Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 09/55/38. The contractual start date was in September 2011. The draft report began editorial review in June 2016 and was accepted for publication in March 2017. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Manny Bagary reports personal fees from Eisai Co., Ltd, and personal fees from UCB Pharma outside the submitted work. Angela Pullen reports grants from GlaxoSmithKline plc., Cyberonics, Inc., Sanofi S.A., Desitin Pharma Ltd and UCB Pharma Ltd outside the submitted work. Sandra Eldridge is a member of the Health Technology Assessment Clinical Trials Board and National Institute for Health Research Clinical Trials Unit Support Funding.
Disclaimer
This report contains transcripts of interviews conducted in the course of the research and contains language that may offend some readers.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2018. This work was produced by Thangaratinam et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2018 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Burden of the problem
Epilepsy complicates 0.6% of all pregnancies in the UK, affecting 0.5–1.0% of the general population. 1 Approximately one-third of people receiving antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are of reproductive age,2 and there has been a rise in the number of pregnancies exposed to AEDs in the past few decades. 3 Maternal mortality is 10-fold higher among pregnant women with epilepsy than among those without epilepsy. 1 In 2009–12, 14 maternal deaths in the UK were attributed to epilepsy4 and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy, accounting for about 80% of deaths in women with epilepsy. 1,4 These were invariably a direct consequence of seizures. The numbers of maternal deaths related to epilepsy in the UK have been stagnant over the last 15 years. Confidential enquiries into maternal deaths have repeatedly highlighted concerns about epilepsy management during pregnancy. 4,5
In addition to major risks to the mother, uncontrolled epilepsy with generalised tonic–clonic convulsions carries risk of harm to the fetus including miscarriage, fetal hypoxia and acidosis, and fetal loss. 6–8 The effect of epilepsy can impact daily living, resulting in loss of driving licence, negative impact on employment and relationships and reduced quality of life (QoL). Seizure control is central to the management of pregnant women with epilepsy, and mothers are often advised to continue the AED in pregnancy.
Antiepileptic drug exposure in utero is associated with congenital malformation,9 with fetal risk related to the number of AEDs, AED type and, probably, AED dose. 10 Furthermore, the magnitude of AED dose exposure to the fetus in utero and the effect of continued AED intake in pregnancy on the long-term neurological development of children is not known. There is a consensus that the risks of uncontrolled convulsive seizures in the mother outweigh the potential teratogenic risk and any other adverse effect on offspring. 11,12
Antiepileptic drug levels decrease in pregnancy in a proportion of women with epilepsy and are hypothesised to aggravate seizures. 13–15 Monitoring of serum AED levels in each trimester, and after delivery, has been recommended by the American Academy of Neurology based on consensus as a good practice. 16 In the UK, however, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network guidelines do not recommend regular AED monitoring in pregnancy because of a paucity of evidence. 12
There are no randomised trials evaluating the effects of additional therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) over clinical features monitoring (CFM) in determining the optimal management of women with epilepsy on AEDs in pregnancy. Furthermore, the acceptability of the two strategies, their impact on the QoL of the mother and pregnancy outcomes is not known.
Objectives
Primary objective
To determine, in pregnant women with epilepsy on AEDs who experience a 25% decrease from baseline in serum AED levels, if a strategy of additional therapeutic drug monitoring compared with clinical features monitoring alone to determine the optimal dose of AED reduces the risk of seizures.
Secondary objectives
-
To determine if there is a relationship between the level of reduction in serum AED levels and seizures, by comparing women in a non-randomised cohort with stable levels with those in randomised cohorts with a decrease in levels.
-
To evaluate the effect of the two monitoring strategies on maternal and fetal outcomes in women with a decrease in serum AED levels.
-
To assess the effect of therapeutic drug monitoring versus clinical features monitoring on QoL in pregnant women with epilepsy on AEDs.
-
To identify any differences in total AED dose exposure between therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring strategies.
-
To assess the adverse effects of AEDs in all women exposed to the drugs.
-
To gain insight into the way pregnant women with epilepsy rationalise and make sense of the management of AEDs in the context of their lives through a qualitative study.
-
To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the two strategies.
Chapter 2 Methods
Study design
A double-blind, randomised trial nested within a cohort study was conducted and a qualitative study of acceptability of the two strategies was undertaken. The study received ethics approval from the National Research Ethics Service Committee West Midlands (reference number 11/WM/0164, trial registration 01253916).
Setting
The trial was conducted across 50 obstetric and/or epilepsy clinics in secondary and tertiary care units in the UK between November 2011 and May 2015.
Patient and public involvement
The Epilepsy Action charity assisted with the trial design and promotion. A member of the charity (APU) contributed in Trial Steering Committee (TSC) meetings to the general management of the project.
A patient representative (NMo) sat on the Trial Management Group and TSC panels and provided input towards the overall supervision of the trial.
Eligibility criteria
For inclusion in the trial, participants had to fulfil the following eligibility criteria.
Inclusion criteria
-
Viable pregnancy of < 24 weeks’ gestation.
-
Confirmed diagnosis of epilepsy including primary, localised or unclassified.
-
Lamotrigine monotherapy/polytherapy (with carbamazepine, phenytoin or levetiracetam) or carbamazepine monotherapy or phenytoin monotherapy or levetiracetam monotherapy.
-
Capable of understanding the information provided.
Exclusion criteria
-
Aged < 16 years.
-
Documented status epilepticus in the last year or non-epileptic seizures in the last 2 years.
-
Non-lamotrigine polytherapy or sodium valproate monotherapy or polytherapy.
-
Participation in any blinded, placebo-controlled trials of investigational medicinal products in pregnancy.
-
Significant learning disability.
-
Unable to complete seizure diaries or recall frequency of seizures accurately.
-
History of alcohol or substance abuse or dependence in the last 2 years.
-
Expressed an intention not to take AEDs in pregnancy.
Health technologies assessed
Women with a decrease in serum AED levels in pregnancy compared with baseline levels at booking or pre-pregnancy were randomised to management based on serum AED levels or to management based on clinical factors only.
Therapeutic drug monitoring group
The monthly levels of serum AED were communicated to the responsible clinicians. Clinicians managed women based on knowledge of serum AED levels in addition to clinical factors. The management involved discussion with the patient of potential risks of reduced serum levels, and the risks and benefits of an increase in AED dose to mother and baby. Women were provided treatment options including more frequent monitoring, increase in dosage of the AED immediately or delayed increase pending early testing.
Clinical features monitoring group
The clinician and mother were not informed of the serum AED levels, unless requested as part of an unblinding procedure. The decision to change the dose of AED was made by a responsible clinician based on clinical features alone.
Randomisation
Participants were allocated in 1 : 1 ratio to therapeutic drug monitoring or clinical features monitoring using a stratified block randomisation, with random block size of two, four or six to reduce predictability. Stratification variables were:
-
baseline AED therapy: (1) lamotrigine monotherapy, (2) carbamazepine, phenytoin or levetiracetam monotherapy, or (3) lamotrigine polytherapy
-
presence or absence of seizures 3 months prior to pregnancy.
Randomisation was carried out online using computer-generated randomisation sequences provided by the Nottingham Clinical Trials Unit.
Outcome
Primary outcome
The primary outcome was seizure deterioration, which was defined as time to first seizure, including first and subsequent seizures after randomisation, over the whole period of monitoring including 6 weeks post delivery.
Secondary outcomes
Maternal
-
Neurological: the proportion of women experiencing seizures who were seizure free in the 3 months prior to consent, number of seizures per week and number of seizure-free days per week, mean daily AED dose exposure and adverse events as measured by the Liverpool Adverse Events Profile (LAEP).
-
Obstetric: maternal death, mode of delivery, pre-term labour, induction of labour, pre-eclampsia, ante- and postpartum haemorrhage, admission to high-dependency/intensive care unit, breastfeeding, infection and gestational diabetes mellitus.
-
QoL: epilepsy-specific QoL [as measured by the Quality Of Life In Epilepsy – 31-item questionnaire (QOLIE-31)] and a generic QoL [as measured by the EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D)].
Fetal and neonatal
-
Stillbirth, neonatal death, major congenital malformations (defined as structural abnormalities with surgical, medical or cosmetic importance diagnosed either antenatally or postnatally17), minor abnormalities, Apgar scores at 1 minute and 5 minutes, admission to neonatal unit, birthweight, head circumference, fetal growth and cord blood levels of AED.
Study conduct
Relevant neurological and obstetric histories were obtained from pregnant women with epilepsy at their booking/antenatal visit. Baseline data were collected on age, ethnicity, age at first seizure (excluding febrile seizures), seizure frequency over the previous 6 months, seizure types, epilepsy syndrome, aetiology of epilepsy, duration of epilepsy, current AED and dose, baseline serum AED level, indications of depression [as measured via the Neurological Disorders Depression Inventory for Epilepsy (NDDI-E)], learning difficulty, school leaving age, educational performance, current employment, previous AED pregnancy exposure, previous pregnancy complications, perinatal outcome, number of children, health of children and educational status of children at the first visit. Indications of depression at baseline were scored by participant responses to the NDDI-E. A score of > 15 out of 24 on the NDDI-E was considered to be indicative of depression and clinicians were requested to refer in accordance with local practice.
Participants were regularly monitored for serum AED levels from baseline at monthly intervals until 6–8 weeks post partum. Women were asked to record seizure activity in diaries specially developed for collecting trial data throughout the course of their participation. Women completed the EQ-5D (maximum score of 1), LAEP (maximum score of 76) and a Patient Costs Questionnaire at baseline, and all follow-up and postnatal visits. Responses to the QOLIE-31 (maximum score of 100 or QOLIE-31 overall health, maximum score of 10) were collected at baseline and in late pregnancy (i.e. 32–36 weeks’ gestation). A higher score indicates a better health state.
Women with a ≥ 25% reduction in serum AED levels at any time in pregnancy, compared with baseline or pre-pregnancy levels, were randomised to therapeutic drug monitoring or clinical features monitoring. Women without a reduction in serum AED levels continued to be monitored in the non-randomised arm, and were randomised if their serum AED levels fell below 25% at any time until delivery. Women and clinicians in the clinical features monitoring arm and non-randomised cohort were blinded to the results. If randomised to the therapeutic drug monitoring arm, the serum levels were communicated to the participating centre within 1 working day of receipt of the test result from the laboratory. If appropriate, the clinician or the research midwife/nurse (on the advice of the clinician) contacted the participant to advise on a course of action within 7 working days of receipt of information from the trial unit. The current daily dose of AED and any adjustment was recorded. In exceptional circumstances, additional serum AED levels were requested from the central laboratory outside the trial visit plan, if deemed appropriate by the treating clinician (e.g. clinical suspicion of toxicity or non-adherence).
We obtained information on seizure status from the seizure diaries, and all maternal and fetal outcomes from clinical records. When women were admitted in labour, blood samples for serum AED levels were obtained alongside routine blood tests at any point from admission in labour up until discharge. After delivery, cord bloods were obtained for serum AED levels and cord pH. Details of the qualitative study are provided in Chapter 4, and details of amendments to study conduct and criteria are provided in Appendix 1.
The study has been reported in line with recommended guidelines. 18,19
Criteria for unblinding of serum levels in the control and non-randomised groups
The serum AED levels were revealed to the clinicians and women in the blinded groups (control and non-randomised) in the following circumstances:
-
deterioration of seizures despite treatment – the serum AED level was revealed in these cases at the request of the clinician, similar to standard clinical practice
-
clinical suspicion of toxicity
-
if levels of AED were found to be above the therapeutic range with risks of toxicity
-
results were requested by the clinician or patient for any other reason.
Withdrawal criteria
If a patient withdrew consent for the study, all data collected up to the point of withdrawal were retained unless the patient requested otherwise. If, for whatever reason, the patient discontinued monitoring, the participant was not withdrawn from the study and data collection continued to allow intention-to-treat analysis, unless consent to do this was withdrawn. Rates were monitored to detect differential dropout, which can bias clinical trial results and reduce the power of the study.
Sample size estimation
A large, prospective registry of pregnant women with epilepsy suggested that around 40% of women experience seizures during pregnancy. 20 We set the outcome-free survival rate under clinical features monitoring at 60% and estimated sample sizes for various effect sizes smaller than what was observed in our systematic review. Table 1 gives a range of estimates of sample sizes for different powers and effect sizes for the primary outcome of time to first seizure.
| Control survival rate (60%) | Total sample size | |
|---|---|---|
| 80% power | 90% power | |
| Increased to 78% (hazard ratio ≈0.60) | 182 | 244 |
| Increased to 76% (hazard ratio ≈0.65) | 258 | 344 |
| Increased to 73% (hazard ratio ≈0.70) | 380 | 508 |
| Increased to 71% (hazard ratio ≈0.75) | 594 | 794 |
We aimed to collect data from at least 594 randomised women, giving 80% power (at p = 0.05) to detect a 25% seizure hazard decrease [hazard ratio (HR) ≈0.75]. We considered 25% to be the minimally important difference in seizure deterioration to be achieved, given the potential drawbacks of increasing AED dose exposure. We assumed a loss to follow-up of 10%, and estimated the need to randomise 660 women with a reduction in serum AED level.
Analysis
Participants were analysed belonging to the group to which they were randomised, unless they were randomised in error. All estimates of effect size (e.g. hazard or risk ratio) were presented as point estimates, with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and p-values. All analyses were carried out using Stata® version 12.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
The primary analysis of time to first seizure was performed using a Cox proportional hazards model. The primary multivariate failure time analysis of time to first seizure was performed using a generalisation of the Cox proportional hazards model, taking into account the correlation of observations within each subject by incorporating robust standard errors for parameter estimates, the Andersen–Gill model. 21 For both models, survival analysis was performed on a daily scale. Multiple seizures of the same or different types on the same day were not considered separately. An event was defined as at least one seizure of any type on a calendar day. Censoring occurred at the first date with missing information on seizure occurrence, or at end of follow-up if no event was recorded and follow-up was complete without missing records.
In addition to the treatment allocation, all primary and secondary models included the randomisation factors of AED type (lamotrigine monotherapy/carbamazepine, phenytoin or levetiracetam monotherapy/lamotrigine polytherapy) and seizures 3 months prior to consent (yes/no) as covariates in the model. To increase the precision of the treatment effect estimate, we also adjusted for the following baseline values that were determined a priori: maternal age, age at first seizure (excluding febrile seizures) and general seizure classification at baseline (tonic–clonic seizure/non-tonic–clonic seizure/unclassified).
Secondary analyses of differences between the two randomised arms for pregnancy outcomes, cord blood serum AED levels and QoL were performed using analysis of covariance. We used Poisson models for analyses of the LAEP, logistic models for binary outcomes, ordered logistic regression for the categorical outcome ‘breastfeeding’ and linear regression for continuous outcomes.
We analysed the association between the reduction in serum AED levels and seizure status using logistic regression models for the binary outcome of seizure-free status by the end of follow-up, and Poisson regression models for weekly seizure rate and number of seizure days per week. Seizure-free status was analysed including randomised and non-randomised participants. Rates were compared between clinical features monitoring and the non-randomised cohort. AED dose exposure was compared between therapeutic drug monitoring, clinical features monitoring and the non-randomised cohort using linear regression. For analysis of participants on multiple AEDs, we used multivariate multiple regression to analyse the two drugs together.
Fetal outcomes were analysed using mixed models to account for clustering of twins by mother (2.7% of pregnancies in study population). Convergence issues were dealt with by using a simpler analysis of covariance model ignoring clustering. We compared these results against a model including only one twin per pair, and in all cases the model results were very similar. The number of twins included in any analysis was very small and the impact of ignoring the clustering in these situations was deemed sufficiently low.
Assumption checks and sensitivity analysis
Extreme values were checked as part of the data cleaning procedure. Any remaining outliers were considered to be true data values and therefore analysed as reported. However, using box plots we identified one participant with extremely large numbers of seizures. We assessed the robustness of the secondary analysis of seizure rates by excluding this value and interpreted the results accordingly. For survival models, the proportional hazards assumption was checked using Schoenfeld residuals, log–log plots and through inclusion of time-dependent effects; subgroup effects were presented to investigate violations and compared using the Wald test for treatment–covariate interactions. We investigated whether or not any treatment effect differed by seizure type by only considering tonic–clonic seizures as outcomes.
Missing values
Withdrawals and those lost to follow-up were included in the analysis up to the last point that data are available. If the number of seizures was unknown for a date or a date range, we contacted the mothers by telephone or in person to obtain missing details. When this was not possible, records were reviewed by two independent neurologists (DM and AK), who commented on the likelihood of seizure and type of seizure in the missing slot. When the neurologists were not able to provide this opinion, or there was a discrepancy in their opinion, the opinion of a third neurologist (Shanika Samarasekera) was sought. When all neurologists were unable to provide estimation on likelihood of seizure, the average seizure rate for tonic–clonic seizures and the rate for non-tonic–clonic seizures over the period of the participant’s completed diary were applied.
When the seizure type was missing or no other data for the seizure type were available, the average rate over any seizure type was used. If multiple seizures occurred during a time frame, they were equally spaced out over the time frame. If the number of seizures was larger than the number of days, the seizures were equally spaced out over each day in the time frame. A sensitivity analysis was conducted for the analysis of time to first seizure to investigate if an interval censoring approach showed a different result. When there were missing data on seizure occurrence, participants were censored at the first date on which seizure occurrence was known. A sensitivity analysis will be performed for the analysis of multiple events ignoring any dates or date ranges in which seizure occurrence is unknown.
Sensitivity analysis for interval analysis for time to first seizure
This sensitivity analysis was planned a priori but not conducted. The reasons are as follows.
The exact date of the first seizure was uncertain in eight women. Three women had substantially more seizures than the number of days in the period of uncertainty. For these women we assumed daily seizures, as the actual number of seizures occurring on a single day is irrelevant for the primary analysis.
Three women reported more than one seizure occurring during a period of 3–6 weeks. Interval censoring approaches standardly available in the statistical packages allow only one event to occur during the period of uncertainty. Allowing for multiple events during the period of uncertainty would require the application of multistate models, which would probably introduce other issues, such as convergence problems. Two women had a single seizure during 1 month. Here, the interval censoring approach standardly available could have been applied. However, as a result of the small number and the issues arising for other women (as described in the previous paragraph), it was decided not to perform this analysis.
Oversight of the trial
The management of our study included an element of expert advice that was entirely independent from the investigators and their host institution(s). The trial was overseen by a 15-member TSC, which included three independent members and a consumer representative from Epilepsy Action. There were three independent members in the five-member Data Monitoring Committee (DMC). The terms of reference and charter for the DMC were determined at the outset, taking into account issues relevant to the monitoring of this study. 22
Health economics analysis
The original sample size for the study was 660 randomised women. In 2014, given the slow rate of recruitment of the trial, the funder, after discussion with the DMC and TSC, decided not to extend the recruitment period of the trial, prior to achievement of the planned sample size. The economic analysis was integral to the initial study design, but given that the planned sample size was not recruited, it was postponed pending results to see if it was justified. Given that the study ultimately found no evidence to support that regular monitoring of AED drug levels in pregnancy offers additional benefit in seizure control than management based only on clinical features, any justification for an economic evaluation has not materialised.
Chapter 3 Results
Flow of women recruited in the study
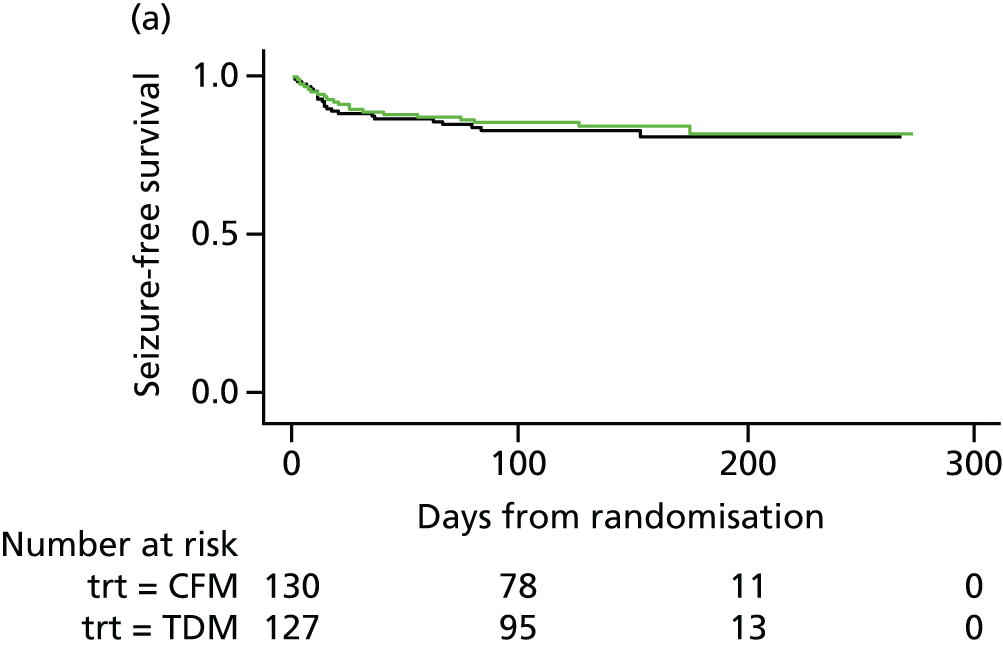
We recruited 593 women: 580 for the cohort and 13 for the qualitative study. The median number of women recruited per centre was nine [interquartile range (IQR) 6–13]. Of the 580 women recruited into the cohort, 20 were recruited but subsequently found to fail the inclusion criteria, resulting in 560 women who were monitored for a reduction in serum AED levels. Less than 1% of participants (n = 6) were recruited twice into the study because they became pregnant again during the trial period. Overall, 263 women had a reduction in serum AED level at some point in their pregnancy and were randomised to therapeutic drug monitoring (n = 130) or clinical features monitoring (n = 133) groups, and the remaining 293 had stable serum AED levels until delivery. Four women who were randomised in error after the end of pregnancy were analysed with the non-randomised group. Complete outcome data for the primary analysis were available from 127 women (98%) in the therapeutic drug monitoring group, 130 (98%) in the clinical features monitoring group and 294 (99%) in the non-randomised group (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials flow chart. CFM, clinical features monitoring; TDM, therapeutic drug monitoring.

Characteristics of women included
A total of 85% of recruited women in the therapeutic drug monitoring, clinical features monitoring and non-randomised groups were white. Around 60% in each of the groups had been educated to Advanced level (A level) or higher. Half of all women in the non-randomised cohort (50%) were nulliparous, and the corresponding figures were 58% and 54% in therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring groups, respectively. The rates of congenital abnormalities in previous pregnancies were between 5% and 8% of women in the therapeutic drug monitoring, clinical features monitoring and non-randomised groups. There was a history of mental illness in about one-tenth of the women (Table 2).
| Variable | Trial group, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomised | Non-randomised (N = 294) | ||
| TDM (N = 130) | CFM (N = 133) | ||
| Ethnic group | n = 130 | n = 133 | n = 294 |
| White | 113 (87) | 118 (89) | 253 (86) |
| Black | 2 (2) | 3 (2) | 6 (2) |
| Asian | 13 (10) | 7 (5) | 25 (9) |
| Mixed | 0 (0) | 2 (2) | 8 (3) |
| Other | 2 (2) | 3 (2) | 2 (1) |
| Highest qualification | n = 127 | n = 133 | n = 292 |
| Degree level | 50 (39) | 49 (37) | 114 (39) |
| A level | 29 (23) | 33 (25) | 68 (23) |
| GCSE | 44 (35) | 48 (36) | 87 (30) |
| Below GCSE | 4 (3) | 3 (2) | 23 (8) |
| Smoking status | n = 130 | n = 133 | n = 294 |
| Smoker | 17 (13) | 14 (11) | 34 (12) |
| Ex-smoker | 30 (23) | 31 (23) | 90 (31) |
| Non-smoker | 83 (64) | 88 (66) | 170 (58) |
| Alcohol units per week | n = 130 | n = 133 | n = 294 |
| 0 | 122 (94) | 117 (88) | 266 (91) |
| 1–9 | 8 (6) | 16 (12) | 25 (9) |
| ≥ 10 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (1) |
| Parity | n = 130 | n = 133 | n = 294 |
| 0 | 75 (58) | 72 (54) | 147 (50) |
| 1–4 | 55 (42) | 59 (44) | 144 (49) |
| ≥ 5 | 0 (0) | 2 (2) | 3 (1) |
| Previous children | n = 76 | n = 100 | n = 225 |
| Neonatal deaths | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 2 (1) |
| Stillbirths | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (1)a |
| At least one congenital abnormality in previous children | 7 (7) | 4 (5) | 17 (8) |
| Medical history | n = 130 | n = 133 | n = 293 |
| Maternal congenital abnormalities | 5 (4) | 5 (4) | 5 (2) |
| Diabetes | 3 (2) | 1 (1) | 9 (3) |
| Chronic hypertension | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | 7 (2) |
| Renal disease | 3 (2) | 2 (2) | 5 (2) |
| HIV infection | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0) |
| Learning difficulties | 3 (2)b | 1 (1) | 11 (4)c |
| Mental illness | 19 (15) | 15 (11) | 33 (11) |
Tonic–clonic seizure was the most common type of seizure, being diagnosed in 80% (100/130) of women in the therapeutic drug monitoring group, 82% (109/133) in the clinical features monitoring group and 81% (237/294) in the non-randomised cohort. One-quarter of women in each of the randomised groups (therapeutic drug monitoring: 26%, 34/130; clinical features monitoring: 24%, 32/133) and one-third in the non-randomised group (29%, 84/294) were seizure free for 3 months before pregnancy. Lamotrigine monotherapy was the most common AED medication taken by around half of the women at baseline. Lamotrigine polytherapy was taken by one-tenth in the therapeutic drug monitoring (11%, 14/130) and clinical features monitoring (9%, 12/133) groups, and by 5% in the non-randomised cohort (15/294). The doses of individual AEDs taken at the time of randomisation in the therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring groups are provided in Table 3.
| Variable | Trial group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomised | Non-randomised cohort | ||
| TDM | CFM | ||
| Age at first seizure (years), mean (SD) [n] | 16.8 (8) [130] | 17.0 (7) [132] | 16.1 (7) [290] |
| Years since first seizure, mean (SD) [n] | 12.2 (8) [121] | 12.1 (7) [124] | 16.1 (8) [261] |
| Seizures 3 months prior to pregnancy [N] | 34.0 (26) [130] | 32.0 (24) [133] | 84.0 (29) [294] |
| Seizure classification,a n (%) | N = 130 | N = 133 | N = 294 |
| TCS | 100 (80) | 109 (82) | 237 (81) |
| Absence | 29 (22) | 35 (26) | 85 (29) |
| Myoclonus | 13 (10) | 20 (15) | 33 (11) |
| Simple | 19 (15) | 20 (15) | 30 (10) |
| Complex | 36 (28) | 19 (14) | 57 (19) |
| Unclassified/other | 6 (5) | 7 (5) | 14 (5) |
| AED intake at baseline, n (%) | N = 130 | N = 133 | N = 294 |
| LTG monotherapy | 68 (52) | 70 (53) | 148 (50) |
| CBZ, PHT or LEV monotherapy | 48 (37) | 51 (38) | 131 (45) |
| LTG polytherapy | 14 (11) | 12 (9) | 15 (5) |
| Type of AED intake at baseline, n (%) | N = 130 | N = 133 | N = 294 |
| CBZ | 16 (12) | 20 (15) | 54 (18) |
| LTG | 68 (52) | 70 (53) | 148 (50) |
| LEV | 31 (24) | 31 (23) | 77 (26) |
| PHT | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| LTG and LEV | 14 (11) | 11 (8) | 15 (5) |
| LTG and CBZ | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) |
| Dose of AED at randomisation (mg), mean (SD) [n] | |||
| CBZ only | 581.3 (339.1) [16] | 695.0 (336.4) [20] | |
| LTG only | 246.3 (124.4) [68] | 242.9 (148.5) [70] | |
| LEV only | 1500.0 (724.6) [31] | 1572.6 (880.8) [31] | |
| PHT only | [0] | 200.0 [1] | |
| LTG and LEV, LTG dose | 448.2 (215.8) [14] | 379.6 (92.8) [11] | |
| LTG and LEV, LEV dose | 1767.9 (846.2) [14] | 2100.0 (1119.3) [10] | |
| LTG and CBZ, LTG dose | [0] | 200.0 [1] | |
| LTG and CBZ, CBZ dose | [0] | 300.0 [1] | |
Baseline QoL measurements are provided in Table 4. Scores for the NDDI-E, QoL (EQ-5D), LAEP and QOLIE-31 were balanced across the therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring groups.
| Variable | Trial group, mean (SD) [n] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomised | Non-randomised (N = 294) | ||
| TDM (N = 130) | CFM (N = 133) | ||
| NDDI-Ea | 9.7 (3.3) [130] | 9.9 (3.6) [133] | 10.1 (3.5) [284] |
| EQ-5Db | 0.90 (0.17) [126] | 0.90 (0.16) [127] | 0.89 (0.18) [267] |
| LAEPc | 34.3 (8.9) [124] | 34.9 (10.4) [121] | 35.3 (9.2) [259] |
| QOLIE-31 scored (UK) | 73.7 (14.6) [128] | 72.8 (15.5) [128] | 71.0 (16.8) [274] |
| QOLIE-31 overall healthe (UK) | 7.0 (1.8) [127] | 7.0 (1.9) [128] | 7.1 (1.8) [273] |
Time to randomisation from consent
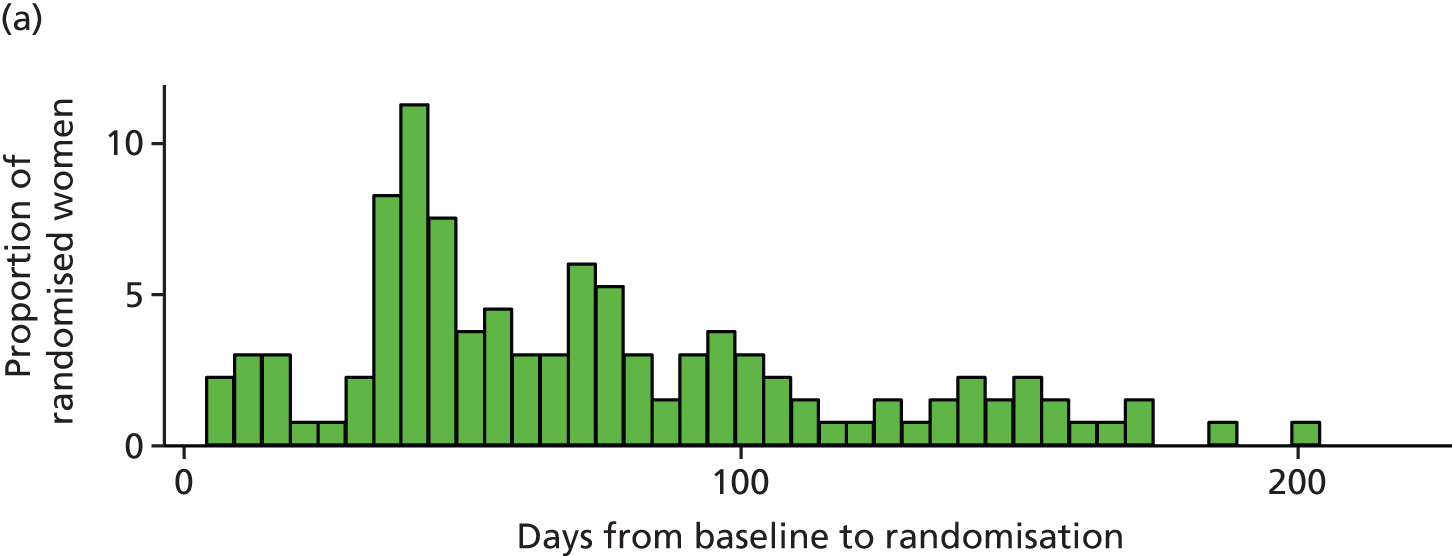
Figure 2 shows the time from baseline to randomisation for randomised participants. Randomisation was performed, on average, 68 days [standard deviation (SD) 43 days] from baseline (median 59 days, IQR 40–96 days).
FIGURE 2.
Time from baseline to randomisation in days. (a) Clinical features monitoring; and (b) therapeutic drug monitoring.

Effects of therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring strategies for antiepileptic drug dosing on maternal seizures
A total of 257 women provided a cumulative analysis time of 35,859 days from randomisation to censoring, with 25,001 days from randomisation to first seizure. The median time of follow-up from randomisation to censoring was 153 (IQR 115–179) and 134 (IQR 84–169) days for the therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring groups, respectively. The number of days with seizure and actual number of seizures that occurred in both groups are provided in Table 5.
| Variable | Randomised group, n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| TDM (N = 127) | CFM (N = 130) | |
| Total observation period (weeks) | ||
| < 12 | 11 (8) | 32 (25) |
| 12 to < 24 | 69 (54) | 65 (50) |
| 24 to < 36 | 46 (36) | 32 (25) |
| ≥ 36 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| Median (IQR) (days) | 153 (115–179) | 134 (84–169) |
| Number of days with any seizures | ||
| 0 | 79 (66) | 80 (63) |
| 1–29 | 36 (30) | 43 (34) |
| 30–59 | 5 (4) | 2 (2) |
| 60–89 | 0 (0) | 2 (2) |
| ≥ 90 | 7 (6) | 3 (2) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–3) | 0 (0–4) |
| Total number of seizures | ||
| 0 | 79 (64) | 80 (62) |
| 1–9 | 29 (24) | 26 (20) |
| 10–99 | 10 (8) | 20 (16) |
| 100–499 | 6 (5) | 3 (2) |
| ≥ 500 | 3 (2) | 1 (1) |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0–4) | 0 (0–5) |
Seizure data were captured from randomisation to the first day of missing data. One-quarter of women in the clinical features monitoring group had a total observation period of < 12 weeks in comparison to 8% of the therapeutic drug monitoring group. A total observation period of 12–24 weeks was seen in half of each randomised group, and one-quarter of the clinical features monitoring and one-third of the therapeutic drug monitoring participants had a total observation period of 24–36 weeks. One woman in each group had seizure data captured for > 36 weeks. The mean number of days with captured seizure data was higher for the therapeutic drug monitoring group by 19 days.
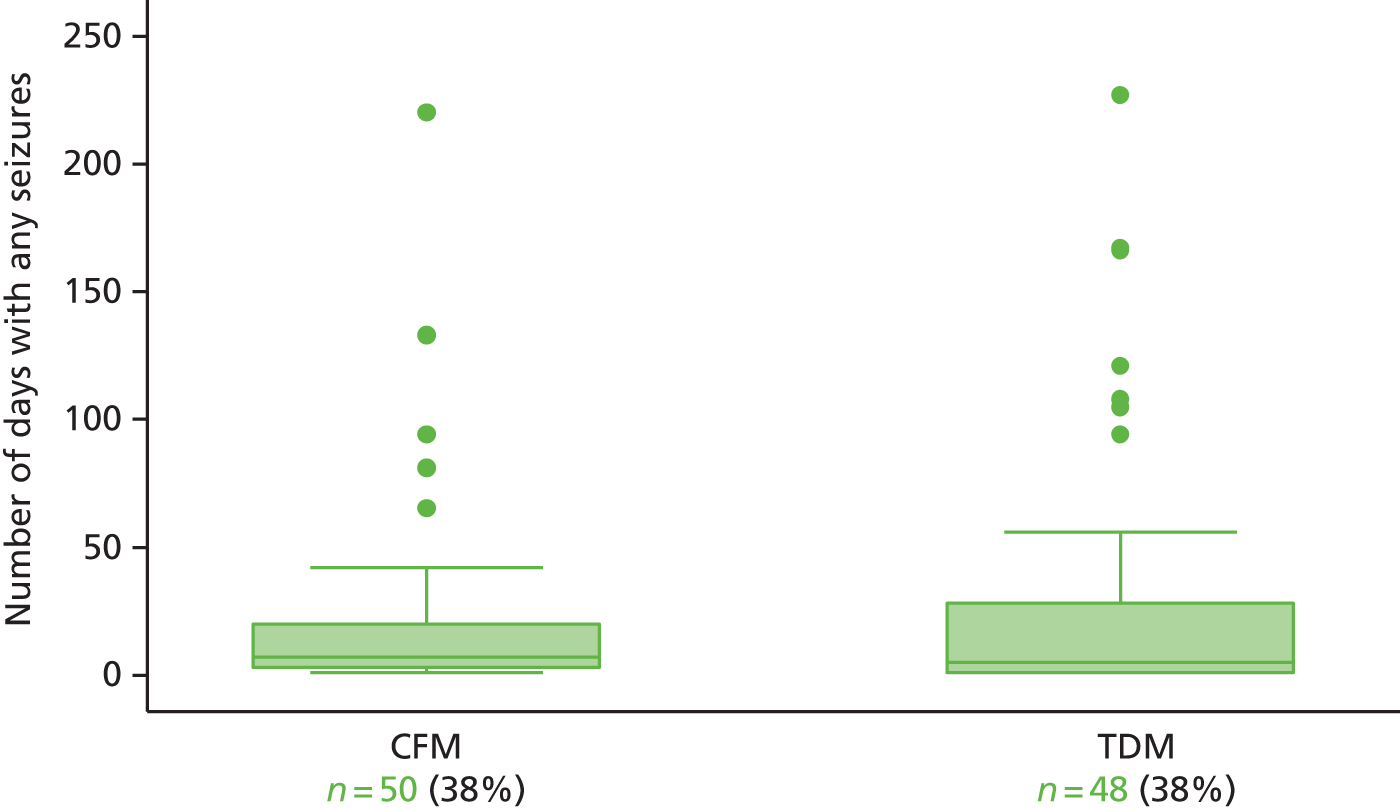
Two-thirds of each randomised group did not experience any seizures after randomisation, whereas approximately one-third of both groups experienced 1–29 days with seizures. Number of days with seizures was similar in both groups (Figure 3). Less than one-quarter of women in both groups had up to nine seizures post randomisation. The proportion of women who experienced 10–99 seizures was twice as high in the clinical features monitoring group (16%) as in the therapeutic drug monitoring group (8%). Small numbers of women in each group experienced > 100 seizures after randomisation and ≥ 30 days of seizures.
FIGURE 3.
Seizure diaries: total number of days with any seizures from randomisation to the end of follow-up by allocation group, excluding women with no seizures. CFM, clinical features monitoring; TDM, therapeutic drug monitoring.
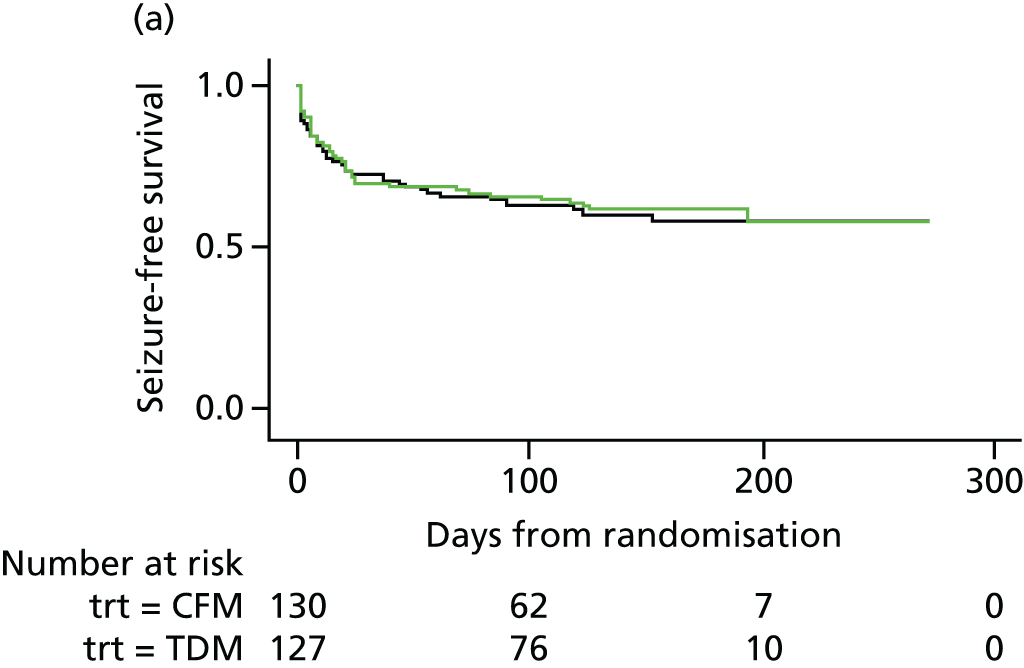
There were no differences in the proportion of women who experienced at least one seizure in the therapeutic drug monitoring (48/127, 38%) and clinical features monitoring (50/130, 38%) groups, with a mean observed time to first seizure of 28 days (SD 42 days) in the therapeutic drug monitoring group and 27 days (SD 36 days) in clinical features monitoring group. There was a 20% reduction in the time to first seizure with therapeutic drug monitoring compared with clinical features monitoring, a difference that was not significant (HR 0.8, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.2). The CI suggests a possible effect of between a 45% decrease and a 20% increase in seizure rate with therapeutic drug monitoring and includes a HR of 0.75; therefore, the possibility of a clinically relevant difference between therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring cannot be rejected. Figure 4 shows the results of the Cox regression of time to first seizure and the corresponding Kaplan–Meier curve. Assumption checks indicated no violation of the proportional hazards assumption globally (p = 0.17). However, some violation was detected for adjustment factor maternal age (p = 0.003), indicating that the influence of age on seizure occurrence changes over time. After including a time-dependent effect for age, the proportional hazards assumption was satisfied for all covariates. Including the time-dependent effect resulted in a minor change to the CI, but not the effect size or statistical significance (HR 0.8, 95% CI 0.54 to 1.3). These investigations supported the use of the Cox model for our analysis.
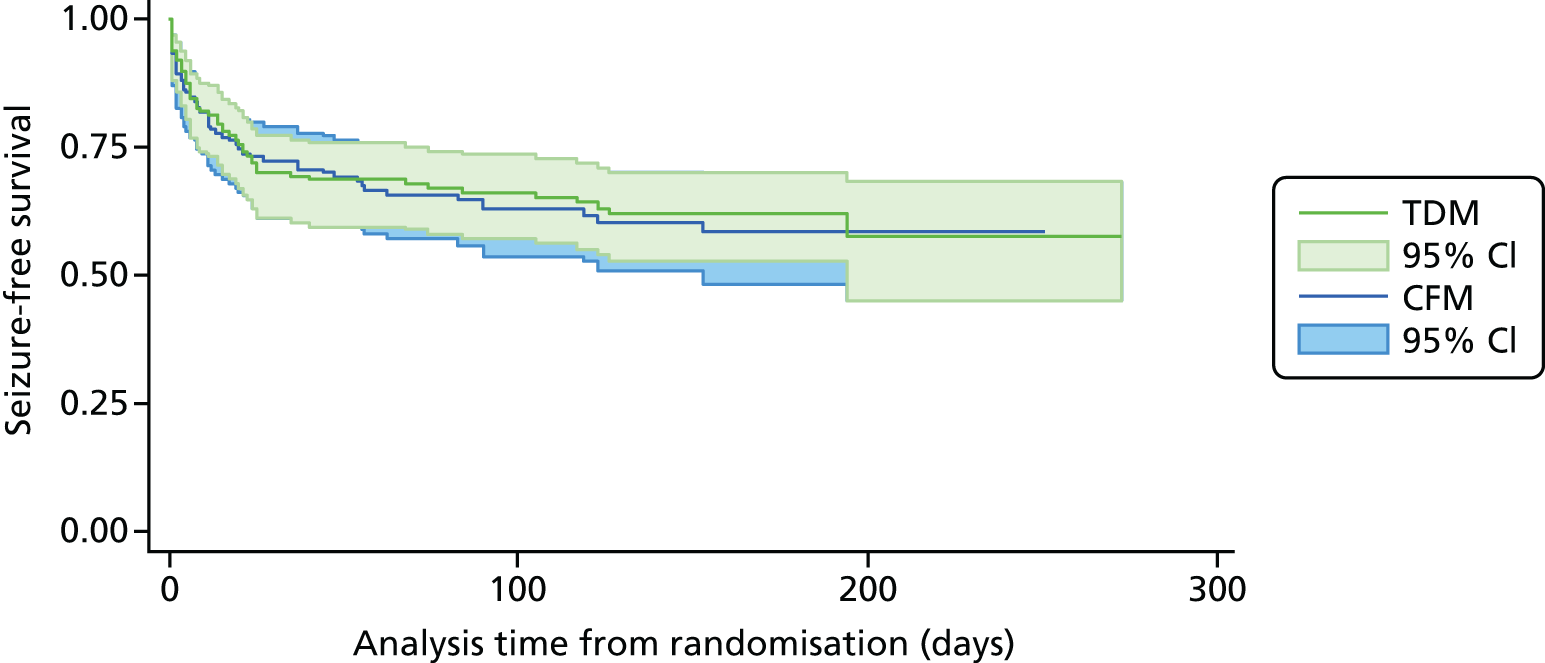
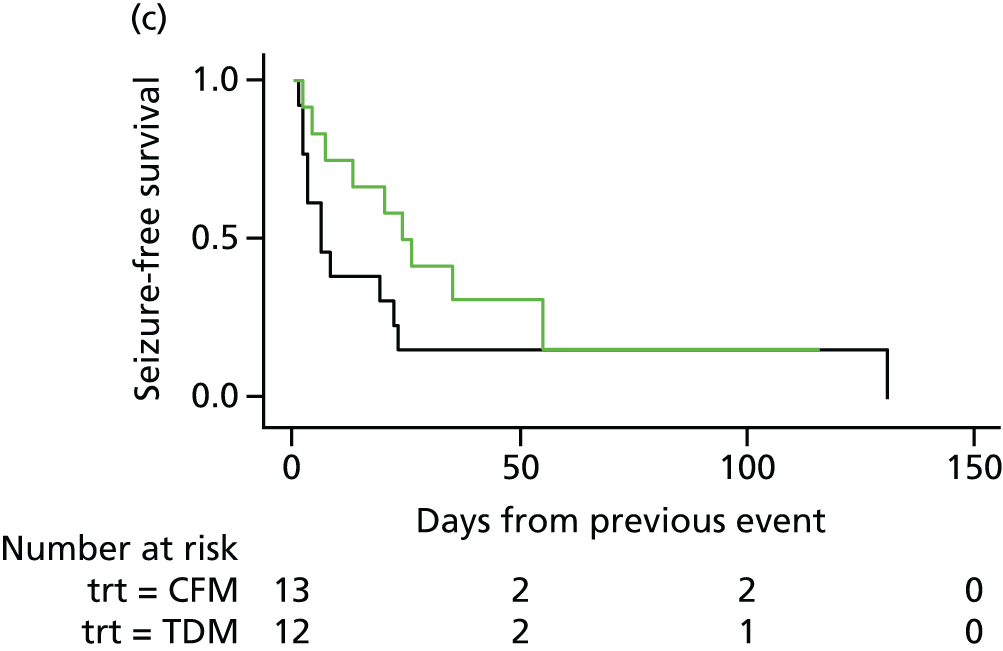
FIGURE 4.
Survival graphs for time to first seizure and subsequent seizures. (a) Event 1; (b) event 2; (c) event 3; and (d) event 4. CFM, clinical features monitoring; TDM, therapeutic drug monitoring; trt, treatment allocation.


Maternal age at baseline slightly increased with date of randomisation over the 3-year study period (p = 0.11), which may explain some of the time-dependent effect. The effect of age as a risk factor may also have varied over time, indicating that higher maternal age at baseline might have carried a larger risk later in the study period than at the start of the study period.
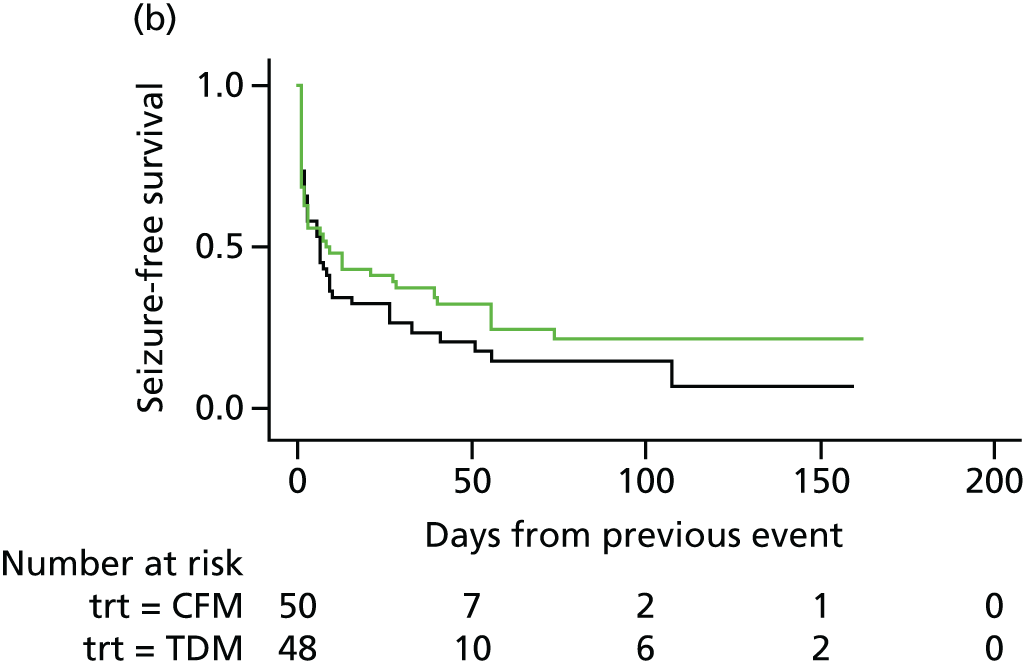
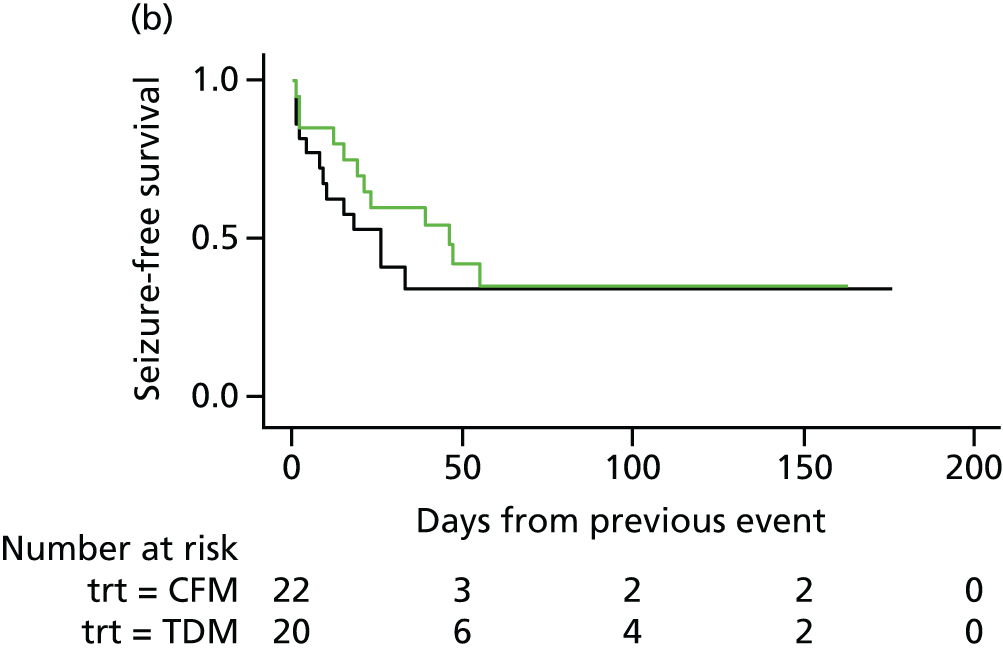
Ninety-eight (38%) women experienced only one seizure, 75 (29%) experienced two or more seizures and 72 (28%) experienced three or more seizures. Of the 98 women who had suffered a first seizure, 75 women experienced a second seizure, 35 in the therapeutic drug monitoring group and 40 in the clinical features monitoring group, with a mean duration to second seizure of 12.1 and 11.6 days, respectively. Subsequently, 72 women with a second seizure had a third seizure, 33 in the therapeutic drug monitoring group (median 3 days, IQR 1–17 days) and 39 in the clinical features monitoring group (median 3 days, IQR 1–13 days).
The analysis of overall time to first seizure and subsequent seizures showed a larger increase with therapeutic drug monitoring than clinical features monitoring, but this was not significant (HR 1.3, 95% CI 0.7 to 2.6). Figure 5 shows the Kaplan–Meier curve of the multiple failure time analysis of time to first seizure and subsequent seizures.
FIGURE 5.
Survival graphs for time to first seizure and time to subsequent seizures after randomisation. Time to (a) event 1; (b) event 2; (c) event 3; and (d) event 4. CFM, clinical features monitoring; TDM, therapeutic drug monitoring; trt, treatment allocation.
Assumption checks indicated violations of the proportional hazards assumption globally and for all covariates. To investigate the source of the violations we performed the Cox regression model including time-dependent effects for all covariates. Only maternal age showed a significant time-dependent effect, which was subsequently included in the Cox regression. The resulting model showed no indication of proportional hazards assumption violation for any covariates. Including the time-dependent effect resulted in a minor change to the effect size and CI, with no changes to statistical significance (HR 1.4, 95% CI 0.73 to 2.6).
Additionally, we investigated treat–covariate interactions by estimating effects within subgroups of each covariate. The subgroup effect sizes were mostly similar and are shown in Table 6. No statistically significant effect modification was detected for any covariate.
| Covariate | Subgroup | n | Subgroup TDM effect, HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seizures 3 months prior to pregnancy | No | 192 | 1.0 (0.35 to 2.8) |
| Yes | 65 | 1.4 (0.68 to 2.8) | |
| Baseline AED group | LTG monotherapy | 133 | 1.1 (0.41 to 3.0) |
| CBZ, PHT or LEV monotherapy | 99 | 1.5 (0.56 to 4.1) | |
| LTG polytherapy | 25 | 1.3 (0.27 to 6.3) | |
| Maternal age (years)a | < 25 | 50 | 1.0 (0.35 to 2.9) |
| 25 to < 35 | 166 | 1.8 (0.68 to 4.6) | |
| ≥ 35 | 41 | 1.1 (0.21 to 5.5) | |
| Age at first seizure (years)a | < 10 | 37 | 0.28 (0.07 to 1.1) |
| 10 to < 20 | 138 | 1.9 (0.90 to 4.2) | |
| ≥ 20 | 82 | 3.3 (0.91 to 12.1) | |
| Baseline broad seizure classification | TCS | 96 | 0.40 (0.11 to 1.4) |
| Non-TCS | 154 | 1.4 (0.71 to 2.8) | |
| Unspecified only | 7 | 0.7 (NA) |
These investigations supported the use of the Cox model for our analysis.
Proportional hazards assumption checks
For time to first seizure, and time to multiple seizures, we did not find any differences between the subgroups based on seizure status 3 months before pregnancy, type of AED intake at baseline and the type of seizure (see Table 6).
Sensitivity analysis
We undertook a sensitivity analysis by including only women with tonic–clonic seizures. For the analysis of time to first tonic–clonic seizure, 257 women provided a total analysis time of 31,572 days from randomisation to first seizure or censoring. Table 7 shows that the risk of time to first seizure was lower in the therapeutic drug monitoring group than in the clinical features monitoring group, but this difference was not statistically significant (HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.43 to 1.5). Figure 6 shows the results of the Cox regression of time to first tonic–clonic seizure and the corresponding Kaplan-Meier curve.
| Model | n | Analysis time (days), mean (SD) | Proportion of women with any seizures | TDM effect, HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDM | CFM | TDM | CFM | |||
| Time to first TCS | 257 | 132 (63) | 114 (65) | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.80 (0.43 to 1.50) |
FIGURE 6.
Survival graph for time to first event analysis on tonic–clonic seizure only. CFM, clinical features monitoring; TDM, therapeutic drug monitoring.
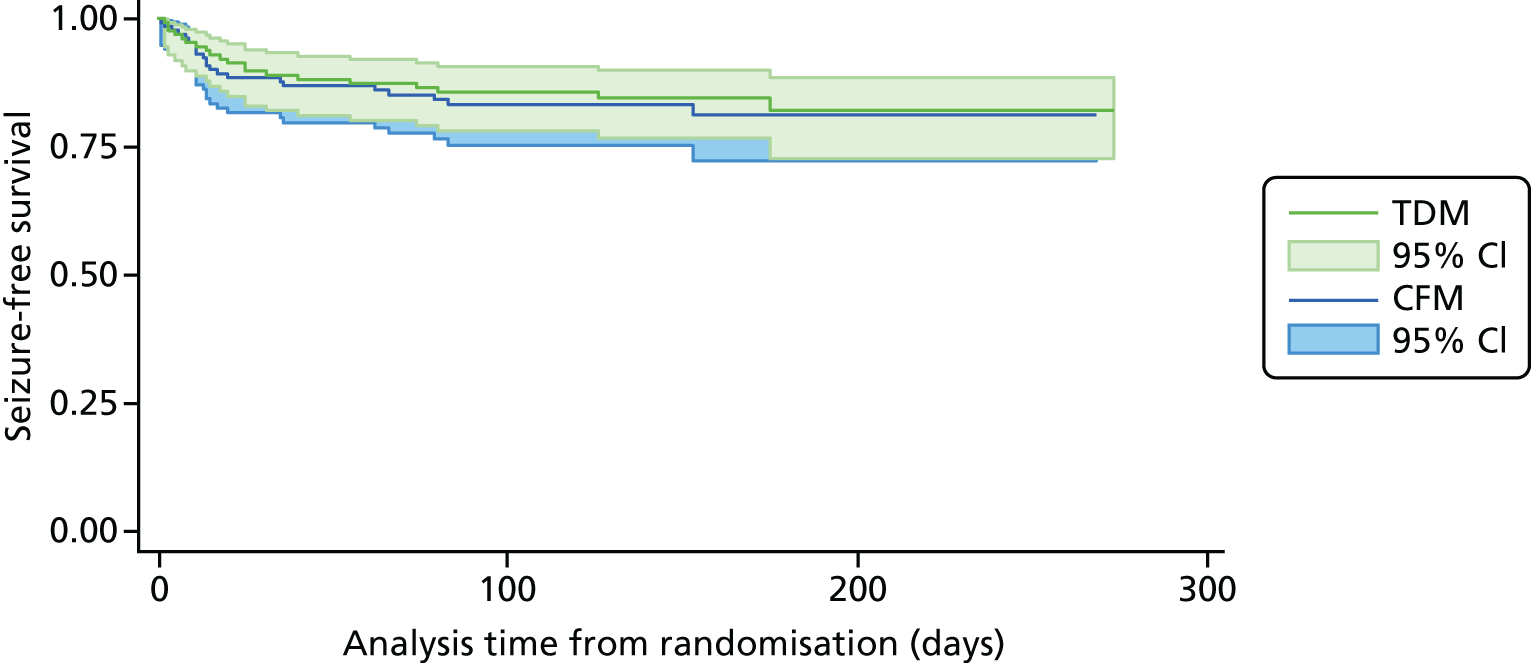
Figure 7 shows the Kaplan–Meier curve of the multiple failure time analysis of time to first tonic–clonic seizure and subsequent seizures.
FIGURE 7.
Survival graphs for time to first tonic–clonic seizure and time to subsequent tonic–clonic seizures. Time to (a) event 1; (b) event 2; (c) event 3; and (d) event 4. CFM, clinical features monitoring; TCS, tonic–clonic seizure; TDM, therapeutic drug monitoring; trt, treatment allocation.

The analysis of time to first and subsequent tonic–clonic seizures showed a decrease with therapeutic drug monitoring compared with clinical features monitoring, which was not significant (Table 8; HR 0.62, 95% CI 0.28 to 1.4).
| Model | n | Analysis time (days), mean (SD) | Number of seizure days, mean (SD) | TDM effect, HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDM | CFM | TDM | CFM | |||
| Multiple seizure rate | 257 | 149 (50) | 130 (55) | 0.54 (1.9) | 0.84 (3.2) | 0.621 (0.28 to 1.4) |
Effects of monitoring strategies on maternal and fetal outcomes
Maternal outcomes
Pregnancy outcomes
There were no differences between the therapeutic drug monitoring or clinical features monitoring groups in mean gestational age at delivery, pre-term birth rate, mode of delivery, rates of ante- or postpartum haemorrhage or admission to a neonatal unit or rate of breastfeeding (Table 9).
| Maternal outcome | Randomised group, n (%) [N] | TDM effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDM | CFM | OR (95% CI) | MD (95% CI) | |
| Maternal death | 0 (0) [130] | 0 (0) [133] | – | |
| Gestational age at delivery (weeks), mean (SD) [n] | 39.2 (2.1) [126] | 39.1 (2.4) [130] | 0.84 (–3.0 to 4.7) | |
| Mode of delivery (effect of CS or instrumental) | 1.3 (0.78 to 2.1) | |||
| Pre-term delivery at < 37 weeks | 8 (6) [127] | 15 (12) [130] | 0.50 (0.20 to 1.2) | |
| Induction of labour | 46 (37) [126] | 39 (30) [130] | 1.4 (0.79 to 2.3) | |
| Pre-eclampsia | 5 (4) [126] | 4 (3) [130] | 1.4 (0.36 to 5.7) | |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | 9 (7) [126] | 3 (2) [130] | 3.2 (0.85 to 12.5) | |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | 2 (2) [127] | 2 (2) [129] | 1.1 (0.14 to 8.7) | |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 19 (15) [127] | 18 (14) [130] | 1.1 (0.55 to 2.3) | |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | 5 (4) [127] | 3 (2) [130] | 1.8 (0.41 to 7.8) | |
| Breastfeeding | [127] | [126] | 0.82 (0.50 to 1.4) | |
| Breast | 75 (58) | 69 (52) | ||
| Mixed | 15 (12) | 20 (15) | ||
| Bottle | 36 (28) | 38 (29) | ||
Maternal exposure to antiepileptic drugs and rates of seizures
One woman received phenytoin monotherapy and one woman received lamotrigine polytherapy with carbamazepine. There were no differences between the therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring groups in the mean daily dose of AEDs prescribed (monotherapy or polytherapy) (Table 10). Appendix 2 shows the effect of increasing the dose of AEDs in women taking monotherapy and polytherapy, and found no significant effect on maternal pregnancy outcomes.
| AED | Daily AED exposure (mg), mean (SD) [n] | TDM effect, mean difference (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TDM | CFM | ||
| CBZ only | 616.7 (355.8) [16] | 695.0 (336.4) [20] | –12.1 (–226.7 to 202.4) |
| LTG only | 290.9 (137.5) [68] | 252.6 (148.0) [70] | 32.3 (–14.4 to 79.0) |
| LEV only | 1735.6 (701.9) [31] | 1628.5 (926.5) [31] | 166.5 (–229.8 to 562.7) |
| LTG and LEV | LTG: 487.5 (206.7); LEV: 1920.1 (858.9) [11] | LTG: 413.8 (91.1); LEV: 2122.2 (1077.5) [14] | LTG: 97.4 (–28.7 to 223.4); LEV: –137.3 (–945.9 to 671.4) |
Fetal outcomes
There were no neonatal deaths in any of the randomised women and two stillbirths in the clinical features monitoring group. The odds of major congenital malformations, small for gestational age fetuses and admission to the neonatal unit did not differ between the two groups (Table 11). We did not observe any differences in birthweight, head circumference, Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes, and cord arterial and venous pH of infants born to mothers exposed to therapeutic drug monitoring or clinical features monitoring strategies. The cord blood levels of the AEDs were available for babies born to women taking lamotrigine (n = 131), carbamazepine (n = 26) and levetiracetam (n = 66). We observed a significant increase in the cord blood levels of lamotrigine [mean difference (MD) 0.55 mg/l, 95% CI 0.11 to 1.0 mg/l) and levetiracetam (MD 7.8 mg/l, 95% CI 0.86 to 14.8 mg/l) in infants born to mothers managed in the therapeutic drug monitoring group compared with in the clinical features monitoring group. There were no differences in cord blood levels of carbamazepine (MD –0.47 mg/l, 95% CI 1.5 to 0.60 mg/l) between the two groups. We quantify the effect of an increase in AED dose on fetal outcomes in Appendix 3. An increase in exposure to AED dose by 1 mg significantly increased the cord blood levels of lamotrigine, by 0.007 mg/l (see Appendix 3), levetiracetam, by 0.008 mg/l, and carbamazepine, by 0.003 mg/l, in women on AED monotherapy. The cord blood levels of lamotrigine and levetiracetam were increased by 0.009 and 0.008 mg/l, respectively, for every 1-mg increase in dose of AED in women on polytherapy. The cord blood venous pH was significantly reduced by –0.0002 per 1-unit increase in dose of carbamazepine, but there were no effects on other fetal outcomes with increasing doses of AED (see Appendix 3).
| Fetal outcomes | Randomised group, n (%) [N] | TDM effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDM | CFM | OR (95% CI) | MD (95% CI) | |
| Stillbirths | 0 (0) [125] | 2 (2) [134] | – | – |
| Neonatal deaths | 0 (0) [126] | 0 (0) [134] | – | |
| Major congenital malformations | 7.0 (6) [125] | 10.0 (8) [134] | 0.66 (0.23 to 1.8) | |
| Admission to neonatal unit | 16.0 (13) [125] | 18.0 (13) [134] | 1.6 (0.29 to 9.5) | |
| Apgar score at 1 minute, mean (SD) [n] | 8.5 (1.4) [123] | 8.5 (1.5) [127] | – | –0.11 (–0.47 to 0.25) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes, mean (SD) [n] | 9.4 (0.87) [124] | 9.3 (0.84) [128] | – | 0.03 (–0.18 to 0.23) |
| Birthweight (kg), mean (SD) [n] | 3.3 (0.60) [124] | 3.3 (0.68) [134] | – | 0.02 (–0.13 to 0.17) |
| Small for gestational age fetus (birthweight < 10th centile) | 13.0 (11) [124] | 22 (16) [134] | 0.43 (0.08 to 2.3) | |
| Head circumference (cm), mean (SD) [n] | 34.2 (1.8) [104] | 34.2 (1.7) [108] | –0.16 (–0.60 to 0.27) | |
| Cord arterial pH, mean (SD) [n] | 7.3 (0.09) [55] | 7.2 (0.07) [46] | 0.01 (–0.02 to 0.04) | |
| Cord venous pH, mean (SD) [n] | 7.3 (0.08) [59] | 7.3 (0.07) [54] | 0.001 (–0.030 to 0.031) | |
| Cord blood levels CBZ (mg/l), mean (SD) [n] | 3.3 (1.5) [13] | 4.3 (1.3) [13] | –0.47 (–1.5 to 0.6) | |
| Cord blood levels LTG (mg/l), mean (SD) [n] | 2.5 (1.6) [63] | 1.9 (1.3) [68] | 0.55 (0.11 to 1.0) | |
| Cord blood levels LEV (mg/l), mean (SD) [n] | 22.5 (17.0) [30] | 13.9 (10.5) [36] | 7.8 (0.86 to 14.8) | |
Maternal quality of life
Table 12 compares the QoL measurements in mothers exposed to the two AED monitoring strategies. There were no differences in the EQ-5D postnatal scores between the two groups (MD 0.002, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.05). The scores for the QOLIE-31 and the overall health score were similar in both groups (see Table 12).
| Outcome | Randomised group, mean (SD) [n] | MDa (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TDM | CFM | ||
| EQ-5D score | 0.90 (0.20) [99] | 0.90 (0.18) [102] | 0.00 (–0.05 to 0.05) |
| QOLIE-31 score (UK) | 71.0 (16.0) [114] | 73.7 (13.5) [110] | –2.5 (–5.1 to 0.0) |
| QOLIE-31 overall health (UK) | 6.9 (1.8) [115] | 7.3 (1.6) [110] | –0.35 (–0.72 to 0.02) |
Effect of a reduction in serum antiepileptic drug levels on maternal seizures
Table 13 compares the seizure status between women in the non-randomised group with stable serum AED levels and women in the clinical features monitoring and therapeutic drug monitoring groups with a decrease in serum AED levels of > 25%. There were no significant differences between the groups in seizure status, which was adjusted for baseline seizures in the 3 months prior to pregnancy.
| Group | N | Seizure status at end of follow-up, n (%) | OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No seizures | Any seizures | |||
| Non-randomised cohort (decrease in serum AED level never exceeding 25%) | 263 | 140 (53) | 123 (47) | Reference group |
| CFM (decrease in serum AED level exceeding 25%) | 130 | 71 (55) | 59 (45) | 0.93 (0.56 to 1.5) |
| TDM (decrease in serum AED level exceeding 25%) | 132 | 74 (56) | 58 (44) | 0.93 (0.56 to 1.5) |
Table 14 shows that there were no differences in the average number of seizures per week and the average number of days with seizures per week, analysed using Poisson models. We removed an extreme outlier who had an average of 256 seizures per week.
| Outcome | n | Group, median (IQR) | Effect of non-randomised cohort, incident rate ratio (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFM | Non-randomised | |||
| Seizure rate per week | 392 | 0 (0–0.26) | 0 (0–0.26) | 1.0 (0.84 to 1.4) |
| Days with seizures per week | 393 | 0 (0–0.23) | 0 (0–0.19) | 0.88 (0.62 to 1.2) |
Serious adverse outcomes
Sixty-one women experienced one or more serious adverse outcomes between the time of consent and 6 weeks postnatally (Table 15).
| SAE description | Trial group, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomised group | Non-randomised (N = 25) | ||
| TDM (N = 19) | CFM (N = 17) | ||
| Admission to HDU/ICU | 1 (5) | 2 (12) | 2 (8) |
| Admission to hospital for seizures | 7 (37) | 8 (47) | 10 (40) |
| Admission to neonatal unit | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Congenital malformation | 5 (26) | 3 (18) | 6 (24) |
| Miscarriage | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) |
| Other fetal adverse outcomea | 1 (5) | 1 (6) | 1 (4) |
| Other maternal adverse outcomeb | 5 (26) | 4 (24) | 6 (24) |
The most frequent serious adverse event was admission to hospital for seizures, which contributed to 37% of serious adverse events in the therapeutic drug monitoring group, 40% of the serious adverse events in the non-randomised group and almost half of the serious adverse events in the clinical features monitoring group.
Other maternal adverse outcomes made up approximately one-quarter of serious adverse outcomes in each group. Similarly, congenital malformation contributed almost one-quarter to each group, although this was less frequent in the clinical features monitoring group at 18%.
The distribution of serious adverse events did not considerably differ between each group. No serious adverse events were related to the trial.
Chapter 4 Qualitative study
Introduction
Women with epilepsy who become pregnant possess an expertise on which to base their expectations of pregnancy and childbirth. Their experience of living with epilepsy influences the ways in which they make sense of their pregnancy, as well as their views on the management of the condition. Thus, women’s position as ‘expert patients’ enables them to balance the risks and benefits to themselves and their baby of AEDs within the context of their lives. This chapter reports on the qualitative study undertaken to capture this expertise and to explore in some depth women’s lived experiences and perspectives of pregnancy while managing their epilepsy. Qualitative data provide an additional dimension to quantitative results, allowing participants to focus on the issues of importance to them and to explain how they make sense of events within the context of their everyday lives. The growth of qualitative studies within a quantitative randomised controlled trial (RCT) framework is important, especially in trials, such as AntiEpileptic drug Monitoring in PREgnancy (EMPiRE), which are conducted within sensitive settings of maternal and fetal medicine, in which participants may be considered ‘vulnerable’. 23 The purpose of this qualitative study is to understand women’s lived experiences and perspectives on managing their epilepsy during pregnancy through interviews with both women who choose to accept participation in the RCT as well as those who declined.
Background
To date, research on epilepsy and pregnancy has been largely investigated using quantitative methods, and this is reflected in evidence-based reviews covering the area. 24,25 Expert reviews26,27 and guidelines28 on the management of epilepsy in pregnancy focus on aspects of care important to health professionals. However, there is a stark absence of research concerning the priorities and perspectives of patients themselves.
A review of qualitative literature29 in this area was conducted in 2013 and found only one study30 that directly investigated women’s experiences of epilepsy during pregnancy. This ‘exploratory qualitative’ study, carried out by Thompson et al. ,30 investigated the experiences of women living with epilepsy of health-care services at key phases of reproduction, including contraception, pre-conceptual care, pregnancy, birth and breastfeeding, and parenting and child safety. Women reported mixed experiences of health care during these stages: some felt that they had received good care, but others were given inadequate information and offered advice from practitioners only after an event, and, thus, they could not take appropriate preventative action. Thompson et al. 30 argue that the management of a chronic illness and reproductive health involves work of a ‘moral dimension’. For example, in relation to their pregnancy, the concern with the effects of AEDs on their unborn babies created a conflict for women between being a ‘good mother’ and being a ‘good patient’. Thompson et al. ’s study30 provides a much needed contribution to understandings of how epilepsy influences women’s experiences of the various stages of pregnancy and reproduction. However, as it is an exploratory study with a small sample size of 15 women, findings remain limited in scope.
The 2013 literature review29 included studies exploring not only women’s experiences of pregnancy, but also their experiences of reproductive health while managing epilepsy. This expansion of the review resulted in 16 additional publications, which were limited in their generalisability because of the small sample sizes and/or poor quality of data. Since the publication of this review, one additional study has been published in this area: Qiang et al. ’s 201631 small qualitative study on the support networks of 12 pregnant women living with epilepsy. There is, therefore, a dearth of high-quality research on the experiences of pregnant women living with epilepsy.
Study aim
To investigate the perspectives and experiences of pregnant women living with, and managing, epilepsy.
Objectives
To gain insight into the way pregnant women with epilepsy rationalise and make sense of the management of AEDs in the context of their lives by addressing the following research questions:
-
How do women experience living with epilepsy before becoming pregnant?
-
What do women perceive as issues of concern for them and their baby in terms of epilepsy management during pregnancy and childbirth?
-
How do women construct and make sense of the risks, and benefits, for themselves and for their baby in terms of medication?
-
How do women perceive maternal responsibility in the context of having epilepsy?
-
What and who influences women’s decision-making in the management of their condition during pregnancy?
-
How do women view their experience of pregnancy and childbirth and the management of their medication during this time?
Methodology
The above research questions were explored empirically through semistructured interviews using participant narratives. 32 This approach allowed research participants some control in the research agenda as they could focus on issues that were of concern to them and elaborate in order to provide context and rationales for the ways in which they make sense of managing their epilepsy over the course of a pregnancy. Reporting was undertaken in line with recommended guidelines. 33
Sample
Theoretical sampling was employed to purposely include women from different geographical regions, with a diversity of sociocultural backgrounds, and who had varied histories with epilepsy and had experienced a range of neurological symptoms. A total of 32 women participated in interviews, of whom 21 had enrolled in the RCT and 11 had declined the trial but agreed to take part in the qualitative study. Recruitment and sampling continued until data saturation was reached and no further analytical categories emerged from ongoing analysis of interview data. 34 Saturation was determined independently by the EMPiRE trial qualitative lead, Elaine Denny, and research fellow, Annalise Weckesser. Women were first approached face to face by research nurses and midwives and given informed consent forms for the qualitative study. Annalise Weckesser then telephoned women who had agreed to take part in the qualitative study and who had signed informed consent forms.
Method
The aim of this research was to gain insight into the way women make sense of living with epilepsy during pregnancy and, thus, a qualitative approach was appropriate. All women were requested to take part in two or three interviews, which were audio-recorded with their permission and transcribed verbatim. Annalise Weckesser or Elaine Denny interviewed the women twice. Annalise Weckesser and Elaine Denny are both women with experience conducting qualitative research. The interviewers did not establish relationships with participants prior to the commencement of the study. Participants knew that Annalise Weckesser and Elaine Denny were non-clinical members of the EMPiRE trial research team, and that both have research interests in gender, reproductive health and chronic illness.
The first interviews took place when women were pregnant and had either entered the trial or refused to enter the trial. The second interviews took place approximately 6 weeks after participants had given birth. First interviews lasted approximately 1 hour and second interviews lasted approximately half an hour. Eight women did not participate in follow-up postnatal interviews: one returned to her country of origin, two withdrew from the RCT and five were unable to be contacted.
Interviews were conducted at places and times convenient to participants. The majority of women were interviewed in their own homes; however, some preferred to be interviewed at hospitals after their antenatal clinic appointments and some interviews took place over the telephone. Most women were interviewed on their own; however, some women asked for their partner (n = 4) or mother (n = 2) to be present to help them remember details of their seizures and medication. Most postnatal interviews were conducted over the telephone as this was most convenient for women with the time constraints of caring for their newborn. In appreciation for their time and participation, women were given a £20 gift voucher following completion of their first interview.
First interviews took place on the women’s entry to or refusal of the randomised trial, and these interviews focused on the six research questions (see Objectives). Additional interviews were originally proposed with women in the qualitative study who had experienced a reduction in serum AED level or who experienced a seizure during pregnancy to explore if these events altered patients’ perspectives on epilepsy and pregnancy and raised new concerns. However, this was not possible as research nurses and midwives did not inform Annalise Weckesser and Elaine Denny when a patient had a seizure during pregnancy. However, in postnatal interviews, Annalise Weckesser and Elaine Denny learned that some participants did have seizures during their pregnancy and we were able to capture these experiences retrospectively. Postnatal interviews concentrated on women’s reflections on the research questions on the presumption that pregnancy experiences can only be fully reflected on once the outcome of the pregnancy is known. Short field notes were taken immediately after the first and second interviews to make note of, and describe, where interviews took place.
Elaine Denny and Annalise Weckesser developed interview guides to ensure data collection on relevant topics (see Appendix 4), but participants were also free to raise issues of importance to them. The interview guide was developed based on themes identified in a review of qualitative literature on the experiences of pregnancy and reproductive health of women living with epilepsy, which was published by Elaine Denny and Annalise Weckesser in 2013. 29 Basic demographic data including current age, parity and years living with epilepsy were collected from participants at the beginning of the first interview.
Ethical considerations
As epilepsy is considered to be a stigmatising condition,35 the researchers avoided stereotyping and discriminatory use of language. Each woman’s guidance was sought at the beginning of interviews concerning acceptable use of terminology. The researchers complied with the British Sociological Association’s statement of ethical practice. 36 Pseudonyms have been used to protect the anonymity of participants.
Analysis
A narrative analysis was adopted as this method has much to contribute to studies of chronic illness. As Riessman notes, ‘[t]elling narratives is a major way that individuals make sense of disruptive events [such as illness] in their lives’. 37 Within this narrative mode of analysis, a thematic approach was undertaken – a method that allowed for the identification of common themes across cases while enabling individual women’s stories to remain intact. 38 To ensure rigour in the analysis process and to establish trustworthiness in the findings, Elaine Denny, Annalise Weckesser and a member of the EMPiRE trial team read all interview transcriptions. Annalise Weckesser took the lead in developing the analysis to increase internal consistency, but all members agreed on coding frames and analytical themes for internal validity. Annalise Weckesser created a coding frame for categorisation of data using NVivo 10 (QSR International, Warrington, UK). Analytical themes and concepts were developed and explored using the constant comparison method. 39 An additional strand of narrative analysis was also conducted, allowing for the integrity of each woman’s interview to be maintained. 38 This analysis of narratives allowed for an understanding of the inter-relatedness of a person’s life story that can be lost and fragmented in the constant comparison method. 38 These two methods of analysis provided insights into how women experience pregnancy and epilepsy, and how they make sense of these events within the context of their lives.
Findings
Sample results
Participants came from urban areas, including London, Birmingham, Cardiff and Liverpool, as well as more rural areas such as Shrewsbury, Gwent and Worcestershire. Table 16 provides the sociodemographic details of participating women. At the time women were first interviewed, over half were becoming mothers for the first time (n = 18) and the rest had at least one child. The youngest participant was aged 19 years and the oldest was aged 42 years (mean age 31 years). More than half of participants were married (n = 18) and others lived with partners (n = 10), lived separate from partners (n = 2) or were single (n = 2). Women worked in professional occupations (n = 17) and in retail (n = 2), or were unemployed and/or full-time mothers (n = 12); one was a full-time student. The majority of participants had been born in the UK and self-identified as white British (n = 21); others identified as British Asian (n = 4) and British black Caribbean (n = 1). A number of women had immigrated to the UK, including three participants who identified as white European and one each as Chinese, black African and white American. One NHS Mandarin interpreter was required to provide an interview translation.
| Demographic | Number of participants |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| Range | 19–42 |
| Mean | 31 |
| Marital status | |
| Married | 18 |
| Cohabiting | 10 |
| Non-cohabiting/with partner | 2 |
| Single | 2 |
| Parity | |
| Primigravida | 18 |
| Gravida 2, parity 1 | 10 |
| Gravida 3, parity 2 | 4 |
| Employment | |
| Professional | 17 |
| Retail | 2 |
| Student | 1 |
| Unemployed/full-time mother | 12 |
| Ethnicity | |
| White British | 21 |
| British Asian | 4 |
| White European | 1 |
| White American | 1 |
| Black African | 1 |
| Chinese | 1 |
| British black Caribbean | 1 |
| Years with epilepsy | |
| Range | 1–29 |
| Mean | 11.2 |
| Types of seizuresa | |
| One-off seizure | 1 |
| Absence seizures | 9 |
| Myoclonic | 9 |
| TCS (self-defined) | 17 |
Participants had varied histories with epilepsy. One mother was diagnosed only within the past year and, at the other end of the spectrum, a participant had lived with the condition for 29 years. On average, women had lived with their condition for 11 years. Women also experienced a wide range of neurological symptoms. Participants self-identified their seizure types, ranging from tonic–clonic seizures (which constitute the more popular images of epileptic convulsive seizures with a person losing consciousness, their muscles stiffening and jerking), myoclonic seizures (involving the brief, shock-like jerking of muscles) and absence seizures (which are absences in awareness and women often described these experiences like ‘déjà vu’ or an ‘aura’). Some women experienced more than one type of seizure at different stages in their life, and the frequency of seizures also differed between women and among individual women over time.
Interview findings
The following findings are based on ante- and postnatal interviews. For the purposes of this chapter, findings are presented thematically rather than as narrative case studies to facilitate the reporting of findings related to the qualitative study’s research objectives of understanding:
-
women’s experiences of living with epilepsy before becoming pregnant
-
women’s concerns in relation to epilepsy management in pregnancy
-
women’s strategies for balancing risks and benefits to themselves and their babies in relation to medication
-
women’s perceptions of maternal responsibility in the context of having epilepsy
-
the influences on women’s decision-making in the management of epilepsy and pregnancy
-
women’s postnatal reflections on the experience of pregnancy and childbirth, and the management of epilepsy
-
women’s reasons for declining trial participation (for participants who declined participation in the randomised trial).
Although reporting findings through this separation of strands of experiences brings clarity, it must be noted that it creates a false distinction; in reality, people’s experiences, feelings and actions are interlinked and, thus, cannot be easily reduced to simple, segregated categories.
Experiences of living with epilepsy before becoming pregnant
Women’s histories of living with epilepsy before becoming pregnant are highly diverse. This diversity is reflected in the spectrum of seizure types and frequencies experienced by participants, and the number of years they have lived with the condition (see Table 16). Although some women had been diagnosed in childhood, others did not receive a diagnosis until more recently and/or after a first pregnancy.
With regard to how the management of their condition impacted on day-to-day life, women’s responses ranged and were shaped by this diversity of seizure types and frequencies. For some, the fear of having a seizure was a daily occurrence:
[I] feel quite nervous and self-conscious all the time because I don’t know when I’m going to have my next seizure.
Cecilia
For some, epilepsy impacted on their work and chosen career paths. For example, one participant reported losing her job in a factory after her diagnosis as she was not allowed to work near the machinery in case she should have a seizure. Another participant had been training as a beautician but was told she could not continue with the course after disclosing her diagnosis, as she would not be allowed to use some of the electrolysis machines.
The majority of participants, however, reported that on a day-to-day basis their condition did not impact on them greatly. Some made modifications to their lifestyle (ensuring that they get enough sleep, refraining from excessive alcohol consumption, not bathing alone, etc.) but saw these as minor adjustments. Riva is one such woman; despite these adjustments, she states that she leads a ‘normal life’:
[Prior to becoming pregnant] I could get up every day, I would have my medication, I could go to work and have a normal life and go back home. And you know, it wasn’t something that would impact me greatly . . . I had a gap of several years between my seizures. So for me the seizures, like it didn’t feel like it had a particularly detrimental impact on my life.
Other participants had such infrequent seizures, some having ever experienced only one seizure, that they reported not feeling they had ‘real epilepsy’ and that they were ‘lucky’ as they believed they faced less hardship and stigma than those with less controlled and more ‘severe’ seizures.
In addition to the diversity of epilepsy experiences, some participants faced additional pregnancy and/or concurrent health concerns that took primacy over their epilepsy. Some women reported fertility issues, challenges having a baby in their forties, undergoing in vitro fertilisation treatments and/or having past experiences of miscarriage. Becoming pregnant was reported, by some, to be more of a challenge and concern than managing their epilepsy:
I thought, ‘OK, I just need to manage my medication and then I’ll get pregnant’ . . . I think more than anything to do with my medication that was the biggest shock for me, that actually it isn’t that easy to get pregnant. Like it’s easy to manage what dosage you take and to keep tabs on what you’re taking, making sure you go and see the specialist and [your epilepsy is] managed. But I think the biggest shock to me was just the process of actually getting pregnant in the first place.
Sonia
Other participants reported additional health concerns that impacted on their day-to-day life, including Tourette syndrome, congenital talipes equinovarus, overactive thyroid and high blood pressure, as well as other related health issues that arose during pregnancy, such as pre-eclampsia and gestational diabetes. One participant felt that managing her Tourette’s affected her more than her epilepsy:
The epilepsy I don’t notice, because if I have a fit, it’s always at night time. So I’ve never had one in the day, I’ve always been fine. Because in the day, I kind of control the Tourette’s.
Tanya
Women’s experiences of epilepsy were also influenced by their different sociocultural and religious backgrounds. One participant believed that her epilepsy had been caused by a curse and attended evangelical faith healing sessions. Another participant, Amina (aged 31 years), after being diagnosed with the condition reported becoming a more ‘devout’ practising Muslim, signified by adopting a hijab. Amina believes that her faith helps her manage her condition; however, she continues to take her AEDs:
I’ve got my religion, but I’ve also got the doctors. This medication’s there for a reason. It’s helped me not have a seizure all this time so I’ll just continue.
Women’s experiences of living with epilepsy prior to becoming pregnant are highly diverse and are shaped by their particular seizure type(s) and history, whether or not they have additional health and fertility concerns and their sociocultural backgrounds.
Concerns in relation to epilepsy management and pregnancy
As discussed in the previous section, for many participants the everyday management of epilepsy prior to becoming pregnant had become routine and normalised. However, pregnancy often becomes a stage at which women have to reflect on their condition and how it impacts on their health and that of their baby. This is illustrated by the case of Philomena (aged 31 years), who states that before becoming pregnant she ‘wasn’t thinking about [her epilepsy] from one day to the next . . .’. After first being diagnosed, she initially took on ‘all the good habits’. She continues:
I never used to drink . . . [I] only took a bath when people were there. So you kind of start with really good practices . . . [A]nd then as the years go by you just stop thinking about it completely and you just take your tablets every night and you’re fine . . . But then as soon as you became pregnant you need to get back into good habits . . . [W]hen you have the baby you need to change [them] on the floor, you shouldn’t do this, you shouldn’t do that, and you were just a bit like, ‘Oh yeah, I completely forgot!’.
Thus, pregnancy is a time that raises many concerns for women living with epilepsy, concerns about things that some may have previously taken for granted.
Participants reported that their primary concern was to give birth to a healthy baby, with no abnormalities:
I think really you worry about everything, you could worry about anything, but I think the main thing is I just want to have a happy and healthy baby at the end of it.
Simone
At the moment I get concerned about whether [the baby’s] going to be normal or not. Otherwise, I haven’t got any concerns.
Mary
The first question I’m asked is, ‘Do you want a girl or a boy?’. And I just say, ‘I want a normal baby’. A healthy, normal baby . . . I don’t care whether it’s a girl or a boy . . . I hope it’s a healthy, fat baby.
Samina
Women also expressed concerns about the effects of their AEDs on their unborn babies. Although participants often reported feeling some reassurance from health practitioners who advised them that the medication they were on were newer AEDs believed to be safer during pregnancy, some still had concerns about possible teratogenic effects, including spina bifida and learning disabilities. This is illustrated in the following extract:
The doctors are like ‘Oh this is a great drug, it’s much better than the one you were on before’. And I’m thinking, ‘Yes, but the one I was on before it’s been around 20, 30 years’. So you know that there’s defects, but you know at what levels those defects occur and how likely it is to happen. Whereas you put me on this new medication, which actually has been around maybe 4 or 5 years so you have a little bit of experience . . . Even though [the doctors’] experience and knowledge is quite valid, but at the same time they don’t have to live with the consequences of it.
Riva
Some women were concerned that they could pass their condition on to their babies, despite the knowledge that genetic inheritance of epilepsy is very rare:
The other thing that you worry about is sometimes it’s like I hope [epilepsy’s] not something I can pass on to my baby because I really wouldn’t want that . . . Even though they say it’s not inherited you just don’t know because they say some forms can be.
Fatimah
Women also expressed concerns about having a seizure during their pregnancy, labour and/or in the early postnatal period. During pregnancy, women were especially concerned about having a seizure in their final trimester, when the baby is seen to be more ‘fully formed’. As Li Min stated:
[I’m] worried that [I’m] going to have a seizure towards the end, when the baby’s like mature . . . [I’m] really scared that it’s going to happen and it’s going to affect the baby and me as well.
Participants worried that a seizure could cause a decrease in the amount of oxygen that gets to the fetus. Tiredness and stress during pregnancy and from the strains of giving birth were also seen as possible seizure triggers. For example, one participant, Laura, feared that she was more likely to have a seizure in her current pregnancy than in her former, as she was now experiencing more sleeplessness as a result of taking care of her firstborn, who was still a baby:
I think I’m probably more concerned this time round because I have it in the back of my mind that I’ll probably have more seizures during this pregnancy because of having [my son] and the sort of stress of looking after him really, as well as the tiredness . . . [T]he end of the day comes and you think ‘I don’t think I’ve even brushed my teeth today to start off with’ . . . So I’m more concerned that I’m going to be more tired, which will lead to me having more seizures, which will lead to me being more tired.
Finally, women were very concerned about having a seizure because this could result in losing driving privileges until they have been seizure free for 1 year:
The main hope is not to have any déjà vu. Because even the slightest déjà vu I need to inform [my medical team] . . . So that is a worry, but mainly for the selfish reasons of driving.
Laura
[If I have a seizure] then I wouldn’t be able to drive, which I think would be a massive issue . . . [T]hat would make everything like a million per cent more difficult.
Philomena
Women in rural areas with little public transport and those who required a vehicle for work were especially concerned about the isolation and inconveniences caused by losing their driver’s licence in the event of a seizure.
Strategies for balancing risks and benefits to themselves and their babies in relation to medication
Many of the participants reported thinking about whether or not they should have children in view of having epilepsy. Most women had planned their pregnancies (n = 22) and two women had been advised against having children because of their condition (one by a doctor and one by their partner). Philomena reflects on her decision to have a baby, stating:
You think about what effects the drugs have on the baby, what if I had a fit . . . There are all of those considerations, but for me none of them outweighs actually having a baby.
In relation to taking AEDs, women made their medication management decisions by weighing up the risks to the health of their baby, their own health and other aspects of their life. Some women felt it was particularly important to keep taking their medication during their pregnancy to minimise the risk of seizures:
I can’t help but think I’m so scared that I’ll have a seizure and somehow or another I will end up hurting either the baby or myself . . . And I think your priorities completely change, you do want to do what is best for your baby, but at the same time if you’re harming yourself you can’t be doing what’s right for your baby. If I fall and if I have a seizure, then I’m risking both anyway. I think you’ve just got to look at it practically.
Fatimah
The risk of me being on the medication is minimal [to the baby] . . . But the risk of me falling down a flight of stairs could kill her really.
Shelly
Thus, although participants saw continuing their AEDs during pregnancy as potentially harmful to the health of their babies, such risks had to be balanced with what some saw as a more likely and harmful risk of having a seizure that could occur if they stopped or reduced their medication. Some women did choose to stop or reduce their medication in the first trimester because of the perception that the fetus was at heightened risk of malformations at this time:
When I found out I was pregnant with [my first child], I did stop taking [the medication] ‘til after my 3-month scan, and I did do this time as well for the current pregnancy . . . I went to the [clinic] at about 10 weeks’ pregnant and [the epilepsy nurse] said, ‘Have you had any seizures?’. I said, ‘No’. She said, ‘You know you’re more susceptible, etc., etc.?’. And I said, ‘Yes’. And she said, ‘Well I’m going to leave you to it’. And then 10 days later I had a bout of seizures, so that just brought me up to my 12-week scan, so I’m back on my medication now, properly.
Laura
Women’s decisions about taking medication in pregnancy to prevent seizures had to be balanced with other aspects of their lives, such as the need to keep their driving licence. One participant, Sandra, had a seizure during her first pregnancy, and during her second pregnancy she stated:
[The seizure] cost me my driving licence. I was a community midwife [in a rural area] . . . It was the most depressing time without a driving licence. I didn’t really know how much it meant to me, and it put me off getting pregnant again because the thought of losing my driving licence again, it was too much of a risk.
Sandra
Sandra believed she had the seizure because her epilepsy specialist midwife had failed to increase her AED dosage during the first pregnancy. She reported that for this current pregnancy her epilepsy specialist midwife had agreed to increase her medication, but if the midwife had not, Sandra would have self-managed her medication and increased her dosage to prevent a seizure.
Perceptions of maternal responsibility in the context of having epilepsy
Although women’s decisions ranged from stopping, reducing, maintaining and increasing their AEDs over the course of their pregnancies, overwhelmingly the rationale for such decisions was based on a feeling of maternal responsibility towards their babies. This is illustrated in the following two contrasting extracts, one from a woman discussing her decision not to take her AEDs in the first trimester, and one woman on why she continues to take her medication during her pregnancy:
If I took the tablets all the time and something happened and [the baby] comes out deformed in some way or had something wrong with it, then I would think that I’ve been a selfish person and feel terrible for doing that when I know I can cope for so long without them.
Mary, on not taking AEDs
[T]here is the odd night I’ll get into bed and every night [think] ’have you taken your tablets? Yes’. But I will remember if I lay there long enough. I’m like, ‘Oh, I didn’t take them’. But it’s not just me I’m thinking about now. So yes, it is a little bit more important. Because I’m not just taking them for me.
Veronica, on taking AEDs
Both women made decisions regarding their medication based on feelings of maternal responsibilities towards their unborn children. The types of seizures that the women experienced also informed their choices. Prior to having full tonic–clonic seizures, Mary would often experience symptoms including auras. Thus, if she had any of these early warning signs she would take her medication. In contrast, Veronica did not have such warning symptoms prior to having a seizure.
Women continuing or increasing their medication to prevent seizures in pregnancy still had concerns about the chance AEDs could affect their baby’s health. These concerns derived from their role as mothers and carers, now looking after the health of their unborn child as well their own. Clara stated, regarding the possible teratogenic effects, that:
[C]hances are very, very low, but then there’s always still that chance. And it’s not just you that you’re talking about any more, it’s an extra person, which took me by surprise at how differently I probably feel about that because, you’re like, it’s not just me any more, it’s another little person.
Participants’ feelings of maternal responsibility were also evident in the form of guilt associated with the possibility of having a baby born with health problems, as illustrated in the following extract:
I worried a lot that if there were problems with the baby that it would be my fault. It wouldn’t necessarily be my fault, but it kind of is if you know what I mean. I worried that the drugs that I took . . . I did have quite sleepless nights thinking, ‘Oh God, what if something happens to the baby and they’re born with defects that I’m going to have to explain to it’. That worries me.
Nicole
Influences on decision-making in the management of epilepsy and pregnancy
Women had a range of influences on their decision-making in the management of epilepsy and pregnancy. In relation to their medication, many made decisions regarding their dosage in consultation with their neurologist, epilepsy nurse or epilepsy midwife, but were also informed by knowledge of their own body, history with the condition and seizure warning symptoms. Women’s decisions, as discussed in Perceptions of maternal responsibility in the context of having epilepsy, were also shaped by considerations for the well-being of their baby. Many participants had partners and key family members (such as mothers) who provided them with care and support in the management of their condition. However, partners and family members did not play key roles in influencing women’s AED management choices. As Fiona replied, in relation to her medication, ‘At the end of the day I make the decisions for what I want and what’s best for me and the child’.
Some women reported using the internet to research the teratogenic effects of the particular AEDs they took, but viewed such information as supplementary to the professional advice of their medical team.
Postnatal reflections on the experience of pregnancy and childbirth, and the management of epilepsy
Women’s perspectives on pregnancy and managing epilepsy were shaped by labour and pregnancy outcomes. The majority of women reported giving birth to babies who, from birth to the point of the postnatal interview, did not have any apparent health problems linked to taking AEDs. For such women, their views on having a pregnancy while managing epilepsy were largely positive. This is reflected by Jeannette, who stated, 6 weeks after giving birth to a healthy baby:
I just don’t think if a woman has epilepsy [that she] should be scared to have a baby because [she] could be like me, everything is fine, no worries at all. So I wouldn’t even worry about thinking, ‘Oh I can’t have a baby because I’ve got epilepsy’. Because it’s twaddle really.
One participant reported early health problems with her baby that she was concerned could be linked to AEDs. Amy had a son ‘born with shaky arms and legs’ and some possible visual impairment. She stated that ‘[At] first, I thought, “Oh was that to do with the medication?” Could that have had an influence because I take these tablets?’. She consulted paediatricians who attributed these complications to an ‘immature neurological system’ and assured her that her son would ‘grow out’ of the ‘shakes’. Amy stated that she now felt ‘pretty reassured’ as the doctors did not believe the medication caused her son’s health impairments and because she is prescribed ‘one of the safest drugs and take[s] quite a relatively low dose’.
Although seizure during labour had been a concern for some women while they were pregnant, only one participant experienced a seizure during childbirth. Many women reported negative experiences in postnatal wards as a result of a lack of sleep and staff shortages. Some women reported feeling ‘abandoned’ and ‘vulnerable’ to seizure in the postnatal ward. They expressed a desire for a partner or family member to remain on the ward to help care for them and their newborn infant. Although a few wards allowed partners/family members to remain outside of visiting hours, this was not universally practised across all wards. One woman reported that she felt that she would not have another baby because of her poor postnatal care experience.
In relation to caring for their newborns, many women reported having to make accommodations as a result of their epilepsy. This was evident in sleeping patterns, breastfeeding strategies and day-to-day care practices for infants. For some participants, sleep deprivation was a seizure trigger. Thus, to ensure they had enough sleep, some had partners, family members or night nannies take the lead in baby care and feeding overnight. Some of these women expressed feelings of guilt that they were not ‘proper’ mothers because they were not doing night feeds.
Many women found mixed feeding (combining breastfeeding and bottle feeding) an effective way to ensure that their babies got the health benefits of breast milk while also being able to ‘top up’ with formula milk. Women felt that this feeding strategy helped babies sleep for longer periods in the night, allowing women to get more sleep. Bottle feeding also allowed partners and family members to share in the feeding duties. A few women reported receiving conflicting advice from health professionals regarding the safety of breastfeeding while taking AEDs.
Precautionary practices in the day-to-day care of newborns, such as breastfeeding or nappy changing while sitting on the floor, refraining from bathing a baby alone and using a car seat when carrying a baby on stairs, were less likely to be taken up by women with a history of well-controlled seizures.
Reasons for declining participation in the randomised trial
Eleven women declined to participate in the RCT. About half (n = 6) of this group chose not to take part in the RCT because the randomisation process was not acceptable to them. They were concerned that they may be streamed into the clinical features monitoring strategy of the trial, and would have their medication dosage increased only after a seizure and not when their blood levels decreased, with negative consequences for them and/or their baby. Such women reported that they felt they would lose control over the management of their epilepsy:
I thought it would be easier to control my seizures if I didn’t go into the study.
Clara
For me it would be quite a bizarre choice not to know what was happening to the levels of lamotrigine in my blood, and not to intervene.
Sandra
These six women also expressed concern that they would be at more risk of a seizure if they were randomised:
Should I require additional medication, that wouldn’t necessarily be prescribed if I was part of the wrong part of the trial.
Nicole
If I could choose which group I was going into that would be fantastic, but I was told I couldn’t choose which group I was going into. So it wasn’t worth the risk [of having a seizure].
Sandra
The five other non-randomised women chose to decline trial participation for the following reasons:
-
work and time commitments (n = 1)
-
lived too far from hospital for required monthly antenatal visits (n = 1)
-
fear of needles (n = 1)
-
stopped taking AEDs prior to pregnancy and did not want to resume (n = 1)
-
believed she did not have epilepsy (n = 1).
Discussion
Women sit on a wide spectrum of seizure types and frequencies, and this makes it difficult to categorise women by epilepsy type. The ways in which women made sense of their pregnancy and epilepsy experiences were shaped by both biography and social context. These varied experiences informed the way participants perceived their condition and how they managed their condition before, during and post pregnancy.
Women who experienced relatively few seizures or who had well-controlled seizures often stated that they felt ‘lucky’ and believed that they faced fewer hardships and stigma than those with more ‘severe’ or ‘real’ epilepsy. Overall, participants did not view their epilepsy as a ‘disability,’ but instead as a chronic health condition that they could manage by taking medication and/or avoiding seizure triggers, including tiredness, excessive alcohol consumption and stress.
For many women, prior to becoming pregnant, the day-to-day management of their condition had become routine and normalised. Pregnancy marked a time when these management routines came to be disrupted. Women had to re-evaluate their drug regime as they now had to consider their increased vulnerability to seizure during pregnancy as well as the risk of teratogenic effects of the AEDs. Women had to weigh up these risks to themselves and to their babies in a context of uncertainty. Risks of seizures and teratogenic effects of medication were possibilities, but not certainties. Participants reported adopting a variety of strategies to mitigate and balance these risks, including reducing, stopping, continuing and increasing their medication during pregnancy. Underlying most of these management strategies was a desire to safeguard the health of their baby.
The findings suggest that a tension may exist between the health professional’s focus on drug adherence and the patient’s experience of doubt. Women may feel that health professionals have different priorities from them, as it is women who will live with the consequences of drug regimens and any teratogenic effects on their babies. As the findings above show, women experience feelings of maternal guilt and responsibility for their babies being born with any health problems or abnormalities. These findings resonate with those of Thompson et al. ’s 30 study, which found that women living with epilepsy undertake ‘moral work’ in relation to their pregnancies and that their concerns with the effects of AEDs on their unborn babies create a conflict between being a ‘good mother’ and being a ‘good patient’.
Strengths and limitations of the qualitative study
As this study was carried out alongside the EMPiRE trial, including only women who chose to have children, there is a risk of bias as those having children may have more well-managed seizures and fewer negative symptoms and side effects associated with their medication. Approximately one-third of women of childbearing age living with epilepsy in the UK consider not having children, or having fewer children, because of their condition. 40
Additional limitations of this qualitative study include the use of a self-selected sample and an inability to capture participants’ experiences of seizure during pregnancy. These seizure experiences were captured only retrospectively through postnatal interviews.
Despite these limitations, the study’s strength lies in the original contribution it makes to further understanding women’s experiences of epilepsy, pregnancy and reproductive health, in which there has previously been a dearth of robust, in-depth qualitative research. 29 To our knowledge, this constitutes one of only two studies to directly examine women’s experiences of pregnancy while managing epilepsy. 30
Chapter 5 Discussion
In pregnant women with epilepsy on AEDs, a strategy of additional therapeutic drug monitoring did not significantly reduce the risk of time to first or to multiple seizures compared with management based on clinical features alone. Babies born to mothers who received therapeutic drug monitoring in pregnancy were exposed to significantly high levels of the AEDs lamotrigine and levetiracetam at birth. The average doses of AEDs prescribed in both groups were similar. There were no differences in pregnancy complications, maternal quality-of-life measure, birthweight and breastfeeding rates between the two strategies. The risk of seizure was not greater in the groups whose serum AED levels were reduced than the stable group when the clinical features monitoring and therapeutic drug monitoring groups were compared with the non-randomised cohort. Women’s decisions on AED intake and increasing the dose of medication were influenced by concerns for the baby.
The EMPiRE study is the largest randomised trial to date on pregnant women with epilepsy. We recruited women across all four nations in the UK, involving centres that had access to joint obstetric epilepsy care. Our findings are generalisable across the UK for the care of women in the NHS.
Strengths and limitations
We included women on AEDs that are commonly prescribed in pregnancy, with evidence of a reduction in levels in pregnancy, and availability of serum level measurements in the NHS. We excluded women on sodium valproate, as sodium valproate levels in pregnancy are considered to be unreliable, and it is not standard practice in the UK to test sodium valproate levels in (or out of) pregnancy. Our chosen design of early consent, and randomisation only when the serum levels fell, ensured that the data on all the randomised patients contributed to an estimation of the effect, enhancing the statistical power to detect a difference. Follow-up of the non-randomised cohort made it possible for us to blind the control group. Our choice of primary outcome, loss of seizure control, could be defined and analysed in various ways, with no consensus on the best approach. 40 The standard approaches to analysis assume a normal distribution. We expected our data to be highly skewed, with a large proportion (50–60%) of women remaining seizure free throughout pregnancy,41 and chose time-to-event analysis incorporating estimation of robust standard errors. Since tonic–clonic seizures are considered to be the most severe, we undertook a sensitivity analysis of the primary outcome when limited to only tonic–clonic seizures. By not prespecifying the level of AED in the therapeutic drug monitoring group at which the dose should be increased, we gave clinicians the flexibility to exercise judgement about whether to adjust the AED dose, and to what extent, taking into account patient preferences and factors other than serum AED level that impinge on the decision. The EMPiRE study assessed the effect of two strategies on pregnancy outcomes and is the first trial to assess QoL in mothers with epilepsy on AEDs.
We randomised fewer women than the required target (n = 660) to provide definitive evidence on the decrease in time to first seizure by at least 25%. An important clinical effect cannot be ruled out, as indicated by the inclusion of target HR in the confidence limits. We involved units that were able to recruit at least one woman per month and took initiatives to set up joint obstetric epilepsy clinics where none existed before. Owing to our inclusion criteria for recruitment being extended until 24 weeks of pregnancy, it is likely that we may have missed randomising women at an earlier gestation when the levels of AEDs had decreased. Although we preferred to use pre-pregnancy levels of AED as the baseline measure against which to compare future levels to detect any decrease, in practice pre-pregnancy levels of AEDs were rarely available. We accepted serum AED levels at baseline in pregnancy as the alternative, but it is likely that we may have missed the decrease in AEDs in these cases. However, our approach was pragmatic, reflecting current clinical practice, in which clinicians have to rely on first levels in pregnancy as the baseline. Given the small numbers of women on individual AEDs, we refrained from providing separate seizure risks that depended on AED intake. We prespecified a 25% reduction in serum AED level as the threshold for randomising women, determined by consensus involving neurologists. It is possible that the effect size would be different for other cut-off points. Although we recruited women from a large number of centres, some centres in the UK refused to participate, as the neurologists from these sites were convinced of the superiority of one strategy over the other. This could be one of the reasons for slow recruitment.
Women’s views for declining participation in the randomised trial
Findings from the qualitative study regarding women’s rationale for declining the trial may also help understand reasons for slow recruitment. Eleven women who participated in the qualitative study declined the RCT; of these, approximately half reported that they found the process of randomisation unacceptable. They expressed concern that randomisation would lead to a ‘loss of control’ over the management of their epilepsy as they could potentially be streamed into the clinical features monitoring strategy of the trial, and would have their medication dosage increased only after a seizure and not when their blood levels fell. They believed that not increasing their medication when their blood levels dropped could potentially lead to a seizure and they or their baby could be harmed. Thus, women’s concerns regarding preventing seizures in pregnancy and maintaining control over their medication regime could also underpin slow recruitment to the trial.
Reductions in serum antiepileptic drug level in pregnancy and seizure deterioration
Serum AED concentrations often decrease during pregnancy. Physiological changes in pregnancy alter AED pharmacokinetics and AED concentrations. There is reduced gastric tone and motility, and increased plasma volume, renal clearance, albumin levels and protein binding. 9,14,42,43 The reductions in serum AED levels are considered to aggravate seizures. 44 Monitoring of serum AED levels in each trimester and after delivery has been recommended by the American Academy of Neurology based on consensus as a good practice. 44 In the UK, however, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network’s guideline does not recommend regular AED monitoring in pregnancy because of a paucity of evidence. 12 Our systematic review on the effect of AED monitoring strategies in pregnant women with epilepsy on AED showed lower rates of seizures with therapeutic drug monitoring than clinical features monitoring strategies. 45 The studies were not randomised, or controlled, results were heterogeneous and there was imprecision, with small numbers of women making findings unreliable.
In our trial, we did not observe any differences in seizure rates and time to first and to multiple seizures with the two strategies. Although the point estimates of hazard to time to first seizure and first tonic–clonic seizure, and to multiple tonic–clonic seizures, showed a trend towards favouring therapeutic drug monitoring, the findings were not significant.
Antiepileptic drug exposure in pregnancy to mother and fetus
The measurement of total AED exposure enabled us to delineate the likelihood of excess exposure under therapeutic drug monitoring, in which dose escalation is expected in response to a known decrease in serum AED levels. However, no differences were observed between the groups. It is likely that, when serum AED levels fell, the intervention in the therapeutic drug monitoring group comprised either close monitoring or dose escalation, whereas, without information on serum AED level, clinicians escalated drug doses in response to their clinical monitoring. Despite similar average AED dose exposure in both groups, the cord blood levels of the commonly prescribed AEDs lamotrigine and levetiracetam were higher in newborns in the therapeutic drug monitoring group. The developmental quotient of infants of mothers exposed to lamotrigine in pregnancy compared with women without epilepsy and women not on AEDs appeared to be similar in a small study. 46 There is limited evidence to assess the effect of levetiracetam or AED polytherapy on long-term neurodevelopment. 47
Quality of life in women using antiepileptic drugs
The effects of seizures extend into daily living, resulting in a loss of driving licence, and are known to have a negative impact on employment and relationships, and reduced QoL. 48 We found no differences in the scores for QoL between the two groups. The additional information on serum AED levels in pregnancy, and the subsequent management based on it, did not appear to adversely affect women’s QoL.
Recommendations for clinical practice
Women with epilepsy on AEDs require management in a multidisciplinary setting, with a team involved in both care of their pregnancy and their seizures. The standards of care for individuals with epilepsy vary widely across the UK. 49 This is particularly relevant for pregnant women with epilepsy. Our survey of epilepsy specialists (n = 29) in the UK showed that one-third of participants managed women with epilepsy on AED with regular therapeutic monitoring of drug levels, one-third adjusted doses based on clinical features only and the rest used therapeutic drug monitoring occasionally. 50 Given the wide CIs, reflecting the imprecision, the absence of differences between the two strategies and similar rates of seizures in women with stable and reduced serum AED levels, we are not able to advocate routine therapeutic drug monitoring monitoring in pregnancy.
Although we randomised only half the number of women required to provide the definitive answer, given the wide imprecision in the CIs, we do not expect one strategy to be shown to be significantly effective compared with the other, even if we had managed to recruit to target. We calculated the fragility index, which is the number of currently randomised women who should have been seizure free, to show a 25% decrease in seizures, as postulated in our sample size calculation. Only 36 women should have suffered seizures, compared with the observed number of 48 women, a significant number that should have been reduced. We also calculated the additional number of women needed to show statistical significance for the effect size as observed. Assuming that the observed effect size and SD holds, we estimate that the number of women that would need to be recruited to demonstrate a significant effect of therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical features monitoring on time to first seizure and time to any seizure was 1038 and 1302, respectively.
The risk of seizure deterioration was not significantly different in the non-randomised group with stable serum AED levels and those with a decrease of ≥ 25%, reinforcing the lack of benefit of routine drug monitoring. Furthermore, we observed a significant increase in the cord blood levels of lamotrigine and levetiracetam in women whose AED doses were managed based on therapeutic drug monitoring. Given the above findings, in the absence of firm evidence on long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes in infants exposed to AEDs, particularly the newer AEDs such as levetiracetam, caution is required prior to routine dose escalation based on serum AED levels alone.
Our qualitative study findings have led to the following recommendations on care for pregnant women living with epilepsy.
-
Pre-conception information: pre-conception counselling interventions need to continue to work towards better identifying, and reaching out to, women who are not accessing this information, and to provide consistent information on whether or not they should start a family.
-
Antenatal care and medication management: women’s varied positions on the spectrum of seizure types need be more fully recognised by health professionals, as this informs how women understand and manage their condition. It should also be recognised that women’s decisions to stop, reduce, maintain or increase their AEDs over the course of their pregnancies are based on a rationale of maternal responsibility towards their babies.
-
Postnatal care: ward practices need to facilitate appropriate access for partners and families of women with epilepsy in order to manage their condition following delivery.
-
Supporting mothers with epilepsy: women would benefit from more advice and information concerning modifying their caregiving practices (changing nappies on the floor, never bathing babies alone, etc.), as these practices were often not considered fully until after the babies were born.
Recommendations for future research
Given the difficulties in achieving the target sample size, despite recruitment in more than 50 centres, conducting future randomised trials with a large sample size will be challenging. Any such trials will need to take into account the core outcomes needed for minimal reporting to enable meaningful evidence synthesis. The risks of seizure deterioration for various threshold levels of decrease in AEDs need further evaluation. A robust risk assessment method, using an individualised prediction model by taking into account mothers’ clinical characteristics including type and duration of seizure, type of AED and change in serum AED levels, will help to identify those women who need close monitoring in pregnancy. Importantly, the long-term neurodevelopment of the infants born to mothers in both randomised groups, and any impact on health-care costs, need further evaluation.
In relation to the qualitative research on pregnant women’s experiences of managing epilepsy, additional research is needed with women with less controlled and/or more frequent seizures. As the qualitative study was carried out alongside the EMPiRE trial, which included only women who had chosen to have children, there is a risk of bias as those women having children may have better-managed seizures and fewer negative symptoms and side effects associated with their medication. Furthermore, there is a need for a more integrated approach in future research in this area to provide a more comprehensive picture of the clinical and experiential aspects of taking AEDs.
Chapter 6 Conclusion
In pregnant women with epilepsy on AEDs such as lamotrigine, carbamazepine, levetiracetam and phenytoin as mono- or polytherapy, regular monitoring of drug levels to inform dosage of AED does not significantly reduce the risk of seizure deterioration or lower maternal and fetal complications compared with management based on clinical features alone. Infants born to women in the therapeutic drug monitoring group were exposed to higher levels of AEDs than those in the clinical features monitoring arm.
The qualitative study sought to address the dearth of research on women’s experiences of pregnancy while managing their epilepsy and, to date, is one of only two studies in this area. 30 Findings suggested that a tension exists between the professional’s focus on drug adherence and the patient’s experience of doubt, as she must live with the consequences of drug regimens. Furthermore, women’s varied positions on the spectrum of seizure types must be more fully recognised, as this informs how they understand and manage their condition. In relation to the trial, qualitative findings on women’s rationales for declining the trial highlight that the randomisation process was not acceptable to some women as they felt they could potentially lose control over the management of their medication, which, in turn, could lead to a seizure during pregnancy.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the principal investigators, co-ordinating midwives, epilepsy specialist nurses, consultant obstetricians and neurologists, co-ordinators and data assistants at each of the recruiting hospitals for their dedication and hard work in promoting the study, recruiting participants and for data entry.
Our thanks to the TSC, chaired by Ben Mol (independent obstetrician), and DMC, chaired by Carl Clarke (independent neurologist), for their constant support throughout the trial.
Acknowledgements also go to the staff at the co-ordinating centre: Women’s Health Research Unit of Queen Mary University of London, Anna Placzek (data administrator), Camille Paulsen (administrator), Joyce Kibaru (data assistant), Malika Barakat (data assistant) and Janet Godfrey (administrator). We also thank the Pragmatic Clinical Trials Unit of Queen Mary University of London for their assistance in the development and management of the study database.
We thank Epilepsy Action for their promotion and guidance in developing the study design.
We would also like to acknowledge the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment programme for their ongoing support and advice during the trial.
Finally, we would like to thank each and every participant who consented to take part in the EMPiRE study.
Contributions of authors
Shakila Thangaratinam (Professor of Maternal and Perinatal Health) designed and led the project, provided clinical direction, and prepared and edited the final report.
Nadine Marlin (Statistician) wrote the statistical analysis plan, provided statistical support, performed the statistical analysis of the study and contributed to the final report.
Sian Newton (Trial Co-ordinator) supervised the general management of the study and its data collection, and assisted with the report.
Annalise Weckesser (Qualitative Researcher) ran the qualitative study, developed the qualitative section of the report and provided input towards the report.
Manny Bagary (Lead Neuropsychiatrist) contributed to the design of the trial and provided clinical advice.
Lynette Greenhill (Lead Epilepsy Specialist Nurse) assisted with the design of the trial, and provided advice and support.
Rachel Rikunenko (Trial Co-ordinator) supervised the general management of the study and contributed to the report.
Maria D’Amico (Research Assistant) entered and cleaned data, and edited the report.
Ewelina Rogozińska (Project Co-ordinator) supported the trial and its data collection, and contributed to the final report.
Andrew Kelso (Neurologist) provided clinical input and contributed to the report.
Kelly Hard (Research and Development Manager) assisted with the design of the trial, and provided advice and support towards the report.
Jamie Coleman (Clinical Pharmacologist) delivered support in developing the trial and provided clinical direction.
Ngawai Moss (Patient and Public Representative) provided support and advice throughout the trial, and provided input towards the final report.
Tracy Roberts (Lead Health Economist) assisted with the design of the trial, and provided advice and support towards the report.
Lee Middleton (Statistician) supported the development of the trial, provided statistical direction and contributed to the report.
Julie Dodds (Senior Research Manager) supervised the running of the trial, provided direction and support, and contributed to the final report.
Angela Pullen (Epilepsy Action Representative) helped draft and review the lay summary of the final report, provided advice and helped promote the study.
Sandra Eldridge (Statistician) delivered statistical supervision, contributed to the analysis plan and the final report.
Alexander Pirie (National Lead in Obstetrics) was involved in conception, design and conduct of the trial, and provided clinical direction.
Elaine Denny (Qualitative Lead) assisted with the development of the study, ran the qualitative study, contributed to the qualitative report and provided input towards the draft.
Doug McCorry (Lead Neurologist) assisted with the development of the study, provided clinical input and support, and contributed to the report.
Khalid S Khan (Professor of Women’s Health and Clinical Epidemiology) designed the project, provided overall direction, and contributed to and edited the report.
Data sharing statement
Study data can be obtained from the corresponding author.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Edey S, Moran N, Nashef L. SUDEP and epilepsy-related mortality in pregnancy. Epilepsia 2014;55:e72-4. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12621.
- Yerby MS, Devinsky O. Epilepsy and pregnancy. Adv Neurol 1994;64:45-63.
- Eurap Study Group . Utilization of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy: comparative patterns in 38 countries based on data from the EURAP registry. Epilepsia 2009;50:2305-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02093.x.
- Knight M, Kenyon S, Brocklehurst P, Neilson J, Shakespeare J, Kurinczuk JJ. Saving Lives, Improving Mother’s Care – Lessons Learned to Inform Future Maternity Care from the UK and Ireland Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths and Morbidity 2009–12. Oxford: University of Oxford; 2014.
- Lewis G. Confidential Enquiry into Maternal and Child Health (CEMACH) Why Mothers Die 2000–2002. The Sixth Report of the Confidential Enquiry into Maternal Deaths in the United Kingdom. London: Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists; 2004.
- Schupf N, Ottman R. Reproduction among individuals with idiopathic/cryptogenic epilepsy: risk factors for spontaneous abortion. Epilepsia 1997;38:824-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1997.tb01470.x.
- Schupf N, Ottman R. Reproduction among individuals with idiopathic/cryptogenic epilepsy: risk factors for reduced fertility in marriage. Epilepsia 1996;37:833-40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1996.tb00035.x.
- Schupf N, Ottman R. Likelihood of pregnancy in individuals with idiopathic/cryptogenic epilepsy: social and biologic influences. Epilepsia 1994;35:750-6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1994.tb02506.x.
- Adab N. Birth defects and epilepsy medication. Expert Rev Neurother 2006;6:833-45. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.6.6.833.
- Tomson T, Battino D, Bonizzoni E, Craig J, Lindhout D, Sabers A, et al. Dose-dependent risk of malformations with antiepileptic drugs: an analysis of data from the EURAP epilepsy and pregnancy registry. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:609-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70107-7.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Epilepsies: Diagnosis and Management Clinical Guideline. NICE Guidelines [CG137] n.d. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg137 (accessed June 2016).
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network . Diagnosis and Management of Epilepsy in Adults. SIGN Publication No. 143 2015. www.sign.ac.uk/pdf/SIGN143.pdf (accessed June 2016).
- Harden CL, Pennell PB, Koppel BS, Hovinga CA, Gidal B, Meador KJ, et al. Practice parameter update: management issues for women with epilepsy-focus on pregnancy (an evidence-based review): vitamin K, folic acid, blood levels, and breastfeeding: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee and Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and American Epilepsy Society. Neurology 2009;73:142-9. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a6b325.
- Pennell PB, Peng L, Newport DJ, Ritchie JC, Koganti A, Holley DK, et al. Lamotrigine in pregnancy: clearance, therapeutic drug monitoring, and seizure frequency. Neurology 2008;70:2130-6. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000289511.20864.2a.
- Tran TA, Leppik IE, Blesi K, Sathanandan ST, Remmel R. Lamotrigine clearance during pregnancy. Neurology 2002;59:251-5. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.59.2.251.
- Greenberg M. Practice parameter: management issues for women with epilepsy (summary statement). Neurology 1998;51:944-8. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.51.4.944.
- Holmes LB, Harvey EA, Coull BA, Huntington KB, Khoshbin S, Hayes AM, et al. The teratogenicity of anticonvulsant drugs. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1132-8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200104123441504.
- Rennie D. CONSORT revised – improving the reporting of randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285:2006-7. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.285.15.2006.
- von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, et al. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int J Surg 2014;12:1495-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.07.013.
- Rawson K, Greenhill L, Bagary M, McCorry D, Pirie AM. Audit of a Joint Epilepsy Obstetric Clinic n.d.:7-9.
- Andersen P, Gill R. Cox’s regression model for counting processes: a large sample study. Ann Stat 1982;10:1100-20. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176345976.
- DAMOCLES study group NHS Health Technology Assessment Programme . A proposed charter for clinical trial data monitoring committees: helping them to do their job well. Lancet 2005;365:711-22.
- Snowdon C, Garcia J, Elbourne D, Lavender T, Edwards G, Alfirevic Z. Demystifying Qualitative Research in Pregnancy and Childbirth. Salisbury: Quay Books; 2001.
- Harden CL, Hopp J, Ting TY, Pennell PB, French JA, Hauser WA, et al. Practice parameter update: management issues for women with epilepsy – focus on pregnancy (an evidence-based review): obstetrical complications and change in seizure frequency: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee and Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and American Epilepsy Society. Neurology 2009;73:126-32. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a6b2f8.
- Meador K, Reynolds MW, Crean S, Fahrbach K, Probst C. Pregnancy outcomes in women with epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published pregnancy registries and cohorts. Epilepsy Res 2008;81:1-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2008.04.022.
- Mawhinney E, Morrow J. Managing epilepsy in pregnancy. Expert Rev Obstet Gynecol 2011;6:667-80. https://doi.org/10.1586/eog.11.66.
- Tomson T, Hiilesmaa V. Epilepsy in pregnancy. BMJ 2007;335:769-73. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39266.473113.BE.
- Nunes VD, Sawyer L, Neilson J, Sarri G, Cross JH. Diagnosis and management of the epilepsies in adults and children: summary of updated NICE guidance. BMJ 2012;344. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e281.
- Weckesser A, Denny E. Women living with epilepsy, experiences of pregnancy and reproductive health: a review of the literature. Seizure 2013;22:91-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2012.11.001.
- Thompson D, Thomas H, Solomon J, Nashef L, Kendall S. Chronic illness, reproductive health and moral work: women’s experiences of epilepsy. Chronic Illn 2008;4:54-6. https://doi.org/10.1177/1742395307086696.
- Qiang JK, Nyhof-Young J, D’Souza R, Bui E. Support systems of women with epilepsy in pregnancy: a retrospective needs assessment. Seizure 2016;36:1-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2015.12.017.
- Riessman CK. Narrative Methods for the Human Sciences. London: Sage Publications, Inc.; 2008.
- Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care 2007;19:349-57. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzm042.
- Bryman A. Social Research Methods. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2008.
- Goffman E. Stigma: Notes on the Management of Spoiled Identity. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall; 1963.
- British Sociological Association . An Introduction to Equality &Amp; Diversity at the BSA 2010. www.britsoc.co.uk/equality (accessed June 2016).
- Riessman CK. Strategic uses of narrative in the presentation of self and illness: a research note. Soc Sci Med 1990;30:1195-200. https://doi.org/10.1016/0277-9536(90)90259-U.
- Reissman C. Narrative Methods for the Human Sciences. London: Sage Publications, Inc.; 2008.
- Corbin J, Strauss A. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory. Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, Inc.; 2008.
- Baker GA, Camfield C, Camfield P, Cramer JA, Elger CE, Johnson AL, et al. Commission on outcome measurement in epilepsy, 1994–1997: final report. Epilepsia 1998;39:213-31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01361.x.
- EURAP Group . Seizure control and treatment in pregnancy: observations from the EURAP epilepsy pregnancy registry. Neurology 2006;66:354-60. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000195888.51845.80.
- Pennell PB. Antiepileptic drug pharmacokinetics during pregnancy and lactation. Neurology 2003;61:35-42. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.61.6_suppl_2.S35.
- Pennell PB, Hovinga CA. Antiepileptic drug therapy in pregnancy I: gestation-induced effects on AED pharmacokinetics. Int Rev Neurobiol 2008;83:227-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7742(08)00013-5.
- Practice parameter: management issues for women with epilepsy (summary statement) . Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Epilepsia 1998;39:1226-31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01316.x.
- Pirie DA, Al Wattar BH, Pirie AM, Houston V, Siddiqua A, Doug M, et al. Effects of monitoring strategies on seizures in pregnant women on lamotrigine: a meta-analysis. Eur J Obst Gynecol Reprod Biol 2014;172:26-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.10.021.
- Bromley RL, Mawer G, Love J, Kelly J, Purdy L, McEwan L, et al. Early cognitive development in children born to women with epilepsy: a prospective report. Epilepsia 2010;51:2058-65. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02668.x.
- Meador KJ, Baker GA, Browning N, Cohen MJ, Clayton-Smith J, Kalayjian LA, et al. Foetal antiepileptic drug exposure and verbal versus non-verbal abilities at three years of age. Brain 2011;134:396-404. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq352.
- Hovinga CA, Asato MR, Manjunath R, Wheless JW, Phelps SJ, Sheth RD, et al. Association of non-adherence to antiepileptic drugs and seizures, quality of life, and productivity: survey of patients with epilepsy and physicians. Epilepsy Behav 2008;13:316-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2008.03.009.
- Dixon PA, Kirkham JJ, Marson AG, Pearson MG. National Audit of Seizure management in Hospitals (NASH): results of the national audit of adult epilepsy in the UK. BMJ Open 2015;5. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007325.
- Thangaratinam S, Rikunenko R, Greenhill L, Bagary M, Pirie A, Khan K, et al. Optimal monitoring of anti epileptic drugs in pregnancy: time for a randomised controlled trial?. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2011;96. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2011.300163.79.
- NIHR Journals Library . Antiepileptic Drug (AED) Management in Pregnancy: An Evaluation of Effectiveness, Cost Effectiveness and Acceptability of Dose Adjustment Strategies 2011. www.nets.nihr.ac.uk/projects/hta/095538 (accessed 6 June 2016).
- Al Wattar BH, Tamilselvan K, Khan R, Kelso A, Sinha A, Pirie AM, et al. Development of a core outcome set for epilepsy in pregnancy (E-CORE): a national multi-stakeholder modified Delphi consensus study. BJOG 2016;124:661-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.14430.
Appendix 1 Amendments to protocol
| What was proposed in original grant application | What was done in the EMPiRE study |
|---|---|
| 1. The original target sample size was 1000 women with epilepsy on AEDs | There were difficulties meeting this target. An extension was requested in order to meet the recruitment target, which was rejected and recruitment stopped at 557 |
| 2. Data were collected for a health economic evaluation | It was decided that the analysis of these data will be parked until further funding is available |
| 3. The BSID was being used to assess mental and motor development of the infant at the 6-week postnatal visit | It was agreed by the TSC that the BSID would not collect valuable data at such an early stage in a child’s development and was removed from the protocol |
| 4. Serum albumin levels were to be checked on visits 1, 3 and 5 | Serum albumin levels are not routinely checked, and committee members felt that the logistics and cost of the test outweighed the research benefits |
| 5. Cord blood was not initially being taken at delivery | Committee members felt strongly that it was important to obtain data on the levels of AED transferred from the mother to baby |
| 6. Suspected non-adherence to AED was not initially being documented | Further clarification of action to be taken regarding suspected non-adherence was necessary. Clinicians of group Ba non-adherent patients were to be unblinded |
| 7. Participants were sent the patient information sheet 7 days before their booking visit to allow time to consider consenting to the trial | Patients were sent the patient information sheet 24 hours before the booking visit in an attempt to increase recruitment |
| 8. There was no option for clinicians to request additional serum levels to be taken | This was added as an option for circumstances in which there is a clinical suspicion of toxicity or non-adherence |
| 9. The NDDI-E tool was not originally being used | The NDDI-E questionnaire was included as part of baseline data collection |
| 10. Serum AED samples for participants in group B were not frozen until the end of the trial | Freezing blood samples in group B was introduced to mirror existing clinical practice, as many units do not routinely check serum AED levels |
| 11. The QOLIE-31 tool was filled out at each monthly visit | The QOLIE-31 questionnaire was lengthy and only necessary to be conducted at baseline and then once between 32 and 36 weeks’ gestation |
| 12. Only clinicians were consenting women in to the trial | Specialist midwives and suitably qualified members of staff at a site were able to consent participants into the trial |
| 13. The original inclusion criteria stated that women who have a confirmed viable pregnancy of < 16 weeks’ gestation can be recruited | This was amended to include women who have a confirmed viable pregnancy of < 24 weeks’ gestation (23 weeks and 6 days) in order to increase recruitment |
| 14. Exclusion criteria included women who have a history of poor adherence | The exclusion criteria were amended to include women who clearly expressed an intention not to take AEDs in pregnancy or come to the clinic regularly. It allowed clinicians not to recruit someone who had a chaotic follow-up and planned to do that for the rest of the pregnancy |
| 15. Clarification was required for unblinding to serum AED levels | Clinicians and participants will automatically be unblinded if there is an undetectable serum AED level at any time for participants in groups Ab and Cc. Clinicians and participants will not be automatically unblinded to undetectable serum AED levels for participants randomised to group B |
| 16. Maternal bloods were to be collected at delivery, and the postnatal visit will be conducted at 6 weeks post delivery | It was clarified that maternal delivery bloods could be collected at any point between labour admission up to discharge. The postnatal visit could be conducted at any point between 6 and 8 weeks post delivery |
The trial protocol is available online. 51
Appendix 2 Maternal outcomes
| Outcome | Number of mothers | Mean lamotrigine exposure in mg (SD) | Measure | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No outcome | Outcome | ||||
| LAEP score | 178 | N/A | N/A | IRR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Gestational age at delivery | 257 | N/A | N/A | MD | 0.00 (–0.00 to 0.02) |
| CS or instrumental delivery | 255 | 273 (153) | 287 (156) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Pre-term labour | 249 | 281 (155) | 253 (149) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Induction of labour | 254 | 273 (151) | 301 (165) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 248 | 279 (154) | 293 (165) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | 248 | 276 (150) | 374 (234) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | 187 | 277 (154) | 351 (172) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 254 | 272 (152) | 312 (159) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | 249 | 277 (154) | 310 (160) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Feeding | 253 | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) | ||
| Breast | 264 (132) | ||||
| Mixed | 300 (177) | ||||
| Bottle | 309 (186) | ||||
| Adverse events | Number of mothers | MD in lamotrigine exposure (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| CS or instrumental delivery | 255 | 24.1 (–12.5 to 60.8) |
| Pre-term labour | 256 | –11.2 (–85.3 to 62.9) |
| Induction of labour | 254 | 22.2 (–20.0 to 64.4) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 255 | 14.8 (–89.4 to 119.0) |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | 255 | 50.0 (–46.0 to 146.0) |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | 254 | 100.9 (–3.8 to 205.6) |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 254 | 49.2 (–0.8 to 99.2) |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | 256 | 31.6 (–49.5 to 112.7) |
| Feeding | 253 | |
| Breast | Reference group | |
| Mixed | 33.3 (–25.7 to 92.3) | |
| Bottle | 38.8 (–4.6 to 82.1) |
| Outcome | Number of mothers | Mean levetiracetam exposure in mg (SD) | Measure | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No outcome | Outcome | ||||
| LAEP score | 88 | N/A | N/A | IRR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Gestational age at delivery | 126 | N/A | N/A | MD | 0.0 (0.0 to 0.0) |
| CS or instrumental delivery | 124 | 1740 (987) | 1548 (641) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Pre-term labour | 96 | 1634 (864) | 1888 (639) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Induction of labour | 125 | 1620 (868) | 1694 (834) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 51 | 1645 (859) | 1825 (459) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | 124 | 1627 (807) | 1471 (611) | OR | 1.0 (0.998 to 1.0) |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | 70 | 1639 (859) | 2033 (454) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 127 | 1684 (890) | 1396 (470) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | 125 | 1662 (858) | 1314 (715) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Feeding | 125 | OR | 1.000 (1.0 to 1.0) | ||
| Breast | 1599 (897) | ||||
| Mixed | 1928 (1022) | ||||
| Bottle | 1611 (592) | ||||
| Adverse events | Number of mothers | MD in levetiracetam exposure (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| CS or instrumental delivery | 126 | –226.4 (–536.3 to 83.5) |
| Pre-term labour | 127 | 23.6 (–644.4 to 691.5) |
| Induction of labour | 127 | 7.7 (–307.4 to 322.8) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 127 | 358.0 (–823.6 to 1539.5) |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | 126 | –109.5 (–815.6 to 596.6) |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | 127 | 507.2 (–459.5 to 1473.9) |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 127 | –365.5 (–817.5 to 86.6) |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | 127 | –431.7 (–1184.8 to 321.5) |
| Breastfeeding | ||
| 126 (128) | 125 | Reference group |
| 97 (98) | 246.5 (–153.4 to 646.5) | |
| 50 (51) | –28.5 (–382.0 to 325.0) |
| Outcome | Number of mothers | Mean carbamazepine exposure in mg (SD) | Measure | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No outcome | Outcome | ||||
| LAEP score | 60 | N/Aa | N/A | IRR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Gestational age at delivery | 86 | N/A | N/A | MD | –0.01 (–0.02 to 0.0) |
| CS or instrumental delivery | 86 | 632 (317) | 711 (290) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Pre-term labour | 82 | 647 (295) | 842 (315) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Induction of labour | 82 | 631 (274) | 747 (340) | OR | 1.0 (0.1 to 1.0) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 81 | 676 (305) | 604 (303) | OR | 1.0 (0.1 to 1.0) |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | 63 | 665 (305) | 831 (249) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | 63 | 671 (305) | 800 (283) | OR | 1.0 (0.98 to 1.06) |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 82 | 664 (297) | 764 (363) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | 63 | 676 (308) | 623 (167) | OR | 1.0 (0.99 to 1.01) |
| Feeding | 85 | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) | ||
| Breast | 689 (336) | ||||
| Mixed | 634 (275) | ||||
| Bottle | 665 (174) | ||||
| Adverse events | Number of mothers | MD in carbamazepine exposure (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| CS or instrumental delivery | 86 | 18.2 (–111.7 to 148.0) |
| Pre-term labour | 86 | 179.0 (4.3 to 353.8) |
| Induction of labour | 86 | 76.0 (–52.9 to 204.9) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 85 | –46.6 (–273.4 to 180.1) |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | 86 | 70.6 (–197.1 to 338.4) |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | 86 | 254.7 (–152.0 to 661.5) |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 86 | 85.8 (–111.4 to 283.0) |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | 86 | 16.4 (–316.4 to 349.2) |
| Feeding | 85 | |
| Breast | Reference group | |
| Mixed | –80.6 (–276.7 to 115.6) | |
| Bottle | –2.2 (–168.4 to 163.9) |
| Outcome | Number of mothers | Measure | Mean lamotrigine exposure in mg (SD) | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | Mean levetiracetam exposure in mg (SD) | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No outcome | Outcome | No outcome | Outcome | |||||
| LAEP score | 22 | IRR | N/A | N/A | 1.0 (1.000 to 1.001) | N/A | N/A | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Gestational age at delivery | 36 | MD | N/A | N/A | –0.01 (–0.050 to 0.030) | N/A | N/A | 0.0 (–0.01 to 0.00) |
| CS or instrumental delivery | 35 | OR | 376 (169) | 451 (177) | 1.0 (1.000 to 1.025) | 1867 (913) | 2060 (1028) | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Pre-term labour | 35 | OR | 421 (175) | 424 (190) | 1.0 (0.995 to 1.008) | 1880 (873) | 2508 (1364) | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Induction of labour | 35 | OR | 420 (205) | 423 (129) | 0.9991.0 (0.99 to 1.0 | 2053 (1137) | 1889 (720) | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 23 | OR | 401 (169) | 518 (34) | Perfect prediction | 2038 (961) | 1743 (1316) | Perfect prediction |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | – | OR | 410 (167) | 450 | Perfect prediction | 1941 (891) | 4462 | Perfect prediction |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | – | OR | 422 (178) | 400 | Perfect prediction | 2013 (976) | 1000 | Perfect prediction |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 24 | OR | 387 (161) | 566 (169) | 1.0 (0.99 to 1.0) | 1967 (963) | 2060 (1106) | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | – | OR | 423 (180) | 400 (0) | Perfect prediction | 2028 (986) | 1250 (354) | Perfect prediction |
| Feeding | 36 | OR | ||||||
| Breast | 446 (186) | 0.99 (0.99 to 1.0) | 2180 (969) | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) | ||||
| Mixed | 523 | 2000 | ||||||
| Bottle | 404 (174) | 1882 (1008) | ||||||
| Adverse events | Number of mothers | MD in lamotrigine exposure (95% CI) | MD in levetiracetam exposure (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS or instrumental delivery | 36 | 87.3 (–46.8 to 221.5) | 30.5 (–771.0 to 832.0) |
| Pre-term labour | 36 | 15.3 (–146.4 to 177.0) | 557.0 (–355.7 to 1469.7) |
| Induction of labour | 36 | –23.1 (–173.1 to 126.9) | 87.0 (–783.1 to 957.2) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 35 | 124.0 (–84.2 to 332.3) | –5.1 (–1337.0 to 1326.8) |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | 35 | –89.4 (–460.1 to 281.4) | 2205.7 (56.8 to 4354.7) |
| Antepartum haemorrhage | 36 | 79.1 (–340.6 to 498.8) | –919.0 (–3331.4 to 1493.4) |
| Postpartum haemorrhage | 36 | 142.8 (–11.6 to 297.2) | –253.6 (–1198.7 to 691.5) |
| Admission to HDU or ICU | 36 | 48.8 (–247.2 to 344.9) | –593.1 (–2296.9 to 1110.8) |
| Feeding | 36 | ||
| Breast | Reference group | Reference group | |
| Mixed | –29.7 (–428.8 to 369.3) | –332.227 (–2680.7 to 2016.2) | |
| Bottle | –74.0 (–209.9 to 61.9) | –250.6 (–1050.4 to 549.3) |
Appendix 3 Fetal outcomes
| Outcome | Number of mothers (number of babies) | Mean lamotrigine exposure in mg (SD) | Measure | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No outcome | Outcome | ||||
| Cord blood levels, lamotrigine (mg/l) | 186 (188) | N/A | N/A | MD | 0.01 (0.01 to 0.01) |
| Major congenital malformations | 247 (254) | 276 (156) | 302 (116) | ORa | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.01) |
| Baby’s admission to neonatal unit | 254 (247) | 279 (153) | 273 (162) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Apgar score at 1 minute | 247 (252) | N/A | N/A | MD | –1 × 10–4 (–0.001 to 0.001) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes | 249 (254) | N/A | N/A | MD | 3 × 10–4 (–0.001 to 0.001) |
| Birthweight (kg) | 254 (261) | N/A | N/A | MD | 4 × 10–4 (–2 × 10–4 to 0.001) |
| Birthweight < 10th centile | 254 (261) | 279 (152) | 268 (170) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Head circumference (cm) | 202 (206) | N/A | N/A | MD | –1 × 10–4 (–0.001 to 0.002) |
| Cord pH A | 103 (104) | N/A | N/A | MD | –2 × 10–4 (–3 × 10–4 to 7 × 10–4) |
| Cord pH V | 109 (110) | N/A | N/A | MDa | –2 × 10–4 (–3 × 10–4 to –3 × 10–5) |
| Adverse events | Number of mothers (number of babies) | MD in lamotrigine exposure (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Major congenital malformations | 247 (254) | 39.0 (–31.6 to 109.6) |
| Baby’s admission to neonatal unit | 254 (247) | 4.2 (–53.5 to 61.8) |
| Apgar score at 1 minute (< 7a) | 247 (252) | 9.0 (–73.5 to 91.5) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes (< 7a) | 249 (254) | 90.9 (–40.5 to 222.3) |
| Birthweight < 10th centile | 254 (261) | –33.4 (–94.5 to 27.7) |
| Cord pH A (< 7a) | 103 (104) | –144.9 (–356.6 to 66.8) |
| Cord pH V (< 7a) | 109 (110) | –77.2 (–388.1 to 233.7) |
| Outcome | Number of mothers (number of babies) | Mean levetiracetam exposure in mg (SD) | Measure | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No outcome | Outcome | ||||
| Cord blood levels, levetiracetam (mg/l) | 94 (95) | N/A | N/A | MDa | 0.01 (0.01 to 0.01) |
| Major congenital malformations | 126 (128) | 1646 (858) | 1859 (593) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.01) |
| Baby’s admission to neonatal unit | 124 (126) | 1626 (789) | 2063 (1415) | OR | 1.0 (1.0,1.0) |
| Apgar score at 1 minute | 123 (125) | N/A | N/A | MDa | –8 × 10–6 (–3 × 10–4 to 3 × 10–4) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes | 123(125) | N/A | N/A | MDa | –4 × 10–5 (–2 × 10–4 to 1 × 10–4) |
| Birthweight (kg) | 126 (128) | N/A | N/A | MD | 6 × 10–5 (–3 × 10–5 to 2 × 10–4) |
| Birthweight < 10th centile | 126 (128) | 1609 (804) | 1928 (1041) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Head circumference (cm) | 97 (98) | N/A | N/A | MDa | 3 × 10–4 (–7 × 10–5 to 0.001) |
| Cord pH A | 50 (51) | N/A | N/A | MDa | –0.005 (–0.01 to 0.00) |
| Cord pH V | 59 (61) | N/A | N/A | MD | –0.003 (–0.01 to 0.00) |
| Adverse events | Number of mothers (number of babies) | MD in levetiracetam exposure (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Major congenital malformations | 126 (128) | 149.3 (–572.1 to 870.6) |
| Baby’s admission to neonatal unit | 124 (126) | 362.2 (–206.5 to 930.9) |
| Apgar score at 1 minute (< 7a) | 123 (125) | –47.5 (–638.2 to 543.2) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes (< 7a) | 123 (125) | Perfect prediction |
| Birthweight centile < 10th centile | 126 (128) | 225.4 (–216.0 to 666.8) |
| Cord pH A (< 7a) | 50 (51) | Perfect prediction |
| Cord pH V (< 7a) | 59 (61) | Perfect prediction |
| Outcome | Number of mothers (number of babies) | Mean carbamazepine exposure in mg (SD) | Measure | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No outcome | Outcome | ||||
| Cord blood levels, carbamazepine (mg/l) | 62 (64) | N/A | N/A | MDa | 0.00 (0.00 to 0.00) |
| Major congenital malformations | 85 (88) | 670 (285) | 688 (398) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Baby’s admission to neonatal unit | 85 (88) | 677 (290) | 644 (358) | OR | 1.0 (0.99 to 1.0) |
| Apgar score at 1 minute | 84 (87) | N/A | N/A | MD | 0.00 (0.00 to 0.00) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes | 84 (87) | N/A | N/A | MDa | –9 × 10–5 (–0.001 to 0.001) |
| Birthweight (kg) | 85 (88) | N/A | N/A | MD | 0.00 (0.00 to 0.00) |
| Birthweight centile < 10th centile | 85 (88) | 640 (299) | 777 (281) | OR | 1.0 (1.0 to 1.0) |
| Head circumference (cm) | 63 (66) | N/A | N/A | MD | 0.00 (0.00 to 0.00) |
| Cord pH A | 35 (36) | N/A | N/A | MD | 1 × 10–5 (–1 × 10–4 to 1 × 10–4) |
| Cord pH V | 40 (40) | N/A | N/A | MDa | 1 × 10–5 (–1 × 10–4 to 1 × 10–4) |
| Adverse events | Number of mothers (number of babies) | MD in carbamazepine exposure (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Major congenital malformations | 85 (88) | –14.1 (–198.9 to 170.8) |
| Baby’s admission to neonatal unit | 85 (88) | –58.8 (–231.4 to 113.7) |
| Apgar score at 1 minute (< 7a) | 84 (87) | –110.7 (–308.7 to 87.4) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes (< 7a) | 84 (87) | 7.7 (–284.7 to 300.2) |
| Birthweight < 10th centile | 85 (88) | 132.1 (–5.7 to 269.9) |
| Cord pH A (< 7a) | 35 (36) | Perfect prediction |
| Cord pH V (< 7a) | 40 (40) | 32.8 (–624.2 to 689.9) |
| Outcome | Number of mothers (number of babies) | Measure | Mean lamotrigine exposure in mg (SD) | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | Mean levetiracetam exposure in mg (SD) | Effect of increasing exposure (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No outcome | Outcome | No outcome | Outcome | |||||
| Cord blood levels, lamotrigine (mg/l) | 27 | MD | N/A | N/A | 0.009 (0.004 to 0.013) | N/A | N/A | –2 × 10–4 (–0.001 to 0.001) |
| Cord blood levels, levetiracetam (mg/l) | 0.008 (–0.026 to 0.041) | 0.008 (0.002 to 0.013) | ||||||
| Major congenital malformations | 22 (24) | OR | 429 (179) | 391 (13) | Perfect prediction | 2011 (989) | 1750 (354) | Perfect prediction |
| Baby’s admission to neonatal unit | 36 (38) | OR | 421 (171) | 440 (188) | 1.005 (0.989 to 1.021) | 1841 (767) | 2297 (1244) | 1.002 (0.998 to 1.006) |
| Apgar score at 1 minute | 35 (37) | MDa | N/A | N/A | 3 × 10–4 (–0.004 to 0.005) | N/A | N/A | 0.000 (0.000 to 0.001) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes | 35 (37) | MDa | N/A | N/A | 0.001 (–0.002 to 0.003) | N/A | N/A | 0.000 (0.000 to 0.001) |
| Birthweight (kg) | 35 (37) | MD | N/A | N/A | –0.001 (–0.002 to 0.000) | N/A | N/A | 0.000 (0.000 to 0.000) |
| Birthweight < 10th centile | 15 (17) | OR | 420 (185) | 473 (115) | Perfect prediction | 1898 (947) | 2218 (685) | Perfect prediction |
| Head circumference (cm) | 27 (28) | MD | N/A | N/A | –0.001 (–0.005 to 0.002) | N/A | N/A | 0.001 (–2 × 10–4 to 0.001) |
| Cord pH A | 13 (14) | MDa | N/A | N/A | 2 × 10–4 (–3 × 10–4 to 0.001) | N/A | N/A | 6 × 10–5 (–1 × 10–4 to 2 × 10–4) |
| Cord pH V | 14 (16) | MD | N/A | N/A | 2 × 10–4 (5 × 10–5 to 3 × 10–4) | N/A | N/A | –3 × 10–5 (–9 × 10–5 to 2 × 10–5) |
| Adverse events | Number of mothers (number of babies) | MD in lamotrigine exposure (95% CI) | MD in levetiracetam exposure (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major congenital malformations | 22 (24) | –11.5 (–288.6 to 265.7) | –317.8 (–1920.0 to 1284.6) |
| Baby’s admission to neonatal unit | 36 (38) | 46.2 (–87.5 to 179.9) | 522.5 (–233.5 to 1278.4) |
| Apgar score at 1 minute (< 7a) | 35 (37) | –42.1 (–239.8 to 155.5) | 964.7 (–53.5 to 1982.9) |
| Apgar score at 5 minutes (< 7a) | 35 (37) | –128.2 (–551.8 to 295.4) | 951.9 (–1351.1 to 3254.9) |
| Birthweight < 10th centile | 15 (17) | 161.3 (–15.4 to 338.0) | 289.6 (–729.1 to 1308.2) |
| Cord pH A (< 7a) | 13 (14) | Perfect prediction | Perfect prediction |
| Cord pH V (< 7a) | 14 (16) | Perfect prediction | Perfect prediction |
Appendix 4 Qualitative interview guide
Appendix 5 Definition of the primary outcome
| Outcome | Definition |
|---|---|
| Time from randomisation to first TCS |
|
| Time from randomisation to any other seizure |
|
Appendix 6 List of core outcomes for studies on pregnant women with epilepsy (Delphi)
| Outcomes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Neurological | Fetal and neonatal | Obstetric |
|
|
|
Appendix 7 List of collaborators
The EMPiRE trial collaborative network:
-
Dr Shanika Samarasekera – Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham
-
Professor Rajat Gupta – Birmingham Children’s Hospital, Birmingham
-
Dr Naghme Adab – University Hospital of Coventry and Warwickshire
-
Professor Ismail Khaled – Keele University Medical School and University of North Staffordshire
-
Mr Lee Middleton – Birmingham University, Birmingham
-
Miss Manjo Doug – Birmingham Women’s NHS Foundation Trust, Birmingham
-
Professor Tracy Baker – Birmingham
-
Dr Salwa El-Taher – Arrowe Park Hospital, Wirral
-
Dr Catharina Schram – Royal Blackburn Hospital, Lancashire; Burnley General Hospital, Lancashire
-
Dr Virginia Beckett – Bradford Royal Infirmary, Bradford
-
Dr Jim Morrow – Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast
-
Mr Alexander Pirie – Birmingham Women’s Hospital, Birmingham
-
Dr Neil Shah – Birmingham City Hospital, Birmingham
-
Dr Fadi Alfhaily – Colchester Hospital, Colchester
-
Ms Sadia Malick – University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire, Coventry
-
Dr Mark Johnson – Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, London
-
Miss Sasha Rajendran – The Royal Derby Hospital, Derby
-
Dr Alastair Campbell – Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh
-
Dr John O’Dwyer – Frimley Park Hospital, London
-
Miss Maggie Armstrong – Glan Clwyd Hospital, Rhyl
-
Dr Charlotte Lawthorn – Royal Gwent Hospital, Newport
-
Dr Janet Brennand – Southern General Hospital, Glasgow
-
Dr Isaac Babarinsa – Gloucester Royal Hospital, Gloucestershire
-
Dr Avideah Nejad – Royal Hampshire County Hospital, Hampshire
-
Dr Gary Dennis – Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield
-
Dr Jacqueline Tay – Leeds General Infirmary, Leeds
-
Dr Manjiri Khare – University Hospitals of Leicester, Leicester
-
Dr Feroza Dawood – Liverpool Women’s Hospital, Liverpool
-
Dr Charlotte Lawthorn – Neville Hall Hospital, Abergavenny
-
Dr Tadala Saukila – University Hospital of Durham, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Mr Wesley McCullough – Northampton General Hospital, Northamptonshire
-
Dr Alpa Shah – Newham Hospital, London
-
Dr Fidelma O’Mahoney – University Hospital of North Staffordshire, Staffordshire
-
Miss Abha Govind – North Middlesex University Hospital, London
-
Dr Oier Aeka and Dr Lucy Mackillop – John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford
-
Dr Karen Brackley – Princess Anne Hospital, Southampton
-
Dr Mukta Bhattacharya – Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth
-
Dr Leye Thompson – Queen’s Hospital, Romford
-
Dr Sophia Stone – St Richard’s Hospital, Chichester
-
Dr Philippa Marsden – Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
-
Dr Rehan Khan – The Royal London Hospital, London
-
Miss Heather Brown – Royal Sussex County Hospital, Brighton
-
Mr Narayanaswamy Raman – Southend Hospital, Westcliff on Sea
-
Dr Hanah Cock – St George’s Hospital, London
-
Dr Robert Powell – Singleton Hospital, Swansea
-
Dr Teresa Kelly – St Mary’s Hospital, Manchester
-
Dr Aarti Ullal – Sunderland Royal Hospital, Sunderland
-
Mr Phil Tittensor – Stafford General Hospital, Stafford
-
Dr Adam Gornall – Royal Shrewsbury Hospital, Shrewsbury
-
Dr Aylur Rajasri – Royal Cornwall Hospital (Treliske), Truro
-
Professor Catherine Nelson-Piercy – St Thomas’ Hospital, London
-
Dr Khalid Hamandi – University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff
-
Dr Rita Arya – Warrington Hospital, Warrington
-
Dr Lakshmi Thirumalaikumar – Worcestershire Royal Hospital, Worcester
-
Dr Sophia Stone – Worthing Hospital, Western Sussex
-
Dr Sujatha Thamban – Whipps Cross Hospital, London.
Appendix 8 Recruitment at each site
| Site | Trial group, n | Total (N = 557), n | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Randomised | Non-randomised (N = 294) | |||
| TDM (N = 130) | CFM (N = 133) | |||
| Arrowe Park Hospital | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Royal Blackburn Hospital | 1 | 4 | 6 | 11 |
| Bradford General Hospital | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Royal Victoria Hospital | 2 | 5 | 5 | 12 |
| Birmingham Women’s Hospital | 12 | 10 | 27 | 49 |
| Burnley General Hospital | 0 | 3 | 5 | 8 |
| Birmingham City Hospital | 5 | 0 | 3 | 8 |
| Colchester General Hospital | 3 | 2 | 6 | 11 |
| University Hospital Coventry | 3 | 0 | 4 | 7 |
| Chelsea & Westminster Hospital | 3 | 3 | 4 | 10 |
| Royal Derby Hospital | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 |
| Royal Edinburgh Infirmary | 1 | 3 | 1 | 5 |
| Frimley Park Hospital | 3 | 0 | 5 | 8 |
| Glan Clwyd Hospital | 5 | 5 | 7 | 17 |
| Royal Gwent Hospital | 2 | 1 | 5 | 8 |
| Southern General Hospital | 2 | 5 | 6 | 13 |
| Gloucester Royal Hospital | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Royal Hampshire County Hospital | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 |
| Jessop Hospital | 5 | 3 | 14 | 22 |
| Leeds General Infirmary | 3 | 2 | 6 | 11 |
| Leicester Royal Infirmary | 1 | 1 | 7 | 9 |
| Liverpool Women’s Hospital | 3 | 4 | 15 | 22 |
| Nevill Hall Hospital | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| University Hospital of North Durham | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 |
| Northampton General Hospital | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Newham University Hospital | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| North Staffordshire Hospital | 4 | 1 | 6 | 11 |
| North Middlesex University Hospital | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| John Radcliffe Hospital | 2 | 3 | 6 | 11 |
| Southampton General Hospital | 3 | 1 | 7 | 11 |
| Queen Alexandra Hospital | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| Queen’s Hospital | 7 | 7 | 13 | 27 |
| St Richard’s Hospital | 3 | 6 | 9 | 18 |
| Royal Victoria Infirmary | 7 | 5 | 10 | 22 |
| Royal London Hospital | 2 | 1 | 5 | 8 |
| Royal Sussex County Hospital | 1 | 0 | 5 | 6 |
| Southend University Hospital | 2 | 6 | 2 | 10 |
| St George’s Hospital | 4 | 3 | 10 | 17 |
| Singleton Hospital | 5 | 4 | 7 | 16 |
| Salford Royal | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 |
| Sunderland Royal Hospital | 6 | 3 | 2 | 11 |
| Stafford Hospital | 7 | 6 | 4 | 17 |
| Royal Shrewsbury Hospital | 3 | 1 | 5 | 9 |
| Royal Cornwall Hospital | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| St Thomas’ Hospital | 1 | 7 | 19 | 27 |
| University Hospital of Wales | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| Warrington Hospital | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| Worcestershire Royal Hospital | 4 | 3 | 6 | 13 |
| Worthing Hospital | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| Whipps Cross University Hospital | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
Appendix 9 Case report form
Baseline booklet
Neurological Disorders Depression Inventory for Epilepsy
Patient questionnaire
Please note that the analogous scale was not used.
Quality Of Life In Epilepsy – 31-item questionnaire
Antenatal follow-up booklet
Delivery booklet
Postnatal follow-up booklet
Purple alert form
Adverse events form
Appendix 10 Seizure diary
List of abbreviations
- AED
- antiepileptic drug
- CI
- confidence interval
- DMC
- Data Monitoring Committee
- EMPiRE
- AntiEpileptic drug Monitoring in PREgnancy
- EQ-5D
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions
- HR
- hazard ratio
- IQR
- interquartile range
- LAEP
- Liverpool Adverse Events Profile
- MD
- mean difference
- NDDI-E
- Neurological Disorders Depression Inventory for Epilepsy
- QoL
- quality of life
- QOLIE-31
- Quality Of Life In Epilepsy – 31-item questionnaire
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- SD
- standard deviation
- TSC
- Trial Steering Committee