Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 08/24/02. The contractual start date was in September 2016. The draft report began editorial review in October 2016 and was accepted for publication in April 2017. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Jonathan Cook reports membership of the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Efficient Study Designs Board outside the submitted work; Malcolm Loudon states that between 2002 and 2004 his research fellowship was sponsored by Ethicon Inc. to carry out a randomised controlled trial evaluating rubber band ligation against stapled haemorrhoidopexy; he received no direct financial support. John Norrie reports membership of the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Journals Library Editorial Group; non-financial support from the HTA commissioning board; and is a member of the NIHR HTA Editorial Board.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2017. This work was produced by Watson et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2017 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Small amounts of text in this report have been adapted from Watson et al. 1 © Watson et al. ; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. 2014. This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited.
The eTHoS study: either Traditional Haemorrhoidectomy or Stapled haemorrhoidopexy for haemorrhoidal disease
In 2010, the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA) programme funded the eTHoS (either Traditional Haemorrhoidectomy or Stapled haemorrhoidopexy for haemorrhoidal disease) study. The study evolved in response to a HTA programme-commissioned call issued in 2008 inviting proposals for a study. The call itself arose after completion of a HTA-commissioned and -funded evidence synthesis written by Burch et al. 2 One of the key recommendations was the need for a well-designed, multicentre, prospective randomised controlled trial (RCT) to inform the evidence for the management of haemorrhoidal disease. This report describes the research.
The eTHoS study was a major multicentre UK-based RCT investigating the clinical effectiveness (including safety) and cost-effectiveness of stapled haemorrhoidopexy (SH) and traditional excisional haemorrhoidectomy (TH) for adult patients with grade II, III or IV haemorrhoids.
This chapter reflects clinical practice, particularly within the NHS, and the evidence available at the time of study inception, and discusses changes in NHS practice and any relevant literature published since 2009.
Background
The burden of the problem
Haemorrhoidal disease is common in all age groups from the mid-teens onwards; however, the direct causes are unclear. Haemorrhoids, or ‘piles’ as they are most commonly known, are defined as enlarged areas of vascular tissue at the top of the anal canal. Symptoms from haemorrhoids include bleeding, pain, itch and prolapse, and these can have an impact on a person’s quality of life. For significantly enlarged and protruding haemorrhoids, surgery is often advised as an effective way to control the symptoms. 3
The most commonly used clinical grading system for haemorrhoids is the one created by Goligher,4 who described four stages of haemorrhoids: grade I – protrusion of piles into anal canal; grade II – prolapse of haemorrhoids externally on defaecation, but return into the anal canal spontaneously; grade III – prolapse of haemorrhoids on defaecation and remain prolapsed until they are manually replaced into the anus; and grade IV – prolapsed and irreducible haemorrhoids.
The treatment of patients with haemorrhoidal disease continues to have considerable workload and cost implications for the NHS. Approximately 25,000 haemorrhoidal procedures were performed as hospital day-case or inpatient admissions in England over the period of 2006–7. 5 The treatment of haemorrhoidal disease is directed at relieving its related symptoms and this remains the current surgical philosophy.
Management of disease
The management of haemorrhoids is initially community-based. For early-grade haemorrhoids (grades I and II) patients are advised to avoid straining at stool and asked to increase the proportion of fruit and fibre in their diets. There is a large range of proprietary treatments that are available ‘over the counter’. These include topical creams and suppositories. Their efficacy is poor. Patients with refractory symptoms, or who have symptoms that cross over with those of bowel cancer and inflammatory bowel disease, are referred to a surgical outpatient clinic for investigation and treatment. Once inflammatory bowel disease and cancer have been excluded, the first line of treatment for grades II–III haemorrhoids is rubber band ligation (RBL). RBL is often offered as a ‘course’ of repeated treatments in the outpatient setting. RBL is successful in treating symptoms around 40% of the time and those patients who remain symptomatic after treatment are offered surgery. There are three main surgical techniques for haemorrhoids. These include excisional (or traditional) haemorrhoidectomy, SH and haemorrhoidal artery ligation (HAL).
In 2009, there were two main standard surgical treatments for haemorrhoids: traditional (or excisional) surgery and SH. A third operation, HAL, had been introduced but was not then in widespread use.
Traditional surgical haemorrhoidectomy
Traditional haemorrhoidectomy involves excision of the haemorrhoidal cushions and has generally been advocated for larger symptomatic haemorrhoids (grades III and IV). The technique involves the excision of haemorrhoid tissue. This is most commonly done by electrocautery, but occasionally sharp dissection with scissors is used. Other energy devices, the Harmonic® scalpel (Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Cincinnati, OH, USA) and the LigaSure™ device (Valleylab, Boulder, CO, USA) can also be used. The resulting wounds can either be sewn up (closed haemorrhoidectomy or Ferguson technique) or left open (open haemorrhoidectomy or Milligan–Morgan technique). This traditional approach, while effective, is nonetheless associated with severe immediate postoperative pain. Improved understanding of the pathogenesis of haemorrhoids6 and of the complications associated with excisional haemorrhoidectomy led to the invention of newer surgical procedures, including SH.
Stapled haemorrhoidopexy
Stapled haemorrhoidopexy was first developed by Longo at the end of the last millennium. 7 Its potential advantages over traditional surgery included a reduction of operating time, length of hospital stay, time to return to work and postoperative pain. 8 These features, compared with traditional haemorrhoid surgery, made SH attractive to patients and health-care providers at the time. However, uncertainties remained concerning complication rates, recurrence of symptoms and costs, which impeded its extensive use in the NHS. The stapling devices used for the procedure have evolved over the last two decades (1997–2017). The design has been refined to reduce the chance of postoperative bleeding and for the gun to be more effectively used in male patients (who have a narrower pelvis). Other manufacturers have also entered the market and produced guns that are significantly cheaper (Chex CPH 32 staple gun; Frankenman, Sheung Wan, Hong Kong) than the leading product, the PPH03 staple gun (Johnson & Johnson, New Brunswick, NJ, USA).
A newer technique, HAL was beginning to be adopted but was not being used across the NHS to any great degree. This surgical technique is also performed under general anaesthetic and involves the identification and ligation of the haemorrhoid arteries that feed haemorrhoids. The procedure is often combined with a suture that ‘pexies’ the prolapsing tissue back into the upper anal canal.
Evidence leading to the inception of the eTHoS study
Multiple RCTs comparing SH with TH and/or other conventional surgeries were analysed in four systematic reviews and a HTA journal publication. 2,9–12 The HTA publication included a review of the clinical effectiveness data from 27 RCTs (n = 2279). When comparing SH with TH, the studies showed equivalent complication and pain rates at day 21 post surgery. However, SH patients had less pain in the immediate postoperative period (first week) than those who received TH. Over the longer term, there was a significantly increased rate of residual prolapse requiring re-intervention with SH; however, there was no evidence of a difference in the number of patients experiencing pain or bleeding between the SH arm and the TH arm. The economic evaluations of the two interventions found that TH dominated SH, but it should be noted that SH and TH had very similar costs and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). 2 The additional cost of the stapling instrument was largely, but not completely, offset by savings in the length of operating time and hospital stay. In terms of QALYs, the improvements in quality of life as a result of lower pain levels in the early postoperative period with SH were offset by losses in quality of life as a result of the higher rate of symptoms over the follow-up period. SH thus appeared to be associated with less pain in the immediate postoperative period, but a higher rate of recurrence in the longer term and an increased need for further surgery. 13 These findings were based on data from small trials, all with methodological flaws, and provided only limited data on quality of life (or, with respect to an economic interpretation, health-state utilities) in the early postoperative period.
At the inception of the eTHoS study there was a reasonable volume of work on grade III and IV haemorrhoids; however, there were limited clinical and economic data regarding SH or TH for grade II haemorrhoids. 14 Members of our group had conducted a small single-centre RCT comparing RBL with SH for grade II haemorrhoids using both clinical and economic outcomes. 15 This had shown a superior clinical effect of SH compared with RBL in terms of recurrence of haemorrhoid symptoms. However, from a health economic standpoint, SH compared with RBL could not be justified, even with a 2-year follow-up. The trend over a longer period, however, suggested that the greater failure rate for RBL may eventually reach a level that justified the increased cost of SH. More robust data on the outcome of RBL have since come from the HubBLe (haemorrhoidal artery ligation versus rubber band ligation for the management of symptomatic second-degree and third-degree haemorrhoids) study16 comparing HAL with RBL, which shows that RBL, when given as a course of two or three treatments, is as clinically effective as HAL.
There was, therefore, a need for an adequately powered, high-quality multicentre RCT comparing the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of SH with that of TH in the NHS setting.
Evidence since the inception of the eTHoS study
Since the start of the eTHoS study there have been very few well-designed, prospective large-scale RCTs comparing SH with TH. 17–19 There were no new trials that included quality-of-life outcomes or looked at the health economics of interventions. These trials included a direct comparison between SH and TH. 20–22 HAL has become more widely used over the course of the eTHoS study and this is reflected in the number of RCTs examining its clinical effectiveness and utility. Results published in 2016 from the HubBle study suggest that HAL is no better than repeat RBL, which challenges the place of HAL in the modern surgical management of haemorrhoid disease. 16
A recent network meta-analysis of 98 RCTs, which included 7827 patients and 11 surgical treatments for grade III and IV haemorrhoids, compared a number of surgical and clinical outcomes23 (Table 1). Patients who had received TH had significantly more postoperative complications than those who had received HAL, LigaSure device and Harmonic scalpel haemorrhoidectomies. Patients who received SH had less pain and resumed normal activities more quickly than those who received TH, but there was a significantly higher chance of recurrent symptoms. The study, however, did not assess patient-reported symptoms nor quality of life.
| Outcome | Ranking | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9th | 10th | 11th | |
| Post-operative complications | Harmonic;p = 0.447 | Harmonic;p = 0.351 | LigaSure; p = 0.291 | LigaSure; p = 0.344 | Stapled; p = 0.263 | Stapled; p = 0.365 | Open; p = 0.377 | Open; p = 0.295 | Closed; p = 0.321 | Closed; p = 0.352 | Radiofrequency; p = 0.484 |
| Post-operative bleeding | Submucosal; p = 0.405 | THD; p = 0.334 | THD; p = 0.332 | Harmonic;p = 0.186 | LigaSure; p = 0.254 | LigaSure; p = 0.240 | Open; p = 0.216 | Open; p = 0.297 | Stapled; p = 0.293 | Radiofrequency; p = 0.259 | Radiofrequency; p = 0.498 |
| Reoperation | THD; p = 0.710 | Laser; p = 0.312 | Harmonic;p = 0.300 | Stapled; p = 0.334 | Open; p = 0.257 | Open; p = 0.355 | Closed; p = 0.390 | Radiofrequency; p = 0.594 | n/a* | n/a | n/a |
| Duration of surgery | Radiofrequency; p = 0.539 | Harmonic; p = 0.381 | Harmonic; p = 0.276 | Stapled; p = 0.293 | Stapled; p = 0.314 | THD; p = 0.293 | THD; p = 0.537 | Open; p = 0.887 | Closed; p = 0.498 | Closed; p = 0.490 | Laser; p = 0.909 |
| Operative blood loss | Bipolar scissors; p = 0.707 | LigaSure; p = 0.280 | LigaSure; p = 0.380 | Stapled; p = 0.300 | Stapled; p = 0.313 | Laser; p = 0.752 | THD; p = 0.335 | Closed; p = 0.481 | Open; p = 0.423 | n/a† | n/a |
| Length of hospital stay | Radiofrequency; p = 0.620 | Submucosal; p = 0.376 | THD; p = 0.308 | Stapled; p = 0.392 | LigaSure; p = 0.228 | LigaSure; p = 0.363 | Open; p = 0.296 | Open; p = 0.308 | Closed; p = 0.220 | Closed; p = 0.428 | Laser; p = 0.392 |
| Time to first bowel movement (days) | THD; p = 0.853 | LigaSure; p = 0.533 | Harmonic;p = 0.470 | Stapled; p = 0.566 | Open; p = 0.596 | Open; p = 0.263 | Bipolar scissors; p = 0.569 | n/a‡ | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Time to normal activities (days) | THD; p = 0.478 | Stapled; p = 0.370 | Stapled; p = 0.333 | LigaSure; p = 0.262 | LigaSure; p = 0.310 | LigaSure; p = 0.198 | Open; p = 0.183 | Open; p = 0.339 | Open; p = 0.284 | Closed; p = 0.322 | Radiofrequency; p = 0.315 |
| Pain on day 1 | THD; p = 0.584 | Starion; p = 0.269 | Stapled; p = 0.292 | Stapled; p = 0.255 | LigaSure; p = 0.292 | LigaSure; p = 0.277 | Radiofrequency; p = 0.254 | Closed; p = 0.427 | Open; p = 0.422 | Submucosal; p = 0.480 | n/a§ |
| Pain on day 7 | THD; p = 0.295 | Stapled; p = 0.342 | Stapled; p = 0.230 | LigaSure; p = 0.222 | LigaSure; p = 0.194 | Closed; p = 0.231 | Open; p = 0.242 | Open; p = 0.285 | Submucosal; p = 0.382 | n/a¶ | n/a |
| Recurrence of haemorrhoids | Submucosal; p = 0.381 | Radiofrequency; p = 0.358 | LigaSure; p = 0.277 | LigaSure; p = 0.315 | Closed; p = 0.273 | Open; p = 0.383 | Stapled; p = 0.287 | Stapled; p = 0.649 | THD; p = 0.785 | n/a¶ | n/a |
| Recurrent haemorrhoidal symptoms | Laser; p = 0.530 | LigaSure; p = 0.333 | Closed; p = 0.296 | THD; p = 0.282 | Open; p = 0.448 | Stapled; p = 0.482 | Harmonic;p = 0.467 | n/a# | n/a | n/a | n/a |
The aim of the eTHoS study was to assess whether or not SH was more clinically effective and cost-effective than TH for patients with grades II, III and IV haemorrhoids.
The primary objective was to compare patient-reported overall health-related quality of life measured using the EuroQol-5 Dimensions, three-level version (EQ-5D-3L) responses over a period of 24 months.
The secondary objective was to compare subdomains of health [Short Form questionnaire-36 items (SF-36) scores, pain and symptoms], disease recurrence, complication rates, direct and indirect costs to the NHS and cost-effectiveness (measured in terms of incremental cost per QALY, when QALYs are derived from responses to the EQ-5D-3L and the SF-36).
Chapter 2 Study design
The eTHoS study was a large multicentre UK pragmatic RCT to assess whether or not SH is more clinically effective and cost-effective than TH for people presenting with haemorrhoids (grades II, III and IV). 1
Participants
Potential participants were adults referred to NHS hospitals for consideration of surgical treatment and identified according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria specified below. Participants could have previously had RBL or HAL, but not undergone any other form of haemorrhoid surgery.
Inclusion criteria
-
Patients with circumferential haemorrhoids of grades II, III or IV.
-
Patients aged ≥ 18 years.
-
Written informed consent obtained.
Exclusion criteria
-
Previous surgery for haemorrhoids (traditional or stapled, except RBL or HAL).
-
Previous surgical treatment for anal sphincter injury repair or symptomatic incontinence or perianal sepsis.
-
Known inflammatory bowel disease.
-
Malignant gastrointestinal disease, within the last 5 years.
-
Medically unfit for surgery or for completion of the study.
-
Pregnant women.
Participants were randomised to one of the two study groups on a 1 : 1 basis. The randomisation minimisation algorithm used centre, grade of haemorrhoidal disease (II, III or IV), baseline EQ-5D-3L score (categorised as < 0.6, 0.6 to < 0.8 and 0.8 to 1.0) and sex. A remote telephone interactive voice response randomisation application, hosted by the Centre for Healthcare Randomised Trials (CHaRT), Health Services Research Unit (HSRU) at the University of Aberdeen, was used to perform the randomisation.
The main criterion for selection of NHS hospital sites across the UK where participant recruitment could take place was that each hospital centre had at least two members of staff to occupy two key research roles. One was that of the research role – a (co-investigating) colorectal consultant; the other was that of a local recruitment officer, for example a nurse or junior doctor. In exceptional circumstances the colorectal consultant performed both roles. At each centre there may have been more than one colorectal consultant (co-investigator) who was fully eTHoS trained and actively screening potential patients (for eligibility) and for subsequent recruitment onto the study. At each centre one of these consultants assumed the leading role of local lead colorectal surgeon for the eTHoS trial. A total of 32 UK NHS sites took part in the study. These were NHS Highland and Islands, Inverness; NHS Grampian, Aberdeen; North Tees and Hartlepool Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Stockton-on-Tees; Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Sheffield; County Durham and Darlington NHS Foundation Trust, Durham; Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, Leeds; Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Norwich; Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester; Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London; NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde, Glasgow; Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board, Rhyl; Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Oxford; Aintree University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Liverpool; Dr Gray’s Hospital, Elgin; Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust, Brighton; South Tees Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Middlesbrough; Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust, Huddersfield; Wirral University Teaching Hospital, Upton, Wirral; Croydon Health Services NHS Trust, Croydon; Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, London; The Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust, Wakefield; Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust, Truro; The Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, London; Bwrdd Iechyd Aneurin Bevan Health Board, Wales; Weston Area Health NHS Trust, Somerset; Derby Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Derby; NHS Forth Valley, Stirling; Gateshead Health NHS Foundation Trust, Gateshead; Colchester Hospital University NHS Foundation Trust, Colchester; Basildon and Thurrock University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Basildon; United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust, Lincoln; and University Hospital of South Manchester NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester.
Study interventions
Eligible participants who consented were placed on the appropriate waiting list by the treating colorectal surgeon or his/her designated team member. Participants received the allocated intervention to which they were randomised:
-
stapled haemorrhoidopexy
-
traditional excisional haemorrhoidectomy.
Each centre’s participating surgeons had undergone appropriate recognised training for both SH and TH surgery. Surgery was performed by surgeons in training: either independently, if signed off by their supervising consultant, or under the direct supervision of their consultant. Pre- and postoperative care followed the respective surgeon’s and/or centre’s standard policies.
Outcome measures
Primary outcome measures
Patient reported
The primary outcome was quality of life gained over the follow-up period [area under the curve (AUC) derived from EQ-5D-3L measurements taken from patient questionnaires distributed at baseline, 1 week, 3 weeks, 6 weeks (postoperatively), 12 months, (EQ-5D-3L only at 18 months if not completed at 12 months) and 24 months post randomisation].
Participants had the opportunity to complete the questionnaires on a secure portal on the eTHoS trial website using log-in details provided by the study team. In the event that the postal questionnaires were not returned or completed via the website, for the 1- and 3-week questionnaires, participants were telephoned to obtain the missing data. Postal reminders were issued if there was no response to the 6-week, 12-month and 24-month questionnaires. A final reminder followed if there was no response to the subsequent reminder. This reminder was shortened to include only the EQ-5D-3L questionnaire.
Health economic
Incremental cost per QALY gained, with QALYs based on the responses to the EQ-5D-3L at 24 months, was measured. QALYs were calculated from participant responses to the EQ-5D-3L completed at baseline, 1 week, 3 weeks and 6 weeks post surgery, and 12 (or 18) and 24 months post randomisation. Costs were collected at baseline, 6 weeks, and 12 and 24 months after randomisation. Participants also provided information about their use of health services via the health-care utilisation questions within the eTHoS trial patient questionnaires (see Appendix 1).
Secondary
Patient reported
Patient-reported secondary outcomes were:
-
generic health profile as measured by the SF-36 and the EQ-5D-3L
-
visual analogue scale (VAS) pain score
-
Cleveland Incontinence Score (CIS)
-
Haemorrhoid Symptom Score (HSS)
-
postoperative analgesia consumption
-
recurrence of haemorrhoids
-
tenesmus.
Clinical
The clinical secondary outcomes were intra-operative and postoperative complications, including:
-
haemorrhage
-
requirement for blood transfusion
-
anal stenosis
-
anal fissure
-
urinary retention (which requires catheterisation)
-
residual anal skin tags
-
difficult defaecation
-
wound discharge
-
pelvic sepsis
-
pruritus
-
recurrence of haemorrhoids.
Economic
The economic secondary outcomes were:
-
costs based on NHS resource use data
-
length of hospital stay
-
use of health services for haemorrhoid-related events or treatments
-
patient costs (treatments, travel to health services, sick leave)
-
need for alternative management for haemorrhoids (e.g. surgery, drugs)
-
other use of health services, such as:
-
visits to general practitioner (GP)
-
visits to practice nurse
-
visits to colorectal surgeon
-
-
QALYs estimated from the EQ-5D-3L at 24 months
-
cost-effectiveness analysis (incremental cost per case of SH and TH excision avoided).
Chapter 3 Methods
Research ethics and regulatory approvals
The eTHoS study was given favourable ethics approval by the North of Scotland Research Ethics Committee (REC) on 18 June 2010 subject to receiving individual research approvals from each host organisation prior to the commencement of the study at site (reference number 10/20802/17). The study was co-sponsored by NHS Highland and the University of Aberdeen. The study was registered and was given an International Standard RCT Number (ISRCTN80061723).
Project management group
The study was supervised by a project management group (PMG). This consisted of the grant holders and representatives from the study office, who provided day-to-day support for the study. Observers were invited to attend at the discretion of the PMG. The PMG met every 6 months, on average, during the course of the study.
Study oversight committees
The study Data Monitoring Committee (DMC) comprised three independent individuals who met initially at the beginning of the study when terms of reference and other committee procedures were agreed. The committee then met an additional four times during the course of the study to monitor unblinded baseline and outcome data provided by the study statistician and details of serious adverse events (SAEs). The DMC reported any recommendations to the chairperson of the Trial Steering Committee (TSC). The TSC comprised four independent individuals who oversaw the study. At the invitation of the chairperson, grant holders and observers/members of the host university (University of Aberdeen) and the funder (HTA programme) could also attend. Terms of reference for the TSC were agreed at the commencement of the study and the group met annually throughout the duration of the study. The terms of reference for the DMC and TSC can be accessed on request from the eTHoS study office.
Patient and public involvement
An independent patient and public involvement representative was a member of the TSC. A patient representative was also involved in the grant application and throughout the study as a grant holder. Patient and public involvement was sought in the development of the participant newsletter. Both members reviewed the paperwork and provided constructive feedback in its development.
Participants
Study flow
The flow of participants through the study is detailed in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
Participant study flow.
Identification of patients and recruitment
Patients were identified by colorectal clinicians in participating sites, and were supported by local clinical research teams.
Colorectal clinicians assessed the eligibility of the participants for surgery according to standard practice. At the initial consultation, the colorectal clinician discussed the various treatment options available and provided information regarding the eTHoS study. Risks and benefits of all treatments were also discussed as part of standard clinical practice. Patients who had undergone RBL or HAL but still had symptoms were eligible for the study. Patients who had received any other form of haemorrhoid surgery were excluded from the study. Participants who expressed a strong preference for one of the interventions were also excluded. Identified eligible patients were then given a patient information leaflet (PIL; see Appendix 2), which contained details of the study and context. The clinician, or a trained member of the local clinical team, was able to answer any questions/discuss the study with the potential participants. Patients were encouraged to take time to read through the PIL and to take it home if they should wish. If the patient agreed to be contacted at home, then a member of the local research team would call to discuss the study. Patients who gave verbal agreement to take part in the study were then requested to complete documents [consent form and baseline questionnaire, which collected data on the EQ-5D-3L, the SF-36, the CIS and the HSS, and patient preference for surgery outcomes (see Appendices 2 and 3)] and return these by post to the local study team at their treating hospital or bring them when they returned to hospital for preoperative assessment or at the time of the operation. The consent form was then countersigned on receipt by the local study team member.
Patients who were able to make a decision to join the study while they were at the initial consultation were provided with the eTHoS study participant baseline questionnaire. This was completed only once a patient was eligible and happy to take part in the study and had signed the consent form. Contact details for both the local and central team were provided on the PIL. Further checking against eligibility criteria was performed by local research staff. Current clinical status was also captured on the baseline case report form (CRF) (see Appendix 3).
Following full written consent and baseline data completion, patients were randomised as near to their surgery date as possible. For those patients who did not consent to participate, an ‘Ineligible/Declined’ form (see Appendix 3) was completed by a local study team member, detailing non-personal data, including the reason(s) for the participant declining (if provided), or the ineligibility criterion. These data were recorded on the study database to inform the consort.
Randomisation
Participants were randomised to one of the two study groups on a 1 : 1 basis. The minimisation algorithm used centre, grade of haemorrhoidal disease (II, III or IV), baseline EQ-5D-3L score and sex. A remote telephone interactive voice response randomisation application hosted by CHaRT, HSRU at the University of Aberdeen was used to perform randomisation. The first participant was randomised on 13 January 2011 and the final participants were randomised on 1 August 2014 when the randomisation system was closed.
Study interventions
Eligible participants who consented were placed on the appropriate waiting list by the treating colorectal surgeon or his/her designated team member. Most participants received the allocated intervention, which was either SH or TH. Some received alternative treatment or did not receive treatment; however, participants were followed up regardless of the intent-to-treat analysis. Treatment data were captured on the hospital and surgery CRF (see Appendix 3). Each centre’s participating surgeons had to have undergone appropriate recognised training for both SH and TH. Surgeries were performed by surgeons in training; either independently, if signed off by their supervising consultant, or under the direct supervision of their consultant. Pre-operative and postoperative care followed the respective surgeon’s and centre’s standard care policies. Although the two procedures being compared are offered as routine care, not all sites provided postoperative information (what to expect after the haemorrhoid treatment) to participants. Therefore, we prepared a participant postoperative leaflet that sites could make available to participants if they wanted to (see Appendix 2).
Data collection
Follow-up consisted of clinical follow-up at 6 weeks after treatment. Postal questionnaires were distributed at 1 week, 3 weeks and 6 weeks after treatment, and 12 months (or 18 months if EQ-5D-3L not completed at 12 months) and 24 months after randomisation (Table 2). The main outcome assessment was planned at 24 months’ (from the date of randomisation) follow-up.
| Outcome | Time point | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Surgical form | 1 week post treatment | 3 weeks post treatment | 6 weeks post treatment | 12 months post randomisation | 24 months post randomisation | 27 months post randomisation | |
| Clinical status | ✓ | |||||||
| Surgical details | ✓ | |||||||
| Patient preference | ✓ | |||||||
| 6 weeks’ clinical follow-up | ✓ | |||||||
| EQ-5D-3La | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| SF-36 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Pain VAS | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| HSS | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| CIS | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Health-care Utilisation questions | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Travel costs questionnaire | ✓ | |||||||
| Recurrence | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Analgesia question | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| DCE | ✓ | |||||||
| Hospital Statistics for further surgery | ✓ | |||||||
Consent was sought from all participants recruited to the study to be flagged for notification of haemorrhoidal recurrence. To evaluate long-term safety, the participants who had further haemorrhoidal surgery were identified via registry databases: Hospital Episode Statistics (HES) in England, Patient Episode Database Wales (PEDW) in Wales and Information Services Division (ISD) data in Scotland, when all participants had reached 12 months post randomisation.
Safety reporting
We reported SAEs in accordance with the guidance from the National Research Ethics Service, which is a subdivision of the National Patient Safety Agency. As such, non-SAEs were not collected or reported. All SAEs were recorded on the SAE report form (see Appendix 3). In addition, SAE forms recorded all deaths during the course of the study whether or not these were related to the research procedures. The following occurrences were potentially expected: intraoperative occurrences associated with the intervention, including anaesthetic-related problems, intraoperative instrument failure, damage to adjacent organs and bleeding. Possible (expected) occurrences associated with either type of surgery occurring at any time during the study included haemorrhage, requirement for blood transfusion, anal stenosis, anal fissure, pain, urinary retention, residual anal skin tags, anal fistula, prolapse, difficult defaecation, faecal urgency, wound discharge, pelvic sepsis, systemic complications and pruritus.
The details of any of the occurrences listed above were recorded on the CRFs and on participant-completed questionnaires and reported to the DMC in annual reports, but were not recorded as a SAE unless defined as an event occurring to a research participant that was related (resulted from administration of any of the research procedures) and was expected or unexpected, which caused death, was life-threatening, required hospitalisation, resulted in significant incapacity/disability or was otherwise considered medically significant by the investigators. Expected and unexpected SAEs were recorded.
Change of status/withdrawal
Participants remained on the study unless they chose to withdraw consent or if the principal investigator, chief investigator or study office felt that it was no longer appropriate for the participant to continue (i.e. the participant became unable to complete the study documentation). Reasons for participant withdrawal from the study were recorded on the ‘withdrawal/change of status’ form (see Appendix 3). Participants could withdraw from treatment but remain in the study for follow-up questionnaires and/or to have relevant outcome data collected from NHS records if consent remained for this.
Data management
Clinical data were collected at the individual hospital centres using hospital-based records and hard-copy CRFs (see Appendix 3). Clinical data were then input onto the eTHoS study database by local researchers using an electronic web-based data capture system [in addition relevant clinical data being collected from registry databases (HES, PEDW and ISD)]. Extensive range and consistency checks enhanced the quality of the data. Staff in the study office provided periodic data queries to local research staff to ensure that the data were as complete and accurate as possible. Questionnaires returned by post to the study office were entered onto the database by data-trained members of the central research team.
Data collected during the course of the research were kept strictly confidential and accessed only by members of the study team. Participants’ details were stored on a secure password-protected and user-specific database under the guidelines of the 1998 Data Protection Act,24 including encryption of any identifiable data. Participants were allocated an individual-specific study number and all data, other than personal data, were identified only by this unique study number.
The content of approximately 10% of CRFs and participant questionnaires entered at sites were checked to ensure accuracy. To ensure that sites had understood the data-entry processes and that they were efficiently entering the data, a sample from the first CRFs entered by each site were selected. Further paper CRFs and questionnaires were selected at random. This was completed at the study office (a copy of the paper forms were sent/faxed from the individual sites to the University of Aberdeen to facilitate this). An error rate of < 5% required no further action; however, if the error rate was > 5%, a 100% check of all forms from that site was undertaken.
Some questionnaires were returned directly to the University of Aberdeen. A 10% random sample of questionnaires returned to the study office were checked by a different data co-ordinator/clerk than the person responsible for the initial data entry, and the action on identified error rate was identical to that described above.
Statistical methods and study analysis
Ground rules for the statistical analysis
Study analyses followed the statistical analysis plan agreed in advance by the TSC. The main statistical analyses were based on all randomised participants, irrespective of subsequent compliance with the treatment allocation. Statistical significance was at the two-sided 5% level with corresponding confidence intervals (CIs) derived.
Sample size
Data on the 24-month AUC (QALYs) for the EQ-5D-3L scores in this patient group were sparse, but an effect size of 0.25 standard deviations (SD) was considered a worthwhile difference in quality-of-life measures. A sample size of 338 per group was required to provide a 90% power to detect a difference in the mean area under the quality-of-life AUC curve with a significance level of 5% (two-sided alpha). To allow for 15% non-response in the outcome, we required 400 participants in each treatment group. This sample size would also give 90% power to assess differences in the secondary outcome of recurrence between the two interventions from around 10% to around 4%. This difference is supported by a recent systematic review,9 which showed a non-statistical trend of higher recurrence in the SH group than in the TH group.
Primary/secondary outcome analysis
The primary outcome, AUC (measured by the EQ-5D-3L), was generated for each participant using the trapezoidal rule and analysed using linear regression. The analysis was adjusted for the minimisation variables, centre was accounted for by using cluster robust standard errors while the others were fixed effects. To be included in the primary analysis, participants had to have at least one short-term measure (1 week, 3 weeks or 6 weeks post surgery) and at least one long-term measure (12, 18 or 24 months post randomisation). In the sensitivity analysis, missing EQ-5D-3L data were estimated using a multiple imputation (MI) by chained equations using the ‘ice’ Stata® version 14 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) command. It also included assessment of the robustness of the treatment effect estimates by altering the minimum number of EQ-5D-3L values needed for each participant and also compliance (using a per-protocol analysis that comprised those participants who received their allocated intervention). Secondary analyses for the primary outcome included the EQ-5D-3L AUC over 6 weeks and 12 months.
Secondary outcomes (SF-36, CIS and HSS) were analysed using linear mixed models with adjustment for minimisation variables. Tenesmus was analysed with the chi-squared test for trend and further surgical intervention was analysed with the chi-squared test. All other secondary outcomes were analysed using either logistic or linear regression. Continuous variables were summarised with mean (SD) or median [interquartile range (IQR)], whereas discrete variables were number and percentages. All analyses were assessed at the two-sided 5% significance level and done using Stata software.
Planned subgroup analyses
Subgroup analyses explored the possible treatment effect modification of clinically important factors (haemorrhoidal grade and sex) through the use of treatment-by-factor interaction, all using a stricter two-sided 1% level of statistical significance.
Patient preference analyses
Baseline data were summarised by treatment preference based on surgical outcome scenarios and the primary and secondary outcomes were analysed using linear regression adjusted for patient preference and minimisation variables. Presence of a treatment-by-preference interaction was assessed. In addition, associations between preference and drop-out were analysed. The patient preference analysis is reported in Chapter 9.
Timing and frequency of analyses
A single principal analysis was carried out when the final participant reached the 24-month time point.
Economics methods
Introduction
Although a de novo economic model was planned to assess the long-term cost-effectiveness (assessed in terms of incremental cost per QALY) and net benefits of SH and TH, the results of the study-based economic evaluation in conjunction with the clinical findings rendered the planned modelling unnecessary. Therefore, the following section describes the methods for the study-based economic evaluation. The question to be addressed by the economic evaluation was ‘what are the relative cost-effectiveness (assessed in terms of incremental cost per QALY) and net benefits of SH and TH?’. The cost-effectiveness analysis follows the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)’s reference case25 and the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research’s recommendations on conducting economic evaluations alongside clinical trials. 26 A secondary analysis also assessed cost to participants. The methods and analysis for the within-trial analysis are described below. The perspective of study was that of the health service provider (the NHS) and the costs are expressed in pounds sterling for the financial year 2014–15. 27 Costs and benefits incurred in the second year were discounted at a rate of 3.5% per annum. 25 The follow-up period for the economic analysis was 24 months.
Within-trial analysis
Health service use was recorded prospectively, and retrospectively, for each participant. Intervention resource use was collected prospectively for every participant in the study using questionnaires at baseline and CRFs, and follow-up resource use was collected retrospectively at 6 weeks, and 12 and 24 months (see Appendix 1). The underlying aim was to keep economic data collection as parsimonious as possible in order to minimise the burden on the participants and the effect on response rates. A postal questionnaire of all participants was used to ascribe participant costs to typical episodes of health service use, and was initially sent at 18 months post randomisation (see Appendix 1), but this was changed during the course of the study to 27 months post randomisation. This was to allow a shortened third reminder to be issued at 18 months for the 12-month questionnaire.
The areas of resource use considered comprised four broad areas:
-
intervention resource use
-
secondary care resource use
-
primary care resource use
-
resource use directly incurred by the participants.
Intervention resource use
The intervention resource use was recorded on a per-patient participant basis. The resources used to provide surgery were established by consulting with relevant staff at participating centres (surgeons, theatre nurses, business managers) and members of the study team to elicit information on:
-
equipment, such as the type of stapler used
-
frequency of use of said equipment
-
consumables used during surgery, such a surgical trays
-
staff mix of the surgical team (e.g. grade of the operating surgeon, grade of the anaesthetist, grade and number of nurses).
In addition to this, the operative information was collected on the CRFs and provided details of the grade of staff involved and the duration of procedure. Length-of-stay information was elicited for each participant through the CRFs by collecting the date of admission and discharge. For the initial intervention, data cost estimation focused on those resources that differed between the two interventions, that is, it was assumed that there would be no difference in time in recovery or time on the ward following the procedure (for those managed as day cases).
Other secondary care resource use
The use of subsequent care, such as inpatient stay (duration of stay), reoperation or other surgical interventions (SH or TH) and outpatient visits over the study follow-up period, was obtained from the CRFs (6 weeks) and patient questionnaire (12 and 24 months).
Primary care resource use
All primary care resource use, such as general practice doctor and nurse contacts and medications prescribed to treat haemorrhoids, was obtained from the participant questionnaire administered at 12 and 24 months.
Derivation of costs
The costs of the health service utilisation were estimated by combining resource use data with unit costs of resource use. Unit costs were based on study-specific estimates in combination with data from standard sources. Unit costs for the equipment used in stapling were obtained from the manufacturers of the products through personal communication with sites using the equipment or from published price lists. Table 3 details the unit costs used, the source of the estimate and any assumptions used to derive them.
| Resource item | Unit cost (£) | Comments | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stapler | |||
| Ethicon PPH03 (Johnson & Johnson, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) | 442.01 | Box of three – £1105.04 excluding VAT | NHS Scotland and NHS England Hub prices (Ewan McDonald, NHS Grampian, 2016, personal communication) |
| Chex CPH 32 | 276.00 | Box of three – £690 excluding VAT | NHS Scotland and NHS England Hub prices |
| EEA™ Staplers with DST™ Series technology (Covidien Ltd, Dublin, Ireland) | 269.62 | Box of three – £674.06 excluding VAT | NHS Scotland and NHS England Hub prices |
| Surgeon and anaesthetist | |||
| Consultant | 2.30 per minute | £138 per hour | PSSRU (2015)28 |
| Specialty doctors and associate specialists | 2.13 per minute | £128 per hour | PSSRU (2015)28 |
| Surgical trainee | 1.20 per minute | £72 per hour | PSSRU (2015)28 |
| Fellow | 0.85 per minute | £51 per hour | PSSRU (2015)28 |
| Nurses | |||
| Band 5 | 0.72 per minute | £43 per hour | PSSRU (2015)28 |
| Band 6 | 0.85 per minute | £51 per hour | PSSRU (2015)28 |
| Anaesthetic drug cost | |||
| General | 14.31 | Various drugs (propofol) | BNF (2016)29 |
| General and block | 15.17 | Various drugs (bupivacaine hydrochloride) | BNF (2016)29 |
| Spinal | 2.25 | Various drugs (lidocaine, etc.) | BNF (2016)29 |
| Interventions at 6 weeks | |||
| Outpatient appointment | 122.5 | Average colorectal specialty | NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015 27 |
| Re-admissions after interventiona | 201 | Admitted VB07Z emergency medicine, category 2 | NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015 27 |
| Emergency outpatient visitsb | 162 | Emergency medicine, category 2 investigation with category 2 treatment | NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015 27 |
| Further interventions at 6 weeks, for example haemorrhoidectomy | 1106 | Day case FZ22E intermediate anal procedures, aged ≥ 19 years, with complications score of 0 | NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015 27 |
| Proctoscopy | 10.99 | – | – |
| Medicines, for example Movicol® (Norgine, Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Uxbridge, UK) | Various | Based on patient report | BNF (2015)30 |
| Glyceryl trinitrate paste | 39.30 | Price per 30-g tube | BNF (2015)30 |
| Diltiazem paste | 78.83 | Price for 2% diltiazem cream per 30-g tube | BNF (2015)30 |
| Repeat SH and TH further interventions | |||
| Day case | 751 | FZ23A minor anal procedures, aged ≥ 19 years | NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015 27 |
| Day case | 1118 | Day case FZ22D intermediate anal procedures, aged ≥ 19 years, with complications score of 1 or 2 | NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015 27 |
| Post discharge events | |||
| Doctor visits | 44 | Per 11.7-minute consultation, including qualification costs | PSSRU (2015)28 |
| Nurse visits | 11 | Per 15.5-minute consultation, including qualification costs | PSSRU (2015)28 |
| Medications | |||
| Analgesic | Various | As reported by participants | BNF (2016)29 |
| Laxative | Various | As reported by participants | BNF (2016)29 |
| Antibiotics | Various | As reported by participants | BNF (2016)29 |
| RBL | 181 | FZ23A minor anal procedures, aged ≥ 19 years, procedures in outpatients | NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015 27 |
Unit costs for outpatient visits were obtained from the NHS reference costs for the period of 2014–15. 27 Unit costs for GP visits were obtained from the Personal Social Services Research Unit28 unit costs of social care. The unit costs of anaesthetic drugs, such as propofol used in the operation and post surgery, were derived from the British National Formulary. 29 For each participant the number of visits was multiplied by the appropriate unit cost. These costs were summed to produce a total cost per patient. The unit cost of the type of stapler used in the intervention was based on the cost of the stapler specified for each patient.
Measurement of resource utilisation for participants’ management of haemorrhoids
Participant resource use comprised three main elements: self-purchased health care; travel costs for making return visit(s) to NHS health care; and time costs of travelling and attending NHS health care.
-
Self-purchased health care is likely to include items such as prescription costs and over-the-counter medications. Information about these was collected through the health-care utilisation questions.
-
Estimation of travel costs requires information from participants about the number of visits to, for example, their GP or consultant (estimated from the health-care utilisation questions) and the cost to the participant of making the return journey to each type of health-care provider. The latter was collected using the participant cost questionnaire (see Appendix 1).
-
The cost of participant time was estimated in a similar manner. The participant was asked, in the participant cost questionnaire, how long they spent travelling to, and attending, their last visit to each type of health-care provider. Participants were also asked what activity they would have been undertaking (e.g. paid work, leisure, housework) had they not attended the health-care provider. Time away from displaced activities was measured in hours and also costed using standard economic conventions, for example the Department of Transport estimates for the value of leisure time. The unit costs used in the estimation of patient time and travel costs are all summarised in Table 4.
| Activity | Unit costs (£) | Assumptions | Source of data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost per mile travelled by car | 0.45 per mile | HMRC-approved mileage rate | HMRC31 |
| Car parking charges | Various | As stated by participant | Participant questionnaire |
| Cost of public transport (fares) | Various | As stated by participant | Participant questionnaire |
| Cost of non-emergency patient transport (ambulance) | 44.50 per journey | – | NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015 27 |
| Cost related to participant and companion time | |||
| Paid work | 13.47 per hour | Based on average economic wage per week of £528 assuming 39.2 hours per working week | ONS’s Average Weekly Earning Time Series Dataset (2015)32 |
| Housework | 10.66 per hour | Cost of housework in the NHS (assumed annual salary of £21,000 gross) | NHS Pay Review Body (2015)33 |
| Child care | 13.47 per hour | As paid work | ONS’s Average Weekly Earning Time Series Dataset (2015)32 |
| Caring for family/friend | 13.47 per hour | As paid work | ONS’s Average Weekly Earning Time Series Dataset (2015)32 |
| Voluntary work | 13.47 per hour | As paid work | ONS’s Average Weekly Earning Time Series Dataset (2015)32 |
| Leisure activities | 6.62 per hour | Value for non-working time (2010 prices inflated to 2015) | WebTAG: TAG Data Book, December 2015 34 |
| Retired | 6.62 per hour | Value for non-working time (2010 prices inflated to 2015) | WebTAG: TAG Data Book, December 2015 34 |
| Unemployed | 6.62 per hour | Value for non-working time (2010 prices inflated to 2015) | WebTAG: TAG Data Book, December 2015 34 |
| Disabled (long-term unrelated to haemorrhoids) | 6.62 per hour | Value for non-working time (2010 prices inflated to 2015) | WebTAG: TAG Data Book, December 2015 34 |
| Incontinence day pads | 1.57 | Mean monthly cost of nappies (the least expensive) £47.10 (three per day) | Fader et al., 200835 |
| Incontinence day pads | 0.66 | Mean monthly cost of nappies (the least expensive) £19.80 (one per night) | Fader et al., 200835 |
Quality of life
Clinical effectiveness in the economic analysis was measured in terms of QALYs. The EQ-5D-3L36 generic quality-of-life instrument was administered to all study participants at baseline, at 1 week, 3 weeks and 6 weeks, and at 12 months and 24 months. The EQ-5D-3L measure divides health status into five dimensions (mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression).
Responses to the EQ-5D-3L are presented in graphical format, illustrating percentage of respondents with any or severe problems on each health domain, split by randomised arms of the study. Results are presented in accordance with EuroQoL guidelines. 37
Responses to the EQ-5D-3L questionnaires were valued using UK general population tariffs,38 based on the time trade-off technique to generate a utility score for every participant within the study. Quality-of-life data derived from the EQ-5D-3L were combined with mortality data from the study, using the standard assumption that all participants who died during the study will have a utility value of zero from the date of death to the end of follow-up. QALYs were then calculated on the basis of these assumptions using an AUC approach, assuming linear extrapolation of utility between time points.
Quality-of-life data were also collected using the SF-36 questionnaire for comparison. SF-36 data were collected at baseline, 6 weeks, and at 12 and 24 months. The SF-36 is a generic measure obtained from a multipurpose, short-form health survey with 36 items. 39 It yields an eight-scale profile of functional health and well-being scores along with psychometrically based physical and mental health summary domains and a preference-based health utility index. These data were converted into a Short Form questionnaire-6 Dimensions (SF-6D) utility index using a published algorithm. 40 As described above for the EQ-5D-3L, QALYs were also derived from these data and a secondary analysis was used.
Cost-effectiveness analysis methods
Economic analyses were consistent with the methods described for the main statistical analyses (primary outcome). All data analyses were conducted using Stata software. The primary economic analysis was based on the imputed data of all participants as randomised, irrespective of the treatment allocation. There was a substantial number of missing data and this posed problems for data analysis, especially surrounding data reported using participant-completed questionnaires. Therefore, statistical MI of missing data was undertaken. The imputation analysis was performed using Stata’s MI procedure. 41 Missing component costs (e.g. cost of primary care, outpatient care) and utility values were imputed at each questionnaire time point (12 and 24 months). The cost–utility analysis was conducted using the MI data. Briggs et al. 42 concluded that imputing the missing data is preferable to a complete or available case analysis.
Components of cost data were imputed based on linear regression models adjusted for minimisation variables, baseline utility and treatment allocation group. Missing utility values were imputed using predictive mean-matching, accounting for the five closest estimates. Chained equations were used for the imputations. The imputation procedure predicted 10 plausible alternative imputed data sets, which was found to be sufficient to provide stable estimates. Analysis of incremental costs and outcomes was undertaken across the 10 imputed data sets and combined to generate one imputed estimate of incremental costs and QALYs. All imputed data sets were plotted on cost-effectiveness acceptability curves (CEACs) using similar methods to the main analyses. Sensitivity analysis was applied in order to assess robustness of the results to realistic variations in the levels of the underlying data and also alternative assumptions, for example QALYs derived from the SF-36.
Data are presented descriptively, and the primary outcome measure was analysed using linear regression with adjustment for the minimisation variables. The minimisation variables are centre, grade of haemorrhoidal disease (II, III or IV), baseline EQ-5D-3L score and sex.
The primary economic analysis presents estimates of the incremental cost per QALY of SH versus TH. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) can be compared with the benchmark willingness-to-pay (WTP) thresholds for cost-effectiveness in the NHS context of £20,000 to £30,000 per QALY gained, as applied by NICE. 43 Regression-based methods (as above) were used to estimate difference in costs for care between SH and TH, over the 24-month study period. CIs (95%) were estimated using parametric methods. To facilitate interpretation of the study results, the within-trial economic analysis is also presented in the form of a balance sheet in which differences in terms of benefits and costs of the two study interventions are presented in their natural or clinical units. Item-level costs are presented descriptively, consistent with the data presentation in the effectiveness analyses.
To explore the skewness of data, a generalised linear model was used; this model allows for heteroscedasticity by selecting an appropriate distributional family for the data. 44 The family offers alternative specifications to reflect the relationship between the mean and the variance of the estimates under considerations. The most appropriate distributional family was selected by (1) performing a modified Parks test, which identified two potentially viable distributional families for costs, namely Gaussian or Gamma; and (2) consulting the Akaike information criterion, which identified a Gaussian model with an identity link as having the lowest Akaike information criterion score and the most appropriate model fit. Regression models applied to cost components (such as ‘other treatments’ and ‘hospital costs’) in the analyses above are also assumed to follow the same distributional assumptions as the total cost data. A standard ordinary least squares model was also identified as the most appropriate model and applied to the analysis of incremental QALY gains. All analyses were conducted using heteroscedastic robust standard errors.
Non-parametric bootstrapping methods were used to estimate CIs to characterise uncertainty surrounding the point estimate of the ICER, using 1000 repetitions. 45 This uncertainty in the ICER is summarised using the following methods.
-
Incremental scatterplots of the 1000 replicates of joint differences in mean costs and QALYs for TH compared with SH compared with TH. 46 The incremental cost-effectiveness scatterplots allow one to see the probability of each intervention falling into each quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane, being (1) less costly and more clinically effective; (2) more costly and less clinically effective; (3) less costly and less clinically effective; or (4) more costly and more clinically effective.
-
The bootstrapped estimates of joint differences in cost effects were further used to generate CEACs. CEACs were generated using estimates of net monetary benefit, generated using the bootstrapped replications, in accordance with the incremental net benefit (INB) statistic given in the following equation:
This is calculated by multiplying the incremental effects (QALYs) by the decision-makers’ WTP cost-effectiveness threshold [lambda (λ)] and subtracting the incremental cost. Although the base-case analysis INB statistic was calculated based on the upper end of the threshold set by NICE (i.e. £30,000), several cost-per-QALY thresholds ranging from £0 to £50,000 are also reported. A positive INB suggests that the intervention is cost-effective versus its comparator at the defined threshold.
Deterministic sensitivity analyses
The presentation of CEACs and scatterplots addresses some of the sampling uncertainty in the data; however, other assumptions surrounding the most appropriate discount rate and analysis models undertaken may create additional uncertainty that is not captured in the presented CEACs. The impact of using MI to impute missing data was also explored by running a complete analysis (including only participants with complete cost and QALY data).
Subgroup analyses
Like the clinical analysis subgroup, analyses explored the possible treatment effect modification of clinically important factors (haemorrhoidal grade and sex) through the use of treatment by factor interaction. We did not identify any additional subgroup analyses that were required to estimate cost-effectiveness for the within-trial analysis.
Chapter 4 Participant baseline characteristics
Study recruitment
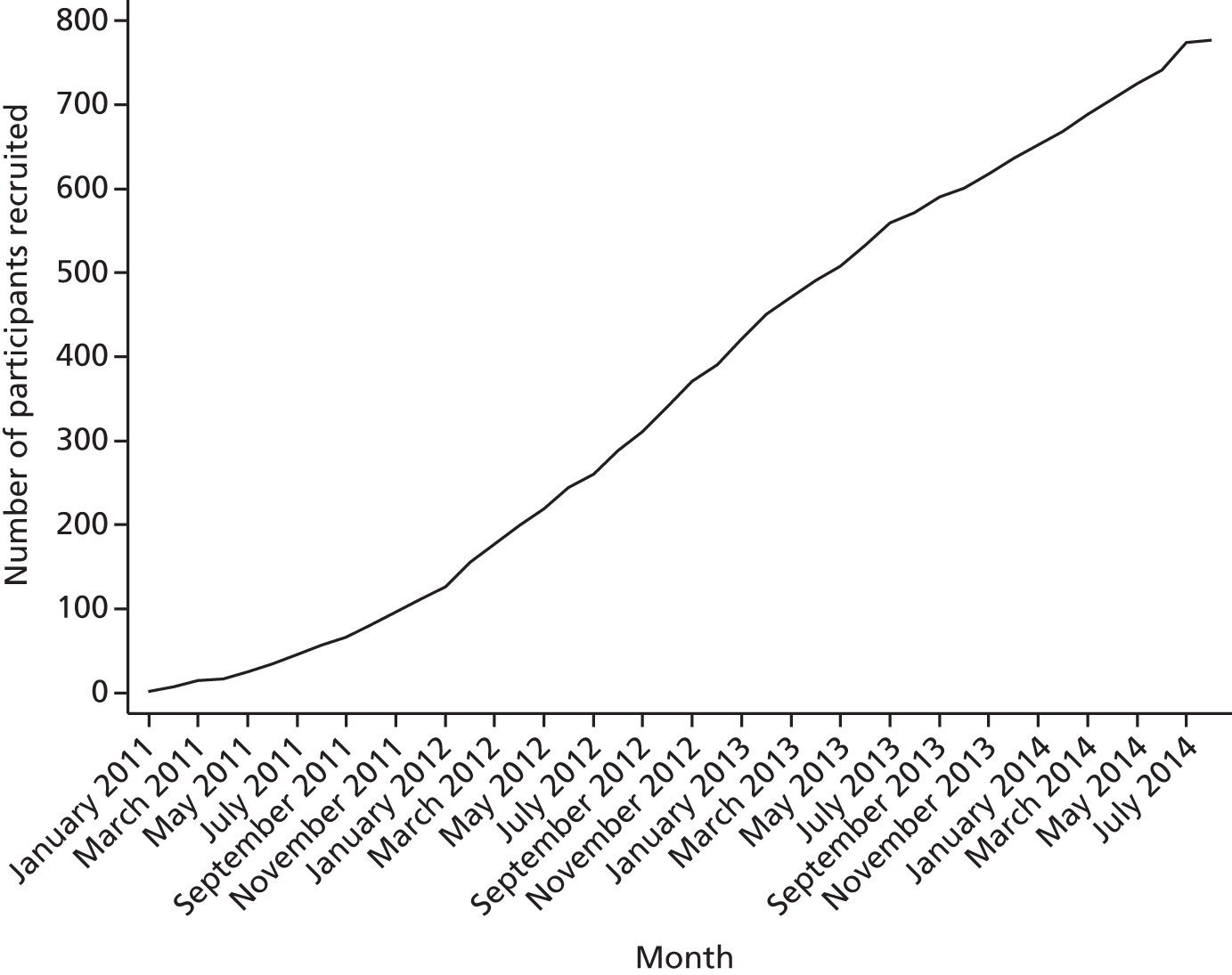
In total, 777 participants were recruited for surgical treatment from 29 out of the 32 UK-wide NHS hospitals that took part in the study (Table 5). Twenty-seven of these centres randomised 389 participants to the SH arm and 28 randomised 388 participants to the TH arm. Participants were recruited to the study between 13 January 2011 and 1 August 2014 and followed up to July 2016; however, not all the centres recruited within this period, owing to staggered introduction and early closure of centres. The trajectory of recruitment from all centres is shown in Figure 2.
| Hospital | Participants, n (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eligible (N = 1056) | Excluded (N = 33) | Declined (N = 225) | Missed (N = 21) | Randomised (N = 777) | Randomised to receive | ||
| SH (N = 389) | TH (N = 388) | ||||||
| Aberdeen Royal Infirmary | 176 | 17 (7.6) | 159 (20.5) | 79 (20.3) | 80 (20.6) | ||
| Arrowe Park Hospital | 4 | 4 (0.5) | 1 (0.3) | 3 (0.8) | |||
| Barnet General Hospital | |||||||
| Basildon University Hospital | |||||||
| Chelsea and Westminster Hospital | 13 | 1(3.0) | 6 (2.7) | 6 (0.8) | 3 (0.8) | 3 (0.8) | |
| Colchester University Hospital | 16 | 13 (5.8) | 1 (4.8) | 2 (0.3) | 2 (0.5) | ||
| Croydon University Hospital | 74 | 14 (6.2) | 1 (4.8) | 59 (7.6) | 30 (7.7) | 29 (7.5) | |
| Dr Gray’s Hospital, Elgin | 6 | 1 (0.4) | 5 (0.6) | 3 (0.8) | 2 (0.5) | ||
| Forth Valley Royal Hospital | 54 | 20 (8.9) | 34 (4.4) | 18 (4.6) | 16 (4.1) | ||
| Glan Clwyd Hospital, Rhyl | 19 | 6 (2.7) | 13 (1.7) | 7 (1.8) | 6 (1.5) | ||
| Glasgow Southern General Hospital | 1 | 1 (0.4) | |||||
| Hillingdon Hospital | 49 | 12 (5.3) | 4 (19.0) | 33 (4.2) | 16 (4.1) | 17 (4.4) | |
| Huddersfield Royal Infirmary | 43 | 16 (7.1) | 3 (14.3) | 24 (3.1) | 12 (3.1) | 12 (3.1) | |
| James Cook University Hospital | 63 | 3 (1.3) | 1 (4.8) | 59 (7.6) | 30 (7.7) | 29 (7.5) | |
| John Radcliffe Hospital | 15 | 4 (1.8) | 11 (1.4) | 6 (1.5) | 5 (1.3) | ||
| Lincoln County Hospital | 12 | 1 (0.4) | 11 (1.4) | 6 (1.5) | 5 (1.3) | ||
| Manchester Royal Infirmary | 29 | 2(6.1) | 11 (4.9) | 16 (2.1) | 8 (2.1) | 8 (2.1) | |
| Nevill Hall Hospital | 6 | 1 (0.4) | 1 (4.8) | 4 (0.5) | 2 (0.5) | 2 (0.5) | |
| Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital | 19 | 12 (5.3) | 1 (4.8) | 6 (0.8) | 3 (0.8) | 3 (0.8) | |
| Northern General Hospital | 25 | 13 (5.8) | 12 (1.5) | 6 (1.5) | 6 (1.5) | ||
| Pinderfields Hospital | 23 | 3 (1.3) | 20 (2.6) | 11 (2.8) | 9 (2.3) | ||
| Queen Elizabeth Hospital | 5 | 5 (0.6) | 2 (0.5) | 3 (0.8) | |||
| Raigmore Hospital | 102 | 7 (21.2) | 8 (3.6) | 87 (11.2) | 44 (11.3) | 43 (11.1) | |
| Royal Cornwall Hospital | 32 | 17 (7.6) | 4 (19.0) | 11 (1.4) | 6 (1.5) | 5 (1.3) | |
| Royal Derby City Hospital | 35 | 35 (4.5) | 18 (4.6) | 17 (4.4) | |||
| Royal Sussex County Hospital | 66 | 66 (8.5) | 33 (8.5) | 33 (8.5) | |||
| St James’s Hospital | 3 | 2 (9.5) | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.3) | |||
| University Hospital Aintree | 7 | 5 (2.2) | 2 (0.3) | 2 (0.5) | |||
| University Hospital of North Durham | 54 | 17 (7.6) | 37 (4.8) | 18 (4.6) | 19 (4.9) | ||
| University Hospital of North Tees | 56 | 9 (4.0) | 47 (6.0) | 23 (5.9) | 24 (6.2) | ||
| Weston Hospital | 3 | 1 (3.0) | 2 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | ||
| Wythenshawe Hospital | 46 | 22 (66.7) | 15 (6.7) | 3 (14.3) | 6 (0.8) | 2 (0.5) | 4 (1.0) |
FIGURE 2.
Recruitment over time.
Participant flow
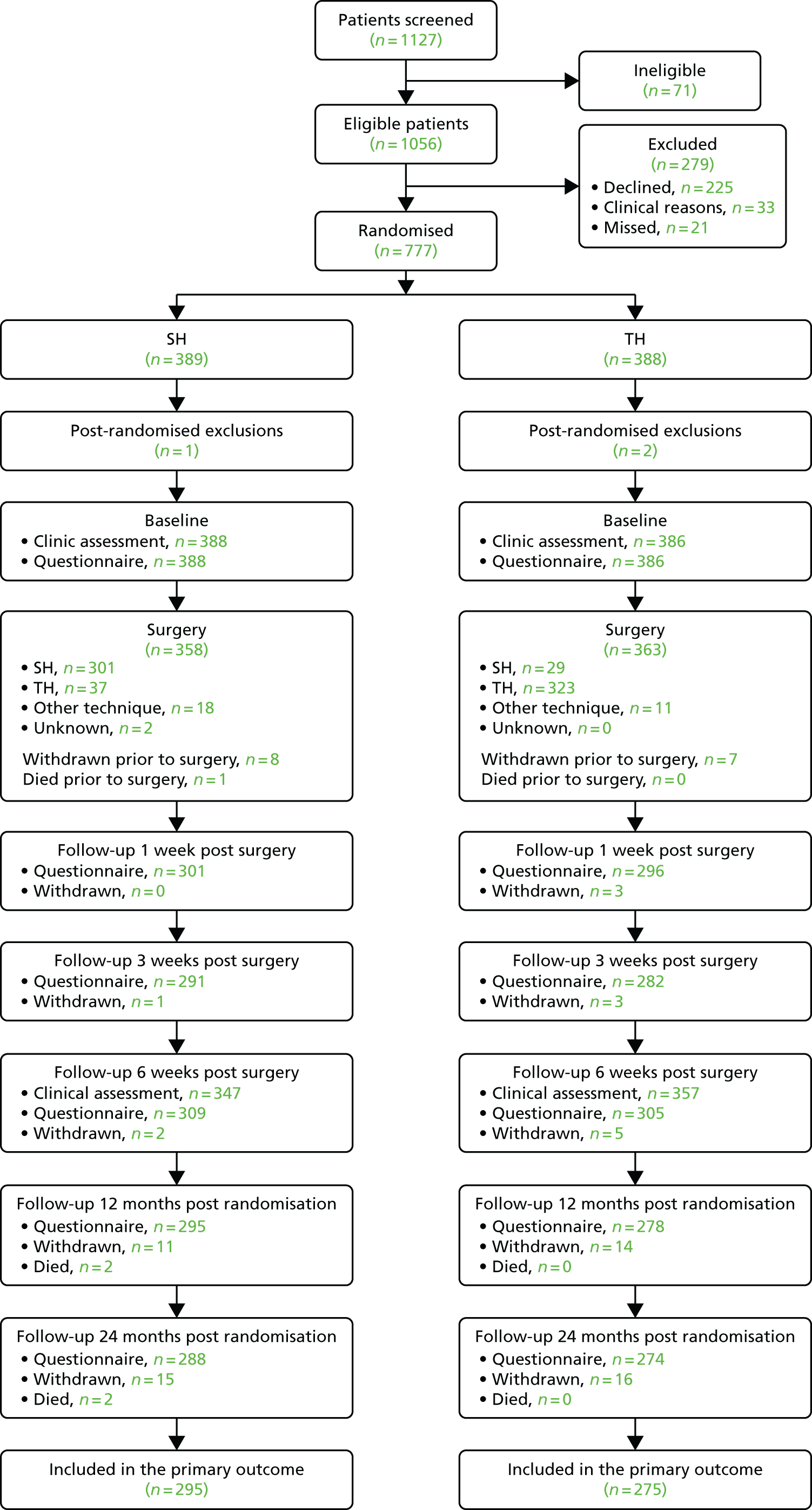
Figure 3 shows the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) diagram for the study. In total, 1127 participants were screened and 1056 were found to be eligible. For the 279 excluded participants, 225 declined, 33 were excluded because of clinical reasons and 21 were missed. The main reasons for ineligibility resulted from the participants having had previous surgery (26.8%) and being unable to complete study questionnaires (23.9%). The most frequent reasons for participants declining resulted from treatment preference (22.2%) and not wanting surgery (14.7%). Further details on reasons why screened participants were not randomised can be found in Table 6. Three participants were excluded post randomisation. One was under the age of 18 years and two withdrew consent within a short period following randomisation. Therefore, 774 participants were included in the study analysis and presentation of findings.
FIGURE 3.
The CONSORT flow diagram.
| Reason | Number of participants, n | % of total number of participants excluded |
|---|---|---|
| Reasons for ineligibility (n = 71) | ||
| Previous surgery | 19 | 26.8 |
| Sphincter injury | 1 | 1.4 |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 5 | 7.0 |
| Malignant colorectal disease | 2 | 2.8 |
| Unable to complete | 17 | 23.9 |
| Other | 27 | 38.0 |
| Reasons for declining to take part (n = 225) | ||
| Participant had a preference for treatment | 50 | 22.2 |
| Participant did not want to be randomised | 16 | 7.1 |
| Participant did not want to have surgery | 33 | 14.7 |
| Participant wanted to have a particular surgeon | 5 | 2.2 |
| Participant had concerns over their health | 4 | 1.8 |
| Participant not interested or did not want to take part in the study | 4 | 1.8 |
| Participant had no time to fill in questionnaires | 3 | 1.3 |
| Participant did not want any treatment | 1 | 0.4 |
| No reason given | 109 | 48.4 |
| Clinical reasons (n = 33) | ||
| Surgeon felt that participant would benefit from a certain procedure | 11 | 33.3 |
| More than one procedure to be performed | 22 | 66.7 |
| Reasons for missing participants (n = 21) | ||
| No response from the participant | 12 | 57.1 |
| Insufficient time to approach the participant | 4 | 19.0 |
| Participant received the information too late | 2 | 9.5 |
| Other | 3 | 14.3 |
All the participants randomised attended the baseline clinical assessment and completed the baseline questionnaire. A total of 31 participants withdrew from the study; one withdrawal was caused by the surgeon’s decision, whereas the remaining were at the participants’ request. Details of the treatment received are described in Chapter 5. Six weeks post surgery, 704 participants attended clinical follow-up appointments and 614 responded to the questionnaire. At the 24-month post-randomisation follow-up, 562 participants responded; a total of 31 participants withdrew from the study by that time point. Two deaths were reported, and none was caused by a study intervention.
Baseline characteristics
The participants’ baseline characteristics are shown for the 774 participants in Table 7 (excluding the post-randomisation exclusions). Sex, grade of haemorrhoids and EQ-5D-3L score were included as minimisation variables; therefore, the balance between the two treatment groups for these covariates was ensured. The median age was 50 years old and the quality-of-life outcomes (SF-36; physical and mental component summary) were balanced between the groups. Over 60% of participants had grade-III haemorrhoids, and 35.8% of participants in the SH arm and 30.1% in the TH arm had had previous haemorrhoid treatment. The majority of participants had either no preference for the type of surgery or preferred an intervention associated with a lower risk of haemorrhoid recurrence.
| Characteristic | Trial arm | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Age (years), n, median (IQR) | 388, 50 (40–60) | 386, 49 (40–59) |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 201 (51.8) | 197 (51.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2), n, mean (SD) | 372, 27.0 (5.2) | 367, 27.0 (4.9) |
| Grade of haemorrhoid, n (%) | ||
| II | 86 (22.2) | 86 (22.3) |
| III | 243 (62.6) | 240 (62.2) |
| IV | 59 (15.2) | 60 (15.5) |
| Previous haemorrhoid surgery, n (%) | 139 (35.8) | 116 (30.1) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | 6 (1.5) | 4 (1.0) |
| Systemic medications, n (%) | ||
| Aspirin | 23 (5.9) | 16 (4.1) |
| Warfarin | 4 (1.0) | 2 (0.5) |
| Clopidogrel | 6 (1.5) | 4 (1.0) |
| Steroids | 5 (1.3) | 2 (0.5) |
| Immunosuppressants | 1 (0.3) | |
| Other | 6 (1.5) | 3 (0.8) |
| Pain (VAS), n, mean (SD) | 379, 2.8 (2.7) | 383, 2.5 (2.6) |
| Analgesia, n (%) | ||
| Yes | 139 (35.8) | 118 (30.6) |
| Missing | 7 (1.8) | 4 (1.0) |
| Number of days in a week with analgesia, n, mean (SD) | 137, 4.1 (2.2) | 117, 4.3 (2.2) |
| EQ-5D-3L, n, mean (SD) | 388, 0.764 (0.264) | 386, 0.762 (0.246) |
| SF-36, n, mean (SD) | ||
| Physical component summary | 380, 48.5 (9.4) | 377, 48.8 (9.5) |
| Mental component summary | 380, 48.8 (11.7) | 377, 49.6 (11.0) |
| CIS, n, mean (SD) | 376, 4.3 (3.9) | 376, 4.1 (4.0) |
| HSS, n, mean (SD) | 370, 10.8 (4.7) | 370, 10.4 (4.7) |
| Patient reporting tenesmus, n (%) | ||
| Always | 15 (3.9) | 9 (2.3) |
| Often | 52 (13.4) | 39 (10.1) |
| Sometimes | 93 (24.0) | 105 (27.2) |
| Rarely | 73 (18.8) | 62 (16.1) |
| Never | 150 (38.7) | 168 (43.5) |
| Missing | 5 (1.3) | 3 (0.8) |
| Patient preference, n (%) | ||
| Strongly prefer better short-term recovery | 23 (5.9) | 38 (9.8) |
| Prefer better short-term recovery | 35 (9.0) | 24 (6.2) |
| No preference | 161 (41.5) | 146 (37.8) |
| Prefer lower risk of recurrence | 95 (24.5) | 85 (22.0) |
| Strongly prefer lower risk of recurrence | 68 (17.5) | 91 (23.6) |
| Missing | 6 (1.5) | 2 (0.5) |
Table 8 summarises the level of experience of the surgeons and is broken down by surgical procedure and not randomisation group. The number of SH and TH operations performed in the previous year per surgeon are similar, whereas the number performed during a surgeon’s career differs.
| Characteristic | Trial arm | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Number of operations performed during career | ||
| n, mean (SD) | 42, 102.7 (98.9) | 42, 200.1 (232.3) |
| Median (IQR) | 85 (30.0–115.0) | 100 (70.0–200.0) |
| Operations performed in previous year | ||
| n, mean (SD) | 43, 12.9 (10.3) | 40, 14.7 (12.6) |
| Median (IQR) | 10 (4.0–21.0) | 10 (4.5–23.0) |
Chapter 5 Outcomes and results
Description of sample
The surgical procedures received by each treatment group are shown in Table 9. Of the 388 participants randomised to receive SH, 358 (92.3%) had surgery and, of these, 301 (84.1%) received their allocated intervention, 37 (10.3%) received TH, 18 (5.0%) had a technique other than the study interventions and two (0.6%) are unknown as they underwent private treatment. For the 386 participants randomised to receive TH, 363 (94.0%) had surgery, 323 (89.0%) received their allocated treatment, 29 (8.0%) received SH and 11 (3.0%) received other treatments. Across both arms 53 (6.8%) participants did not receive surgery, and the reasons are shown in Table 10.
| Surgery details | Trial arm | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Received surgery, n (%) | ||
| Yes | 358 (92.3) | 363 (94.0) |
| No | 30 (7.7) | 23 (6.0) |
| Surgical technique, n (%) | ||
| Stapling | 301 (84.1) | 29 (8.0) |
| Ethicon | 155 (51.5) | 22 (75.9) |
| Chex CPH 32 staple gun | 117 (38.9) | 6 (20.7) |
| EEA Staplers with DST Series technology | 9 (3.0) | – |
| Other | 10 (3.3) | 1 (3.4) |
| Missing | 10 (3.3) | – |
| Traditional | 37 (10.3) | 323 (89.0) |
| Open (Milligan–Morgan) | 36 (97.3) | 272 (84.2) |
| Closed (Ferguson) | 1 (2.7) | 41 (12.7) |
| Other conventional technique | – | 5 (1.5) |
| Missing | – | 5 (1.5) |
| Other technique | 18 (5.0) | 11 (3.0) |
| Surgery technique unknown | 2 (0.6) | – |
| Surgeon grade, n (%) | ||
| Consultant | 256 (71.5) | 225 (62.0) |
| Specialty doctor | 32 (8.9) | 37 (10.2) |
| Surgical trainee | 58 (16.2) | 89 (24.5) |
| Fellow | 4 (1.1) | 5 (1.4) |
| Other | 5 (1.4) | 6 (1.7) |
| Missing | 3 (0.8) | 1 (0.3) |
| Anaesthetist present, n (%) | ||
| Yes | 356 (99.4) | 363 (100.0) |
| Missing | 2 (0.6) | – |
| Anaesthetist grade, n (%) | ||
| Consultant | 287 (80.2) | 297 (81.8) |
| Specialty doctor | 45 (12.6) | 36 (9.9) |
| Fellow | – | 1 (0.3) |
| Registrar | 10 (2.8) | 21 (5.8) |
| Other | 2 (0.6) | – |
| Missing | 14 (3.9) | 8 (2.2) |
| Type of anaesthesia, n (%) | ||
| General | 236 (65.9) | 223 (61.4) |
| General and local anaesthetic block | 105 (29.3) | 127 (35.0) |
| Spinal | 15 (4.2) | 11 (3.0) |
| Other | – | 1 (0.3) |
| Missing | 2 (0.6) | 1 (0.3) |
| Duration of operation (hours), n, mean (SD) | 346, 0.4 (0.2) | 359, 0.4 (0.2) |
| Length of hospital stay (days), n, mean (SD) | 356, 0.4 (0.3) | 363, 0.4 (0.4) |
| Day cases, n (%) | 305 (85.6) | 317 (87.3) |
| Time from randomisation to surgery (days), n, mean (SD) | 358, 68.2 (78.3) | 363, 68.8 (81.1) |
| Reason | Number of participants, n (%) (N = 53) |
|---|---|
| Patient reasons | 39 (73.6) |
| Opted out of surgery | 15 |
| Cancelled surgery | 10 |
| Did not attend | 7 |
| Went private | 3 |
| Moved away | 2 |
| Withdrew prior to surgery (withdrew outcome data) | 1 |
| Withdrew consent | 1 |
| Clinical reasons | 10 (18.9) |
| Underlying health condition | 5 |
| Following preoperative consultation conservative management was decided | 1 |
| Pregnancy | 1 |
| Following preoperative consultation did not require surgery | 3 |
| Unknown | 3 (5.7) |
| Death prior to surgery | 1 (1.9) |
Surgical details
For the SH procedure, the most common staplers used were the Ethicon and the Chex staplers, used on 177 (53.6%) and 123 (37.3%) patients, respectively. For the TH procedure, the Milligan–Morgan approach was the main surgical approach, performed on 308 (85.6%) patients. The majority of participants were operated on by consultant surgeons (71.5% in the SH arm and 62.0% in the TH arm). Specialty doctors performed 8.9% of operations in the SH arm and 10.2% in the TH arm and surgical trainees performed 16.2% of the SH surgeries and 24.5% of the TH surgeries. Most procedures were performed either under general anaesthesia (65.9% in the SH arm and 61.4% in the TH arm) or with an additional local anaesthetic block in 29.3% of the SH arm and 35.0% of the TH arm. The mean duration of the operation was the same in both groups (0.4 hours), 305 (85.6%) in the SH arm and 317 (87.3%) in the TH arm were day cases and the mean number of days to surgery was similar for both groups (68.2 days in the SH arm and 68.8 days in the TH arm).
Primary outcome
The EQ-5D-3L values at each time point are shown in Table 11. Figure 4 shows the profile for the two treatment groups over the study period, whereas Figure 5 shows the profile for the earlier follow-up time points. The SH arm had higher EQ-5D-3L scores for 1 week and 3 weeks, but this changed to higher scores in the TH arm from 6 weeks onwards. The primary outcome, EQ-5D-3L AUC over 24 months post randomisation, reported as QALYs (Table 12), favoured TH (–0.073 QALYs, 95% CI –0.140 to –0.006 QALYs; p = 0.034). The secondary analysis of AUC over 6 weeks post surgery favoured SH and the AUC over 12 months post randomisation showed no evidence of a difference between the two interventions. The analyses restricted to participants with at least one long-term measure were similar, and exploring the sensitivities to assumptions (per-protocol and MI analyses) gave similar results (Tables 13–16).
| Time point | Trial arm, n, mean (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Baseline | 388, 0.762 (0.247) | 386, 0.764 (0.264) |
| 1 week | 298, 0.592 (0.315) | 291, 0.458 (0.337) |
| 3 weeks | 285, 0.802 (0.244) | 276, 0.750 (0.244) |
| 6 weeks | 305, 0.843 (0.226) | 303, 0.853 (0.228) |
| 12 months | 296, 0.816 (0.258) | 280, 0.877 (0.212) |
| 24 months | 283, 0.830 (0.251) | 272, 0.872 (0.195) |
FIGURE 4.
Participant EQ-5D-3L scores up to 2 years. Participants need to have at least one short-term and one long-term follow-up score over 2 years.
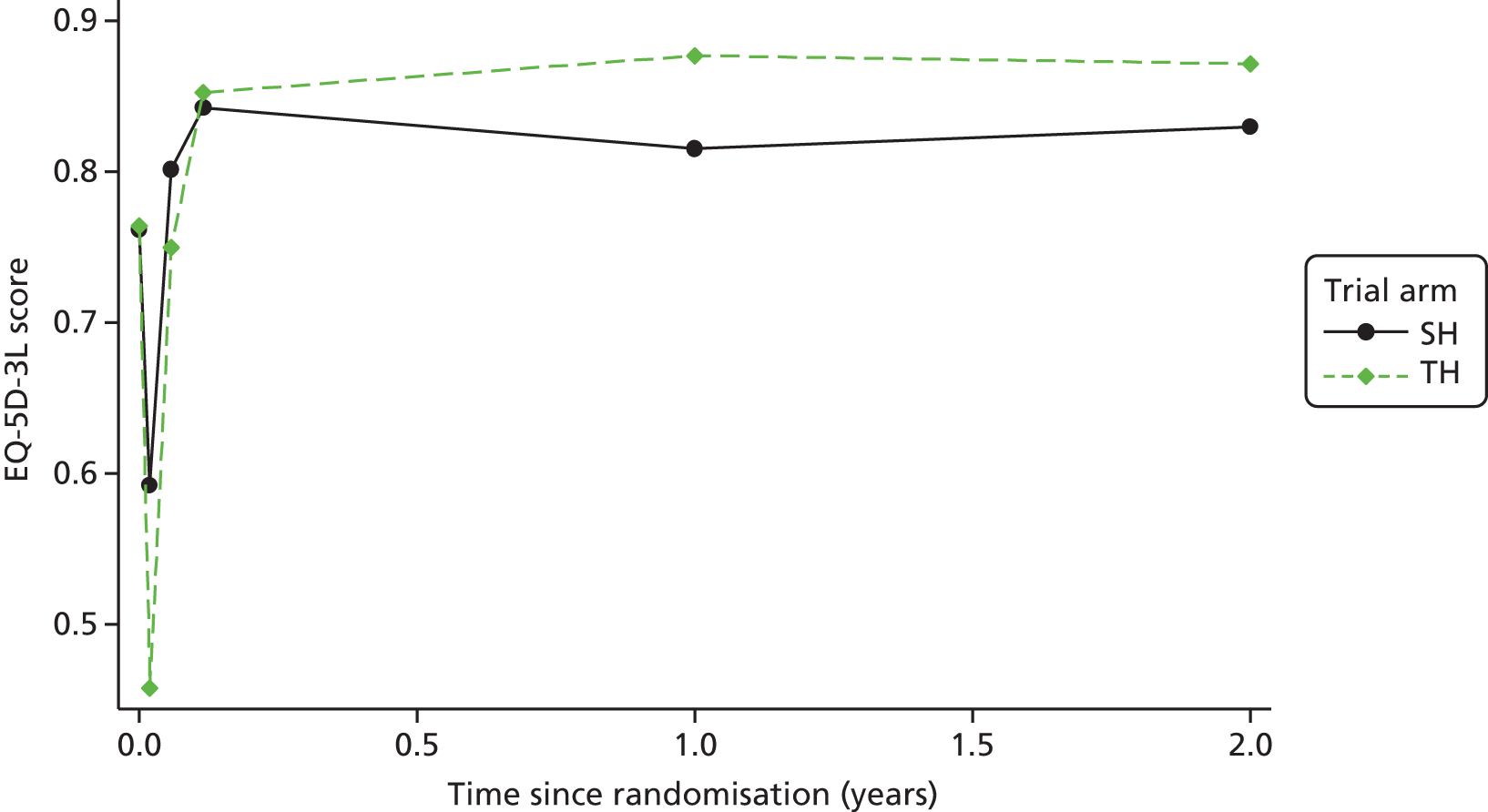
FIGURE 5.
Participant EQ-5D-3L scores up to 6 weeks. Participants need to have at least one short-term follow-up score over 6 weeks.
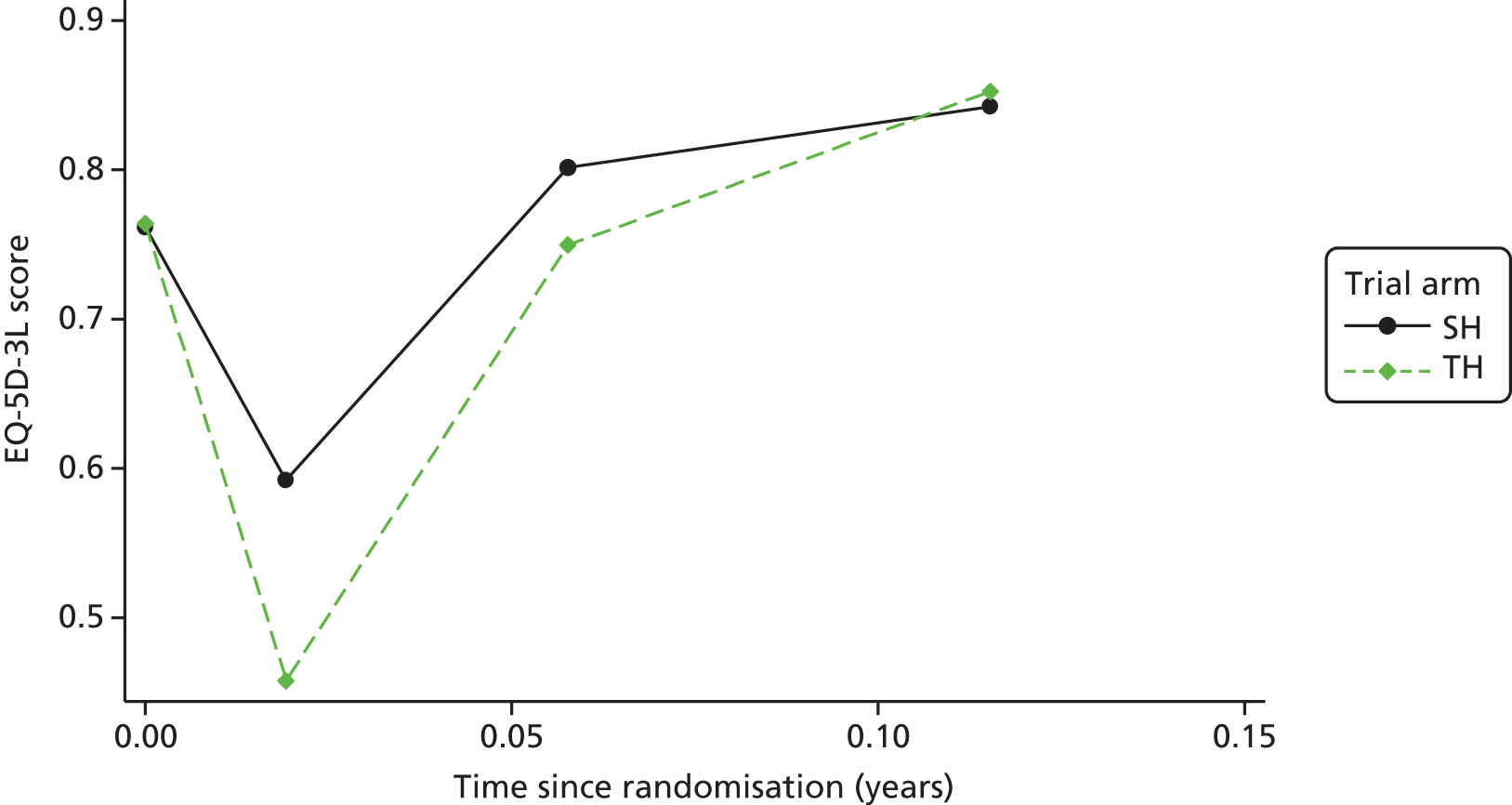
| Time point | Trial arm, n, mean AUC (SD) | MD (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| 6 weeks | 331, 0.215 (0.150) | 328, 0.197 (0.143) | 0.020 (0.003 to 0.038) | 0.024 |
| 12 months | 282, 0.824 (0.218) | 262, 0.828 (0.225) | –0.010 (–0.039 to 0.019) | 0.483 |
| 24 months | 295, 1.556 (0.483) | 275, 1.618 (0.431) | –0.073 (–0.140 to –0.006) | 0.034 |
| Time point | Trial arm, n, mean AUC (SD) | MD (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| 12 months | 29, 0.821 (0.219) | 280, 0.828 (0.225) | –0.015 (–0.040 to 0.011) | 0.249 |
| 24 months | 315, 1.541 (0.489) | 294, 1.609 (0.435) | –0.077 (–0.137 to –0.017) | 0.013 |
| Time point | Trial arm, n, mean AUC (SD) | MD (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| 6 weeks | 282, 0.225 (0.151) | 299, 0.197 (0.142) | 0.029 (0.010 to 0.048) | 0.004 |
| 12 months | 240, 0.823 (0.217) | 243, 0.827 (0.219) | –0.009 (–0.040 to 0.022) | 0.565 |
| 24 months | 251, 1.555 (0.478) | 256, 1.623 (0.418) | –0.078 (–0.153 to –0.002) | 0.045 |
| Time point | Trial arm, n, mean AUC (SD) | MD (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| 12 months | 247, 0.824 (0.215) | 246, 0.828 (0.219) | –0.011 (–0.041 to 0.020) | 0.467 |
| 24 months | 258, 1.550 (0.479) | 260, 1.616 (0.429) | –0.078 (–0.152 to –0.004) | 0.039 |
| Time point | Trial arm, n | MD (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| Participants who either had surgery or at least one follow-up | ||||
| 6 weeks | 354 | 358 | 0.024 (0.004 to 0.043) | 0.020 |
| 12 months | 360 | 367 | –0.012 (–0.038 to 0.014) | 0.350 |
| 24 months | 363 | 369 | –0.063 (–0.111 to –0.015) | 0.013 |
| All participants randomised | ||||
| 6 weeks | 388 | 386 | 0.020 (–0.002 to 0.042) | 0.071 |
| 12 months | 388 | 386 | –0.007 (–0.345 to 0.018) | 0.571 |
| 24 months | 388 | 386 | –0.054 (–0.107 to –0.000) | 0.049 |
Secondary outcomes
Quality of life
The SF-36 mental and physical component summary scores, CIS and HSS are shown in Table 17. Six weeks after surgical intervention, the physical and mental components scores were either similar to, or less than, the baseline scores, and there was no evidence of a difference between the two interventions. At 12 and 24 months after randomisation both scores improved, and there is evidence of a difference in favour of TH at 12 months [physical summary: mean difference (MD) –1.79, 95% CI –3.06 to –0.5, p = 0.006; mental summary: MD –1.71, 95% CI –3.34 to –0.08, p = 0.040].
| Time point | Trial arm, n, mean score (SD) | MD (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| SF-36 | ||||
| Physical component summary | ||||
| Baseline | 380, 48.5 (9.4) | 377, 48.8 (9.5) | – | – |
| 6 weeks | 294, 48.2 (10.4) | 293, 48.9 (9.2) | –0.58 (–1.77 to 0.61) | 0.342 |
| 12 months | 265, 49.7 (10.1) | 255, 51.2 (9.4) | –1.79 (–3.06 to –0.51) | 0.006 |
| 24 months | 250, 50.3 (10.1) | 234, 51.1 (9.4) | –1.15 (–2.47 to 0.16) | 0.086 |
| Mental component summary | ||||
| Baseline | 380, 48.8 (11.7) | 377, 49.6 (11.0) | – | – |
| 6 weeks | 294, 47.3 (12.7) | 293, 48.7 (11.7) | –0.55 (–2.07 to 0.97) | 0.480 |
| 12 months | 265, 48.8 (12.2) | 255, 51.2 (10.4) | –1.71 (–3.34 to –0.08) | 0.040 |
| 24 months | 250, 49.8 (11.2) | 234, 51.0 (10.9) | –0.89 (–2.57 to 0.80) | 0.303 |
| CIS | ||||
| Baseline | 376, 4.3 (3.9) | 376, 4.1 (4.0) | – | – |
| 6 weeks | 288, 5.1 (4.5) | 290, 5.0 (4.3) | –0.16 (–0.74 to 0.42) | 0.584 |
| 12 months | 266, 4.4 (4.3) | 247, 2.9 (3.5) | 1.20 (0.58 to 1.81) | < 0.001 |
| 24 months | 249, 3.8 (3.8) | 235, 3.0 (3.4) | 0.78 (0.15 to 1.42) | 0.015 |
| HSS | ||||
| Baseline | 370, 10.8 (4.7) | 370, 10.4 (4.7) | – | – |
| 6 weeks | 288, 8.2 (5.1) | 291, 7.9 (5.0) | 0.15 (–0.60 to 0.91) | 0.691 |
| 12 months | 263, 6.6 (5.1) | 243, 4.3 (4.3) | 2.09 (1.28 to 2.90) | < 0.001 |
| 24 months | 250, 6.4 (5.0) | 240, 4.8 (4.4) | 1.46 (0.64 to 2.28) | < 0.001 |
The CIS at 6 weeks was similar for both groups [SH arm: 5.1 (SD 4.5); TH arm: 5.0 (SD 4.3)], but at 12 and 24 months post randomisation there is evidence of a difference between the two groups (12 months: MD 1.20, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.81, p < 0.001; 24 months: MD 0.78, 95% CI 0.15 to 1.42, p = 0.015). The HSS favours TH over SH at all time points (6 weeks: MD 0.15, 95% CI –0.60 to 0.91, p = 0.691; 12 months: MD 2.09, 95% CI 1.28 to 2.90, p < 0.001; 24 months: MD 1.46, 95% CI 0.64 to 2.28, p < 0.001).
Patient-reported pain measures
There is evidence that pain, recorded on the VAS, was lower in the SH arm than in the TH arm at both 1 week (MD –1.35, 95% CI –1.81 to –0.89; p < 0.001) and 3 weeks after surgery (MD –0.72, 95% CI –1.16 to –0.028; p = 0.003). The number of days with analgesia was significantly different and in favour of SH at 1 week (MD –0.59, 95% CI –0.98 to –0.20; p = 0.004), but not at 3 weeks. Pain scores and the number of days with analgesia at 6 weeks showed no difference between the arms and the proportion of participants returning to usual activities was the same (89%). Results are shown in Table 18.
| Time point | Trial arm | Effect sizeb (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388)a | TH (N = 386)a | |||
| Pain at 1 week post surgery | ||||
| Number of patients followed up, n (%) | 301 (77.6) | 296 (76.7) | – | – |
| Worst pain (VAS) | 298, 6.9 (2.5) | 295, 7.9 (2.2) | –1.04 (–1.59 to –0.49) | 0.001 |
| Pain (VAS) | 299, 4.0 (2.5) | 296, 5.3 (2.6) | –1.35 (–1.81 to –0.89) | < 0.001 |
| Analgesia, n (%) | 285 (94.7) | 286 (96.6) | 0.57 (0.27 to 1.19) | 0.134 |
| Number of days with analgesia | 285, 5.8 (1.7) | 286, 6.4 (1.3) | –0.59 (–0.98 to –0.20) | 0.004 |
| Pain at 3 weeks post surgery | ||||
| Number of patients followed up, n (%) | 291 (75.0) | 282 (73.1) | – | – |
| Pain (VAS) | 290, 1.8 (2.2) | 281, 2.6 (2.5) | –0.72 (–1.16 to –0.28) | 0.003 |
| Analgesia, n (%) | 111 (38.1) | 145 (51.4) | 0.58 (0.45 to 0.75) | < 0.001 |
| Number of days with analgesia | 111, 4.3 (2.1) | 145, 4.5 (2.2) | –0.24 (–0.75 to 0.27) | 0.340 |
| Pain at 6 weeks post surgery | ||||
| Number of patients followed up, n (%) | 309 (79.6) | 305 (79.0) | – | – |
| Pain (VAS) | 304, 1.3 (2.0) | 301, 1.3 (1.9) | –0.01 (–0.35 to 0.33) | 0.961 |
| Analgesia, n (%) | 73 (23.6) | 67 (22.0) | 1.11 (0.73 to 1.68) | 0.620 |
| Number of days in a week with analgesia | 72, 4.7 (2.3) | 67, 4.0 (2.3) | 0.58 (–0.22 to 1.37) | 0.146 |
| Returned to usual activities after 6 weeks, n (%) | 276 (89.3) | 271 (88.9) | 1.05 (0.64 to 1.71) | 0.854 |
Participant-reported recurrence
At 12 months post randomisation more participants in the SH arm reported that their haemorrhoids had recurred (n = 94, 31.9%) than in the TH arm (n = 39, 14.0%) [odds ratio (OR) 2.96, 95% CI 2.02 to 4.32; p < 0.001]. This was also the case at 24 months; 134 (42.3%) reoccurrences were reported in the SH arm compared with 76 (25.3%) in the TH arm (Table 19).
| Time point | Trial arm, n (%) | ORa (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| 12 months post randomisation | ||||
| Participants followed up | 295 | 278 | – | – |
| Haemorrhoids reoccurred | 94 (31.9) | 39 (14.0) | 2.96 (2.02 to 4.32) | < 0.001 |
| 24 months post randomisation | ||||
| Participants followed up | 317 | 300 | – | – |
| Haemorrhoids reoccurred | 134 (42.3) | 76 (25.3) | 2.25 (1.46 to 3.46) | < 0.001 |
Tenesmus
Table 20 shows that tenesmus at 6 weeks post surgery, and 12 and 24 months post randomisation was more prevalent in the SH arm.
| Time point | Trial arm, n (%) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | ||
| 6 weeks | |||
| Participants followed up | 309 | 305 | 0.001 |
| Always | 17 (5.5) | 9 (3.0) | |
| Often | 42 (13.6) | 20 (6.6) | |
| Sometimes | 82 (26.5) | 75 (24.6) | |
| Rarely | 58 (18.8) | 68 (22.3) | |
| Never | 109 (35.3) | 131 (43.0) | |
| Missing | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.7) | |
| 12 months | |||
| Participants followed up | 295 | 278 | < 0.001 |
| Always | 11 (3.7) | 4 (1.4) | |
| Often | 27 (9.2) | 7 (2.5) | |
| Sometimes | 60 (20.3) | 46 (16.5) | |
| Rarely | 65 (22.0) | 43 (15.5) | |
| Never | 113 (38.3) | 154 (55.4) | |
| Missing | 19 (6.4) | 24 (8.6) | |
| 24 months | |||
| Participants followed up | 288 | 274 | 0.001 |
| Always | 6 (2.1) | 3 (1.1) | |
| Often | 27 (9.4) | 13 (4.7) | |
| Sometimes | 51 (17.7) | 36 (13.1) | |
| Rarely | 55 (19.1) | 47 (17.2) | |
| Never | 119 (41.3) | 143 (52.2) | |
| Missing | 30 (10.4) | 32 (11.7) | |
Further haemorrhoid surgery
In total, 34 (9.3%) participants in the SH arm had to have further surgery compared with 23 (6.2%) in the TH arm (p = 0.111; Table 21).
| Time point | Trial arm, n (%) | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | ||||||
| Participant | Registrya | Combinedb | Participant | Registrya | Combinedb | ||
| Participants followed up at 6 weeks | 348 | 343 | 348 | 356 | 354 | 357 | |
| Within 6 weeks of surgery | |||||||
| TH | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | – | – | – | – |
| RBL | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | |
| At 6 weeks | |||||||
| TH | 6 (1.7) | – | 6 (1.7) | 2 (0.6) | – | 2 (0.6) | – |
| SH | 3 (0.9) | – | 3 (0.9) | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | |
| RBL | 4 (1.1) | – | 4 (1.1) | 6 (1.7) | – | 6 (1.7) | |
| Skin tags | 5 (1.4) | – | 5 (1.4) | 4 (1.1) | – | 4 (1.1) | |
| Type of haemorrhoid surgery unknown | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | – | |||
| 12 months post randomisation | |||||||
| Participants followed up at 12 months | 288 | 374 | 299 | 272 | 379 | 283 | – |
| TH | 6 (2.1) | 5 (1.3) | 11 (3.7) | – | 3 (0.8) | 3 (1.1) | |
| SH | – | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.4) | |
| RBL | 3 (1.0) | – | 3 (1.0) | 3 (1.1) | 2 (0.5) | 5 (1.8) | |
| Skin tags | 1 (0.3) | 5 (1.3) | 6 (2.0) | 2 (0.7) | 4 (1.1) | 6 (2.1) | |
| 24 months post randomisation | |||||||
| Participants followed up at 24 months | 286 | 374 | 289 | 273 | 379 | 274 | |
| TH | 2 (0.7) | – | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.4) | – | 1 (0.4) | |
| SH | 2 (0.7) | 2 (0.5) | 4 (1.4) | – | – | – | |
| RBL | 2 (0.7) | – | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.4) | – | 1 (0.4) | |
| Skin tags | – | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.4) | |
| Type of haemorrhoid surgery unknown | 1 (0.3) | – | 1(0.3) | 1 (0.4) | – | 1 (0.4) | |
| Number of participants who had further surgical treatment | – | – | 34/364 (9.3) | – | – | 23/371 (6.2) | 0.111 |
Further interventions: non-surgical
In total, 94 (25.8%) participants in the SH arm had to have further non-surgical interventions compared with 70 (18.9%) in the TH arm (Table 22). This included patients who had received intramuscular onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox®; Allergan, Marlow, UK) injections and other medical treatments.
| Time point | Trial arm, n (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||||
| Participant | Registrya | Combinedb | Participant | Registrya | Combinedb | |
| Participants followed up at 6 weeks | 348 | 343 | 348 | 356 | 354 | 356 |
| Within 6 weeks of surgery | ||||||
| Botox | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | – | – | – |
| Medical treatment | 11 (3.2) | – | 11 (3.2) | 16 (4.5) | – | 16 (4.5) |
| At 6 weeksc | ||||||
| Medical treatment | 33 (9.5) | – | 33 (9.5) | 33 (9.3) | – | 33 (9.3) |
| 12 months post randomisation | ||||||
| Participants followed up | 288 | 374 | 288 | 272 | 379 | 272 |
| Botox | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | – |
| Medical treatment | 53 (18.4) | 2(0.5) | 53 (18.4) | 31 (11.4) | 2 (0.5) | 31 (11.4) |
| 24 months post randomisation | ||||||
| Participants followed up | 286 | 374 | 286 | 273 | 379 | 273 |
| Botox | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | – | – | – |
| Medical treatment | 38 (13.3) | – | 38 (13.3) | 19 (7.0) | – | 19 (7.0) |
| Number of participants who had further non-surgical treatment | – | – | 94/364 (25.8) | – | – | 70/371 (18.9) |
Perioperative and postoperative complications
The number of participants who had complications before discharge was similar in both groups [18 (5.0%) in the SH arm; 19 (5.2%) in the TH arm; p = 0.9], but after discharge there were slightly more in the TH arm [96 (24.9%) in the SH arm; 117 (30.6%) in the TH arm; OR 0.75, 95% CI 0.57 to 0.98; p = 0.034] (Table 23). Further details of the other complications (perioperative, post operative and within 6 weeks) are given in Tables 24 and 25, and details of the complications at 12 and 24 months post randomisation are given in Table 26.
| Complication | Trial arm, n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||||||
| Participant | Registrya | Combinedb | Participant | Registrya | Combinedb | |||
| Participants who received surgery | 358 | – | 358 | 363 | – | 363 | ||
| Perioperative complication | ||||||||
| Anaesthetic | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.6) | – | 2 (0.6) | – | – |
| Bleeding | 6 (1.7) | – | 6 (1.7) | 6 (1.7) | – | 6 (1.7) | – | |
| Other | 4 (1.1) | – | 4 (1.1) | – | – | |||
| Postoperative complications prior to discharge | ||||||||
| Bleeding | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | – | |
| Need for blood transfusion | – | – | – | 1 (0.3) | – | 1 (0.3) | – | |
| Urinary retention | – | – | – | 3 (0.8) | – | 3 (0.8) | – | |
| Other | 7 (2.0) | – | 7 (2.0) | 8 (2.2) | – | 8 (2.2) | – | |
| Number of participants with a complication before discharge | – | – | – | 18 (5.0) | – | 19 (5.2) | – | 0.900 |
| Complications since discharge (at 6 weeks) | ||||||||
| Number of patients followed up | 348 | 374 | 349 | 357 | 379 | 358 | – | |
| Residual haemorrhoidal tissue | 36 (10.3) | – | 36 (10.3) | 37 (10.4) | – | 37 (10.3) | – | |
| Surgery for complications | 7 (2.0) | 2(0.5) | 8 (2.3) | 7 (2.0) | 4 (1.1) | 10 (2.8) | – | |
| Anal stenosis | 6 (1.7) | – | 6 (1.7) | 2 (0.6) | – | 2 (0.6) | – | |
| Anal fistula | 2 (0.6) | – | 2 (0.6) | 2 (0.6) | – | 2 (0.6) | – | |
| Anal fissure | 11 (3.2) | – | 11 (3.2) | 13 (3.6) | – | 13 (3.6) | – | |
| Wound discharge | 6 (1.7) | – | 6 (1.7) | 27 (7.6) | – | 27 (7.5) | – | |
| Pelvic sepsis | – | – | – | 2 (0.6) | – | 2 (0.6) | – | |
| Need for blood transfusion | 2 (0.6) | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.6) | 2 (0.6) | – | 2 (0.6) | – | |
| Urinary retention requiring catheterisation | 9 (2.6) | – | 9 (2.6) | 8 (2.2) | – | 8 (2.2) | – | |
| Other | 31 (8.9) | 1 (0.3) | 31 (8.9) | 42 (11.8) | – | 39 (10.9) | – | |
| Further surgery required for complications at 6 weeks | 8 (2.3) | – | 8 (2.3) | 3 (0.8) | – | 3 (0.8) | – | |
| Responded at 12 months and received surgery | 295 | 374 | 295 | 278 | 379 | 278 | – | |
| Complications | 8 (2.7) | 4 (1.1) | 9 (3.1) | 8 (2.9) | 2 (0.5) | 8 (2.9) | – | |
| Complications requiring surgery | 3 (1.0) | 6 (1.6) | 8 (2.7) | 1 (0.4) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.4) | – | |
| Responded at 24 months and received surgery | 288 | 374 | 288 | 274 | 379 | 275 | – | |
| Complications | 3 (1.0) | 2 (0.5) | 3 (1.0) | – | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.4) | – | |
| Complications requiring surgery | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.5) | 2 (0.7) | – | – | – | – | |
| Number of participants with a complication after discharge | – | – | 96 (24.9) | – | – | 117 (30.6) | 0.75 (0.57 to 0.98) | 0.034 |
| Complication | Trial arm, n | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Perioperative complication | 4 | – |
| Haematoma | 1 | – |
| Low staple line | 1 | – |
| Purse string snapped and redone | 2 | – |
| Postoperative complications prior to discharge | 7 | 8 |
| Pain | 5 | 4 |
| Anaesthetic | 1 | 3 |
| Urinary retention | – | 1 |
| Not specified | 1 | – |
| Complication | Trial arm, n | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Other complications | 31 | 39 |
| Pain | 6 | 11 |
| Bleeding | 7 | 3 |
| Pain and bleeding | 1 | 6 |
| Constipation | – | 4 |
| Pain and constipation | – | 2 |
| Bleeding and constipation | 1 | 1 |
| Faecal urgency | 3 | 2 |
| Incontinence | 2 | – |
| Infection | 4 | 7 |
| Other | 7 | 3 |
| Surgery within 6 weeks for complications | 8 | 10 |
| Pain | 1 | 3 |
| Pain and bleeding | 1 | – |
| Infection | 1 | – |
| Other | 5 | 7 |
| Further surgery required for complications at 6 weeks | 8 | 3 |
| Pain | – | 1 |
| Bleeding | 1 | – |
| Fissure | 1 | – |
| Other | 6 | 2 |
| Complication | Trial arm, n | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Complications at 12 months | 9 | 8 |
| Bleeding | 4 | 2 |
| Pain | – | 1 |
| Anal fissure | 2 | 3 |
| Urinary retention | 1 | 1 |
| Other | 2 | 1 |
| Surgery within 12 months for complications | 8 | 1 |
| Pain | 1 | 1 |
| Stricture | 2 | – |
| Anal fissure | 2 | – |
| Other | 3 | – |
| Complications at 24 months | 3 | 1 |
| Bleeding | 1 | – |
| Anal fissure | 1 | 1 |
| Other | 1 | – |
| Surgery within 24 months for complications | 2 | 0 |
| Stricture | 1 | – |
| Anal fissure | – | – |
| Other | 1 | – |
Adverse events
In total, there were 61 SAEs during the study; 59 participants [28 (7.2%) in the SH arm and 31 (8.0%) in the TH arm] had an event (Table 27). Table 28 gives details by randomisation group and Table 29 by the treatment received. There were two deaths in the SH arm, both unrelated to haemorrhoid surgery. One patient died while abroad 1 year after surgery, with the cause unknown; the other participant was randomised to receive SH but did not receive surgery, and the cause of death was ketoacidosis. The majority of SAEs by treatment received were related to pain (six in the SH arm and 10 in the TH arm), bleeding (six in the SH arm and one in the TH arm) and participants requiring catheterisation for urinary retention (seven in the SH arm and four in the TH arm). Two participants in each surgery arm had two episodes of pain, two required a blood transfusion; one had a low haemoglobin concentration prior to surgery and the other was readmitted 1 week post surgery with severe postoperative bleeding, which required extensive hospital stay. A combination of pain, constipation and bleeding occurred in a small number of participants, and one participant who received SH and two who received TH had pain caused by fissure.
| SAE | Trial arm | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Participants who had a SAE, n (%) | 28 (7.2) | 31 (8.0) |
| Total number of SAEs | 29 | 32 |
| Participant died,a n | 2 | – |
| Hospitalisation, n | 18 | 17 |
| Prolongation, n | 7 | 13 |
| Medically significant, n | 1 | 2 |
| Expected,b n | 26 | 31 |
| SAE | Trial arm, n | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Death (unrelated to the study) | 2 | – |
| Infection | 1 | – |
| Urinary retention | 3 | 8 |
| Difficulty passing urine | 2 | – |
| Paina | 6 | 10 |
| Pain and bleeding | 1 | 1 |
| Pain and stenosis | 1 | – |
| Stenosis | 1 | – |
| Pain caused by fissure | 1 | 2 |
| Constipation and urinary retention | – | 2 |
| Bleeding | 7 | – |
| Constipation | – | 3 |
| Pain and constipation | – | 1 |
| Constipation and bleeding | 1 | 1 |
| Pain, constipation and bleeding | – | 1 |
| Anaesthesia | – | 2 |
| Haemorrhoid symptoms | 1 | – |
| Fissure | 1 | – |
| SAE | Trial arm | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 352) | |
| Participants who had a SAE, n (%) | 25 (7.6) | 33 (9.2) |
| Total number of SAEs | 26 | 34 |
| Death (unrelated to the study), n | 1 | – |
| Infection, n | – | 1 |
| Urinary retention, n | 4 | 7 |
| Difficulty passing urine, n | 2 | – |
| Pain,a n | 6 | 10 |
| Pain and bleeding, n | 1 | 1 |
| Pain and stenosis, n | 1 | – |
| Stenosis, n | 1 | – |
| Pain caused by fissure, n | 1 | 2 |
| Constipation and urinary retention, n | – | 2 |
| Bleeding, n | 6 | 1 |
| Constipation, n | – | 3 |
| Pain and constipation, n | – | 1 |
| Constipation and bleeding, n | – | 2 |
| Pain, constipation and bleeding, n | – | 1 |
| Anaesthesia, n | – | 2 |
| Haemorrhoids symptoms, n | 1 | – |
| Fissure, n | 1 | – |
Subgroup analysis
Two subgroup analyses were planned on the primary outcome (EQ-5D-3L AUC over 24 months): sex and grade of haemorrhoid.
A stricter level of statistical significance (two-sided 1% significance level) was applied given the exploratory nature of the analyses.
There was no evidence that any of the subgroups were statistically different at the 1% level; the results are shown in Tables 30 and 31.
| Outcome | Trial arm, n, mean (SD) | MD (99% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 147, 1.531 (0.502) | 126, 1.626 (0.414) | – | – |
| Male | 148, 1.582 (0.464) | 149, 1.612 (0.446) | 0.055 (–0.087 to 0.197) | 0.295 |
| Grade of haemorrhoid | ||||
| II | 56, 1.545 (0.492) | 60, 1.532 (0.467) | – | – |
| III | 196, 1.564 (0.483) | 171, 1.657 (0.408) | –0.072 (–0.300 to 0.155) | 0.388 |
| IV | 43, 1.536 (0.482) | 44, 1.585 (0.458) | 0.050 (–0.302 to 0.403) | 0.696 |
| Outcome | Trial arm, n, mean (SD) | MD (99% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 388) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 158, 1.510 (0.505) | 139, 1.613 (0.427) | – | – |
| Male | 157, 1.572 (0.472) | 155, 1.605 (0.444) | 0.056 (–0.083 to 0.196) | 0.272 |
| Grade of haemorrhoid | ||||
| II | 61, 1.518 (0.507) | 67, 1.544 (0.446) | – | – |
| III | 206, 1.546 (0.491) | 183, 1.638 (0.425) | –0.036 (–0.265 to 0.192) | 0.663 |
| IV | 48, 1.548 (0.465) | 44, 1.585 (0.458) | 0.090 (–0.249 to 0.430) | 0.468 |
Chapter 6 Health economics
The perspective of the analyses is primarily that of the UK NHS. A supplementary analysis incorporates wider perspective costs, including participant travel costs, opportunity costs of time spent attending appointments for participants and companions, self-purchased health care and time off work as a result of haemorrhoidal surgery. The last analysis provides a wider scope on the economic consequences of haemorrhoidal surgery.
Over the 24-month study period, some participants were missing data from the key parameters for the analysis, such as the EQ-SD-3L score at the different time points, as well as resource use data. The results (Table 32) show that the number of missing data was broadly similar between arms and also increased over time.
| Variable | Trial arm, n (%) | % difference | All participants, n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 389) | TH (N = 386) | |||
| EQ-5D-3L | ||||
| Baseline | 1 (0.26) | 0 (0) | 0.26 | 1 (0.13) |
| 1 week | 91 (23.39) | 95 (24.61) | –1.22 | 186 (23.94) |
| 3 weeks | 104 (26.74) | 110 (28.5) | –1.76 | 214 (27.54) |
| 6 weeks | 84 (21.59) | 83 (21.5) | 0.09 | 167 (21.49) |
| 12 months | 98 (25.19) | 112 (29.02) | –3.83 | 210 (27.03) |
| 24 months | 106 (27.25) | 114 (29.53) | –2.28 | 220 (28.31) |
| QALYs | 183 (47.04) | 192 (49.74) | –2.7 | 375 (48.26) |
| Costs | ||||
| Intervention | 48 (12.34) | 26 (6.74) | 5.6 | 74 (9.52) |
| 12 months | 174 (44.73) | 171 (44.30) | 0.43 | 345 (44.40) |
| 24 months | 145 (37.28) | 153 (39.64) | –2.36 | 298 (38.35) |
| Total cost | 213 (54.76) | 208 (53.89) | 0.87 | 421 (54.18) |
Resource use
The details of the resources used for the surgical procedure, such as type of surgery, type of stapler used, operating surgeon grade, anaesthetist grade, type of anaesthesia, duration of operation and length of hospital stay, are reported (see Table 9). On average, the use of resources was similar across both arms. Details of the number of participants receiving further surgical interventions, such as removal of skin tags, TH, SH and RBL, are reported (see Table 21). The number of further interventions, was low over the 24-month period. For example, at the 6-week time point, eight participants received TH: six in the SH arm and two in the TH arm. Three participants (in the SH arm) and one (in the TH arm) received SH, while four (in the SH arm) and six (in the TH arm) had RBL. Five participants (in the SH arm) and four (in the TH arm) had further treatments for skin tags. The number of participants receiving non-surgical treatments, such as Botox and medical treatments, are reported (see Table 22). Further non-surgical interventions resource use was similar for both arms at 6 weeks post treatment. Further non-surgical interventions resource use was higher in the SH arm at 12 months (54 vs. 31 participants) and 24 months (39 vs. 19 participants). Table 33 below details participant-reported visits to outpatient department and GP. On average there were more visits in the SH arm.
| Resource | Trial arm, n, mean (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 389) | TH (N = 386) | |
| 12 months | ||
| Visit to outpatient department | 80, 1.74 (1.00) | 55, 1.51 (0.81) |
| Visit to GP (doctor) | 63, 2.02 (1.24) | 47, 1.85 (1.43) |
| Visit to GP (nurse) | 12, 1.58 (1.24) | 8, 1.38 (0.74) |
| Visit to other professionals | 11, 2.45 (1.75) | 7, 2.86 (3.24) |
| 24 months | ||
| Visit to outpatient department | 27, 1.89 (1.15) | 15, 1.47 (0.92) |
| Visit to GP (doctor) | 46, 2.00 (1.74) | 20, 1.70 (0.86) |
| Visit to GP (nurse) | 6, 2.17 (1.47) | 2, 1.50 (0.71) |
| Visit to other professionals | 5, 1.60 (0.89) | 3, 1.00 (0.00) |
The average surgery time used in the economic analysis was estimated using all available data. A few participants were missing either time of entry into the operating room and/or the time of leaving the operating room, so their time was estimated using available data. No data were collected on the time spent in the recovery room as it was assumed that this would have been similar in both treatment arms; it was therefore not included in the estimation of resource use.
Tables 34 and 35 detail the conversions of all the resource use into costs to the NHS and cost differences between the two arms. The estimates are reported in terms of NHS costs (see Table 34) incurred after the participant received the treatments. The mean total cost per patient in the SH arm was £921.80 (SD £586.90) and the mean cost of treatment in the TH arm was £620.65 (SD £582.98). There was a statistically significant difference in the (adjusted) total mean costs (£323, 95% CI £237 to £409) of the interventions.
| Resource | Trial arm, n, mean cost (£) (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 389) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Intervention | ||
| Staff time at operation | 349, 207.94 (81.76) | 360, 212.53 (87.69) |
| Anaesthetic used | 356, 14.06 (2.51) | 361, 14.25 (2.17) |
| Stapler | 346, 306.70 (153.83) | 362, 32.20 (111.10) |
| Admissions during intervention | 354, 51.45 (134.22) | 362, 48.57 (145.33) |
| Total intervention cost | 341, 581.06 (230.22) | 360, 308.00 (215.47) |
| 6-week follow-up | ||
| 6-week clinic visit | 348, 102.79 (45.08) | 357, 98.14 (48.97) |
| Additional hospital visit | 348, 10.32 (42.11) | 357, 12.55 (46.07) |
| Proctoscopy | 305, 3.03 (4.92) | 305, 3.03 (4.92) |
| Further intervention | 348, 12.67 (99.61) | 356, 18.91 (134.37) |
| Admissions | 348, 25.26 (253.27) | 355, 46.88 (279.80) |
| Prescribed medicines | 348, 3.45 (14.77) | 356, 3.31 (15.24) |
| Total 6-week cost | 305, 150.89 (313.94) | 304, 175.49 (389.75) |
| 12 months | ||
| Outpatient appointments | 274, 62.02 (117.10) | 258, 39.33 (88.37) |
| GP (doctor) | 276, 20.25 (45.38) | 259, 14.78 (41.16) |
| GP (nurse) | 278, 0.83 (4.93) | 259, 0.52 (3.25) |
| Other health professionals | 277, 6.01 (44.02) | 250, 1.51 (13.70) |
| Medicines prescribed | 258, 2.16 (7.71) | 236, 1.63 (6.58) |
| Admissions | 264, 61.77 (306.51) | 249, 32.73 (204.92) |
| Total after 6-week visit | 243, 138.28 (334.77) | 227, 80.56 (251.56) |
| Total cost to 12 months | 197, 869.23 (578.73) | 188, 547.42 (446.67) |
| 24 monthsa | ||
| Further intervention | 257, 36.18 (191.37) | 241, 20.75 (144.20) |
| Admissions | 256, 30.67 (238.69) | 241, 16.22 (111.87) |
| Outpatient appointments | 258, 25.64 (81.99) | 244, 10.65 (49.12) |
| GP (doctor) | 258, 15.98 (45.04) | 244, 5.92 (22.37) |
| GP (nurse) | 258, 0.59 (4.53) | 245, 0.19 (1.83) |
| Other health professionals | 258, 3.12 (26.51) | 245, 1.03 (10.14) |
| Medicines prescribed | 245, 0.67 (2.94) | 236, 0.29 (1.27) |
| Total 12–24 monthsa | 244, 102.41 (365.79) | 233, 56.49 (219.22) |
| Total over the 2 years | 158, 921.80 (586.90) | 156, 620.65 (582.98) |
| Resource | MDa (95% CI) | Standard error | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | |||
| Time of staff at operation | –4.95 (–18.40 to 8.50) | 6.57 | 0.46 |
| Anaesthetic used | –0.19 (–0.53 to 0.15) | 0.17 | 0.27 |
| Stapler | 274.52 (207.35 to 341.70) | 32.79 | 0.00 |
| Admissions | 2.56 (–21.62 to 26.75) | 11.81 | 0.83 |
| Total intervention | 272.62 (239.74 to 305.66) | 36.79 | 0.00 |
| 6-week follow-up | |||
| Proctoscopy | 0.05 (–0.51 to 0.61) | 0.27 | 0.85 |
| 6-week follow-up visit | 4.35 (–0.18 to 8.90) | 2.21 | 0.06 |
| Additional hospital visit | –2.31 (–9.69 to 5.07) | 3.60 | 0.53 |
| Further intervention | –5.87 (–21.28 to 9.55) | 7.53 | 0.44 |
| Inpatient stay | –21.91 (–53.30 to 9.48) | 15.32 | 0.16 |
| Prescribed medicines | 0.12 (–1.49 to 1.73) | 0.78 | 0.88 |
| Intervention: 6-week costs | –25.34 (–67.80 to 17.12) | 20.73 | 0.23 |
| 12 months | |||
| Further interventions | 25.69 (–23.30 to 74.67) | 23.91 | 0.29 |
| Outpatient appointment | 23.73 (7.39 to 40.06) | 7.98 | 0.01 |
| GP (doctor) | 5.86 (–1.64 to 13.36) | 3.66 | 0.12 |
| GP (nurse) | 0.39 (–0.31 to 1.08) | 0.34 | 0.26 |
| Other health professionals | 4.39 (1.47 to 7.32) | 1.43 | 0.01 |
| Medicines prescribed | 0.54 (–0.70 to 1.78) | 0.60 | 0.38 |
| Inpatient stay | 1.43 (–4.52 to 7.38) | 2.91 | 0.63 |
| 6-week: 12-month costs | 32.96 (–1.82 to 67.74) | 16.95 | 0.06 |
| Total 12-month costs | 308.50 (237.08 to 379.93) | 34.75 | 0.00 |
| 24 months | |||
| Further interventions | 16.86 (–11.94 to 45.67) | 14.06 | 0.24 |
| Outpatient appointment | 15.45 (3.52 to 27.38) | 5.82 | 0.01 |
| GP (doctor) | 10.20 (5.73 to 14.67) | 2.18 | 0.00 |
| GP (nurses) | 0.40 (–0.14 to 0.93) | 0.26 | 0.14 |
| Other health professionals | 2.18 (–0.73 to 5.09) | 1.42 | 0.14 |
| Medicines prescribed | 0.40 (0.03 to 0.76) | 0.18 | 0.03 |
| Inpatient stay | 15.86 (–10.93 to 42.66) | 13.08 | 0.24 |
| 12–24b months costs | 47.57 (13.32 to 81.82) | 16.72 | 0.01 |
| Total cost over the 24 months | 323.38 (237.11 to 409.64) | 41.97 | 0.00 |
The cost results reflect resource use results. A low level of resource use means that total cost data were skewed to the right, as most of the participants had low or no costs at all, but a few had high costs. Figures 6 and 7 illustrate the distribution of SH and TH costs, respectively.
FIGURE 6.
Distribution of cost data in the SH arm.

FIGURE 7.
Distribution of data in the TH arm.
Although cost of resource use measured during the intervention was similar in both arms, the mean cost of interventions was £272.62 higher in the SH arm (95% CI £239.74 to £305.66) because of the additional costs of the staplers (see Table 35). The costs reported at the 6-week visit were £25.34 lower in the SH arm (95% CI –£67.80 to £17.12), but not statistically significant. The other patient-reported costs between 6 months and 12 months were higher for SH (MD £32.96, 95% CI –£1.82 to £67.74) but not statistically significant, and the total 12-month costs were significantly higher in the SH arm (MD £308.50, 95% CI £237.08 to £379.93) than in the TH arm. The 12- to 24-month costs were significantly higher in the SH arm (MD £47.57, 95% CI £13.32 to £81.82). Total mean costs over the 24-month follow-up period were significantly higher in the SH arm (MD £323.38, 95% CI £237.11 to £409.64) than in the TH arm. The incremental differences are based on linear regression models, namely ordinary least squares with adjustments for baseline covariates, including baseline EQ-5D-3L score.
Quality-adjusted life-years
The EQ-5D-3L scores for the study arms at baseline, at 1 week, 3 weeks, 6 weeks, and at 12 and 24 months are shown in Table 36. The EQ-5D-3L scores were higher in the SH arm at 1 week and 3 weeks. However, the scores were lower at 6 weeks, 12 months and 24 months. From these data it was estimated that the mean QALYs over the 2 years were 1.676 (SD 0.384) in the SH arm and 1.738 (SD 0.334) in the TH arm.
| Time point | Trial arm, n, mean (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 389) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Baseline | 388, 0.762 (0.247) | 386, 0.764 (0.264) |
| 1 week | 298, 0.592 (0.315) | 291, 0.458 (0.337) |
| 3 weeks | 285, 0.802 (0.244) | 276, 0.750 (0.244) |
| 6 weeks | 305, 0.846 (0.220) | 303, 0.851 (0.235) |
| 12 months | 291, 0.822 (0.252) | 274, 0.880 (0.209) |
| 24 monthsa | 283, 0.802 (0.242) | 272, 0.841 (0.192) |
| QALYsb | 206, 1.676 (0.384) | 194, 1.738 (0.334) |
The MD between the arms in EQ-5D-3L score at 1 week, 3 weeks, 6 weeks, and at 12 and 24 months are reported below (Table 37). The MD in EQ-SD-3L scores after adjusting for minimisation factors and baseline EQ-SD-3L scores was statistically significantly higher for SH at 1 week (MD 0.135, 95% CI 0.082 to 0.188) and 3 weeks (MD 0.05, 95% CI 0.008 to 0.091), but was significantly lower at 12 months and 24 months. The QALY difference was –0.071 (95% CI –0.127 to –0.016) and was statistically significantly lower for the SH arm than the TH arm.
| Time point | MD (95% CI) | Standard error | t | p > t |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | 0.135 (0.082 to 0.188) | 0.026 | 5.230 | 0.000 |
| Week 3 | 0.050 (0.008 to 0.091) | 0.020 | 2.460 | 0.021 |
| Week 6 | –0.004 (–0.037 to 0.029) | 0.016 | –0.230 | 0.817 |
| 12 months | –0.064 (–0.095 to –0.033) | 0.015 | –4.210 | 0.000 |
| 24 monthsa | –0.046(–0.079 to –0.013) | 0.016 | –2.860 | 0.008 |
| QALYsb | –0.071 (–0.127 to –0.016) | 0.027 | –2.650 | 0.013 |
Cost–utility results
The base-case analysis was based on multiple imputed data. The estimated costs and QALYs are reported below (Table 38). Total cost was £337 (95% CI £251 to £423). Total QALYs were lower in the SH group (MD –0.074, 95% CI –0.127 to –0.011). Both these differences are statistically significant.
| Arm | Cost (£), mean (SD) | Cost (£) difference (£) (standard error), 95% CI | QALY, mean (SD) | Difference (standard error), 95% CI | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (n = 389) | 941 (415) | – | 1.62 (0.43) | – | Dominateda |
| TH (n = 386) | 602 (507) | 337 (41), 251 to 423 | 1.69 (0.38) | –0.070 (0.027), 0.127 to –0.011 | – |
The CEAC generated from the base-case cost-effectiveness analysis (Figure 8) shows that there is no probability of SH being cost-effective at the thresholds of £20,000 and £30,000.
FIGURE 8.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability that SH is cost-effective, given the different values of WTP thresholds.

The scatterplot (Figure 9) shows the point estimate and the distribution of the joint differences in costs and effects. The ICER point estimate and almost all of the bootstrapped estimates fall in the north-west quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane, suggesting that SH is significantly more costly and less clinically effective than TH.
FIGURE 9.
Cost-effectiveness scatterplot illustrating the distribution of differences in costs and QALYs.
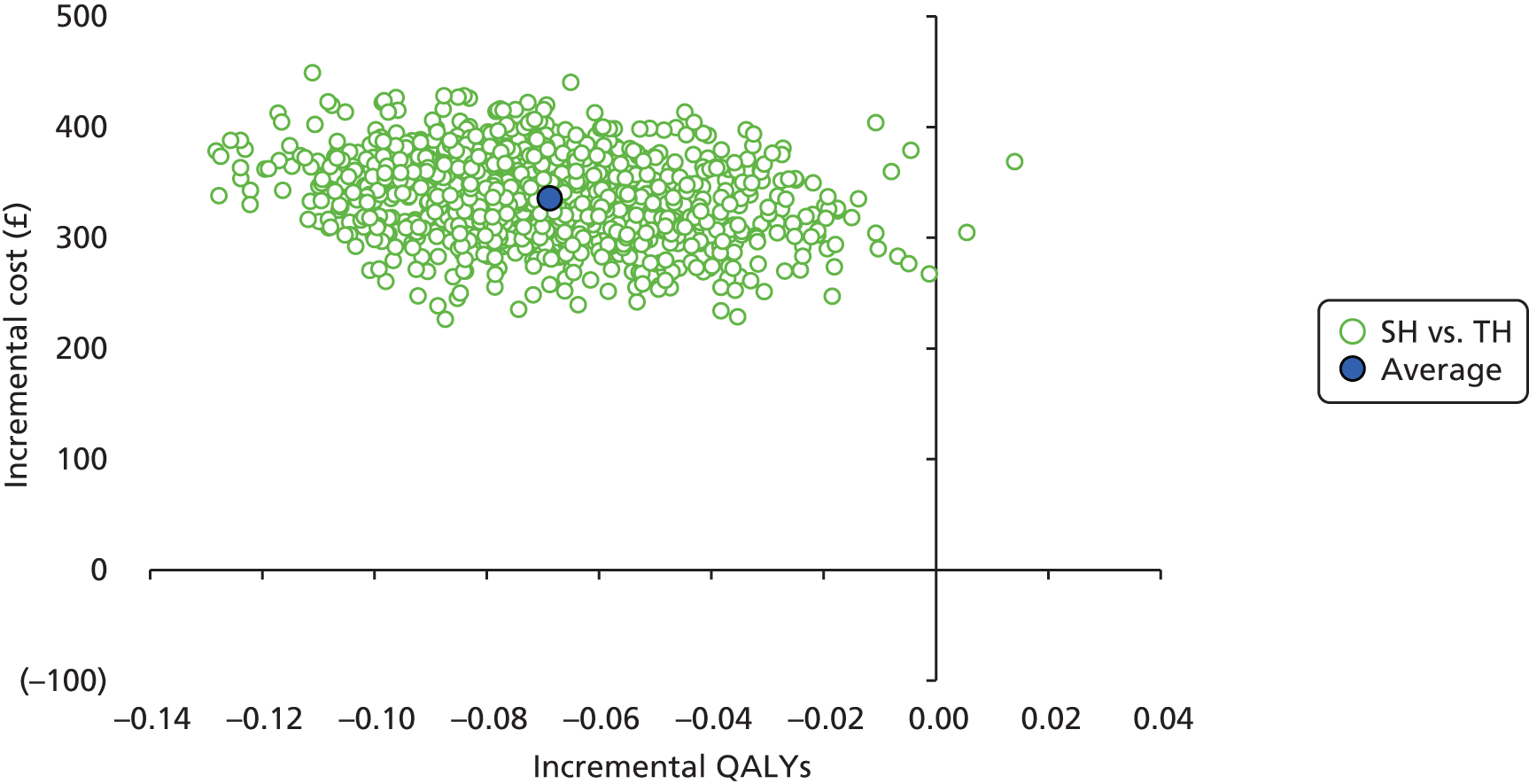
Cost-effectiveness results: number of recurrences averted
The results of the cost-effectiveness analysis based on the number of recurrences averted were similar to those of the base-case analysis (Table 39). On average, there were more recurrences in the SH arm and SH was more costly than TH. SH was dominated by TH.
| Arm | Cost (£), mean (SD) | Cost (£) difference (standard error), 95% CI | Recurrences, mean (SD) | Difference (standard error), 95% CI | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (n = 389) | 941 (415) | – | 0.327 (0.008) | – | Dominateda |
| TH (n = 386) | 602 (507) | 337 (41), 251 to 423 | 0.142 (0.006) | –0.18 (0.030), –0.245 to –0.120 | – |
Subgroup analysis
The results allowing for a treatment interaction with sex provide similar results to those of the base-case analysis. On average, SH cost £334.78 more than TH and had –0.069 QALYs fewer than TH. There was a 2.4% probability of being considered cost-effective at a £30,000 threshold (Figure 10).
FIGURE 10.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability that SH is cost-effective, given the different values of WTP thresholds for subgroup analysis investigating the influence of sex.

The ICER plot estimate falls in the north-west quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane, suggesting that SH is more costly and less clinically effective than TH (Figure 11).
FIGURE 11.
Cost-effectiveness scatterplot illustrating the distribution differences of costs and QALYs for the analysis interacting treatment with sex.

The results of the subgroup analysis incorporating a treatment interaction with haemorrhoidal grade were broadly similar to those of the base-case analysis. Allowing for grade-specific effects, on average, SH had higher costs and lower QALYs than TH. However, the chance that SH might be considered to be cost-effective at the £30,000 threshold increased to 6% (Figure 12).
FIGURE 12.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability that SH is cost-effective, given the different values of WTP thresholds for subgroup analysis incorporating a treatment interaction with haemorrhoidal grade.

The ICER plot estimate falls in the north-west quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane, suggesting that SH is more costly and less clinically effective than TH (Figure 13).
FIGURE 13.
Cost-effectiveness scatterplot illustrating the distribution of differences in costs and QALY for the analysis incorporating a treatment interaction with haemorrhoidal grade.
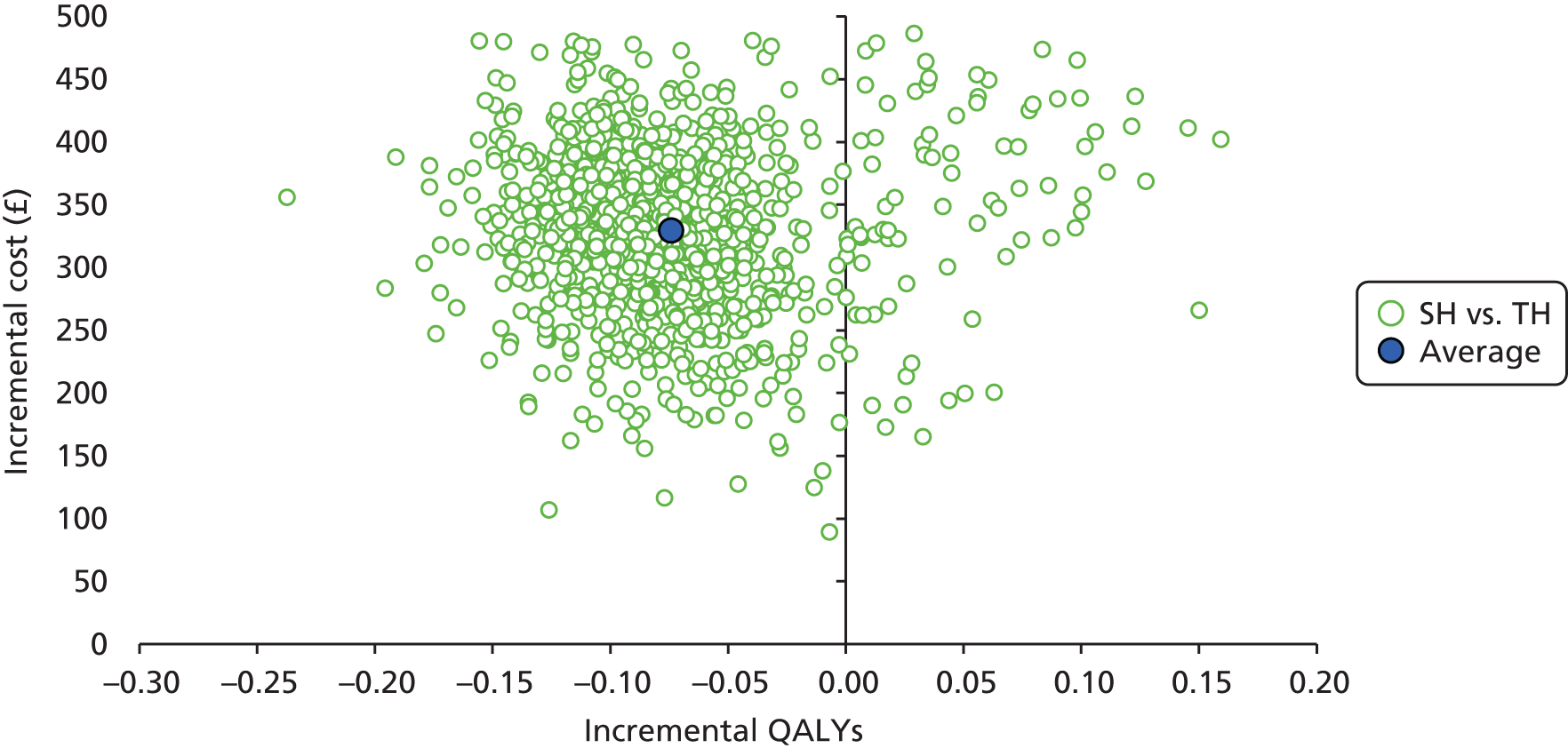
Sensitivity analysis
Complete-case analysis
The results of the analysis considering the complete cases (based on participants with both cost and QALY data) are presented in Table 40. On average, SH cost £287.87 (95% CI £190.17 to £385.56) more than TH and had –0.060 (95% CI –0.113 to –0.007) fewer QALYs than TH.
| Trial arm | Costs (£), n, mean (SD) | Cost (£) difference (standard error), 95% CI | QALY, n, mean (SD) | Difference (standard error), 95% CI | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 389) | 148, 863.91 (415) | – | 148, 1.72 (0.33) | – | Dominateda |
| TH (N = 386) | 149, 573.27 (507) | 287.87 (47.33), 190.17 to 385.56 | 149, 1.77(0.30) | –0.060 (0.026), –0.113 to –0.007 | – |
The results of the complete-case analysis were broadly similar to those of the base-case analysis. On average, SH had higher costs and fewer QALYs than TH. The probability that SH might be considered to be cost-effective at the £30,000 threshold was 1.7% (Figure 14).
FIGURE 14.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability that SH is cost-effective, given the different values of WTP thresholds (complete-case analysis).

The ICER plot estimate falls in the north-west quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane, showing SH to be more costly and less clinically effective than TH (Figure 15).
FIGURE 15.
Cost-effectiveness scatterplot illustrating the distribution of differences in costs and QALYs for sensitivity analysis (complete-case analysis).

Sensitivity analysis using Short Form questionnaire-36 items data
The utility and QALY scores derived from the SF-36D followed a similar pattern to those of the EQ-5D-3L (Table 41). On average, the 6-week utility score in the SH arm was –0.015 lower than that in the TH arm, but this did not meet statistical significance. However, the utility score was also lower at 12 months (–0.040) and 24 months (–0.034), and these differences were statistically significant (p < 0.05) (Table 42). The number of QALYs was –0.063 (95% CI –0.107 to –0.018) lower in the SH arm than in the TH arm.
| Time point | Trial arm, n, mean score (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| SH (N = 389) | TH (N = 386) | |
| Baseline | 376, 0.736 (0.144) | 370, 0.745 (0.143) |
| 6 weeks | 255, 0.741 (0.142) | 268, 0.747 (0.148) |
| 12 months | 254, 0.758 (0.154) | 241, 0.796 (0.147) |
| 24 months | 239, 0.776 (0.144) | 222, 0.800 (0.131) |
| QALYs | 161, 1.540 (0.263) | 156, 1.600 (0.238) |
| Time point | MD (95% CI) | Standard error | t | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 weeks | –0.015 (–0.37 to 0.007) | 0.010 | –1.32 | 0.168 |
| 12 months | –0.040 (–0.070 to –0.010) | 0.015 | –2.73 | 0.012 |
| 24 monthsa | –0.034 (–0.062 to –0.006) | 0.013 | –2.52 | 0.019 |
| QALYs | –0.063 (–0.107 to –0.018) | 0.021 | –2.92 | 0.008 |
The CEAC (Figure 16) indicates that there is only a 0.1% chance of SH being considered cost-effective at WTP thresholds of £20,000 or £30,000 (based on QALYs derived from the SF-6D). The ICER plot estimate falls in the north-west quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane, suggesting that SH is more costly and less clinically effective than TH (Figure 17).
FIGURE 16.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability that SH is cost-effective, given the different values of WTP thresholds: sensitivity analysis using SF-6D data.

FIGURE 17.
Cost-effectiveness scatterplot illustrating distribution of cost and QALY differences for sensitivity analysis (SF-6D data).
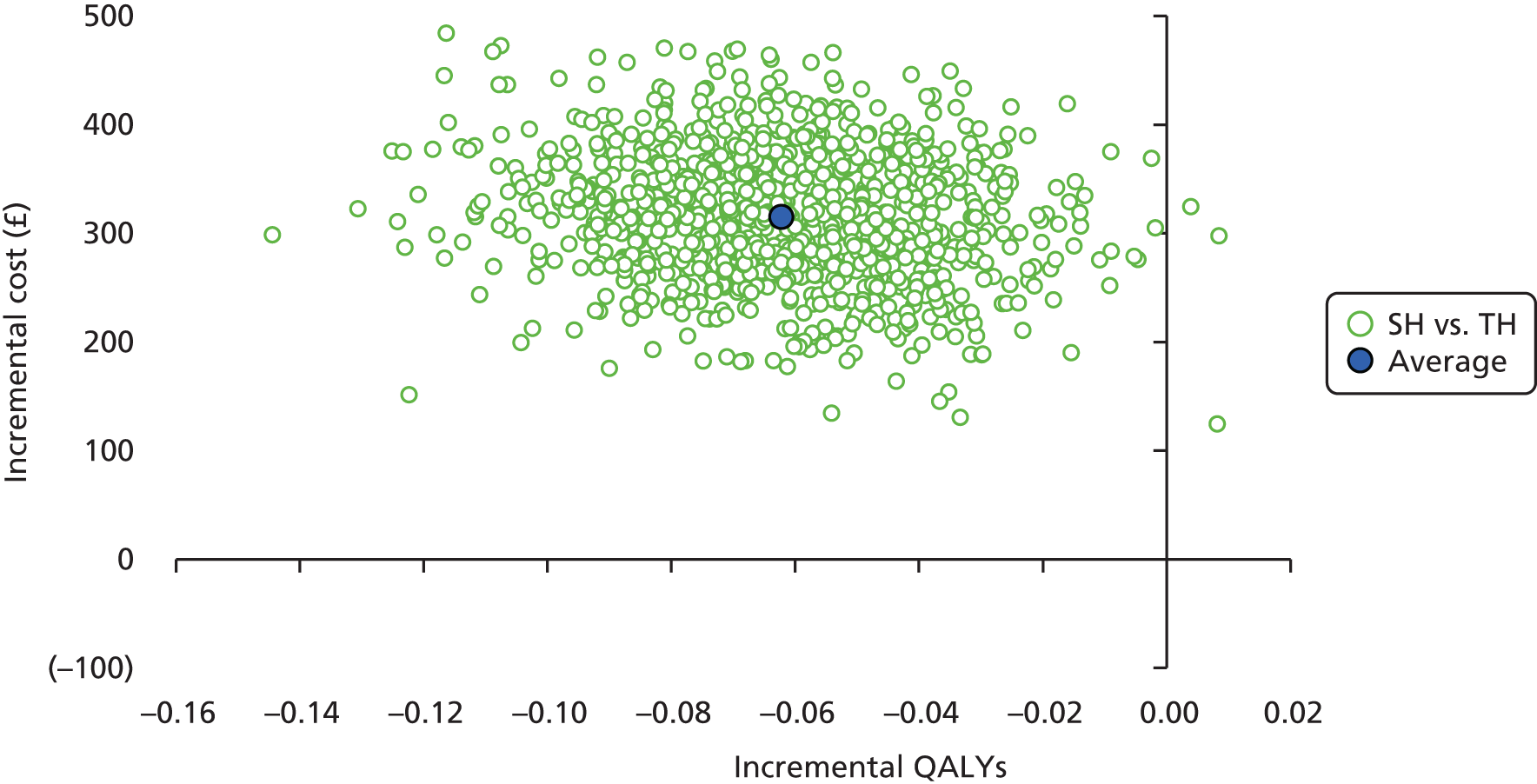
Sensitivity relating to cost of staplers
Further analysis was undertaken varying the cost of the staplers and using the least expensive of those used in the study (Table 43). The QALY difference remains the same as before (–0.070, 95% CI –0.127 to –0.011) (see Table 38). The results were similar to those of the base-case analysis. For costs of ≥ £125, SH costs significantly more and has fewer QALYs than TH. SH remains marginally more costly than TH, unless the cost of the stapler falls to zero.
| Cost of stapler (£) | Cost (£) difference (95% CI) | Standard error | t | p-value | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 269 | 216.45 (123.62 to 309.28) | 45.07 | 4.80 | 0.000 | SH dominated |
| 150 | 118.55 (30.83 to 206.28) | 42.60 | 2.78 | 0.010 | SH dominated |
| 125 | 98.10 (11.14 to 185.05) | 42.22 | 2.32 | 0.029 | SH dominated |
| 100 | 77.64 (–8.67 to 163.93) | 41.90 | 1.85 | 0.076 | SH dominated |
| 75 | 57.18 (–28.57 to 142.92) | 41.64 | 1.37 | 0.182 | SH dominated |
| 50 | 36.72 (–48.61 to 122.03) | 41.42 | 0.89 | 0.384 | SH dominated |
| 45 | 32.62 (–52.62 to 117.87) | 41.40 | 0.79 | 0.438 | SH dominated |
| 0 | –4.20 (–89.0 to 80.59) | 41.17 | –0.10 | 0.919 | 60 |
The results of the analysis in which it was assumed that there was no additional cost of staplers suggest that SH has a 0.1% chance of being considered cost-effective at the £20,000 and £30,000 thresholds (Figure 18).
FIGURE 18.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability that SH is cost-effective, given the different values of WTP thresholds: assuming no cost of stapler.

The ICER plot estimate falls in the north-west quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane, suggesting that SH is more costly and less clinically effective than TH (Figure 19). The cost difference estimate is lower (£216) than that of the base case (£323), so the ellipse is lower than that of the base case.
FIGURE 19.
Cost-effectiveness scatterplot illustrating the distribution of cost and QALY differences: sensitivity analysis assuming no cost of stapler.

Participant costs
The distribution patterns of the participant costs are similar to those of the main analysis (Figures 20 and 21). There are many participants with low costs and very few with high costs. The average participant costs were £31.48 (95% CI £5.00 to £57.00) higher for SH (£69.83, SD 229.33) than for TH (£38.35, SD 72.80). This further increases the total cost difference between the arms.
FIGURE 20.
Distribution of total participant costs in the SH arm.

FIGURE 21.
Distribution of total participant costs in the TH arm.
The cost–utility analysis based on the imputed data is reported in Table 44. On average, the cost indicates that the SH arm has £326.11 higher costs and –0.070 fewer QALYs than the TH arm. Like the base-case analysis, there was no chance that SH would be cost-effective at the £20,000 threshold and a 0.1% chance that it would be cost-effective at the £30,000 threshold (Figure 22).
| Variable | MD (95% CI) | Standard error | p-value | ICER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Costs (£) | 326.11 (215.02 to 437.20) | 53.94 | 0 | – |
| QALYs | –0.070 (–0.127 to –0.011) | 0.027 | 0.11 | SH dominated |
FIGURE 22.
Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability that SH is cost-effective, given the different values of WTP thresholds: sensitivity analysis including societal cost.

The ICER plot estimate falls in the north-west quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane, suggesting that SH is more costly and less clinically effective than TH (Figure 23).
FIGURE 23.
Cost-effectiveness scatterplot illustrating the distribution of cost and QALY differences as per sensitivity analysis: including societal costs.
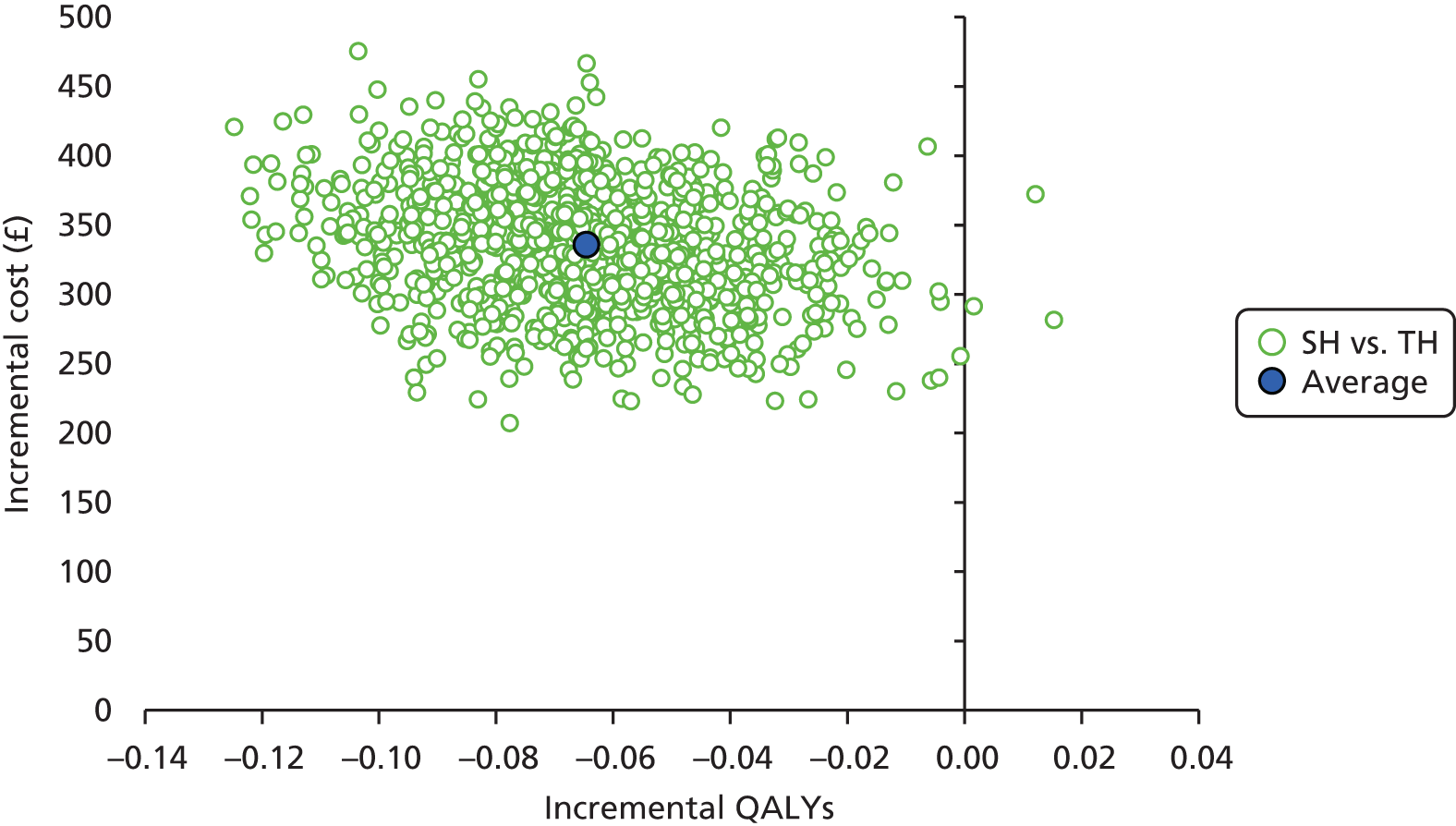
Discussion
Summary of the main findings
The results of the base-case analysis suggest that, on average, SH costs £337 more than TH and has –0.0704 fewer QALYs than TH. The cost–utility analysis suggests that there is no chance of SH being considered cost-effective at £20,000, and a very low chance of being considered cost-effective (0.01%) at the £30,000 WTP threshold. Similar results are seen in all the analyses that were conducted. The sensitivity analyses using the complete cases and SF-6D were similar to the base-case results: SH always costs more than TH and generates fewer QALYs than TH. Results of the analysis incorporating subgroup interaction terms relating to sex were similar to those of the base-case analysis, but those of the analysis incorporating an interaction for the grade of haemorrhoid had a higher chance (6%) of SH being considered to be cost-effective at a WTP threshold of £30,000.
The major driver for the increased cost of SH was the cost of staplers, but the sensitivity analysis shows that the cost-effectiveness conclusions are not particularly sensitive to this parameter, because of the superior QALY estimates for TH. This was a pragmatic study and study sites were allowed to use the stapler of their choice. Sensitivity analyses varying the cost of the stapler suggest that the cost of the stapler would have to fall to zero for the difference in cost results to change in favour of SH. However, the cost-effectiveness results would lie in the segment of the south-west quadrant of the cost-effectiveness plane (SH would cost less than TH, but have fewer QALYs than TH) where the cost savings do not outweigh the associated QALY losses.
Strengths
A key strength of the study was that it was a multicentre study with centres across the UK that followed up participants for 24 months. In addition, it is the first RCT to compare SH with TH. The incorporation of a wider economic perspective on costs as a secondary analysis adds value in terms of a broader economic perspective and understanding of the non-health-care costs to participants, their families and the economy more generally, of haemorrhoid symptoms and treatments. The analysis of QALYs based on EQ-5D-3L patient-level responses follows best practice and is another advantage. It is also reassuring that QALYs based on the alternative SF-6D instrument produce similar results.
Challenges
One of the challenges of the economic analysis was the number of missing data. Summaries of missing data indicated that the number of missing data was similar in both arms. MI methods that assumed the data to be missing at random were conducted to address this challenge. However, the results of the two analyses presented for imputed data set and complete case were similar, and the main conclusion remained the same irrespective of the approach.
Conclusion
The results of the within-trial analysis show that SH costs more and is less clinically effective than TH. These results were conclusive and supported by the sensitivity analyses and the fact that secondary outcomes such as tenesmus were more prevalent in the SH arm (p < 0.001), and more participants reported recurrence of haemorrhoids at both 12 and 24 months.
Chapter 7 Delivering person-centred care: what do the public and patients want (discrete choice experiment)
Background
Discrete choice experiments (DCEs) were introduced into health economics to value aspects of care beyond QALYs, and thus inform the delivery of public- and patient-centred care. 47,48 Research funding programmes such as the NIHR HTA programme (UK)49 are increasingly using applications of DCEs to assess what the public and patients want from the delivery of health care to inform key stakeholders such as policy-makers (NICE), researchers, NHS health professionals and the general public.
The DCE method can be used to assess the values of outcomes beyond QALYs in the delivery of treatment for haemorrhoids. Burch et al. 2 found that the outcomes of SH and TH differed in terms of short-term outcomes (earlier return to usual activities, pain) and the risk of recurrence. There was some concern that the recommended quality-of-life measurement (and QALYs based on it)25 may not fully measure the change in quality of life, as it would not capture all the aspects that represent patients’ preferences for treatments and their associated outcomes. The objectives of the DCE were to:
-
investigate the outcomes of haemorrhoidal treatment that matter to individuals and their relative importance
-
estimate the value of such outcomes using WTP, a monetary measure of value for outcomes
-
compare costs and benefits in monetary terms, within a cost–benefit analysis framework, using this person and patient-centred measure of value
-
compare the results from the standard cost–utility analysis approach (cost per QALY) with the cost–benefit analysis results.
The DCE included an additional surgical intervention, HAL, to take into account all the treatment options currently available to patients with haemorrhoids (and considered within the study).
Methods
Developing the discrete choice experiment
Discrete choice experiments involve four stages: (1) identification of attributes and levels; (2) questionnaire development; (3) data collection; and (4) data analysis and interpretation. 50,51
Stage 1: identification of attributes and levels
The first stage is to define the attributes or factors important in the treatment of haemorrhoids. The attributes, derived from a previous study2 and expert advice, are shown in Table 45. Time in postoperative pain had an impact as it could last up to 4 weeks post surgery. Chance of serious complications took account of post-surgery effects such as skin tags, which can cause pruritus and difficulty with personal hygiene, and may need further intervention to remove. Other complications that could lead to hospitalisation, such as bleeding, wound and systemic infections, faecal and urinary incontinence, anal stenosis and anastomotic stricture, were also important. Time taken to return to usual activities would have an impact on patients, particularly those of working age. Chance of recurrent prolapse might lead to the need for further treatment. To allow the estimation of WTP for attributes, and thus monetary values of different treatments within a cost–benefit analysis framework, a cost-of-treatment attribute was included.
| Attribute and description | Level |
|---|---|
| Time in postoperative pain | |
| This describes the number of days in which you are in pain during the first 6 weeks after your operation. This is pain that requires taking painkillers for relief. For example, the pain may last for: |
|
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation | |
| This refers to complications/side effects of the treatment that could lead to visiting a health-care provider, such as accident and emergency department visits or spending a few days in hospital. These complications could include severe bleeding/haemorrhage, abscess after operation, infection and urinary or faecal incontinence. For example, the chance might be that of: |
|
| Time taken to return to usual activities | |
| This describes the time that it may take you to return to your usual activities, such as work, housekeeping, leisure or studying |
|
| Chance of a recurrence of haemorrhoidal symptoms | |
| This describes the chance that in 12 months’ time the symptoms you had before your surgery might come back. These symptoms include minor bleeding, itching, pain and skin tags |
|
| Cost of treatment | |
| This refers to how much you would value the surgical interventions. One way of finding out the value is to find out how much you would be willing to pay for such a service. Please consider what you would be personally willing and able to pay for the service you choose. Remember that any money you spend on this service will not be available to spend on other things |
|
Levels for the attributes were derived from the study data and discussions with gastroenterology experts. Levels were anchored on the minimum and maximum number of days in pain postoperatively and time to return to usual activities, and the chance of serious complications or recurrence cited in the literature. Levels for the cost attribute were defined from a pre-pilot WTP survey (see Table 45).
Stage 2: questionnaire development
The five attributes and four levels yield 1024 possible profiles (55), too many to present to individuals. SAS version 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used to develop a D-efficient fractional factorial design to reduce the profiles to a manageable level while still being able to infer utilities (or benefit) for all possible choices. 52 The experimental design maximises the precision of estimated parameters (by maximising the D efficiency, a summary measure of the variance–covariance matrix) for a given number of choice sets. The design had 32 choice sets, which were randomly split into four questionnaires, each containing eight choice tasks (see Appendix 1). For each choice, respondents were asked to state which option they would choose: excisional (TH), artery ligation (HAL), stapled (SH) or no treatment. The no-treatment or opt-out alternative was included to reflect reality, as patients can choose not to be treated. An example of a choice set is shown in Table 46.
| Attribute | Excisional | Artery ligation | Stapled | No treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (days) in postoperative pain | 7 | 21 | 30 | If you do not seek treatment your symptoms will persist and possibly become worse |
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation | 20 in 1000 people (2%) | 30 in 1000 people (3%) | 10 in 1000 people (1%) | |
| Time (days) taken to return to usual activities | 21 | 30 | 42 | |
| Chance of a recurrence of haemorrhoidal symptoms | 21 in 1000 people (2.1%) | 15 in 1000 people (1.5%) | 18 in 1000 people (1.8%) | |
| Cost (£) of treatment | 300 | 400 | 200 | |
| Which would you choose (please tick one) | Excisional | Artery ligation | Stapled | No treatment |
| ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
The questionnaire also contained a description of the DCE task, a description of the attributes and levels and an example of a completed choice set. Information was also collected on respondents’ sex, age, income, health status (EQ-5D-3L) and experience of haemorrhoids.
Stage 3: respondent recruitment and data collection
An important consideration in preference elicitation is whose preferences to elicit. 53 Should it be the general population, whose resources are being allocated (and whose values are used for the EQ-5D-3L), or patients who have experience of the disease? If preferences differ across groups, making decisions based on one group’s preferences may be suboptimal for the other. Therefore, patients who have the experience of both disease and treatment and the general population were considered appropriate for this study.
The patient sample was recruited from the study participants. A total of 293 study participants were sent a pen-and-paper questionnaire 24 months after treatment. The general population sample was recruited from members of a commercial online panel (Research Now). 54 Panel members were sent an e-mail inviting them to complete the online survey. The survey was pre-piloted among a small sample of the research group and the HSRU, University of Aberdeen, to refine all practical aspects of the survey, such as explanations and presentation of choices and to ensure that respondents were understanding and making trade-offs between the attributes. The pilot questionnaire was sent to 50 members of the online survey panel to ensure that respondents would trade and to ensure that the results were meaningful (with estimated parameters moving in the expected direction).
Stage 4: data analysis
The following model was used to analyse the responses:
in which ‘U’ is the utility (or benefit) for a defined profile, given levels of each attribute.
The parameters β1 to β8 are the coefficients of the model to be estimated and their interpretation depends on their unit of measurement. Parameters β1 to β3 are the treatment options TH, HAL and SH, which are measured relative to no treatment. The coefficients β4 to β8 are continuous, indicating their relative importance, or weight, for a unit change such as a 1% change in chance of recurrence of haemorrhoidal symptom on utility.
The rate at which respondents are willing to trade between these attributes (i.e. how much of the attribute they are willing to give up for the improvements in other attributes), is shown by the ratio of the coefficients; for example, β4 divided by –β6 indicates how much longer respondents are willing to wait before returning to usual activities in order to have reduced days in postoperative pain. The trade-offs respondents make between the cost of haemorrhoids and other attributes represents respondents’ WTP for (or their value of) a unit change in attribute level. The marginal WTP (mWTP) for a unit change in one of the attributes is estimated as:
For example, (β4/β8) is respondents’ mWTP for reducing the time in postoperative pain by 1 day and (β5/β8) is respondents’ WTP for reducing the risk of complications by 1%. The mWTP was estimated for all attribute levels, and CIs for these values were calculated using a parametric bootstrap with 1000 replications of the model. 55
Equation 2 was estimated using the mixed-logit regression model, using Stata. This model allows for unobserved preference heterogeneity (variation in preferences across the sample, meaning that preferences cannot be adequately represented by the sample mean). We allowed for preference heterogeneity with respect to TH, HAL and SH, and assumed a normal distribution. Statistically significant SDs provide evidence of preference heterogeneity.
Cost–benefit analysis
A cost–benefit analysis was undertaken to compare costs and benefits, in monetary terms, of the two treatment options valued within the trial: SH and TH. To estimate total WTP for a defined option (SH or TH treatment) mWTP values for all attributes were combined with the average levels for each attribute for each treatment option. Actual levels for attributes and average treatment costs were informed by the trial data. A net benefit (benefits minus costs) was generated for SH and TH.
Results
Respondent characteristics
Although 1394 individuals accessed the web-based survey, 364 respondents dropped out and seven declined to take part, resulting in 1010 respondents (77.5%) completing the online questionnaire. Table 47 presents a summary of respondents’ characteristics. The mean age was 46 years, 51% were male (n = 511) and 44% reported that they had experienced haemorrhoids (n = 441). The respondents had an average utility score of 0.84. Over half of respondents (61%) were in some form of employment and 70% had at least secondary school-level education. Respondents were evenly distributed across income groups.
| Participant characteristics | Respondents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Web-based survey, n | % | Study participants, n | % | |
| Total sample size | 1010 | 100 | 193 | 100 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 511 | 51 | 101 | 52 |
| Female | 499 | 49 | 92 | 47 |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 1010 | 46 (16) | 193 | 54 (13) |
| Education | ||||
| 1–4 O levels/CSEs/GCSEs (any grades) | 188 | 19 | 7 | 4 |
| NVQ/SVQ Level 1 or 2, GNVQ/GSVQ | 94 | 9 | 11 | 6 |
| ≥ 5 O levels (passes) | 253 | 25 | 10 | 5 |
| Apprenticeship | 39 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| ≥ 2 A levels/VCE | 217 | 21 | 1 | 1 |
| NVQ/SVQ Level 3 | 113 | 11 | 16 | 8 |
| Degree | 400 | 40 | 19 | 10 |
| Professional qualifications | 169 | 17 | 34 | 18 |
| Other qualifications | 122 | 12 | 47 | 25 |
| Foreign qualifications | 12 | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| No qualifications | 34 | 3 | 30 | 16 |
| Prefer not to say | 12 | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| Employment status in the last week | ||||
| Employee | 497 | 49 | 60 | 33 |
| Self-employed or freelance | 122 | 12 | 1 | 1 |
| On a government training scheme | 6 | 1 | 10 | 5 |
| Working alone or family’s business | 21 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Away from work: ill, maternity leave, on holiday or temporarily laid off | 17 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Doing any other kind of paid work | 16 | 2 | 68 | 37 |
| Actively looking for a job | 36 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Unemployed | 36 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| Retired | 187 | 19 | 4 | 2 |
| Student | 56 | 6 | 18 | 10 |
| Looking after home or family | 82 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Long-term sick or disabled | 46 | 5 | 7 | 4 |
| Other: please specify | 8 | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| Annual income | ||||
| Up to £5199 per year | 70 | 6 | 6 | 3 |
| £5200 and up to £10,399 per year | 109 | 11 | 27 | 14 |
| £10,400 and up to £15,599 per year | 114 | 11 | 22 | 12 |
| £15,600 and up to £20,799 per year | 107 | 11 | 28 | 15 |
| £20,800 and up to £25,999 per year | 112 | 11 | 17 | 9 |
| £26,000 and up to £31,199 per year | 91 | 9 | 13 | 7 |
| £31,200 and up to £36,399 per year | 68 | 7 | 9 | 5 |
| £36,400 and up to £51,999 per year | 107 | 10 | 19 | 10 |
| £52,000 and above per year | 109 | 11 | 12 | 6 |
| Prefer not to say | 123 | 13 | 36 | 19 |
| Experienced haemorrhoids | ||||
| Yes | 441 | 44 | 193 | 100 |
| No | 569 | 56 | 0 | 0 |
| General health | ||||
| Mean EQ-5D score (SD) | 1010 | 0.839 (0.023) | 191 | 0.880 (0.19) |
| Study treatment allocation | ||||
| SH | NA | NA | 93 | 48 |
| TH | NA | NA | 100 | 52 |
Of the 293 questionnaires sent to the eTHoS study participants, 66% (n = 193) were returned. The mean age was 54 years old and 52% were male (n = 101). The respondents’ average utility score was 0.88. Respondents were evenly distributed across income groups (Table 47).
Results: web-based sample
Over all of the choices presented in the web-based DCE, 32% were for TH treatment, 30% for HAL treatment, 31% for SH treatment and 7% for no treatment. Very few respondents chose no treatment (8%). Table 48 reports the results of the DCE analyses.
| Attribute | Coefficient (95% CI) | Standard error | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean preferencesa | |||
| TH | 5.043 (4.802 to 5.284) | 0.123 | < 0.001 |
| HAL | 4.995 (4.761 to 5.228) | 0.119 | < 0.001 |
| SH | 4.709 (4.482 to 4.936) | 0.116 | < 0.001 |
| Time in postoperative pain | –0.043 (–0.046 to –0.040) | 0.002 | < 0.001 |
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation | –0.369 (–0.411 to –0.326) | 0.022 | < 0.001 |
| Time taken to return to usual activities | –0.030 (–0.033 to –0.028) | 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Chance of a recurrence of haemorrhoidal symptoms | –0.030 (–0.033 to –0.028) | 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Cost of treatment | –0.568 (–0.636 to –0.501) | 0.034 | < 0.001 |
| Measures of variability in preferences (SD) | |||
| TH | 1.238 (1.118 to 1.359) | 0.061 | < 0.001 |
| HAL | 1.119 (1.005 to 1.233) | 0.058 | < 0.001 |
| SH | 1.248 (1.125 to 1.372) | 0.063 | < 0.001 |
The coefficients for treatment options (TH, 5.043; HAL, 4.995; and SH, 4.709) are all statistically significant and positive. This indicates that everything else being equal, respondents have a general preference for being treated over not being treated. However, the coefficients for TH, HAL and SH are not significantly different from each other, with CIs overlapping. This suggests that respondents did not distinguish between the three treatment options (everything else being equal).
The SDs for TH, SH and HAL (see the lower part of Table 48) are statistically significant, indicating preference heterogeneity for treatment options. Under the mixed-logit model assumptions in which TH, HAL and SH are normally distributed, these results still suggest that almost 100% of the population prefer treatment over no treatment. The coefficients for all the attributes are statistically significant and, as expected, negative. This indicates face validity for the model, with increases in all attributes reducing the utility and probability of take-up of a given treatment option. The magnitude of the coefficients show the impact of a unit change in the attribute. For example, a 1% increase in the chance of recurrence of haemorrhoids reduces utility by –0.568 and a 1% increase in chance of serious complications needing hospitalisation reduces utility by –0.369.
Willingness to pay: a monetary measure of value
Marginal WTP values are shown in Table 49. Respondents are willing to pay £1802 to move from no treatment to TH, £1785 to move to HAL and £1683 to move to SH. Although WTP is highest for TH, the values are not statistically significantly different. Everything else being equal, respondents were willing to pay £203 for a 1% reduction in the chance of recurrence of haemorrhoidal symptoms; £132 for a 1% reduction in the chance of serious complications requiring readmission; £15 for a 1-day reduction in time spent in postoperative pain; and £11 for a 1-day reduction in time taken to return to usual activities.
| Attribute | WTP (£) (95%CI) | Preference interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| TH | 1802 (1636 to 1968) | Willing to pay £1802 to move from no treatment to TH |
| HAL | 1785 (1623 to 1946) | Willing to pay £1785 to move from no treatment to HAL |
| SH | 1683 (1533 to 1833) | Willing to pay £1683 to move from no treatment to SH |
| Time in postoperative pain | –15 (–17 to –13) | If time increases by 1 day, then WTP decreases by £15 |
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation | –132 (–151 to –112) | If risk increases by 1%, then WTP decreases by £132 |
| Time taken to return to usual activities | –11 (–12 to –9) | If time increases by 1 day, then WTP decreases by £11 |
| Chance of a recurrence of haemorrhoidal symptoms | –203 (–233 to –173) | If risk increases by 1%, then WTP decreases by £203 |
Results from eTHoS participants
The study participants’ results were similar to those of the web-survey group (Table 50). All treatment attributes were significant at the 5% level, suggesting that they all influenced preferences for haemorrhoidal treatments. Although the cost attribute was negative, it was not statistically significant. It was therefore not possible to calculate WTP values for the trial participants.
| Attribute | Coefficient (95% CI) | p > z | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean preferences | |||
| THa | 7.173 (6.300 to 8.046) | p < 0.001 | |
| HAL | 6.669 (5.881 to 7.457) | p < 0.001 | |
| SH | 7.029 (6.222 to 7.837) | p < 0.001 | |
| Time in postoperative pain | –0.047 (–0.056 to –0.038) | p < 0.001 | |
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation | –0.520 (–0.642 to –0.397) | p < 0.001 | |
| Time taken to return to usual activities | –0.036 (–0.043 to –0.029) | p < 0.001 | |
| Chance of a recurrence of haemorrhoidal symptoms | –1.175 (–1.373 to –0.977) | p < 0.001 | |
| Cost of treatment | 0.000 (–0.001 to 0.001) | 0.776 | |
| Measures of variability in preferences (SD) | |||
| TH | 2.271 (1.737 to 2.805) | p < 0.001 | |
| HAL | 1.934 (1.438 to 2.430) | p < 0.001 | |
| SH | 2.180 (1.636 to 2.723) | p < 0.001 | |
Cost–benefit analysis
Table 51 shows the results of the cost–benefit analysis. Total WTP for the two treatment options, SH and TH, can be defined as:
| Parameters used to estimate net benefit | WTP (DCE) | Trial arm (study outcome) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SH | TH | ||
| SH | £1683 | – | – |
| TH | £1802 | – | – |
| Time in postoperative pain | –£15 | 8.14 days | 8.92 days |
| Chance of serious complications requiring hospitalisation | –£132 | 0.25 | 0.30 |
| Time taken to return to usual activities | –£11 | 15.47 days | 19.05 days |
| Chance of a recurrence of haemorrhoidal symptoms | –£203 | 0.42 | 0.25 |
| Total WTP | – | £1271 | £1367 |
| Cost from study | – | £941 | £602 |
| Net benefita | – | £330 | £765 |
While the total WTP estimates were positive for both treatments (£1277 and £1367, SH and TH, respectively), the net benefit was higher for TH than SH (£765 vs. £330).
Discussion
Following the standard approach to valuation in trials (costs per QALY), we estimated a broader measure of value using the DCE. Following this, we generated a monetary measure of value that took account of factors important to users in the delivery of treatments for haemorrhoids (for the general population). Overall, respondents in both groups had a general preference to have treatment over no treatment, but did not distinguish between the three treatment options. However, they also had preferences for the attributes identified, with decreases in all four treatment attributes, as expected, reducing the benefit of treatment. The magnitude of coefficients indicated that the most important marginal change was chance of recurrence, followed by chance of complications.
An interesting finding was that cost was not significant to study participants. This may be explained by study participants having experienced treatment at zero cost to them (at the point of consumption). If DCEs are to be used to estimate a broader measure of value, this raises questions regarding who should complete the DCE and when. We leave this to future research.
The results of the within-study analysis reported in Chapter 6 suggested that the EQ-5D-3L captured differences in quality of life, and that TH costs less (–£337) and is associated with more (0.07) QALYs than SH. The standard cost–utility analysis thus suggested TH as the optimal treatment. These cost–utility analysis results were confirmed by the cost–benefit analysis, which indicated that TH had a higher INB.
Conclusions
Respondents from both the general population and the trial participants valued aspects of treatment beyond those captured in the QALYs. Respondents across groups also had similar preferences for treatment attributes. New haemorrhoidal treatments should aim at reducing the chance of recurrence and complications, as well as the time in postoperative pain and time taken to return to usual activities. The cost–benefit analysis results suggesting TH as the optimal treatment concur with the cost-per-QALY results.
Chapter 8 Use of monetary incentives to boost participant questionnaire response rates in the eTHoS study: the ‘to incentivise or not to incentivise’ studies
Introduction
Response rates to the questionnaires administered at follow-up in the eTHoS study were routinely monitored at monthly in-house team meetings. Although response rates to the two early questionnaires were acceptable, there was no further contact with participants until the 12-month follow-up questionnaire and no contact between the 12- and 24-month questionnaires. The response rate to the 12-month follow-up questionnaire was observed to be lower than expected part way through the recruitment period. Options to improve the response rates were therefore considered by the study team. Literature reviews looking at methods to increase response rates were reviewed, and it was found that monetary incentives were likely to increase response rates. 56 However, there was limited evidence from studies in the UK and RCTs. It was therefore decided to conduct a formal evaluation of whether or not using a monetary incentive improved the response rate. This study was called ‘to incentivise or not to incentivise’ (IONTI). Surprisingly, the response rates continued to be low, and a need to protect the response rates in the main study was paramount; hence, the IONTI study was stopped early after 15 months. Subsequently, after a further review of the literature, a second incentive approach was implemented and its impact was assessed in the IONTI-2 study. The background, design and findings from both of these ‘studies within a trial’ (SWATs) are described in this chapter. Appendix 4 gives an overview of the timeline for both the IONTI and IONTI-2 studies.
‘To incentivise or not to incentivise’
In early 2013, the response rates to the 12-month follow-up questionnaire were found to be lower than expected at 69% (97/140 as of 25 February 2013); the expected response rate was 85%. Following discussion at the PMG meeting on 26 March 2013, it was decided that action needed to be taken in order to increase the response rate as much as possible. In order to choose the most effective intervention to increase the follow-up response rates in the eTHoS study, the team turned to the literature. A review published by The Cochrane Library56 evaluating strategies to boost response rates looked at 110 different strategies in 481 trials using postal questionnaires and 27 different strategies in 32 trials using electronic questionnaires. Although the eTHoS study follow-up data were collected using self-report by postal and electronic means, the largest proportion of responses were postal and, therefore, this mode of administration was also prioritised when designing the SWAT.
The literature review showed that in postal but not electronic questionnaire studies, monetary incentives were suggested to be the most likely to be effective in increasing response rates (OR 1.87, 95% CI 1.73 to 2.04), although there was significant heterogeneity among results. 56 The amount of the incentive might also affect the impact of monetary incentives. The review showed that in the 37 studies included, in which larger and smaller monetary incentives were compared, larger amounts were more effective. A further variation in studies using monetary incentives is whether the incentive is conditional or unconditional, that is, whether or not a voucher can be forwarded on the condition that the participant returns a completed questionnaire, or the voucher can be sent with the questionnaire to be completed and the participant does not have to do anything before receiving it. The review found that unconditional monetary incentives were more effective than conditional monetary incentives. However, very few studies used gift vouchers, few were clinical trials and only a small number were carried out in the UK; therefore, the generalisability of the findings could be questioned.
One study carried out, in the UK, by Gates et al. 57 showed a positive impact on response rates following the introduction of a monetary incentive, a £5 gift voucher, into their RCT on advice for whiplash patients. Participants (n = 2144) were randomised to two groups: one group received a gift voucher at both follow-up points and the other group did not receive any incentive. Participants in the former group (n = 1070) received the gift voucher unconditionally with their questionnaire at the 4- and 8-month follow-up points. The results showed that the incentive group was more likely to return the questionnaires (relative risk 1.10, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.16), an absolute increase of 7% of questionnaires returned. However, the authors acknowledged that further research was needed in order to establish whether or not the findings were generalisable to different populations and different types of trials.
In addition, the eTHoS study also presented an opportunity to assess the introduction of an incentive part way through a study to address the lower than anticipated response rate to a postal questionnaire; this is a scenario that triallists regularly face. Further steps were also taken in order to protect the response rate of the main study during the IONTI study; however, these were not randomised.
Based on the limited evidence available, the eTHoS study team decided to conduct a SWAT looking at the impact of an unconditional and, therefore, small £5 high-street gift voucher on questionnaire response rates at the 12- and 24-month follow-up points, and whether or not the timing of the incentive has an impact. The specific research questions are explored in detail in the following sections.
Aim
The overall aim was to assess whether or not sending an unconditional £5 high-street gift voucher improves the response rate to the 12- and 24-month patient questionnaires.
The specific research questions were as follows.
-
Does sending an unconditional £5 high-street gift voucher with the 12-month follow-up questionnaire improve the response rate to this questionnaire?
-
Does sending an unconditional £5 high-street gift voucher with the 24-month follow-up questionnaire improve the response rate to this questionnaire?
-
Is there any indication of an interaction when a £5 high-street gift voucher is sent at 12 and 24 months?
Methods: ‘to incentivise or not to incentivise’
Participants/eligibility
As of 5 June 2013, patients enrolled in the eTHoS study, across all clinical sites, who had yet to receive their 12-and 24-month follow-up questionnaires, were randomised into one of four groups described in Table 52.
| Follow-up time point | Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 12-month follow-up | Voucher | Voucher | No voucher | No voucher |
| 24-month follow-up | No voucher | Voucher | Voucher | No voucher |
Materials
All participants who were randomised to receive a voucher were sent a covering letter describing the purpose of the 12- or 24-month follow-up questionnaire and why a voucher was included (see Appendix 4).
The IONTI study participants received the same standard 12- and 24-month follow-up questionnaires as described in Chapter 3, and the same reminders (postal then telephone reminders).
A £5 Love2Shop (Park Group plc, London, UK) voucher was included with the postal questionnaire according to group allocation. This brand of vouchers was chosen as they would be accepted in a range of high-street shops across the UK and should therefore be convenient to use for all participants.
Randomisation
Simple randomisation (1 : 1 : 1 : 1) was completed to allocate the eTHoS study participants to one of the four groups.
NHS research ethics and other permissions
Ethics approval was sought for the IONTI study and submitted as a substantial amendment to the main study. Ethics approval was received on 25 April 2013 for amendment 16 of the REC reference number 10/S0802/17.
Sites also had to approve the IONTI study. Sites were informed about the IONTI study as standard practice for all substantial amendments and had 35 days of submission to object to the amendment, otherwise approval would be assumed.
One of the co-sponsors (University of Aberdeen) required a statement regarding the possible tax implications to be included in the IONTI study questionnaire cover letters. This was included as of June 2013. However, this was removed in April 2014, as the sponsor reviewed its guidelines for this statement to be applicable only to amounts exceeding £10.
Primary outcomes
The primary outcome was the response rates at 12 and 24 months for the four groups.
In addition, through the routine study management system, the following information was collected: date questionnaire sent, if a reminder was sent and date sent, if a second reminder was sent and date sent, if a response was received along with mode utilised (postal or online) and date of receipt.
Statistical analysis
The response rates to questionnaires at 12 and 24 months between the incentive and the non-incentive groups were compared using logistic regression. Two separate analyses were carried out, one each for the return of the 12- and 24-month questionnaires. For the analysis of return of the 12-month questionnaire, only a 12-month incentive main effect was included. The analysis of return of the 24-month questionnaire included both a 12-month and a 24-month incentive main effect. The possibility of an interaction was explored using an additional incentive at 12 months by incentive at 24-month interaction effect. Models were adjusted for the minimisation variables (sex, baseline EQ-5D-3L score, haemorrhoid grade and centre) and 95% CIs are reported.
In addition, a non-randomised comparison of the impact of the IONTI study on the response rates was completed. This was also analysed using logistic regression with the IONTI study viewed as a single intervention (ignoring each individual’s randomised allocation) with the pre- and post-IONTI study responses compared.
Estimated sample size
A total of 600 participants were anticipated to be recruited or still to have 12-month questionnaires sent by 1 May 2013, and could potentially have been included in the IONTI study subject to approval and implementation. A sample of 300 per group would have allowed a difference of 10% (70–80%) to be detected with 80% statistical power at the two-sided 5% significance level. Seventy per cent was the estimated proportion, as of February 2013, of participants returning their 12-month questionnaire. The 24-month level was uncertain, given the low numbers that had reached that time point.
Stopping rules
If the monetary incentive was found to be effective, the IONTI study would be stopped and all participants due a 12- or 24-month follow-up questionnaire would receive a voucher. The possibility of the IONTI study being detrimental was not considered and a date for interim analysis was not set.
Study within a trial registration
The SWAT was registered on the SWAT repository store held by the Northern Ireland hub for Trials Methodology Research [this was referenced as SWAT13 Jonathan Cook (2013 February 01 1237)].
Other initiatives taken to improve response rates in the main study
As of September 2013, the effectiveness of the reminders was reviewed by the study team. Telephone reminders for 12 and 24 months were found to be ineffective and expensive. For this reason, the second reminder was changed to a postal reminder.
As of December 2013, both reminders for the 12- and 24-month questionnaires were shortened to contain only the primary outcome measure (EQ-5D-3L). The second shortened reminder (EQ-5D-3L) was also introduced at this time to replace telephone call reminders, and was to be sent at 18 months, replacing the participant travel cost questionnaire, which was now postponed to be sent after the 24-month follow-up questionnaire at 27 months.
As of May 2014, a newsletter was sent to participants 1 week before their 12- or 24-month follow-up questionnaires, highlighting that they would soon, approximately 1 week later, receive their next follow-up questionnaire. Participants who had completed their follow-up received a version of the newsletter without a pre-notification.
Results
Two sites did not approve the amendment for the IONTI study and, therefore, participants from 27 sites were eligible and randomised in the IONTI study. One site objected because of the possibility that participants’ confidentiality might be breached as the sponsor is legally required to share details of individuals who have received payments if requested by HM Revenue & Customs, whereas the other site objected on ethical grounds.
In addition, one participant who was randomised to receive the voucher returned it, as he felt that as he did not receive surgical treatment, he was not eligible to receive the voucher.
Flow of participants
Figure 24 shows the flow of participants who were included in the IONTI study. There were 142 participants randomised to group 1 (voucher at 12 months but not at 24 months); 124 participants randomised to group 2 (voucher at 12 and 24 months); 123 randomised to group 3 (no voucher at 12 months but voucher at 24 months); and 132 participants randomised to group 4 (no voucher at 12 or 24 months). In total, 25 participants withdrew by the end of the study and one had died (unrelated). Baseline data are shown in Table 53.
FIGURE 24.
Flow of participants in the IONTI study. a, Participants eligible while the IONTI study was running from June 2013 until it was stopped in October 2014. Withdrawal refers to withdrawal from main study.
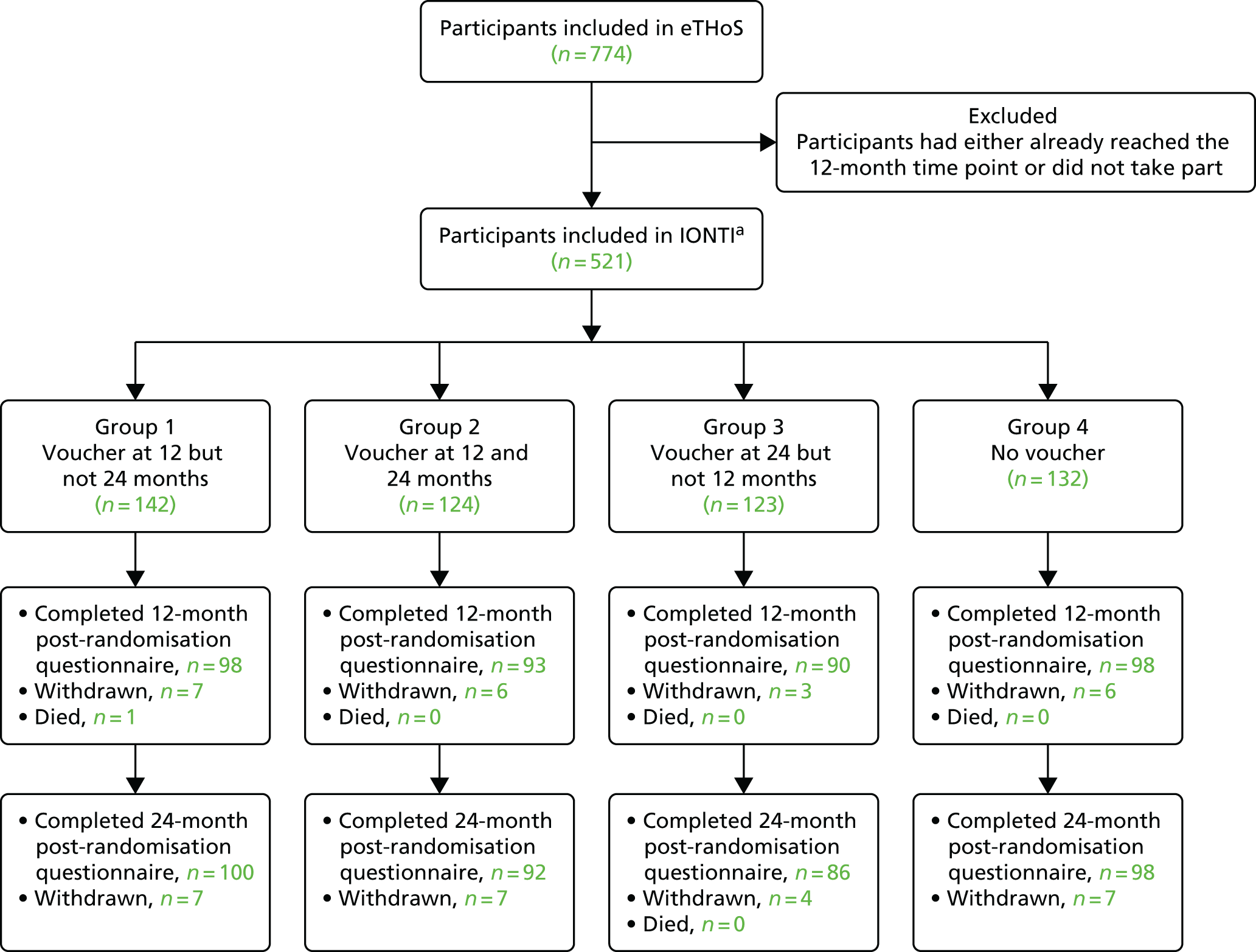
| Characteristic | Trial arm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No voucher (N = 132) | 12 months only (N = 142) | 24 months only (N = 123) | Both time points (N = 124) | |
| Age (years), n, median (IQR) | 132, 50 (40–59) | 142, 48 (38–58) | 123, 50 (41–60) | 124, 50 (42–61) |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 62 (47.0) | 73 (51.4) | 64 (52.0) | 63 (50.8) |
| BMI, n, mean (SD) | 127, 26.8 (4.9) | 137, 27.7 (5.2) | 121, 26.6 (5.0) | 120, 27.1 (5.3) |
| Grade of haemorrhoid, n (%) | ||||
| II | 27 (20.5) | 37 (26.1) | 27 (22.0) | 26 (21.0) |
| III | 85 (64.4) | 83 (58.5) | 81 (65.9) | 78 (62.9) |
| IV | 20 (15.2) | 22 (15.5) | 15 (12.2) | 20 (16.1) |
| Previous haemorrhoid surgery, n (%) | 37 (28.0) | 52 (36.6) | 45 (36.6) | 31 (25.0) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | 1 (0.8) | – | 2 (1.6) | 2 (1.6) |
| Systemic medications, n (%) | ||||
| Aspirin | 7 (5.3) | 1 (0.7) | 7 (5.7) | 7 (5.6) |
| Warfarin | 2 (1.5) | 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.8) | 1 (0.8) |
| Clopidogrel | 2 (1.5) | 1 (0.7) | 4 (3.3) | 2 (1.6) |
| Steroids | – | 2 (1.4) | 1 (0.8) | – |
| Other | 3 (2.3) | – | 1 (0.8) | 1 (0.8) |
| Pain (VAS), n, mean (SD) | 131, 2.6 (2.4) | 140, 3.0 (2.5) | 121, 2.4 (2.7) | 121, 2.8 (2.9) |
| Analgesia, n (%) | ||||
| Yes | 42 (31.8) | 44 (31.0) | 40 (32.5) | 37 (29.8) |
| Missing | 1 (0.8) | 1 (0.7) | 3 (2.4) | 2 (1.6) |
| Number of days in a week with analgesia, n, mean (SD) | 42, 3.8 (2.0) | 44, 4.3 (2.2) | 40, 5.1 (2.2) | 36, 4.4 (2.1) |
| EQ-5D-3L, n, mean (SD) | 132, 0.812 (0.216) | 142, 0.735 (0.264) | 123, 0.771 (0.262) | 124, 0.751 (0.266) |
| SF-36, n, mean (SD) | ||||
| Physical component summary | 130, 49.6 (9.3) | 139, 48.5 (9.5) | 119, 48.3 (10.0) | 124, 48.3 (10.4) |
| Mental component summary | 130, 50.4 (10.1) | 139, 49.1 (11.1) | 119, 50.2 (11.7) | 124, 47.9 (12.3) |
| CIS, n, mean (SD) | 129, 3.9 (3.6) | 137, 4.5 (3.7) | 118, 3.4 (3.7) | 120, 4.6 (4.5) |
| HSS, n, mean (SD) | 129, 12.9 (3.7) | 134, 12.5 (3.9) | 116, 12.5 (3.7) | 120, 12.5 (4.3) |
| Patient reporting tenesmus, n (%) | ||||
| Always | 2 (1.5) | 6 (4.2) | 4 (3.3) | 3 (2.4) |
| Often | 18 (13.6) | 18 (12.7) | 14 (11.4) | 14 (11.3) |
| Sometimes | 36 (27.3) | 36 (25.4) | 33 (26.8) | 28 (22.6) |
| Rarely | 19 (14.4) | 30 (21.1) | 17 (13.8) | 19 (15.3) |
| Never | 57 (43.2) | 51 (35.9) | 50 (40.7) | 60 (48.4) |
| Missing | – | 1 (0.7) | 5 (4.1) | – |
| Patient preference, n (%) | ||||
| Strongly prefer better short-term recovery | 11 (8.3) | 12 (8.5) | 11 (8.9) | 10 (8.1) |
| Prefer better short-term recovery | 11 (8.3) | 11 (7.7) | 6 (4.9) | 3 (2.4) |
| No preference | 42 (31.8) | 57 (40.1) | 51 (41.5) | 47 (37.9) |
| Prefer lower risk of recurrence | 33 (25.0) | 38 (26.8) | 28 (22.8) | 28 (22.6) |
| Strongly prefer lower risk recurrence | 35 (26.5) | 23 (16.2) | 24 (19.5) | 34 (27.4) |
| Missing | – | 1 (0.7) | 3 (2.4) | 2 (1.6) |
In general, the groups were well balanced. Table 54 provides the IONTI study response rate results. There were no statistically significant differences between the groups at 12 or 24 months. Similarly, there was no evidence of an interaction effect (Tables 55 and 56).
| Response time point | Time point of voucher, n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 months | 24 months | |||
| No | Yes | No | Yes | |
| Response at 12 months | ||||
| No | 62 (24.3) | 69 (25.9) | – | – |
| Yes | 193 (75.7) | 197 (74.1) | – | – |
| Response at 24 months | ||||
| No | 71 (27.8) | 74 (27.8) | 76 (27.7) | 69 (27.9) |
| Yes | 184 (72.2) | 192 (72.2) | 198 (72.3) | 178 (72.1) |
| Response time point | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Response at 12 months | ||
| Voucher at 12 months | 0.99 (0.72 to 1.37) | 0.962 |
| Response at 24 months | ||
| Voucher at 12 months | 0.93 (0.60 to 1.44) | 0.760 |
| Voucher at 24 months | 0.85 (0.48 to 1.52) | 0.586 |
| Interaction | 1.39 (0.69 to 2.79) | 0.358 |
| Time point post randomisation | Responded to questionnaire, n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |||
| 12 months | ||||
| Before | 178 (72.1) | 69 (27.9) | – | – |
| After | 408 (77.4) | 119 (22.6) | 1.31 (0.84 to 2.04) | 0.237 |
| 24 months | ||||
| Before | 30 (71.4) | 12 (28.6) | – | – |
| After | 532 (72.7) | 200 (27.3) | 1.01 (0.55 to 1.86) | 0.980 |
The ‘to incentivise or not to incentivise’-2 study
Response rates remained lower, at 75% (375/498) for the 12-month questionnaire and 60% (127/212) for the 24-month questionnaire, than the expected rate of 85%, despite the fact that the IONTI study ran for 1 year. The eTHoS study team turned to the literature again for guidance.
A systematic literature review suggested that higher-value incentives were effective in increasing response rates to postal questionnaires in randomised trials. In their review, Brueton et al. 58 looked at randomised SWATs that compared strategies with increase response rates to follow-up questionnaires in RCTs. They identified 38 eligible SWATs, of which 14 tested incentives and two compared size of incentive. The two trials (n = 902) showed that those receiving a higher-value incentive were more likely to respond to questionnaires than those who received lower-value incentives (relative risk 1.12, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.22; p < 0.005), irrespective of how the incentive was delivered.
Based on the evidence reviewed above, the study team decided to conduct another monetary incentive study, IONTI-2. In the IONTI-2 study a high-value gift voucher (£30) was sent to participants who returned a fully completed 12- or 24-month questionnaire or associated reminders. A fully completed questionnaire was defined as one in which the primary outcome measure, the EQ-5D-3L, was completed.
Aim
The aim of the IONTI-2 study was to investigate the impact of a conditional £30 gift voucher on response rates at the 12- and 24-month follow-up points.
Methods: the ‘to incentivise or not to incentivise’-2 study
Participants/eligibility
As of 17 October 2014, patients enrolled in the eTHoS study across all clinical sites, who had yet to receive their 1-year and/or 2-year follow-up questionnaire, were eligible.
Materials
All participants received a covering letter describing the purpose of the 12- or 24-month follow-up questionnaire and were informed that on return of a completed questionnaire they would receive a £30 gift voucher as a token of appreciation for their time spent completing the questionnaire (see Appendix 4).
The IONTI-2 participants received the same standard 12- and 24-month follow-up questionnaires as described in Chapter 3, and the same reminders (by this time amended to two postal reminders containing only the EQ-5D-3L, and an 18-month reminder if no return at 12 months).
On receipt of a completed questionnaire (12- or 24-month questionnaire reminders or 18-month reminder), the primary outcome measure had to be completed, a £30 gift voucher was triggered and sent to the participant.
The Love2Shop brand of vouchers was chosen as these would be accepted in a range of high-street shops across the UK and should therefore be convenient to use for all participants.
As of 21 January 2015 a label was added to the front of questionnaires, giving participants a choice to opt out from receiving the gift voucher (see Appendix 4). The team felt that this option should be made available for participants who were taking part in the study solely for altruistic reasons.
NHS research ethics and other permissions
Ethics approval was sought for the IONTI-2 study and a substantial amendment was submitted to the main study. Ethics approval was received on 8 September 2014 for amendment 27 for REC reference number 10/S0802/17.
Sites also had to approve the IONTI-2 study. Sites were informed about the IONTI-2 study as standard practice for all substantial amendments and could object within 35 days of submission of the amendment, otherwise approval would be assumed.
As vouchers had a value of more than £10, the sponsor required a statement regarding the possible tax implications to be included with the vouchers. A compliment slip was included in the mailing with the voucher informing participants of possible tax implications (see Appendix 4).
Primary outcomes
The main primary outcome was response rates at 12 and 24 months for participants included in the IONTI-2 study.
In addition, through the routine study management system, the following information was collected: date questionnaire was sent, if a reminder was sent and date sent, if a second reminder was sent and date sent, if a response was received along with mode utilised (postal or online) and date of receipt.
Statistical analysis
The primary analysis was a before-and-after analysis of the impact of the £30 gift voucher at 12 and/or 24 months using logistic regression with adjustment for the minimisation variables. The primary analysis included all participants who had not already reached the 12- and/or 24-month time point.
A further analysis using the preceding IONTI study period data along with all of the data up to the end of the 24-month follow-up period was carried out.
A post hoc sensitivity analysis was carried out as a result of the overlapping influence of the IONTI study. For the 12-month analysis, this included participants not included in the IONTI-2 study, participants who were randomised to no voucher and those who received the voucher at 24 months only. For the 24-month analysis, this included participants not included in the IONTI-2 study and participants who were randomised to receive no vouchers in the IONTI-2 study. Data on responses were collected and compared.
One interim analysis for futility was planned once the outcome for 75% of the anticipated participants in the IONTI-2 study was known at 24 months. Based on this, it was decided to continue the study to completion.
Owing to a system error, the shortened reminders (introduced in December 2013) were not issued to participants at 24 months for a period of 12 months during the IONTI study. This might have impacted on the response rate at 24 months. To protect the host study, eTHoS, these missed 24-month reminders were sent out during the IONTI-2 study and these included the conditional voucher incentive to maximise response rates. These returned reminders were not included in the final analysis for the IONTI-2 study.
Estimated sample size
A total of 440 recruits were anticipated to still be due to receive their 24-month questionnaires at the time of design. Based on a simple pre–post comparison of the return rate, a sample of 216 per group would allow a difference of 16% (60–75%) to be detected with 90% statistical power at the two-sided 5% significance level. This may be reduced slightly because of the single interim analysis, although it is anticipated to be over 80%.
Study within a trial registration
The SWAT was registered on the SWAT repository store held by the Northern Ireland hub for Trials Methodology Research [reference: SWAT13 Jonathan Cook (2013 February 01 1237)].
Other initiatives taken to improve the response rates in the main study
No new steps were taken during the IONTI-2 study.
Results
‘To incentivise or not to incentivise’-2
All sites agreed to take part in the IONTI-2 study. The IONTI-2 study began on 17 October 2014 when the IONTI study ceased. A total of 5% of participants (24/481) who completed the questionnaire opted not to receive the voucher. Table 57 provides the IONTI-2 study results, which showed no statistical evidence of a change in the response rate.
| Time point post randomisation | Responded to questionnaire, n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |||
| 12 months | ||||
| Before | 443 (75.1) | 147 (24.9) | – | – |
| After | 143 (77.7) | 41 (22.3) | 1.13 (0.75 to 1.69) | 0.559 |
| 24 months | ||||
| Before | 205 (69.3) | 91 (30.7) | – | – |
| After | 357 (74.7) | 121 (25.3) | 1.31 (0.97 to 1.76) | 0.074 |
Owing to the different follow-up points that individuals were at in that point in time, a small proportion of participants took part in both SWATs – ‘a middle group’. Table 58 provides the IONTI-2 sensitivity analyses results, exploring this ‘middle group’. There was no evidence of a difference in the 12-month response rates after the incentive was given. This was also the same at 24 months, but there was a slight increase in response rates (71.4% before the incentive, 75.9% after the incentive).
| Time point post randomisation | Responded to questionnaire, n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |||
| 12 months | ||||
| Before | 434 (77.1) | 129 (22.9) | – | – |
| After | 143 (77.7) | 41 (22.3) | 1.01 (0.66 to 1.55) | 0.974 |
| 24 months | ||||
| Before | 205 (71.4) | 82 (28.6) | – | – |
| After | 349 (75.9) | 111 (24.1) | 1.25 (0.87 to 1.80) | 0.230 |
Discussion
Findings from the IONTI and IONTI-2 studies were inconclusive with regard to the overall question. The IONTI study was stopped early as a result of concerns that it was having a negative impact on retention, based on anecdotal information and interim results. The overall response rates for the main study (eTHoS) were prioritised over the value of continuing the IONTI study. Findings from the IONTI study were statistically inconclusive. The overall analysis of IONTI-2 was similarly inconclusive, including the sensitivity analysis, which might be viewed as the purer analysis (excluding the group that had received an incentive in the IONTI study), which also showed no difference in response rate at 12 months. The 24-month finding was also statistically significant, but there was a slightly higher post-incentive response rate in both analyses.
As both SWATs were found not to be effective, the cost of these incentives per participant has not been calculated.
Taken together, the findings were, at best, inconclusive, and, from the study team’s perspective, clearly disappointing. No positive effect was observed and there was the suspicion and possibility of a negative impact, despite previous work evaluating incentives as being very favourable. 56,58 It is possible, however, that the negative finding here was only a chance finding. Alternatively, they could reflect something specific to the study and the way in which the incentives were delivered. There are a number of possible contributing factors. Of particular note was the requirement of the sponsor to include a statement in the covering letter regarding possible tax implications in the IONTI study. Anecdotal feedback from participants suggested that this caused concern to some participants. This institutional judgement was later revised on appeal, and the cover letter used was modified accordingly most of the way through the IONTI study intervention period. The eTHoS study participants received multiple questionnaires early in the follow-up period with a number of similar outcomes, which may have resulted in lower response rates. Introducing a relatively low-value incentive at 12 or 24 months might be viewed as too little and/or too late. It was later hoped that the study team could carry out qualitative research to fully explore the cause of the negative impact. This was not followed through, because of the substantial regulatory barriers and lack of resources. Further research in this area is recommended, preferably in a variety of settings to allow disease- and population-specific cohorts, along with features of follow-up, to be explored.
Multiple strategies to improve recruitment and response rate are regularly used in multicentre trials in which recruitment and/or response rates are lower than hoped. Often these are used without much evidence to support their use. It was the investigators’ expectation at the initiation of the IONTI study that the use of incentives could be only positive (or, at worst, that they would have no impact). The findings from the IONTI studies question this assumption and points to the need for care when introducing new interventions part way through a study. Bower et al. 59 suggested that SWATs or ‘nested’ trials are needed to test the effectiveness of retention strategies. However, triallists should be aware of the challenges of implementing SWATs part way through pragmatic trials. As noted by others in Glidewell et al. ;60 ‘Interventions to increase response rates may incur negative consequences’ contrary to the intuitive expectation.
Both studies had a number of limitations in terms of the evaluation of an intervention. A confounding factor during the conduct of the IONTI study was the use of pre-notification newsletters, which were also employed as a method to boost retention. There is some limited evidence that these are beneficial to boosting response rates. 56 Newsletters were issued 1 week prior to the 12- and 24-month questionnaire being distributed across all IONTI study groups; as such, it was not possible to untangle what impact this would have had upon the overall study. The IONTI and IONTI-2 studies were carried out in a fully ‘open’ manner, with the interim results monitored as part of the routine study management process by the study team. This reflected their primary aim to address the lower-than-anticipated response rate, with the main study being the priority. The decision to stop the study was not according to a prespecified stopping rule, but a corporate judgement of the study team. As such, this monitoring process increased the possibility of a misleading finding.
The IONTI-2 study had a number of limitations. As a before-and-after study, its findings are susceptible to secular trends and other concurrent changes. In particular, some participants were involved in both studies, ‘a middle group’, which makes the interpretation more difficult. We carried out a sensitivity analysis that excluded this group; however, such exclusion of data is not without its own risks in terms of bias. More generally, recruitment to trials often has ebb and flows during the life cycle of a trial for various reasons, and this could have led to some bias being included in the comparison.
Participants in the IONTI-2 study were given an ‘opt-out’ option when receiving the £30 voucher. This was taken up by a small proportion [5% (24/481)] of participants, but the true ‘opt-out’ level may include some who did not respond.
Summary
The IONTI studies did not find any evidence in favour of the use of incentives to increase the response rate, and there was some suggestion of a negative impact. There are a number of contextual aspects that may explain this unexpected finding. Care is needed when introducing a new intervention into an ongoing study. Future evaluations of incentives are needed to explore the impact of contextual issues that may moderate their impact.
Chapter 9 Patient preference
Introduction
Patients’ preference regarding treatment is well acknowledged to have a potential impact on the generalisability of randomised trials. 61 This can occur if an unrepresentative group of individuals (when compared with the patient population, who would potentially receive the treatments under evaluation) participate in the study. Perhaps less well recognised is the potential for patients’ treatment to have an impact on the study results. 62,63 Participants within trials who receive their preferred treatment may have different outcomes from those who do not, as they may be more motivated to continue participating in the study (e.g. complying with the treatment) or simply perceive their outcome as being better as a result of receiving their preference. Those who do not receive their preferred treatment may experience resentful demoralisation and be more likely to drop out of the study. 62
Various modifications to study design have been proposed to allow exploration of the impact of patients’ treatment preference. These include preference study design (a form of comprehensive cohort in which those who do not consent to take part in a RCT receive their preferred treatment) and the fully randomised patient preference design. 62,64,65 Various advantages and disadvantages of these approaches have been considered elsewhere. 62,65
Previous work has suggested, as noted in Chapter 1, that TH and SH procedures have different outcome profiles; one (SH) potentially leads to less pain and better quality of life in the short term, and the other (TH) potentially leads to less recurrence and need for further intervention. The eTHoS study aimed to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of these procedures over 24 months and, as shown in Chapters 5 and 6, this was confirmed by the study. Given this, there was reason to anticipate that patients’ preferences had the potential to have an impact on the study findings as well as on recruitment. 62 We were unaware of any assessment of the impact of patients’ preference for the treatment of haemorrhoids. To address this, we adopted a fully randomised patient preference design in which participants’ preferences were recorded at baseline, prior to randomisation. This enabled an analysis that takes preference into account. In this chapter, we report the findings of the fully randomised patient preference evaluation. Consideration of the impact of preference is briefly made in Chapter 5, in which reasons for not participating are recorded. An alternative evaluation of patient preferences was undertaken in the DCE reported in Chapter 7.
Methods
Measuring participants’ treatment preference
We recorded the preference in an indirect way by including a question about preference in the baseline question. The questionnaire was framed around two hypothetical treatments, A and B. It was stated that treatment A was believed to have better short-term recovery (up to 6 weeks), but over the longer term (up to 5 years) patients may be more likely to have haemorrhoids again and need further surgery. Treatment B was believed to have poorer short-term recovery (up to 6 weeks), but over the longer term (up to 5 years) patients were less likely to have haemorrhoids again and need further surgery. Participants were asked for their choice of treatment on a five-point Likert scale (the options were ‘strongly prefer operation A’, ‘prefer A but not strongly’, ‘no preference’, ‘prefer B but not strongly’ and ‘strongly prefer B’). These scenarios (A and B) were a simplification of the expectation regarding SH and TH at the initiation of the study, given previous evidence. 2,13 Details of how the baseline questionnaire data were collected and information relating to the study design are provided in Chapter 3.
Statistical analysis
Participants’ treatment preferences were separated by the two interventions, SH and TH, and important baseline characteristics were summarised according to the preference choice. The primary outcome, EQ-5D-3L, key patient-reported secondary outcomes at 24 months (CIS, HSS and recurrence) and treatment by preference group interactions were included. Compliance with treatment allocation and retention were compared between groups using a logistic regression with interaction effects for the preference groups as above. Continuous variables were summarised with number, mean (SD) or median and IQR, and discrete variables were number and percentages. All analyses were at the 5% two-sided significance level with 95% CIs provided as appropriate and analysed using Stata.
Results
Of the 774 participants randomised (after three post-randomisation exclusions), 766 completed the preference question. A total of 307 (40.1%) had no preference, with more participants strongly preferring operation B [159 (20.8%)] over A [61 (8.0%)] (Table 59). Preference groups were balanced between the two randomised interventions.
| Treatment preference | Trial arm, n (%) | Total, n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SH | TH | ||
| No preference | 161 (41.5) | 146 (37.8) | 307 (40.1) |
| Prefer operation A but do not feel very strongly | 35 (9.0) | 24 (6.2) | 59 (7.7) |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 23 (5.9) | 38 (9.8) | 61 (8.0) |
| Prefer operation B but do not feel very strongly | 95 (24.5) | 85 (22.0) | 180 (23.5) |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 68 (17.5) | 91 (23.6) | 159 (20.8) |
| Total | 382 | 384 | 766 (100.0)a |
There was no sign of a difference in outcome between the participants’ treatment preference at baseline in terms of overall or disease-specific quality of life (Table 60). Those who preferred operation A (strongly or not) were slightly younger, and more men strongly preferred A.
| Characteristic | Treatment preference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No preference (N = 307) | Prefer operation A but do not feel very strongly (N = 59) | Strongly prefer operation A (N = 61) | Prefer operation B but do not feel very strongly (N = 180) | Strongly prefer operation B (N = 159) | |
| Age (years), n, median (IQR) | 307, 51 (41–62) | 59, 46 (36–55) | 61, 47 (40–56) | 180, 49 (40–60) | 159, 49 (40–59) |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 159 (51.8) | 28 (47.5) | 41 (67.2) | 84 (46.7) | 82 (51.6) |
| EQ-5D-3L, n, mean score (SD) | 307, 0.754 (0.255) | 59, 0.797 (0.202) | 61, 0.756 (0.287) | 180, 0.801 (0.221) | 159, 0.727 (0.295) |
| SF-36, n, mean score (SD) | |||||
| Physical component summary | 299, 48.5 (9.7) | 59, 51.6 (6.2) | 59, 50.2 (7.7) | 176, 49.3 (8.8) | 158, 46.8 (10.7) |
| Mental component summary | 299, 49.4 (11.0) | 59, 48.7 (10.7) | 59, 49.1 (10.4) | 176, 50.1 (10.6) | 158, 48.0 (13.2) |
| CIS | 297, 4.3 (3.9) | 59, 4.3 (3.7) | 60, 4.3 (4.0) | 175, 3.8 (3.8) | 155, 4.2 (4.4) |
| HSS | 289, 12.7 (4.1) | 58, 12.7 (3.6) | 58, 12.4 (3.4) | 175, 12.5 (3.5) | 154, 12.7 (4.2) |
The EQ-5D-3L data according to the participants’ preference across all time points are given in Table 61. At baseline, the groups differed noticeably in EQ-5D-3L score, although not in a manner consistent with a preference effect. As was observed in the main study analysis (see Chapter 5), the scores were lower at 1 week and 3 weeks post surgery. At 3 weeks, preference of operation A (but not strongly) had a higher score than the other preference groups, and at 12 months post randomisation, the score was lower in the strongly preferring operation A group. Results of the analyses that assessed the impact of the preference on the randomised group comparison of the primary outcome are given in Table 62.
| Time point | Treatment preference, n, mean score (SD) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No preference (N = 307) | Prefer operation A but do not feel very strongly (N = 59) | Strongly prefer operation A (N = 61) | Prefer operation B but do not feel very strongly (N = 180) | Strongly prefer operation B (N = 159) | |
| Baseline | 307, 0.754 (0.255) | 59, 0.797 (0.202) | 61, 0.756 (0.287) | 180, 0.801 (0.221) | 159, 0.727 (0.295) |
| 1 week | 233, 0.529 (0.340) | 49, 0.520 (0.315) | 41, 0.588 (0.293) | 141, 0.546 (0.323) | 120, 0.478 (0.352) |
| 3 weeks | 229, 0.765 (0.281) | 47, 0.814 (0.224) | 37, 0.723 (0.258) | 129, 0.794 (0.218) | 115, 0.784 (0.182) |
| 6 weeks | 243, 0.828 (0.265) | 46, 0.890 (0.140) | 44, 0.849 (0.170) | 147, 0.877 (0.184) | 123, 0.839 (0.223) |
| 12 months | 227, 0.828 (0.262) | 45, 0.866 (0.184) | 34, 0.794 (0.250) | 146, 0.877 (0.190) | 118, 0.858 (0.246) |
| 24 months | 225, 0.851 (0.228) | 40, 0.846 (0.235) | 35, 0.835 (0.214) | 134, 0.876 (0.172) | 115, 0.836 (0.257) |
| Time point and treatment preference | n, mean AUC (SD) | Interaction effect | Within-preference-subgroup treatment effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD (95% CI) | p-value | MD (95% CI) | p-value | ||
| 6 weeks | |||||
| No preference | 261, 0.205 (0.137) | – | – | 0.043 (–0.001 to 0.087) | 0.057 |
| Prefer operation A but do not feel very strongly | 55, 0.192 (0.149) | –0.083 (–0.188 to 0.023) | 0.121 | –0.040 (–0.118 to 0.039) | 0.309 |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 48, 0.212 (0.134) | –0.026 (–0.096 to 0.044) | 0.451 | 0.017 (–0.060 to 0.094) | 0.655 |
| Prefer operation B but do not feel very strongly | 155, 0.216 (0.155) | –0.005 (–0.079 to 0.068) | 0.880 | 0.038 (–0.004 to 0.079) | 0.072 |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 135, 0.203 (0.162) | –0.052 (–0.118 to 0.014) | 0.115 | –0.009 (–0.058 to 0.039) | 0.695 |
| 12 months | |||||
| No preference | 216, 0.800 (0.236) | – | – | 0.048 (–0.010 to 0.105) | 0.099 |
| Prefer operation A but do not feel very strongly | 44, 0.888 (0.258) | –0.123 (–0.322 to 0.076) | 0.228 | –0.076 (–0.264 to 0.112) | 0.415 |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 30, 0.845 (0.164) | –0.127 (–0.227 to –0.028) | 0.014 | –0.080 (–0.163 to 0.003) | 0.057 |
| Prefer operation B but do not feel very strongly | 136, 0.849 (0.187) | –0.057 (–0.124 to 0.009) | 0.088 | –0.010 (–0.059 to 0.039) | 0.681 |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 113, 0.822 (0.221) | –0.120 (–0.226 to –0.014) | 0.027 | –0.072 (–0.147 to 0.003) | 0.058 |
| 24 months | |||||
| No preference | 230, 1.565 (0.471) | – | – | 0.025 (–0.081 to 0.131) | 0.629 |
| Prefer operation A but do not feel very strongly | 47, 1.575 (0.504) | –0.174 (–0.436 to 0.089) | 0.187 | –0.148 (–0.374 to 0.077) | 0.188 |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 34, 1.582 (0.416) | –0.165 (–0.454 to 0.124) | 0.252 | –0.140 (–0.418 to 0.138) | 0.312 |
| Prefer operation B but do not feel very strongly | 137, 1.633 (0.410) | –0.117 (–0.228 to –0.005) | 0.042 | –0.091 (–0.180 to –0.002) | 0.045 |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 117, 1.590 (0.474) | –0.187 (–0.372 to –0.002) | 0.048 | –0.162 (–0.334 to 0.010) | 0.064 |
The EQ-5D-3L preference analyses at 6 weeks and 12 months did not show any clear statistical evidence of an interaction between treatment and preference (at most one of the interaction effects was statistically significant at the 5% level). Although the observed difference within subgroups did differ somewhat, at 12 and 24 months they all tended towards favouring TH. The pattern was not consistent in terms of a preference effect.
The randomised treatment by participants’ preference analyses for HSS and CIS are given in Table 63. The CIS and HSS preference analyses at 24 months did not show any clear statistical evidence of an interaction between treatment and preference (none and one of the interaction effects, respectively, were statistically significant at the 5% level). All within-subgroup effects tended in the direction of favouring TH.
| Outcome and treatment preference | n, mean score (SD) | Interaction effect | Within-preference-subgroup treatment effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD (95% CI) | p-value | MD (95% CI) | p-value | ||
| CIS | |||||
| No preference | 196, 3.67 (3.82) | – | – | 0.452 (0.355 to 0.549) | < 0.001 |
| Prefer operation A but not feel very strongly | 32, 3.25 (2.98) | –0.14 (–2.02 to 1.73) | 0.875 | 0.356 (–1.042 to 1.754) | 0.606 |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 28, 4.11 (2.95) | –0.43 (–2.04 to 1.18) | 0.589 | 0.072 (–1.318 to 1.462) | 0.916 |
| Prefer operation B but not feel very strongly | 121, 2.98 (3.25) | 0.26 (–1.03 to 1.54) | 0.686 | 0.758 (–0.066 to 1.582) | 0.070 |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 103, 3.44 (3.95) | 1.27 (–0.09 to 2.62) | 0.066 | 1.768 (0.458 to 3.078) | 0.010 |
| HSS | |||||
| No preference | 198, 5.46 (4.64) | – | – | 0.52 (–0.591 to 1.628) | 0.347 |
| Prefer operation A but not feel very strongly | 33, 6.12 (4.86) | 0.47 (–1.66 to 2.60) | 0.654 | 0.99 (–0.726 to 2.704) | 0.247 |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 30, 6.90 (4.72) | 2.92 (0.20 to 5.65) | 0.036 | 3.44 (0.932 to 5.951) | 0.009 |
| Prefer operation B but not feel very strongly | 119, 5.77 (4.99) | 1.99 (–0.02 to 4.01) | 0.052 | 2.51 (1.141 to 3.886) | 0.001 |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 105, 5.23 (4.81) | 1.57 (–0.29 to 3.43) | 0.094 | 2.09 (0.373 to 3.813) | 0.019 |
Table 64 shows the patient-reported recurrence preference analyses at 24 months, which did not show any clear statistical evidence of an interaction between treatment and preference (none of the respective interaction effects was statistically significant at the 5% level). All within-subgroup effects tended in the direction of favouring TH.
| Treatment preference | n (%) | Interaction effect | Within-preference-subgroup treatment effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | ||
| No preference | 89 (36.6) | – | – | 2.77 (1.66 to 4.63) | < 0.001 |
| Prefer operation A but not feel very strongly | 14 (28.6) | 0.78 (0.21 to 2.82) | 0.700 | 2.15 (0.64 to 7.24) | 0.217 |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 11 (27.5) | 0.55 (0.18 to 1.64) | 0.283 | 1.52 (0.44 to 5.20) | 0.509 |
| Prefer operation B but not feel very strongly | 57 (37.7) | 0.69 (0.36 to 1.34) | 0.278 | 1.92 (1.01 to 3.64) | 0.046 |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 36 (28.3) | 0.78 (0.31 to 1.95) | 0.594 | 2.16 (0.88 to 5.26) | 0.091 |
The compliance with treatment preference analyses (Table 65) did not show any clear statistical evidence of an interaction between treatment and preference (none of the respective interaction effects were statistically significant at the 5% level). All within-subgroup effects tended in the direction of favouring TH. Table 66 shows the association between compliance and retention and participants’ treatment preferences. There was some suggestion of a preference effect (for the ‘strongly prefer B’ group), which might have lead to differential retention.
| Treatment preference | Compliance within subgroup, n (%) | Interaction effect | Within-preference subgroup treatment effect | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | OR (95% CI) | p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| No preference | 51 (16.6) | 256 (83.4) | – | – | – | – |
| Prefer operation A but not feel very strongly | 11 (18.6) | 48 (81.4) | 2.392 (0.591 to 9.678) | 0.222 | 1.264 (0.437 to 3.659) | 0.665 |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 18 (29.5) | 43 (70.5) | 3.631 (0.785 to 16.805) | 0.099 | 1.920 (0.559 to 6.590) | 0.300 |
| Prefer operation B but not feel very strongly | 35 (19.4) | 145 (80.6) | 1.015 (0.334 to 3.085) | 0.978 | 0.537 (0.266 to 1.083) | 0.082 |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 32 (20.1) | 127 (79.9) | 1.123 (0.266 to 4.739) | 0.874 | 1.594 (0.275 to 1.283) | 0.185 |
| Treatment preference | Response to questionnaire, n (%) | Interaction effect | Within-preference subgroup treatment effect | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | OR (95% CI) | p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| No preference | 80 (26.1) | 227 (73.9) | – | – | 1.14 (0.70 to 1.84) | 0.597 |
| Prefer operation A but not feel very strongly | 19 (32.2) | 40 (67.8) | 1.004 (0.341 to 2.958) | 0.994 | 1.14 (0.36 to 3.67) | 0.822 |
| Strongly prefer operation A | 25 (41.0) | 36 (59.0) | 0.925 (0.378 to 2.264) | 0.865 | 1.05 (0.46 to 2.40) | 0.901 |
| Prefer operation B but not feel very strongly | 43 (23.9) | 137 (76.1) | 0.860 (0.390 to 1.900) | 0.710 | 0.98 (0.55 to 1.73) | 0.943 |
| Strongly prefer operation B | 43 (27.0) | 116 (73.0) | 1.488 (0.931 to 2.378) | 0.097 | 1.69 (1.08 to 2.65) | 0.021 |
Discussion
Patient preference was collected in the eTHoS study, prior to randomisation, by asking participants to give their preference for a hypothetical scenario that reflected general belief at the time of the study’s initiation. The majority of participants in the eTHoS study expressed a preference, with more participants favouring longer-term over short-term outcomes. It is worth noting that among all patients who would receive SH or TH, this proportion could well be higher, as some with stronger preferences are likely to not have consented to participate in the study.
Overall, there was no clear sign of a preference effect for any of the outcomes. This finding held for all of the outcomes (EQ-5D-3L, CIS, HSS, recurrence compliance and retention). There was also no sign of a difference at baseline according to preference group. Similar to other work, we have found that the overall RCT results were not modified by treatment preference. 66 There was some suggestion of an effect on retention for strong preference in favour of those who favour long-term reduced recurrence over short-term recovery.
Several trials have been undertaken using this approach to assess the effect of patients’ preference on outcome,63,67–69 with the proportion expressing a preference varying substantially. Findings regarding whether or not the existence of preferences has affected the treatment effect have been mixed. 62,63
Our study is one of the largest to look at within-trial preferences and to assess the possible impact on the treatment effect. 63 We are aware of only one previous fully randomised surgery preference study, which was reported for incontinence surgery. 70 None looked at preference for treatment of haemorrhoids. It may be the condition that explains the lack of preference or that the treatments were of a similar (surgical) nature, though they did differ in expected and realised outcome. The DCE reported in Chapter 7 explored preferences in a more subtle way and showed a specific preference for particular attributes (lower recurrence and complications). Differences in the included participants may explain this difference in findings, or that while there were some preferences for the nature of treatment outcome, this did not affect the treatment comparison of SH and TH.
There were a number of limitations to this work. First, the preference of participants was measured indirectly and fairly crudely. The terminology we used may not have produced a fully balanced response and contributed to some degree to the favouring of B over A, aside from solely the participants’ general preference for longer-term resolution even at the cost of poor short-term outcome. The response would link to the timings we used, which reflected the views on the relative impact of the operation and the anticipated last timing of outcome assessed (6 weeks and 2 years). We asked participants in the eTHoS study directly about any preference, whereas in other studies this was assessed by the health professional. 71
Summary
No clear evidence of a treatment preference effect was observed. These analyses further support the generalisability of the main study results and that TH has a better outcome over 24 months than SH. Further work exploring which types of treatment choices are more likely to have stronger associated patient preferences would be beneficial.
Chapter 10 Discussion
Summary of findings
The eTHoS study is one of the largest studies conducted in the field of haemorrhoidal disease worldwide. The findings from the study, along with those from HubBLe and LingaLongo,16,72 have added greatly to our understanding of the management of haemorrhoids. This study showed better overall generic quality of life over the 24-month follow-up period for TH over SH. Drawing on previous work concerning clinically important differences in the EQ-5D-3L, the magnitude of difference in favour of TH was found to be clinically important. The minimum important difference for the EQ-5D-3L has been estimated to be around 0.07, based on an anchor method applied to a range of patient populations. 73,74 The participants who were randomised to receive TH also reported fewer haemorrhoid symptoms and less incidence of further surgery in the 24-month follow-up period. Incontinence symptoms and tenesmus also occurred less frequently in this arm. In the immediate postoperative period, those who were randomised to receive SH reported less pain, but this difference disappeared by 6 weeks. Short-term post-surgery quality of life (measured by the EQ-5D-3L) scores also favoured SH, reflecting the lower rates of pain and analgesic consumption. At 12 months, the EQ-5D-3L AUC quality-of-life scores were similar; however, the physical and mental health domains of the SF-36 favoured TH (see Table 17). By the end of the 24-month follow-up period, the primary outcome favoured TH. This, along with lower residual symptoms, re-interventions and costs, indicates that TH may be the surgical treatment of choice for grades II–IV haemorrhoids. Overall, this suggests that TH is the better treatment option in terms of clinical effectiveness.
The operating time, length of stay and return to normal activity by 6 weeks were the same in both arms of the study. This differs from the previously published economic studies that suggested that a shorter operating time, and associated length of hospital stay after SH, offset the cost of a stapler. 2 This fact, taken alone, draws into question the continued use of the technique, as it implies higher costs for a similar surgical outcome. The ongoing use of SH within publicly funded health services is also challenged by the other findings from this study that demonstrate a higher recurrence rate, more tenesmus, higher cost and otherwise equivocal incontinence scores and complications. Even the reduced pain after SH was equivalent by 6 weeks postoperatively.
Strengths and limitations
In the eTHoS study, the clinical recurrence of haemorrhoids and severity of symptoms were measured using the HSS, a patient-reported, dichotomous outcome measure, which was supplemented with recurrence data from both national registry databases (HES, PEDW and ISD) and patients’ self-reported further interventions. HSS is not a validated tool; however, it was adopted in the HubBLe study,16 and at the inception of the eTHoS study it was arguably the best assessment tool available. An initial follow-up period of 24 months for the evaluation of outcomes was used, given the expectation of a trade-off between short- and longer-term outcomes as transpired. We expected the majority of recurrences of haemorrhoids to happen in the first 24 months of the study; however, there were very few data available concerning the long-term success rates of haemorrhoid surgery. Extending the follow-up period to 60 months could be advantageous, although it seems unlikely that the direction of effect would change. In addition, after 24 months it would be important to distinguish between those symptoms caused by inadequate initial treatment and the occurrence of new disease. 23
Incontinence and tenesmus are significant symptoms for patients after haemorrhoid surgery. The anal sphincter complex comprises two concentric muscles, the internal and external anal sphincters. Anal cushions (the abnormal swelling of which form the basis of haemorrhoids) in the upper part of the canal contribute to continence by acting as ‘washers’ helping to form a seal. Prolapsed haemorrhoids, therefore, interfere with continence by disrupting the sealing mechanism of the sphincters and cushions working in concert. TH involves removing tissue close to the internal sphincter. Damage and subsequent impairment of continence is widely reported after TH. 74 The optimal technique for SH involves the accurate placement of the staple line 3–4 cm from the anal verge and above the dentate line in the columnar mucosa of the anal canal. Staple lines lower than this may encroach on the squamous mucosa of the anal canal (which has the sensory inputs of normal skin), contributing to relatively more postoperative pain and a greater chance of injuring the internal sphincter. 75 In the immediate postoperative period, continence was relatively impaired when compared with the baseline, reasonably attributable to subsequent pain and healing in this sensitive area (see Table 17). However, continence scores were significantly better in the TH arm up to 24 months after randomisation. High-quality surgery and the avoidance of sphincter injury in both arms, as well as reducing the volume of haemorrhoid tissue, would explain the slight improvement in continence scores over the course of the study.
Meaning of the study
The economic analysis convincingly demonstrated that TH dominates SH, as it costs £337 less than SH and is 0.07 QALYs more clinically effective than SH. SH has a < 1% probability of being considered cost-effective at the £30,000 threshold. Taken together with the HubBLe study’s health-care cost analysis, this suggests that neither of the newer surgical techniques are cost-effective. The results of the economic analysis differ from those published in Burch et al. 2, in which it was reported that TH and SH had similar costs and QALYs, but that the costs of the staple gun were offset by savings in hospital stay. In our study, the inpatient stay was similar in both arms, so there were no cost-savings in inpatient stay, and our QALY results, based on a 24-month follow-up, indicate that SH had fewer QALYs than TH (see Tables 34–36). There is a paucity of robust economic data available on haemorrhoid surgery; however, if the results of the eTHoS and HubBLe studies are adopted into practice, substantial annual cost-savings in publicly funded health services could be achieved. Given the current financial status of the NHS, commissioners of health care may consider being more prescriptive about procedures being offered for haemorrhoids.
Study design and conduct
Within this study we ran two substudies (SWATs) examining the effectiveness of incentives in maximising questionnaire returns. The SWATs were developed and conducted using vouchers with different monetary values, £5 and £30. The first SWAT, the IONTI study, was stopped early as the study team feared that it was having a negative impact on retention. The monetary value was increased to £30 (IONTI-2 study), but, again, this had little impact on response rates. The use of financial incentives is an under-researched but important area in the recruitment and continued participation of patients within trials. Based on the IONTI studies, we are uncertain of whether or not the financial incentives met a high enough threshold value to influence participant behaviour, if the participants’ motives to take part in research trials were more altruistic, if the negative result of the IONTI study was a chance finding, if there were study-specific factors or if a combination of these explain the unanticipated findings.
Participants’ treatment preferences have been suggested to potentially have a substantial impact on the outcome. As part of the study we explored this in two ways. The design of the eTHoS study included a DCE. We wanted to use this methodology to explore what attributes about an operation may influence patient choice. The DCE data were collected iteratively through a user group, a public group (on the internet) and then through participants who had completed their 24-month questionnaires. The attributes and levels were developed robustly. Overall, respondents in both groups had a general preference to have treatment over no treatment, but did not distinguish between the three treatment options. However, they also had preferences for the attributes identified, with decreases in all four treatment attributes, as expected, reducing the benefit of treatment. The magnitude of coefficients indicated that the most important marginal changes were chance of recurrence followed by chance of complications. A further novel addition to the eTHoS study was the patient preference study embedded within it. We believe this to be the first prospectively conducted preference study of patients with haemorrhoids within a RCT. Participants were asked, prior to randomisation, if they had a preference for one of the treatment modalities. Although the choices of treatments were described abstractly as surgeries ‘A’ and ‘B’, participants were more likely to favour an operation that gave them longer-term disease control but poorer short-term outcomes. Pre-randomisation preferences had no clear influence on retention or outcomes within this study.
Taken together, the findings from these two approaches to explore preferences further support the strength of the overall findings of the eTHoS study.
Results in context
The interventions compared in the eTHoS study reflected clinical practice in the UK NHS at the time of its design. During the recruitment period a new intervention, HAL, was being adopted. The HubBLe trial recently showed no benefit to HAL over RBL. 16 The HUbBLe and eTHoS studies suggest a pattern of failure of new, and purportedly better, interventions to achieve sufficient clinical outcome at an appropriate cost. They provide a cautious warning about the widespread adoption of relatively expensive and unproven new procedures. The IDEAL framework76–78 provides a potential pathway from idea to robust evaluation; however, to date, while perhaps improving, surgical evaluation is still often too late and lacking in rigour.
The introduction of new surgical treatments for haemorrhoids has been accompanied by the greater incidence of reporting of adverse events. There have been some published postoperative complications, after surgery for a benign condition, which have been severe, particularly with regard to pelvic sepsis, rectal perforation and rectovaginal fistula formation. 79 There were no reports of these complications within this study, which may reflect safe surgical practice within study centres, or that complications occur more frequently within the earlier stages of surgical learning curves. SAEs were equally distributed through both arms of the eTHoS study. All the events were expected and largely consisted of pain, bleeding, constipation and urinary retention.
A number of decisions were made reflecting the pragmatic nature of the study’s conception and design and its aim to reflect routine care. First, the study was unblinded; there was no attempt to blind either the participants (who were generally the outcome assessors) or the surgeon to the intervention. Also, the presence or absence of perianal wounds would have rendered blinding impossible, even in the short term. No prescriptive entry criteria were set for hospital inclusion; we are therefore confident that the results are generalisable across health services. A 24-month follow-up period was used to capture symptom recurrence and further interventions, giving a median follow-up of 731 days, which is an additional strength of this study.
A pragmatic approach to surgeon’s credentials was adopted. At the inception of the study, both techniques were established in common surgical practice and surgeons had to have undergone appropriate recognised training for both procedures. Ideally, this would also have included attendance at a ‘masterclass’. The effect of surgical experience on outcomes can partially be mitigated by the high level of consultant involvement in performing the surgery (71.5% in the SH arm and 62.0% in the TH arm) and the low incidence of adverse events.
There were perhaps four key potential sources of bias. First, the study was, as noted above, unblinded. However, given the lack of the evidence to support a patient preference effect, this seems unlikely to have given a biased effect. Second, final recruitment to the eTHoS study was just short (97%) of the target number; and third, there were a substantial number of missing data at the 24-month follow-up despite multiple strategies to mitigate this (IONTI and IONTI-2 studies). This perhaps reflected the population (working age), the nature of the condition (chronic and considered by some to be a sensitive subject) and the nature of the follow-up. Nevertheless, the study still had sufficient statistical precision to detect a clinically relevant difference between treatment groups. The presence of a substantial number of missing data could have led to bias being introduced into the comparison. Various secondary analyses explored plausible imputation and missing data assumptions regarding quality of life, and there was a consistent pattern of benefit in favour of TH over 24 months. Fourth, there was also a noticeable amount of non-compliance with allocation (some participants not receiving surgery, and some receiving a different operation), reflecting perhaps a mixture of clinical reality and also some surgeon and patient preferences regarding treatment. Such non-compliance tends to dilute a genuine effect. Despite this, the primary analysis still supported a difference in favour of TH, and the per-protocol analysis of only those who complied with allocation was consistent in the findings. More generally, it is worth noting that the delivery of the interventions reflected routine clinical practice across a range of UK centres in terms of the surgeons participating (their experience) and how the interventions were delivered (specific technique and centre practices). Taken together, we believe the findings are robust and generalisable.
Recommendations
The findings in this study can be compared with a recent network meta-analysis that included 98 trials of procedures for grade III and IV haemorrhoids in the analysis. 23 The authors suggested that TH was associated with fewer haemorrhoid recurrences, and that SH was associated with less postoperative pain and with a higher rate of recurrence. However, the eTHoS study findings refute the data on higher complications rates, return to normal activity, length of operation and length of stay in TH. Taken together, the HubBLe16 and eTHoS trials also answer the authors’ call for further high-quality RCTs incorporating economic cost comparisons. Our recommendation for future work would be to update a network meta-analysis incorporating these two large trials, with the addition of the LingaLongo study, which would add further value to the existing literature.
Conclusions
In conclusion, excisional surgery (TH) was both more clinically effective and less costly than SH. It was more painful in the short term, but this level of pain can be adequately managed at home. Return to normal activity rates were equal. In addition to superior quality-of-life scores, haemorrhoid symptoms scores, continence and tenesmus rates and the need for further surgery were all lower in TH. TH is, therefore, a superior surgical treatment for the management of grades II–IV haemorrhoids when compared with SH in terms of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness.
Acknowledgements
The eTHoS authors thank the NIHR HTA programme for funding the eTHoS study and the staff for their support and advice during the course of the study.
The authors would like to thank the staff of the study office past and present, that is, Julie Murdoch, Joy Eldridge, Kathryn Starr, Jackie Ellington, Margery Heath and Kirsty McCormack, based at CHaRT within the HSRU, University of Aberdeen. We would also like to thank Gladys McPherson, Mark Forrest and the programming team at CHaRT for their information technology and database support during the course of the study.
Sincere thanks are also due to the staff of the North East of Scotland Research Ethics Service (NoSRES) for considering our application and amendments during the course of the study.
The eTHoS study team acknowledges the support of the NIHR, through the Comprehensive Local Research Networks in England, Wales and Scotland.
We would also like to acknowledge the work of Mandy Ryan (Health Economics Research Unit, University of Aberdeen) and Euan MacDonald (NHS Forth Valley), who contributed to the development of the DCE questionnaire.
Sincere thanks to Andrew Elders, who was the eTHoS statistician until May 2014.
We would like to acknowledge the members of the PMG for their ongoing advice and support of the study; the independent members of the TSC and the DMC, and the staff at recruitment sites who facilitated recruitment, treatment and follow-up of study participants.
Grant holders
Angus JM Watson, Malcolm Loudon, David Jayne, Ramesh Rajagopal (who replaced Andrew Maw on 21 February 2012), Finlay Curran, Steven Brown, Jonathan Cook, John Norrie (who replaced Jennifer Burr as CHaRT director) and Brian Buckley. Other original grant holders who we wish to acknowledge include Luke Vale and Laura Ternent.
Project management group
The eTHoS study group comprises Angus JM Watson, Kathleen MacLeod, Malcolm Loudon, David Jayne, Ramesh Rajagopal, Finlay Curran, Steven Brown, Jonathan Cook, John Norrie, Brian Buckley, Mary Kilonzo, Jessica Wood, Alison McDonald and Mark Forrest (who replaced Gladys McPherson on 1 July 2015).
Independent members of the Trial Steering Committee
Robert Steele (Chairperson), Laura Magill, James Hill and Robert Arnott.
Independent members of the Data Monitoring Committee
Ajith Siriwardena (Chairperson), Angela Crook and Diane Whitham (who replaced Shaun Treweek on 1 February 2013).
Recruitment sites
Principal investigators
Malcolm Loudon and Craig Parnaby (who replaced Malcolm Loudon on 30 December 2014), Anil Agarwal, Steven Brown, Jag Varma and Venkatesh Shanmugan (who replaced Jag Varma on 1 March 2012), David Jayne, Sandeep Kapur, Finlay Curran, Paris Tekkis, Graham Sunderland, Ramesh Rajagopal, Ian Lindsey, Christopher Barben, Alan Grant, Marc Lamah, Madan Jha, Suhail Anwar, Liviu Titu, Al Mutaz Abulafi, Pawan Mathur Harjeet Narula and Adeshina Fawole (who replaced Harjeet Narula on 8 April 2014), Ponnandai Arumugam, Yaser Mohsen, Ray Delicata, Reuben West, William Speake, Euan MacDonald, Mark Mercer-Jones, Matthew Tutton, Mark Zammit, Suresh Pillai and Abhiram Sharma.
Research nurses/fellows/clinical trial assistants
Kathleen MacLeod (lead research nurse), Louise Hunter, Carole Edwards, Angela Lee, Michael Agymang, John Humphreys, Nathaniel Mills, Julie Dorell, Michelle Deighton, Sharon Kennison, Rachel Mottram, Emily Calton, Kelsey Armitage, Claire Shaw, Anthony Kennedy, Amanda Cowton, Gillian Horner, Lyndsey Taylor, Glynis Rose, Mohammed Shazad Khalid, Catherine Moriarty, Holly Speight, Louise White, Laura Wilkinson, Georgina Glister, Melissa Rosbergen, David Tomlinson, Jocelyn Keshet-Price, Glaxy Grey, Olga Colaco, Rojy Santosh, Karen Breislin, Hayley Brooks, Darwisa Abulla, Joanne Mangan, Katherine McGuigan, Elaine Cant, Karen Duffy, Paul Cofie, Helen Ingram, Simona Fourie, Melanie Harrison, Maxine Handford, Shirley Cooper, Tracey Kramer-Taylor, Chris Macdonald, Richard Rye, Mary Flowerdew, Julie Tregonning, Marie Branch, Rachel Clarkson, Julie McGivern, Allison Holmes, Helyn Evans, Michael Chang, Ajeet Kumar, Rebecca Bryne, Rebecca Foster, Stephani Lupton, Aimee Hayton-Bott, Barbara Burlace, Karen Simeson, Jackie Ward, Annette Jones, Lynsey Bourner, Kerri Robinson, Alyson Andrew, Amanda Datson, Kirsty Bond, Lisa Trembath, Leanne Welch, Jessica Summers, T Lynne Graves, Mariam Nasseri, Roz Gill, Polly Needs, Daniel McVeigh, Tom Clifford, Alexandra Diaz, Graham Sturgeon, Donna Cotterill, Dawn Simmons, Hugh Lloyd-Jones, Harvey Dymond, Glenn Saunders, Sarah Kidd, Charlotte Downes,Lindsey Kimber, Shirley Pyke, Ryan Humphries, Maggie Hughes, Bola Oyebanjo, , Joanne Donnachie, Alison Gosh, Natalie Wheatley, Aine Turner, Marianne Morgan, Orla Turner, Cathleen Chabo, Clare Bullock, Stacey Pepper, Amanda Solebury, Karen Warner, Victoria Sherburn, Sarah Ford, Kathryn Fellows, Stephen Preston, Anna Gipson, Alison Walker, Cheryl Berrisford, Tracey Platt and Deirdre Leonard. Special thanks to Angela Allan, Joan Henderson and Christine Dallas, who completed the participant questionnaire reminder telephone calls.
NHS trusts and health boards
NHS Highland and Islands, Inverness; NHS Grampian, Aberdeen; North Tees and Hartlepool Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Stockton-on-Tees; Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Sheffield; County Durham and Darlington NHS Foundation Trust, Durham; Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, Leeds; Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Norwich; Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester; Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London; NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde, Glasgow; Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board, Rhyl; Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Oxford; Aintree University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Liverpool; Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust, Brighton; South Tees Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Middlesbrough; Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust, Huddersfield; Wirral University Teaching Hospital, Upton, Wirral; Croydon Health Services NHS Trust, Croydon; Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, London; The Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust, Wakefield; Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust, Truro; The Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, London; Bwrdd Iechyd Aneurin Bevan Health Board, Wales; Weston Area Health NHS Trust, Somerset; Derby Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Derby; NHS Forth Valley, Stirling; Gateshead Health NHS Foundation Trust, Gateshead; Colchester Hospital University NHS Foundation Trust, Colchester; Basildon and Thurrock University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Basildon; United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust, Lincoln; and University Hospital of South Manchester NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester.
The eTHoS study participants
Finally, we would like to acknowledge the contribution of the eTHoS study participants, without whom we would not have been able to complete this research.
Contributions of authors
Professor Angus JM Watson (Consultant Colorectal Surgeon) was the chief investigator of the study; he had complete involvement and oversight of the study design, execution and data collection, and was responsible for the final report.
Professor Jonathan Cook (Senior Statistician/Triallist) contributed his methodological expertise to the design of the study, recruitment and interpretation of the study findings, and to the writing and delivery of the final report.
Miss Jemma Hudson (Statistician) contributed to the statistical analysis of the study and writing of the results and discussion chapters.
Ms Mary Kilonzo (Research Fellow, Health Economics and co-investigator) contributed to the analysis of the health economics component of the study and also to the writing of the health economics chapters.
Mrs Jessica Wood (Trial Manager) was responsible for the day-to-day management and delivery of the study, and the writing and delivery of the final report.
Dr Hanne Bruhn (Research Fellow) contributed to the delivery of the study and the writing and delivery of the final report.
Mr Steven Brown (Consultant Colorectal Surgeon) contributed to the design and delivery of the study, and to the writing of the final report.
Dr Brian Buckley (Patient representative) contributed to the design and delivery of the study, and to the writing of the final report.
Mr Finlay Curran (Consultant Colorectal Surgeon) contributed to the design of the study, delivery of the study and to the writing of the final report.
Mr David Jayne (Consultant Colorectal Surgeon) contributed to the design and delivery of the study, and to the writing of the final report.
Mr Malcolm Loudon (Consultant Colorectal Surgeon) contributed to the design and delivery of the study, and to the writing of the final report.
Mr Ramesh Rajagopal (Consultant Colorectal Surgeon) contributed to the design and delivery of the study, and to the writing of the final report.
Mrs Alison McDonald (Senior Trial Manager) contributed to the delivery of the study and to the writing of the final report.
Professor John Norrie (Director of CHaRT) contributed to the design and delivery of the study, and to the writing of the final report.
The HSRU is core funded by the Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health and Social Care Directorates; however, the opinions expressed in this publication are those of the authors, and may not be shared by the Chief Scientist Office or the Department of Health and Social Care.
Publication
Watson AJM, Hudson J, Wood J, Kilonzo M, Brown SR, McDonald A, et al. Comparison of stapled haemorrhoidopexy with traditional excisional surgery for haemorrhoidal disease (eTHoS): a pragmatic, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;388:2375–85.
Data sharing statement
All available data can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Watson AJM, Bruhn H, MacLeod K, McDonald A, McPherson G, Kilonzo M, et al. A pragmatic, multicentre, randomised controlled trial comparing stapled haemorrhoidopexy to traditional excisional surgery for haemorrhoidal disease (eTHoS): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2014;15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-15-439.
- Burch J, Epstein D, Baba-Akbari A, Weatherly H, Fox D, Golder S, et al. Stapled haemorrhoidectomy (haemorrhoidopexy) for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2008;12. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta12080.
- Jóhannsson HO, Graf W, Påhlman L. Long-term results of haemorrhoidectomy. Eur J Surg 2002;168:485-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/110241502321116505.
- Goligher J. Surgery of the Anus, Rectum and Colon. London: Bailliere Tindall; 1984.
- NHS Digital . Hospital Episode Statistics, Admitted Patient Care – England, 2006–07 2007. www.content.digital.nhs.uk/article/2021/Website-Search?productid=92&q=haemorrhoid+procedure&sort=Relevance&size=10&page=2&area=both#top (accessed 23 June 2016).
- Thomson WH. The nature of haemorrhoids. Br J Surg 1975;62:542-52. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.1800620710.
- Longo A. Treatment of Haemorrhoidal Disease by Reduction of Mucosa and Haemorrhoidal Prolapse With a Circular Suturing Device: A New Procedure n.d.
- Lacerda-Filho A, Silva RG. Stapled hemorrhoidectomy: present status. Arq Gastroenterol 2005;42:191-4. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0004-28032005000300013.
- Shao WJ, Li GC, Zhang ZH, Yang BL, Sun GD, Chen YQ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing stapled haemorrhoidopexy with conventional haemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg 2008;95:147-60. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.6078.
- Jayaraman S, Colquhoun PHD, Malthaner RA. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy is associated with a higher long-term recurrence rate of internal hemorrhoids compared with conventional excisional hemorrhoid surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 2007;50:1297-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-007-0308-4.
- Laughlan K, Jayne DG, Jackson D, Rupprecht F, Ribaric G. Stapled haemorrhoidopexy compared to Milligan–Morgan and Ferguson haemorrhoidectomy: a systematic review. Int J Colorectal Dis 2009;24:335-44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-008-0611-0.
- Jayaraman S, Colquhoun PH, Malthaner RA. Stapled versus conventional surgery for hemorrhoids. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;4. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005393.pub2.
- Thaha MA, Campbell KL, Kazmi SA, Irvine LA, Khalil A, Binnie NR, et al. Prospective randomised multi-centre trial comparing the clinical efficacy, safety and patient acceptability of circular stapled anopexy with closed diathermy haemorrhoidectomy. Gut 2009;58:668-78. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.151266.
- Technology Appraisal Guidance [TA128]. Chapter 6 – Recommendations for Further Research. London: NICE; 2007.
- Shanmugam V, Muthukumarasamy G, Cook JA, Vale L, Watson AJM, Loudon MA. Randomized controlled trial comparing rubber band ligation with stapled haemorrhoidopexy for Grade II circumferential haemorrhoids: long-term results. Colorectal Dis 2010;12:579-86. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1318.2009.01841.x.
- Brown SR, Tiernan JP, Watson AJM, Biggs K, Shephard N, Wailoo AJ, et al. Haemorrhoidal artery ligation versus rubber band ligation for the management of symptomatic second-degree and third-degree haemorrhoids (HubBLe): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;388:356-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30584-0.
- Nyström PO, Qvist N, Raahave D, Lindsey I, Mortensen N. Randomized clinical trial of symptom control after stapled anopexy or diathermy excision for haemorrhoid prolapse. Br J Surg 2010;97:167-76. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.6804.
- Kim JS, Vashist YK, Thieltges S, Zehler O, Gawad KA, Yekebas EF, et al. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy versus Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy in circumferential third-degree hemorrhoids: long-term results of a randomized controlled trial. J Gastrointest Surg 2013;17:1292-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2220-7.
- Ripetti V, La Vaccara V, Greco S, Arullani A. A randomized trial comparing stapled rectal mucosectomy versus open and semiclosed hemorrhoidectomy. Dis Colon Rectum 2015;58:1083-90. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0000000000000454.
- De Nardi P, Capretti G, Corsaro A, Staudacher C. A prospective, randomized trial comparing the short- and long-term results of Doppler-guided transanal hemorrhoid dearterialization with mucopexy versus excision hemorrhoidectomy for grade III hemorrhoids. Dis Colon Rectum 2014;57:348-53. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0000000000000085.
- Lucarelli P, Picchio M, Caporossi M, De Angelis F, Di Filippo A, Stipa F, et al. Transanal haemorrhoidal dearterialisation with mucopexy versus stapler haemorrhoidopexy: a randomised trial with long-term follow-up. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2013;95:246-51. https://doi.org/10.1308/003588413X13511609958136.
- Infantino A, Altomare DF, Bottini C, Bonanno M, Mancini S. Prospective randomized multicentre study comparing stapler haemorrhoidopexy with Doppler-guided transanal haemorrhoid dearterialization for third-degree haemorrhoids. Colorectal Dis 2012;14:205-11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1318.2011.02628.x.
- Simillis C, Thoukididou SN, Slesser AA, Rasheed S, Tan E, Tekkis PP. Systematic review and network meta-analysis comparing clinical outcomes and effectiveness of surgical treatments for haemorrhoids. Br J Surg 2015;102:1603-18. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.9913.
- Data Protection Act 1998. London: The Stationery Office; 1998.
- Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal. London: NICE; 2013.
- Ramsey S, Willke R, Briggs A, Brown R, Buxton M, Chawla A, et al. Good research practices for cost-effectiveness analysis alongside clinical trials: The ISPOR RCT-CEA Task Force report. Value Health 2005;8:521-33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2005.00045.x.
- NHS Reference Costs 2014 to 2015. London: Department of Health; 2007.
- Curtis L, Burns A. Unit Costs of Health of Social Care 2015. Canterbury: PSSRU, University of Kent; 2015.
- British National Formulary. London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press; 2016.
- British National Formulary. London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press; 2015.
- Travel-Mileage and Fuel Rates and Allowances. London: HM Revenue & Customs; 2013.
- Office for National Statistics . Average Weekly Earning Time Series Dataset 2017. www.ons.gov.uk/employmentandlabourmarket/peopleinwork/earningsandworkinghours/datasets/averageweeklyearnings (accessed 23 May 2016).
- NHS . Pay Review Body 29th Report: 2016 2016. www.gov.uk/government/publications/national-health-service-pay-review-body-29th-report-2016 (accessed 25 May 2016).
- Department for Transport . WebTAG: TAG Data Book, December 2015 2015. www.gov.uk/government/publications/webtag-tag-data-book-december-2015 (accessed 23 May 2016).
- Fader M, Cottenden A, Getliffe K, Gage H, Clarke-O’Neill S, Jamieson K, et al. Absorbent products for urinary/faecal incontinence: a comparative evaluation of key product designs. Health Technol Assess 2008;12. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta12290.
- EuroQol Group . Euroqol – a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16:199-208. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-8510(90)90421-9.
- EQ-5D-3L User Guide – Basic Information on How to Use the EQ-5D-3L Instrument. Rotterdam: EuroQoL Group; 2015.
- Kind P, Hardman G, Macran S. UK Population Norms for EQ-5D. York: University of York; 1999.
- Garratt AM, Ruta DA, Abdalla MI, Russell IT. SF-36 health survey questionnaire: II. Responsiveness to changes in health status in four common clinical conditions. Qual Health Care 1994;3:186-92. https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.3.4.186.
- Brazier JE, Roberts J. The estimation of a preference-based measure of health from the SF-12. Med Care 2004;42:851-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlr.0000135827.18610.0d.
- Royston P. Multiple imputation of missing values: update of ice. Stata J 2005;5:527-36.
- Briggs A, Clark T, Wolstenholme J, Clarke P. Missing. presumed at random: cost-analysis of incomplete data. Health Econ 2003;12:377-92. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.766.
- Earnshaw J, Lewis G. NICE guide to the methods of technology appraisal: pharmaceutical industry perspective. PharmacoEconomics 2008;26:725-7. https://doi.org/10.2165/00019053-200826090-00002.
- Glick HA, Doshi JA, Sonnad SS, Polsky D. Economic Evaluation in Clinical Trials. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2007.
- Briggs AH, Wonderling DE, Mooney CZ. Pulling cost-effectiveness analysis up by its bootstraps: a non-parametric approach to confidence interval estimation. Health Econ 1997;6:327-40. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1050(199707)6:4<327::AID-HEC282>3.0.CO;2-W.
- Briggs AH, O’Brien BJ, Blackhouse G. Thinking outside the box: recent advances in the analysis and presentation of uncertainty in cost-effectiveness studies. Annu Rev Public Health 2002;23:377-401. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.publhealth.23.100901.140534.
- Clark MD, Determann D, Petrou S, Moro D, de Bekker-Grob EW. Discrete choice experiments in health economics: a review of the literature. PharmacoEconomics 2014;32:883-902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-014-0170-x.
- de Bekker-Grob EW, Ryan M, Gerard K. Discrete choice experiments in health economics: a review of the literature. Health Econ 2012;21:145-72. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.1697.
- Adams J, Bateman B, Becker F, Cresswell T, Flynn D, McNaughton R, et al. Effectiveness and acceptability of parental financial incentives and quasi-mandatory schemes for increasing uptake of vaccinations in preschool children: systematic review, qualitative study and discrete choice experiment. Health Technol Assess 2015;19. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta19940.
- Lancsar E, Louviere J. Conducting discrete choice experiments to inform healthcare decision making: a user’s guide. PharmacoEconomics 2008;26:661-77. https://doi.org/10.2165/00019053-200826080-00004.
- Bridges JF, Hauber AB, Marshall D, Lloyd A, Prosser LA, Regier DA, et al. Conjoint analysis applications in health – a checklist: a report of the ISPOR Good Research Practices for Conjoint Analysis Task Force. Value Health 2011;14:403-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2010.11.013.
- Kuhfeld WF. Marketing Research Methods in SAS. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc; 2010.
- Mott DJ, Najafzadeh M. Whose preferences should be elicited for use in health-care decision-making? A case study using anticoagulant therapy. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res 2016;16:33-9. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737167.2016.1115722 (accessed March 2016).
- Research Now . Market Research Solutions 2016. www.researchnow.com (accessed 10 October 2016).
- Hole AR. A comparison of approaches to estimating confidence intervals for willingness to pay measures. Health Econ 2007;16:827-40. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.1197.
- Edwards PJ, Roberts I, Clarke MJ, Diguiseppi C, Wentz R, Kwan I, et al. Methods to increase response to postal and electronic questionnaires. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;3. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.MR000008.pub4.
- Gates S, Williams MA, Withers E, Williamson E, Mt-Isa S, Lamb SE. Does a monetary incentive improve the response to a postal questionnaire in a randomised controlled trial? The MINT incentive study. Trials 2009;10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-10-44.
- Brueton VC, Tierney J, Stenning S, Harding S, Meredith S, Nazareth I, et al. Strategies to improve retention in randomised trials. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;12. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.MR000032.pub2.
- Bower P, Brueton V, Gamble C, Treweek S, Smith CT, Young B, et al. Interventions to improve recruitment and retention in clinical trials: a survey and workshop to assess current practice and future priorities. Trials 2014;15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-15-399.
- Glidewell L, Thomas R, MacLennan G, Bonetti D, Johnston M, Eccles MP, et al. Do incentives, reminders or reduced burden improve healthcare professional response rates in postal questionnaires? two randomised controlled trials. BMC Health Serv Res 2012;12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-12-250.
- Prescott RJ, Counsell CE, Gillespie WJ, Grant AM, Russell IT, Kiauka S, et al. Factors that limit the quality, number and progress of randomised controlled trials. Health Technol Assess 1999;3.
- King M, Nazareth I, Lampe F, Bower P, Chandler M, Morou M, et al. Conceptual framework and systematic review of the effects of participants’ and professionals’ preferences in randomised controlled trials. Health Technol Assess 2005;9. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta9350.
- Preference Collaborative Review Group . Patients’ preferences within randomised trials: systematic review and patient level meta-analysis. BMJ 2008;337. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.a1864.
- Grant AM, Wileman SM, Ramsay CR, Mowat NA, Krukowski ZH, Heading RC, et al. Minimal access surgery compared with medical management for chronic gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: UK collaborative randomised trial. BMJ 2008;337. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.a2664.
- Torgerson DJ, Klaber-Moffett J, Russell IT. Patient preferences in randomised trials: threat or opportunity?. J Health Serv Res Policy 1996;1:194-7.
- Cockayne S, Curran M, Denby G, Hashmi F, Hewitt C, Hicks K, et al. EVerT: Cryotherapy versus salicylic acid for the treatment of verrucae – a randomised controlled trial. Health Technol Assess 2011;15. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta15320.
- Hardy GE, Barkham M, Shapiro DA, Reynolds S, Rees A, Stiles WB. Credibility and outcome of cognitive-behavioural and psychodynamic-interpersonal psychotherapy. Br J Clin Psychol 1995;34:555-69. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8260.1995.tb01489.x.
- Moffett JAK, Jackson DA, Richmond S, Hahn S, Coulton S, Farrin A, et al. Randomised trial of a brief physiotherapy intervention compared with usual physiotherapy for neck pain patients: outcomes and patients’ preference. BMJ 2005;330:75-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38286.493206.82.
- Thomas E, Croft PR, Paterson SM, Dziedzic K, Hay EM. What influences participants’ treatment preference and can it influence outcome? Results from a primary care-based randomised trial for shoulder pain. Br J Gen Pract 2004;54:93-6.
- Kitchener HC, Dunn G, Lawton V, Reid F, Nelson L, Smith ARB. Laparoscopic versus open colposuspension – results of a prospective randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2006;113:1007-13. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.01035.x.
- Cockayne S, Hicks K, Kangombe AR, Hewitt C, Concannon M, Thomas K, et al. The effect of patients’ preference on outcome in the EVerT cryotherapy versus salicylic acid for the treatment of plantar warts (verruca) trial. J Foot Ankle Surg 2012;5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-1146-5-28.
- Lehur PA, Didnée AS, Faucheron JL, Meurette G, Zerbib P, Siproudhis L, et al. Cost-effectiveness of new surgical treatments for hemorrhoidal disease: a multicentre randomised controlled trial comparing transanal Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation with monopexy and circular stapled hemorrhoidopexy. Ann Surg 2016;264:710-6. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000001770.
- Cook JA, Hislop J, Adewuyi TE, Harrild K, Altman DG, Ramsay CR, et al. Assessing methods to specify the target difference for a randomised controlled trial: DELTA (Difference ELicitation in TriAls) review. Health Technol Assess 2014;18. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta18280.
- Walters SJ, Brazier JE. Comparison of the minimally important difference for two health state utility measures: EQ-5D and SF-6D. Qual Life Res 2005;14:1523-32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-004-7713-0.
- Shanmugam V, Watson AJ, Chapman AD, Binnie NR, Loudon MA. Pathological audit of stapled haemorrhoidopexy. Colorectal Dis 2005;7:172-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1318.2004.00748.x.
- McCulloch P, Cook JA, Altman DG, Heneghan C, Diener MK. IDEAL Group . IDEAL framework for surgical innovation 1: the idea and development stages. BMJ 2013;346. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f3012.
- Cook JA, McCulloch P, Blazeby JM, Beard DJ, Marinac-Dabic D, Sedrakyan A. IDEAL Group . IDEAL framework for surgical innovation 3: randomised controlled trials in the assessment stage and evaluations in the long term study stage. BMJ 2013;346. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f2820.
- McCulloch P, Altman DG, Campbell WB, Flum DR, Glasziou P, Marshall JC, et al. No surgical innovation without evaluation: the IDEAL recommendations. Lancet 2009;374:1105-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61116-8.
- Faucheron JL, Voirin D, Abba J. Rectal perforation with life-threatening peritonitis following stapled haemorrhoidopexy. Br J Surg 2012;99:746-53. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.7833.
Appendix 1 The eTHoS study participant questionnaire
Appendix 2 The eTHoS study patient information sheet
Appendix 3 The eTHoS study case report form
Appendix 4 ‘To incentivise or not to incentivise’ and ‘to incentivise or not to incentivise’-2 appendices
Appendix 5 The eTHoS study trial consent form
Appendix 6 The eTHoS study amendments
List of abbreviations
- AUC
- area under the curve
- CEAC
- cost-effectiveness acceptability curve
- CHaRT
- Centre for Healthcare Randomised Trials
- CI
- confidence interval
- CIS
- Cleveland Incontinence Score
- CONSORT
- Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials
- CRF
- case report form
- DCE
- discrete choice experiment
- DMC
- Data Monitoring Committee
- EQ-5D-3L
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions, three-level version
- eTHoS
- either Traditional Haemorrhoidectomy or Stapled haemorrhoidopexy for haemorrhoidal disease
- GP
- general practitioner
- HAL
- haemorrhoidal artery ligation
- HES
- Hospital Episode Statistics
- HSRU
- Health Services Research Unit
- HSS
- Haemorrhoid Symptom Score
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- HubBLe
- haemorrhoidal artery ligation versus rubber band ligation for the management of symptomatic second-degree and third-degree haemorrhoids
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- INB
- incremental net benefit
- IONTI
- ‘to incentivise or not to incentivise’
- IQR
- interquartile range
- ISD
- Information Services Division
- MD
- mean difference
- MI
- multiple imputation
- mWTP
- marginal willingness to pay
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NIHR
- National Institute for Health Research
- OR
- odds ratio
- PEDW
- Patient Episode Database Wales
- PIL
- patient information leaflet
- PMG
- project management group
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- RBL
- rubber band ligation
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- REC
- Research Ethics Committee
- SAE
- serious adverse event
- SD
- standard deviation
- SF-36
- Short Form questionnaire-36 items
- SF-6D
- Short Form questionnaire-6 Dimensions
- SH
- stapled haemorrhoidopexy
- SWAT
- study within a trial
- TH
- traditional haemorrhoidectomy
- TSC
- Trial Steering Committee
- VAS
- visual analogue scale
- WTP
- willingness to pay
