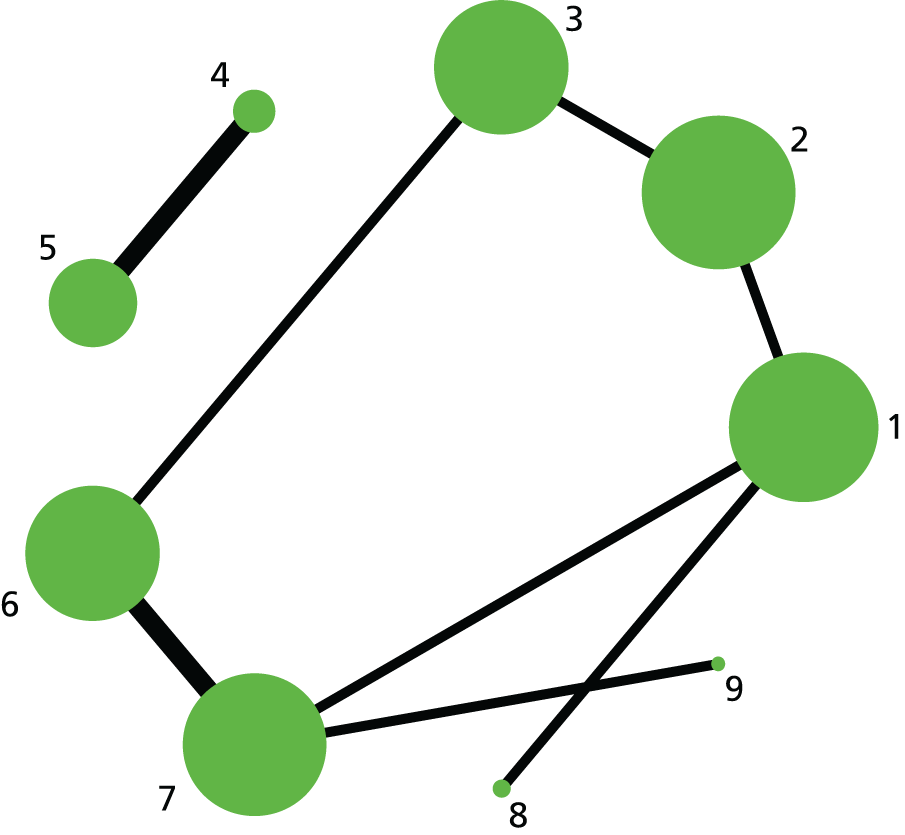
Model would not converge because of sparse network and small number of events on some arms.
Appendix 16 Joint estimation of intervention efficacy for use in economic model
After induction of labour there are three mutually exclusive outcomes that can occur: VD within 24 hours (VD24), VD after 24 hours (VD > 24) and CS. If a study reports all outcomes then we can jointly estimate the probability of each of these outcomes using a multinomial likelihood, which ensures that the three outcome probabilities sum to 1. However, not all of our included studies report all of these outcomes. Restricting to only studies that report all three outcomes substantially reduces the number of studies that are included to 86. In order to include as many studies as possible, we note that the multinomial likelihood with three outcomes can be written as two conditionally independent binomial likelihoods. We therefore first estimate the relative effects (ORs) for CS using the NMA presented in Chapter 3 (including 307 studies). Then, conditional on not having a CS, we estimate the relative effects (ORs) for a VD within 24 hours compared with after 24 hours, in an additional NMA performed specifically for the economic model (including 86 studies – see below). Care is required to ensure that the correct denominator (number of women who did not have a CS) is used in this analysis.
Given estimates of the probability of (1) a VD within 24 hours and (2) CS conditional on failure to achieve a VD in 24 hours, for the reference treatment, ref, we can apply the ORs estimated in the NMA to obtain probabilities for these outcomes for any intervention k using the relationship: log–odds (probability(k)) = log–odds (probability(ref)) + log–odds ratio.
We can then find the overall p(VD24) = (1 – p(CS)) x p(VD24 given no CS). The probability of a VD in > 24 hours, p(VD > 24), can be computed as p(VD > 24) = 1 – p(VD24) – p(CS).
For the additional NMA for a VD within 24 hours given no CS, after excluding trials with zero events in all arms and those that did not report both CS and failure to deliver vaginally within 24 hours, 86 trials of 21 interventions were incorporated, including placebo and no intervention comparisons. The network plot is shown in Figure 34.
FIGURE 34.
Vaginal delivery within 24 hours, given no CS. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials comparing directly each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). Interventions are numbered as follows: 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 16, NO; 17, mifepristone; 18, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 19, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 20, extra-amniotic PGE2; 21, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.

For the additional NMA for a VD within 24 hours given no CS, in the subgroup of women with intact membranes only, 33 trials of 13 interventions were included. The network plot is shown in Figure 35.
FIGURE 35.
Subgroup analysis (i): women with intact membranes only. VD within 24 hours, given no CS. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. The width of the lines is proportional to the number of trials comparing directly each pair of interventions. The size of each node is proportional to the number of randomised participants (sample size). Interventions are numbered as follows: 1, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 2, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 3, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 4, intracervical PGE2; 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 6, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 7, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 8, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 9, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 10, i.v. oxytocin plus amniotomy; 11, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 12, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 13, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.

For the additional NMA for a VD within 24 hours given no CS in the subgroup of women with an unfavourable cervix only, 63 trials of 19 interventions were incorporated, including placebo and no intervention. The network plot is shown in Figure 36.
FIGURE 36.
Subgroup analysis (ii): women with an unfavourable cervix only. VD within 24 hours given no CS. Network diagram of all of the studies included in analysis. Interventions are numbered as follows: 1, no intervention; 2, placebo; 3, vaginal PGE2 (tablet); 4, vaginal PGE2 (gel); 5, vaginal PGE2 pessary (slow release); 6, intracervical PGE2; 7, vaginal PGE2 pessary (normal release); 8, vaginal misoprostol (dose < 50 µg); 9, vaginal misoprostol (dose ≥ 50 µg); 10, oral misoprostol tablet (dose < 50 µg); 11, oral misoprostol tablet (dose ≥ 50 µg); 12, titrated (low-dose) oral misoprostol solution; 13, sustained-release misoprostol insert; 14, i.v. oxytocin; 15, NO; 16, mifepristone; 17, mechanical methods – Foley catheter; 18, mechanical methods – double-balloon or Cook’s catheter; 19, buccal/sublingual misoprostol.
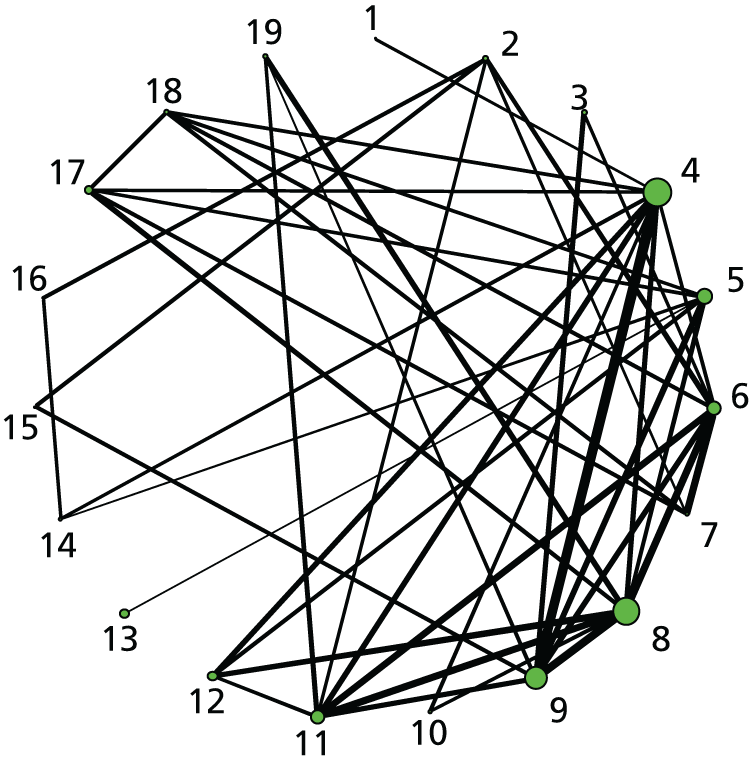
Appendix 17 Review of economic evidence
The economic search strategy is shown below for The Cochrane Library. The same strategy was translated for the other databases searched. Table 76 gives a list of excluded studies for model inputs for utilities, with reasons.
| ID | Search | Hits |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | MeSH descriptor: [Pregnancy] explode all trees | 5896 |
| #2 | MeSH descriptor: [Pregnancy Complications] explode all trees | 8008 |
| #3 | MeSH descriptor: [Infant, Newborn] explode all trees | 13,392 |
| #4 | MeSH descriptor: [Maternal Health Services] explode all trees | 1652 |
| #5 | MeSH descriptor: [Maternal-Child Nursing] explode all trees | 194 |
| #6 | MeSH descriptor: [Perinatal Care] explode all trees | 436 |
| #7 | pregnan* (Word variations have been searched) | 31,254 |
| #8 | birth or childbirth | 16,329 |
| #9 | labour or laboring | 4572 |
| #10 | labour* | 4470 |
| #11 | caesar* | 3126 |
| #12 | cesar* | 6306 |
| #13 | obstetric* | 26,797 |
| #14 | matern* | 12,662 |
| #15 | (#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14) | 64,641 |
| #16 | Economics | 23,886 |
| #17 | (exp "Costs and Cost Analysis") | 15 |
| #18 | exp Models, Economic | 662 |
| #19 | Decision Trees | 2207 |
| #20 | econom$ | 12 |
| #21 | cba | 404 |
| #22 | cea | 861 |
| #23 | cua | 70 |
| #24 | (monteadjcarlo) | 30 |
| #25 | (decision adj3 (tree$ or analys$)) | 90 |
| #26 | (cost or costs or costing$ or costly or costed) | 60,137 |
| #27 | #16 or #17 or #18 or #19 or #20 or #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 | 63,745 |
| #28 | "Quality of Life" | 43,721 |
| #29 | quality of life | 50,815 |
| #30 | “Value of Life” | 168 |
| #31 | Quality-Adjusted Life Years | 6281 |
| #32 | quality adjusted life | 10,178 |
| #33 | (qaly$ or qald$ or qale$ or qtime$) | 3670 |
| #34 | Health Status Indicators | 2532 |
| #35 | (sf36 or sf 36 or short form 36 or shortform 36 or sf thirtysix or sf thirty six or shortformthirtysix or shortform thirty six or short form thirtysix or short form thirty six) | 9841 |
| #36 | sf6 or sf 6 or short form 6 or shortform 6 or sf six or sfsix or shortform six or short form six | 11718 |
| #37 | sf12 or sf 12 or short form 12 or shortform 12 or sf twelve or sftwelve or shortform twelve or short form twelve | 9713 |
| #38 | sf16 or sf 16 or short form 16 or shortform 16 or sf sixteen or sfsixteen or shortform sixteen or short form sixteen | 6468 |
| #39 | sf20 or sf 20 or short form 20 or shortform 20 or sf twenty or sftwenty or shortform twenty or short form twenty | 7651 |
| #40 | euroqol or euro qol or eq5d or eq 5d | 2773 |
| #41 | qol or hql or hqol or hrqol | 7840 |
| #42 | hye or hyes | 53 |
| #43 | health$ year$ equivalent$ | 2861 |
| #44 | utilit* | 11,896 |
| #45 | hui or hui1 or hui2 or hui3 | 1263 |
| #46 | disutili* | 205 |
| #47 | quality of well-being | 996 |
| #48 | quality of well-being | 3585 |
| #49 | qwb | 68 |
| #50 | willingness-to-pay | 1337 |
| #51 | standard gamble$ | 528 |
| #52 | time trade-off | 66 |
| #53 | time trade-off | 939 |
| #54 | tto | 95 |
| #55 | #28 or #29 or #30 or #31 or #32 or #33 or #34 or #35 or #36 or #37 or #38 or #39 or #40 or #41 or #42 or #43 or #44 or #45 or #46 or #47 or #48 or #49 or #50 or #51 or #52 or #53 or #54 | 67,456 |
| #56 | #27 or #55 | 109,206 |
| #57 | #15 and #27 | 8908 |
| #58 | #56 and #57 | 8908 |
| Study | NICU | VD | Emergency CS | How derived | Reason for inclusion/exclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chung et al. 2001 Cost-effectiveness of a trial of labour after previous cesarean. Obstet Gynecol 97:932–41 |
Neonatal health state: no/mild or moderate morbidity – 1, range: 0.9–1 | Successful trial of labour – per diem disutility of 0.35 for 7 days | Elective repeat caesarean delivery – per diem disutility of 0.45 over 21 days | Quality of Well-being classification system | Excluded, as utilities not elicited from patients |
| Wymer et al. 2014 The cost-effectiveness of a trial of labour accrues with multiple subsequent vaginal deliveries. Am J Obstet Gynecol 211:211:e.1–56.e12 |
0.92, range 0.88–0.96 | 0.9973, range 0.9919–0.9987 | 0.9954, range 0.9931–0.9977 | NICU admission from Hamel 2000; VD and CS from Plunkett and Grobman 2005 | Excluded, as no utilities measured, utilities taken from excluded studies |
| Hamel et al. 2000 Outcomes and cost-effectiveness of ventilator support and aggressive care for patients with acute respiratory failure due to pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Med 109:614–20 |
ICU utility – median: 0.92; 25th, 75th percentile 0.92, 1 | Time trade-off by 225 patients with acute respiratory failure | Excluded due to wrong patient population | ||
| Kaimal et al. 201112 Cost-effectiveness of elective induction of labor at 41 weeks in nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:137.e1–9 |
VD – 1 | Caesarean delivery – 0.99 (0.9–1.0) | Vaginal assumed. CS assumed from Caughey et al.975 no utilities given in paper | Excluded as no utilities measured, unclear where utility values taken from | |
| Fawsitt et al. 2013 At what price? A cost-effectiveness analysis comparing trial of labour after previous caesarean versus elective repeat cesarean delivery. PLOS ONE 8:e58577 |
Successful trial of labour – 0.41 for 7 days | Emergency CS – 0.58 for 21 days | Adapted from Chung et al. 2001 | Excluded, as no utilities measured, utilities taken from excluded studies | |
| Ohno et al. 2011 Treating mild gestational diabetes mellitus: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 205:282.e1–7 |
NICU admission – 1 | VD – 1 | Caesarean delivery – 0.99 | VD assumed, CS assumed based on Caughey et al. 2006, NICU assumed | Excluded, as no utilities measured |
| Tan et al. 2010 Cost-effectiveness of external cephalic version for term breech presentation. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 10:3 |
0.76/0.75 – derived from an assumed 2-day ICU or NICU stay at a utility of 0.17 and 0.20, respectively, for mother and child, followed by utility of 0.60 for the subsequent 2 weeks post delivery and a utility of 0.77 for the following 8 weeks until return to perfect health | 0.86 – based on the first 7 days at a utility of 0.50 and the remainder of the 6 weeks for recovery at a utility of 0.77 Assumed that the mother would subsequently return to perfect health at a utility of 1.00 |
0.78 – based on the first 21 days at a utility of 0.41 and the remainder of the 8 weeks for recovery at a utility of 0.77 Assumed that the mother would subsequently return to perfect health at a utility of 1.00 |
Estimated through observation and simulation of a mother and child experiencing each of the four health states used in the model | Excluded, as utilities not elicited from patients |
| Gilbert et al. 2013 Cost-effectiveness of trial of labor after previous cesarean in a minimally biased cohort. Am J Perinatol 30:11–20 |
Successful trial of labour – per diem disutility of 0.35 for 7 days | Elective Repeat Caesarean Delivery – per diem disutility of 0.45 over 21 days | From Chung et al. 2001 | Excluded as no utilities measured, utilities taken from excluded studies | |
| Culligan et al. 2005 Elective cesarean section to prevent anal incontinence and brachial plexus injuries associated with macrosomia: a decision analysis. Int Urogynecol J 16:19–28 |
Uncomplicated VD and healthy child – 1, range: 0.9–1, VD including first or second degree episiotomy that heals normally and healthy child – 0.995, range: 0.90–1 | Assigned by a panel of five experts | Excluded, because of lack of instrument to value health states | ||
| Xu et al. 2010 Pelvic floor consequences of caesarean delivery on maternal request in women with a single birth: a cost-effectiveness analysis. J Women Health 19:147–60 |
Admission to neonatal nursery – 0.99, range 0.70–0.99 | VD – 0.92, range 0.69–1.00 | Emergency CS – 0.59, range 0.44–0.74 | From Pham and Crowther and Vandenbussche 1999; from Turner et al. 2008 | Excluded, as no utilities measured, utilities taken from other studies |
Appendix 18 Elicitation of utilities
Visual analogue scale
The VAS consists of a single line with anchors representing best possible health and death (or some alternative). Respondents are asked to place each health state on the line, such that the intervals between the placements reflect their perceived differences between the health states. Our VAS depicted a 10-point horizontal line ranging from ‘worst imaginable health state’ (lower anchor) to ‘best imaginable health state’ (upper anchor). Each respondent was asked to draw a horizontal line on the VAS to indicate where they thought the described maternal and neonatal health states should be positioned, taking the top and bottom anchors into consideration.
Utility elicitation questionnaire
Statistical analysis
The responses for each of the 10 respondents are plotted in Figure 37. Overall utility scores are very variable across respondents, but similar patterns are seen between health states. We fitted a normal distribution to the utility scores for the first state (VD from the mother’s perspective), giving an estimated mean score 0.65, across respondents, and estimated between respondent SD of 2.05. Then for each of the other health states we estimate the mean difference in score relative to state 1 (VD from the mother’s perspective) and between-respondent SD in these differences. Modelling differences in this way accounts for the variability between respondents and allows for correlations between scores from the same respondent. Adding the estimated mean difference to the mean score for health state 1 gives an absolute score for each health state, and dividing by 10 gives a value on the interval 0–1. The OpenBUGS code is given below.
FIGURE 37.
Utility scores from the VAS questionnaire. Each line represents a different respondent. The health states valued are given on the x-axis, where CS = caesarean section, IC = intensive care, HD = high dependency, TC = transitional care. ‘Mother’ indicates the perspective of the mother, and ‘Baby’ indicates the perspective of the baby. If not specified then score represents the perspective of the mother.

Table 77 shows how the utility scores from the questions in the VAS questionnaire are combined to obtain the utility scores for the health states required in our model. Note that to obtain the utility scores for the mother’s perspective only the first term is used for each state, whereas for the utilities from the baby’s perspective only the second term is used for each state.
| Health state | Derivation |
|---|---|
| VD with no neonatal complications | utility1 + 1 |
| Emergency CS with no neonatal complications | utility3 + 1 |
| VD with transitional care | utility1*utility8 + utility9 |
| VD with intensive care | utility1*utility6 + utility7 |
| VD with high-dependency care | utility1*utility4 + utility5 |
| Emergency CS with transitional care | utility3*utility8 + utility9 |
| Emergency CS with intensive care | utility3*utility6 + utility7 |
| Emergency CS with high-dependency care | utility3*utility4 + utility5 |
OpenBUGS Code for analysis of utility scores from visual analogue scale questionnaire
Glossary
- Amniotomy
- Surgical rupture of the amniotic membranes.
- Apgar score
- A scoring system (0–10) to describe the condition of the newborn. A score > 7 at 5 minutes after the birth suggests that the infant is in a good condition.
- Bishop score
- A scoring system to measure changes in the cervix (cervical length and dilatation); a Bishop score < 6 is often referred to as an unripe cervix (unfavourable), whereas ≥ 6 is referred to as a ripe cervix (favourable).
- Catheter
- A length of rubberised tubing with an inflatable balloon to anchor the tubing in place. Urinary catheters are used to drain urine from the bladder (a Foley catheter is a type of urinary catheter). A catheter can be passed through the cervical canal and small balloon(s) is (are) inflated with sterile solution to hold the catheter in place. Catheters used for the induction of labour may have a single balloon (e.g. Foley catheter) or specially designed catheters with two balloons can be used.
- Cluster randomised trial
- A type of randomised trial in which groups rather than individual participants are randomised to intervention or control.
- Cochrane Collaboration
- International not-for-profit organisation preparing, maintaining and promoting the accessibility of systematic reviews of the effects of health-care interventions.
- Consistency
- The fundamental assumption underpinning a network meta-analysis. The assumption is also known as transitivity and states that (the benefit of A over B) is equal to (the benefit of A over C) minus (the benefit of B over C). Consistency suggests that the sets of studies used to obtain the indirect comparison are sufficiently similar in characteristics that potentially moderate the intervention effect.
- Direct comparison
- A comparison of two or more interventions made within a study.
- Direct evidence
- Evidence on the relative effects of interventions derived entirely from direct comparisons.
- Expectant management
- Care that involves a period of observation rather than immediate intervention. In the context of planned induction of labour, this would give time to allow for the spontaneous onset of labour.
- Gestational age
- The length of the pregnancy from the date of the last menstrual period; gestational age is usually recorded in weeks plus days.
- Indirect comparison
- A comparison of two interventions via one or more common comparator. For example, the combination of intervention effects from AB and intervention effects from BC studies may (in some situations) be used to learn about the intervention effect AC.
- Indirect evidence
- Evidence on the relative effectiveness of two interventions derived entirely from indirect comparisons. Indirect evidence may be available via more than one intermediate comparator.
- Induction of labour
- Interventions (pharmacological, mechanical, complementary or alternative) to artificially stimulate the start of labour.
- Intra
- Into (e.g. intravaginal, intracervical; when drugs are introduced into the vagina or cervical canal).
- Laminaria
- Devices that can be introduced into the cervical canal, which expand to stimulate cervical dilatation.
- Membrane sweep
- Membrane sweeping or stripping involves the midwife or doctor detaching the amniotic membranes from the lower section of the uterus by a circular movement of an examining finger; this has been used to stimulate labour.
- Meta-analysis
- Synthesis (pooling) of data from more than one study to estimate an overall result.
- Network diagram
- A graphical depiction of how each intervention is connected to the others through direct comparisons. Each line, or edge, depicts a direct comparison between two intervention nodes.
- Network meta-analysis
- The simultaneous comparison of multiple competing treatments in a single statistical analysis (also known as a mixed-treatment comparison). The method uses both direct and indirect evidence to estimate the relative effects of each treatment compared with all others in the network, even though some treatments may not have been directly compared with each other in trials.
- Nitric oxide donors
- Chemicals produced by the body that have a role in many functions. Commercially produced nitric oxide donors are used to stimulate changes in the cervix as part of induction of labour. Types of nitric oxide donors include isosorbide mononitrate, isosorbide dinitrate, nitroglycerin and sodium nitroprusside.
- Oxytocin
- A hormone produced by the body that has an important role in childbirth. Commercially manufactured oxytocin is used in the induction of labour to stimulate cervical dilatation and uterine contractions.
- Parity
- Relates to the number of times a woman has given birth. A nulliparous woman has not given birth before; a multiparous woman has given birth at least once before.
- Post term
- A pregnancy continuing beyond 41+0 weeks (also known as post dates).
- Preterm birth
- Birth before 37+0 weeks of pregnancy.
- Prostaglandin E1
- A type of Q4 prostaglandin (misoprostol is a synthetic analogue of PGE1 used in the induction of labour).
- Prostaglandin E2
- A type of prostaglandin used in the induction of labour (dinoprostone).
- Prostaglandin F2
- A type of prostaglandin used in the induction of labour.
- Prostaglandin F2 alpha
- A naturally occurring prostaglandin, pharmaceutically termed dinoprost, used in medicine to induce labour and as an abortifacient.
- Prostaglandins
- Hormones produced by the body, which are important in the onset of labour; synthetically manufactured prostaglandins can be used to start labour.
- Rankogram
- A two-dimensional treatment-specific plot, presenting on the horizontal axis the possible ranks of the treatment and on the vertical axis the probability for the treatment to assume each of the possible ranks according to a specific outcome.
- Systematic review
- A review of literature focused on a research question that uses prespecified methods to identify, evaluate, select and synthesise research evidence. A systematic review may include meta-analysis.
- Transitivity
- See Consistency.
- Uterine hyperstimulation
- Contractions of the uterus that are too strong, too long or too frequent. Uterine hyperstimulation can result in changes in the fetal heart rate (uterine hyperstimulation syndrome).
- Uterine hypersystole
- Uterine contractions that are too strong.
- Uterine tachysystole
- Uterine contractions that are too frequent.
List of abbreviations
- CCT
- clinical controlled trial
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CENTRAL
- Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials
- CPCG
- Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group
- CrI
- credible interval
- CS
- caesarean section
- DIC
- deviance information criterion
- EQ-5D™
- European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions
- EVPI
- expected value of perfect information
- EVPPI
- expected value of partial perfect information
- FHR
- fetal heart rate
- HIV
- human immunodeficiency virus
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- ICU
- intensive care unit
- ISMN
- isosorbide mononitrate
- i.v.
- intravenous
- MCMC
- Markov chain Monte Carlo
- NHS EED
- NHS Economic Evaluation Database
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NICU
- neonatal intensive care unit
- NMA
- network meta-analysis
- NO
- nitric oxide
- OR
- odds ratio
- PGE1
- prostaglandin E1
- PGE2
- prostaglandin E2
- PGF2
- prostaglandin F2
- PGF2α
- prostaglandin F2 alpha
- PICO
- population, intervention and relevant comparators, outcomes
- PRISMA
- Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PROM
- prelabour rupture of the amniotic membranes
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RE
- random effect
- SD
- standard deviation
- VAS
- visual analogue scale
- VD
- vaginal delivery
- VD24
- vaginal delivery within 24 hours
- VD > 24
- vaginal delivery after 24 hours