Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the HTA programme as project number 13/96/07. The contractual start date was in March 2015. The draft report began editorial review in February 2019 and was accepted for publication in July 2019. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The HTA editors and publisher have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the draft document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Oliver Rivero-Arias, Ursula Bowler, Edmund Juszczak, Marian Knight, Louise Linsell and Julia Sanders report receipt of funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) outside the submitted work. Edmund Juszczak reports Clinical Trials Unit infrastructure support funding received from NIHR and active membership of the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Commissioning Board and the HTA General Board while the study was being undertaken.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2019. This work was produced by Knight et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
2019 Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO
Chapter 1 Introduction
Sepsis is a leading cause of direct and indirect maternal death in the UK, and, globally, is estimated to cause almost 20,000 maternal deaths annually. 1,2 In addition to very maternal death, an estimated 70 women have severe sepsis (requiring level 2 or 3 critical care) but survive. 3 An increased risk of sepsis in association with caesarean section has been recognised for many years,4 and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)’s guidance recommends the use of prophylactic antibiotics at all caesarean births,5 based on substantial randomised controlled trial (RCT) evidence of clinical effectiveness. 6 Three separate studies, conducted as part of a previous National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Programme Grants for Applied Research programme, using both UK and US data, have documented an additional risk associated with operative vaginal birth (forceps or ventouse/vacuum extraction),3,7–9 particularly in relation to group A streptococcal infection, one of the most rapidly progressive causes of maternal infection. 2,3 A Cochrane review,10 updated in 2017, identified only one small previous trial of prophylactic antibiotics following operative vaginal birth, including a total of 393 women, with a relative risk of 0.07 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.00 to 1.21] for post-partum endometritis; given the small study size and extreme result, the authors suggested that further robust evidence is needed.
Further work suggests that the burden of localised infection following operative vaginal birth is also significant,11 with > 10% of women experiencing symptoms of perineal wound infection in the 3 weeks after giving birth. Women prioritising childbirth-related perineal trauma outcomes have rated ’fear of perineal infection’ as the most important outcome they are concerned about in the first few weeks after childbirth. 12
Latest figures show that approximately 12% of women have an operative vaginal (forceps or ventouse) birth in England, representing a significant burden of potentially preventable morbidity. 13 Current NICE guidelines for intrapartum care make no reference to prophylactic antibiotics following instrumental vaginal birth. 14 The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG)’s guidance on operative vaginal delivery15 states that there are insufficient data to justify the use of prophylactic antibiotics in operative vaginal birth, referencing the Cochrane review10 identified above. Recognising the importance of antibiotic stewardship, the World Health Organization (WHO)’s recommendations on prevention and treatment of maternal peripartum infections explicitly state that routine antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended for women undergoing operative vaginal birth, again citing a lack of evidence of benefit. 16 The RCOG’s guidance on bacterial sepsis following pregnancy does not identify operative vaginal birth as a risk factor for post-partum infection;17 a lack of awareness of the associated risk may contribute to a delay in diagnosis. Evidence suggests that progression to severe sepsis following birth, particularly in association with group A streptococcal infection, can be very rapid. 2,3 This emphasises the importance of urgent investigation of potential prophylactic measures.
Women with generalised and localised infection following operative vaginal birth incur additional health-care resources compared with those without infection. Although there are no studies quantifying these additional resources accurately, women with post-surgical infection after undergoing caesarean section follow a similar treatment pathway to women with localised infection after instrumental vaginal birth. Research has estimated that infection after caesarean section costs, annually, an additional £226 per patient compared with women with no post-surgical infection. 18 These extra health-care costs are attributable to additional hospital length of stay, re-admissions and community care. Therefore, there remains the potential for a reduction in health-care costs if routine antibiotic prophylaxis prevents post-partum infection.
Presentations of the data from the NIHR programme studies3,7–9 at national meetings clearly showed that the natural response of the clinical community is to introduce prophylactic management with antibiotics, without clear evidence for the effectiveness of this approach following operative birth, because antibiotic prophylaxis been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of infection following caesarean birth. 10 Giving antibiotic prophylaxis after operative vaginal birth has thus been introduced into local guidance unsupported by evidence. Although similar in some ways, there are clear differences between the wound sites and potential contaminating organisms at caesarean section and instrumental birth, so it cannot be assumed that single-dose prophylactic antibiotics will be equally effective in both circumstances. In addition, in the context of growing concerns about antibiotic resistance,19–21 it is vital that there is robust evidence behind any prophylactic use of antibiotics.
Recent recommendations suggest that antibiotic prophylaxis for caesarean section should be given prior to delivery. This trial specifically aimed to investigate the use of antibiotic prophylaxis after operative vaginal birth of the infant for the following reasons:
-
The potential risks of in utero exposure to antibiotics are now widely recognised. The risk of necrotising enterocolitis22 and cerebral palsy23 is known to be increased among the children of women managed with antibiotics for suspected preterm labour. Maternal antibiotic use in late pregnancy has also been associated with an increased risk of asthma in early childhood24 and with very early-onset inflammatory bowel disease. 25 Reports have identified differences in the infant microbiome with maternal antibiotic administration and the potential for long-term impacts on other disease states is a concern. 26
-
The major difference between the episiotomy wound and the caesarean section wound is the fact that there is ongoing contamination of the surgical field. Thus, with caesarean section, as soon as the operation is completed and a wound dressing applied, the major risk of infection is over. In contrast, an episiotomy wound is impossible to cover and, therefore, our rationale is to actually increase the length of time that there would be therapeutic levels of antibiotic from a single dose by giving it post delivery, to cover for ongoing contamination for as long as possible.
-
There have been several cases of anaphylaxis relating to antibiotics given prophylactically for caesarean birth identified in a NIHR-funded study. 27 Although the incidence is extremely low, this is of concern, particularly with antenatal administration, in which there is the potential for fetal compromise.
Twelve per cent of women in the UK undergo forceps or ventouse deliveries,13 which is an estimated 90,000 women annually. The conservatively estimated incidence of maternal infection following operative vaginal birth is 4%, based on the one previous trial,10 which results in an estimated 3600 women potentially having an infection after instrumental vaginal birth. Of these women, around 200 will be diagnosed with severe infection7 and up to four may die from their infection. 28 There is, therefore, considerable scope for direct patient benefit from an effective preventative strategy. Other non-randomised studies suggest higher infection rates of up to 16%,29 which would correspondingly lead to an even greater potential benefit from a preventative therapy.
Objective
The objectives of this research were to investigate whether or not a single dose of prophylactic antibiotic following operative vaginal birth is clinically effective for preventing confirmed or presumed maternal infection and to investigate the associated impact on health-care costs.
Chapter 2 Methods
The trial protocol28 and results30 have been previously published and parts of the published articles are reproduced throughout this report. These have been reproduced with permission from Knight et al. 28 [This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.] and Knight et al. 30 [This article is available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0) ‘Beyond maternal death’. You may copy and distribute the article, create extracts, abstracts and new works from the article, alter and revise the article, text or data mine the article and otherwise reuse the article commercially (including reuse and/or resale of the article) without permission from Elsevier. You must give appropriate credit to the original work, together with a link to the formal publication through the relevant DOI and a link to the Creative Commons user license above. You must indicate if any changes are made but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use of the work.]
Design
The A randomised controlled trial of prophylactic ANtibiotics to investigate the prevention of infection following Operative vaginal DElivery (ANODE) trial was a multicentre, randomised, blinded, placebo-controlled trial conducted in the UK.
Ethics approval and research governance
The ANODE trial protocol was approved by the Health Research Authority National Research Ethics Service Committee South Central – Hampshire B (study reference number 15/SC/0442).
Local approval and site-specific assessments were obtained from each NHS hospital site.
Patient and public involvement
The research question was initially prioritised by the user advisory group to the NIHR ‘Beyond maternal death’ programme, which generated the initial information about sepsis risk in association with operative vaginal birth. 9 To obtain the perspective of a group more representative of the wider maternity population, we contacted the PRIME (Public and Researchers Involvement in Maternity and Early pregnancy) group. PRIME is a patient and public involvement group that was set up in collaboration with the University of Birmingham Collaborations for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care (CLAHRC). PRIME group members helped design the trial processes and materials, particularly assisting with designing our approach to consent. The group was represented among the co-applicant group to continue to advise throughout the trial.
Participants
Inclusion criteria
-
Women aged ≥ 16 years who were willing and able to give informed consent.
-
Women who had had an operative vaginal delivery at ≥ 36+0 weeks’ gestation.
Exclusion criteria
Women were not eligible to enter the trial if any of the following applied:
-
A clinical indication for ongoing antibiotic administration post delivery [e.g. because of a confirmed antenatal or intrapartum infection, third- or fourth-degree tears (obstetric anal sphincter injury)]. Note that receiving antenatal antibiotics (e.g. for maternal group B streptococcal carriage or prolonged rupture of membranes) was not considered a reason for exclusion if there was no indication for ongoing antibiotic prescription post delivery.
-
Known allergy to penicillin or to any of the components of co-amoxiclav, as documented in hospital notes.
-
History of anaphylaxis (a severe hypersensitivity reaction) to another β-lactam agent (e.g. cephalosporin, carbapenem or monobactam), as documented in hospital notes.
Setting
The trial was conducted in 27 consultant-led obstetric units in England and Wales (see Appendix 1).
Informed consent and recruitment
Information about the trial was made widely available throughout the maternity units in the form of posters and leaflets [with QR (Quick Response) codes to the trial website]. Written information about the trial was available to all women at participating centres during their pregnancy through different routes, depending on the centre, for example at their antenatal booking visit, as part of their hand-held notes or at their 19- to 21-week scan visit.
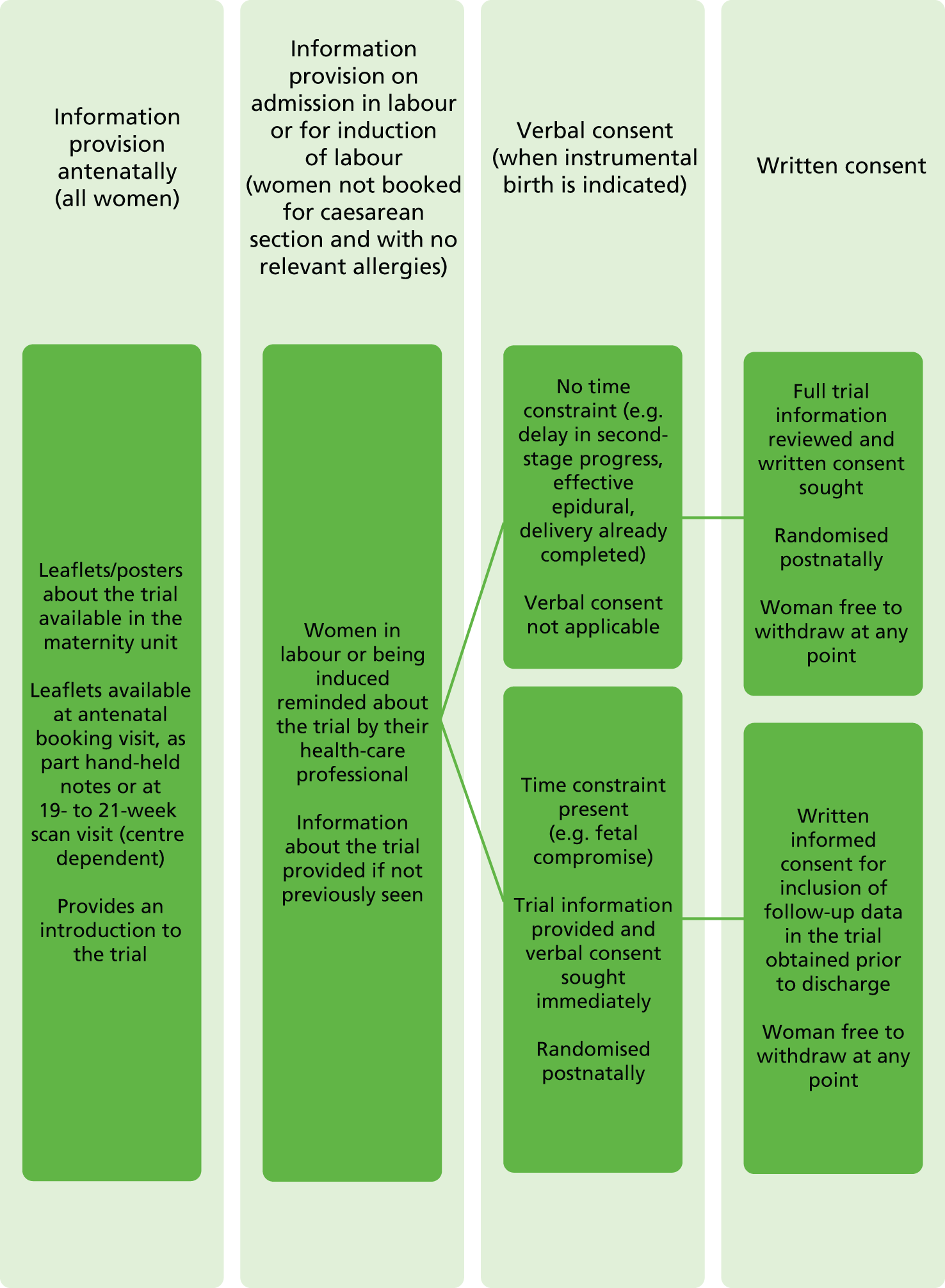
On admission, women in labour or admitted for induction were reminded about the trial by their health-care professional and information about the trial could be provided if not previously seen. After the clinical decision for operative vaginal birth had been made, the following approaches were used by the woman’s midwife, obstetrician or anaesthetist to obtain informed consent, depending on the clinical circumstances (Figure 1):
-
If there was no time constraint (e.g. in cases of operative vaginal birth for delayed second-stage progress or if birth was already completed), the health-care professional discussed the trial with the woman and provided her with the participant information leaflet. If she was happy to join the trial, then informed written consent was obtained.
-
If there was a time or other constraint (e.g. in cases of operative vaginal birth for suspected fetal compromise, or if an approach for written consent was considered inappropriate by the health professionals in attendance), women were approached to give verbal consent. It is possible that urgent deliveries are associated with a lower standard of asepsis, and so it was particularly important that these women were able to participate in the trial. If the attending obstetrician or midwife felt that it was appropriate, the woman was provided with verbal information about the trial and asked if she was willing to participate, in principle; if she agreed, she was randomised. Verbal consent was documented by the clinician recruiting the woman and countersigned by a witness. All women enrolled under this procedure were approached before discharge by trial midwives to give full written consent for inclusion of their data in the trial and for participation in the planned follow-up.
FIGURE 1.
Consent and randomisation processes. Reproduced from Knight et al. 28 This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt and build upon this work, for commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The text includes minor additions and formatting changes to the original text.
Intervention
Centres were supplied with sealed sequentially numbered indistinguishable packs containing trial treatment [a single dose of intravenous co-amoxiclav (1 g of amoxicillin/200 mg of clavulanic acid)] or placebo (a single dose of intravenous sterile saline), as designated. Bottles of 1000 mg/200 mg of co-amoxiclav, in the form of sterile powder for solution, were supplied for making up as an injection reconstituted with sterile water, which was also supplied. The placebo (0.9% saline) was supplied as 20 ml single-use vials of clear liquid. Reconstitution was not required.
As co-amoxiclav, when reconstituted, has a distinct colour and odour, it was impossible to blind those preparing and checking the intervention to women’s allocation. The investigational medicinal product (IMP) (co-amoxiclav or placebo) was made up in an opaque-coloured syringe so that the woman herself remained blinded to allocation. To ensure that awareness of allocation could not influence outcomes, it was specified that the research nurse/midwife conducting telephone follow-up should not have prepared or checked the intervention. Sites were instructed to give the intervention as soon as possible after women had given birth, and no later than 6 hours after birth of the baby.
Randomisation, blinding and code-breaking
A randomisation list was generated by the Senior Trials Statistician at the National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit Clinical Trials Unit (NPEU CTU) using permuted blocks of variable size to ensure balance and unpredictability overall. Pack numbers were added by the Senior Trials Programmer at the NPEU CTU, who liaised directly with the packaging and distribution company. Sites were provided with a series of sequential packs and stocks were replenished from the global sequence as required. Women were randomised by the allocation of the next sequentially numbered indistinguishable pack once consent and eligibility were established. Pack use was recorded by the recruiting site and reviewed by NPEU CTU.
An emergency code-breaking procedure was not required. As only a single dose of co-amoxiclav was administered, there was no need to code-break if further antibiotics were required. Centres were advised that if a woman had an anaphylactic reaction, she should be treated as if she had been given the active drug.
Internal pilot
We conducted an internal pilot during the first 9 months of the trial, when 1034 recruits were predicted, to test our recruitment and retention assumptions. The predefined stop–go criteria were:
-
If recruitment was ≥ 75% (n ≥ 775), then the target sample size was clearly achievable and Trial Steering Committee (TSC) recommendation to Health Technology Assessment (HTA) programme would be to continue directly with the main trial.
-
If recruitment was between 50% and 75% (517 ≤ n ≤ 775), then the TSC recommendation to the HTA programme would be to recruit more centres and review again in 6 months.
-
If recruitment was < 50% (n < 517), then urgent discussions were required between the Project Management Group and the TSC to undertake a detailed review of options to subsequently recommend to the HTA programme.
Outcomes
Primary outcome
Confirmed or suspected maternal infection within 6 weeks of delivery, as defined by one of the following:
-
a new prescription of antibiotics for presumed perineal wound-related infection, endometritis or uterine infection, urinary tract infection with systemic features or other systemic infection
-
confirmed systemic infection on culture
-
endometritis, as defined by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 31
An episode of endometritis defined according to the CDC required meeting at least one of the following criteria:
-
Organisms are cultured from fluid (including amniotic fluid) or tissue from endometrium obtained during an invasive procedure or biopsy.
-
The woman exhibits at least two of the following signs or symptoms: fever (> 38 °C), abdominal pain (with no other recognised cause), uterine tenderness (with no other recognised cause) or purulent drainage from uterus (with no other recognised cause).
Secondary outcomes
Systemic sepsis
This was defined according to modified systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria for pregnancy used in previous population-based surveillance studies,3,32 namely:
-
any woman dying from infection or suspected infection
-
any woman requiring level 2 or 3 critical care (or obstetric high-dependency unit-type care) because of severe sepsis or suspected severe sepsis
-
a clinical diagnosis of severe sepsis (two or more of the following) –
-
a temperature of > 38 °C or < 36 °C measured on two occasions at least 4 hours apart
-
a heart rate of > 100 beats per minute measured on two occasions at least 4 hours apart
-
a respiratory rate of > 20 breaths per minute measured on two occasions at least 4 hours apart
-
a white cell count of > 17 × 109/l or < 4 × 109/l or with > 10% immature band forms, measured on two occasions.
-
Perineal wound infection
This was defined according to the Public Health England Surveillance definition of surgical site infection (SSI),33 which falls under the following headings.
Superficial incisional infection
Superficial incisional infection is a SSI that occurs within 30 days of surgery, involves only the skin or subcutaneous tissue of the incision and meets at least one of the following criteria:
-
purulent drainage from superficial incision
-
culture of organisms and pus cells present in fluid/tissue from superficial incision or wound swab from superficial incision
-
at least two symptoms of inflammation – pain, tenderness, localised swelling, redness, heat AND EITHER (1) incision deliberately opened to manage infection OR (2) clinician’s diagnosis of superficial SSI.
Deep incisional infection
Deep incisional infection is a SSI involving the deep tissues (i.e. fascial and muscle layers) within 30 days of surgery (or 1 year if an implant is in place), and the infection appears to be related to the surgical procedure and meets at least one of the following criteria:
-
purulent drainage from deep incision (not organ space)
-
organisms from culture and pus cells present in fluid/tissue from deep incision or wound swab from deep incision
-
deep incision dehisces or deliberately opened and patient has at least one symptom of fever or localised pain/tenderness
-
abscess or other evidence of infection in deep incision – re-operation/histopathology/radiology
-
clinician’s diagnosis of deep incisional SSI.
Organ/space infection
Organ/space infection is a SSI involving the organ/space (other than the incision) opened or manipulated during the surgical procedure, that occurs within 30 days of surgery and the infection appears to be related to the surgical procedure and meets at least one of the following criteria:
-
purulent drainage from drain (through stab wound) into organ space
-
organisms from culture and pus cells present in fluid or tissue from organ/space or swab from organ/space
-
abscess or other evidence of infection in organ/space – re-operation/histopathology/radiology
-
clinician’s diagnosis of organ/space infection.
Perineal pain/use of pain relief/dyspareunia/ability to sit comfortably to feed the baby/need for additional perineal care/breastfeeding
This was identified using standard questions developed for the HOOP study34 and the PREVIEW study. 35
Maternal quality of life
This was elicited by the EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version (EQ-5D-5L), questionnaire. 36
Hospital bed stay/hospital and general practitioner visits/wound breakdown/antibiotic side effects
This was identified through specific questions included in the maternal questionnaire.
Sample size
Observational studies of operative vaginal birth estimate postnatal infection to occur in between 2% and 16% of women. 29 The single existing trial of antibiotic prophylaxis at operative vaginal birth found a 4% rate of postnatal infection. 10 We therefore used this more conservative estimate of the maternal infection rate following operative vaginal birth. We assumed an estimated relative risk reduction of 50% in this rate with antibiotics to 2% in the treatment arm. The single trial relating to operative vaginal birth suggests a greater reduction than this, but this rate of reduction is based on that seen in the more robust antibiotic prophylaxis for caesarean section trials. 6 We used the absolute difference (i.e. a reduction from 4% to 2%) to calculate the sample size. To detect such a difference with 90% statistical power at the two-sided 5% level of significance required 1626 participants per group; with an estimated 5% loss to follow-up, the trial required 1712 participants per group, which was a total of 3424 women.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were carried out according to a prespecified statistical analysis plan finalised and agreed prior to unblinding. In summary, demographic and clinical data were summarised with counts and percentages for categorical variables, means [standard deviations (SDs)] for normally distributed continuous variables and medians (with interquartile or simple ranges) for other continuous variables. Women were analysed in the groups to which they were randomly assigned, comparing the outcome of all women allocated to active treatment with all those allocated to placebo, regardless of deviation from the protocol or treatment received (referred to as the intention-to-treat population). Binary outcomes were analysed using risk ratios, while continuous outcomes were analysed using either a mean or a median difference, as appropriate. As randomisation did not involve stratification or minimisation, the primary analysis was based on unadjusted estimates of effect. Two-sided statistical testing was performed throughout. A 5% level of statistical significance was used for analyses of the primary outcome, and 1% for secondary outcomes. 95% CIs are presented for analyses of the primary outcome and 99% CIs for secondary outcomes.
Sensitivity analyses
Four planned sensitivity analyses were carried out:
-
examining the primary outcome restricted to women who had not received antibiotics in the 7 days prior to birth, in case any masking of a prophylactic effect occurred by inclusion of pre-treated women
-
examining the primary outcome excluding women prescribed antibiotics (other than the trial intervention) within 24 hours of birth in case these women were already infected prior to administration of the intervention
-
a repeat analysis of the primary outcome restricted to women whose primary outcome was obtained based on data obtained between 6 and 10 weeks after women had given birth
-
a sensitivity analysis including centre as a random effect.
Data collection
Data were collected at hospital discharge by extraction of information from a woman’s clinical records by the research midwife and at 6 weeks post partum by telephone interview with a research midwife to obtain information on the primary outcome. Following this, each woman was sent a postal or online questionnaire (as preferred by each woman) for collection of data on secondary outcomes.
Text reminders for completion of the questionnaire were sent and women were offered the option for telephone completion in the event of a delayed response to ensure a high response rate. Information about any hospital re-admissions and results of any microbiological investigations when a woman indicated that she had a suspected or confirmed infection were collected from hospital records by the site research midwife.
Basic demographic, medical and obstetric details were collected for all women, including details of any antibiotic treatment in the 7 days before women gave birth and the indication for antibiotic prescription.
Data on maternal anaphylaxis were collected up until hospital discharge. Data on other secondary outcomes were collected at 6 weeks post partum using standard instruments, when possible, as detailed below.
Surgical site infection (perineal)
This was identified using the items included in the Public Health England ’surgical wound healing post discharge questionnaire’. 33
Perineal pain/use of pain relief/dyspareunia/ability to sit comfortably to feed the baby/need for additional perineal care/breastfeeding
This was identified using standard questions developed for the HOOP (Hands On Or Poised) study34 and the PREVIEW (PREVention of diabetes through lifestyle intervention and population studies In Europe and around the World) study. 37
Maternal quality of life
This was elicited by the EQ-5D-5L. 36
Hospital bed stay/hospital and general practitioner visits/wound breakdown/antibiotic side effects
This was identified through specific questions included in the maternal questionnaire, to include medications prescribed, critical care admission, hospital inpatient admissions, outpatient visits, and midwife and practice nurse visits. All side effects of the IMP were recorded.
Indications for maternal antibiotic prescription and causes of infection were independently coded by two clinical reviewers, blinded to allocation, into the following categories:
-
perineal wound-related infection (including deep infections, such as abscess)
-
endometritis/uterine infection
-
urinary tract infection with systemic features (e.g. pyelonephritis)
-
other systemic infection (sepsis)
-
uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection (urinary tract infection with no other features specified)
-
breast infection/mastitis
-
respiratory infection (e.g. chest/throat)
-
other infection (e.g. meningitis)
-
other reason (non-infective)
-
unknown reason.
Any discrepancies or disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved by discussion or referral to a third reviewer.
A ’blinded end-point review’ (BER) was conducted to derive the primary outcome for women who returned a questionnaire but did not complete a telephone interview. Two clinical reviewers, who were blinded to allocation, independently assessed each questionnaire to see if there was any evidence that might indicate that the woman had experienced the primary outcome (i.e. evidence of any condition that might have led to antibiotic prescription, endometritis or any hospital re-admission). Any discrepancies or disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved by discussion or referral to the BER committee chairperson. If there was a potential, but not definite, indication that a woman had experienced the primary outcome, information about any hospital re-admissions and the results of any microbiological investigations were collected from hospital records by the site research midwife.
Adverse event reporting
The safety reporting window for this trial was from administration of intervention to 6 hours post administration or discharge (whichever was sooner). Non-serious adverse events were not routinely recorded as the IMP is a licensed product being given at a standard dose. However, adverse events that were part of the trial outcomes were recorded in the case report form.
All serious adverse events (SAEs) were reported immediately, at least within 24 hours, except the following SAEs (which were not considered to be causally related to the trial intervention because these events occurred prior to the trial intervention being administered):
-
birth defect/congenital anomaly
-
hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (e.g. pre-eclampsia/eclampsia)
-
post-partum haemorrhage with onset before the intervention.
Development safety update report
A development safety update report was submitted each year to the Competent Authority, the Ethics Committee and the sponsor.
Health-care resource use and cost analysis
As an additional analysis, not specified in the trial protocol, we conducted a within-trial comparison of health-care resource use and associated costs between trial arms. The perspective of the analysis was that of the UK NHS and the following categories of resource use were collected using the telephone interview and postal questionnaire at 6 weeks post delivery: antibiotic use (co-amoxiclav prophylaxis and new prescriptions), health-care professional visits [general practitioner (GP), nurse, midwife, health visitor and district nurse], outpatient hospital visits and all-cause hospital re-admissions.
Unit costs for co-amoxiclav were collected and estimated using the British National Formulary 2017. 38 We did not have details of the antibiotics used for new prescriptions and, therefore, assumed that all new prescriptions were co-amoxiclav, a low-cost generic antibiotic, so that our estimate of costs was conservative. Although some women may have received more than one course of antibiotics, we assumed that all women who had a new prescription of antibiotics had a single 7-day course of co-amoxiclav with three daily doses, again so that our estimate of costs was conservative. Unit costs for GP visits and nurse/midwife services at general practice were collected from Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2017. 39 For other health-care resource categories, the unit cost was taken from NHS Reference Costs 2017/18. 40 More details on sources and associated estimates of unit costs (expressed in 2017/18 Great British pounds) for the different categories of resource use are presented in Appendix 2, Tables 17 and 18. The costs associated with each category of resource use were estimated by multiplying resource use by unit costs.
We calculated the mean and SD of resource uses (number of visits for health-care professional and outpatient hospital visits, number of days for re-admissions) and costs for each category by trial arms. We also calculated overall mean (SD) costs at 6 weeks following delivery by adding up all individual cost categories, together with the cost for intervention (a single dose of intravenous co-amoxiclav). Mean differences in health-care resource use and costs were calculated and associated 99% parametric CIs were estimated.
The main analysis was based on complete cases among women who returned the postal questionnaire at 6 weeks post delivery and completed questions on usage for each specific health-care resource category. We compared the characteristics of women who returned the postal questionnaire with those who did not using the t-test for continuous variables and Pearson’s chi-squared test for categorical variables. A sensitivity analysis using multiple imputation with chained equations was conducted to evaluate the impact of missing data on our complete-case results. Fifty values were imputed for each missing data point by specifying separate regression models for each variable with missing data. Within each model, the remaining variables with missing data were used as predictors along with selected patient characteristics [maternal age, gestational age at randomisation in weeks, ethnic group, body mass index (BMI), any previous pregnancies of ≥ 22 weeks’ gestation, labour induction, episiotomy in current delivery, perineal tear in current delivery]. Imputation was performed using prediction mean matching (using five nearest neighbours) and for each trial arm separately.
Governance and monitoring
A monitoring plan for the trial, including responsibilities, was developed prior to the start of recruitment. Remote monitoring was carried out, with at least one monitoring assessment of each site. Site monitoring visits were carried out if remote monitoring identified any discrepancies.
The trial was supervised on a day-to-day basis by a Project Management Group. A TSC was convened comprising an independent chairperson, four other independent members, a patient and public involvement representative, the NPEU CTU Director and the chief investigator. A Data Monitoring Committee (DMC), independent of the applicants and of the TSC, reviewed the progress of the trial annually and provided the TSC with advice on the conduct of the trial.
Summary of changes to the trial protocol
The initial planned primary outcomes were defined as follows.
Confirmed or suspected maternal infection within 6 weeks of delivery, as defined by one of:
-
a new prescription of antibiotics
-
confirmed systemic infection on culture
-
endometritis as defined by the US CDC. 31
Following an interim review of the data by the DMC in February 2017, a change to the primary outcome was recommended to exclude women who were prescribed antibiotics for unrelated indications. This was because of concerns that the noise arising from antibiotic prescriptions for unrelated indications would mask the effect of the intervention. The primary outcome was therefore revised to the following.
Confirmed or suspected maternal infection within 6 weeks of delivery, as defined by one of:
-
a new prescription of antibiotics for presumed perineal wound-related infection, endometritis or uterine infection, urinary tract infection with systemic features or other systemic infection
-
confirmed systemic infection on culture
-
endometritis as defined by the US CDC. 31
Indications for antibiotic prescription were coded independently as described in Data collection by two clinically qualified staff, based on responses to the telephone questionnaire, the infection form or the postal questionnaire. The revised primary outcome could, therefore, be derived for all women already recruited into the trial and no additional processes were needed.
A summary of the other changes made to the original protocol is presented in Appendix 3.
Chapter 3 Results
Recruitment and retention
Between March 2016 and June 2018, 3427 women were randomised: 1719 to the antibiotic arm and 1708 to the placebo arm (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2.
Flow of participants. Figure modified from Knight et al. 30 This article is available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). You may copy and distribute the article, create extracts, abstracts and new works from the article, alter and revise the article, text or data mine the article and otherwise reuse the article commercially (including reuse and/or resale of the article) without permission from Elsevier. You must give appropriate credit to the original work, together with a link to the formal publication through the relevant DOI and a link to the Creative Commons user license above. You must indicate if any changes are made but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use of the work.

The number of participants recruited at each site varied from 22 to 388 (Table 1).
| Site | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1715), n (%) | Placebo (N = 1705), n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| James Cook University Hospital | 128 (7.5) | 132 (7.7) |
| Royal Berkshire Hospital, Reading | 30 (1.7) | 31 (1.8) |
| Sunderland Royal Hospital | 191 (11.1) | 197 (11.6) |
| Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne | 150 (8.7) | 148 (8.7) |
| University Hospital of North Tees | 50 (2.9) | 51 (3.0) |
| John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford | 86 (5.0) | 88 (5.2) |
| Bradford Royal Infirmary | 111 (6.5) | 103 (6.0) |
| Burnley General Hospital | 12 (0.7) | 10 (0.6) |
| Darlington Memorial Hospital | 59 (3.4) | 58 (3.4) |
| Derriford Hospital, Plymouth | 42 (2.4) | 40 (2.3) |
| East Surrey Hospital, Redhill | 28 (1.6) | 24 (1.4) |
| Liverpool Women’s Hospital | 111 (6.5) | 114 (6.7) |
| Princess Anne Hospital, Southampton | 83 (4.8) | 85 (5.0) |
| Princess of Wales Hospital, Bridgend | 21 (1.2) | 17 (1.0) |
| Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead | 53 (3.1) | 56 (3.3) |
| Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital | 25 (1.5) | 20 (1.2) |
| Singleton Hospital, Swansea | 32 (1.9) | 30 (1.8) |
| South Tyneside District General Hospital | 23 (1.3) | 22 (1.3) |
| St Thomas’ Hospital, London | 90 (5.2) | 89 (5.2) |
| Stoke Mandeville Hospital, Aylesbury | 40 (2.3) | 39 (2.3) |
| University Hospital of North Durham | 41 (2.4) | 37 (2.2) |
| University Hospital of Wales | 114 (6.6) | 113 (6.6) |
| Warrington Hospital | 21 (1.2) | 22 (1.3) |
| Whittington Hospital, London | 27 (1.6) | 30 (1.8) |
| Royal Stoke University Hospital | 17 (1.0) | 17 (1.0) |
| Croydon University Hospital | 110 (6.4) | 111 (6.5) |
| Northumbria Specialist Emergency Care Hospital | 20 (1.2) | 21 (1.2) |
Characteristics of participants
Characteristics of participants were similar between the two trial arms (Table 2) and appeared to be representative of the general population of women undergoing operative vaginal birth. Women had a mean age of 30 years, approximately half were of normal BMI and more than four-fifths were of white ethnicity. Overall, 77% of women were primiparous, and 49% had labour induced. Sixty-five per cent of births were assisted by forceps and 35% were assisted by vacuum extraction. Eighty-eight per cent of women had an episiotomy, 31% had a perineal tear and > 99% of women had suturing of a perineal wound.
| Characteristic | Allocated to co-amoxiclav (N = 1715), n (%) unless otherwise indicated | Allocated to placebo (N = 1705), n (%) unless otherwise indicated |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal age (years) mean (SD) | 30.3 (5.37) | 30.2 (5.49) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Gestational age at randomisation (weeks) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 40 (39–41) | 40 (39–41) |
| 36+ 0 to 37+ 6 | 136 (7.9) | 123 (7.2) |
| 38+ 0 to 39+ 6 | 568 (33.1) | 555 (32.6) |
| 40+ 0 to 41+ 6 | 964 (56.2) | 968 (56.8) |
| ≥ 42+ 0 | 46 (2.7) | 59 (3.5) |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 0 (0) |
| Ethnic group | ||
| White | 1436 (84.1) | 1474 (86.8) |
| Indian | 36 (2.1) | 34 (2.0) |
| Pakistani | 73 (4.3) | 54 (3.2) |
| Bangladeshi | 8 (0.5) | 14 (0.8) |
| Black Caribbean | 6 (0.4) | 8 (0.5) |
| Black African | 32 (1.9) | 29 (1.7) |
| Any other ethnic group | 116 (6.8) | 85 (5.0) |
| Missing | 8 (0.5) | 7 (0.4) |
| BMI at booking (kg/m2) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 25 (22–28) | 25 (22–29) |
| < 18.5 | 46 (2.8) | 48 (2.9) |
| 18.5 to 24.9 | 851 (51.0) | 842 (50.6) |
| 25 to 29.9 | 460 (27.5) | 446 (26.8) |
| 30 to 34.9 | 207 (12.4) | 216 (13.0) |
| 35 to 39.9 | 74 (4.4) | 77 (4.6) |
| ≥ 40 | 32 (1.9) | 34 (2.0) |
| Missing | 45 (2.6) | 42 (2.5) |
| Twin pregnancy | 11 (0.6) | 9 (0.5) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Any previous pregnancies of ≥ 22 weeks’ gestation | 402 (23.5) | 373 (21.9) |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 3 (0.2) |
| Previous caesarean section | 137 (8.0) | 123 (7.2) |
| Missing | 2 (0.1) | 3 (0.2) |
| Previous episiotomy | 147 (8.7) | 141 (8.4) |
| Missing | 26 (1.5) | 25 (1.5) |
| Previous tear | 81 (4.8) | 80 (4.8) |
| Missing | 24 (1.4) | 26 (1.5) |
| Rupture of membranes before giving birth | 1692 (98.7) | 1683 (98.7) |
| < 24 hours | 1461 (85.2) | 1466 (86.0) |
| ≥ 24 to < 48 hours | 191 (11.1) | 175 (10.3) |
| ≥ 48 hours | 35 (2.0) | 36 (2.1) |
| Unknown | 5 (0.3) | 6 (0.4) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Labour induction | 819 (47.8) | 852 (50.0) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Actual mode of birtha | ||
| Spontaneous vaginalb | 7 (0.4) | 3 (0.2) |
| Forceps | 1086 (62.9) | 1148 (67.0) |
| Vacuum extraction | 633 (36.7) | 563 (32.8) |
| Caesarean section | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Sequential instruments used | 77 (4.5) | 78 (4.6) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Reason for instrumental birth (non-exclusive) | ||
| Failure to progress | 855 (49.9) | 870 (51.0) |
| Fetal compromise | 861 (50.3) | 817 (47.9) |
| Other medical reason | 134 (7.8) | 131 (7.7) |
| Missing | 2 (0.1) | 0 (0) |
| Episiotomy in current birth | 1519 (88.6) | 1525 (89.4) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Perineal tear in current birth | 493 (28.7) | 560 (32.8) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Perineal wound sutured | 1645 (99.0) | 1665 (99.6) |
| Missing | 54 (3.1) | 33 (1.9) |
| Location suturing carried out | ||
| Operating theatre | 571 (34.7) | 588 (35.3) |
| Delivery ward/room | 1074 (65.3) | 1076 (64.7) |
| Missing | 70 (4.1) | 41 (2.4) |
Outcomes
Primary outcome data were available for 3225 out of 3420 women (94.3%). There were no substantive differences between women for whom primary outcome data were available (Table 3). Questionnaires were received for 2593 women (75.8%).
| Characteristic | Missing primary outcome data (N = 195), n (%) unless otherwise indicated | Complete primary outcome data (N = 3225), n (%) unless otherwise indicated |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal age (years) | ||
| Mean (SD) | 28.2 (5.97) | 30.4 (5.37) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Gestational age at randomisation (weeks) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 40 (39–41) | 40 (39–41) |
| 36+ 0 to 37+ 6 | 18 (9.2) | 241 (7.5) |
| 38+ 0 to 39+ 6 | 68 (34.9) | 1055 (32.7) |
| 40+ 0 to 41+ 6 | 104 (53.3) | 1828 (56.7) |
| ≥ 42+ 0 | 5 (2.6) | 100 (3.1) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 1 (0) |
| Ethnic group | ||
| White | 164 (84.1) | 2746 (85.5) |
| Indian | 2 (1.0) | 68 (2.1) |
| Pakistani | 7 (3.6) | 120 (3.7) |
| Bangladeshi | 3 (1.5) | 19 (0.6) |
| Black Caribbean | 1 (0.5) | 13 (0.4) |
| Black African | 5 (2.6) | 56 (1.7) |
| Any other ethnic group | 13 (6.7) | 188 (5.9) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 15 (0.5) |
| BMI at booking (kg/m2) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 24 (22–30) | 25 (22–28) |
| < 18.5 | 8 (4.2) | 86 (2.7) |
| 18.5 to 24.9 | 93 (49.2) | 1600 (50.9) |
| 25 to 29.9 | 45 (23.8) | 861 (27.4) |
| 30 to 34.9 | 32 (16.9) | 391 (12.4) |
| 35 to 39.9 | 9 (4.8) | 142 (4.5) |
| ≥ 40 | 2 (1.1) | 64 (2.0) |
| Missing | 6 (3.1) | 81 (2.5) |
| Twin pregnancy | 3 (1.5) | 17 (0.5) |
| Any previous pregnancies of ≥ 22 weeks’ gestation | 57 (29.2) | 718 (22.3) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 4 (0.1) |
| Previous caesarean section | 15 (7.7) | 245 (7.6) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 5 (0.2) |
| Previous episiotomy | 20 (10.3) | 268 (8.4) |
| Missing | 1 (0.5) | 50 (1.6) |
| Previous tear | 17 (8.8) | 144 (4.5) |
| Missing | 1 (0.5) | 49 (1.5) |
| Rupture of membranes before giving birth | 195 (100.0) | 3180 (98.6) |
| < 24 hours | 178 (91.3) | 2749 (85.2) |
| ≥ 24 to < 48 hours | 14 (7.2) | 352 (10.9) |
| ≥ 48 hours | 1 (0.5) | 70 (2.2) |
| Unknown | 2 (1.0) | 9 (0.3) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Labour induction | 101 (51.8) | 1570 (48.7) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Actual mode of birtha | ||
| Spontaneousb | 0 (0) | 10 (0.3) |
| Forceps | 129 (65.2) | 2105 (65.3) |
| Ventouse | 69 (34.8) | 1127 (34.9) |
| Caesarean section | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Sequential instruments used | 7 (3.6) | 148 (4.6) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Reason for instrumental birth (non-exclusive) | ||
| Failure to progress | 82 (42.1) | 1643 (51.0) |
| Fetal compromise | 111 (56.9) | 1567 (48.6) |
| Other medical reason | 16 (8.2) | 249 (7.7) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 2 (0.1) |
| Episiotomy in current birth | 174 (89.2) | 2870 (89.0) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Tear in current birth | 50 (25.6) | 1003 (31.1) |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Wound sutured | 184 (98.9) | 3126 (99.3) |
| Missing | 9 (4.6) | 78 (2.4) |
| Location suturing carried out | ||
| Operating theatre | 61 (33.2) | 1098 (35.1) |
| Delivery ward/room | 123 (66.8) | 2027 (64.9) |
| Missing | 11 (5.6) | 100 (3.1) |
Primary outcomes
There was a 42% reduction in the risk of the overall primary outcome (risk difference 7.9%, 95% CI 5.5% to 10.4%) among the antibiotic arm compared with the placebo arm, noting that the overall primary outcome rate was substantially higher in the placebo arm than we had hypothesised (19% vs. an estimated 4%) (Table 4). The primary outcome was principally driven by one of the three components of the primary outcome: new prescription of antibiotics with specific indication. However, all components of the primary outcome showed the same direction of effect, and there was a statistically significant 56% reduction in confirmed systemic infection on culture from 1.5% (25/1606) in the placebo arm to 0.6% (11/1619) in the antibiotic arm.
| Outcome | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1715), n (%) | Placebo (N = 1705), n (%) | Risk ratioa (95% CI unless otherwise indicated) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmed or suspected maternal infection | 180 (11.1) | 306 (19.1) | 0.58 (0.49 to 0.69) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 96 (5.6) | 99 (5.8) | ||
| Confirmed systemic infection on culture | 11 (0.6) | 25 (1.5) | 0.44 (0.22 to 0.89) | 0.018 |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| Endometritis | 15 (0.9) | 23 (1.3) | 0.65 (0.34 to 1.24) | 0.186 |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| New prescription of antibiotics with relevant indication | 180 (11.1) | 306 (19.1) | 0.58 (0.49 to 0.69) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 96 (5.6) | 99 (5.8) | ||
| Systemic sepsis according to modified SIRS criteria for pregnancy | 6 (0.4) | 10 (0.6) | 0.59 (0.16 to 2.24)b | 0.307 |
| Missing | 9 (0.5) | 16 (0.9) | ||
| Perineal wound infection | ||||
| Superficial incisional infection | 75 (4.4) | 141 (8.3) | 0.53 (0.37 to 0.76)b | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 3 (0.2) | 5 (0.3) | ||
| Deep incisional infection | 36 (2.1) | 77 (4.5) | 0.46 (0.28 to 0.77)b | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 5 (0.3) | 11 (0.6) | ||
| Organ/space infection | 0 | 4 (0.2) | 0.00 | 0.044 |
| Missing | 7 (0.4) | 11 (0.6) | ||
Secondary outcomes
There were statistically significant reductions in the secondary outcomes superficial perineal infection and deep perineal wound infection in the antibiotic arm. There was no significant difference in the incidence of systemic sepsis according to the modified SIRS criteria for pregnancy (see Table 4).
Considering the secondary outcomes reported on the postal/online questionnaire (Table 5), women in the antibiotic arm reported significantly lower levels of perineal pain, less use of pain relief for perineal pain, a less frequent need for additional perineal care and lower rates of wound breakdown than those in the placebo arm. There were no differences in reported dyspareunia between the groups, noting that only 41% of women had resumed intercourse at the time of returning their questionnaire. There was no statistically significant difference in breastfeeding rates between the two groups, but a greater proportion of women in the placebo arm reported times at which their perineum was too uncomfortable to feed their baby. Women in the antibiotic arm had fewer primary care or home visits, or hospital outpatient visits, in relation to their perineum than women in the placebo arm. There was no statistically significant difference in hospital re-admissions between the two arms, and no difference in mean EQ-5D-5L score (using the significance level p < 0.01 for secondary outcomes).
| Outcome | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1296), n (%) unless otherwise indicated | Placebo (N = 1297), n (%) unless otherwise indicated | Effect measurea (99% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perineal pain | 592 (45.7) | 707 (54.5) | 0.84 (0.76 to 0.93) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Use of pain relief for perineal pain | 99 (7.7) | 138 (10.8) | 0.72 (0.52 to 0.99) | 0.007 |
| Missing | 13 (1.0) | 18 (1.4) | ||
| Need for additional perineal care | 390 (31.1) | 543 (43.1) | 0.72 (0.63 to 0.83) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 42 (3.2) | 38 (2.9) | ||
| Wound breakdown | 142 (11.0) | 272 (21.1) | 0.52 (0.41 to 0.67) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 4 (0.3) | 7 (0.5) | ||
| Dyspareuniab | 299 (55.0) | 280 (54.5) | 1.01 (0.87 to 1.17) | 0.873 |
| Missing | 5 (0.4) | 8 (0.6) | ||
| Breastfeeding at 6 weeks | 662 (51.2) | 657 (50.8) | 1.01 (0.91 to 1.11) | 0.828 |
| Missing | 4 (0.3) | 4 (0.3) | ||
| Perineum ever too painful/uncomfortable to feed baby | 136 (11.3) | 198 (16.5) | 0.69 (0.53 to 0.90) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 96 (7.4) | 98 (7.6) | ||
| Hospital bed stay to discharge | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 0.00 (0.00 to 0.00) | 0.318 |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Any primary care or home visits in relation to perineum | 361 (27.9) | 496 (38.4) | 0.73 (0.63 to 0.84) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 3 (0.2) | 5 (0.4) | ||
| Any outpatient visits in relation to perineum | 95 (7.4) | 173 (13.4) | 0.55 (0.40 to 0.75) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 5 (0.4) | 6 (0.5) | ||
| Maternal hospital re-admission | 63 (5.0) | 84 (6.7) | 0.75 (0.49 to 1.14) | 0.072 |
| Missing | 47 (3.6) | 51 (3.9) | ||
| Maternal health-related quality of life | ||||
| EQ-5D-5L score, mean (SD) | 0.935 (0.098) | 0.927 (0.111) | 0.008 (–0.003 to 0.019) | 0.048 |
| Missing | 16 (1.2) | 18 (1.4) | ||
Adverse events and side effects
Only three women reported side effects of the intervention: 2 out of 1715 in the antibiotic arm (0.12%) and 1 out of 1705 (0.06%) in the placebo arm (risk difference 0.06%, 95% CI –0.14% to 0.25%). The woman in the placebo arm reported a skin rash, and the women in the antibiotic arm reported other reactions (e.g. itching, swollen throat). There were no cases of anaphylaxis. Three SAEs were reported (Table 6), but only one was thought to be causally related to the intervention.
| Treatment allocation | Description | Severity | Related |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co-amoxiclav | Immediate reaction to the active IMP: itching and swollen throat. | Moderate | Definitely |
| Placebo | Woman admitted to intensive care unit 15 days post natal with severe sepsis | Severe | Not related |
| Placebo | Post-partum haemorrhage with blood transfusion | Moderate | Not related |
Adherence
The intervention was administered a median of 3 hours after women had given birth (Table 7). Thirty-three women (1.0%) received the intervention > 6 hours after giving birth. Overall, 33 telephone follow-up interviews (1.0%) were conducted by staff who had prepared or checked the ANODE intervention and may, theoretically, have been unblinded to allocation. Similarly, as antibiotic prescription was part of the primary outcome, we checked whether or not the person prescribing antibiotics was also the person who had checked or prepared the ANODE intervention and would therefore have been unblinded. Only one woman, in the antibiotic arm, was prescribed further antibiotics by a member of staff who may have been unblinded.
| Adherence factor | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1715), n (%) unless otherwise indicated | Placebo (N = 1705), n (%) unless otherwise indicated |
|---|---|---|
| Time between giving birth and the administration of the intervention (hours) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 3.2 (2.2–4.5) | 3.1 (2.1–4.4) |
| ≤ 6 | 1649 (98.9) | 1651 (99.2) |
| > 6 | 19 (1.1) | 14 (0.8) |
| Missing | 47 (2.7) | 40 (2.3) |
| Telephone interviewer at 6 weeks prepared or checked the ANODE intervention | 14 (0.9) | 19 (1.2) |
| Missing | 130 (7.6) | 132 (7.7) |
| Same person who prescribed further antibiotics prepared or checked the trial intervention | 1 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 4 (0.2) |
Sensitivity analyses
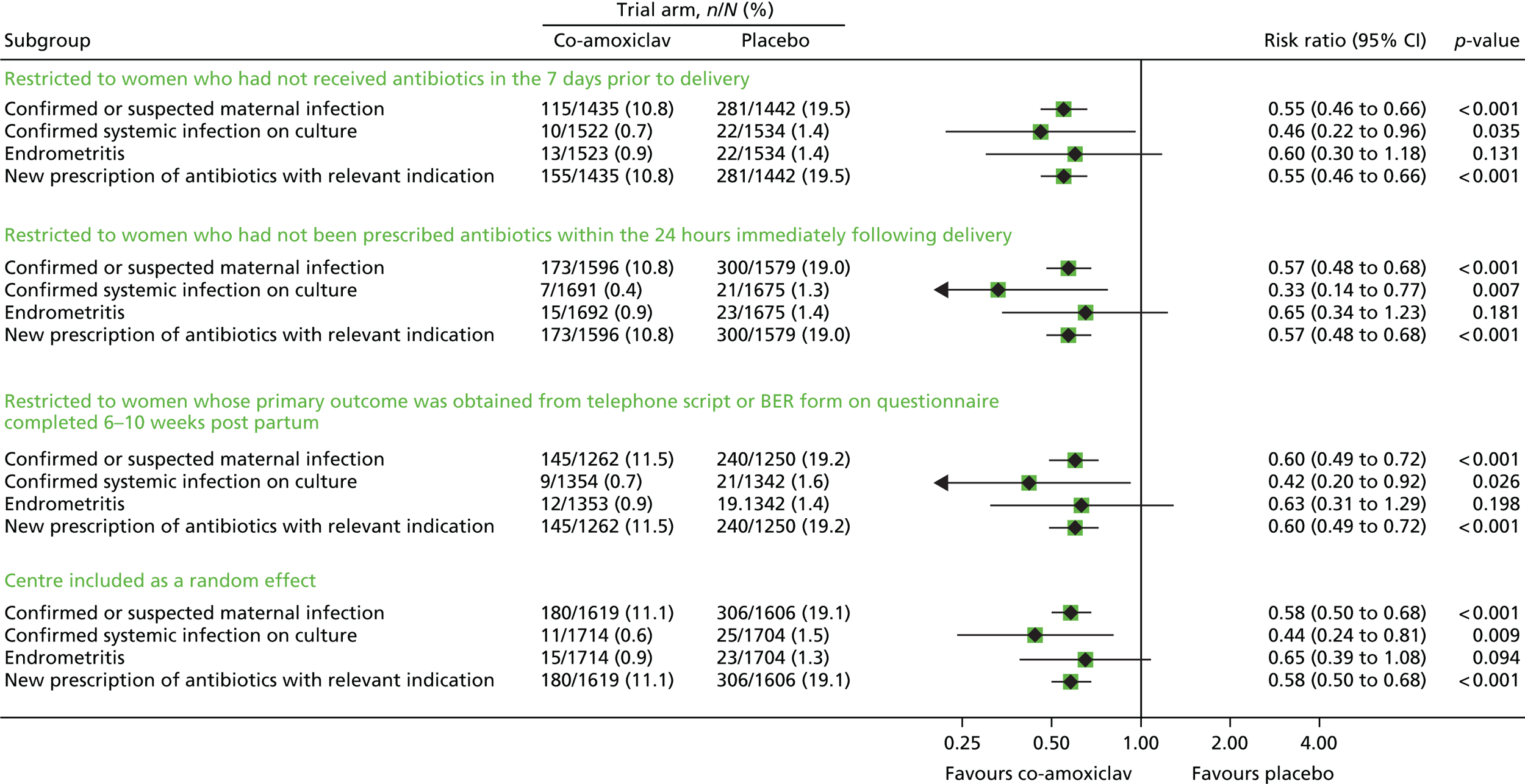
There were no material changes to the primary outcome with any of the sensitivity analyses (Tables 8–11 and Figure 3).
| Outcome | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1523), n (%) | Placebo (N = 1535), n (%) | Risk ratio (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmed or suspected maternal infection | 155 (10.8) | 281 (19.5) | 0.55 (0.46 to 0.66) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 88 (5.8) | 93 (6.1) | ||
| Confirmed systemic infection on culture | 10 (0.7) | 22 (1.4) | 0.46 (0.22 to 0.96) | 0.035 |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| Endometritis | 13 (0.9) | 22 (1.4) | 0.60 (0.30 to 1.18) | 0.131 |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| New prescription of antibiotics with relevant indication | 155 (10.8) | 281 (19.5) | 0.55 (0.46 to 0.66) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 88 (5.8) | 93 (6.1) |
| Outcome | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1692), n (%) | Placebo (N = 1676), n (%) | Risk ratio (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmed or suspected maternal infection | 173 (10.8) | 300 (19.0) | 0.57 (0.48 to 0.68) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 96 (5.7) | 97 (5.8) | ||
| Confirmed systemic infection on culture | 7 (0.4) | 21 (1.3) | 0.33 (0.14 to 0.77) | 0.007 |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| Endometritis | 15 (0.9) | 23 (1.4) | 0.65 (0.34 to 1.23) | 0.181 |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| New prescription of antibiotics with relevant indication | 173 (10.8) | 300 (19.0) | 0.57 (0.48 to 0.68) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 96 (5.7) | 97 (5.8) |
| Outcome | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1354), n (%) | Placebo (N = 1343), n (%) | Risk ratio (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmed or suspected maternal infection | 145 (11.5) | 240 (19.2) | 0.60 (0.49 to 0.72) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 92 (6.8) | 93 (6.9) | ||
| Confirmed systemic infection on culture | 9 (0.7) | 21 (1.6) | 0.42 (0.20 to 0.92) | 0.026 |
| Missing | 0 (0) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| Endometritis | 12 (0.9) | 19 (1.4) | 0.63 (0.31 to 1.29) | 0.198 |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| New prescription of antibiotics with relevant indication | 145 (11.5) | 240 (19.2) | 0.60 (0.49 to 0.72) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 92 (6.8) | 93 (6.9) |
| Outcome | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1715), n (%) | Placebo (N = 1705), n (%) | Risk ratio (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmed or suspected maternal infection | 180 (11.1) | 306 (19.1) | 0.58 (0.50 to 0.68) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 96 (5.6) | 99 (5.8) | ||
| Confirmed systemic infection on culture | 11 (0.6) | 25 (1.5) | 0.44 (0.24 to 0.81) | 0.009 |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| Endometritis | 15 (0.9) | 23 (1.3) | 0.65 (0.39 to 1.08) | 0.094 |
| Missing | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | ||
| New prescription of antibiotics with relevant indication | 180 (11.1) | 306 (19.1) | 0.58 (0.50 to 0.68) | < 0.001 |
| Missing | 96 (5.6) | 99 (5.8) |
FIGURE 3.
Forest plot showing the results of the sensitivity analyses.
Health-care resource use and cost analysis
Among the 2593 women who returned the questionnaire, we found evidence that, at 6 weeks post delivery, women randomised to the antibiotic arm consumed fewer NHS health-care resources than those in the placebo arm (Table 12). The mean difference in all categories of resource use favoured the antibiotic arm, with the number of visits to the GP (p < 0.001), nurse or midwife home visits (p < 0.001) and outpatient hospital visits (p < 0.001) being statistically significantly different between groups. No statistically significant mean differences were detected in the length of stay for all-cause hospital re-admissions.
| Health-care resource use category | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1296) | Placebo (N = 1297) | Mean difference (99% CI) | p-value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Minimum | Maximum | Mean (SD) | n | Minimum | Maximum | Mean (SD) | |||
| Health-care professional number of visits in relation to perineum | ||||||||||
| GP | 1235 | 0 | 4 | 0.161 (0.500) | 1239 | 0 | 7 | 0.266 (0.689) | –0.11 (–0.17 to –0.04) | < 0.001 |
| Midwife/nurse at general practice | 1240 | 0 | 23 | 0.115 (0.771) | 1243 | 0 | 6 | 0.142 (0.546) | –0.03 (–0.10 to 0.04) | 0.298 |
| Midwife/nurse at home | 1219 | 0 | 15 | 0.373 (1.079) | 1226 | 0 | 10 | 0.551 (1.189) | –0.18 (–0.30 to –0.06) | < 0.001 |
| Health visitor/district nurse | 1240 | 0 | 23 | 0.071 (0.731) | 1253 | 0 | 11 | 0.081 (0.550) | –0.01 (–0.08 to 0.06) | 0.710 |
| Outpatient hospital number of visits | 1229 | 0 | 12 | 0.168 (0.828) | 1231 | 0 | 17 | 0.310 (1.042) | –0.14 (–0.24 to –0.04) | < 0.001 |
| Length of stay hospital re-admissions (in days) | 1234 | 0 | 29 | 0.079 (0.954) | 1235 | 0 | 10 | 0.124 (0.761) | –0.05 (–0.14 to 0.04) | 0.192 |
Similar results were found for costs. Among different health-care categories, the highest cost was estimated for hospital re-admissions, followed by nurse or midwife home visits and outpatient hospital visits (Table 13). Compared with the women allocated to the placebo arm, the health-care costs for women in the antibiotic arm were, on average, a significant £0.40 (99% CI £0.20 to £0.50) less for new prescriptions of antibiotic, £3.90 (99% CI £1.60 to £6.20) less for GP visits, £12.10 (99% CI £4.00 to £20.10) less for nurse or midwife home visits and £15.40 (99% CI £5.20 to £25.50) less for outpatient hospital visits. The mean cost of hospital re-admissions was also found to be lower in the antibiotic arm (£50.30 vs. £81.60), but the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.164). The total mean cost at 6 weeks following delivery was estimated to be £102.50 (SD £652.40) per woman in the antibiotic arm and £155.10 (SD £497.40) per woman in the placebo arm. The mean difference in the total health-care cost was –£52.60 (99% CI –£115.10 to £9.90) per woman, which was not statistically significantly different at the 1% level (p = 0.030).
| Health care cost | Co-amoxiclav (N = 1296) | Placebo (N = 1297) | Mean difference (99% CI) | p-value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Minimum | Maximum | Mean (SD) | n | Minimum | Maximum | Mean (SD) | |||
| Health-care cost category | ||||||||||
| Co-amoxiclav for prevention | 1296 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 (0.0) | 1297 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 (0.0) | 2.3 (2.3 to 2.3) | – |
| New prescription of antibiotic | 1283 | 0 | 4.8 | 0.5 (1.5) | 1281 | 0 | 4.8 | 0.9 (1.9) | –0.4 (–0.5 to –0.2) | < 0.001 |
| Health-care professional number of visits | ||||||||||
| GP | 1235 | 0 | 148.0 | 6.0 (18.5) | 1239 | 0 | 259.0 | 9.9 (25.5) | –3.9 (–6.2 to –1.6) | < 0.001 |
| Midwife/nurse at general practice | 1240 | 0 | 250.7 | 1.2 (8.4) | 1243 | 0 | 65.4 | 1.6 (5.9) | –0.3 (–1.1 to 0.4) | 0.298 |
| Midwife/nurse at home | 1219 | 0 | 1020.0 | 25.4 (73.4) | 1226 | 0 | 680.0 | 37.4 (80.8) | –12.1 (–20.1 to –4.0) | < 0.001 |
| Health visitor/district nurse | 1240 | 0 | 874.0 | 2.7 (27.8) | 1253 | 0 | 418.0 | 3.1 (20.9) | –0.4 (–2.9 to 2.2) | 0.710 |
| Outpatient hospital number of visits | 1229 | 0 | 1303.1 | 17.3 (84.1) | 1231 | 0 | 1846.1 | 32.7 (109.3) | –15.4 (–25.5 to –5.2) | < 0.001 |
| Hospital re-admissions | 1234 | 0 | 18568.7 | 50.3 (610.6) | 1235 | 0 | 6403.0 | 81.6 (498.7) | –31.3 (–89.1 to 26.6) | 0.164 |
| Total health-care costsa | ||||||||||
| Total costs at 6-weeks following delivery | 1148 | 2.3 | 19084.0 | 102.5 (652.4) | 1144 | 0.0 | 6403.0 | 155.1 (497.4) | –52.6 (–115.1 to 9.9) | 0.030 |
On the basis of the estimated number of doses of co-amoxiclav used for the costs analysis (see Table 13), we estimated the potential effect of a policy of universal prophylaxis with a single dose of co-amoxiclav after operative vaginal birth on overall antibiotic use. In the placebo arm, 19% of women had a confirmed or suspected infection and 1297 women received an estimated 5166 doses of co-amoxiclav to treat infection (three daily doses for 7 days in 246 women). In the antibiotic arm, 11% of women had a confirmed or suspected infection and 1296 women received an estimated 3003 doses of co-amoxiclav to treat infection (three daily doses for 7 days in 143 women), as well as 1296 prophylactic doses; therefore, a total of 4299 doses. A policy of universal prophylaxis would therefore be associated with an estimated net reduction of 867 doses of antibiotic (17% reduction).
There were statistically significant differences in the characteristics of women who had missing secondary resource outcomes compared with those who did not (Table 14). However, the comparisons of post-delivery health-care resource use and costs after multiple imputation were similar to those generated by using complete cases (Tables 15 and 16). Compared with women allocated to the placebo arm, women in the antibiotic arm had significantly fewer GP visits, nurse or midwife visits at home, and outpatient hospital visits. The total mean costs after multiple imputation were estimated to be £117.30 (SE £20.23) in the co-amoxiclav group and £168.30 (SE £15.07) in the placebo group. The mean difference in the total cost was –£50.90 (99% CI–£114.70 to £12.90; p = 0.040).
| Characteristic | Secondary outcome missing (N = 827), n (%) unless otherwise indicated | Secondary outcome present (N = 2593), n (%) unless otherwise indicated | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mother’s age at randomisation (years), mean (SD) | 28.2 (5.8) | 30.9 (5.1) | < 0.001 |
| Gestational age at randomisation (weeks) | |||
| 36+0 to 37+6 | 74 (8.9) | 185 (7.1) | 0.036 |
| 38+0 to 39+6 | 294 (35.6) | 829 (32.0) | |
| 40+0 to 41+6 | 438 (53.0) | 1494 (57.6) | |
| > 42 | 21 (2.5) | 84 (3.2) | |
| Ethnic group | |||
| Bangladeshi | 12 (1.5) | 10 (0.4) | < 0.001 |
| Black African | 25 (3.0) | 36 (1.4) | |
| Black Caribbean | 9 (1.1) | 5 (0.2) | |
| Indian | 26 (3.2) | 44 (1.7) | |
| Other | 47 (5.7) | 154 (6.0) | |
| Pakistani | 54 (6.6) | 73 (2.8) | |
| White | 648 (78.9) | 2262 (87.5) | |
| BMI at booking (kg/m2) | |||
| < 18.5 | 30 (3.7) | 64 (2.5) | < 0.001 |
| 18.5 to 24.9 | 383 (47.3) | 1310 (51.9) | |
| 25 to 29.9 | 199 (24.6) | 707 (28.0) | |
| 30 to 34.9 | 133 (16.4) | 290 (11.5) | |
| 35 to 39.9 | 41 (5.1) | 110 (4.4) | |
| ≥ 40 | 23 (2.8) | 43 (1.7) | |
| Multiple pregnancy | |||
| No | 821 (99.3) | 2579 (99.5) | 0.54 |
| Yes | 6 (0.7) | 14 (0.5) | |
| Previous pregnancies of ≥ 22 weeks’ gestation | |||
| No | 587 (71.1) | 2054 (79.3) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 239 (28.9) | 536 (20.7) | |
| Previous caesarean section | |||
| No | 744 (90.1) | 2411 (93.1) | 0.004 |
| Yes | 82 (9.9) | 178 (6.9) | |
| Previous episiotomy | |||
| No | 727 (89.4) | 2354 (92.1) | 0.017 |
| Yes | 86 (10.6) | 202 (7.9) | |
| Previous tear | |||
| No | 758 (93.2) | 2451 (95.9) | 0.002 |
| Yes | 55 (6.8) | 106 (4.1) | |
| Rupture of membranes before giving birth | |||
| < 24 hours | 718 (87.9) | 2209 (86.4) | 0.36 |
| 24 to < 48 hours | 76 (9.3) | 290 (11.3) | |
| ≥ 48 hours | 20 (2.4) | 51 (2.0) | |
| Unknown | 3 (0.4) | 8 (0.3) | |
| Labour induced | |||
| No | 401 (48.5) | 1348 (52.0) | 0.080 |
| Yes | 426 (51.5) | 1245 (48.0) | |
| Sequential instruments used | |||
| No | 796 (96.3) | 2469 (95.2) | 0.21 |
| Yes | 31 (3.7) | 124 (4.8) | |
| Episiotomy in current birth | |||
| No | 101 (12.2) | 275 (10.6) | 0.20 |
| Yes | 726 (87.8) | 2318 (89.4) | |
| Tear in current birth | |||
| No | 603 (72.9) | 1764 (68.0) | 0.008 |
| Yes | 224 (27.1) | 829 (32.0) | |
| Wound sutured | |||
| No | 8 (1.0) | 15 (0.6) | 0.22 |
| Yes | 786 (99.0) | 2524 (99.4) | |
| Health-care resource | Co-amoxiclav | Placebo | Mean difference (99% CI) | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean (SE) | n | Mean (SE) | |||
| Health-care professional number of visits in relation to perineum | ||||||
| GP | 1715 | 0.170 (0.014) | 1705 | 0.270 (0.018) | –0.100 (–0.161 to –0.039) | < 0.001 |
| Midwife/nurse at general practice | 1715 | 0.114 (0.018) | 1705 | 0.152 (0.015) | –0.038 (–0.098 to 0.022) | 0.101 |
| Midwife/nurse at home | 1715 | 0.404 (0.031) | 1705 | 0.568 (0.032) | –0.163 (–0.277 to –0.049) | < 0.001 |
| Health visitor/district nurse | 1715 | 0.073 (0.016) | 1705 | 0.082 (0.015) | –0.009 (–0.067 to 0.049) | 0.699 |
| Outpatient hospital number of visits | 1715 | 0.173 (0.022) | 1705 | 0.317 (0.028) | –0.145 (–0.236 to –0.053) | < 0.001 |
| Duration of stay for hospital re-admissions (in days) | 1715 | 0.099 (0.031) | 1705 | 0.134 (0.022) | –0.035 (–0.131 to 0.060) | 0.339 |
| Health-care cost | Co-amoxiclav | Placebo | Mean difference (99% CI) | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean (SE) | n | Mean (SE) | |||
| Health-care cost category | ||||||
| Co-amoxiclav for prevention | 1715 | 2.3 (0.0) | 1705 | 0.0 (0.0) | 2.3 (2.3 to 2.3) | – |
| New prescription of antibiotic | 1715 | 0.5 (0.038) | 1705 | 0.9 (0.047) | –0.4 (–0.5 to –0.2) | < 0.001 |
| Health-care professional visits in relation to perineum | ||||||
| GP | 1715 | 6.3 (0.524) | 1705 | 10.0 (0.681) | –3.7 (–5.9 to –1.4) | < 0.001 |
| Midwife/nurse at general practice | 1715 | 1.2 (0.194) | 1705 | 1.7 (0.164) | –0.4 (–1.1 to 0.2) | 0.101 |
| Midwife/nurse at home | 1715 | 27.5 (2.084) | 1705 | 38.6 (2.203) | –11.1 (–18.9 to –3.4) | < 0.001 |
| Health visitor/district nurse | 1715 | 2.8 (0.625) | 1705 | 3.1 (0.579) | –0.3 (–2.5 to 1.9) | 0.699 |
| Outpatient hospital visits | 1715 | 13.6 (1.826) | 1705 | 26.0 (2.487) | –12.4 (–20.3 to –4.5) | < 0.001 |
| Hospital re-admissions | 1715 | 63.1 (19.634) | 1705 | 88.0 (14.216) | –24.9 (–86.4 to 36.7) | 0.296 |
| Total health-care costs | ||||||
| Total costs at 6 weeks following delivery | 1715 | 117.3 (20.228) | 1705 | 168.3 (15.069) | –50.9 (–114.7 to 12.9) | 0.040 |
Chapter 4 Discussion and conclusions
Summary of main findings
This trial showed clear evidence of benefit of a single dose of intravenous co-amoxiclav administered to women a median of 3 hours after operative vaginal birth. Women in the antibiotic arm had a 42% relative reduction, from 19% to 11%, in the risk of suspected or confirmed infection. This was principally driven by the prescription of antibiotics for presumed perineal wound-related infection, endometritis or uterine infection, urinary tract infection with systemic features or other systemic infection, but women in the antibiotic arm also had a statistically significant 56% reduction in the risk of confirmed systemic infection on culture, from 1.5% to 0.6%. Secondary outcomes also favoured the active (co-amoxiclav) arm, with significant reductions in rates of both deep and superficial perineal infection, perineal pain, wound breakdown and the need for additional perineal care.
At 6 weeks post delivery, women who were randomised to the antibiotic arm consumed fewer NHS health-care resources than women randomised to the placebo arm, with significantly fewer visits to the GP, midwife/nurse home visits and outpatient hospital visits. The mean total health-care cost per woman was £52.60 lower in the antibiotic arm than in the placebo arm, but this was not statistically significantly different at the 1% level.
Limitations
We took the pragmatic approach in this trial of defining suspected or confirmed maternal infection using a composite outcome, including a new prescription of antibiotics for confirmed or suspected infection, which can be interpreted as equating to a clinical diagnosis of infection. This clinical diagnosis of infection drove the overall outcome and resulted in a substantially higher than anticipated event rate, which may suggest overprescription of antibiotics in the postnatal period. The use of this clinical definition rather than microbiologically confirmed infection could be regarded as a limitation; however, we observed a statistically significant decrease in the rate of microbiologically confirmed systemic infection following culture from a sterile site, which supports the assumption that the findings represent a genuine decrease in infection, despite our pragmatic primary outcome definition.
We achieved a 76% follow-up rate for the majority of our secondary outcomes, which represents the main limitation of this trial. There were statistically significant differences in the characteristics of the women who completed the 6-week questionnaire and those who did not. Most notably, a greater proportion of women who returned the 6-week questionnaire were primiparous. It is possible that their consultation behaviour differed from multiparous women; thus, rates of some of the reported secondary outcomes may be higher than would be seen in the general population. This difference in characteristics between those with follow-up data and those without is, however, unlikely to account for the magnitude of difference we observed between the antibiotic and placebo arms.
The population of women included in the trial was representative of the population of women undergoing operative vaginal birth and thus appear broadly generalisable. The trial was limited to women who were not penicillin-allergic and, therefore, is not directly applicable to women who are allergic to penicillin. However, it would be anticipated that another antibiotic with a similar spectrum of activity would have a similar protective effect in women for whom co-amoxiclav is contraindicated. Options for penicillin-allergic women that offer a comparable spectrum of activity to co-amoxiclav would include cefuroxime with metronidazole or clindamycin with gentamicin. Similarly, we included only women giving birth at ≥ 36 weeks’ gestation. However, there are no clear reasons why the results would not also be generalisable to women who had an instrumental vaginal birth at lower gestations than this.
We asked sites to administer the intervention as soon as possible after women had given birth, and no later than 6 hours after women had given birth. In practice, it was administered a median of 3 hours after women had given birth. It is possible that administration this length of time after women had given birth made the co-amoxiclav less effective than it might have been, given that caesarean section trials suggest that pre-delivery administration is more effective at preventing wound infection and endometritis. 41 However, as noted earlier, the perineal wound, which is highly likely to become contaminated, is very different from the caesarean section wound, and later administration may have allowed for a longer duration of protective effect and greater efficacy. Further analyses are needed to investigate the mechanism of effect, as described in Implications for research.
Comparison with existing literature
The single previous trial of antibiotic prophylaxis after operative vaginal birth42 reported on endometritis only, noting a rate of 4% in the no antibiotic arm. This is considerably lower than the rate of suspected or confirmed infection we observed in the ANODE trial but, interestingly, using the strict CDC surveillance definition,31 we observed a lower endometritis rate. The estimate of effect we observed for endometritis (relative risk 0.65, 95% CI 0.34 to 1.24) in the ANODE trial is compatible with the effect estimate in the Heitmann and Benrubi trial42 (relative risk 0.07, 95% CI 0.00 to 1.17). Combining the results of the two trials using Mantel–Haenszel fixed-effect meta-analysis gives an overall relative risk 0.50 (95% CI 0.27 to 0.93) for endometritis.
Women in the ANODE trial who received placebo had a 19% rate of confirmed or suspected infection at 6 weeks post partum. This is higher than the infection rate reported in most other studies of complications following instrumental vaginal birth. 29 As noted previously, very few of these observational studies followed women beyond discharge, yet post-partum wound infections and endometritis have been reported to occur at a peak of 7 days post discharge in large data-linkage studies. 43 The ANODE trial shows very clearly a significant burden of confirmed or suspected infection and, most notably, both superficial and deep perineal wound infection after initial hospital discharge.
Although a single dose of co-amoxiclav almost halved the infection rate, 11% of women still had a confirmed or suspected infection after receiving antibiotic prophylaxis. The question therefore arises as to whether or not other, non-pharmaceutical interventions might reduce this further. We did not collect information about the aseptic techniques used at the time of operative vaginal birth, nor whether or not gloves and instrument trollies were changed between birth and perineal repair; the RCOG guidelines simply state that good standards of hygiene and aseptic technique are recommended. 15 It is possible that further attention to aseptic technique at the time of birth may influence later outcomes. A Cochrane review identified no difference in infection rates in surgical wounds cleansed with water versus other solutions (saline, procaine spirit) or no cleansing. 44 The review identified only one small trial of wound-cleansing post episiotomy, which randomised 100 women to cleanse their episiotomy wounds with either water or procaine spirit;45 the authors report no difference in infection rates, but did not give exact figures. They note that women cleaned their wounds an average of five times per day and that all wounds were healed well by 14 days post partum. Therefore, there may be a place for further investigation of wound-cleansing after operative vaginal birth to see if infection rates are lower.
There is an apparent discrepancy between the proportion of women who were diagnosed with systemic sepsis in the ANODE trial, defined by the modified SIRS criteria for pregnancy, and those with a microbiologically confirmed systemic infection. There are several possible reasons for this. The modified SIRS criteria in pregnancy3,32 have never been validated against microbiological or other diagnostic tests, and work is ongoing to establish a clear and actionable definition of maternal sepsis. 46,47 It is possible that women with microbiologically confirmed systemic infection are false negative cases of maternal sepsis when using the modified SIRS criteria. Conversely, with the substantially raised awareness of maternal sepsis, which has followed the UK Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths and Morbidity48 and the work of the UK Sepsis Trust [https://sepsistrust.org (accessed 12 December 2018)], women with microbiologically confirmed systemic infection may have been diagnosed and treated early, before progression to infection sufficiently severe to meet the modified SIRS criteria.
Women reported a range of other complications after operative vaginal birth, the majority of which were also less frequent among women who were randomised to receive antibiotic prophylaxis. A very high proportion of women reported perineal pain at 6 weeks after giving birth (46% in the antibiotic arm and 55% in the placebo arm), although a much lower proportion reported use of pain relief for their perineal pain (8% in the antibiotic arm vs. 11% in the placebo arm). A recent US study of women undergoing vaginal birth noted that operative vaginal birth was associated with opioid prescription in the 7 days after discharge (adjusted odds ratio 1.52, 95% CI 1.49 to 1.54), indicating a significant degree of pain. A trial of restrictive versus routine use of episiotomy at operative vaginal birth noted very similar rates of perineal pain at 6 weeks post partum (44%), but this had decreased to 18% at 1 year post partum. 49 Notably, women reported higher levels of pain with restrictive use of episiotomy compared with routine use; however, almost 90% of women included in the ANODE trial had an episiotomy, suggesting that restricted use is unlikely to be a potential underlying reason for the high rates of perineal pain observed.
One in five women in the placebo arm and one in 10 in the antibiotic arm reported that they had experienced perineal wound breakdown. Although a previous feasibility study reported that most women whose perineal wound had dehisced had healed by 6–8 weeks,35 women described long-term impacts 6–9 months later,37 including psychosexual morbidity. It is therefore probable that the almost 50% reduction in wound breakdown reported in the antibiotic arm is associated with longer-term benefit on sexual function, even though we observed no difference in dyspareunia between the groups at 6 weeks post partum. Only 40% of women had resumed intercourse, which may also mask any potential beneficial effect of the active intervention, but our results highlight the high levels of ongoing maternal morbidity following childbirth.
The mean total health-care cost per woman was £52.60 lower in the antibiotic arm than in the placebo arm, but this was not statistically significantly different at the 1% level. However, considering the probable long-term persistence of some complications, and the likelihood that the intervention dominates, it is probable that co-amoxiclav prophylaxis will prove cost-effective as well as clinically effective in the longer term. In the light of current concerns over antimicrobial stewardship and the emergence of antimicrobial resistance,21 an assessment of the impact of the single prophylactic dose on overall antibiotic use is important. The additional health-care cost and resource analysis conducted for the ANODE trial estimates that, for each additional 100 doses of antibiotic used in prophylaxis, 168 treatment doses will be avoided, representing a 17% overall reduction in antibiotic use with a policy of universal prophylaxis.
Sensitivity analyses
None of the sensitivity analyses we conducted materially affected the assessment of the primary outcome. A number of women were prescribed antibiotics in labour, for indications such as prophylaxis against group B streptococcal infection or maternal pyrexia. Exclusion of these women from the analysis did not change the estimate of effect of antibiotic prophylaxis, indicating that the effect we observed was not caused by a protective effect of prior antibiotic administration. We additionally examined whether or not exclusion from the primary outcome of any women who were prescribed antibiotics within the first 24 hours after giving birth had any impact, to test if the effect was solely due to prevention of infection among women who were already infected at or around the time of giving birth. As this had no substantial effect on the results, it suggests that the protective effect of a single dose of antibiotic is not caused by treatment of early or already established infections alone.
We also examined whether or not the exclusion of data that were obtained < 6 weeks or > 10 weeks after women had given birth had an impact on the results. There was no major influence, suggesting that the results were not biased by any over-reporting of outcomes from data returned at a later time point or under-reporting of outcomes in data returned at an earlier time point.
As a final sensitivity analysis we included site as a random effect; there was no suggestion that the results differed by site.
Implications for practice
Current national guidance on operative vaginal birth in the UK,15 the USA,50 Australia and New Zealand51 either do not mention or do not recommend antibiotic prophylaxis after instrumental vaginal birth. The WHO guidelines on prevention of maternal infection explicitly state that antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended after instrumental vaginal birth based on a lack of evidence of effectiveness. The ANODE trial provides clear evidence of effectiveness of a single dose of prophylactic intravenous co-amoxiclav on prevention of confirmed or suspected maternal infection, a range of secondary outcomes and a potential impact on health service costs. On the basis of this evidence, reconsideration of official policy/guidance about whether or not routine prophylaxis with a single dose of intravenous antibiotic after operative vaginal birth should be considered.
Implications for research
Further analyses of the ANODE trial data
A number of questions remain that could be addressed by further analyses of the ANODE trial data:
-
The intervention was given a median of 3 hours after women had given birth; as discussed earlier, theoretically, either earlier or later intervention may have been more effective. Further investigation of whether or not the efficacy of prophylaxis varied with timing of administration is warranted to further guide advice on how rapidly antibiotic prophylaxis should be administered, and to assess whether or not there is any evidence to suggest that pre-delivery or repeated administration may be more effective.
-
The ANODE trial intervention showed clear evidence of benefit in reducing incidence of suspected or confirmed maternal infection. Nevertheless, it is possible that it had different effects among different groups of women, for example, women who had a forceps birth compared with those having a ventouse birth, or those who had an episiotomy compared with those who did not. Further investigation of these subgroups is important.
-
Eleven per cent of women in the antibiotic arm had confirmed or suspected maternal infection. Investigation of the factors associated with maternal infection may give additional indications as to future preventative interventions, or specific risk groups towards whom preventative interventions may be focused.
-
Similarly, detailed examination of the microorganisms causing infection in the ANODE trial cohort, together with their resistance patterns, would provide further information about the mechanism of action, and the optimal spectrum of antibacterial activity, of this single prophylactic antibiotic dose.
-
A high proportion of women in the ANODE trial were prescribed antibiotics in the absence of a confirmed infection, or for non-infective indications. Further detailed examination of these prescription patterns may indicate areas of practice that could be the focus of future antimicrobial stewardship interventions.
-
A number of assumptions were made during the cost analysis, for example, in relation to the duration of antibiotic treatment and the type of antibiotic used in women who had infection or suspected infection. Further sensitivity analyses could be conducted to investigate the impact of these assumptions on the cost analysis.
Further research questions raised
-
In this trial, the prophylactic antibiotic was administered intravenously. The commonest reason for women not receiving the planned intervention was cannula failure. Similarly, a significant number of women declined to participate in the trial because it would require placement of a cannula to administer antibiotics. In other settings where operative vaginal delivery is undertaken, for example in low- and middle-income countries, intravenous administration of antibiotics may be difficult or impossible. This raises the question of whether or not oral antibiotic prophylaxis would be as effective as intravenous, either as a single dose or as multiple doses.
-
The substantial residual burden of infection after antibiotic prophylaxis indicates a need for investigation of additional preventative measures and/or early identification to prevent associated wound breakdown. It is possible that multiple doses of antibiotic may be more effective, but this needs to be carefully evaluated against the risk of driving emergence of antimicrobial resistance. This would also need to be robustly investigated in a future RCT if further analysis of the ANODE trial data suggests that there is a potential place for multiple doses. Currently, both 1- and 3-day courses are being prescribed with no clear evidence. Further investigation of cleansing/aseptic measures is also warranted.
-
The evidence from this trial suggests that there could be a change of policy to recommend universal antibiotic prophylaxis at operative vaginal birth. The effect of such a change of policy on patterns of infection and emerging antimicrobial resistance would, however, need careful evaluation.
-
The women participating in the ANODE trial reported high rates of perineal pain and wound breakdown as well as confirmed or suspected infection at 6 weeks postnatally. Nevertheless, it is unclear whether women will continue to have long-term morbidity or if these outcomes are problematic only in the short term. Assessment of the long-term costs and outcomes for women will be essential in assessing the cost-effectiveness of any prophylaxis policies.
Conclusions
The ANODE trial has shown clear evidence of the benefit of a single intravenous dose of prophylactic co-amoxiclav after operative vaginal birth; these results indicate the need for reconsideration of official policy/guidance. Further analysis of the mechanism of action of this single dose of antibiotic is needed to investigate whether earlier, pre-delivery or repeated administration could be more effective. Until these analyses are completed, there is no indication for administration of more than a single dose of prophylactic antibiotic, or for pre-delivery administration.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge all the women who participated in the trial and the site staff, without whom this research would not have been possible.
Sponsorship
The ANODE trial was sponsored by the University of Oxford.
Independent Trial Steering Committee
Fiona Denison (chairperson), Simon Cousens, Timothy Overton, Rachel Plachinski, Donna Southam and Matthew Wilson.
Independent Data Monitoring Committee
Siladitya Bhattacharya (chairperson), Carrol Gamble and Michael Millar.
ANODE Trial Collaborative Group
-
Marian Knight, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford.
-
Helen Enderby, lay member, PRIME group.
-
Derek Tuffnell, Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Kim Hinshaw, Sunderland Royal Hospital, Tyne and Wear.
-
Ranee Thakar, Croydon University Hospital.
-
Abdul H Sultan, Croydon University Hospital and St George’s, University of London.
-
Julia Sanders, Cardiff University.
-
Dharmintra Pasupathy, King’s College London.
-
Philip Moore, Birmingham Women’s Hospital.
-
James Gray, Birmingham Women’s and Children’s NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Oliver Rivero-Arias, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford.
-
Ed Juszczak, NPEU CTU, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford.
-
Louise Linsell, NPEU CTU, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford.
-
Aethele Khunda, James Cook University Hospital, Middlesbrough.
Contributions of authors
Marian Knight wrote the first draft of the manuscript with contributions from Virginia Chiocchia, Oliver Rivero-Arias and Xinyang Hua.
Virginia Chiocchia, Christopher Partlett, Louise Linsell and Edmund Juszczak developed the analysis plan and conducted the analyses.
Marian Knight, Virginia Chiocchia, Christopher Partlett, Oliver Rivero-Arias, Xinyang Hu, Ursula Bowler, James Gray, Shan Gray, Kim Hinshaw, Aethele Khunda, Philip Moore, Linda Mottram, Nelly Owino, Dharmintra Pasupathy, Julia Sanders, Abdul H Sultan, Ranee Thakar, Derek Tuffnell, Louise Linsell and Edmund Juszczak contributed to the development and conduct of the trial and edited and approved the final version of the manuscript.
All members of the collaborative group contributed to the development and conduct of the trial.
Publications
Knight M, Mottram L, Gray S, Partlett C, Juszczak E, ANODE collaborative group. Prophylactic antibiotics for the prevention of infection following operative vaginal delivery (ANODE): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2018;19:395.
Knight M, Ciocchia V, Partlett C, Rivero-Arias O, Hua X, Hinshaw, et al. Prophylactic antibiotics in the prevention of infection after operative vaginal delivery (ANODE): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019;393:2395–403.
Data-sharing statement
Data will be shared in accordance with the National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit Data Sharing policy. Requests for access to the data will be considered by the National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit Data Sharing committee. Access to anonymised data can be requested from general@npeu.ox.ac.uk.
Patient data
This work uses data provided by patients and collected by the NHS as part of their care and support. Using patient data is vital to improve health and care for everyone. There is huge potential to make better use of information from people’s patient records, to understand more about disease, develop new treatments, monitor safety, and plan NHS services. Patient data should be kept safe and secure, to protect everyone’s privacy, and it’s important that there are safeguards to make sure that it is stored and used responsibly. Everyone should be able to find out about how patient data are used. #datasaveslives You can find out more about the background to this citation here: https://understandingpatientdata.org.uk/data-citation.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the HTA programme or the Department of Health and Social Care.
References
- Global Burden of Disease Causes of Death Collaborators . Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017;390:1151-210.
- Knight M, Bunch K, Tuffnell D, Jayakody H, Shakespeare J, Kotnis R, et al. Saving Lives, Improving Mothers’ Care – Lessons Learned to Inform Maternity Care From The UK and Ireland Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths and Morbidity 2014–16. Oxford: National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, University of Oxford; 2018.
- Acosta CD, Kurinczuk JJ, Lucas DN, Tuffnell DJ, Sellers S, Knight M. United Kingdom Obstetric Surveillance System. Severe maternal sepsis in the UK, 2011–2012: a national case-control study. PLOS Med 2014;11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001672.
- Declercq E, Barger M, Cabral HJ, Evans SR, Kotelchuck M, Simon C, et al. Maternal outcomes associated with planned primary caesarean births compared with planned vaginal births. Obstet Gynecol 2007;109:669-77. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000255668.20639.40.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Caesarean Section. NICE Clinical Guideline 132 2011.
- Smaill FM, Grivell RM. Antibiotic prophylaxis versus no prophylaxis for preventing infection after caesarean section. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;10. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007482.pub3.
- Acosta CD, Bhattacharya S, Tuffnell D, Kurinczuk JJ, Knight M. Maternal sepsis: a Scottish population-based case-control study. BJOG 2012;119:474-83. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2011.03239.x.
- Acosta CD, Knight M, Lee HC, Kurinczuk JJ, Gould JB, Lyndon A. The continuum of maternal sepsis severity: incidence and risk factors in a population-based cohort study. PLOS ONE 2013;8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067175.
- Knight M, Acosta C, Brocklehurst P, Cheshire A, Fitzpatrick K, Hinton L, et al. Beyond maternal death: improving the quality of maternal care through national studies of ‘near-miss’ maternal morbidity. Programme Grants Appl Res 2016;4. https://doi.org/10.3310/pgfar04090.
- Liabsuetrakul T, Choobun T, Peeyananjarassri K, Islam QM. Antibiotic prophylaxis for operative vaginal delivery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;8. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004455.pub4.
- Johnson A, Thakar R, Sultan AH. Obstetric perineal wound infection: is there underreporting?. Br J Nurs 2012;21. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2012.21.Sup5.S28.
- Perkins E, Tothill S, Kettle C, Bick D, Ismail K. Women’s views of important outcomes following perineal repair. BJOG 2008;115.
- NHS Digital . NHS Maternity Statistics, England 2017–18 2018. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/nhs-maternity-statistics/2017-18 (accessed 12 December 2018).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Intrapartum Care for Healthy Women and Babies. Clinical Guidance 190 (CG190) 2014. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg190 (accessed 15 April 2015).
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists . Green-Top Guideline Number 26: Operative Vaginal Delivery 2011. www.rcog.org.uk/globalassets/documents/guidelines/gtg_26.pdf (accessed 17 April 2018).
- World Health Organization . WHO Recommendations for Prevention and Treatment of Maternal Peripartum Infections 2015.
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) . Green-Top Guideline No. 64b. Bacterial Sepsis Following Pregnancy 2012.
- Wloch C, Lamagni T, Connelly J, Harrington P, Elgohari S, van Hoek AJ, et al. Estimating the Healthcare Costs of Post-Surgical Infection in Patients Undergoing Caesarean Section in England 2012.
- Department of Health and Social Care . Getting Ahead of the Curve 2002.
- Department of Health and Social Care . UK Five Year Antimicrobial Resistance Strategy 2013 to 2018 2013. www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/244058/20130902_UK_5_year_AMR_strategy.pdf (accessed 23 October 2013).
- Chief Medical Officer . Annual Report of the Chief Medical Officer, Volume Two, 2011, Infections and the Rise of Antimicrobial Resistance 2013.
- European Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (ECDC) . Poor Pregnancy Outcomes Associated With Maternal Infection With the A(H1N1) 2009 Virus During the Pandemic – Findings from a European Cohort Study 2011. www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/activities/sciadvice/Lists/ECDC%20Reviews/ECDC_DispForm.aspx?List=512ff74f-77d4-4ad8-b6d6-bf0f23083f30&ID=1157&MasterPage=1 (accessed 31 July 2011).
- McCulloch P, Altman DG, Campbell WB, Flum DR, Glasziou P, Marshall JC, et al. No surgical innovation without evaluation: the IDEAL recommendations. Lancet 2009;374:1105-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61116-8.
- Stensballe LG, Simonsen J, Jensen SM, Bønnelykke K, Bisgaard H. Use of antibiotics during pregnancy increases the risk of asthma in early childhood. J Pediatr 2013;162:832-8.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.09.049.
- Örtqvist AK, Lundholm C, Halfvarson J, Ludvigsson JF, Almqvist C. Fetal and early life antibiotics exposure and very early onset inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Gut 2019;68:218-25. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314352.
- Gülmezoglu AM, Duley L. Use of anticonvulsants in eclampsia and pre-eclampsia: survey of obstetricians in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland. BMJ 1998;316:975-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.316.7136.975.
- McCall SJ, Bunch KJ, Brocklehurst P, D’Arcy R, Hinshaw K, Kurinczuk JJ, et al. The incidence, characteristics, management and outcomes of anaphylaxis in pregnancy: a population-based descriptive study. BJOG 2018;125:965-71. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.15041.
- Knight M, Mottram L, Gray S, Partlett C, Juszczak E. ANODE collaborative group. Prophylactic antibiotics for the prevention of infection following operative vaginal delivery (ANODE): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2018;19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-018-2787-0.
- Mohamed-Ahmed O, Hinshaw K, Knight M. Operative vaginal delivery and post-partum infection. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2018;56:93-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2018.09.005.
- Knight M, Chiocchia V, Partlett C, Rivero-Arias O, Hua X, Hinshaw K, et al. Prophylactic antibiotics in the prevention of infection after operative vaginal delivery (ANODE): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019;393:2395-403. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30773-1.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCP) . CDC/NHSN/Surveillance/Definitions/for/Specific/Types/of/Infections 2013. www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/17pscnosinfdef_current.pdf (accessed 15 November 2013).
- Waterstone M, Bewley S, Wolfe C. Incidence and predictors of severe obstetric morbidity: case-control study. BMJ 2001;322:1089-93. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1089.
- Public Health England (Health Protection Agency) . Protocol for the Surveillance of Surgical Site Infection 2013. http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/10080709222242/http://www.hpa.org.uk/web/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1194947388966 (accessed 18 April 2019).
- McCandlish R, Bowler U, van Asten H, Berridge G, Winter C, Sames L, et al. A randomised controlled trial of care of the perineum during second stage of normal labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1998;105:1262-72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb10004.x.
- Dudley L, Kettle C, Thomas PW, Ismail KM. Perineal resuturing versus expectant management following vaginal delivery complicated by a dehisced wound (PREVIEW): a pilot and feasibility randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2017;7. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012766.
- Devlin NJ, Shah KK, Feng Y, Mulhern B, van Hout B. Valuing health-related quality of life: an EQ-5D-5L value set for England. Health Econ 2018;27:7-22. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.3564.
- Dudley L, Kettle C, Waterfield J, Ismail KM. Perineal resuturing versus expectant management following vaginal delivery complicated by a dehisced wound (PREVIEW): a nested qualitative study. BMJ Open 2017;7. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013008.
- Joint Formulary Committee . British National Formulary n.d. www.medicinescomplete.com (accessed August 2019).
- Curtis L, Burns A. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2017. University of Kent, Personal Social Services Research Unit; 2017.
- NHS Improvement . NHS Reference Costs 2017 18 n.d. https://improvement.nhs.uk/resources/reference-costs/#rc1718 (accessed 17 January 2019).
- Mackeen AD, Packard RE, Ota E, Berghella V, Baxter JK. Timing of intravenous prophylactic antibiotics for preventing postpartum infectious morbidity in women undergoing caesarean delivery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;12. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009516.pub2.
- Heitmann JA, Benrubi GI. Efficacy of prophylactic antibiotics for the prevention of endomyometritis after forceps delivery. South Med J 1989;82:960-2. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007611-198908000-00007.
- Axelsson D, Brynhildsen J, Blomberg M. Postpartum infection in relation to maternal characteristics, obstetric interventions and complications. J Perinat Med 2018;46:271-8. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpm-2016-0389.
- Fernandez R, Griffiths R. Water for wound cleansing. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;2. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003861.pub3.
- Tay SK, Soong SL, Choo BM. Is routine procaine spirit application necessary in the care of episiotomy wound?. Singapore Med J 1999;40:581-3.
- Bonet M, Nogueira Pileggi V, Rijken MJ, Coomarasamy A, Lissauer D, Souza JP, et al. Towards a consensus definition of maternal sepsis: results of a systematic review and expert consultation. Reprod Health 2017;14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-017-0321-6.
- Bonet M, Souza JP, Abalos E, Fawole B, Knight M, Kouanda S, et al. The global maternal sepsis study and awareness campaign (GLOSS): study protocol. Reprod Health 2018;15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-017-0437-8.
- Knight M, Kenyon S, Brocklehurst P, Neilson J, Shakespeare J, Kurinczuk J, et al. Saving Lives, Improving Mothers’ Care – Lessons Learned to Inform Future Maternity Care from the UK and Ireland Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths and Morbidity 2009–12. Oxford: National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, University of Oxford; 2014.
- Macleod M, Goyder K, Howarth L, Bahl R, Strachan B, Murphy DJ. Morbidity experienced by women before and after operative vaginal delivery: prospective cohort study nested within a two-centre randomised controlled trial of restrictive versus routine use of episiotomy. BJOG 2013;120:1020-6. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12184.
- Committee on Practice Bulletins – Obstetrics . ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 154: Operative Vaginal Delivery. Obstet Gynecol 2015;126:e56-65. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000001147.
- Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists . Instrumental Vaginal Birth 2015.
- Joint Formulary Committee . British National Formulary 2017. https://bnf.nice.org.uk/medicinal-forms/co-amoxiclav.html (accessed 22 January 2019).
- Curtis L, Burns A. Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2015. Canterbury: Personal Social Services Research Unit, University of Kent; 2015.
Appendix 1 Recruiting units, principal investigators and site midwives
Bradford Royal Infirmary
Derek Tuffnell (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Jennifer Syson (Local Research Midwife).
Burnley General Hospital
Manisha Golash (Consultant Obstetrician).
Rebekah McCrimmon (Local Research Midwife).
Croydon University Hospital
Ranee Thakar (Subspecialist in Urogynaecology and Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Hana Kleprlikova (Local Research Midwife).
Darlington Memorial Hospital
Poornima Ranka (Consultant Obstetrician).
Jacqui Jennings (Local Research Midwife).
Derriford Hospital
Alex Taylor (Consultant Obstetrician).
Heidi Hollands (Local Research Midwife).
East Surrey Hospital
Mahalakshmi Gorti (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Linda Bailey (Local Research Midwife).
Guy’s and St Thomas’ Hospital
Dharmintra Pasupathy (Consultant and Reader in Maternal and Fetal Medicine).
Cathryn Marsh (Local Research Midwife).
John Radcliffe Hospital
Christos Ioannou (Consultant in Obstetrics and Fetal Medicine).
Clare Edwards (Local Research Midwife).
Liverpool Women’s Hospital
Mark Clement-Jones (Consultant Obstetrician).
Siobhan Holt (Local Research Midwife).
Northumbria Specialist Emergency Care Hospital
Jonathan Brady (Consultant).
Helen Howlett (Local Research Midwife).
Princess Anne Hospital
James Hounslow (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Fiona Walbridge/Nicki Martin (Local Research Midwife).
Queen Elizabeth Hospital
Vaideha M Deshpande (Consultant Obstetrician/Gynaecologist and Reproductive Medicine Specialist).
Barbara Lynam (Local Research Midwife).
Royal Berkshire
Patrick Bose (Consultant).
Fidelma Lee (Local Research Midwife).
Royal Devon and Exeter Wonford Hospital
Tracey Kay (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Jacqui Tipper (Local Research Midwife).
Royal Stoke University Hospital
Simon Cunningham (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Donna Brayford (Local Research Midwife).
Royal Victoria Infirmary
Suzanne Jackson (Consultant Obstetrician).
Michelle Perkins (Local Research Midwife).
Singleton Hospital – Swansea/Princess of Wales – Bridgend
Madhuchanda Dey (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Sharon Jones (Local Research Midwife).
South Tyneside District Hospital
Umo Esen (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Judith Ormonde (Local Research Midwife).
Stoke Mandeville Hospital
Nutan Mishra (Consultant Obstetrician).
Julie Tebbutt (Local Research Midwife).
Sunderland Royal Hospital
Kim Hinshaw (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Lesley Hewitt (Local Research Midwife).
The James Cook University Hospital
Aethele Khunda (Consultant Obstetrician and Urogynaecologist).
Hazel Alexander (Research Practitioner).
University Hospital of North Durham
Tadala Saukila (Consultant Obstetrician).
Vicki Atkinson (Local Research Midwife).
University Hospital of North Tees
Mihraban Bapir (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Sharon Gowans (Local Research Midwife).
University Hospital of Wales
Julia Sanders (Consultant Midwife).
Anouk Ridgway (Local Research Midwife).
Warrington Hospital
Rita Arya (Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist).
Rachel Crone/Lindsay Roughley (Local Research Midwife).
Whittington Health
Meg Wilson (Consultant).
Osi Egole (Local Research Midwife).
Appendix 2 Sources of unit costs (Great British pounds 2017/18) used in the cost analysis
| Health-care resource use item | Unit cost (£) | Sources (notes) |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | ||
| Single dose of co-amoxiclav assigned to intervention | 2.30 | British National Formulary 201752 (average of three brands with NHS indicative prices for 1000 mg of amoxicillin/200 mg of clavulanic acid powder for solution for injection vials) |
| Course of co-amoxiclav assigned to prescriptions following delivery | 4.80 | British National Formulary 201752 (average of 14 brands with NHS indicative prices for oral suspension and tablet courses of co-amoxiclav) |
| Health-care professionals | ||
| GP | 37.00 | Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2017 39 |
| Nurse/midwife at general practice | 10.90 | Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201739 (duration of visit extracted from Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 201553) |
| Nurse/midwife in home | 68.00 | NHS Reference Costs 2017–1840 (code N01P) |
| Health visitor/district nurse | 38.00 | NHS Reference Costs 2017–1840 (code N02AF) |
| Outpatient visits | ||
| Outpatient visit doctor | 138.20 | NHS Reference Costs 2017–1840 (weighted average of codes 501 and 502, total) |
| Outpatient visit nurse or midwife | 73.00 | NHS Reference Costs 2017–1840 (560, non-consultant led) |
| Outpatient physiotherapy | 55.00 | NHS Reference Costs 2017–1840 (code 650) |
| Hospital re-admissions | ||
| Stay including intensive care | 936.90 | NHS Reference Costs 2017–1840 (weighted average of codes XC03Z–XC07Z) |
| Non-elective short stay | 640.30 | NHS Reference Costs 2017–1840 (weighted average of codes NZ26A and NZ26B) |
| Medicinal forms for co-amoxiclav | Unit cost (£) (NHS indicative price) |
|---|---|
| Powder for solution for injection | |
| Augmentin intravenous 1.2 g of powder for solution for injection vials (GlaxoSmithKline plc, Brentford, UK) (size 10) | 10.60 |
| Co-amoxiclav 1000 mg/200 mg of powder for solution for injection vials (Bowmed Ibisqus Ltd, Wrexham, UK) (size 10) | 27.50 |
| Co-amoxiclav 1000 mg/200 mg of powder for solution for injection vials (Wockhardt UK Ltd, Wrexham, UK) (size 10) | 29.70 |
| Oral suspension | |
| Augmentin 125/31 SF oral suspension (GlaxoSmithKline plc) | 3.54 |
| Co-amoxiclav 125 mg/31 mg/5 ml oral suspension (AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Coventry, UK) | 2.15 |
| Co-amoxiclav 125 mg/31 mg/5 ml oral suspension (Mylan, Canonsburg, PA, USA) | 5.00 |
| Co-amoxiclav 125 mg/31 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd) | 1.79 |
| Co-amoxiclav 125 mg/31 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Alliance Healthcare, Surrey, UK) | 1.79 |
| Co-amoxiclav 125 mg/31 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Almus Pharmaceuticals, Surrey, UK) | 1.79 |
| Co-amoxiclav 125 mg/31 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Sandoz Ltd, Frimley, UK) | 1.48 |
| Augmentin 250/62 SF oral suspension (GlaxoSmithKline plc) | 3.60 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250 mg/62 mg/5 ml oral suspension (AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd) | 2.15 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250 mg/62 mg/5 ml oral suspension (Mylan) | 5.00 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250 mg/62 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd) | 1.63 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250 mg/62 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Alliance Healthcare) | 1.63 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250 mg/62 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Almus Pharmaceuticals) | 1.63 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250 mg/62 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Sandoz Ltd) | 1.65 |
| Augmentin-Duo 400/57 oral suspension (GlaxoSmithKline plc) (size 35) | 4.13 |
| Augmentin-Duo 400/57 oral suspension (GlaxoSmithKline plc) (size70) | 5.79 |
| Co-amoxiclav 400 mg/57 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd) (size 35) | 4.13 |
| Co-amoxiclav 400 mg/57 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd) (size 70) | 5.79 |
| Co-amoxiclav 400 mg/57 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Brown & Burk UK Ltd, Hounslow, UK) | 6.97 |
| Co-amoxiclav 400 mg/57 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Sandoz Ltd) (size 35) | 4.13 |
| Co-amoxiclav 400 mg/57 mg/5 ml oral suspension sugar free (Sandoz Ltd) (size 70) | 5.79 |
| Tablet | |
| Augmentin 375 mg tablets (GlaxoSmithKline plc) | 5.03 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250-mg/125-mg tablets (AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd) | 2.18 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250-mg/125-mg tablets (Alliance Healthcare) | 1.97 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250-mg/125-mg tablets (Almus Pharmaceuticals) | 1.97 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250-mg/125-mg tablets (Brown & Burk UK Ltd) | 6.00 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250-mg/125-mg tablets (Consilient Health Ltd, Surrey, UK) | 5.03 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250-mg/125-mg tablets (Mylan) | 5.00 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250-mg/125-mg tablets [Rivopharm (UK) Ltd, London, UK] | 4.02 |
| Co-amoxiclav 250-mg/125-mg tablets (Sandoz Ltd) | 3.55 |
| Augmentin 625-mg tablets (GlaxoSmithKline plc) | 9.60 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd) | 2.29 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Actavis UK Ltd) | 3.15 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Alliance Healthcare) | 2.29 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Almus Pharmaceuticals) | 2.29 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Aurobindo Pharma, Hyderabad, India) | 1.65 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Brown & Burk UK Ltd) | 12.00 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Consilient Health Ltd) | 8.00 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Creo Pharma Ltd, Cock Green, UK) | 9.60 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Kent Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Kent, UK) | 15.00 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Medreich plc, Feltham, UK) | 7.90 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Mylan) | 8.00 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Rivopharm (UK) Ltd) | 7.68 |
| Co-amoxiclav 500-mg/125-mg tablets (Sandoz Ltd) | 2.86 |
| Co-amoxiclav 875-mg/125-mg tablets (Brown & Burk UK Ltd) | 18.00 |
Appendix 3 Summary of changes to the trial protocol
| Amendment number | Protocol version number | Date issued | Author(s) of changes | Details of changes made |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not applicable | Version 2.0 | Not applicable | Changes made on behalf of Project Management Group | Subsequent to protocol version 1.0 being approved by the REC, the MHRA requested several edits to the ANODE protocol when it was submitted as part of the initial Clinical Trials Authorisation application. These edits were made to create version 2.0 on 17 October 2015 (see summary of changes below). Version 2.0 on 17 October 2015 was approved by the MHRA and Clinical Trials Authorisation awarded (Clinical Trials Authorisation acceptance letter dated 29 October 2015) |
The following changes have been made to create protocol version 2.0 17 October 2015.
Exclusion criteria (page 16)
The exclusion criterion was amended to exclude all participants who have the contraindications listed in the Summary of Medicinal Product Characteristics for co-amoxiclav as requested by the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).
Reporting serious adverse events and procedure for immediate reporting of serious adverse events (pages 25–26)
The section was amended in response to a request made by the MHRA on reviewing the initial ANODE trial Clinical Trials Authorisation application.
A list of SAEs that were not considered to be causally related to the trial intervention were agreed with Professor Bhattacharya (chairperson of the ANODE trial DMC). The SAE reporting procedure was also amended to include the ability to report SAEs via the Clinical Database OpenClinica© (Enterprise edition, OpenClinica LLC, Waltham, MA, USA) on page 26.
Listed below are all edits reviewed by the MHRA prior to the Clinical Trials Authorisation being granted (ANODE trial protocol version 2.0):
-
The Ethics Reference number was added to page 1.
-
Social care visits were removed from the secondary outcomes; they had been included in error.
-
The spelling of amoxicillin has been made consistent throughout the document.
-
The duration of the study on page 16 was amended to reflect changes made to the recruitment start date (changed from 1 September 2015 to 1 December 2015).
-
A reference was deleted on page 34 of the protocol because it was duplicated in error.
| Amendment number | Protocol version number | Date issued | Author(s) of changes | Details of changes made |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Version 3.0 | 6 January 2016 | Changes made on behalf of the Project Management Group | Substantial amendment 1 was reviewed by both REC and MHRA |
The following changes have been made to create protocol version 3.0 3 December 2015.
Exclusion criteria (page 16)
In the point ’Note that receiving antenatal or postnatal antibiotics e.g. for maternal Group B Streptococcal carriage or prolonged rupture of membranes, is not a reason for exclusion if there is no indication for ongoing antibiotic prescription post-delivery’, the words ’or postnatal’ have been removed because this wording was incorrect and contradicts the previous sentence.
Reporting serious adverse events and procedure for immediate reporting of serious adverse events (pages 25–26)
Wording was amended to improve consistency and to make it clear that events that commence prior to the administration of the trial intervention do not require reporting as a SAE.
Randomisation, blinding and code-breaking (page 20)
Text edited regarding balance and unpredictability from ’within centre’ to ’overall’ by trial statistician.
Text edited to show that an emergency code-breaking procedure will not be required; as only a single dose of co-amoxiclav will be administered, there is no need to code-break if further antibiotics are required. If a woman was to have an anaphylactic reaction, she would be treated as if she had been given the active drug.
Other edits to the protocol in version 3.0 are listed below
-
The list of investigators was removed from the cover page to make the protocol clearer and to ensure that the ANODE trial team at the Clinical Trials Unit were approached with any protocol queries in the first instance rather than a co-investigator. The investigators will be listed on the ANODE trial website.
-
The confidentiality statement was removed from page 2 as the protocol is no longer confidential and is available publicly.
| Amendment number | Protocol version number | Date issued | Author(s) of changes | Details of changes made |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Version 4.0 | 22 April 2016 | Changes made on behalf of the Project Management Group | Changes listed below |
The following changes have been made to create protocol version 4.0 22 April 2016.
Section 7.0 trial design (page 15)
Edits to this section were made to specify exactly who would not be blinded to allocation to clarify that this also includes the person responsible for checking the intervention. The people not blinded to intervention were the person who prepared the trial intervention and the person who checked the intervention prior to administration. Training was provided to all unblinded staff on the importance of maintaining blinding and unblinded staff were not involved in the collection of outcomes information.
Other edits to the ANODE trial protocol
-
Page 1 – ISRCTN added and signature blocks for the chief investigator and the statistician removed; they were documented separately and filed with the protocol in the trial master file.
-
Global edit – where Hospital Episode Statistics (HES) are referenced, ’or NHS Wales Informatics Service’ was added. HES were accessed for participants recruited in England; NHS Wales Informatics Service were accessed for those participants recruited in Wales.
-
Pages 15–16 and appendix A – duration of study edited to reflect the change in start date agreed with the HTA programme.
-
Page 19 – edited to clarify that the original signed consent forms would be sent the co-ordinating centre and a copy retained at site.
-
Page 20 – section 9.5 edited to clarify the roles of the senior trials statistician and the senior trial programmer with regard to their responsibilities regarding the randomisation schedule generation.
| Amendment number | Protocol version number | Date issued | Author(s) of changes | Details of changes made |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Version 5.0 | 30 November 2017 | Changes made on behalf of the Project Management Group | Changes listed below |
The following changes have been made to create protocol version 5.0 30 November 2017.
Amendment to the definition of the primary outcome [pages 7, 9 (in flow chart), 14 and 20]
Primary outcome refined to the amended text below:
-
A new prescription of antibiotics for presumed perineal wound-related infection, endometritis or uterine infection, urinary tract infection with systemic features or other systemic infection.
-
Confirmed systemic infection on culture.
-
Endometritis as defined by the US CDC. 31
Trial timeline updated to reflected changes following an extension to the duration of the trial (pages 16 and 39)
Description of statistical methods (page 27)
The statistics section of the protocol was updated to make it consistent with the current strategy detailed in the statistical analysis plan as requested by the ANODE trial DMC in a meeting held on 27 November 2017.
List of abbreviations
- ANODE
- A randomised controlled trial of prophylactic ANtibiotics to investigate the prevention of infection following Operative vaginal DElivery
- BER
- blinded end-point review
- BMI
- body mass index
- CDC
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- CI
- confidence interval
- DMC
- Data Monitoring Committee
- EQ-5D-5L
- EuroQol-5 Dimensions, five-level version
- GP
- general practitioner
- HTA
- Health Technology Assessment
- IMP
- investigational medicinal product
- MHRA
- Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NIHR
- National Institute for Health Research
- NPEU CTU
- National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit Clinical Trials Unit
- PRIME
- Public and Researchers Involvement in Maternity and Early pregnancy
- RCOG
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- SAE
- serious adverse event
- SD
- standard deviation
- SIRS
- systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- SSI
- surgical site infection
- TSC
- Trial Steering Committee
- WHO
- World Health Organization
