Notes
Article history
The research reported in this issue of the journal was funded by the PHR programme as project number 12/3070/13. The contractual start date was in October 2013. The final report began editorial review in May 2016 and was accepted for publication in December 2016. The authors have been wholly responsible for all data collection, analysis and interpretation, and for writing up their work. The PHR editors and production house have tried to ensure the accuracy of the authors’ report and would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the final report document. However, they do not accept liability for damages or losses arising from material published in this report.
Declared competing interests of authors
Lorna Guinness reports grants from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine during the conduct of the study. Matthew Hickman is a member of the Public Health Research Funding Board. Sharon Hutchinson reports grants from the National Institute for Health Research during the conduct of the study and personal fees from AbbVie Inc. and Gilead Sciences, Inc., outside the submitted work. Avril Taylor reports grants from NHS National Services Scotland during the conduct of the study. Alison Munro reports personal fees from Janssen UK outside the submitted work. John Parry reports grants from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine during the conduct of the study.
Permissions
Copyright statement
© Queen’s Printer and Controller of HMSO 2017. This work was produced by Platt et al. under the terms of a commissioning contract issued by the Secretary of State for Health. This issue may be freely reproduced for the purposes of private research and study and extracts (or indeed, the full report) may be included in professional journals provided that suitable acknowledgement is made and the reproduction is not associated with any form of advertising. Applications for commercial reproduction should be addressed to: NIHR Journals Library, National Institute for Health Research, Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre, Alpha House, University of Southampton Science Park, Southampton SO16 7NS, UK.
Chapter 1 Introduction
Evidence shows that injecting with used needles or syringes and sharing injecting equipment is the main risk factor for infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) among people who inject drugs (PWID). 1,2 The current primary interventions for reducing HIV/HCV infection transmission among PWID are opioid substitution therapy (OST) and needle and syringe programmes (NSPs). 3 In 2005, there were an estimated 1700 NSPs in England, 70% of which were provided by community pharmacies, with the rest offered by specialist community-based services and outreach/mobile services and in custody suites. 4 NSPs in England are funded through Drug Action Teams and Local Strategic Partnerships, which are multiagency bodies involving local government, the police and health services.
Needle and syringe programmes are often a first point of contact with health services for PWID. They provide support to minimise drug and sexual risk-related harms, including the provision of clean needles/syringes and condoms in order to prevent blood-borne virus transmission, bacterial infections and other adverse health outcomes. By maximising the amount of clean injecting equipment in circulation, it is possible to minimise the time that contaminated equipment remains in use and the proportion of unsafe injections. 5,6 NSPs operate through a range of modalities including via fixed sites, outreach, peer PWID networks, vending machines and pharmacies. Engaging in behaviours that are socially stigmatised and illegal, PWID often have high rates of unemployment, homelessness and incarceration. NSPs also provide access to longer-term support by referring clients to medical, drug treatment or social support services.
Drug treatment for opioid addiction and dependence also encompasses a range of strategies to manage injecting drug use and to reduce associated harms, including medication-assisted treatment such as OST, medication-assisted treatment combined with psychosocial approaches and residential rehabilitation. The most commonly prescribed forms of OST are opioid agonist treatments, namely methadone maintenance therapy and partial agonist buprenorphine maintenance treatment, or the increasingly popular naloxone and buprenorphine (Subuxone®, Indivior Inc., Richmond, VA, USA). OST is prescribed to dependant users to diminish the use and effects of illicitly acquired opioids. It is usually taken orally and therefore reduces the frequency of injection and unsafe injecting practices. 7 As a treatment for opioid dependence, OST has been shown to increase health and social functioning, decrease crime and reduce the frequency of injection and unsafe injecting practices. 8,9 Evidence suggests that OST is most effective when it is continuous and provided at adequate doses. 10,11 In the UK, OST is prescribed by medically qualified clinicians or nurses and dispensed in both primary care or community settings (sometimes co-located at NSPs).
Both NSPs and OST are complex interventions that not only seek to reduce immediate harms caused by unsafe injecting practices, such as reducing HIV, HCV or bacterial infections, but also aim to address more complex social problems experienced by PWID by providing integrated care and referrals to other agencies including housing, social welfare, legal advocacy and sexual and mental health services. This report takes a more focused definition of how the interventions reduce the risk of infection with HCV infection and does not take into account the indirect routes or causal pathways through which the interventions might work by addressing the underlying social issues that might lead to injecting risk behaviours.
Although there is good evidence that NSPs and OST in combination reduce injecting risk behaviours and some evidence to show the impact on HIV incidence, there is little evidence of their impact on HCV infection incidence among PWID. 3,12–15 In 2012 and 2014, two reviews were published that estimated a moderate effect of NSPs on reducing HIV transmission by 48% [95% confidence interval (CI) 3% to 72%] and strong evidence for OST reducing HIV transmission by 54% (95% CI 33% to 68%). 16,17 Similar evidence is lacking for the effect of NSPs or OST on HCV infection. Previous reviews7,15,18 have synthesised evidence for use of NSPs but have focused primarily on HIV as the main outcome and, as a consequence, have failed to include all the available evidence on HCV infection. 3 More recently, evidence on a range of risk-reduction interventions on HCV infection seroconversion, including behavioural interventions, NSP and OST, were reviewed. 19 This study measured the effect of NSP use, defined inconsistently as any attendance at a NSP or attendance at one point in time, and showed an increased risk of seroconversion. Limitations of this review included substantial heterogeneity across studies, a lack of clarity on the measure of NSP use and a focus on evidence from North America, which limits the generalisability of findings to other settings, including the UK. Our review on the effect of OST use on HIV transmission detected many more studies than earlier Cochrane reviews. 17 We also expect that not all evidence on the effect of NSP on HCV infection transmission has been identified, so extending previous reviews would strengthen the evidence base as well as provide a more refined measure of coverage of NSP that accounts for frequency and the degree to which NSPs meet individuals’ requirement for needles/syringes.
A recent analysis of pooled data presented a clearer definition of NSP use, defining coverage in terms of the proportion of injections with a sterile syringe. This analysis suggested that high coverage of NSPs (‘100% NSP’, i.e. obtaining ≥ 1 sterile syringes per injection) or OST can each reduce HCV infection risk by 50%; and NSPs and OST in combination can reduce HCV infection risk by 80%. 20 However, owing to a small number of incident HCV infection cases (n = 40), the efficacy estimate for 100% coverage of NSPs was weak (95% CI 0.22 to 1.12) and there was insufficient power to evaluate whether or not a dose–response relationship exists. This project will provide a more robust understanding of the likely impact of existing coverage levels of NSPs and changes in the extent of provision.
There have been no attempts to estimate the cost-effectiveness of NSP provision in England, although NSPs and OST are the current primary interventions for reducing HIV/HCV transmission among PWID in the UK. 3 In addition, although a recent National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) evaluation considered the cost-effectiveness of NSPs, they were unable to estimate the incremental cost-effectiveness of increasing coverage because of ‘a paucity of evidence underpinning effectiveness’. 21 Internationally, of the economic evaluations of NSPs, none has been undertaken in Western Europe, few have considered the costs saved as a result of care and treatment averted, and all studies have relied on weak measures of NSP effectiveness, such as using either changes in self-reported syringe sharing or ecological data relating NSP exposure to HCV infection prevalence or incidence in the population, which are unreliable and subject to substantial bias (Guinness L, Martin N, Harker M, Greco G, Vickerman P, 2012, unpublished). There is an urgent need to fill this evidence gap by producing the first Western European evidence for the cost-effectiveness of NSPs and an economic evaluation to use empirical data on NSP effectiveness in reducing HCV infection transmission at the individual level.
Rationale for current study
Evidence for the effect of NSP use on HIV and HCV infection incidence is inconsistent. 22,23 Studies have lacked sufficient evidence on the frequency of use of the intervention, the quantity of needles/syringes distributed24 or insufficient sample sizes to accurately measure the effect. 3 Economic evaluations of NSPs have not focused on Western European data, and existing studies have relied on weak measures of NSP effectiveness. Further evidence is essential in order to accurately estimate what level and combination of intervention is needed to substantially reduce HCV infection in PWID and the costs associated with increasing coverage to the optimal level.
Research objectives
The aim of this project was to assess the impact and different coverage levels of needle and syringe provision with and without OST on the incidence of HCV infection among PWID as well as the costs and cost-effectiveness of NSPs.
There were six linked objectives.
-
Objective 1: use pooled data sets and a deterministic model to measure the impact of different NSP coverage levels in the presence and absence of OST on the incidence of HCV infection among PWID in the UK.
-
Objective 2: estimate the contribution of risk factors (e.g. homelessness and crack cocaine use) to HCV infection incidence and the overall transmission of HCV infection among PWID.
-
Objective 3: conduct a systematic review of international evidence on the impact of NSPs with and without OST on the incidence of HCV infection among PWID.
-
Objective 4: estimate the costs associated with existing NSP provision in three UK settings.
-
Objective 5: estimate the impact and cost-effectiveness of existing provision of NSPs, compared with no provision, on HCV and HIV transmission and disease burden among PWID in three UK settings.
-
Objective 6: determine possible strategies to increase the coverage of NSP provision in three UK settings, and the probable impact and cost-effectiveness of these strategies.
Research design
The aims and objectives listed above were achieved through the implementation of five linked data collection activities and analyses. The findings from each study are summarised in the individual chapters below. Chapter 2 details the systematic review, Chapter 3 provides an analysis of pooled data sets, Chapter 4 outlines the costing analysis, Chapter 5 details the impact modelling and Chapter 6 outlines the cost-effectiveness analysis.
Chapter 2 Systematic review of the effectiveness of needle and syringe programmes and opioid substitution therapy in preventing hepatitis C transmission among people who inject drugs
Objectives
Our primary objective was to assess the impact of NSPs and OST together and alone on the incidence of HCV infection among PWID. Our secondary objective involved exploring the effect of sample characteristics (e.g. experience of prison, homelessness, use of stimulant injection) on the transmission of HCV infection among PWID.
Research questions
The specific research questions to be answered through the review were:
-
How effective is OST in reducing HCV infection incidence among PWID?
-
How effective are NSPs with and without the use of OST for reducing HCV infection incidence among PWID?
-
How does the effect of NSP and OST vary according to the duration of treatment (i.e. weekly vs. monthly attendance for NSPs)?
-
How does the effect of NSPs vary according to the type of service (fixed vs. mobile site; high vs. low coverage)?
-
How does the effect of OST vary according to the dosage of OST, the type of substitution used and adherence to treatment?
International evidence supports the use of combination interventions to prevent and treat HIV among PWID with the provision of NSPs, OST and HIV antiretroviral treatment as the key interventions. 25 There is good evidence that NSPs and OST reduce injecting risk behaviours and increasing evidence to show an impact on HIV incidence. 16,17 However, evidence of their impact on HCV infection incidence among PWID, in combination or alone, is limited. 3,8,12–15,20
Methods
The full methods used in the review are published in Platt et al. 26,27 This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes. Here, we summarise the methods in brief as well as some of the key findings of the review. We conducted two primary searches of the literature based on key search terms identified by the review of reviews and the recent review of the effect of OST and NSPs on the risk of HIV and HCV infection among PWID. 3,17 The purpose of the two searches was to (1) identify studies that directly measured the impact of NSPs/OST on HCV infection incidence and (2) identify longitudinal studies that measured HCV infection incidence and report the impact of NSPs/OST as part of an adjusted analysis.
We searched MEDLINE (1946 to November 2015), PsycINFO (1806 to November 2015), EMBASE (1980 to November 2015), Global Health (1910 to November 2015), Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, NHS Economic Evaluation Database, Health Technology Assessment database, The Cochrane Library, the Cochrane Drug and Alcohol Register and Web of Science for observational and experimental studies measuring exposure to NSPs and/or OST (compared with no intervention) among PWID and HCV infection incidence. All searches were conducted in November 2015. When no measure was reported in observational studies, authors of studies were contacted and asked to provide unpublished data. We also searched publications of key international agencies as well as conference abstracts. Reference lists of all included articles were reviewed for eligible papers. A copy of the search strategy is published in Platt et al. 26
Selection criteria
We included all observational (prospective and retrospective cohorts, cross-sectional surveys and case–control studies) and experimental studies [randomised controlled trials (RCTs)] that measured exposure to either intervention versus no intervention or a reduced exposure, and that reported HCV infection incidence as an outcome.
We included cross-sectional surveys if they included a serological measure of recent infection [e.g. through positive ribonucleic acid (RNA) results on antibody-negative samples]. We excluded cross-sectional studies (including serial cross-sectional studies) reporting HCV infection prevalence only. We excluded studies relying on self-reported data for the outcome.
Participants
We focused on studies of PWID (opioids and/or stimulants). Studies that include participants undergoing opportunistic HCV infection testing (outside the study setting) were excluded, as were those relating to PWID in the prison setting, because addiction services and treatment provision in this setting differ significantly from community and health-care settings.
Outcome
Our outcome of interest was incidence of HCV infection in PWID as measured via repeat testing such as the detection of HCV RNA-positive status among HCV antibody-negative results or antibody avidity. Studies were also included if they reported a minimum of two HCV seroconversions (HCV antibody negative to HCV antibody positive) among the study participants from tests conducted at different time points.
Methods used in this systematic review in relation to the search strategies and approaches to data synthesis follow methods applied in a similar review to assess the impact of OST on HIV incidence. 17
Intervention
Exposure to NSPs was defined as the proportion of injections that are covered by a clean needle/syringe or attendance at a NSP. When it was not possible to estimate the proportion of injections covered by a clean needle/syringe, we defined exposure accounting for frequency of injection and the degree to which the NSP meets the individual’s requirement for needles/syringes.
Exposure to OST was defined as current or recent continuous or interrupted treatment (past 6 months or for the duration of HCV infection observation period), or any past treatment with methadone or buprenorphine.
Interventions were defined as current OST (within past 6 months) or lifetime use of OST, and high NSP coverage (regular attendance at a NSP or all injections covered by a new needle or syringe) or low NSP coverage (irregular attendance at a NSP or < 100% of injections covered by a new needle or syringe).
Control intervention
-
No OST.
-
Low coverage NSP or no NSP.
Types of comparisons
-
OST versus no OST.
-
High NSP coverage with no OST versus low coverage NSP.
-
Low NSP coverage with no OST versus no NSP.
-
Combined high/low NSP coverage with OST versus no OST and low/no coverage NSP.
Data collection and analysis
Two reviewers screened all title and abstracts, and disagreements were resolved following discussion. Full texts were screened by two people to assess eligibility. Data were extracted independently by two people and then checked for consistency. Full-text papers in languages other than English were translated by individuals fluent in those languages.
Meta-analysis was conducted using random-effects models, pooling univariable and multivariable models separately. We examined heterogeneity with the I2-statistic and explored reasons for heterogeneity using univariable random-effects metaregression. We examined heterogeneity with the I2 and τ2 statistics, and explored reasons for heterogeneity using univariable random-effects metaregression to evaluate the impact of the following covariates on intervention effect: geographical region of study; recruitment setting (community based or treatment); percentage of female participants; main drug injected; type of NSP; frequency of injecting; dose, duration and adherence to NSP/OST (i.e. continuous or interrupted treatment); and study design. There was insufficient information to assess the impact of adherence to NSPs/OST (i.e. continuous or interrupted treatment). We used Stata® version 14.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) in all analyses and transferred the data into RevMan software version 5.3 (Cochrane, The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen, Denmark).
Grading of evidence
Risk of bias for all studies was assessed using the ACROBAT-NRSI tool (A Cochrane Risk Of Bias Assessment Tool: for Non-Randomized Studies of Interventions), which is in development by the Methods Groups of Cochrane. 28 We assessed the overall quality of the evidence for the primary outcome using the Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) system. The GRADE Working Group developed a system for grading the quality of evidence,29–32 which takes into account issues related not only to internal validity but also to external validity, such as the directness of results. In particular, they provide key information concerning the quality of evidence, the magnitude of effect of the interventions examined and the sum of available data on the main outcomes.
The GRADE system uses the following criteria for assigning grades of evidence:
-
High – we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect.
-
Moderate – we are moderately confident in the effect estimate. The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different.
-
Low – our confidence in the effect estimate is limited. The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect.
-
Very low – we have very little confidence in the effect estimate. The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect.
Grading is decreased for the following reasons:
-
serious (–1) or very serious (–2) study limitation for risk of bias
-
serious (–1) or very serious (–2) inconsistency between study results
-
some (–1) or major (–2) uncertainty about directness (the correspondence between the population, the intervention or the outcomes measured in the studies actually found and those under consideration in our systematic review)
-
serious (–1) or very serious (–2) imprecision of the pooled estimate (–1)
-
publication bias strongly suspected (–1).
Grading is increased for the following reasons:
-
Strong evidence of association – significant relative risk of > 2 (< 0.5) based on consistent evidence from two or more observational studies, with no plausible confounders (+1). Very strong evidence of association – significant relative risk of > 5 (< 0.2) based on direct evidence with no major threats to validity (+2).
-
Evidence of a dose–response gradient (+1).
-
All plausible confounders would have reduced the effect (+1).
Results
Text in this section is reproduced from Platt et al. 26 and Platt et al. 28 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
Study selection
Figure 1 shows the number of studies identified, reviewed and selected and the reasons for exclusion for both searches.
FIGURE 1.
Flow chart of included studies. CDAG, Cochrane Drug and Alcohol Register; CENTRAL, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials; CINAHL, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature; CLib, Cochrane Library; DARE, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects; HTA, Health Technology Assessment; NHS EED, NHS Economic Evaluation Database; WOS, Web of Science. Reproduced from Platt et al. ,26,27 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
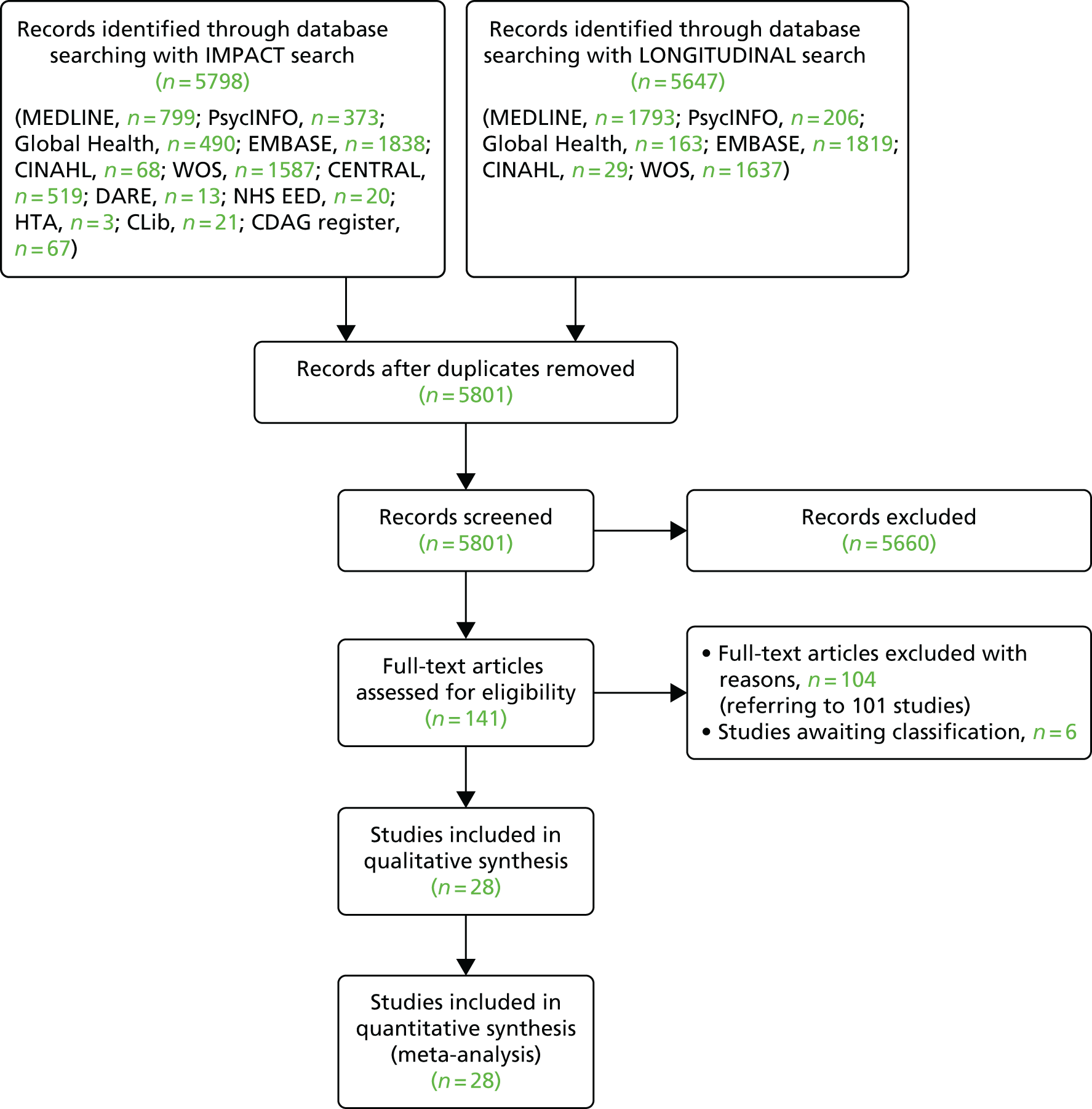
We identified 21 papers that directly included measures of the impact of exposure to either OST or NSPs on HCV infection transmission. In addition, we identified 11 eligible prospective studies that measured HCV infection incidence and contacted authors of these articles. Of these, unpublished data were obtained from seven cohort studies in Montreal, Canada;33 Baltimore, USA;34 San Francisco, USA;35 London, UK;36 and Sydney and Melbourne, Australia. 37,38 The full text of 141 papers was reviewed. A total of 19 papers were included, and 120 papers were excluded for the following reasons: no HCV infection incidence data (n = 55); no measure of intervention exposure (n = 34); contain no primary data (n = 20); the sample was not PWID (n = 1); all the sample were recruited from the intervention (n = 9); and the article could not be obtained in its original language (Japanese) (n = 1).
In total, we included 21 published studies14,39–58 and seven unpublished studies33–37,59,60 comprising 1827 HCV incident infections and 8789.7 person-years of follow-up. Overall HCV infection incidence ranged between 0.09 and 42 cases per 100 person-years across the studies.
Excluded studies
A total of 101 studies (104 articles) were excluded in which there was no outcome of interest assessed (43 studies); no intervention of interest (32 studies); no comparison of interest (all participants on OST) (nine studies); no outcome and no intervention of interest (11 studies); no outcome and no comparison of interest (four studies); or when the study was an editorial or overview (two studies).
Description of studies
Participants and setting
We included studies undertaken in the USA (n = 8), the UK (n = 5), Canada (n = 5), the Netherlands (n = 1), France (n = 1), Italy (n = 1), Spain (n = 1), Australia (n = 5) and China (n = 1). Twenty-five studies reported the sex of participants, for which the mean proportion of female participants was 32% (range 2.8–55.9%). Across 14 studies, on average, 40.7% (range 9.2–69.2%) of participants had experience of recent or past homelessness and 35% (range 18.2–90%) had past or recent experience of prison (n = 12 studies). The mean reported use of stimulants was 32.7% (range 0–75%, n = 19 studies) and a mean of 50.5% (range 18.2–100%) of participants reported heroin use (n = 13). Across 14 studies, a mean of 50.6% of participants reported injecting daily (range 18.2–84%).
Type of interventions
Twenty-one of the included studies reported the impact of OST,14,20,39,40,45–47,49,51–53,55,57,58 including seven unpublished estimates. 33–37,59,60 Seventeen studies reported the impact of NSPs,14,20,41–44,47,48,50,54,56,58 including five unpublished sources,33–35,59,60 and four reported combined measures of NSPs with OST,14,33,44,47 including one unpublished data source. 33 One study looked at the impact of distributing injecting paraphernalia (defined as spoons and filters) by itself, with needles/syringes and in combination with OST. 47
Study design
There was much variation in the included studies in terms of sample size (range 46–2788), method of recruitment involving street outreach (n = 12), respondent-driven sampling (RDS) alone (n = 2), street outreach, snowball sampling or RDS combined (n = 4), and service attenders (n = 7). A range of study designs were included, such as case–control studies (n = 2), cross-sectional studies (n = 3), prospective cohort studies (n = 20), retrospective cohort studies (n = 2) and serial cross-sectional surveys (n = 1). For cohort studies, the duration of follow-up time ranged between 1 and 22 years. Included studies were published between 1995 and 2014. Key study characteristics are included in Table 1.
| Author and year | Country | Study design | Sex (% female) | Age (years) | Sample | HCV per 100 person-years | New HCV cases/person-years | Interventions | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aitken et al., 201737 | Australia | Cohort | 31.7 | 29.4 (median) | 98 | 8.6 | 17/196 | OST current | No OST in past month |
| Use of OST in past month | |||||||||
| Bruneau, 201533 | Canada | Cohort | NA | < 30 (37.4%) | 285 | 17.3 | 102/589.35 | OST; NSP (high); combined NSP/OST | No OST in past 6 months; low (< 100%) NSP coverage |
| (1) Use of OST in past 6 months; (2) high NSP (> 100% coverage); (3) OST in past 6 months and high (> 100% coverage) | |||||||||
| Craine et al., 200939 | Wales | Cohort | 29.0 | 27.2 (mean) | 286 | 5.9 | 17/287.33 | OST current | Not in OST |
| In OST at interview | |||||||||
| Crofts et al., 199740 | Australia | Cohorta | 41.9 | 29.2 (mean) | 73 | 22.2 | 13/85.4 | OST current | Not on OST |
| Continuous OST during follow-up | |||||||||
| Hagan et al., 199541 | USA | Case–control | 45.0 | < 25 (24%) | 46 | 20/NA | NSP (low) | Never used NSP | |
| Ever used NSP | |||||||||
| Hagan et al., 199942 | USA | Cohort | 38.0 | < 25 (19%) | 187 | 20.8 | 26/209 | NSP (high, low) | Never used NSP |
| Current, regular or sporadic NSP use | |||||||||
| Holtzman et al., 200943 | USA | Cohort | 38.0 | < 21 (28%) | 1288 | 139/NA | NSP (low) | No use of NSP in past 6 months | |
| NSP participation in the past 6 months | |||||||||
| Hope et al., 201144 | UK | Cross-sectional | 23.0 | < 25 (17%) | 119 | 40 | 14/35 | OST current; NSP alone (low, high); NSP/OST combined | No OST, low or no NSP coverage |
| Use of OST in past 4 weeks; high NSP (≥ 100% coverage) or low NSP (< 100% coverage) | |||||||||
| Hope, 201559 | UK | Cross-sectional | 25.0 | 919 | 9.9 | 30.3 | OST current; NSP | Low NSP, no OST | |
| Use of OST in past 4 weeks; high NSP coverage (≥ 100% coverage) | |||||||||
| Judd, 201536 | UK | Cohort | 29.0 | 27.4 | 149 | 42 | 49/116.7 | OST current | |
| Use of methadone in past 6 months or longer | |||||||||
| Lucidarme et al., 200445 | France | Cohort | 17.6 | 26.9 (mean) | 165 | 11 | 16/178.4 | OST current | No OST |
| No definition | |||||||||
| Maher, 201560 | Australia | Cohort | 38.0 | 24 (median) | 368 | 24.9 | 53/212.86 | OST current | No OST |
| OST in past 6 months | |||||||||
| Mehta, 201534 | USA | Cohort | 34 (median, baseline) | 324 | 17.8 | 27/166.5 | OST current | No OST | |
| OST in past 6 months | |||||||||
| Nolan et al., 201446 | Canada | Cohort | 30.4 | 23–34 | 1004 | 6.32 | 184/2108.4 | OST current | No OST |
| Active participation in MMT in past 6 months | |||||||||
| Page, 201535 | USA | Cohort | 21.7 | 33.7 (mean) | 552 | 25.1 | 171/681.3 | NSP (low) | No NSP |
| NSP use in the past 3 months | |||||||||
| Palmateer et al., 201447 | Scotland | Cross-sectional | 27.5 | 34 (mean) | 2788 | 7.3 | 392/602.7 | OST current; NSP (high) OST/NSP combined; OST at time of survey; high NSP (> 200%) coverage and not on OST; low NSP (< 200%) | No OST; low NSP coverage |
| Patrick et al., 200148 | Canada | Cohort | 30.3 | 34 (median) | 155 | 29.1 | 62/207.95 | NSP (high) | No attendance at NSP |
| Attendance at least once per week at NSP in past 6 months | |||||||||
| Rezza et al., 199649 | Italy | Case–control | 2.8 | > 28 (21%) | 106 | 28.6 | 21/73.4 | OST current | No OST |
| OST in past 6 months | |||||||||
| Ruan et al., 200751 | China | Cohort | < 28 (44%) | 86 | 33.0 | 47/258 | OST other | Never used OST | |
| Ever used OST | |||||||||
| Use of NSP in past 6 monthsb | |||||||||
| Roy et al., 200750 | Canada | Cross-sectional | 27.0 | 31.8 (mean) | 359 | 27.1 | 94/267 | NSP (low) | No NSP use in past 6 months |
| Spittal et al., 201252 | Canada | Cohort | 53.4 | 23 (median) | 148 | 11.6 | 45/338.6 | OST current | Not in MMT |
| In OST at time of survey | |||||||||
| Thiede et al., 200053 | USA | Cohort | 48.9 | < 25 (5.4%) | 80 | 0.09 | 4/80 | OST current and other | Left treatment and not enrolled at follow-up |
| Continuous treatment during follow-up. Interrupted treatment; left treatment at least once during follow-up but had re-entered by end of study | |||||||||
| Thorpe et al., 200254 | USA | Cohort | 39.7 | 18–22 (52%) | 353 | 10 | 29/327.2 | NSP (low) | No use of NSP in last 6 months |
| Use of NSP in past 6 months | |||||||||
| Tsui et al., 201455 | USA | Cohort | 31.9 | 15–18 (16%) | 552 | 25.1 | 145/680 | OST current and other | No OST |
| Opioid agonist therapy maintenance treatment in past 3 months; OST other opioid agonist detoxification in past 3 months | |||||||||
| Vallejo et al., 201556 | Spain | Cohort | 27.3 | ≥ 25 (40%) | 137 | 39.8 | 42/105.4 | OST other | Never used OST |
| Lifetime use of OST | |||||||||
| Van Den Berg et al., 200714 | The Netherlands | Cohort | 33.0 | 31.4 (median) | 168 | 6.78 | 57/598.56 | OST current; NSP alone; combined OST/NSP | No OST or no injecting; low (1–99%) or no NSP coverage (0%) |
| OST ≥ 60 mg of methadone daily | |||||||||
| High NSP (100% coverage); low NSP (1–99% coverage) | |||||||||
| van Beek et al., 199857 | Australia | Cohorta | 55.9 | < 20 (61.5%) | 152 | 20.9 | 26/148.2 | OST other | Never used OST |
| Ever used OST | |||||||||
| White et al., 201458 | Australia | Cohort | 25.0 | 27 (median) | 127 | 7.9 | 20/215.2 | OST; NSP (low) | No NSP. (1) No OST, mainly injected heroin, (2) no OST, mainly injected another drug |
| Accessed NSP in past 6 months; OST in past 6 months |
Methodological quality: risk-of-bias assessment
Twenty-one original non-randomised published studies were assessed. Two were judged as being at moderate overall risk of bias, 17 were judged as being at serious risk of bias and seven were judged as being at critical risk of bias. For two studies, we did not have sufficient information to make a judgement. A summary of the risk-of-bias assessment is included in Table 2.
| Study | Confounding | Selection bias | Measurement of interventions | Departures from intended interventions | Missing data | Measurement of outcomes | Selection of reported result | Overall risk of bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aitken et al., 201737 | Critical | Critical | Serious | No information | Critical | Low | No information | Critical |
| van Beek et al., 199857 | Critical | Serious | Serious | No information | Critical | Low | Low | Critical |
| Bruneau, 201533 | Moderate | Serious | Moderate | No information | No information | Low | Low | Serious |
| Craine et al., 200939 | Serious | Serious | Serious | No information | Serious | Low | Low | Serious |
| Crofts et al., 199740 | Critical | Serious | Low | No information | Serious | Serious | Low | Critical |
| Hagan et al., 199541 | Serious | Serious | Serious | No information | Low | Low | Low | Serious |
| Hagan et al., 199942 | Moderate | Serious | Low | No information | Low | Low | Low | Serious |
| Holtzman et al., 200943 | Serious | Serious | Moderate | No information | No information | Low | Low | Serious |
| Hope et al., 201144 | Moderate | Moderate | Serious | No information | Low | Low | Low | Serious |
| Hope, 201559 | Moderate | Moderate | Serious | No information | No information | Low | Low | Serious |
| Judd, 201536 | Moderate | Critical | Critical | No information | Critical | Low | Low | Critical |
| Lucidarme et al., 200445 | Moderate | Serious | Serious | No information | Serious | Low | Low | Serious |
| Maher, 201560 | Moderate | Serious | Serious | No information | No information | Low | Low | Serious |
| Mehta, 201534 | Moderate | No information | No information | No information | No information | Low | Low | No information |
| Nolan et al., 201446 | Serious | Serious | Moderate | No information | Low | Low | Low | Serious |
| Page, 201535 | Moderate | No information | No information | No information | No information | Low | Low | No information |
| Palmateer et al., 201447 | Serious | Serious | Moderate | No information | Serious | Low | Low | Serious |
| Patrick et al., 200148 | Serious | Moderate | Serious | No information | Serious | Low | Low | Serious |
| Rezza et al., 199649 | Serious | Low | Serious | No information | Critical | Low | Low | Critical |
| Roy et al., 200750 | Serious | Serious | Serious | No information | Critical | Low | Low | Critical |
| Ruan et al., 200751 | Critical | Critical | Serious | No information | Serious | Low | Low | Critical |
| Spittal et al., 201252 | Serious | Serious | Moderate | No information | Low | Low | Low | Serious |
| Thiede et al., 200053 | Moderate | Moderate | Low | No information | Low | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Thorpe et al., 200254 | Serious | Serious | Serious | No information | Moderate | Low | Low | Serious |
| Tsui et al., 201455 | Moderate | Moderate | Low | No information | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Vallejo et al., 201556 | Serious | Serious | Low | No information | Serious | Low | Low | Serious |
| Van Den Berg et al., 200714 | Serious | Serious | Moderate | No information | Serious | Low | Low | Serious |
| White et al., 201458 | Moderate | Serious | Moderate | No information | No information | Low | Low | Serious |
Effects of interventions
Current use of opioid substitution therapy versus no current opioid substitution therapy
Of the 28 studies, we pooled data from a total of 17 studies to assess the impact of current OST use on HCV infection incidence,14,39,40,45–47,49,52,53,55,56,58 including five unpublished estimates. 33,36,37,59,60 Current use of OST was defined as reporting use of OST within the past 6 months (yes or no)33,46,49,58,60 or as reporting use of OST either within 6 months or > 6 months ago,36 use of methadone at the time of survey,39,47,52,59 continuous use of OST throughout the follow-up period,40,45,53 with one study defining continuous use as daily use of methadone (any dosage) in the past 6 months14 or in the past month. 37 One study used a 3-month time frame to measure the use of opioid agonist therapy maintenance treatment. 55 One study measured current use of buprenorphine. 34
All comparison groups were made against no intervention. All the included studies were longitudinal studies, with the exception of one case–control study49 and two cross-sectional surveys. 47,59
The 17 studies included a minority of women (range 3–53%), a high proportion of the samples had experience of prison (range 18–60%) and homelessness (9–70%), and use of stimulants ranged between 1% and 51% across the studies. A total of 1073 HCV infection incident cases were included over 4990.29 person-years of follow-up.
Of these 17 studies, 12 presented adjusted estimates on which the primary analyses were focused. Adjusted estimates controlled for potentially confounding effects of the following factors: duration of injection; frequency of injection;33,36,60 area of residence, homelessness, sharing injecting equipment or needles;2 sex, geographical region, use of condoms, injection of cocaine, duration of injection and sharing injecting equipment;45 duration of injection, frequency of injection and age of whole cohort;34 unstable housing, cocaine, heroin or methamphetamine injection, cohort of recruitment, year of recruitment and follow-up time;46 survey year, homelessness, stimulant injection and duration of injection;47 sex, age, duration of drug use and injection of cocaine;49 age, duration of injection, sex, ethnicity, homelessness or prison in the past 3 months;55 sex, ethnicity, age, frequency of injecting, sharing needles/syringes, not receiving OST while reporting opioid use,58 injected at follow-up, pooled money to buy drugs, injection with used needles and backloading. 53
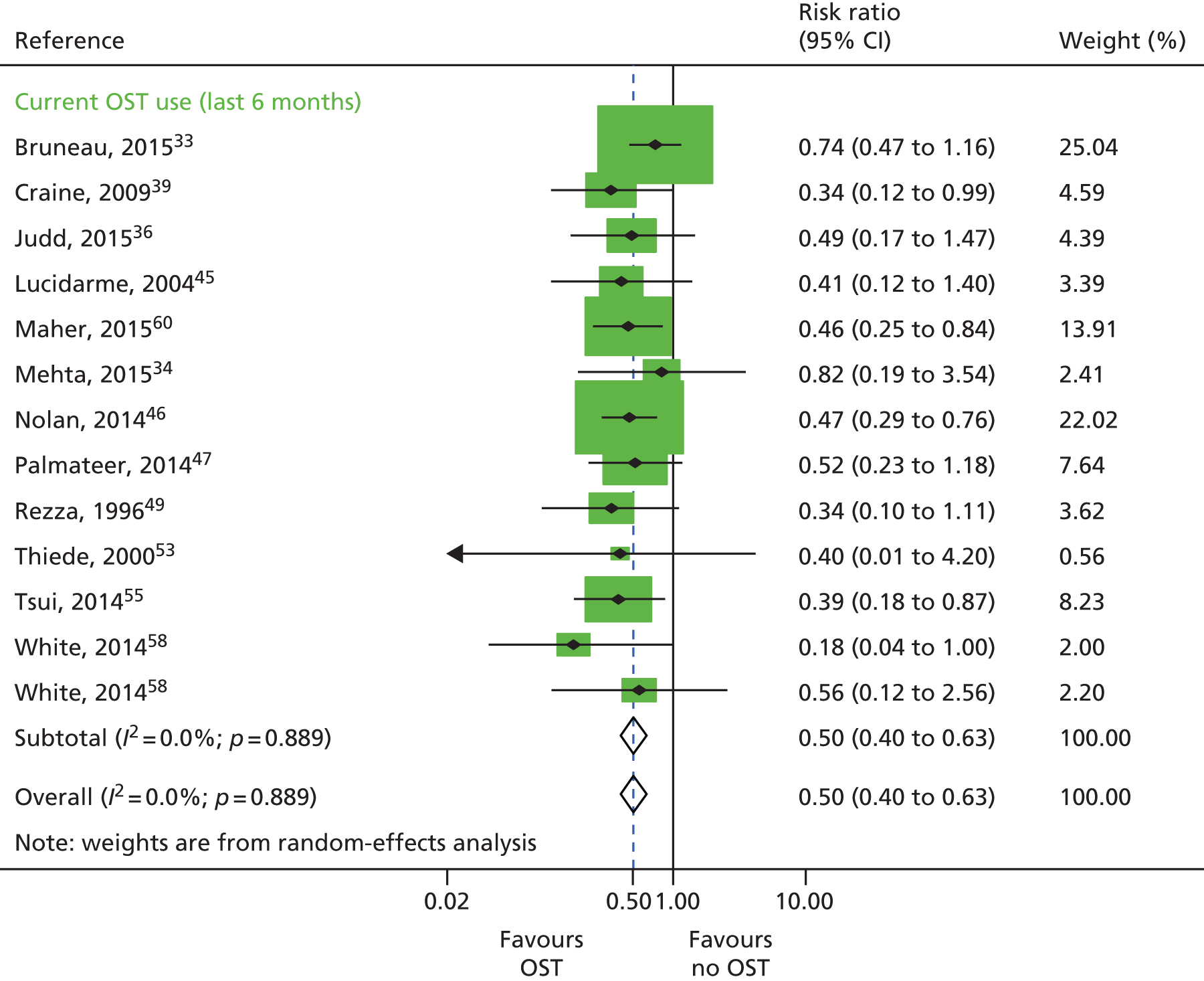
Random-effects meta-analysis of multivariable estimates shows that OST was associated with a 50% reduction in the risk of HCV infection [rate ratio (RR) 0.50, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.63] with little evidence of heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 0; p = 0.889) (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2.
Impact of current use of OST vs. non-OST use on HCV infection incidence from adjusted analyses. Reproduced from Platt et al. ,26,27 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
Sensitivity analyses
This effect was increased when excluding estimates from four unpublished data sources33,34,36,53 (RR 0.42, 95% CI 0.31 to 0.58) and little evidence of heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 0%; p = 0.96). The effect was maintained when limiting the analysis to exclude all unpublished data sets as well as one study that was judged to be at critical risk of bias49 (RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.31 to 0.59; I2 = 0%; p = 0.93). The effect was slightly reduced when limiting the analysis to exclude two studies47,49 that reported baseline measures of effect only (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.65; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.807) and two studies that reported incident RRs only34,39 (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.64; I2 = 0%; p = 0.853). These data are not shown.
A random-effects meta-analysis of 16 studies that presented univariable estimates suggests that OST was associated with a 40% reduction in the risk of HCV infection (RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.47 to 0.76), with only moderate evidence of heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 31.7; p = 0.09) (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3.
Impact of current use of OST vs. no OST on HCV infection incidence findings from unadjusted analyses. Reproduced from Platt et al. ,26,27 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
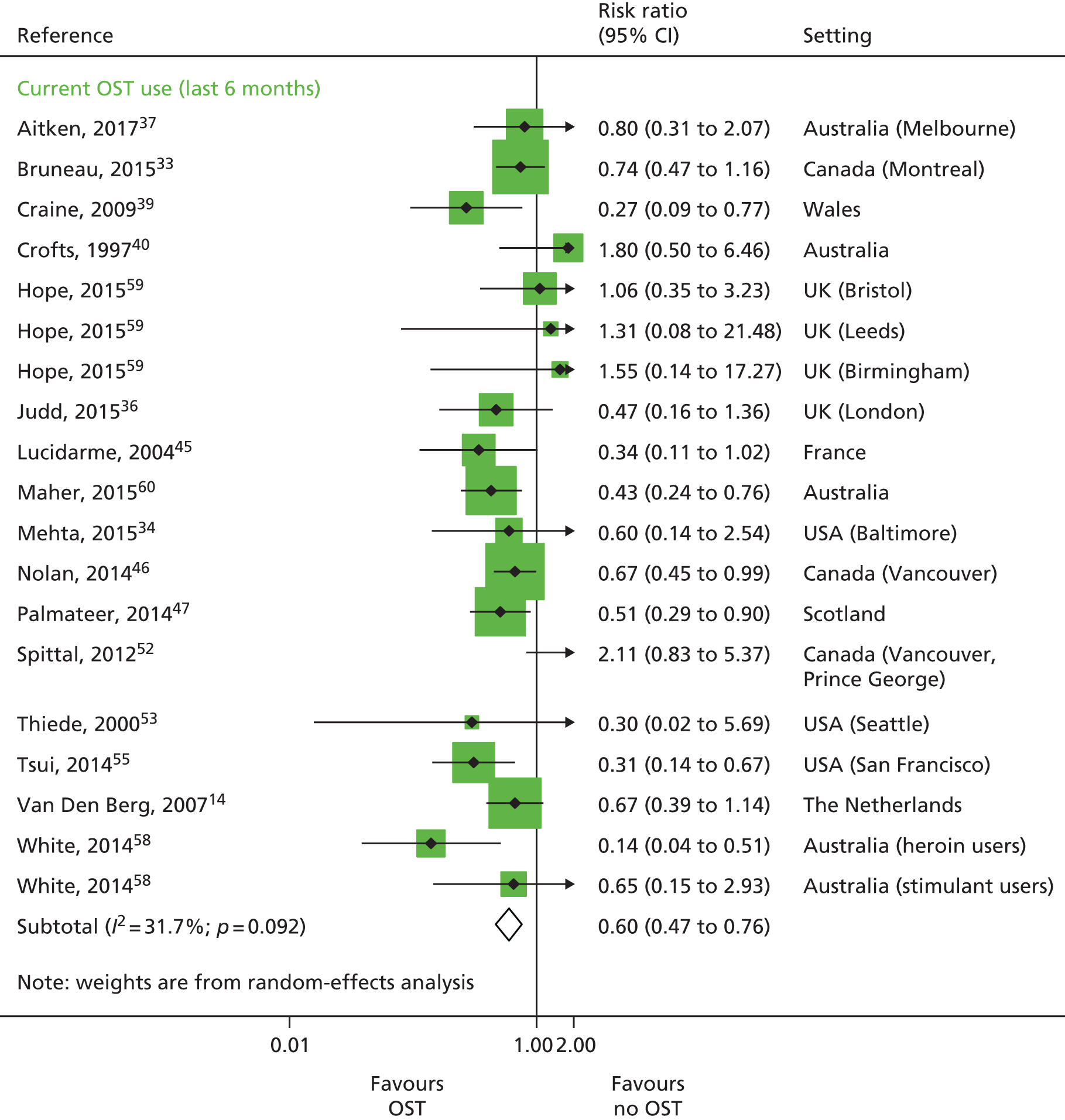
Metaregression
Based on univariable metaregression of unadjusted estimates, we found no evidence that effectiveness varied by other covariates including geographical location. We did find evidence of differential impact in the proportion of female participants in the sample. With each 10% increase of female participants in the sample, the effect of intervention exposure was reduced (RR 1.59, 95% CI 1.13 to 2.29) (see Table 15).
History of opioid substitution therapy
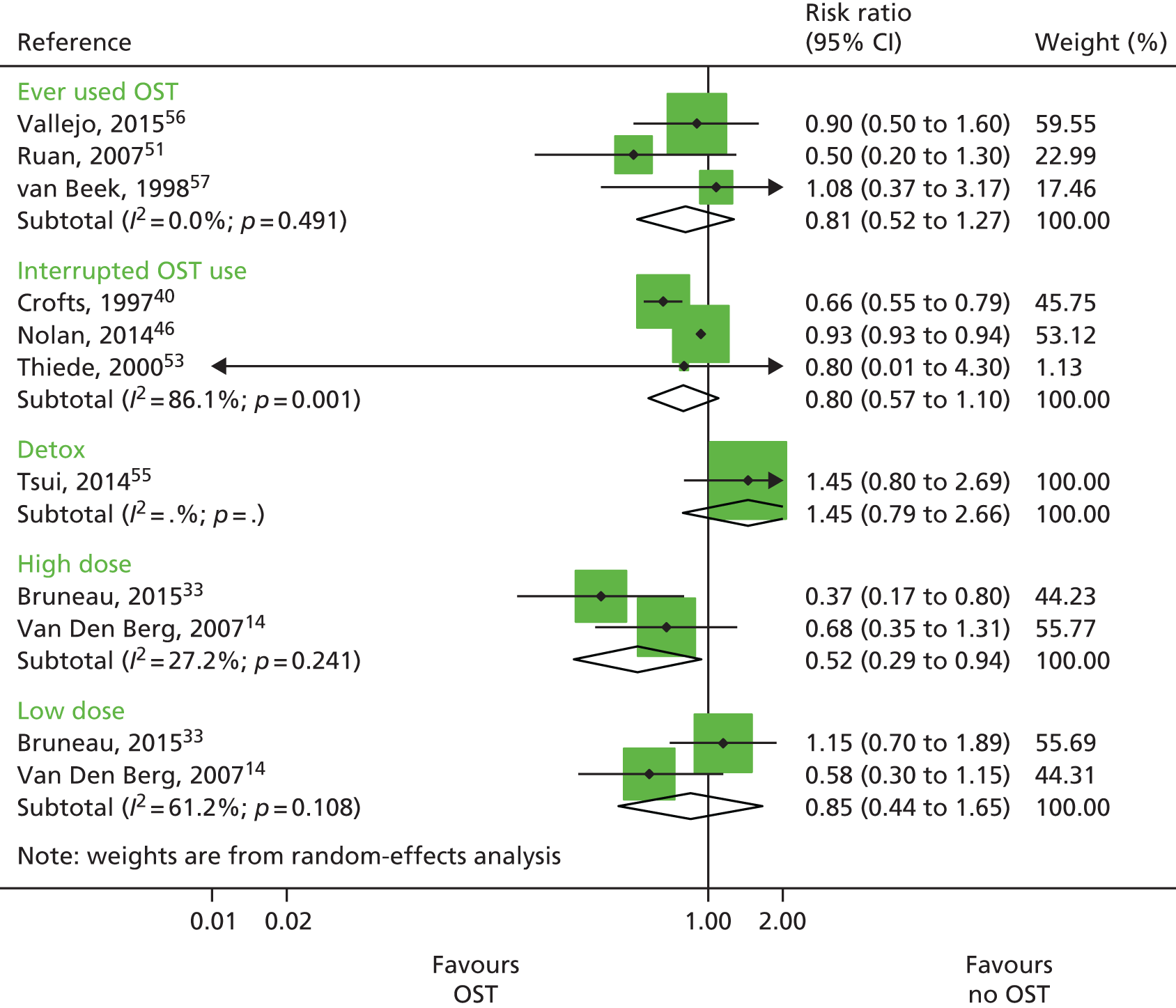
Three studies published unadjusted estimates of history of OST use, comprising 115 HCV infection cases over 511.6 person-years and from three prospective cohorts. 51,56,57 One study did not define the time frame and was coded as past experience of OST. 56
Three studies published unadjusted estimates of interrupted OST use. 40,46,53 Two of these studies were prospective cohorts and one was retrospective, and a total of 200 HCV infection cases were included over 2273.8 person-years. Interrupted OST use was defined as use of OST at baseline but not at follow-up,46 or leaving OST at least once during follow-up. 40,53 One prospective cohort study comprising 149 HCV infection cases over 680 person-years examined OST for detoxification,55 and two studies measured high dosage (≥ 60 mg) or low dosage (1–59 mg) of methadone for daily use14 or use some time in the past 6 months. 33 Both these studies were prospective cohorts and included 148 HCV infection cases over 598.6 person-years.
A random-effects meta-analysis showed no impact among studies measuring historical use of OST (RR 0.81 95% CI 0.52 to 1.27) or among those measuring interrupted use (RR 0.80 95% CI 0.57 to 1.10). 51,56,57 The one study measuring the impact of OST used for detoxification was not associated with reduced HCV infection risk acquisition (RR 1.45, 95% CI 0.79 to 2.66). 55 High dosage with OST was associated with a reduction of HCV infection acquisition (RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.29 to 0.94) but low dosage was not (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.44 to 1.65) (Figure 4). 14,33
FIGURE 4.
Impact of other modes of OST on HCV infection risk acquisition. Reproduced from Platt et al. 26 This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
Needle and syringe programmes versus lower or no needle and syringe programmes coverage
A total of 15 studies reported measures of NSP exposure and HCV infection incidence,14,20,41–44,47,48,50,54,58 including five unpublished estimates. 33–35,59,60 Only five studies published adjusted estimates,33,42,44,47,48 restricting the sensitivity analysis that could be conducted. We therefore focused our primary analyses on pooling unadjusted estimates.
Comparison groups consisted of non-attendance in the NSP14,34,35,41–43,48,50,54,60 or lower coverage of injections covered by a clean needle or syringe,14,44,47,59 or a needle or syringe obtained from a safe source. 33
High coverage versus non-attendance or lower coverage
We pooled data from seven studies that reported unadjusted measures of high NSP exposure and HCV infection incidence,14,42,44,47,48 including two unpublished data sets. 33,59 High NSP coverage was defined as obtaining 100% of needles and syringes from a safe source33 or reporting ≥ 100% of injections covered by a clean needle or syringe,14,44,59 or ≥ 200% of injections covered by a clean needle/syringe. 47 Other measures of high coverage were defined as regular attendance at least once per week at a NSP48 or obtaining most of all needles/syringes from a NSP in the past 6 months. 42 The seven included studies consisted of four prospective cohorts14,33,42,48 and three cross-sectional surveys,44,47,59 comprising 641 HCV infection cases over 1015.51 person-years.
The primary analysis focused on seven studies that measured high-level uptake of NSP coverage. This primary analysis compared the effect of high-level NSP coverage versus no intervention33,42,48 or lower levels of coverage. 14,44,47,59 These seven studies included a median of 27% of women (range 23–38%), a high proportion of the samples had experience of prison (range 26–60%) and homelessness (range 2–58%), and use of stimulants ranged between 17% and 63% across the studies.
A random-effects meta-analysis suggested no evidence of high coverage of NSPs associated with a reduction in the risk of HCV infection (RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.38 to 1.54) with evidence of high heterogeneity between studies. (I2 = 78.8; p < 0.001) (Figure 5).
FIGURE 5.
Impact of high NSP coverage vs. low or no NSP coverage on HCV infection risk acquisition from unadjusted analysis. Reproduced from Platt et al. ,26,27 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.

Sensitivity analyses
This effect remained the same when excluding the unpublished data sets (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.23 to 2.19; p < 0.001). 33,59 The effect was also maintained when limiting the analysis to a subset of four studies that excluded three studies assessed to be at critical risk of bias or that were unpublished data sets (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.17 to 2.98), with evidence of within-study heterogeneity (I2 = 89.6%, p < 0.001). 14,33,59 The effect was increased when we excluded studies that reported only incident rate ratios (RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.35 to 1.74; I2 = 80.3%; p < 0.001). 14 The effect was further decreased when we excluded studies that reported baseline measures only (RR 1.26, 95% CI 0.55 to 2.93; I2 = 87.0%; p < 0.001). 44,47,59 Limiting the analysis to a further subset of four studies that adjusted for confounders, the effect remained the same (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.61; I2 = 77%, p = 0.022; τ2 = 0.4482) (data not shown).
Metaregression
Based on univariable metaregression analyses, we found some evidence that the effectiveness of high NSP coverage varied according to geographical region. After removing studies from North America, high NSP coverage in Europe was associated with a 54% reduction in HCV infection acquisition risk (RR 0.44, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.80) with less heterogeneity (I2 = 12.3%; p = 0.337), whereas in North America it remained insignificant (RR 1.58, 95% CI 0.57 to 4.42, I2 = 89.9%; p < 0.001).
Based on univariable metaregression analyses, the differential impact of NSPs according to geographical region remained, with studies from North America having less impact (ratio of RRs 3.73, 95% CI 0.95 to 14.7; p = 0.06). There was no differential impact by recruitment site (p = 0.89), by proportion of participants reporting stimulant use, homelessness, injection of stimulants or sex. (These data are presented in Appendix 1, Table 16.)
Low-level coverage of needle and syringe programmes versus no needle and syringe programme coverage
Ten studies reported unadjusted measures of low-level NSP coverage and HCV infection incidence. Eight were prospective cohorts14,34,35,42,43,54,58,60 and one was a case–control study. 41 A total of 531 cases were included in the analyses over 1617 person-years. One prospective cohort was dropped because it did not report 95% CIs around the effect estimate or the number of new HCV infection cases in international and comparison groups required to estimate it. 50
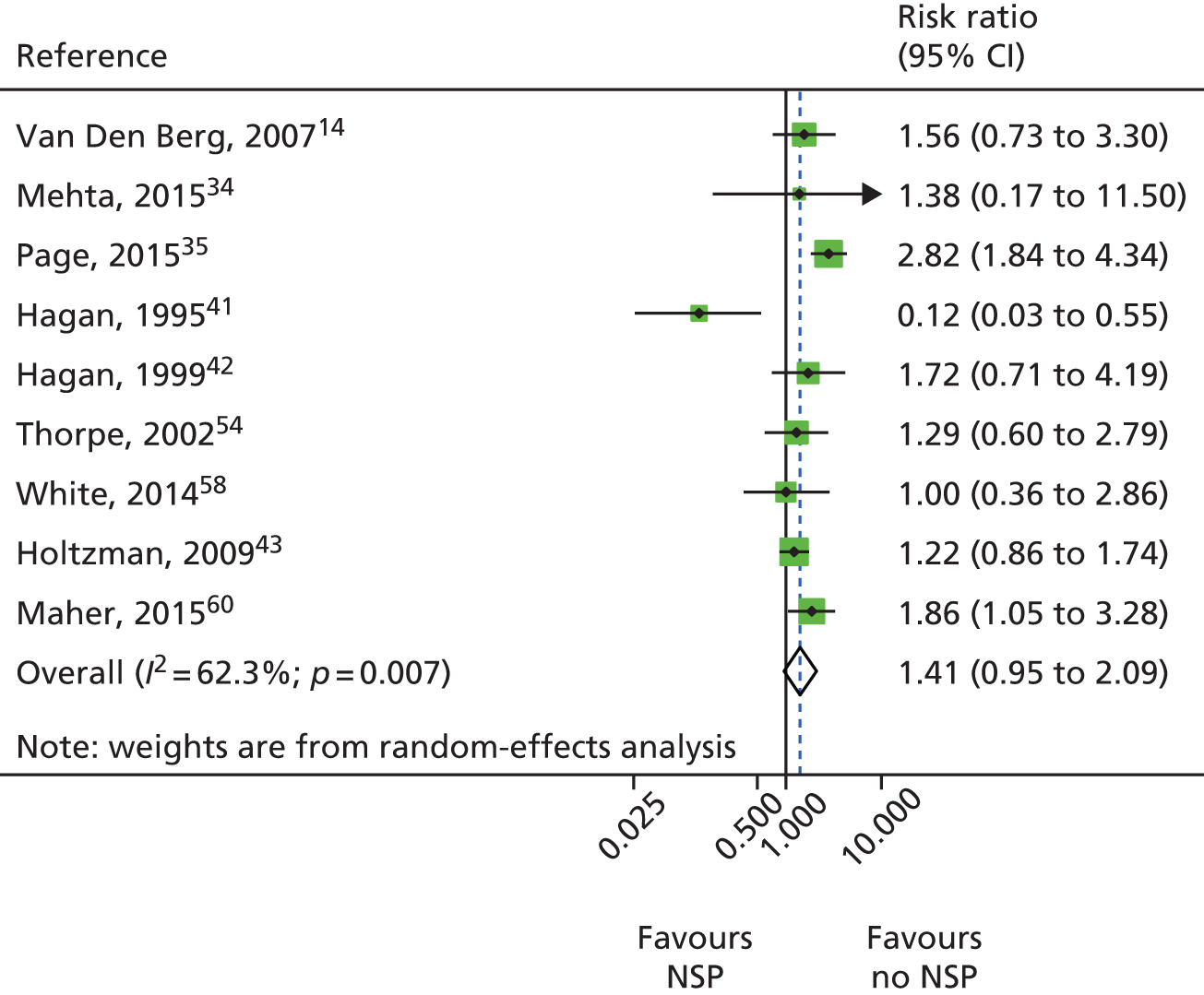
A random-effects meta-analysis showed no evidence of an intervention effect of low NSP coverage on HCV infection risk acquisition with moderate levels of heterogeneity (RR 1.41, 95% CI 0.95 to 2.09; I2 = 62.3%; p = 0.007; τ2 = 0.19) derived from nine studies with a total of 3414 participants (Figure 6).
FIGURE 6.
Impact of low NSP coverage on HCV infection risk acquisition. Reproduced from Platt et al. 26 This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
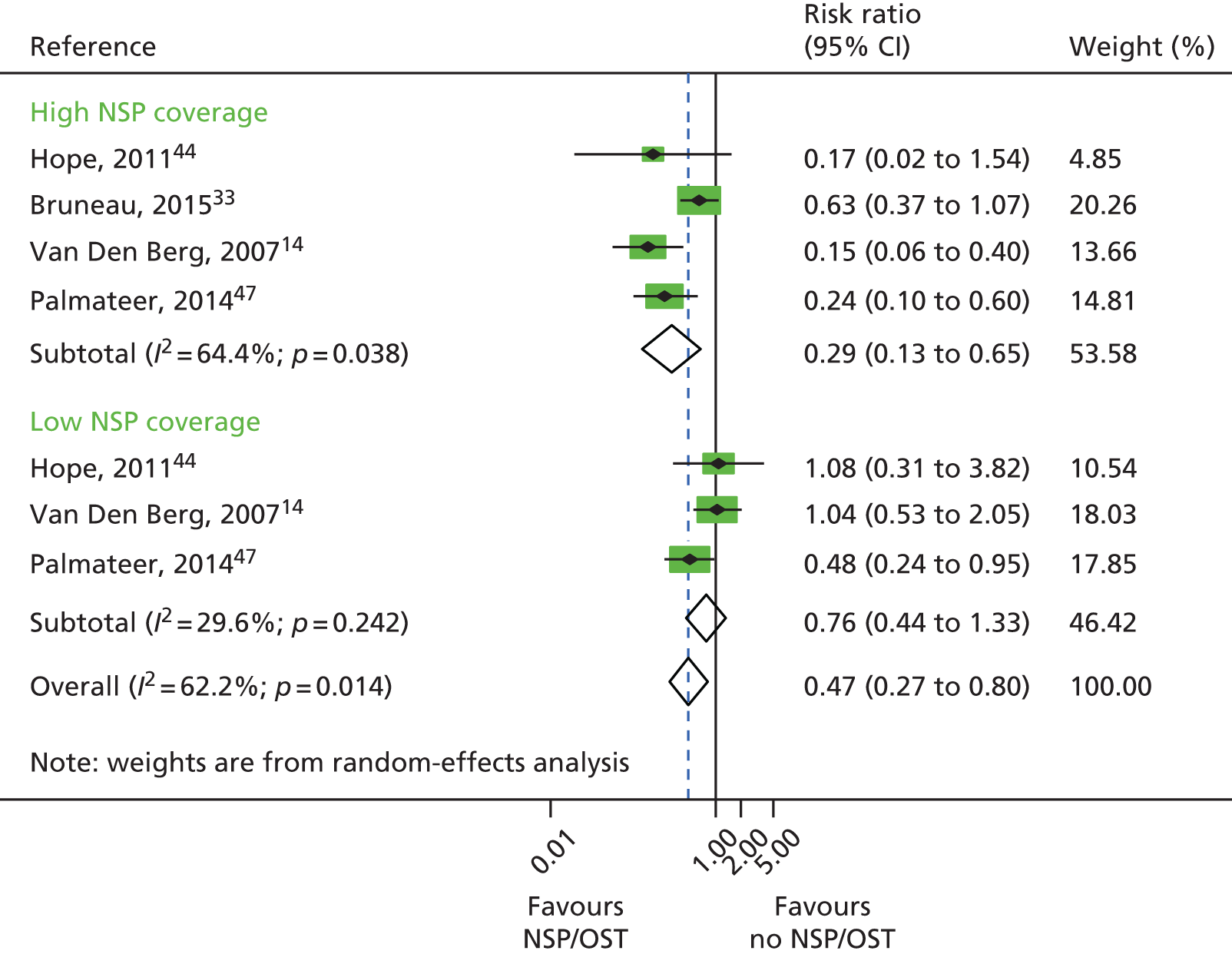
Combined needle and syringe programmes with opioid substitution therapy versus low or no needle and syringe programme coverage and no opioid substitution therapy
A total of four studies reported combined exposure to both NSPs and OST,14,44,47 including one unpublished data set. 33 These categories were defined as high coverage (≥ 100% or ≥ 200%) of injections using clean needles or syringes14,44,47 or obtaining 100% of needles and syringes from a safe source33 plus current use of OST at the point of survey44,47 or within the past 6 month,33 or daily use of methadone during the past 6 months. 14 OST use and low coverage (< 100% of injections covered by a clean needle or syringe) was reported by three studies. 14,44,47 A total of 518 HCV infection incident cases were included in the analysis examining high NSP coverage and 449 for low NSP coverage. Only one study reported the number of person-years. 14 A random-effects meta-analysis showed that combined use of OST and high coverage of NSP was associated with a 71% risk reduction in HCV infection acquisition (RR 0.29, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.65). The effect of exposure to OST and low coverage of NSP was less and non-significant (RR 0.76, 95% CI 0.44 to 1.33) (Figure 7).
FIGURE 7.
Combined OST and high-coverage NSPs. Reproduced from Platt et al. ,26,27 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
Publication bias
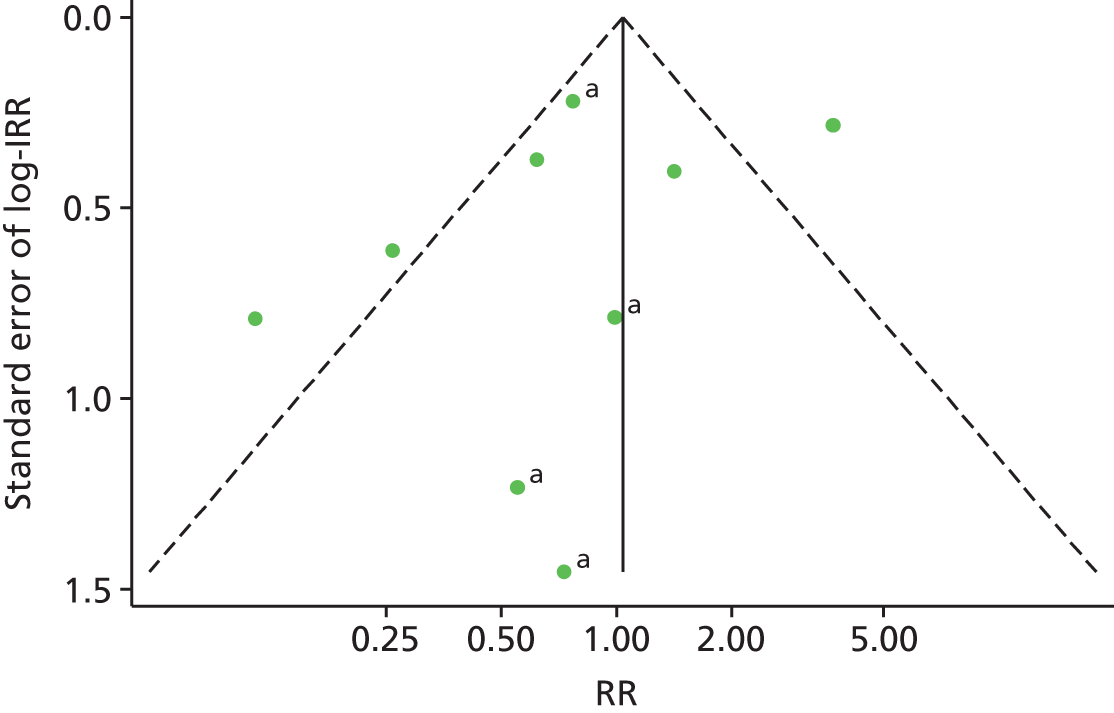
A funnel plot of 13 estimates (12 studies) suggested no evidence of publication bias in studies of current OST exposure (Figure 8). A funnel plot of nine estimates (eight studies) suggested no evidence of publication bias in studies of high NSP coverage (Figure 9).
FIGURE 8.
Funnel plot with pseudo-95% confidence limits assessing publication bias in 12 studies of current OST exposure. a, Unpublished data sets. IRR, incident rate ratio. Reproduced from Platt et al. ,26,27 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
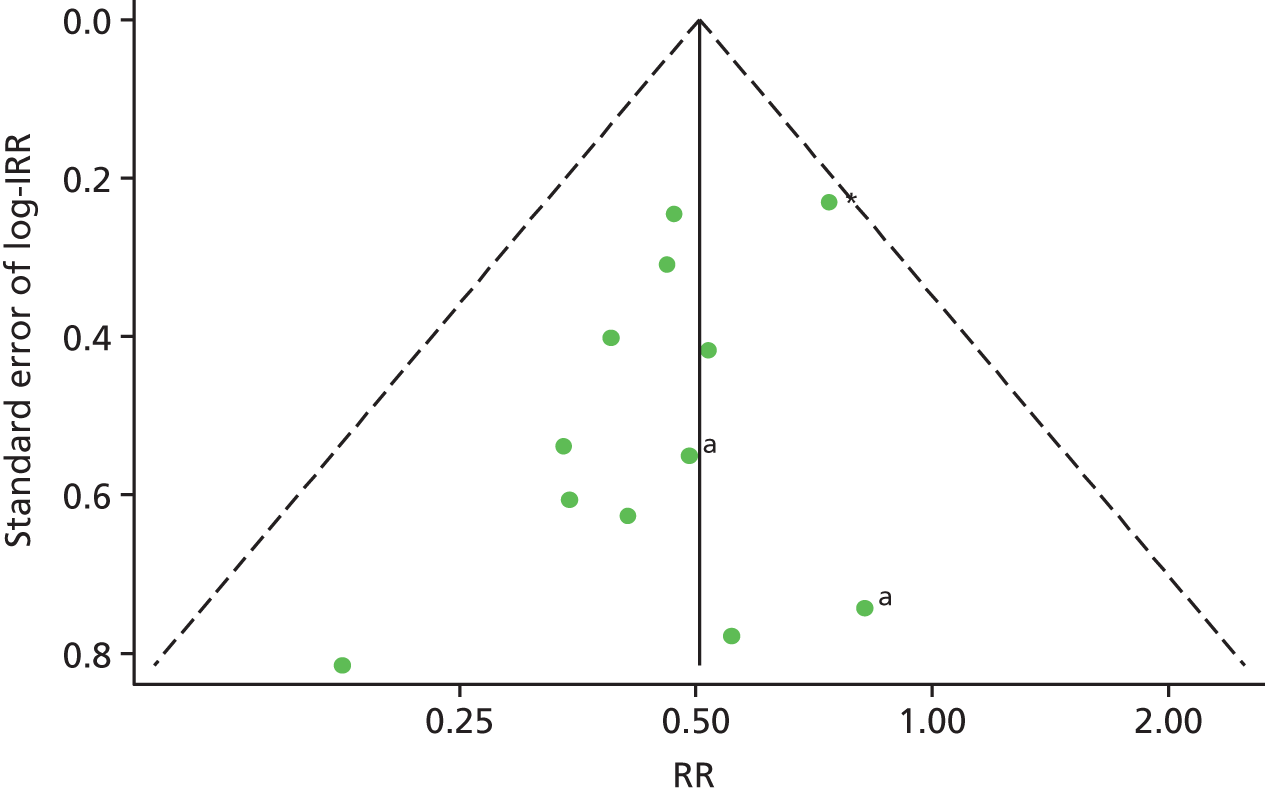
FIGURE 9.
Funnel plot with pseudo-95% confidence limits assessing publication bias in 15 studies of high NSP exposure. The central line is plotted at the fixed-effect summary effect (RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.0.75 to 1.28). a, Unpublished data sets. IRR, incident rate ratio. Reproduced from Platt et al. ,26,27 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
Discussion
Text in this section is reproduced from Platt et al. 26,27 which are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial Licence, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
A primary meta-analysis of 12 observational studies, adjusting for key confounders and enrolling 5910 anti-HCV negative participants, showed that current use of OST compared with no intervention reduced the risk of HCV infection acquisition by 50% (RR 0.50, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.63). The intervention effect is strong, but the evidence is considered to be of low quality because it was derived from observational studies with serious risk of bias. Nonetheless, the findings were robust to sensitivity analyses, excluding studies judged to be at critical risk of bias, studies drawing on unpublished data, case–control and cross-sectional studies reporting only baseline data and studies reporting only unadjusted estimates. There also was no evidence of publication bias. All of these sensitivity analyses showed a statistically significant benefit of OST. A funnel plot (see Figure 8) showed no evidence of publication bias.
A few studies reported other types of exposure to OST. Three studies reported past exposure to OST,51,56,57 three reported interrupted OST use,40,46,53 one measured OST use for detoxification,55 and two measured high dosage (≥ 60 mg) or low dosage (1–59 mg) of methadone for daily use. 14,33 Among these exposures, only high dosage of OST was associated with a reduction in risk of HCV infection acquisition.
A primary meta-analysis of seven observational studies pooling unadjusted estimates and enrolling 5669 anti-HCV-negative participants show weak and low-quality evidence that NSP exposure did not reduce risk of HCV infection acquisition. This effect remained consistent in sensitivity analyses. After removing studies from North America, high NSP coverage in Europe was associated with a 61% reduction in HCV infection acquisition risk (RR 0.39, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.64) with less heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; p = 0.428).
There was low-quality evidence for the impact of combined high coverage of NSP and OST from studies comprising 3356 anti-HCV-negative participants, which suggested a 71% reduction in risk of HCV infection acquisition (risk ratio 0.29, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.65). There were insufficient data to conduct a sensitivity analysis with this intervention group. A summary of key findings and quality of evidence is presented in Table 3.
| Outcomes | Comparison | Relative effect (95% CI) | Number of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCV infection incidence adjusted analyses: number of HCV seroconversion follow-up – mean 440.5 patient-years | Current OST vs. no OST for PWID | Risk ratio 0.50 (0.40 to 0.63) | 5910 (12 studies) | Low |
| HCV infection incidence unadjusted analyses: number of HCV seroconversion follow-up – mean 269 patient-years | High NSP coverage vs. no/low NSP coverage for PWID | Risk ratio 0.70 (0.38 to 1.54) | 5669 (7 studies) | Very low |
| HCV infection incidence unadjusted analyses: number of HCV seroconversions follow-up – mean 356 patient-years | Combined OST and high NSP vs. no OST and low/no NSP | Risk ratio 0.29 (0.13 to 0.65) | 3356 (4 studies) | Low |
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
There is a substantial body of observational evidence that reviews the effectiveness of NSPs and OST in reducing HCV infection acquisition among PWID. The majority of evidence was identified in North America and Western Europe. Only one study was identified from China51 and no studies were identified from Eastern Europe or South-East Asia, where the largest populations of PWID are located and where there is a high prevalence of HIV, HCV and HIV/HCV co-infection among PWID. 61–63
Quality of the evidence
Many studies included in the review were assessed as being at severe risk of bias. Of the studies that were assessed, only two were judged as being at moderate overall risk of bias, 17 were judged as being at serious risk and seven were judged as being at critical risk. There is a need to improve transparency and consistency in the reporting of observational studies to facilitate systematic reviews of observational studies. Only a few studies report the effect of exposure to NSPs adjusted for confounders (5/7), which limited the sensitivity analyses that we could conduct. Therefore, efficacy estimates relating to NSP exposure are limited to unadjusted estimates.
Potential biases in the review process
A potential bias in the review was the heterogeneity across the studies in the use of multiple effect measures. Effect measures were converted into risk ratios in the meta-analysis, but this may have introduced bias into our findings because we had to assume that risk ratios approximated odds ratios (ORs), which may be inappropriate for some sites given the high incidence of HCV seroconversion. We removed cross-sectional study designs that identified serological markers of incidence infection as part of our sensitivity analysis. Effect estimates remained the same for current use of OST versus no intervention, but not for high coverage of NSPs. The majority of studies recruited PWID currently or have done so recently, which may not be representative of all PWID exposed to OST and may lead to an underestimate of the effect of OST on HCV infection transmission. For example, in the Amsterdam cohort, people who reported being on OST and having ceased injecting had a lower risk of HCV infection transmission. 14
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
Our review corroborates and underpins an earlier review that showed consistent and large effects of NSP and OST on injecting risk behaviours associated with blood-borne virus transmission. 8 Two recent reviews focused on the effectiveness of OST and NSPs in reducing HCV infection incidence. 3,19 Our findings corroborate the most recent pooled analysis, which suggested that receiving OST and high coverage of NSPs can reduce HCV infection risk alone, but that the effect of OST and NSPs is greater in combination. 20 The estimate for association between exposure to NSPs and HCV infection incidence was weak in the pooled analysis and focused on studies from the UK only. Findings from our subgroup analysis suggested a stronger effect of high NSP coverage in Europe. This finding builds directly on the Turner et al. 20 analysis through the addition of one earlier paper14 and more recent studies and data sets59 to the meta-analysis, and strengthens the effectiveness estimate for Europe suggesting reduced risk of HCV infection acquisition (risk ratio 0.44, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.80). We found no effect of high NSP coverage when pooling estimates from North America as well as greater heterogeneity across the studies. This corroborates findings from another review that found an increased risk of seroconversion associated with NSP attendance and that relied on evidence predominantly from North America. 19
The lack of evidence for NSPs from studies in North America can be attributed to a mixture of confounding, differences in injecting patterns, potential selection bias and misclassification of exposure. It has been shown that people who attend NSPs regularly also report greater injecting risk behaviour and that, after adjustment for injecting risk, any positive association between HCV infection transmission and NSP attendance is removed. The effect of this residual confounding has been demonstrated in further analyses of a cohort of PWID in Vancouver, which demonstrated that higher HIV seroconversion rates observed among daily NSP attenders was associated with high-risk behaviours of attenders (including regular cocaine injection, sex work involvement and homelessness), rather than use of the NSP. 64 A study based in Seattle showed that people who were homeless or who injected with used needles or syringes were more likely to become new NSP users. 65 The higher proportion of stimulant injecting users in North America also means that the additional protective effect of OST is absent, which may contribute to the impact of NSPs on HCV infection risk in European studies. Potential selection bias may occur because samples of cohort studies are to some degree self-selected, particularly when participants are lost to follow-up over time; they may be inherently different in terms of the demographic characteristics and risk behaviours that can influence the outcome. Misclassification of exposure may also occur because it is difficult to make a clear distinction between exposed and unexposed groups: unexposed populations may have access to clean needles/syringes through other sources than NSPs. Consistent measures of NSP exposure through coverage of injections by clean needles/syringes were used across the European studies, whereas the North American studies drew on varied definitions of NSP use, which focused on the frequency of attendance at NSPs. Comparability in the measurement of intervention exposure is reflected in the higher heterogeneity observed among studies measuring exposure to NSPs (I2 = 80.9%; p < 0.001) compared with OST exposure (I2 = 0%; p = 0.959). This is particularly relevant in relation to measures of intervention exposure that focus on the frequency of attendance at an NSP rather than a measure of injections covered by clean needles and syringes, and further explains the lack of effect between high NSP coverage and HCV infection incidence observed in North America.
Findings also corroborate two recent systematic reviews that measured the impact of NSPs and OST on HIV transmission. These previous analyses of 12 observational studies estimated a moderate effect of NSPs on reducing HIV transmission by 48% (95% CI 3% to 72%) and strong evidence for OST reducing HIV transmission by 54% (95% CI 33% to 68%). 16,17
A previous review of reviews from 2010 concluded that there was insufficient evidence to assess the effectiveness of NSPs in reducing HCV infection incidence. This ‘meta’ review synthesised findings from four primary reviews, three of which focused primarily on HIV as an outcome missing much of the relevant data and the fourth of which predominantly relied on weaker study designs. 3
Implications for practice
Opioid substitution treatment reduces the risk of HCV infection acquisition among PWID. The evidence for the effectiveness of high coverage NSP was more mixed, with good evidence from studies in Europe that NSPs reduce HCV infection transmission. The intervention effect is strengthened by the combination of OST and high-coverage NSP. OST and NSPs are recommended as key interventions for preventing drug-related harm, including HCV infection transmission, by the World Health Organization (WHO), the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. However, OST is not widely implemented in many countries, is prohibited in the Russian Federation and is often restricted by age or duration of dependence prior to treatment entry. 23
Our findings show the need to remove restrictions on the concurrent use of both NSPs and OST to maximise reduction in HCV infection transmission. Distribution of needles/syringes through NSPs needs to be maintained alongside the provision of OST. NSP and OST services need to recognise the role of sex and to develop appropriate policies and practices to encourage women to use services addressing the specific injecting-related risk behaviours that they face and addressing other health and social welfare needs. We identified only three studies that examined effectiveness of interrupted use of OST, but effectiveness was reduced. Similarly, available evidence to examine differences in effect by dosage was limited.
Implications for research
There is good evidence demonstrating the effectiveness of OST in reducing risk behaviour and the transmission of HCV and HIV. However, there is a need to understand the role of the duration of OST use in reducing the risk of both HIV and HCV. For NSPs, evidence needs to be strengthened, including more consistent measurement in the coverage of NSPs across epidemiological studies to obtain better effect estimates as well as to gain an understanding of how the injection of stimulants or prescription opioids changes their effectiveness. Given the body of observational evidence on the effect of OST and NSPs on reducing HIV and HCV infection incidence and other injecting-related harms, it is no longer ethical to individually randomise exposure to OST or NSPs, so future trial evidence can be derived only from stepped wedge clustered RCTs or using wait-list controls, if at all. Current guidance means that the quality of the evidence typically will be assessed as low.
However, priorities for research needs to turn to implementation, the delivery of services and their cost-effectiveness to ensure that existing services are maintained and to promote the introduction and scale-up of services in countries and settings with emerging or growing epidemics of injecting and opioid drug use. We need to understand the pathways between contextual factors and mechanisms of service delivery, and the extent to which these influence effectiveness across different outcomes and settings. For example, HIV and HCV infection epidemics continue unchecked in Eastern Europe, despite the implementation of OST and NSP in some countries. 66 Epidemics of HCV and HIV among PWID are growing in Sub-Saharan African countries, including Tanzania and Kenya, where OST is currently being implemented, but little formal evaluation is being undertaken. Research is needed here that does not employ experimental designs but rather designs that take into account the specific economic, social and political context and different epidemiology of HIV and HCV infection transmission in those contexts. We identified only one study conducted in a middle-income country (China) and no studies in low-income countries.
There was insufficient evidence to examine differences in effectiveness by NSP modality or setting of OST. This reflects a lack of evaluation of provision of OST or NSP in other settings. Further research is needed to examine how the effect of NSPs differs by service modality including pharmacies, mobile clinics or outreach services. Similarly, research into the effectiveness of OST delivered in specialist services, community settings and prisons is needed.
Although evidence for the combined effect of OST and high NSP coverage seemed to be of higher quality, we identified only four studies. Further evidence is needed to understand how effectiveness may differ by modality and duration of OST, as well as by its impact on other health outcomes associated with injecting drug use, such as bacterial infections and mental health.
Finally, given the low quality of evidence, there is a need to improve transparency and consistency in the reporting of observational studies to facilitate systematic reviews of observational studies.
Changes from original protocol
We have changed the title of the review to refer to opioids instead of opiates. Opioid encompasses synthetic opiates as well as those derived from opium, whereas opiates includes only drugs derived from opium. The original protocol specified that one sensitivity analysis would be to remove studies that reported only incident rate ratios as effect estimates. We did not do this because only three studies used incident rate ratios. Instead, we removed estimates derived from unpublished data sets as part of our sensitivity analyses because seven estimates were derived in this way, making them a more substantive part of the analysis.
There was insufficient evidence to answer some of the research questions that sought to examine differences in effectiveness in terms of the following factors: duration of treatment, dosage of OST, type of substitution used, NSP modality (fixed vs. mobile site) or setting of OST. This reflects a lack of evaluation of the provision of OST or NSPs in other settings.
Chapter 3 The impact of needle and syringe provision on hepatitis C transmission among people who inject drugs in the UK and Australia: an analysis of pooled data sets
The aim of the study was to update a previous analysis of pooled data sets to provide a more robust understanding of the extent to which OST and NSP, alone or in combination, can reduce the risk of HCV infection acquisition.
Methods
We collated six data sets previously used in a pooled analysis, methods for which have been published previously. 20 We added an additional three data sets, including a community survey of PWID in Bristol (n = 336), Public Health England’s Unlinked Anonymous Monitoring Programme (UAMP) survey of PWID from England and Wales (n = 3408), the Australian Needle Syringe Programme Survey (ANSPS) (n = 2391) and replaced one of the studies with updated data from Public Health Scotland’s Needle Exchange Surveillance Initiative (NESI) (n = 6988), adding in an additional 6041 individuals. These data are presented in Table 4. We excluded one cohort data set used in the original analysis of recent initiates into injecting because the data set did not contain information on use of NSPs and the population focused on young and recent initiates into injecting, and were less comparable with the other samples. 67
| Characteristic | Bristol 144 | Leeds59 | Birmingham59 | aBristol 259 | Wales39 | aEngland and Wales, UAMP70 | aScotland, NESI68 | aAustralia, ANSP69 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2006 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2004–6 | 2011–12 | 2008–12 | 2012 |
| Study design | Cross sectional: RDS | Cohort: NSP and community | Cross-sectional: NSP, treatment | Cross-sectional: NSP | ||||
| Inclusion criteria | Injected in past 4 weeks | Injected in past 12 months | Ever injected | Ever injected | ||||
| Total participants | 299 | 302 | 310 | 336 | 406 (700) | 3408 | 6988 | 2391 |
| HCV infection prevalence, % (n/N) | 59 (177/299) | 60 (182/302) | 42 (130/310) | 60 (201/336) | 26 (184/700) | 46 (1567/3408) | 54 (3709/6909)b | 53 (1184/2243) |
| Female (%) | 23 | 24 | 12 | 22 | 26 | 24 | 28 | 32 |
| Age, years (median) | 32 (26–37) | 32 (27–37) | 32 (28–38) | 34 (29–39) | 29 (24–34) | 34 (29–40) | 34 (29–39) | 38 (31–45) |
| Duration injecting, median (IQR) | 10 (6–16) | 11 (7–16) | 9 (4–13) | 13 (7–18) | 6 (3–12) | 12 (6–18) | 10.4 (6–16) | 17 (11–25) |
| Ever homeless, % (n/N) | 90 (270/299) | 86 (260/301) | 93 (287/310) | 88 (295/336) | 39 (158/405) | 80 (2664/3331) | 68 (4748/6985) | NA |
| Homeless in past 12 months, % (n/N) | 58 (174/299) | 52 (156/301) | 63 (194/310) | 60 (175/295 | 39 (158/405) | 36 (1209/3331) | 24 (1654/6980) | NA |
| Ever exchanged sex, % (n/N) | 11 (34/299) | 5 (16/302) | 2 (5/310) | 7 (24/336) | 3 (18/599) | 14 (343/2370) | 5 (119/2314) | |
| Ever been in prison, % (n/N) | 81 (242/299) | 81 (245/301) | 85 (263/310) | 77 (260/336) | 71 (494/693) | 72 (2401/3329) | 60 (4188/6973) | 51 (1192/2354) |
| Prison in the past 12 months, % (n/N) | 42 (101/240) | 36 (89/245) | 43 (114/263) | 32 (82/260) | 46 (225/489) | NA | 15 (1070/6988) | 23 (2206/9621) |
| New HCV infectionc | 14/115 | 2/120 | 2/180 | 3/135 | 17/285 | 34/1809 | 51/3104 | 62/477 |
| HCV infection incidence (per 100 person-years) | 40 | 7.6 | 5.2 | 9.9 | 5.6 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 42.0 |
| Abscess or sore at injection site, % (n/N) | 59 (176/299) | 45 (135/302) | 49 (153/310) | 46 (155/336) | 72 (505/700) | 28 (866/3092 | ||
| Injection risk (past 4 weeks) | ||||||||
| Injection in past 4 weeks, % (n/N) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 75 (2500/3346) | 79 (5512/6987) | 91 (2166/2379) |
| Number of injections, median (IQR) | 39 (14–84) | 33 (12–60) | 28 (8–83) | 42 (18–84) | 35 (8–84) | 27 (8–63) | 20 (4–76) | 22 (9–50) |
| Injection with used needle/syringe, % (n/N) | 28 (83/299) | 7 (20/302) | 3 (10/310) | 8 (28/335) | 35 (35/407) | 11 (231/2187) | 69 (209/304) | 16 (342/2073) |
| Shared filters, % (n/N) | 47 (141/298) | 28 (83/301) | 33 (103/307) | 49 (165/334) | 40 (279/690) | 23 (570/2454) | 15 (199/1338)d | 11 (228/1987) |
| Shared spoon/container, % (n/N) | 94 (279/297) | 96 (289/301) | 41 (125/308) | 86 (285/333) | 50 (343/688) | 27 (672/2465) | 18 (299/1639) | 23 (454/1987) |
| Injected while in prison, % (n/N) | 21 (52/242) | 17 (41/245) | 12 (31/263) | 24 (62/260) | 7 (32/486) | 16 (394/2451) | 12 (509/4187) | 34 (90/261)e |
| Injected crack cocaine, % (n/N) | 62 (178/299) | 61 (185/302) | 56 (174/310) | 75 (251/336) | 12 (86/700) | 55 (1840/3372) | 6.5 (458/5581) | 27 (642/2391) |
| Access to services | ||||||||
| Tested for HIV, % (n/N) | 77 (230/299) | 73 (220/301) | 71 (219/309) | 83 (274/329) | 79 (2563/3251) | 73 (4911/6650) | 87 (1997/2296) | |
| Tested for HCV, % (n/N) | 81 (235/291) | 83 (250/301) | 76 (231/303) | 91 (303/332) | 47 (317/669) | 84 (2654/3169) | 80 (5364/6694) | 92 (2086/2267) |
| Never used a NSP, % (n/N) | 8 (41/299) | 5 (26/275) | 5.7 (29/310) | 5 (25/336) | 18 (92/696) | 32 (165/3378) | 0 | 0 |
| Low NSP coverage: (< 100%), % (n or n/N)f | 46 (137) | 36 (108) | 36 (111) | 51 (172) | 39 (126/325) | 49 (1214) | 22 (1180) | 25 (500) |
| High NSP coverage: (> 100%), % (n) | 54 (160) | 64 (190) | 64 (198) | 49 (163) | 54 (177) | 51 (1222) | 78 (4307) | 74 (1466) |
| Currently on OST, % (n) | 57 (172) | 60 (180) | 65 (203) | 81 (241) | 52 (149) | 69 (2535) | 82 (5106) | 43 (1029) |
Two studies recruited PWID through NSPs (NESI, ANSPS) and one through both NSPs and drug treatment clinics (UAMP). 68–70 The remaining studies recruited via community settings (Wales) and through RDS (Bristol, Leeds, Birmingham). 20,39,44 Five of the studies included people who had injected in the past 4 weeks, whereas the UAMP, NESI and ANSPS included people who had ever injected drugs.
All studies, except for one, contained data on recent HCV infection, defined for cross-sectional surveys as individuals who tested HCV RNA-positive among those who tested HCV antibody-negative from dried blood spot (DBS) samples. The one cohort study defined incident infection as those who were HCV antibody negative at baseline and were retested as antibody positive at 12-month follow-up. 39 All samples from the UAMP survey were tested for the purpose of the analysis. Anti-HCV testing was performed using a previously published method, the accuracy of which is close to that achieved on venous blood specimens. 71 The residual DBS had been stored in the refrigerator with desiccant since anti-HCV antibody testing, which has been shown to stabilise both anti-HCV and nucleic acids in DBS. Nucleic acid was extracted from an area of approximately 28 mm2 punched from each DBS, using an automated platform [Qiagen MDx (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany)]. Samples were tested for HCV RNA using nested polymerase chain reaction amplification of the NS5B (non-structural protein 5B) region, which provides a product suitable for differentiating different lineages of HCV infection. 72
Outcomes
The primary outcome was new HCV infection (yes/no) based on the definitions described above. Secondary outcomes were based on self-reported injecting risk behaviours (frequency of injecting, injecting with a used needle or syringe, use of shared spoons or filters for drug preparation, injecting site infection) and HIV/HCV infection testing.
Interventions
We used previously published outcome measures of OST use and NSP coverage. 20 OST was defined as current use of OST for all cross-sectional surveys, whereas in the cohort study it was defined as > 6 months of OST in the past year (yes/no). An internationally used standardised measure of an individual’s NSP coverage was defined as the percentage of injections for which a new needle had been obtained (calculated as the average number of new needles obtained divided by the average number of injections in past four weeks, with the exception of the NESI survey, which measures coverage over 6 months, and the Birmingham study, which uses a 2-week time frame). 5,73,74 The total number of needles or syringes obtained from any source was taken, not limiting data to those needles/syringes obtained from a NSP. We examined the effect of both interventions in two ways. First, we measured the impact of binary measures of NSP and OST to assess their individual effect without considering the influence of the other intervention. Second, we combined these binary measures to form a measure of harm reduction coverage with four categories as used in the original analysis and comparable studies with high coverage defined as ≥ 100% of injections covered by a clean syringe for all sites (Table 5). 14,20,68
| Intervention | NSP coverage ≥ 100% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||
| OST | Yes | Full harm reduction | Partial harm reduction |
| No | Partial harm reduction | Minimal harm reduction | |
Statistical analyses
Of the total 14,734 included participants across the eight studies, a total of 7173 were considered in the primary analysis with an initial HCV antibody-negative result. The analysis involved (1) a meta-analysis of the (unadjusted) effect of OST on new HCV infection incidence limited to 5543 participants; (2) a meta-analysis of the (unadjusted) effect of high NSP coverage limited to 4947 participants; (3) a pooled analysis of the (unadjusted and adjusted) effects of NSP and OST on new HCV incident infections confined to 5280 estimates; and (4) a meta-analysis of the pooled effect estimates alongside estimates from a recent systematic review. 26 A flow chart summarising the numbers of HCV infection cases included in analyses (1) to (3) is summarised in Figure 10. We also conducted a pooled analysis focusing on the effects of NSP and OST on secondary outcomes (see below).
FIGURE 10.
Flow chart summarising the combined HCV antibody and RNA test results among PWID in the UK and Australia. +, positive.
Meta-analysis
We conducted a meta-analysis to test for study heterogeneity in the effects of OST and high NSP coverage on new HCV infection. Separate logistic regression models using fixed-effect meta-analyses were used to estimate the study-specific associations of the (unadjusted) effects of OST and NSP on new HCV infection and to examine levels of heterogeneity between study sites. As published elsewhere, counts of new HCV infection cases were small, resulting in no cases in one intervention group in Birmingham20 and in the 2009 Bristol survey. We added one case and three controls to the intervention group with zero cases. 75,76 We used the I2-statistic to assess between-study heterogeneity in the effects of the interventions on new HCV infection. 77
Pooled analysis of the effects of opioid substitution therapy and needle and syringe programmes on new hepatitis C infection
There was no evidence of heterogeneity between the studies for OST (I2 = 13.6%; p = 0.324) or NSP (I2 = 0%; p = 0.659) so the data were pooled in subsequent analyses and the augmented data points were removed. We used logistic regression to model the odds of recent infection by NSP and joint effects of OST exposure adjusting for key confounders of HCV infection risk including sex,41,45,51,67 injecting duration,41,44,45,67 injecting crack cocaine45,67 and experience of prison. 55
Secondary outcomes
We also examined the risk of self-reported injecting risk behaviour and access to services according to exposure to different levels of harm reduction (OST and NSP) as defined above. Measures of risk included: (1) the proportion of needle/syringe sharing (n = 6217); (2) the frequency of injecting (n = 11,786); (3) reuse of the same needle/syringe more than once for injecting (n = 1242); (4) used of shared filters or spoons for the preparation of drugs (n = 7223); (5) self-reported symptoms of bacterial infections (n = 5039); (6) receiving testing for HIV (n = 13,435); and (7) receiving testing for HCV infection (n = 14,026). We used logistic regression for binary outcomes (measures 1, 2, 4–7) and linear regression for continuous variables (measure 3). All models were adjusted for key confounders listed in the previous analysis (sex,41,45,51,67 injecting duration,41,44,45,67 injecting crack cocaine45,67 and experience of prison55).
Pooled effects and systematic review findings
We conducted a meta-analysis using fixed-effects models to assess the pooled effects of study-level associations between intervention exposure and new HCV infection incidence cases with findings from the Cochrane systematic review reported in Chapter 1. Estimates from the review of European studies that employed the same definition of high NSP coverage were extracted and combined with our additional estimates from the UAMP and ANSP surveys. We used the I2-statistic to assess between-study heterogeneity in the effects of the interventions on new HCV infection.
Findings
The eight studies in Table 4 summarise the characteristics of participants in each study. Approximately 26% of the participants were female, the median age ranged between 29 and 38 years, and the median duration of injecting ranged between 6 and 17 years. The majority of participants had experience of homelessness, ranging from 39% in Wales to 90% in the Bristol 2006 data set. Similar proportions had experience of prison, ranging between 51% in the Australian data set and 90% in the Bristol 2006 data set. Between 2% and 14% had ever engaged in sex work. The background prevalence of HCV infection was highest in the 2009 survey in Bristol and Leeds (60%) and lowest in Wales (26%). Incidence of HCV infection was highest in the Australian data set (42 per 100 person-years) and in the Bristol 2006 data set (40 per 100 person-years) and between 5 and 10 per 100 person-years in all the other sites. Approximately 66% of participants currently injecting reported obtaining at least as many clean needles/syringes as injections and 70% were currently receiving OST.
Meta-analysis to test for study heterogeneity in the effect of opioid substitution therapy and needle and syringe programmes on the risk of hepatitis C acquisition
The meta-analysis shows that high NSP coverage was associated with a slight reduction in the risk of HCV infection but this was not significant (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.54 to 1.06). Exposure to OST was associated with a 45% reduction in the risk of HCV infection (OR 0.55, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.77). There was no evidence of heterogeneity between the studies for the effect of either intervention (NSP: I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.659; OST: I2 = 13.6%; p = 0.324). (These findings are summarised in Figures 11 and 12.)
FIGURE 11.
Meta-analysis summarising study-level estimates of the effect of high NSP coverage (> 100%) on HCV infection incidence.
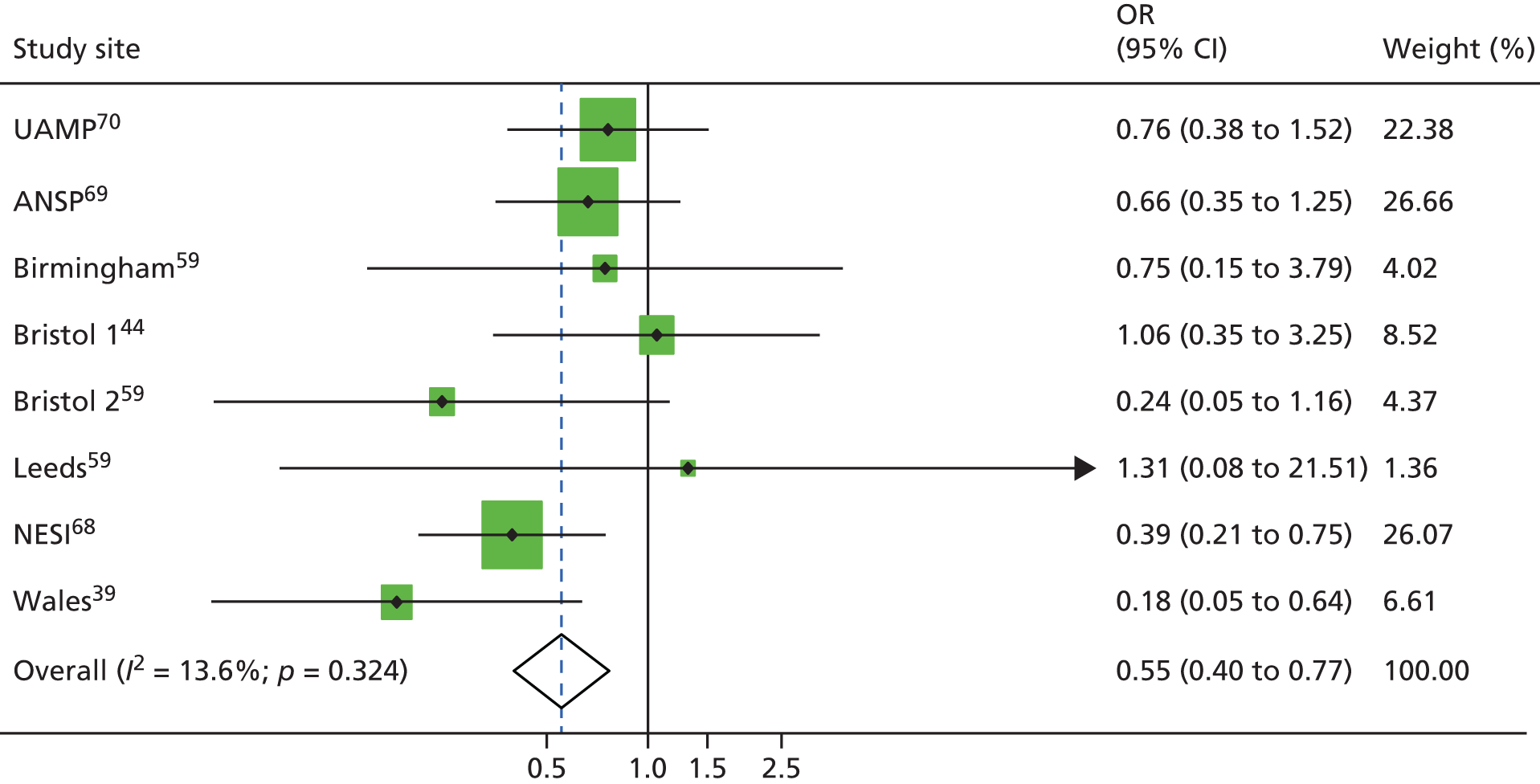
FIGURE 12.
Meta-analysis summarising study-level estimates of the effect of current OST use on HCV infection incidence.
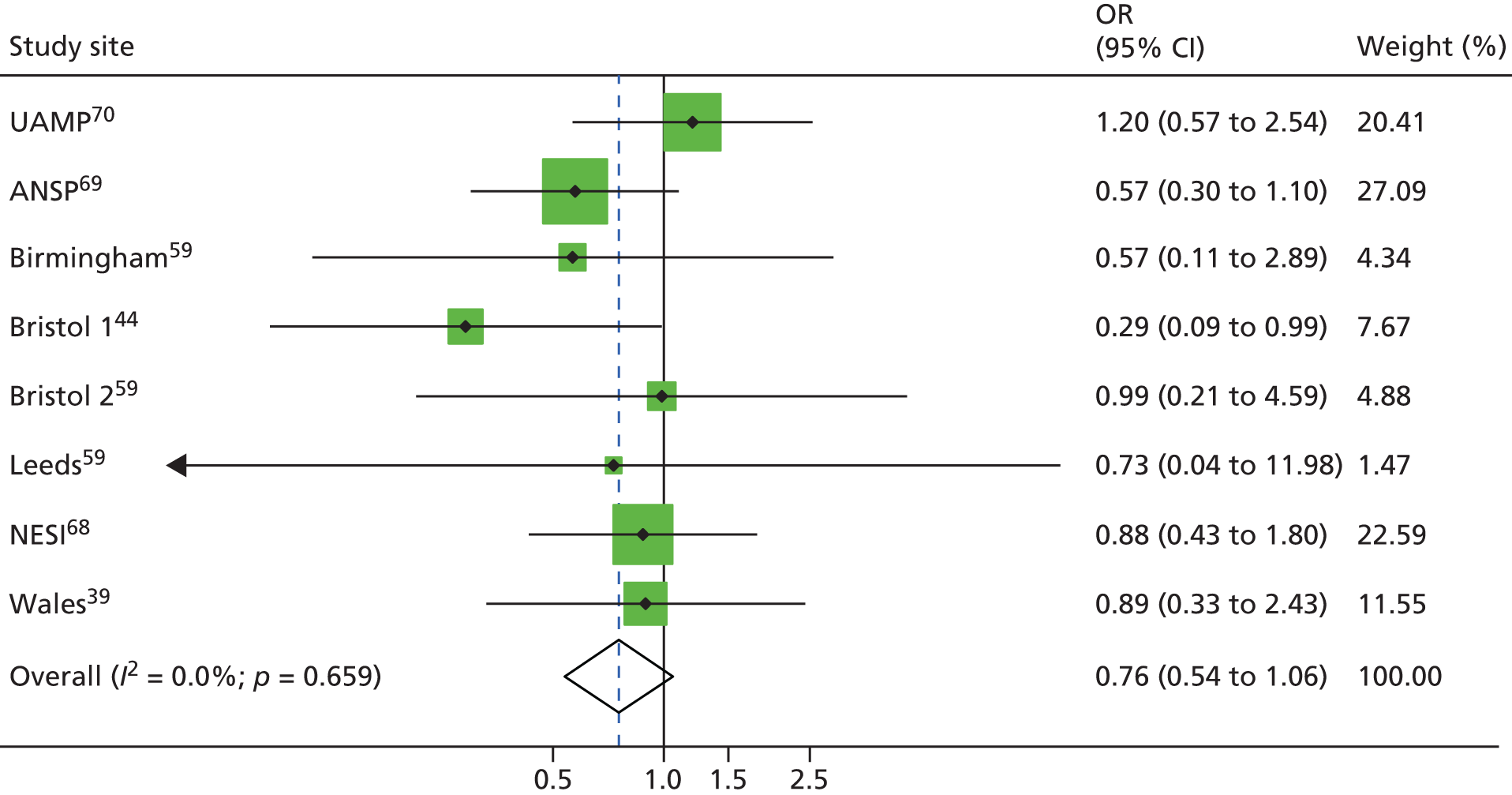
Pooled analysis of the effect of opioid substitution therapy and needle and syringe programmes on new hepatitis C infection
The impact of OST and NSP coverage on new HCV infections is summarised in Table 6 for the complete case data (n = 5280). In the unadjusted analysis, PWID currently using OST had only a 65% reduced odds of HCV infection (OR 0.35, 95% CI 0.26 to 0.48). High coverage with needle/syringes (≥ 100%) alone was not significantly associated with reduced odds of HCV infection (OR 0.83, 95% CI 0.60 to 1.16). Following adjustment for sex, experience of prison or injecting crack cocaine, the intervention effects of OST alone was reduced [adjusted odds ratio (AOR) 0.61, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.87], but the effect of NSP alone was not altered.
| Explanatory factors | n | Total | % | OR | 95% CI | p-value | AOR | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 NSP, no OST | 36 | 577 | 6 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| > 100 NSP, no OST | 47 | 905 | 5 | 0.8 | 0.53 to 1.29 | 0.39 | 0.6 | 0.36 to 0.96 | 0.03 |
| < 100 NSP, OST | 19 | 896 | 2 | 0.3 | 0.18 to 0.57 | < 0.001 | 0.4 | 0.22 to 0.75 | < 0.001 |
| > 100 NSP, OST | 56 | 2902 | 2 | 0.3 | 0.19 to 0.45 | < 0.001 | 0.4 | 0.27 to 0.71 | < 0.001 |
| Female | 1.3 | 0.92 to 1.74 | 0.14 | 1.1 | 0.73 to 1.56 | 0.73 | |||
| History of prison | 0.9 | 0.69 to 1.24 | 0.59 | 1.4 | 0.98 to 2.05 | 0.06 | |||
| Injection of crack cocaine | 1.8 | 1.35 to 2.49 | 0.00 | 1.6 | 1.09 to 2.40 | 0.02 | |||
| Duration of injection (years) | |||||||||
| 0–3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| 3.1–5 | 0.9 | 0.55 to 1.36 | 0.54 | 1.0 | 0.67 to 1.47 | 0.953 | |||
| 6–10 | 0.5 | 0.30 to 0.75 | 0.00 | 1.1 | 0.78 to 1.45 | 0.6853 | |||
| 11+ | 0.8 | 0.53 to 1.10 | 0.15 | 1.1 | 0.86 to 1.49 | 0.361 | |||
| Study | |||||||||
| Bristol 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| Leeds | 0.1 | 0.03 to 0.55 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.03 to 0.54 | 0.01 | |||
| Birmingham | 0.1 | 0.02 to 0.36 | < 0.001 | 0.1 | 0.02 to 0.35 | < 0.001 | |||
| Wales | 0.5 | 0.22 to 0.96 | 0.04 | 0.6 | 0.26 to 1.21 | 0.14 | |||
| Bristol 2 | 0.2 | 0.05 to 0.59 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 0.06 to 0.75 | 0.02 | |||
| NESI | 0.1 | 0.06 to 0.22 | < 0.001 | 0.2 | 0.10 to 0.38 | < 0.001 | |||
| UAMP | 0.1 | 0.07 to 0.27 | < 0.001 | 0.2 | 0.08 to 0.31 | < 0.001 | |||
| ANSP | 1.1 | 0.58 to 2.00 | 0.81 | 1.3 | 0.64 to 2.54 | 0.49 | |||
| On OST | 0.4 | 0.26 to 0.48 | < 0.001 | 0.6 | 0.43 to 0.87 | 0.007 | |||
| High NSP coverage | 0.8 | 0.60 to 1.16 | 0.27 | 0.8 | 0.55 to 1.12 | 0.182 | |||
When examining the effects of combined harm reduction interventions, the risk of new HCV infection was halved among those on full harm reduction (defined as receiving OST and ≥ 100% NSP coverage) (AOR 0.44, 95% CI 0.27 to 0.71) compared with those on minimal harm reduction (≤ 100% NSP coverage). There were reduced odds of HCV infection acquisition among those on partial harm reduction exposed to high NSP coverage but not among those on OST (AOR 0.59, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.96) and a higher effect for those on OST but with low NSP coverage (AOR 0.41, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.75).
Pooled analysis of the effect of opioid substitution therapy and needles/syringe programmes on injecting risk behaviours
A total of 15% of the sample reported injecting with a used needle/syringe in the past 4 weeks (958/6217), 20% had shared spoons or filters during the preparation of drugs (3018/14,734) and 30% had injected with the same needle/syringe more than once (377/1242). The mean number of injections in the past month was 44. Across five studies, 39.5% of participants had an abscess or sore at the injection site (1990/5039). The majority (77.5%) reported ever having an HIV test (10,414/13,435) and a test for HCV infection (81%, 11,440/14,026).
Injecting with a used needle or syringe
Participants in full harm reduction (≥ 100% NSP, OST) or partial harm reduction (≥ 100% NSP, no OST) had a 50% lower risk of injecting with a used needle/syringe (AOR 0.5, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.62) than those in minimal harm reduction (< 100%, no OST; AOR 0.5, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.65). Participants on OST but with lower NSP coverage had a 30% reduced risk of injecting with a used needle/syringe (AOR 0.7, 95% CI 0.57 to 0.94) compared with those without OST. Current use of OST without taking into account NSP coverage was not associated with reduced odds of injecting with a used needle/syringe (AOR 0.9, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.07). High compared with low needle/syringe programme coverage was associated with a reduced odds of sharing a used needle/syringe (AOR 0.6, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.69). (These findings are presented in Appendix 2, Table 18.)
Reuse of the same needles or syringes for injection
Across the five community cross-sectional surveys (n = 1195), full harm reduction compared with minimal harm reduction was associated with a 40% reduction in the odds of reusing the same needle/syringe for injection more than once (AOR 0.59, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.88). Partial measures of harm reduction were not significantly associated with reuse of the same needle/syringe. Current use of OST alone was not significantly associated with a reduction in reuse of the same needle/syringe (AOR 0.93, 95% CI 0.70 to 1.22). However, high coverage (≥ 100%) with needle/syringes was associated with a 40% reduction in reuse of the same needle/syringe more than once (AOR 0.59, 95% CI 0.46 to 0.76). (These findings are presented in Appendix 2, Table 19.)
Frequency of injecting
Among 10,514 participants reporting frequency of injection, we found that participation in full harm reduction was associated with a mean reduction in injecting frequency compared with those in minimal harm reduction (AOR –41.2, 95% CI –45.5 to –38.0). Participation in partial harm reduction with ≥ 100% NSP coverage but no OST was associated with a reduction in injecting frequency compared with lower NSP coverage and no OST (i.e. minimal harm reduction AOR –21.6, 95% CI 26.2 to –17.0). (These findings are presented in Appendix 2, Table 20.)
Shared used of spoons and filters
Participants on full harm reduction had a 28% lower odds of sharing filters or spoons to prepare drugs (AOR 0.78, 95% CI 0.66 to 0.98). The effect of partial harm reduction with or without OST or higher coverage of needles/syringes results in the same proportional decrease in the risk of sharing filters or spoons. Current use of OST without taking into account NSP coverage was not associated with a reduction in the risk of sharing spoons and filters (AOR 0.94, 95% CI 0.83 to 1.06). High compared with low NSP coverage was associated with a 12% reduction in the use of shared spoons and filters (AOR 0.88, 95% CI 0.78 to 0.98). (These findings are presented in Appendix 2, Table 21.)
Injecting site infections
There was a weaker association between the harm reduction intervention variable and injecting site infections across the four community surveys, the Welsh cohort and the UAMP data set (n = 4259). There was some evidence that current use of OST was associated with increased odds of an injecting site infection (AOR 1.3, 95% CI 1.11 to 1.50). There was no association with the NSP coverage variable. (These findings are presented in Appendix 2, Table 21.)
Hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus testing
Full harm reduction was associated with increased odds of testing for HCV infection. Odds of HCV infection testing increased with greater harm reduction coverage, with participants on full harm reduction having almost twice the odds of reported testing for HCV infection compared with those on minimal harm reduction (AOR 1.9, 95% CI 1.56 to 2.23). Participants on OST had 1.5 times higher odds of being tested for HCV infection (95% CI 1.36 to 1.71) and those with ≥ 100% NSP coverage had a 20% higher chance of being tested for HCV infection (AOR 1.2, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.31). Similar associations were observed with HIV testing. Participants on full harm reduction had twice the odds of reporting undergoing testing for HIV (AOR 1.9, 95% CI 1.6 to 2.20) and odds of testing for HIV were 50% higher among those on OST (AOR 1.5, 95% CI 1.36 to 3.04) and 20% higher among those with high NSP coverage (AOR 1.2, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.30). (These findings are presented in Appendix 2, Tables 22 and 23.)
Pooling estimates with systematic review findings
Combining estimates of NSP coverage from the systematic review with two data sets69,70 not already represented in the review strengthened the evidence for the effect of high needle syringe programme coverage on reducing the risk of HCV infection acquisition to 39% (RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.87) with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 30%; p = 0.189). The systematic review data comprised a total of 438 new HCV infection cases from a sample of 3990. Similarly, the addition of 12 estimates from a systematic review that examined the effectiveness of current use of OST comprising 998 new HCV infection cases from a sample of 5910 supported the evidence for the effect of OST in reducing HCV infection risk acquisition (RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.45 to 0.69; I2 = 0%; p = 0.620). These findings are summarised in Figures 13 and 14.
FIGURE 13.
Meta-analysis combining pooled analyses with systematic review findings to measure the impact of high NSP coverage (> 100%) on HCV infection incidence.
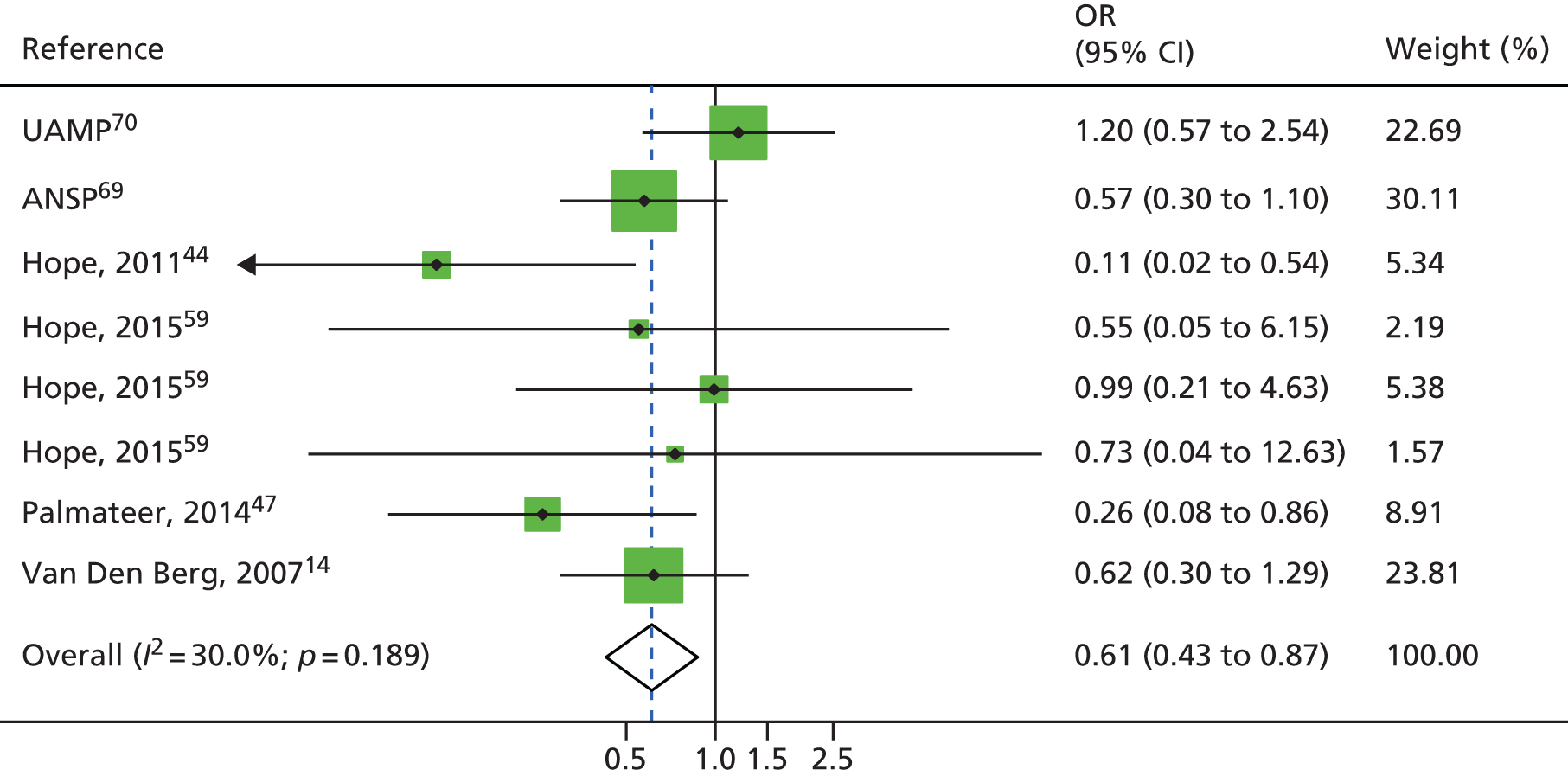
FIGURE 14.
Meta-analysis combining pooled analyses with systematic review findings to measure impact of current OST exposure on HCV infection incidence.
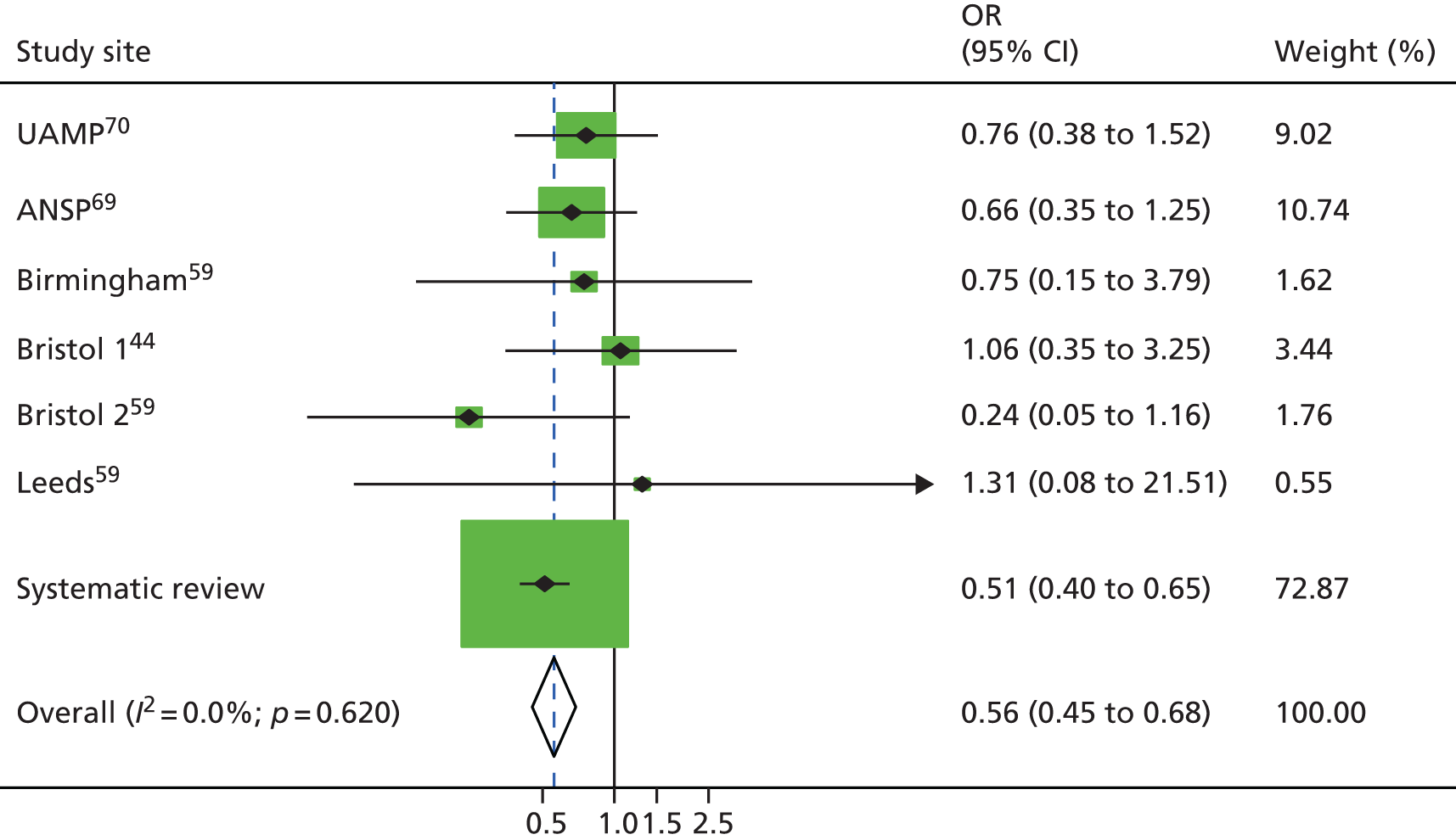
Conclusion
The analyses of pooled data sets from the UK and Australia showed strong evidence for the impact of full harm reduction (OST with ≥ 100% NSP coverage) in reducing the risk of HCV infection acquisition, injecting with used needles/syringes, frequency of injecting and increasing access to HIV/HCV infection testing among PWID in the UK and Australia. The impact of high (≥ 100%) NSP coverage without OST reduced the risk of HCV infection acquisition by 40% compared with no OST and low (< 100%) NSP coverage. Our meta-analysis showed a weaker effect of the effect of NSP coverage on HCV infection incidence at the study level (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.54 to 1.06). However, when this was combined with the systematic review, the effect was stronger (OR 0.61, 95% CI 0.42 to 0.87).
Limitations
Our findings suggest a weaker effect of full harm reduction than reported previously, despite having a sample size five times larger and greater study power. One reason for this may be that the majority of new observations were derived from routine surveillance sets (UAMP, ANSP, NESI) that recruit from NSPs and drug treatment centres. First, these data sets cover wide geographic areas for which the effectiveness of interventions is likely to differ, and this variation is not accounted for in the analysis. Second, the reported numbers of needles/syringes obtained from the UAMP were 3–4 times lower than those reported by community surveys, reflecting different inclusion criteria and settings. The community surveys were undertaken in larger urban areas, whereas the UAMP include smaller towns and rural areas. Third, findings clearly point to difficulties in accurately measuring the use of NSP coverage, which relies on correct recall of the frequency of injecting and the numbers of needles/syringes obtained in a time period and does not take into account secondary distribution (people taking additional needle/syringes to give to their peers).
Concluding remarks
This is the largest national UK-wide analysis of the effectiveness of OST and NSP among PWID on HCV infection incidence. Findings clearly underline the importance of OST in combination with NSP as cornerstone interventions to reduce HCV transmission among PWID and the need to prioritise these interventions to prevent HCV. Findings also provide important new evidence of the role of high NSP coverage in reducing not only HCV incidence but also injecting with used needles/syringes and show that increasing the circulation of clean needles/syringes does not increase injecting frequency among PWID. The inclusion of the Australian data set shows that findings are generalisable to other contexts.
Chapter 4 Costing of needle and syringe programmes
Introduction
Needle and syringe programmes have been shown to be cost-effective for the reduction of HIV transmission in a wide range of settings. 13,78,79 Recent studies indicate that NSPs could also substantially reduce HCV infection rates. 20,80 To date, there have been no economic evaluations of NSPs for HCV infection reduction in Western Europe. This chapter aims to fill this gap by providing robust estimates of the cost of NSP programmes in order to facilitate a cost-effectiveness analysis (see Chapter 5).
Methods
Needle and syringe programme costing
Description of the intervention
The intervention evaluated is NSPs. NSPs in England are funded through Drug Action Teams and Local Strategic Partnerships, which are multiagency bodies involving local government, the police and health services, and that can be provided through pharmacies, mobile vans or specialist fixed sites. In Scotland, regional commissioning bodies are responsible for commissioning co-ordinated services for the region.
Needle and syringe distribution takes place through a range of modalities in the UK. There are three levels of needle distribution detailed in NICE guidance. 81 Level 1 includes the distribution of either loose or packaged injecting equipment. Level 2 includes the distribution of injecting equipment in a bespoke ‘pick and mix’ style and the dissemination of health promotion advice. Finally, Level 3 includes the distribution of ‘pick and mix’ injecting equipment and health promotion advice, as well as the provision of ‘specialist services’ (e.g. vaccinations, drug treatment and secondary care, including treatment for HCV and HIV).
The two most common modalities include pharmacy distribution and fixed-site distribution. Fixed-site NSP programmes are contracted by commissioning bodies to provide needle and syringe exchange at Level 3 as described in the NICE guidance. Fixed sites are generally contained within substance misuse services, which offer a wide range of drug and alcohol treatment interventions. These may include blood-borne virus testing and treatment, pregnancy testing, one-to-one support, structured day care and group-work programmes, OST prescription, relapse prevention services, and training volunteering and employment services. All injecting equipment is offered free of charge, usually in a ‘pick and mix’ style, from which clients may choose their own equipment to take away. Fixed sites also accept used injecting equipment for safe disposal and provide health promotion advice regarding the location and care of the injecting site, overdose avoidance and general welfare.
Pharmacies are contracted by local commissioning bodies to provide needle and syringe exchange, usually at Levels 1 and 2 as described in the NICE guidance. Injecting equipment is distributed to clients free of charge, either in a ‘pick and mix’ style or in pre-made pharmacy packs. Pharmacy packs contain various size needles depending on the colour of the pack and usually come in quantities of 5, 10 or 20 needles per pack. Some pharmacies are also now beginning to provide ‘one-hit kits’, which contain one needle and are intended to reduce drug-related litter. Pharmacies also accept used injecting equipment for safe disposal. Pharmacies may also provide health promotion advice, either verbally or in the form of health education materials, which are distributed alongside injecting equipment. Pharmacies are usually paid an ‘incentive’ by commissioning bodies to distribute needles and syringes, which can range from £1 to £3 per exchange. Pharmacies also receive administrative and overhead support either from local commissioning bodies or from fixed sites operating in the area; this support includes ordering and delivery of pre-made needle packs, the collection and disposal of waste, and the administration and collation of service statistics.
Alternative modes of delivery not mentioned by the NICE guidance include peer-led and drop-in centre distribution, mobile outreach, vending machines and drop-box schemes. Peer-led and drop-in centres function as places for those with drug and alcohol dependencies to feel safe and comfortable, receive support in the form of hot meals, washing facilities and/or clean clothes, and find referrals for medical, legal or housing services. Mobile outreach services have the capability to visit sites in the outer areas of the city during afternoons and evenings, targeting areas where pharmacy NSP provision is less accessible or where there is a particularly high need for services. Vending machines are potential mechanisms by which to allow people to access injecting equipment out of hours and can complement or supplement existing services.
Sites and settings
Cost data collection took place in three UK cities, namely Bristol, Dundee and Walsall. Sites were selected through a combination of convenience sampling based on the availability of impact data for the cost-effectiveness analysis, existing relationships with service managers and the feasibility of conducting a costing study. The three settings reflected variation in the primary modality through which needles were distributed, and a range of ‘other’ modalities intended to expand coverage.
The Bristol Drugs Project (BDP) is responsible for all harm reduction and substance misuse treatment in the Bristol area. They have a fixed site providing a needle exchange as well as other services. Pharmacy co-ordination is carried out by the BDP, and pharmacy-distributed NSP supplies are provided by the BDP. Pharmacies in Bristol exclusively distribute equipment in pre-made packs, rather than in a pick and mix style. Packs are available in two sizes: 10 needles or 20 needles. Most pharmacies in Bristol will also distribute OST, although commissioning for this is managed separately.
Services in Dundee are commissioned through NHS Tayside and the Sexual Health & Blood-Borne Virus Managed Care Network Prevention Sub-Group. The Managed Care Network Sub-Group is a multiprofessional group with representation from secondary care, primary care, the local authority, the voluntary sector and patient/carer/client representatives throughout Tayside, which has a remit for blood-borne virus prevention and sexual health improvement. This includes public awareness, education and harm reduction. The Tayside Substance Misuse Service is made up of two specialist harm reduction nurses, an administrator and a lead pharmacist. The service helps to co-ordinate pharmacy-based NSP services in addition to having several other responsibilities. The Cairn Centre is the busiest fixed-site injecting equipment provider in the Dundee area. Needle exchange services within CAIR Scotland are funded exclusively by the Managed Care Network. There are 15 pharmacies providing needle exchange services throughout Tayside, six of which are in Dundee. Pharmacies will offer injecting equipment either in packs or in pick and mix format. Most pharmacies in Dundee will also distribute OST; however, commissioning for this is managed separately.
Finally, in Walsall, the council commissions all NSP/harm reduction services through Public Health England. During the period of data collection, Addaction was commissioned to provide all needle/syringe exchange services in Walsall. Owing to recommissioning occurring after the period of data collection, Addaction Walsall are no longer in operation. Addaction co-ordinated other agencies providing NSP, including pharmacies and Hi’s ‘n’ Lows (a drop-in centre; Walsall, UK). There are 12 pharmacies in Walsall offering needle and syringe exchange services. Most pharmacies in Walsall also distribute OST, although commissioning for this is managed separately. Hi’s ‘n’ Lows is a peer-run drop-in service, offering a safe space for people to be and also offering a number of different services including a cheap meal, advice and counselling, and clothes. They provided needle exchange in co-operation with Addaction (which provided the needles and handled waste management).
Data collection
Data collected incorporates the costs for different modalities of NSP provision (pharmacy, specialised and mobile sites) within each city. In total, we collected cost data for three fixed sites, six pharmacies and three ‘other’ modalities, which could potentially enable scale-up of output and coverage levels. Other modalities include a mobile outreach service, a drop-in centre and an out-of-hours pharmacy. For pharmacies, only a subsample was costed in detail owing to the existence of multiple pharmacy NSPs in each setting. The costs of other pharmacies in each city were estimated using their output data and unit cost data from the pharmacies where detailed costings were undertaken to give an overall cost estimate per city. The cost analysis covers a period of 1 financial year (2013–14), the most recent year for which data were fully available, and takes a provider perspective.
We estimated the total and unit economic costs for distributing clean needles to PWID. Our approach to costing was incremental to existing services and was particularly focused on needle and syringe exchange. We followed standard methods for costing in an economic evaluation of a health intervention; we include all costs regardless of the payer and estimate a ‘shadow cost’ when the price does not accurately represent the value of resources. 82,83
In collecting resource use data, when possible, data were extracted from existing reporting mechanisms, including budget and expenditure records, human resources records and the management information system. In addition, we carried out direct observations of staff time and activities in order to confirm supply use estimations and to allocate resources that are shared between the NSP and other harm reduction services (such as staff time, building space, equipment or vehicle operation). Shared resources were allocated to services as a proportion of total services delivered and total time spent on each service. Current market prices [2014 UK pounds sterling (GBP)] were applied to all resources in order to estimate a cost. Overhead and support costs were estimated from programme records and a portion allocated to NSP services. Data were collated in a standardised Microsoft Excel® Version 3 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) spreadsheet. Data collection was primarily conducted by one researcher and quality-controlled by a second researcher.
Owing to the nature of pharmacy-based needle exchange, there was far less detailed output data available within pharmacies. We therefore made a number of assumptions in estimating the outputs at pharmacies. The type of data available for pharmacy-based needle distribution in each city varied: in Bristol, pharmacies reported on the total number of visits, whereas in Dundee, pharmacies reported on both the number of visits and the total number of needles distributed. Walsall pharmacies reported on the number of packs distributed. Based on feedback from both pharmacies and fixed sites, we assumed that 100% of clients obtaining needles at pharmacies were opioid users. Information on the distribution by sex of clients accessing pharmacies was available at two sites; this distribution was used to estimate the approximate breakdown between male and female clients at the other two sites. In order to estimate the total number of clients at pharmacies, we further assumed that an average of eight visits were made per client at pharmacies over the course of 1 year; again, this assumption was based on observations at two pharmacies for which this information was available. We assumed that pharmacies distributed an average of 1.12 needle packs per transaction. The out-of-hours pharmacy had begun the distribution of ‘one-hit kits’ shortly before the data collection period; as there was very little information on the quantity of ‘one-hit kits’ distributed per visit, we varied our assumption of ‘one-hit kits’ per transaction between 1 and 10 (the minimum and maximum quantities distributed per visit in the 2 weeks prior to the site visit).
Similarly, data on the proportion of needles distributed to opioid versus image and performance enhancing drug (IPED) clients at Addaction Walsall were unavailable. We therefore assumed a proportion based on data in other fixed sites. Detailed information on the sex distribution at the out-of-hours pharmacy and the peer-led site was also not available; we therefore estimated the same sex distribution as observed in the two pharmacies for which information on the sex breakdown was available.
Data analysis
Fixed and variable costs
Costs at all sites were classified as fixed and variable costs to facilitate analysis. Fixed costs are defined as those costs that are not easily changed in the short term. Fixed costs included the following ingredients:
-
Overhead costs for pharmacy/fixed-site management – estimated as the percentage of needle exchange services delivered compared with other services delivered in the pharmacy/the local area.
-
Co-ordination by commissioners – included as an overhead and allocated to the site as the percentage of needle exchange services delivered, compared with other services delivered in the pharmacy/the local area.
-
Training as a minimum – includes awareness of the need for discretion, but this should also include an understanding of how to treat people in a non-judgemental way, and may include further education on common injecting practices and harm reduction messages. Training costs were estimated using an ingredients-based approach.
-
Health and safety training – included as a cost for fixed-site staff but not for pharmacists, who as a part of their normal job will already have received health and safety training (e.g. needle stick injuries) and hepatitis B vaccines.
-
Vehicle purchase – estimated using an ingredients approach and allocated as the proportion of mileage used for NSP services compared with for other services.
Variable costs are those costs that vary depending on the volume of services provided and can change in the short term. Variable costs included in the analysis are:
-
Injecting equipment in pre-made packs or ‘pick and mix’ as appropriate to the site/service. Equipment and paraphernalia distributed varied between pharmacies and fixed sites and from site to site. Equipment distributed includes pots, water, citric acid, needles/syringes (various types and sized), condoms and sharps bins. The cost of this equipment will be estimated using a combination of the ingredients-based approach and step-down accounting. For pharmacies distributing needle packs, the base-case analysis assumes that packs of 10 are routinely distributed. This is varied to packs of 20 needles in the sensitivity analysis.
-
Staff time costs, including service and administrative staff, allocated to NSP services as a percentage of their time use for NSP services compared with other services, using a combination of observational and interview data.
-
Waste management and disposal of returned needles.
-
Vehicle fuel, insurance and maintenance costs, estimated using an ingredients approach, and allocated as the proportion of mileage used for NSP services compared with for other services.
Estimating city-level costs
In order to input into the cost-effectiveness model, we estimated the total cost for distribution of needles to opioid users in each of the three commissioning areas included in the study. We take the assumption that IPED users are at less risk of HCV infection via shared needles. 84 This is based on low reported prevalence of HCV infection in IPED users.
Our estimate of total costs for distributing needles to non-IPED users is estimated using total fixed costs at the city level, plus a weighted average variable cost per needle distributed to opioid clients. This estimation approach is intended to proxy the equivalent costs of providing needles only to opioid users (i.e. it represents the full fixed cost of the infrastructure necessary to provide needle and syringe exchange, and the variable cost attributable to non-IPED users). We anticipate this to be a conservative approach, which does not account for the benefit of distributing needles to IPED users.
Total fixed costs at city level are estimated accounting for the fixed site in each city, as well as all pharmacies and other modalities operating in each city. For pharmacies not included in our costing sample, we estimated an average fixed cost per pharmacy for each commissioning area using the two or three pharmacies sampled for detailed cost data collection. We then applied an average fixed cost to all pharmacies across the commissioning area; this information was provided by fixed sites in each city. When incentive payments were less than or equal to the costs of staff time for transactions, these were treated as a transfer and not included as an additional cost. When incentive payments were greater than the costs of staff time, any additional amount was considered an additional cost and was factored into the total cost estimate.
Average variable costs per opioid needle distributed were estimated for each service modality in each city and weighted to reflect the total proportion of opioid needles distributed through that service modality citywide. This weighted average variable cost was then applied to the total number of needles distributed citywide to come to an estimate of the total citywide variable cost.
Uncertainty analysis
In order to reflect the uncertainty encountered in collecting NSP costs, we conducted a univariate sensitivity analysis. We included factors in the sensitivity analysis that could not be directly observed or that varied substantially between sites, including supply wastage, staff time taken for needle distribution, opportunity costs of volunteer time, equipment wastage, opioid/IPED client mix, number of needles distributed per visit and discount rate. In addition, we conducted a multivariate analysis of all factors mentioned above, simultaneously varying all factors with uniform distribution between the minimum and the maximum values observed over 1000 iterations. (The costing parameters varied in the uncertainty analysis, along with their minimum and maximum values, are located in Appendix 3, Table 25.)
Results
Needle and syringe programme outputs
The size of fixed-site services varied substantially across the three cities. The largest fixed site handled > 10,000 visits in the financial year, whereas the smallest fixed site handled only 1756 visits in the same year (see Appendix 3, Table 26). The client mix at fixed sites also varied between sites. The majority of clients attending BDP and CAIR Scotland were users of opioids and other drugs, whereas the majority of clients at Addaction Walsall were IPED users. The total number of clients in 1 year at fixed sites varied from 569 to 1134; however, it is possible that the number of clients was distorted within fixed sites by clients giving different names on different visits.
The majority of clients at all sites were male: 87% of clients visiting BDP, 62% of clients at CAIR Scotland and 91% of clients at Addaction Walsall. At BDP, detailed information on the sex breakdown was available by opioid vs. IPED users. When looking at this breakdown, the sex balance is much more extreme among IPED users, with 98% of IPED users being male. It is possible that the large number of IPED users at Addaction Walsall will have resulted in a greater majority of male clients.
There was considerably less variation in outputs within the pharmacies sampled for the collection of cost data (see Appendix 3, Table 27). The pharmacies for which detailed data were collected reported between 1405 and 2316 visits per year. Pharmacies distributed between 18,518 and 36,100 needles. Two pharmacies distributed needles in ‘pick and mix’ form; the remaining pharmacies distributed needles in pack form only.
Finally, the three ‘other’ modalities distributed a wide range of needles – between 6816 and 101,326 needles per year (see Appendix 3, Table 28). Although detailed information was not available in the out-of-hours pharmacy or the drop-in centre on the breakdown of clients using either opioid and IPEDs, based on feedback from the sites we assumed that 100% of clients at these two sites were opioid users. The outreach service saw a greater mix of opioid/IPED users, with 72% of clients using opioids and 28% of clients using IPEDs. The outreach service saw mostly male clients; this imbalance was more exaggerated among IPED users (at 98% male) than opioid users (84% male).
Needle and syringe programme costs
Total costs
Total annual costs for the distribution of needles to all users (of both opioids and IPEDs) at fixed sites ranged from £25,613 to £65,630 per year, depending on the different sizes and reaches of the different fixed sites (Table 7). Pharmacies saw much less variation in total costs, ranging from £6815 to £10,690 per annum. Total annual costs for the out-of-hours pharmacy in Walsall were slightly less than the total costs for day pharmacies, at £5235. The costs for the distribution of needles using the mobile outreach service in Bristol were £32,887. Total costs for the drop-in centre in Walsall (Hi’s ‘n’ Lows) were lowest, at £2138.
| Site | Total annual cost (£) | Total fixed costs (£) | Total variable costs (£) | Total opioid cost (£) | Unit cost per opioid needle (£) | Unit cost per opioid client (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed site | ||||||
| BDP | 55,854.41 | 12,229.50 | 43,624.91 | 51,860.77 | 0.21 | 68.69 |
| CAIR Scotland | 65,630.81 | 5859.49 | 59,771.32 | 60,285.41 | 1.65 | 86.49 |
| Addaction Walsall | 25,613.22 | 1347.35 | 24,265.87 | 23,584.95 | 0.37 | 124.13 |
| Other | ||||||
| Out-of-hours pharmacy (Walsall) | 5235.09 | 519.79 | 4715.30 | 5235.09 | 0.77 | 24.58 |
| Outreach service (Bristol) | 32,887.50 | 536.63 | 32,350.87 | 22,361.89 | 0.24 | 78.19 |
| Drop-in centre (Walsall) | 2138.19 | 421.68 | 1716.51 | 2138.19 | 0.27 | 19.01 |
| Pharmacy | ||||||
| Pharmacy 1 (Bristol) | 8541.67 | 860.31 | 7681.36 | 9802.99 | 0.31 | 48.81 |
| Pharmacy 2 (Bristol) | 10,276.01 | 1262.25 | 9013.76 | 11,171.30 | 0.29 | 48.36 |
| Pharmacy 3 (Dundee) | 6814.59 | 901.52 | 5913.07 | 6814.59 | 0.31 | 23.74 |
| Pharmacy 4 (Dundee) | 9019.88 | 2449.12 | 6570.76 | 9019.88 | 0.37 | 31.15 |
| Pharmacy 5 (Walsall) | 10,690.48 | 650.80 | 10,039.68 | 10,690.48 | 0.58 | 50.91 |
| Pharmacy 6 (Walsall) | 7506.43 | 443.77 | 7062.66 | 7506.43 | 0.43 | 36.27 |
The primary cost driver in most settings was the cost of supplies; this accounted for an average of 60% of total costs across sites (range 23–80%) (Figure 15). Supplies costs for the out-of-hours pharmacy were less than those for day pharmacies, owing to the fact that this pharmacy distributed only one-hit kits, whereas the remaining pharmacies all distributed packs of 5, 10 or 20 needles during the costing period. This was followed in most cases by administrative and overhead costs, which accounted for 6–45% of total costs. Mobile outreach service costs were largely driven by transport costs, making up 47% of total costs.
FIGURE 15.
Cost drivers as a proportion of total costs.
Table 7 shows the fixed and variable costs per site, and the total cost for needle distribution to non-IPED users at each site (methods for this estimation are described previously; see Methods). The total opioid cost varied from £23,584 at Addaction Walsall to £60,285 at CAIR Scotland, and from £6815 at Pharmacy 3 in Dundee to £10,690 at Pharmacy 5, also in Dundee.
The unit cost per opioid needle distributed varied from £0.21 to £1.65, and the unit cost per non-IPED client (annually) varied from £19.01 to £124.13. There was no consistent ranking across sites in terms of unit costs; sites that had high unit costs per client did not necessarily also have high costs per needle, and vice versa.
City-level costs: non-IPED users
Table 8 shows estimates of the total number of needles distributed to non-IPED users at the city level, total fixed costs and average variable costs per needle, and estimated total annual costs for needle distribution to non-IPED users by mode of distribution. Bristol and Walsall spent proportionally more on pharmacies (68% and 69% of total city-wide costs, respectively) than on fixed-site distribution (22% and 24% of total city-wide costs, respectively). In contrast, Dundee spent 58% of total city-wide costs on fixed-site distribution, and only 42% of total city-wide costs on pharmacy distribution. Pharmacies in all three cities distributed the majority of needles; pharmacies accounted for 59%, 73% and 66% of total citywide needle distribution in Bristol, Dundee and Walsall, respectively. The fixed site in Dundee had the highest average variable cost per opioid needle at £1.49. The lowest cost per needle was observed at the fixed site in Bristol, at £0.16 per needle.
| City and site type | Total needles | Total fixed costs (£) | Average variable cost per needle (£) | Total cost (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bristol | ||||
| Fixed site | 252,039 | 12,229.50 | 0.16 | 51,861 |
| Pharmacies (n = 25) | 495,500 | 28,392.32 | 0.26 | 157,894 |
| Other | 92,171 | 536.63 | 0.24 | 22,362 |
| Total citywide | 839,710 | 41,158.44 | 0.23 | 232,117 |
| Dundee | ||||
| Fixed site | 36,455 | 5859.49 | 1.49 | 60,285 |
| Pharmacies (n = 5) | 100,604 | 3880.79 | 0.41 | 44,210 |
| Other | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Total citywide | 137,059 | 9740.28 | 0.69 | 104,496 |
| Walsall | ||||
| Fixed site | 63,644 | 1347.35 | 0.35 | 23,585 |
| Pharmacies (n = 12) | 151,460 | 17,357.32 | 0.46 | 67,690 |
| Other | 14,628 | 941.47 | 0.34 | 7373 |
| Total citywide | 229,732 | 19,646.14 | 0.35 | 98,649 |
Total city-wide costs for distribution to non-IPED users varied from £104,496 in Dundee to £232,117 in Bristol. Table 9 presents the total number of needles and total costs distributed compared with the total opioid injecting population in 2014, as predicted by the impact model. Looking at the total costs incurred in each city compared with the 2014 population size estimates included in the cost-effectiveness model, the amount of investment per person injecting non-IPEDs varied across cities (see Table 9). Bristol spent between £89 and £126 annually per person in the total non-IPED injecting population citywide, whereas Dundee spent £127–155 per person and Walsall spent £60–86 per person. The variation in investment at the city level is to some extent a reflection of varying coverage and intensity of interaction. Walsall distributed an average of 12 needles per visit but had the lowest number of visits per user overall in the city (12–17 visits per person in the injecting population citywide). In comparison, Dundee distributed an average of only 10 needles per visit, but saw clients much more frequently (17–20 visits per person). Finally, Bristol had between 13 and 18 visits per person citywide, but distributed an average of 26 needles per visit.
| City | Total number of needles | Average variable cost per opioid needle (£) | Total cost (£) | Population size | Visits per user | Cost per user (£) | Needles per user |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bristol | 883,524 | 0.23 | 232,116.78 | 1847–2595 | 13–18 | £89.45–125.67 | 340–478 |
| Dundee | 150,790 | 0.69 | 104,495.75 | 675–825 | 17–20 | £126.66–154.81 | 183–223 |
| Walsall | 245,002 | 0.35 | 98,649.03 | 1144–1646 | 12–17 | £59.93–86.23 | 149–214 |
Uncertainty analysis
Figure 16 provides an illustration of our univariate and multivariate uncertainty analyses for the NSP costing, showing the impact of varying each parameter for which there was uncertainty on the estimated unit cost per opioid needle. The parameter with the greatest effect on costs was that of equipment wastage; this is to be expected, as injecting equipment is the primary cost driver at most sites. Similarly, varying assumptions of the total number of ‘one-hit kits’ distributed per client at the out-of-hours pharmacy impacted the cost per needle substantially. Varying all parameters simultaneously gave a relatively wide estimate of unit costs per needle. The out-of-hours pharmacy was most sensitive to assumptions, with the unit cost per needle varying between –229% and +56% of the base-case cost in the multivariate sensitivity analysis.
FIGURE 16.
Needle and syringe programme costing uncertainty analysis.

Conclusions
We observed a degree of variation in costs across the three different commissioning areas evaluated, with variation in cost and outputs being observed across fixed sites and pharmacies. This was due to substantial variation in the set-up of NSP services. There is no ‘standard’ for NSP administration in the UK and, as such, each setting had different types of services, with different degrees of interaction with opioid users. Although cities varied in their modality of focus (i.e. pharmacy vs. fixed site), there was not a clear correlation between the primary modality though which needles were distributed in the city and the estimated cost per opioid user citywide.
Some variation was also due to case mix across the three cities. Addaction Walsall handled a larger number of IPED users who made very few visits each. This increased the fixed costs, resulting in a greater cost per opioid client. However, providing needles to IPED users did not necessarily increase the unit cost per opioid needle distributed; for example, Addaction Walsall distributed a large number of needles to opioid users, so the unit cost per opioid needle was relatively small.
The difference in costs observed between cities is likely to be driven partly by the type of needle distribution and ease of access to needles for people injecting drugs. We observed a large variation in the number of visits per user across cities and in the number of needles distributed at each visit. The variation observed, however, should be taken in the context of the different characteristics of the injecting population in each setting and not necessarily reduced efficiency in distribution. A higher number of visits per person in the injecting population citywide did appear to increase the costs of distribution; however, an increase in the level of investment per user citywide did not necessarily lead to reduced cost-effectiveness. In fact, the city with the greatest investment per user (Dundee) also saw the greatest savings as a result of implementing NSPs in the long term.
Limitations
The primary outcome of interest for this study is needle exchange for the prevention of HCV infection transmission; we therefore include only those costs and benefits that are relevant to this outcome in this costing study. We do not include any costs or benefits from other engagement programmes as delivered by the fixed sites and the peer-led service, such as one-to-one support, sexual health services, legal advocacy, etc. A larger number of visits per person in the injecting population may be necessary for these benefits; further research on the impact of these services is required in order to come to any recommendation on the optimal frequency of visits for injecting populations. These additional services are also likely to bring in more clients to the needle exchange. This may especially be the case for women, who might access sexual health-related services at the sites.
We also do not estimate the costs for the clean-up of drug-related litter, which can also be a substantial investment, and without which some councils would not politically be able to continue the provision of needle exchange. Drug-related litter is a key reason for implementing the distribution of ‘one-hit kits’ in some pharmacies, including the out-of-hours pharmacy, as there have been a number of discarded unused needles found in some study sites. Councils may need to consider the additional costs of litter pick-up schemes; this can vary widely depending on the number of staff employed and the size of the city. In one city, we estimated the salary costs for litter pickup to be approximately £4064 per year, not including transport and equipment costs. In another (larger) city, the overall costs of a dedicated sex- and drug-related litter pickup scheme are reported to be £80,000 per year.
Our analysis also does not consider any potential impact of the prevention of HCV cases in people injecting IPEDs, and excludes variable costs encountered by NSPs in providing needles and syringes for IPED use. Research from Australia indicates that IPED users are at some, albeit reduced, risk of HCV transmission. 85
Finally, we encountered a lack of detailed information on the client mix receiving needle exchange services through pharmacies and we could not obtain any estimates on the relative proportion of IPED to opioid injectors accessing pharmacy needle exchanges. Moreover, we could not find information on male-to-female ratios in pharmacies. Feedback from pharmacies and fixed sites during the costing process indicated that IPED users rarely access pharmacies and that the proportion of opioid visits to pharmacies is likely to be close to 100%.
All findings were presented to each site mid-way through the project, when results were presented and plausibility was discussed. Permission was sought to present the potentially sensitive nature of the findings. It was agreed not to publish the costings separately but to present these alongside cost-effectiveness analyses in any public dissemination or peer-reviewed output.
Chapter 5 Impact modelling
Introduction
Previous modelling for the UK has shown that OST and NSP is likely to have had a large impact on reducing HCV infection prevalence in the past, whereas further scaling up of these interventions will have only a modest effect on HCV infection prevalence. 86 However, this analysis did not estimate the current ongoing impact of NSPs and how that may vary in specific UK settings, or assess the impact of scaling up OST and NSP in terms of HCV infection incidence and HCV infections averted.
The prevalence of HCV infections and the coverage of harm reduction interventions such as NSPs and OST varies across the UK,16,20,39,44,70,73,87–90 and although the coverage of OST has increased in the past 10 years, the level of high-coverage NSPs has remained relatively constant. 70 In this chapter, a HCV infection transmission and progression model, incorporating new evidence on intervention effectiveness, is used to assess the impact of current levels of OST and NSP on HCV infection prevalence, incidence and HCV-related morbidity among current and ex-injecting drug users in three UK settings, and the probable impact of scaling up NSP coverage.
Methods
Model description
We developed a dynamic ordinary differential equation model of HCV infection transmission and disease progression among PWID and ex-injecting drug users. The model simulates the movement of PWID through different injecting durations, intervention, risk and HCV infection disease states, and also follows them after they have ceased injecting to capture HCV morbidity outcomes.
Stratifications by injecting duration are included in the model to capture higher rates of injecting cessation during the first few years of injecting,91 and the heightened level of HCV infection acquisition risk among recently initiated PWID. 20,92 There are four injecting duration categories: < 3 years, ≥ 3 years to < 10 years, ≥ 10 years and ex-injecting drug users. All PWID enter the model as recently initiated PWID (< 3 years injecting category) at a constant rate θ, and then transition to non-recent PWID (at rate 1/3 year–1) and then to long-term PWID (at a rate of 1/7 year–1 from the non-recent PWID). Each of these categories also has specific cessation rates of injecting, which results in users entering the ex-injecting drug user class, as well as death rates that vary by injecting duration, giving a total proportion of PWID leaving the current injector category, µi. (Figure 17 shows the schematic for this aspect of the model structure. Ex-injecting drug users are also stratified by the same infection and disease progression states so that morbidity benefits can be tracked.)
FIGURE 17.
Schematic of injecting duration and infection components of model. (a) Injectors cease injecting (cessation or death) at rate µi, where i = 1, 2 or 3 for recent, non-recent and long-term injectors, respectively. Injecting duration is modelled in three categories with progression at rate τi, where i = 1 or 2 for recent and non-recent injectors, respectively; (b) schematic of the intervention component of the model. It is assumed that the recruitment rates β and η are independent of the current intervention state; and (c) schematic of disease progression component of the model. Each of the disease states is stratified by injecting duration, n; risk category, m; OST category, i; and NSP category, j. Progression through the disease states is by a rate determined by the current disease state, as are disease-related death rates. In addition to current injectors, ex-injecting drug users are followed through the model when they cease injecting with an identical pathway, except that reinfection is excluded. All states have a cessation rate from injecting and a background death rate that is not disease related. Reinfection can occur at any stage but these lines are not shown after compensated cirrhosis. C, chronically infected; DC, decompensated cirrhosis; F0, F1, F2, F3, chronic infection states; F4, compensated cirrhosis; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; LT, liver transplant; PLT, post liver transplant; S, susceptible.
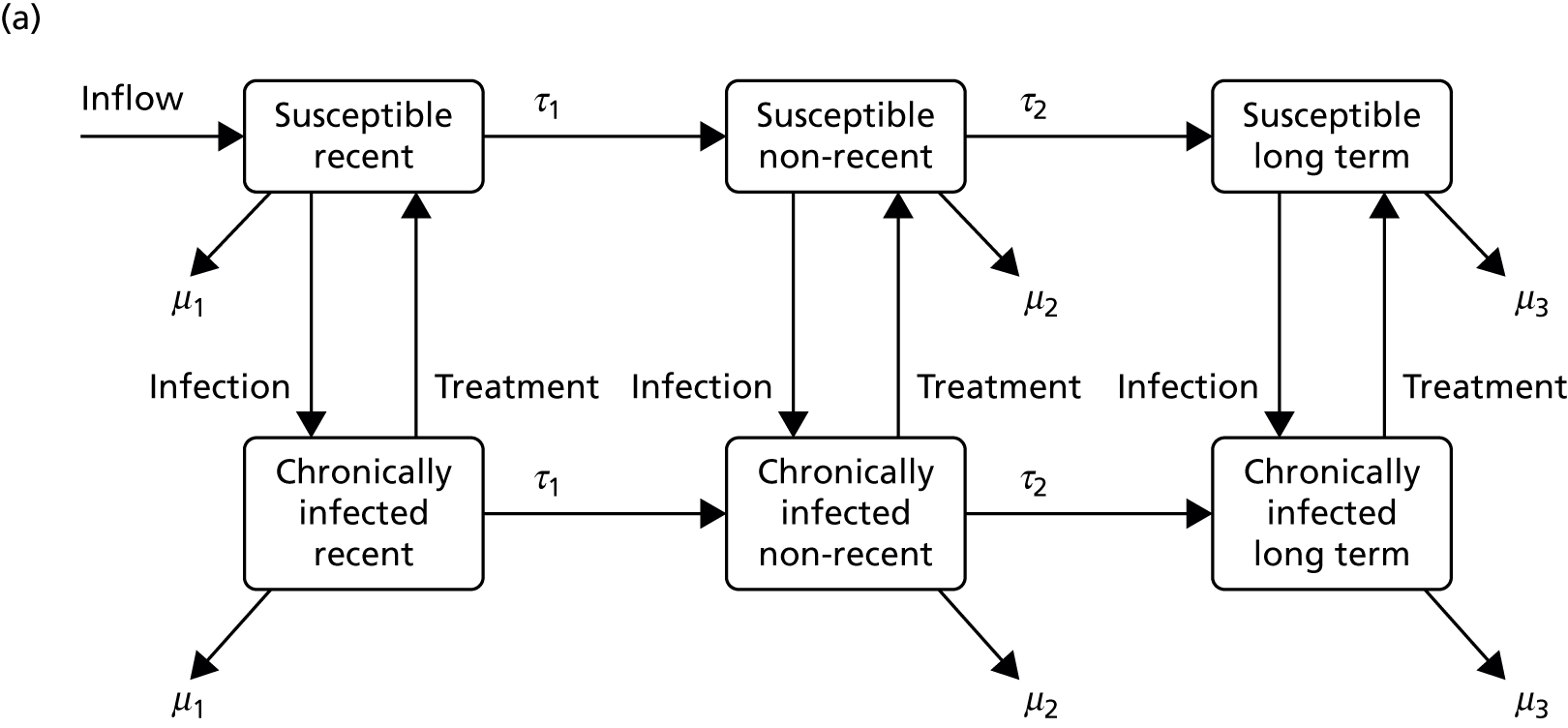
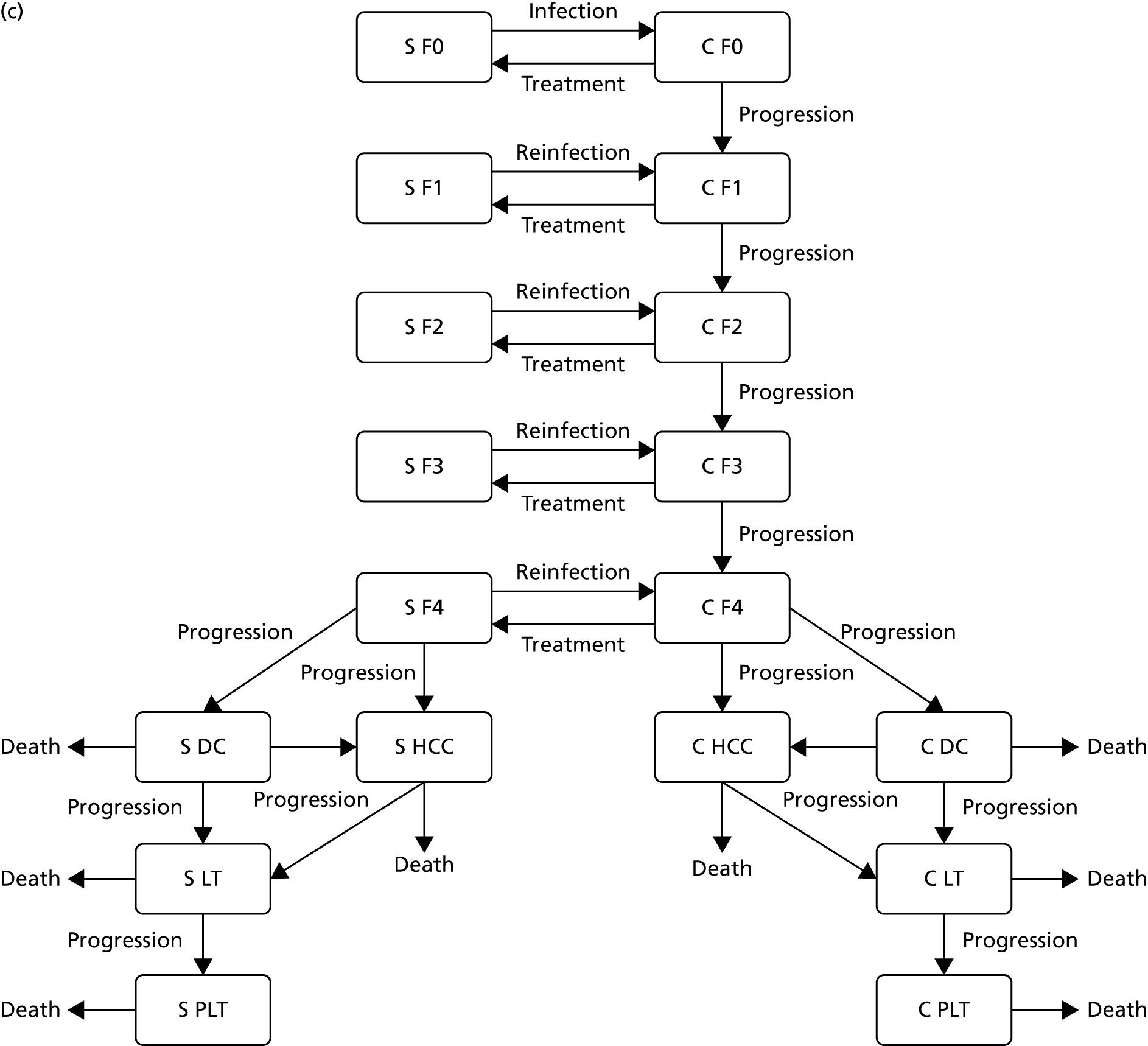
People who inject drugs are also tracked through different intervention states: no intervention, on OST only, > 100% NSP only, and on both OST and > 100% NSP. When PWID start injecting they are assumed to be in the ‘no intervention’ state. Recruitment on to OST and > 100% NSP occurs at per capita rates β and η, respectively, with both being assumed to be independent of current risk state for simplicity and lack of data. The rates of leaving OST and > 100% NSP are γ and κ, respectively. (See Figure 17b for the schematic for this component of the model structure.)
The model is further stratified by high and low injecting risk, with high-risk behaviours being defined by characteristics that have been shown to increase the risk of HCV infection acquisition among PWID in the UK. High risk is defined as being homeless and/or a crack cocaine injector, and low risk is defined as being neither homeless nor a crack cocaine injector. A proportion of individuals, ϕ, enter the model in the high-risk category. Movement from the low- to the high-risk category and vice versa occurs at per capita rates σ and ζ, respectively.
All PWID enter the model as susceptible individuals and become infected at a per capita rate, (λn,mi,j) or force of infection, which depends on the intervention state, injecting duration category and risk category of the individual, as well as the prevalence of infection. The force of infection for each susceptible state is defined by the relative risk in that state, such that infectivity and susceptibility are multiplied by the following factors: Γ, Π, B if the injecting drug user is on OST, ≥ 100% NSP or both, respectively; X1 and X2 if the injecting drug user is a recent injector or non-recent injector, respectively; and Ξ if the injecting drug user is a high-risk individual. Because assortative mixing has been shown to have little effect on transmission when there is movement between high- and low-risk groups, we do not include it here. 86 In addition, evidence from Bristol88 suggests that there is little assortative mixing by injecting duration, so we assumed random mixing between all categories. For this, the chance of an injecting drug user having a transmission event with an injecting drug user in a specific risk category is assumed to be proportional to the overall transmission risk of PWID in that state.
Once infected, a proportion of newly infected PWID, δ, spontaneously clear the infection and remain in the susceptible category, and the remainder enter the chronically infected category (ln,mi,j) and remain infected until they die or are treated. The progression of HCV infection for any PWID who enters the chronically infected PWID category is modelled as shown in Figure 17c. The disease states modelled are METAVIR stages F0, F1, F2, F3 (chronically infected), F4 (compensated cirrhosis), decompensated cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), liver transplant and post liver transplant. Individuals progress from F0 through each METAVIR stage to compensated cirrhosis, from which they progress either to decompensated cirrhosis or to HCC. Individuals with decompensated cirrhosis can then progress to HCC or can be considered for liver transplant (as can individuals with HCC), which, if successful, results in the individual moving to the post liver-transplant stage. HCV disease-related death occurs from the decompensated cirrhosis, HCC, liver transplant and post liver-transplant stages with disease stage-specific death rates.
Treatment of HCV infection is allowed only in the F0–F3 and compensated cirrhosis (F4) stages, as it is unclear whether or not treatment in later disease stages is beneficial. 93 A number of PWID, Φ, are assumed to be treated each year and on treatment a proportion, α, achieve a sustained virological response (SVR) and re-enter the susceptible non-infectious category. Treatment of ex-injecting drug users occurs at per capita rate r, with the same proportion, α, achieving SVR. Those who do not attain SVR remain in the infected category and are eligible for retreatment. This simplifying assumption was made based on the influx of new treatment regimes becoming available. On successful treatment, individuals enter the respective susceptible category with the same disease stage (see Figure 17c). Disease progression still occurs among these individuals if they have compensated cirrhosis, but at a slower rate. We assume no further disease progression if treatment is successful in the F0–F3 chronically infected non-cirrhotic stages. 94,95 The disease progression of ex-injecting drug users is also tracked to assess the long-term impact that interventions will have on this subpopulation. It is assumed that ex-injecting drug users who are susceptible or who have been successfully treated cannot be reinfected.
Model parameterisation
The model parameters can be found in Table 10. The model was calibrated to the following parameters estimated from survey data: HCV infection prevalence, coverage of OST and NSP, proportion of PWID with high-risk behaviour and injecting duration distribution of PWID over time.
| Parameter | Symbol | Value/range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epidemiological and demographic parameters | |||
| Number of new injectors per year | θ | Fitted to obtain population sizes | See Appendix 4, Table 29 and supporting information |
| Combined death and cessation rates per year | µi | Fitted to obtain injecting duration profiles for each setting | See Appendix 4, Table 29 and supporting information |
| Infection rate per year | π | Fitted to obtain HCV infection prevalence required in each setting | See Appendix 4, Table 29 and supporting information |
| Proportion of new infections that spontaneously clear | δ | Sampled from uniform distribution (0.22–0.29) | Micallef et al., 200696 |
| Leaving rate per year from high- to low-risk behaviour | ζ | Sampled range (0.6761–1.617) | Data from cohort study97 found that 78 out of 145 injectors were no longer homeless after 8 months. Transition probability sampled from beta distribution α = 78 and β = 67 and converted to instantaneous rate |
| Recruitment rate per year from low- to high-risk behaviour | σ | Fitted to obtain required high-risk proportions in each setting | See Appendix 4, Table 29 and supporting information |
| Intervention-related parameters | |||
| Leaving rate per year off OST | γ | 1–3 | Duration on OST was 8 months (4–12 months) in a cohort of PWID in the UK98 |
| Leaving rate per year off high-coverage NSP | κ | 0.37–0.77 | Welsh cohort study: 61% of PWID were still > 100% NSP after 1 year39 |
| Recruitment rate per year on OST | β | Fitted to obtain required OST coverage proportions in each setting | See Appendix 4, Table 29 and supporting information |
| Recruitment rate per year on high-coverage NSP | η | Fitted to obtain required high NSP coverage proportions in each setting | See Appendix 4, Table 29 and supporting information |
| Proportion of treatments achieving SVR prior to 2015 | α | Sampled from uniform distribution (0.3992–0.6653) | Weighted mean of pooled intention to treat SVR for genotypes 1 and 2/3 taken from treatment data for PWID in the UK99 |
| Proportion of treatments achieving SVR post 2015 | α | Sampled from uniform distribution (0.859–0.915) | Harris et al., 2014100 |
| Proportion of infected ex-injecting drug users treated in chronic and compensated cirrhosis stages | r | 0.03 | Harris et al., 2014100 |
| Number of PWID treated per year | Φ | Bristol: 18 Dundee: 34 (2009–15) and 40 (2015 onwards) Walsall: 2 |
Number of HCV infection treatments in 2011. Assumed treatment of PWID commenced in 2009.99 More recent values for Dundee from correspondence with John Dillon (John Dillon, University of Dundee, 2016, personal communication). Walsall value assumed to be same rate per infected PWID as Bristol |
| Relative transmission risk parameters | |||
| Risk associated with being on OST only | Γ | 0.41 (0.22–0.75) sampled from log-normal distribution | OR and 95% CI from pooled analysis (see Chapter 2) |
| Risk associated with being on high-coverage NSP only | Π | 0.59 (0.36–0.96) sampled from log-normal distribution | OR and 95% CI from pooled analysis (see Chapter 2) |
| Risk associated with being on both OST and high-coverage NSP | Γ × Π | 0.26 (0.09–0.64) | Calculated as product of risk associated with being solely on OST or NSP. Compares well with estimate for systematic review 0.29 (0.13–0.65) |
| Risk associated with being a recent injector compared with being a long-term injector | χ1 | 1.53 (0.93–2.52) sampled from log-normal distribution | OR from pooled analysis (Lucy Platt, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, 2015, personal communication) |
| Risk associated with being in the high-risk category | Ξ | For Dundee: 2.13 (1.40–3.24) | OR from pooled analysis. For Dundee, the OR is just for homelessness because there is little crack cocaine injection, whereas it is for crack cocaine injection or homelessness for Bristol and Walsall |
| For Bristol and Walsall: 2.75 (1.97–4.22) | |||
| Sampled from log-normal distribution | |||
| Disease progression parameters | |||
| Yearly progression rate from F0 to F1 | ρ 1 | 0.529–0.2095 sampled from normal distribution | PWID-specific instantaneous rates from Smith et al., 2015101 |
| Yearly progression rate from F1 to F2 | ρ 2 | 0.0216–0.1013 sampled from normal distribution | |
| Yearly progression rate from F2 to F3 | ρ 3 | 0.0450–0.1145 sampled from normal distribution | |
| Yearly progression rate from F3 to compensated cirrhosis | ρ 4 | 0.0513–0.1838 sampled from normal distribution | |
| Yearly progression rate from compensated cirrhosis to decompensated cirrhosis | ρ 5 | 0.0166–0.0921 | Instantaneous rates calculated from sampled beta distributions of transition probabilities in Shepherd et al., 200793 |
| Yearly progression rate from compensated cirrhosis or decompensated cirrhosis to HCC | ρ 6 | 0.0003–0.0684 | |
| Yearly progression rate from decompensated cirrhosis or HCC to liver transplant | ρ 7 | 0.0062–0.0962 | |
| Yearly progression rate from liver transplant to post liver transplant | ρ 8 | 1.0423–2.4412 | |
| Decompensated cirrhosis-related death rate per year | d 9 | 0.1063–0.1842 | |
| HCC-related death rate per year | d 7 | 0.3904–0.7697 | |
| Liver transplant-related death rate per year | d 8 | 0.0911–0.4348 | |
| Post liver transplant-related death rate per year | d 6 | 0.0280–0.1016 | |
| Relative risk for progression rate from compensated to decompensated cirrhosis (ρ5) following SVR | e 5 | 0.07 (95% CI 0.03 to 0.2) | Sampled from transformed log-normal distribution102 |
| Relative risk for progression rate from compensated cirrhosis to HCC (ρ5) following SVR | e 6 | 0.23 (95% CI 0.16 to 0.35) | Sampled from transformed log-normal distribution95 |
Odds ratio effect estimates for the degree to which the risk of HCV infection transmission is modified when an injecting drug user is on OST or there is ≥ 100% NSPs in the high-risk category or for different injecting durations were taken from a pooled analysis of UK and Australian data (see Chapter 2). The OR combined effect of OST and ≥ 100% NSP was calculated by multiplying together the effects estimates for OST and ≥ 100% NSP alone, to reflect the assumption that both interventions together would be more beneficial than alone, giving a range comparable to that from the systematic review (see Chapter 1).
Hepatitis C treatment was assumed to occur in all settings since 2009 at context-specific rates based on recent data from those settings, except for Walsall where data from Bristol was used because of a lack of data from that setting. Before 2015, we estimated the SVR rate for pegylated interferon and ribavirin from a recent study of PWID in the UK. 99 After 2015, we assumed that treatment would involve using the new direct-acting antiviral (DAA) drugs, and so assumed a high SVR rate of 90% for all genotypes. 103
Instantaneous HCV infection disease stage progression rates were calculated from a recent meta-analysis of PWID-specific progression probabilities to compensated cirrhosis101 and a systematic review of general progression probabilities for other disease stages,101 and, similarly, the spontaneous clearance probability came from a published meta-analysis. 96 Non-HCV-related death and injecting cessation were combined into one rate for each injecting duration strata, with the death rates being estimated from a cohort study of PWID in Scotland,91 and the cessation rates being estimated through fitting the model to the observed distribution of PWID by injecting duration.
The leaving rate from the high-risk category, characterised as homelessness or crack cocaine injection, came from two studies among PWID in the UK. 39,97 The leaving rates from NSP and OST came from a Welsh cohort study. 39 Conversely, the recruitment rates to these states were obtained through calibration.
Model calibration and uncertainty
The model was calibrated to data on PWID population size, historical coverage levels of OST and NSP, prevalence of high-risk behaviours (crack cocaine injection and homelessness), HCV infection prevalence and the distribution of injecting duration. These calibration data were collated from various sources (Appendix 4, Table 29 summarises the data used), including size estimation studies,104–107 three Bristol community surveys in 2004, 2006 and 2009,44,73,88,89 yearly UAMP surveys from 1991 (Bristol) or 2006 (Walsall) to 2014,70 and four surveys from NESI for Dundee from 2008 to 2014. 70 Data on incidence for Dundee (NESI) and Bristol (community survey 2009) were used for model validation as well as for prevalence data post 2006 for Bristol and Walsall (UAMP).
Model calibration was carried out in three steps with 1000 parameter sets obtained at each step:
-
population size and injecting duration fitting using a PWID demographic submodel without infection
-
NSP and OST coverage fitting using a submodel that includes HCV infection transmission but no disease progression
-
HCV infection prevalence fitting using the full model with disease progression.
Step 1
In Dundee, survey data70 suggested that the proportion of the PWID population in each injecting duration category was stable from 2008 to 2014, and so we assumed a constant population size estimated from unpublished data from Scotland. In Bristol and Walsall, size estimation data suggest that the PWID population has decreased by between 10% and 30% between 2009 and 2011. 104–106,108 Concurrently, survey data44,70,73,88,89 suggest that the proportion of PWID injecting for > 10 years has increased, whereas the proportion injecting for between 3 and 10 years has decreased (Figure 18). There has been little change in the proportion injecting for < 3 years. It was assumed that these changes were partly attributable to a decrease in the initiation rate of new injectors and a change in the cessation rates of non-recent and long-term injectors. We allowed for uncertainty around these parameters and estimated them by fitting the model to the population size and injecting duration profile (proportion of PWID in each injecting duration category) at two time points for Walsall and Bristol and one time point for Dundee. This fitting was done with a demographic submodel, which had only three injecting duration categories and no other stratification. We assumed that the PWID population size was at equilibrium initially (before 2004, 2006 and 2008 for Bristol, Walsall and Dundee, respectively). We sampled 1000 values for this ‘stable’ initial population size and the cessation rate from the recent injector category for each setting. For each of these 1000 parameter sets, the wide prior distributions for the cessation rates from non-recent and long-term injectors (see Appendix 4, Table 29) were then sampled, and for each sample the model was fit to the initial population size by calculating a suitable PWID recruitment rate, using the steady state equations for the demographic submodel (for more details, see Appendix 4). Parameter sets were retained if the resulting injecting duration profile lay within the ranges suggested from the data, otherwise the cessation rates were resampled. We then sampled 1000 estimates for the later population size in 2011 for Bristol and Walsall, as well as new cessation rates for non-recent and long-term injectors, and the PWID recruitment rate was recalibrated to fit to this new sampled population size for the 2011 data (for Bristol and Walsall only). This refitting of the demographic submodel was done using the Matlab release 2014b (The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA, USA) algorithm fzero applied to the analytic solution of the model with initial conditions from the first step of fitting. Parameter sets were retained if the resulting injecting duration profile lay within ranges suggested from data for the years 2004 and 2011 for Bristol and 2008 and 2011 for Walsall, otherwise the new cessation rates for this second step were resampled to obtain a fit to each of the first step parameter sets (1000 each for Bristol and Walsall).
FIGURE 18.
Graphs showing model fitting of the baseline scenarios in each setting. Error bars in black are data points from surveys, error bars in blue are the ranges used for model calibration (for NSP coverage this was the service provision estimate). (a) Bristol; (b) Walsall; and (c) Dundee.
Step 2
Coverage levels for PWID currently on OST have increased over the past 12 years. In Bristol, the proportion of PWID currently on OST increased from 40% in 200473 to 81% in 2009. 88 In Walsall, OST coverage increased from 40% in 2006 to 70% in 2009,70 and in Dundee it increased from 43% in 2008 to 72% in 2014. 87 Conversely, over this same time period, the proportion of PWID with > 100% NSP coverage remained stable in both Bristol (55%)70,73,88 and Walsall (38%),70 although it increased over time in Dundee from 41% in 2008 to 60% in 2014. 70 Modelled OST coverage levels for each city were calibrated to this coverage data by varying the recruitment rate onto each intervention. A service provision estimate of NSP coverage was calculated for each setting using data on needles distributed from the costings analysis (2014 data), population size (calculated from the model in 2014) and injecting frequency from survey data. Bootstrap samples of the mean injecting frequency were calculated for each setting using UAMP (Bristol and Walsall) and NESI (Dundee) data. In addition, the mean injecting frequency in Dundee has decreased from 717 injections per year in 2008 to 388 injections per year in 2014. Therefore, an estimate of NSP coverage was calculated for each time point. The average service provision estimates of NSP coverage were 56% and 28% in Bristol and Walsall, respectively, in 2014 and 27% and 49% in 2008 and 2014, respectively, for Dundee (see Appendix 4, Table 29 for more details). The recruitment rates were estimated using an intervention submodel that incorporated no onward disease progression, as these mechanisms have little effect on the coverage levels obtained. Using the Matlab fitting algorithm lsqnonlin, recruitment rates were found to fit the submodel to the initial and end-point coverage of each intervention (as shown in Appendix 4, Table 29), while assuming that coverage levels were quasi-stable. In the full model, the recruitment rates for the initial coverage level were first used to obtain initial conditions for the first time point for each city, and then the recruitment rate was gradually varied linearly between the two values to obtain the required increase in coverage for that city.
Survey data suggest that the prevalence of crack cocaine injecting and/or homelessness, our markers of high HCV infection transmission risk, have remained stable in Dundee (33% homeless) and Walsall (52% homeless or crack cocaine injection), whereas it has increased in Bristol from 75% in 2004 to 87% in 2014 (homeless or crack cocaine injection). We assumed that a proportion of injectors are high risk when they initiate injecting, which is consistent with available data. 97 The leaving rate from these high-risk categories was estimated from a cohort study on homelessness, which found that approximately two-thirds of homeless PWID are no longer homeless after 1 year. 97 This agrees with unpublished findings from a Welsh cohort study for both crack cocaine injecting and homelessness. 39,86 The leaving rate was sampled 1000 times and used for all three settings. The proportion of PWID that are high risk was also sampled 1000 times for each setting. The recruitment rates were then calculated for each parameter set using the steady-state solution of the high- and low-risk submodel (two variables). In Bristol, where the proportion of high-risk PWID has increased, we calculated a second recruitment rate for the second time point (2014) using the same method. For Bristol, the recruitment rate was gradually varied linearly to obtain the increase in the proportion of PWID that are high risk.
Step 3
The last step of the model calibration involved fitting the full model to the HCV infection prevalence data from each setting (sampled 1000 times from the ranges given in Appendix 4, Table 29). This incorporated the 1000 parameter sets from the previous model calibration steps, and involved calibrating the model’s infection rate using the lsqnonlin function in Matlab. The model was first fit to the initial prevalence estimate (sampled from the ranges given in Appendix 4, Table 29) in 2004, 2006 and 2008 for Bristol, Walsall and Dundee, respectively (see Figure 18 and Appendix 4, Table 29), while assuming that the epidemic was in a stable state at that time. For Walsall and Bristol, this one infection rate well captured the subsequent baseline epidemic dynamics (slightly increasing in Bristol and Walsall) and, therefore, no change in the infection rate was assumed after that point. The baseline transmission rates in Bristol and Walsall were comparable (0.07–0.21 and 0.09–0.22, respectively), whereas Dundee had a slightly higher baseline transmission risk (0.16–0.39). However, for Dundee, we needed to fit a second increased infection rate (0.36–0.94) to capture the increase in HCV infection prevalence from 2008 to 2014 (using the parameters from the first prevalence fitting step as the initial conditions). This suggests either that the epidemic was not stable in 2008 or that there has been a change in the risk profile of PWID in Dundee that is not fully captured by changes in intervention coverage or the prevalence of high-risk behaviours. Table 29 in Appendix 4 and Figure 18 show the model parameters that were fitted in the model.
Impact analysis
First, the model was used to estimate the impact of current intervention activities over the next 15 years, from 2016 to 2031. This included the impact of current coverage levels of OST, NSP and HCV infection treatment. To estimate the impact of each intervention, the baseline epidemic projections with these interventions incorporated were compared with what would happen if the effect of these interventions were removed from the start of 2016 (i.e. either the efficacy parameter for a specific intervention was set to one from 2016 or no additional PWID were HCV infection treated). Following this, we also assessed the detrimental impact of current levels of high-risk behaviours. This was evaluated in the same way over 15 years. The impact of each scenario was assessed in terms of the relative change in prevalence and incidence, and the relative change in the number of incident infections and the number of disease-related deaths. Specifically, we investigated how the epidemic in each setting would change from 2016 to 2031 if the following interventions or behaviours had no effect on HCV infection transmission rates:
-
> 100% NSP
-
OST intervention
-
> 100% NSP and OST intervention
-
HCV infection treatment of PWID
-
all high-risk behaviours.
Following this, we then considered the potential impact to 2031 of increasing the coverage of > 100% NSP from 2016 to 80% or 90% over the next 5 years.
Sensitivity analysis
The model calibration algorithm involved probabilistic sampling over a large number of the model parameters, and we fit the model across the full uncertainty of the calibration data. The different runs from this model calibration exercise were used to assess those parameters that effected the model projections most. We undertook a linear regression analysis of covariance109 to determine those parameter uncertainties that contribute most to uncertainty in the 15-year impact of current NSP coverage levels on the relative change in the number of infections. The proportion of each model outcome’s sum-of-squares contributed by each parameter was calculated to estimate the importance of individual parameters to the overall uncertainty.
Results
Baseline epidemic projections and model validation
In agreement with available recent HCV infection prevalence data up to 2014, we projected a slightly increasing HCV infection prevalence in Bristol and Walsall when fitting prevalence to only the first time point (2004 and 2006, respectively), as shown in Figure 19. The increasing HCV infection prevalence in Dundee was obtained by fitting the prevalence to two time points. The incidence of HCV infection calculated from the model in 2014 was used to validate the model and varies between the three settings, with the highest incidence in Dundee [16.8, 95% credible interval (CrI) 10.7 to 24.7 per 100 person-years], which agrees with incidence estimates from NESI (14.3, 95% CI 4.9 to 25.9 per 100 person-years). In Bristol, we project a lower HCV infection incidence of 6.9 (95% CrI 3.9 to 11.5) per 100 person-years, slightly lower than the most recent HCV infection incidence estimate from 2009 (10.0, 95% CI 9.7 to 14.0 per 100 person-years). 88 In Walsall, we project an even lower HCV infection incidence of 3.4 (95% CrI 1.7 to 6.5) per 100 person-years, corresponding to the low and decreasing prevalence in that setting. Unfortunately, no empirical estimates of HCV infection incidence exist for Walsall against which to compare these estimates.
FIGURE 19.
Impact of each intervention scenario on HCV infection prevalence and incidence in each setting. (a) Bristol incidence; (b) Bristol prevalence; (c) Walsall incidence; (d) Walsall prevalence; (e) Dundee incidence; and (f) Dundee prevalence. The solid line is the median of the baseline model scenario, with the shaded region representing the 95% CrIs around those projections. Error bars in black are data points and those in blue are the ranges used for calibration. py, person-years.
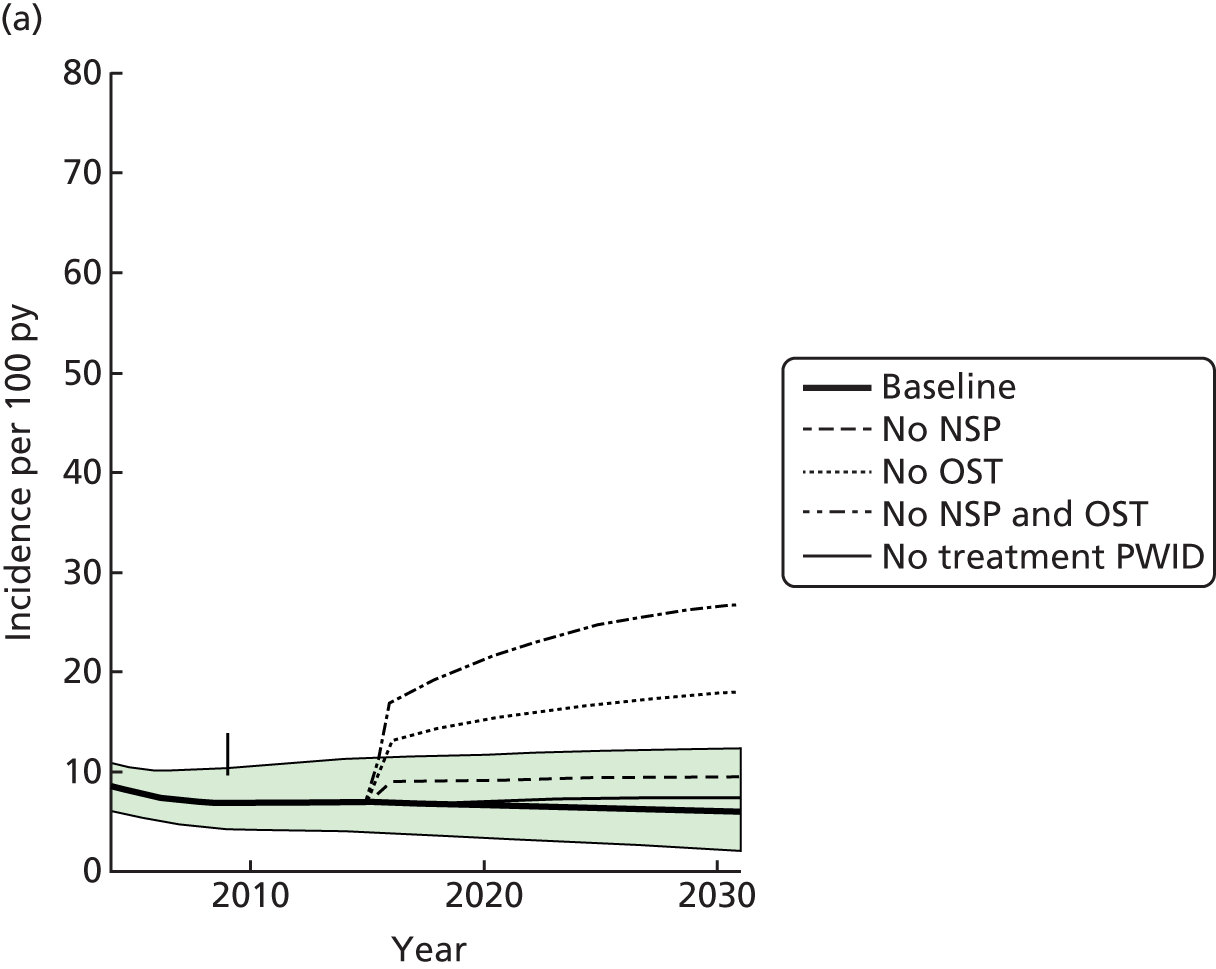
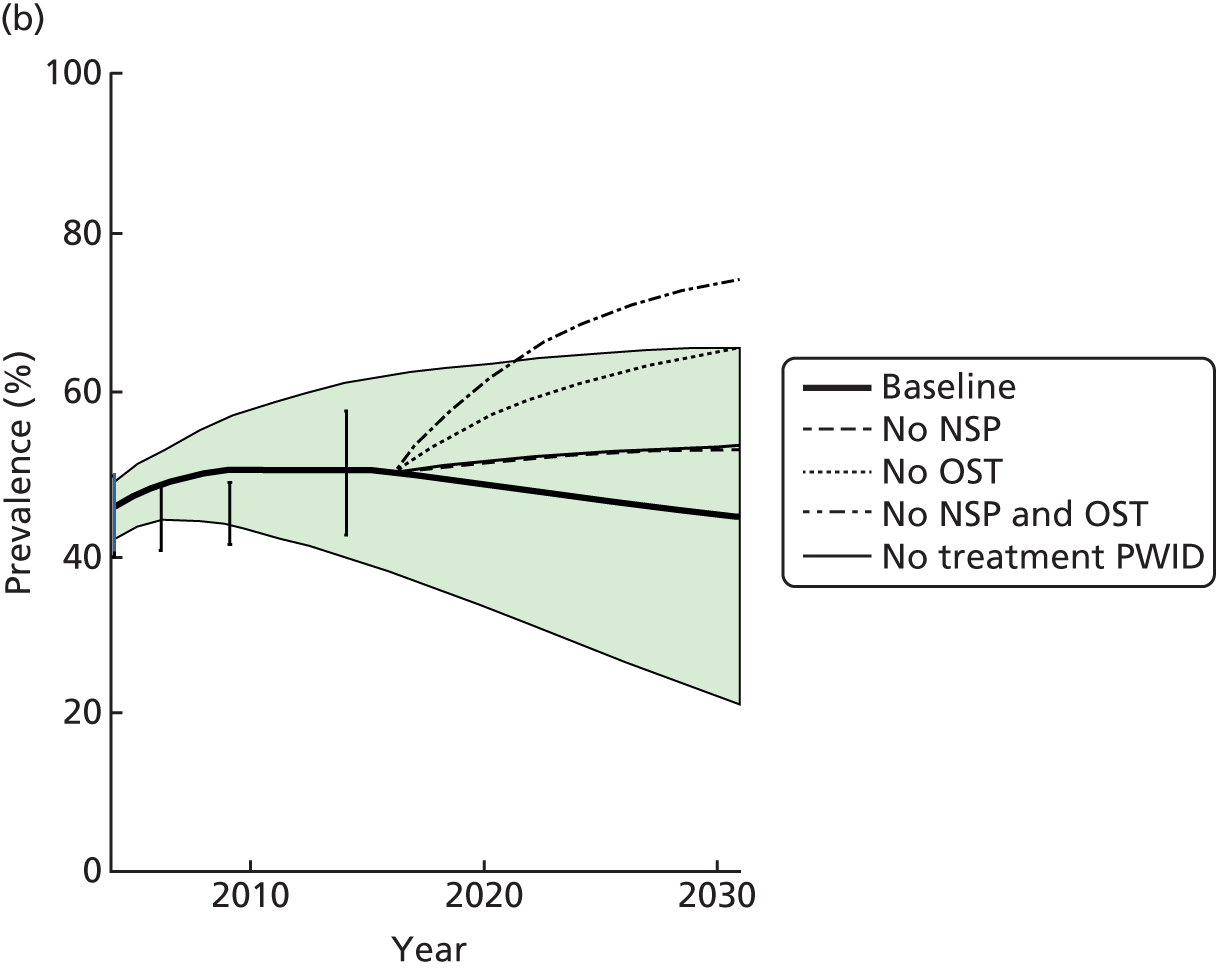
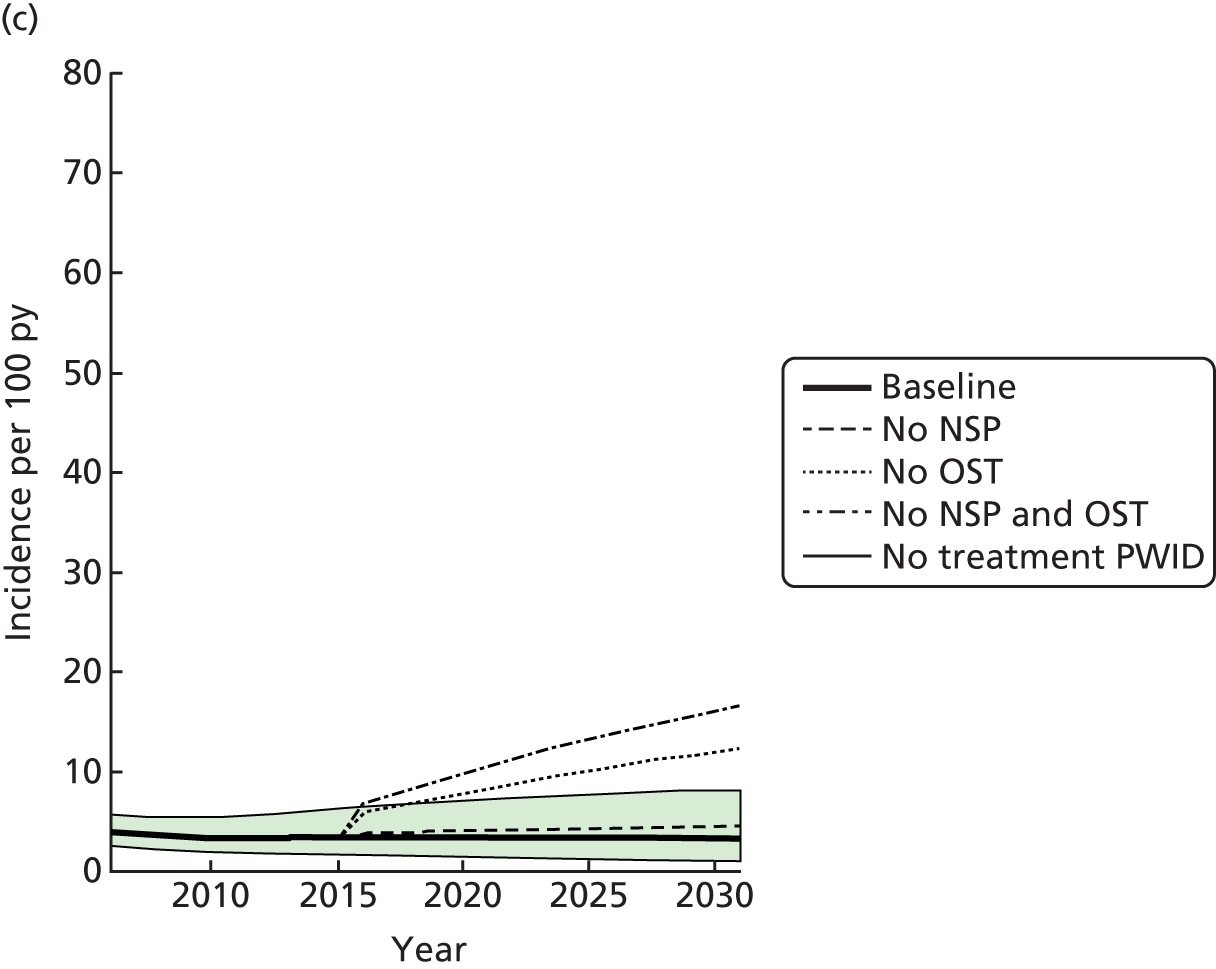
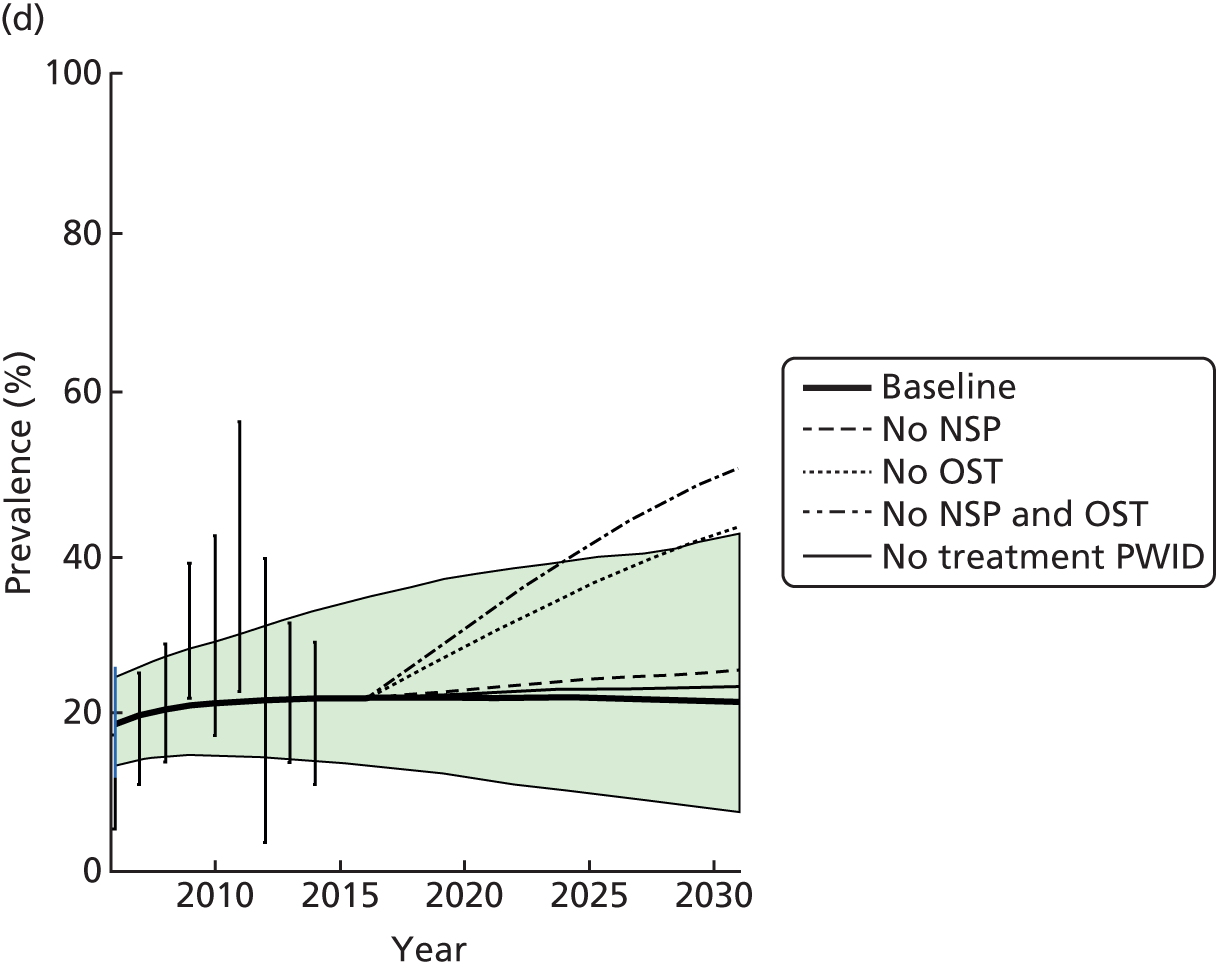
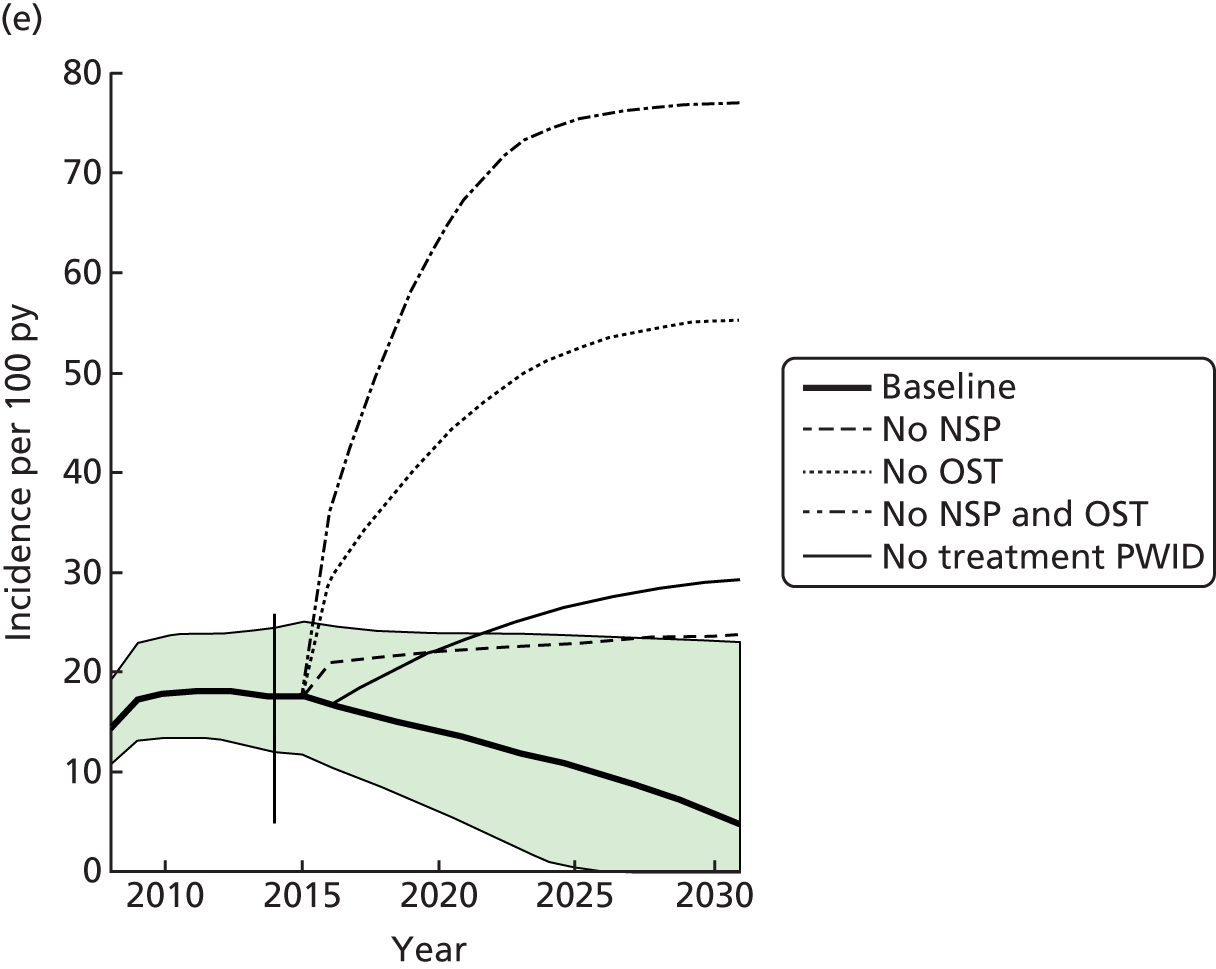
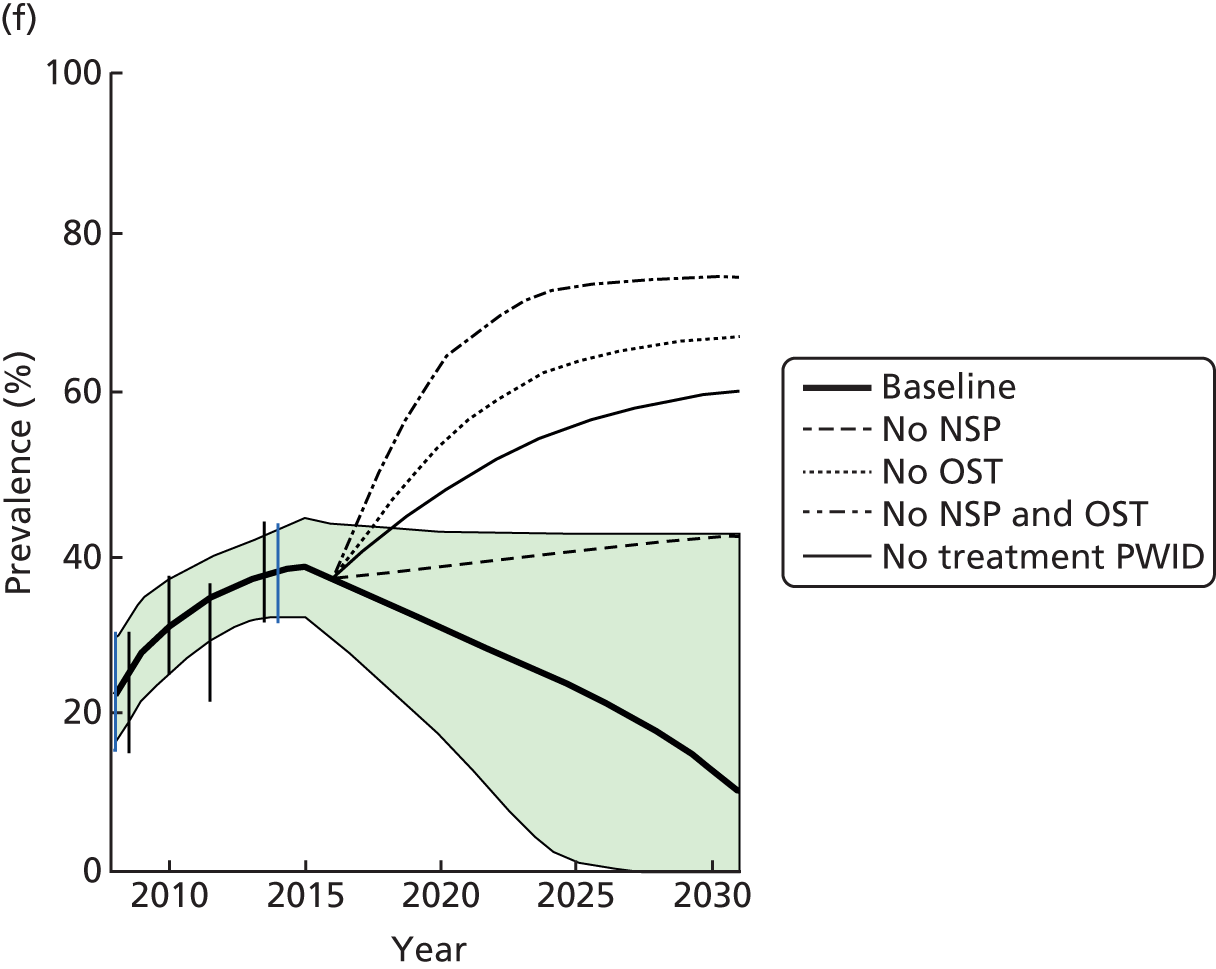
Over the period from 2016 to 2031, the model suggests that HCV infection prevalence will slightly decrease in Bristol and Walsall, and decrease markedly in Dundee from 36.9% (95% CrI 28.7% to 43.5%) to 10.1% (95% CrI 0.0% to 42.3%). The decreases in all settings are attributable to the use of more effective DAA treatment commencing in 2015, with the larger decrease in Dundee being attributable to treatment already being scaled up as part of a trial intervention. Over each year, the models project that 32 (95% CrI 21 to 43), 6 (95% CrI 1 to 11) and 14 (95% CrI 9 to 20) HCV-related deaths will occur among PWID and ex-injecting drug users in Bristol, Dundee and Walsall, respectively, with most (> 85%) of these deaths occurring among ex-injecting drug users. Baseline prevalence, incidence and disease-related mortality can be found in Table 11.
| Setting | Prevalence 2016 (%), median (95% CrI) | Prevalence 2031 (%), median (95% CrI) | Incidence 2016 per 100 person-years, median (95% CrI) | Incidence 2031 per 100 person-years, median (95% CrI) | Disease-related deaths per year 2016, median (95% CrI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bristol | 49.8 (37.4 to 62.2) | 44.5 (21.0 to 65.6) | 6.9 (3.9 to 11.5) | 6.1 (2.2 to 12.3) | 32 (21 to 44) |
| Walsall | 21.7 (13.4 to 34.2) | 21.2 (7.5 to 42.2) | 3.4 (1.7 to 6.5) | 4.8 (0 to 23.1) | 14 (9 to 20) |
| Dundee | 36.7 (29.2 to 43.6) | 10.2 (0.02 to 42.3) | 16.9 (10.7 to 24.7) | 3.3 (0.9 to 8.2) | 6 (1 to 11) |
Impact of existing interventions
Regardless of setting, removing either or both of NSP and OST would have a large detrimental impact on both prevalence and incidence in all three settings by 2031, as shown in Figure 19. As expected, removing both interventions has the biggest effect on the epidemics, with the model suggesting at least a 337% (range 337–1525% between settings) relative increase in incidence by 2031 compared with baseline 2031 levels, a 125% (range 125–166%) relative increase in the number of new HCV infections over the period 2016 to 2031 and a 35% (range 65–636%) relative increase in prevalence compared with baseline projections in all settings from 2016 to 2031. Following this, removing OST has the next biggest impact, resulting in at least a 196% (range 196–1034%) relative increase in incidence, an 86% (range 86–125%) increase in the number of HCV infections and a 46% (range 46–562%) relative increase in prevalence in 2031. The next biggest impact is removing NSP, which increases incidence by at least 35% (range 35–372%) and prevalence by at least 17% (range 17–275%). NSP has a smaller impact than OST because it has lower coverage in each setting and lower efficacy (NSP lowers transmission risk by 41% vs. 59% for OST) as suggested by our pooled analysis. Removing NSP still results in a large relative increase in the number of new HCV infections by 2031, with a 30% (95% CrI 7.0% to 67.0%) increase in Bristol, a 22% (95% CrI 6% to 40%) increase in Walsall and 59% (95% CrI 12% to 219%) increase in Dundee, as seen in Figure 20.
FIGURE 20.
Impact of removing NSP, OST, NSP and OST or treatment of PWID on the number of new infections from 2016 to 2031 for each setting. The box plots signify the uncertainty (the middle line is the median, the limits of the box are 25% and 75% percentiles, and the whiskers 2.5% and 97.5% percentiles).
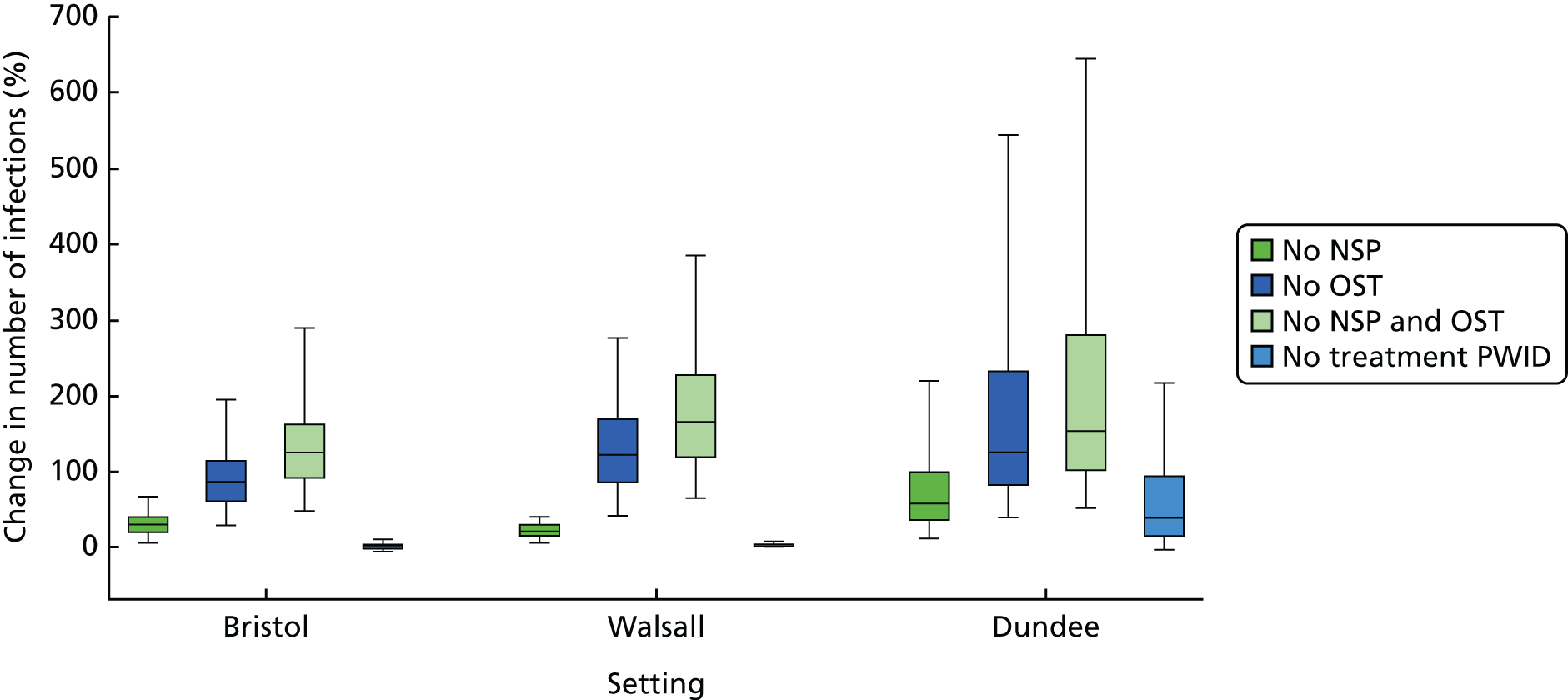
Across the cities, a greater relative impact on prevalence and incidence is seen by removing NSP and/or OST in Dundee, then Walsall and, finally, Bristol. Removing NSP and/or OST has the greatest impact in Dundee because HCV infection prevalence and incidence were otherwise decreasing to low levels by 2031, whereas removing the interventions causes prevalence to increase, as seen in Figure 19.
Removing treatment of PWID in each setting has similar impacts on prevalence and incidence to removing NSP, as seen in Figure 19. However, less impact is seen on the number of new infections, as seen in Figure 20. This is explained by treatments lowering incidence indirectly through reducing prevalence, as opposed to directly reducing the incidence of new infections, which is the case for NSP and OST.
The impact of current high-risk behaviours
When the increased transmission risk associated with homelessness and crack cocaine injecting (or homelessness only in Dundee) is removed, a decrease in incidence and prevalence of HCV infection occurs. The biggest relative decrease is seen in Dundee, where incidence decreases by 99% (95% CrI 86% to 100%) and the number of new infections decreases by 58% (95% CrI 29% to 77%) between 2016 and 2031 (Figure 21). Similarly, the number of new infections decreases by 59% (95% CrI 40% to 75%) in Walsall and 64% (95% CrI 45% to 78%) in Bristol. However, despite Bristol having the highest proportion (> 80%) of high-risk PWID, the smallest relative decrease in prevalence (35%, 95% CrI 22% to 53%) occurs here when we remove the elevated risk among high-risk PWID; this is compared with a 99% (95% CrI 69% to 99.7%) decrease in Dundee and a 45% (95% CrI 28% to 64%) decrease in Walsall. This could be due in part to the longer injecting duration predicted by the model in Bristol, with a median of 15 years injecting in Bristol compared with 8 years in Dundee and Walsall.
FIGURE 21.
Impact of removing transmission risk associated with high-risk behaviour on decreasing the number of new infections from 2016 to 2031 for each setting. The box plots signify the uncertainty (the middle line is the median, the limits of the box are the 25% and 75% percentiles, and the whiskers are the 2.5% and 97.5% percentiles).
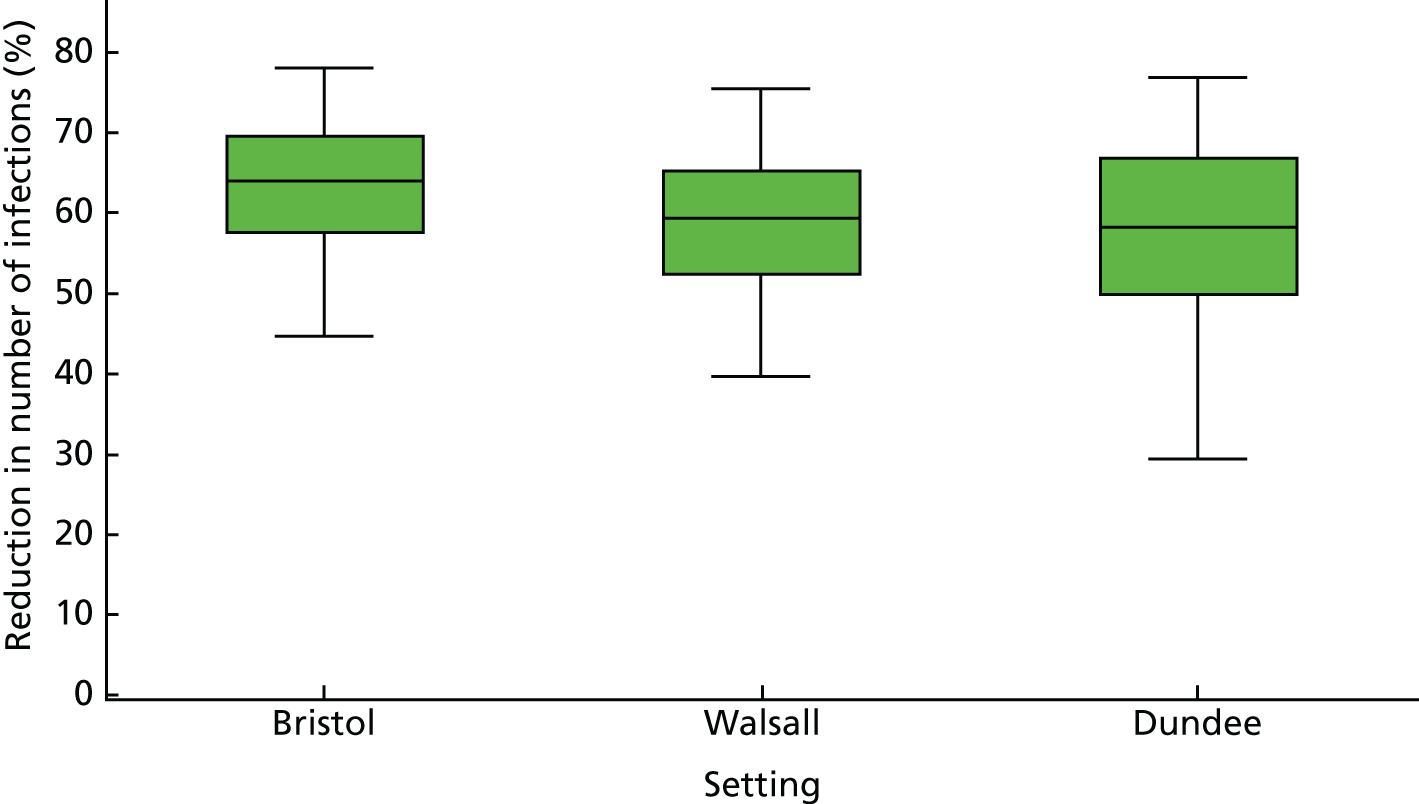
Impact of scaling up needle and syringe programmes
Scaling up > 100% NSP coverage to 80% or 90% has a substantial impact on the number of new infections by 2031, as shown in Figure 22. For instance, a large impact is seen in Walsall because of the low current coverage of NSP (21–42%), in which the number of new infections is decreased by 25% (95% CrI 7% to 40%) and incidence decreases by 41% (95% CrI 12% to 61%) when NSP is scaled up to 80% coverage. Conversely, increasing NSP coverage in Bristol and Dundee has less impact because of the higher current coverage in both settings (38–82% in Bristol and 34–79% in Dundee), with the number of infections decreasing by 10% (95% CrI 2.0% to 22%) in Bristol and 26% (95% CrI 6.0% to 48%) in Dundee. Less impact is always seen on prevalence, with an absolute drop of approximately 4% in all three settings.
FIGURE 22.
Impact of increasing NSPs in each setting on the number of new infections from 2016 to 2031. The box plots signify the uncertainty (the middle line is the median, the limits of the box are 25% and 75% percentiles, and the whiskers 2.5% and 97.5% percentiles).
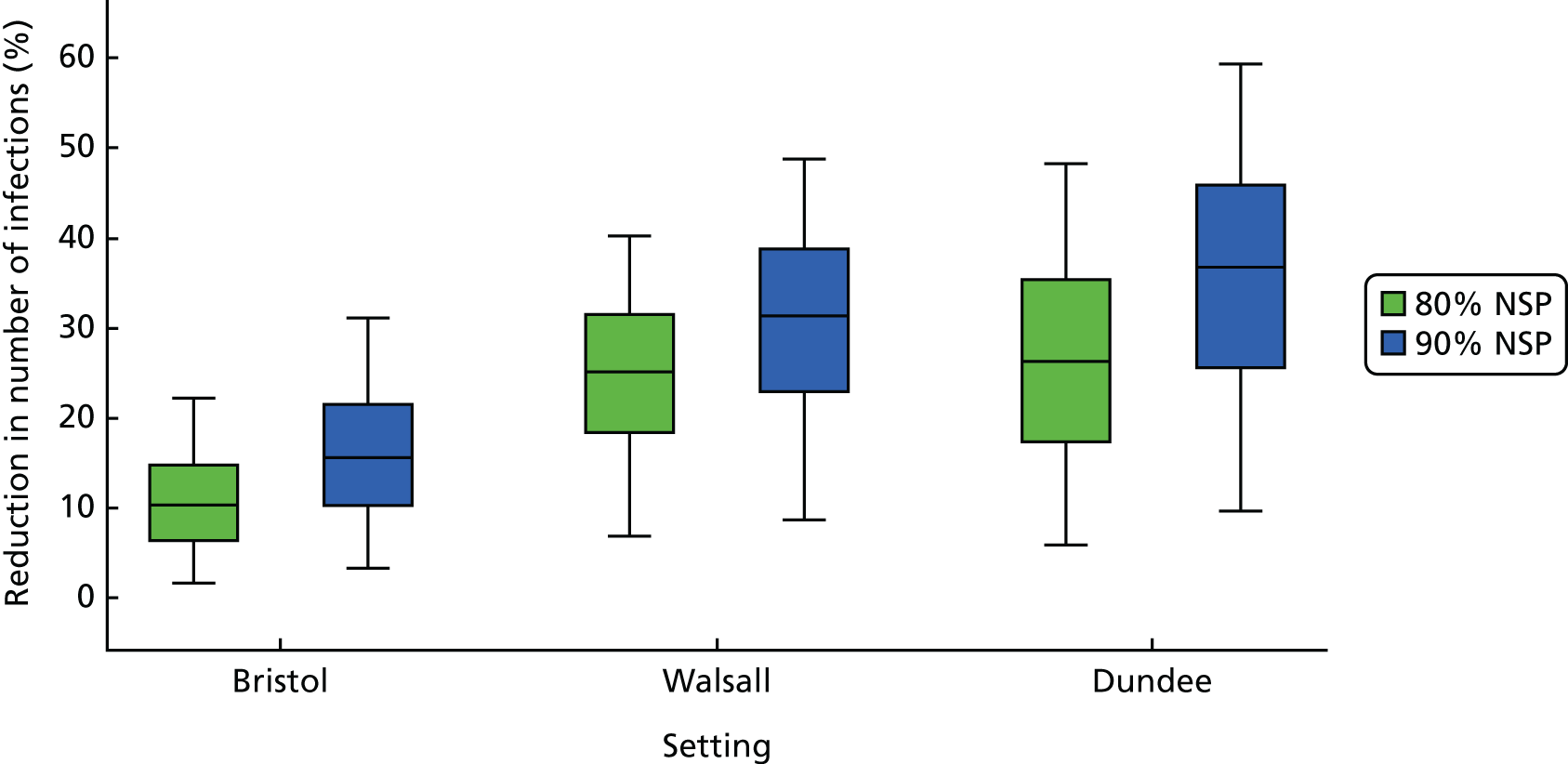
Sensitivity analysis
The results of the sensitivity analysis are shown in Figure 23. In Bristol and Walsall, the model parameter with the largest percentage contribution to the variability in the relative number of infections averted from current coverage levels of NSP is the efficacy estimate for NSP (which accounts for 41%, 20% and 48% of variation in Bristol, Dundee and Walsall, respectively). In Bristol and Walsall, the next most important input was the 2014 coverage of NSP (32% of variation in Bristol and 39% in Walsall). Conversely, for Dundee, HCV infection prevalence in 2014 had the largest contribution (36%) to the variability, followed by NSP effectiveness, OST effectiveness then NSP and OST effectiveness (20%, 10% and 6%, respectively). In Bristol and Dundee, the population size estimate contributed 3% and 5%, respectively, to the variability. All other parameters and inputs contributed < 5% to the variability in the impact of NSPs on the number of infections averted. The different patterns seen between Bristol/Walsall and Dundee could be attributable to the differences in the fitting procedures for each setting. Dundee required an extra fitting step to calibrate the model to the increasing prevalence from 2008 to 2014 and had a constant population size, which would account for the impact of those parameters. The presence of the OST and OST + NSP effectiveness parameters can be explained by the impact of these parameters when NSP is removed, which results in the OST + NSP effectiveness becoming the same value as the OST effectiveness parameter.
FIGURE 23.
Sensitivity analysis results: percentage contribution of the uncertainty in different model parameters to the overall variation in the relative increase in number of infections when NSP is removed (only those aspects with > 3% contribution in any of the settings are shown). (a) Bristol; (b) Walsall; and (c) Dundee.
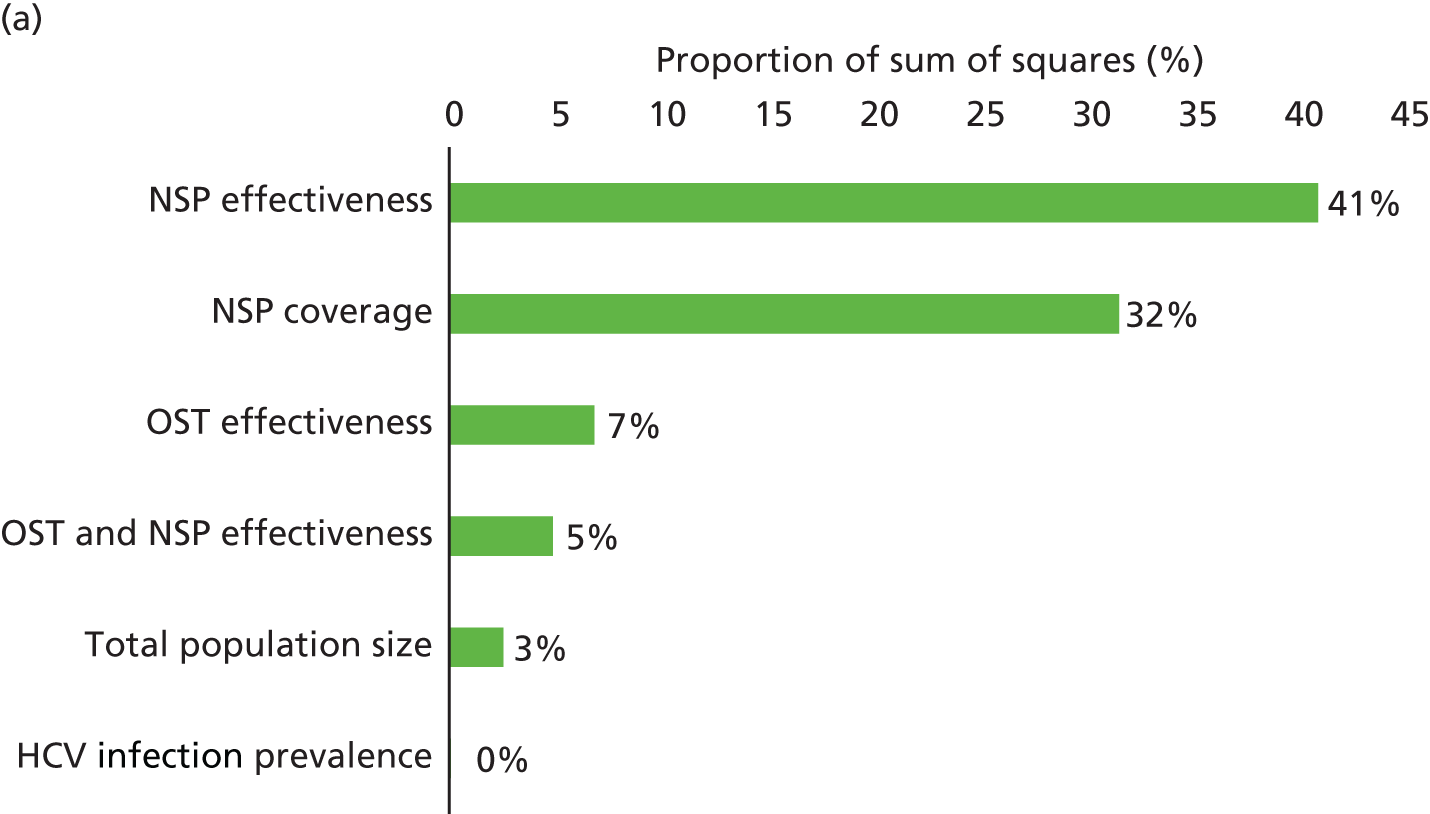
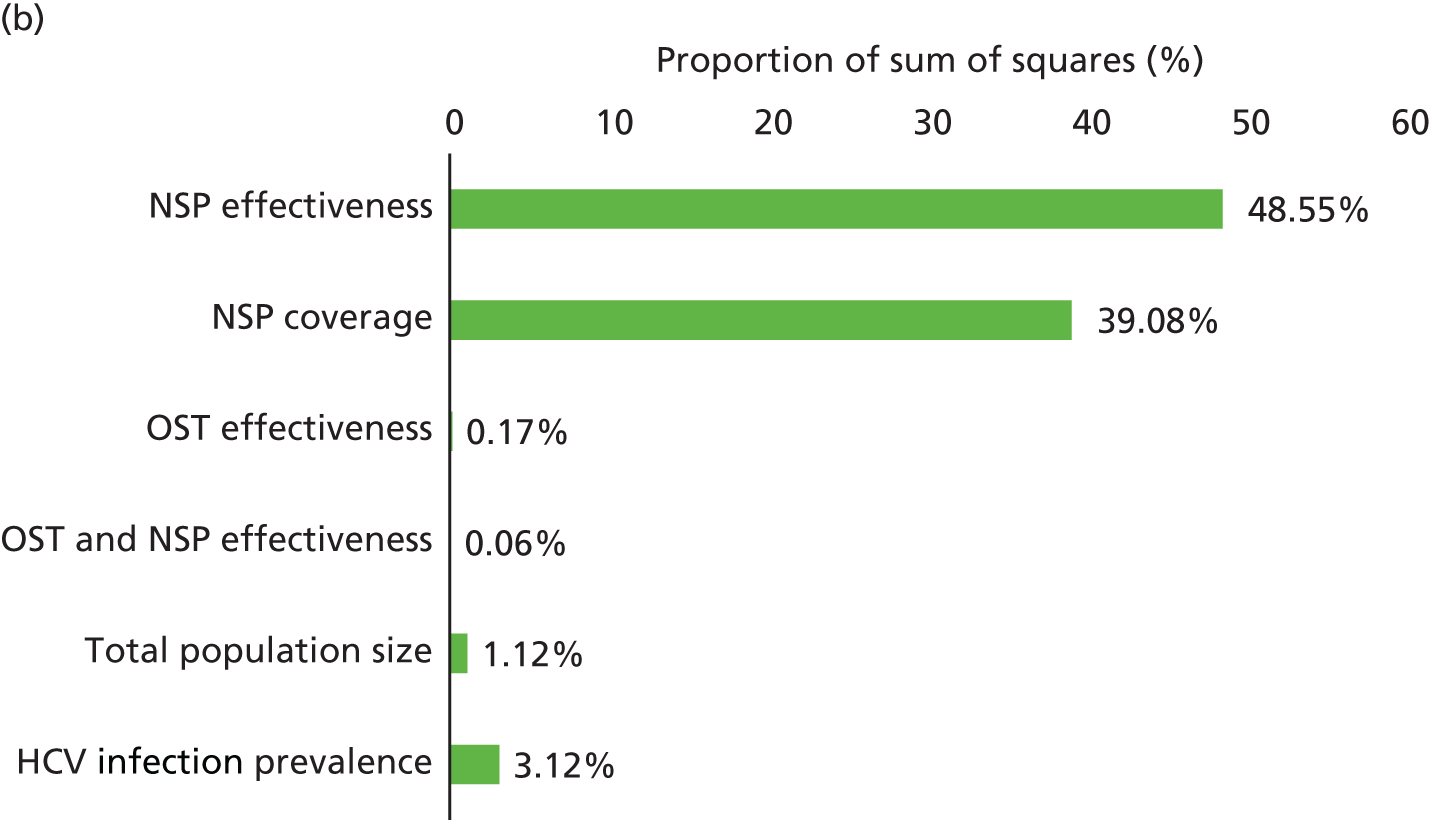
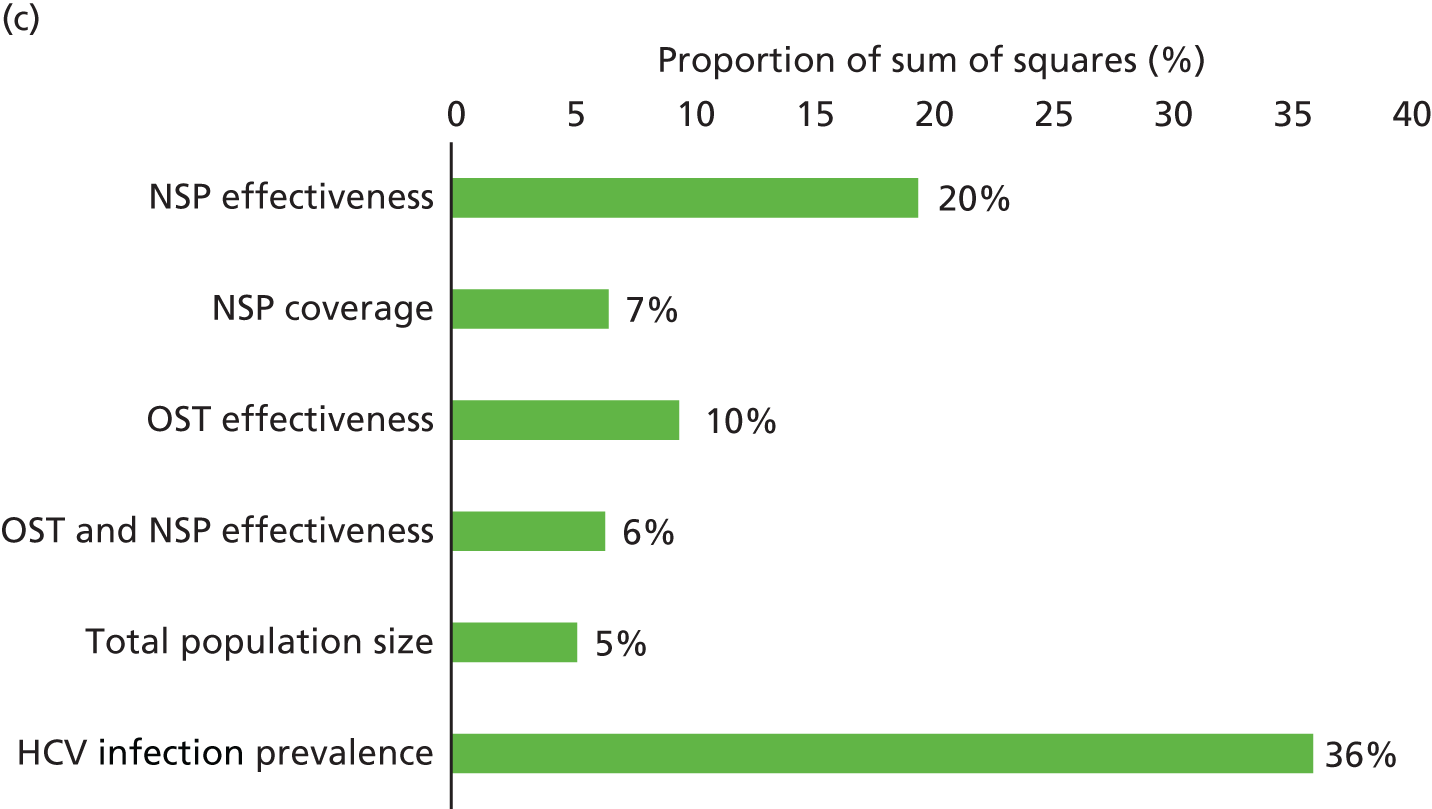
Conclusions
This analysis for three contrasting UK settings suggests that existing coverage levels of > 100% NSP and OST in combination and separately are currently preventing considerable transmission of HCV infection in these cities, with their combined removal resulting in at least a 125% increase in the number of new HCV infections over the next 15 years. Less impact is achieved from NSP on its own, but in combination with OST, synergistic benefits are generally achieved that increase impact further than would be expected from each intervention separately. Despite the large impact already achieved, our analyses suggest that the impact could be increased further, with a relative decrease in new infections by 2031 of 10–26% if NSP coverage is increased to 80% in all settings. Increasing NSP coverage has a larger effect in low prevalence and coverage settings, such as Dundee where local elimination is a feasible possibility, with incidence decreasing by 99% compared with 2016 levels by 2031. In the other settings, these increases in NSP in parallel with DAA treatments being used at current treatment rates are still likely to reduce incidence considerably (by 29% and 42% in Bristol and Walsall, respectively), but more will be needed to approach local elimination. Conversely, less impact is achieved on prevalence by 2031, with a sustained increase in NSP coverage as well as other interventions being needed to result in large decreases in HCV infection prevalence among PWID if the trend in longer-term injecting continues. Finally, current factors linked to high transmission risk, homelessness and crack cocaine injection should also be considered targets for intervention activities because our projections suggest that if the heightened transmission risk associated with these behaviours is removed it could avert about 60% of HCV infections over the next 15 years.
Strengths and limitations
Our detailed modelling of contrasting settings gives a better understanding of how the impact of interventions vary across the UK, with the use of updated empirical efficacy estimates for OST and NSP consistent with the included systematic review, thereby lending added strength to the results. In addition, our model stratified and calibrated PWID by injecting duration, allowing it to incorporate possible important changes in injecting recruitment and cessation over recent years, thus giving more realism to the model projections.
As with all modelling, there are several limitations. The main limitation is the sparsity of data on how injecting cessation and recruitment has changed; we thus had to extrapolate from imperfect data on size estimates and changes in the sample distributions by injecting duration in successive surveys. Importantly, we incorporated the uncertainty in these parameters, and our model projections were informative despite this. However, better data on these hard-to-quantify parameters would improve the accuracy of our model projections. Second, we did not consider any impact of OST on injecting cessation or mortality rates. Long-term OST use has been shown to increase injecting duration and lower mortality rates,91 while being associated with increased incidences of temporary cessation. 110 It is possible that the increasing proportion of long-term injectors seen in Bristol and Walsall may in part be due to the high current levels of OST in these settings. Future modelling could consider temporary cessation as well as permanent cessation, with current OST use impacting on the rates of cessation.
infectionThird, we assumed that the whole population of PWID would be eligible for OST, but there is a growing proportion (from 3.9% in 2004 to 12% in 2014) of PWID in the UK who inject non-opioid substances, such as amphetamines, as their main drug. 70 This is likely to have diluted the effect estimates from the pooled analysis, meaning that we may have underestimated the impact of current OST levels on HCV infection incidence. Fourth, we did not model incarceration, which can be associated with HCV infection transmission risk in the UK. 111 The role of incarceration in driving HCV infection transmission in the UK is the focus of current research. Finally, we did not consider IPED injectors in this model because the HCV infection prevalence in this subpopulation of PWID is much lower than psychoactive drug injectors (3.6% HCV antibody prevalence compared with 50%). 70 It is likely that their contribution to the overall HCV infection epidemic in the UK is small.
Other evidence and implications
Other models have looked at the impact of NSP or OST on HCV infection transmission, but have generally lacked empirical efficacy estimates for the effect of these interventions on HCV infection acquisition risk,79,112–114 or have not considered impact in specific cities parameterised with detailed data. 86 Our modelling extends existing analyses by including detailed context-specific modelling of the impact of OST, NSP and HCV infection treatment, as well as the disabling effect of high-risk behaviours and how it varies across UK settings.
Summary
Our projections are important for showing how the current impact of interventions vary across settings and where the scale-up of interventions should be targeted. They emphasise the crucial need to avoid any scale-back in the coverage of current interventions, which could result in huge increases in HCV infection transmission across these settings. Despite coverage being high in many settings, the projections also suggest that important benefits could still be achieved from scaling up NSP further, especially in settings with current low coverage levels. In addition, as suggested by other recent modelling analyses,99,114 scaling up other interventions such as HCV infection treatment could also have a large impact on HCV transmission, although treatment will need to scale up considerably to see a large impact on incident infections. Importantly, strategies need to be devised to tackle or reduce the harms associated with homelessness and crack cocaine injection among PWID, which our modelling suggests is doubling the level of transmission in each setting. Reducing the risk of HCV transmission among these vulnerable subpopulations should be a priority for any strategy attempting to reduce HCV transmission or hoping to achieve HCV elimination, as recently set out by WHO. 115 There is now a realistic possibility to reduce HCV to low levels, even in higher-prevalence settings, and mathematical models could be useful for guiding these efforts.
Chapter 6 Cost-effectiveness analysis
Methods
The cost data described in Chapter 3 were used to populate a cost-effectiveness model to estimate the incremental cost-effectiveness of NSPs in each of the three cities described previously.
Model calibration
The model was calibrated for each city using survey data from each city (see Chapter 4 for more detail). The model was used to estimate the cost-effectiveness of existing levels of NSP compared with if they were removed from 2016, with the removal of NSP being simulated for 10 years (2016 to end 2025) and then the subsequent transmission effects simulated for a further 40 years (2026 to end 2065). For the baseline intervention scenario, we assumed that OST and > 100% NSP coverage levels remained at current levels and kept other model parameters constant. In the sub-baseline counterfactual scenario, the lower transmission risk associated with > 100% NSP was set to one, and the transmission risk for current OST and > 100% NSP use was set to the transmission risk associated with just current OST use. This was done for 10 years to investigate the detrimental impact of removing current levels of > 100% NSP in each city. No costs of NSP were assumed over this time. After 10 years, the transmission risks associated with > 100% NSP, and current OST and > 100% NSP were set to baseline levels again to simulate the resumption of NSP activities, with the estimated costs of NSP being included for subsequent years. We calculated the costs and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) over two time horizons. First, we calculated costs and QALYs for a further 40 years after NSP was reintroduced, giving a total time horizon of 50 years. We also calculated costs and QALYs for a further 90 years after NSP was reintroduced, giving a total time horizon of 100 years. The numbers of individuals in each category of the model were recorded, and QALYs and costs were attached to each category as appropriate. Both time horizons are presented in the results.
Uncertainty in the underlying parameters was accounted for, such that demographic and epidemiological parameters, disease progression rates, costs and health utilities were randomly sampled from appropriate distributions. For each city, we obtained 1000 matched simulations for the costs and QALYs of the baseline intervention scenario and the sub-baseline counterfactual scenario.
Using the sampled simulation sets, we calculate the total costs and the total QALYs gained for the baseline scenario with NSP coverage, and for the scenario removing NSP services for a period of 10 years. These scenarios are presented as ‘NSP’ and ‘no NSP’ respectively for clarity. All future costs and QALYs were discounted using a baseline discount rate of 3.5%.
Cost data
The fixed city-level cost and cost per needle of NSP programmes was estimated over 1000 iterations, simultaneously varying all parameters described in the costing sensitivity analysis, and these 1000 estimates for costs were input into the model. The number of needles distributed each year was calculated by multiplying the total number of PWID with > 100% NSP coverage from the model by the mean injecting frequency per year (see Chapter 4 for details). The total NSP cost per year is then the total number of needles distributed per year multiplied by the cost per needle, added to the fixed city-level cost. (The sampled values of the cost per needle and the fixed city-level cost are shown in Appendix 5, Table 30.)
To enable use of the model for the cost-effectiveness analyses, HCV infection care costs were assigned to different HCV infection stages in the model. These costs were drawn from previously published estimates of the costs of treatment and care for HCV infection in the UK (see Appendix 5, Tables 31 and 32 for data used). Detailed estimates of total cost for each disease stage were drawn from the literature and inflated to 2014 GBP using the hospital and community health services index (see Appendix 5, Table 31 for the cost values used in the cost-effectiveness model). We assumed that 50% of chronic infections (F0–F3 disease stages) in PWID and ex-injecting drug users are diagnosed and incur a cost. We also assumed that treatment costs for active PWID were higher than those for ex-injecting drug users or non-injecting drug users. Costs associated with the supportive care of compensated cirrhosis were applied to all individuals in that disease stage.
Effectiveness
Health utility values (QALY weights) are sourced from previous economic evaluations of HCV infection treatment interventions (see Appendix 5, Table 32). Following previous analyses, we assume that the baseline quality of life for active injectors is lower than that for ex- or non-injectors. As for the model fitting for the impact analyses, the HCV infection disease utility and costs were sampled for each run.
Sensitivity analysis
Seven different scenarios were tested in the sensitivity analysis: increasing time horizon to 100 years, no chronic HCV infection disease (F0–F3) stage cost (baseline was 50% of those infected incurred cost), no associated disease cost for chronic HCV infection or compensated cirrhosis disease states (F0–F3 and compensated cirrhosis), a discount rate of 0% for costs and QALYs instead of 3.5%, the same treatment cost for PWID as for ex-injecting drug users; and, finally, assuming a reduction of 50% in the drug cost component of the treatment costs from 2016.
Results
Model outputs
Table 12 shows the total deaths and HCV infections averted through NSP compared with no NSP in each city. Bristol has a median anticipated 21 deaths averted over 50 years and Dundee has a median 23 deaths averted; Walsall has a median anticipated 5.8 deaths averted over the same time horizon. The number of infections averted varies by city, from 93 infections in Walsall to 749 infections in Dundee. Walsall has the smallest prevalence of HCV infection within the injecting population and, therefore, saw the smallest number of deaths and infections averted, despite the fact that the proportion of deaths and infections averted through NSP was similar in each city, as shown in Chapter 4. There was wide uncertainty in the outputs in all cities.
| Site | Deaths averted | Infections averted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 2.5% CrI | 97.5% CrI | Median | 2.5% CrI | 97.5% CrI | |
| Bristol | 20.5 | 4.3 | 51.1 | 199.5 | 42.5 | 505.2 |
| Dundee | 23.1 | 3.8 | 57.5 | 749 | 119.1 | 1637.6 |
| Walsall | 5.8 | 1.2 | 14.9 | 92.7 | 22.3 | 200.5 |
Table 13 shows the total health-related costs incurred over the 50-year time horizon for Bristol, Dundee and Walsall, discounted to reflect their current value. Removing NSPs consistently increases health-related costs across all cities, including costs of health care for early-stage HCV infection, costs for HCV infection treatment among PWID and costs for HCV infection treatment among ex-/non-injecting drug users. These increased costs reflect an increase in HCV infection transmission in the ‘no NSP’ scenario, including to people who then cease injecting. The costs of NSP are higher in the ‘NSP’ scenario. In Dundee, this additional cost for NSPs increases the total cost marginally compared with the ‘no NSP’ scenario; however, in Walsall the total median costs for the ‘NSP’ scenario are lower than those for the ‘no NSP’ scenario, despite additional NSP costs. In Bristol, total median costs are the same in both scenarios.
| Setting and health-care category | Projected total health-related costs (£) over 50-year time horizon | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSPs | No NSPs | |||||
| Mean | 2.5% CrI | 97.5% CrI | Mean | 2.5% CrI | 97.5% CrI | |
| Bristol | ||||||
| Health-care costs | 130.4 | 60.0 | 289.8 | 131.6 | 60.3 | 292.6 |
| HCV infection treatment cost | 39.9 | 23.5 | 58.8 | 41.1 | 24.3 | 60.6 |
| HCV infection treatment PWID cost | 9.3 | 6.6 | 11.2 | 9.3 | 6.7 | 11.2 |
| NSP cost | 6.0 | 3.7 | 8.3 | 3.8 | 2.3 | 5.3 |
| OST cost | 112.3 | 86.8 | 142.5 | 112.2 | 86.8 | 142.4 |
| Total cost | 297.8 | 298.0 | ||||
| Dundee | ||||||
| Health-care costs | 27.1 | 5.8 | 66.5 | 28.9 | 6.5 | 70.3 |
| HCV infection treatment cost | 15.5 | 8.1 | 28.2 | 18.7 | 9.5 | 31.1 |
| HCV infection treatment PWID cost | 12.9 | 5.5 | 24.2 | 16.2 | 7.3 | 24.5 |
| NSP cost | 2.9 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 2.8 |
| OST cost | 37.1 | 32.1 | 44.3 | 37.1 | 32.1 | 42.3 |
| Total cost | 95.4 | 102.9 | ||||
| Walsall | ||||||
| Health-care costs | 64.1 | 31.2 | 131.5 | 64.5 | 31.3 | 132.3 |
| HCV infection treatment cost | 23.3 | 14.4 | 34.0 | 23.9 | 14.8 | 34.7 |
| HCV infection treatment PWID cost | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| NSP cost | 3.0 | 1.6 | 5.3 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 3.5 |
| OST cost | 61.7 | 38.3 | 96.5 | 61.7 | 38.3 | 96.5 |
| Total cost | 153.1 | 153.0 | ||||
Cost-effectiveness
Table 14 presents the average total costs, QALYs and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) for the 50-year time horizon. In Bristol and Dundee, providing NSP services is cost-saving; keeping NSP services is estimated to save an average of £137,949 in Bristol and nearly £7.5M over the 50-year time horizon in Dundee. NSPs are also anticipated to contribute 502 and 958 incremental QALYs in comparison to the ‘no NSP’ scenario in Bristol and Dundee, respectively. In Bristol and Dundee, an additional £10M and £26M, respectively, could be spent on NSP without any additional impact, and NSPs would still fall under the commonly cited willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of £20,000 per QALY gained.
| Setting | Total cost (£) | Incremental cost (£) | Total QALYs | Incremental QALYs | ICER (£) | Net monetary benefit (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bristol | ||||||
| No NSP | 297,970,375 | 187,663 | ||||
| NSP | 297,832,426 | –137,949 | 188,165 | 502 | –274.76 | 10,179,353 |
| Dundee | ||||||
| No NSP | 102,891,384 | 124,208 | ||||
| NSP | 95,420,292 | –7,471,093 | 125,165 | 958 | –7799.19 | 26,629,720 |
| Walsall | ||||||
| No NSP | 153,007,364 | 142,702 | ||||
| NSP | 153,122,615 | 115,250 | 142,894 | 192 | 600.68 | 3,722,082 |
In Walsall, the mean incremental costs of the NSP scenario compared with the ‘no NSP’ scenario are estimated at £115,250. NSPs are expected to contribute 192 incremental QALYs compared with the scenario removing NSPs. The mean incremental cost-effectiveness of NSPs in Walsall is estimated at £601 per QALY gained. Our central estimate for the ICER in Walsall is well below the commonly cited NICE WTP threshold of £20,000–30,000 per QALY gained and, therefore, can be regarded as highly cost-effective. In fact, an additional £3.7M could be spent with no impact, and NSPs would still fall under the £20,000 per QALY threshold. It has recently been suggested that a more appropriate WTP threshold in a UK setting would be £13,000, as this is the rate at which the NHS is able to turn costs into QALYs. 116 Our central estimate for Walsall also falls well below this threshold, indicating a high return on investment in the current NHS setting.
Table 15 presents the average total costs, QALYs and ICERs for the 100-year time horizon. Over the 100-year time horizon, NSPs are cost-saving in all cities, saving £687,351, £8,800,186 and £177,778 in Bristol, Dundee and Walsall, respectively, and contributing 699, 1326, and 278 QALYs, respectively, in that time. Using the lower WTP threshold of £20,000 per QALY gained, this represents a net monetary benefit of > £14.6M in Bristol, £35M in Dundee and £5.7M in Walsall over the 100-year time horizon.
| Setting and intervention scenario | Total cost (£) | Incremental cost (£) | Total QALYs | Incremental QALYs | ICER (£) | Net monetary benefit (£) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bristol | ||||||
| No NSP | 334,009,891 | 225,720 | ||||
| NSP | 333,322,534 | –687,357 | 226,419 | 699 | –982.81 | 14,675,014 |
| Dundee | ||||||
| No NSP | 114,678,850 | 151,461 | ||||
| NSP | 105,878,665 | –8,800,186 | 152,787 | 1326 | –6634.97 | 35,326,845 |
| Walsall | ||||||
| No NSP | 173,478,543 | 176,097 | ||||
| NSP | 173,300,765 | –177,778 | 176,375 | 278 | –638.61 | 5,745,412 |
The ICERs for Bristol, Dundee and Walsall over 1000 baseline runs for the 50-year time horizon are shown in Figures 24–26. All cities show some uncertainty in the ICER; however, across all cities there were no estimates in the bottom-left quadrant (indicating that NSPs are dominated). In Dundee, 99% of iterations are located in the bottom-right quadrant, indicating that NSPs are cost-saving. In Bristol, 45% of iterations are cost-saving, and in Walsall, 40% of iterations are cost-saving.
FIGURE 24.
Incremental cost-effectiveness: Bristol.
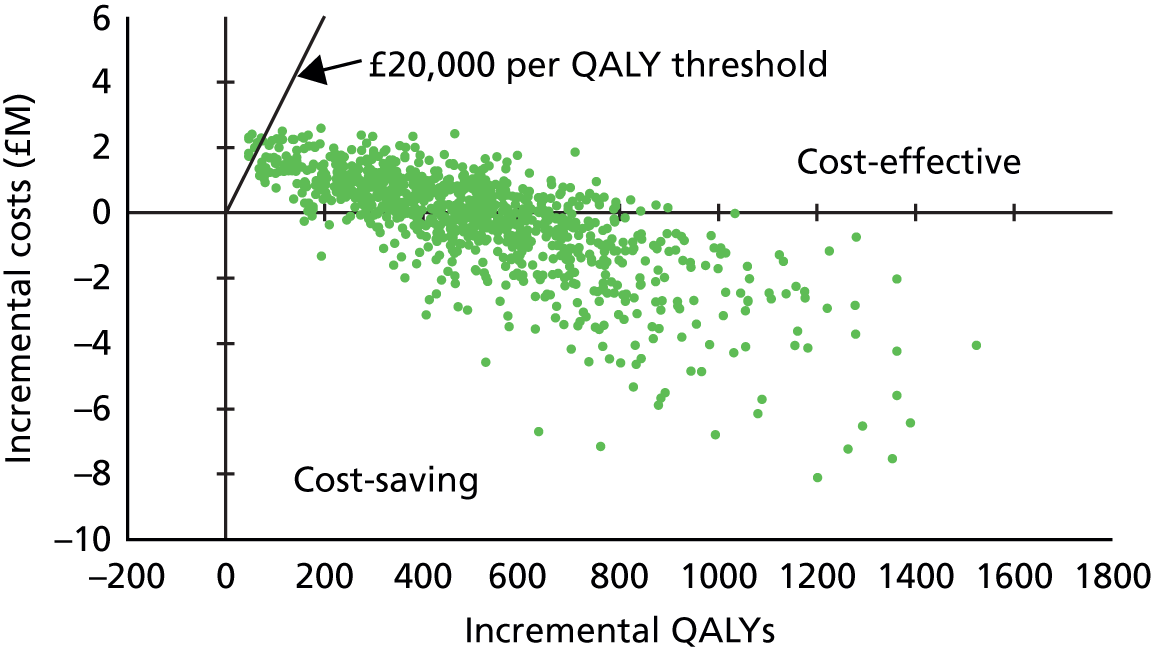
FIGURE 25.
Incremental cost-effectiveness: Dundee.
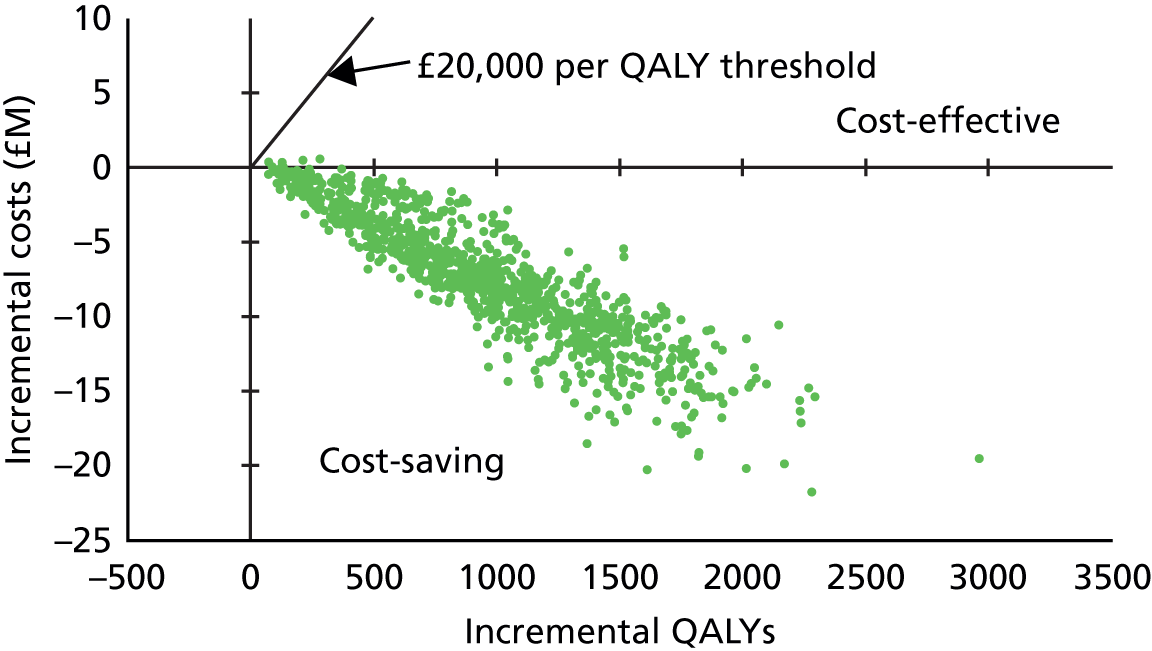
FIGURE 26.
Incremental cost-effectiveness: Walsall.
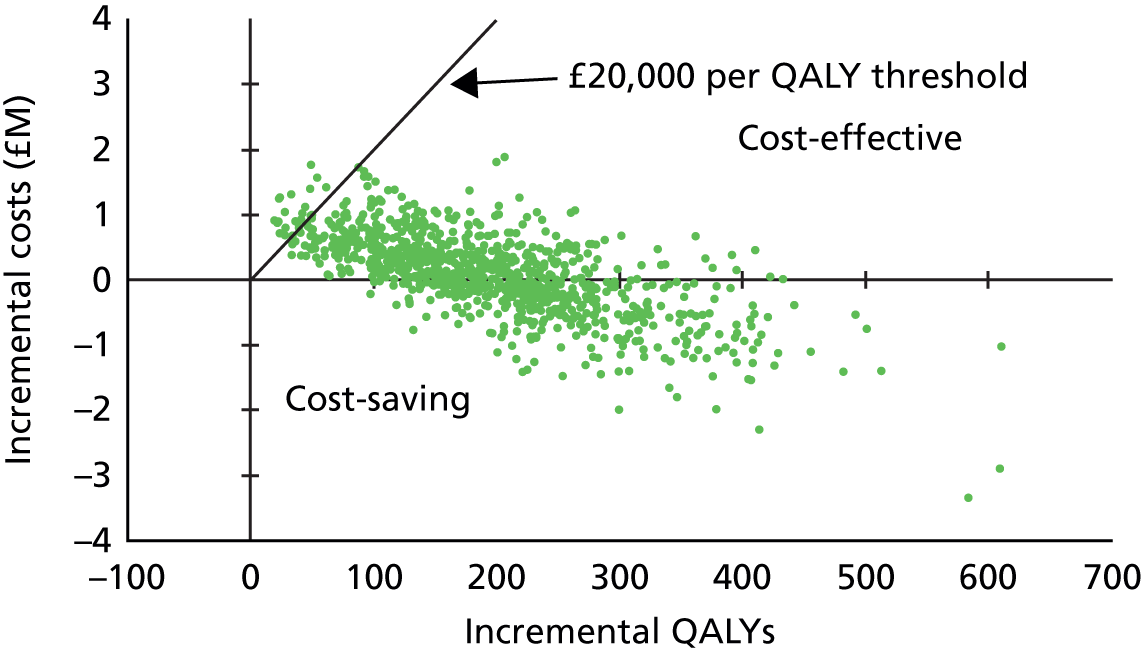
Sensitivity analysis
Figures 27–29 show cost-effectiveness acceptability curves over a range of sensitivity analysis scenarios for Bristol, Dundee and Walsall, respectively. As indicated in the figures, our model was relatively robust to assumptions, and the likelihood of cost-effectiveness was not substantially altered in the sensitivity analysis scenarios. In the base case, 96% of iterations in Bristol, 100% of iterations in Dundee and 95% of iterations in Walsall are located below the WTP threshold of £13,000 per QALY saved. Using the more commonly cited lower-bound threshold of £20,000 per QALY saved, 98% of iterations from Bristol, 100% of iterations from Dundee and 98% of iterations from Walsall are below the threshold.
FIGURE 27.
Cost-effectiveness sensitivity analysis: Bristol.
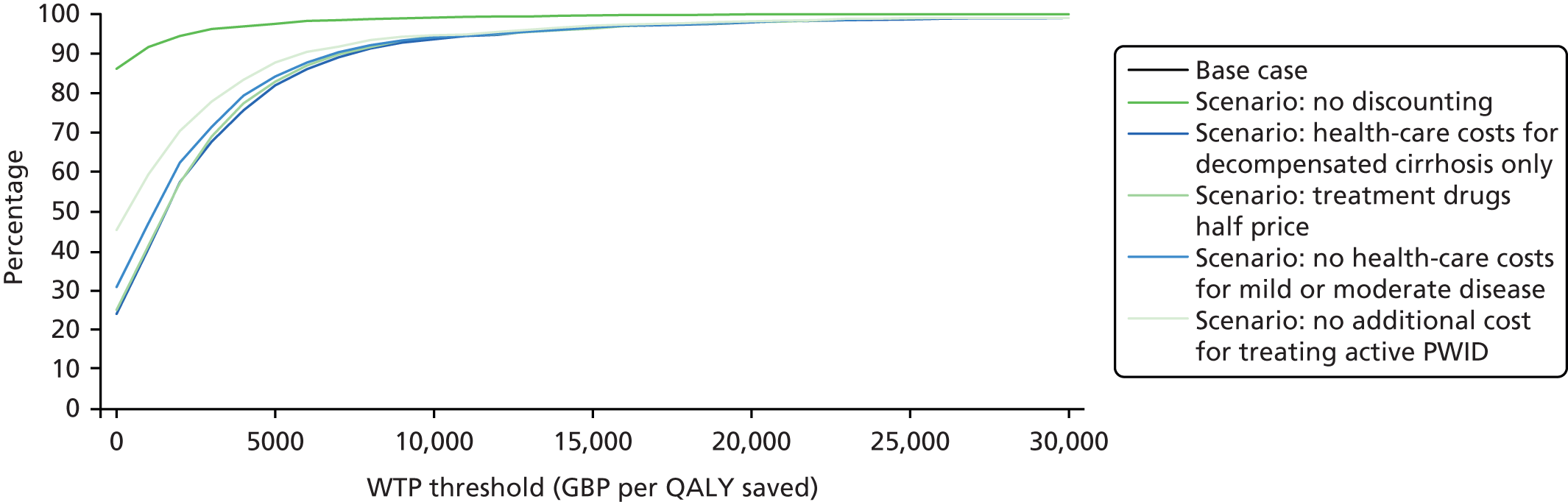
FIGURE 28.
Cost-effectiveness sensitivity analysis: Dundee.
FIGURE 29.
Cost-effectiveness sensitivity analysis: Walsall.
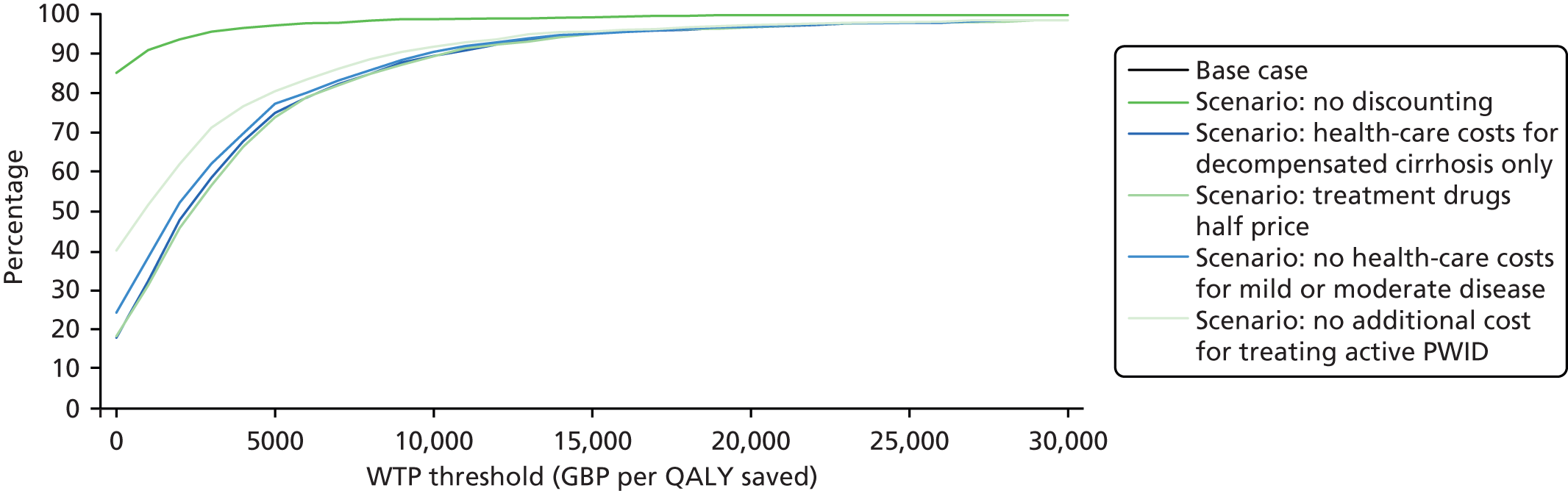
The sensitivity analysis scenario with the greatest impact on the ICER assumes a discount rate of 0% for both costs and QALYs. Under this scenario, 86% of iterations in Bristol, 100% of iterations in Dundee and 85% of iterations in Walsall are below a WTP threshold of £0. The scenario reducing HCV infection treatment drugs to half of their listed price returns the lowest proportion of iterations below any given WTP threshold overall. However, even under this scenario, the large majority of iterations are below a WTP threshold of £20,000 (98% in Bristol, 100% in Dundee and 97% in Walsall).
Conclusions
Overall, we found NSPs to be highly likely to be cost-effective at low WTP thresholds and, in fact, to be cost-saving in some settings. In both Bristol and Dundee, the large majority of iterations from the model were cost-saving, and in Walsall the large majority of iterations were considerably below a WTP threshold of £13,000 per QALY gained.
The difference in ICERs between cities is likely to be driven partly by population size and HCV infection prevalence in each study setting. Walsall had the lowest population of people injecting drugs citywide, so NSPs had a lesser impact in the form of a reduction in infections and deaths and, therefore, had less of an overall impact on cost. There was also a larger amount of uncertainty in the NSP costs for this city owing to the fact that the out-of-hours pharmacy had only recently begun providing services at the time of data collection; this generated substantial uncertainty, as we extrapolated observations from the past month to an annual estimate.
The unit costs presented do not reflect the substantial gains from averting other health problems. Most importantly, there is substantial evidence that NSPs are highly effective in averting HIV infection. 13 Incorporating HIV infections averted through NSPs into our model would further increase the number of QALYs averted through NSPs, thereby increasing the cost-effectiveness of our estimates. These estimates also do not reflect the supportive nature of transactions, or any other measures of quality. Quality of transactions will vary substantially across sites and may be reflected in the costs; for example, a service might take more time per visit if practitioners engage the client in discussions about their injecting behaviour and safe practices. Services offering a wider range of injecting equipment may also encounter higher supply costs; however, this wide range of supplies may draw additional clients in or improve the quality of services. For example, a number of fixed sites are looking into offering so-called ‘crack packs’ as a harm-reduction mechanism to encourage clients to smoke rather than inject drugs. Similarly, two fixed sites offered water for injection in order to enable clients to use clean water when injecting heroin; this will increase the overall supply costs but will possibly reduce the costs related to injection-site infections.
Furthermore, fixed-site NSPs also commonly provide other services such as wound care, vaccination, links to social and welfare services, and psychosocial support. Similarly, the drop-in centre offered other services, including a safe place, psychosocial support, food and bedding for rough sleepers, and a sense of community. Many of these benefits have not been evaluated for their effectiveness, but are likely to contribute to well-being among PWID. A co-financing approach whereby funding is split across the multiple sectors benefiting from an intervention, such as that suggested by Remme et al. ,117 would further improve WTP for NSPs, for example across the health-care and social care sectors in the UK.
Finally, this analysis does not investigate the cost-effectiveness of OST in detail, as it does for NSP. Costs for OST were not collected in detail as they were for NSP and were instead drawn from published unit cost estimates from the Personal Social Services Research Unit in the UK. Other benefits of OST, such as reducing drug-related mortality or incarceration and social costs, have also not been included in the model. More expansive analyses have shown OST to be cost-saving when these other outcomes are included. Further research to evaluate the combined impact and cost-effectiveness of both NSP and OST across both social care and health-care sectors would fill a major gap in current understanding.
This report presents model projections rather than empirical evidence, and caution is advised in interpretation of our findings. Key limitations relate to the simplifying assumptions of the model and uncertainty around several parameters. There was some uncertainty in our estimates of the cost of NSP programmes and in the anticipated impact for all cities. This was partly due to uncertainty in the primary data collection in terms of costs and outputs. This was especially true for pharmacies, where detailed records of needle exchanges are not usually kept. There was also substantial uncertainty in NSP coverage estimates in the UK. The pooled analysis (see Chapter 2) suggested that estimates of coverage varied widely, with a median coverage of 2.5 needles distributed per injection (interquartile range 1.4–4.7) reported in community-recruited surveys of PWID in Leeds but a median of 1 (interquartile range 0.48–2.5) from the UAMP survey, which primarily recruits from NSPs and low-threshold treatment settings. Coverage estimates per site were presented at the National Needle Exchange Forum annual meeting in November 2014, and responses from practitioners suggested that coverage estimated through community surveys was far higher than reported by services.
Nonetheless, this modelling exercise indicates that NSP services are highly likely to be cost-effective at almost any WTP threshold and, in some settings, are cost-saving. Policies to ensure that NSPs can be accessed widely alongside the provision of OST are needed, and obstacles preventing the concurrent use of both NSP and OST could be removed to maximise the reduction in HCV infection transmission. Further research is also needed to improve our understanding of the mechanisms through which NSPs and OST achieve their effect and of the optimum contexts to support their implementation.
Chapter 7 Conclusions and recommendations
Although there is good evidence that NSPs and OST in combination reduce injecting risk behaviours and some evidence to show their impact on HIV incidence, there is little evidence for their impact on HCV infection incidence among PWID. There have been no economic evaluations of NSPs undertaken in Western Europe and few have considered the costs saved as a result of care and treatment being averted. All existing studies have relied on weak measures of NSP effectiveness, with most using changes in self-reported risk behaviour, which can be biased. This project filled a gap in the evidence by attempting to provide more robust estimates of the efficacy of NSP and OST on reducing the risk of HCV infection transmission, and an assessment of the probable impact of existing coverage levels of NSPs and changes in the extent of provision. It also provided the first assessment of the costs and cost-effectiveness of needle and syringe provision in UK, and ICERs associated with increasing coverage on HCV infection transmission among PWID.
Opioid substitution therapy and needle and syringe programme efficacy estimates
Primary meta-analysis of 12 observational studies adjusting for key confounders enrolling 5910 anti-HCV negative participants showed that the current use of OST compared with no intervention reduced the risk of HCV infection acquisition by 50% (RR 0.50, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.63). The intervention effect is strong, but the evidence is considered to be of low quality because it was derived from observational studies with serious risk of bias. Nonetheless, the findings were robust to sensitivity analyses excluding studies judged to be at critical risk of bias, studies drawing on unpublished data, case–control and cross-sectional studies reporting only baseline data, and studies reporting only unadjusted estimates. There also was no evidence of publication bias. All of these sensitivity analyses showed a statistically significant benefit of OST.
A few studies reported other types of exposure to OST. Three studies reported past exposure to OST and three reported interrupted OST use [one study measuring OST use for detoxification and two studies measuring high dosage (≥ 60 mg) or low dosage (1–59 mg) of methadone for daily use]. Among these exposures, only high dosage of OST was associated with a reduction in risk of HCV infection acquisition.
Primary meta-analysis of seven observational studies pooling unadjusted estimates and enrolling 5669 anti-HCV negative participants showed weak and low-quality evidence that NSP exposure did not reduce the risk of HCV infection acquisition. This effect remained consistent in sensitivity analyses. After removing studies from North America, high NSP coverage in Europe was associated with a 61% reduction in HCV infection acquisition risk (RR 0.39, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.64) with less heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; p = 0.428).
There was moderate-quality evidence for the impact of combined high coverage of NSP and OST from studies comprising 3356 anti-HCV negative participants, which suggested a 71% reduction in the risk of HCV infection acquisition (RR 0.29, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.65). There were insufficient data to conduct a sensitivity analysis with this intervention group. A summary of key findings and quality of evidence is presented in Table 3.
Findings from a pooled analysis of full harm reduction compared with minimal exposure reduced the risk of injecting with a used needle/syringes by 50% (AOR 0.5, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.62), as well as reuse of the same needle/syringe for injecting by 40% (AOR 0.59, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.88) and frequency of injecting. There was weaker evidence for an association with injecting-site infections or shared used of filters and spoons for drug preparation. Full harm reduction was associated with twice the odds of testing for both HCV and HIV (AOR 1.9, 95% CI 1.56 to 2.23 and AOR 1.9 95% CI 1.6 to 2.20, respectively). Combining estimates of NSP coverage from the systematic review with two data sets69,70 not already represented in the review strengthened the evidence for the effect of high NSP coverage on reducing the risk of HCV infection acquisition to 39% (RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.87) with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 30%; p = 0.189).
Costs of needle and syringe programme provision through different modalities
Evidence showed a degree of variation in costs across the three different commissioning areas evaluated; variation in cost and outputs was observed across fixed sites and pharmacies. The primary cost driver in most settings was the cost of supplies, which accounted for an average of 60% of total costs across sites (range 28–78%). This was followed in most cases by administrative and overhead costs, which accounted for 9–28% of total costs. There was some considerable uncertainty in our estimates owing to the fact that cost and output data on NSP distribution are not routinely collected for some distribution modalities within the UK.
The difference in costs is likely to be driven partly by the type of needle distribution and the ease of access to needles for PWID. We observed a large variation in the number of visits per user across cities and in the number of needles distributed at each visit. A higher number of visits per person in the injecting population citywide did appear to increase the costs of distribution, suggesting that distributing a greater number of needles in fewer visits may be more efficient than restricting the number of needles distributed at each visit, assuming that there is demand for greater quantities of needles within a visit.
Cost-effectiveness of needle and syringe programme provision
Overall, we found that needle and syringe exchange services are highly likely to be cost-effective at almost any WTP threshold and, in fact, are cost-saving in some settings, despite some uncertainty in total outputs. Under the 50-year time horizon, in Dundee the large majority of iterations from the model were cost-saving, and in Bristol and Walsall the large majority of iterations were below a WTP threshold of £13,000 per QALY gained. Under the 100-year time horizon, NSP services in all three cities were cost-saving.
The difference in cost-effectiveness between cities is also likely to be driven partly by population size and HCV infection prevalence in each study setting. Walsall had the lowest population of people injecting drugs citywide, so a reduction in infections and deaths had less of an overall impact on cost-effectiveness. There was also greater uncertainty in the NSP costs for this city.
These cost-effectiveness estimates do not reflect the substantial gains from averting other health problems associated with injecting drug use, including HIV and other infections. Previous research has indicated that NSPs are highly effective in averting HIV infection; incorporating these health gains would substantially improve cost-effectiveness.
Impact modelling of needle and syringes programmes and opioid substitution therapy
Regardless of setting, removing either or both of NSP and OST would have a large detrimental impact on both prevalence and incidence of HCV infection in all three settings by 2031. As expected, removing both interventions has the biggest effect on the epidemics, with the model suggesting at least a 109% relative increase in incidence, a 51% relative increase in the number of new HCV infections and a 23% relative increase in prevalence being projected in all settings from 2016 to 2031. Following this, removing OST has the next biggest impact, resulting in at least a 59% relative increase in incidence, a 31% increase in the number of HCV infections and a 14% relative increase in prevalence by 2031. This is followed by removing NSPs, which increases relative incidence by at least 8% and prevalence by at least 3%. NSP has a smaller impact than OST because it has lower coverage in each setting, and lower efficacy (NSP lowers transmission risk by 41% vs. 59% for OST), as suggested by our pooled analysis. However, removing NSPs still generally results in a large relative increase in the number of new HCV infections, with a median increase of 32% (95% CrI 7% to 71%) in Bristol, 23% (95% CrI 6% to 43%) in Walsall and 61% (95% CrI 12% to 219%) in Dundee.
Scaling up > 100% NSP coverage to 80% or 90% has a substantial impact on the number of new infections by 2031. The largest relative impact is seen in Walsall, where the number of new infections is decreased by 27% (95% CrI 7% to 43%) and incidence decreases by 40% (95% CrI 11% to 59%) when NSP is scaled up to 80% coverage. This is due to the low current coverage of NSP (21–42%) and the low prevalence of HCV infections in Walsall. Increasing NSP coverage from the current level of between 38% and 80% in Bristol up to 80% coverage from 2021 onwards, results in a decrease in actual prevalence of 3% (95% CrI 0.7% to 6.9%) by 2031, corresponding to a relative decrease of 6% (95% CrI 1% to 14%); however, the number of infections is reduced by 11% (95% CrI 2% to 24%).
Limitations
We have discussed individual limitations of the methods separately in each of the results chapters. Here, we discuss some overarching limitations that cross all the methods and that stem from the complex nature of NSPs and OST that do not lend themselves to evaluation through traditional evaluation study designs. This produced the following limitations.
First, the evidence synthesised in the systematic review was drawn from observational studies. The ACROBAT-NRSI tool that we applied to assess the risk of bias28 assesses studies according to seven domains [(1) confounding, (2) selection bias, (3) measurement of interventions, (4) departures from intervention, (5) missing data, (6) measurement of outcomes and (7) selection of reported results] to give an overall risk of bias, which can be classified into four categories (ranging from low to critical). A study categorised as being at low risk of bias would be comparable to a well-performed randomised trial, whereas one that is at critical risk is defined as being too problematic to provide any useful evidence and should be excluded from the synthesis. It is worth noting that observational studies are unlikely to be rated as being at ‘low’ risk of bias because they will always score poorly on the confounding domain, as it is impossible to ensure that an observational study has adjusted for all possible residual confounding. Assessing quality of study designs alongside RCTs as a gold standard reduces the strength of the assertions that we can make about observational evidence. The use of the GRADE system to assess the overall quality draws heavily on the risk-of-bias assessment, further reducing confidence in the strength of the evidence. Many of the studies included in the systematic review were assessed as being at severe risk of bias and only two were judged as being at moderate overall risk of bias. It is questionable how appropriate it is to apply this quality assessment system to complex interventions such as NSP and OST, which rely on observational study designs to measure effect. Individual random allocation to the intervention would be unethical, as there is sufficient evidence of their effectiveness in relation to other adverse health outcomes. Other reviews conducted outside Cochrane that do not assess quality against a RCT as a gold standard conclude that there is much stronger evidence of effect, although they present comparable results and are drawn from comparable study designs. 17
Second, it is clear from both the systematic review and the pooled analysis that there are difficulties in accurately measuring the use of NSPs. We used a simple definition of NSP use, encompassing coverage that requires correct recall of frequency of injecting and the numbers of needles/syringe obtained in the same time period. It is clear that the use of NSPs purely for obtaining clean needles/syringes oversimplifies its benefits for PWID. This definition does not consider any of the other engagement programmes delivered by the fixed-site NSP services, such as one-to-one support, sexual health services, help with housing, welfare benefits, legal advocacy or other social welfare issues. These linked support services are key to bringing people into the NSP and providing the necessary enabling environment for both participants and providers to reduce behaviours that lead to HCV infection. The oversimplification of the use of NSPs may further explain the weaker efficacy estimates that we found in the pooled analysis and systematic review. This has subsequent implications for the mathematical modelling that estimated the impact of NSPs on HCV infection transmission, because the modelling estimates are only as strong as the parameters on which the model draws. These additional services were not evaluated in the cost-effectiveness analysis but are likely to contribute to well-being among PWID and to further improve WTP.
Finally, another limitation of the project was that we set out to consider strategies for achieving improved coverage of the interventions, including different methods of delivery, and to consider this as part of the cost-effectiveness analysis. However, we were unable to source any estimate on the potential effect of strategies to improve coverage in order to parameterise the model and, thus, we were unable to do this.
Patient and public involvement
People who inject drugs and NSP/OST service providers were consulted on the research at several stages of the project. We convened an advisory group consisting of members of the National Needle Exchange Forum, Addaction and the Hepatitis C Trust, who we met to consult on the study design and emerging findings. Through close consultation with them, we selected the NSP sites across the UK in which to conduct the costing analysis. These sites were selected to represent a range of NSP delivery modalities, different types of injecting drug use and epidemiology of HCV infection, as well as being driven by pragmatic reasons and the availability of data. Preliminary findings of the pooled analysis and the costing analysis were also presented at the annual meeting of the National Needle Exchange Forum, attended by NSP employees and service users. They provided some feedback on the initial findings and commented on the plausibility of our NSP coverage estimates derived from the pooled analysis and for use in the impact modelling. Further consultation on the findings of the costing analysis and results of the systematic review were elicited from each of the collaborating sites (Bristol, Dundee and Walsall) through sites visits. As well as receiving feedback on the findings, we sought opinion on appropriate strategies for scale-up from staff and service users. However, further input from PWID would have been beneficial and its absence should be recognised as a limitation of the project.
Implications for service and local decision-makers
Findings emphasise the crucial need to avoid any scale-back in the coverage of current interventions, which, if it occurred, could result in huge increases in HCV infection transmission across these settings. Despite NSP and OST coverage being high in many settings, model projections also suggest that important benefits could still be achieved from scaling up NSP further, especially in settings with current low coverage levels. NSPs are neglected in most countries by government officials and funders, and are often underprioritised by drug treatment organisations. 23 This can be seen clearly in the UK, where priorities have shifted to treatment and recovery interventions, and these policies need to be addressed to prioritise harm reduction and the provision of NSPs and OST. 118,119 Policies to ensure that NSPs can be accessed widely alongside provision of OST are needed. Policies that insist on the cessation of injection to qualify for OST prescriptions could be stopped to encourage ongoing use of NSPs alongside OST. Evidence shows that the co-location of NSPs with OST provision services can act as a disincentive to the use of NSPs. Preventing the concurrent use of both NSP and OST needs to be removed to maximise reduction in HCV infection transmission.
Strategies are needed to reduce the harms associated with homelessness and crack cocaine injection among PWID, which our modelling suggests is doubling the level of transmission in each setting. Reducing the risk of HCV infection transmission among these vulnerable subpopulations should be a priority for any strategy attempting to reduce HCV infection transmission or hoping to achieve HCV infection elimination as recently set out by WHO. 115
Research priorities
Given the body of evidence demonstrating the effectiveness of OST and NSPs in reducing the transmission of HCV and HIV shown here and elsewhere,16,17 research needs to turn to understanding how NSPs and OST can be most effective and efficient in responding to HIV/HCV and the other health needs that PWID have. Improving our understanding of the mechanisms through which NSPs and OST achieve their effect and the optimum contexts in which to support their implementation is integral to reducing the health inequalities experienced by PWID in the UK and internationally.
We know that the effectiveness of NSP varies by geographical location, and without the provision of counselling, education and drug treatment services including OST, NSPs are not sufficient to reduce epidemics of HIV and HCV infection among PWID, even when sufficient clean needles are distributed to cover each injection. 120 There is a need to understand the pathways between contextual factors and mechanisms of service delivery, and the extent to which these influence effectiveness across different outcomes. This is particularly relevant in the UK in the current austerity climate and ongoing financial pressure on health and social care services. Further research on what happens to distributed needles/syringes, how much wastage there is and whether it is better to distribute single needle/syringes or packs is needed. Better information on this would facilitate decision-making around service provision and improve efficiency. There is also a need to improve the understanding of the ways in which the coverage of NSPs might be expanded and the potential impact of these various methods of expanding coverage.
Finally, routine data collection on costs associated with NSP provision is needed to reduce uncertainty in NSP costings and to facilitate cost-effective analyses incorporating costs associated with other health gains that NSPs bring. Particularly in pharmacies, there is currently little tracking of the numbers and types of patients accessing needle exchange.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Craig Moss from Addaction; Rachel Ayres, Jane Neale, Joseph Fisher and Tracy Chamberlain from the BDP; Ingrid Hainey and Mike Burns from CAIR Scotland, Dundee, who were our key collaborators in Bristol, Dundee and Walsall for facilitating data collection for the costing analysis and who provided ongoing feedback on the study design and findings. We would also like to thank Jamie Bridge from the National Needle Exchange Forum, and Charles Gore and Grace Everest from the Hepatitis C Trust who advised on the selection of NSP sites and provided critical insights into the analyses. They are currently reviewing the policy brief and advising on future dissemination strategies.
Contributions of authors
Lucy Platt, Matthew Hickman and Peter Vickerman devised the overall study design.
Lucy Platt, with help from Matthew Hickman, Vivian Hope, Lisa Maher and Peter Vickerman, conducted the pooled analysis.
Jenny Iversen and Alison Munro cleaned data sets for inclusion in the pooled analysis, and with Avril Taylor commented on findings and helped with the interpretation of the results.
Vivian Hope and John Parry were responsible for the reanalysis of the DBSs to provide measures of new HCV infection cases.
Lucy Platt, with help from Matthew Hickman, Sharon Hutchinson, Lisa Maher and Peter Vickerman, conducted the systematic review.
Sedona Sweeney and Lorna Guinness were responsible for the collection of NSP costing data as well as for the write up and interpretation of the cost-effectiveness analysis.
Noel Craine and Josie Smith advised on the collation of costing data.
Zoe Ward and Peter Vickerman developed and parameterised the mathematical model for use in the impact modelling and cost-effectiveness analysis.
Lucy Platt led the write up of the report with individuals leading on specific chapters including the systematic review and pooled analysis (Lucy Platt), the costing analysis and cost-effectiveness (Sedona Sweeney), and the impact modelling (Zoe Ward and Peter Vickerman). All authors commented on a draft of the report.
Publications
Platt L, Reed J, Minozzi S, Vickerman P, Hagan H, French C, et al. Effectiveness of needle/syringe programmes and opiate substitution therapy in preventing HCV transmission among people who inject drugs. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;1:CD012021.
Platt L, Minozzi S, Reed J, Vickerman P, Hogan H, French C, et al. Needle syringe programmes and opioid substitution therapy for preventing HCV transmission among people who inject drugs: findings from a Cochrane Review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print 11 September 2017]. Addiction 2017.
Platt L, Minozzi S, Reed J, Vickerman P, Hagan H, French C, et al. Needle syringe programmes and opioid substitution therapy for preventing hepatitis C transmission in people who inject drugs [published online ahead of print 18 September 2017]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017.
Planned publications
Platt L, Vickerman P, Hope V, Ingle SN, Craine J, Iversen A, et al. The effect of needle/syringe provision and opiate substitution therapy on HCV incidence: update on a pooled analysis from the UK and Australia. Addiction 2016.
Sweeney S, Ward Z, Platt L, Guinness L, Hickman Smith JM, Ayres R, et al. Cost-effectiveness of needle and syringe provision to prevent transmission of HCV.
Ward Z, Platt L, Sweeney S, Hutchinson S, Hickman M, Smith J, et al. Impact of current and scaled up levels of needle and syringe programmes and Opiate substitution therapy in three UK settings.
Policy brief
Preventing Hepatitis C: the role of needle syringe programmes and opiate substitution therapy.
Conference dissemination
Sweeney S, Ward Z, Platt L, Hope V, Maher L, Hutchinson S, et al. The Cost-Effectiveness of Needle and Syringe Provision in Preventing Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus in People who Inject Drugs. Public Health England Research and Applied Epidemiology Conference, Warwick, UK, March 2017.
Ward Z, Platt L, Sweeney S, Hope V, Maher L, Hutchinson S, et al. Impact of Current and Scaled Up Levels of Needle and Syringe Programmes and Opiate Substitution Therapy in Three UK Settings. Fifth International Symposium on Hepatitis Care in Substance Users, Oslo, Norway, September 2016.
Platt L, Reed J, Minozzi S, Hickman M, French C, Hope V, et al. Effectiveness of Needle/Syringe Programmes and Opiate Substitution Therapy in Preventing HCV Transmission Among People who Inject Drugs. International Harm Reduction Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2015.
Platt L, Reed J, Minozzi S, Hickman M, French C, Hope V, et al. Effectiveness of Needle/Syringe Programmes and Opiate Substitution Therapy in Preventing HCV Transmission Among People who Inject Drugs. Fourth International Symposium on Hepatitis Care in Substance Users, Sydney, NSW, Australia, October 2015.
Platt L. Effectiveness of NSPs and OST on HCV Incidence. National Needle Exchange Forum, High Wycombe, UK, December 2014.
Data sharing statement
All data will be made available following publication in peer-reviewed journals on request to the corresponding author (lucy.platt@lshtm.ac.uk).
All data requests should be submitted to the corresponding author (lucy.platt@lshtm.ac.uk) for consideration. Access to anonymised data may be granted following review.
Disclaimers
This report presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views and opinions expressed by authors in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the PHR programme or the Department of Health. If there are verbatim quotations included in this publication the views and opinions expressed by the interviewees are those of the interviewees and do not necessarily reflect those of the authors, those of the NHS, the NIHR, NETSCC, the PHR programme or the Department of Health.
References
- Pouget ER, Hagan H, Des Jarlais DC. Meta-analysis of hepatitis C seroconversion in relation to shared syringes and drug preparation equipment. Addiction 2012;107:1057-65. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03765.x.
- Strathdee SA, Hallett TB, Bobrova N, Rhodes T, Booth R, Abdool R, et al. HIV and risk environment for injecting drug users: the past, present, and future. Lancet 2010;376:268-84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60743-X.
- Palmateer N, Kimber J, Hickman M, Hutchinson S, Rhodes T, Goldberg D. Evidence for the effectiveness of sterile injecting equipment provision in preventing hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus transmission among injecting drug users: a review of reviews. Addiction 2010;105:844-59. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02888.x.
- Needle and Syringe Programmes (2009). London: NICE; 2014.
- Bluthenthal RN, Anderson R, Flynn NM, Kral AH. Higher syringe coverage is associated with lower odds of HIV risk and does not increase unsafe syringe disposal among syringe exchange program clients. Drug Alcohol Depend 2007;89:214-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.12.035.
- Kaplan EH, Heimer R. A model-based estimate of HIV infectivity via needle sharing. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1992;5:1116-18.
- Tilson H, Aramrattana A, Bozzette SA. Preventing HIV Infection Among Injecting Drug Users in High-risk Countries: An Assessment of the Evidence. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine; 2007.
- Gowing L, Farrell MF, Bornemann R, Sullivan LE, Ali R. Oral substitution treatment of injecting opioid users for prevention of HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004145.pub4.
- Vorma H, Sokero P, Aaltonen M, Turtiainen S, Hughes LA, Savolainen J. Participation in opioid substitution treatment reduces the rate of criminal convictions: evidence from a community study. Addict Behav 2013;38:2313-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.03.009.
- Amato L, Davoli M, Minozzi S, Ferroni E, Ali R, Ferri M. Methadone at tapered doses for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003409.pub4.
- Faggiano F, Vigna-Taglianti F, Versino E, Lemma P. Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002208.
- Gibson DR, Flynn NM, McCarthy JJ. Effectiveness of methadone treatment in reducing HIV risk behavior and HIV seroconversion among injecting drug users. AIDS 1999;13:1807-18. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002030-199910010-00002.
- Jones L, Pickering L, Sumnall H, McVeigh J, Bellis MA. A Review of the Effectiveness and Cost-effectiveness of Needle and Syringe Programmes for Injecting Drug Users. Liverpool: Centre for Public Health, Liverpool John Moores University; 2008.
- Van Den Berg C, Smit C, Van Brussel G, Coutinho R, Prins M. Amsterdam Cohort . Full participation in harm reduction programmes is associated with decreased risk for human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus: evidence from the Amsterdam Cohort Studies among drug users. Addiction 2007;102:1454-62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.01912.x.
- Gibson DR, Flynn NM, Perales D. Effectiveness of syringe exchange programs in reducing HIV risk behavior and HIV seroconversion among injecting drug users. AIDS 2001;15:1329-41. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002030-200107270-00002.
- Aspinall E, Nambiar D, Goldberg DJ, Hickman M, Weir A, Van Velzen E, et al. Are needle and syringe programmes associated with a reduction in HIV transmission among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol 2014;43:235-48. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyt243.
- MacArthur GJ, Minozzi S, Martin N, Vickerman P, Deren S, Bruneau J, et al. Opiate substitution treatment and HIV transmission in people who inject drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2012;345. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e5945.
- Wodak A, Cooney A. Effectiveness of Sterile Needle and Syringe Programming in Reducing HIV/AIDS Among Injecting Drug Users. Geneva: WHO; 2004.
- Hagan H, Pouget ER, Des Jarlais DC. A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventions to prevent hepatitis C virus infection in people who inject drugs. J Infect Dis 2011;204:74-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jir196.
- Turner KM, Hutchinson S, Vickerman P, Hope V, Craine N, Palmateer N, et al. The impact of needle and syringe provision and opiate substitution therapy on the incidence of hepatitis C virus in injecting drug users: pooling of UK evidence. Addiction 2011;106:1978-88. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03515.x.
- Vickerman P, Miners A, Williams J. Assessing the Cost-effectiveness of Interventions Linked to Needle and Syringe Programmes for Injecting Drug Users: An Economic Modelling Report. NICE; 2008.
- Preventing HIV Infection Among Injecting Drug Users in High-Risk Countries: An Assessment of the Evidence. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine; 2007.
- Mathers BM, Degenhardt L, Ali H, Wiessing L, Hickman M, Mattick RP, et al. HIV prevention, treatment, and care services for people who inject drugs: a systematic review of global, regional, and national coverage. Lancet 2010;375:1014-28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60232-2.
- Lurie P. Invited commentary: le mystère de Montréal. Am J Epidemiol 1997;146:1003-6. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009227.
- Degenhardt L, Mathers B, Vickerman P, Rhodes T, Latkin C, Hickman M. Prevention of HIV infection for people who inject drugs: why individual, structural, and combination approaches are needed. Lancet 2010;376:285-301. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60742-8.
- Platt L, Minozzi S, Reed J, Vickerman P, Hagan H, French C, et al. Needle syringe programmes and opiate substitution therapy for preventing hepatitis C transmission in people who inject drugs [published online ahead of print 18 September 2017]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD012021.
- Platt L, Minozzi S, Reed J, Vickerman P, Hogan H, French C, et al. Addiction. 2017.
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928.
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:383-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026.
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE Working Group . GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008;336:924-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD.
- Schünemann HJ, Jaeschke R, Cook DJ, Bria WF, El-Solh AA, Ernst A, et al. An official ATS statement: grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in ATS guidelines and recommendations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006;174:605-14. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200602-197ST.
- Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004;328:1490-4. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7454.1490.
- Bruneau J. Analyses Received from Julie Bruneau and Her Study Team 2015.
- Mehta S. Analyses Received from Shruti Mehta and Her Study Team 2015.
- Page K. Analyses Received from Kim Page and Her Study Team 2015.
- Judd A. Data Set Obtained from Ali Judd and Analyses Conducted by the Review Team 2015.
- Aitken CK, Agius PA, Higgs PG, Stoové MA, Bowden DS, Dietze PM. The effects of needle-sharing and opioid substitution therapy on incidence of hepatitis C virus infection and reinfection in people who inject drugs. Epidemiol Infect 2017;145:796-801. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268816002892.
- Maher L, Jalaludin B, Chant KG, Jayasuriya R, Sladden T, Kaldor JM, et al. Incidence and risk factors for hepatitis C seroconversion in injecting drug users in Australia. Addiction 2006;101:1499-508. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01543.x.
- Craine N, Hickman M, Parry JV, Smith J, Walker AM, Russell D, et al. Incidence of hepatitis C in drug injectors: the role of homelessness, opiate substitution treatment, equipment sharing, and community size. Epidemiol Infect 2009;137:1255-65. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S095026880900212X.
- Crofts N, Nigro L, Oman K, Stevenson E, Sherman J. Methadone maintenance and hepatitis C virus infection among injecting drug users. Addiction 1997;92:999-1005. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.1997.tb02979.x.
- Hagan H, Jarlais DC, Friedman SR, Purchase D, Alter MJ. Reduced risk of hepatitis B and hepatitis C among injection drug users in the Tacoma syringe exchange program. Am J Public Health 1995;85:1531-7. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.85.11.1531.
- Hagan H, McGough JP, Thiede H, Weiss NS, Hopkins S, Alexander ER. Syringe exchange and risk of infection with hepatitis B and C viruses. Am J Epidemiol 1999;149:203-13. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009792.
- Holtzman D, Barry V, Ouellet LJ, Des Jarlais DC, Vlahov D, Golub ET, et al. The influence of needle exchange programs on injection risk behaviors and infection with hepatitis C virus among young injection drug users in select cities in the United States, 1994–2004. Prev Med 2009;49:68-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2009.04.014.
- Hope VD, Hickman M, Ngui SL, Jones S, Telfer M, Bizzarri M, et al. Measuring the incidence, prevalence and genetic relatedness of hepatitis C infections among a community recruited sample of injecting drug users, using dried blood spots. J Viral Hepat 2011;18:262-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2893.2010.01297.x.
- Lucidarme D, Bruandet A, Ilef D, Harbonnier J, Jacob C, Decoster A, et al. Incidence and risk factors of HCV and HIV infections in a cohort of intravenous drug users in the North and East of France. Epidemiol Infect 2004;132:699-708. https://doi.org/10.1017/S095026880400247X.
- Nolan S, Dias Lima V, Fairbairn N, Kerr T, Montaner J, Grebely J, et al. The impact of methadone maintenance therapy on hepatitis C incidence among illicit drug users. Addiction 2014;109:2053-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/add.12682.
- Palmateer N, Hutchinson S, McAllister G, Munro A, Cameron S, Goldberg D, et al. Risk of transmission associated with sharing drug injecting paraphernalia: analysis of recent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection using cross-sectional survey data. J Viral Hepat 2014;21:25-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jvh.12117.
- Patrick DM, Tyndall MW, Cornelisse PG, Li K, Sherlock CH, Rekart ML, et al. Incidence of hepatitis C virus infection among injection drug users during an outbreak of HIV infection. CMAJ 2001;165:889-95.
- Rezza G, Sagliocca L, Zaccarelli M, Nespoli M, Siconolfi M, Baldassarre C. Incidence rate and risk factors for HCV seroconversion among injecting drug users in an area with low HIV seroprevalence. Scand J Infect Dis 1996;28:27-9. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365549609027145.
- Roy E, Alary M, Morissette C, Leclerc P, Boudreau JF, Parent R, et al. High hepatitis C virus prevalence and incidence among Canadian intravenous drug users. Int J STD AIDS 2007;18:23-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/095646207779949880.
- Ruan Y, Qin G, Yin L, Chen K, Qian HZ, Hao C, et al. Incidence of HIV, hepatitis C and hepatitis B viruses among injection drug users in southwestern China: a 3-year follow-up study. AIDS 2007;21:39-46. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.aids.0000304695.54884.4f.
- Spittal PM, Pearce ME, Chavoshi N, Christian WM, Moniruzzaman A, Teegee M, et al. The Cedar Project: high incidence of HCV infections in a longitudinal study of young Aboriginal people who use drugs in two Canadian cities. BMC Public Health 2012;12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-632.
- Thiede H, Hagan H, Murrill CS. Methadone treatment and HIV and hepatitis B and C risk reduction among injectors in the Seattle area. J Urban Health 2000;77:331-45. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386744.
- Thorpe LE, Ouellet LJ, Hershow R, Bailey SL, Williams IT, Williamson J, et al. Risk of hepatitis C virus infection among young adult injection drug users who share injection equipment. Am J Epidemiol 2002;155:645-53. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/155.7.645.
- Tsui JI, Evans JL, Lum PJ, Hahn JA, Page K. Association of opioid agonist therapy with lower incidence of hepatitis C virus infection in young adult injection drug users. JAMA Intern Med 2014;174:1974-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.5416.
- Vallejo F, Barrio G, Brugal MT, Pulido J, Toro C, Sordo L, et al. High hepatitis C virus prevalence and incidence in a community cohort of young heroin injectors in a context of extensive harm reduction programmes. J Epidemiol Community Health 2015;69:599-603. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2014-205070.
- van Beek I, Dwyer R, Dore GJ, Luo K, Kaldor JM. Infection with HIV and hepatitis C virus among injecting drug users in a prevention setting: retrospective cohort study. BMJ 1998;317:433-7. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.317.7156.433.
- White B, Dore GJ, Lloyd AR, Rawlinson WD, Maher L. Opioid substitution therapy protects against hepatitis C virus acquisition in people who inject drugs: the HITS-c study. Med J Aust 2014;201:326-9. https://doi.org/10.5694/mja13.00153.
- Hope V. Data Set Obtained from Vivian Hope and Analyses Conducted by the Review Team 2015.
- Maher L. Data Set Obtained from the International Collaborative of Prospective Studies of HIV and Hepatitis in IDU and Analyses Conducted by Meghan Morris 2015.
- Gower E, Estes C, Blach S, Razavi-Shearer K, Razavi H. Global epidemiology and genotype distribution of the hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol 2014;61:45-57. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.027.
- Mathers BM, Degenhardt L, Phillips B, Wiessing L, Hickman M, Strathdee SA, et al. Global epidemiology of injecting drug use and HIV among people who inject drugs: a systematic review. Lancet 2008;372:1733-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61311-2.
- Platt L, Easterbrook P, Gower E, McDonald B, Sabin K, McGowan C, et al. Prevalence and burden of HCV co-infection in people living with HIV: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2016;16:797-808. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00485-5.
- Wood E, Lloyd-Smith E, Li K, Strathdee SA, Small W, Tyndall MW, et al. Frequent needle exchange use and HIV incidence in Vancouver, Canada. Am J Med 2007;120:172-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.02.030.
- Hagan H, McGough JP, Thiede H, Hopkins SG, Weiss NS, Alexander ER. Volunteer bias in nonrandomized evaluations of the efficacy of needle-exchange programs. J Urban Health 2000;77:103-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02350966.
- Vickerman P, Platt L, Jolley E, Rhodes T, Kazatchkine MD, Latypov A. Controlling HIV among people who inject drugs in Eastern Europe and Central Asia: insights from modeling. Int J Drug Policy 2014;25:1163-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2014.09.013.
- Judd A, Hickman M, Jones S, McDonald T, Parry JV, Stimson GV, et al. Incidence of hepatitis C virus and HIV among new injecting drug users in London: prospective cohort study. BMJ 2005;330:24-5. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38286.841227.7C.
- Palmateer NE, Taylor A, Goldberg DJ, Munro A, Aitken C, Shepherd SJ, et al. Rapid decline in HCV incidence among people who inject drugs associated with national scale-up in coverage of a combination of harm reduction interventions. PLOS ONE 2014;9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104515.
- Iversen J, Maher L. NSP Survey National Data Report 1995–2014. Prevalence of HIV, HCV and Injecting and Sexual Behaviour Among Needle and Syringe Program Attendees. Sydney, NSW: Kirby Institute, University of New South Wales; 2015.
- Shooting Up: Infections Among People who Inject Drugs in the UK. London: Public Health England; 2015.
- Judd A, Parry J, Hickman M, McDonald T, Jordan L, Lewis K, et al. Evaluation of a modified commercial assay in detecting antibody to hepatitis C virus in oral fluids and dried blood spots. J Med Virol 2003;71:49-55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jmv.10463.
- Mellor J, Holmes EC, Jarvis LM, Yap PL, Simmonds P. Investigation of the pattern of hepatitis C virus sequence diversity in different geographical regions: implications for virus classification. The International HCV Collaborative Study Group. J Gen Virol 1995;76:2493-507. http://dx.doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-76-10-2493.
- Aceijas C, Hickman M, Donoghoe MC, Burrows D, Stuikyte R. Access and coverage of needle and syringe programmes (NSP) in Central and Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Addiction 2007;102:1244-50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.01848.x.
- Heimer R, Khoshnood K, Bigg D, Guydish J, Junge B. Syringe use and reuse: effects of syringe exchange programs in four cities. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol 1998;18:37-44. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042560-199802001-00008.
- Lewis JR, Sauro J. When 100% really isn’t 100%: improving the accuracy of small-sample estimates of completion rates. J Usability Stud 2010;1:136-50.
- Wilson EB. Probable inference, the law of succession, and statistical inference. J Am Stat Assoc 1927;22:209-12. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1927.10502953.
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002;21:1539-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186.
- Guinness L, Vickerman P, Quayyum Z, Foss A, Watts C, Rodericks A, et al. The cost-effectiveness of consistent and early intervention of harm reduction for injecting drug users in Bangladesh. Addiction 2010;105:319-28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02755.x.
- Kwon JA, Anderson J, Kerr CC, Thein HH, Zhang L, Iversen J, et al. Estimating the cost-effectiveness of needle-syringe programs in Australia. AIDS 2012;26:2201-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283578b5d.
- Bruggmann P, Grebely J. Prevention, treatment and care of hepatitis C virus infection among people who inject drugs. Int J Drug Policy 2015;26:22-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2014.08.014.
- Needle and Syringe Programmes. London: NICE; 2014.
- Drummond M. Return on Investment in Needle and Syringe Programs in Australia: Report. Canberra, ACT: Commonwealth Department of Health and Ageing; 2002.
- Guide to Starting and Managing Needle and Syringe Programmes. Geneva: WHO; 2007.
- Hope VD, McVeigh J, Marongiu A, Evans-Brown M, Smith J, Kimergård A, et al. Prevalence of, and risk factors for, HIV, hepatitis B and C infections among men who inject image and performance enhancing drugs: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2013;3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003207.
- Aitken C, Delalande C, Stanton K. Pumping iron, risking infection? Exposure to hepatitis C, hepatitis B and HIV among anabolic-androgenic steroid injectors in Victoria, Australia. Drug Alcohol Depend 2002;65:303-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-8716(01)00174-0.
- Vickerman P, Grebely J, Dore GJ, Sacks-Davis R, Page K, Thomas DL, et al. The more you look, the more you find: effects of hepatitis C virus testing interval on reinfection incidence and clearance and implications for future vaccine study design. J Infect Dis 2012;205:1342-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jis213.
- Information Services Division Scotland . Injecting Equipment Provision in Scotland Survey 2013 14 2015. www.isdscotland.org/Health-Topics/Drugs-and-Alcohol-Misuse/Publications/2015-06-23/2015-06-23-IEP-Report.pdf (accessed 1 March 2016).
- Mills HL, Colijn C, Vickerman P, Leslie D, Hope V, Hickman M. Respondent driven sampling and community structure in a population of injecting drug users, Bristol, UK. Drug Alcohol Depend 2012;126:324-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.05.036.
- Mills HL, Johnson S, Hickman M, Jones NS, Colijn C. Errors in reported degrees and respondent driven sampling: implications for bias. Drug Alcohol Depend 2014;142:120-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.06.015.
- Cullen KJ, Hope VD, Croxford S, Shute J, Ncube F, Parry JV. Factors associated with recently acquired hepatitis C virus infection in people who inject drugs in England, Wales and Northern Ireland: new findings from an unlinked anonymous monitoring survey. Epidemiol Infect 2015;143:1398-407. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0950268814002040.
- Kimber J, Copeland L, Hickman M, Macleod J, McKenzie J, De Angelis D, et al. Survival and cessation in injecting drug users: prospective observational study of outcomes and effect of opiate substitution treatment. BMJ 2010;341. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c3172.
- Sutton AJ, Gay NJ, Edmunds WJ, Hope VD, Gill ON, Hickman M. Modelling the force of infection for hepatitis B and hepatitis C in injecting drug users in England and Wales. BMC Infect Dis 2006;6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-6-93.
- Shepherd J, Jones J, Hartwell D, Davidson P, Price A, Waugh N. Interferon alpha (pegylated and non-pegylated) and ribavirin for the treatment of mild chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2007;11. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta11110.
- Bruno S, Zuin M, Crosignani A, Rossi S, Zadra F, Roffi L, et al. Predicting mortality risk in patients with compensated HCV-induced cirrhosis: a long-term prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:1147-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2009.31.
- Morgan RL, Baack B, Smith BD, Yartel A, Pitasi M, Falck-Ytter Y. Eradication of hepatitis C virus infection and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Intern Med 2013;158:329-37. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-158-5-201303050-00005.
- Micallef JM, Kaldor JM, Dore GJ. Spontaneous viral clearance following acute hepatitis C infection: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. J Viral Hepat 2006;13:34-41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2893.2005.00651.x.
- Kemp PA, Neale J, Robertson M. Homelessness among problem drug users: prevalence, risk factors and trigger events. Health Soc Care Community 2006;14:319-28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2524.2006.00624.x.
- Cornish R, Macleod J, Strang J, Vickerman P, Hickman M. Risk of death during and after opiate substitution treatment in primary care: prospective observational study in UK General Practice Research Database. BMJ 2010;341. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c5475.
- Martin NK, Foster GR, Vilar J, Ryder S, Cramp ME, Gordon F, et al. HCV treatment rates and sustained viral response among people who inject drugs in seven UK sites: real world results and modelling of treatment impact. J Viral Hepat 2015;22:399-408. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jvh.12338.
- Harris RJ, Thomas B, Griffiths J, Costella A, Chapman R, Ramsay M, et al. Increased uptake and new therapies are needed to avert rising hepatitis C-related end stage liver disease in England: modelling the predicted impact of treatment under different scenarios. J Hepatol 2014;61:530-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.05.008.
- Smith DJ, Combellick J, Jordan AE, Hagan H. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) disease progression in people who inject drugs (PWID): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Drug Policy 2015;26:911-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2015.07.004.
- van der Meer AJ, Veldt BJ, Feld JJ, Wedemeyer H, Dufour JF, Lammert F, et al. Association between sustained virological response and all-cause mortality among patients with chronic hepatitis C and advanced hepatic fibrosis. JAMA 2012;308:2584-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.144878.
- Kohli A, Shaffer A, Sherman A, Kottilil S. Treatment of hepatitis C: a systematic review. JAMA 2014;312:631-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.7085.
- Jones HE, Welton NJ, Ades AE, Pierce M, Davies W, Coleman B, et al. Problem drug use prevalence estimation revisited: heterogeneity in capture–recapture and the role of external evidence. Addiction 2016;111:438-47. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13222.
- Hay G, Gannon M, MacDougall J, Millar T, Eastwood C, McKeganey N. National and Regional Estimates of the Prevalence of Opiate Use and/or Crack Cocaine Use 2006/07: A Summary of Key Findings. London: Home Office; 2008.
- Hay G, Rael dos Santos A, Millar T. Estimates of the Prevalence of Opiate Use and/or Crack Cocaine Use, 2010/11: Sweep 7 Report. London: Centre for Public Health, Liverpool John Moores University; 2013.
- King R, Bird SM, Overstall A, Hay G, Hutchinson SJ. Injecting drug users in Scotland, 2006: listing, number, demography, and opiate-related death-rates. Addict Res Theory 2013;21:235-46. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/16066359.2012.706344.
- Hickman M, Hope V, Coleman B, Parry J, Telfer M, Twigger J, et al. Assessing IDU prevalence and health consequences (HCV, overdose and drug-related mortality) in a primary care trust: implications for public health action. J Public Health 2009;31:374-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdp067.
- Briggs A, Claxton K, Sculpher MJ. Decision Modelling for Health Economic Evaluation. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2006.
- Xia Y, Seaman S, Hickman M, Macleod J, Robertson R, Copeland L, et al. Factors affecting repeated cessations of injecting drug use and relapses during the entire injecting career among the Edinburgh Addiction Cohort. Drug Alcohol Depend 2015;151:76-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.03.005.
- Allen EJ, Palmateer NE, Hutchinson SJ, Cameron S, Goldberg DJ, Taylor A. Association between harm reduction intervention uptake and recent hepatitis C infection among people who inject drugs attending sites that provide sterile injecting equipment in Scotland. Int J Drug Policy 2012;23:346-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2012.07.006.
- Vickerman P, Hickman M, Judd A. Modelling the impact on hepatitis C transmission of reducing syringe sharing: London case study. Int J Epidemiol 2007;36:396-405. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyl276.
- Vickerman P, Platt L, Hawkes S. Modelling the transmission of HIV and HCV among injecting drug users in Rawalpindi, a low HCV prevalence setting in Pakistan. Sex Transm Infect 2009;85:23-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/sti.2008.034660.
- Martin NK, Vickerman P, Grebely J, Hellard M, Hutchinson SJ, Lima VD, et al. Hepatitis C virus treatment for prevention among people who inject drugs: modeling treatment scale-up in the age of direct-acting antivirals. Hepatology 2013;58:1598-609. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hep.26431.
- Draft Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis, 2016–2021 – The First of its Kind. Geneva: WHO; 2015.
- Claxton K, Martin S, Soares M, Rice N, Spackman E, Hinde S, et al. Methods for the estimation of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence cost-effectiveness threshold. Health Technol Assess 2015;19. http://dx.doi.org/10.3310/hta19140.
- Remme M, Vassall A, Lutz B, Luna J, Watts C. Financing structural interventions: going beyond HIV-only value for money assessments. AIDS 2014;28:425-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000000076.
- Drug Treatment in England 2013–2014. London: Public Health England; 2014.
- Substance Misuse Treatment Framework (SMTF) Recovery Oriented Integrated Systems of Care. Cardiff: Welsh Government; 2013.
- Strathdee SA, Patrick DM, Currie SL, Cornelisse PG, Rekart ML, Montaner JS, et al. Needle exchange is not enough: lessons from the Vancouver injecting drug use study. AIDS 1997;11:F59-65. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002030-199708000-00001.
- Hickman M, Hope V, Brady T, Madden P, Jones S, Honor S, et al. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) prevalence, and injecting risk behaviour in multiple sites in England in 2004. J Viral Hepat 2007;14:645-52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2893.2007.00855.x.
- Unit Costs of Health and Social Care 2013. Canterbury: PSSRU, University of Kent; 2013.
- Wright M, Forton D, Main J, Goldin R, Torok E, Tedder R, et al. Treatment of histologically mild hepatitis C virus infection with interferon and ribavirin: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. J Viral Hepat 2005;12:58-66. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2893.2005.00575.x.
- Martin NK, Vickerman P, Dore GJ, Hickman M. How should HCV treatment be prioritized in the direct-acting antiviral era? An economic evaluation including population prevention benefits. J Hepatol 2016;65:17-25.
Appendix 1 Supplementary material for Chapter 2
| Variable | Number of studies | Univariable RR (95% CI) | Ratio of RRs (95% CI) | p-value | τ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic region | |||||
| Europe | 8 | 0.51 (0.37 to 0.70) | 1.0 (reference) | ||
| Australia | 5 | 0.55 (0.28 to 1.11) | 1.12 (0.52 to 2.41) | ||
| North America | 6 | 0.69 (0.44 to 1.08) | 1.42 (0.73 to 2.78) | 0.53 | 0.103 |
| Site of recruitment | |||||
| Service attenders | 12 | 0.67 (0.49 to 0.92) | 1.0 (reference) | ||
| Community | 7 | 0.49 (0.33 to 0.73) | 0.73 (0.42 to 1.27) | 0.256 | 0.06 |
| Females | 9 | 1.59 (1.13 to 2.29) | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
| Prison | 7 | 1.06 (0.61 to 1.79) | 0.821 | 0.4303 | |
| Homelessness | 6 | 1.08 (0.83 to 1.40) | 0.521 | 0.2327 | |
| Injection of stimulants | 7 | 0.89 (0.65 to 1.22) | 0.405 | 0.15 | |
| Daily injection | 4 | 0.88 (0.64 to 1.22) | 0.373 | 0.17 | |
| Variable | Number of studies | Univariable RR (95% CI) | Ratio of RRs (95% CI) | p-value | τ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic region | |||||
| Europe | 5 | 0.44 (0.24 to 0.80) | 1.0 (reference) | ||
| North America | 3 | 1.58 (0.57 to 4.42) | 3.73 (0.95 to 14.7) | 0.057 | 0.41 |
| Site of recruitment | |||||
| Service attenders | 3 | 0.67 (0.28 to 1.59) | 1.0 (reference) | ||
| Community | 5 | 0.82 (0.29 to 2.32) | 0.76 (0.12 to 4.88) | 0.74 | 0.89 |
| Females | 7 | 2.97 (0.38 to 23.1) | 0.24 | 0.87 | |
| Prison | 3 | NA | |||
| Homelessness | 6 | 1.01 (0.38 to 2.67) | 0.976 | 1.53 | |
| Injection of stimulants | 7 | 1.08 (0.47 to 2.51) | 0.827 | 1.15 | |
| Daily injection | 5 | 3.66 (0.22 to 61.3) | 0.239 | 1.15 | |
Appendix 2 Supplementary material for Chapter 3
| Explanatory factors | n | Total | % | OR | 95% CI | p-value | AOR | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 NSP, no OST | 181 | 911 | 20 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| > 100 NSP, no OST | 196 | 1462 | 13 | 0.6 | 0.50 to 0.78 | < 0.001 | 0.5 | 0.38 to 0.62 | < 0.001 |
| < 100 NSP, OST | 219 | 1301 | 17 | 0.8 | 0.66 to 1.02 | 0.0682 | 0.7 | 0.57 to 0.94 | 0.0155 |
| > 100 NSP, OST | 313 | 2126 | 15 | 0.7 | 0.57 to 0.85 | 0.0004 | 0.5 | 0.41 to 0.65 | < 0.001 |
| Female | 1.2 | 1.00 to 1.37 | 0.0431 | 1.1 | 0.95 to 1.37 | 0.1644 | |||
| History of prison | 1.2 | 1.00 to 1.35 | 0.0516 | 1.4 | 1.19 to 1.73 | 0.0002 | |||
| Injection of crack cocaine | 0.8 | 0.67 to 0.89 | 0.0004 | 1.2 | 1.00 to 1.42 | 0.0501 | |||
| Duration of injection (years) | |||||||||
| 0–3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| 3.1–5 | 1.1 | 0.82 to 1.58 | 0.4498 | 1.0 | 0.67 to 1.47 | 0.953 | |||
| 6–10 | 1.1 | 0.85 to 1.44 | 0.4456 | 1.1 | 0.78 to 1.45 | 0.6853 | |||
| 11+ | 1.2 | 0.96 to 1.49 | 0.1014 | 1.1 | 0.86 to 1.49 | 0.3613 | |||
| Study | |||||||||
| Bristol 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| Leeds | 0.2 | 0.11 to 0.31 | < 0.001 | 0.2 | 0.11 to 0.32 | < 0.001 | |||
| Birmingham | 0.1 | 0.04 to 0.17 | < 0.001 | 0.1 | 0.05 to 0.18 | < 0.001 | |||
| Wales | 0.2 | 0.16 to 0.38 | < 0.001 | 0.3 | 0.17 to 0.48 | < 0.001 | |||
| Bristol 2 | 0.2 | 0.15 to 0.38 | < 0.001 | 0.2 | 0.12 to 0.34 | < 0.001 | |||
| NESI | 5.7 | 4.03 to 8.13 | < 0.001 | 7.7 | 5.24 to 11.37 | < 0.001 | |||
| UAMP | 0.3 | 0.23 to 0.41 | < 0.001 | 0.3 | 0.22 to 0.40 | < 0.001 | |||
| ANSPS | 0.5 | 0.39 to 0.68 | < 0.001 | 0.7 | 0.50 to 0.92 | 0.0121 | |||
| On OST | 1.0 | 0.87 to 1.16 | 0.929 | 0.9 | 0.76 to 1.07 | 0.2319 | |||
| High NSP coverage | 0.8 | 0.65 to 0.86 | < 0.001 | 0.6 | 0.50 to 0.69 | < 0.001 | |||
| Explanatory factors | n | Total | % | OR | 95% CI | p-value | AOR | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 NSP, no OST | 62 | 181 | 34 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| > 100 NSP, no OST | 62 | 224 | 28 | 0.73 | 0.48 to 1.12 | 0.154 | 0.71 | 0.45 to 1.09 | 0.1187 |
| < 100 NSP, OST | 125 | 318 | 39 | 1.24 | 0.85 to 1.82 | 0.2625 | 1.11 | 0.74 to 1.66 | 0.6196 |
| > 100 NSP, OST | 116 | 472 | 25 | 0.63 | 0.43 to 0.91 | 0.0133 | 0.59 | 0.40 to 0.88 | 0.0088 |
| Female | 0.79 | 0.58 to 1.07 | 0.1287 | 0.8 | 0.56 to 1.13 | 0.1997 | |||
| History of prison | 1.21 | 0.88 to 1.65 | 0.2484 | 1.06 | 0.74 to 1.52 | 0.7349 | |||
| Injection of crack cocaine | 1.48 | 1.14 to 1.91 | 0.0032 | 1.5 | 1.13 to 2.00 | 0.0055 | |||
| Duration of injection (years) | |||||||||
| 0–3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| 3.1–5 | 1.41 | 0.81 to 2.46 | 0.2201 | 1.24 | 0.68 to 2.26 | 0.4791 | |||
| 6–10 | 1.8 | 1.19 to 2.73 | 0.0054 | 1.72 | 1.10 to 2.70 | 0.0178 | |||
| 11+ | 1.54 | 1.05 to 2.27 | 0.0275 | 1.37 | 0.89 to 2.10 | 0.1511 | |||
| Study | |||||||||
| Bristol 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| Leeds | 0.38 | 0.27 to 0.54 | < 0.001 | 0.39 | 0.27 to 0.56 | < 0.001 | |||
| Birmingham | 0.33 | 0.23 to 0.47 | < 0.001 | 0.35 | 0.24 to 0.51 | < 0.001 | |||
| Bristol 2 | 0.59 | 0.42 to 0.81 | 0.0012 | 0.57 | 0.40 to 0.81 | 0.0018 | |||
| On OST | 0.98 | 0.76 to 1.27 | 0.8821 | 0.93 | 0.70 to 1.22 | 0.5873 | |||
| > 100 NSP | 0.58 | 0.45 to 0.73 | < 0.001 | 0.59 | 0.46 to 0.76 | < 0.001 | |||
| High NSP coverage | 0.58 | 0.45 to 0.73 | < 0.001 | 0.59 | 0.46 to 0.76 | < 0.001 | |||
| Explanatory factors | Mean (n) | OR | 95% CI | p-value | OR | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 NSP, no OST | 72.4 (1156) | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
| > 100 NSP, no OST | 48.6 (2184) | –23.8 | –28.3 to –19.3 | < 0.001 | –21.6 | –26.2 to –17.0 | < 0.001 |
| < 100 NSP, OST | 56.1 (2083) | –16.2 | –20.8 to –11.7 | < 0.001 | –18.4 | –23.1 to –13.8 | < 0.001 |
| > 100 NSP, OST | 30.3 (5091) | –42 | –46.1 to –37.9 | < 0.001 | –41.2 | –45.5 to –37.0 | < 0.001 |
| Female | 0.2 | –2.4 to 2.85 | 0.882 | –0.14 | –10.0 to 9.71 | 0.2 | |
| History of prison | 7.9 | 5.5 to 10.3 | < 0.001 | 6.3 | 3.58 to 9.07 | < 0.001 | |
| Injection of crack cocaine | 15.7 | 13.1 to 18.2 | < 0.001 | 11.7 | 8.59 to 14.8 | < 0.001 | |
| Duration of injection (years) | |||||||
| 0–3 | Reference | Reference | |||||
| 3.1–5 | 1.6 | –3.06 to 6.18 | 0.508 | 2.3 | –2.8 to 7.38 | 0.384 | |
| 6–10 | 3.2 | –0.63 to 7.03 | 0.101 | 3.82 | –0.44 to 8.09 | 0.079 | |
| 11+ | 2.6 | –0.78 to 5.92 | 0.132 | 4.35 | 0.44 to 8.27 | 0.029 | |
| Study | |||||||
| Bristol 1 | Reference | Reference | |||||
| Leeds | –3.08 | –13.3 to 7.12 | 0.554 | –0.14 | –9.98 to 9.71 | 0.978 | |
| Birmingham | –10.63 | –20.7 to –0.51 | 0.04 | –5.32 | –15.1 to 4.45 | 0.286 | |
| Bristol 2 | –1.85 | –10.5 to 6.80 | 0.674 | 4.21 | –6.15 to 14.6 | 0.426 | |
| On OST | 7.29 | –2.64 to 17.22 | 0.150 | 7.98 | –1.94 to 17.90 | 0.115 | |
| High NSP coverage | –13.3 | –20.7 to –5.87 | < 0.001 | 1.82 | –5.62 to 9.26 | 0.632 | |
| Explanatory factors | n | Total | % | OR | 95% CI | p-value | AOR | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 NSP, no OST | 442 | 1027 | 43 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| > 100 NSP, no OST | 572 | 1684 | 34 | 0.68 | 0.58 to 0.80 | < 0.001 | 0.77 | 0.63 to 0.93 | 0.0063 |
| < 100 NSP, OST | 644 | 1606 | 40 | 0.89 | 0.76 to 1.04 | 0.1353 | 0.8 | 0.66 to 0.97 | 0.0252 |
| > 100 NSP, OST | 1021 | 2906 | 35 | 0.72 | 0.62 to 0.83 | < 0.001 | 0.78 | 0.66 to 0.93 | 0.0066 |
| Female | 0.93 | 0.84 to 1.03 | 0.1855 | 1.08 | 0.95 to 1.24 | 0.2457 | |||
| History of prison | 1.46 | 1.32 to 1.61 | < 0.001 | 1.15 | 1.01 to 1.31 | 0.0417 | |||
| Injection of crack cocaine | 1.72 | 1.56 to 1.88 | < 0.001 | 1.11 | 0.98 to 1.27 | 0.1099 | |||
| Duration of injection (years) | |||||||||
| 0–3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| 3.1–5 | 1.09 | 0.90 to 1.32 | 0.3731 | 1.01 | 0.79 to 1.29 | 0.9344 | |||
| 6–10 | 1.27 | 1.09 to 1.49 | 0.0021 | 0.95 | 0.78 to 1.16 | 0.6396 | |||
| 11 + | 0.93 | 0.81 to 1.06 | 0.2796 | 0.87 | 0.73 to 1.04 | 0.127 | |||
| Study | |||||||||
| Bristol 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| Leeds | 0.78 | 0.29 to 2.12 | 0.6227 | 0.78 | 0.29 to 2.12 | 0.624 | |||
| Birmingham | 0.04 | 0.02 to 0.08 | < 0.001 | 0.04 | 0.02 to 0.08 | < 0.001 | |||
| Wales | 0.03 | 0.01 to 0.06 | < 0.001 | 0.03 | 0.01 to 0.06 | < 0.001 | |||
| Bristol 2 | 0.18 | 0.08 to 0.41 | < 0.001 | 0.19 | 0.08 to 0.45 | 0.0001 | |||
| NESI | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.01 | < 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.02 | < 0.001 | |||
| UAMP | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.02 | < 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.02 | < 0.001 | |||
| ANSPS | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.02 | < 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.02 | < 0.001 | |||
| On OST | 1.01 | 0.91 to 1.11 | 0.8797 | 0.94 | 0.83 to 1.06 | 0.3343 | |||
| High NSP coverage | 0.69 | 0.63 to 0.76 | < 0.001 | 0.88 | 0.78 to 0.98 | 0.0244 | |||
| Explanatory factors | n | Total | % | OR | 95% CI | p-value | AOR | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 NSP, no OST | 213 | 621 | 34 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| > 100 NSP, no OST | 254 | 596 | 43 | 1.42 | 1.13 to 1.79 | 0.0029 | 1.2 | 0.90 to 1.51 | 0.2524 |
| < 100 NSP, OST | 450 | 1082 | 42 | 1.36 | 1.11 to 1.67 | 0.003 | 1.4 | 1.14 to 1.81 | 0.002 |
| > 100 NSP, OST | 698 | 1960 | 36 | 1.06 | 0.88 to 1.28 | 0.5509 | 1.2 | 0.99 to 1.52 | 0.0603 |
| Female | 1.29 | 1.13 to 1.48 | 0.0002 | 1.3 | 1.12 to 1.58 | 0.0011 | |||
| History of prison | 1.02 | 0.90 to 1.16 | 0.7517 | 0.9 | 0.77 to 1.08 | 0.2929 | |||
| Injection of crack cocaine | 0.94 | 0.84 to 1.05 | 0.2946 | 1.4 | 1.18 to 1.58 | < 0.001 | |||
| Duration of injection (years) | |||||||||
| 0–3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| 3.1–5 | 1.15 | 0.91 to 1.46 | 0.2518 | 0.99 | 0.74 to 1.33 | 0.9442 | |||
| 6–10 | 1.01 | 0.84 to 1.22 | 0.9081 | 0.94 | 0.74 to 1.18 | 0.5745 | |||
| 11+ | 0.93 | 0.79 to 1.09 | 0.3797 | 1.22 | 0.99 to 1.50 | 0.0637 | |||
| Study | |||||||||
| Bristol 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| Leeds | 0.56 | 0.41 to 0.78 | 0.0005 | 0.58 | 0.42 to 0.80 | 0.001 | |||
| Birmingham | 0.68 | 0.49 to 0.94 | 0.0188 | 0.72 | 0.52 to 1.00 | 0.0509 | |||
| Wales | 1.81 | 1.36 to 2.40 | < 0.001 | 2.76 | 1.89 to 4.03 | < 0.001 | |||
| Bristol 2 | 0.6 | 0.44 to 0.82 | 0.0014 | 0.55 | 0.39 to 0.76 | 0.0004 | |||
| ANSPS | 0.27 | 0.21 to 0.35 | < 0.001 | 0.26 | 0.20 to 0.33 | < 0.001 | |||
| On OST | 1.12 | 0.98 to 1.28 | 0.0843 | 1.29 | 1.11 to 1.50 | 0.0007 | |||
| High NSP coverage | 0.87 | 0.77 to 0.98 | 0.0262 | 1.03 | 0.89 to 1.18 | 0.7318 | |||
| Explanatory factors | n | Total | % | OR | 95% CI | p-value | AOR | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 NSP, no OST | 858 | 1126 | 76 | Reference | 1.0 | ||||
| > 100 NSP, no OST | 1748 | 2101 | 83 | 1.6 | 1.29 to 1.85 | < 0.001 | 1.4 | 1.13 to 1.69 | 0.0015 |
| < 100 NSP, OST | 1727 | 2028 | 85 | 1.8 | 1.49 to 2.15 | < 0.001 | 1.7 | 1.41 to 2.12 | < 0.001 |
| > 100 NSP, OST | 5833 | 6781 | 86 | 1.9 | 1.65 to 2.24 | < 0.001 | 1.9 | 1.56 to 2.23 | < 0.001 |
| Female | 1.2 | 1.08 to 1.32 | 0.0004 | 1.4 | 1.22 to 1.57 | < 0.001 | |||
| History of prison | 1.9 | 1.77 to 2.11 | < 0.001 | 1.6 | 1.45 to 1.83 | < 0.001 | |||
| Injection of crack cocaine | 1.6 | 1.42 to 1.76 | < 0.001 | 1.4 | 1.20 to 1.62 | < 0.001 | |||
| Duration of injection (years) | |||||||||
| 0–3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| 3.1–5 | 1.9 | 1.63 to 2.21 | < 0.001 | 1.7 | 1.41 to 2.06 | < 0.001 | |||
| 6–10 | 2.8 | 2.43 to 3.15 | < 0.001 | 2.2 | 1.83 to 2.52 | < 0.001 | |||
| 11+ | 5.5 | 4.86 to 6.15 | < 0.001 | 3.3 | 2.82 to 3.80 | < 0.001 | |||
| Study | |||||||||
| Bristol 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| Leeds | 1.2 | 0.77 to 1.78 | 0.4674 | 1.1 | 0.72 to 1.73 | 0.6138 | |||
| Birmingham | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.13 | 0.1813 | 0.8 | 0.55 to 1.26 | 0.3816 | |||
| Wales | 0.2 | 0.15 to 0.30 | < 0.001 | 0.3 | 0.21 to 0.46 | < 0.001 | |||
| Bristol 2 | 2.5 | 1.54 to 4.02 | 0.0002 | 2.6 | 1.47 to 4.45 | 0.0009 | |||
| NESI | 1.0 | 0.71 to 1.29 | 0.7937 | 1.3 | 0.93 to 1.78 | 0.1267 | |||
| UAMP | 1.2 | 0.90 to 1.67 | 0.1888 | 1.3 | 0.94 to 1.80 | 0.1136 | |||
| ANSPS | 2.8 | 1.98 to 3.81 | < 0.001 | 3.6 | 2.52 to 5.20 | < 0.001 | |||
| On OST | 1.5 | 1.36 to 1.65 | < 0.001 | 1.5 | 1.36 to 1.71 | < 0.001 | |||
| High NSP coverage | 1.4 | 1.27 to 1.54 | < 0.001 | 1.2 | 1.04 to 1.31 | 0.0098 | |||
| Explanatory factors | n | Total | % | OR | 95% CI | p-value | AOR | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 NSP, no OST | 765 | 1092 | 70 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| > 100 NSP, no OST | 1586 | 2037 | 78 | 1.5 | 1.27 to 1.78 | < 0.001 | 1.3 | 1.10 to 1.58 | 0.0028 |
| < 100 NSP, OST | 1582 | 1975 | 80 | 1.7 | 1.45 to 2.04 | < 0.001 | 1.7 | 1.40 to 2.02 | < 0.001 |
| > 100 NSP, OST | 5452 | 6732 | 81 | 1.8 | 1.58 to 2.10 | < 0.001 | 1.9 | 1.60 to 2.20 | < 0.001 |
| Female | 1.2 | 1.12 to 1.36 | < 0.001 | 1.4 | 1.22 to 1.53 | < 0.001 | |||
| History of prison | 1.6 | 1.51 to 1.78 | < 0.001 | 1.4 | 1.25 to 1.54 | < 0.001 | |||
| Injection of crack cocaine | 1.3 | 1.20 to 1.46 | < 0.001 | 1.2 | 1.04 to 1.34 | 0.0121 | |||
| Duration of injection (years) | |||||||||
| 0–3 | |||||||||
| 3.1–5 | 1.7 | 1.48 to 2.01 | < 0.001 | 1.6 | 1.31 to 1.88 | < 0.001 | |||
| 6–10 | 2.2 | 1.92 to 2.48 | < 0.001 | 1.8 | 1.52 to 2.05 | < 0.001 | |||
| 11+ | 3.8 | 3.41 to 4.29 | < 0.001 | 2.7 | 2.33 to 3.07 | < 0.001 | |||
| Study | |||||||||
| Bristol 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||
| Leeds | 0.8 | 0.56 to 1.18 | 0.2786 | 0.8 | 0.52 to 1.12 | 0.1644 | |||
| Birmingham | 0.7 | 0.51 to 1.05 | 0.0903 | 0.8 | 0.53 to 1.13 | 0.1824 | |||
| Bristol 2 | 1.5 | 1.01 to 2.22 | 0.0463 | 1.3 | 0.83 to 1.94 | 0.2724 | |||
| NESI | 0.9 | 0.64 to 1.11 | 0.2365 | 1.0 | 0.70 to 1.27 | 0.7086 | |||
| UAMP | 1.1 | 0.84 to 1.48 | 0.4395 | 1.1 | 0.83 to 1.50 | 0.4803 | |||
| ANSPS | 2.0 | 1.49 to 2.69 | < 0.001 | 2.2 | 1.61 to 3.04 | < 0.001 | |||
| On OST | 1.4 | 1.27 to 1.53 | < 0.001 | 1.5 | 1.36 to 1.68 | < 0.001 | |||
| High NSP coverage | 1.2 | 1.04 to 1.27 | 0.0044 | 1.2 | 1.05 to 1.30 | 0.0037 | |||
Appendix 3 Supplementary material for Chapter 4
| Parameter | Base case | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discount rate (%) | 4 | 1 | 6 |
| Salaries multiplier (%) | 100 | 50 | 200 |
| Equipment wastage (%) | 100 | 50 | 200 |
| Opportunity cost of volunteer time (annual) | 18,992.87 | – | 18,992.87 |
| Opportunity cost of volunteer time (hourly) | 0 | 0 | 12.5 |
| Per cent of visits for non-IPED users | |||
| Fixed sites | 92 | 75 | 90 |
| Pharmacies | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Walk-in centres | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Per cent of needles to non-IPED users | |||
| Fixed sites | 81 | 75 | 90 |
| Pharmacies | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Walk-in centres | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Visits per client | |||
| Pharmacies | 8 | 6 | 10 |
| Walk-in centres | 8 | 6 | 10 |
| Needle distribution | |||
| Needle pack size | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Needle packs per transaction | 1.06 | 1.00 | 1.12 |
| ‘One hit kit’ packs per transaction | 4 | 1 | 10 |
| Site and output type | Total outputs | Opioids and other | IPEDs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, N | Male, n (%) | Female, n (%) | Total | Male, n (%) | Total | Male, n (%) | |
| BDP | |||||||
| Total clients | 1134 | 991 (87) | 143 (13) | 755 (67) | 618 (82) | 379 (33) | 373 (98) |
| Total visits | 10,796 | 9353 (87) | 1443 (13) | 9937 (92) | 8502 (86) | 859 (8) | 851 (99) |
| Total needles | 286,698 | 252,039 (88) | 34,659 (12) | ||||
| CAIR Scotland | |||||||
| Total clients | 817 | 504 (62) | 201 (25) | 697 (85) | 121 (15) | ||
| Total visits | 6251 | 5692 (91) | 559 (9) | ||||
| Total needles | 50,186 | 36,455 (73) | 13,731 (27) | ||||
| Addaction Walsall | |||||||
| Total clients | 569 | 520 (91) | 44 (8) | 190 (33) | 379 (67) | ||
| Total visits | 1756 | 1609 (92) | 147 (8) | ||||
| Total needles | 78,914 | 63,644 (81)a | 15,270 (19)a | ||||
| Site | Distribution style | Total clients (all opiate users) | Total visits | Total needles distributed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, N | Male, n (%) | Female, n (%) | ||||
| Pharmacy 1 (Bristol) | Packs | 176a | 132 (75)a | 44 (25)a | 1405 | 28,100a |
| Pharmacy 2 (Bristol) | Packs | 213a | 160 (75)a | 53 (25)a | 1705 | 36,100a |
| Pharmacy 3 (Dundee) | Pick and mix | 287 | 224 (78) | 62 (22) | 1940 | 21,982 |
| Pharmacy 5 (Dundee) | Pick and mix | 210 | 149 (71) | 61 (29) | 1914 | 18,518 |
| Pharmacy 4 (Walsall) | Packs | 290a | 217 (75)a | 72 (25)a | 2316a | 24,520 |
| Pharmacy 6 (Walsall) | Packs | 207a | 155 (75)a | 52 (25)a | 1656a | 17,530 |
| Site and output type | Total | Opioids and other | IPEDs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, N | Male, n (%) | Female, n (%) | Total, n (%) | Male, n (%) | Total, n (%) | Male, n (%) | |
| Out-of-hours pharmacy (Walsall) | |||||||
| Total clients | 213 | 160 (75)a | 53 (25)a | 213 (100) | 0 | ||
| Total visits | 1704 | 1704 (100) | 0 | ||||
| Total needles | 6816 | 6816 (100) | 0 | ||||
| Drop-in centre (Walsall) | |||||||
| Total clients | 113 | 84 (75)a | 28 (25)a | 113 (100) | 0 | ||
| Total visits | 900 | 900 (100) | 0 | ||||
| Total needles | 7812 | 7812 (100) | 0 | ||||
| Outreach service (Bristol) | |||||||
| Total clients | 396 | 348 (88) | 48 (12) | 286 (72) | 240 (84) | 110 (28) | 108 (98) |
| Total visits | 1778 | 1438 (81) | 340 (19) | 1207 (68) | 1248 (79) | 192 (11) | 190 (99) |
| Total needles | 101,326 | 92,171 (91) | 9155 (9) | ||||
Appendix 4 Supplementary material for Chapter 5
Model equations
Sn,mi,j,k and Cn,mi,j,k are the number of susceptible and chronically infected individuals in the model, in which i = 0,1 for off OST and on OST respectively, j = 0,1 for < 100% NSP and > 100% NSP, respectively, n = 1,2,3,4 for recent and non-recent or long-term injectors and ex-injecting drug users, m = l,h for low and high risk, respectively, and k = 1,2 . . . 6 for the disease progression states chronic infected, compensated cirrhosis, decompensated cirrhosis, HCC, liver transplant and post liver transplant, respectively.
The ordinary differential equation model is made up of 300 equations, which are described below for different aspects of the model.
Inflow of injectors
There are only two variables in the model that allow an inflow of new injectors. These are low- and high-risk susceptible individuals in the first disease progression category with no intervention: the number of new low-risk individual per year is θ(1 – ϕ) and the number of new high-risk individuals per year is θϕ.
Injecting duration progression
These terms in the equations are concerned with movement from one injecting duration category to another as well as PWID-related and background mortality. IDn,mi,j,k denotes the terms in an ordinary differential equation of injecting duration category n. It occurs for all values of m,i,j,k. Yn,mi,j,k is used to describe one of the variables in the model, in which Y = S or C and the subscripts and superscripts are as described previously.
When n = 4 (ex-injecting), the terms have a different form:
Interventions: opioid substitution therapy and needle and syringe programmes
These terms in the equations are concerned with the movement of injectors from one intervention category to another. ITi,j,kn,m denotes the terms in the ordinary differential equation of OST intervention category i and NSP intervention category j. These terms can be found for all values of m,k and current injector categories but not for the ex-injecting drug user category (n = 4):
High and low risk
These terms in the equations are concerned with movement of current injectors between low and high risk. HRn,mi,j,k denotes the terms in the ordinary differential equation of risk category m. These terms can be found in the equations for all values of i, j, k and n = 1,2,3.
Disease progression
These terms in the equations are concerned with movement through the disease states. Infection and treatment are described separately. DSn,mi,j,k denotes the terms in the ordinary differential equation of disease category k for susceptible individuals and DCn,mi,j,k for infected individuals. These terms can be found in the equations for all values of I,j,n,m.
Infection terms
The forces of infection below are concerned with acquiring infection. The terms are of the form:
When the ordinary differential equation is for susceptible, the force of infection term is subtracted and the same term is added to the matching infectious category.
Define:
to give
Treatments
There are a fixed number of treatments per year, given by Φ. When the total number of infected individuals in the model is greater than this number, the treatments are allocated proportionately. When the total number of infected individuals is less than the number of possible treatments per year, all are treated. Only the first two disease progression categories are eligible for treatment and will have treatment terms. If the ordinary differential equation is for an infected category, the treatment term will be subtracted and for a susceptible category, the term will be added. If:
for k = 1,2, then n = 1,2,3.
Otherwise:
for k = 1,2, n = 1,2,3.
For ex-injecting drug users, treatment is more straightforward, with a proportion, r, of the chronically infected and compensated cirrhosis individuals being treated each year.
for k = 1,2.
As an example, below is the ordinary differential equation for the susceptible category for the first disease progression category, with no interventions, a recent injector (< 3 years) and at low risk. On the right-hand side in order from left to right there is an inflow term, injecting duration terms, intervention terms, high- and low-risk terms, disease progression terms, infection term and treatment term.
Submodels used in the fitting procedure
Injecting duration model
A model with three injecting duration categories was used to fit the population data and the injecting duration profiles from survey data. Here, Si is the number of susceptible injectors in the i category. The categories are: r, recent injector; n, non-recent injector; and l, long-term injector. The µi and τi, are as described above.
The steady state solution of this model is given below:(16)Sr=θµ1+τ1,Sn=θτ1(µ1+τ1)(µ2+τ2),Sl=θτ1τ2(µ3(µ1+τ1)(µ2+τ2)).
With total population N=Sr+Sn+Sl, the analytical solution of this system is: Sr(t)=Sr(0)e−(µ1+τ1)t+θµ1+τ1(1−e−(µ1+τ1)t),Sn(t)=τ1θ(µ1+τ1)(µ2+τ2)+Sn(0)e−(µ2+τ2)t+τ1µ1+τ1−µ2−τ2Sr(0)(e−(µ2+τ2)t−e−(µ1+τ1)t)+τ1θµ1+τ1−µ2−τ2*(e−(µ1+τ1)t/(µ1+τ1)−e−(µ2+τ2)t/(µ2+τ2)),Sl(t)=e−µ3t(Sl(0)+τ2µ2+τ2−µ3. (τ1Sr(0)µ1+τ1−µ3−τ1θµ3(µ1+τ1−µ3)+Sn(0)))+e−(µ2+τ2)tτ2µ2+τ2−µ3(τ1Sr(0)µ2−τ2+µ1+τ1+τ1θ(µ2+τ2)(−µ2−τ2+µ1+τ1)−Sn(0)). +e−(µ1+τ1)tτ1τ2θ(µ1+τ1)(µ1+τ1−mu3)(µ1+τ1−µ2−τ2)+τ1τ2θµ3(µ1+τ1)(µ2+τ2).
High-risk model
A model with a high and low risk only was used to calculate parameter values in the calibration process. The variable Sh denotes high risk and Sl denotes low risk:(17)dShdt=−ζSh+σSldSldt=ζSh−σSl.
As this is a closed system, we can use N−Sh=Sl, which gives:(18)dShdt=−ζSh+σ(N−Sh).
Setting the left-hand side to zero and rearranging gives the proportion of the total population that are high risk (Φ):(19)Φ=σσ+ζ.
This expression was used to calculate the required value of the recruitment rate σ from the sampled values of the proportion of high-risk individuals and the leaving rate σ.
| Parameter | Bristol | Walsall | Dundee | Relevant parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current PWID population size | 2004: sampled 111–125%106 of 2011 value104 | 2006: 125%106 of 2011 value | Constant level: 675–825 local estimate adjusted from King et al. (2013)107 Sampled uniformly |
θ, number of new injectors per year. Value of θ found using steady-state equations of population submodel for the first time point in all three settings. In Bristol and Walsall, a second value of θ is found using Matlab fzero and analytical solution to population submodel that gives population size required with sampled cessation rates |
| 2011: 2025–2564 adjusted from Jones et al. (2016)104 to include only 60% of people on OST not in contact with other services.104 Sampled uniformly | 2011: 1296–1623 estimated from local number on OST and unpublished PWID prevalence estimates for West Midlands. Sampled uniformly | |||
| Injecting duration profile: proportion of PWID that are R, NR or LT | 2004: R, 0.04–0.2; NR, 0.25–0.45; LT, 0.4–0.6573 | 2006: R, 0.1–0.3; NR, 0.45–0.65; LT, 0.2–0.3 | Constant level: R, 0.15–0.35; NR, 0.36–0.65; LT, 0.12–0.35 (NESI) | Death and cessation rates (µi) (per year). Prior distribution for µ1 (0.0351–0.1702) calculated from assumption that between 10% and 40% of recent initiates cease injecting within 3 years.91 A large upper bound of 0.4 was assumed for the prior distributions of µ2 and µ3 owing to a lack of information. Lower bounds of 0.004 and 0.008 were chosen to ensure that the leaving rate was greater than the likely death rate.98 Parameter sets were accepted if PWID demographic submodel fits were within the ranges for each injecting duration |
| 2014: R, 0.075–0.2; NR, 0.05–0.22; LT, 0.55–0.85 (UAMP) | 2014: R, 0.1–0.3; NR, 0.15–0.4; LT, 0.4–0.6 (UAMP) | |||
| Chronic HCV infection prevalence (75% of HCV antibody prevalence) | Constant level 40–50% (community surveys, UAMP); sampled from truncated beta (305.25,364.75) | 2006: 11–26% (UAMP); sampled from truncated beta (30.75,132.25) | 2008: 15–30% (NESI); sampled from truncated beta (18.75,64.25) | π, infection rate used to fit the HCV infection prevalence estimates |
| 2014: 15–39% (no fitting required) | 2014: 31–44% adjusted from (NESI); sampled from truncated beta (54.6.90.4) | |||
| Proportion high risk | 2004: 70–80% (2004, 2006 community surveys and UAMP). Sampled uniformly | Constant level of 40–65% (UAMP); sampled uniformly | Constant level of 26–42% (NESI); sampled from beta (156,315) | ϕ, proportion of injectors initially high risk assumed to be the same as sampled proportion high risk σ, recruitment rate per year from low- to high-risk behaviour, calculated from sampled leaving rate, ζ, and proportion high risk, ϕ |
| 2014: 80–95% (UAMP); sampled uniformly | ||||
| Proportion on OST | 2004: 33.3–46.7%121 sampled from truncated beta (81,121) | 2006: 30–50% (UAMP); sampled from truncated beta (32,48) | 2008: 433–53% (NESI) sampled from beta (36,47) | β, recruitment rate per year on to OST |
| 2009: 76.5–86.3% (community survey, 2009) sampled from truncated beta (241,55) | 2009: 61–82% (UAMP); sampled from truncated beta (47,18) | 2014: 65–79% (NESI) sampled from beta (106,40) | ||
| Proportion > 100% NSP [needles distributed/(population size × injecting frequency)] | Needles distributed in 2014 (786,542–844,646), population size in 2014 and injecting frequency (470–859 per year from UAMP) sampled. Mean calculated coverage 56% | Needles distributed in 2014 (225,275–237,111), population size in 2014 and injecting frequency (435–716 per year from UAMP) sampled. Mean calculated coverage 28% | Needles distributed in 2014 (assumed to be the same as in 2008), population size in 2008 and injecting frequency (517–999 per year from NESI) sampled. Mean calculated coverage 27%. Needles distributed in 2014 (138,246–145,768), population size in 2014 and injecting frequency (251–533 per year from NESI) sampled. Mean calculated coverage 49% | η, recruitment rate per year onto high-coverage NSP |
Appendix 5 Supplementary material for Chapter 6
| Setting | Fixed citywide cost (£) | Cost per needle distributed (£) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Minimum | Maximum | Median | Minimum | Maximum | |
| Bristol | 44,142 | 36,758 | 49,890 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.42 |
| Dundee | 10,159 | 8672 | 11,807 | 0.78 | 0.37 | 1.19 |
| Walsall | 21,068 | 16,320 | 26,318 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 1.03 |
| Disease stage | Annual costs (2014 GBP) | Distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| OST (specialist prescribing) | 2839.28 | Gamma | PSSRU122 |
| Uninfected | 0.00 | Gamma | Wright et al., 2005123 |
| F0 and F1 mild HCV infection | 187.59 | Gamma | Wright et al., 2005123 |
| F2 and F3 moderate HCV infection | 974.68 | Gamma | Wright et al., 2005123 |
| Compensated cirrhosis | 1546.98 | Gamma | Wright et al., 2005123 |
| Decompensated cirrhosis | 12,397.57 | Gamma | Wright et al., 2005123 |
| HCC | 11,170.04 | Gamma | Wright et al., 2005123 |
| Liver transplant | 40,273.00 | Gamma | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Post transplant | 2041.00 | Gamma | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Hospital costs year of transplant | 13,937.00 | Gamma | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Treatment | Gamma | ||
| Sofosbuvir + Ledipasvir (Harvoni®, Gilead) – PWID | 48,816.00 | Gamma | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Sofosbuvir + Ledipasvir – ex- or non-injecting drug user | 40,680.00 | Gamma | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Liver-related death | 0.00 | Gamma | Assumption |
| Disease stage | QALYs | Distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uninfected | |||
| Ex- or non-injecting drug user | 0.94 | Constant | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Injecting drug user | 0.85 | Uniform(0.8, 0.9) | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Mild HCV infection | |||
| Without treatment (F0 and F1) | 0.77 | Beta(521.2375, 155.6943) | |
| SVR (F1 only) | 0.82 | Beta(65.8678, 14.4588) | |
| Moderate HCV (F2 and F3) | Martin et al., 2016124 | ||
| Without treatment | 0.66 | Beta(168.2461, 86.6723) | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| SVR | 0.72 | Beta(58.0608, 22.592) | |
| Compensated cirrhosis | |||
| Without treatment | 0.55 | Beta(47.1021, 38.5381) | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| SVR | 0.61 | Beta(58.0608, 37.1124) | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Decompensated cirrhosis | 0.45 | Beta(123.75, 151.25) | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| HCC | 0.45 | Beta(123.75, 151.25) | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Liver transplant | 0.45 | Beta(123.75, 151.25) | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Post transplant | 0.67 | Beta(59.2548, 29.1852) | Martin et al., 2016124 |
| Liver-related death | 0 | Martin et al., 2016124 | |
Glossary
- Australian Needle Syringe Programme Survey
- An annual survey of people who inject drugs conducted by the University of New South Wales.
- Needle Exchange Surveillance Initiative
- An annual survey of people who inject drugs conducted by Public Health Scotland.
- Unlinked Anonymous Monitoring Programme
- An annual survey of people who inject drugs conducted by Public Health England.
List of abbreviations
- ACROBAT-NRSI
- A Cochrane Risk Of Bias Assessment Tool: for Non-Randomized Studies of Interventions
- ANSPS
- Australian Needle Syringe Programme Survey
- AOR
- adjusted odds ratio
- BDP
- Bristol Drugs Project
- CI
- confidence interval
- CrI
- credible interval
- DAA
- direct acting antiviral
- DBS
- dried blood spot
- GBP
- UK pounds sterling
- GRADE
- Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation
- HCC
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- HCV
- hepatitis C virus
- HIV
- human immunodeficiency virus
- ICER
- incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- IPED
- image and performance enhancing drug
- NESI
- Needle Exchange Surveillance Initiative
- NICE
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NSP
- needle and syringe programme
- OR
- odds ratio
- OST
- opioid substitution therapy
- PWID
- people who inject drugs
- QALY
- quality-adjusted life-year
- RCT
- randomised controlled trial
- RDS
- respondent-driven sampling
- RNA
- ribonucleic acid
- RR
- rate ratio
- SVR
- sustained virological response
- UAMP
- Unlinked Anonymous Monitoring Programme
- WHO
- World Health Organization
- WTP
- willingness to pay