Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 11/01/30. The contractual start date was in August 2012. The draft report began editorial review in July 2017 and was accepted for publication in February 2018. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Peter JD Andrews reports grants from the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine during the conduct of the study and personal fees from BARD Medical (Covington, GA, USA) and INTEGRA Neurosciences Ltd (Andover, UK) outside the submitted work. H Louise Sinclair, Bridget Harris, Gordon Murray and Aryelly Rodríguez report grants from the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine during the conduct of the study.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2018. This work was produced by Andrews et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2018 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Literature review: from bench to bedside
Background and objectives
This chapter provides a summary of the evidence that has supported the design of the Eurotherm3235 Trial. 1 This trial was a large, multinational, prospective, randomised controlled trial (RCT) of patients with raised intracranial pressure (ICP) after traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Traumatic brain injury is a major cause of death and severe disability throughout the world and leads to around 1 million hospital admissions per annum throughout the European Union (EU). It causes the majority of the 50,000 deaths from road traffic accidents each year and leaves 10,000 patients severely disabled; three-quarters of these victims are young people. 2 Additionally, TBI results in 290,000 hospital admissions and 51,000 deaths and leaves 80,000 patients with permanent neurological disabilities in the USA annually. 3 The consequence of TBI is both a devastating emotional and physical impact and an enormous financial burden. 4
Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) has been shown to improve outcome after cardiac arrest;4 therefore, both the European Resuscitation Council5 and the American Heart Association guidelines6 recommend the use of hypothermia in these patients. Hypothermia is also thought to improve neurological outcome after neonatal birth asphyxia. 7 Cardiac arrest and neonatal asphyxia patient populations present to health-care services rapidly and without posing a diagnostic dilemma; therefore, systemic TH may be implemented relatively quickly. As a result of this, the use of hypothermia in these two populations is similar to the laboratory models in which systemic TH is commenced very soon after the injury and has shown so much promise. 8
The need for resuscitation and computed tomography (CT) imaging to confirm the diagnosis in patients with TBI are factors that delay intervention with temperature reduction strategies. Treatments in TBI have traditionally focused on restoring and maintaining adequate brain perfusion, surgically evacuating large haematomas when necessary, and preventing or promptly treating oedema. 4 Brain swelling can be monitored by measuring ICP, and in most centres ICP is used to guide treatments and to monitor their success. There is an absence of evidence for the five most commonly used treatments for raised ICP (hypertonics, sedation, muscle relaxants, barbiturates and decompressive craniectomy) and all are potential ‘double-edged swords’ with significant disadvantages. The use of hypothermia in patients with TBI may have beneficial effects in terms of both ICP reduction and possible neuroprotection.
Pathophysiology
Ischaemia has a key role in all forms of brain injury, and preventing ischaemic (or secondary) injury is at the core of all neuroprotective strategies. 4 A complex cascade of processes ensues at the cellular level after a period of ischaemia, beginning from minutes to hours after injury and continuing for 72 hours or longer. Thus, there may be a window of opportunity of several hours, or even days, during which injury can be mitigated by treatments such as hypothermia. 4
Early studies that used profound hypothermia in models of brain trauma used treatment paradigms that were not feasible in clinical practice. 9 More recent studies have shown that moderate/mild hypothermia appears to be neuroprotective in well-characterised rodent models of TBI. The effects of systemic hypothermia (30–36 °C) following fluid percussion brain injury in rats were first investigated by Clifton et al.,10 who showed that hypothermia of 33 °C resulted in reduced mortality rates and attenuated deficits in motor function and weight loss compared with normothermia. Dietrich et al. 8 showed that post-traumatic hypothermia (30 °C) initiated 5 minutes after fluid percussion brain injury reduced overall contusion volume and preserved survival of the overlying cortical neurons. Therefore, these studies demonstrated that cooling after a TBI provided histological/cellular protection, improved motor and cognitive function and reduced mortality. Moderate hypothermia (30 °C), initiated 5 minutes after TBI, improved hippocampal-dependent learning and memory using the Morris water maze. 11 An important predictor of outcome in TBI patients, traumatic axonal pathology, is reduced with moderate post-injury hypothermia therapy. 12 Therefore, post-traumatic hypothermia modulates the major pathologies in TBI such as contusions, neuronal vulnerability and traumatic axonal injury. Mild hypothermia is therefore potentially attractive as a treatment for TBI as it modulates multiple mechanisms or pathways and has advantages over unipolar pharmacological attempts to provide neurological protection.
Blood–brain barrier
Alterations in blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability after acute injury result in water, electrolytes, blood-borne substances and potential neurotoxic agents passing across the vascular system and into the brain parenchyma. Many studies have demonstrated the importance of brain and body temperature on the microvascular consequences of cerebral ischaemia and trauma. One study that assessed the effects of intra-ischaemic brain temperature (mild hypothermia) on the BBB found a reduction in extravasation of the protein tracer horseradish peroxidase. 13 Brain water content is significantly reduced with hypothermia after focal cerebral ischaemia. 14,15 This has been assessed in imaging studies, with magnetic resonance imaging finding that reductions in the apparent diffusion coefficient of water (cellular oedema) are also reduced by hypothermia. 16
In models of post-traumatic injury, hypothermia has also been shown to reduce BBB permeability. Hypothermia may be attenuating BBB permeability by altering matrix metalloproteinases, which are critical extracellular enzymes that can disrupt the BBB. 17 Given that BBB permeability, formation of vasogenic oedema and the extravasation of circulating inflammatory cells can adversely affect post-injury outcome, the effects of hypothermia are an important underlying mechanism for the beneficial effects of hypothermia.
Inflammation and oedema
The inflammatory response after TBI is significantly attenuated by hypothermia in laboratory and clinical studies. As well as attenuating the increase in BBB permeability and leucocyte margination, the endogenous inflammatory response of the central nervous system (CNS) is also reduced by hypothermia. Astrocytes and microglia respond to CNS injury by proliferating around the injury areas and releasing pro-inflammatory communication molecules as an endogenous repair mechanism. Hypothermia significantly attenuates the activation of both astrocytes and microglia. 18–21 Combination therapy with the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin 10 (IL-10) and hypothermia therapy was attempted in both TBI and focal cerebral ischaemia. 22 Synergistic effects were seen in focal cerebral ischaemia but not in TBI, suggesting that the cellular biology of inflammation in these two major CNS injuries has an influence on the effect of subsequent hypothermia.
Another major aspect of the inflammatory response to CNS injury is the release of reactive oxygen species by astrocytes and microglia. Hypothermia reduces increases in tissue levels of superoxide, nitric oxide and the hydroxyl radical. 23,24 The level of the superoxide dismutase, the enzyme responsible for scavenging superoxide, is increased by hypothermia,25,26 and the level of the enzyme responsible for synthesising nitric oxide, nitric oxide synthase, is attenuated by hypothermia. 27
Metabolism
By exploiting local measures of glucose metabolism using 2-deoxyglucose techniques, researchers have shown that moderate hypothermia (30 °C) results in reduced glucose utilisation compared with normothermia. 28 Metabolic effects of mild hypothermia have also been demonstrated using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. 29 Therefore, hypothermia appears to lower metabolic and energy demands, which has potentially beneficial effects on cytoplasmic adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the maintenance of normal transmembrane ion and neurotransmitter gradients. The magnitude of preservation of ATP levels depends on both the temperature reduction and the severity of the injury. Therefore, an important mechanism for the neuroprotective effects of hypothermia is a reduction or delay in metabolic demand during and after an acute CNS injury.
Excitotoxicity
The effects of moderate hypothermia on glutamate excitotoxicity were reported using microdialysis to assay extracellular/extravascular concentrations of neurotransmitters after global ischaemia. A middle cerebral artery occlusion model is considered a reasonable model for haemorrhagic contusion. Busto et al. 30 showed that intra-ischaemic hypothermia (33 °C and 30 °C) attenuated the rise in extracellular levels of glutamate and dopamine after global cerebral ischaemia. These studies have been replicated in a variety of models of ischaemia, indicating that one of the major mechanisms by which temperature affects neuronal vulnerability is through reducing excitotoxicity following cerebral ischaemia. 23,31,32 Delayed pharmacological treatments that reduce excitotoxicity further improve outcome in combination with hypothermia;33 this may be a promising strategy for further studies. The glutamatergic receptors alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) are also modulated by hypothermia. Expression of hippocampal glutamate receptors is decreased after transient global ischaemia and this is completely blocked by intra-ischaemic hypothermia. 34
Other neurotransmitters are also modulated by hypothermia. Lyeth et al. 35 demonstrated that hypothermia (30 °C) reduced elevations in cerebrospinal levels of acetylcholine after TBI. Conversely, hypothermia delayed decreases in dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin after global cerebral ischaemia. 36 However, other studies have demonstrated that hypothermia (32 °C) can improve outcome after CNS injury without attenuating extracellular levels of glutamate and aspartate. 12,29,37 Although the neurotransmitter response in various injury models may be temperature dependent, attenuating other injury cascades may be more important in delivering possible beneficial effects of hypothermia.
Cerebrovascular effects
The effects of hypothermia on cerebral blood flow are controversial. In 1954, Rosomoff and Holaday38 demonstrated that systemic hypothermia at 25 °C significantly lowered cerebral blood flow. However, in a model of selective brain cooling (30.9 °C), cortical blood flow measured by laser Doppler flowmetry was shown to increase above control levels. 39 Cerebrovascular changes secondary to cooling of the brain are important because reductions in blood flow to critical levels could have adverse effects on tissue survival and functional outcome.
Intracellular calcium-dependent signalling
There are pronounced changes in calcium-dependent intracellular signalling pathways after CNS injury. Normal neuronal activity is mediated by signalling through protein kinases and several of these have been documented to be disrupted by TBI and cerebral ischaemia. Temporary cerebral ischaemia inhibits the activity of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), a key protein kinase that mediates synaptic strength, and this is attenuated by hypothermia. 40 Protein kinase C (PKC) translocates to the membrane after cerebral ischaemia and undergoes inhibition; hypothermia rescues the inhibition of PKC activity and its translocation to the membrane. 41 Recently, various transcription factors that participate in normal neuronal functioning have been shown to be sensitive to temperature. The immediate early gene c-Fos, which regulates key genetic responses of neurons, is activated by hypothermia after transient global ischaemia. 18,42,43
These studies suggest that temperature may have profound effects on events associated with neuronal injury as well as the normal processing of neuronal signals throughout brain circuits.
Neuronal cell death
Although neuronal necrosis is commonly seen in most CNS injury models, evidence for apoptotic cell death has also been documented using various histochemical and molecular techniques. As with necrosis, apoptotic cell death appears to be sensitive to post-injury hypothermic treatment strategies. Recent studies have indicated that apoptotic cell death is another important target by which temperature may affect long-term outcome in various models of CNS injury. Various gene families [genes with a similar sequence of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) nucleotides] have been shown to be sensitive to post-injury temperature manipulations in models of ischaemia and trauma. 44 The ability of post-injury temperature to affect the acute and more delayed genetic response to injury is important because these genes may play an important role in determining the cellular response(s) that results in secondary injury. Using high-throughput screening and bioinformatics, genomic studies are ongoing in many laboratories; these contemporary technologies will help to determine how hypothermia may protect, and potentially repair, CNS tissues after injury.
The Collaborative Approach to Meta-Analysis and Review of Animal Data from Experimental Studies
The Collaborative Approach to Meta-Analysis and Review of Animal Data from Experimental Studies (CAMARADES) group has a mission statement:
It is our contention that there is significant scope for improvements in the design, conduct, analysis and reporting of animal experiments. By minimising bias, such improvements would improve the amount of valid information gained from those animals used. By providing (using systematic review and meta-analysis) a precise and robust overview of existing data the need for further experiments, and the precise areas in which those experiments should focus, this approach would ensure that unnecessary replication did not occur. The proposed research is therefore crucial to the development of ‘reduction’ strategies.
Reproduced with permission from CAMARADES45
To date, this approach has not been rigorously applied to TBI models. Such an approach would enhance translational research and, hopefully, reduce futile clinical studies.
Therefore, with the proviso above, numerous animal experiments across different species have shown that induced hypothermia improves recovery outcome after experimental TBI. This has led to the undertaking of a large number of clinical trials. 4 Interpretation of these results is complicated by the fact that these trials have enrolled different categories of patients, with different types of injuries, and have used widely diverging treatment protocols. 46 Most have used elevated ICP as an inclusion criterion, although some have used CT scan criteria. The duration of cooling has varied from 24 hours to > 5 days and rewarming rates have also varied. Some studies have used ICP to guide the depth and duration of treatment, although responses to rebound intracranial hypertension have differed. 4 Use of co-interventions such as osmotic therapy, sedation, analgesia, paralysis and targets for mean arterial pressure (MAP) and cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) have also varied considerably. 4 All of these factors can affect outcome after TBI in general and the potential efficacy of cooling in particular. Thus, interpreting, comparing and aggregating the results of these studies presents a number of complex challenges.
Review of clinical evidence
In total, 29 clinical studies have been performed to assess the effects of hypothermia in TBI. 47–76 Twenty-seven of these were performed in adult patients, 18 of which included a control group. Data from one pilot study were subsequently included in a larger study, therefore leaving 17 studies. As outlined above, study protocols have differed considerably and not all studies were properly randomised.
Eighteen studies, with outcome data available for 2096 patients, used hypothermia in patients with high ICP that was refractory to ‘conventional’ treatments (usually sedation/analgesia, paralysis, osmotic therapy and sometimes barbiturates). 58–61,63–71,73–77 All studies observed decreases in ICP during cooling. Thirteen of these studies reported significant improvements in outcome associated with hypothermia. 58–61,63,65,67–71,74,77 All of these studies were performed in specialised neurotrauma centres with experience in applying hypothermia and managing its side effects. Ten were single-centre studies58–60,65,67,68,70,71,74,77 and three (all performed in China) were multicentre studies. 61,63,69 Four additional studies observed a trend towards improved outcome, but these differences were not statistically significant. 61,64,66,73
In contrast, one of the two largest multicentre RCTs failed to show that induced hypothermia improved outcome at 6 months after TBI [poor outcome RR (risk ratio) 1, 95% CI (confidence interval) 0.8 to 1.2; p = 0.99]. 76 The proportion of patients experiencing a poor outcome was significantly higher among those admitted to hospital with hypothermia who were randomised to normothermia and consequently rewarmed (78%, n = 31) than among the group admitted with hypothermia and treated with hypothermia (61%, n = 38) (p = 0.09).
On subsequent analysis, it became clear that, although this study was methodologically well designed, there was marked intercentre variance in the treatment effect of hypothermia, age of participants, severity of illness scoring between groups, management of intracranial hypertension and haemodynamic and fluid management. 10 Induced hypothermia in the hypothermia group was started relatively late, with a slow speed of cooling (average time to target temperature > 8 hours) in all centres.
Hypotension (lasting > 2 hours) and hypovolaemia occurred three times more frequently in the hypothermia group than in the normothermia group. Bradycardia associated with hypotension also occurred four times more frequently in this group and electrolyte disorders and hyperglycaemia were also found more frequently in the hypothermia group76 than in the normothermia group. All of these complications are known side effects of hypothermia. Most are easily preventable with good intensive care and should not be regarded as inevitable consequences of hypothermia treatment. As even very brief episodes of hypotension or hypovolaemia can adversely affect outcome in TBI, these and other issues may have significantly affected the results of this trial. 10,78–80 One possible problem was that some of the participating centres had little or no previous experience in using hypothermia; large centres, familiar with cooling, showed apparently favourable neurological outcomes whereas smaller centres showed poor outcomes.
Induction of hypothermia
The most widely accepted use of hypothermia is after cardiac arrest. Two RCTs in this patient group found significant neurological improvements in patients whose initial cardiac rhythm was ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia and who were treated with hypothermia many hours after injury. 81,82 Subsequent data from a large study of patients treated after myocardial infarction suggest that infarct size was reduced in patients who were cooled to < 35 °C before coronary intervention;83 therefore, these studies suggest that faster cooling rates may be beneficial to patient outcome.
Methods of cooling can be broadly divided into two different techniques: surface cooling and core cooling. 84 The above study used surface cooling devices alone and found that a large number of patients did not reach the target temperature quickly enough before the start of the coronary intervention to demonstrate a benefit. 83 Despite advancing technology in surface cooling devices, and the introduction of endovascular catheters for core cooling, average periods of 2–3 hours are still required to reach temperatures of 32–34 °C. 84 The currently available surface cooling devices are also relatively large and cumbersome. This, coupled with the need for staff with specialist knowledge of the management of induced hypothermia, may prevent its use outside the intensive care unit (ICU). 84
One study has examined the feasibility, speed and complication rates of infusing refrigerated fluids intravenously to quickly induce hypothermia in patients with various neurological injuries. 84 The results showed that a 1500-ml infusion of 0.9% saline in patients without cardiogenic shock, administered over 30 minutes, reduced core temperature from 36.9 ± 1.9 °C to 34.6 ± 1.5 °C at 30 minutes and to 32.9 ± 0.9 °C at 60 minutes. Continuous monitoring of arterial blood pressure, heart rhythm, central venous pressure, arterial blood gasses and serum levels of electrolytes, platelets and white blood cells showed no significant adverse events (AEs). 84
When hypothermia develops, the body will immediately try to counteract the temperature drop to maintain homeostasis. 85 One of the key mechanisms of heat production is shivering; this can lead to an increased oxygen consumption of 40–100%, which may be detrimental in this patient population. Sedation drugs are known to increase peripheral blood flow, which, in turn, will increase the transfer of heat from the core to the peripheries, thus reducing the core temperature. 85 Therefore, shivering may be counteracted by the administration of sedatives, anaesthetic agents, opiates and/or paralysing agents. 85
It should be noted, however, that the capacity and effectiveness of the mechanisms of controlling body temperature decrease with age. Younger patients will therefore react earlier, and with greater intensity, than older patients. For this reason, induction of hypothermia in younger patients often requires high doses of sedation drugs to neutralise the counter-regulatory mechanisms. 85
Together with TH therapy, all patients in the intervention group continued to be treated with stage 1 and 2 therapies as required to reduce intracranial hypertension. 86,87 If raised ICP became resistant to these therapies, even when the depth of hypothermia was increased, then care was escalated to include stage 3 interventions. If this was required, TH treatment could be terminated for patients allocated to the treatment group and the patients rewarmed using the rewarming guideline. The reason for treatment escalation was then documented on the daily data collection form.
Meta-analyses
Six meta-analyses were published between 2002 and 2008. 86–91 These included various numbers of trials with varying quality of randomisation and blinding procedures. All found a trend towards positive effects of hypothermia on neurological outcome, although statistical significance was reached in only two reviews (improved neurological outcome: RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.63 to 0.98;86 RR 0.68, 95% CI 0.52 to 0.8987).
The most recent meta-analysis91 included eight trials that studied comparable patient groups at baseline. Hypothermia was shown to reduce mortality by 20%, although this finding was not statistically significant (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.59 to 1.09). Subgroup analysis showed that this effect was most significant when hypothermia was maintained for > 48 hours (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.33 to 0.79). Hypothermia was also associated with a non-significant increase of 25% in neurological outcome when measured by the Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) at 6 months (RR 1.25, 95% CI 0.96 to 1.62). Despite not reaching statistical significance, the results showed an increased likelihood of improved neurological outcome when cooling was maintained for > 48 hours (RR 1.91, 95% CI 1.28 to 2.85). Another key finding of this meta-analysis was that hypothermia was only of significant benefit to those patients who had not received barbiturate therapy (RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.85).
A criticism of these analyses is that most failed to take account of important differences in patient groups, such as the presence or absence of intracranial hypertension, and differences in treatment protocols, with the exception of the use of hypothermia. Only one differentiated between studies that enrolled patients with normal ICP and those that enrolled patients with intracranial hypertension; this study found no neurological improvement associated with hypothermia. 90 Only two assessed the effects of treatment duration and speed of rewarming,86,87 concluding that cooling for > 48 hours and rewarming rates of 24 hours, or 1 °C per 4 hours, were both key factors in reducing mortality (RR 0.70, 95% CI 0.56 to 0.87) and improving neurological outcome (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.63 to 0.98).
In summary, the evidence from previous research shows that induced hypothermia may be effective in patients with severe TBI and intracranial hypertension, provided that the treatment is continued for long enough (between 48 hours and 5 days) and that patients are rewarmed slowly (1 °C per 4 hours). Experience with cooling also appears to be important if complications, which may outweigh the benefits of hypothermia, are to be avoided.
Rationale for the Eurotherm3235 Trial
One of the most harmful consequences of TBI is cell injury and cell death in the brain. When this occurs, it starts a complex sequence of harmful, and potentially irreversible, processes at the cellular level. These processes can cause swelling (oedema) in the brain. This swelling increases the pressure inside the head and makes the injury worse. Preventing cell injury and cell death is therefore an important part of treatment. Cell death can occur from minutes to hours after injury and the harmful effects can last for 72 hours or longer. Thus, there may be a window of opportunity of several hours, or even days, during which cell death can be prevented by treatments such as hypothermia. Hypothermia treatment lowers the patient’s temperature to below normal, which has a potentially beneficial effect on a number of problems caused by injury to brain cells.
The evidence from previous research shows that hypothermia treatment may be an effective therapy to improve outcome in patients who have suffered a TBI. Many trials have been carried out in this patient group, but none has been large enough to prove whether or not hypothermia is effective in preventing further brain damage and reducing death and disability. The Eurotherm3235 Trial aimed to provide a clear answer to this question.
Chapter 2 Trial design
Specific trial objectives and hypotheses
The Eurotherm3235 Trial tested the efficacy of hypothermia to reduce ICP after TBI and the effect of hypothermia treatment on functional recovery at 6 months after injury compared with standard care alone.
Hypothesis
Patients treated with TH (32–35 °C) will have reduced morbidity and mortality rates compared with those receiving standard care alone after TBI.
Research questions
-
Does TH (32–35 °C) reduce morbidity and mortality rates at 6 months after TBI as assessed by the Glasgow Outcome Scale – Extended (GOSE) questionnaire?
-
Does TH (32–35 °C) reduce intracranial hypertension?
-
Is TH a cost-effective treatment to improve outcome after TBI?
Methods
Trial design
This was a pragmatic, multicentre RCT to examine the effects of hypothermia (32–35 °C) on outcome after TBI. Participants were randomised to receive either standard care alone or standard care with the addition of TH (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
Study flow chart. EEG, electroencephalogram.

The experience from previous hypothermia trials underscores the potential difficulties in using TH treatment for TBI. 10 For this reason, and to reduce intercentre variance, only centres experienced in the care of TBI patients and the use of hypothermia in this patient group were initiated.
At the time of designing the trial protocol in 2008, previous studies had found that TH lasting for at least 48 hours showed a trend towards reduced mortality and improved neurological function after TBI. 91 Hypothermia (32–35 °C) was therefore continued for at least 48 hours in the trial and for as long as was necessary to reduce and maintain ICP at < 20 mmHg. This ICP threshold was used because the Brain Trauma Foundation guidelines86 define intracranial hypertension as an ICP of > 20 mmHg. When ICP was stable, patients were then slowly rewarmed at a rate of 0.25 °C per hour (1 °C per 4 hours).
There are three recognised stages of TBI management (Figure 2). 86,92
FIGURE 2.
Three stages of ICP management after TBI. CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; EEG, electroencephalogram; GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale.
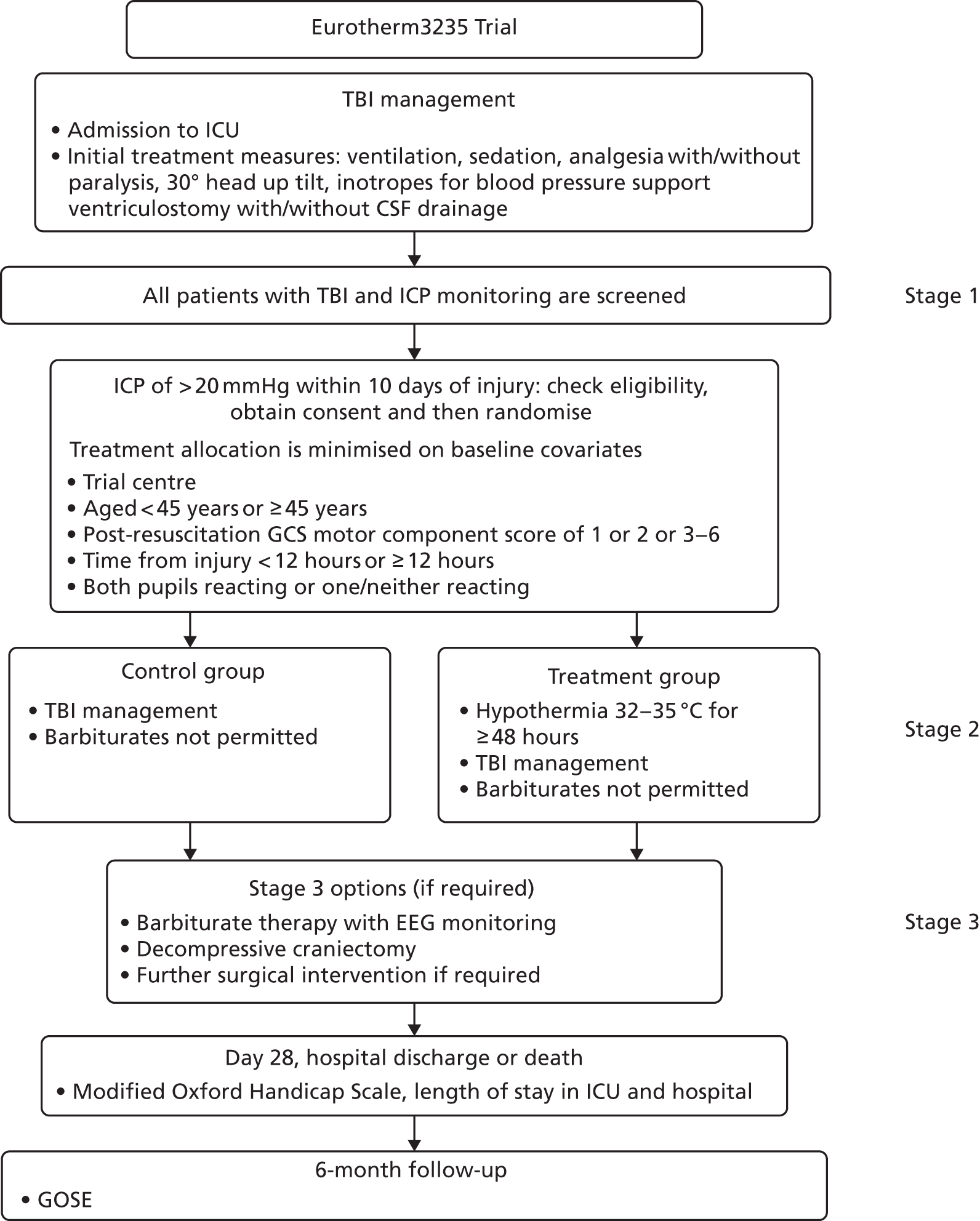
Participants in the hypothermia group continued to be treated with stage 1 and 2 therapies as required to reduce intracranial hypertension. 86,87 If raised ICP was resistant to these therapies, despite increasing the depth of hypothermia, care could be escalated to include stage 3 interventions.
During the preparation of the protocol, evidence suggested that patients were three times more likely to develop complications if hypothermia treatment was continued in conjunction with stage 3 interventions, that is, surgery or continuous infusion of barbiturates (the drugs used to treat ICP). Thus, we advised that the cooling intervention was withdrawn and the patient was rewarmed using the rewarming guideline as soon as it was safe to do so when the patient’s care was escalated. The reason for treatment escalation was then documented on the daily data collection form.
The primary end point of the Eurotherm3235 Trial was the outcome 6 months after TBI using the GOSE questionnaire. Participants were sent the GOSE questionnaire with a covering letter by post 6 months after randomisation by the co-ordinating centre.
Important changes to methods after trial commencement
The inclusion criteria were changed in January 2012, based on the pilot phase findings,93 to remove the upper age limit (previously 65 years) and increase the time from injury from 72 hours to 10 days. These changes provided important information on older patients and allowed patients with evolving brain swelling up to 10 days from injury to be included.
Participants
A total of 387 patients were recruited between January 2009 and October 2014.
The inclusion/exclusion criteria for the trial are given in the following sections.
Inclusion criteria
-
Believed to be legal age to consent to take part in research.
-
Primary closed TBI.
-
Raised ICP of > 20 mmHg for ≥ 5 minutes after first-line treatments with no obvious reversible cause (e.g. patient position, coughing, inadequate sedation).
-
≤ 10 days from the initial head injury.
-
Cooling device or technique available for > 48 hours.
-
Core temperature of ≥ 36 °C (at the time of randomisation).
-
An abnormal CT scan of the brain, defined as one that shows haematoma, contusion, swelling, herniation or compressed basal cisterns.
Exclusion criteria
-
Patient already receiving TH treatment.
-
Administration of barbiturate infusion prior to randomisation.
-
Unlikely to survive for the next 24 hours in the opinion of the ICU consultant or consultant neurosurgeon treating the patient.
-
Temperature of ≤ 34 °C at hospital admission.
-
Pregnancy.
All female patients of childbearing age who met the inclusion criteria underwent a urine pregnancy test. This was performed by the investigator or research nurse in the ICU as part of the screening for eligibility procedure.
The Eurotherm3235 Trial enrolled patients after TBI who had an ICP of > 20 mmHg for ≥ 5 minutes, despite first-line treatments, with no obvious reversible cause, for example patient position, coughing or inadequate sedation. Although early cooling after injury is considered to be beneficial, this is offset by failure to show benefit from hypothermia in the absence of raised ICP. Enrolment to the Eurotherm3235 Trial was therefore allowed up to 10 days following injury.
The trial recruited incapacitated adult patients who were admitted to the neurological ICU. It was not possible to obtain consent from the patients before enrolment to the study as they were sedated and attached to a ventilator. Information booklets were therefore made available in the waiting area of the ICU and the patient’s legal surrogate decision-maker, their next of kin/nearest relative/welfare guardian (in accordance with the laws of each country) was informed about the study by the ICU team soon after their relative was admitted. If they wanted further information about the trial or wished for their relative to participate, then the relative/welfare guardian contacted the researcher.
During this discussion, all stages of the trial were explained and the researcher explained that the patient may not have been eligible at that time, as they must have developed brain swelling before entering the study. Brain swelling can cause further brain damage if not treated quickly, so it was desirable that consent was obtained before any brain swelling occurred so that treatment could be allocated and started very soon after meeting the eligibility criteria. Patients who were consented early entered the study only if they developed brain swelling and met all the inclusion criteria for the trial at that time.
In accordance with the Good Clinical Practice guidelines,94 the patient’s nearest relative or welfare guardian was given the opportunity to ask questions and was given a copy of the trial information sheet to read and keep.
In some cases, the patient’s nearest relative/welfare guardian was not present when the patient was admitted to the ICU. In usual circumstances, the health-care team contacted them to update them on the patient’s condition soon after the patient was admitted. During this call, basic information was provided about the trial and they were asked if they would like more information. If further information was requested, the local investigator or research nurse obtained telephone consent and followed this up with written consent as soon as possible afterwards.
Premature withdrawal
Participation in any research trial is voluntary; therefore, the participant or their legal representative was able to withdraw from the trial at any point. In this case, it was clearly documented on the premature withdrawal form whether or not any previously collected data could still be used in the analysis and which part of the trial the participant was being withdrawn from, using the following options:
-
withdraw entirely – the hypothermia intervention will be safely terminated, no further data will be collected and previously collected data will not be used in the analysis
-
withdraw entirely – the intervention will be safely terminated and no further data will be collected, but previously data collected may be used in the analysis
-
withdraw from the intervention but be willing to be followed up
-
withdraw from being followed up only.
Settings and locations where the data were collected
Induced hypothermia treatment is a specialist intervention; therefore, this study involved only neurological ICUs that were familiar with the use of hypothermia treatment in this patient group. Potential centres were asked to complete a centre survey that allowed the trial management team to assess the expertise at each centre before allowing a centre to take part.
A total of 61 specialist neurological ICUs were opened as recruiting centres across 18 countries between 2009 and 2015: Belgium (n = 8), England (n = 21), Estonia (n = 1), Germany (n = 1), Greece (n = 6), Hungary (n = 1), India (n = 3), Ireland (n = 1), Italy (n = 5), Northern Ireland (n = 1), the Netherlands (n = 1), Portugal (n = 1), Russia (n = 1), Saudi Arabia (n = 1), Scotland (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Abu Dhabi (n = 1) and Wales (n = 1). Of these initiated centres, 54 centres screened patients and 46 centres randomised patients.
Once it was confirmed by the trial management team that a centre was eligible to participate, the process of obtaining ethics and hospital approvals varied between UK and non-UK centres. In the UK, ethics approval was obtained for the whole of the UK at the beginning of the trial, so that only hospital management approval was required for each new centre. To obtain this, the trial manager completed a site-specific information (SSI) form for each hospital and amended the consent documents to include the local hospital logos, contact details, etc. The trial manager then contacted the National Institute for Health Research Coordinated System for gaining NHS permission (NIHR CSP) network to ask for each hospital to be added to the list of participating centres. When this was approved, the local documents and SSI form were submitted to the local hospital research and development office for approval.
The process of obtaining approval in the non-UK centres was different as ethics approval was required for each hospital and the documents needed to be completed in the language of the country. For this reason, the local principal investigator (PI) had to complete the application form while the trial manager arranged for the trial documents to be translated into the appropriate language by an external translation company. The only exception to this was in Belgium, where the ethics process is centralised and, therefore, similar to that in the UK: one ethics application is submitted with a list of possible participating centres. When approval was given, each hospital submitted its own consent documents with its logo and contact details to its local hospital research office or independent review board for approval.
Trial site initiation visits
As soon as hospital approval was given for a site to participate in the trial, the trial manager contacted the PI and research team to arrange a site initiation visit. In the UK, the trial manager visited each site in person to conduct this visit. The visit lasted approximately 2 hours, during which time the staff were taught the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the consenting process, how to randomise a patient, the trial interventions, how to complete the data collection forms on the internet-based electronic database, how to complete a serious adverse event (SAE) form and how to report a SAE. Staff were also given access to the test database to practise completing data input. Follow-up procedures were also discussed and staff were told about the importance of maintaining contact details for the participants and their nearest relative after discharge from the ICU. The procedure for withdrawing a participant from the trial if required was also discussed.
Site initiation visits for the non-UK sites
Owing to the variability of access to the non-UK sites, we developed an alternative method for site initiation in these centres. When it was feasible in terms of travel time, cost and language barrier, the trial manager visited each of the non-UK centres to carry out the trial initiation visit. When this was not feasible, the trial manager arranged a web conference with the PI and research team at each hospital. This meeting lasted for at least 2 hours and was conducted in English.
The countries that we visited were:
-
Belgium – as the process of ethics approval was centralised for Belgian centres, we arranged a single site initiation meeting in Brussels and invited all centres to attend. Two additional centres joined the trial after this meeting. In this case, the trial manager arranged one meeting in one of the hospitals and both PIs and research staff from the two hospitals attended.
-
Germany and Italy – because of the language barrier in two sites, we felt that the staff at these sites would benefit more from a face-to-face meeting rather than a teleconference.
-
Republic of Ireland – the trial manager visited the site in Ireland as it was very similar to centres in the UK and was very easy to travel to.
-
Portugal – a trial initiation meeting was possible at this site because the chief investigator was invited to attend the Portuguese Intensive Care Society meeting and so carried out the visit while attending the local conference.
-
Spain – because of the language barrier in one site, we felt that the local staff would benefit more from a face-to-face meeting rather than a teleconference.
Once a site was initiated and activated on the database system, hospital staff could start to screen and recruit patients. Ongoing support was provided to the sites by the chief investigator and trial managers, either by e-mail or office telephone (available Monday–Friday, 09.00–17.00). We also set up a trial helpline using a separate mobile phone account, which was available out of hours and at weekends. The helpline was held by the chief investigator and trial managers on a rotational basis.
Interventions
Participants were randomised using minimisation criteria to either standard care (including ventilation, increased sedation and osmotherapy) or standard care with titrated TH (range 32–35 °C).
Prior to the induction of hypothermia, participants:
-
were sedated and attached to a ventilator
-
had probes inserted to monitor their blood pressure, fluid status and intracranial (brain) pressure
-
had been assessed, including measurement of all laboratory values, by the doctor in charge of their care
-
had continuous core body temperature monitoring in place using a probe in the pulmonary artery, oesophagus, bladder or rectum.
Hypothermia was then initiated with a bolus of 20–30 ml/kg of intravenous, refrigerated sodium chloride (0.9%) and maintained using each site’s usual cooling technique. The core temperature was reduced by the minimum required to control ICP at ≤ 20 mmHg, within the limits of 32–35 °C. This ICP threshold was used as intracranial hypertension is defined as an ICP of > 20 mmHg in the Brain Trauma Foundation guidelines. 86 If a participant’s ICP was not controlled after cooling to 35 °C, then the temperature was incrementally decreased to a minimum temperature of 32 °C to control ICP.
Hypothermia was maintained for at least 48 hours and continued for as long as necessary to maintain ICP at < 20 mmHg. Rewarming was considered after 48 hours at a rate of 0.25 °C per hour provided ICP was ≤ 20 mmHg. The reason for this timeline was that previous studies have reported that TH that lasts for at least 48 hours showed a trend towards a reduction in mortality and improved neurological function after TBI. 86,87,91
A flow chart was designed for the induction and maintenance of TH in the intervention group (see Appendix 1). The depth of hypothermia (32–35 °C) was guided by ICP, with a higher pressure level warranting a cooler target temperature. A guideline was also designed for the detection and treatment of shivering (see Appendix 2). This was designed specifically for this trial, drawing on:
-
the hospital protocol of the Mission Hospital, Orange County, CA, USA (permission given by Mary Kay Bader, Neuroclinical Nurse Specialist, Mission Hospital, Orange County, CA, USA)
-
the hospital protocol of the University Medical Centre, Utrecht, the Netherlands (permission given by Dr Kees Polderman, University Medical Centre, Utrecht, the Netherlands)
-
the Bedside Shivering Assessment Scale. 95
All participants in the intervention group also continued to be treated with stage 1 and 2 therapies as required to reduce intracranial hypertension. 86,87 If ICP became resistant to these therapies, and despite increasing the depth of hypothermia, care was then escalated to include stage 3 interventions.
Evidence suggests, however, that a patient is three times more likely to develop complications if hypothermia treatment is given in conjunction with stage 3 interventions, namely surgery or the drugs used to treat severe brain swelling (known as barbiturates). 91 If care was escalated, the participant was rewarmed using the rewarming guideline as soon as it was safe to do so. The reason for treatment escalation was then documented on the daily data collection form.
Outcomes
Primary
-
Outcome at 6 months using the GOSE questionnaire.
Secondary
-
Six-month mortality rate.
-
Intracranial pressure control.
-
Incidence of pneumonia across both groups.
-
Length of stay in the ICU and hospital.
-
Modified Oxford Handicap Scale score at 1 month, discharge from the randomising hospital or death, whichever took place first.
-
Correlation between the predicted outcome using the MOHS score at hospital discharge and the predicted outcomes using the GOSE score at 6 months post injury.
-
Health economics.
Primary end-point data collection
-
Outcome at 6 months using the GOSE questionnaire.
To collect this information, a questionnaire was sent to all participants 6 months after injury.
This study recruited a very challenging patient group; patients who have suffered a head injury can have personality changes after the injury, which can make it challenging to follow them up. Therefore, drawing on our previous experience of the follow-up of brain-injured patients who had been admitted to the ICU, we knew that it was unlikely that all patients would be able to complete and return the questionnaire by themselves. Depending on the severity of their injury, many patients would still be in hospital at the 6-month follow-up. For this reason, we designed the follow-up procedures very carefully and included these processes in the initial consenting discussion.
At the same time as sending the questionnaire to participants at 6 months, we also sent a letter to those who gave consent for participants to enter the study. This letter informed them that the questionnaire had been sent to participants and asked them to help with completion of the questionnaire.
This procedure was discussed with those giving consent at the time of providing consent for a patient to enter the study. This procedure was also discussed with patients at the time of obtaining their subsequent consent (if applicable).
The procedures for the follow-up of participants varied between those who were recruited in the UK and those who were recruited in non-UK centres.
Follow-up procedure for UK centres
The first process for follow-up, before we sent anything to participants, was for the trial manager to ask the research nurse at each participant’s centre to check the participant’s vital status by determining whether the participant was still an inpatient or had been transferred to a rehabilitation centre. If the participant had been discharged home, the research nurse was then asked to contact the participant’s GP to find out their vital status.
A GOSE questionnaire was then sent by post from the trial office in Edinburgh to all surviving participants 6 months after injury. At this time, we also sent a letter to those who gave consent for participants to enter the study, asking them to help with completion of the questionnaire.
In the pilot stage of the trial, if we did not receive a response from a participant within 3 weeks, we sent a shorter GOS questionnaire to the participant by post. If this was not returned after 2 weeks, then an independent and blinded researcher based in Edinburgh telephoned the participant to complete the short questionnaire with them over the telephone. The steps taken if a participant could not be contacted at this time varied depending on whether or not the participant had regained capacity and had given subsequent consent themselves:
-
If the participant had regained capacity and had given retrospective consent, then the process ended here and the participant was documented as lost to follow-up.
-
If the participant had not regained capacity and had not given follow-on consent, then the independent researcher telephoned the person who had given consent and asked them to complete the short questionnaire over the telephone.
This process was streamlined at the beginning of the main phase of the trial in January 2012. At this time, we decided to remove the process of sending the shorter questionnaire to participants and instead moved straight to telephoning participants if the first GOSE questionnaire was not returned after 3 weeks. In this case, the independent/blinded researcher based in Edinburgh telephoned participants if they had been discharged from hospital and completed the longer GOSE questionnaire with them over the telephone. If a participant was still in hospital and had not regained capacity to give follow-on consent, then the independent researcher telephoned the person who gave consent for the participant to enter the study and completed the longer GOSE questionnaire with them over the telephone.
Follow-up procedure for non-UK centres
Owing to the language barrier in the participating non-UK centres, it was not possible for the independent/blinded researcher in Edinburgh to contact the non-UK patients for follow-up. We therefore devised a slightly different process for the non-UK centres depending on their local procedures.
The procedure for follow-up was specifically outlined and discussed by the trial manager at the trial initiation meeting with the PI and research team at each of the non-UK centres.
Each PI was asked to identify someone in their hospital who would be blind to the participants’ intervention and could carry out the follow-up. All centres, except those in Belgium, had an independent person at their hospital who carried out the follow-up over the telephone at 6 months. Belgium had a similar procedure to that in the UK in that a letter was sent to both the participant and the person who gave consent at 6 months and, if this was not returned after 3 weeks, an independent person at the centre contacted the participant by telephone and completed the longer GOSE questionnaire with them over the telephone.
Secondary end-point data collection
Data collection for the secondary end points comprised:
-
intracranial pressure control
-
incidence of pneumonia across both groups
-
length of stay in the ICU and hospital
-
Modified Oxford Handicap Scale score at 1 month, discharge from the randomising hospital or death, whichever took place first, collected using the daily data collection forms that were completed by the research team at each centre
-
correlation between the predicted outcome using the MOHS score at hospital discharge and the predicted outcome using the GOSE score at 6 months post injury; this correlation was conducted by the trial statistician during the final analysis of the data
-
health economics.
Owing to the unexpected result of the trial, with a higher rate of poor outcome in the hypothermia group, a health economic analysis was not deemed to be necessary.
Any changes to trial outcomes after the trial commenced, with reasons
No changes were made to the trial outcomes after commencement of the trial.
Sample size
The main evidence for the sample size calculation was the six meta-analyses published between 2002 and 2008. 86–91 These included varying numbers of clinical trials and examined each trial based on an assessment of the quality of randomisation and blinding procedures. All meta-analyses found a trend towards positive effects of hypothermia on neurological outcome, but statistical significance was reached in only two. 86,87
With a conventional dichotomous analysis of the GOSE, comparing the proportions of participants with an unfavourable outcome in the two groups, a 600-patient trial had 81% power at the 5% significance level (two-sided) to detect an absolute reduction of 12% (60% reducing to 48%). There was 87% power to detect an absolute reduction of 13% (60% reducing to 47%).
These calculations are conservative compared with the Peterson et al. 91 systematic review of optimised therapeutic cooling.
Using an ordinal analysis of the GOSE together with covariate adjustment, there was the potential to increase the statistical efficiency of the analysis. If we achieve the efficiency gains suggested by simulations run by the IMPACT (International Mission on Prognosis and Clinical Trial Design in Traumatic Brain Injury) investigators96 and demonstrated in a reanalysis of the CRASH (Corticosteroid Randomisation After Significant Head Injury) trial,97 then a trial of 600 patients would have equivalent power to a trial of 1000 patients. This would give 80% power at the 5% significance level (two-sided) to detect an absolute reduction of 9% (60% reducing to 51%).
Data monitoring
The trial did not include any predefined interim analyses. The trial Data and Safety Monitoring Committee (DSMC) met regularly, however, to discuss the unblinded trial data and monitor the progress of the trial.
This committee was assembled using the Medical Research Council (MRC) guidelines for the development of a Data Monitoring and Ethics Committee (DMEC) and comprised three members:
-
an expert clinician in intensive care (chairperson)
-
an expert trial statistician
-
an expert triallist.
A DSMC charter was developed and agreed by all members at the first DSMC meeting in 2010 (see Appendix 3). This charter included the guidelines for early termination, the quorum for decision-making and the reporting of the DSMC recommendations.
Statistical guidelines for termination: Data and Safety Monitoring Committee charter
The DSMC has the responsibility for deciding whether, while randomisation is in progress, the unblinded results (or the unblinded results for a particular subgroup) should be revealed to the Trial Steering Committee.
The DSMC terms of reference stated that it would do this if, and only if, two conditions were satisfied:
-
The blinded results provide proof beyond reasonable doubt that treatment is, on balance, either definitely harmful or definitely favourable for all, or for a particular category of, patients in terms of the major outcome.
-
The blinded results would, if revealed, be expected to substantially change the prescribing patterns of doctors who are already familiar with any other trial results that exist.
Exact criteria for ‘proof beyond reasonable doubt’ are not, and cannot be, specified by a purely mathematical stopping rule, but they are strongly influenced by such rules. DSMC members expressed sympathy with the stopping rule proposed in Part I of the 1976 report to the MRC Leukaemia Committee,98 whereby an interim analysis of major end points would generally need to involve a difference between treatment and control of at least three standard errors to justify premature disclosure. An interim subgroup analysis would, of course, have to be even more extreme to justify disclosure. This rule has the advantage that the exact number and timing of interim analyses need not be prespecified. In summary, the stopping rules as specified in the CRASH trial protocol99 (as successfully applied in other trials including the MRC International Stroke Trial,100 which randomised 19,436 acute stroke patients) require extreme differences to justify premature disclosure and involve an appropriate combination of mathematical stopping rules and scientific judgement.
The DSMC met a total of nine times between February 2010 and October 2014. Of note is that the data showed a trend towards harm in the hypothermia group during the seventh and eighth DSMC meetings but the results did not become significant (difference of three standard errors) until the data were reviewed during the ninth meeting in October 2014.
At this time, the DSMC came to the following conclusions:
-
There is no evidence of benefit for the patient group receiving the treatment to be evaluated.
-
At best, a result of futility can be expected if the study is continued.
-
There are signs of harm by the new treatment investigated including differences in mortality rate and a smaller number of patients achieving a relatively good outcome in the new treatment group, for those surviving the 6-month period after inclusion.
The DSMC therefore proposed that ‘appropriate action is taken rapidly, as a consequence of the analysis done . . . in order to protect patients to be potentially included in this trial from now on’ (abbreviated excerpt from the DSMC letter to the Trial Steering Committee).
This recommendation was sent to the chairperson of the Trial Steering Committee who convened an urgent Trial Steering Committee meeting. The meeting concluded that recruitment to the trial should be stopped early on the basis of futility and possible harm to participants. Recruitment was therefore stopped on 14 October 2014.
Randomisation
The randomisation of participants to either the hypothermia or the standard-care group was undertaken using a central internet-based randomisation service provided by Lincoln (Paris, France).
Type of randomisation
Participant allocation to either the hypothermia or the standard-care group by the online randomisation service used a minimisation technique with a random element using the following stratification variables:
-
trial centre
-
aged < 4–5 years or ≥ 45 years
-
post-resuscitation Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) motor component 1 or 2 or 3–6
-
time from injury of < 12 hours or ≥ 12 hours
-
pupils – both reacting or one or neither reacting
-
allocation concealment mechanism.
It was not possible to conceal the allocated group from local investigators and study teams as it was clinically obvious which participants were receiving hypothermia, for example from the equipment required, participant temperature, blood results and fluid requirements.
To overcome potential bias, outcome data assessment were blinded.
Implementation
The central internet-based randomisation service provided by Lincoln generated the random allocation sequence (using minimisation with a random element) and assigned participants to groups.
Patients at each site were enrolled by either the PI or their deputy (e.g. research nurse or research doctor).
Blinding
It was not possible to blind local investigators, study teams or the participants’ next of kin to group allocation as it was clinically obvious which participants were receiving hypothermia.
Outcome data assessment was blinded as the GOSE questionnaire was, in the first instance, posted to participants by the trial office in Edinburgh. If it was not returned in the post within 3 weeks, then an independent researcher who was blind to treatment allocation telephoned the participant and/or their next of kin to complete the questionnaire with them over the telephone.
There were some similarities between interventions in the hypothermia group and interventions in the standard-care group of this trial. Both groups received stage 1 and stage 2 therapy (see Figure 2) throughout the trial period. It was also possible that participants in the standard-care group received temperature reduction, to a minimum of 36 °C, to treat fever using the same cooling technique as for participants in the hypothermia group. If this was required, the centres followed their local guidelines for fever management; no guidelines were provided as part of the trial.
Statistical methods
Overall statistical principles
The trial statistician performed the statistical programming and analysis to produce all summary tables and figures using the statistical package SAS® (version 9.2 or a more recent version; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA; SAS and all other SAS Institute Inc. product or service names are registered trademarks or trademarks of SAS Institute Inc. in the USA and other countries. ® indicates USA registration).
In general terms, categorical data are presented using counts and percentages, whereas continuous variables are presented using the mean, median, standard deviation (SD), minimum, maximum, interquartile points at 25% and 75% (Q1 and Q3) and number of participants with an observation (n). Data are split by time point when applicable.
All applicable statistical tests are two-sided and have been performed using a 5% significance level, leading to 95% (two-sided) CIs, unless otherwise specified.
Distributional assumptions underlying the statistical analyses are assessed by visual inspection of residual plots. Normality is examined by normal probability plots. If the distributional assumptions for the parametric approach were not satisfied, further data transformation (for achieving normality), or other suitable methods, were considered.
The intention-to-treat (ITT) and per-protocol (PP) populations are used to summarise all data and all analyses unless otherwise specified.
There has been no imputation of the data with regard to missing values or withdrawals for the statistical summaries and statistical analysis unless otherwise specified.
Statistical analysis plan
A detailed statistical analysis plan, setting out full details of the proposed analyses, was finalised before the trial database was locked for analysis.
As a result of the internal pilot phase,93 the sample size for the full trial was reduced from 1800 to 600 participants. Two factors contributed to this decision:
-
The original sample size may have underestimated the possible benefit of hypothermia as, unlike participants in most previous hypothermia trials, participants in the Eurotherm3235 Trial had to have evidence of brain swelling (raised ICP of > 20 mmHg) to be eligible for randomisation.
-
We showed that an enhanced cooling intervention could be delivered, as described by Peterson et al. 91
These data therefore informed the revised power calculation.
Population for analysis
Intention-to-treat population
The ITT population included all participants randomised into the Eurotherm3235 Trial. Participants were analysed in the group to which they were randomised, regardless of treatment received.
Per-protocol population
The PP population comprised those members of the ITT population who completed the study without a major protocol violation and who adequately complied with the administered treatment. Participants were analysed depending on the treatment that they actually received.
List of analyses
Recruitment and retention
No formal statistical testing was performed to look at recruitment and retention. A Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) flow chart is provided in Chapter 3. The numbers of participants screened, consented, randomised, treated, completed and discontinued by treatment and overall are also presented in Chapter 3. The number of participants discontinued early from the study is summarised by reason for withdrawal and treatment.
Baseline data: demographics and baseline/clinical characteristics
No formal statistical testing was performed. The following baseline characteristics are presented and summarised in the ITT report by treatment and overall (see Chapter 3):
-
characteristic used in minimisation algorithm
-
time from TBI to randomisation
-
age and gender
-
ICP, body temperature, post-resuscitation GCS and diagnosis details.
Protocol deviations/violations
No formal statistical testing was performed. All protocol deviations/violations are listed in the ITT statistical report (see Chapter 3).
Compliance with allocated treatment
Treatment compliance was determined using the following strategy:
-
Step 1 – if a participant was allocated to a treatment then he or she should have received the allocated treatment.
-
Step 2 – if a participant was allocated to the control then his or her core temperature should be ≥ 36 °C for all of the temperature observations for the first 48 hours from randomisation or until death (whichever event happens first).
-
Step 3 – if a participant was allocated to the hypothermia group then his or her core temperature should strictly be ≥ 32 °C and < 35 °C for all of the temperature observations from 4 hours after hypothermia started until the first 48 hours from randomisation or until death (whichever event happens first). Additionally, the participant could not have a barbiturate infusion within the first 48 hours from randomisation.
No formal statistical testing was performed. The number of treatment-compliant participants is summarised by treatment group as part of the ITT statistical report (see Chapter 3).
Primary outcome
Using an ordinal analysis of the GOSE scores, together with covariate adjustment (primary efficacy analysis), we were able to increase the statistical efficiency of the analysis101,102 so that a trial involving 600 participants would have power equivalent to that of a trial involving 1000 participants that assessed a binary outcome. We calculated that, with such an analysis, the study would have the equivalent of 80% power to detect a rate of unfavourable outcome (GOSE score of 1–4) that was 9 percentage points lower with hypothermia than with standard care (51% vs. 60%) at the 5% significance level (two-sided).
Data were analysed on an ITT basis. All randomised participants for whom outcome data were available were therefore included.
Participants were analysed depending on their allocated intervention, irrespective of whether or not their actual management complied with the allocated intervention.
The distributions of the 6-month GOSE scores between the two randomised groups (hypothermia vs. standard care) were compared using ordinal regression, adjusting for the following baseline covariates that were included in the minimisation algorithm:
-
age (included as a continuous variable using a linear term in the regression model)
-
post-resuscitation GCS motor component 1 or 2 compared with 3–6
-
time from injury of < 12 hours compared with ≥ 12 hours
-
pupils: both reacting compared with one reacting compared with neither reacting (included as an unordered categorical variable in the regression model).
As the covariates specified for the statistical analyses were required to inform the minimisation algorithm, there were no missing data for baseline covariates. A strenuous effort by the trial managers was also made to obtain complete outcome data at 6 months.
For this analysis, the eight-point GOSE was collapsed to six categories by pooling the ‘death with vegetative state’ and ‘lower severe disability’ categories. This was carried out to ensure that the analysis could not give ‘credit’ to an intervention that reduces mortality at the expense of increasing the proportion of severely disabled survivors.
The treatment effect was reported as an estimated adjusted common odds ratio (OR) with its corresponding 95% CI. The treatment groups are ordered in such a way that a common OR of < 1 corresponds to a benefit for hypothermia over standard care.
If there is strong evidence that the treatment effect does not satisfy the proportional odds assumption, which is required for the ordinal analysis, then this in itself will demonstrate that the distribution of the GOSE score differs between the two randomised groups. In such a situation, the distribution of the GOSE score in the two groups will be explored descriptively to give an insight into the nature of the treatment effect.
Sensitivity analyses
The unadjusted common OR and its corresponding 95% CI, derived by fitting an ordinal regression model with treatment as the only covariate included, is reported as a sensitivity analysis.
A binary logistic regression, using the same baseline covariates as set out in List of analyses, was also performed, using the conventional split of the GOSE as ‘lower moderate disability’ or better (‘favourable’) compared with ‘upper severe disability’ or worse (‘unfavourable’).
In a further exploratory analysis, the impact of missing outcome data was examined using an imputation technique, based on the simple IMPACT model96 and the MOHS value and/or shorter GOS, if available, for imputing the missing GOSE data.
Secondary outcomes
The following outcome measures were tested for differences between the two treatment groups:
Six-month mortality rate
Survival from ICU admission to 6 months post randomisation (analysis of mortality) is presented using a Kaplan–Meier plot split by treatment group. The two survival curves have been compared formally using a log-rank test. If distributional assumptions hold, this will be analysed using Cox proportional hazards regression and the result presented as an estimated hazard ratio (HR) with its corresponding 95% CI.
Intracranial pressure control
The proportion of recorded ICP measurements of ≤ 20 mmHg were calculated for each participant. These proportions are summarised by treatment group in the ITT statistical report (see Chapter 3).
The effect of the intervention was estimated using a linear model adjusted by the minimisation variables. The effect of treatment allocation is reported as an adjusted mean difference with its corresponding 95% CI.
The above analysis was also repeated for an ICP of ≤ 25 mmHg as a sensitivity analysis.
Incidence of pneumonia across both groups
The number and proportion of participants who developed pneumonia were calculated by treatment group. The effect of the intervention was then estimated using binary logistic regression adjusted by minimisation variables. The effect of treatment allocation is reported as an adjusted OR with its corresponding 95% CI in the ITT statistical report (see Chapter 3).
Additionally, the first time (from day 3 to day 7) that pneumonia manifested is reported but statistical significance was not assessed.
Length of stay in the intensive care unit and hospital
The length-of-stay variables were calculated as follows:
-
date/time from TBI (inclusion visit form) to randomisation
-
date/time from randomisation to discharge from hospital (follow-up form)
-
date/time from TBI (inclusion visit form) to discharge from hospital (follow-up form)
-
studied ICU stay = date/time from randomisation to discharge from ICU (follow-up form)
-
overall ICU stay = date/time of admission to ICU (inclusion visit form) to discharge from ICU (follow-up form)
-
hospital stay = date/time from TBI (inclusion visit form) to discharge from hospital (follow-up form).
A linear regression model has been used to compare the mean lengths of stay between groups, adjusting by minimisation variables. The result are presented as an adjusted difference in mean length, together with its corresponding 95% CI, in the ITT statistical report (see Chapter 3).
Modified Oxford Handicap Scale score at 28 days, discharge from the randomising hospital or death, whichever took place first
This outcome was analysed as per the primary outcome using an adjusted ordinal regression. In this analysis, the six-point MOHS was collapsed to four categories by pooling ‘death’ with ‘fully dependent, requiring attention day and night’ and ‘dependent, but not requiring constant attention’.
Correlation between the predicted outcome using the Modified Oxford Handicap Scale score at hospital discharge and the predicted outcome using the Glasgow Outcome Scale – Extended score at 6 months post injury
The Kendall tau-b correlation coefficient with its 95% CI between the MOHS score and the GOSE score is presented as part of the ITT statistical report (see Chapter 3).
A priori subgroups for the primary analysis were explored as follows:
-
aged < 45 years compared with ≥ 45 years
-
post-resuscitation GCS motor component 1 or 2 compared with 3–6
-
time from injury of < 12 hours compared with ≥ 12 hours
-
pupillary response: both or one reacting compared with none reacting
-
UK centres compared with non-UK centres
-
centres with high numbers of patients (i.e. 10 patients) compared with centres with low numbers (i.e. 10 patients).
These analyses were performed by including an interaction term between treatment and the relevant covariate in the ordinal regression model described above. A stricter level of statistical significance (p < 0.01) has been used in these analyses to reflect their exploratory nature.
Quality control of summary tables and statistical analysis
Isolated data errors, detected in the database as a result of the quality control checks, that were deemed significant were submitted for enquiry to the trial manager or designee.
Systematic data errors in the data reporting were investigated further; the data were corrected if necessary and the appropriate table was then rechecked.
Quality control/validation: summary tables
A random selection of unique analysis and summary tables was quality controlled using manual methods (e.g. comparison of results in the table with results calculated using a calculator, spreadsheet, database output or any alternative summarisation tool).
Quality control/validation: statistical analysis
Quality control/validation of statistical analyses was performed by peer review of program code, log and output. Additionally, the primary outcome analysis was replicated independently by a second statistician.
Unblinding procedures
Unblinding procedures were not applicable.
Chapter 3 Results
Results
Participant flow
Of the 2498 participants who were assessed for trial eligibility, 387 were randomly assigned, 386 received the intended treatment (after a withdrawal pre intervention) and 387 were analysed for the primary outcome (Figure 3). The most common reasons for exclusion from the trial were that ICP remained at ≤ 20 mmHg (41% of 2111 exclusions), the participant was unlikely to survive (8%) or the participant was already receiving hypothermia treatment (6%).
FIGURE 3.
The CONSORT flow diagram. Adapted with permission from Andrews et al. 1 Copyright © (2015) Massachusetts Medical Society.

Recruitment
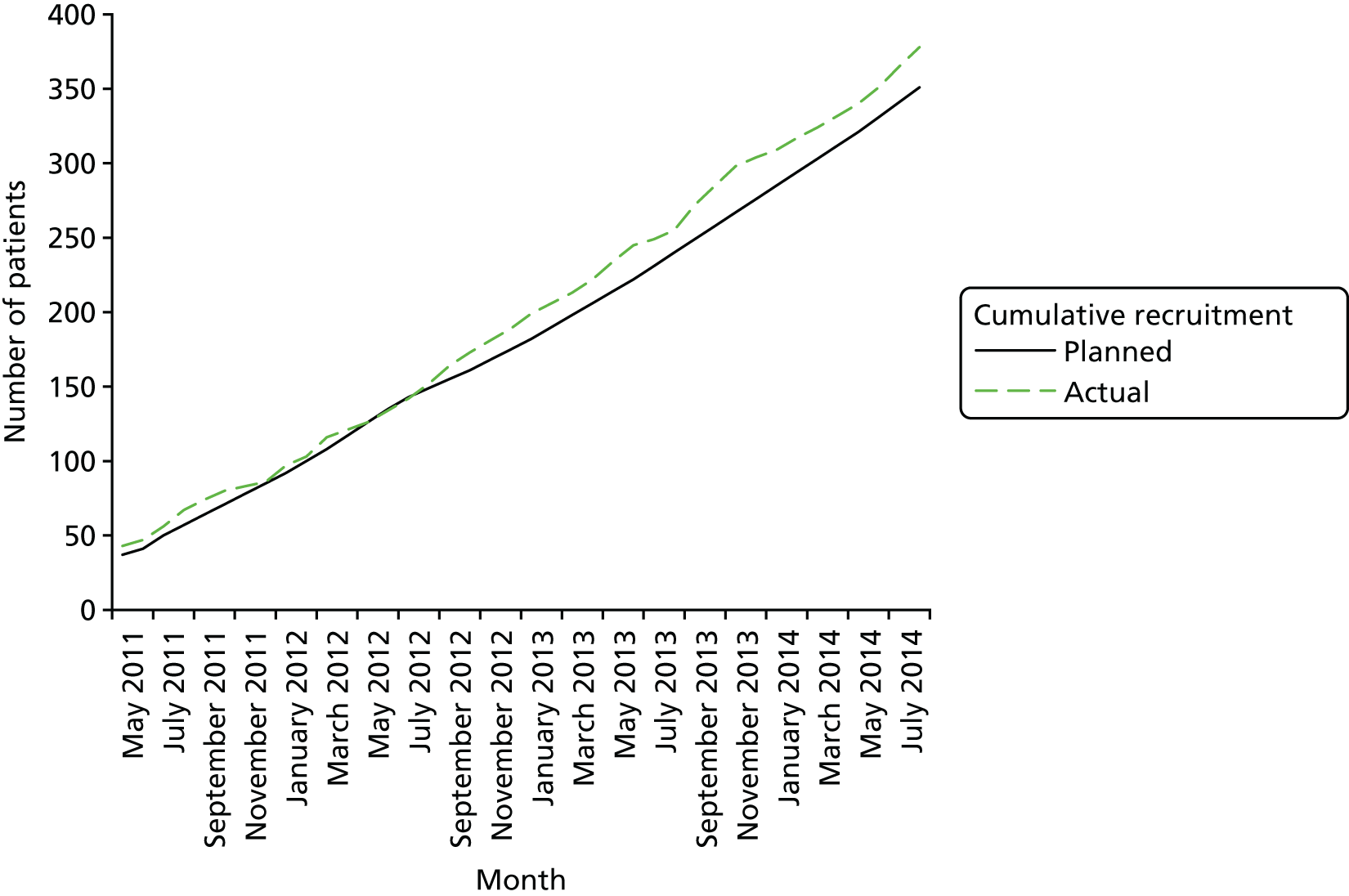
A total of 64 centres were initiated in 18 countries worldwide, with a target recruitment at each centre of four participants per year. A total of 387 participants were randomised from 47 of these centres between November 2009 (pilot phase from 10 January 2009 to 15 September 201193) and October 2014, when recruitment was stopped. Of these 387 participants, 53% (n = 205) were recruited in the UK. Follow-up ended 6 months after recruitment stopped, in April 2015.
Figure 4 shows the predicted versus actual recruitment throughout the trial.
FIGURE 4.
Recruitment graph. Adapted with permission from Andrews et al. 1 Copyright © (2015) Massachusetts Medical Society.
Why the trial was ended
Recruitment was stopped in October 2014 when the Trial Steering Committee, in concurrence with the original recommendations of the DMEC, concluded that there were signs of harm with the induced hypothermia treatment and, at best, a result of futility would be expected if the trial were to continue. These findings were apparent when the study’s designated primary outcome measure, analysed in accordance with the study’s pre-stated statistical analysis plan, was examined.
Baseline data
On an ITT basis, a total of 195 participants were randomised to hypothermia and 192 participants were randomised to standard care. Table 1 shows that there were no significant differences between groups in baseline characteristics.
| Demographic details | Treatment group | Overall (N = 387) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia (N = 195) | Control (N = 192) | |||
| Exact age (years), mean (SD) | 37.4 (15.4) | 36.7 (14.9) | 37.0 (15.1) | 0.65 |
| Age compliance, n (%) | ||||
| < 45 years | 131 (67.2) | 131 (68.2) | 262 (67.7) | |
| ≥ 45 years | 64 (32.8) | 61 (31.8) | 125 (32.3) | |
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 157 (80.5) | 164 (85.4) | 321 (82.9) | 0.20 |
| Female | 38 (19.5) | 28 (14.6) | 66 (17.1) | |
| Time from TBI (hours), mean (SD) | 77.96 (267.7) | 211.9 (1421.7) | 144.58 (1021.5) | 0.50 |
| Time from TBI compliance, n (%) | ||||
| < 12 hours | 19 (9.7) | 15 (7.8) | 34 (8.8) | |
| ≥ 12 hours | 176 (90.3) | 177 (92.2) | 353 (91.2) | |
| ICP at randomisation (mmHg), mean (SD) | 25.2 (4.8) | 25.5 (6.4) | 25.3 (5.6) | 0.77 |
| Temperature at randomisation (°C), mean (SD) | 37.01 (0.7) | 37.10 (0.72) | 37.05 (0.7) | 0.19 |
| GCS eyes,a n (%) | ||||
| None | 117 (60.0) | 113 (58.9) | 230 (59.4) | 0.96 |
| To pain | 17 (8.7) | 24 (12.5) | 41 (10.6) | |
| To sound | 29 (14.9) | 26 (13.5) | 55 (14.2) | |
| Spontaneous | 32 (16.4) | 29 (15.1) | 61 (15.8) | |
| GCS verbal,a n (%) | ||||
| None | 109 (55.9) | 108 (56.3) | 217 (56.1) | 0.91 |
| Incomprehensible | 36 (18.5) | 35 (18.2) | 71 (18.3) | |
| Inappropriate | 21 (10.8) | 14 (7.3) | 35 (9.0) | |
| Confused | 21 (10.8) | 25 (13.0) | 46 (11.9) | |
| Orientated | 8 (4.1) | 10 (5.2) | 18 (4.7) | |
| GCS motor,a n (%) | ||||
| None | 38 (19.5) | 38 (19.8) | 76 (19.6) | 0.61 |
| Extension | 18 (9.2) | 12 (6.3) | 30 (7.8) | |
| Abnormal flexion | 13 (6.7) | 18 (9.4) | 31 (8.0) | |
| Normal flexion | 22 (11.3) | 32 (16.7) | 54 (14.0) | |
| Localises | 70 (35.9) | 61 (31.8) | 131 (33.9) | |
| Obeys command | 34 (17.4) | 31 (16.1) | 65 (16.8) | |
| GCS sum (eyes + verbal + motor), n (%) | ||||
| 3–8 | 125 (64.1) | 129 (67.2) | 254 (65.6) | 0.70 |
| 9–12 | 45 (23.1) | 34 (17.7) | 79 (20.4) | |
| 13–15 | 25 (12.8) | 29 (15.1) | 54 (14.0) | |
| Isolated TBI, n (%) | ||||
| Yes | 123 (63.1) | 133 (69.3) | 256 (66.1) | 0.20 |
| No | 72 (36.9) | 59 (30.7) | 131 (33.9) | |
| Mechanism of injury, n (%) | ||||
| Missing | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.87 |
| Road traffic accident – pedestrian | 22 (11.3) | 31 (16.1) | 53 (13.7) | |
| Road traffic accident – motor vehicle | 68 (35.1) | 51 (26.6) | 119 (30.8) | |
| Push bike | 7 (3.6) | 10 (5.2) | 17 (4.4) | |
| Fall | 78 (40.2) | 78 (40.6) | 156 (40.4) | |
| Sports injury | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 2 (0.5) | |
| Assault | 18 (9.3) | 21 (10.9) | 39 (10.1) | |
| CT scan appearance – Marshall classification,b n (%) | ||||
| Diffuse injury Ic (no visible pathology) | 2 (1.0) | 0 | 2 (0.5) | 0.47 |
| Diffuse injury IId | 31 (15.9) | 36 (18.8) | 67 (17.3) | |
| Diffuse injury IIIe (swelling) | 39 (20.0) | 42 (21.9) | 81 (20.9) | |
| Diffuse injury IVf (shift) | 21 (10.8) | 15 (7.8) | 36 (9.3) | |
| Any lesion surgically removed | 46 (23.6) | 52 (27.1) | 98 (25.3) | |
| High- or mixed-density lesion | 56 (28.7) | 47 (24.5) | 103 (26.6) | |
| Any neurosurgery this admission, n (%) | ||||
| Yes | 83 (42.6) | 73 (38.0) | 156 (40.3) | 0.36 |
| No | 112 (57.4) | 119 (62.0) | 231 (59.7) | |
| Number of neurosurgeries, n (%) | ||||
| 0 | 112 (57.4) | 119 (62.0) | 231 (59.7) | 0.61 |
| 1 | 68 (34.9) | 51 (26.6) | 119 (30.7) | |
| 2 | 12 (6.2) | 18 (9.4) | 30 (7.8) | |
| 3 | 3 (1.5) | 4 (2.1) | 7 (1.8) | |
Numbers analysed
Table 2 shows the breakdown of recruitment and treatment allocation by centre and Table 3 shows the total number of participants screened and recruited at each centre.
| Trial centre | Treatment group, n (%) | Overall, n (%) (N = 387) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia (N = 195) | Control (N = 192) | ||
| Western General Hospital, Edinburgh, UK | 24 (12.3) | 18 (9.4) | 42 (10.9) |
| Aberdeen Royal Infirmary, Aberdeen, UK | 2 (1.0) | 3 (1.6) | 5 (1.3) |
| Charing Cross Hospital, London, UK | 1 (0.5) | 2 (1.0) | 3 (0.8) |
| Derriford Hospital, Plymouth, UK | 9 (4.6) | 7 (3.6) | 16 (4.1) |
| Royal Berkshire Hospital, Reading, UK | 0 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.3) |
| Hull Royal Infirmary, Hull, UK | 2 (1.0) | 4 (2.1) | 6 (1.6) |
| Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield, UK | 2 (1.0) | 1 (0.5) | 3 (0.8) |
| University Hospital of North Staffordshire, UK | 6 (3.1) | 6 (3.1) | 12 (3.1) |
| Leeds General Infirmary, Leeds, UK | 2 (1.0) | 4 (2.1) | 6 (1.6) |
| Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK | 8 (4.1) | 4 (2.1) | 12 (3.1) |
| North Estonia Medical Centre, Tallinn, Estonia | 7 (3.6) | 12 (6.3) | 19 (4.9) |
| Thriassio General Hospital of Eleusis, Magoula, Greece | 2 (1.0) | 3 (1.6) | 5 (1.3) |
| Albert Szent-Gyorgyi Medical Centre, Szeged, Hungary | 3 (1.5) | 2 (1.0) | 5 (1.3) |
| Hurstwood Park Neurological Centre, Haywards Heath, UK | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 1 (0.3) |
| Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast, UK | 4 (2.1) | 3 (1.6) | 7 (1.8) |
| CHU de Charleroi, Charleroi, Belgium | 2 (1.0) | 2 (1.0) | 4 (1.0) |
| Evangelismos General Hospital, Athens, Greece | 1 (0.5) | 3 (1.6) | 4 (1.0) |
| Cliniques Universitaires UCL de Mont-Godinne, Dinant, France | 3 (1.5) | 2 (1.0) | 5 (1.3) |
| University Hospital Brussels, Brussels, Belgium | 2 (1.0) | 3 (1.6) | 5 (1.3) |
| CSL Clinique Saint Joseph, Arlon, Spain | 0 | 2 (1.0) | 2 (0.5) |
| CHR Citadelle, Liege, Belgium | 0 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.3) |
| St Mary’s Hospital, London, UK | 3 (1.5) | 5 (2.6) | 8 (2.1) |
| King’s College Hospital, London, UK | 14 (7.2) | 16 (8.3) | 30 (7.8) |
| Hôpital ERASME, Brussels, Belgium | 14 (7.2) | 13 (6.8) | 27 (7.0) |
| Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milan, Italy | 3 (1.5) | 1 (0.5) | 4 (1.0) |
| Sklifosovsky Research Institute, Moscow, Russia | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 1 (0.3) |
| University Hospital of Ioannina, Ioannina, Greece | 0 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.3) |
| Cork University Hospital, Cork, Ireland | 6 (3.1) | 5 (2.6) | 11 (2.8) |
| University Hospital of Thessaly, Larissa | 5 (2.6) | 5 (2.6) | 10 (2.6) |
| BG Kliniken Bergmannstrost, Halle, Germany | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 2 (0.5) |
| Salford Royal NHS Trust, Salford, UK | 8 (4.1) | 7 (3.6) | 15 (3.9) |
| Complejo Universitario de Burgos, Burgos, Spain | 6 (3.1) | 6 (3.1) | 12 (3.1) |
| University Hospital of Coventry and Warwickshire, Coventry, UK | 0 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.3) |
| Policlinico A. Gemelli, Rome, Italy | 2 (1.0) | 0 | 2 (0.5) |
| General Hospital of Kavala, Greece | 2 (1.0) | 0 | 2 (0.5) |
| Jai Prakash Narain Apex Trauma Centre, AIIMS, New Delhi, India | 20 (10.3) | 18 (9.4) | 38 (9.8) |
| University Hospital of Wales, UK | 9 (4.6) | 11 (5.7) | 20 (5.2) |
| Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, United Arab Emirates | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 2 (0.5) |
| Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands | 4 (2.1) | 4 (2.1) | 8 (2.1) |
| UCIP, Hospital de Santo Antonio, Portugal | 1 (0.5) | 4 (2.1) | 5 (1.3) |
| Queen’s Hospital, Romford, UK | 3 (1.5) | 1 (0.5) | 4 (1.0) |
| Royal London Hospital, UK | 3 (1.5) | 4 (2.1) | 7 (1.8) |
| Royal Preston Hospital, UK | 3 (1.5) | 2 (1.0) | 5 (1.3) |
| King Abdulaziz Medical City, Saudi Arabia | 2 (1.0) | 1 (0.5) | 3 (0.8) |
| Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 1 (0.3) |
| The Walton Centre, Liverpool, UK | 0 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.3) |
| Trial centre | Participants (n) | |
|---|---|---|
| Randomised | Screened | |
| Western General Hospital, Edinburgh, UK | 42 | 137 |
| Jai Prakash Narain Apex Trauma Centre, AIIMS, New Delhi, India | 38 | 38 |
| King’s College Hospital, London, UK | 30 | 144 |
| Hôpital Erasme, Brussels, Belgium | 27 | 27 |
| University Hospital of Wales, UK | 20 | 115 |
| North Estonia Medical Centre, Estonia | 19 | 107 |
| Derriford Hospital, Plymouth, UK | 16 | 143 |
| Salford Royal NHS Trust, UK | 15 | 155 |
| Royal Stoke University Hospital, UK | 12 | 127 |
| Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle, UK | 12 | 112 |
| Complejo Universitario de Burgos, Spain | 12 | 25 |
| Cork University Hospital, Ireland | 11 | 58 |
| University Hospital of Thessaly, Larissa, Greece | 10 | 13 |
| St Mary’s Hospital, London, UK | 8 | 157 |
| Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands | 8 | 81 |
| Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast, UK | 7 | 98 |
| Royal London Hospital, UK | 7 | 142 |
| Leeds General Infirmary, UK | 6 | 83 |
| Hull Royal Infirmary, UK | 6 | 74 |
| Aberdeen Royal Infirmary, UK | 5 | 77 |
| Thriassio General Hospital of Eleusis, Attica, Greece | 5 | 43 |
| Albert Szent-Gyorgyi Medical Centre, Hungary | 5 | 7 |
| Cliniques Universitaires UCL de Mont Goddine, Belgium | 5 | 5 |
| UCIP Hospital de Santo António, Porto, Portugal | 5 | 8 |
| University Hospital Brussels, Belgium | 5 | 20 |
| Royal Preston Hospital, UK | 5 | 59 |
| CHU de Charleroi, Belgium | 4 | 10 |
| Evangelismos General Hospital, Greece | 4 | 22 |
| Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milan, Italy | 4 | 9 |
| Queen’s Hospital, Romford, UK | 4 | 31 |
| Charing Cross Hospital, London, UK | 3 | 23 |
| King Abdulaziz Medical City, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia | 3 | 35 |
| Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield, UK | 3 | 20 |
| G. Gennimatas General Hospital of Athens, Greece | 3 | 3 |
| Policlinico A. Gemelli, Rome, Italy | 2 | 11 |
| CSL Clinique St Joseph Arlon, Belgium | 2 | 11 |
| BG Kliniken Bergmannstrost, Halle, Germany | 2 | 12 |
| General Hospital of Kavala, Greece | 2 | 5 |
| Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates | 2 | 4 |
| Royal Berkshire Hospital, Reading, UK | 1 | 5 |
| Hurstwood Park Neurological Centre, Haywards Heath, UK | 1 | 31 |
| CHR Citadelle, Liège, Belgium | 1 | 2 |
| Sklifosovsky Research Institute, Moscow, Russia | 1 | 23 |
| University Hospital of Ioannina, Greece | 1 | 1 |
| University Hospital of Coventry and Warwickshire, UK | 1 | 115 |
| Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain | 1 | 2 |
| The Walton Centre, Liverpool, UK | 1 | 1 |
| Ospedale San Gerardo di Monza, Italy | 0 | 15 |
| Medisch Centrum Haaglanden, the Netherlands | 0 | 11 |
| Hospital Germans Trias I Pujol, Badalona, Spain | 0 | 10 |
| University General Hospital of Alexandroupolis, Greece | 0 | 9 |
| Queen’s Medical Centre, Nottingham, UK | 0 | 9 |
| Southern General Hospital, Glasgow, UK | 0 | 8 |
| St George’s Hospital, London, UK | 0 | 3 |
| CHL-Apollo Hospitals, India | 0 | 2 |
| All centres | 387 | 2498 |
The breakdown of participants recruited in the UK and non-UK centres was 53% and 47%, respectively.
Outcomes and estimation
All analyses were performed with SAS software. Analyses were performed on an ITT basis, incorporating all participants who underwent randomisation and for whom outcome data were available, with participants evaluated depending on their assigned intervention.
For the primary analysis, the distribution of the 6-month GOSE scores between the two groups (hypothermia vs. control) was compared with the use of ordinal logistic regression and with adjustment for the following baseline covariates:
-
age (included as a continuous variable with the use of a linear term in the regression model)
-
post-resuscitation GCS motor score [1 or 2 (no response or extensor response) vs. 3 to 6 (flexion or better response)]
-
time from injury (< 12 hours vs. ≥ 12 hours)
-
pupillary response (both reacting vs. one reacting vs. neither reacting; included as an unordered categorical variable in the regression model).
For this analysis, we collapsed the eight-point GOSE to six categories by pooling ‘death with a vegetative state’ and ‘lower severe disability’. This ensured that the analysis would not favour an intervention that reduced mortality at the expense of increasing the proportion of severely disabled survivors. Figure 5 shows the survival curves between groups.
FIGURE 5.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves per group.

Table 4 shows a detailed breakdown of the score category per group for both the full eight-point GOSE, the collapsed six-category GOSE and the dichotomised GOSE.
| Parameter | Categories | Treatment group, n (%) | Overall, n (%) (N = 387) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia (N = 195) | Control (N = 192) | |||
| GOSE score at 6 months | Dead | 68 (34.9) | 51 (27.3) | 119 (31.7) |
| Vegetative state | 0 | 3 (1.6) | 3 (0.8) | |
| Lower severe disability | 46 (24.5) | 43 (23.0) | 89 (23.7) | |
| Upper severe disability | 26 (13.8) | 21 (11.2) | 47 (12.5) | |
| Lower moderate disability | 16 (8.5) | 17 (9.1) | 33 (8.8) | |
| Upper moderate disability | 12 (6.4) | 15 (8.0) | 27 (7.2) | |
| Lower good recovery | 10 (5.3) | 20 (10.7) | 30 (8.0) | |
| Upper good recovery | 10 (5.3) | 17 (9.1) | 27 (7.2) | |
| GOSE score 2: vegetative state | 0 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.3) | |
| GOSE score 3: severe disability | 2 (1.0) | 1 (0.5) | 3 (0.8) | |
| GOSE score 4: moderate disability | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 1 (0.3) | |
| Lost to follow-up | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 2 (0.5) | |
| Alive at follow-up, GOSE data not available | 2 (1.0) | 2 (1.0) | 4 (1.0) | |
| Withdrawn pre treatment | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 1 (0.3) | |
| GOSE score at 6 months: collapseda | Dead, vegetative state, lower severe disability | 114 (60.6) | 98 (52.1) | 212 (56.4) |
| Upper severe disability | 26 (13.8) | 21 (11.2) | 47 (12.5) | |
| Lower moderate disability | 16 (8.5) | 17 (9.0) | 33 (8.8) | |
| Upper moderate disability | 12 (6.4) | 15 (8.0) | 27 (7.2) | |
| Lower good recovery | 10 (5.3) | 20 (10.6) | 30 (8.0) | |
| Upper good recovery | 10 (5.3) | 17 (9.0) | 27 (7.2) | |
| Dichotomised GOSE scorea | Unfavourable: dead, vegetative state, lower severe disability, upper severe disability | 142 (74.3) | 120 (63.5) | 262 (68.9) |
| Favourable: lower moderate disability, upper moderate disability, lower good recovery, upper good recovery | 49 (25.7) | 69 (36.5) | 118 (31.1) | |
Table 5 shows the results of the primary analysis and primary subgroup analyses for the ITT population.
| Analysis | Estimate (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Adjusted common ORa for GOSE score at 6 monthsb,c | 1.53 (1.02 to 2.30) | 0.04 |
| Adjusted ORa for unfavourable outcomeb,d | 1.69 (1.06 to 2.70) | 0.03 |
| Treatment with hypothermia vs. control (unadjusted) | 1.53 (1.02 to 2.30) | 0.04 |
| Treatment with hypothermia vs. control (collapsed) | 1.55 (1.05 to 2.29) | 0.03 |
| Treatment with hypothermia vs. control (dichotomised) | 1.67 (1.06 to 2.70) | 0.027 |
| Subgroup analyses | ||
| Aged < 45 vs. ≥ 45 yearsd | 1.03 (1.01 to 1.04) | < 0.001 |
| Post-resuscitation GCS motor component [score of 1 or 2 (or no extension or response) vs. 3–6 (flexion or better response)]d | 0.23 (0.13 to 0.40) | < 0.001 |
| Time from injury (< 12 hours vs. ≥ 12 hours)d | 0.71 (0.35 to 1.44) | 0.34 |
| Pupillary response (both reacting vs. one reacting vs. neither reacting)d | 0.91 (0.36 to 2.31) | 0.0029 |
The results of the primary analysis were unexpected and showed that participants in the hypothermia group had significantly poorer outcomes at 6 months (p = 0.04) and a higher mortality rate (p = 0.05) than those treated with standard care alone. Furthermore, the primary subgroup analysis showed that age and post-resuscitation GCS motor component were specifically linked to outcome; in this patient population, these findings would be expected.
Secondary analyses
Secondary outcomes of the trial were:
-
6-month mortality rate
-
intracranial pressure control
-
incidence of pneumonia across both groups
-
length of stay in the ICU and hospital
-
modified Oxford Handicap Scale score at 1 month, discharge from the randomising hospital or death, whichever took place first
-
correlation between the predicted outcome using the MOHS at hospital discharge and the GOSE score at 6 months post injury
-
health economics.
The results of the secondary end-point analyses are shown in Table 6.
| Analysis of secondary outcomes: hypothermia vs. control | Estimate (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted HR for death incidence between randomisation and 6 months | 1.45 (1.01 to 2.10) | 0.047 |
| Physiological measuresa | ||
| Adjusted mean difference in ICP on days 1–7 (mmHg) | –0.48 (–2.04 to 1.08) | 0.55 |
| Adjusted mean difference in core temperature on days 1–7 (°C) | –2.14 (–2.34 to –1.94) | < 0.001 |
| Adjusted mean difference in MAP on days 1–7 (mmHg) | 1.20 (–0.46 to 2.86) | 0.16 |
| Adjusted mean difference in CPP on days 1–7 (mmHg) | 1.61 (–0.36 to 3.58) | 0.11 |
| Adjusted mean difference in squared proportion of ICP measurements of ≤ 20 mmHg on days 1–7 | 440 (–1.60 to 1000) | 0.47 |
| Incidence of patients who had presence of pneumonia on days 3–7 | 1.04 (0.69 to 1.58) | 0.84 |
| Adjusted mean difference in log-transformed length of ICU stay (log-hours)c | 0.05 (0.11 to 0.22) | 0.54 |
| Adjusted common ORb for MOHS grade at 28 daysc,d | 1.65 (0.91 to 3.02) | 0.10 |
The physiological measures detailed in Table 5 are also shown as trends in Figures 6 and 7.
FIGURE 6.
Intracranial pressure control per group. Adapted with permission from Andrews et al. 1 Copyright © (2015) Massachusetts Medical Society.
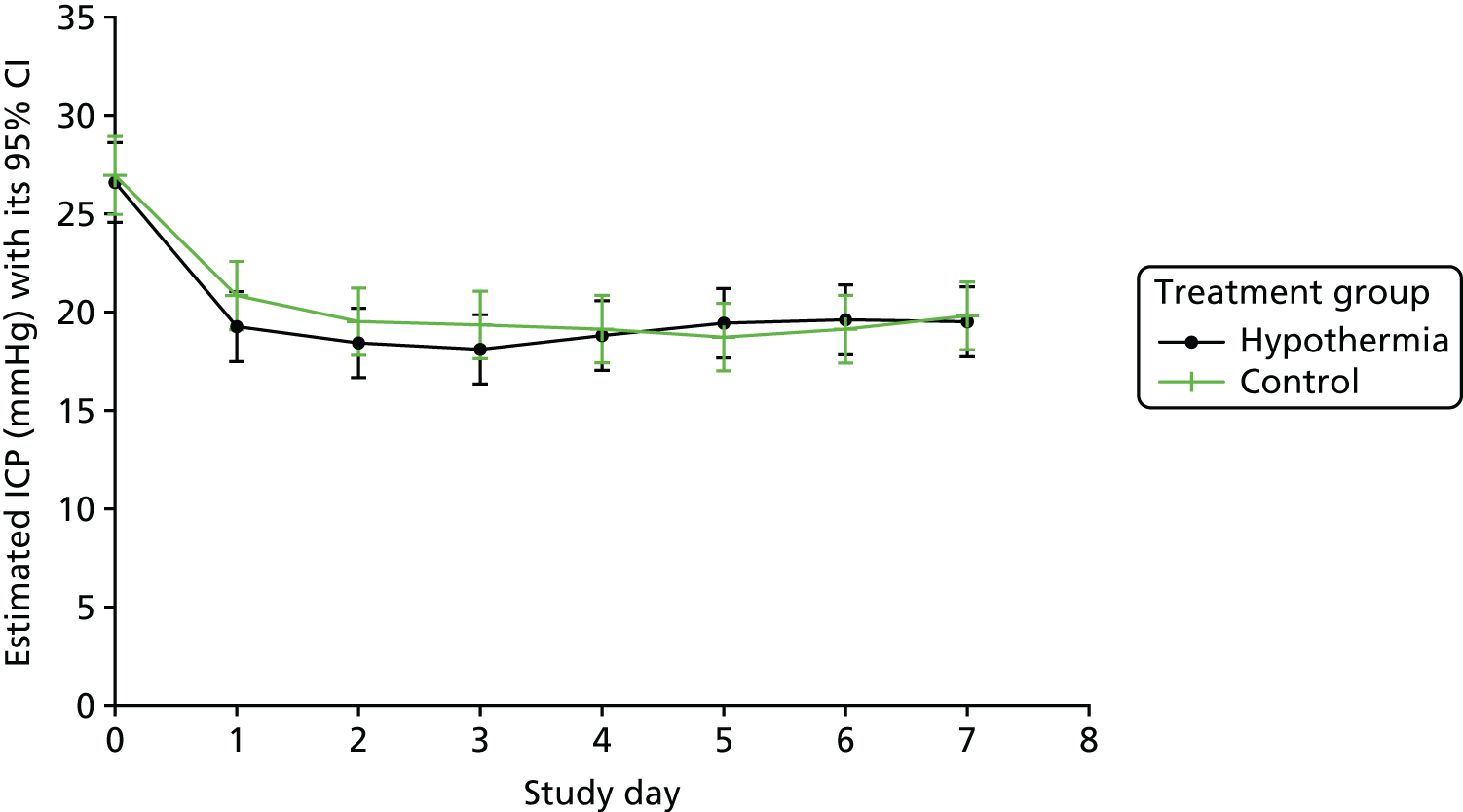
FIGURE 7.
Temperature control per group. Adapted with permission from Andrews et al. 1 Copyright © (2015) Massachusetts Medical Society.

Per-protocol analysis
We also carried out a PP analysis. Participants from the ITT population were included in this analysis if they completed the study without a major protocol violation and adequately complied with the prescribed treatment group. Participants were analysed depending on the treatment they actually received. A total of 257 participants were included in this analysis: 125 in the hypothermia group and 132 in the control group.
Table 7 shows that, as with the ITT population (see Table 5), there were no significant differences in baseline characteristics in the PP population. Table 8 shows the breakdown of GOSE score category for the full eight-point GOSE, the collapsed six-point GOSE and the dichotomised GOSE in this population.
| Demographic details | Treatment group | Overall (N = 257) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia (N = 125) | Control (N = 132) | |||
| Exact age (years), mean (SD) | 38.3 (15.5) | 37.0 (15.0) | 37.6 (15.2) | 0.46 |
| Age compliance, n (%) | ||||
| < 45 years | 83 (66.4) | 90 (68.2) | 173 (67.3) | 0.76 |
| ≥ 45 years | 42 (33.6) | 42 (31.8) | 84 (32.7) | |
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 98 (78.4) | 115 (87.1) | 213 (82.9) | 0.06 |
| Female | 27 (21.6) | 17 (12.9) | 44 (17.1) | |
| Time from TBI (hours), mean (SD) | 91.54 (332.71) | 264.68 (1315.76) | 180.82 (974.83) | 0.63 |
| Time from TBI compliance, n (%) | ||||
| < 12 hours | 10 (8.0) | 8 (6.1) | 18 (7.0) | 0.02 |
| ≥ 12 hours | 115 (92.0) | 124 (93.9) | 239 (93.0) | |
| ICP at randomisation (mmHg), mean (SD) | 25.1 (4.8) | 25.1 (6.0) | 25.1 (5.5) | 0.86 |
| Temperature at randomisation (°C), mean (SD) | 37.01 (0.74) | 37.17 (0.67) | 37.09 (0.71) | 0.65 |
| GCS eyes,a n (%) | ||||
| None | 78 (62.4) | 76 (57.6) | 154 (59.9) | 0.39 |
| To pain | 10 (8.0) | 16 (12.1) | 26 (10.1) | |
| To sound | 23 (18.4) | 17 (12.9) | 40 (15.6) | |
| Spontaneous | 14 (11.2) | 23 (17.4) | 37 (14.4) | |
| GCS verbal,a n (%) | ||||
| None | 67 (53.6) | 73 (55.3) | 140 (54.5) | 0.93 |
| Incomprehensible | 26 (20.8) | 24 (18.2) | 50 (19.5) | |
| Inappropriate | 13 (10.4) | 10 (7.6) | 23 (8.9) | |
| Confused | 16 (12.8) | 16 (12.1) | 32 (12.5) | |
| Orientated | 3 (2.4) | 9 (6.8) | 12 (4.7) | |
| GCS motor,a n (%) | ||||
| None | 22 (17.6) | 25 (18.9) | 47 (18.3) | 0.67 |
| Extension | 10 (8.0) | 10 (7.6) | 20 (7.8) | |
| Abnormal flexion | 9 (7.2) | 10 (7.6) | 19 (7.4) | |
| Normal flexion | 17 (13.6) | 24 (18.2) | 41 (16.0) | |
| Localises | 48 (38.4) | 41 (31.1) | 89 (34.6) | |
| Obeys command | 19 (15.2) | 22 (16.7) | 41 (16.0) | |
| GCS sum (eyes + verbal + motor), n (%) | ||||
| 3–8 | 82 (65.6) | 89 (67.4) | 171 (66.5) | 0.93 |
| 9–12 | 29 (23.2) | 20 (15.2) | 49 (19.1) | |
| 13–15 | 14 (11.2) | 23 (17.4) | 37 (14.4) | |
| Isolated TBI, n (%) | ||||
| Yes | 74 (59.2) | 96 (72.7) | 170 (66.1) | 0.23 |
| No | 51 (40.8) | 36 (27.3) | 87 (33.9) | |
| Mechanism of injury, n (%) | ||||
| Missing | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.91 |
| Road traffic accident – pedestrian | 13 (10.5) | 19 (14.4) | 32 (12.5) | |
| Road traffic accident – motor vehicle | 46 (37.1) | 37 (28.0) | 83 (32.4) | |
| Push bike | 3 (2.4) | 8 (6.1) | 11 (4.3) | |
| Fall | 49 (39.5) | 54 (40.9) | 103 (40.2) | |
| Sports injury | 0 | 1 (0.8) | 1 (0.4) | |
| Assault | 13 (10.5) | 13 (9.8) | 26 (10.2) | |
| CT scan appearance – Marshall classification,b n (%) | ||||
| Diffuse injury Ic (no visible pathology) | 1 (0.8) | 0 | 1 (0.4) | 0.59 |
| Diffuse injury IId | 19 (15.2) | 27 (20.5) | 46 (17.9) | |
| Diffuse injury IIIe (swelling) | 21 (16.8) | 25 (18.9) | 46 (17.9) | |
| Diffuse injury IVf (shift) | 17 (13.6) | 10 (7.6) | 27 (10.5) | |
| Any lesion surgically removed | 37 (29.6) | 39 (29.5) | 76 (29.6) | |
| High- or mixed-density lesion | 30 (24.0) | 31 (23.5) | 61 (23.7) | |
| Any neurosurgery this admission, n (%) | ||||
| Yes | 60 (48.0) | 52 (39.4) | 112 (43.6) | 0.16 |
| No | 65 (52.0) | 80 (60.6) | 145 (56.4) | |
| Number of neurosurgeries, n (%) | ||||
| 0 | 65 (52.0) | 80 (60.6) | 145 (56.4) | |
| 1 | 49 (39.2) | 35 (26.5) | 83 (32.7) | |
| 2 | 8 (6.4) | 14 (10.6) | 22 (8.6) | |
| 3 | 3 (2.4) | 3 (2.3) | 6 (2.3) | |
| Parameter | Categories | Treatment group, n (%) | Overall (N = 257) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia (N = 125) | Control (N = 132) | |||
| GOSE score at 6 months | Dead | 41 (33.6) | 29 (22.7) | 70 (28.0) |
| Vegetative state | 0 | 1 (0.8) | 1 (0.4) | |
| Lower severe disability | 30 (24.6) | 32 (25.0) | 62 (24.8) | |
| Upper severe disability | 16 (13.1) | 15 (11.7) | 31 (12.4) | |
| Lower moderate disability | 11 (9.0) | 9 (7.0) | 20 (8.0) | |
| Upper moderate disability | 10 (8.2) | 12 (9.4) | 22 (8.8) | |
| Lower good recovery | 6 (4.9) | 16 (12.5) | 22 (8.8) | |
| Upper good recovery | 8 (6.6) | 14 (10.9) | 22 (8.8) | |
| GOSE score at 6 months: collapsed | Dead, vegetative state, lower severe disability | 71 (58.2) | 62 (48.4) | 133 (53.2) |
| Upper severe disability | 16 (13.1) | 15 (11.7) | 31 (12.4) | |
| Lower moderate disability | 11 (9.0) | 9 (7.0) | 20 (8.0) | |
| Upper moderate disability | 10 (8.2) | 12 (9.4) | 22 (8.8) | |
| Lower good recovery | 6 (4.9) | 16 (12.5) | 22 (8.8) | |
| Upper good recovery | 8 (6.6) | 14 (10.9) | 22 (8.8) | |
| Dichotomised GOSE score | Unfavourable: dead, vegetative state, lower severe disability, upper severe disability | 88 (71.0) | 78 (60.5) | 166 (65.6) |
| Favourable: lower moderate disability, upper moderate disability, lower good recovery, upper good recovery | 36 (29.0) | 51 (39.5) | 87 (34.4) | |
Tables 9 and 10 show the results of the primary analysis (hypothermia vs. standard care), primary subgroup analyses and secondary analyses of the PP population.
| Analysis of primary outcome for hypothermia vs. control | Estimate (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Adjusted common OR for GOSE score at 6 monthsa,b,c | 1.61 (0.98 to 2.61) | 0.06 |
| Adjusted OR for unfavourable outcomea,b,d | 1.62 (0.93 to 2.83) | 0.09 |
| Treatment hypothermia vs. control (unadjusted) | 1.63 (1.02 to 2.62) | 0.04 |
| Treatment hypothermia vs. control (collapsed) | 1.61 (0.98 to 2.61) | 0.06 |
| Treatment hypothermia vs. control (dichotomised) | 1.62 (0.93 to 2.83) | 0.09 |
| Subgroup analyses | ||
| Aged < 45 vs. ≥ 45 yearsd | NP | 0.03 |
| Post-resuscitation GCS motor component [score of 1 or 2 (or no extension or response) vs. 3–6 (flexion or better response)]d | NP | 0.79 |
| Time from injury (< 12 hours vs. ≥ 12 hours)d | NP | 0.02 |
| Pupillary response (both reacting vs. one reacting vs. neither reacting)d | NP | 0.64 |
| Analysis of secondary outcomes: hypothermia vs. control | Estimate (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted HR for death incidence between randomisation and 6 months | 1.62 (1.01 to 2.60) | 0.05 |
| Adjusted mean difference in squared proportion of ICP measurements of ≤ 20 mmHg on days 1–7 | 183.30 (–545.32 to 911.92) | 0.62 |
| Incidence of patients who had presence of pneumonia on days 3–7 | 1.04 (0.62 to 1.73) | 0.89 |
| Adjusted mean difference in log-transformed length of ICU stay (log-hours)a | 0.02 (–1.16 to 0.20) | 0.80 |
| Adjusted common OR for MOHS grade at 28 daysa,b | 1.93 (0.93 to 4.00) | 0.08 |
For binary outcomes, presentation of both absolute and relative effect sizes is recommended103 (see Tables 6–10 for all data).
Ancillary analyses
Prespecified subgroups for the primary analysis were defined on the basis of the baseline covariates described (see Table 1), the location of the centre (UK vs. non-UK) and the volume of the centre (≥ 10 vs. < 10 participants). We performed these analyses by including an interaction term between each intervention and the relevant covariate in the ordinal logistic–regression model; a stricter level of statistical significance (p < 0.01) was used because of their exploratory nature.
The results of this subanalysis showed no statistically significant difference in patient outcome between UK centres and non-UK centres (p = 0.17) and no statistically significant difference in outcome between high-volume recruiting centres and low-volume recruiting centres (p = 0.12).
Modified Oxford Handicap Scale grades were analysed in the same way as GOSE scores, but we collapsed the six grades to four categories by grouping together dependent, fully dependent and death. In the analysis of the between-group difference in mortality, Cox proportional hazards regression was used to estimate the intervention effect.
Other continuous outcomes were tested with an analysis of covariance; for binary outcomes, logistic regression was used. ICP, core temperature, MAP and CPP on days 1–7 were analysed post hoc with the use of a linear model, with study days as repeated measurements with a compound symmetry covariance matrix. All of these analyses used the same covariates as were prespecified for GOSE scores, together with the baseline value of the relevant variable.
Occasionally, participants who have suffered a brain injury have severe brain swelling that does not respond to the usual treatment methods. In these cases, participants require further treatment with either drugs (barbiturates) or surgery (decompressive craniectomy).
A further covariance analysis that was carried out was the incidence of treatment escalation or stage 2 therapy failure across groups. Table 11 shows the proportion of participants in the Eurotherm3235 Trial who developed severe brain swelling and the days on which the therapy failure occurred.
| Parameter | Treatment group, n (%) | Overall, n (%) (N = 387) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia (N = 195) | Standard care (N = 192) | ||
| First occurrence | |||
| Day 1 | 15 (7.8) | 31 (16.4) | 46 (12.1) |
| Day 2 | 15 (7.8) | 22 (11.6) | 37 (9.7) |
| Day 3 | 14 (7.3) | 17 (9.0) | 31 (8.1) |
| Day 4 | 13 (6.8) | 14 (7.4) | 27 (7.1) |
| Day 5 | 7 (3.6) | 7 (3.7) | 14 (3.7) |
| Day 6 | 11 (5.7) | 4 (2.1) | 15 (3.9) |
| Day 7 | 9 (4.7) | 7 (3.7) | 16 (4.2) |
| Missing | 3 (1.5) | 3 (1.6) | 6 (1.6) |
| Never occurred | 108 (56.3) | 87 (46.0) | 195 (51.2) |
Harms
An AE is any untoward medical occurrence in a clinical trial subject. Many untoward events are expected in patients admitted to the ICU because of the severity of their illness and/or injury.
The treatment of any untoward medical occurrence is part of the standard care for patients admitted to the ICU. Therefore, the decision was made in the design stage of the trial that no AE data would be collected in this study.
A SAE is defined by the National Research Ethics Service in the UK104 as any AE that:
-
results in death
-
is life-threatening
-
necessitates hospitalisation or prolongation of existing hospitalisation
-
results in persistent or significant disability or incapacity
-
is a congenital abnormality or birth defect.
Death is an expected outcome in approximately 25% of all critically ill patients with severe TBI105 and, therefore, it was not reported as a SAE in this study.
The specific SAE data that we collected were:
-
bleeding – defined as a new haemorrhage requiring ≥ 2 units of packed red cells
-
cardiovascular instability – defined as a systolic blood pressure of < 90 mmHg for ≥ 30 minutes86 (of note, terminal hypotension data was not collected)
-
thermal burns on > 5% of body surface area using the Lund–Browder chart
-
cerebral perfusion pressure of < 50 mmHg for ≥ 15 minutes.
Unexpected events considered to be SAEs, that are not described above, could also be collected by investigators by using the ‘other’ option on the SAE form. Table 12 shows all SAEs that were collected throughout the trial.
| Parameter | Category | Treatment group, n (%) | Overall, n (%) (N = 387) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia (N = 195) | Control (N = 192) | |||
| Participants who had at least one SAEa | All | 19 (9.7) | 10 (5.2) | 29 (7.5) |
| Number of SAEs | All | 33 | 10 | 43 |
| Number of specific SAEs | Bleeding – defined as a new haemorrhage requiring ≥ 2 units of packed red cells | 3 (9.1) | 0 | 3 (7.0) |
| Cardiovascular instability – defined as a MAP of ≤ 90 mmHg for ≥ 30 minutes | 5 (15.2) | 2 (20.0) | 7 (16.3) | |
| CPP of < 50 mmHg for ≥ 15 minutes | 11 (33.3) | 6 (60.0) | 17 (39.5) | |
| Other | 14 (14.2) | 2 (20.0) | 16 (37.2) | |
| SAE causality | Not related | 25 (75.8) | 9 (90.0) | 34 (79.1) |
| Possibly related | 8 (24.2) | 1 (10.0) | 9 (20.9) | |
Reporting of SAEs was low throughout the trial, with an overall incidence of 7.5%. Most of these events were collected in the hypothermia group. We believe that the reason for this is that the four specific SAEs that we outlined were all possible side effects of hypothermia; therefore, these SAEs may have been thought to be physiological effects of the brain injury in the standard-care group rather than being related to the trial, especially as treatment in the standard-care group was not protocolised.
Economic evaluation
Owing to the early stopping of this trial, as a result of likely futility and possible harm, it was considered by the investigators and Trial Steering Committee that an economic analysis would not make a useful contribution to the outcomes of the study; the results of the ITT analysis supported this view.
Chapter 4 Discussion
Discussion
The use of induced hypothermia in addition to standard care did not result in improved patient outcomes at 6 months after injury compared with standard care alone. Consequently, the trial was stopped early, after 387 of the intended 600 participants had been randomised, when the Trial Steering Committee and the trial sponsor agreed with the recommendations of the DSMC:
-
At best, a result of futility would be expected if the trial were to continue.
-
There were signs of harm with the treatment being evaluated.
-
These signs included increased mortality in participants assigned to the treatment being evaluated and fewer participants assigned to the treatment being evaluated achieving ‘good recovery’ on the GOSE at the designated outcome assessment point of 6 months after inclusion.
-
These findings were apparent when examining the study’s designated primary outcome measure analysed in accordance with the study’s pre-stated statistical analysis plan.
We acknowledge that the early termination of recruitment to this trial introduces the risk of bias; however, the reason for termination was accepted by the authors.
The Eurotherm3235 Trial was a large RCT that tested TH as the primary (stage 2) intervention to reduce ICP after TBI. Literature at the time of protocol development indicated that at least one episode of ICP of > 20 mmHg occurred in 50% of participants with TBI who received mechanical ventilation and ICP monitoring. 10 In contrast to this, participant screening data collected during this trial indicated that fewer participants than expected (only 16% of screened participants) developed raised ICP of > 20 mmHg.
Standard care followed the best practice recommended in the Brain Trauma Foundation guidelines86 but was not prescribed in the protocol. Guidelines for induction and maintenance of hypothermia and for control of shivering were developed and discussed with centres during their site initiation meeting. It should be noted that the hypothermia guideline only prescribed the technique for the induction of hypothermia rather than the maintenance; centres were able to use whichever cooling technique they would normally use for maintenance of hypothermia. If a participant was randomised to the hypothermia group, copies of these guidelines were given to the relevant centre to use.
We found no significant between-group difference regarding to the time from injury to initiation of hypothermia (< 12 or ≥ 12 hours). This differs from a previous review, which found that outcome was improved when hypothermia was initiated within 12 hours of injury. 36 However, there were not enough participants randomised within 12 hours after injury in this trial to be confident of having excluded a subgroup effect for the time from injury. Those trials in which hypothermia for neuroprotection was induced very soon after injury and which were judged to be of higher quality and to have a lower risk of bias13 also showed trends towards unfavourable outcomes15,16 or were stopped for futility. 17,18
In this trial, barbiturate infusion was reserved for participants who had uncontrolled raised ICP despite treatment with all stage 1 and 2 treatments. We found that barbiturate infusion to reduce ICP was used more frequently, and earlier, in the control group than in the hypothermia group. It is plausible that barbiturate infusion may have somehow been beneficial to participants in the control group, but this hypothesis is not within the remit of this trial and requires further testing. There was no statistical difference in the use of decompressive craniectomy between the two groups.
The trial was designed to be pragmatic and to focus on functional outcome rather than on detailed mechanistic pathways throughout the participants’ ICU stays. In usual practice, the intensity of a stage 2 therapy is adjusted in the ICU setting depending on its effect on haemodynamic variables: ICP, MAP and CPP. As there were no, or limited, data on the benefits and harms of standard stage 2 interventions at the time of writing the protocol, we decided not to record which and/or how many stage 2 therapies were delivered to participants. Our findings show that there were no clinically important differences in these variables between the two groups.
We accept that the result, which suggests the possible harm of hypothermia, could be attributable to a biological effect of hypothermia or to the harms or benefits of the other therapies used differentially in the two groups. This trial did not assess the biological effects of other treatments administered during hypothermia; therefore, no conclusion regarding this hypothesis could be made. Furthermore, the main entry criterion for this trial was raised ICP of ≥ 20 mmHg, which is the definition of raised ICP given in the Brain Trauma Foundation guidelines. 86 Consequently, the benefits and risks of hypothermia, when used to treat severe intracranial hypertension that is not responsive to any stage 2 treatments applied before initiation of hypothermia, were not assessed as part of this trial.
This trial found that ICP was well controlled in both groups (see Figure 6). Detailed results show, however, that ICP was more difficult to control in the standard-care group, with more stage 2 therapy failures observed in this group. This suggests that TH was effective in reducing ICP; however, it did not improve functional recovery more than treatment with standard care alone. The benefits and harms of any other interventions that successfully reduce ICP have not been assessed as part of this trial. We now believe that more adequately powered clinical trials of common therapies used to reduce ICP, such as hypertonic therapy, barbiturates and hyperventilation, are required to assess their potential benefits and risks to patients.
Limitations
A limitation of this study was the inability to blind the hypothermia intervention. This is problematic for any trial of TH and is primarily because of the equipment required and the obvious physiological differences between groups including, but not limited to, participants’ core temperature. Cooling to normothermia was, however, permitted in the standard-care group; therefore, it is possible that some relatives were masked from the intervention/allocated group. We believe that this limitation was overcome, however, by blinding the follow-up and GOSE scoring.
A further limitation in the design of the trial is that we allowed SAEs to be collected in both groups when the four specific SAEs that we outlined (see Chapter 3, Harms) were all possible side effects of induced hypothermia. This resulted in more frequent SAE reporting in the hypothermia group and introduced reporting bias. The same clinical events may have been seen in the control group but may have been considered expected consequences of admission to intensive care following severe brain injury, and may not have been reported as SAEs linked to being in the trial.
Generalisability
The Trial Steering Committee and trial sponsor accepted the recommendation of the DSMC after its ninth meeting in full and terminated recruitment early. Early stopping of any trial can potentially reduce the external validity of the results; however, the burden of proof required for early stopping for possible harm is considerably lower than that for overwhelming evidence of efficacy. 106 In this case, the GOSE scores collected after the decision to terminate confirmed the result of the trial detailed earlier.
Although the trial was open, we believe that the external validity was strong, as centres:
-
were able to use their own technique for maintenance of hypothermia
-
could rewarm the participant based on their physiological parameters and condition from day 3 onwards
-
could cool participants to normothermia in the control group for fever control
-
could escalate care to stage 3 interventions if/as soon as was required in both groups.
The prescribed induction of hypothermia means that the same technique was used to initiate hypothermia in all participants. We know that compliance with the guideline was good, as Figure 7 shows the rapid reduction in temperature to 35 °C, and treatment compliance showed that 97.1% of core temperature observations were within range in the hypothermia group. This strengthens the internal validity of the trial and its result. The use of a blinded outcome assessor also improved the internal validity of the trial as the same method for scoring was used for all GOSE questionnaires and scoring was carried out by the same researcher throughout the trial. Furthermore, the imputed algorithm in the trial online database was used to ensure that there was no human error/bias in scoring.
The trial involved 387 participants from 47 centres across 18 countries worldwide, and all were able to use their own maintenance technique for hypothermia without a protocolised control group. We therefore believe that the results can be generalised to any global setting. The cooling intervention studied was already being used in clinical practice in each of these centres and was tested in the way that centres normally used it.
Chapter 5 Updated systematic review of therapeutic hypothermia for adult patients following traumatic brain injury
The protocol and Cochrane domain-based assessment of bias for this systematic review can be found in Report Supplementary Material 1 and 2.
Evidence before this study
Therapeutic hypothermia is commonly used in the treatment of adult TBI. There has been debate over the efficacy of TH following the publication of two multicentre RCTs107,108 that showed either harm or no clinical benefit from the use of TH.
The following databases were searched from 1 January 2011 to 31 March 2016: CENTRAL (Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials), MEDLINE, PubMed and EMBASE. Only foreign articles published in the English language were included. Only articles that were RCTs investigating adult TBI sustained following an acute, closed head injury were included. Quality was assessed using the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool109 for assessing the risk of bias and a modified Jadad score.
Added value of this study
This study adds key knowledge to the evidence base that may go some way to explain discrepancies in results between the most recent published RCTs and reviews. When high-quality studies are analysed together, they do not support the role of TH as a treatment for adult TBI with respect to resultant mortality, outcomes and incidences of pneumonia. Crucially, this review is able to highlight the importance of the control group, as fever in the control group led to significantly more poor outcomes; therefore, potentially overemphasising the benefit of TH.
Implications of all the available evidence
Overall, this systematic review of RCTs does not support the role of TH in adult TBI patients, which is in keeping with the conclusions of the two most recent RCTs. 1,107
Introduction
There has been debate over both the overall efficacy of TH and the degree of hypothermia required to gain any positive clinical effect in the treatment of adult TBI. A previous study found some clinical benefit to TH in TBI,110 however the Eurotherm3235 Trial1 was stopped early concerns over participant safety. 1,110 Additionally, a RCT published in 2016111 showed that strict fever control resulted in similar clinical outcomes as prolonged TH. The most recent systematic reviews1,112 have also reported conflicting results. 110 A 2016 meta-analysis111 was unable to demonstrate improved survival and suggested that TH may increase the risk of new pneumonia and cardiovascular complications. Conversely, a large meta-analysis reported a benefit of TH but it was discussed that this benefit may be attributable to the fact that a large number of observational studies were included in this analysis. 113 Despite this discourse, TH is still routinely used in the treatment of raised ICP in the context of adult TBI.
Aims
The primary aim of this systematic review was to use RCTs to update the evidence base on the use of TH when administered to adult patients in intensive care following TBI. The main outcomes of interest were mortality, poor (unfavourable) outcomes and new pneumonia.
Secondary aims were (1) comparison of control group, (2) early (< 24 hours from injury) compared with late (> 24 hours from injury) TH, (3) the effect of duration of follow-up on mortality outcomes and (4) whether or not the date of publication had any effect on the outcomes of TH trials.
Materials and methods
Search methods for identification of trials
Searches were not restricted by date or by publication status. The search strategy is recorded in the protocol (see Report Supplementary Material 1). The dates were chosen to be complementary to, and have an overlap of 12 months with, the previous systematic review110 conducted by one of the co-authors; this was to capture any trials that were in the process of publication.
Other sources
Reference lists of all included trials and relevant review articles were hand-searched by the authors. When appropriate, authors were contacted directly for further information.
Ethics approval and consent
This study did not require ethics approval or individual participant consent.
Methodological criteria for selection of randomised controlled trials
The inclusion criteria were that trials must (1) be RCTs, (2) investigate adult moderate (i.e. a GCS of 9–12) or severe (i.e. a GCS of ≤ 8) TBI and (3) investigate TBI that was sustained following an acute, closed head injury. The use of TH was the intervention of interest. RCTs that did not have two treatment arms with TH compared with a control group were excluded. For the purpose of this review TH is defined as any intervention with the intention of reducing core body temperature to below the physiological norm (36 °C). The method of temperature reduction was noted during data extraction. Participant outcomes at follow-up were assessed using mortality and poor outcome data. There was a particular emphasis on outcomes recorded on a scale, for example the GOS, the Ranchos Los Amigos Scale or an equivalent scale. Reporting of poor outcomes includes mortality figures, in accordance with the usual reporting methodology.
Participants/population
To be included in the review, participants must be adults and must have sustained an acute, closed head injury. Adults were defined as being at the legal age for consent in the country the study was conducted in. Articles were excluded if they contained only neonatal or paediatric participants or participants with open head injuries (including gunshot wounds).
Only trials that met all inclusion criteria, and that did not meet any of the exclusion criteria, were included.
Data extraction
The output of all searches was exported into Microsoft Word (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) and two co-authors were involved at each stage of review. The PRISMA statement114 was followed at all three stages of review. First, duplicates from across the databases were removed. Following duplicate removal, the abstracts and titles were assessed against our inclusion and exclusion criteria. Second, abstracts were read in detail against the defined criteria. Third, the remaining articles were read in full and the final decision on inclusion or exclusion was made. A third reviewer was available to resolve any discrepancies in agreement. See Figure 9 for the PRISMA flow diagram.
Bias
The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing the risk of bias109 was used during the data extraction process. The following areas were assessed: selection, performance, detection, attrition and reporting bias. This covered the relevant areas of allocation concealment, blinding, ITT analysis and completeness of follow-up. In comparison to the previous review,110 academic bias was also included at this stage; academic bias was considered to be present if two or more RCTs included in this systematic review were by the same author.
The included RCTs were put into a domain-based assessment of risk of bias (see Report Supplementary Material 2), which included potential confounding factors. The maximum score available was 18 points, with a high score equating to the least risk of bias. Those scoring 14–18 (top quartile) had a low risk of bias and those scoring < 14 had a high risk of bias, as assessed by the domains.
Quality
A modified Jadad score was used to assess the quality of the included RCTs. 14 Blinding was not possible because of the nature of the intervention. Regarding randomisation, 1 point was awarded for randomisation being mentioned and a further point was awarded if randomisation was appropriate. No points were awarded if randomisation was not stated. Then, 1 point was given if all participants entered into the trial were accounted for at the end of the trial. This gave a maximum modified quality score of 3 points per RCT. Studies scoring 0, 1 or 2 points were considered low quality, with those scoring 3 points considered high quality. The quality of included RCTs was also assessed using the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing the risk of bias. 109
Data synthesis
Review Manager (RevMan; version 5.3; Cochrane Collaboration, The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen, Denmark) was used for data analysis.
Statistical analyses
Mortality, poor outcomes (including mortality) and pneumonia data were extracted and the RR and corresponding 95% CIs were calculated. The Mantel–Haenszel approach was used to assess the significance of the overall RR (RRoverall) as an effect estimate using the null hypothesis RRoverall = 1 using the z-test.
As per the Cochrane Handbook,109 both fixed and random effects were generated in the first instance for each analysis.
Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using the chi-squared and I2-index tests to estimate the degree of trial variability. Thresholds for interpretation of heterogeneity were also taken from the Cochrane Handbook, with 0–40% representing possible low heterogeneity, 30–60% representing possible moderate heterogeneity, 50–90% representing possible substantial heterogeneity and 75–100% representing possible high heterogeneity.
Sensitivity analysis
Forest plot analyses were performed for all studies and were performed separately for those deemed at least risk of bias as assessed using a Cochrane-based evaluation.
Results
The final analyses included 21 trials,1,48,59,60,63,64,69,71,73–77,107,108,115–120 including data for two new trials. 1,107 Figure 8 shows the PRISMA flow diagram for inclusion. One trial included in the 2014 review has now been published with additional data. 107 These trials enrolled 2299 participants. Only one trial did not include mortality data. 48,107 The quality of included RCTs and the characteristics and data extraction of the included studies is shown in Appendix 5 . The primary and secondary aims are addressed below. All subgroup analyses had fixed- and random-effects models generated. There was no difference in statistical significance so fixed-effects models have been used throughout. When RCTs had ‘not estimable’ in the RevMan plots, they were removed from the graph as they did not contribute statistically. Appendix 6 details the RCT inclusion differences between this systematic review and previous large reviews.
FIGURE 8.
The PRISMA flow diagram.

Risk of bias of included randomised controlled trials
There were two methods used for assessing the quality of included RCTs: the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing the risk of bias and a modified Jadad score. 109
Using the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing the risk of bias, each RCT was given a score out of 18. Two RCTs scored ≥ 14 (top quartile) so were considered as having a low risk of bias. Conversely, 18 RCTs scored ≤ 13 and so were considered as having a high risk of bias. See Appendix 7 on assessment of bias. These scores were used for further analysis of risk of bias for the primary outcomes of mortality, poor outcomes and new pneumonia.
Quality of included randomised controlled trials
On the modified Jadad score, those scoring 3 were high quality and those scoring 0, 1 or 2 were low quality. In total, six of the included studies were classed as high quality and 14 studies were classed as low quality. These scores were used for further analysis of quality for the primary outcomes of mortality, poor outcomes and new pneumonia.
Primary aims
Mortality results
Mortality was reported in 20 studies. Figure 9 shows mortality data for 20 studies, totalling 2270 participants. When the results of these 20 RCTs were statistically aggregated, there was a significant reduction in mortality in the TH group (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.74 to 0.96; p = 0.01). A fixed-effects model was used and supported by a moderate I2-index (I2 = 43%).
FIGURE 9.
Forest plot of mortality data for 20 studies. M–H, Mantel–Haenszel.

Mortality results with quality and risk-of-bias analysis
Six of the included studies were classed as high quality and 14 studies were classed as low quality, as per the modified Jadad score assessment of risk of bias (Figure 10). The high-quality studies showed a higher mortality in the TH group (RR 1.22, 95% CI 0.99 to 1.57), but this result was not significant (p = 0.06). The low-quality studies showed a higher mortality in the control group (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.58 to 0.81; p < 0.00001). There was significant heterogeneity between the two subgroups (I2 = 94.2%).
FIGURE 10.
Mortality results with quality and modified Jadad score assessment of risk-of-bias analysis. M–H, Mantel–Haenszel.
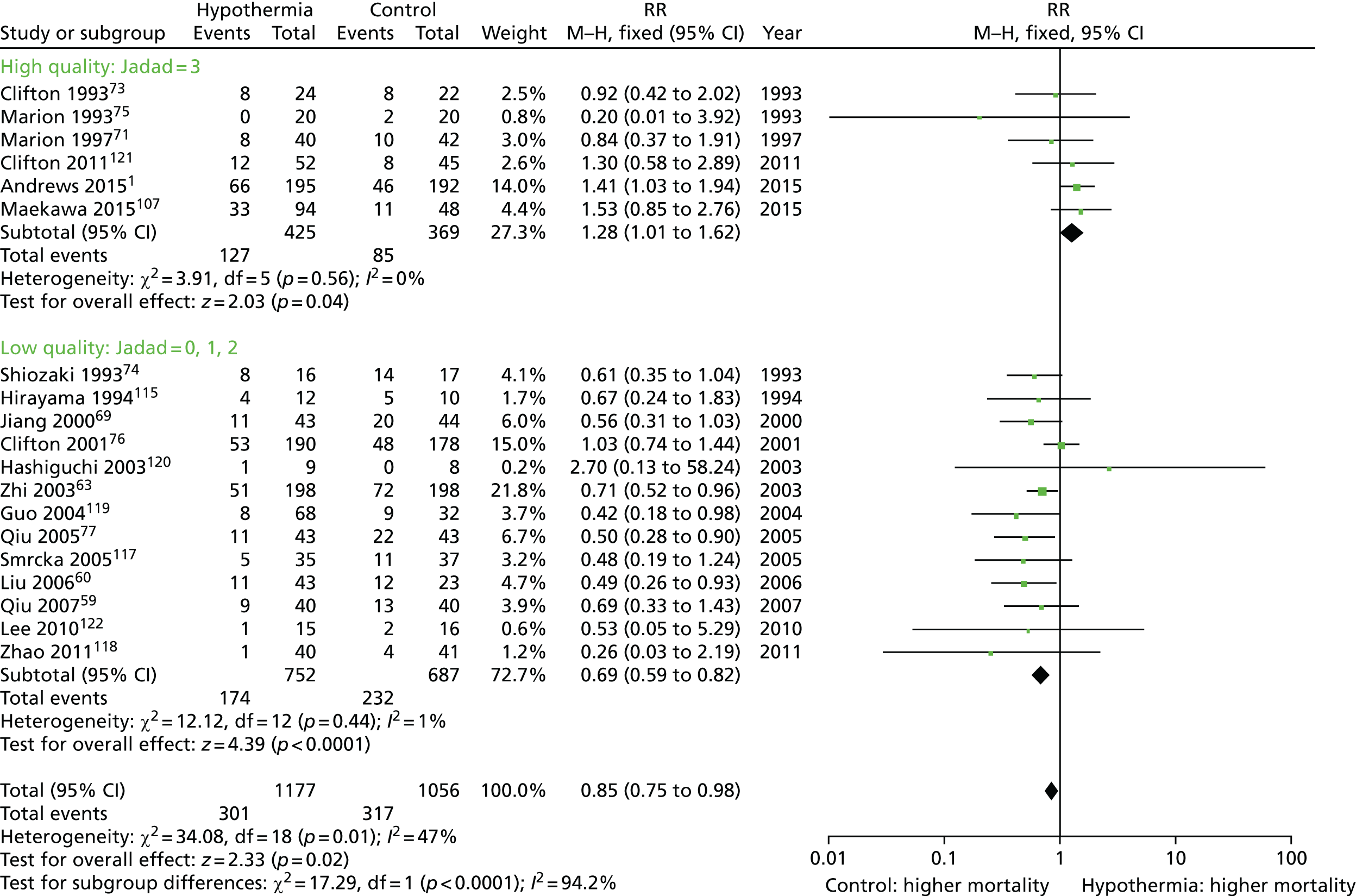
Risk-of-bias assessment was also undertaken using the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool and again affected mortality outcomes (Figure 11). Two studies had a low risk of bias and showed a higher mortality in the TH group (RR 1.37, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.79; p = 0.02), whereas the 18 studies having a high risk of bias showed a higher mortality in the control group (RR 0.72, 95% CI 0.62 to 0.84; p < 0.0001).
FIGURE 11.
Forest plot of mortality results with quality and Cochrane Collaboration assessment of risk-of-bias analysis. M–H, Mantel–Haenszel.

Poor outcomes
Twenty-one trials reported on poor outcome involving 2286 participants. There were significantly more poor outcomes in the control group than in the TH group (RR 0.81, 95% CI 0.75 to 0.87; p ≤ 0.00001) (Figure 12), with possible substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 72%).
FIGURE 12.
Forest plot of poor outcome. M–H, Mantel–Haenszel.

Poor outcome results with quality and risk-of-bias analysis
There were six high-quality studies that showed no significant difference in poor outcomes between the control and TH groups (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.92 to 1.16; p = 0.56). However, when the 15 low-quality studies were analysed together, they showed more poor outcomes in the control group (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.62 to 0.76; p < 0.00001).
When the two low-risk-of-bias studies were analysed, they showed that poor outcomes were more likely in the TH group (RR 1.16, 95% CI 1.02 to 1.32; p = 0.03). Conversely, when the 19 studies with a high risk of bias were analysed together, they showed significantly more poor outcomes in the control than the TH group (RR 0.70, 95% CI 0.64 to 0.77; p < 0.00001).
New pneumonia results
Thirteen studies reported new pneumonia, accounting for 1128 participants. There was significantly more new pneumonia in the TH group (RR 1.43, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.78; p = 0.001) (Figure 13) when all studies were analysed together.
FIGURE 13.
Forest plot of new pneumonia data. M–H, Mantel–Haenszel.

New pneumonia results with quality and risk-of-bias analysis
There were three high-quality studies that, when analysed together, showed no significance in new pneumonia between the two groups (RR 1.33, 95% CI 0.79 to 2.25; p = 0.28). In contrast, the 10 low-quality studies suggested significantly more new pneumonia in the TH group (RR 1.35, 95% CI 1.07 to 1.69; p = 0.01).
The two low-risk-of-bias studies showed no significant difference in new pneumonia between the two groups (RR 1.41, 95% CI 0.72 to 1.84; p = 0.32), whereas the 11 studies having a high risk of bias suggested significantly more new pneumonia in the TH group (RR 1.47, 95% CI 1.17 to 1.84; p = 0.0008).
Secondary aims
Mortality: comparison of control groups and comparison of controlled normothermia temperature ranges
The first subanalysis on mortality specifically assessed the methodology used for temperature management in the control groups. There was no significant difference in mortality between the TH group and the control group with controlled normothermia (RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.08; p = 0.25) with possible low heterogeneity (I2 = 25%). However, there was significantly greater mortality in the no temperature control group than in the TH group (RR 0.81, 95% CI 0.68 to 0.97; p = 0.02) with possible substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 63%).
The results for those RCTs that implemented controlled normothermia of any degree were analysed in isolation. The groups were split into those that ensured that their control groups were < 38 °C and those that included 38 °C within their normothermia control range. Those studies that stated controlled normothermia without specific temperature ranges were placed in the latter group. Those studies that controlled to < 38 °C showed no significant difference in mortality outcomes between the control group and TH group (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.32; p = 0.73). Contrastingly, those control groups that included 38 °C within their normothermia range showed significantly more mortality in their control groups (RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.44 to 0.87; p = 0.005).
Early therapeutic hypothermia compared with late therapeutic hypothermia
When mortality was analysed accounting for timing of TH from time of TBI, there were significant differences between the subgroups (Figure 14). For those participants with early hypothermia (< 24 hours from injury), there was significantly greater mortality in the control group than in the TH group [RR 0.76, 95% CI 0.64 to 0.90; p = 0.001 (1542 participants)] with possible low heterogeneity (I2 = 2%). Whereas, among those participants with TH induced ≥ 24 hours after injury, there was no significant difference in mortality between the control and TH groups [RR 1.08, 95% CI 0.86 to 1.34; p = 0.51 (641 participants)] with possible substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 79%). There was also possible substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 83.5%) between the early and late hypothermia subgroups.
FIGURE 14.
Forest plot of mortality analysed accounting for timing of TH from time of TBI. M–H, Mantel–Haenszel.

Mortality: effect of duration of follow-up
There was variation between the RCTs regarding duration of follow-up. Two groups were created that analysed those RCTs with follow-up for 3 months (five studies; 271 participants) compared with those with follow-up for > 6 months (14 studies; 1999 participants) (Figure 15). For those followed up for 3 months, there was no significant difference in mortality between the control and TH groups (RR 0.73, 95% CI 0.47 to 1.17; p = 0.20) with possible low heterogeneity (I2 = 0%), whereas studies with follow-up for > 6 months showed significantly greater mortality in the control group (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.74 to 0.98; p = 0.02), there was possible moderate heterogeneity in this subgroup (I2 = 55%). There was no heterogeneity between the two subgroups (I2 = 0%).
FIGURE 15.
Forest plot of the effect of duration of follow-up on trial results. M–H, Mantel–Haenszel.

Mortality: date of publication
Those studies that reported mortality data were split into two groups: five were published before 2000 (223 participants) and 15 were published in or after 2000 (2047 participants). Those published before 2000 showed no significant difference in mortality between the groups (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.49 to 1.04; p = 0.08), whereas those studies published in or after 2000 found higher mortality in the control group than the TH group (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.74 to 0.99; p = 0.03) (Figure 16).
FIGURE 16.
Forest plot of the effect of date of publication on outcome. M–H, Mantel–Haenszel.
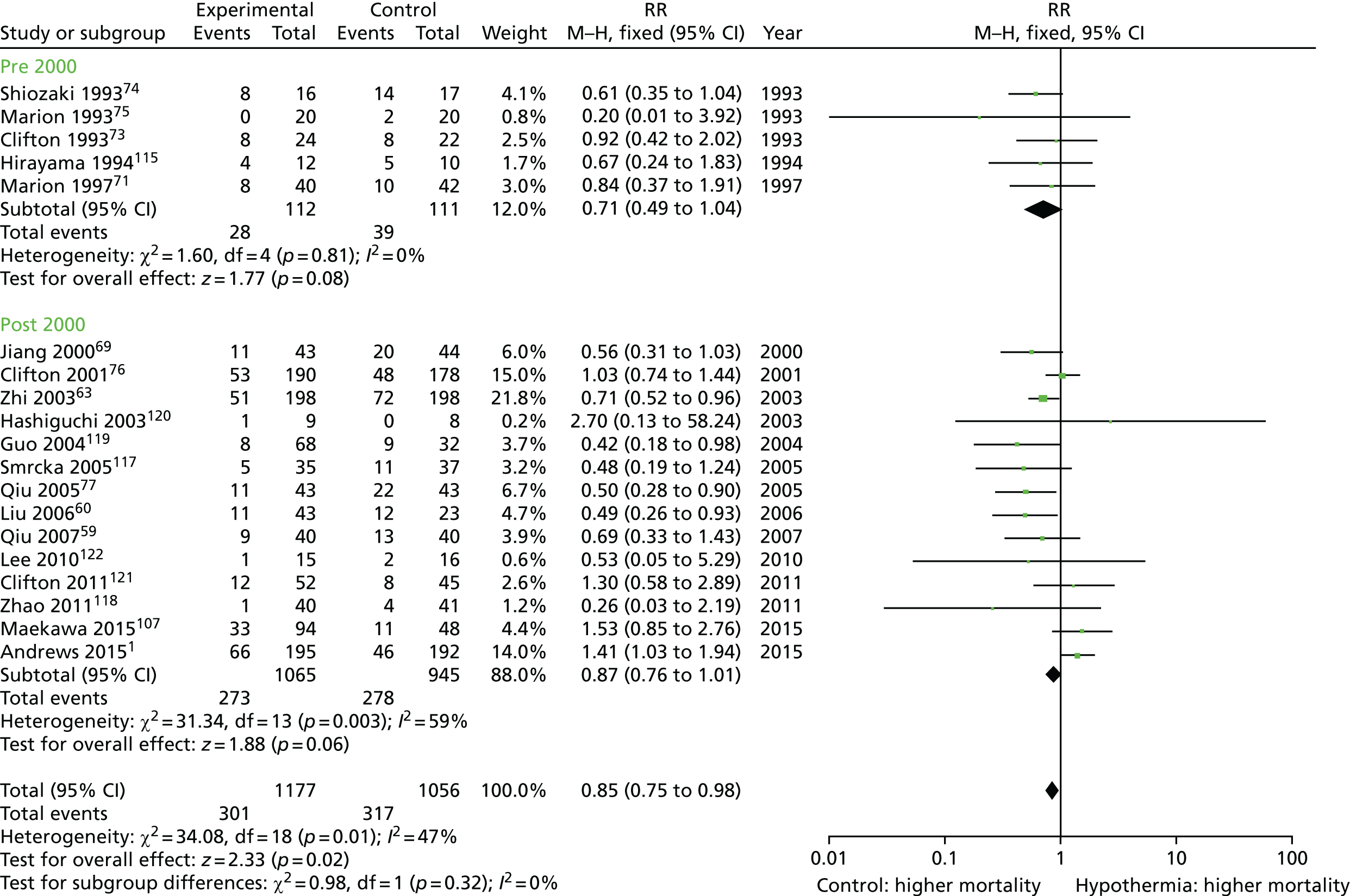
Discussion
Summary of results
Overall, the results of this systematic review shed doubt on the overall outcome benefits of TH. Low-quality studies are more likely than high-quality studies to show that TH improves mortality. In addition, this review also highlights the importance of temperature management in the control group of TH trials and, in particular, the avoidance of fever.
Explanation of results
Adding to the literature, this review has shown that the control group management is important in assessing the efficacy of TH. When the temperature of the control group is controlled (controlled normothermia), avoiding fever, then TH was no longer beneficial. Furthermore, when controlled normothermia included ‘fever’ temperatures then the control group had a greater mortality. This is significant because it suggests that it is not just the implementation of TH that is important, but also the maintenance of adequate fever control. The importance of fever control has implications for the conclusions suggested by RCTs; for example, the Eurotherm3235 Trial had a control population with values of normothermia and the results showed harm from TH. Studies that do not adequately maintain normothermia in their control groups may be overestimating the benefits of TH, as worse overall outcomes in the control groups may be down to poor fever control rather than lack of TH.
Subgroup heterogeneity appears to be important in a variety of analyses. When looking at the induction of TH, there is a lower mortality in those who had TH implemented within 24 hours; however, cooling after 24 hours conferred no mortality benefit compared with the control treatment. This could suggest that cooling early is most beneficial or that there are differences between the subgroups; this is supported by the possible substantial heterogeneity. The results of the ongoing POLAR (Prophylactic Hypothermia trial to Lessen Traumatic Brain Injury) study123 of early hypothermia for neuroprotection could provide further evidence to support this hypothesis. Those patients with late TH may have more severe injuries with more difficult to control ICP meaning that treatment was less likely to be successful regardless of time of TH onset. The two most recent RCTs both investigated late-onset TH. 1,107
Other studies have shown that subgroup differences are important in relation to surgical intervention; this is not always accounted for during statistical analysis of mortality and poor outcomes. These studies have provided evidence that TH may be more beneficial in those patients who are cooled after surgical haematoma evacuation than in those with diffuse brain injury. This review was unable to investigate this further because diffuse and focal TBI patients were commonly grouped together during data analysis.
Overall, this finding is important as it suggests that there may be certain subgroups of TBI patients who are more likely to benefit from TH. Differences could depend on the type of injury, surgical intervention before TH, early or late cooling and the temperature management within the control group. With all of these possible confounding factors, it is unsurprising that there are conclusion discrepancies among the most recent reviews.
Quality of evidence
Two methods were used to assess quality and the risk of bias: a modified Jadad score was used in conjunction with a domain-based assessment for risk of bias. The two latest RCTs1,107 were of high quality and had a low risk of bias. However, all other studies showed a high risk of bias as assessed by the objective domains. Previously, concern has been expressed that small, single-centre studies are distorting the conclusions. 110 This review highlights the importance of this as, when the larger, higher-quality RCTs were analysed separately, they showed consistently different conclusions to other trials.
Deviation from systematic review protocol
The original primary and secondary outcomes remained as published in the protocol (see Report Supplementary Material 1). However, several additional subgroup analyses were added as secondary outcomes following protocol publication.
Of the original secondary aims, some subgroup analyses could not take place because of a lack of information supplied within RCTs or homogeneity between the studies. These were depth of cooling on outcomes, effect of rate of rewarming, the duration of cooling on outcomes and the use of propofol sedation.
Data extraction was completed as per protocol. There was always agreement between the two co-authors undertaking the data extraction but a reason for exclusion of an article was not always documented.
The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing the risk of bias109 was used rather than the 1998 Downs and Black checklist. 124 The modified Jadad score for trial quality was added to increase the objectivity for claims of quality and risk of bias.
Limitations of the review
The main limitations of the previous reviews were the inclusion of many single-centre, low-quality RCTs; this has now been partly addressed with the addition of the two latest RCTs. However, as discussed above, underlying subgroup differences may be affecting the overall conclusions.
There was significant variation in the length of follow-up post injury, ranging from 3 months to 2 years. This has also been a factor in other systematic reviews. It is not possible to control this confounder because of the variations in the standalone RCT protocols. In the context of hypothermia after cardiac arrest, it has been suggested that 6 months is the earliest time point that neurological status should be assessed. 125
This review updated some of the original data used in the Crossley et al. 110 paper and these data extraction amendments have been included and analysed in this paper.
Similarities to, and differences from, other reviews
Although this review has several similarities to recent review papers, it also has some significant differences. Crossley et al. 110 were able to demonstrate a significant reduction in mortality and poor outcomes with the use of TH. However, Zhu et al. 111 found no difference in either of these outcomes between the TH and control groups. The latter systematic review is in agreement with other RCTs published since 2015: the Eurotherm3235 Trial found evidence of harm from TH,1 whereas B-HYPO (Brain Hypothermia study)107 found no improvement in outcomes from TH when compared with strict fever control or controlled normothermia; both studies assessed the use of late TH post TBI. Importantly, both of these RCTs avoided fever in their control groups, which does differ from the control groups of previous RCTs. 110,111 Previous systematic reviews reported a general belief that TH was associated with new pneumonia. However, until this review, only Zhu et al. 111 had been able to show significance from this result. This current systematic review has gone some way to explain the varying conclusions on the effectiveness of TH in TBI by analysing the main subgroups.
Ongoing trials of therapeutic hypothermia for traumatic brain injury
There are two ongoing RCTs that are yet to be published: the POLAR RCT126 and the RCT of Long-term Mild Hypothermia for Severe Traumatic Brain Injury trial (LTH-1). 127 Both author groups were contacted during the production of this systematic review.
The POLAR RCT is a neuroprotection study, the results of which may support the finding of this review that early hypothermia is beneficial.
In the earlier 2014 systematic review,110 the B-HYPO107 investigators kindly provided preliminary data from their RCT. The full RCT has now been published and has been included in this updated systematic review.
Conclusions
Overall, this updated systematic review shows that, when high-quality studies of the use of TH in TBI are reviewed together, they show no significant differences in mortality, poor outcomes or new pneumonia; therefore, the use of TH is not evidenced. Conversely, the low-quality studies are more likely to show a benefit of TH in TBI. In addition, this review highlights the importance of fever control as, in those studies that included control groups with no temperature control, there was a higher rate of mortality than in those controlled to normothermia.
Key messages
-
High-quality studies show no significant difference in mortality, poor outcomes or new pneumonia.
-
When temperature in the control group is controlled normothermia, there is no difference in mortality.
Chapter 6 A biological effect or an imbalance of co-interventions? Exploratory analyses of the Eurotherm3235 Trial
Introduction
The Eurotherm3235 Trial was pragmatic and data collection was not overburdensome. We believe that this is one reason for the success of the trial; however, our data collection was not sufficiently comprehensive to allow investigation of possible mechanisms of the unexpected result. We are grateful to the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment programme for extending our funding to allow us to conduct a separate, retrospective study of the details of individual patient care in the main trial and mode of death, when appropriate. We considered this ‘additional data collection’ to be an important exercise for allowing full implementation of the trial results.
Background
Although early trials of TH after TBI showed that this treatment improved functional outcome, two recent multicentre trials, NABISH (National Acute Brain Injury Study: Hypothermia) and B-HYPO,76,107 have failed to confirm a neuroprotective effect. In a systematic review, Crossley et al. 110 reported that TH might be beneficial in the treatment of TBI, although most of the positive trials that were included were of low quality and probably overestimated the effects of hypothermia. Madden and DeVon128 showed that controlled normothermia, avoiding fever, improved functional outcomes, whereas hypothermia was associated with unfavourable outcomes. Additionally, three large, paediatric multicentre trials have not found evidence of benefit of TH, showing an increment in mortality in this population. 129–131
The Eurotherm3235 Trial was not designed to investigate why TH was associated with a poorer outcome; however, this relationship may arise because of either a biological effect of TH or an imbalance in co-interventions used in the hypothermia or control groups.
We therefore undertook a retrospective additional data collection exercise with the following aims:
-
to assess the mode of death by treatment allocation
-
to compare aspects of clinical management by treatment allocation including surgical intervention(s), medical treatments and drug dosages for management of raised ICP
-
to compare the incidence of comorbidities and complications of care by treatment allocation
-
to compare the available physiological data (not available in the original study) by treatment allocation.
Material and methods
Ethics approval for the collection of additional data through a bespoke case report form (CRF) was obtained from the Scotland Research Ethics Committee and the Bradford Research Ethics Committee in November 2015. A total of 47 centres in 18 countries that had randomised 387 participants from November 2009 to October 2014 were contacted. A total of 21 UK recruiting sites were invited to participate on 4 December 2015, whereas the 26 non-UK centres were required to obtain permission from their ethics/hospital committee prior to beginning participation.
The data collection started on 1 January 2016 and the deadline for completion of the CRFs was set to 31 July 2016. This was 6 years and 2 months after the beginning of the main trial and 1 year and 3 months after the last 6-month outcome assessment. Paper CRFs were used for the retrospective data collection and they were completed from the participant’s medical notes, imaging and 24-hour ICU charts. There were 15 areas of interest, including comorbidities, (likely) cause of death and, for days 1–7, post randomisation information on medical and surgical interventions for raised ICP (ICP of > 20 mmHg), sedation and analgesia regimes, cardiovascular support, blood results and infection(s).
The additional data collection exercise provided sufficient information to calculate a modified and abbreviated sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) to assess organ dysfunction. The full SOFA is composed of six domains, scoring respiratory, cardiovascular, hepatic, coagulation, renal and neurological systems, graded from 0 to 4 depending on the degree of dysfunction/failure. For this exploratory analysis, we defined a modified SOFA excluding the respiratory and neurological domains. The rationale for this was that in the Eurotherm3235 Trial all participants were sedated (masking neurological assessment) and mechanically ventilated (affecting respiratory system SOFA) to control ICP at stage I. Formal assessment of GCS was not practical in many cases as a result of concerns about the likely effect of a sedation break on ICP. For the abbreviated SOFA, each of the remaining four organ domains were scored either as normal (0) or abnormal (1) and the sum of these was calculated. These scores were then used to characterise participants as having either minimal organ dysfunction (modified SOFA score of ≤ 1) or significant organ dysfunction (SOFA score of > 1).
Completed CRFs were sent by e-mail or post to the Eurotherm3235 Trial office at the Western General Hospital in Edinburgh. Eurotherm3235 Trial staff (Claire Battison, Trial Manager, and Irene Puddu, Research Fellow) worked closely with local clinicians to obtain complete and accurate data within the set time frame.
Statistical analysis
For all data collected, descriptive statistics by allocated treatment and dichotomised by GOSE outcome (favourable vs. unfavourable) were generated.
Results
Data
Responses were received from a total of 33 centres out of the 47 centres in the main trial, of which 16 (48%) were UK and 17 (52%) were non-UK sites. A total of 286 anonymised CRFs (UK, n = 163; and non-UK, n = 123) were returned by e-mail or post to the Eurotherm3235 Trial office by 31 July 2016. Data were returned on 143 participants randomised to TH and 143 participants randomised to the control groups. This distribution was similar to the main trial.
Demographics and baseline characteristics
The demographics of this sample were well matched between the TH and control group and were very similar to those of the main trial ITT population. Table 13 shows that the baseline characteristics of the two ‘additional data collection’ groups were similar in all respects. Furthermore, the TH and control groups were well balanced for comorbidities (see Table 13).
| Data | Treatment group | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia (N = 143)a | Control (N = 143) | ||
| Characteristic | |||
| Aged < 45 years, n (%) | 95 (66.4) | 95 (66.4) | 0.900 |
| Age (years), median (interquartile range) | 35 (24–49) | 36 (26–48) | 0.966 |
| Male, n (%) | 115 (80.4) | 120 (83.9) | 0.537 |
| Mechanism of injury, n (%) | |||
| Road traffic accident: pedestrian | 17 (12.0) | 22 (15.4) | 0.319 |
| Road traffic accident: motor vehicle | 46 (32.4) | 34 (23.8) | |
| Cycling accident | 5 (3.5) | 9 (6.3) | |
| Fall | 62 (43.7) | 61 (42.7) | |
| Sports injury | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Assault | 11 (7.7) | 17 (11.9) | |
| Isolated TBI, n (%) | 88 (61.5) | 99 (69.2) | 0.214 |
| GCS motor score, n (%) | |||
| 1 or 2 | 41 (28.7) | 35 (24.5) | 0.503 |
| 3–6 | 102 (71.3) | 108 (75.5) | |
| Pupillary response, n (%) | |||
| Both reacting | 106 (74.1) | 107 (74.8) | 1.0 |
| One or neither reacting | 37 (25.9) | 36 (25.2) | |
| Marshall classification, n (%) | |||
| Diffuse axonal injury I–III | 55 (38.5) | 58 (40.6) | 0.918 |
| Diffuse axonal injury IV | 16 (11.2) | 13 (9.1) | |
| Any lesion surgically removed | 32 (22.4) | 34 (23.8) | |
| High-density or mixed-density lesion | 40 (28.0) | 38 (26.6) | |
| At randomisation | |||
| Time from injury ≥ 12 hours, n (%) | 130 (90.9) | 133 (93.0) | 0.664 |
| Intracranial pressure at randomisation (mmHg), median (interquartile range) | 24 (22–27) | 23 (22–26) | 0.473 |
| Core temperature at randomisation (°C), median (interquartile range) | 36.9 (36.4–37.4) | 37.1 (36.6–37.6) | 0.051 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Arthritis, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 3 (2.2) | 5 (3.6) | 0.712 |
| No | 135 (97.8) | 132 (96.4) | |
| Osteoporosis, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0.997 |
| No | 138 (99.3) | 140 (100) | |
| Asthma, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 8 (5.8) | 5 (3.6) | 0.561 |
| No | 129 (94.2) | 133 (96.4) | |
| COPD/emphysema, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 6 (4.3) | 4 (2.9) | 0.739 |
| No | 133 (95.7) | 136 (97.1) | |
| Angina, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.7) | 0.481 |
| No | 138 (99.3) | 139 (99.3) | |
| CCF, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 4 (2.9) | 3 (2.1) | 0.992 |
| No | 135 (97.1) | 137 (97.9) | |
| MI, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 3 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.243 |
| No | 136 (97.8) | 140 (100) | |
| Neurological disease, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 6 (4.3) | 3 (2.1) | 0.491 |
| No | 133 (95.7) | 137 (97.9) | |
| Stroke/TIA, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 1 (0.7) | 2 (1.4) | 0.995 |
| No | 138 (99.3) | 138 (98.6) | |
| PVD, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 2 (1.4) | 2 (1.4) | 0.62 |
| No | 137 (98.6) | 138 (98.6) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 8 (5.8) | 5 (3.6) | 0.561 |
| No | 131 (94.2) | 135 (96.4) | |
| GI disease, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 5 (3.6) | 2 (1.4) | 0.438 |
| No | 134 (96.4) | 138 (98.6) | |
| Depression, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 16 (11.5) | 12 (8.6) | 0.537 |
| No | 123 (88.5) | 128 (91.4) | |
| Anxiety, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 6 (4.3) | 8 (5.7) | 0.795 |
| No | 133 (95.7) | 132 (94.3) | |
| Visual impairment, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0.997 |
| No | 138 (99.3) | 140 (100) | |
| Hearing impairment, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.7) | 0.481 |
| No | 138 (99.3) | 139 (99.3) | |
| Disc disease, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 1 (0.7) | 2 (1.4) | 0.995 |
| No | 137 (99.3) | 137 (98.6) | |
| BMI of > 30 kg/m2, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 4 (2.9) | 6 (4.3) | 0.756 |
| No | 135 (97.1) | 134 (95.7) | |
| Secondary insults pre ICU admission | |||
| Hypoxia, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 27 (20.9) | 17 (13.2) | 0.136 |
| No | 102 (79.1) | 112 (86.8) | |
| Hypoxia detected, n (%) | |||
| Arterial gases | 13 (48.2) | 13 (81.3) | 0.031 |
| Clinical signs | 12 (44.4) | 1 (6.3) | |
| Both | 2 (7.4) | 2 (12.5) | |
| Hypotension, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 15 (12.0) | 11 (8.6) | 0.493 |
| No | 110 (88.0) | 117 (91.4) | |
| Hypotension detected, n (%) | |||
| Blood pressure | 10 (55.6) | 7 (53.9) | 0.638 |
| Clinical signs | 1 (5.6) | 2 (15.4) | |
| Both | 7 (38.9) | 4 (30.8) | |
The incidence of pre-ICU admission of secondary brain injuries because of either hypoxia [n = 27 (20.9%) in TH vs. n = 17 (13.2%) in the control group; p = 0.136] or hypotension [n = 15 (12.0%) in TH vs. n = 11 (8.6%) in the control group; p = 0.493] was not different between the groups. However, clinical signs of hypoxia were proportionally more frequent in the TH group (n = 12, 44.4%) than in the control group (n = 1, 6.3%), and blood gas evidence of hypoxia was more frequent in the control group [13 (48.2%) in TH vs. 13 (81.3%) in the control group; p = 0.031], although the absolute number of arterial gases identifying hypoxia were identical in both groups (see Table 13).
Additional data collection sample mortality
Hypothermia was associated with a statistically significant increased risk of death at 6 months (Figure 17). In the additional data collection sample, a total of 78 participants died: 46 participants in the TH group (32.2%) and 32 participants in the control group (22.5%) (HR 1.624, 95% CI 1.025 to 2.573; p = 0.0388). These data were consistent with the ITT study population and suggest no reporting bias in this retrospective cohort.
FIGURE 17.
Survival curve between randomisation and 6 months by treatment allocation in the additional data collection cohort.

Cause of death
Table 14 shows that the number of deaths due to brain stem death (BSD) was the same in both groups, but because of other causes of death with TH, BSD represented a greater proportion in the control group [12 (28.6%) deaths in TH vs.12 (42.3%) deaths in control group]. In the TH group, pathologies with a strong inflammatory component, including multiorgan failure (MOF), infection and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), were more commonly attributed to causing death in the TH group [15 (35.7%) deaths in TH vs. 5 (19.1%) deaths in control group; p = 0.618].
| Cause of Death | Treatment group, n (%) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| BSD | 12 (28.6) | 11 (42.3) | 0.618 |
| MOF/sepsis/ARDS | 15 (35.7) | 5 (19.2) | |
| Neurological/withdrawal | 11 (26.2) | 7 (26.9) | |
| Cardiac event | 2 (4.8) | 2 (7.7) | |
| Other | 2 (4.8) | 1 (3.9) | |
Clinical management and interventions
Intracranial pressure management: medical therapy
The main trial results showed that the mean daily ICP was similar in the two groups. During the first 4 days after randomisation, there were fewer failures of stage II therapy to control ICP in TH than in the control group (57 vs. 84 participants). In this exploratory analysis, the use of medical treatments to control ICP was similar in both groups over days 1–7 after randomisation: 128 participants (92.1%) in the TH group received medical treatments for raised ICP compared with 124 participants (91.9%) in the control group (p = 0.88) (see Table 15). There was no significant difference in the average number of participants treated with hypertonic saline per day [mean 35.0 (SD 6.2) in the TH group vs. mean 39.6 (SD 10.9) in the control group; p = 0.353] or the average number of daily treatments given [mean 1.9 (SD 0.7) in TH group vs. mean 2.5 (SD 0.9) in the control group; p = 0.15]. Similarly, for mannitol, the average number of participants treated (mean 37.0 (SD 9.4) in the TH group vs. [mean 43.3 (SD 16.0) in the control group; p = 0.388)] and the average number of daily treatments [2.0 (2.0–2.0) in the TH group vs. 2.0 (2.0–2.0) in the control group; p = 0.71] were not significantly different. The average number of daily treatments with furosemide was statistically significantly higher in the control group than the TH group [mean 1.2 (SD 0.4) in the TH group vs. mean 1.9 (SD 0.4) in the control group; p = 0.004], but there was no difference in the average number of participants treated per day [mean 13.3 (SD 4.3) in the TH group vs. mean 15.7 (SD 5.6) in the control group; p = 0.384] (Table 15).
| Management | Treatment group | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Treatment for raised ICP, mean (SD) | |||
| Yes | 128 (92.1) | 124 (91.9) | 0.88 |
| No | 11 (7.9) | 11 (8.1) | |
| ICP treatments | |||
| Hypertonic saline, mean (SD) | 35.0 (6.2) | 39.6 (10.9) | 0.353 |
| Hypertonic saline (treatments/day), mean (SD) | 1.9 (0.7) | 2.5 (0.9) | 0.15 |
| Mannitol, median (SD) | 37.0 (9.4) | 43.3 (16) | 0.388 |
| Mannitol (treatments/day) (range) | 2.0 (2.0–2.0) | 2.0 (2.0–2.0) | 0.71 |
| Frusemide, mean (SD) | 13.3 (4.3) | 15.7 (5.6) | 0.384 |
| Frusemide (treatments/day), mean (SD) | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.9 (0.4) | 0.004 |
| Decompressive craniectomy, mean (SD) | |||
| Before randomisation | |||
| Yes | 21 (15.4) | 23 (16.4) | 0.952 |
| No | 115 (84.6) | 117 (83.6) | |
| After randomisation | |||
| Yes | 34 (24.8) | 37 (26.2) | 0.893 |
| No | 103 (75.2) | 104 (73.8) | |
| Craniectomy type, mean (SD) | |||
| Hemicraniectomy | 29 (58.0) | 37 (64.9) | 0.593 |
| Bifrontal | 21 (42.0) | 20 (35.1) | |
Intracranial pressure management: surgical treatment
The surgical management of raised ICP was also similar between groups. The number of participants undergoing decompressive craniectomy before randomisation was 21 (15.4%) in the TH group, compared with 23 (16.3%) in the control group (p = 0.952), and after randomisation was 34 (24.8%) in the TH group, compared with 37 (26.2%) in the control group (p = 0.893) (see Table 15). The proportion of participants undergoing hemicraniectomy was slightly greater in the control group than in the TH group [29 (58.0%) in TH group vs. 37 (64.9%) in the control group], whereas bifrontal craniectomy was more common in the TH group than in the control group [21 (42.0%) in the TH group vs. 20 (35.1%) in the control group]. Only one participant in each group underwent decompressive craniectomy before and after randomisation. However, these distributions were not significantly different between the groups (p = 0.593) (see Table 15).
Follow-up computed tomography
Follow-up CT was performed in significantly more participants in the control group than the TH group: 105 (80.8%) in TH group compared with 120 (90.2%) in the control group (p = 0.045) (Table 16). The distribution of Marshall scores based on the second CT scan was similar in both groups, with no statistically significant differences (p = 0.323). In both the TH and CG groups of the additional collection exercise, type II diffuse injury and high- or mixed-density lesion not evacuated were the most common pathologies observed [26 participants (24.8%) in the TH group vs. 31 participants (26.7%) in the control group, for both] (see Table 16). For both the TH group and the control group, the distribution of Marshall scores with the type of decompressive craniectomy was not significantly different (p = 0.506 in the TH group; p = 0.189 in the control group) (see Table 16). In the TH group, removable lesions were most frequently associated with both hemicraniectomy and bifrontal craniectomy [10 participants (41.7%) had a hemicraniectomy vs. five participants (38.5%) who had a bifrontal procedure]. By contrast, in the control group, removable lesions were most commonly associated with hemicraniectomy (14 participants, 46.7%), but a type II diffuse injury was slightly more common in those receiving bifrontal craniectomy (four participants, 28.6%). For both hemicraniectomy and bifrontal craniectomy, the distribution of Marshall scores by treatment allocation was also not significantly different (p = 0.787 for hemicraniectomy; p = 0.598 for bifrontal craniectomy) (see Table 16).
| CBT classification of TBI lesion | Craniectomy type, n (%) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Follow-up CT | |||
| Yes | 105 (80.8) | 120 (90.2) | 0.045 |
| No | 25 (19.2) | 13 (9.8) | |
| Marshall classification | |||
| Diffuse injury I (no visible pathology) | 2 (1.9) | 2 (1.7) | 0.323 |
| Diffuse injury II | 26 (24.8) | 31 (26.7) | |
| Diffuse injury III (swelling) | 18 (17.1) | 8 (6.9) | |
| Diffuse injury IV (shift) | 13 (12.4) | 16 (13.8) | |
| Any lesion surgically removed | 20 (19.0) | 28 (24.1) | |
| High- or mixed-density lesion | 26 (24.8) | 31 (26.7) | |
| Hypothermia, n (%) | |||
| Hemicraniectomy | Bifrontal | ||
| Marshall classification | |||
| Diffuse injury I (no visible pathology) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.506 |
| Diffuse injury II | 3 (12.5) | 2 (15.4) | |
| Diffuse injury III (swelling) | 1 (4.2) | 3 (23.1) | |
| Diffuse injury IV (shift) | 4 (16.7) | 2 (15.4) | |
| Any lesion surgically removed | 10 (41.7) | 5 (38.5) | |
| High- or mixed-density lesion | 5 (20.8) | 1 (7.7) | |
| Control, n (%) | |||
| Hemicraniectomy | Bifrontal | ||
| Marshall classification | |||
| Diffuse injury I (no visible pathology) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (7.1) | 0.189 |
| Diffuse injury II | 2 (6.7) | 4 (28.6) | |
| Diffuse injury III (swelling) | 3 (10.0) | 1 (7.1) | |
| Diffuse injury IV (shift) | 5 (16.7) | 3 (21.4) | |
| Any lesion surgically removed | 14 (46.7) | 3 (21.4) | |
| High- or mixed-density lesion | 6 (20.0) | 2 (14.3) | |
| Treatment group, n (%) | |||
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Marshall classification | |||
| Diffuse injury I (no visible pathology) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.787 |
| Diffuse injury II | 3 (12.5) | 2 (6.7) | |
| Diffuse injury III (swelling) | 1 (4.2) | 3 (10.0) | |
| Diffuse injury IV (shift) | 4 (16.7) | 5 (16.7) | |
| Any lesion surgically removed | 10 (41.7) | 14 (46.7) | |
| High- or mixed-density lesion | 5 (20.8) | 6 (20.0) | |
| Bifrontal: treatment group, n (%) | p-value | ||
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Marshall classification | |||
| Diffuse injury I (no visible pathology) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (7.1) | 0.598 |
| Diffuse injury II | 2 (15.4) | 4 (28.6) | |
| Diffuse injury III (swelling) | 3 (23.1) | 1 (7.1) | |
| Diffuse injury IV (shift) | 2 (15.4) | 3 (21.4) | |
| Any lesion surgically removed | 5 (38.5) | 3 (21.4) | |
| High- or mixed-density lesion | 1 (7.7) | 2 (14.3) | |
Sedation and analgesia
Midazolam infusion was used more often in the TH group: the mean number of participants per day was 96.0 (SD 12.8) in the TH group compared with 78.7 (SD 16.0) in the control group (p = 0.046), with the same hourly infusion rate in both groups [median 10.0 (IQR 10.0–10.0) mg/hour in the TH group vs. median 10.0 (IQR 10.0–10.0) mg/hour in the control group; p = 0.71) (Table 16). Alfentanil and fentanyl were the most commonly used opioids in all centres. The number of participants receiving alfentanil each day was higher in the TH group than in the control group [mean 37.1 (SD 4.7) in the TH group vs. mean 27.7 (SD 5.2) in the control group; p = 0.004], but the hourly dose was the same in both groups [median 2.5 (IQR 2.5–2.5) mg/hour in the TH group vs. median 2.5 (IQR 2.5–2.5) mg/hour in the control group; p = 1.0]. In contrast, the number of participants treated per day with fentanyl was not significantly different between groups [mean 56.0 (SD 6.9) in the TH group vs. mean 58.4 (SD 7.7) in the control group; p = 0.545] or the hourly dose [median 250 (IQR 250–250) µg/h in the TH group vs. median 250 (IQR 250–250) µg/h in the control group; p = 0.71] (see Table 17).
The average number of participants sedated with propofol per day was similar in both groups: a total of 89.9 (SD 14.2) participants in the TH group, compared with 79.1 (SD 17.8) participants in the control group (p = 0.236). The mean daily dose of 4615.3 (SD 658.8) mg/day in the TH group compared with 4801.4 (SD 657.0) mg/day in the control group (p = 0.606) (see Table 15). Correcting the daily dose for the participants’ weight did not reveal any between-group difference: 60.0 (SD 8.6) mg/kg/day in the TH group compared with 62.7 (SD 5.4) mg/kg/day in the control group (p = 0.5). After adjustment for age, post resuscitation GCS motor component, time from injury and pupil reactivity, no significant differences in the average daily dose of propofol in each group were found. A potentially toxic level infusion rate of propofol (> 5mg/kg/hour) was used in a few participants per day in both groups [median 3.0 participants (IQR 2.3–5.3) in the TH group and median 4.0 participants (IQR 3.0–4.0) in the control group; p = 0.535].
Atracurium was the predominant neuromuscular blocking agent used in all 33 centres. The number of participants receiving atracurium was significantly greater in the TH group [mean 31.1 (SD 6.8)] than in the control group [mean 22.0 (SD 4.5)] (p = 0.012) after randomisation. However, the median hourly infusion rate was slightly higher in the control group than in the TH group: median 50.0 (IQR 50.0–50.0) mg/hour in the TH group, compared with median 60.0 (IQR 50.8–60.0) mg/hour in the control group (p = 0.017) (see Table 17).
| Intervention | Treatment group | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Sedation | |||
| Midazolam, mean (SD) | 96.0 (12.8) | 78.7 (16.0) | 0.046 |
| Midazolam (mg/hour), median (IQR) | 10.0 (10.0–10.0) | 10.0 (10.0–10.0) | 0.71 |
| Analgesia | |||
| Fentanyl, mean (SD) | 56 (6.9) | 58.4 (7.7) | 0.545 |
| Fentanyl (µg/hour), median (IQR) | 250.0 (250.0–250.0) | 250.0 (250.0–250.0) | 0.71 |
| Alfentanil, mean (SD) | 37.1 (4.7) | 27.7 (5.2) | 0.004 |
| Alfentanil (mg/hour), median (IQR) | 2.5 (2.5–2.5) | 2.5 (2.5–2.5) | 1 |
| Sedation, mean (SD) | |||
| Propofol | 89.9 (14.2) | 79.1 (17.8) | 0.236 |
| Propofol (mg/day) | 4615.3 (658.8) | 4801.4 (657.0) | 0.606 |
| Propofol (mg/kg/day), mean (SD) | 60.0 (8.6) | 62.7 (5.4) | 0.5 |
| Propofol (mg/kg/hour), mean (SD) | 2.5 (0.4) | 2.6 (0.2) | 0.495 |
| Propofol number reaching toxic dose (> 5 mg/kg/hour), median (IQR) | 3.0 (2.3–5.3) | 4.0 (3.0–4.0) | 0.535 |
| NMB | |||
| Atracurium, mean (SD) | 31.1 (6.8) | 22.0 (4.5) | 0.012 |
| Atracurium (mg/hour), median (IQR) | 50.0 (50.0–50.0) | 60.0 (50.8–60.0) | 0.017 |
Cardiovascular support
The use of drugs to support the cardiovascular system was greater in the TH group than in the control group. The average number of participants receiving noradrenaline per day [mean 95.4 (SD 12.9) in the TH group vs. mean 78.1 (SD 18.7) in the control group] and the daily infusion rate [mean 15.3 (SD 3.5) mg/day in the TH group vs. mean 12.2 (SD 2.5) mg/day in the control group] were not significantly different (p = 0.067 and p = 0.078, respectively) (Table 18). Dobutamine was used in more TH participants [mean 7.3 (SD 3.1) participants/day] than control group participants [mean 2.3 (SD 1.0) participants/day] (p = 0.002), although the daily infusion rates were similar [median 292.5 (IQR 221.3–466.9) mg/day in the TH group vs. median 315.0 (IQR 193.9–441.9) mg/day in the control group; p = 0.71]. Similarly, more participants received daily vasopressin in the TH group [mean 5.7 (SD 2.4)] than in the control group [mean 1.9 (SD 0.9)] (p = 0.002), with a daily dose of median 24.9 (IQR 16.7–31.6) UI/day in the TH group compared with median 60.4 (IQR 6.0–778.8) UI/day in the control group (p = 0.71) (see Table 18).
| Cardiovascular support | Treatment group | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Noradrenaline, mean (SD) | 95.4 (12.9) | 78.1 (18.7) | 0.067 |
| Noradrenaline (mg/day), mean (SD) | 15.3 (3.5) | 12.2 (2.5) | 0.078 |
| Dobutamine, mean (SD) | 7.3 (3.1) | 2.3 (1.0) | 0.002 |
| Dobutamine (mg/day), median (IQR) | 292.5 (221.3–466.9) | 315.0 (193.9–441.9) | 0.71 |
| Vasopressin, mean (SD) | 5.7 (2.4) | 1.9 (0.9) | 0.002 |
| Vasopressin (units/day), median (IQR) | 24.9 (16.7–31.6) | 60.4 (6.0–778.8) | 0.71 |
Steroids
The number of participants receiving steroids was greater in the TH group [23 (17.8%)] than in the control group [9 (6.7%)] (p = 0.01) (Table 19). The most frequently used steroid was hydrocortisone: 20 participants, with a median daily dose of 100 mg (range 25–600 mg), used this steroid in the TH group compared with six participants, with a median daily dose of 125 mg (range 50–200 mg), in the control group.
| Intervention | Treatment group | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Receiving steroids, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 23 (17.8) | 9 (6.7) | 0.01 |
| No | 106 (82.2) | 125 (93.3) | |
| Receiving hydrocortisone, n (%) | 2.9 (3.19) | 0.9 (0.90) | 0.136 |
| Fluid balance during randomisation | |||
| Patients with a positive daily balance, n (%) | 84.4 (19.2) | 87.3 (17.0) | 0.773 |
| Patients with a negative daily balance, n (%) | 32.9 (13.9) | 30.9 (11.3) | 0.773 |
| Fluid balance (ml/day) mean (SD) | 781.7 (409.9) | 657.3 (406.6) | 0.579 |
Fluid balance
Daily fluid balance was similar in both groups. The number of participants per day with a positive fluid balance [mean 84.4 participants (SD 19.2) in the TH group vs. mean 87.3 (SD 17.0) in the control group; p = 0.773] or negative fluid balance [mean 32.9 (SD 13.9) in the TH group vs. mean 30.9 (SD 11.3) in the control group; p = 0.773] was similar. Average daily fluid balance was also similar between the groups [mean 781.7 (SD 409.9) ml in TH vs. mean 657.3 (SD 406.6) ml in control group; p = 0.579] (Table 19).
Laboratory results and organ failure
There were no significant differences in the average daily haemoglobin [mean 102.4 (SD 2.8) g/l in the TH group vs. mean 102.8 (SD 4.6) g/l in the control group; p = 0.839], haematocrit [mean 0.3 (SD 0.0) in the TH group vs. mean 0.3 (SD 0.0) in the control group; p = 0.139] or platelet count [mean 163.1 (SD 15.2) × 109/l in the TH group vs. mean 195.5 (SD 36.9) × 109/l in the control group; p = 0.053] between the two groups (Table 20).
| Analysis | Treatment group | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Haemoglobin (g/l), mean (SD) | 102.4 (2.8) | 102.8 (4.6) | 0.839 |
| Haematocrit (%), mean (SD) | 0.3 (0.0) | 0.3 (0.0) | 0.139 |
| White cell count (× 109/l), mean (SD) | 9.9 (0.9) | 11.0 (0.7) | 0.031 |
| Neutrophils (× 109/l), mean (SD) | 7.8 (0.6) | 9.0 (0.7) | 0.005 |
| Platelets (× 109/l), mean (SD) | 163.1 (15.2) | 195.5 (36.9) | 0.053 |
| APTT (seconds), mean (SD) | 33.2 (2.1) | 31.2 (1.3) | 0.046 |
| APTTr, mean (SD) | 1.2 (0.1) | 1.1 (0.0) | 0.037 |
| Urea (mmol/l), mean (SD) | 4.30 (0.83) | 4.33 (1.00) | 0.959 |
| Sodium (mmol/l), median (range) | 145.2 (144.2–145.4) | 145.0 (142.8–145.6) | 0.62 |
| Potassium (mmol/l), mean (SD) | 4.03 (0.14) | 4.03 (0.11) | 1 |
| Creatinine (µmol/l), mean (SD) | 54.9 (4.9) | 57.9 (3.3) | 0.205 |
| Bilirubin (µmol/l), mean (SD) | 8.22 (0.65) | 8.34 (1.29) | 0.832 |
| ALT (U/l), median (range) | 32.0 (29.3–41.5) | 30.5 (29.0–44.8) | 1 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/l), mean (SD) | 81.9 (21.1) | 85.5 (20.1) | 0.751 |
| Calcium (mmol/l), mean (SD) | 2.04 (0.04) | 2.08 (0.08) | 0.232 |
| Albumin (g/l), median (range) | 25.8 (25.5–27.4) | 26.9 (26.5–28.5) | 0.128 |
| Phosphate (mmol/l), mean (SD) | 1.10 (0.17) | 1.04 (0.11) | 0.444 |
| Magnesium (mmol/l), mean (SD) | 0.83 (0.02) | 0.85 (0.03) | 0.269 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/l), mean (SD) | 148.8 (31.9) | 160.4 (31.9) | 0.511 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/l), mean (SD) | 23.0 (0.7) | 23.6 (0.5) | 0.101 |
| Lactate (mmol/l), mean (SD) | 1.20 (0.10) | 1.06 (0.11) | 0.027 |
Liver function was not significantly different in the two groups. There were no significant differences between the two groups for average daily bilirubin [mean 8.2 (SD 0.7) µmol/l in the TH group vs. mean 8.3 (SD 1.3) µmol/l in the control group; p = 0.832], alanine transaminase (ALT) [median 32.0 (IQR 29.3–41.5) U/l in the TH group vs. median 30.5 (IQR 29.0–44.8) U/l in the control group; p = 1.0] and albumin [median 25.8 (IQR 25.5–27.4) g/l in the TH group vs. median 26.9 (IQR 26.5–28.5) g/l in the control group; p = 0.128] (see Table 20). Average daily APTT (activated partial thromboplastin time) [mean 33.2 (SD 2.1) seconds in the TH group vs. mean 31.2 (SD 1.3) seconds in the control group; p = 0.046] and APTTr (activated partial thromboplastin time ratio) [mean 1.2 (SD 0.1) in the TH group vs. mean 1.1 (SD 0.0) in the control group; p = 0.037] were significantly increased in the TH group.
Renal function was not significantly different in the two groups for average daily serum urea [mean 4.30 (SD 0.83) mmol/l in the TH group vs. mean 4.33 (SD 1.0) mmol/l in the control group; p = 0.959] or creatinine [mean 54.9 (SD 4.9) µmol/l in the TH group vs. mean 57.9 (SD 3.3) µmol/l in the control group; p = 0.205] (see Table 20). Electrolyte concentrations were identical in the TH and control groups: serum sodium was median 145.2 (range 144.2–145.4) mmol/l in the TH group, compared with median 145.0 (range 142.8–145.6) mmol/l in the control group (p = 0.62) and potassium was mean 4.03 (SD 0.14) mmol/l in the TH group, compared with mean 4.03 (SD 0.11) mmol/l in the control group; p = 1].
There was no difference in the number of participants requiring renal replacement therapy (RRT). Seven participants (5.5%) in the TH group required RRT, compared with three participants (2.4%) in the control group (p = 0.33) (see Table 20). Evidence of rhabdomyolysis was reported in the same number of participants in each group [11 (9.1%) in the TH group vs. 11 (8.9%) in the control group; p = 0.87]. Additionally, elevated levels of creatine kinase and/or troponin T were reported in a similar proportion of participants across the two groups [37 (33.9%) in the TH group vs. 30 (28.6%) in the control group; p = 0.484]. The average serum creatinine kinase level was median 753 (IQR 505–1280) U/l in the TH group, compared with median 1013 (IQR 606–1554) U/l in the control group (p = 0.336), and the troponin T level was median 41.0 (IQR 10.0–142.0) ng/l in the TH group, compared with median 15.0 (IQR 3.755–38.3) ng/l in the control group (p = 0.46).
Acid–base estimation
Metabolic acidosis was reported significantly more often in the TH group than in the control group [45 participants (36.9%) in the TH group vs. 27 participants (22.1%) in the control group; p = 0.017], as was the use of an infusion of bicarbonate [17 (13.7%) in the TH group vs. 5 (4.2%) in the control group; p = 0.018]. Average daily lactate concentrations were significantly greater in the TH group than in the control group [mean 1.2 (SD 0.1) mmol/l in the TH group vs. mean 1.1 (SD 0.1) mmol/l in the control group; p = 0.027], although serum bicarbonate concentrations were similar in both groups [mean 23.0 (SD 0.7) mmol/l in the TH group vs. mean 23.6 (SD 0.5) mmol/l in the control group; p = 0.10].
Organ dysfunction
Organ dysfunction was quantified using a modified abbreviated SOFA score. All analyses were made comparing minimal (SOFA score of ≤ 1) with significant (SOFA score of > 1) organ dysfunction. There was no significant difference in the distribution of SOFA scores between the TH group and the control group; 47 participants (32.9%) in the TH group and 55 participants (38.5%) in the control group had a SOFA score of ≤ 1, and 96 participants (67.1%) in the TH group and 88 participants (61.5%) in the control group had a SOFA score of > 1 (p = 0.388) (Table 21). In the TH group, there were significantly more participants who died with a SOFA score of > 1 [39 (84.8%) died vs. 57 (58.8%) survived] than with a SOFA score of ≤ 1 [7 (15.2%) died vs. 40 (41.2%) survived] (p = 0.004). This was not seen in the control group: 21 participants (65.6%) died compared with 66 participants (60.0%) survived with a SOFA score of > 1, and 11 participants (34.4%) died compared with 44 participants (40.0%) survived with a SOFA score of ≤ 1 (p = 0.712). The distribution of SOFA scores was not significantly different for the dichotomised GOSE in either the TH group [73 (71.6%) unfavourable vs. 23 (59.0%) favourable with a SOFA score of > 1, and 29 (28.4%) poor vs. 16 (41.0%) good outcome with a SOFA score of ≤ 1; p = 0.218] or the control group [53 (60.2%) poor vs. 33 (62.3%) good outcome with a SOFA score of > 1 and 35 (39.8%) poor vs. 20 (37.7%) good outcome with a SOFA score of ≤ 1; p = 0.951].
| Complications | Treatment group | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Haemofiltration, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 7 (5.5) | 3 (2.4) | 0.333 |
| No | 120 (94.5) | 124 (97.6) | |
| Rhabdomyolysis, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 11 (9.1) | 11 (8.9) | 0.87 |
| No | 110 (90.9) | 113 (91.1) | |
| Metabolic acidosis, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 45 (36.9) | 27 (22.1) | 0.017 |
| No | 77 (63.1) | 95 (77.9) | |
| Bicarbonate infusion, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 17 (13.7) | 5 (4.2) | 0.018 |
| No | 107 (86.3) | 114 (95.8) | |
| Troponin and/or CK elevation, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 37 (33.9) | 30 (28.6) | 0.484 |
| No | 72 (66.1) | 75 (71.4) | |
| CK (units/l) n = 35/29, mean (range) | 769 (505–1478) | 1004 (606–1554) | – |
| Troponin (ng/l) n = 9/3, mean (range) | 41.0 (10.0–133.0) | 15.0 (0.0–46.0) | – |
| SOFA of ≤ 1, n (%) | 47 (32.9) | 55 (38.5) | 0.388 |
| SOFA of > 1, n (%) | 96 (67.1) | 88 (61.5) | |
| SOFA score and survival – hypothermia | |||
| Died | Survived | ||
| SOFA of ≤ 1, n (%) | 7 (15.2) | 40 (41.2) | 0.004 |
| SOFA of > 1, n (%) | 39 (84.8) | 57 (58.8) | |
| SOFA score and survival – control group | |||
| Died | Survived | ||
| SOFA of ≤ 1, n (%) | 11 (34.4) | 44 (40.0) | 0.712 |
| SOFA of > 1, n (%) | 21 (65.6) | 66 (60.0) | |
Immunity and infection
Therapeutic hypothermia was associated with a significantly lower average daily leucocyte count [mean 9.9 (SD 0.9) × 109/l in the TH group vs. 11.0 (SD 0.7) × 109/l in the control group; p = 0.031]. Similarly, the neutrophil count was also reduced [mean 7.8 (SD 0.6) x109/l in the TH group vs. mean 9.0 (SD 0.7) ×109/l in the control group; p = 0.005]. However, there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups for average daily C-reactive protein [mean 148.8 (SD 31.9) mg/l in the TH group vs. mean 160.4 (SD 31.9) mg/l in the control group; p = 0.511].
The number of participants suspected of having infection was similar over days 1–7 of data collection [111 (81.6%) in the TH group vs. 106 (78.5%) in the control group; p = 0.627]. Confirmed infections were also similar [98 (79.0%) in the TH group vs. 94 (77.0%) in the control group; p = 0.825] (Table 22). Pneumonia was the most common infection in both groups, although there was no significant difference in the number of episodes between the two groups [84 (58.7%) episodes in the TH group vs. 78 (54.5%) in the control group; p = 0.551]. Endotracheal aspiration was the technique most frequently used to confirm a respiratory infection [35 participants (44.3%) in the TH group vs. 29 participants (40.8%) in the control group; p = 0.754]. There was no significant difference between the two groups in the number of participants who received antibiotics [116 (89.2%) in the TH group vs. 113 (87.6%) in the control group; p = 0.828].
| Intervention | Treatment group, n (%) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | Control | ||
| Suspected infection | |||
| Yes | 111 (81.6) | 106 (78.5) | 0.627 |
| No | 25 (18.4) | 29 (21.5) | |
| Confirmed infection | |||
| Yes | 98 (79.0) | 94 (77.0) | 0.825 |
| No | 26 (21.0) | 28 (23.0) | |
| Respiratory infection | |||
| Yes | 84 (58.7) | 78 (54.5) | 0.551 |
| No | 59 (41.3) | 65 (45.5) | |
| Respiratory sample type | |||
| Formal bronchoalveolar lavage | 19 (24.1) | 16 (22.5) | 0.754 |
| Mini bronchoalveolar lavage | 5 (6.3) | 8 (11.3) | |
| Endotracheal aspiration | 35 (44.3) | 29 (40.8) | |
| Sputum | 20 (25.3) | 18 (25.4) | |
| Infections | |||
| Respiratory infection | |||
| Yes | 84 (58.7) | 78 (54.5) | 0.551 |
| No | 59 (41.3) | 65 (45.5) | |
| Urinary infection | |||
| Yes | 4 (2.8) | 9 (6.3) | 0.256 |
| No | 139 (97.2) | 134 (93.7) | |
| Catheter-related bloodstream infection | |||
| Yes | 4 (2.8) | 5 (3.5) | 0.756 |
| No | 139 (97.2) | 138 (96.5) | |
| Sepsis of uncertain origin | |||
| Yes | 2 (1.4) | 1 (0.7) | 1 |
| No | 141 (98.6) | 142 (99.3) | |
| Other infection | |||
| Yes | 8 (5.6) | 7 (4.9) | 1 |
| No | 135 (94.4) | 136 (95.1) | |
| Antibiotics | |||
| Antibiotics prescribed | |||
| Yes | 116 (89.2) | 13 (87.6) | 0.828 |
| No | 14 (10.8) | 16 (12.4) | |
Coenrolment
The number of participants coenrolled in other trials was similar in the two groups: 16 out of 143 participants (11.4%) in the TH group and 12 out of 143 participants (8.6%) in the control group (p = 0.55). The distribution of trials to which participants were coenrolled was not different. Coenrolment was not more frequent in non-survivors than in survivors in either the TH group [5 (11.1%) non-survivors vs. 11 (11.6%) survivors; p = 0.839] or the control group [3 (9.7%) non-survivors vs. 8 (7.4%) survivors; p = 0.972]. Similarly, coenrolment was not more common in those participants with an unfavourable outcome by GOSE in the TH group [11 (11.2%) unfavourable outcome vs. 3 (7.9%) good outcome; p = 0.796] or the control group [7 (8.2%) poor outcome vs. 4 (7.7%) good outcome; p = 0.833].
Method of cooling
The majority of participants were cooled with an automated device and surface cooling; Blanketrol® (Patient Temperature Management Solutions, Cincinnati, OH, USA) and ARCTIC SUN® 5000 Temperature Management System (Bard Medical Division, Covington, GA, USA) were the most commonly used devices (58.2% of the TH group sample), although a small percentage of participants were cooled with an intravascular device (ZOLL®; ZOLL, Pitsburgh, PA, USA) (23.9% of the TH group sample).
Unfavourable outcome at 6 months by GOSE was not associated with the type of cooling device used (p = 0.441).
Discussion
This exploratory analysis collected additional information not considered in the original Eurotherm3235 Trial in order to explore possible reasons for the original trial results. Consistent with the ITT population, analysis of this additional data sample also showed that there was a statistically significant increase in the mortality within 6 months of randomisation in the hypothermia group. Treatment allocation, demographics and outcomes were similar to the ITT population.
The main observation that stands out from these results is that hypothermia was associated with an excess number of deaths as a consequence of sepsis/ARDS/MOF. In the case of non-surviving participants, study centres were asked to give a likely cause of death. Hypothermia was associated with an excess number of deaths as a consequence of sepsis/ARDS/MOF. In the TH group, significantly more participants who died had increased organ dysfunction scores, but this study cannot prove causality. With an absence of any difference in comorbidities or cointerventions between groups, the differences in the cause of death and the incidence of non-neurological organ dysfunction among those who died point to profound systemic consequences of hypothermia in this population of participants.
The harmful systemic effects of inflammation, linking sepsis, lung injury and MOF as a pathogenic consequence of TH, might explain the greater requirement for cardiovascular support, the evidence of tissue hypoperfusion and greater incidence of organ dysfunction associated with TH deaths.
One trigger for inflammation and organ dysfunction with TH may stem from a reduction in oxygen availability at a cellular level. Hypothermia causes a decrease in the tension/partial pressure of dissolved gases in the blood because of their increased solubility. This is accompanied by an increase in blood pH. A reduction in PaCO2, pH and temperature causes a leftward shift in the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve (OHDC),132 making less oxygen available in tissues. 133
The alpha-stat blood gas management is a simple and reliable method used by the 33 centres that participated in the Eurotherm3235 Trial and also in other hypothermia trials, such as the NABISH II and TTM trials. 108,134 It may be beneficial for participants with cerebrovascular disease or derangements of cerebral autoregulation. Murkin et al. 135 compared pH-stat and alpha-stat strategies and found that flow–metabolism coupling was preserved using alpha-stat. Conversely, Kiziltan et al. 136 found that the pH-stat management might suppress the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen more than the alpha-stat. In addition, under pH-stat conditions, there is a decrease in haemoglobin affinity for oxygen compared with alpha-stat, which could provide more dissolved oxygen for tissues. Similarly, Sakamoto et al. 137 showed that the pH-stat management increases cerebral oxygenation through improved oxygen delivery compared with alpha-stat. Higher oxyhaemoglobin and lower deoxyhaemoglobin levels were identified on cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy. The optimal strategy for blood gas management in TH remains uncertain and was not addressed in the majority of laboratory studies we reviewed prior to studying this intervention.
In order to maintain cerebral autoregulation, the alpha-stat acid–base management for arterial blood gases analysis was used in this trial and will have exacerbated tissue oxygen delivery. For example, a cooled participant with an alpha-stat PaCO2 of 40 mmHg (measured at 37 °C) will have a substantially lower PaCO2 at actual tissue temperature (32–35 °C) and a higher pH. A reduction in tissue oxygen delivery will be compounded by the reduction in cerebral blood flow (due to autoregulation) as PaCO2 decreases. The net result of this is a failure in oxygen delivery, tissue acidosis and a pro-inflammatory state. This relative tissue hypoxia will affect not only the brain, but every organ system. Hypothermia creates a new and heterogeneous blood flow distribution, with areas of hypoxia and lactic acid generation. Such systematic effects might explain the greater use of vasopressors and inotropes in the TH group and the increased use of steroids. This would also be in keeping with the small but significant increase in the average daily lactate concentration and the greater prevalence of metabolic acidosis in the TH group.
During rewarming, there is a rightward shift of the OHDC, which facilitates oxygen dissociation. Morray et al. 138 documented an increase in VO2 during rewarming and found that oxygen delivery failed to keep pace with this VO2. Prolonged hypothermia may reduce blood flow through arterioles because of local factors such as a decrease in oxygen requirement, vasoconstriction and a reduction in plasma volume. Heterogeneous areas of blood flow distribution, tissue oxygen debt, an increment in lactate concentration and a metabolic acidosis will result. During rewarming, lactate re-enters normal oxidative pathways, consuming oxygen during this process. With a return to normothermia, free radical oxidation resumes, leading to non-respiratory utilisation of oxygen and an increase in VO2.
To detect and prevent brain hypoxia, the use of brain tissue oxygen tension (PbtO2) monitoring as part of a multimodality array of advanced cerebral monitoring is becoming increasingly common. Frequent and long duration of cerebral hypoxaemic episodes in trauma patients have been repeatedly found to be significantly associated with poor outcome. 139 By manipulating CPP and ICP, and optimising PaO2, PaCO2 and blood haemoglobin concentration, it is possible to improve PbtO2. 112
In a small, single-centre, retrospective analysis of the first 17 participants enrolled in the Eurotherm3235 Trial, Flynn et al. 140 found that there was a significant decline in mean PbtO2 from 30.2 mmHg to 22.4 mmHg in the TH group, from induction to stable hypothermia. In five out of the nine TH participants, PbtO2 fell below the target value of 20 mmHg but was unaffected by cooling in the remainder of the TH group. This raises the possibility that the response to cooling could be heterogeneous. For some patients, TH might reduce oxygen delivery to the brain to a greater degree than the reduction in metabolic oxygen consumption that occurs with cooling. However, this effect is not universal. A greater understanding of why cooling might be better tolerated in some patients, how to mitigate the effects of cooling on oxygen supply and of the use of cooling to a target PbtO2 might improve the results of TH in this group of patients.
Although anaemia has also been associated with a decrease in PbtO2 following TBI, this exploratory analysis found no statistically significant difference in the average daily mean of haemoglobin and haematocrit levels in the two groups. 141
We found no evidence of a significant imbalance in propofol use or infusion rate between the treatment allocations. 142 Similarly, there was no significant difference in propofol dose after adjustment for age, post resuscitation GCS motor component, time from injury and pupil reactivity. Furthermore, there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the number of participants receiving potentially toxic (> 5 mg/kg/hour) rates of propofol in the first 48 hours. 143,144
These comparisons, however, do not consider the effect of cooling on the metabolism of propofol, which, by slowing clearance, could potentially promote toxicity. Leslie et al. 145 demonstrated an approximate 28% increase in the serum concentration of propofol in six patients cooled to 34 °C. Moreover, the study showed a decrease in the hepatic blood flow by 10% with cooling. Bjelland et al. 146 showed that propofol clearance was significantly lower during hypothermia than normothermia (median 2046 vs. 2665 ml/minute; p < 0.035) in 14 patients treated with TH following cardiac arrest.
That said, the average daily liver and kidney function tests did not differ between the groups and there were no differences in the need for RRT, evidence of rhabdomyolysis or cardiac damage by treatment allocation. These findings would argue against the effect of propofol-related infusion syndrome (PRIS) in the TH group. The greater use of vasopressors and inotropes in the TH group may reflect a response to cardiovascular compromise because of an inflammatory state rather than the cardiotoxic effects of PRIS.
Hypothermia can also affect the clearance of other drugs, including neuromuscular blocking agents. 147 In this analysis, we found that atracurium was used more often in the TH group, possibly in an effort to manage shivering, than in the control group. However, the median hourly infusion rate was significantly lower with TH than with standard treatment; this could be explained by the reduction in the clearance of atracurium, which is temperature dependent by Hofmann degradation.
Decompressive craniectomy is performed in many neurotrauma centres worldwide. Over the course of our study, two important trials148,149 were either published or nearing completion. These trials found that decompressive craniectomy was associated with either a worse GOSE score at 6 months or greater survival but no improvement in the proportion of patients with good recovery. In our study, the number of participants undergoing decompressive craniectomy before and after randomisation was similar in the two groups. The use of hemicraniectomy and bifrontal craniectomy did not vary by CT appearance in either the TH group or the control group, nor was there a difference in Marshall scores by treatment allocation for either decompressive technique.
The literature at the time of the Eurotherm3235 Trial did not recommend the use of steroids to improve outcomes or reduce ICP. 86 The large, multicentre CRASH trial150 found worse outcomes at 6 months and a higher mortality within 2 weeks in patients treated with methylprednisolone (Consilient Health Ltd, Surrey, UK). The mechanism and cause of the increase in death rate were not clear. The data from the exploratory analysis in this report revealed that the number of participants receiving steroids was significantly greater in the TH group than in the control group. However, when used, the steroids were of a relatively low dose compared with those used in the CRASH trial, and more in keeping with an adrenocortical replacement dose, such as what might be used in severe sepsis.
The Eurotherm3235 Trial was stopped early because of futility and safety concerns. The main trial was designed to be pragmatic, namely focused on functional outcome rather than on detailed mechanistic pathways. The fact that the study was stopped earlier than intended may introduce the risk of bias, reducing the validity of the results. 151 For this exploratory analysis, the Eurotherm3235 Trial team successfully collected data on 74% of the ITT population, and received 286 anonymised CRFs out of 387 by post or e-mail to the Eurotherm3235 Trial office by the deadline of 31 July 2016. The main reasons that we received a smaller number of data than initially hoped for were that, among the 33 centres that took part in the main trial, three sites were closed, three did not have the capacity for collecting data and eight were inactive.
Chapter 7 Conclusions
Hypothermia with alpha-stat blood gas management is associated with important systemic effects, manifested as an inflammatory condition similar to sepsis/ARDS/MOF. This condition is associated with increased mortality and poorer outcomes after TBI.
Impact of patient and public involvement, challenges of patient and public involvement and lessons learnt
The Eurothern3235 Trial recruited patient populations that were very challenging for two main reasons:
-
Patients were incapacitated because they were sedated and connected to a ventilator at the time of recruitment to the trial.
-
There is a high probability of a poor outcome following TBI; therefore, patients who have survived their injury generally have many problems, either cognitively or physically, that impair their ability to contribute to the design of a research trial.
This made patient involvement in the design and structure of the trial very difficult. For these reasons, it was not possible to have a patient representative as part of the protocol design group; however, we did involve a group of patients who had suffered a TBI and their relatives in the design and writing of the patient and relative documentation. The patients and relatives involved were suggested to us by the Edinburgh Headway Group, and time since suffering the TBI ranged from 2 to 25 years.
The trial manager (H Louise Sinclair) visited the Edinburgh Headway Group on a day, arranged by the group, when the suggested patients and relatives would attend. The patients were given the draft patient consent forms and patient information sheets to read, and the relatives were given the draft patient and relative consent forms and information sheets to comment on. The patients were interviewed individually by H Louise Sinclair and any comments were documented. The main comment from patients was that the forms were too complicated; they struggled to understand some of the wording and could not read the forms because of the font (Times New Roman) and the small font size that was used.
The relatives were also interviewed individually and their comments were documented. The main concerns were:
-
The length of the information sheets for both patients and relatives.
-
The formal layout of the information sheets – A4 size double-sided documents.
-
The complexity of the wording used for patients – we needed to use much more basic language (approximately at the level of an 8-year-old).
-
The complexity of the wording used for relatives. The concerns were that, at the time of reading the documents and consent forms, relatives would be in a state of shock so would be unable to process a lot of information.
The consent documents were then amended, taking into account all of the comments and concerns raised. We could not reword the consent forms because they were written in accordance with the NRES guidelines for wording consent forms and information sheets;152 however, we were able to change the layout of these documents. In doing so, we changed the font used and increased the font size of the consent forms, and changed the layout of the information sheets to an A5-sized booklet using basic language, an informal, larger font and the use of colour text boxes. H Louise Sinclair then met with the same cohort and the forms were approved by the group.
We also appointed a patient’s relative as a lay member of the Trial Steering Committee. She was recommended by Edinburgh Headway Group and attended the steering committee meetings in person. She did, however, find being a member of the committee difficult at times because she is her husband’s main carer and could not leave him at home alone for the duration of the meeting. She therefore had to arrange for carers to be with him while she attended the meetings. She also found the role upsetting at times because she described how it brought back memories of her husband’s brain injury, his stay in intensive care and subsequent difficult recovery with the adaptations she has had to make to their lives.
Conclusions
In patients with TBI, TH plus standard care successfully reduced ICP. This intervention, however, did not improve functional recovery as compared with standard care alone.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients who participated in this trial and their families. We thank Lindsay Wilson, PhD, for support with training and adjudication of GOSE scoring; Corrie Roberts and Dawn Grey for assistance with trial management and administration; and the staff of the Wellcome Trust Clinical Research Facility in Edinburgh for research nurse support.
Contributions of authors
Peter JD Andrews was responsible for the conception of the work and the design of the database for the acquisition, analysis or interpretation of data, drafting the work and revising it for important intellectual content and giving final approval of the published version.
H Louise Sinclair made substantial contributions to the design of the work, and the acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. She was responsible for drafting the work, revising it critically for important intellectual content and giving final approval of the published version.
Aryelly Rodríguez was responsible for the analysis of data, drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content and giving final approval of the published version.
Bridget Harris made substantial contributions to the design of the work, and the acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. She was responsible for drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content.
Jonathan Rhodes made substantial contributions to the analysis and interpretation of data (author of Chapter 6) and gave final approval of the published version.
Hannah Watson made substantial contributions to the analysis and interpretation of data (author of Chapter 4) and gave final approval of the published version.
Gordon Murray created the trial design and was the author of the statistical analysis plan. He was responsible for drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content.
All authors agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work were appropriately investigated and resolved.
Publications
Andrews PJ, Citerio G. EUROTHERM3235Trial. Intensive Care Med 2010;36:1990–2.
Sinclair HL, Andrews PJD. Bench-to-bedside review: hypothermia in traumatic brain injury. Crit Care 2010;14:204.
Robinson K, Andrews PJD. The European Clinical Trials Directive and its impact on critical care and emergency research. Current Opin Crit Care 2011;17:141–5.
Pitoni S, Sinclair HL, Andrews PJD. Aspects of thermoregulation physiology. Current Opin Crit Care 2011;17:115–21.
Andrews PJ, Sinclair HL, Battison CG, Polderman KH, Citerio G, Mascia L, et al. European Society of Intensive Care Medicine study of therapeutic hypothermia (32–35 °C) for intracranial pressure reduction after traumatic brain injury (the Eurotherm3235Trial). Trials 2011;12:8.
Andrews PJ, Sinclair LH, Harris B, Baldwin MJ, Battison CG, Rhodes JK, et al. Study of therapeutic hypothermia (32 to 35 °C) for intracranial pressure reduction after traumatic brain injury (the Eurotherm3235Trial): outcome of the pilot phase of the trial. Trials 2013;14:277.
Carlotta Bagna F, Pitoni S, Andrews PJD. Therapeutic mild hypothermia and the pharmacokinetics of drugs in trauma brain injury (TBI) patients with a focus on sedation, anticonvulsant and antibiotic therapy. Open Crit Care Med J 2013;6:31–8.
Stocchetti N, Le Roux P, Vespa P, Oddo M, Citerio G, Andrews PJ, et al. Clinical review: neuromonitoring – an update. Crit Care 2013;17:201.
Harris BA, Andrews PJD. A lesson on induction of hypothermia and measurement of efficacy. Crit Care 2014;18:710.
Crossley S, Reid J, McLatchie R, Hayton J, Clark C, MacDougall M, Andrews PJD. A systematic review of therapeutic hypothermia for adult patients following traumatic brain injury. Crit Care 2014;18:R75.
Saxena M, Andrews PJ, Cheng A, Deol K, Hammond N. Modest cooling therapies (35 °C to 37.5 °C) for traumatic brain injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;8:CD006811.
Flynn LM, Rhodes J, Andrews PJ. Therapeutic hypothermia reduces intracranial pressure and partial brain oxygen tension in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: preliminary data from the Eurotherm3235 Trial. Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag 2015;5:143–51.
Andrews PJ, Sinclair HL, Rodríguez A, Harris BA, Battison CG, Rhodes JK, et al. Hypothermia for intracranial hypertension after traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2403–12.
Andrews PJ, Harris BA, Murray GD. Hypothermia for intracranial hypertension after traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med 2016;374:1385.
Andrews PJD, Rodríguez A, Suter P, Battison CG, Rhodes JKJ, Puddu I, Harris BA. Mortality risk stratification after traumatic brain injury and hazard of death with titrated hypothermia in the Eurotherm3235Trial. Crit Care Med 2017;45:883–90.
Rhodes J, Sinclair L, Puddu I, Rodríguez A, Andrews P. The whole is greater than the sum of its parts . . . ? Crit Care Med 2017;45:e741–2.
Abu-Arafeh A, Rodríguez A, Paterson RL, Andrews PJD. Temperature variability in a modern targeted temperature management trial. Crit Care Med 2018;46:223–8.
Watson H, Shepherd A, Rhodes J, Andrews PJD. Revisited: a systematic review of therapeutic hypothermia for adult patients following traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med 2018;46:972–9.
Data-sharing statement
All data requests should be submitted to the corresponding author for consideration. Access to anonymised data may be granted following review.
Patient data
This work uses data provided by patients and collected by the NHS as part of their care and support. Using patient data is vital to improve health and care for everyone. There is huge potential to make better use of information from people’s patient records, to understand more about disease, develop new treatments, monitor safety, and plan NHS services. Patient data should be kept safe and secure, to protect everyone’s privacy, and it’s important that there are safeguards to make sure that it is stored and used responsibly. Everyone should be able to find out about how patient data are used. #datasaveslives You can find out more about the background to this citation here: https://understandingpatientdata.org.uk/data-citation.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Andrews PJD, Sinclair HL, Rodríguez A, Harris BA, Battison CG, Rhodes JKJ, et al. Hypothermia for intracranial hypertension after traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2403-12. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1507581.
- Society EBI . European Brain Injury Society 2004. www.ebissociety.org/index-eng.html (accessed 9 August 2018).
- Ghajar J. Traumatic brain injury. Lancet 2000;356:923-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02689-1.
- Polderman KH. Induced hypothermia and fever control for prevention and treatment of neurological injuries. Lancet 2008;371:1955-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60837-5.
- Nolan JP, Deakin CD, Soar J, Böttiger BW, Smith G. European Resuscitation Council . European Resuscitation Council guidelines for resuscitation 2005. Section 4. Adult advanced life support. Resuscitation 2005;67:39-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2005.10.009.
- American Heart Association . Guidelines for CPR and ECC. Part 7.5 post-resuscitation support. Circulation 2005;112:84-8.
- Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, Tarnow-Mordi W, Inder TE, Davis PG. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;1. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003311.pub2.
- Dietrich WD, Bramlett HM. Hyperthermia and central nervous system injury. Prog Brain Res 2007;162:201-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(06)62011-6.
- Dietrich WD, Atkins CM, Bramlett HM. Protection in animal models of brain and spinal cord injury with mild to moderate hypothermia. J Neurotrauma 2009;26:301-12. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2008.0806.
- Clifton GL, Choi SC, Miller ER, Levin HS, Smith KR, Muizelaar JP, et al. Intercenter variance in clinical trials of head trauma experience of NABIS hypothermia. J Neurosurg 2001;95:751-55. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.95.5.0751.
- Bramlett HM, Green EJ, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Globus MY, Ginsberg MD. Posttraumatic brain hypothermia provides protection from sensorimotor and cognitive behavioral deficits. J Neurotrauma 1995;12:289-98. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.1995.12.289.
- Koizumi H, Fujisawa H, Ito H, Maekawa T, Di X, Bullock R. Effects of mild hypothermia on cerebral blood flow-independent changes in cortical extracellular levels of amino acids following contusion trauma in the rat. Brain Res 1997;747:304-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(96)01240-1.
- Dietrich WD, Busto R, Halley M, Valdes I. The importance of brain temperature in alterations of the blood–brain barrier following cerebral ischemia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1990;49:486-97. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005072-199009000-00004.
- Kawai N, Nakamura T, Nagao S, Czosnyka M, Pickard JD, Kirkpatrick PJ, et al. Intracranial Pressure and Brain Biochemical Monitoring. Vienna: Springer Vienna; 2002.
- Park CK, Jun SS, Kim MC, Kang JK, Marmarou A, Bullock R, et al. Intracranial Pressure and Neuromonitoring in Brain Injury: Proceedings of the Tenth International ICP Symposium, Williamsburg, VA, USA, May 25–9, 1997. Vienna: Springer Vienna; 1998.
- Mancuso A, Derugin N, Hara K, Sharp FR, Weinstein PR. Mild hypothermia decreases the incidence of transient ADC reduction detected with diffusion MRI and expression of c-Fos and hsp70 mRNA during acute focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res 2000;887:34-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02963-2.
- Nagel S, Su Y, Horstmann S, Heiland S, Gardner H, Koziol J, et al. Minocycline and hypothermia for reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat: effects on BBB breakdown and MMP expression in the acute and subacute phase. Brain Res 2008;1188:198-206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2007.10.052.
- Kumar K, Wu X, Evans AT. GFAP-immunoreactivity following hypothermic forebrain ischemia. Metab Brain Dis 1997;12:21-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02676351.
- Goss JR, Styren SD, Miller PD, Kochanek PM, Palmer AM, Marion DW, et al. Hypothermia attenuates the normal increase in interleukin 1 beta RNA and nerve growth factor following traumatic brain injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 1995;12:159-67. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.1995.12.159.
- Kinoshita K, Chatzipanteli K, Alonso OF, Howard M, Dietrich WD. The effect of brain temperature on hemoglobin extravasation after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 2002;97:945-53. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.97.4.0945.
- Vitarbo EA, Chatzipanteli K, Kinoshita K, Truettner JS, Alonso OF, Dietrich WD. Tumor necrosis factor alpha expression and protein levels after fluid percussion injury in rats: the effect of injury severity and brain temperature. Neurosurgery 2004;55:416-24. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000130036.52521.2C.
- Kline AE, Bolinger BD, Kochanek PM, Carlos TM, Yan HQ, Jenkins LW, et al. Acute systemic administration of interleukin-10 suppresses the beneficial effects of moderate hypothermia following traumatic brain injury in rats. Brain Res 2002;937:22-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(02)02458-7.
- Globus MY, Alonso O, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Ginsberg MD. Glutamate release and free radical production following brain injury: effects of posttraumatic hypothermia. J Neurochem 1995;65:1704-11. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65041704.x.
- Sakamoto KI, Fujisawa H, Koizumi H, Tsuchida E, Ito H, Sadamitsu D, et al. Effects of mild hypothermia on nitric oxide synthesis following contusion trauma in the rat. J Neurotrauma 1997;14:349-53. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.1997.14.349.
- DeKosky ST, Abrahamson EE, Taffe KM, Dixon CE, Kochanek PM, Ikonomovic MD. Effects of post-injury hypothermia and nerve growth factor infusion on antioxidant enzyme activity in the rat: implications for clinical therapies. J Neurochem 2004;90:998-1004. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02575.x.
- Lei B, Tan X, Cai H, Xu Q, Guo Q. Effect of moderate hypothermia on lipid peroxidation in canine brain tissue after cardiac arrest and resuscitation. Stroke 1994;25:147-52. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.25.1.147.
- Van Hemelrijck A, Hachimi-Idrissi S, Sarre S, Ebinger G, Michotte Y. Post-ischaemic mild hypothermia inhibits apoptosis in the penumbral region by reducing neuronal nitric oxide synthase activity and thereby preventing endothelin-1-induced hydroxyl radical formation. Eur J Neurosci 2005;22:1327-37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04331.x.
- Tohyama Y, Sako K, Yonemasu Y. Hypothermia attenuates hyperglycolysis in the periphery of ischemic core in rat brain. Exp Brain Res 1998;122:333-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050521.
- Lo EH, Steinberg GK, Panahian N, Maidment NT, Newcomb R. Profiles of extracellular amino acid changes in focal cerebral ischaemia: effects of mild hypothermia. Neurol Res 1993;15:281-7. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.1993.11740149.
- Busto R, Globus MY, Dietrich WD, Martinez E, Valdés I, Ginsberg MD. Effect of mild hypothermia on ischemia-induced release of neurotransmitters and free fatty acids in rat brain. Stroke 1989;20:904-10. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.20.7.904.
- Mitani A, Kataoka K. Critical levels of extracellular glutamate mediating gerbil hippocampal delayed neuronal death during hypothermia: brain microdialysis study. Neuroscience 1991;42:661-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(91)90035-M.
- Rokkas CK, Cronin CS, Nitta T, Helfrich LR, Lobner DC, Choi DW, et al. Profound systemic hypothermia inhibits the release of neurotransmitter amino acids in spinal cord ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1995;110:27-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5223(05)80006-6.
- Zhu H, Meloni BP, Bojarski C, Knuckey MW, Knuckey NW. Post-ischemic modest hypothermia (35 degrees C) combined with intravenous magnesium is more effective at reducing CA1 neuronal death than either treatment used alone following global cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol 2005;193:361-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.01.022.
- Friedman LK, Ginsberg MD, Belayev L, Busto R, Alonso OF, Lin B, et al. Intraischemic but not postischemic hypothermia prevents non-selective hippocampal downregulation of AMPA and NMDA receptor gene expression after global ischemia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2001;86:34-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-328X(00)00252-7.
- Lyeth BG, Jiang JY, Robinson SE, Guo H, Jenkins LW. Hypothermia blunts acetylcholine increase in CSF of traumatically brain injured rats. Mol Chem Neuropathol 1993;18:247-56. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160117.
- Zhang H, Zhou M, Zhang J, Mei Y, Sun S, Tong E. Therapeutic effect of post-ischemic hypothermia duration on cerebral ischemic injury. Neurol Res 2008;30:332-6. https://doi.org/10.1179/174313208X300279.
- Winfree CJ, Baker CJ, Connolly ES, Fiore AJ, Solomon RA. Mild hypothermia reduces penumbral glutamate levels in the rat permanent focal cerebral ischemia model. Neurosurgery 1996;38:1216-22.
- Rosomoff HL, Holaday DA. Cerebral blood flow and cerebral oxygen consumption during hypothermia. Am J Physiol 1954;179:85-8. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.179.1.85.
- Kuluz JW, Prado R, Chang J, Ginsberg MD, Schleien CL, Busto R. Selective brain cooling increases cortical cerebral blood flow in rats. Am J Physiol 1993;265:H824-H27. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.3.H824.
- Hu BR, Kamme F, Wieloch T. Alterations of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and its messenger RNA in the rat hippocampus following normo- and hypothermic ischemia. Neuroscience 1995;68:1003-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(95)00213-3.
- Shimohata T, Zhao H, Steinberg GK. εPKC may contribute to the protective effect of hypothermia in a rat focal cerebral ischemia model. Stroke 2007;38:375-80. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000254616.78387.ee.
- Akaji K, Suga S, Fujino T, Mayanagi K, Inamasu J, Horiguchi T, et al. Effect of intra-ischemic hypothermia on the expression of c-Fos and c-Jun, and DNA binding activity of AP-1 after focal cerebral ischemia in rat brain. Brain Res 2003;975:149-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(03)02622-2.
- Pabello NG, Tracy SJ, Snyder-Keller A, Keller RW. Regional expression of constitutive and inducible transcription factors following transient focal ischemia in the neonatal rat: influence of hypothermia. Brain Res 2005;1038:11-2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2004.12.047.
- Gressens P, Dingley J, Plaisant F, Porter H, Schwendimann L, Verney C, et al. Analysis of neuronal, glial, endothelial, axonal and apoptotic markers following moderate therapeutic hypothermia and anesthesia in the developing piglet brain. Brain Pathol 2008;18:10-2. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00095.x.
- Collaborative approach to meta analysis and review of animal data from experimental stroke (CAMARADES) n.d. www.dcn.ed.ac.uk/camarades/default.htm (accessed 17 July 2018).
- Polderman KH, Ely EW, Badr AE, Girbes AR. Induced hypothermia in traumatic brain injury: considering the conflicting results of meta-analyses and moving forward. Intensive Care Med 2004;30:1860-4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-004-2383-5.
- Wang WP, Ren HJ, Chi JY, Xu FL, Quan Y. Effects of mild hypothermia on patients with lower intracranial pressure following severe brain injury. Chin J Traumatol 2005;8:54-6.
- Shiozaki T, Kato A, Taneda M, Hayakata T, Hashiguchi N, Tanaka H, et al. Little benefit from mild hypothermia therapy for severely head injured patients with low intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg 1999;91:185-91. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.91.2.0185.
- Shiozaki T, Hayakata T, Taneda M, Nakajima Y, Hashiguchi N, Fujimi S, et al. A multicenter prospective randomized controlled trial of the efficacy of mild hypothermia for severely head injured patients with low intracranial pressure. Mild Hypothermia Study Group in Japan. J Neurosurg 2001;94:50-4. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.94.1.0050.
- Tokutomi T, Morimoto K, Miyagi T, Yamaguchi S, Ishikawa K, Shigemori M. Optimal temperature for the management of severe traumatic brain injury: effect of hypothermia on intracranial pressure, systemic and intracranial hemodynamics, and metabolism. Neurosurgery 2003;52:102-11.
- Yamamoto T, Mori K, Maeda M. Assessment of prognostic factors in severe traumatic brain injury patients treated by mild therapeutic cerebral hypothermia therapy. Neurol Res 2002;24:789-95. https://doi.org/10.1179/016164102101200906.
- Bernard SA, Mac C, Jones B, Buist M. Experience with prolonged induced hypothermia in severe head injury. Crit Care 1999;3:167-72. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc371.
- Shiozaki T, Sugimoto H, Taneda M, Oda J, Tanaka H, Hiraide A, et al. Selection of severely head injured patients for mild hypothermia therapy. J Neurosurg 1998;89:206-11. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1998.89.2.0206.
- Tateishi A, Soejima Y, Taira Y, Nakashima K, Fujisawa H, Tsuchida E, et al. Feasibility of the titration method of mild hypothermia in severely head-injured patients with intracranial hypertension. Neurosurgery 1998;42:1065-69. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199805000-00066.
- Metz C, Holzschuh M, Bein T, Woertgen C, Frey A, Frey I, et al. Moderate hypothermia in patients with severe head injury: cerebral and extracerebral effects. J Neurosurg 1996;85:533-41. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1996.85.4.0533.
- Adelson PD, Ragheb J, Kanev P, Brockmeyer D, Beers SR, Brown SD, et al. Phase II clinical trial of moderate hypothermia after severe traumatic brain injury in children. Neurosurgery 2005;56:740-54. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000156471.50726.26.
- Biswas AK, Bruce DA, Sklar FH, Bokovoy JL, Sommerauer JF. Treatment of acute traumatic brain injury in children with moderate hypothermia improves intracranial hypertension. Crit Care Med 2002;30:2742-51. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200212000-00020.
- Qiu W, Shen H, Zhang Y, Wang W, Liu W, Jiang Q, et al. Noninvasive selective brain cooling by head and neck cooling is protective in severe traumatic brain injury. J Clin Neurosci 2006;13:995-1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2006.02.027.
- Qiu W, Zhang Y, Sheng H, Zhang J, Wang W, Liu W, et al. Effects of therapeutic mild hypothermia on patients with severe traumatic brain injury after craniotomy. J Crit Care 2007;22:229-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2006.06.011.
- Liu WG, Qiu WS, Zhang Y, Wang WM, Lu F, Yang XF. Effects of selective brain cooling in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: a preliminary study. J Int Med Res 2006;34:58-64. https://doi.org/10.1177/147323000603400107.
- Jiang JY, Xu W, Li WP, Gao GY, Bao YH, Liang YM, et al. Effect of long-term mild hypothermia or short-term mild hypothermia on outcome of patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2006;26:771-6. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600253.
- Qiu WS, Liu WG, Shen H, Wang WM, Hang ZL, Zhang Y, et al. Therapeutic effect of mild hypothermia on severe traumatic head injury. Chin J Traumatol 2005;8:27-32.
- Zhi D, Zhang S, Lin X. Study on therapeutic mechanism and clinical effect of mild hypothermia in patients with severe head injury. Surg Neurol 2003;59:381-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-3019(03)00148-4.
- Gal R, Cundrle I, Zimova I, Smrcka M. Mild hypothermia therapy for patients with severe brain injury. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2002;104:318-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0303-8467(02)00023-9.
- Polderman KH, Tjong Tjin JR, Peerdeman SM, Vandertop WP, Girbes ARJ. Effects of artificially induced hypothermia on intracranial pressure and outcome in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Intensive Care Med 2002;28:1563-67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1511-3.
- Polderman KH, Peerdeman SM, Girbes AR. Hypophosphatemia and hypomagnesemia induced by cooling in patients with severe head injury. J Neurosurg 2001;94:697-705. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.94.5.0697.
- Yan Y, Tang W. Changes of evoked potentials and evaluation of mild hypothermia for treatment of severe brain injury. Chin J Traumatol 2001;4:8-13.
- Aibiki M, Maekawa S, Yokono S. Moderate hypothermia improves imbalances of thromboxane A2 and prostaglandin 12 production after traumatic brain injury in humans. Crit Care Med 2000;28:3902-06. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200012000-00029.
- Jiang J, Yu M, Zhu C. Effect of long-term mild hypothermia therapy in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: 1-year follow-up review of 87 cases. J Neurosurg 2000;93:546-9. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.4.0546.
- Zhang K, Wang JX. Comparitive study on mild hypothermia in patients with severe head injury and the most severe head injury. Inn Mongol Med J 2000;32:4-6.
- Marion DW, Penrod LE, Kelsey SF, Obrist WD, Kochanek PM, Palmer AM, et al. Treatment of traumatic brain injury with moderate hypothermia. N Engl J Med 1997;336:540-6. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199702203360803.
- Resnick DK, Marion DW, Darby JM. The effect of hypothermia on the incidence of delayed traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 1994;34:252-55. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-199402000-00007.
- Clifton GL, Allen S, Barrodale P, Plenger P, Berry J, Koch S, et al. A Phase II study of moderate hypothermia in severe brain injury. J Neurotrauma 1993;10:263-71. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.1993.10.263.
- Shiozaki T, Sugimoto H, Taneda M, Yoshida H, Iwai A, Yoshioka T, et al. Effect of mild hypothermia on uncontrollable raised intracranial hypertension after severe head injury. J Neurosurg 1993;79:363-86. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1993.79.3.0363.
- Marion DW, Obrist WD, Carlier PM, Penrod LE, Darby JM. The use of moderate therapeutic hypothermia for patients with severe head injuries: a preliminary report. J Neurosurg 1993;79:354-62. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1993.79.3.0354.
- Clifton GL, Miller ER, Choi SC, Levin HS, McCauley S, Smith KR, et al. Lack of effect of induction of hypothermia after acute brain injury. N Engl J Med 2001;344:556-63. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200102223440803.
- Qiu WS, Liu WG, Shen H, Wang WM, Hang ZL, Zhang Y, et al. Therapeutic effect of mild hypothermia on severe traumatic head injury. Chin J Traumatol 2005;8:27-32.
- Fearnside MR, Cook RJ, McDougall P, McNeil RJ. The Westmead Head Injury Project outcome in severe head injury. A comparative analysis of pre-hospital, clinical and CT variables. Br J Neurosurg 1993;7:267-79. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688699309023809.
- Chesnut RM, Marshall SB, Piek J, Blunt BA, Klauber MR, Marshall LF. Early and late systemic hypotension as a frequent and fundamental source of cerebral ischemia following severe brain injury in the Traumatic Coma Data Bank. Acta Neurochir Suppl 1993;59:121-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-9302-0_21.
- Ducrocq SC, Meyer PG, Orliaguet GA, Blanot S, Laurent-Vannier A, Renier D, et al. Epidemiology and early predictive factors of mortality and outcome in children with traumatic severe brain injury: experience of a French paediatric trauma centre. Peadiatr Crit Care Med 2006;7:461-67. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PCC.0000235245.49129.27.
- Bernard SA, Gray TW, Buist MD, Jones BM, Silvester W, Gutteridge G, et al. Treatment of comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with induced hypothermia. N Engl J Med 2002;346:557-63. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa003289.
- Hypothermia After Cardiac Arrest Study Group . Mild therapeutic hypothermia to improve the neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med 2002;346:549-56. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa012689.
- Dixon SR. Infarct angioplasty: beyond stents and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors. Heart 2005;91:iii2-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2005.060251.
- Polderman KH. Application of therapeutic hypothermia in the intensive care unit. Opportunities and pitfalls of a promising treatment modality – part 2: practical aspects and side effects. Intensive Care Med 2004;30:757-69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-2151-y.
- Polderman KH, Rijnsburger ER, Peerdeman SM, Girbes AR. Induction of hypothermia in patients with various types of neurologic injury with use of large volumes of ice-cold intravenous fluid. Crit Care Med 2005;33:2744-51. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000190427.88735.19.
- American Association of Neurological Surgeons and Congress of Neurological Surgeons . Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 2007;24:S1-06.
- McIntyre LA, Fergusson DA, Hébert PC, Moher D, Hutchison JS. Prolonged therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury in adults: a systematic review. JAMA 2003;289:2992-9. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.22.2992.
- Harris OA, Colford JM, Good MC, Matz PG. The role of hypothermia in the management of severe brain injury: a meta-analysis. Arch Neurol 2002;59:1077-83. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.59.7.1077.
- Henderson WR, Dhingra VK, Chittock DR, Fenwick JC, Ronco JJ. Hypothermia in the management of traumatic brain injury. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med 2003;29:1637-44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1848-2.
- Alderson P, Gadkary C, Signorini DF. Therapeutic hypothermia for head injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004;4. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001048.pub2.
- Peterson K, Carson S, Carney N. Hypothermia treatment for traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurotrauma 2008;25:62-71. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2007.0424.
- Maas AI, Dearden M, Teasdale GM, Braakman R, Cohadon F, Iannotti F, et al. EBIC-guidelines for management of severe head injury in adults. European Brain Injury Consortium. Acta Neurochir 1997;139:286-94. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808823.
- Andrews PJ, Sinclair LH, Harris B, Baldwin MJ, Battison CG, Rhodes JK, et al. Study of therapeutic hypothermia (32 to 35°C) for intracranial pressure reduction after traumatic brain injury (the Eurotherm3235Trial): outcome of the pilot phase of the trial. Trials 2013;14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-14-277.
- MRC Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice in Clinical Trials. London: Medical Research Council; 1998.
- Badjatia N, Strongilis E, Gordon E, Prescutti M, Fernandez L, Fernandez A, et al. Metabolic impact of shivering during therapeutic temperature modulation: the Bedside Shivering Assessment Scale. Stroke 2008;39:3242-7. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.523654.
- Steyerberg EW, Mushkudiani N, Perel P, Butcher I, Lu J, McHugh GS, et al. Predicting outcome after traumatic brain injury: development and international validation of prognostic scores based on admission characteristics. PLOS Med 2008;5. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0050165.
- Roozenbeek B, Lingsma HF, Perel P, Edwards P, Roberts I, Murray GD, et al. The added value of ordinal analysis in clinical trials: an example in traumatic brain injury. Crit Care 2011;15. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc10240.
- Peto R, Pike MC, Armitage P, Breslaw NE, Cox DR, Howard SV, et al. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. I. Introduction and design. Br J Cancer 1976;34:585-612.
- The CRASH trial management group on behalf of the CRASH trial collaborators . The CRASH trial protocol (corticosteroid randomisation after significant head injury) [ISRCTN74459797]. BMC Emerg Med 2001;11.
- International Stroke Trial Collaborative Group . The International Stroke Trial (IST): a randomised trial of aspirin subcataneous heparin, both, or neither among 19435 patients with acute ischaemic stroke. Lancet 1997;349:1569-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(97)04011-7.
- Murray GD, Barer D, Choi S, Fernandes H, Gregson B, Lees KR, et al. Design and analysis of phase III trials with ordered outcome scales: the concept of the sliding dichotomy. J Neurotrauma 2005;22:511-17. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2005.22.511.
- Ilodigwe D, Murray GD, Kassell NF, Torner J, Kerr RS, Molyneux AJ, et al. Sliding dichotomy compared with fixed dichotomization of ordinal outcome scales in subarachnoid hemorrhage trials. J Neurosurg 2013;118:3-12. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.9.JNS111383.
- Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D. CONSORT Group . CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Trials 2010;11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-11-32.
- Health Research Authority . Progress and Safety Reporting 2017. www.hra.nhs.uk/resources/during-and-after-your-study/progress-and-safety-reporting (accessed 17 July 2018).
- Grieve R, Sadique Z, Gomes M, Smith M, Lecky FE, Hutchinson PJA, et al. An evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of alternative care locations for critically ill adult patients with acute traumatic brain injury. Br J Neurosurg 2016;30:388-96. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688697.2016.1161166.
- Peto R, Pike MC, Armitage P, Breslow NE, Cox DR, Howard SV, et al. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. Analysis and examples. Br J Cancer 1977;35:1-39. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1977.1.
- Maekawa T, Yamashita S, Nagao S, Hayashi N, Ohashi Y. Brain-Hypothermia Study Group . Prolonged mild therapeutic hypothermia versus fever control with tight hemodynamic monitoring and slow rewarming in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: a randomized controlled trial. J Neurotrauma 2015;32:422-9. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2013.3197.
- Clifton GL, Valadka A, Zygun D, Coffey CS, Drever P, Fourwinds S, et al. Very early hypothermia induction in patients with severe brain injury (the National Acute Brain Injury Study: Hypothermia II): a randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:131-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70300-8.
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Book Series. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Crossley S, Reid J, McLatchie R, Hayton J, Clark C, MacDougall M, et al. A systematic review of therapeutic hypothermia for adult patients following traumatic brain injury. Crit Care 2014;18. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc13835.
- Zhu Y, Yin H, Zhang R, Ye X, Wei J. Therapeutic hypothermia versus normothermia in adult patients with traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis. Springerplus 2016;5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2391-2.
- Rhodes JK, Chandrasekaran S, Andrews PJ, Ang BT. Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XV. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2016.
- Crompton EM, Lubomirova I, Cotlarciuc I, Han TS, Sharma SD, Sharma P. Meta-analysis of therapeutic hypothermia for traumatic brain injury in adult and pediatric patients. Crit Care Med 2017;45:575-83. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000002205.
- Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009;339. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700.
- Hirayama TKY, Kano T, Hayashi N, Tsubokawa T, Nagai HIS, Maeda M. Intracranial Pressure IX. Tokyo: Springer-Verlag; 1994.
- Lee HC, Chuang HC, Cho DY, Cheng KF, Lin PH, Chen CC. Applying cerebral hypothermia and brain oxygen monitoring in treating severe traumatic brain injury. World Neurosurg 2010;74:654-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2010.06.019.
- Smrcka M, Vidlák M, Máca K, Smrcka V, Gál R. The influence of mild hypothermia on ICP, CPP and outcome in patients with primary and secondary brain injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl 2005;95:273-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-211-32318-X_56.
- Zhao QJ, Zhang XG, Wang LX. Mild hypothermia therapy reduces blood glucose and lactate and improves neurologic outcomes in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Crit Care 2011;26:311-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2010.08.014.
- Guo W, Wang LL, Cai KH. A control study on mild hypothermia in treament of severe craniocerebral injury. Journal of Xianxiang Medical College 2004;21:269-71.
- Hashiguchi N, Shiozaki T, Ogura H, Tanaka H, Koh T, Noborio M, et al. Mild hypothermia reduces expression of heat shock protein 60 in leukocytes from severely head-injured patients. J Trauma 2003;55:1054-60. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.TA.0000033252.43742.8B.
- Clifton MG, Valadka PA, Aisuku IP, Okonkwo DO. Future of rewarming in therapeutic hypothermia for traumatic brain injury: a personalized plan. Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag 2011;1:3-7. https://doi.org/10.1089/ther.2010.1500.
- Lee BK, Jeung KW, Lee SC, Min YI, Ryu HH, Kim MJ, et al. Augmentation of the cooling capacity of refrigerated fluid by minimizing heat gain of the fluid using a simple method of cold insulation. Acad Emerg Med 2010;17:673-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1553-2712.2010.00748.x.
- Presneill J, Gantner D, Nichol A, McArthur C, Forbes A, Kasza J, et al. Statistical analysis plan for the POLAR-RCT: the Prophylactic hypOthermia trial to Lessen trAumatic bRain injury–Randomised Controlled Trial. Trials 2018;19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-018-2610-y.
- Downs SH, Black N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health 1998;52:377-84. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.52.6.377.
- Temple A, Porter R. Predicting Neurological Outcome and Survival Cardiac Arrest. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care and Pain 2012;12:283-7. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjaceaccp/mks029.
- Nichol A GD, Presneill J, Murray L, Trapani T, Bernard S, Cameron P, et al. Protocol for a multicentre RCT of early and sustained prophylactic hypothermia. Crit Care Resusc 2015;17:92-100.
- ClinicalTrials.gov . Randomised Controlled Trial of Long-Term Mild Hypothermia for Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (LTH-I) n.d. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01886222 (accessed 18 July 2018).
- Madden LK, DeVon HA. A systematic review of the effects of body temperature on outcome after adult traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Nurs 2015;47:190-203. https://doi.org/10.1097/JNN.0000000000000142.
- Hutchison JS, Guerguerian AM. Cooling of children with severe traumatic brain injury. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:527-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70058-9.
- Adelson PD, Wisniewski SR, Beca J, Brown SD, Bell M, Muizelaar JP, et al. Comparison of hypothermia and normothermia after severe traumatic brain injury in children (Cool Kids): a Phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:546-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70077-2.
- Adelson PD. Hypothermia following pediatric traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 2009;26:429-36. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2008.0571.
- Morgan TJ. The oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve in critical illness. Critical Care Resusc 1999;1.
- Abdul Aziz KA, Meduoye A. Is pH-stat or alpha-stat the best technique to follow in patients undergoing deep hypothermic circulatory arrest?. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2010;10:271-82. https://doi.org/10.1510/icvts.2009.214130.
- Nielsen N, Wetterslev J, Cronberg T, Erlinge D, Gasche Y, Hassager C, et al. Targeted temperature management at 33 °C versus 36 °C after cardiac arrest. N Eng J Med 2013;369:2197-206. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1310519.
- Murkin JM, Farrar JK, Tweed WA, McKenzie FN, Guiraudon G. Cerebral autoregulation and flow/metabolism coupling during cardiopulmonary bypass: the influence of PaCO2. Anesth Analg 1987;66:825-32. https://doi.org/10.1213/00000539-198709000-00003.
- Kiziltan HT, Baltali M, Bilen A, Seydaoglu G, Incesoz M, Tasdelen A, et al. Comparison of alpha-stat and pH-stat cardiopulmonary bypass in relation to jugular venous oxygen saturation and cerebral glucose-oxygen utilization. Anesth Analg 2003;96:644-50. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ANE.0000048826.67870.85.
- Sakamoto T, Kurosawa H, Shin’oka T, Aoki M, Isomatsu Y. The influence of pH strategy on cerebral and collateral circulation during hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass in cyanotic patients with heart disease: results of a randomized trial and real-time monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004;127:12-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.08.033.
- Morray JP, Pavlin EG. Oxygen delivery and consumption during hypothermia and rewarming in the dog. Anesthesiology 1990;72:510-16. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-199003000-00020.
- Oddo M, Frangos S, Milby A, Chen I, Maloney-Wilensky E, Murtrie EM, et al. Induced normothermia attenuates cerebral metabolic distress in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and refractory fever. Stroke 2009;40:1913-16. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.534115.
- Flynn LM, Rhodes J, Andrews PJ. Therapeutic hypothermia reduces intracranial pressure and partial brain oxygen tension in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: preliminary data from the Eurotherm3235 Trial. Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag 2015;5:143-51. https://doi.org/10.1089/ther.2015.0002.
- Oddo M, Levine JM, Kumar M, Iglesias K, Frangos S, Maloney-Wilensky E, et al. Anemia and brain oxygen after severe traumatic brain injury. Intensive Care Med 2012;38:1497-504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-012-2593-1.
- Dengler B, Garvin R, Seifi A. Can therapeutic hypothermia trigger propofol-related infusion syndrome?. J Crit Care 2015;30:823-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.03.027.
- Fudickar A, Bein B, Tonner PH. Propofol infusion syndrome in anaesthesia and intensive care medicine. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2006;19:404-10. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aco.0000236140.08228.f1.
- Vasile B, Rasulo F, Candiani A, Latronico N. The pathophysiology of propofol infusion syndrome: a simple name for a complex syndrome. Intensive Care Med 2003;29:1417-25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1905-x.
- Leslie K, Sessler DI, Bjorksten AR, Moayeri A. Mild hypothermia alters propofol pharmacokinetics and increases the duration of action of atracurium. Anesth Analg 1995;80:1007-14.
- Bjelland TW, Klepstad P, Haugen BO, Nilsen T, Dale O. Effects of hypothermia on the disposition of morphine, midazolam, fentanyl, and propofol in intensive care unit patients. Drug Metab Dispos 2013;41:214-23. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.112.045567.
- Heier T, Caldwell JE. Impact of hypothermia on the response to neuromuscular blocking drugs. Anesthesiology 2006;104:1070-80. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200605000-00025.
- Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, Arabi YM, Davies AR, Urso P, et al. Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury. N Eng J Med 2011;364. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1102077.
- Hutchinson PJ, Kolias AG, Timofeev IS, Corteen EA, Czosnyka M, Timothy J, et al. Trial of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic intracranial hypertension. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1119-30. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1605215.
- Roberts I, Yates D, Sandercock P, Farrell B, Wasserberg J, Lomas G, et al. Effect of intravenous corticosteroids on death within 14 days in 10008 adults with clinically significant head injury (MRC CRASH trial): randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2004;364:1321-28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17188-2.
- Andrews PJ, Sinclair HL, Battison CG, Polderman KH, Citerio G, Mascia L, et al. European Society of Intensive Care Medicine study of therapeutic hypothermia (32–35 °C) for intracranial pressure reduction after traumatic brain injury (the Eurotherm3235Trial). Trials 2011;12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-12-8.
- NHS Scotland . Research Ethics Structure in Scotland n.d. www.nhsresearchscotland.org.uk/services/research-ethics (accessed 9 August 2018).
- Sydenham E, Roberts I, Alderson P. Hypothermia for traumatic head injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;2. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001048.pub3.
- Watson H, Shepherd A, Rhodes J, Andrews PJD. Revisited: a systematic review of therapeutic hypothermia for adult patients following traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med 2018;46:972-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/ccm.0000000000003125.
- Harris OA, Muh CR, Surles MC, Pan Y, Rozycki G, Macleod J, et al. Discrete cerebral hypothermia in the management of traumatic brain injury: a randomized controlled trial. J Neurosurg 2009;110:1256-64. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.1.JNS081320.
- Hutchison JS, Ward RE, Lacroix J, Hébert PC, Barnes MA, Bohn DJ, et al. Hypothermia therapy after traumatic brain injury in children. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2447-56. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0706930.
- Ishikura H, Yamagami K, Akahori M, Shoji Y, Fukui H, Tanaka T. Changes in blood platelet count and serum thrombopoetin (TPO) level under moderate hypothermic therapy in traumatic severe closed head injury. Crit Care Med 1998;26. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199801001-00209.
- Maekawa T. Tsuyoshi Maekawa hwms . BHYPO Study 2009.
Appendix 1 Induction and maintenance of therapeutic hypothermia
Continue stage 1 and 2 therapy as indicated throughout the hypothermia/rewarming interventions.
Prior to induction of hypothermia-
Opiate and propofol (suggested dosage of 10 µg/kg/minute) or midazolam infusions.
-
Paracetamol (1 g/6 hours oral/rectal/intravenously).
-
Ensure that extremities are covered.
-
Ensure that the maintenance method of hypothermia is in place and ready for use.
-
Core temperature monitoring in place – bladder, oesophageal, pulmonary artery catheter or rectum.
-
Assess baseline laboratory values as appropriate.
-
Infuse 20–30 ml/kg of refrigerated 0.9% saline intravenously within 30 minutes.
-
Closely monitor all vital signs during the induction phase of hypothermia.
-
Observe continuously for obvious signs of shivering.
-
Assess for signs of shivering using the shivering assessment tool every 30 minutes during the first 2 hours and hourly thereafter, and if there is any indication of shivering between these times.
-
Maintain hypothermia for > 48 hours.
-
Maintain ICP of ≤ 20 mmHg by adjusting temperature (32–35 °C) (i.e. higher ICP may require a lower temperature).
-
Assess laboratory values as appropriate during hypothermia therapy.
-
Observe continuously for obvious signs of shivering.
-
Assess for signs of shivering using the shivering assessment tool every 30 minutes during the first 2 hours and hourly thereafter, and if there is any indication of shivering between these times.
-
Please note that all participants should be closely monitored and their care assessed to avoid any side effects of induced hypothermia therapy:
-
hypovolaemia
-
respiratory and metabolic acidosis
-
hypokalaemia
-
relative drug overdose
-
hypotension
-
coagulopathy.
-
There is no maximum duration of hypothermia; however, rewarming should first be considered 48 hours from induction of hypothermia only if ICP is ≤ 20 mmHg.
Rewarming rate: 1 °C/4 hours (0.25 °C per hour) until core temperature is ≥ 36 °C.
Assess laboratory values as appropriate.
All patients should be closely monitored and their care assessed to avoid any side effects:
-
hypotension
-
hypovolaemia
-
hyperkalaemia
-
arrhythmias.
Pause rewarming if ICP is > 20 mmHg and if necessary recool to maintain ICP of ≤ 20 mmHg.
Consider stage 3 options if necessary:
-
barbiturate infusion
-
decompressive craniectomy.
Appendix 2 Detection and treatment of shivering
-
Opiate and propofol or midazolam infusions.
-
Paracetamol (1 g/6 hours enterally/intravenously).
-
Ensure that extremities are covered.
-
Observe continuously for obvious signs of shivering.
-
Assess for signs of shivering using the shivering assessment tool every 15 minutes until target temperature achieved.
-
Observe continuously for obvious signs of shivering.
-
Assess for signs of shivering using the shivering assessment tool every 30 minutes during the first 2 hours and hourly thereafter, and if there is any indication of shivering between these times.
Observe ECG and/or BIS trace continuously for artefact.
Formal assessment.
Observe patient for 2 minutes, during which time visually inspect and palpate jaw, neck, chest, arms and legs.
Score shivering as follows:
-
0 = no shivering
-
1 = mild: shivering localised to jaw, neck and/or chest only
-
2 = moderate: shivering involves gross movement of arms or legs, in addition to neck, chest and two extremities
-
3 = severe: shivering involves gross movements of the trunk and arms and legs.
If the patient scores ≥ 1 using this scale, please refer to the Prevention of Shivering Guideline overleaf.
BIS, Bispectral Index; ECG, electrocardiogram.
Based on recommendations in Badjatia et al. 95
FIGURE 18.
Shivering treatment guideline. a, Definition of ‘deeply sedated’ – no response to voice, but movement or eye opening to physical stimulation. b, Increase in propofol dose every 10 minutes until deeply sedated state is achieved and/or Bispectral Index. b.p.m., beats per minute.
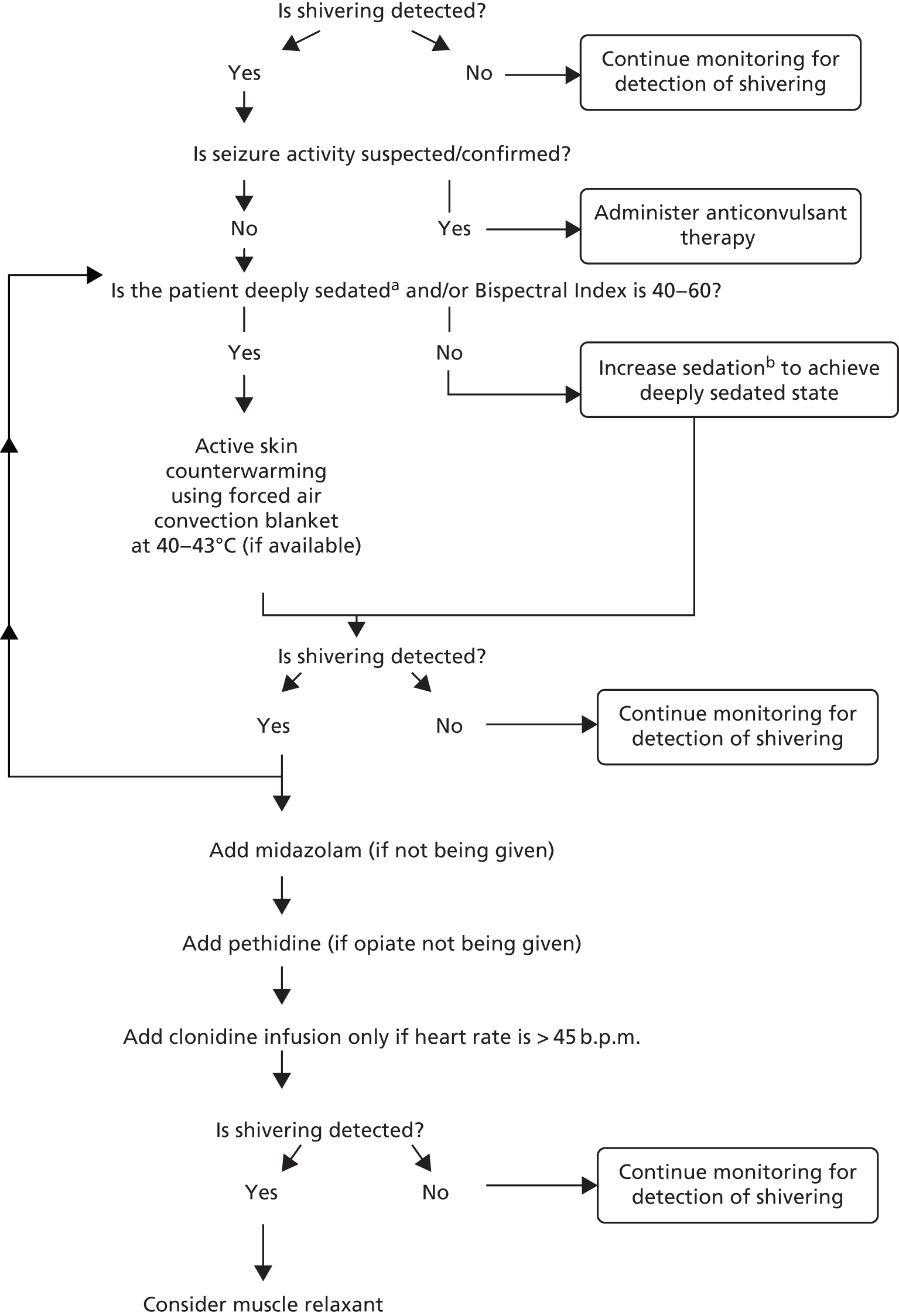
Appendix 3 Data Safety Monitoring Committee charter
Appendix 4 Systematic review protocol: PROSPERO international prospective register of systematic reviews
Appendix 5 Characteristics of included randomised controlled trials
The table below shows the characteristics of the included RCTs.
| Study: first author and year of publication | Method of intervention | Target or lowest body temperature achieved (°C) | Duration of TH | Maximum time between TBI and TH | Temperature management of control group (°C) | Lowest GCS score on admission (GCS score of 3–15) | Rate of rewarming |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andrews 20151 | i.v. cooling and individual centre techniques | 32–35 | 48 hours | 72 hours to 10 days | No temperature control | 3 | 0.25 °C/hour |
| Clifton 199373 | Cooling blankets | 32–33 | 48 hours | 6 hours | CN to 37 | 4 | 0.25 °C/hour |
| Clifton 200176 | Application of ice and gastric lavage | 33.2 ± 1.0 | 47.2 ± 3.0 hours | 6 hours | CN to 37 | 3 | 0.25 °C/hour |
| Clifton 2011121 | i.v. cooling, surface cooling and gastric lavage | 33 | 48 hours | 2.5 hours | CN to 37 | 3 | 0.25 °C/hour |
| Gal 200264 | Forced air cooling and circulating-water mattress cooling | 34 | 72 hours | 15 hours | CN 36.5–37.5 | 3 | – |
| Guo 2004119 | Cooling blankets | 32–34 | 24–48 hours extra following ‘normal’ ICP | 24 hours | No temperature control | TH: 5.3 ± 1.5 | – |
| Control: 5.2 ± 1.4 | |||||||
| Hashigushi 2003120 | Water blankets | 33.5 | 48 hours | – | CN | 3 | 1 °C/24 hours |
| Hirayama 1994115 | Cooling blankets | 32–33 | 48 hours | 6 hours | Normothermia 37–38, no further detail | GCS score of ≤ 8 | 0.25 °C/hour |
| Jiang 200069 | Cooling blankets | 33 | 3–14 days | – | CN 37–38 | 3 | – |
| Lee 2010122 | Surface cooling and ice pillows | 33 | – | – | Unclear | 4 | – |
| Liu 200660 | Cooling blankets and ice bags | 33–35 | 0–6 hours (average 4.5 hours) on 3 consecutive days | 2 hours | No temperature control | 3 | – |
| Maekawa 2015107 | Cooling blankets | 32–34 | Ideally > 72 hours | 92 hours | CN 35.5–37 | 4 | – |
| Marion 199375 | Cooling blankets and gastric lavage | 32–33 | 24 hours | 10 hours | CN 37–38 | 3 | – |
| Marion 199771 | Cooling blankets and nasogastric lavage | 32–33 | 24 hours | 6 hours | CN | 3 | 1 °C/hour |
| Qiu 200577 | Cooling blanket and/or cooling cap and/or ice bags | Brain 33–35, rectal 34.5–36 | Natural rewarming after 3–5 days (average 4.3 days) | ‘Immediately’ or 3–5 days (average 4.3 days) after craniotomy | Controlled to 38 | 3 | – |
| Qiu 200759 | Cooling blanket and/or cooling cap and/or ice bags | Brain 33–35, rectal 34.5–36 | 4 days | Started immediately after unilateral craniotomy | CN to 37.5 | < 6 | – |
| Shiozaki 199374 | Surface cooling | Core 34, bladder 33.5–34.5 | 48 hours | 2 hours | Unclear | – | – |
| Shiozaki 1999117 | Surface cooling | 33.5–34.5 | 48 hours | – | CN 36.5–37.5 | 4 | 1 °C/24 hours |
| Smrcka 2005117 | Surface cooling | 34 | 72 hours | 15 hours | Unclear | – | – |
| Zhao 2011118 | Cooling blankets | 32.5–33 | 72 hours | 6 hours | Unclear | 3 | – |
| Zhi 200363 | Cooling blankets | 32 | 1–7 days (average 62.4 hours ± 27.6 hours) | 20 hours | Unclear | – | 0.25 °C/hour |
Appendix 6 Comparison of included trials from previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses
| Study: first author and year of publication | Study: first author and year of publication | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sydenham 2009153 (Cochrane review) | Crossley 2014110 | Zhu 2016112 | Watson 2018154 | |
| Adelson 2005 (HYPO1)56 | Y | N | N | N |
| Adelson 2005 (HYPO2)56 | Y | N | N | N |
| Aibiki 200068 | Y | N | N | N |
| Andrews 20151 | - | - | Y | Y |
| Biswas 200257 | Y | N | N | N |
| Clifton 1992 | Y | N | N | N |
| Clifton 199373 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Clifton 200176 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Clifton 2011121 | - | Y | N | Y |
| Gal 200264 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Guo 2004119 | Y | Y | N | Y |
| Harris 2009155 | Y | N | N | N |
| Hashigushi 2003120 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Hirayama 1994115 | Y | Y | N | Y |
| Hutchison 2008156 | Y | N | N | N |
| Ishikura 1998157 | Y | N | N | N |
| Jiang 200069 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Lee 2010122 | – | Y | Y | Y |
| Liu 200660 | N | Y | N | Y |
| Maekawa 2009158 | N | Y | N (Maekawa 2015107) | N (Maekawa 2015107) |
| Maekawa 2015107 | – | – | Y | Y |
| Marion 199375 | N | Y | N | Y |
| Marion 199771 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Qiu 200577 | N | Y | Y | Y |
| Qiu 200658 | N | N | Y | N |
| Qiu 200759 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Shiozaki 199374 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Shiozaki 1999117 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Shiozaki 200149 | Y | N | Y | N |
| Smrcka 2005117 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Yan 200167 | Y | N | N | N |
| Zhang 200070 | Y | N | N | N |
| Zhao 2011118 | – | Y | Y | Y |
| Zhi 200363 | N | Y | Y | Y |
| Total studies (n) | 23 | 20 | 18 | 21 |
Appendix 7 Quality assessment with academic bias
Academic bias for all 21 included RCTs is shown below. The first table outlines the quality assessment of the two new RCTs added to update the systematic review. The second table shows the characteristics of the other 19 previously included RCTs. Those scoring 14–18 were considered studies having a low risk of bias and those scoring ≤ 13 were considered having a high risk of bias.
| Quality assessment | Study: first author and year of publication | |
|---|---|---|
| Andrews 20151 | Maekawa 2015107 | |
| Has the control group been managed to normothermia? | Yes | Yes |
| Yes = 1; no/NS = 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Was the control group actively warmed on admission if hypothermic? | NS | NS |
| Yes = 0; NS = 1; no = 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Has the treatment arm received barbiturates in addition to TH? | No | No |
| Yes = 0; NS = 1; no = 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Are there significant differences between the treatment and control sample populations? | No | No |
| Yes = 0; no = 1; NS = 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Has the standard treatment that the control group received been clearly outlined? | Yes | Yes |
| Yes = 1; no = 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Adequacy of randomisation technique? | Adequate | Adequate |
| Adequate = 1; inadequate/unclear = 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Blinding of investigators | No | No |
| Yes = 1; no/NS = 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Blinding of participants | No | No |
| Yes = 1; no/NS = 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Blinding of outcome assessor | Yes | Yes |
| Yes = 1; no/NS = 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Blinding of data analysis | Yes | Yes |
| Yes = 1; no/NS = 0 | 1 | 1 |
| ITT analysis | Yes | Yes |
| Yes = 1; not stated but confirmed on study assessment = 1; stated but not confirmed on study assessment = 0; no/NS = 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Completion of follow-up (at 6 months if possible) | Yes, loss of 10 cases to follow-up | Yes, 100% |
| 100% = 2; > 95% = 1; < 95% = 0; no/NS = 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Reasons given when patients were excluded from enrolment, allocation follow-up or analysis? | Yes | Yes |
| Yes = 1; no = 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Has the first author published two or more RCTs that have been included in this review? | No | No |
| Yes = 0; no = 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Total score | 14 | 15 |
| Maximum score | 18 | 18 |
| Study; first author and year of publication | Has the first author published at least two RCTs that have been included in this review? | Yes = 0; no = 2 | Original score from Crossley 2014110 | Following assessment of academic bias (maximum score = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clifton 199373 | Y | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| Clifton 200176 | Y | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| Clifton 2011121 | Y | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Gal 200264 | N | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| Guo 2004119 | N | 2 | 10 | 12 |
| Hashigushi 2003120 | N | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| Hirayama 1994115 | N | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| Jiang 200069 | N | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| Lee 2010122 | N | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| Liu 200660 | N | 2 | 6 | 8 |
| Marion 199375 | Y | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| Marion 199771 | Y | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| Qiu 200577 | Y | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| Qiu 200759 | Y | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| Shiozaki 199374 | Y | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| Shiozaki 1999117 | Y | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| Smrcka 2005117 | N | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| Zhao 2011118 | N | 2 | 7 | 9 |
| Zhi 200363 | N | 2 | 6 | 8 |
Appendix 8 Modified Jadad scores for included randomised controlled trials
| Study: first author and year of publication | Randomisation (2, 1 or 0 points) | Blinding (2, 1 or 0 points) | Accounting for all patients (1 point) | Total modified Jadad score (maximum 3 points) | Low quality (0, 1 or 2 points) or high quality (3 points) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andrews 20151 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | High |
| Clifton 199373 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | High |
| Clifton 200176 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Low |
| Clifton 2011121 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | High |
| Gal 200264 | 1 – inadequate | 0 | 0 | 1 | Low |
| Guo 2004119 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Low |
| Hashigushi 2003120 | 1 – method not stated | 0 | 1 | 2 | Low |
| Hirayama 1994115 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Low |
| Jiang 200069 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Low |
| Lee 2010116 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Low |
| Liu 200660 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Low |
| Maekawa 2015107 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | High |
| Marion 199375 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | High |
| Marion 199771 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | High |
| Qiu 200577 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Low |
| Qiu 200759 | 1 – unclear if adequate | 0 | 1 | 2 | Low |
| Shiozaki 199374 | 1 – inadequate | 0 | 1 | 2 | Low |
| Shiozaki 1999117 | 1 – inadequate | 0 | 1 | 2 | Low |
| Smrcka 2005117 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Low |
| Zhao 2011118 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Low |
| Zhi 200363 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Low |
List of abbreviations
- AE
- adverse event
- ARDS
- acute respiratory distress syndrome
- ATP
- adenosine triphosphate
- BBB
- blood–brain barrier
- B-HYPO
- Brain Hypothermia study
- CENTRAL
- Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials
- CI
- confidence interval
- CNS
- central nervous system
- CONSORT
- Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials
- CPP
- cerebral perfusion pressure
- CRASH
- Corticosteroid Randomisation After Significant Head Injury
- CRF
- case report form
- CT
- computed tomography
- DMEC
- Data Monitoring and Ethics Committee
- DSMC
- Data and Safety Monitoring Committee
- EU
- European Union
- GCS
- Glasgow Coma Scale
- GOS
- Glasgow Outcome Scale
- GOSE
- Glasgow Outcome Scale – Extended
- HR
- hazard ratio
- ICP
- intracranial pressure
- ICU
- intensive care unit
- IMPACT
- International Mission on Prognosis and Clinical Trial Design in Traumatic Brain Injury
- IQR
- interquartile range
- ITT
- intention to treat
- MAP
- mean arterial pressure
- MOF
- multiorgan failure
- MOHS
- Modified Oxford Handicap Scale
- MRC
- Medical Research Council
- OHDC
- oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve
- OR
- odds ratio
- PbtO2
- brain tissue oxygen tension
- PKC
- protein kinase C
- POLAR
- Prophylactic Hypothermia trial to Lessen Traumatic Brain Injury
- PP
- per protocol
- PRIS
- propofol-related infusion system
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RR
- risk ratio
- RRT
- renal replacement therapy
- SAE
- serious adverse event
- SOFA
- sequential organ failure assessment
- TBI
- traumatic brain injury
- TH
- therapeutic hypothermia
